Antarctic Climate Change and Stratospheric Ozone Depletion. Karen L. Smith Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory Earth 2 Class October 19, 2013
|
|
|
- Daniella Lambert
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Antarctic Climate Change and Stratospheric Ozone Depletion Karen L. Smith Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory Earth 2 Class October 19, 2013
2 Antarctic Climate Change Antarctic climate change over the past several decades has been dominated by the effects of stratospheric ozone depletion Thompson et al. 2011
3 The Antarctic Ozone Hole (2012) Movie courtesy of NASA: from the OMI instrument on board the AURA satellite
4 Outline Introduction to Ozone Ozone Depletion The Montreal Protocol ODP vs. GWP Ozone and Climate The World Avoided Antarctic Sea Ice and Ozone UNEP, The Ozone Story, 1998
5 Introduction to Ozone
6 Ozone (O 3 ) Blue colored, strong smelling molecule Absorbs UV radiation Unstable: constantly breaks down, reforms in stratosphere Breakdown can be accelerated by certain chemicals (catalysts) Also a primary constituent of photochemical smog in the troposphere
7 Atmospheric Pressure Altitude (km) Felix Baumgartner Weather Balloons Stratosphere U2 Spy Plane Stealth Bomber Commercial Airliners Mt. Everest Denver Atmospheric Pressure (atm) Troposphere
8 Thermal Structure of the Atmosphere
9 Ozone in the Atmosphere
10 Ozone Formation in the Atmosphere Solar radiation striking the Earth s atmosphere is absorbed by air molecules O 2 strongly absorbs in the UV band Absorption of UV by molecular oxygen splits the O=O bond, forming O free radicals These O free radicals combine with molecular oxygen to form O 3 (ozone)
11 Ozone Absorption in the UV Band UV radiation includes wavelengths from 200 to 400 nm UV-A UV-B UV-C nm nm nm UV-C Nearly all UV-C is absorbed in the upper atmosphere UV-B 90% of UV-B is absorbed by the atmosphere, mostly by O 3 UV-A Not strongly absorbed by the atmosphere
12 Anthropogenic Ozone Depletion
13 CFC s (1928) Wonder Gas! UNEP, The Ozone Story, 1998
14 CFC s (1928) Wonder Gas! UNEP, The Ozone Story, 1998
15 Stratospheric Ozone Depletion Results from large-scale industrial manufacture and release of synthetic compounds (chlorofluorocarbons, CFCs) in quantities that can interfere with chemical processes in the Earth s atmosphere Unanticipated side effects of CFCs like acid rain, global warming, etc., were not expected only appreciated in hindsight Environmental success story?
16 Polar Ozone Destruction Ozone Hole : term for regional, seasonal thinning of O 3 layer over the poles Cause: catalytic destruction of O 3 by Cl and Br Mechanisms are complex: Ice clouds form in frigid stratospheric winter air, absorb HNO 3, ClONO 2, HCl Surface reactions on ice convert these to reactive Cl 2, HOCl, which accumulate, trapped in ice Spring daylight returns, solar radiation converts Cl 2 to Cl and HOCl to HO and Cl Sudden burst of Cl reacts with O 3, produces ClO which forms ClO-OCl, which forms ClOO and Cl Abundant Cl destroys lots of ozone Chain is broken when sunlight evaporates polar clouds, releasing bound HNO 3 ; NO 2 reacts with ClO and traps it again
17 The Ozone Hole through Time 194 DU 108 DU DU 118 DU
18 Ozonesondes
19 Ozonesonde Measurements 2012 Courtesy of NOAA
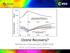
20 Ozone Hole Recovery? 2012 Ozone Hole 2 nd smallest in last 20 years! Courtesy of NOAA
21 Ozone and UV Ozone in the atmosphere is directly correlated with the UV intensity at the Earth s surface Most of the biologically harmful effects of ozone depletion are due to an increase in UV-B at the Earth s surface. Too much UV-B at the Earth s surface can lead to an increase in skin cancer, cataracts and other health problems.
22 The Montreal Protocol
23 History 1974: Molina & Rowland (1974) Nature 249, Paper calls attention to dangers of CFC s in ozone breakdown 1978: U.S., Canada, Sweden and Norway ban CFCs as propellants 1987: Montreal Protocol calls for decrease in CFCs to 50% of 1986 levels by : London Amendments call for complete CFC phase-out by : Copenhagen Amendments accelerate phase-out to : Molina & Rowland win Nobel Prize in Chemistry
24 Montreal Protocol (1987) The 1987 Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer (as agreed in 1987) Preamble The Parties to this Protocol, Being Parties to the Vienna Convention for the Protection of the Ozone Layer, Mindful of their obligation under that Convention to take appropriate measures to protect human health and the environment against adverse effects resulting or likely to result from human activities which modify or are likely to modify the ozone layer, Recognizing that world-wide emissions of certain substances can significantly deplete and otherwise modify the ozone layer in a manner that is likely to result in adverse effects on human health and the environment, Conscious of the potential climatic effects of emissions of these substances, Aware that measures taken to protect the ozone layer from depletion should be based on relevant scientific knowledge, taking into account technical and economic considerations, Determined to protect the ozone layer by taking precautionary measures to control equitably total global emissions of substances that deplete it, with the ultimate objective of their elimination on the basis of developments in scientific knowledge, taking into account technical and economic considerations, Acknowledging that special provision is required to meet the needs of developing countries for these substances, Noting the precautionary measures for controlling emissions of certain chlorofluorocarbons that have already been taken at national and regional levels, Considering the importance of promoting international co-operation in the research and development of science and technology relating to the control and reduction of emissions of substances that deplete the ozone layer, bearing in mind in particular the needs of developing countries, HAVE AGREED AS FOLLOWS:
25 Ratification of Montreal Protocol (July 2003) Countries that have NOT Ratified the Montreal Protocol (11 Countries)
26 Ozone-Depleting Substances (ODS) The Montreal Protocol has slowed and reversed the emission and accumulation of ODSs in the stratosphere. Ozone Assessment, 2010
27 ODP vs. GWP
28 AR4, 2007 Radiative Forcing (RF)
29 AR4, 2007 Radiative Forcing (RF)
30 AR4, 2007 Radiative Forcing (RF)
31 ODP and GWP The Montreal Protocol has a dual benefit: protecting ozone and climate!
32 Mass-Weighted Emissions ODP-Weighted Emissions GWP-Weighted Emissions Ozone Assessment, 2010
33 Montreal Protocol Protects Climate Montreal Protocol decreases CO 2 -eq emissions by 11 Gt in 2010! Ozone Depletion Offset 3.0 HFC Offset 0.9 ~11 Gt Ozone Assessment, 2010; Velders 2007 N.B. The reduction target for the Kyoto Protocol for is 2 Gt.
