Executive Summary. Inorder to avert a major crisis, key actions at the recommended in the immediate term (upto 3 months), Among the urgent actions
|
|
|
- Phebe Stephany Quinn
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Executive Summary Acute water scarcity has developed into a severe drought situation. While there has been monsoon deficit of 2014, differential rainfall pattern 1, hail storm in Feb-Mar of 2015 crop losses have turned more macabre due to the subsequent rainfall deficit in many places during Jan-Feb of 2016; to untimely snowballing into major crisis that most of the most vulnerable in Bundelkhand find themselves sucked into, some of whom are out of options. This document is an attempt to capture key findings of the Inter-Agency assessment of impact of drought on men, women, children, families, communities. It has tried to capture key aspects of migration during this period, water-sanitation and hygiene, food security, nutrition and IYCF, and key observations on government response. Please refer to Annexure 1 for Terms of reference of the Assessment There is need for urgent attention being paid to the region in view of acute food security challenges being faced by the most vulnerable in the region. The situation is alarming with severe repercussions for children as well as women whose social status. Timely action is needed to avert a looming crisis. In the absence of regular growth monitoring, severe malnutrition among children abounds. The most vulnerable people are bearing repressions of the acute crisis every single day. Inorder to avert a major crisis, key actions at the recommended in the immediate term (upto 3 months), Among the urgent actions Area/districts of Uttar Pradesh that are declared drought hit are highlighted in orange recommended to be implemented, the key ones are: implementation of provisions of National Food Security Act, immediate supplementation of mid-day meals, provision of subsidized fodder and monitoring nutrition levels of children across all affected districts. It is absolutely essential that life saving drugs for children are available free of cost, micro-nutrients be made available to children Mobile Health Units be operationalized and atleast two Fair Price shops are started in each affected district in line with good practice from West Bengal Medium term (3-12 months) and long term (12-48 months) actions are also recommended to prepare for and mitigate the drought situation in future. 1 Differential rainfall patterns, in large part being ascribed to climate change are such that even within a Panchayat, while one part get some rain while another doesn t.
3 1.0 Background Water scarcity is nothing new to Bundelkhand, a region home to 18 million people 2 spread over 7 districts of Uttar Pradesh and 6 districts of Madhya Pradesh. For a small farmer, it is not the most favourable place to be in, with interplay of factors pitted against him. Little wonder then, that the area has a population density of less than one-third of the UP state average. 79% live in the rural areas of which one-third households are officially Below Poverty Line (BPL) entitling them to state s welfare schemes. Over 75% of Bundelkhand s population continues to depend on agriculture, while 96% of the total income is raised from agriculture and livestock together. 30% of this population has a land holding between 1-2 acres. As is well documented, the region experienced a major drought in every 16 years during the 18th and 19th centuries, which increased by three times during the period 1968 to 1992 (Samra, 2008) 3. The last time India experienced back to back droughts was in It was only the fourth time in a century that the country battled two consecutive years of scant rainfall. The drought of 2015 was the worst India has experienced in recent years. Nearly half the districts in the country recorded a rainfall deficit of 20% or more. More recently, the Drought Crisis Management plan, 2015 of Government of India recognizes a more than three-fold increase in drought occurrence in Bundelkhand region to once in 5 years. The drought of 2015 was the worst India has experienced in recent years. Nearly half the districts in the country recorded a rainfall deficit of 20% or more. However efforts at mitigating drought are yet to bear visible fruit at a large scale 4 Drought is widely recognized as no longer a mere absence of or scarcity of rainfall but related to inefficient water resource management 5. It is worth noting that December 15 and January 16 are considered the warmest winter months in the last 100 years. The deficiency of more than 50% rainfall has greatly reduced the ground water level, as a result the availability of water for irrigation dropped considerably, which has led to severe crop failure. The districts of Bundelkhand region suffer particularly severely, as their economy relies heavily on agriculture. 6 2 Figures as per 2011 census of India figures 3According to Inter-ministerial Central Team s report on drought mitigation strategies for UP and MP Bundelkhand under Dr. J. S. Samra 4 As a response to the chronic drought like conditions, a Special package for implementation of drought mitigation strategies in the region was approved by the Central government in As part of the package, Rs 7266 crores (approx. 121 million USD) were allocated for Uttar Pradesh and Rs 3760 crores (approx. 627 million USD) for Madhya Pradesh. A further one hundred crore rupees each for Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh were approved in 2011 under the 12thFive year plan. 5 Management of drought, National Disaster Management Guidelines, September 2010, NDMA 6 Verbatim quoted from version 8 of the unpublished report of the Rapid Impact Assessment Mission of Drought in Budelkhand region, by Dr. D. Caravotta, Health Consultant at UNICEF, Uttar Pradesh and others
4 Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Social consequences of such high levels of distress are many. Media has for years reported the distress of young men of marriageable age not getting bride due to acute water stress in their village. In the current situation on the other hand, crop failure and lack of employment has led to migration of working adults leaving children and elderly behind and as rapid assessment has revealed, large scale desertion of livestock to save them from starvation! Water bearing ponds of Bundelkhand, many of them silted during the course of Independent India, still provide precious water, thus forming the backbone of an otherwise precarious living in Bundelkhand. Furthermore, fast depleting ground water reserves that have anyways been widely categorized as the ultimate last resort, low productivity of land, recent dependencies on high investment crops by the farmers and the continued increased need for irrigated fields along with a challenged development scenario of the region are other important factors within the context of Bundelkhand. Debt burden upon farmers is forcing suicides. Rainfall data of the state for 2014 and 2015, although aggregated, highlights the deficit in rainfall in the last three cropping seasons in the state Uttar Pradesh Rainfall pattern Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Actual Normal Deficit % Uttar Pradesh Rainfall pattern-2015 Actual Normal Deficit Despite years of well-intentioned Central and State level funding allocations, Meterological failure has repeatedly causing drought disaster in Bundelkhand despite years of Central and State level schemes, funding allocations and hosting of international level institutions within the region with large financial outlays. 7 Acute scarcity has caused crippling effect on the food security and livelihood support system beyond the level of community resilience. Anecdotal references as well as British era gazetteers from as recent as 1860s provide mention of forest reserves and high cotton yields in Bundelkhand, both of which are critical components of livelihoods for the rural poor. As a response to the critical situation, 50 districts of Uttar Pradesh have been officially declared as drought affected. Independent figures point to 40% of the country being under drought like conditions. 7 While the rate of its occurrence varies, researchers point to the stoic inevitability of its occurrence. Currently 39% of the country s landmass is suffering due to drought. As per the National Drought Manual, 2009, three hundred and twenty nine million hectare of land covering 103 districts and 16 states of India are chronically drought prone. (An area close to 70% of the net sown area of the country).
5 As rain Gods turn away ( a run up to the current drought situation) Overall, there is a below normal rainfall of about 14% across the country, with vast regional and intrastate variations (Even at the national aggregate level, while normal rainfall is mm, actual rainfall was mm). Definitely, the Gangetic belt of India is the worst affected with severe shortage of rainfall. State of Uttar Pradesh is the worst affected with all the districts receiving less than normal rain. 32 of its districts received scanty rainfall of less than 50% of normal rainfall, 35 of them less than 20% rainfall and just four of them normal rainfall (i.e. less than average, but within -20% range). It must be noted that states like Punjab, Haryana, Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Maharashtra and Bihar are also severely affected. Madhya Pradesh, Chattishgarh, Gujarat, Karnataka, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh, Telengana and Jharkhand have several districts with deficient rainfall (between 20% to 50%). Only the State of Jammu & Kashmir has had excess rainfall across all districts but for a few. Intra-state variations are also highly visible. The state of Arunachal Pradesh has districts varying between 68% (deficit rain) to % (excess) rainfall. Tamilnadu, Meghalaya, Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan too have 2 to 4 districts receiving excess rainfall, with others getting deficit rainfall. In the case of West Bengal, the usually high rainfall fed sub-himalayan West Bengal (normal mm), including Darjeeling hills have received a - 19% (deficit) rainfall (actual mm); the Gangetic West Bengal has received about +13 % (actual 1299 mm) rainfall from normal ( mm). States with exposure to higher climate variability seem to have been impacted by the severe shortage and high intrastate deviations of rainfall. This is closely in line with the ranking based on Exposure related indicators of ICAR (Central Research Institute for Dryland Agriculture) on Climate change: Vulnerability & Implications to Drought Programming in India that considers rainfall variations, heat wave conditions, dry spell period, intensity of rainfall and other climate variable indicators for ranking the districts.
6 Development scenario in Bundelkhand, Uttar Pradesh While this document pertains specifically to the impact of prevailing drought condition in Bundelkhand on men, women and children; development deficits, particularly those relating to child survival, development and growth have been a challenge in the whole of Uttar Pradesh. Figures indicate that 21.6 % children of Uttar Pradesh are born under-weight and so are in need of additional support. Please refer Annexure 2 for Urban Rural Divide of Low Birth Weight among Children in Drought Affected Districts Children born underweight in Uttar Pradesh Nearly one-third of India s child laborers come from Uttar Pradesh. More than 55 % of children are Source: Census of India, 2011 stunted, and the state has the highest neo-natal mortality in the country. It is to be noted that children breast fed within one hour of birth in Uttar Pradesh is 39.4% (In rural areas it is 38.9%). Exclusive breastfeeding in first six months is just 20.8 % across the state. About 20 million people of the state practice open defecation 8. It is also recorded that over 45% of adolescents in the state do not go to school. Even at an aggregate level, only about 19 % of households have access to treated piped water. Understandably, this water supply is limited to urban and semi-urban areas. 22 districts among the drought affected districts have less than 15% of their households covered by tap water supply. Please refer Annexure 3: State wise comparison of development indices Source: Census of India, 2011 Percentage of households accessing water from tubewells 8 Source:
7 Methodology for assessment In view of the worsening drought situation in the state, Inter-Agency group took upon itself to conduct rapid needs assessment from 09 th -11 th February of a drought situation that has become a matter of immediate and urgent attention for all. Below mentioned five most affected districts selected for RNA are indicated in Figure XXX - DISTRICT BANDA CHITRAKOOT SIDDHARTHNAGAR SONBHADRA MOHOBA BLOCK Naraini, Tindwari Manikpuri Bansi Duddhi Kabrai
8 Criteria for selection of blocks The following were the criteria for selection of the blocks for the rapid assessment: o o o Among areas with highest water stress and with highest vulnerabilities Presence of CSO partners and therefore logistically feasible to conduct assessment Discussion with district administration officials for selection of target blocks. e.g. The district Magistrate of District Chitrakoot also suggested to pick Manik Pur as one of the block for assessment. Five teams comprising of members from - Action Aid, Water Aid, UNICEF and Oxfam partner agencies were formed and a common field tool was used. Orientation of the field staff/enumerators was conducted on 8th of February 2016 by Action Aid & UNICEF on IRA methodology. The assessment team met with district officials (List of people met is attached in Annexure 4) and conducted house visits in the most affected 22 villages. Key findings and recommendations arising from this exercise are given in the following sections.
