BUILDING RETROFITS: BREATHING NEW LIFE INTO EXISTING BUILDING STRUCTURES
|
|
|
- Cecily McCormick
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BUILDING RETROFITS: BREATHING NEW LIFE INTO EXISTING BUILDING STRUCTURES CLIFFORD SCHWINGER Clifford Schwinger Clifford Schwinger, P.E. is Vice President and Quality Assurance Manager at Cagley Harman & Associates. Mr. Schwinger received his BSCE degree from Lehigh University and has been with Cagley, Harman & Associates for 20 years. He s on the AISC Manuals and Textbooks Committee. Abstract Steel building structures often undergo modifications to accommodate new uses and occupancies during their lifespan. This paper discusses methods and procedures used for analyzing and strengthening the framing in existing steel structures including: procedures for reviewing the load capacity of existing framing and connections; weldability issues related to welding to existing steel structures; and tips and techniques for strengthening existing beams, columns and connections. 1
2 Introduction The modification of existing building structures to accommodate new uses presents structural engineers with a variety of interesting challenges. Engineers working on such projects must take on an investigative role to ascertain existing conditions, followed by an analysis phase to determine the load capacity. When additional load capacity is required of an existing structure, engineers have the option of either strengthening the existing framing or adding new framing to replace or supplement the existing. Most building codes require existing structures undergoing substantial modifications or a change of occupancy to be upgraded to meet current building code requirements. Code Issues Chapter 34 of the 2006 International Building Code (International Code Council, 2006) stipulates the requirements for additions and modifications to existing structures. The main points related modifications or additions to existing structures are as follows: 1. Alterations or additions must comply with the requirements of the code for new construction. (Section ) 2. Additions or alterations to an existing structure shall not cause a stress increase of more than 5 percent in any existing member unless the member can resist the increased load in accordance with the requirements of the code for new structures. (Section ) 3. Existing members found to be unsound or structurally deficient shall be repaired so that they can support the required loads in accordance with the requirements of the code for new structures. (Section ) 4. Additions to existing buildings that are seismically independent from adjacent existing structures shall be designed in accordance to the code for new structures. (Upgrades to the lateral load resisting system of the independent existing structure are not required.) (Section ) 5. Where an addition is added to an existing structure and that addition is not seismically independent from the existing structure, then the lateral load resisting system of the entire structure shall be upgraded to conform to the requirements of the code for new construction unless all of the following conditions are met (Section ): a. The new addition conforms to the requirements for new structures. b. The addition does not increase seismic forces in any member in the existing structure by more than 10 percent unless that increased force can be supported in accordance with the requirements of the code for new construction. c. The addition does not decrease the seismic force resisting strength in any existing member by more than 10 percent unless there is sufficient residual strength in those members to support the seismic forces in accordance with the requirements of the code for new construction. 6. Where alterations are made to an existing structure the existing lateral load resisting system need not be upgraded as long as the seismic forces in any element do not increase by more than 10 percent or as long as the strength of any existing member resisting seismic forces is not diminished by more than 5 percent. (Section ) Assessing Existing Structures The availability of existing structural drawings makes the task of engineering modifications to existing structures easier. Unfortunately these drawings are often not available. Architectural drawings for pre-1940 buildings often showed a substantial amount of accurate information related to the structural framing. Occasionally some original architectural drawings are available even when the structural drawings are gone. At a minimum, architectural drawings provide engineers a good starting point for determining column locations, floor-to-floor heights and an approximation of the loads for which the structure may have been designed. Dates on original drawings can give a clue as to what building code may have been in effect and what AISC Specification may have been used when the building was designed. Architectural plans showing floor layouts will give insight as to what design live loads may have been used. 2
3 A site visit should always be performed to inspect the structure especially for structures more than 30 years old. These site visits are required to assess the condition of the structure and to obtain all measurements required to perform the necessary structural analysis. Some key things to look for when assessing the existing condition of a structure are as follows: 1. Any damage to framing? 2. Any noticeable corrosion? 3. Any signs that modifications to the structure that may have been performed without engineering review? 4. Any unusual deflections in floor framing? 5. Any cracks in supported slabs? 6. Any signs of foundation settlement? 7. Any signs that new rooftop equipment, heavy hung piping loads, folding partitions, rigging, or other suspended loads that may have been added without structural engineering review. The following information must be obtained: 1. Floor-to-floor heights 2. Floor slab thicknesses 3. Column bay dimensions 4. Spacing and configuration of all floor framing 5. Dimensions of all floor framing members 6. Connection details 7. Joist sizes and geometry (look for joist tags). Review of existing conditions during the survey should also be performed to ascertain the constraints and limitations for gaining access to the existing framing for the purposes of installing supplemental framing and/or reinforcing to the existing framing. Such access constraints may dictate what type of structural reinforcement would be most appropriate. A valuable resource available to structural engineers working with existing building structures is AISC Steel Design Guide 15 AISC Rehabilitation and Retrofit Guide (Brockenbrough, 2002). This publication is available free to AISC members. Design Guide 15 lists section properties of all beam and column shapes produced since 1873, provides a summary of all allowable stresses published and beam and column design equations published in every AISC specification since 1923, lists grades and yield strengths of all structural steel produced since 1900 and provides tables listing the in chronological order the allowable stresses in bolts, rivets and welds throughout the twentieth century. Another valuable source of information is the Structural Engineers Handbook by Milo S. Ketchum (1924). This book provides a wealth of knowledge for those working on building structures constructed prior to Copies of this publication are frequently available from used book dealers on the internet. Determining Load Capacity of Existing Structures Knowing the yield strength of the steel used in the framing is essential for computing the load capacity. A good starting point for establishing the probable yield strength is provided in Table A. Testing should be performed to ascertain and verify the actual yield strength. One technique for finding additional strength in existing steel framed structures is to test the steel to determine its actual yield strength, in hope of finding it to be of a higher value than was used in the original design. Probable F y of W shapes Year Constructed F y (ksi) Present 36/50 Table A. This table is a guide that lists the most probable yield strength for W shapes. Actual yield strength of existing framing members should be defined from existing drawings or verified by testing. 3
4 Mill certification tests for A36 steel were quite often 40 ksi or higher. Likewise, many tons of steel produced in the mid-eighties through mid-nineties had dual certification that is, the steel met the requirements of both ASTM A36 and ASTM A572, Grade 50. While dual certified steel may have been designed as A36 material, the actual yield strength was at least 50 ksi. Taking advantage of the actual yield strength can provide a substantial increase in member capacity. Another technique for finding more strength in existing structures is to analyze the framing using LRFD. LRFD useable strength is approximately 1.5 times greater than ASD service level strength. If the average load factor is less than 1.5, then LRFD design will provide greater load carrying capacity than ASD via the relative lower required strength. Per Chapter 2 of ASCE 7-05, the required strength for a member supporting only dead and live gravity loads is 1.2D+1.6L. When the live load is the same magnitude as the dead load (D = L), the average load factor is 1.4. In most steel buildings the design live load is usually close to or less than the dead load. For members such as girders and columns supporting large tributary areas of floor framing, live load reductions permitted by building codes will usually reduce the average load factor to a value lower than 1.4. An average load factor of 1.4 yields a 7% decrease (1 (1.4/1.5) = 0.07) in required strength versus a 1.5 average load factor, resulting in an effective 7% increase in load capacity using LRFD design. For columns in multistory structures where full live load reductions can be taken, the ratio of dead load / live load can often be 2 or more. When DL/LL=2, the average load factor is An average load factor of 1.33 yields a 11% decrease (1 (1.33/1.5) = 0.11) in required strength versus a 1.5 average load factor, resulting in an effective 11% increase in load capacity using LRFD design. To reiterate, the increased load capacity achievable using LRFD is not an increase in member strength per se but is a reduction in the required strength relative to usable strength that s realized when the average load factor is less than 1.5. The Allowable Stress Design and the newer Allowable Strength Design methodologies provide a constant safety factor of 1.5 (safety factor = nominal strength / usable strength) for all load combinations. LRFD design provides a variable factor of safety that decreases as the ratio between dead load and live load increases. Accordingly, analysis of structures using LRFD design will result in more efficient design than ASD design when the average load factor is less than 1.5. When investigating the load carrying capacity of existing structures the economic advantages of using LRFD design can be substantial especially when additional load carrying capacity can be justified that can eliminate or minimize the need for reinforcing the existing framing. Weldability Issues An excellent resource available to structural engineers for issues related to welding to existing structures is the paper Field Welding to Existing Structures by David Ricker. This publication is available at no charge to AISC members via the AISC website. The following are several important points with regards to welding to existing structures: 1. If the original framing has welded connections, then welding to the steel is acceptable. 2. Don t weld to cast iron or wrought iron (Ricker, 1988). 3. Weldability is verified by mechanical and chemical testing (Ricker, 1988). a. Mechanical testing measures ductility. b. Chemical testing determines the carbon equivalent value a value that is a measure of weldability. c. Steel buildings constructed between 1900 and 1962 were most likely constructed using ASTM A7 or A9 steel. The ASTM A7 and A9 specifications placed no limits on carbon content and other elements that affect weldability (Garlich, 2000). Although A7 and A9 steel is generally weldable, it should be tested. 4
