Supplementary Information Titles
|
|
|
- Loraine Cain
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Supplementary Information Titles Please list each supplementary item and its title or caption, in the order shown below. Note that we do NOT copy edit or otherwise change supplementary information, and minor (nonfactual) errors in these documents cannot be corrected after publication. Please submit document(s) exactly as you want them to appear, with all text, images, legends and references in the desired order, and check carefully for errors. Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Contributing Authors: A Novel Technique for In Vivo Mapping of Myocardial Creatine Kinase Metabolism Ravinder Reddy Mohammad Haris, Anup Singh, Kejia Cai, Feliks Kogan, Jeremy McGarvey, Catherine DeBrosse, Gerald A Zsido, Walter RT Witschey, Kevin Koomalsingh, James J Pilla, Julio A. Chirinos, Victor A. Ferrari, Joseph H Gorman, Hari Hariharan, Robert C Gorman, Ravinder Reddy Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Discussion Supplementary Methods Title or Caption [NO DESCRIPTIVE TITLE NECESSARY [NO DESCRIPTIVE TITLE NECESSARY]
2 2 Supplementary Discussion The chemical-exchange-saturation-transfer (CEST) technique has been widely used to map different metabolites and macromolecules in vivo 1-6. Briefly, chemical exchange between bulk water and amine/amide/hydroxyl protons from different amino acids, proteins and other molecules have been exploited to measure ph in vivo 1, hepatic glycogen 2, cartilage glycosaminglycans 3, gene expression in vivo 4, myoinositol and glutamate in the brain 5,6. Comparison with hyperpolarized 13 C MRI Hyperpolarized 13 C MRI, using the techniques of parahydrogen induced polarization (PHIP) or dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP), has been used to study cardiac angiography, perfusion, catheter tracking and metabolic imaging 7,8. It is worth comparing the CrEST technique with hyperpolarization as an alternative method for metabolic imaging. While the hyperpolarized 13 C MRI probes the pyruvate metabolic products such as lactate, alanine, bicarbonate, and carbon dioxide 8-10, it does not detect either free creatine (Cr), phosphocreatine (PCr) or their inter-conversion. The major advantages of hyperpolarized 13 C MRI is that due to its high signal to noise ratio (SNR) and zero background signal, it provides high contrast-to-noise-ratio images of a specific metabolite. However, due to the four times lower gyromagnetic ratio of 13 C compared to 1 H, it requires 4 times higher gradient strength that limits its resolution in its applications in large animals and humans. On the other hand, CrEST images water signal and can be performed on standard clinical scanners
3 3 (3T) without requirement of any additional gradient strength. Furthermore, 13 C NMR requires exogenous injection of the 13 C labeled pyruvate and other metabolites and on-site polarizing instrument while the CrEST exploits the endogenous Cr. Tissue heterogeneity In the current study, ex vivo tissues showed (30 40%) variation on CrEST contrast, which could be due to the intrinsic tissue heterogeneity as well as inhomogeneous tissue degradation caused by the delay between the animal sacrifice and experiment time. This variation can be minimized by reducing the 24 hours delay significantly. Supplementary Methods Animal handling and preparation All animals were treated under experimental protocols approved by the University of Pennsylvania s Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) and in compliance with National Institutes of Health Publication No , revised Three male Yorkshire swine and two male Dorset sheep weighing between 35 and 40 kg were used in this study. For myocardial infarction (MI) creation (n = 3), animals were sedated with intramuscular ketamine injection (25 30 mg/kg), intubated, and mechanically ventilated. General anesthesia was maintained with