34 Ozone and Climate
35 Geopotential Height Trends and the Southern Annular Mode of Variability Thompson and Solomon 2002
36 Climate Change Attribution How do we attribute climate changes to greenhouse gases versus ozone depletion? Use a global climate model, e.g.) Table of GCM simulations (Polvani et al., 2011)
37 Climate Change Attribution How do we attribute climate changes to greenhouse gases versus ozone depletion? Use a global climate model, e.g.) Table of GCM simulations (Polvani et al., 2011)
38 Climate Change Attribution How do we attribute climate changes to greenhouse gases versus ozone depletion? Use a global climate model, e.g.) Table of GCM simulations (Polvani et al., 2011)
39 Climate Change Attribution How do we attribute climate changes to greenhouse gases versus ozone depletion? Use a global climate model, e.g.) Table of GCM simulations (Polvani et al., 2011)
40 Climate Change Attribution How do we attribute climate changes to greenhouse gases versus ozone depletion? Use a global climate model, e.g.) Table of GCM simulations (Polvani et al., 2011)
41 Climate Change Attribution How do we attribute climate changes to greenhouse gases versus ozone depletion? Use a global climate model, e.g.) Table of GCM simulations (Polvani et al., 2011)
42 20 th Century Change: Attribution to Ozone and GHG Polvani et al. 2011a
43 20 th Century Change: Attribution to Ozone and GHG Polvani et al. 2011a
44 21 st Century Change: Attribution to Ozone and GHG Polvani et al. 2011b
45 The World Avoided
46 The World Avoided No Montreal Protocol EECL Equivalent effective Chlorine (think of it as CFC s) Garcia et al., 2012
47 World Avoided Global Warming 21 st Century T s Change (a) Control (Montreal Protocol) (b) World Avoided (No Montreal Protocol) (a) Averaged Over Longitudes Garcia et al., 2012
48 UV Index World Avoided Values over 11 are considered extreme Present-day levels of ozone Garcia et al., 2012
49 Ozone Depletion and Antarctic Sea Ice
50 Antarctic sea ice extent is increasing Small + positive trend in Antarctic sea ice Data: NSIDC;
51 What about changes in other components of the Antarctic climate system? Sea Ice
52 Is there a connection between trends in stratospheric ozone depletion and the observed trend in Antarctic sea ice?
53 Future Antarctic sea ice loss GCM simulations using Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model Version 4 (WACCM4; Marsh et al. 2012) 1.9 x 2.5 horizontal resolution 66 vertical levels up to 140 km coupled middle atmosphere chemistry coupled ocean and sea ice components
54 Future Antarctic sea ice loss GCM simulations using Whole Atmosphere Community Climate Model Version 4 (WACCM4; Marsh et al. 2012). 1.9 x 2.5 horizontal resolution 66 vertical levels up to 140 km coupled middle atmosphere chemistry coupled ocean and sea ice components Two 3-member ensembles of 21 st century ( ) integrations with and without ozone recovery. 1 st Ensemble, RCP4.5: Standard RCP 4.5 including ozone recovery. 2 nd Ensemble, FixODS: RCP 4.5 with surface ozone-depleting substances fixed at year 2000 levels. Response is ensemble mean FixODS RCP4.5 averaged over last 10 years of integration.
55 Stratospheric ozone recovers in RCP 4.5 October-November-December Polar Cap Total Column Ozone Year
56 Ozone recovery mitigates Antarctic sea ice loss Austral Autumn Sea Ice Extent
57 Monthly sea ice extent response (FixODS RCP4.5) Absolute Difference Relative Difference Month Month
58 Monthly sea ice extent response (FixODS RCP4.5) Absolute Difference Relative Difference Annual Mean Response to climate change in RCP4.5: ~-11% Annual Mean Response to Fixed Ozone: ~-4% Month Month
59 Monthly sea ice extent response (FixODS RCP4.5) Absolute Difference Relative Difference Ozone recovery decreases magnitude of SIE loss by: ~33% Month Month
60 Fixing ODS s leads to a poleward shift in the large-scale atmospheric circulation Summer Zonal Mean Zonal Wind Response Latitude Contour interval is 1 m/s. Gray shading indicates 95% statistical significance.
61 Poleward shifted surface Westerlies induce a surface wind stress response Summer Sea ice concentration response (%; shading) Surface wind stress (black vectors) Surface temperature (black curves)
62 Ozone depletion induces Ekman-driven oceanic meridional overturning circulation Summer
63 Upper ocean warming persists throughout the year Summer Autumn Winter Spring
64 The Southern Ocean response to fixing ODS s Atmosphere Sea Ice Ocean Meridional Overturning Circulation
65 Robust response in models to stratospheric ozone perturbations Three different modeling studies that show Antarctic sea ice decreases in the presence of an ozone hole: Sigmond and Fyfe (2010) stratosphere-resolving GCM; ocean eddies parameterized. Smith et al. (2012) stratosphere-resolving GCM with interactive middle atmosphere chemistry; ocean eddies parameterized. Bitz and Polvani (2012) standard low-top GCM with resolved ocean eddies
66 How do we reconcile models and observations? Observations: sea ice is increasing Models: both GHG and stratospheric ozone depletion melt sea ice!
67 How do we reconcile models and observations? Observations: sea ice is increasing Models: both GHG and stratospheric ozone depletion melt sea ice! LARGE INTERNAL VARIABILITY!
68 Natural variability? 27-year trends are highlighted
69 Natural variability?
70 Conclusions The Montreal Protocol is one of the great success stories of international climate protection policy. Scientists and policy-makers have regulated the dual protection of the ozone layer and the climate. The climate of the Antarctic has changed dramatically as a consequence of ozone depletion. Future changes will reflect both ozone recovery and GHG warming.
71 References UNEP, Ozone Assessment 2010: ent_2010/index.shtml NASA Ozone Watch: US EPA: The Ozone Story, UNEP, 1998 Velders et al., PNAS 2007 Polvani et al., J. Climate, 2011 Polvani et al., GRL, 2011 Smith et al., GRL, 2012 Kang et al., Science, 2011 Garcia et al., JGR, 2012 Wu et al., J. Climate, 2013 Smith et al., GRL, 2012 Polvani and Smith, GRL, 2013