5 d. Steel buildings constructed after 1962 were constructed with weldable steel (A36 and A572). Testing to verify the weldability of this steel is not necessary. Increasing Flexural Strength Floor Framing Members There are two options for reinforcing existing floors to support additional loads: Option #1: Option #2: Add new framing to supplement the existing framing. Reinforce the existing beams, girders and connections. Provided that the floor slab has sufficient capacity to carry the loads, the easiest solution is usually that of reinforcing the existing beams and girders. Figure 1 shows several ways of reinforcing existing W shapes to increase their flexural strength. The easiest and most cost effective method for reinforcing these members is to weld rectangular HSS s to the bottom flanges (Figure 1(a)). The advantages of using HSS in this manner are as follows: 1. Easy down-hand welding when the HSS is wider than beam flange. 2. Only one piece of steel to handle. 3. Easy to obtain, fabricate, handle and install in long lengths. (Plates generally have to be cut and spliced.) 4. Installation of a single HSS to the bottom flange is less labor intensive than welding plates to the bottom of the top and bottom flanges. 5. The fabrication cost of HSS s is less than that of plates. (Narrow plates are usually cut from wider plates. 6. HSS s provide a greater increase in moment of inertia per dollar than do top and bottom field welded flange plates. 7. Welding new steel to the underside of the top flanges of existing girders is very difficult where other members frame to sides of the girders. 8. The yield strength of rectangular HSS shapes is 42 ksi, compared to 36 ksi for A36 plate material. Increasing axial load capacity of columns (a) (b) (c) (d) Figure 1. Column axial load capacity is usually dictated by the column buckling limit state, of which slenderness kl/r is a variable. Column buckling in pinned-pinned gravity load only columns occurs at the mid-height of the column. Accordingly, when gravity columns require reinforcing to support additional loads, the reinforcing usually does not need to be installed continuous through the floor framing, provided that the factored load in the column through the floor is less than 0.90 x Fy x As, and the column is braced in both directions by the floor framing. Column reinforcing serves both to reduce slenderness (by increasing the radius of gyration of the section) as well as to reduce stress. Since column buckling in pinned-pinned gravity columns is a mid-height P phenomenon increasing column stiffness between the supports, not at the supports, is required to increase column capacity. 5
6 Figure 2(a) shows the most cost effective method for increasing the weak axis stiffness of a W shaped column. While the plates could be welded parallel and flush with the column flanges in Figure 2(b), this reinforcing configuration is not as efficient in reducing slenderness as it that shown in Figure 2(a). For either detail, the reinforcing plates can terminate several inches below the underside of the framing at the top of the column and several inches above the existing floor slab when the column is braced in both directions by the floor framing. (a) Figure 2. (b) Increasing Capacity of Connections The capacities of existing connections must be determined when existing framing is modified or additional load capacity is sought. If additional load capacity is required, existing connections must either be reinforced or supplemented to provide the required capacity. The manner by which existing shear connections can be reinforced is limited only by the imagination of the engineer. Such reinforcing however usually consists of either adding welds to the existing connections (Figure 3), welding seat brackets to the ends of beams (Figure 4), replacing rivets or A307 bolts with high strength bolts (Figure 5), or a combination thereof. AISC Design Guide 15 (Brockenbrough, 2002) provides historic data on design capacities that have been used for design of riveted, bolted and welded connections. Figure 3. 6
7 Figure 4. Figure 5. Connecting New Framing To Existing Framing As is the case with reinforcing existing connections there are many ways that new framing can be connected to existing framing. If the existing steel is weldable, the best connection is most likely one that involves a welded connection to the existing structure. Welding new connection elements to existing steel is simpler and requires less precision as compared to the process of field drilling new holes through existing steel and field bolting connections to the steel. Various details for connecting new framing to existing framing are shown in Figures 6 through 13. 7
8 Figure 6. Figure 7. Figure 8. 8
9 Figure 9. Figure 10. Figure 11. 9
10 Figure 12. Figure 13. REFERENCES 1. Ricker, David T., Field Welding to Existing Steel Structures, AISC Engineering Journal, 1 st Quarter Garlich, Michael J., Welding to Existing Structures, Presented at North American Steel Construction Conference Las Vegas, February 24 and 25, Brockenbrough, Roger L., AISC Rehabilitation and Retrofit Guide A Reference for Historic Shapes and Specifications, Steel Design Guide Series 15, American Institute for Steel Construction, Ketchum, Milo S., Structural Engineers Handbook, Data for the Design and Construction of Steel Bridges and Buildings, McGraw-Hill Book Company, International Building Code, International Code Council, 2006, pp 541,
CVEN 483. Structural System Overview
 CVEN 483 Structural System Overview Dr. J. Bracci Fall 2001 Semester Presentation Overview 1. Building system primary function 2. Types of load 3. Building materials 4. Structural members 5. Structural
CVEN 483 Structural System Overview Dr. J. Bracci Fall 2001 Semester Presentation Overview 1. Building system primary function 2. Types of load 3. Building materials 4. Structural members 5. Structural
THE BRACE CONNECTION THE BOLTED OPTION FIGURE 1 MODEL SHOWING THE BOILER AND THE STRUCTURAL SUPPORT SYSTEM (BOILER BUILDING)
 Comparative Study of Bolted versus Welded SCBF Connections Authors: Robert P. Krumpen III P.E., Bechtel Corporation, rpkrumpe@bechtel.com Dr. Peter J. Carrato P.E. S.E., Bechtel Corporation, pcarrato@bechtel.com
Comparative Study of Bolted versus Welded SCBF Connections Authors: Robert P. Krumpen III P.E., Bechtel Corporation, rpkrumpe@bechtel.com Dr. Peter J. Carrato P.E. S.E., Bechtel Corporation, pcarrato@bechtel.com
SJI Updates Expanded Load Tables for Noncomposite Joists / Joist Girders and Development of New Composite Joist Series
 SJI Updates Expanded Load Tables for Noncomposite Joists / Joist Girders and Development of New Composite Joist Series SUMMARY David Samuelson Steel joists are growing in recognition as being a very economical
SJI Updates Expanded Load Tables for Noncomposite Joists / Joist Girders and Development of New Composite Joist Series SUMMARY David Samuelson Steel joists are growing in recognition as being a very economical
STATE UNIVERSITY CONSTRUCTION FUND. UNIVERSITY CON DIRECTIVE 5-1 Issue date: October 2014
 STATE STRUCTION FUND DIRECTIVE 5-1 Issue date: October 2014 STRUCTURAL STEEL 1. General: It is the Fund's policy that the design of the structural steel is the prime responsibility of the project's Structural
STATE STRUCTION FUND DIRECTIVE 5-1 Issue date: October 2014 STRUCTURAL STEEL 1. General: It is the Fund's policy that the design of the structural steel is the prime responsibility of the project's Structural
Figure 1 Example of HSS column splice
 HSS Column Splices Mike Manor, PE, MLSE FORSE Consulting Technical Consultant to the Steel Tube Institute Hollow Structural Sections (HSS) columns are prevalent in many types of construction, especially
HSS Column Splices Mike Manor, PE, MLSE FORSE Consulting Technical Consultant to the Steel Tube Institute Hollow Structural Sections (HSS) columns are prevalent in many types of construction, especially
xiii Preface to the Fifth Edition Preface to the Second Edition Factors for Conversion to SI Units of
 Structural Steel Designer's Handbook Table Of Contents: Contributors xiii Preface to the Fifth Edition xv Preface to the Second Edition xvii Factors for Conversion to SI Units of xix Measurement Chapter
Structural Steel Designer's Handbook Table Of Contents: Contributors xiii Preface to the Fifth Edition xv Preface to the Second Edition xvii Factors for Conversion to SI Units of xix Measurement Chapter
Supplemental Structural Correction Sheet Steel Moment Frame Design (2017 LABC)
 Supplemental Structural Correction Sheet Steel Moment Frame Design (2017 LABC) Plan Check/PCIS Application No.: Checked By: Your feedback is important, please visit our website to complete a Custom Survey
Supplemental Structural Correction Sheet Steel Moment Frame Design (2017 LABC) Plan Check/PCIS Application No.: Checked By: Your feedback is important, please visit our website to complete a Custom Survey
There are countless ways to improve constructability on your next project. Here are 50 of them. the need for it or specify it on the design drawings.
