Contrasting physical-biological interactions in the central gyres and ocean margins
|
|
|
- Carmel Sullivan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Contrasting physical-biological interactions in the central gyres and ocean margins Anand Gnanadesikan NOAA/Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Lab AOSC Seminar University of Maryland Nov. 11, 2010
2 Key points Well ventilated ocean gyres and poorly ventilated ocean margins have Different physics to leading order. Different biogeochemical sensitivity to changes in circulation. Different physical impacts from changes in biogeochemistry/ocean color.
3 Motivation: What do we mean by ventilated? Well ventilated waters- low age, high CFC and oxygen Poorly ventilated- high age, low CFC and oxygen
4 Consider a spinning earth If you look down on a column of water at the north pole, it will seem to spin counterclockwise. Animation courtesy of NASA But a column of water at the equator won t seem to spin at all, it will just move eastward. And a column of water at the south pole will spin clockwise.
5 How can this happen? Stretching or squashing Stretching a column pulls fluid in towards the center. Coriolis force results in torque on column in same direction as rotation. Squashing a column pushes fluid out from center. Coriolis force causes column to spin in opposite direction
6 Implication Change in spin given by torque Change in height given by inward flow So a stretching can balance a poleward flow and a squashing an equatorward flow
7 Potential thickness In absence of frictional, bottom torques, this quantity is conserved! Alternatively- flows that do not conserve this quantity are unsteady.
8 Boundaries and potential thickness N W L E H Eq Radius of deformation Planetary waves homogenize pressure (layer thickness). This creates gradients in potential thickness H/f!
9 Observed potential thickness at 300m
10 Summary: Part 1 Well ventilated ocean has potential thickness contours that connect to outcrop regions directly, are relatively high PT. Isopycnal dynamics dominate. Poorly ventilated ocean has potential thickness contours that connect with boundaries, are relatively low PT. Diapycnal processes can be more important. Oxygen minimum zones are dynamically controlled! (Physics shapes chemistry)
11 Part 2-Anoxia and global warming Higher T gives lower saturation Higher stratification means lower circulation, flux. Temperature should win.
12 Recent example We find that climate feedbacks within the Earth system amplify the strength and duration of global warming, ocean heating and oxygen depletion. Decreased oxygen solubility from surface-layer warming accounts for most of the enhanced oxygen depletion in the upper 500m of the ocean. Possible weakening of ocean overturning and convection lead to further oxygen depletion, also in the deep ocean. We conclude that substantial reductions in fossil-fuel use over the next fewgenerations are needed if extensive ocean oxygen depletion for thousands of years is to be avoided. Shaffer et al., Nature Geosciences, 2009
13 GFDL s new Ocean BGC model (TOPAZ) Deposition (N, Fe) Runoff (CaCO3,N) Nutrients Remineralization/ dissolution Phytoplankton Dissolved components Oxygen DOP,DON CaCO3 Burial (CaCO3, Fe) NO3 NH4 Si Small plankton Zooplankton (parameterized) PO4 Fe Large Plankton Sinking particles Denitrification Remineralization/ dissolution N fixation Dunne et al., in prep. Diazotrophs Oxygen DOP, DON (POM, CaCO3, Opal, Fe)
14 Some key features of TOPAZ Grazing is parameterized so as to produce scaling between large and small plankton (Dunne et al., 2005). Remineralization slows down when oxygen is low. N:P ratios vary according to demand for various cellular components (Klausmeier et al., 2004).
15 Model solution
16 Oxygen change at 300m Subtropical gyres and margins show opposite response!
17 Ideal age simulations in previous coupled model Ideal age: Set to zero in top layer at each time step. Age one year/year below that level. Run in mainstream coupled models at GFDL for over a decade.
18 Pattern of oxygen change and age Gnanadesikan, Dunne, Rykaczewksi and John in prep.
19 Not just a feature seen in this model! Similar features also seen in NCAR model Gnanadesikan, Russell and Zeng, 2007
20 Why the change? Potential thickness explains part Easier for surface waters to enter oxygen minimum zones.
21 ..and slowdown of deep overturning explains the other Less old water coming up from below
22 Result Easier exchange with gyre waters Margins get younger! Key point: When many sources contribute to a watermass, changes in the mix matter! Less upwelling of old waters from below
23 What about remineralization? Smaller sink at depth opposes oxygen change.
24 Remineralization fails to explain change at 300m Some inverse correlation (coefficient =-0.21)
25 Summary- Part 2 In well ventilated regions, higher temperature under global warming leads to lower oxygen content. In poorly ventilated regions, less upwelling under global warming can lead to higher oxygen content. OMZs don t necessarily become more intense under global warming! (Physics shapes chemistry)
26 Part 3- Ocean water clarity and climate 10m e-folding ~40-50m e-folding Morel (1988) extinction coefficients How big is this effect?
27 Ocean color and ENSO Timmermann and Jin (2002)- ocean color leads to weaker ENSO (biothermostat hypothesis) Marzeion et al. (2005) interactive ocean color leads to stronger ENSO. Lengaigne et al. (2007) finds same thing as Marzeion but concludes that it is shift of mean state that matters. In GFDL ESM2.1, interactive ocean color leaves ENSO spectrum unchanged.
28 Our strategy Use a chlorophyll-dependent shortwave absorption parameterization within a circulation model. Set chlorophyll to zero (should always cool surface, warm deep locally) Evaluate change in ocean-only models forced with observed atmosphere Evaluate change in fully coupled climate model (CM2.1 Atmosphere, isopycnal ocean) Look at sensitivity to regional changes in color.
29 Ocean only vs. coupled Coupled (CM2.2) 100 year mean SST Coupling enhances off-equatorial response. Anderson et al, GRL, L11609, 2007
30 Gyres and margins show opposite response! In gyres Less mixing Lower chlorophyll Lower stratification Negative feedback! In margins Less mixing Lower chlorophyll More stratification Positive feedback!
31 Ocean color can alter ENSO Clear gyre= Weaker ENSO Clear margin= stronger ENSO
32 Initial hypothesis- thermocline depth BlueMargin (strong ENSO) and BluePGyre (weak ENSO) both have deeper thermocline!
33 Brief review of ENSO physics
34 Wind stress/speed changes Clear Gyre Clear Margin SON DJF Response of wind stress to changes in equatorial SST is stronger over Central Pacific in Clear Margin (BlueMargin) case.
35 Why the difference?- A hypothesis Weaker Walker cell when margin is clear Tighter, more intense Hadley cell when gyres are clear
36 When different winds are run over the same ocean Clear margin- 1C SST gives 1.2C response at depth (positive feedback!) Clear Gyre-1C SST change gives 0.7 C response at depth (damped). Anderson, Gnanadesikan and Wittenberg, 2009
37 Other consequences of Hadley cell change Both SST and atmospheric response project onto cyclogenesis
38 What s the impact on cyclogenesis? Away from equator SSTs go down Shear goes up RH goes down Sinking goes up-> Vorticity goes down Genesis Potential Index (Camargo, Emanuel and Sobel, 2007)
39 Downscaling techniques simulate aspects of observed distribution Right-hand plot shows statistical-dynamical downscale from Kerry Emanuel
40 Cyclogenesis change Gnanadesikan, Emanuel, Vecchi, Anderson and Hallberg, GRL, 2010 Presence of ocean color in gyres makes huge difference in cyclogenesis!