9 Section 2: Key Findings Food Security The following are the key findings from the rapid assessment related to food security issues: There is a high degree of stress prevalent in the region on account of access to food. In two out of every three villages, report of eating smaller meals (less filling meals) and fewer meals was reported. In addition to this, the cultural practice in the region of women eating leftovers at the end of the meals, is sure to have adverse impact on the health of women in general and pregnant and lactating women in particular. In all the places visited, people are concerned that they are not able to purchase the type of food according to their choice due to lack of resources. People are presently reporting to be eating same type of food day after day. In about 50% of cases, people reported to be eating things that they would not like to eat in normal circumstances. Grain quality in the local market is not good, yet high prices are being charged. In about 40% cases, people reported to have gone to bed hungry as they had no or inadequate food. Nearly 50% families have limited their regular intake of food to potatoes and rice, or wheat and potato with some salt. Lentils, which are a source of essential protein have been taken off their menu. Affordability is limited to a few families, the differentiation is evident in the fodder quality too The following coping mechanisms were observed: About one-fourth families are borrowing money/food from others About 15% in total are coping from collecting wild fruits and other produce Only about 50% were working for the food As high as 30% were seen bartering/ exchange of good with others for foods In general food aid/dependency on PDS of government is in about 20% cases fall back on stored food at family level (10%) loan from money lenders was specifically mentioned in one case; purchase food with existing resources and earnings from work (over 70%). Most people use one or more strategies. It is clear that there is high degree of stress in the current situation, and if timely and appropriate action is not taken, the situation is likely to get much worse as people run out of options
10 Suggestions from community: Proper and regular opening of the PDS shops has been suggested by most as they find irregular opening of PDS shops as a critical constraint. Suggestions are also for (a) increase the quantity of food supplies per person until the coming monsoon; (b) make more materials available through the PDS Nutrition The following are the key findings from the rapid assessment related to nutrition and IYCF issues: Only 10 % of the villages reported of regular growth monitoring having been conducted in the recent months, which has been undertaken only after the declaration of drought by the state In a test in 6 locations, 17 undernourished children and 35 severely malnourished children could be recorded at an average of about 9 per hamlet. This is a clear sign that the risk to children is high in the present situation. In about 40% of locations, supplementary nutrition programs in the form of dry ration through ICDS etc are available to children of 7 months to 6 years age group. Considering the severity of the problem, ground reality of ICDS is too dismal- new evidence suggests, however, that large numbers of children with severe acute malnutrition can be treated in their communities without being admitted to a health facility or a therapeutic centre! In 25 % of cases, children are said to be moving with parents, which could have implications for their nutrition, access to health services and development. In 30% places people confirmed Vitamin A Supplement being provided to children under five years. At about 10 % places children showed signs of Vitamin A deficiency. At least in 50% of places children s eye had been tested for Vitamin Deficiency, and only in 20% of cases people confirmed distribution of de-worming tablets. People are being supported in some locations by locally wealthy people, money lenders and other well intended persons. However, these resources are expected to run out soon. In few places people have begun to change the way they manage their food habits. In 65% cases informants mostly mothers stated that their milk was insufficient to meet the demand of the infant and they resorted to buying expensive commercial products from the market In the case of young child feeding, 25 % of families reported non-availability of (poor capacity to purchase) lentils as a key issue for inadequate feeding of children. In other cases families reported that the children had same food as family (with addition of milk, where possible). It must be noted that, as per RSOC report of % % newborns in Uttar Pradesh have
11 low weight at the time of birth. The report mentions that nearly 65% families give water and animal milk / supplementary milk products within the first six months of children; about 10% receive semi-solid food or adult food in that period. Suggestions from Community: Make supplementary nutrition (micro-nutrient fortified food ) available regularly for children at the ICDS centers; monitoring of child growth should be regular and timely referral of malnourished children is important for early management. All anganwadi centres should be opened regularly and food be provided. Health The following are the key findings from the rapid assessment related to Health issues: In 70% of cases surveyed, families had access to primary health (health sub-center or PHC), as the point of access. Others had access to secondary services and facilities such as the CHC. 30% people only mentioned of having access to doctors, and others have access to an ANM or the pharmacist as the highest level of staff that provides services to them. 40% families can access health facilities within 5 kms of their house; 10 % need to travel between 5 10 kms and the rest need to travel more than 10 kms. About 45 % mention that the access to health facilities is very difficult. They identified difficulties relating to transportation as the critical issue; about 5 % marked lack of roads to access health centers as the primary problem. Cold & fever, acute respiratory problems and diarrhea besides cases of jaundice and malaria are the main problems for which people visit the health services. This is in tune with the information available from health centers, and corresponds to AHS to a large extent. Unclean water is identified (marked in questionnaire) by nearly everyone as the main cause of morbidity among children and adults. 20 % also mentioned trauma and other non-infectious diseases as the reason for morbidity. Outreach for routine immunization and polio immunization seems to be much better as people had the immunization cards with adequately updated information. Whereas the initial immunization such as BCG is mentioned to be at about 85% (as per AHS reports), the drop is in measles vaccination, which is around 15% 9 in the case of areas surveyed, marking sharp decline from BCG to Measles. In 80 % of the cases mortality surveillance is not done, especially in the case of children. In case of adults; accidents, respiratory diseases, complications arising from alcohol abuse, communicable diseases such as AIDS, malaria, diarrhea, non-communicable diseases, other diseases and unnatural deaths (suicide) are reported as major reasons. In the case of children under 5 years, respiratory diseases, diarrhea, pneumonia, under-nutrition, lack of care of 9 This resonates with the findings of the study undertaken in 2008 on the drought conditions in Bundelkhand region.
12 children, not availing timely treatment for diseases, measles and rickets are considered major contributors to child mortality. This also goes well with the behavioral issue of open defecation and contamination of water and environment, and its negative results. Three major contributors to limited availability of health services are: (a) poverty / lack of finance; (b) lack of transportation / distance from health services; and (c) lack of facilities at the health institutions. Suggestions from Community: Mobile health facilities and mobile health camps need to be increased to improve access to services. Separate health camps for women and children may be organized from time to time. Government must also focus on building health awareness among people. Make more medicines available at hospitals so that people need not purchase most medicines with their own money. Water, sanitation and hygiene The following are the key findings from the rapid assessment related to water, sanitation and hygiene issues: Hand pumps are the most common source of water However, on an average, 1/3rd of the pumps are dysfunctional due to depletion of water table up to feet in some areas. In about 40% cases, open wells are being used for water collection. U n c l e Dysfunctional hand pumps due to steep drop in ground water level, and dysfunctional abandoned toilet Location: Chheria Khhurd/Buzurg an water was reported from Banda district. In all villages assessed, open defecation is the common practice. In 8 out of 10 places, animals are sharing water with the humans from the same water sources.
13 Remnants of ambitious water supply schemes dot the landscape. Meanwhile, the current situation of acute water scarcity is pushing people to the brink. There is drastic drop in water level in the wells, the only source in many cases. Women spend an average of 1-2 hours collecting litres of water, barely sufficient to meet family needs Open defecation is common practice this can be substantiated with numbers. With high open defecation in rural areas and less availability of water, potential for contamination of remaining water sources is high. In 1/3 rd of the houses, toilet is very close to the water source, indicating high possibility of water source contamination. Basic cleanliness and maintaining hygienic environment in and around family toilets also is a challenge. Suggestions from community: Government needs to make water available to the people for their consumption and that of animals in places where the situation is severe; tube wells may be further deepened (deep tube wells) and re-boring of tube wells may be of undertaken. The government needs to concentrate on water purification. Construction of toilets and provision for soaps may be considered urgently. Migration One out of five families is moving out with families. This is mainly visible in Banda district, and could be an indication of stress in the region. In large numbers, cattle and livestock are seen wandering as they are being left by the owners as there is dire paucity of fooder. Brick kilns have been a source of livelihood for the people of the region. However, most brick kilns are under closure under direction of the National Green Tribunal (NGT) for lack of clearance from Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB). This has also brought about additional stress On Government response 10 Nearly everyone felt that no additional efforts have been done to improve access to water and sanitation related services. 55 % felt that some non-food items such as blankets have been provided by the government, and 50% felt that food items are being provided through PDS for people. Others felt that nothing significant is being done to improve availability and access to food by the people. 45 % of the respondents feel that supplementary nutrition is available through ICDS centers (mostly in the form of khichidi, daliya and lentils) 40 % feel that the Health department is working to promote Infant and Young Child Feeding (IYCF) 10 For Central and State level efforts in drought response, please refer to Annexure 5
14 Suggestions from community: (a) There is a need for more frequent visits by concerned government officials to affected villages so that the needs and emerging situations are monitored, and people s needs are taken up on priority. (b) Streamline relief supplies so that people get access to supplies in due time with less delays and in right quantity. (c) Be prepared to provide for water and fodder for the needs of animals. (d) Work to improve irrigation systems to avoid / minimize crop failures. (e) The government also needs to take steps to improve transparency and accountability of revenue department in provisioning of relief supplies. Improve the system for verification of beneficiaries. (f) Review the functioning of government service providers (such as PHC, ICDS centers and PDS shops), to make them functional immediately.