 There are countless ways to improve constructability on your next project. Here are 50 of them. Tips to Take your Team to the Top By Matthew D. Brady, P.E., and Cliff Schwinger, P.E. We hear the word constructability
There are countless ways to improve constructability on your next project. Here are 50 of them. Tips to Take your Team to the Top By Matthew D. Brady, P.E., and Cliff Schwinger, P.E. We hear the word constructability
Survey and Testing of Pre-1988 Braced Frame Structures From The West Coast of the United States
 Survey and Testing of Pre-1988 Braced Frame Structures From The West Coast of the United States Dan Sloat 1, Charles W. Roeder 2, Dawn E. Lehman 3, and Jeffrey W. Berman 4 1 Graduate Student, Dept. of
Survey and Testing of Pre-1988 Braced Frame Structures From The West Coast of the United States Dan Sloat 1, Charles W. Roeder 2, Dawn E. Lehman 3, and Jeffrey W. Berman 4 1 Graduate Student, Dept. of
Tech Tips SidePlate Connections FAQ 09/30/2017
 Tech Tips SidePlate Connections FAQ 09/30/2017 Page 1 of 15 Introduction to SidePlate Connection Technology SidePlate Connection Technology is ideally suited to protect structures against seismic events,
Tech Tips SidePlate Connections FAQ 09/30/2017 Page 1 of 15 Introduction to SidePlate Connection Technology SidePlate Connection Technology is ideally suited to protect structures against seismic events,
Tips For Designing Constructable Concrete Buildings
 Tips For Designing Constructable Concrete Buildings by Clifford Schwinger, P.E. The Harman Group, Structural Engineers King of Prussia, Pa. Structural Engineers Association of Ohio Annual Conference Presentation
Tips For Designing Constructable Concrete Buildings by Clifford Schwinger, P.E. The Harman Group, Structural Engineers King of Prussia, Pa. Structural Engineers Association of Ohio Annual Conference Presentation
fifteen steel construction: materials & beams ARCHITECTURAL STRUCTURES: FORM, BEHAVIOR, AND DESIGN DR. ANNE NICHOLS SUMMER 2016 lecture
 ARCHITECTURAL STRUCTURES: FORM, BEHAVIOR, AND DESIGN DR. ANNE NICHOLS SUMMER 2016 lecture fifteen steel construction: materials & beams Steel Beams 1 Steel Beam Design American Institute of Steel Construction
ARCHITECTURAL STRUCTURES: FORM, BEHAVIOR, AND DESIGN DR. ANNE NICHOLS SUMMER 2016 lecture fifteen steel construction: materials & beams Steel Beams 1 Steel Beam Design American Institute of Steel Construction
Structural System. Design Criteria Fire Resistance Concrete designed for 2 HR rating (worst case) Geotechnical Report Allowable Bearing Capacity
 System Codes and Criteria Design Codes and Standards The design code used is the Wisconsin Administrative Code along with the State of Wisconsin Department of Commerce-Safety & Buildings Chapters Comm
System Codes and Criteria Design Codes and Standards The design code used is the Wisconsin Administrative Code along with the State of Wisconsin Department of Commerce-Safety & Buildings Chapters Comm
Spring Hill Suites Marriott
 Spring Hill Suites Marriott Project Location: Amarillo, TX Prepared for: Girder Slab Technologies Contact: Daniel Fisher, Sr. January 15, 2008 Prepared by: Monica Stockmann Regional Engineer: Erika Winters-Downey
Spring Hill Suites Marriott Project Location: Amarillo, TX Prepared for: Girder Slab Technologies Contact: Daniel Fisher, Sr. January 15, 2008 Prepared by: Monica Stockmann Regional Engineer: Erika Winters-Downey
Supplemental Structural Correction Sheet Steel Brace Frame Design (2017 LABC)
 Supplemental Structural Correction Sheet Steel Brace Frame Design (2017 LABC) Plan Check Submittal Date: Plan Check / PCIS App #: Job Address: Applicant: P.C. Engineer: (print first / last name) E-mail:
Supplemental Structural Correction Sheet Steel Brace Frame Design (2017 LABC) Plan Check Submittal Date: Plan Check / PCIS App #: Job Address: Applicant: P.C. Engineer: (print first / last name) E-mail:
80 Fy (ksi)= 50 2 nd Floor = 61. Length (ft) Plan View. Penthouse
 SUBJECT: CORNER SHEET 62 of 131 Design Columns for the lightest W10's and W12's section. Columns are to be sized for two options: Option I Continuous, Option II with Splices. Then prices are to be compared
SUBJECT: CORNER SHEET 62 of 131 Design Columns for the lightest W10's and W12's section. Columns are to be sized for two options: Option I Continuous, Option II with Splices. Then prices are to be compared
Pro-Con Structural Study for Alternative Floor Systems October 27, 2004
 Ismail Al-Hadhrami Structural Option Faculty Consultant: Dr. Thomas Boothby Agricultural Hall and Annex East Lansing, MI Pro-Con Structural Study for Alternative Floor Systems October 27, 2004 Executive
Ismail Al-Hadhrami Structural Option Faculty Consultant: Dr. Thomas Boothby Agricultural Hall and Annex East Lansing, MI Pro-Con Structural Study for Alternative Floor Systems October 27, 2004 Executive
U.S. General Services Administration Progressive Collapse Design Guidelines Applied to Concrete Moment-Resisting Frame Buildings
 2004 ASCE Structures Congress Nashville, Tennessee May 18-22, 2004 U.S. General Services Administration Progressive Collapse Design Guidelines Applied to Concrete Moment-Resisting Frame Buildings By David
2004 ASCE Structures Congress Nashville, Tennessee May 18-22, 2004 U.S. General Services Administration Progressive Collapse Design Guidelines Applied to Concrete Moment-Resisting Frame Buildings By David
Structural Redesign Gravity System
 Redesign Gravity System Design Considerations A composite floor system was used for this design to maximize the efficiency of the material being used. This type of system requires less material and provides
Redesign Gravity System Design Considerations A composite floor system was used for this design to maximize the efficiency of the material being used. This type of system requires less material and provides
Structural vs Nonstructural Members. Roger LaBoube, Ph.D., P.E. Wei-Wen Yu Center for Cold-Formed Steel Structures
 Structural vs Nonstructural Members Roger LaBoube, Ph.D., P.E. Wei-Wen Yu Center for Cold-Formed Steel Structures Behavior of Cold-Formed Steel Members STEEL DESIGN SPECIFICATIONS Type of steel Specification
Structural vs Nonstructural Members Roger LaBoube, Ph.D., P.E. Wei-Wen Yu Center for Cold-Formed Steel Structures Behavior of Cold-Formed Steel Members STEEL DESIGN SPECIFICATIONS Type of steel Specification
Brent Ellmann Structural Option 200 Minuteman Park, Andover, MA Structural Consultant: Dr. Hanagan
 Executive Summary: 200 Minuteman Park currently stands as a three story commercial building. The original design was limited to three stories by an industrial zoning law in Andover, Massachusetts. If this
Executive Summary: 200 Minuteman Park currently stands as a three story commercial building. The original design was limited to three stories by an industrial zoning law in Andover, Massachusetts. If this
SECTION PLATE CONNECTED WOOD TRUSSES