41 Summary-Part 2 In well ventilated regions additional penetration of heat results in surface cooling leading to strengthened Hadley cell, weaker ENSO, strong decrease in tropical cyclones. In poorly ventilated regions additional penetration of heat results in surface warming leading to weaker Walker cell, stronger ENSO/ moderate increase in tropical cyclones. Ocean water clarity plays an important role in climate! (Chemistry shapes physics!)
42 Key points Well ventilated and poorly ventilated regimes have Different physics (isopycnal/advective vs. diapycnal/diffusive) Different biogeochemical sensitivity to changes in circulation. Global warming gives lower oxygen vs. higher oxygen. Different physical sensitivity to changes in water clarity. More clarity gives surface cooling, lower TC activity,strong Hadley cell vs. surface warming,higher TC activity, weaker Walker cell.
43 Open questions How much deep water actually upwells in the shadow zones? (He-3, radiocarbon) Sensitivity to parameterized mixing opposite in margins vs. gyres- why? What s the impact of eddies on the shadow zone (do they break through the front)? How much anoxia is there in the open ocean? How strong are feedbacks between remineralization and oxygen in/above margins?
44 References Ventilation and Age Gnanadesikan, Russell and Zeng, Ocean Science, Anoxia and global warming Gnanadesikan, Rykaczewski, Dunne and John, in prep. Water clarity Anderson, Gnanadesikan, Hallberg, Dunne and Samuels., GRL, 2007 Anderson, Gnanadesikan and Wittenberg, Ocean Science, 2009 Gnanadesikan and Anderson, J. Phys. Oceanogr., Gnanadesikan, Emanuel, Vecchi, Anderson and Hallberg, GRL,2010.
45 Mixing sensitivity
Ocean Production and CO 2 uptake
 Ocean Production and CO 2 uptake Fig. 6.6 Recall: Current ocean is gaining Carbon.. OCEAN Reservoir size: 38000 Flux in: 90 Flux out: 88+0.2=88.2 90-88.2 = 1.8 Pg/yr OCEAN is gaining 1.8 Pg/yr Sum of the
Ocean Production and CO 2 uptake Fig. 6.6 Recall: Current ocean is gaining Carbon.. OCEAN Reservoir size: 38000 Flux in: 90 Flux out: 88+0.2=88.2 90-88.2 = 1.8 Pg/yr OCEAN is gaining 1.8 Pg/yr Sum of the
Oceans OUTLINE. Reading: White, Chapter 15 Today Finish estuaries and particles, then: 1. The oceans: currents, stratification and chemistry
 Oceans OUTLINE Reading: White, Chapter 15 Today Finish estuaries and particles, then: 1. The oceans: currents, stratification and chemistry Next Time Salinity Exercise bring something to calculate with
Oceans OUTLINE Reading: White, Chapter 15 Today Finish estuaries and particles, then: 1. The oceans: currents, stratification and chemistry Next Time Salinity Exercise bring something to calculate with
The Carbon cycle. Atmosphere, terrestrial biosphere and ocean are constantly exchanging carbon
 The Carbon cycle Atmosphere, terrestrial biosphere and ocean are constantly exchanging carbon The oceans store much more carbon than the atmosphere and the terrestrial biosphere The oceans essentially
The Carbon cycle Atmosphere, terrestrial biosphere and ocean are constantly exchanging carbon The oceans store much more carbon than the atmosphere and the terrestrial biosphere The oceans essentially
Part 3. Oceanic Carbon and Nutrient Cycling
 OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems (11.03.11) (Schlesinger: Chapter 9) Part 3. Oceanic Carbon and Nutrient Cycling Lecture Outline 1. Models of Carbon in the Ocean 2. Nutrient Cycling in the Ocean Atmospheric-Ocean
OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems (11.03.11) (Schlesinger: Chapter 9) Part 3. Oceanic Carbon and Nutrient Cycling Lecture Outline 1. Models of Carbon in the Ocean 2. Nutrient Cycling in the Ocean Atmospheric-Ocean
Production vs Biomass
 Patterns of Productivity OCN 201 Biology Lecture 5 Production vs Biomass Biomass = amount of carbon per unit area (= standing stock * C/cell) Units (e.g.): g C m -2 Primary Production = amount of carbon
Patterns of Productivity OCN 201 Biology Lecture 5 Production vs Biomass Biomass = amount of carbon per unit area (= standing stock * C/cell) Units (e.g.): g C m -2 Primary Production = amount of carbon
The Global Carbon Cycle
 The Global Carbon Cycle In a nutshell We are mining fossil CO 2 and titrating into the oceans, (buffered by acid-base chemistry) Much of the fossil CO 2 will remain in the atmosphere for thousands of years
The Global Carbon Cycle In a nutshell We are mining fossil CO 2 and titrating into the oceans, (buffered by acid-base chemistry) Much of the fossil CO 2 will remain in the atmosphere for thousands of years
Patterns of Productivity
 Patterns of Productivity OCN 201 Biology Lecture 8 Primary Production - the production of autotrophic biomass Secondary Production - the production of heterotrophic biomass Production vs Biomass Biomass
Patterns of Productivity OCN 201 Biology Lecture 8 Primary Production - the production of autotrophic biomass Secondary Production - the production of heterotrophic biomass Production vs Biomass Biomass
ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007
 ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007 Name This examination consists of a total of 100 points. In each of the first two sections, you have a choice of which questions to answer. Please note that you
ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007 Name This examination consists of a total of 100 points. In each of the first two sections, you have a choice of which questions to answer. Please note that you
MEDUSA. Model of Ecosystem Dynamics, nutrient Utilisation, Sequestration and Acidification. Julien Palmiéri, Andrew Yool, Katya Popova
 MEDUSA Model of Ecosystem Dynamics, nutrient Utilisation, Sequestration and Acidification Julien Palmiéri, Andrew Yool, Katya Popova Oxford 1-12-2015 UKESM1 and imarnet Development of UKESM1 required the
MEDUSA Model of Ecosystem Dynamics, nutrient Utilisation, Sequestration and Acidification Julien Palmiéri, Andrew Yool, Katya Popova Oxford 1-12-2015 UKESM1 and imarnet Development of UKESM1 required the
The Ocean Carbon Cycle. Doug Wallace Dalhousie University, Halifax, Canada
 The Ocean Carbon Cycle Doug Wallace Dalhousie University, Halifax, Canada KISS Satellite to Seafloor Workshop, Pasadena, 6 October, 2013 Premise: There are Two Flavours (or Colours) of Carbon Natural carbon
The Ocean Carbon Cycle Doug Wallace Dalhousie University, Halifax, Canada KISS Satellite to Seafloor Workshop, Pasadena, 6 October, 2013 Premise: There are Two Flavours (or Colours) of Carbon Natural carbon
What ocean biogeochemical models can tell us about bottom-up control of ecosystem variability
 ICES Journal of Marine Science (2011), 68(6), 1030 1044. doi:10.1093/icesjms/fsr068 What ocean biogeochemical models can tell us about bottom-up control of ecosystem variability A. Gnanadesikan*, J. P.
ICES Journal of Marine Science (2011), 68(6), 1030 1044. doi:10.1093/icesjms/fsr068 What ocean biogeochemical models can tell us about bottom-up control of ecosystem variability A. Gnanadesikan*, J. P.