15 3.0 Key Recommendations In view of the acute crisis that the region is going through, there is need for all stakeholders to work together in well coordinated manner inorder to avert the large scale humanitarian crisis. The following key recommendations have come up from the rapid assessment. The list of medium and long term actions is not exhaustive, but serves as a good starting point: Coordination Immediate term (0-3 months) To Government The Government has a member of Committees at the district level. Participation by CSO s in these committees will help improve coordination between the government and the civil society. District Magistrate, Hamirpur has constituted a committee called Samvedna where two NGO s are members. The Committee meets twice a week on designated days. District level water scarcity task force under the chairmanship of District Magistrate should be constituted with representation from NGO s/cso s and subject experts. Food Security National Food Security Act should be implemented ; pulses, edible oils and other basic food items should be provided through an improved Public Distribution System until end of July An older system of the BPL categorisation for PDS is widely considered notoriously restrictive, unreliable and outdated and therefore is in dire need for updation. Mid Day Meal should include the provision of eggs and milk for children. In addition, it should be run continuously throughout the summer when the schools close. In addition to the crop compensation, subsidised animal fodder should be provided to the distressed farmers. Train anganwadi workers, (if not possible, engage trained volunteers from select NGOs), to monitor nutrition level of children across all affected districts, and set regulated reporting system Ensure cooking of hot cooked meal at AWC daily. Supplementary nutrition should be distributed for the recommended 25 days. Health Ensure more varieties of generic medicines for common ailments and all life saving drugs for children are available free of cost at all health centers Make micro-nutrients available to children through anganwadis and to women in reproductive age through health institutions. Corporate engagement to provide for additional micro-nutrients may be sought in case of lack of funds. Start at least two Fair Price Medicine shops (as done in West Bengal) in each district Mobile Health Units should be operationalized.
16 Water Sanitation and Hygiene Monitor water availability in villages and towns, and provide for additional solutions such as (a) providing water through water tankers (b) availability of water purification systems with engagement of civil society participation; (c) marking of drinkable water from water for other human and animal needs; (d) temporary mitigation measures in areas where above solutions are inadequate Others Provide free bus passes to all students for the purpose of attending schools and colleges in the affected districts till end of June 2016 To Humanitarian Agencies Undertake sectoral assessments, especially for Nutrition and WASH immediately, and design further plan of action as per the detailed sectoral assessment. An assessment on Livelihood and Food Security is also recommended. Monitor emerging situation through IAG partnership and village volunteers and establish a daily reporting mechanism for collation of qualitative and quantitative observations to be operational till mid-june 2016 Support in monitoring child health and nutrition levels, and provide for additional support as may be necessary in the case of malnourished children and pregnant women Undertake random school attendance along with Education Department to monitor and report any trends in lowering of school attendance. Organize awareness programs on maintaining sanctity of clean water, water purification and culturally acceptable locally available nourishment for children, aged and others in need. IAG to put together a Who s Doing What matrix to guide further action by humanitarian agencies Medium term (3-12 months) Take support of higher academic institutions to design employment generating programs in large numbers in order to increase coverage under MNREGA, and provide for speedy payment of wages. Ensure, in parallel on an urgent basis that eligible households are identified and appropriation of BPL cards brought to an end to stem the downward slide that only points towards hunger and deprivation in the region. UP State drought SoP should be drafted. There should be due acknowledgement that not only are the rainfall different in different districts, but also the possibility of differential possibility within the district itself. Indicators for emergency response must be setup for instance relating to loss of cropping due to less rainfall, withdrawal of monsoon and delay in monsoon for more
17 than four weeks, and percentage reduction in rainfall. There is a need to setup indicators for different stages of crisis: 1. Watch or alert Indicator based on meteorological data. 2. Warning Indicator based on meteorological as well as water scarcity levels. 3. Emergency Indicators linking water scarcity, livelihood vulnerability on the basis of risk scenario develop response scenario accordingly. 4. Acute Indicators should lead to response action being initiated on war footing. Detailed assessment of governed programs should be carried out on a pilot basis with the government in one district of Bundelkhand. Crop Insurance should be made mandatory and institutional arrangements should be made so that timely payment of insurance premiums can be made. Banking and insurance mechanisms should be dovetailed to ensure that credit is disbursed to the farmer after not only deduction of the premium amount, but immediate issuance of crop insurance/ premium paid receipt. There is also need for large scale disssmination of Package of Practice (PoP) for drought resistant cropping and demonstrable examples from within the region should be viewed as leaning opportunities. Peer learning and exchange mechanisms should be developed within and across districts Long term (12-48months) As a local resource, the indigenous bovine population has been largely viewed as a low milk yielding variety and almost never viewed as a farm resource of sustainable farming. As a remnant of the Green revolution of the seventies, there are many reported instances of Artificial Insemination (AI) efforts have had undesirable negative fallouts such as cattle loss owing to high temperatures in the region. In the absence of a cattle insurance outreach in the region, such losses are a difficult setback! Cattle insurance should be rolled out on pilot basis in one block on pilot basis in each of the Bundelkhand districts. Farming practices have largely ignored local farm based, small scale ponds, while favouring large irrigation structures. Farm ponds are good instruments for recharge of ground water and protective irrigation. Micro irrigation practices are yet to be sizeably up scaled. In the long term there is need for mainstreaming frugal technology and making it accessible to people for ensuring rural livelihoods. All micro-irrigation schemes of the GoI should be implemented in totality in Bundelkhand. Micro-irrigation and drip-irrigation projects should be implemented on a 100% saturation basis. Farm Pond (JalKhets) technology are being promoted by the civil society and NGO s efforts as a drought proofing measure. For instance, in Dewas district of Madhya Pradesh nearly 6000 farmers had invested on ponds since 2006, and it was determined that they were able to recover their initial investment in just 3 years on account for agricultural economy of the region due to the significant improvement in availability of irrigation water. Sustainable Livelihood options are a pressing need. With the growing awareness of environmental sustainability and regulatory frameworks coming into force, alternate rural livelihoods are needed in large numbers.
18 Not only tanks, canals also need to be de-silted and enough measures be undertaken to ensure that tail end villages receive water.
19 Annexure 1: Terms of Reference, Rapid Assessment (Drought) Bundelkhand 1. Background Uttar Pradesh has been roiled by three successive crop failures due to drought and unseasonal rains. The situation caused by extensive damage to Rabi crop in the month of April 2015 as a result of hailstorm and unseasonal rains and current drought has led to extensive crop damage worsened the life of small and marginal farmers and poor people of Bundelkhand. The successive crop failures have a convulsive impact on people: from worsening hunger to mass exodus of entire villages in Bundelkhand region. Due to the current situation of drought, the evidence of widespread intense crises of food, nutrition, drinking water, health ailments, and fodder for animals is visible in villages, small and marginal farmers are unable to pay off their mounting crop debts, due to recurring crop failure. The crisis of feeding the destitute, especially old persons, women and children has been critical and they are suffering the most in this situation. The state government has declared 50 districts as drought-hit in Uttar Pradesh. Inter-Agency coordination meeting of UP was conducted to discuss the drought situation in the state. IAG has decided to conduct rapid needs assessment on prevailing drought situation in 5 worst affected districts of Uttar Pradesh 2. Terms of Reference: In the view of above, the terms of reference for mission is provided below: To assess the impact of the drought situation in Bundelkhand region in the UP affected and selected districts/villages). To assess the Government response to the drought. To assess the quantity and quality of the Health System and structure and the capacity of response in case of emergency/outbreak drought related. To study the coping mechanisms and resilience response of the population. To recommend sector-wise actions for (W&S,Nutrition,Health-Immunization) to the GOUP to decrease the impact of the drought to the affected populations in Bundelkhand region. Meeting with key stakeholders to assess the impact of the drought conditions on the population especially on women and children in the worst affected districts. An evaluation of the food availability, potable drinking water availability, health and nutrition status of the affected population with clear focus on the needs of children and action taken by the State/District authorities. The team should also study the coping mechanisms of the population. Availability of health and social services. To assess prevalence of morbidity, mortality and under nutrition by using standardized tools of assessment and the status of immunisation and child health services. To indicate the vulnerable areas where quick corrective action can be implemented. To recommend IAG support for mitigating the adverse impact of the drought, both in immediate response needs and in mid-term if required.
20 Annexure 2: Urban Rural Divide of Low Birth Weight among Children in Drought Affected Districts 11 S.No Affected District Rural Urban Total 1 Agra Allahabad Ambedkar Nagar Auraiya Baghpat Ballia Balrampur Banda Barabanki Basti Chandauli Chitrakoot Deoria Etah Etawah Faizabad Farrukhabad Fatehpur Ghaziabad Gonda Gorakhpur Hamirpur Jalaun Jaunpur Jhansi Kannauj Kanpur Nagar Kaushambi Kushinagar Lalitpur Lucknow Mahamaya Nagar Mahoba Mahrajganj Mainpuri Mau Mirzapur Pilibhit Pratapgarh Rae Bareli Information for the district of Amethi is not available, and so, is not integrated in the table.