 SECTION 06173 PLATE CONNECTED WOOD TRUSSES PART 1 GENERAL 1.01 SUMMARY A. Section Includes: 1. Shop fabricated wood trusses for roof and floor framing. 2. Bridging, bracing, and anchorage. B. Related Sections:
SECTION 06173 PLATE CONNECTED WOOD TRUSSES PART 1 GENERAL 1.01 SUMMARY A. Section Includes: 1. Shop fabricated wood trusses for roof and floor framing. 2. Bridging, bracing, and anchorage. B. Related Sections:
Steel Column Analysis and Design
 Architecture 324 Structures II Steel Column Analysis and Design Failure Modes Effects of Slenderness Stress Analysis of Steel Columns Capacity Analysis of Steel Columns Design of Steel Columns University
Architecture 324 Structures II Steel Column Analysis and Design Failure Modes Effects of Slenderness Stress Analysis of Steel Columns Capacity Analysis of Steel Columns Design of Steel Columns University
North Mountain IMS Medical Office Building
 North Mountain IMS Medical Office Building Phoenix, Arizona Michael Hopple Technical Assignment 2 October 29 th, 2007 AE 481W-Senior Thesis The Pennsylvania State University Faculty Adviser: Dr. Ali Memari,
North Mountain IMS Medical Office Building Phoenix, Arizona Michael Hopple Technical Assignment 2 October 29 th, 2007 AE 481W-Senior Thesis The Pennsylvania State University Faculty Adviser: Dr. Ali Memari,
INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF PLUMBING AND MECHANICAL OFFICIALS UNIFORM EVALUATION SERVICE EVALUATION CRITERIA FOR
 INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF PLUMBING AND MECHANICAL OFFICIALS UNIFORM EVALUATION SERVICE EVALUATION CRITERIA FOR HELICAL PILES FOR USE UNDER THE INTERNATIONAL RESIDENTIAL CODE EC027-2017 (Adopted November
INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF PLUMBING AND MECHANICAL OFFICIALS UNIFORM EVALUATION SERVICE EVALUATION CRITERIA FOR HELICAL PILES FOR USE UNDER THE INTERNATIONAL RESIDENTIAL CODE EC027-2017 (Adopted November
Bjorhovde, R. Stub Girder Floor Systems Structural Engineering Handbook Ed. Chen Wai-Fah Boca Raton: CRC Press LLC, 1999
 Bjorhovde, R. Stub Girder Floor Systems Structural Engineering Handbook Ed. Chen Wai-Fah Boca Raton: CRC Press LLC, 1999 Stub Girder Floor Systems Reidar Bjorhovde Department of Civil and Environmental
Bjorhovde, R. Stub Girder Floor Systems Structural Engineering Handbook Ed. Chen Wai-Fah Boca Raton: CRC Press LLC, 1999 Stub Girder Floor Systems Reidar Bjorhovde Department of Civil and Environmental
Buckling Restrained Brace
 Buckling Restrained Brace Retrofitting Reinforced Concrete structures In lack of suitable seismic code, existing reinforced concrete structures had been traditionally designed for gravity forces only.
Buckling Restrained Brace Retrofitting Reinforced Concrete structures In lack of suitable seismic code, existing reinforced concrete structures had been traditionally designed for gravity forces only.
Structural Technical Report #2 Pro/Con Study of Alternate Floor Systems
 Christopher McCune Structural Option Eight Tower Bridge Faculty Advisor: Dr. Hanagan October 31 st, 2005 Structural Technical Report #2 Pro/Con Study of Alternate Floor Systems Executive Summary This technical
Christopher McCune Structural Option Eight Tower Bridge Faculty Advisor: Dr. Hanagan October 31 st, 2005 Structural Technical Report #2 Pro/Con Study of Alternate Floor Systems Executive Summary This technical
Structural Tests and Special Inspections Form. Inspection of Fabricators (1704.2)
 Inspection of Fabricators (1704.2) Furnish inspection reports (1704.2.1) - Fabricators that have not been approved Provide a Certificate of Compliance (1704.2.2) - Approved Fabricators Steel Construction
Inspection of Fabricators (1704.2) Furnish inspection reports (1704.2.1) - Fabricators that have not been approved Provide a Certificate of Compliance (1704.2.2) - Approved Fabricators Steel Construction
PORTAL FRAMES 1.0 INTRODUCTION
 36 PORTAL FRAMES 1.0 INTRODUCTION The basic structural form of portal frames was developed during the Second World War, driven by the need to achieve the low - cost building envelope. Now they are the
36 PORTAL FRAMES 1.0 INTRODUCTION The basic structural form of portal frames was developed during the Second World War, driven by the need to achieve the low - cost building envelope. Now they are the
CE 549 Building Design Project Spring Semester 2010
 CE 549 Building Design Project Spring Semester 2010 Instructor: Farzad Naeim, Ph.D., S.E., Esq. E-Mail: naeim@usc.edu Syllabus Overview: We will design a mid-rise office building using a team-approach
CE 549 Building Design Project Spring Semester 2010 Instructor: Farzad Naeim, Ph.D., S.E., Esq. E-Mail: naeim@usc.edu Syllabus Overview: We will design a mid-rise office building using a team-approach
DESIGN CALCULATIONS INSTA-FOOTING LOAD BEARING CAPACITIES ON CONCRETE SLAB. January 14, 2017 Rev -
 DESIGN CALCULATIONS INSTA-FOOTING LOAD BEARING CAPACITIES ON CONCRETE SLAB January 14, 2017 Rev - Projection Name: Owner: Prepared by: Insta-Footing Design Calculations Insta-footing, LLC Richard Nolan,
DESIGN CALCULATIONS INSTA-FOOTING LOAD BEARING CAPACITIES ON CONCRETE SLAB January 14, 2017 Rev - Projection Name: Owner: Prepared by: Insta-Footing Design Calculations Insta-footing, LLC Richard Nolan,
MATERIALS. Moment-resisting Frames. Key Words Historical steelwork, old steelwork, retrofit, appraisal, rehabilitation, assessment,
 Properties and Assessment of Historical Structural Steelwork Author: Kevin Cowie Affiliation: Steel Construction New Zealand Inc. Date: 3 rd July 2009 Ref.: MAT1005 MATERIALS Key Words Historical steelwork,
Properties and Assessment of Historical Structural Steelwork Author: Kevin Cowie Affiliation: Steel Construction New Zealand Inc. Date: 3 rd July 2009 Ref.: MAT1005 MATERIALS Key Words Historical steelwork,
A-Series Aluminum Gantry Crane
 SPANCO PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS 1 A-Series Aluminum Gantry Crane This guide can be used to prepare a bid specification for the incorporation of an A-Series Gantry Crane into a competitive bid project or
SPANCO PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS 1 A-Series Aluminum Gantry Crane This guide can be used to prepare a bid specification for the incorporation of an A-Series Gantry Crane into a competitive bid project or
Reinforced Concrete Design. A Fundamental Approach - Fifth Edition
 CHAPTER REINFORCED CONCRETE Reinforced Concrete Design A Fundamental Approach - Fifth Edition Fifth Edition REINFORCED CONCRETE A. J. Clark School of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
CHAPTER REINFORCED CONCRETE Reinforced Concrete Design A Fundamental Approach - Fifth Edition Fifth Edition REINFORCED CONCRETE A. J. Clark School of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
90% Design Submittal Structural Calculations Parking Garage CDRL
 NORTH METRO RAIL LINE PROJECT Thornton Crossroads at 104 th Avenue Station 90% Design Submittal Structural Calculations Parking Garage CDRL 03-037.11.06 June 2, 2017 Prepared by: Regional Rail Partners