4 4 a mixture of inhaled isoflurane ( %) and oxygen, delivered by volumecontrolled ventilation at a tidal volume of ml/kg. Via a left thoracotomy, animals underwent selective ligation of the circumflex artery or its branches with non-absorbable suture to produce a postereolateral infarct of uniform shape involving approximately 20 25% of the left ventricular (LV) wall. Hemodynamic and echocardiographic data were recorded pre- and post-infarction. After ensuring hemodynamic and electrophysiologic stability, all animals were then recovered for anesthesia. Prior to imaging, anesthesia was again initiated with ketamine and mixed isoflurane (1.5 3%) and maintained continuously throughout the imaging procedures. A high-fidelity pressure transducer (Millar Instruments, Houston, TX, USA) was guided into the left ventricle for cardiac gating. The animal was transported to a 3T MRI scanner connected to a ventilator and underwent cardiac imaging. In vivo image acquisition protocol description All animals were imaged at 3T Siemens scanner under an approved Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) protocol. The real challenge with in vivo cardiac experiments is tissue motion. This has been addressed in two ways: use of gated segmented image acquisition and use of z spectral fitting during post processing. Specialized hardware to provide combined respiratory and cardiac gating of image acquisition was used. Initial set up consisted of the following scans: (i) a general 3 plane multi-slice large FOV (50 cm) localizer, (ii) a smaller FOV (35 40 cm) oblique localizer to get the short axis heart orientation
5 5 and (iii) a multi-slice multi-phase Cine MRI scan with 12 phases along the short axis orientation. From the Cine images, the position and diastolic phase delay time for the slice of interest were determined. The diastolic phase delay time was used to fix the CEST acquisition protocol including trigger delay and the number of acquisition segments. The trigger delay time was adjusted such that the saturation duration and the acquisition duration fall in the diastolic phase. In the current study, after trigger delay, 250 ms saturation pulse was applied at peak B 1rms of 155 Hz (3.6 µt) followed by a ~50 ms readout period (8 segments with a segment TR ~6 ms) for a total time of ~300 ms. A delay of several seconds was allowed for the restoration of longitudinal magnetization, which was adjusted by respiratory gating. We need images with about 48 saturation frequency offsets for z-spectral fitting. Each image acquisition with cardiac and respiratory gating takes about 16 respiratory periods (~ 48 s to 60 s based on the rate of respiration of animal) due to the need for keeping the segment size small enough (n = 8) to reduce motion artifacts. Thus the total acquisition time for the entire protocol is minutes. The CrEST pulse sequence diagram is shown in Figure 1.
6 6 Figure 1. CrEST imaging pulse sequence. The basic sequence consists of an outer shot loop containing the frequency selective saturation pulse train followed by an inner loop of segmented fast low angle shot (FLASH) gradient echo acquisitions and ending with a delay (T1/SAR delay). Shot loops are repeated using the number of shots required per image acquisition. In each shot 8 segments of k space were acquired. The saturation pulse was applied just after trigger delay following the cardiac trigger pulse. We use a centric phase encoding order scheme to maintain the best CEST contrast. The whole sequence can be repeated to generate images with saturation applied at different offset frequencies. In Vivo Myocardial Wall Identification
7 7 CEST weighted images obtained at +/-2 p.p.m. show good contrast between myocardial wall and chambers. Hence we used a manual procedure to identify the boundaries of myocardial wall as shown below in figure 2. Figure 2. In vivo myocardial wall identification for color overlay. First, the myocardial wall was identified on anatomical CEST weighted image (2 p.p.m.) and was circumscribed manually (red polygon) as shown in (a) and a mask was generated. The CrEST map corresponding to the mask of myocardial wall was overlaid on the anatomical image without saturation as shown in (b). Post Processing details All image processing and data analysis was performed using in house written MATLAB (version 7.5, R2007b) routines. B 0 and B 1 maps were also obtained for the same slice position in case of ex vivo tissue and skeletal muscles and were used to correct the CEST asymmetry maps using the method described previously 5,6. CrEST was computed using asymmetry analysis and normalized with negative frequency offset.