21 41 Rampur SantKabir Nagar SantRavidas Nagar (Bhadohi) Shahjahanpur Siddharthnagar Sonbhadra Sultanpur Unnao
22 ANNEXURE 3: State wise comparison of development indices Uttar Pradesh is one of the states with high development deficits, with less access to education, health and nutrition; this is compounded by existential poverty and social discrimination. A detailed analysis measuring Uttar Pradesh against other states of the country in terms of multiple indicators (prepared by DRR Section of UNICEF Delhi Office in 2015) shows that the state is in most vulnerable position with high vulnerability and low capacity as shown in the table below: Area Name Risk Index Child Protection Education Hazard Health Nutrition WASH Tamil Nadu Karnataka Assam Maharashtra Jharkhand Chhattisgarh Gujarat West Bengal Orissa Andhra Pradesh Rajasthan Madhya Pradesh Bihar Uttar Pradesh
23
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF DRINKING WATER & SANITATION LOK SABHA UNSTARRED QUESTION NO.450 TO BE ANSWERED ON Piped Water Supply
 GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF DRINKING WATER & SANITATION LOK SABHA UNSTARRED QUESTION NO.450 TO BE ANSWERED ON 19.07.2018 Piped Water Supply 450. SHRI BHAIRON PRASAD MISHRA: Will the Minister of DRINKING
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF DRINKING WATER & SANITATION LOK SABHA UNSTARRED QUESTION NO.450 TO BE ANSWERED ON 19.07.2018 Piped Water Supply 450. SHRI BHAIRON PRASAD MISHRA: Will the Minister of DRINKING
SITREP-: Drought in Bundelkhand Region of UP & MP and Maharashtra 30 th March 2016
 Situation Report SITREP-: Drought in Bundelkhand Region of UP & MP and Maharashtra 30 th March 2016 The Bundelkhand region (comprising seven districts of Uttar Pradesh and six districts of Madhya Pradesh)
Situation Report SITREP-: Drought in Bundelkhand Region of UP & MP and Maharashtra 30 th March 2016 The Bundelkhand region (comprising seven districts of Uttar Pradesh and six districts of Madhya Pradesh)
PROGRAMMES AND SCHEMES Monsoon and Crop Sowing Situation during Kharif-2012
 PROGRAMMES AND SCHEMES Monsoon and Crop Sowing Situation during Kharif-2012 As per India Meteorological Department (IMD) data SW Monsoon rainfall for the country as a whole during June- September, 2012
PROGRAMMES AND SCHEMES Monsoon and Crop Sowing Situation during Kharif-2012 As per India Meteorological Department (IMD) data SW Monsoon rainfall for the country as a whole during June- September, 2012
NREGA: A Component of Full Employment Strategy in India. Prof. Indira Hirway Center For Development Alternatives Ahmedabad
 NREGA: A Component of Full Employment Strategy in India Prof. Indira Hirway Center For Development Alternatives Ahmedabad This Paper This paper argues that NREGA could be an important first step of a full
NREGA: A Component of Full Employment Strategy in India Prof. Indira Hirway Center For Development Alternatives Ahmedabad This Paper This paper argues that NREGA could be an important first step of a full
DROUGHT (INDIA) SURINDER KAUR INDIA METEOROLOGICAL DEPARTMENT
 DROUGHT (INDIA) SURINDER KAUR INDIA METEOROLOGICAL DEPARTMENT WATER AVAILIBILITY IN INDIA AREA OF THE COUNTRY 32,87,263 SQ. KMs RAINFALL 4000 KM³ SURFACE WATER POTENTIAL 684 KM³ GROUND WATER POTENTIAL
DROUGHT (INDIA) SURINDER KAUR INDIA METEOROLOGICAL DEPARTMENT WATER AVAILIBILITY IN INDIA AREA OF THE COUNTRY 32,87,263 SQ. KMs RAINFALL 4000 KM³ SURFACE WATER POTENTIAL 684 KM³ GROUND WATER POTENTIAL
NCERT Class 9th Social Science Economics Chapter 4: Climate
 NCERT Class 9th Social Science Economics Chapter 4: Climate Question 1. How is food security ensured in India? Food security is ensured in India by Creation of buffer stock. Introduction of the Public
NCERT Class 9th Social Science Economics Chapter 4: Climate Question 1. How is food security ensured in India? Food security is ensured in India by Creation of buffer stock. Introduction of the Public
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF RURAL DEVELOPMENT DEPARTMENT OF LAND RESOURCES LOK SABHA STARRED QUESTION NO. 70 TO BE ANSWERED ON
 GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF RURAL DEVELOPMENT DEPARTMENT OF LAND RESOURCES LOK SABHA STARRED QUESTION NO. 70 TO BE ANSWERED ON 20.07.2017 Development of Wasteland *70. SHRI KUNWAR PUSHPENDRA SINGH
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF RURAL DEVELOPMENT DEPARTMENT OF LAND RESOURCES LOK SABHA STARRED QUESTION NO. 70 TO BE ANSWERED ON 20.07.2017 Development of Wasteland *70. SHRI KUNWAR PUSHPENDRA SINGH
Growth and Inclusion: Theoretical and Applied Perspectives
 THE WORLD BANK WORKSHOP Growth and Inclusion: Theoretical and Applied Perspectives Session I Food Inflation: Drivers and Policy Implications Subir Gokarn Reserve Bank of India January 12, 212 The Claridges
THE WORLD BANK WORKSHOP Growth and Inclusion: Theoretical and Applied Perspectives Session I Food Inflation: Drivers and Policy Implications Subir Gokarn Reserve Bank of India January 12, 212 The Claridges
IN THE SUPREME COURT OF INDIA CIVIL ORIGINAL JURISDICTION WRIT PETITION (CIVIL) NO. 857 OF 2015 VERSUS WRITTEN NOTE ON BEHALF OF PETITIONER
 IN THE SUPREME COURT OF INDIA CIVIL ORIGINAL JURISDICTION WRIT PETITION (CIVIL) NO. 857 OF 2015 IN THE MATTER OF: SWARAJ ABHIYAN UNION OF INDIA & ORS VERSUS...PETITIONER...RESPONDENTS WRITTEN NOTE ON BEHALF
IN THE SUPREME COURT OF INDIA CIVIL ORIGINAL JURISDICTION WRIT PETITION (CIVIL) NO. 857 OF 2015 IN THE MATTER OF: SWARAJ ABHIYAN UNION OF INDIA & ORS VERSUS...PETITIONER...RESPONDENTS WRITTEN NOTE ON BEHALF
Downloaded from INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX CHAPTER: 4 Food Security in India
 INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX CHAPTER: 4 Food Security in India WORKSHEET NO: 19 FOOD SECURITY AVAILABILITY OF FOOD Q.No Questions Mark 1 What is meant by food
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX CHAPTER: 4 Food Security in India WORKSHEET NO: 19 FOOD SECURITY AVAILABILITY OF FOOD Q.No Questions Mark 1 What is meant by food
5. ENDEMIC POVERTY AND STARK INEQUALITIES
 5. ENDEMIC POVERTY AND STARK INEQUALITIES One of every 3 persons in India is officially poor, and 2 of 3 are undernourished or malnourished. If you count those who are deprived of safe drinking water,
5. ENDEMIC POVERTY AND STARK INEQUALITIES One of every 3 persons in India is officially poor, and 2 of 3 are undernourished or malnourished. If you count those who are deprived of safe drinking water,
Acute Food Insecurity Situation Overview
 (Sudan) Current - map Key Outcomes for the Worst affected Area Republic of Sudan Integrated Food Security Phase Classification (IPC) Acute Food Insecurity Situation Overview Food consumption: South Kordofan:
(Sudan) Current - map Key Outcomes for the Worst affected Area Republic of Sudan Integrated Food Security Phase Classification (IPC) Acute Food Insecurity Situation Overview Food consumption: South Kordofan:
Reducing Vulnerabilities and Building Resilience in Drought. Experiences from India
 Reducing Vulnerabilities and Building Resilience in Experiences from India 51 Europe Eastern 78 Northern 13 Southern 80 Western 30 Total 201 Asia Eastern 88 South-Central 125 South East 57 Western 35 Total
Reducing Vulnerabilities and Building Resilience in Experiences from India 51 Europe Eastern 78 Northern 13 Southern 80 Western 30 Total 201 Asia Eastern 88 South-Central 125 South East 57 Western 35 Total
WFP India Food Security Bulletin
 Fighting Hunger Worldwide WFP India Food Security Bulletin Quarter 4 (October December 2015) HIGHLIGHTS In 2015-16, food grains production is estimated to be 4.1% less than the target. Despite increase
Fighting Hunger Worldwide WFP India Food Security Bulletin Quarter 4 (October December 2015) HIGHLIGHTS In 2015-16, food grains production is estimated to be 4.1% less than the target. Despite increase
Impact Assessment of Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY)
 Impact Assessment of Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) correlation between road improvements and GDP per capita growth is extensive. Executiive Summary Rural roads provide basic inputs for all-round
Impact Assessment of Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) correlation between road improvements and GDP per capita growth is extensive. Executiive Summary Rural roads provide basic inputs for all-round
Status of Poverty in India A State wise Analysis
 Status of Poverty in India A State wise Analysis Dr Waheeda Sunny Thomas Faculty Economics, SEMCOM, Gujarat, India ABSTRACT First millennium development goal is to eradicate extreme poverty and hunger.
Status of Poverty in India A State wise Analysis Dr Waheeda Sunny Thomas Faculty Economics, SEMCOM, Gujarat, India ABSTRACT First millennium development goal is to eradicate extreme poverty and hunger.
11. Area specific mineral mixture formulation for the state of Area specific mineral mixture formulation for the state of 13
 Area specific mineral mixture formulations developed based on the mineral mapping programme taken up by NDDB and various centres under the ICAR Micro-Nutrients Network Programme Content Page Number 1.
Area specific mineral mixture formulations developed based on the mineral mapping programme taken up by NDDB and various centres under the ICAR Micro-Nutrients Network Programme Content Page Number 1.
UNICEF Namibia. Drought Situation Report #1 Issued on 24 July 2013
 UNICEF Namibia Drought Situation Report #1 Issued on 24 July 2013 Highlights Emergency Food Security Assessment conducted in April/ May and Drought Emergency declared on 17 May 2013, affecting all 13 regions.
UNICEF Namibia Drought Situation Report #1 Issued on 24 July 2013 Highlights Emergency Food Security Assessment conducted in April/ May and Drought Emergency declared on 17 May 2013, affecting all 13 regions.