72 Thank you!
Lovelock detects CCl 3. F (CFC-11) in the atmosphere of both hemispheres Rowland & Molina's Nature paper. CFC + hυ Cl + CCl 2
 1972-1974 1972 Lovelock detects CCl 3 F (CFC-11) in the atmosphere of both hemispheres. 1974 Rowland & Molina's Nature paper Review suggests that tropospheric sinks for CFC's (e.g. oxidation, dissolution
1972-1974 1972 Lovelock detects CCl 3 F (CFC-11) in the atmosphere of both hemispheres. 1974 Rowland & Molina's Nature paper Review suggests that tropospheric sinks for CFC's (e.g. oxidation, dissolution
Stratospheric Chemistry HS 2017 Solution to Homework Problem Set 3
 Stratospheric Chemistry HS 2017 Solution to Homework Problem Set 3 For questions: andrea.stenke@env.ethz.ch (CHN P14) Problem 1: The Montreal Protocol and Climate (a) Chemical Formulas CFC-11 : CFCl 3
Stratospheric Chemistry HS 2017 Solution to Homework Problem Set 3 For questions: andrea.stenke@env.ethz.ch (CHN P14) Problem 1: The Montreal Protocol and Climate (a) Chemical Formulas CFC-11 : CFCl 3
4. Stratospheric ozone depletion
 112 4. Stratospheric ozone depletion The thickness of the ozone layer above Europe has decreased significantly since the beginning of the 198s, and is declining at a rate of 4 5 % per decade. The gradual
112 4. Stratospheric ozone depletion The thickness of the ozone layer above Europe has decreased significantly since the beginning of the 198s, and is declining at a rate of 4 5 % per decade. The gradual
The role of the Montreal Protocol in protecting present and future climate: A scientific perspective
 ATOC4800/ATOC5000/ENVS5830: Policy Implications of Climate : Critical Issues in Climate and the Environment, Prof. Weiqing Han University of Colorado Boulder Boulder, CO 20 February 2019 The role of the
ATOC4800/ATOC5000/ENVS5830: Policy Implications of Climate : Critical Issues in Climate and the Environment, Prof. Weiqing Han University of Colorado Boulder Boulder, CO 20 February 2019 The role of the
The Effects of Volcano-Induced Ozone Depletion on Short-Lived Climate Forcing in the Arctic
 C53C-0852 The Effects of Volcano-Induced Ozone Depletion on Short-Lived Climate Forcing in the Arctic Peter L. Ward US Geological Survey Retired Teton Tectonics Jackson, WY 307-733-3664 cell 307-413-4055
C53C-0852 The Effects of Volcano-Induced Ozone Depletion on Short-Lived Climate Forcing in the Arctic Peter L. Ward US Geological Survey Retired Teton Tectonics Jackson, WY 307-733-3664 cell 307-413-4055
Air Pollution Chapter 21. Atmosphere as a Resource
 Air Pollution Chapter 21 Atmosphere as a Resource Atmospheric Composition Nitrogen 78.08% Oxygen 20.95% Argon 0.93% Carbon dioxide 0.04% Ecosystem services Blocks UV radiation Moderates the climate Redistributes
Air Pollution Chapter 21 Atmosphere as a Resource Atmospheric Composition Nitrogen 78.08% Oxygen 20.95% Argon 0.93% Carbon dioxide 0.04% Ecosystem services Blocks UV radiation Moderates the climate Redistributes
Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part III
 Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part III A Story of Anthropogenic Disruption of a Natural Steady State p 77-79 in Class Notes TODAY: The STORY OF THE DISCOVERY OF THE OZONE HOLE:
Topic # 13 (cont.) OZONE DEPLETION IN THE STRATOSPHERE Part III A Story of Anthropogenic Disruption of a Natural Steady State p 77-79 in Class Notes TODAY: The STORY OF THE DISCOVERY OF THE OZONE HOLE:
Why are there large quantities of the un-natural (Man Made) CFCs in Antarctica?
 Ozone Depletion and Climate Change Why are there large quantities of the un-natural (Man Made) CFCs in Antarctica? In a recent (last August 2016) BBC documentary on the Antarctic weather changes, it has
Ozone Depletion and Climate Change Why are there large quantities of the un-natural (Man Made) CFCs in Antarctica? In a recent (last August 2016) BBC documentary on the Antarctic weather changes, it has
The 2018 WMO/UNEP Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion
 The 2018 WMO/UNEP Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion Co-chairs: David Fahey Paul A. Newman John Pyle Bonfils Safari Scientific Steering Committee: Co-chairs + Martyn Chipperfield David Karoly Doug
The 2018 WMO/UNEP Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion Co-chairs: David Fahey Paul A. Newman John Pyle Bonfils Safari Scientific Steering Committee: Co-chairs + Martyn Chipperfield David Karoly Doug
A MODEL STUDY OF THE IMPACT OF WELL-MIXED GREENHOUSE GASES (GHGS) ON TROPOSPHERIC CHEMISTRY FROM THE PREINDUSTRIAL ERA TO THE PRESENT DAY
 6.6 A MODEL STUDY OF THE IMPACT OF WELL-MIXED GREENHOUSE GASES (GHGS) ON TROPOSPHERIC CHEMISTRY FROM THE PREINDUSTRIAL ERA TO THE PRESENT DAY Fernanda Ramos-Garcés 1 * Vaishali Naik 2 Larry W. Horowitz
6.6 A MODEL STUDY OF THE IMPACT OF WELL-MIXED GREENHOUSE GASES (GHGS) ON TROPOSPHERIC CHEMISTRY FROM THE PREINDUSTRIAL ERA TO THE PRESENT DAY Fernanda Ramos-Garcés 1 * Vaishali Naik 2 Larry W. Horowitz
Gases and the atmosphere
 Gases and the atmosphere Chemical reactions in the atmosphere Ozone cycle Ozone depletion Greenhouse effect Global Warming Pollution in the troposphere 1 Gases and the atmosphere Review Composition of
Gases and the atmosphere Chemical reactions in the atmosphere Ozone cycle Ozone depletion Greenhouse effect Global Warming Pollution in the troposphere 1 Gases and the atmosphere Review Composition of
September 16 th 2010 International Day for the Preservation of the Ozone Layer
 September 16 th 2010 International Day for the Preservation of the Ozone Layer Next 16 th of September it will be celebrated the 2010 edition of the International Day for the Preservation of the Ozone
September 16 th 2010 International Day for the Preservation of the Ozone Layer Next 16 th of September it will be celebrated the 2010 edition of the International Day for the Preservation of the Ozone
Name: Class: Date: 6. Most air pollution is produced by a. thermal inversions. c. ozone layer depletion. b. fuel burning. d. volcanic eruptions.
 Name: Class: Date: Air Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is often used to remove poisonous gases from industrial
Name: Class: Date: Air Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is often used to remove poisonous gases from industrial
SCIAMACHY book. Ozone Recovery? Michel Van Roozendael, BIRA- IASB. ATC14, October, Jülich, Germany
 SCIAMACHY book Ozone Recovery? Michel Van Roozendael, BIRA- IASB ATC14, 27-31 October, Jülich, Germany 1928: start of CFC production 1971: 1 st observation of CFC in the atmosphere (J. Lovelock) 1974:
SCIAMACHY book Ozone Recovery? Michel Van Roozendael, BIRA- IASB ATC14, 27-31 October, Jülich, Germany 1928: start of CFC production 1971: 1 st observation of CFC in the atmosphere (J. Lovelock) 1974:
Stratospheric Ozone. Science Concepts. Stratospheric Ozone. Ozone Chemistry Creation Process Destruction Processes Equilibrium.
 Stratospheric Ozone 12-1 Stratospheric Ozone Ozone Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) CFCs Science Concepts Ozone Chemistry Creation Process Destruction Processes Equilibrium CFC Chemistry Antarctic Ozone Hole
Stratospheric Ozone 12-1 Stratospheric Ozone Ozone Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) CFCs Science Concepts Ozone Chemistry Creation Process Destruction Processes Equilibrium CFC Chemistry Antarctic Ozone Hole
I. Pollutants A. Harmful substances the enter the environment
 I. Pollutants A. Harmful substances the enter the environment II. Two Classifications A. Particulates 1. Tiny substances (liquid or solid) suspended in the atmosphere 2. Examples: Dust, Ash, and Soot 3.
I. Pollutants A. Harmful substances the enter the environment II. Two Classifications A. Particulates 1. Tiny substances (liquid or solid) suspended in the atmosphere 2. Examples: Dust, Ash, and Soot 3.
Chapter 15 Air Pollution and Stratospheric Ozone Depletion
 Chapter 15 Air Pollution and Stratospheric Ozone Depletion Air Pollution Air pollution- the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or microorganisms into the atmosphere at concentrations high enough
Chapter 15 Air Pollution and Stratospheric Ozone Depletion Air Pollution Air pollution- the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or microorganisms into the atmosphere at concentrations high enough
Lecture 29 Air Pollution. Air Pollution. Clean Boundary Layer. Clean Boundary Layer
 Lecture 29 Air Pollution Air Pollution Conditions that promote air pollution episodes Ozone Hole Air Pollution Elevated levels of aerosols and harmful gases Most pollution enters atmosphere near the surface.