NORTH METRO RAIL LINE PROJECT Thornton Crossroads at 104 th Avenue Station 90% Design Submittal Structural Calculations Parking Garage CDRL 03-037.11.06 June 2, 2017 Prepared by: Regional Rail Partners
EVALUATION REPORT. PFC-5551 Reissued April 1, Filing Category: DESIGN Steel (038)
 ICBO Evaluation Service, Inc. 5360 WORKMAN MILL ROAD WHITTIER, CALIFORNIA 90601-2299 A subsidiary corporation of the International Conference of Building Officials EVALUATION REPORT Copyright 2001 ICBO
ICBO Evaluation Service, Inc. 5360 WORKMAN MILL ROAD WHITTIER, CALIFORNIA 90601-2299 A subsidiary corporation of the International Conference of Building Officials EVALUATION REPORT Copyright 2001 ICBO
On Cold-Formed Steel Construction. Light Gauge Steel Engineers Association Washington, D.C Toll Free (866)
 TECHNICAL NOTE On Cold-Formed Steel Construction $5.00 Light Gauge Steel Engineers Association Washington, D.C. 20005 Toll Free (866) 465-4732 www.lgsea.com DESIGN OF BY-PASS SLIP CONNECTORS IN COLD-FORMED
TECHNICAL NOTE On Cold-Formed Steel Construction $5.00 Light Gauge Steel Engineers Association Washington, D.C. 20005 Toll Free (866) 465-4732 www.lgsea.com DESIGN OF BY-PASS SLIP CONNECTORS IN COLD-FORMED
Totaling approximately 617,000
 Totaling approximately 617,000 sq. ft, the mixed-use Embassy Suites hotel development is among the largest of several newly built hotels in the business district adjoining New York s bustling Wall Street
Totaling approximately 617,000 sq. ft, the mixed-use Embassy Suites hotel development is among the largest of several newly built hotels in the business district adjoining New York s bustling Wall Street
Anchor bolts ASTM F1554, Gr. 36 Wide flange beams ASTM A992, Fy = 50 ksi Misc. structural steel ASTM A36, Fy = 36 ksi
 STRUCTURAL NOTES MATERIAL STRENGTHS Structural Steel Reinforcing Steel Concrete Masonry Structural Lumber Anchor bolts ASTM F1554, Gr. 36 Wide flange beams ASTM A992, Fy = 50 ksi Misc. structural steel
STRUCTURAL NOTES MATERIAL STRENGTHS Structural Steel Reinforcing Steel Concrete Masonry Structural Lumber Anchor bolts ASTM F1554, Gr. 36 Wide flange beams ASTM A992, Fy = 50 ksi Misc. structural steel
Tables with Allowable ASD Seismic Values For Design at R = 6.5. Special Moment Frame MF1-12
 Tables with Allowable ASD Seismic Values For Design at R = 6.5 Special Moment Frame MF1-12 Hardy Frames, Inc manufactures and markets pre-fabricated shear wall systems. We have been the innovative leader
Tables with Allowable ASD Seismic Values For Design at R = 6.5 Special Moment Frame MF1-12 Hardy Frames, Inc manufactures and markets pre-fabricated shear wall systems. We have been the innovative leader
COFS Mission. AISI Standards Hierarchy. North American Standards for Cold-Formed Steel Framing. Member versus System Design. Specification 10/21/2016
 COFS Mission North American Standards for Cold-Formed Steel Framing Roger LaBoube, Ph.D., P.E. Curators Distinguished Teaching Professor Emeritus Director, Wei-Wen Yu Center for Cold-Formed Steel Structures
COFS Mission North American Standards for Cold-Formed Steel Framing Roger LaBoube, Ph.D., P.E. Curators Distinguished Teaching Professor Emeritus Director, Wei-Wen Yu Center for Cold-Formed Steel Structures
June 1, 2012 PARTIES INTERESTED IN COLD-FORMED STEEL FRAMING MEMBERS
 June 1, 2012 TO: PARTIES INTERESTED IN COLD-FORMED STEEL FRAMING MEMBERS SUBJECT: Proposed Revisions to the Acceptance Criteria for Cold-formed Steel Framing Members, Subject AC46-0612-R1 (WM/DM) Dear
June 1, 2012 TO: PARTIES INTERESTED IN COLD-FORMED STEEL FRAMING MEMBERS SUBJECT: Proposed Revisions to the Acceptance Criteria for Cold-formed Steel Framing Members, Subject AC46-0612-R1 (WM/DM) Dear
Steel Joist Floor Systems Best Practices
 Steel Joist Floor Systems Best Practices APRIL 20, 2016 Copyright 2016 Steel Joist Institute. All Rights Reserved. Presented by: Michael A. West, P.E., F.ASCE David Samuelson, P.E. Learning Objectives
Steel Joist Floor Systems Best Practices APRIL 20, 2016 Copyright 2016 Steel Joist Institute. All Rights Reserved. Presented by: Michael A. West, P.E., F.ASCE David Samuelson, P.E. Learning Objectives
CIVIL BREADTH Exam Specifications
 NCEES Principles and Practice of Engineering Examination CIVIL BREADTH and STRUCTURAL DEPTH Exam Specifications Effective Beginning with the April 2015 Examinations The civil exam is a breadth and depth
NCEES Principles and Practice of Engineering Examination CIVIL BREADTH and STRUCTURAL DEPTH Exam Specifications Effective Beginning with the April 2015 Examinations The civil exam is a breadth and depth
The Ultimate Structural Engineering Software Package!
 RCsolver Superior Concrete Design Software by Deep Excavation LLC in association with Civil Engineering Department of A.U.TH. The Ultimate Structural Engineering Software Package! Deep Excavation LLC proudly
RCsolver Superior Concrete Design Software by Deep Excavation LLC in association with Civil Engineering Department of A.U.TH. The Ultimate Structural Engineering Software Package! Deep Excavation LLC proudly
151 First Side. Technical Assignment 2 November 16 th, William J. Buchko. AE 481w Senior Thesis The Pennsylvania State University
 November 16 th, 2007 William J. Buchko AE 481w Senior Thesis The Pennsylvania State University Thesis Advisor: Kevin Parfitt Table of Contents Executive Summary... 3 Structural System Overview Foundation...
November 16 th, 2007 William J. Buchko AE 481w Senior Thesis The Pennsylvania State University Thesis Advisor: Kevin Parfitt Table of Contents Executive Summary... 3 Structural System Overview Foundation...
The American Institute
 Cynthia J. Lanz Cynthia J. Lanz is Director of Specifications at the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) in Chicago. The American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) will welcome the new
Cynthia J. Lanz Cynthia J. Lanz is Director of Specifications at the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) in Chicago. The American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) will welcome the new
Lightweight Steel Framing. Composite DeltaStud Load Tables
 Lightweight Steel Framing Composite DeltaStud Load Tables January 2011 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction and Scope...3 Design Responsibility...3 Design Criteria and Technical Data...3 Composite Action / Materials
Lightweight Steel Framing Composite DeltaStud Load Tables January 2011 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction and Scope...3 Design Responsibility...3 Design Criteria and Technical Data...3 Composite Action / Materials
E-Series Steel Gantry Crane
 SPANCO PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS 1 E-Series Steel Gantry Crane This guide can be used to prepare a bid specification for the incorporation of an E-Series Gantry Crane into a competitive bid project or application.
SPANCO PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS 1 E-Series Steel Gantry Crane This guide can be used to prepare a bid specification for the incorporation of an E-Series Gantry Crane into a competitive bid project or application.