CO 2. and the carbonate system II. Carbon isotopes as a tracer for circulation. The (solid) carbonate connection with. The ocean climate connection
 CO 2 and the carbonate system II Carbon isotopes as a tracer for circulation The (solid) carbonate connection with ocean acidity Climate The ocean climate connection The carbon cycle the carbon cycle involves
CO 2 and the carbonate system II Carbon isotopes as a tracer for circulation The (solid) carbonate connection with ocean acidity Climate The ocean climate connection The carbon cycle the carbon cycle involves
Quantifying Sources & Sinks of Atmospheric CO 2. Uptake and Storage of Anthropogenic Carbon
 Quantifying Sources & Sinks of Atmospheric CO 2 Uptake and Storage of Anthropogenic Carbon by Christopher L. Sabine ; NOAA/PMEL, Seattle, WA USA Acknowledgements: Richard A. Feely (PMEL), Frank Millero
Quantifying Sources & Sinks of Atmospheric CO 2 Uptake and Storage of Anthropogenic Carbon by Christopher L. Sabine ; NOAA/PMEL, Seattle, WA USA Acknowledgements: Richard A. Feely (PMEL), Frank Millero
SOLAR PASSIVE DESIGN: PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE
 SOLAR PASSIVE DESIGN: PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE Understanding Climate and Atmosphere Human impact on global weather Energy outlook in India Energy needs in buildings Comfort zone Solar passive design- Case
SOLAR PASSIVE DESIGN: PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICE Understanding Climate and Atmosphere Human impact on global weather Energy outlook in India Energy needs in buildings Comfort zone Solar passive design- Case
Lakes, Primary Production, Budgets and Cycling
 OCN 401-Biogeochemical Systems Lecture #10 (9.22.11) Lakes, Primary Production, Budgets and Cycling (Schlesinger: Chapter 7) 1. Primary Production and Nutrient Cycling in Lakes Physical aspects and nomenclature
OCN 401-Biogeochemical Systems Lecture #10 (9.22.11) Lakes, Primary Production, Budgets and Cycling (Schlesinger: Chapter 7) 1. Primary Production and Nutrient Cycling in Lakes Physical aspects and nomenclature
Lakes, Primary Production, Budgets and Cycling Schlesinger and Bernhardt (2013): Chapter 8, p
 OCN 401-Biogeochemical Systems Lecture #12 (10.8.13) Angelos Hannides, hannides@hawaii.edu Lakes, Primary Production, Budgets and Cycling Schlesinger and Bernhardt (2013): Chapter 8, p. 288-308 1. Physical
OCN 401-Biogeochemical Systems Lecture #12 (10.8.13) Angelos Hannides, hannides@hawaii.edu Lakes, Primary Production, Budgets and Cycling Schlesinger and Bernhardt (2013): Chapter 8, p. 288-308 1. Physical
Curriculum Guide. National Science Education Standards Grades 5-8 Earth and Space Science
 National Science Education Standards Grades 5-8 Earth and Space Science Curriculum Guide Structure of the Earth system: Global patterns of atmospheric movement influence local weather. Oceans has a major
National Science Education Standards Grades 5-8 Earth and Space Science Curriculum Guide Structure of the Earth system: Global patterns of atmospheric movement influence local weather. Oceans has a major
Carbon cycling and climate: the CO 2. connection
 Carbon cycling and climate: the C 2 connection Gasses in the ocean The carbonate system (and buffering in the ocean) Carbon dioxide and the climate connection. Importance of C 2 to climate C 2 acts like
Carbon cycling and climate: the C 2 connection Gasses in the ocean The carbonate system (and buffering in the ocean) Carbon dioxide and the climate connection. Importance of C 2 to climate C 2 acts like
Lecture 22: Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate
 Lecture 22: Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate Required Reading: FP Chapter 14 (only sections that I cover) Suggested Introductory Reading: Jacob Chapter 7 Atmospheric Chemistry CHEM-5151 / ATOC-5151 Spring
Lecture 22: Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate Required Reading: FP Chapter 14 (only sections that I cover) Suggested Introductory Reading: Jacob Chapter 7 Atmospheric Chemistry CHEM-5151 / ATOC-5151 Spring
Causes of Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia
 Causes of Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Nancy N. Rabalais 1 R. Eugene Turner 2 1 Louisiana Universities Marine Consortium 2 Louisiana State University Center for Sponsored Coastal Ocean Research, Coastal Ocean
Causes of Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Nancy N. Rabalais 1 R. Eugene Turner 2 1 Louisiana Universities Marine Consortium 2 Louisiana State University Center for Sponsored Coastal Ocean Research, Coastal Ocean
The Global Carbon Cycle
 The Global Carbon Cycle Laurent Bopp LSCE, Paris Introduction CO2 is an important greenhouse gas Contribution to Natural Greenhouse Effect Contribution to Anthropogenic Effect 1 From NASA Website 2 Introduction
The Global Carbon Cycle Laurent Bopp LSCE, Paris Introduction CO2 is an important greenhouse gas Contribution to Natural Greenhouse Effect Contribution to Anthropogenic Effect 1 From NASA Website 2 Introduction
Primary Production in the Ocean
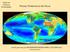 Primary Production in the Ocean A global composite of sea surface chlorophyll concentration Oligotrophic gyre (LNLC) Seasonal Phytoplankton blooms Coastal Upwelling High-nutrient, low chlorophyll (HNLC)
Primary Production in the Ocean A global composite of sea surface chlorophyll concentration Oligotrophic gyre (LNLC) Seasonal Phytoplankton blooms Coastal Upwelling High-nutrient, low chlorophyll (HNLC)
Lakes: Primary Production, Budgets and Cycling. Lecture Outline
 OCN 401-Biogeochemical Systems (10.06.16) Lakes: Primary Production, Budgets and Cycling Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 8 Lecture Outline 1. Seasonal cycle of lake stratification Temperature / density relationship
OCN 401-Biogeochemical Systems (10.06.16) Lakes: Primary Production, Budgets and Cycling Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 8 Lecture Outline 1. Seasonal cycle of lake stratification Temperature / density relationship
Lakes: Primary Production, Budgets and Cycling
 OCN 401-Biogeochemical Systems (9.28.17) Lakes: Primary Production, Budgets and Cycling Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 8 Lecture Outline 1. Seasonal cycle of lake stratification Temperature / density relationship
OCN 401-Biogeochemical Systems (9.28.17) Lakes: Primary Production, Budgets and Cycling Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 8 Lecture Outline 1. Seasonal cycle of lake stratification Temperature / density relationship
Life in Water. Chapter 3
 Life in Water Chapter 3 Outline Hydrologic Cycle Oceans Shallow Marine Waters Marine Shores Estuaries, Salt Marshes, and Mangrove Forests Rivers and Streams Lakes 2 The Hydrologic Cycle Over 71% of the
Life in Water Chapter 3 Outline Hydrologic Cycle Oceans Shallow Marine Waters Marine Shores Estuaries, Salt Marshes, and Mangrove Forests Rivers and Streams Lakes 2 The Hydrologic Cycle Over 71% of the
Primary Production in the Ocean
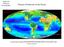 Primary Production in the Ocean A global composite of sea surface chlorophyll concentration Oligotrophic gyre (LNLC) Seasonal Phytoplankton blooms Coastal Upwelling High-nutrient, low chlorophyll (HNLC)
Primary Production in the Ocean A global composite of sea surface chlorophyll concentration Oligotrophic gyre (LNLC) Seasonal Phytoplankton blooms Coastal Upwelling High-nutrient, low chlorophyll (HNLC)
Why are there large quantities of the un-natural (Man Made) CFCs in Antarctica?