8 8 Background noise of image without saturation was removed by applying a threshold on signal intensity and a mask was generated. The mask was then applied on entire data to remove noise regions. Noise in image regions was reduced by applying an averaging kernel of size 3 3 spatially. After spatial noise reduction, data corresponding to both +ve and ve frequencies over a limited range around ±1.8 p.p.m. were fitted, separately, with a linear function. The linear function was used to generate B 0 inhomogeneity corrected CEST images. Finally, the corrected CEST images were used to generate CrEST contrast map using asymmetry analysis as given in equation [1] 6. S ve S+ ve CrEST (%) = 100 Eq [1] S ve where S -ve and S +ve are the B 0 inhomogeneity corrected MR signals at -1.8 p.p.m. and +1.8 p.p.m. respectively. To account for and minimize the contribution from direct saturation and magnetization transfer effects, we used S -ve instead of S 0 for normalization. The animal data with more than 10% heart rate fluctuation and/ or more than 2 mm heart wall displacement during the course of imaging were excluded from this study. Even on the included data, CEST contrast obtained by asymmetry analysis is somewhat unreliable due to subtraction artifacts caused by residual respiratory and left ventricular wall motion and fluctuations of B 0 during gated CEST imaging. z-spectral fitting based methods can mitigate these artifacts. In this study, we adopted an approach of fitting a probabilistic combination of Lorentzian functions, corresponding to direct saturation (DS), magnetization
9 9 transfer (MT) and CrEST components as described below. This model is a modification to the previously published combination of Lorentzian functions for CEST z-spectral fitting 11. Probabilistic model (PM) for z-spectrum Let A, B and C are non-mutually exclusive events. According to additive law of probability 12, the probability of union of these three events is given by following equation: p(a U B UC) = p(a) + p(b) + p(c) [p(a B) + p(b C) + p(a C) ] + p(a B C) Eq [2] where U and represents union and intersection respectively. Since DS, MT and CrEST are non- mutually exclusive events, probability of union of these events can be obtained using equation [2]. Z-spectrum corresponds to the probability distribution of union of DS, MT and CrEST. Let s assume Lorentzian (L i, i = 1,2, 3) distributions for DS, MT and CrEST. Where, A =amplitude, W=width, C =center of Lorentzian, =offset frequency. Using probabilistic model and Lorentzian functions corresponding to DS, MT and CrEST events, the following equations are used to fit z-spectral data over [-5, 5] p.p.m. frequency offset range: f = 1- p(ds U MT U CrEST) Eq [4]
10 10 Where is frequency offset? The center of CEST component was fixed at 1.8 p.p.m. relative to DS center. The PM model fitting was validated for z-spectral data obtained using standard 3pool model Bloch equations with exchange terms13. Next, we experimentally demonstrated the equivalent performance of this approach to the standard asymmetry analysis using ex vivo tissue results. Ex vivo Z-spectral data over -5 to 5 p.p.m. range were fitted with PM function using a non-linear fitting routine in MATLAB (lsqnonlin) as shown in Figure 3 below. Figure 3. Ex vivo tissue data: Anatomical CEST weighted image (2 p.p.m.) of a non-infarcted lamb myocardium (a). gray scale and color coded CrEST contrast map generated through asymmetry-based analysis (b, c). Fitting of z-spectra
11 11 along with fitted components (DS, direct water saturation; MT, magnetization transfer; and CEST) in a voxel in ex vivo tissue using PM model. Gray scale and color coded CrEST map of the same tissue obtained using PM based approach (e, f). The CrEST contrast calculated using both approaches are comparable and within ~10% of variation. Procedure for PM fitting in vivo data: Here we adopted a two-step fitting procedure. In the first step, z-spectra corresponding to 4 small ROIs on the myocardial wall are fitted and the results from the ROI with the best fit are used to set constraints and initial guess for voxel wise z-spectra fitting of entire myocardium tissue. Upper and lower bound for constraints were set at ±10% of the initial guess. In cases of animals with infarct, ROIs were drawn in both healthy and infarcted regions and best-fit parameters were obtained separately for both types of tissues. Scan time considerations There is a substantial difference in total scan times between in vivo skeletal muscle and in vivo cardiac studies. In the case of cardiac studies, we need images with about 48 saturation frequency offsets for z-spectral fitting. Each image acquisition with cardiac and respiratory gating takes about 16 respiratory periods (~ 48 s to 60 s based on the rate of respiration of animal). Thus the total acquisition time for the entire protocol is minutes. In the case of skeletal muscle, since the data are acquired in the absence of motion, we can use CEST
12 12 asymmetry analysis with B 0 correction as given in Equation 1. This requires a total of 6 saturation-offset frequencies (3 on the positive side and 3 on the negative side). We also use a single shot readout of a whole image with respect to saturation pulse with a TR of 4 s for each offset frequency. Hence, in the case of calf muscle, in essence, we can gather the CrEST map in about 24 s. The B 0 and B 1 maps collected either pre- or post exercise can be used for correcting the B 0 and B 1 field heterogeneities. Spectroscopy data processing 1 H and 31 P MR spectra were phased and baseline corrected and fitted using nonlinear least-squares method with Gaussian functions. Unsuppressed water signal from the same voxel was used to derive absolute concentration of creatine in tissue as well as PCA extracts. Sample size As this is a methodology development study, the sample sizes were chosen to illustrate feasibility and no randomization or group categorization was done.