Statement of Special Inspections Michigan Building Code 2012 (MBC 2012)
 Gaines Charter Township 8555 Kalamazoo Ave SE Caledonia MI 49316 PH: 616 698-6640 Fax: 616 698-2490 www.gainestownship.org Building Department Statement of Special Inspections Michigan Building Code 2012
Gaines Charter Township 8555 Kalamazoo Ave SE Caledonia MI 49316 PH: 616 698-6640 Fax: 616 698-2490 www.gainestownship.org Building Department Statement of Special Inspections Michigan Building Code 2012
THE FORENSIC MEDICAL CENTER
 THE FORENSIC MEDICAL CENTER Image courtesy of Gaudreau, Inc. TECHNICAL REPORT #2 OCTOBER 26, 2007 KEENAN YOHE STRUCTURAL OPTION DR. MEMARI FACULTY ADVISOR EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Image courtesy of Gaudreau,
THE FORENSIC MEDICAL CENTER Image courtesy of Gaudreau, Inc. TECHNICAL REPORT #2 OCTOBER 26, 2007 KEENAN YOHE STRUCTURAL OPTION DR. MEMARI FACULTY ADVISOR EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Image courtesy of Gaudreau,
CE 549 Building Design Project Spring Semester 2013
 CE 549 Building Design Project Spring Semester 2013 Instructor: Farzad Naeim, Ph.D., S.E., Esq. E-Mail: naeim@usc.edu Syllabus Overview: We will design a mid-rise office building using a team-approach
CE 549 Building Design Project Spring Semester 2013 Instructor: Farzad Naeim, Ph.D., S.E., Esq. E-Mail: naeim@usc.edu Syllabus Overview: We will design a mid-rise office building using a team-approach
Interpretation of SECTION 12 DESIGN AND DETAILING FOR EARTHQUAKE LOADS IS
 Interpretation of SECTION 12 DESIGN AND DETAILING FOR EARTHQUAKE LOADS 12.1 General IS 800-2007 Steel frames shall be so designed and detailed as to give them adequate strength, stability and ductility
Interpretation of SECTION 12 DESIGN AND DETAILING FOR EARTHQUAKE LOADS 12.1 General IS 800-2007 Steel frames shall be so designed and detailed as to give them adequate strength, stability and ductility
SPECIFICATIONS FOR THE CONSTRUCTION OF NEW PASSENGER EQUIPMENT CARS PREFACE
 SPECIFICATIONS FOR THE CONSTRUCTION OF NEW PASSENGER EQUIPMENT CARS Standard ADOPTED 1939; ADVANCED TO STANDARD, 1945. PREFACE The specifications have been prepared on the basis that they will be used
SPECIFICATIONS FOR THE CONSTRUCTION OF NEW PASSENGER EQUIPMENT CARS Standard ADOPTED 1939; ADVANCED TO STANDARD, 1945. PREFACE The specifications have been prepared on the basis that they will be used
THE PLAZA AT PPL CENTER HAMILTON BOULEVARD AT 9 TH STREET - ALLENTOWN, PA
 THE PLAZA AT PPL CENTER HAMILTON BOULEVARD AT 9 TH STREET - ALLENTOWN, PA Amy Graver, Structural Option - Dr. Hanagan, Advisor 12.16.2002 THESIS PROPOSAL Executive Summary Architecture The Plaza at PPL
THE PLAZA AT PPL CENTER HAMILTON BOULEVARD AT 9 TH STREET - ALLENTOWN, PA Amy Graver, Structural Option - Dr. Hanagan, Advisor 12.16.2002 THESIS PROPOSAL Executive Summary Architecture The Plaza at PPL
REPORT HOLDER: ispan SYSTEMS LP 70 BRENTWOOD DRIVE PRINCETON, ONTARIO N0J 1V0 CANADA EVALUATION SUBJECT:
 0 Most Widely Accepted and Trusted ICC-ES Evaluation Report ICC-ES 000 (800) 2-6587 (562) 699-05 www.icc-es.org ESR-787 Issued 07/2017 This report is subject to renewal 07/2018. DIVISION: 05 00 00 METALS
0 Most Widely Accepted and Trusted ICC-ES Evaluation Report ICC-ES 000 (800) 2-6587 (562) 699-05 www.icc-es.org ESR-787 Issued 07/2017 This report is subject to renewal 07/2018. DIVISION: 05 00 00 METALS
Great Lakes District
 Great Lakes District Gregory D. Carnaghi, PE Senior Structural Engineer Detroit, Michigan 586-782-9293 gcarnaghi@uis-usa.com EDUCATION: Lawrence Technological University Southfield, Michigan Bachelors
Great Lakes District Gregory D. Carnaghi, PE Senior Structural Engineer Detroit, Michigan 586-782-9293 gcarnaghi@uis-usa.com EDUCATION: Lawrence Technological University Southfield, Michigan Bachelors
Project Address: Name of Person Completing Form:
 Statement of Inspections This form is provided as a way to list aspects of the project that require special inspection and testing in accordance with IBC Sections 107.1, 1704, and 1705 and define duties
Statement of Inspections This form is provided as a way to list aspects of the project that require special inspection and testing in accordance with IBC Sections 107.1, 1704, and 1705 and define duties
Overview of Presentation. SCBFs are Conceptually Truss Structures
 Ultimate Strength and Inelastic Behavior of Braced Frame Gusset Plate Connections Charles W. Roeder University of Washington Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Seattle, WA 98195 Structural
Ultimate Strength and Inelastic Behavior of Braced Frame Gusset Plate Connections Charles W. Roeder University of Washington Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Seattle, WA 98195 Structural
Bijan Khaleghi, Ph, D. P.E., S.E.
 0 Submission date: July, 0 Word count: 0 Author Name: Bijan Khaleghi Affiliations: Washington State D.O.T. Address: Linderson Way SW, Tumwater WA 0 INTEGRAL BENT CAP FOR CONTINUOUS PRECAST PRESTRESSED
0 Submission date: July, 0 Word count: 0 Author Name: Bijan Khaleghi Affiliations: Washington State D.O.T. Address: Linderson Way SW, Tumwater WA 0 INTEGRAL BENT CAP FOR CONTINUOUS PRECAST PRESTRESSED
One-Way Wide Module Joist Concrete Floor Design
 One-Way Wide Module Joist Concrete Floor Design A 1 3 4 30'-0" 30'-0" 30'-0" 3' B 3' C 3' D 3' E 4" 4" (typ.) 3' F 0" 0" (typ.) Figure 1 One-Way Wide Module Joist Concrete Floor Framing System 1 Overview
One-Way Wide Module Joist Concrete Floor Design A 1 3 4 30'-0" 30'-0" 30'-0" 3' B 3' C 3' D 3' E 4" 4" (typ.) 3' F 0" 0" (typ.) Figure 1 One-Way Wide Module Joist Concrete Floor Framing System 1 Overview
Structural Design of Dam Sluice Gate Walkway Slabs: Retrofit and Replacement Options
 Structural Design of Dam Sluice Gate Walkway Slabs: Retrofit and Replacement Options A local utility company issued a Request for Proposal to our university s capstone design class for structural improvements
Structural Design of Dam Sluice Gate Walkway Slabs: Retrofit and Replacement Options A local utility company issued a Request for Proposal to our university s capstone design class for structural improvements
This guide can be used to prepare a specification for incorporating free standing jib cranes into a competitively bid construction project.
 SECTION 14651 FREE STANDING JIB CRANE ***** Gorbel, Inc. manufacturers a broad range of material handling cranes including monorail, bridge, gantry, and jib cranes. Numerous work station and industrial
SECTION 14651 FREE STANDING JIB CRANE ***** Gorbel, Inc. manufacturers a broad range of material handling cranes including monorail, bridge, gantry, and jib cranes. Numerous work station and industrial
STANDARD SPECIFICATIONS
 American National Standard SJI-K 1.1 STANDARD SPECIFICATIONS FOR OPEN WEB STEEL JOISTS, K-SERIES Adopted by the Steel Joist Institute November 4, 1985 Revised to November 10, 2003 - Effective March 01,
American National Standard SJI-K 1.1 STANDARD SPECIFICATIONS FOR OPEN WEB STEEL JOISTS, K-SERIES Adopted by the Steel Joist Institute November 4, 1985 Revised to November 10, 2003 - Effective March 01,
GUIDE SPECIFICATIONS FOR SEISMIC DESIGN OF STEEL BRIDGES
 GUIDE FOR SEISMIC DESIGN OF STEEL BRIDGES First Edition State of California Department of Transportation December 2001 TABLE OF CONTENTS PREFACE i DEFINITIONS iv NOTATION vii 1. INTRODUCTION 1 1.1. Scope