 Ozone Depletion and Climate Change Why are there large quantities of the un-natural (Man Made) CFCs in Antarctica? In a recent (last August 2016) BBC documentary on the Antarctic weather changes, it has
Ozone Depletion and Climate Change Why are there large quantities of the un-natural (Man Made) CFCs in Antarctica? In a recent (last August 2016) BBC documentary on the Antarctic weather changes, it has
Nitrate Dynamics at ALOHA and K2. Karen Casciotti Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Department of Marine Chemistry and Geochemistry
 Nitrate Dynamics at ALOHA and K2 Karen Casciotti Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Department of Marine Chemistry and Geochemistry VERTIGO 24 Experiments Nitrate isotopic profiles Coupled δ 15 N and
Nitrate Dynamics at ALOHA and K2 Karen Casciotti Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Department of Marine Chemistry and Geochemistry VERTIGO 24 Experiments Nitrate isotopic profiles Coupled δ 15 N and
Stable versus unstable planktonic food webs in oceans
 Stable versus unstable planktonic food webs in oceans L. Legendre 1, F. Rassoulzadegan 2 1 Département de biologie, Université Laval, Québec, QC G1K 7P4, Canada 2 Station Zoologique, BP 28, F-06230 Villefranche-sur-Mer,
Stable versus unstable planktonic food webs in oceans L. Legendre 1, F. Rassoulzadegan 2 1 Département de biologie, Université Laval, Québec, QC G1K 7P4, Canada 2 Station Zoologique, BP 28, F-06230 Villefranche-sur-Mer,
Implications of global climate change for estuarine & coastal ecosystems (Gulf of Mexico in particular)
 - The cumulative effects of global change, including climate change, increased population, & more intense industrialization & agribusiness, will likely continue & intensify the course of eutrophication
- The cumulative effects of global change, including climate change, increased population, & more intense industrialization & agribusiness, will likely continue & intensify the course of eutrophication
Representation of the carbon cycle in box models and GCMs: 1. Solubility pump
 GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 17, NO. 1, 1026, doi:10.1029/2001gb001401, 2003 Representation of the carbon cycle in box models and GCMs: 1. Solubility pump J. R. Toggweiler, A. Gnanadesikan, and S.
GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 17, NO. 1, 1026, doi:10.1029/2001gb001401, 2003 Representation of the carbon cycle in box models and GCMs: 1. Solubility pump J. R. Toggweiler, A. Gnanadesikan, and S.
Revisiting nutrient trapping in global coupled biogeochemical ocean circulation models
 GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 27, 1 20, doi:10.1002/gbc.20029, 2013 Revisiting nutrient trapping in global coupled biogeochemical ocean circulation models 1 1,2 H. Dietze and U. Loeptien Received
GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 27, 1 20, doi:10.1002/gbc.20029, 2013 Revisiting nutrient trapping in global coupled biogeochemical ocean circulation models 1 1,2 H. Dietze and U. Loeptien Received
Observations of Growth Rate of Carbon Reservoirs. Keeling et al. (2000) & Marland et al. (2000)
 Carbon Science A new synthesis of the present carbon budget. Building an earth system model for century time scale scenarios An examination of the long term consequences of continued fossil fuel use Scouts
Carbon Science A new synthesis of the present carbon budget. Building an earth system model for century time scale scenarios An examination of the long term consequences of continued fossil fuel use Scouts
Chapter 4 Guided Notes and presentations
 Module 9: The Unequal Heating of Earth Definitions Troposphere: Chapter 4 Guided Notes and presentations Stratosphere: Albedo: Ozone Graph the following temperature data and corresponding layers of the
Module 9: The Unequal Heating of Earth Definitions Troposphere: Chapter 4 Guided Notes and presentations Stratosphere: Albedo: Ozone Graph the following temperature data and corresponding layers of the
Chapter Two: Cycles of Matter (pages 32-65)
 Biology 20 Chapter 2.1_keyed Chapter Two: Cycles of Matter (pages 32-65) 2.1 The Role of Water in the Cycles of Matter (pages 34 40) Due to its ability to form hydrogen bonds, water has several unique
Biology 20 Chapter 2.1_keyed Chapter Two: Cycles of Matter (pages 32-65) 2.1 The Role of Water in the Cycles of Matter (pages 34 40) Due to its ability to form hydrogen bonds, water has several unique
CTD (CONDUCTIVITY-TEMPERATURE-DEPTH)
 CTD (CONDUCTIVITY-TEMPERATURE-DEPTH) Related lesson plan Fresh and Seawater Density What is this sensor? CTD is an acronym for Conductivity, Temperature and Depth. However, this is somewhat misleading
CTD (CONDUCTIVITY-TEMPERATURE-DEPTH) Related lesson plan Fresh and Seawater Density What is this sensor? CTD is an acronym for Conductivity, Temperature and Depth. However, this is somewhat misleading
Greenhouse Gas Measurements from Space. Chris O Dell Colorado State University
 Greenhouse Gas Measurements from Space Chris O Dell Colorado State University 1 Climate Forcings & Feedbacks Forcings Greenhouse Gases Aerosols Volcanic Eruptions Solar Forcing Temperature Change Feedbacks
Greenhouse Gas Measurements from Space Chris O Dell Colorado State University 1 Climate Forcings & Feedbacks Forcings Greenhouse Gases Aerosols Volcanic Eruptions Solar Forcing Temperature Change Feedbacks
Measuring Ocean Color: The Basics
 Measuring Ocean Color: The Basics Radiation of energy from the Sun and the Earth s surface. Recall from previous lectures that the Sun (6000 K), radiates energy in three portions of the energy spectrum:
Measuring Ocean Color: The Basics Radiation of energy from the Sun and the Earth s surface. Recall from previous lectures that the Sun (6000 K), radiates energy in three portions of the energy spectrum:
Oceanography Page 1 of 6 Lab: Ocean Salinity and Density M.Sewell rm #70
 Oceanography Page 1 of 6 Salty Water! Description: This lab is designed to demonstrate the formation of the world s oceans and why the oceans are salty, as well as the changes that take place in density
Oceanography Page 1 of 6 Salty Water! Description: This lab is designed to demonstrate the formation of the world s oceans and why the oceans are salty, as well as the changes that take place in density
Ocean Literacy The ocean is a major influence on weather and climate.