Lecture 29 Air Pollution Air Pollution Conditions that promote air pollution episodes Ozone Hole Air Pollution Elevated levels of aerosols and harmful gases Most pollution enters atmosphere near the surface.
Green Chemistry Five ways in which the Chemical industry can become Greener Changing to renewable sources Use of alternatives to hazardous chemicals
 Green Chemistry Green Chemistry refers to the processes in the chemical industry that are being reinvented to make them more sustainable. The term sustain means to keep going. If we use resources faster
Green Chemistry Green Chemistry refers to the processes in the chemical industry that are being reinvented to make them more sustainable. The term sustain means to keep going. If we use resources faster
PHY392S Physics of Climate. Lecture 1. Introduction
 PHY392S Physics of Climate Lecture 1 Introduction Slides based on material from Prof. K. Strong PHY392S - Physics of Climate Lecture 1, Page 1 Some Definitions Weather the fluctuating state of the atmosphere
PHY392S Physics of Climate Lecture 1 Introduction Slides based on material from Prof. K. Strong PHY392S - Physics of Climate Lecture 1, Page 1 Some Definitions Weather the fluctuating state of the atmosphere
HUMAN IMPACT ON THE ENVIRONMENT 02 OCTOBER 2013
 HUMAN IMPACT ON THE ENVIRONMENT 02 OCTOBER 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Look at the Human influence on the environment in terms of: o Composition of the atmosphere and ozone layer (Depleting
HUMAN IMPACT ON THE ENVIRONMENT 02 OCTOBER 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Look at the Human influence on the environment in terms of: o Composition of the atmosphere and ozone layer (Depleting
3/4/2014. Air Pollution. Chapter 15 Air Pollution and Stratospheric Ozone Depletion. Major Air Pollutants. Primary Pollutants
 Air Pollution Air pollution- the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or microorganisms into the atmosphere at concentrations high enough to harm plants, animals, and materials such as buildings,
Air Pollution Air pollution- the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or microorganisms into the atmosphere at concentrations high enough to harm plants, animals, and materials such as buildings,
polar stratospheric ozone & Southern Hemisphere climate change l.m. polvani
 polar stratospheric ozone & Southern Hemisphere climate change l.m. polvani atmospheric circulation changes for the last several decades observations indicate: + strengthening of the Southern Annual Mode
polar stratospheric ozone & Southern Hemisphere climate change l.m. polvani atmospheric circulation changes for the last several decades observations indicate: + strengthening of the Southern Annual Mode
History of significant air pollution events
 Ch17 Air Pollution A thick layer of smoke and haze covers Santiago, Chile. History of significant air pollution events Many of the worst air pollution episodes occurred in the last two centuries in London
Ch17 Air Pollution A thick layer of smoke and haze covers Santiago, Chile. History of significant air pollution events Many of the worst air pollution episodes occurred in the last two centuries in London
Environmental Science Std.-9 Chp.7 Atmosphere and Climate
 Environmental Science Std.-9 Chp.7 Atmosphere and Climate 2018-19 Q.1. Name the layers of the atmosphere. Troposphere Stratosphere Mesosphere Thermosphere Exosphere GREENHOUSE EARTH: Q.2. (a) What is the
Environmental Science Std.-9 Chp.7 Atmosphere and Climate 2018-19 Q.1. Name the layers of the atmosphere. Troposphere Stratosphere Mesosphere Thermosphere Exosphere GREENHOUSE EARTH: Q.2. (a) What is the
Gases and the atmosphere
 Gases and the atmosphere Chemical reactions in the atmosphere Ozone cycle Ozone depletion Greenhouse effect Global Warming Pollution in the troposphere 1 Gases and the atmosphere Review Composition of
Gases and the atmosphere Chemical reactions in the atmosphere Ozone cycle Ozone depletion Greenhouse effect Global Warming Pollution in the troposphere 1 Gases and the atmosphere Review Composition of
Scenarios of ODSs and ODS substitutes. Guus Velders
 Scenarios of ODSs and ODS substitutes Guus Velders 1 02 May 2011 Chapter 5: WMO/UNEP Ozone assessment: 2010 A focus on information and options for policymakers: Metrics: update of lifetimes, GWPs, ODPs
Scenarios of ODSs and ODS substitutes Guus Velders 1 02 May 2011 Chapter 5: WMO/UNEP Ozone assessment: 2010 A focus on information and options for policymakers: Metrics: update of lifetimes, GWPs, ODPs
Mitigation of 21st century Antarctic sea ice loss by stratospheric ozone recovery
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl053325, 2012 Mitigation of 21st century Antarctic sea ice loss by stratospheric ozone recovery Karen L. Smith, 1 Lorenzo M. Polvani, 1,2 and Daniel
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl053325, 2012 Mitigation of 21st century Antarctic sea ice loss by stratospheric ozone recovery Karen L. Smith, 1 Lorenzo M. Polvani, 1,2 and Daniel
Environmental Science 101 Air Resources. Fall Learning Objectives: Reading Assignment:
 1 Environmental Science 101 Air Resources Fall 2012 Lecture Outline: 11. OZONE DEPLETION A. Nature and Importance of the Ozone Shield B. Formation and Breakdown of the Shield 1. Ozone Formation 2. Chloroflourocarbons
1 Environmental Science 101 Air Resources Fall 2012 Lecture Outline: 11. OZONE DEPLETION A. Nature and Importance of the Ozone Shield B. Formation and Breakdown of the Shield 1. Ozone Formation 2. Chloroflourocarbons
Announcements. Pollution week continues. Thinking about pollution. Why are polar bears so contaminated?
 Announcements Grades for exam 2 have been posted March 7 th - Last day to submit LEAD summary to TA, extra credit videos due next Tuesday (no late videos will be accepted) Next Thursday, Environmental
Announcements Grades for exam 2 have been posted March 7 th - Last day to submit LEAD summary to TA, extra credit videos due next Tuesday (no late videos will be accepted) Next Thursday, Environmental
2 Atmospheric Heating
 CHAPTER 15 2 Atmospheric Heating SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How does energy travel from the sun to Earth? What are
CHAPTER 15 2 Atmospheric Heating SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How does energy travel from the sun to Earth? What are
Earth's Atmosphere. Atmospheric Layers. Atmospheric Layers
 Earth's Atmosphere Today we will talk about the part of Earth that is most important to our survival - the atmosphere Earth's atmosphere is unique in the Solar System and has changed greatly over time
Earth's Atmosphere Today we will talk about the part of Earth that is most important to our survival - the atmosphere Earth's atmosphere is unique in the Solar System and has changed greatly over time
The Earth s Atmosphere-I. GEOL 1350: Introduction To Meteorology
 The Earth s Atmosphere-I GEOL 1350: Introduction To Meteorology 1 Overview What is the composition of Atmosphere? How did the atmosphere arrive at its current state? 2 Earth s Atmosphere Earth s atmosphere
The Earth s Atmosphere-I GEOL 1350: Introduction To Meteorology 1 Overview What is the composition of Atmosphere? How did the atmosphere arrive at its current state? 2 Earth s Atmosphere Earth s atmosphere
Chapter 19 Global Change. Wednesday, April 18, 18
 Chapter 19 Global Change Module 62 Global Climate Change and the Greenhouse Effect After reading this module you should be able to distinguish among global change, global climate change, and global warming.