Farmers Suicides In India
 Research Paper - Economics Farmers Suicides In India Vol. 1, Issue. 1 / February 2011, pp. 113-117 - Dr. P. V. Deshmukh Dept. of Economics, Dr. Babasaheb Amedkar Marathwada University, Aurangabad Agriculture
Research Paper - Economics Farmers Suicides In India Vol. 1, Issue. 1 / February 2011, pp. 113-117 - Dr. P. V. Deshmukh Dept. of Economics, Dr. Babasaheb Amedkar Marathwada University, Aurangabad Agriculture
National Drought Management Authority MANDERA COUNTY DROUGHT EARLY WARNING BULLETIN FOR SEPTEMBER 2017
 National Drought Management Authority MANDERA COUNTY DROUGHT EARLY WARNING BULLETIN FOR SEPTEMBER 2017 SEPTEMBER EW PHASE Drought Situation & EW Phase Classification Biophysical Indicators One-day Rainfall
National Drought Management Authority MANDERA COUNTY DROUGHT EARLY WARNING BULLETIN FOR SEPTEMBER 2017 SEPTEMBER EW PHASE Drought Situation & EW Phase Classification Biophysical Indicators One-day Rainfall
SUBJECT: MINUTES OF THE MEETING OF THE CROP WEATHER WATCH GROUP HELD ON
 F. No. 31/ 201819CFCCES GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF AGRICULTURE AND FARMERS WELFARE DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE, COOPERATION AND FARMERS WELFARE (CROP FORECAST COORDINATION CENTRE) Room No. 344A Krishi
F. No. 31/ 201819CFCCES GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF AGRICULTURE AND FARMERS WELFARE DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE, COOPERATION AND FARMERS WELFARE (CROP FORECAST COORDINATION CENTRE) Room No. 344A Krishi
TPDS, GOI Highlights. Summary and Analysis
 TPDS, GOI 2011-12 In order to ensure food security, the Government of India (GOI) provides food subsidy to citizens. The Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS) is the primary vehicle used for delivery
TPDS, GOI 2011-12 In order to ensure food security, the Government of India (GOI) provides food subsidy to citizens. The Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS) is the primary vehicle used for delivery
UNICEF Lesotho Situation Report
 UNICEF Lesotho Situation Report Mid-year update: Situation Report #3 Reporting Period: 01 January to 31 July 2013 Highlights Health, Nutrition and Hygiene: A total of 791 children with acute and severe-
UNICEF Lesotho Situation Report Mid-year update: Situation Report #3 Reporting Period: 01 January to 31 July 2013 Highlights Health, Nutrition and Hygiene: A total of 791 children with acute and severe-
WAJIR COUNTY DROUGHT EARLY WARNING BULLETIN FOR JULY 2017
 National Drought Management Authority WAJIR COUNTY DROUGHT EARLY WARNING BULLETIN FOR JULY 2017 JULY EW PHASE 2017 Drought Situation & EW Phase Classification Biophysical Indicators Generally the county
National Drought Management Authority WAJIR COUNTY DROUGHT EARLY WARNING BULLETIN FOR JULY 2017 JULY EW PHASE 2017 Drought Situation & EW Phase Classification Biophysical Indicators Generally the county
Progress and Potential of Horticulture in India
 Ind. Jn. of Agri.Econ. Vol.63, No.3, July-Sept. 2008 SUBJECT I TRIGGERING AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT THROUGH HORTICULTURE CROPS Progress and Potential of Horticulture in India Ramesh Chand, S.S. Raju and
Ind. Jn. of Agri.Econ. Vol.63, No.3, July-Sept. 2008 SUBJECT I TRIGGERING AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT THROUGH HORTICULTURE CROPS Progress and Potential of Horticulture in India Ramesh Chand, S.S. Raju and
Drought Rapid Assessment Report. Western Afghanistan Badghis province
 Drought Rapid Assessment Report Western Afghanistan Badghis province October, 2014 Drought Assessment Report [Badghis Province] Contents Overview... 3 Geographical Area:... 3 Summary of key findings:...
Drought Rapid Assessment Report Western Afghanistan Badghis province October, 2014 Drought Assessment Report [Badghis Province] Contents Overview... 3 Geographical Area:... 3 Summary of key findings:...
Drought Conditions and Management Strategies in Botswana
 Drought Conditions and Management Strategies in Botswana Dr. M. Manthe-Tsuaneng Acting Deputy Permanent Secretary- Natural Resources Ministry of Environment, Wildlife and Tourism Private Bag BO 199 Gaborone,
Drought Conditions and Management Strategies in Botswana Dr. M. Manthe-Tsuaneng Acting Deputy Permanent Secretary- Natural Resources Ministry of Environment, Wildlife and Tourism Private Bag BO 199 Gaborone,
Guidelines for Implementation of fisheries Scheme under the National Mission for Protein Supplements (NMPS) in States during
 Annexure-III Guidelines for Implementation of fisheries Scheme under the National Mission for Protein Supplements (NMPS) in States during 2012-13 The Department of Animal Husbandry, Dairying & Fisheries,
Annexure-III Guidelines for Implementation of fisheries Scheme under the National Mission for Protein Supplements (NMPS) in States during 2012-13 The Department of Animal Husbandry, Dairying & Fisheries,
Sugar Industry, Co-generation and Distillery Promotion Policy, 2013
 Sugar Industry, Co-generation and Distillery Promotion Policy, 2013 Introduction: Spread over an area of 2.43 lakh sq. km. and with a population aggregating 20 crore, Uttar Pradesh is one of the largest
Sugar Industry, Co-generation and Distillery Promotion Policy, 2013 Introduction: Spread over an area of 2.43 lakh sq. km. and with a population aggregating 20 crore, Uttar Pradesh is one of the largest
Influence of climate uncertainties on hinterland of Orissa
 Coping strategy and vulnerability reduction to Climate Extremes Objective: Better understanding of the coping mechanism of the community to climatic changes in a micro level. Preserve the current knowledge
Coping strategy and vulnerability reduction to Climate Extremes Objective: Better understanding of the coping mechanism of the community to climatic changes in a micro level. Preserve the current knowledge
VECTOR BORNE DISEASES AND CLIMATIC CHANGES
 VECTOR BORNE DISEASES AND CLIMATIC CHANGES Dr. Neeraj Dhingra Additional Director National Vector Borne Disease Control Porgramme (NVBDCP Ministry of Health & Family Welfare Government of India PREVENTION
VECTOR BORNE DISEASES AND CLIMATIC CHANGES Dr. Neeraj Dhingra Additional Director National Vector Borne Disease Control Porgramme (NVBDCP Ministry of Health & Family Welfare Government of India PREVENTION
INTERNATIONAL FOOD POLICY RESEARCH INSTITUTE. Page 1
 Page 1 Food and Energy Security for Development in India Ashok Gulati & Kavery Ganguly Presentation at Third IBSA Summit Academic Forum IBSA Partnership for Shared Prosperity and Inclusive Globalization
Page 1 Food and Energy Security for Development in India Ashok Gulati & Kavery Ganguly Presentation at Third IBSA Summit Academic Forum IBSA Partnership for Shared Prosperity and Inclusive Globalization
MEMBERS' REFERENCE SERVICE LARRDIS LOK SABHA SECRETARIAT, NEW DELHI REFERENCE NOTE. No.56/RN/Ref./Nov/2017
 MEMBERS' REFERENCE SERVICE LARRDIS LOK SABHA SECRETARIAT, NEW DELHI REFERENCE NOTE No.56/RN/Ref./Nov/2017 For the use of Members of Parliament NOT FOR PUBLICATION 1 DAIRY SECTOR: PRESENT SCENARIO AND NEW
MEMBERS' REFERENCE SERVICE LARRDIS LOK SABHA SECRETARIAT, NEW DELHI REFERENCE NOTE No.56/RN/Ref./Nov/2017 For the use of Members of Parliament NOT FOR PUBLICATION 1 DAIRY SECTOR: PRESENT SCENARIO AND NEW
FOOD SECURITY MONITORING, TAJIKISTAN
 Fighting Hunger Worldwide BULLETIN July 2017 ISSUE 19 Tajikistan Food Security Monitoring FOOD SECURITY MONITORING, TAJIKISTAN July 2017 - ISSUE 19 Fighting Hunger Worldwide BULLETIN July 2017 ISSUE 19
Fighting Hunger Worldwide BULLETIN July 2017 ISSUE 19 Tajikistan Food Security Monitoring FOOD SECURITY MONITORING, TAJIKISTAN July 2017 - ISSUE 19 Fighting Hunger Worldwide BULLETIN July 2017 ISSUE 19
Sudan acute Food insecurity Situation
 Integrated Food Security Phase Classification (IPC) Sudan acute Food insecurity Situation Analysis Date: October 2017 - Valid to: End of December2017 Outcomes for more affected areas:(phase 3 and worse)
Integrated Food Security Phase Classification (IPC) Sudan acute Food insecurity Situation Analysis Date: October 2017 - Valid to: End of December2017 Outcomes for more affected areas:(phase 3 and worse)
APPENDIX-A Questionnaire (Drought-Primary Data) (i) Questionnaire for Farmers
 APPENDIX-A Questionnaire (Drought-Primary Data) (i) Questionnaire for Farmers Name: Age: Sex: Educational Level: Land Holding: Family Size (number and char): Address: Agricultural Impact: - Q1. What is
APPENDIX-A Questionnaire (Drought-Primary Data) (i) Questionnaire for Farmers Name: Age: Sex: Educational Level: Land Holding: Family Size (number and char): Address: Agricultural Impact: - Q1. What is
Nearly one-quarter of the population lives on less than USD 1 per day
 Nearly one-quarter of the population lives on less than USD 1 per day 32 Nepal Background Nepal suffers from chronic food insecurity, severe and recurrent natural disasters, poor health and sanitation
Nearly one-quarter of the population lives on less than USD 1 per day 32 Nepal Background Nepal suffers from chronic food insecurity, severe and recurrent natural disasters, poor health and sanitation
Hunger and Malnutrition among Women and Children in India
 Hunger and Malnutrition among Women and Children in India Jagdev Singh (Research Scholar, Department of Economics, Punjabi University, Patiala, Punjab, India) Abstract: The present paper is an attempt
Hunger and Malnutrition among Women and Children in India Jagdev Singh (Research Scholar, Department of Economics, Punjabi University, Patiala, Punjab, India) Abstract: The present paper is an attempt
22: List of Studies Conducted by Agro-Economic Research Centres
 22: List of Studies Conducted by Agro-Economic Research Centres 2006-07 1 India s Global Tea Trade Reducing Share, Declining Competitiveness. 2 Developing India s Strategic Responses to the Global Debate
22: List of Studies Conducted by Agro-Economic Research Centres 2006-07 1 India s Global Tea Trade Reducing Share, Declining Competitiveness. 2 Developing India s Strategic Responses to the Global Debate
Soil Health Management in India
 Soil Health Management in India Soil Health Management in India Soil Health Management In order to improve the soil health of the Indian soils, gov- The nature and extent of deficiencies of nutrients in
Soil Health Management in India Soil Health Management in India Soil Health Management In order to improve the soil health of the Indian soils, gov- The nature and extent of deficiencies of nutrients in
Regional Pattern of Agricultural Growth and Rural Employment in India: Have Small Farmers Benefitted?
 Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 26 (Conference Number) 2013 pp 1-11 Regional Pattern of Agricultural Growth and Rural Employment in India: Have Small Farmers Benefitted? M.L. Nithyashree* and
Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 26 (Conference Number) 2013 pp 1-11 Regional Pattern of Agricultural Growth and Rural Employment in India: Have Small Farmers Benefitted? M.L. Nithyashree* and
P r e s e n t a t i o n. Water Systems. Myanmar, Laos and Cambodia
 P r e s e n t a t i o n Water Systems Myanmar, Laos and Cambodia 2 Overview Chronic fresh water scarcity and contamination are among the predominant challenges in the least-developed and remote villages
P r e s e n t a t i o n Water Systems Myanmar, Laos and Cambodia 2 Overview Chronic fresh water scarcity and contamination are among the predominant challenges in the least-developed and remote villages
Early warning and Acute food insecurity analysis: introduction to CH process
 Famine Early Warning Systems Network Early warning and Acute food insecurity analysis: introduction to CH process Nigeria CH Foundational Training Overview What is early warning? Some concepts Guiding
Famine Early Warning Systems Network Early warning and Acute food insecurity analysis: introduction to CH process Nigeria CH Foundational Training Overview What is early warning? Some concepts Guiding
WORLD HEALTH DAY CHALLENGE 2014 SPECIAL HEALTH REPORT
 WORLD HEALTH DAY CHALLENGE 2014 SPECIAL HEALTH REPORT FOOD SECURITY AND NUTRITION Nutrition challenges are not only about a lack of food. Malnutrition often arises when there is a gap in knowledge about
WORLD HEALTH DAY CHALLENGE 2014 SPECIAL HEALTH REPORT FOOD SECURITY AND NUTRITION Nutrition challenges are not only about a lack of food. Malnutrition often arises when there is a gap in knowledge about
National Drought Management Authority GARISSA COUNTY
 National Drought Management Authority GARISSA COUNTY DROUGHT EARLY WARNING BULLETIN FOR JANUARY 215 Drought early warning Flag- Phase Alarm Drought Situation & EW Phase Classification Biophysical Indicators
National Drought Management Authority GARISSA COUNTY DROUGHT EARLY WARNING BULLETIN FOR JANUARY 215 Drought early warning Flag- Phase Alarm Drought Situation & EW Phase Classification Biophysical Indicators
Rampur: Village Economy
 Chapter 9 Rampur: Village Economy Key Points: 1. Rampur lies in the fertile alluvial plains of the Gengetic basin in the Western part of U.P. Farming is the main production activity in Rampur. Majority
Chapter 9 Rampur: Village Economy Key Points: 1. Rampur lies in the fertile alluvial plains of the Gengetic basin in the Western part of U.P. Farming is the main production activity in Rampur. Majority
Quality of Water and Water Related Diseases in Urban Areas
 5.1.2 Incidence of water borne diseases in states of India The water borne diseases in India are occurring over the years despite various water quality management plans by the Government of India. Regardless
5.1.2 Incidence of water borne diseases in states of India The water borne diseases in India are occurring over the years despite various water quality management plans by the Government of India. Regardless
Somalia Famine Appeal
 Somalia Famine Appeal FAMINE SPREADING IN SOUTHERN SOMALIA USD 70 MILLION URGENTLY NEEDED TO AVERT A REGIONAL DISASTER FAO Somalia Emergency Requirements - Nairobi: 21 July 2011 On 20 July, the United
Somalia Famine Appeal FAMINE SPREADING IN SOUTHERN SOMALIA USD 70 MILLION URGENTLY NEEDED TO AVERT A REGIONAL DISASTER FAO Somalia Emergency Requirements - Nairobi: 21 July 2011 On 20 July, the United
IMPO P RT R AN A C N E C E O F G RO R UN U D N W
 Introduction IMPORTANCE OF GROUNDWATER Global Groundwater Situation ACWADAM s database Sources for presentation CGWB, various publications FAO-database Various United Nations publications. UN World Water
Introduction IMPORTANCE OF GROUNDWATER Global Groundwater Situation ACWADAM s database Sources for presentation CGWB, various publications FAO-database Various United Nations publications. UN World Water
DEPENDENCE ON AGRICULTURAL EMPLOYMENT: A REGIONAL ANALYSIS. Bal Krishan Research Scholar Centre for study of regional development, JNU, New Delhi
 DEPENDENCE ON AGRICULTURAL EMPLOYMENT: A REGIONAL ANALYSIS Bal Krishan Research Scholar Centre for study of regional development, JNU, New Delhi Abstract After six decade of independence there has been
DEPENDENCE ON AGRICULTURAL EMPLOYMENT: A REGIONAL ANALYSIS Bal Krishan Research Scholar Centre for study of regional development, JNU, New Delhi Abstract After six decade of independence there has been
Agustinho da Costa Ximenes National Consultant for Food Security Ministry Of Agriculture and Fisheries Timor Leste
 Agustinho da Costa Ximenes National Consultant for Food Security Ministry Of Agriculture and Fisheries Timor Leste INTRODUCTION The country has an area of 14,609 square kilometers, It is divided in thirteen
Agustinho da Costa Ximenes National Consultant for Food Security Ministry Of Agriculture and Fisheries Timor Leste INTRODUCTION The country has an area of 14,609 square kilometers, It is divided in thirteen
food security bill: Way forward to optimal nutrition Prema ramachandran NutritioN foundation of india, New delhi. 21 st November, 2013
 food security bill: Way forward to optimal nutrition Prema ramachandran NutritioN foundation of india, New delhi. 21 st November, 2013 Perspective Food price inflation Food security act NSI s Comments
food security bill: Way forward to optimal nutrition Prema ramachandran NutritioN foundation of india, New delhi. 21 st November, 2013 Perspective Food price inflation Food security act NSI s Comments
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF MARGINAL FARMS IN INDIA VIS-A-VIS WEST BENGAL DURING LAST DECADE
 Journal of Economic & Social Development, Vol. - XIII, No. 2, Dec. 2017 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF MARGINAL FARMS IN INDIA VIS-A-VIS WEST BENGAL DURING LAST DECADE Amit Mandal* ISSN 0973-886X Agriculture is
Journal of Economic & Social Development, Vol. - XIII, No. 2, Dec. 2017 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF MARGINAL FARMS IN INDIA VIS-A-VIS WEST BENGAL DURING LAST DECADE Amit Mandal* ISSN 0973-886X Agriculture is
Rice Production and Nutrient Management in India
 I n d i a Rice Production and Nutrient Management in India By K.N. Tiwari The demand for rice in India is projected at 28 million tonnes (M t) for the year 202 and will require a production level of 3,000
I n d i a Rice Production and Nutrient Management in India By K.N. Tiwari The demand for rice in India is projected at 28 million tonnes (M t) for the year 202 and will require a production level of 3,000
Ethiopia. July Eritrea. Sudan. Djbouti. Somalia. Kenya ETHIOPIA. at a glance. summary. Tigray. Region. Amhara. Region. Somali. Oromiya.
 EMERGENCY UPDATE Ethiopia July 2000 Sudan Wolayita Eritrea Tigray Amhara Addis Ababa ETHIOPIA Konso N. Wollo S. Wollo Djbouti East Haraghe Jijiga Oromiya Fik Red Sea Somali Gode Kenya Somalia at a glance
EMERGENCY UPDATE Ethiopia July 2000 Sudan Wolayita Eritrea Tigray Amhara Addis Ababa ETHIOPIA Konso N. Wollo S. Wollo Djbouti East Haraghe Jijiga Oromiya Fik Red Sea Somali Gode Kenya Somalia at a glance
National Drought Management Authority MERU COUNTY DROUGHT EARLY WARNING BULLETIN FOR JULY 2017
 National Drought Management Authority MERU COUNTY DROUGHT EARLY WARNING BULLETIN FOR JULY 2017 JULY EW PHASE Drought Situation & EW Phase Classification Biophysical Indicators July remained generally cold
National Drought Management Authority MERU COUNTY DROUGHT EARLY WARNING BULLETIN FOR JULY 2017 JULY EW PHASE Drought Situation & EW Phase Classification Biophysical Indicators July remained generally cold
SUBJECT: MINUTES OF THE MEETING OF THE CROP WEATHER WATCH GROUP HELD ON
 F. No. 31/ 201718CFCCE&S GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF AGRICULTURE AND FARMERS WELFARE DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE, COOPERATION AND FARMERS WELFARE (CROP FORECAST COORDINATION CENTRE) Room No. 344A, Krishi
F. No. 31/ 201718CFCCE&S GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF AGRICULTURE AND FARMERS WELFARE DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE, COOPERATION AND FARMERS WELFARE (CROP FORECAST COORDINATION CENTRE) Room No. 344A, Krishi
National Afforestation Programme (NAP) Scheme: At A Glance
 National Afforestation Programme (NAP) Scheme: At A Glance (1) Background: MoEF was operating four centrally sponsored afforestation schemes during the 9 th Plan, i.e. Integrated Afforestation and Eco-development
National Afforestation Programme (NAP) Scheme: At A Glance (1) Background: MoEF was operating four centrally sponsored afforestation schemes during the 9 th Plan, i.e. Integrated Afforestation and Eco-development
Amita Shah. Gujarat Institute of Development Research Gota, Ahmedabad
 Patterns, Processes of Reproduction and Policy Implications for Poverty in Remote Rural Areas in India: A Case Study of Southern Orissa Amita Shah Gujarat Institute of Development Research Gota, Ahmedabad
Patterns, Processes of Reproduction and Policy Implications for Poverty in Remote Rural Areas in India: A Case Study of Southern Orissa Amita Shah Gujarat Institute of Development Research Gota, Ahmedabad
Safe Water Network is recognized as a National Key Resource Center by the Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation KNOWLEDGE PARTNER GRANT PARTNER
 Safe Water Network is recognized as a National Key Resource Center by the Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation KNOWLEDGE PARTNER GRANT PARTNER 1 Dream of Har Ghar Jal will be realized by 2030:
Safe Water Network is recognized as a National Key Resource Center by the Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation KNOWLEDGE PARTNER GRANT PARTNER 1 Dream of Har Ghar Jal will be realized by 2030:
Comparative Study of Marginal Farms in India vis-a-vis West Bengal; Evidences from Last Decade
 Economic Affairs, Vol. 61, No. 4, pp. 589-598, December 2016 DOI: 10.5958/0976-4666.2016.00073.5 2016 New Delhi Publishers. All rights reserved Comparative Study of Marginal Farms in India vis-a-vis West
Economic Affairs, Vol. 61, No. 4, pp. 589-598, December 2016 DOI: 10.5958/0976-4666.2016.00073.5 2016 New Delhi Publishers. All rights reserved Comparative Study of Marginal Farms in India vis-a-vis West
ANNUAL REPORT OF THE RESIDENT/HUMANITARIAN COORDINATOR ON THE USE OF CERF GRANTS. Reporting Period 1 January December 2009
 Country ANNUAL REPORT OF THE RESIDENT/HUMANITARIAN COORDINATOR ON THE USE OF CERF GRANTS Resident/Humanitarian Coordinator Syria Ismail Ould Cheikh Ahmed Reporting Period 1 January 2009 31 December 2009
Country ANNUAL REPORT OF THE RESIDENT/HUMANITARIAN COORDINATOR ON THE USE OF CERF GRANTS Resident/Humanitarian Coordinator Syria Ismail Ould Cheikh Ahmed Reporting Period 1 January 2009 31 December 2009
Public Expenditures and Subsidies in Indian Surface Irrigation: Who Benefits?