 Freshand Salt Principle 3 Ocean Literacy The ocean is a major influence on weather and climate. Great Lakes Literacy The Great Lakes influence local and regional weather and climate. 49 Fresh Salt and
Freshand Salt Principle 3 Ocean Literacy The ocean is a major influence on weather and climate. Great Lakes Literacy The Great Lakes influence local and regional weather and climate. 49 Fresh Salt and
25 years of Hawaii Ocean Time-series carbon flux determinations: Insights into productivity, export, and nutrient supply in the oligotrophic ocean
 25 years of Hawaii Ocean Time-series carbon flux determinations: Insights into productivity, export, and nutrient supply in the oligotrophic ocean MATTHEW CHURCH, ROBERT BIDIGARE, JOHN DORE, DAVID KARL,
25 years of Hawaii Ocean Time-series carbon flux determinations: Insights into productivity, export, and nutrient supply in the oligotrophic ocean MATTHEW CHURCH, ROBERT BIDIGARE, JOHN DORE, DAVID KARL,
Detection of anthropogenic climate change in satellite records of ocean chlorophyll and productivity
 Author(s) 2010. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Biogeosciences Detection of anthropogenic climate change in satellite records of ocean chlorophyll and productivity
Author(s) 2010. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Biogeosciences Detection of anthropogenic climate change in satellite records of ocean chlorophyll and productivity
A sense of place N, W LNLC region two layered system. < 50m mixed layer ~125 m euphotic zone/nutricline. Station ALOHA (1988 onwards)
 STATION ALOHA 1. Introduction to the region 2. Types of blooms (enhanced biomass/growth emphasis on the mixed layer) 3. Drivers of variability 4. Beyond biomass towards productivity angelicque white, oregon
STATION ALOHA 1. Introduction to the region 2. Types of blooms (enhanced biomass/growth emphasis on the mixed layer) 3. Drivers of variability 4. Beyond biomass towards productivity angelicque white, oregon
Trace Metal Iron (Fe), an important element to measure at sea. Dr. Thato Nicholas Mtshali
 Trace Metal Iron (Fe), an important element to measure at sea Dr. Thato Nicholas Mtshali Southern Atlantic Ocean and Antarctic Seminar (Cape Town): 5 December 2017 A CSIR-led multidisciplinary and multi-institutional
Trace Metal Iron (Fe), an important element to measure at sea Dr. Thato Nicholas Mtshali Southern Atlantic Ocean and Antarctic Seminar (Cape Town): 5 December 2017 A CSIR-led multidisciplinary and multi-institutional
Includes the coastal zone and the pelagic zone, the realm of the oceanographer. I. Ocean Circulation
 Includes the coastal zone and the pelagic zone, the realm of the oceanographer I. Ocean Circulation II. Water Column Production A. Coastal Oceans B. Open Oceans E. Micronutrients F. Harmful Algal Blooms
Includes the coastal zone and the pelagic zone, the realm of the oceanographer I. Ocean Circulation II. Water Column Production A. Coastal Oceans B. Open Oceans E. Micronutrients F. Harmful Algal Blooms
Unit III Nutrients & Biomes
 Unit III Nutrients & Biomes Nutrient Cycles Carbon Cycle Based on CO 2 cycling from animals to plants during respiration and photosynthesis. Heavy deposits are stored in wetland soils, oceans, sedimentary
Unit III Nutrients & Biomes Nutrient Cycles Carbon Cycle Based on CO 2 cycling from animals to plants during respiration and photosynthesis. Heavy deposits are stored in wetland soils, oceans, sedimentary
Chapter Two: Cycles of Matter (pages 32-65)
 Chapter Two: Cycles of Matter (pages 32-65) 2.2 Biogeochemical Cycles (pages 42 52) In order to survive and grow, organisms must obtain nutrients that serve as sources of energy or chemical building blocks,
Chapter Two: Cycles of Matter (pages 32-65) 2.2 Biogeochemical Cycles (pages 42 52) In order to survive and grow, organisms must obtain nutrients that serve as sources of energy or chemical building blocks,
Air-Sea Gas Exchange
 Air-Sea Gas Exchange OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 25 Feb 2016 Reading: Libes, Chapter 6 pp. 158-168 2016 David Ho and Frank Sansone Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs) At the completion of this module, students
Air-Sea Gas Exchange OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 25 Feb 2016 Reading: Libes, Chapter 6 pp. 158-168 2016 David Ho and Frank Sansone Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs) At the completion of this module, students
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL: Spatial and temporal variability in nutrients and carbon uptake during 2004 and 2005 in the eastern equatorial Pacific Ocean
 Manuscript prepared for Biogeosciences Discuss. with version 3.5 of the LATEX class copernicus discussions.cls. Date: August SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL: Spatial and temporal variability in nutrients and carbon
Manuscript prepared for Biogeosciences Discuss. with version 3.5 of the LATEX class copernicus discussions.cls. Date: August SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL: Spatial and temporal variability in nutrients and carbon
Nitrogen Cycling, Primary Production, and Water Quality in the New River Estuary. Defense Coastal/Estuarine Research Program (DCERP)
 Nitrogen Cycling, Primary Production, and Water Quality in the New River Estuary Defense Coastal/Estuarine Research Program (DCERP) Introduction: A key theme of the ongoing DCERP program is monitoring
Nitrogen Cycling, Primary Production, and Water Quality in the New River Estuary Defense Coastal/Estuarine Research Program (DCERP) Introduction: A key theme of the ongoing DCERP program is monitoring
SUMMARY OF THE COPERNICUS MARINE ENVIRONMENT MONITORING SERVICE OCEAN STATE REPORT 2016
 SUMMARY OF THE COPERNICUS MARINE ENVIRONMENT MONITORING SERVICE OCEAN STATE REPORT 2016 C O P E RNICUS M ARINE E NVIRO N MEN T M ONIT ORING SE R VICE OCEAN STATE REPORT No.1, 2016 Journal of Operational
SUMMARY OF THE COPERNICUS MARINE ENVIRONMENT MONITORING SERVICE OCEAN STATE REPORT 2016 C O P E RNICUS M ARINE E NVIRO N MEN T M ONIT ORING SE R VICE OCEAN STATE REPORT No.1, 2016 Journal of Operational
CHEMICAL: NITROGEN AND PHOSPHORUS (read pp in Dodson)
 BIOE 155, Fall 010 BACKGROUND CHEMICAL: NITROGEN AND PHOSPHORUS (read pp39-50 in Dodson) Lakes are often classified according to trophic status, specifically how much energy or food is available for the
BIOE 155, Fall 010 BACKGROUND CHEMICAL: NITROGEN AND PHOSPHORUS (read pp39-50 in Dodson) Lakes are often classified according to trophic status, specifically how much energy or food is available for the
Water Quality Monitoring:
 Water Quality Monitoring: Lesson Plan for Exploring Time Series Data Presenters: Janet Vail, Fallon Januska, Dirk Koopmans Lake Michigan Center in Muskegon, Michigan Home of Annis Water Resources Institute
Water Quality Monitoring: Lesson Plan for Exploring Time Series Data Presenters: Janet Vail, Fallon Januska, Dirk Koopmans Lake Michigan Center in Muskegon, Michigan Home of Annis Water Resources Institute
10 Productivity and Food Webs in the Sea. Notes for Marine Biology: Function, Biodiversity, Ecology By Jeffrey S. Levinton
 10 Productivity and Food Webs in the Sea Notes for Marine Biology: Function, Biodiversity, Ecology By Jeffrey S. Levinton Microbial Loop 2 Larger consumers Microbial loop DOC & POC Viruses Bacteria Herbivores
10 Productivity and Food Webs in the Sea Notes for Marine Biology: Function, Biodiversity, Ecology By Jeffrey S. Levinton Microbial Loop 2 Larger consumers Microbial loop DOC & POC Viruses Bacteria Herbivores
Earth & Space Science (Water Cycle) Grade 7 Science Grade 7 Science Start Date: November 04, 2013 End Date : November 22, 2013