GUIDE FOR SEISMIC DESIGN OF STEEL BRIDGES First Edition State of California Department of Transportation December 2001 TABLE OF CONTENTS PREFACE i DEFINITIONS iv NOTATION vii 1. INTRODUCTION 1 1.1. Scope
ACCEPTANCE CRITERIA FOR HELICAL PILE SYSTEMS AND DEVICES PREFACE
 www.icc-es.org (800) 423-6587 (562) 699-0543 A Subsidiary of the International Code Council ACCEPTANCE CRITERIA FOR HELICAL PILE SYSTEMS AND DEVICES AC358 Approved June 2012 Compliance date December 1,
www.icc-es.org (800) 423-6587 (562) 699-0543 A Subsidiary of the International Code Council ACCEPTANCE CRITERIA FOR HELICAL PILE SYSTEMS AND DEVICES AC358 Approved June 2012 Compliance date December 1,
Gusset Plate Stability Using Variable Stress Trajectories
 Gusset Plate Stability Using Variable Stress Trajectories Bo Dowswell, P.E., Ph.D. ARC International, 300 Cahaba Park Circle, Suite 116, Birmingham, AL 35242, USA bo@arcstructural.com Abstract Gusset plates
Gusset Plate Stability Using Variable Stress Trajectories Bo Dowswell, P.E., Ph.D. ARC International, 300 Cahaba Park Circle, Suite 116, Birmingham, AL 35242, USA bo@arcstructural.com Abstract Gusset plates
Council on Tall Buildings
 Structure Design of Sino Steel (Tianjin) International Plaza Xueyi Fu, Group Chief Engineer, China Construction Design International 1 1 Brief of Project 2 Location: Tianjin Xiangluowan Business District
Structure Design of Sino Steel (Tianjin) International Plaza Xueyi Fu, Group Chief Engineer, China Construction Design International 1 1 Brief of Project 2 Location: Tianjin Xiangluowan Business District
CHAPTER 22 STEEL SECTION 2204 SECTION 2201 CONNECTIONS GENERAL
 CHAPTER 22 STEEL SECTION 2201 GENERAL 2201.1 Scope. The provisions of this chapter govern the quality, design, fabrication and erection of steel used structurally in buildings or structures. Exception:
CHAPTER 22 STEEL SECTION 2201 GENERAL 2201.1 Scope. The provisions of this chapter govern the quality, design, fabrication and erection of steel used structurally in buildings or structures. Exception:
June 19, 2012 PARTIES INTERESTED IN SCREW FOUNDATION SYSTEMS
 June 19, 2012 TO: PARTIES INTERESTED IN SCREW FOUNDATION SYSTEMS SUBJECT: Acceptance Criteria for Screw Foundation Systems (SFSs), Subject AC443-0612-R1 (DZ/KS)] Dear Colleague: We are enclosing the new
June 19, 2012 TO: PARTIES INTERESTED IN SCREW FOUNDATION SYSTEMS SUBJECT: Acceptance Criteria for Screw Foundation Systems (SFSs), Subject AC443-0612-R1 (DZ/KS)] Dear Colleague: We are enclosing the new
CBC SECTION/TABLE NUMBER NEW -CHANGE COMMENTARY. X Flexible and Rigid definitions removed and found in ASCE 7-10
 2016 Chapter 16 Structural Design- Changes include new plan content requirements for Photovoltaic Panel Systems as well as guidance on how to determine the dead and live loads. For mid- and high-rise designs
2016 Chapter 16 Structural Design- Changes include new plan content requirements for Photovoltaic Panel Systems as well as guidance on how to determine the dead and live loads. For mid- and high-rise designs
SEISMIC APPLICATIONS OF HOLLOW STRUCTURAL SECTIONS (HSS) IN MOMENT RESISTING FRAMES
 SEISMIC APPLICATIONS OF HOLLOW STRUCTURAL SECTIONS (HSS) IN MOMENT RESISTING FRAMES By Emily Guglielmo, SE, Martin/Martin, STI Technical Committee Member Use of Hollow Structural Section (HSS) members
SEISMIC APPLICATIONS OF HOLLOW STRUCTURAL SECTIONS (HSS) IN MOMENT RESISTING FRAMES By Emily Guglielmo, SE, Martin/Martin, STI Technical Committee Member Use of Hollow Structural Section (HSS) members
Types Of Roofs - Vault
 1 Types Of Roofs - Vault Implementation Of the Concrete On Vault Implementation Of Vault Earthquake Damage 2 Types Of Roofs - Joist And Block 3 Types Of Coverage Roofs-Composite 4 5 Building Structure
1 Types Of Roofs - Vault Implementation Of the Concrete On Vault Implementation Of Vault Earthquake Damage 2 Types Of Roofs - Joist And Block 3 Types Of Coverage Roofs-Composite 4 5 Building Structure
Top Things To Know About HSS Connections
 Top Things To Know About HSS Connections SEAoPA Philadelphia, PA Wednesday, December 2, 2015 Brad Fletcher, S.E. Atlas Tube Market Leader Largest size range in North America 1 16 square, up to 5/8 wall
Top Things To Know About HSS Connections SEAoPA Philadelphia, PA Wednesday, December 2, 2015 Brad Fletcher, S.E. Atlas Tube Market Leader Largest size range in North America 1 16 square, up to 5/8 wall
Seismic Behaviour of RC Shear Walls
 Ductile Detailing of RC Structures :: IS:13920-1993 1993 Short Course on Seismic Design of RC Structures Durgesh C. Rai Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Kanpur The material contained in this lecture
Ductile Detailing of RC Structures :: IS:13920-1993 1993 Short Course on Seismic Design of RC Structures Durgesh C. Rai Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Kanpur The material contained in this lecture
DESIGN CRITERIA. Allowable Stress Design (ASD) AISC-1999.
 DESIGN CRITERIA 1. INTRODUCTION This appendix summarizes the codes, standards, criteria, and practices that are generally used in the design and construction structural engineering system for the Sarker
DESIGN CRITERIA 1. INTRODUCTION This appendix summarizes the codes, standards, criteria, and practices that are generally used in the design and construction structural engineering system for the Sarker
Originally Issued: 09/28/2017 Valid Through: 09/30/2018
 SIDEPLATE SYSTEMS, INC. SidePlate Steel Frame Connection Technology: Field-Welded and Field-Bolted Connections CSI Sections: 05 12 00 Structural Steel Framing 1.0 RECOGNITION SidePlate Steel Frame Connection
SIDEPLATE SYSTEMS, INC. SidePlate Steel Frame Connection Technology: Field-Welded and Field-Bolted Connections CSI Sections: 05 12 00 Structural Steel Framing 1.0 RECOGNITION SidePlate Steel Frame Connection
Product Designation As specified in the AISI standard for cold formed steel framing General provisions A5.2.
 Steel Structural Systems (TRI-S) was founded in 2004 to meet the service needs of a growing industry. The company is a world-class manufacturer of light gauge steel framing components for the commercial
Steel Structural Systems (TRI-S) was founded in 2004 to meet the service needs of a growing industry. The company is a world-class manufacturer of light gauge steel framing components for the commercial
AIA St. Louis January 4 th, 2017 Phillip Shinn, PE Jacobs Engineering Washington University in St. Louis, Sam Fox School of Design and Visual Arts
 AIA St. Louis January 4 th, 2017 Phillip Shinn, PE Jacobs Engineering Washington University in St. Louis, Sam Fox School of Design and Visual Arts Owners are NOT Architects (but they ARE the Owners) Steel
AIA St. Louis January 4 th, 2017 Phillip Shinn, PE Jacobs Engineering Washington University in St. Louis, Sam Fox School of Design and Visual Arts Owners are NOT Architects (but they ARE the Owners) Steel
Supplement No. 1 to AISC Prequalified Connections for Special and Intermediate Steel Moment Frames for Seismic Applications
 1 1 DRAFT AISC 358-16s1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 Supplement No. 1 to AISC 358-16 Prequalified Connections for Special and Intermediate
1 1 DRAFT AISC 358-16s1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 Supplement No. 1 to AISC 358-16 Prequalified Connections for Special and Intermediate
DIVISION: EARTHWORK SECTION: BORED PILES REPORT HOLDER: GEOTECH ENTERPRISES, INC.