 Public Expenditures and Subsidies in Indian Surface Irrigation: Who Benefits? Mona Sur and Dina Umali-Deininger South Asia Rural Development Unit March 5, 2003 India: An overview 1 billion popn,72% rural
Public Expenditures and Subsidies in Indian Surface Irrigation: Who Benefits? Mona Sur and Dina Umali-Deininger South Asia Rural Development Unit March 5, 2003 India: An overview 1 billion popn,72% rural
From Rooftops to Farmtops. Augmenting India s Distributed Solar Goals through net-metered solar pumps
 From Rooftops to Farmtops Augmenting India s Distributed Solar Goals through net-metered solar pumps Introduction The Government of India has recently announced a scheme for solar water pumps known as
From Rooftops to Farmtops Augmenting India s Distributed Solar Goals through net-metered solar pumps Introduction The Government of India has recently announced a scheme for solar water pumps known as
Inter-Linkages Among Agricultural Research Investment, Agricultural Productivity and Rural Poverty in India
 Inter-Linkages Among Agricultural Research Investment, Agricultural Productivity and Rural Poverty in India Kiresur V.R and Melinamani V.P. Paper prepared for presentation at the 12 th EAAE Congress People,
Inter-Linkages Among Agricultural Research Investment, Agricultural Productivity and Rural Poverty in India Kiresur V.R and Melinamani V.P. Paper prepared for presentation at the 12 th EAAE Congress People,
AGRICULTURE SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS]
![AGRICULTURE SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS] AGRICULTURE SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS]](/thumbs/79/79737240.jpg) AGRICULTURE SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS] 1. Distinguish between primitive subsistence farming and intensive subsistence farming. The following are the differences between primitive subsistence
AGRICULTURE SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS] 1. Distinguish between primitive subsistence farming and intensive subsistence farming. The following are the differences between primitive subsistence
End poverty in all its forms everywhere
 End poverty in all its forms everywhere 1.1 By 2030, eradicate extreme poverty for all people everywhere, currently measured as people living on less than $1.25 a day 1.2 By 2030, reduce at least by half
End poverty in all its forms everywhere 1.1 By 2030, eradicate extreme poverty for all people everywhere, currently measured as people living on less than $1.25 a day 1.2 By 2030, reduce at least by half
National Drought Management Authority KILIFI COUNTY DROUGHT EARLY WARNING BULLETIN, AUGUST 2017
 National Drought Management Authority KILIFI COUNTY DROUGHT EARLY WARNING BULLETIN, AUGUST 2017 AUGUST EW PHASE Early Warning(EW) Phase Classification Livelihood Zone Stage Trend Drought situation and
National Drought Management Authority KILIFI COUNTY DROUGHT EARLY WARNING BULLETIN, AUGUST 2017 AUGUST EW PHASE Early Warning(EW) Phase Classification Livelihood Zone Stage Trend Drought situation and
National Integrated Food Security and Nutrition Policy (NIFSNP) Manoj Thibbotuwawa, Research Economist
 National Integrated Food Security and Nutrition Policy (NIFSNP) Manoj Thibbotuwawa, Research Economist Food Security When all people, at all times, have physical and economic access to sufficient, safe
National Integrated Food Security and Nutrition Policy (NIFSNP) Manoj Thibbotuwawa, Research Economist Food Security When all people, at all times, have physical and economic access to sufficient, safe
Chapter 9: Farmers in drought-prone areas. I. The special problems of farmers in drought-prone regions
 Chapter 9: Farmers in drought-prone areas I. The special problems of farmers in drought-prone regions Although drought is thought of as a natural phenomenon, it is often as much due to human intervention
Chapter 9: Farmers in drought-prone areas I. The special problems of farmers in drought-prone regions Although drought is thought of as a natural phenomenon, it is often as much due to human intervention
Weather Risks Insurance for Agriculture
 Weather Risks Insurance for Agriculture International Workshop on Agrometeorological Risk Management, Delhi Oct 26, 2006 Presented by: Pranav Prashad ICICI Lombard General Insurance Co. Mumbai, India Weather
Weather Risks Insurance for Agriculture International Workshop on Agrometeorological Risk Management, Delhi Oct 26, 2006 Presented by: Pranav Prashad ICICI Lombard General Insurance Co. Mumbai, India Weather
ACT ALLIANCE AFRICA REGION - STATEMENT ON HORN OF AFRICA DROUGHT
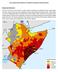 ACT ALLIANCE AFRICA REGION - STATEMENT ON HORN OF AFRICA DROUGHT Background Information The Horn of Africa is in the midst of a major drought resulting from La Niña and Indian Ocean Dipole reducing moisture
ACT ALLIANCE AFRICA REGION - STATEMENT ON HORN OF AFRICA DROUGHT Background Information The Horn of Africa is in the midst of a major drought resulting from La Niña and Indian Ocean Dipole reducing moisture
AGRICULTURAL DROUGHTS AND THEIR MANAGEMENT
 AGRICULTURAL DROUGHTS AND THEIR MANAGEMENT YS Ramakrishna Director (Retd.), CRIDA, Hyderabad Drought is a disaster in slow motion covering large areas. It is characterized by deficient supply of moisture
AGRICULTURAL DROUGHTS AND THEIR MANAGEMENT YS Ramakrishna Director (Retd.), CRIDA, Hyderabad Drought is a disaster in slow motion covering large areas. It is characterized by deficient supply of moisture
Borlaug Dialogue 2008
 Borlaug Dialogue 2008 Managing Climate Change, Agriculture and Rural Poverty Rita Sharma Secretary to Government of India Ministry of Rural Development Des Moines, 16 October 2008 Mahatma Gandhi s Talisman
Borlaug Dialogue 2008 Managing Climate Change, Agriculture and Rural Poverty Rita Sharma Secretary to Government of India Ministry of Rural Development Des Moines, 16 October 2008 Mahatma Gandhi s Talisman
PEO Study No.122 EVALUATION OF RURAL ELECTRIFICATION PROGRAMME - VOLUME - I The Study
 PEO Study No.122 EVALUATION OF RURAL ELECTRIFICATION PROGRAMME - VOLUME - I - 1982 1. The Study Rural Electrification, aimed at bringing about a rural urban continuum by bridging the gulf between them,
PEO Study No.122 EVALUATION OF RURAL ELECTRIFICATION PROGRAMME - VOLUME - I - 1982 1. The Study Rural Electrification, aimed at bringing about a rural urban continuum by bridging the gulf between them,
SUBJECT: MINUTES OF THE MEETING OF THE CROP WEATHER WATCH GROUP HELD ON
 F. No. 31/ 201718CFCCE&S GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF AGRICULTURE AND FARMERS WELFARE DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE, COOPERATION AND FARMERS WELFARE (CROP FORECAST COORDINATION CENTRE) Room No. 344A, Krishi
F. No. 31/ 201718CFCCE&S GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF AGRICULTURE AND FARMERS WELFARE DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE, COOPERATION AND FARMERS WELFARE (CROP FORECAST COORDINATION CENTRE) Room No. 344A, Krishi
OPM India. In summary
 OPM India In summary About Oxford Policy Management s In summary series Our In summary publications aim to give an introduction to a key area of our expertise and the capabilities we offer in supporting
OPM India In summary About Oxford Policy Management s In summary series Our In summary publications aim to give an introduction to a key area of our expertise and the capabilities we offer in supporting
Potato Short Note. 31 Jan Introduction. Seasonality
 31 Jan 2008 Potato Short Note Introduction Potato is the world's fourth important food crop after wheat, rice and maize because of its higher yield potential along with high nutritive value. With an annual
31 Jan 2008 Potato Short Note Introduction Potato is the world's fourth important food crop after wheat, rice and maize because of its higher yield potential along with high nutritive value. With an annual
Assessing Poverty in Kenya
 Findings reports on ongoing operational, economic and sector work carried out by the World Bank and its member governments in the Africa Region. It is published periodically by the Africa Technical Department
Findings reports on ongoing operational, economic and sector work carried out by the World Bank and its member governments in the Africa Region. It is published periodically by the Africa Technical Department
Constrains Perceived by the Dairy Farmers in Irrigated Ecosystem: A Case Study from Damodar Command Area, West Bengal
 www.stmjournals.com Constrains Perceived by the Dairy Farmers in Irrigated Ecosystem: A Case Study from Damodar Command Area, West Bengal R. Bera*, A. Seal, T.H. Das, D. Sarkar National Bureau of Soil
www.stmjournals.com Constrains Perceived by the Dairy Farmers in Irrigated Ecosystem: A Case Study from Damodar Command Area, West Bengal R. Bera*, A. Seal, T.H. Das, D. Sarkar National Bureau of Soil
ACF INTEGRATED MULTI-SECTOR APPROACH TO MALNUTRITION
 ACF INTEGRATED MULTI-SECTOR APPROACH TO MALNUTRITION Overall program goal To contribute to the reduction of malnutrition-related morbidity and mortality WATER SANITATION HYGIENE NUTRITION FOOD SECURITY
ACF INTEGRATED MULTI-SECTOR APPROACH TO MALNUTRITION Overall program goal To contribute to the reduction of malnutrition-related morbidity and mortality WATER SANITATION HYGIENE NUTRITION FOOD SECURITY