 Unit Overview Hydrologic Cycle, Thermal Energy Transfer. Content Elaborations The movement of water through the spheres of E water changes state and energy is transferred, it water transfers from the hydrosphere
Unit Overview Hydrologic Cycle, Thermal Energy Transfer. Content Elaborations The movement of water through the spheres of E water changes state and energy is transferred, it water transfers from the hydrosphere
Carbon Dioxide, Alkalinity and ph
 Carbon Dioxide, Alkalinity and ph OCN 62 Chemical Oceanography Reading: Libes, Chapter 15, pp. 8 94 (Remainder of chapter: Biogenic production, carbonate saturation and sediment distributions ) 1. CO 2
Carbon Dioxide, Alkalinity and ph OCN 62 Chemical Oceanography Reading: Libes, Chapter 15, pp. 8 94 (Remainder of chapter: Biogenic production, carbonate saturation and sediment distributions ) 1. CO 2
Seasonal Anoxia over the Western Indian Continental Shelf
 Seasonal Anoxia over the Western Indian Continental Shelf S.W.A. Naqvi, Hema Naik, A.K. Pratihary, M. Gauns, Witty D Souza, Gayatree Narvenkar, D.A. Jayakumar, M.S. Shailaja & P.V. Narvekar National Institute
Seasonal Anoxia over the Western Indian Continental Shelf S.W.A. Naqvi, Hema Naik, A.K. Pratihary, M. Gauns, Witty D Souza, Gayatree Narvenkar, D.A. Jayakumar, M.S. Shailaja & P.V. Narvekar National Institute
Chapter 2 9/15/2015. Chapter 2. Penny Boat. 2.1 The Role of Water in Cycles of Matter
 Chapter 2 Chapter 2 Cycles of Matter 2.1 The Role of Water in Cycles of Matter 2.2 Biogeochemical Cycles 2.3 the Balance of the Matter and Energy Exchange 2.1 The Role of Water in Cycles of Matter In this
Chapter 2 Chapter 2 Cycles of Matter 2.1 The Role of Water in Cycles of Matter 2.2 Biogeochemical Cycles 2.3 the Balance of the Matter and Energy Exchange 2.1 The Role of Water in Cycles of Matter In this
Introduction (Welcome!)
 Introduction (Welcome!) OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems LECTURES Lectures will generally be given using PowerPoint presentations. As a convenience to students, copies of the PowerPoint slides will be
Introduction (Welcome!) OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems LECTURES Lectures will generally be given using PowerPoint presentations. As a convenience to students, copies of the PowerPoint slides will be
Phytoplankton! Zooplankton! Nutrients!
 Phytoplankton! Zooplankton! Nutrients! Phytoplankton! Zooplankton! Critical Depth Recycled Nutrients! Oxidized Nutrients! Detritus! Rest of Ocean Biological and Solubility Pumps New (Export) vs. Regenerated
Phytoplankton! Zooplankton! Nutrients! Phytoplankton! Zooplankton! Critical Depth Recycled Nutrients! Oxidized Nutrients! Detritus! Rest of Ocean Biological and Solubility Pumps New (Export) vs. Regenerated
TRANSFER PROCESSESAND TIME SCALES IN BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES tt
 Svensson, B.H. & SOderlund, R. (eds.) 1976. Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Sulphur - Global Cycles. SCOPE Report 7. Ecol. Bull. (Stockholm) 22:17-22 TRANSFER PROCESSESAND TIME SCALES IN BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES
Svensson, B.H. & SOderlund, R. (eds.) 1976. Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Sulphur - Global Cycles. SCOPE Report 7. Ecol. Bull. (Stockholm) 22:17-22 TRANSFER PROCESSESAND TIME SCALES IN BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES
The Hawaii Ocean Time-series (HOT): Highlights and perspectives from two decades of ocean observations
 The Hawaii Ocean Time-series (HOT): Highlights and perspectives from two decades of ocean observations MATTHEW CHURCH UNIVERSITY OF HAWAII OCB SCOPING WORKSHOP SEPTEMBER 2010 A Dedicated HOT Team NSF What
The Hawaii Ocean Time-series (HOT): Highlights and perspectives from two decades of ocean observations MATTHEW CHURCH UNIVERSITY OF HAWAII OCB SCOPING WORKSHOP SEPTEMBER 2010 A Dedicated HOT Team NSF What
Chapter Concepts LIFE IN WATER. The Hydrologic Cycle. The Hydrologic Cycle
 Chapter Concepts Chapter 3 LIFE IN WATER The hydrologic cycle exchanges water among reservoirs The biology of aquatic environments corresponds broadly to variations in physical factors such as light, temperature,
Chapter Concepts Chapter 3 LIFE IN WATER The hydrologic cycle exchanges water among reservoirs The biology of aquatic environments corresponds broadly to variations in physical factors such as light, temperature,
AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System
 AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System Next: How can we explain Earth s unique atmosphere. What kept Earth s climate stable? How did Earth's atmosphere end up so different? 1. Why did Earth retain most
AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System Next: How can we explain Earth s unique atmosphere. What kept Earth s climate stable? How did Earth's atmosphere end up so different? 1. Why did Earth retain most
The summertime subpycnocline dissolved oxygen budget in the western Long Island Sound. Grant McCardell and James O Donnell
 The summertime subpycnocline dissolved oxygen budget in the western Long Island Sound Grant McCardell and James O Donnell MAPBOM 2013 Overview WLIS hypoxia SWEM model Data-based transport estimates WLIS
The summertime subpycnocline dissolved oxygen budget in the western Long Island Sound Grant McCardell and James O Donnell MAPBOM 2013 Overview WLIS hypoxia SWEM model Data-based transport estimates WLIS
Carbon Cycle Midterm Exam April 1, Answer Key
 Carbon Cycle Midterm Exam April 1, 2008 Answer Key 1. a. What process dominates the seasonal cycle in atmospheric O 2 at 41 S? Southern summer release and southern winter uptake by the ocean. Part due
Carbon Cycle Midterm Exam April 1, 2008 Answer Key 1. a. What process dominates the seasonal cycle in atmospheric O 2 at 41 S? Southern summer release and southern winter uptake by the ocean. Part due
Particulate Soil Phosphorus and Eutrophication in Lakes and Streams
 Particulate Soil Phosphorus and Eutrophication in Lakes and Streams Paul R. Bloom Soil, Water, & Climate Department University of Minnesota With contributions by John Moncrief, Carl Rosen and David Mulla
Particulate Soil Phosphorus and Eutrophication in Lakes and Streams Paul R. Bloom Soil, Water, & Climate Department University of Minnesota With contributions by John Moncrief, Carl Rosen and David Mulla
- geographic patterns of energy balance
 (1 of 10) Further Reading: Chapter 04 of the text book Outline - geographic patterns of energy balance - net radiation - meridional transport (2 of 10) Introduction Previously, we discussed the energy
(1 of 10) Further Reading: Chapter 04 of the text book Outline - geographic patterns of energy balance - net radiation - meridional transport (2 of 10) Introduction Previously, we discussed the energy
Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter (CDOM) In The Global Ocean. Norm Nelson, Dave Siegel, UCSB
 Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter (CDOM) In The Global Ocean Norm Nelson, Dave Siegel, UCSB Outline CDOM: Definitions, rationale, methodology, research questions CDOM distribution and dynamics in the
Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter (CDOM) In The Global Ocean Norm Nelson, Dave Siegel, UCSB Outline CDOM: Definitions, rationale, methodology, research questions CDOM distribution and dynamics in the
NOTEBOOK. Table of Contents: 9. Properties of Water 9/20/ Water & Carbon Cycles 9/20/16
 NOTEBOOK Table of Contents: 9. Properties of Water 9/20/16 10. Water & Carbon Cycles 9/20/16 NOTEBOOK Assignment Page(s): Agenda: Tuesday, September 20, 2016 Properties of Water Water & Carbon Cycles 1.