13 13 References: 1. Zhou, J., Payen, J.F., Wilson, D.A., Traystman, R.J. & van Zijl, P.C. Using the amide proton signals of intracellular proteins and peptides to detect ph effects in MRI. Nat Med 9, (2003). 2. van Zijl, P.C., Jones, C.K., Ren, J., Malloy, C.R. & Sherry, A.D. MRI detection of glycogen in vivo by using chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging (glycocest). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104, (2007). 3. Ling, W., Regatte, R.R., Navon, G. & Jerschow, A. Assessment of glycosaminoglycan concentration in vivo by chemical exchange- dependent saturation transfer (gagcest). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105, (2008). 4. Gilad, A.A., et al. Artificial reporter gene providing MRI contrast based on proton exchange. Nat Biotechnol 25, (2007). 5. Haris, M., Cai, K., Singh, A., Hariharan, H. & Reddy, R. In vivo mapping of brain myo- inositol. NeuroImage 54, (2011). 6. Cai, K., et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of glutamate. Nature medicine 18, (2012). 7. Tyler, D.J. Cardiovascular Applications of Hyperpolarized MRI. Current cardiovascular imaging reports 4, (2011). 8. Golman, K., et al. Cardiac metabolism measured noninvasively by hyperpolarized 13C MRI. Magnetic resonance in medicine : official journal of the Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine / Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 59, (2008). 9. Merritt, M.E., et al. Hyperpolarized 13C allows a direct measure of flux through a single enzyme- catalyzed step by NMR. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 104, (2007). 10. Lau, A.Z., et al. Rapid multislice imaging of hyperpolarized 13C pyruvate and bicarbonate in the heart. Magnetic resonance in medicine : official journal of the Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine / Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 64, (2010). 11. Zaiss, M., Schmitt, B. & Bachert, P. Quantitative separation of CEST effect from magnetization transfer and spillover effects by Lorentzian- line- fit analysis of z- spectra. J Magn Reson 211, (2011). 12. Dennis D. Wackerly, William Mendenhall & Scheaffer, R.L. Mathematical Statistics with Applications. 13. Woessner, D.E., Zhang, S., Merritt, M.E. & Sherry, A.D. Numerical solution of the Bloch equations provides insights into the optimum design of PARACEST agents for MRI. Magnetic resonance in medicine : official journal of the Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine / Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 53, (2005).
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Nat Med. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2012 August 01.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nat Med. ; 18(2): 302 306. doi:10.1038/nm.2615. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Glutamate Kejia Cai 1,**, Mohammad Haris 1,**, Anup
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nat Med. ; 18(2): 302 306. doi:10.1038/nm.2615. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Glutamate Kejia Cai 1,**, Mohammad Haris 1,**, Anup
Clinical Translation of Tumor Acidosis Measurements with AcidoCEST MRI
 Electronic Supplementary Material Clinical Translation of Tumor Acidosis Measurements with AcidoCEST MRI Journal: Molecular Imaging and Biology Kyle M. Jones, B.S., 1 Edward A. Randtke, Ph.D., 2 Eriko
Electronic Supplementary Material Clinical Translation of Tumor Acidosis Measurements with AcidoCEST MRI Journal: Molecular Imaging and Biology Kyle M. Jones, B.S., 1 Edward A. Randtke, Ph.D., 2 Eriko
Background. Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS) non invasively measures metabolite concentrations
 Applying FID navigators to high field MRS in the body AAPM North Central Chapter Spring Meeting April 7th, 2017 Ryan M. Kalmoe Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Minnesota Advisor: Dr. Gregory
Applying FID navigators to high field MRS in the body AAPM North Central Chapter Spring Meeting April 7th, 2017 Ryan M. Kalmoe Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Minnesota Advisor: Dr. Gregory
Artifacts Caused by Eddy Current in Diffusion MRI
 Artifacts Caused by Eddy Current in Diffusion MRI Xi Tan ABSTRACT Magnetic resonance diffusion imaging is potentially an important tool for the noninvasive characterization of normal and pathological tissue.