Chapter 19 Global Change Module 62 Global Climate Change and the Greenhouse Effect After reading this module you should be able to distinguish among global change, global climate change, and global warming.
TROPICS: insolation high year round, high sun angle and ~ constant duration
 GE 101, February 6, 14 Finish insolation variation Global environmental issues associated with insolation TRPICS: insolation high year round, high sun angle and ~ constant duration MID-LATITUDES: insolation
GE 101, February 6, 14 Finish insolation variation Global environmental issues associated with insolation TRPICS: insolation high year round, high sun angle and ~ constant duration MID-LATITUDES: insolation
Chapter 17: Atmospheric Science and Air Pollution I. Central Case: The 1952 Killer Smog of London
 Chapter 17: Atmospheric Science and Air Pollution I. Central Case: The 1952 Killer Smog of London A. Thick smog first settled over the city on December 5, 1952, when many residents stoked: B. A wind finally
Chapter 17: Atmospheric Science and Air Pollution I. Central Case: The 1952 Killer Smog of London A. Thick smog first settled over the city on December 5, 1952, when many residents stoked: B. A wind finally
How is the atmosphere different from outer space? a mixture of gases that surrounds the Earth
 Chapter 15 Atmosphere Section 1 Objectives Describe the composition of Earth's atmosphere. Explain why air pressure changes with altitude. Explain how air temperature changes with atmospheric composition.
Chapter 15 Atmosphere Section 1 Objectives Describe the composition of Earth's atmosphere. Explain why air pressure changes with altitude. Explain how air temperature changes with atmospheric composition.
Climate Change and Ozone Loss
 Climate Change and Ozone Loss During the past 900,000 years, the earth has undergone a series of cold glacial periods followed by warmer interglacial periods. The past 10,000 years has been an interglacial
Climate Change and Ozone Loss During the past 900,000 years, the earth has undergone a series of cold glacial periods followed by warmer interglacial periods. The past 10,000 years has been an interglacial
3 - Environmental Ozone Indicators
 3 - Environmental Ozone Indicators A. Introduction: Ozone (O3) is a triatomic allotrope of oxygen. It is naturally occurring process called photochemical analysis; the ozone exists throughout the year
3 - Environmental Ozone Indicators A. Introduction: Ozone (O3) is a triatomic allotrope of oxygen. It is naturally occurring process called photochemical analysis; the ozone exists throughout the year
Lecture Presentation. Chapter 18. Chemistry of the Environment. James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 18 James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Atmosphere The atmosphere consists of the troposphere, stratosphere (combined 99.9 mass %), mesosphere, and thermosphere.
Lecture Presentation Chapter 18 James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Atmosphere The atmosphere consists of the troposphere, stratosphere (combined 99.9 mass %), mesosphere, and thermosphere.
Introduction to Photolysis AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433/633 Ross Salawitch. Importance of Radicals
 Introduction to Photolysis AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433/633 Ross Salawitch Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~rjs/class/spr2013 Lecture 10 5 March 2013 1 Importance of Radicals With a few exceptions,
Introduction to Photolysis AOSC 433/633 & CHEM 433/633 Ross Salawitch Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~rjs/class/spr2013 Lecture 10 5 March 2013 1 Importance of Radicals With a few exceptions,
Overview of Chapter 19
 19 Air Pollution Overview of Chapter 19 Atmosphere as a Resource Types and Sources of Air Pollution Effects of Air Pollution Controlling Air Pollution in the US Ozone Depletion in the Stratosphere Acid
19 Air Pollution Overview of Chapter 19 Atmosphere as a Resource Types and Sources of Air Pollution Effects of Air Pollution Controlling Air Pollution in the US Ozone Depletion in the Stratosphere Acid
Section 4 The Air We Breathe
 Section 4 The Air We Breathe Key Concept Air is an important natural resource that is affected by human activities. What You Will Learn Air pollution is caused by human activities, such as burning fossil
Section 4 The Air We Breathe Key Concept Air is an important natural resource that is affected by human activities. What You Will Learn Air pollution is caused by human activities, such as burning fossil
Large climate-induced changes in ultraviolet index and stratosphere-totroposphere
 Yale-NUIST Center on Atmospheric Environment Large climate-induced changes in ultraviolet index and stratosphere-totroposphere ozone flux By Michaela I. Hegglin and Theodore G. Shepherd (Nature geoscience,
Yale-NUIST Center on Atmospheric Environment Large climate-induced changes in ultraviolet index and stratosphere-totroposphere ozone flux By Michaela I. Hegglin and Theodore G. Shepherd (Nature geoscience,
SAP-2010-FAQs-update.pdf
 ATM 507 Lecture 10 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 4 due Oct. 23 Midterm Oct. 25? Today s topics Polar Ozone, Global Ozone Trends Required reading: 20 Questions and Answers from the 2010 WMO report
ATM 507 Lecture 10 Text reading Section 5.7 Problem Set # 4 due Oct. 23 Midterm Oct. 25? Today s topics Polar Ozone, Global Ozone Trends Required reading: 20 Questions and Answers from the 2010 WMO report
Chapter 20 Air Pollution
 Chapter 20 Air Pollution Overview of Chapter 20 Atmosphere as a Resource Types and Sources of Air Pollution Effects of Air Pollution Controlling Air Pollution in the US Ozone Depletion in the Stratosphere
Chapter 20 Air Pollution Overview of Chapter 20 Atmosphere as a Resource Types and Sources of Air Pollution Effects of Air Pollution Controlling Air Pollution in the US Ozone Depletion in the Stratosphere
Earth s Atmosphere Lecture 14 3/6/2014
 Earth s Atmosphere Lecture 14 3/6/2014 MRS 1 Due Tuesday Second exam will be postponed until after spring break The sun drives the climate of Earth http://www.spaceweather.com/images2002/18mar02/cme_c3_big.gif
Earth s Atmosphere Lecture 14 3/6/2014 MRS 1 Due Tuesday Second exam will be postponed until after spring break The sun drives the climate of Earth http://www.spaceweather.com/images2002/18mar02/cme_c3_big.gif
WMO/UNEP Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion: 2010 OF THE MONTREAL PROTOCOL ON SUBSTANCES
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY WMO/UNEP Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion: 2010 PREPARED BY THE SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT PANEL OF THE MONTREAL PROTOCOL ON SUBSTANCES THAT DEPLETE THE OZONE LAYER **************************
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY WMO/UNEP Scientific Assessment of Ozone Depletion: 2010 PREPARED BY THE SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT PANEL OF THE MONTREAL PROTOCOL ON SUBSTANCES THAT DEPLETE THE OZONE LAYER **************************
Questions 1 4 refer to the diagram of the earth s atmosphere shown above. 3. The section of the atmosphere responsible for our daily weather.
 Unit 6 Practice Test Questions 1 4 refer to the diagram of the earth s atmosphere shown above 1. The ozone layer is found at this location. 2. The atmosphere is at its warmest point at this location. 3.
Unit 6 Practice Test Questions 1 4 refer to the diagram of the earth s atmosphere shown above 1. The ozone layer is found at this location. 2. The atmosphere is at its warmest point at this location. 3.