NOTEBOOK Table of Contents: 9. Properties of Water 9/20/16 10. Water & Carbon Cycles 9/20/16 NOTEBOOK Assignment Page(s): Agenda: Tuesday, September 20, 2016 Properties of Water Water & Carbon Cycles 1.
79. Cone- bearing trees are characteristic of the a) taiga. b) tropical rain forest. c) temperate deciduous forest. d) savanna.
 73. The portion of a species resource (biological, chemical, and physical) which a particular species actually utilizes is known as the: a) Reserve niche b) Conservation niche c) Basic niche d) Fundamental
73. The portion of a species resource (biological, chemical, and physical) which a particular species actually utilizes is known as the: a) Reserve niche b) Conservation niche c) Basic niche d) Fundamental
Carbon Dioxide, Alkalinity and ph
 Carbon Dioxide, Alkalinity and ph OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 31 January 2013 Reading: Libes, Chapter 15, pp. 383 394 (Remainder of chapter will be used with the lecture: Biogenic production, carbonate
Carbon Dioxide, Alkalinity and ph OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 31 January 2013 Reading: Libes, Chapter 15, pp. 383 394 (Remainder of chapter will be used with the lecture: Biogenic production, carbonate
The unnatural carbon dioxide cycle and oceanic processes over the last few hundred years. OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography
 The unnatural carbon dioxide cycle and oceanic processes over the last few hundred years OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography In the 19th century, scientists realized that gases in the atmosphere cause a "greenhouse
The unnatural carbon dioxide cycle and oceanic processes over the last few hundred years OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography In the 19th century, scientists realized that gases in the atmosphere cause a "greenhouse
DOC and major carbon reservoirs and fluxes
 The Composition and cycling of Dissolved organic matter-i Review of DOC distribution Review of radiocarbon in DOC Sources of DOC Seasonal cycling of DOC above the permanent thermocline Composition of DOC
The Composition and cycling of Dissolved organic matter-i Review of DOC distribution Review of radiocarbon in DOC Sources of DOC Seasonal cycling of DOC above the permanent thermocline Composition of DOC
Leif Backman HENVI Seminar February 19, 2009
 Methane Sources and Sinks Leif Backman HENVI Seminar February 19, 2009 Background Atmospheric methane Sources & Sinks Concentration variations & trends Objective & methods Objective & Goals Research plan
Methane Sources and Sinks Leif Backman HENVI Seminar February 19, 2009 Background Atmospheric methane Sources & Sinks Concentration variations & trends Objective & methods Objective & Goals Research plan
What is the carbon cycle?
 What is the carbon cycle? By NASA Earth Observatory, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.29.17 Word Count 1,160 Carbon is both the foundation of all life on Earth and the source of the majority of energy consumed
What is the carbon cycle? By NASA Earth Observatory, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.29.17 Word Count 1,160 Carbon is both the foundation of all life on Earth and the source of the majority of energy consumed
OCN 201 Chemical Oceanography Class Notes, Fall Chemical Distributions: the roles of biology and physics
 The Nutrients OCN 201 Chemical Oceanography Class Notes, Fall 2001 Chemical Distributions: the roles of biology and physics Chris Measures Department of Oceanography The phytoplankton in the surface waters
The Nutrients OCN 201 Chemical Oceanography Class Notes, Fall 2001 Chemical Distributions: the roles of biology and physics Chris Measures Department of Oceanography The phytoplankton in the surface waters
The Global Carbon Cycle
 The Global Carbon Cycle Tom Bibby September 2003 bibby@imcs.rutgers.edu falko@imcs.rutgers.edu The Carbon Cycle - Look at past climatic change; as controlled by the carbon cycle. - Interpret the influence
The Global Carbon Cycle Tom Bibby September 2003 bibby@imcs.rutgers.edu falko@imcs.rutgers.edu The Carbon Cycle - Look at past climatic change; as controlled by the carbon cycle. - Interpret the influence
Marine Biogeochemical Modeling
 Marine Biogeochemical Modeling Scott Doney (WHOI) NCAR ASP Colloquium 2009 Talk Outline Science Motivation Philosophy of Modeling Model Construction Evaluation Against Data Supported by: Ocean Biological
Marine Biogeochemical Modeling Scott Doney (WHOI) NCAR ASP Colloquium 2009 Talk Outline Science Motivation Philosophy of Modeling Model Construction Evaluation Against Data Supported by: Ocean Biological
What is the carbon cycle?