Artifacts Caused by Eddy Current in Diffusion MRI Xi Tan ABSTRACT Magnetic resonance diffusion imaging is potentially an important tool for the noninvasive characterization of normal and pathological tissue.
Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy from fundamental developments to improved noninvasive diagnosis and characterisation of children s brain tumours.
 Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy from fundamental developments to improved noninvasive diagnosis and characterisation of children s brain tumours. Martin Wilson IOP Medical Physics Group Scientific and
Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy from fundamental developments to improved noninvasive diagnosis and characterisation of children s brain tumours. Martin Wilson IOP Medical Physics Group Scientific and
emission tomography (PET) and single photon emission tomography (SPECT).
 Supplementary Notes for Manuscript NMED-NT53311 Title: Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Glutamate Authors: Kejia Cai, Mohammad Haris, Anup Singh, Feliks Kogan, Joel H. Greenberg, Hari Hariharan, John A. Detre,
Supplementary Notes for Manuscript NMED-NT53311 Title: Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Glutamate Authors: Kejia Cai, Mohammad Haris, Anup Singh, Feliks Kogan, Joel H. Greenberg, Hari Hariharan, John A. Detre,
In Vivo 13 Carbon Metabolic Imaging at 3T With Hyperpolarized 13 C-1-Pyruvate
 Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 58:65 69 (2007) In Vivo 13 Carbon Metabolic Imaging at 3T With Hyperpolarized 13 C-1-Pyruvate S.J. Kohler, 1 * Y. Yen, 1 J. Wolber, 2 A.P. Chen, 3 M.J. Albers, 4 R. Bok,
Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 58:65 69 (2007) In Vivo 13 Carbon Metabolic Imaging at 3T With Hyperpolarized 13 C-1-Pyruvate S.J. Kohler, 1 * Y. Yen, 1 J. Wolber, 2 A.P. Chen, 3 M.J. Albers, 4 R. Bok,
Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL)
 Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) Imaging Seminars Series Stony Brook University, Health Science Center Stony Brook, NY - December 11 th, 2012 Francesca Zanderigo, PhD Layout BASIC PRINCIPLES ACQUISITION SEQUENCES
Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) Imaging Seminars Series Stony Brook University, Health Science Center Stony Brook, NY - December 11 th, 2012 Francesca Zanderigo, PhD Layout BASIC PRINCIPLES ACQUISITION SEQUENCES
P hosphorus (31P) magnetic resonance (MR) is a unique non-invasive tool for studying muscle physiology,
 OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: PHYSIOLOGY BIOPHYSICS BIOENERGETICS Received 17 March 2014 Accepted 19 May 2014 Published 9 June 2014 Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to P.P. (prodromos.
OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: PHYSIOLOGY BIOPHYSICS BIOENERGETICS Received 17 March 2014 Accepted 19 May 2014 Published 9 June 2014 Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to P.P. (prodromos.