Chemistry in the Environment
 Chemistry in the Environment Section 261 Earth s Atmosphere In your textbook, read about the terms used to describe the physical and chemical properties of Earth s atmosphere Complete each statement 1
Chemistry in the Environment Section 261 Earth s Atmosphere In your textbook, read about the terms used to describe the physical and chemical properties of Earth s atmosphere Complete each statement 1
ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007
 ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007 Name This examination consists of a total of 100 points. In each of the first two sections, you have a choice of which questions to answer. Please note that you
ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007 Name This examination consists of a total of 100 points. In each of the first two sections, you have a choice of which questions to answer. Please note that you
Lecture 14 Stratospheric Ozone Loss ATOC/CHEM 5151
 Lecture 14 Stratospheric Ozone Loss ATOC/CHEM 5151 1 Setting the Stage: An Historical Perspective To begin, we need to go back to the 1970s Concern about the environment is high and people are starting
Lecture 14 Stratospheric Ozone Loss ATOC/CHEM 5151 1 Setting the Stage: An Historical Perspective To begin, we need to go back to the 1970s Concern about the environment is high and people are starting
Atmospheric Chemistry (Option 1B)
 Atmospheric Chemistry (Option 1B) Introduction Option 1B consists of the following subsections: 1B.1 Oxygen 1B.2 Nitrogen 1B.3 Carbon Dioxide 1B.4 Atmospheric Pollution 1B.5 The Ozone Layer Some chemistry
Atmospheric Chemistry (Option 1B) Introduction Option 1B consists of the following subsections: 1B.1 Oxygen 1B.2 Nitrogen 1B.3 Carbon Dioxide 1B.4 Atmospheric Pollution 1B.5 The Ozone Layer Some chemistry
K EY F INDING #9. Arctic Ozone Depletion
 K EY F INDING #9 Ultraviolet radiation (UV) reaching the earth s surface is a growing concern in the Arctic, largely due to depletion of stratospheric ozone caused by emissions of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
K EY F INDING #9 Ultraviolet radiation (UV) reaching the earth s surface is a growing concern in the Arctic, largely due to depletion of stratospheric ozone caused by emissions of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
Large cancellation, due to ozone recovery, of future Southern Hemisphere atmospheric circulation trends
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl046712, 2011 Large cancellation, due to ozone recovery, of future Southern Hemisphere atmospheric circulation trends Lorenzo M. Polvani, 1,2 Michael
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl046712, 2011 Large cancellation, due to ozone recovery, of future Southern Hemisphere atmospheric circulation trends Lorenzo M. Polvani, 1,2 Michael
Climate Change and Ozone Depletion
 Climate Change and Ozone Depletion Troposphere 78% N 2, 21% O 2, 0.09% Ar,, 0.035% CO 2 Global warming occurs here Stratosphere global sunscreen (ozone layer) Keeps 95% of the sun s s harmful UV radiation
Climate Change and Ozone Depletion Troposphere 78% N 2, 21% O 2, 0.09% Ar,, 0.035% CO 2 Global warming occurs here Stratosphere global sunscreen (ozone layer) Keeps 95% of the sun s s harmful UV radiation
ASTRONOMY 161. Introduction to Solar System Astronomy. Class 16
 ASTRONOMY 161 Introduction to Solar System Astronomy Class 16 Earth s Atmosphere Monday, February 19 Earth s Atmosphere: Key Concepts (1) The Earth s atmosphere consists mainly of nitrogen (N 2 ) and
ASTRONOMY 161 Introduction to Solar System Astronomy Class 16 Earth s Atmosphere Monday, February 19 Earth s Atmosphere: Key Concepts (1) The Earth s atmosphere consists mainly of nitrogen (N 2 ) and
Introduction. Introduction. Introduction. Outline Last IPCC report : 2001 Last IPCC report :
 Introduction Greenhouse Gases & Climate Change Laurent Bopp LSCE, Paris When did the story start? ¾1827 Fourier hypothesizes greenhouse effect ¾1860 Tyndal identifies CO2 and water vapor as heat trapping
Introduction Greenhouse Gases & Climate Change Laurent Bopp LSCE, Paris When did the story start? ¾1827 Fourier hypothesizes greenhouse effect ¾1860 Tyndal identifies CO2 and water vapor as heat trapping
Do Now pg 89. List 3 ways you think air pollution affects human health
 Do Now pg 89 List 3 ways you think air pollution affects human health Lesson 15.2 Pollution of the Atmosphere Types of Air Pollutants Primary air pollutants: Released directly into the atmosphere; example:
Do Now pg 89 List 3 ways you think air pollution affects human health Lesson 15.2 Pollution of the Atmosphere Types of Air Pollutants Primary air pollutants: Released directly into the atmosphere; example:
Name SID Number Final VERSION B
 Name SID Number Final VERSION B 1. Greenhouses. (1) absorb infrared and absorb ultraviolet radiation (2) does not absorb infrared and does not absorb ultraviolet radiation (3) does not absorb infrared
Name SID Number Final VERSION B 1. Greenhouses. (1) absorb infrared and absorb ultraviolet radiation (2) does not absorb infrared and does not absorb ultraviolet radiation (3) does not absorb infrared
Name SID Number Final VERSION B
 Name SID Number Final VERSION B 1. Which of the following is true: (1) The world population is about 15 billion people (2) Half of the energy used on earth today comes from fossil fuel (3) Reducing all
Name SID Number Final VERSION B 1. Which of the following is true: (1) The world population is about 15 billion people (2) Half of the energy used on earth today comes from fossil fuel (3) Reducing all
Modelling the stratospheric polar vortex and its changes for GHGs increase and ozone depletion. Elisa Manzini
 Modelling the stratospheric polar vortex and its changes for GHGs increase and ozone depletion. Elisa Manzini (manzini@ingv.it) National Institute for Geophysics and Volcanology (Bologna, Italy) Thanks:
Modelling the stratospheric polar vortex and its changes for GHGs increase and ozone depletion. Elisa Manzini (manzini@ingv.it) National Institute for Geophysics and Volcanology (Bologna, Italy) Thanks:
Greenhouse Effect. The Greenhouse Effect
 Greenhouse Effect The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse gases let short-wavelength radiation come into the Earth s atmosphere from the sun. However, they absorb and re-radiate Earth s long-wavelength radiation
Greenhouse Effect The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse gases let short-wavelength radiation come into the Earth s atmosphere from the sun. However, they absorb and re-radiate Earth s long-wavelength radiation
The September Equinox is today: Sep 23rd! It s considered the traditional end of Summer and the beginning of Fall
 More coming up in Topic #11 (class notes p 61) The September Equinox is today: Sep 23rd! It s considered the traditional end of Summer and the beginning of Fall The Sun s rays have greatest intensity right
More coming up in Topic #11 (class notes p 61) The September Equinox is today: Sep 23rd! It s considered the traditional end of Summer and the beginning of Fall The Sun s rays have greatest intensity right
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT OF OZONE DEPLETION: 1998
 World Meteorological Organization Global Ozone Research and Monitoring Project Report No. 44 SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT OF OZONE DEPLETION: 1998 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
World Meteorological Organization Global Ozone Research and Monitoring Project Report No. 44 SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT OF OZONE DEPLETION: 1998 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
Topic # 7 Part II ATMOSPHERIC STRUCTURE & CHEMICAL COMPOSITION
 Topic # 7 Part II ATMOSPHERIC STRUCTURE & CHEMICAL COMPOSITION All about the GASES IN THE ATMOSPHERE, esp. GREENHOUSE GASES! Class Notes pp 37-41 REVIEW: ATMOSPHERIC STRUCTURE The changes in temperature
Topic # 7 Part II ATMOSPHERIC STRUCTURE & CHEMICAL COMPOSITION All about the GASES IN THE ATMOSPHERE, esp. GREENHOUSE GASES! Class Notes pp 37-41 REVIEW: ATMOSPHERIC STRUCTURE The changes in temperature
Atmosphere and Climate Change Section 1. Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Section 1: Climate and Climate Change DAY ONE
 Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Section 1: Climate and Climate Change DAY ONE Climate Climate is the average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time. Climate is determined by
Chapter 13 Atmosphere and Climate Change Section 1: Climate and Climate Change DAY ONE Climate Climate is the average weather conditions in an area over a long period of time. Climate is determined by
Threats to Our Atmosphere
 Threats to Our Atmosphere A Reading A Z Level W Leveled Reader Word Count: 1,831 LEVELED READER W Written by Shaun Taylor Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. www.readinga-z.com
Threats to Our Atmosphere A Reading A Z Level W Leveled Reader Word Count: 1,831 LEVELED READER W Written by Shaun Taylor Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials. www.readinga-z.com
Ozonesonde. Ozonesonde
 Ozonesonde Introduction In this exercise you will participate in a group activity which involves measuring and then interpreting the profile of ozone in the atmosphere from the ground to the stratosphere.