 0 Most Widely Accepted and Trusted ICC ES Report ICC ES 000 (800) 423 6587 (562) 699 0543 www.icc es.org ESR 3623 Reissued 04/2017 This report is subject to renewal 04/2018. DIVISION: 31 00 00 EARTHWORK
0 Most Widely Accepted and Trusted ICC ES Report ICC ES 000 (800) 423 6587 (562) 699 0543 www.icc es.org ESR 3623 Reissued 04/2017 This report is subject to renewal 04/2018. DIVISION: 31 00 00 EARTHWORK
22. DESIGN OF STEEL BRACED FRAMES Eccentrically Braced Steel Frames
 22. DESIGN OF STEEL BRACED FRAMES 22.1 Eccentrically Braced Steel Frames Objective is to dissipate energy in the shear or moment links and to protect the remainder of the frame from inelastic action, including
22. DESIGN OF STEEL BRACED FRAMES 22.1 Eccentrically Braced Steel Frames Objective is to dissipate energy in the shear or moment links and to protect the remainder of the frame from inelastic action, including
SECTION VIBRATION CONTROLS FOR HVAC PIPING AND EQUIPMENT
 SECTION 230548 - PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 SUMMARY A. This Section includes the following: 1. Elastomeric Isolation pads. 2. Elastomeric Isolation mounts. 3. [Freestanding] [Restrained] [Freestanding and restrained]
SECTION 230548 - PART 1 - GENERAL 1.1 SUMMARY A. This Section includes the following: 1. Elastomeric Isolation pads. 2. Elastomeric Isolation mounts. 3. [Freestanding] [Restrained] [Freestanding and restrained]
SJI Code of Standard Practice
 Standard Practice CODE OF STANDARD PRACTICE FOR STEEL JOISTS AND JOIST GIRDERS SECTION 1 GENERAL 1.1 SCOPE Adopted by the Steel Joist Institute April 7, 1931 Revised to May 18, 2010 - Effective December
Standard Practice CODE OF STANDARD PRACTICE FOR STEEL JOISTS AND JOIST GIRDERS SECTION 1 GENERAL 1.1 SCOPE Adopted by the Steel Joist Institute April 7, 1931 Revised to May 18, 2010 - Effective December
one structural behavior, systems and design Course Description Course Description Syllabus & Student Understandings statics mechanics of materials
 ARCHITECTURAL STRUCTURES: FORM, BEHAVIOR, AND DESIGN DR. ANNE NICHOLS SUMMER 2014 lecture one Syllabus & Student Understandings structural behavior, systems and design Introduction 1 Architectural Structures
ARCHITECTURAL STRUCTURES: FORM, BEHAVIOR, AND DESIGN DR. ANNE NICHOLS SUMMER 2014 lecture one Syllabus & Student Understandings structural behavior, systems and design Introduction 1 Architectural Structures
P. Armaos & D.M. Thomson
 Seismic strengthening of commercial warehouse with slender precast concrete panels, utilizing knowledge from the observed performance of similar buildings during the 2010/2011 Christchurch earthquakes:
Seismic strengthening of commercial warehouse with slender precast concrete panels, utilizing knowledge from the observed performance of similar buildings during the 2010/2011 Christchurch earthquakes:
Analysis and Design of One-way Slab System (Part-I)
 Lecture-02 Analysis and Design of One-way Slab System (Part-I) By: Prof Dr. Qaisar Ali Civil Engineering Department UET Peshawar www.drqaisarali.com 1 Topics Addressed Concrete Floor Systems Analysis and
Lecture-02 Analysis and Design of One-way Slab System (Part-I) By: Prof Dr. Qaisar Ali Civil Engineering Department UET Peshawar www.drqaisarali.com 1 Topics Addressed Concrete Floor Systems Analysis and
CE 3150 Reinforced Concrete Design Design Project
 Problem Description For this design project you will work in your project groups to complete a partial design of an office building. Specifically, you will design and fully detail three components: 1.
Problem Description For this design project you will work in your project groups to complete a partial design of an office building. Specifically, you will design and fully detail three components: 1.
STRUCTURAL-STEEL DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION
 9 Roger L. Brockenbrough R. L. Brockenbrough & Associates, Inc. Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania STRUCTURAL-STEEL DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION T he many desirable characteristics of structural steels has led to their
9 Roger L. Brockenbrough R. L. Brockenbrough & Associates, Inc. Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania STRUCTURAL-STEEL DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION T he many desirable characteristics of structural steels has led to their
Steel Seismic Force Resisting Systems
 Steel Seismic Force Resisting Systems Ontario Building Officials Association 2007 Annual Meeting and Training Sessions Fairmont Chateau Laurier, Ottawa, ON September 24, 2007 David H. MacKinnon, M.A.Sc.,
Steel Seismic Force Resisting Systems Ontario Building Officials Association 2007 Annual Meeting and Training Sessions Fairmont Chateau Laurier, Ottawa, ON September 24, 2007 David H. MacKinnon, M.A.Sc.,
Structural Engineering
 Structural Engineering 4 4.0 TABLE OF CONTENTS 4.1 General Approach 115 Submission Requirements 4.2 Codes and Standards 116 Structural Design of New Buildings 116 Use of Recycled Materials 4.3 Structural
Structural Engineering 4 4.0 TABLE OF CONTENTS 4.1 General Approach 115 Submission Requirements 4.2 Codes and Standards 116 Structural Design of New Buildings 116 Use of Recycled Materials 4.3 Structural
Mark L. Reno, P.E. September 11, 2015
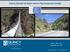 Ogden Ogden Siphon Canyon Pipe Siphon Suspension Structural Assessment Bridge Mark L. Reno, P.E. September 11, 2015 Seismic Retrofit of Designed in 1936 by U.S. Bureau of Reclamation 1,044 feet of 31.25
Ogden Ogden Siphon Canyon Pipe Siphon Suspension Structural Assessment Bridge Mark L. Reno, P.E. September 11, 2015 Seismic Retrofit of Designed in 1936 by U.S. Bureau of Reclamation 1,044 feet of 31.25
LIFE SCIENCES BUILDING STRUCTURAL CONCEPTS AND EXISTING CONDITIONS
 Structural Technical Report 1 LIFE SCIENCES BUILDING STRUCTURAL CONCEPTS AND EXISTING CONDITIONS Prepared for: Dr. Aly M. Said Dr. Thomas Boothby Professor Kevin Parfitt Dr. Charles D. Cox Prepared by:
Structural Technical Report 1 LIFE SCIENCES BUILDING STRUCTURAL CONCEPTS AND EXISTING CONDITIONS Prepared for: Dr. Aly M. Said Dr. Thomas Boothby Professor Kevin Parfitt Dr. Charles D. Cox Prepared by:
DIVISION: METALS SECTION: STEEL DECKING REPORT HOLDER: EPIC METALS CORPORATION 11 TALBOT AVENUE RANKIN, PENNSYLVANIA 15104
 0 Most Widely Accepted and Trusted ICC ES Evaluation Report ICC ES 000 (800) 423 6587 (562) 699 0543 www.icc es.org ESR 2047 Reissued 07/207 This report is subject to renewal 07/209. DIVISION: 05 00 00
0 Most Widely Accepted and Trusted ICC ES Evaluation Report ICC ES 000 (800) 423 6587 (562) 699 0543 www.icc es.org ESR 2047 Reissued 07/207 This report is subject to renewal 07/209. DIVISION: 05 00 00
REPORT HOLDER: MITEK USA, INC. (FORMERLY USP STRUCTURAL CONNECTORS) SOUTHCROSS DRIVE, SUITE 200 BURNSVILLE, MINNESOTA EVALUATION SUBJECT:
 0 Most Widely Accepted and Trusted ICC ES Evaluation Report ICC ES 000 (800) 43 6587 (56) 699 0543 www.icc es.org ESR 3754 Reissued 09/07 This report is subject to renewal 09/09. DIVISION: 03 00 00 CONCRETE
0 Most Widely Accepted and Trusted ICC ES Evaluation Report ICC ES 000 (800) 43 6587 (56) 699 0543 www.icc es.org ESR 3754 Reissued 09/07 This report is subject to renewal 09/09. DIVISION: 03 00 00 CONCRETE
Structural Inspection
 General: Background: An inspection and structural analysis have been performed for the purpose of evaluating the buildings structural systems and components. A full set of structural drawings was utilized
General: Background: An inspection and structural analysis have been performed for the purpose of evaluating the buildings structural systems and components. A full set of structural drawings was utilized
A Guide for the Interpretation of Structural Design Options for Residential Concrete Structures
 CFA Technical Note: 008-2010 A Guide for the Interpretation of Structural Design Options for Residential Concrete Structures CFA Technical This CFA Technical Note is intended to serve as a guide to assist
CFA Technical Note: 008-2010 A Guide for the Interpretation of Structural Design Options for Residential Concrete Structures CFA Technical This CFA Technical Note is intended to serve as a guide to assist
SECTION SEISMIC RESTRAINT REQUIREMENTS FOR NON-STRUCTURAL COMPONENTS REVISED PART 1 GENERAL 1.1 DESCRIPTION:
 SECTION 13 05 41 SEISMIC RESTRAINT REQUIREMENTS FOR NON-STRUCTURAL COMPONENTS REVISED 1-25-13 PART 1 GENERAL 1.1 DESCRIPTION: A. Provide seismic restraint in accordance with the requirements of this section
SECTION 13 05 41 SEISMIC RESTRAINT REQUIREMENTS FOR NON-STRUCTURAL COMPONENTS REVISED 1-25-13 PART 1 GENERAL 1.1 DESCRIPTION: A. Provide seismic restraint in accordance with the requirements of this section
UNIFIED FACILITIES GUIDE SPECIFICATIONS
 USACE / NAVFAC / AFCEC / NASA UFGS-05 21 00 (May 2015) --------------------------- Preparing Activity: USACE Superseding UFGS-05 21 13 (August 2009) UFGS-05 21 16 (August 2009) UFGS-05 21 19 (July 2007)
USACE / NAVFAC / AFCEC / NASA UFGS-05 21 00 (May 2015) --------------------------- Preparing Activity: USACE Superseding UFGS-05 21 13 (August 2009) UFGS-05 21 16 (August 2009) UFGS-05 21 19 (July 2007)