European Journal of Radiology
 European Journal of Radiology 81 (2012) e653 e664 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect European Journal of Radiology jo ur n al hom epage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrad In vivo proton magnetic resonance
European Journal of Radiology 81 (2012) e653 e664 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect European Journal of Radiology jo ur n al hom epage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrad In vivo proton magnetic resonance
Disease Detection in MRS (Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy)
 Disease Detection in MRS (Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy) Hariram Vyas 1, Shivam Thakur 2, Dr. S.K.Pathan 3 Hariram Vyas Department of computer Engineering Smt. Kashibai Navale College Of Engineering
Disease Detection in MRS (Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy) Hariram Vyas 1, Shivam Thakur 2, Dr. S.K.Pathan 3 Hariram Vyas Department of computer Engineering Smt. Kashibai Navale College Of Engineering
Final Project
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.584J: Magnetic Resonance Analytic, Biochemical, and Imaging Techniques, Spring 2006 Course Directors: Dr. Bruce Rosen and Dr. Lawrence Wald 22.561
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.584J: Magnetic Resonance Analytic, Biochemical, and Imaging Techniques, Spring 2006 Course Directors: Dr. Bruce Rosen and Dr. Lawrence Wald 22.561
Magnetic Resonance Imaging at 7T in Glasgow. A unique opportunity!
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging at 7T in Glasgow A unique opportunity! An NHS MR Physicist's perspective... What is different about 7T scanners? What has already been achieved? Imaging Centre of Excellence
Magnetic Resonance Imaging at 7T in Glasgow A unique opportunity! An NHS MR Physicist's perspective... What is different about 7T scanners? What has already been achieved? Imaging Centre of Excellence
Optimization of 31 P magnetic resonance spectroscopy in vivo
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Optimization of 31 P magnetic resonance spectroscopy in vivo To cite this article: A V Manzhurtsev et al 2018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 945 012005 View
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Optimization of 31 P magnetic resonance spectroscopy in vivo To cite this article: A V Manzhurtsev et al 2018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 945 012005 View
Pre-clinical and postmortem diffusion MRI
 manisha.aggarwal@jhu.edu Pre-clinical and postmortem diffusion MRI Manisha Aggarwal, Ph.D. Department of Radiology Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Diffusion and tissue microstructure? signal
manisha.aggarwal@jhu.edu Pre-clinical and postmortem diffusion MRI Manisha Aggarwal, Ph.D. Department of Radiology Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Diffusion and tissue microstructure? signal
ClinScan. think forward. Small Animal MRI Solution for Molecular Imaging and Translational Research. Preclinical MRI
 ClinScan Small Animal MRI Solution for Molecular Imaging and Translational Research think forward Preclinical MRI Be Clinical from the Very Beginning With ClinScan you enter the field of translational
ClinScan Small Animal MRI Solution for Molecular Imaging and Translational Research think forward Preclinical MRI Be Clinical from the Very Beginning With ClinScan you enter the field of translational
N. Gopa1sami. S.L. Dieckman. and W. A. Ellingson Materials and Components Technology Division
 QUANTITATIVE MRI MEASUREMENT OF BINDER DISTRIBUTIONS IN GREEN-STATE CERAMICS N. Gopa1sami. S.L. Dieckman. and W. A. Ellingson Materials and Components Technology Division R.E. Botto Chemistry Division
QUANTITATIVE MRI MEASUREMENT OF BINDER DISTRIBUTIONS IN GREEN-STATE CERAMICS N. Gopa1sami. S.L. Dieckman. and W. A. Ellingson Materials and Components Technology Division R.E. Botto Chemistry Division
Pulsed NMR of Paramagnetic Terbium. Cheyenne Michael Yari
 Pulsed NMR of Paramagnetic Terbium Cheyenne Michael Yari June 26, 2012 1 - Introduction The magnetic properties of atomic nuclei have proven to provide very useful information which can directly be used
Pulsed NMR of Paramagnetic Terbium Cheyenne Michael Yari June 26, 2012 1 - Introduction The magnetic properties of atomic nuclei have proven to provide very useful information which can directly be used
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Alenina et al. 10.1073/pnas.0810793106 SI Materials and Methods In Vivo Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). In vivo brain MRI was performed in 6-month-old Tph2 / and control
Supporting Information Alenina et al. 10.1073/pnas.0810793106 SI Materials and Methods In Vivo Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). In vivo brain MRI was performed in 6-month-old Tph2 / and control
Table S1. Dystrophin antibodies.