Ozonesonde Introduction In this exercise you will participate in a group activity which involves measuring and then interpreting the profile of ozone in the atmosphere from the ground to the stratosphere.
Human Activity and Climate Change
 Human Activity and Climate Change Textbook pages 482 501 Section 11.1 11.2 Summary Before You Read How might climate change affect the region where you live? Record your thoughts in the lines below. What
Human Activity and Climate Change Textbook pages 482 501 Section 11.1 11.2 Summary Before You Read How might climate change affect the region where you live? Record your thoughts in the lines below. What
The ozone hole leaves a lasting impression on southern climate
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health - Papers Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2014 The ozone hole leaves a lasting impression on southern climate Sharon
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health - Papers Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2014 The ozone hole leaves a lasting impression on southern climate Sharon
9th Period Environmental Science Chapter 15: The Atmosphere
 Section 15.1: Earth s Atmosphere 9th Period Environmental Science Chapter 15: The Atmosphere Properties of the Atmosphere: nitrogen, oxygen, water vapor and 1% other gases. air pressure is higher at the
Section 15.1: Earth s Atmosphere 9th Period Environmental Science Chapter 15: The Atmosphere Properties of the Atmosphere: nitrogen, oxygen, water vapor and 1% other gases. air pressure is higher at the
Chapter 18 Chemistry of the Environment
 Chapter 18 Chemistry of the Environment Earth s Atmosphere Outer Regions of the Atmosphere Ozone in the Upper Atmosphere Chemistry of the Troposphere You will need to read the Course Pack to compliment
Chapter 18 Chemistry of the Environment Earth s Atmosphere Outer Regions of the Atmosphere Ozone in the Upper Atmosphere Chemistry of the Troposphere You will need to read the Course Pack to compliment
Physics 100 Lecture 17. The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming April 2, 2018
 1 Physics 100 Lecture 17 The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming April 2, 2018 2 Class Quiz Ch. 7: Suppose your car burned bituminous coal instead of gasoline. How much coal would provide the same energy
1 Physics 100 Lecture 17 The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming April 2, 2018 2 Class Quiz Ch. 7: Suppose your car burned bituminous coal instead of gasoline. How much coal would provide the same energy
Overview of Global Warming, Ozone Depletion, and Air Quality AOSC 433 & 633. Ross Salawitch
 Overview of Global Warming, Ozone Depletion, and Air Quality AOSC 433 & 633 Ross Salawitch Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~rjs/class/spr2017 Note: An entry for CHEM 433 has appeared on Testudo
Overview of Global Warming, Ozone Depletion, and Air Quality AOSC 433 & 633 Ross Salawitch Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~rjs/class/spr2017 Note: An entry for CHEM 433 has appeared on Testudo
Explain how human activities can impact chemical cycles. Explain how pollution can affect food chains.
 Objectives Explain how human activities can impact chemical cycles. Explain how pollution can affect food chains. Key Terms deforestation greenhouse effect global warming eutrophication acid rain pollution
Objectives Explain how human activities can impact chemical cycles. Explain how pollution can affect food chains. Key Terms deforestation greenhouse effect global warming eutrophication acid rain pollution
Air Pollution. Asian Brown Cloud. Developed Countries have reduced emissions recently
 Study Questions 1. Compare and contrast primary vs. secondary pollutants, giving examples of each. 2. Compare and contrast indoor vs. outdoor pollution, listing specific examples and sources of each. 3.
Study Questions 1. Compare and contrast primary vs. secondary pollutants, giving examples of each. 2. Compare and contrast indoor vs. outdoor pollution, listing specific examples and sources of each. 3.
Environmental Impacts of. Energy Production
 CH2356 Energy Engineering Environmental Impacts of Energy Production Dr. M. Subramanian Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College of Engineering Kalavakkam
CH2356 Energy Engineering Environmental Impacts of Energy Production Dr. M. Subramanian Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College of Engineering Kalavakkam
Human Impact on the Environment: Part I
 Human Impact on the Environment: Part I The late Alan Gregg pointed out that human population growth within the ecosystem was closely analogous to the growth of malignant tumor cells, that man was acting
Human Impact on the Environment: Part I The late Alan Gregg pointed out that human population growth within the ecosystem was closely analogous to the growth of malignant tumor cells, that man was acting
Chapter outline. introduction. Reference. Chapter 6: Climate Change Projections EST 5103 Climate Change Science
 Chapter 6: Climate Change Projections EST 5103 Climate Change Science Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of Science & Technology Chapter outline Future Forcing and Scenarios,
Chapter 6: Climate Change Projections EST 5103 Climate Change Science Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of Science & Technology Chapter outline Future Forcing and Scenarios,
COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT. Reviewing Regulation (EC) No 2037/2000 on substances that deplete the ozone layer
 EN EN EN COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, 1.8.2008 SEC(2008) 2367 final COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT Reviewing Regulation (EC) No 2037/2000 on substances that deplete the ozone layer
EN EN EN COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, 1.8.2008 SEC(2008) 2367 final COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT Reviewing Regulation (EC) No 2037/2000 on substances that deplete the ozone layer
Science 30 Unit B Chemistry and the Environment
 Science 30 Unit B Chemistry and the Environment Outcome 2: Students will analyze the sources of organic compounds and their effects on the environment. Specific Outcome 2.3: Identify organic compounds
Science 30 Unit B Chemistry and the Environment Outcome 2: Students will analyze the sources of organic compounds and their effects on the environment. Specific Outcome 2.3: Identify organic compounds
Name SID Number Final VERSION A
 Name SID Number Final VERSION A 1. The main source of energy, that is heating planet earth is (1) renewable energy (2) natural gas (3) the sun (4) oil (5) coal 2. Which of the following mainly causes acid
Name SID Number Final VERSION A 1. The main source of energy, that is heating planet earth is (1) renewable energy (2) natural gas (3) the sun (4) oil (5) coal 2. Which of the following mainly causes acid
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY FINAL UNEP/WMO "SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT OF OZONE DEPLETION: 2002" PREPARED BY THE SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT PANEL