 What is the carbon cycle? By NASA Earth Observatory, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.29.17 Word Count 1,454 Carbon is both the foundation of all life on Earth and the source of the majority of energy consumed
What is the carbon cycle? By NASA Earth Observatory, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.29.17 Word Count 1,454 Carbon is both the foundation of all life on Earth and the source of the majority of energy consumed
WHY CARBON? The Carbon Cycle 1/17/2011. All living organisms utilize the same molecular building blocks. Carbon is the currency of life
 The Carbon Cycle WHY CARBON? Inventories: black text Fluxes: purple arrows Carbon dioxide (+4) AN = 6 (6P/6N) AW = 12.011 Oxidation: -4 to +4 Isotopes: 11 C, 12 C, 1 C, 14 C Methane (-4) Carbon is the
The Carbon Cycle WHY CARBON? Inventories: black text Fluxes: purple arrows Carbon dioxide (+4) AN = 6 (6P/6N) AW = 12.011 Oxidation: -4 to +4 Isotopes: 11 C, 12 C, 1 C, 14 C Methane (-4) Carbon is the
Composition and Energy AOSC 200 Tim Canty
 Composition and Energy AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Atmospheric composition cont. Energy transfer Lecture 03 Sept 5 2017 1 Today s Weather
Composition and Energy AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Atmospheric composition cont. Energy transfer Lecture 03 Sept 5 2017 1 Today s Weather
People, Oceans and Climate Change
 People, Oceans and Climate Change A deeper look at the carbon dioxide cycle, greenhouse gases, and oceanic processes over the last 150 years OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 18 April 2013 Reading: Libes,
People, Oceans and Climate Change A deeper look at the carbon dioxide cycle, greenhouse gases, and oceanic processes over the last 150 years OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 18 April 2013 Reading: Libes,
1 The marine nitrogen cycle:
 1 The marine nitrogen cycle: Overview and challenges NICOLAS GRUBER 1 1 Environmental Physics, Institute of Biogeochemistry and Pollution Dynamics, ETH Zürich, Switzerland 1.1 INTRODUCTION The marine nitrogen
1 The marine nitrogen cycle: Overview and challenges NICOLAS GRUBER 1 1 Environmental Physics, Institute of Biogeochemistry and Pollution Dynamics, ETH Zürich, Switzerland 1.1 INTRODUCTION The marine nitrogen
Responses of Marine Ecosystems to a Changing Climate
 Responses of Marine Ecosystems to a Changing Climate Ken Denman Fisheries and Oceans Canada EC Canadian Centre for Climate Modelling and Analysis c/o University of Victoria, BC, Canada & Institute of Ocean
Responses of Marine Ecosystems to a Changing Climate Ken Denman Fisheries and Oceans Canada EC Canadian Centre for Climate Modelling and Analysis c/o University of Victoria, BC, Canada & Institute of Ocean
Preliminary calculations: Lake morphometry Gas Transfer
 Preliminary calculations: Lake morphometry For all individual processes it will be necessary to know the depth of the epilimnion and hypolimnion. You have been given the following information: Epilimnion
Preliminary calculations: Lake morphometry For all individual processes it will be necessary to know the depth of the epilimnion and hypolimnion. You have been given the following information: Epilimnion
CLIMATE MODELS: LARGE SCALE AND PREDICTABLE
 CCS 5-1 CLIMATE MODELS: LARGE SCALE AND PREDICTABLE 1. Print this file (and associated linked images if any). Also answer the "Concept of the Week" questions in the Weekly Climate News File. (Check for
CCS 5-1 CLIMATE MODELS: LARGE SCALE AND PREDICTABLE 1. Print this file (and associated linked images if any). Also answer the "Concept of the Week" questions in the Weekly Climate News File. (Check for
Effects of Solar Variability on the Stratosphere
 Effects of Solar Variability on the Stratosphere Cora Randall, LASP, University of Colorado, Boulder, USA Lon Hood, LPL, University of Arizona, Tucson, USA Variations in solar and magnetospheric particle
Effects of Solar Variability on the Stratosphere Cora Randall, LASP, University of Colorado, Boulder, USA Lon Hood, LPL, University of Arizona, Tucson, USA Variations in solar and magnetospheric particle
Marine Primary Productivity: Measurements and Variability
 Why should we care about productivity? Marine Primary Productivity: Measurements and Variability Photosynthetic activity in oceans created current O 2 -rich atmosphere Plankton form ocean sediments & fossil
Why should we care about productivity? Marine Primary Productivity: Measurements and Variability Photosynthetic activity in oceans created current O 2 -rich atmosphere Plankton form ocean sediments & fossil
Carbon Science Highlights 2004
 Carbon Science Highlights 2004 THE PAST Understanding the Ice Ages THE PRESENT Observations of Atmospheric Gases Estimating CO 2 Sources and Sinks Processes Controlling CO 2 Fluxes Processes Determining
Carbon Science Highlights 2004 THE PAST Understanding the Ice Ages THE PRESENT Observations of Atmospheric Gases Estimating CO 2 Sources and Sinks Processes Controlling CO 2 Fluxes Processes Determining
Chapter 11: Atmosphere
 To get you thinking This is our atmosphere. All life on Earth exists within this tiny protective blanket. Why is the atmosphere important to us? What do you think it does for us? Chapter 11: Atmosphere
To get you thinking This is our atmosphere. All life on Earth exists within this tiny protective blanket. Why is the atmosphere important to us? What do you think it does for us? Chapter 11: Atmosphere
Biology 13- Marine Biology
 Introductions Biology 13- Marine Biology Instructor: Dr. Kevin Raskoff Email: kraskoff@mpc.edu Phone: (831) 646-4132 Office: Life Science, 203B (upstairs) Office hours: Mon-Thurs- 10-11; Thur 5-6pm; or
Introductions Biology 13- Marine Biology Instructor: Dr. Kevin Raskoff Email: kraskoff@mpc.edu Phone: (831) 646-4132 Office: Life Science, 203B (upstairs) Office hours: Mon-Thurs- 10-11; Thur 5-6pm; or
WATER QUALITY ENGINEERING
 WATER QUALITY ENGINEERING Zerihun Alemayehu (AAiT-CED) Water Quality Management The control of pollution from human activities so that the water is not degraded to the point that it is no longer suitable
WATER QUALITY ENGINEERING Zerihun Alemayehu (AAiT-CED) Water Quality Management The control of pollution from human activities so that the water is not degraded to the point that it is no longer suitable
The Ocean: a Carbon Pump
 The Ocean: a Carbon Pump Laurent Bopp*, Chris Bowler*, Lionel Guidi, Éric Karsenti, Colomban de Vargas *lead authors The ocean contains 50 times more carbon than the atmosphere and exchanges large amounts
The Ocean: a Carbon Pump Laurent Bopp*, Chris Bowler*, Lionel Guidi, Éric Karsenti, Colomban de Vargas *lead authors The ocean contains 50 times more carbon than the atmosphere and exchanges large amounts
Aquatic respiration and ocean metabolism
 Aquatic respiration and ocean metabolism Remember what life is all about: Energy (ATP) Reducing power (NADPH) Nutrients (C, N, P, S, Fe, etc., etc.) Photosynthetic organisms use sunlight, H 2 O, and dissolved
Aquatic respiration and ocean metabolism Remember what life is all about: Energy (ATP) Reducing power (NADPH) Nutrients (C, N, P, S, Fe, etc., etc.) Photosynthetic organisms use sunlight, H 2 O, and dissolved
People, Oceans and Climate Change
 People, Oceans and Climate Change or the unnatural carbon dioxide cycle and oceanic processes over the last few hundred years OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography Reading: Libes, Chapter 25 (a good summary) In
People, Oceans and Climate Change or the unnatural carbon dioxide cycle and oceanic processes over the last few hundred years OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography Reading: Libes, Chapter 25 (a good summary) In
Announcements. What are the effects of anthropogenic CO 2 on the ocean? 12/7/2017. UN Commitment to plastics in the ocean
 Announcements UN Commitment to plastics in the ocean http://www.bbc.com/news/scienceenvironment-42239895 Today: Quiz on paper by Lee et al. 2009 Climate change and OA Review for final exam (Tuesday 8 AM)
Announcements UN Commitment to plastics in the ocean http://www.bbc.com/news/scienceenvironment-42239895 Today: Quiz on paper by Lee et al. 2009 Climate change and OA Review for final exam (Tuesday 8 AM)
How will we measure the response of carbon export in the ocean to climate change? Ken Johnson MBARI
 How will we measure the response of carbon export in the ocean to climate change? Ken Johnson MBARI johnson@mbari.org Outline: Why care about ocean carbon flux? Future changes? How would we measure changes
How will we measure the response of carbon export in the ocean to climate change? Ken Johnson MBARI johnson@mbari.org Outline: Why care about ocean carbon flux? Future changes? How would we measure changes
1) The Changing Carbon Cycle
 1) The Changing Carbon Cycle WG1 Chapter 6, figure 1 The numbers represent carbon reservoirs in Petagrams of Carbon (PgC; 10 15 gc) and the annual exchanges in PgC/year. The black numbers and arrows show
1) The Changing Carbon Cycle WG1 Chapter 6, figure 1 The numbers represent carbon reservoirs in Petagrams of Carbon (PgC; 10 15 gc) and the annual exchanges in PgC/year. The black numbers and arrows show