 Table S1. Dystrophin antibodies. name clone immunogen (human dystrophin) epitope exons region amino acids vendor (catalogue number) references for characterization of antibodies MANEX1A 4C7 recombinant
Table S1. Dystrophin antibodies. name clone immunogen (human dystrophin) epitope exons region amino acids vendor (catalogue number) references for characterization of antibodies MANEX1A 4C7 recombinant
The first MR with IQ Philips Intera 1.5T With SmartExam
 The first MR with IQ Philips Intera 1.5T With SmartExam Smart Exam reproducibility 2 consistency, and efficiency Philips Intera 1.5T gives you the image quality, patient comfort and range of clinical applications
The first MR with IQ Philips Intera 1.5T With SmartExam Smart Exam reproducibility 2 consistency, and efficiency Philips Intera 1.5T gives you the image quality, patient comfort and range of clinical applications
Physicists Quality Control for MR Equipment
 Physicists Quality Control for MR Equipment Geoffrey D. Clarke, Ph.D. University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio 1 Overview ABR and the role of the Qualified Medical Physicist/ MR Scientist
Physicists Quality Control for MR Equipment Geoffrey D. Clarke, Ph.D. University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio 1 Overview ABR and the role of the Qualified Medical Physicist/ MR Scientist
MRI CryoProbe. "c_ MAl. Innovation with lntegri~ Unrivaled Sensitivity in Preclinical MRI
 MRI CryoProbe Unrivaled Sensitivity in Preclinical MRI "c_ MAl. Innovation with lntegri~ \!A!itffi)~~ Lnl:@ [!JITill~ ~ @he1? For the ultimate image; for the best in resolution; for unmatched performance
MRI CryoProbe Unrivaled Sensitivity in Preclinical MRI "c_ MAl. Innovation with lntegri~ \!A!itffi)~~ Lnl:@ [!JITill~ ~ @he1? For the ultimate image; for the best in resolution; for unmatched performance
High-resolution functional magnetic resonance imaging of the animal brain
 Methods 30 (2003) 28 41 www.elsevier.com/locate/ymeth High-resolution functional magnetic resonance imaging of the animal brain Seong-Gi Kim a, * and Kamil Ugurbil b a Department of Neurobiology, University
Methods 30 (2003) 28 41 www.elsevier.com/locate/ymeth High-resolution functional magnetic resonance imaging of the animal brain Seong-Gi Kim a, * and Kamil Ugurbil b a Department of Neurobiology, University
Preclinical MRI. Solutions for Small Animal Imaging. Molecular Imaging
 Preclinical MRI Solutions for Small Animal Imaging Molecular Imaging The Power of Imaging Applications Resolution Typical resolution in MRI is less than 200μm, to more than 20μm with 2D slices or full
Preclinical MRI Solutions for Small Animal Imaging Molecular Imaging The Power of Imaging Applications Resolution Typical resolution in MRI is less than 200μm, to more than 20μm with 2D slices or full
2018 REVIEW CATEGORIES
 2018 REVIEW CATEGORIES 100 Neuro 101 Neuro: Acquisition 102 Neuro: Processing 103 Neuro: Neonatal & Pediatric - Normal Development 104 Neuro: Neonatal & Pediatric - Clinical Studies 105 Neuro: Normal Aging
2018 REVIEW CATEGORIES 100 Neuro 101 Neuro: Acquisition 102 Neuro: Processing 103 Neuro: Neonatal & Pediatric - Normal Development 104 Neuro: Neonatal & Pediatric - Clinical Studies 105 Neuro: Normal Aging
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING OF IN VIVO FLOW PHENOMENA
 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING OF IN VIVO FLOW PHENOMENA So far we have seen that magnetic resonance can Locate the positions of spins (mainly water) with the aid of one or multiple field gradient: MRI Characterize
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING OF IN VIVO FLOW PHENOMENA So far we have seen that magnetic resonance can Locate the positions of spins (mainly water) with the aid of one or multiple field gradient: MRI Characterize
PRINCIPLES OF CT AND MR IMAGING Marc-André d Anjou, DMV, DACVR Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Montreal Saint-Hyacinthe, Quebec, Canada
 PRINCIPLES OF CT AND MR IMAGING Marc-André d Anjou, DMV, DACVR Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Montreal Saint-Hyacinthe, Quebec, Canada CT and MR imaging offer superior diagnostic possibilities