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY FINAL UNEP/WMO "SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT OF OZONE DEPLETION: 2002" PREPARED BY THE SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT PANEL OF THE MONTREAL PROTOCOL ON SUBSTANCES THAT DEPLETE THE OZONE LAYER Released
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY FINAL UNEP/WMO "SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT OF OZONE DEPLETION: 2002" PREPARED BY THE SCIENTIFIC ASSESSMENT PANEL OF THE MONTREAL PROTOCOL ON SUBSTANCES THAT DEPLETE THE OZONE LAYER Released
Geo-engineering of climate
 CREATE Summer School Tim Canty Geo-engineering of climate Today: Climate change Geo-engineering of climate How this may affect the polar regions Will it really work? Lecture C 27 July 2012 1 Is the climate
CREATE Summer School Tim Canty Geo-engineering of climate Today: Climate change Geo-engineering of climate How this may affect the polar regions Will it really work? Lecture C 27 July 2012 1 Is the climate
AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System
 AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System Next: How can we explain Earth s unique atmosphere. What kept Earth s climate stable? How did Earth's atmosphere end up so different? 1. Why did Earth retain most
AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System Next: How can we explain Earth s unique atmosphere. What kept Earth s climate stable? How did Earth's atmosphere end up so different? 1. Why did Earth retain most
Climate Change, Greenhouse Gases and Aerosols
 Climate Change, Greenhouse Gases and Aerosols J Srinivasan J Srinivasan is a Professor at the Centre for Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences at Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. He was a lead author
Climate Change, Greenhouse Gases and Aerosols J Srinivasan J Srinivasan is a Professor at the Centre for Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences at Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. He was a lead author
Topic # 7 ATMOSPHERIC STRUCTURE & CHEMICAL COMPOSITION
 Topic # 7 ATMOSPHERIC STRUCTURE & CHEMICAL COMPOSITION All about the GASES IN THE ATMOSPHERE, esp. GREENHOUSE GASES! Class Notes pp 37-41 OBJECTIVES: To understand: -- the VERTICALSTRUCTURE of the atmosphere
Topic # 7 ATMOSPHERIC STRUCTURE & CHEMICAL COMPOSITION All about the GASES IN THE ATMOSPHERE, esp. GREENHOUSE GASES! Class Notes pp 37-41 OBJECTIVES: To understand: -- the VERTICALSTRUCTURE of the atmosphere
Lecture 2: Greenhouse Gases - Basic Background on Atmosphere - GHG Emission and Concentration Rise - California Regulation (AB32)
 Lecture 2: Greenhouse Gases - Basic Background on Atmosphere - GHG Emission and Concentration Rise - California Regulation (AB32) METR 113/ENVS 113 Spring Semester 2011 February 15, 2011 Suggested Reading
Lecture 2: Greenhouse Gases - Basic Background on Atmosphere - GHG Emission and Concentration Rise - California Regulation (AB32) METR 113/ENVS 113 Spring Semester 2011 February 15, 2011 Suggested Reading
FINAL EXAM STUDYING JUMP START REVIEW. Some review from earlier in the semester and some Q s on more recent topics...
 FINAL EXAM STUDYING JUMP START REVIEW Some review from earlier in the semester and some Q s on more recent topics.... The wavelength range of infrared 1. < 0.4 micrometers radiation. 2. > 0.7 micrometers
FINAL EXAM STUDYING JUMP START REVIEW Some review from earlier in the semester and some Q s on more recent topics.... The wavelength range of infrared 1. < 0.4 micrometers radiation. 2. > 0.7 micrometers
Directed Reading. Section: Global Change. than in the rest of the United States. b. In the United States and Canada, many lakes are dying as their ph
 Section: Global Change In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1. Scientists have discovered that acid rain is caused
Section: Global Change In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1. Scientists have discovered that acid rain is caused
Environmental Engineering Atmosphere & pollution 2
 Environmental Engineering Atmosphere & pollution 2 Global radiation Greenhouse effect Kyoto protocol David Zumr Dpt. of Drainage, Irrigation and Landscape Eng. 1/ insolation from the Sun Electromagnetic
Environmental Engineering Atmosphere & pollution 2 Global radiation Greenhouse effect Kyoto protocol David Zumr Dpt. of Drainage, Irrigation and Landscape Eng. 1/ insolation from the Sun Electromagnetic
Effect of Aviation on Atmospheric Composition
 Effect of Aviation on Atmospheric Composition Cynthia Whaley, Kimberly Strong, Zen Mariani, and Steven Barrett (MIT) UTIAS Colloquium on Sustainable Aviation 15-16 May 2013 Outline Introduction Composition
Effect of Aviation on Atmospheric Composition Cynthia Whaley, Kimberly Strong, Zen Mariani, and Steven Barrett (MIT) UTIAS Colloquium on Sustainable Aviation 15-16 May 2013 Outline Introduction Composition
Depleting The Ozone Layer. environmentalists have extensively studied the effects of the depletion of the ozone layer for the
 Abdul 1 Paula Abdul Dr. Koster CRTW 201 19 April 2005 Depleting The Ozone Layer What would the Earth be like if the ozone layer were to be non existent? Scientists and environmentalists have extensively
Abdul 1 Paula Abdul Dr. Koster CRTW 201 19 April 2005 Depleting The Ozone Layer What would the Earth be like if the ozone layer were to be non existent? Scientists and environmentalists have extensively
Assessing Rates of Climate Change
 Assessing Rates of Climate Change What is the difference between climate and weather Climate = average weather over many years (ex: 30 year averages) Climate forcings (things that affect global temperatures)
Assessing Rates of Climate Change What is the difference between climate and weather Climate = average weather over many years (ex: 30 year averages) Climate forcings (things that affect global temperatures)
TODAY: TOPIC #6 WRAP UP!! Atmospheric Structure & Composition
 TODAY: TOPIC #6 WRAP UP!! Atmospheric Structure & Composition There s one more thing to correct in our the depiction of incoming Solar....... the atmosphere is NOT totally TRANSPARENT to INCOMING Solar
TODAY: TOPIC #6 WRAP UP!! Atmospheric Structure & Composition There s one more thing to correct in our the depiction of incoming Solar....... the atmosphere is NOT totally TRANSPARENT to INCOMING Solar
Aerosol from biomass burning and mineral aerosols. 1. What are aerosols from biomass burning?
 Lectures 40-41. Global change due to anthropogenic aerosols: Aerosol from biomass burning and mineral aerosols. Objectives: 1. What are aerosols from biomass burning? 2. What is mineral aerosol? 3. Direct
Lectures 40-41. Global change due to anthropogenic aerosols: Aerosol from biomass burning and mineral aerosols. Objectives: 1. What are aerosols from biomass burning? 2. What is mineral aerosol? 3. Direct
Air Pollution. Air Pollution 3/11/2015. Our Atmosphere IS a Resource. March 10, 2015 Mr. Alvarez
 Air Pollution March 10, 2015 Mr. Alvarez Air Pollution Air Pollution- the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter or microorganisms into the atmosphere at concentrations high enough to harm plants,
Air Pollution March 10, 2015 Mr. Alvarez Air Pollution Air Pollution- the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter or microorganisms into the atmosphere at concentrations high enough to harm plants,