CHAPTER V CONCLUSIONS
 CHAPTER V CONCLUSIONS The farm sector in India is in crises and it is reflected through the growing number of suicides by farmers in some states. Karnataka State is one of the states hit by the epidemic
CHAPTER V CONCLUSIONS The farm sector in India is in crises and it is reflected through the growing number of suicides by farmers in some states. Karnataka State is one of the states hit by the epidemic
Organic Cotton in India. Facts and figures 9/6/09. Organic cotton in India: facts and figures. General Issues in organic cotton sector of India
 Organic Cotton in India Facts, figures and issues By: H. Lanting, MSc. ETC Consultants India Pvt Ltd mans.lanting@planet.nl, www.etc-india.org Organic cotton in India: facts and figures India produces
Organic Cotton in India Facts, figures and issues By: H. Lanting, MSc. ETC Consultants India Pvt Ltd mans.lanting@planet.nl, www.etc-india.org Organic cotton in India: facts and figures India produces
Tata Trusts. Impacting quality of life of poor communities
 Tata Trusts Impacting quality of life of poor communities Tata Trusts Sir Ratan Tata Trust, 1919 Navajbai Ratan Tata Trust Sir Dorabji Tata Trust, 1932 Other Allied Trusts: 7 of them Annual investment
Tata Trusts Impacting quality of life of poor communities Tata Trusts Sir Ratan Tata Trust, 1919 Navajbai Ratan Tata Trust Sir Dorabji Tata Trust, 1932 Other Allied Trusts: 7 of them Annual investment
Chapter 4 Agriculture
 Chapter 4 Agriculture Types of Farming Primitive Subsistence Farming Practiced on small patches of land. Involves family/community labour. Uses primitive tools such as hoe, digging sticks etc. Predominance
Chapter 4 Agriculture Types of Farming Primitive Subsistence Farming Practiced on small patches of land. Involves family/community labour. Uses primitive tools such as hoe, digging sticks etc. Predominance
NAKAPIRIPIRIT OCTOBER DROUGHT BULLETIN 2012
 NAKAPIRIPIRIT OCTOBER DROUGHT BULLETIN 2012 AGRICULTURAL AGRO-PASTORAL PASTORAL TREND: IMPROVE TREND: IMPROVE TREND: WORSEN SECTORS LIVESTOCK ALARM CROPS NORMAL WATER NORMAL LIVELIHOODS ALARM SECTORS LIVESTOCK
NAKAPIRIPIRIT OCTOBER DROUGHT BULLETIN 2012 AGRICULTURAL AGRO-PASTORAL PASTORAL TREND: IMPROVE TREND: IMPROVE TREND: WORSEN SECTORS LIVESTOCK ALARM CROPS NORMAL WATER NORMAL LIVELIHOODS ALARM SECTORS LIVESTOCK
The New Face of Hunger
 The New Face of Hunger Josette Sheeran Executive Director, World Food Programme a revolution in food aid Not your grandmother s food aid : WFP is transforming the way it does business Needs assessments
The New Face of Hunger Josette Sheeran Executive Director, World Food Programme a revolution in food aid Not your grandmother s food aid : WFP is transforming the way it does business Needs assessments
Food Security and the Public Distribution System. Pranab Banerji
 Food Security and the Public Distribution System Pranab Banerji Evolution of the PDS Genesis: food problem of late 50s & 60s Green revolution Economic reforms 1991 Revamped public distribution systems
Food Security and the Public Distribution System Pranab Banerji Evolution of the PDS Genesis: food problem of late 50s & 60s Green revolution Economic reforms 1991 Revamped public distribution systems
2. Theme A Critical Analysis of Farmers' Conditions in Punjab
 2. Theme A Critical Analysis of Farmers' Conditions in Punjab Abstract Agriculture sector has been recognized as engine of economic growth. Punjab economy is predominant in agriculture and has been a forerunner
2. Theme A Critical Analysis of Farmers' Conditions in Punjab Abstract Agriculture sector has been recognized as engine of economic growth. Punjab economy is predominant in agriculture and has been a forerunner
Solar pumps for sustainable irrigation Supporting policymakers and enterprises to scale adoption and ensure sustainable use
 Solar pumps for sustainable irrigation Supporting policymakers and enterprises to scale adoption and ensure sustainable use Sasmita Patnaik Programme Lead Council on Energy, Environment and Water ISA,
Solar pumps for sustainable irrigation Supporting policymakers and enterprises to scale adoption and ensure sustainable use Sasmita Patnaik Programme Lead Council on Energy, Environment and Water ISA,
SOUTH ASIA: Drought. The situation. Needs: the Assessment Mission s Report. 6 June India
 SOUTH ASIA: Drought 6 June 2000 The situation Severe drought is currently affecting vast areas of South Asia, and the effects on the livelihoods of inhabitants are particularly evident in western India,
SOUTH ASIA: Drought 6 June 2000 The situation Severe drought is currently affecting vast areas of South Asia, and the effects on the livelihoods of inhabitants are particularly evident in western India,
Aao Jal Sanchay Karein. Boond - Boond se Dharti Bharein.
 Aao Jal Sanchay Karein Boond - Boond se Dharti Bharein Ravindra Kumar ravindra53@yahoo.co.in Major GW Issues Quality Problems Declining Water Levels & Depleting first aquifer Over Exploitation of Ground
Aao Jal Sanchay Karein Boond - Boond se Dharti Bharein Ravindra Kumar ravindra53@yahoo.co.in Major GW Issues Quality Problems Declining Water Levels & Depleting first aquifer Over Exploitation of Ground
Water-Food-Energy Nexus in the context of groundwater use in India: Experience from three Indian States
 Photo: :Tom David van Brazier/IWMI Cakenberghe/IWMI Water-Food-Energy Nexus in the context of groundwater use in India: Experience from three Indian States Aditi Mukherji, IWMI Water for a food-secure
Photo: :Tom David van Brazier/IWMI Cakenberghe/IWMI Water-Food-Energy Nexus in the context of groundwater use in India: Experience from three Indian States Aditi Mukherji, IWMI Water for a food-secure
India s Positioning in the Global Fertilizer Industry
 Market Update Kg/Hectare Arable Land India s Positioning in the Global Fertilizer Industry Country-Wise Consumption of Fertilizers 8,000 7,000 6,000 5,000 4,000 3,000 2,000 1,000-6898.7 2759.6 1750 157.52
Market Update Kg/Hectare Arable Land India s Positioning in the Global Fertilizer Industry Country-Wise Consumption of Fertilizers 8,000 7,000 6,000 5,000 4,000 3,000 2,000 1,000-6898.7 2759.6 1750 157.52
Gender Participation and Role of Women in Livestock Management Practices in Bundelkhand Region of Central India
 Gender Participation and Role of Women in Livestock Management Practices in Bundelkhand Region of Central India Seema Mishra*, Satyawati Sharma, Padma Vasudevan, R. K. Bhatt, Sadhna Pandey, Maharaj Singh,
Gender Participation and Role of Women in Livestock Management Practices in Bundelkhand Region of Central India Seema Mishra*, Satyawati Sharma, Padma Vasudevan, R. K. Bhatt, Sadhna Pandey, Maharaj Singh,
Farmer Suicides in India: Levels and Trends across Major States,
 University of Massachusetts - Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Economics Department Working Paper Series Economics 2016 Farmer Suicides in India: Levels and Trends across Major States, 1995-2011 Deepankar
University of Massachusetts - Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Economics Department Working Paper Series Economics 2016 Farmer Suicides in India: Levels and Trends across Major States, 1995-2011 Deepankar
RUCHI. Submitted to. Gender Analysis. for. PF1/290 Baddi Township Integrated Water Project. in Himachal Pradesh, India
 Gender Analysis for PF1/290 Baddi Township Integrated Water Project in Himachal Pradesh, India Submitted to RUCHI Study Conducted and Submitted by Table of Contents Introduction 3 The Activity 3 Profile
Gender Analysis for PF1/290 Baddi Township Integrated Water Project in Himachal Pradesh, India Submitted to RUCHI Study Conducted and Submitted by Table of Contents Introduction 3 The Activity 3 Profile
Angola Impact of Drought on Food Security and Nutrition Situation Report No May 2012
 Angola Impact of Drought on Food Security and Nutrition Situation Report No. 1 24 May 2012 This report is produced by OCHA in collaboration with humanitarian partners. It was issued by the Regional Office
Angola Impact of Drought on Food Security and Nutrition Situation Report No. 1 24 May 2012 This report is produced by OCHA in collaboration with humanitarian partners. It was issued by the Regional Office
COCOA LIFE COTE D IVOIRE NEEDS ASSESSMENT. Executive summary
 COCOA LIFE COTE D IVOIRE NEEDS ASSESSMENT Executive summary April 2015 1. The purpose of the needs assessment A needs assessment is carried out for each Cocoa Life origin in the early stages of program
COCOA LIFE COTE D IVOIRE NEEDS ASSESSMENT Executive summary April 2015 1. The purpose of the needs assessment A needs assessment is carried out for each Cocoa Life origin in the early stages of program
National Drought Management Authority EMBU COUNTY
 National Drought Management Authority EMBU COUNTY EARLY WARNING BULLETIN FOR EMBU 215 AUGUST EW PHASE Early Warning Phase Classification Drought Situation & EW Phase Classification Biophysical Indicators
National Drought Management Authority EMBU COUNTY EARLY WARNING BULLETIN FOR EMBU 215 AUGUST EW PHASE Early Warning Phase Classification Drought Situation & EW Phase Classification Biophysical Indicators