PRINCIPLES OF CT AND MR IMAGING Marc-André d Anjou, DMV, DACVR Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Montreal Saint-Hyacinthe, Quebec, Canada CT and MR imaging offer superior diagnostic possibilities
Phased array 3D MR spectroscopic imaging of the brain at 7 T
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Magnetic Resonance Imaging 26 (2008) 1201 1206 Original contributions Phased array 3D MR spectroscopic imaging of the brain at 7 T Duan Xu a,b,, Charles H. Cunningham
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Magnetic Resonance Imaging 26 (2008) 1201 1206 Original contributions Phased array 3D MR spectroscopic imaging of the brain at 7 T Duan Xu a,b,, Charles H. Cunningham
AN AUTOMATED SYRINGE PUMP SYSTEM FOR IMPROVING THE REPRODUCIBILITY OF DYNAMIC HYPERPOLARIZED MRI PHANTOMS
 Texas Medical Center Library DigitalCommons@TMC UT GSBS Dissertations and Theses (Open Access) Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences 8-2016 AN AUTOMATED SYRINGE PUMP SYSTEM FOR IMPROVING THE REPRODUCIBILITY
Texas Medical Center Library DigitalCommons@TMC UT GSBS Dissertations and Theses (Open Access) Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences 8-2016 AN AUTOMATED SYRINGE PUMP SYSTEM FOR IMPROVING THE REPRODUCIBILITY
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Magn Reson Imaging. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2010 February 12.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Magn Reson Imaging. 2008 November ; 26(9): 1201. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2008.03.006. Phased Array 3D MR Spectroscopic Imaging of the Brain
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Magn Reson Imaging. 2008 November ; 26(9): 1201. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2008.03.006. Phased Array 3D MR Spectroscopic Imaging of the Brain
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: magnetic_resonance_spectroscopy 12/1997 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Magnetic
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: magnetic_resonance_spectroscopy 12/1997 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Magnetic
Original Article. imri 2017;21: Ji Eun Park 1, Ho Sung Kim 1, Seung Chai Jung 1, Jochen Keupp 2, Ha-Kyu Jeong 3, Sang Joon Kim 1
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2017;21:65-70 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2017.21.2.65 Depiction of Acute Stroke Using 3-Tesla Clinical Amide Proton Transfer Imaging: Saturation Time Optimization
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2017;21:65-70 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2017.21.2.65 Depiction of Acute Stroke Using 3-Tesla Clinical Amide Proton Transfer Imaging: Saturation Time Optimization
Photoacoustic imaging of vascular networks in transgenic mice
 Photoacoustic imaging of vascular networks in transgenic mice J.G. Laufer 1, J.O. Cleary 1,2, E.Z. Zhang 1, M.F. Lythgoe 2, P.C. Beard 1 1. Department of Medical Physics and Bioengineering, University
Photoacoustic imaging of vascular networks in transgenic mice J.G. Laufer 1, J.O. Cleary 1,2, E.Z. Zhang 1, M.F. Lythgoe 2, P.C. Beard 1 1. Department of Medical Physics and Bioengineering, University
BIOMEDICAL SIGNAL AND IMAGE PROCESSING
 BIOMEDICAL SIGNAL AND IMAGE PROCESSING EE 5390-001 SYLLABUS Instructor: Wei Qian, Ph.D. Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering Medical Signal and Image Computerized Processing Scheme for Medical
BIOMEDICAL SIGNAL AND IMAGE PROCESSING EE 5390-001 SYLLABUS Instructor: Wei Qian, Ph.D. Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering Medical Signal and Image Computerized Processing Scheme for Medical
High-Speed 3T MR Spectroscopic Imaging of Prostate With Flyback Echo-Planar Encoding
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 25:1288 1292 (2007) Clinical Note High-Speed 3T MR Spectroscopic Imaging of Prostate With Flyback Echo-Planar Encoding Albert P. Chen, PhD, 1,2 Charles H. Cunningham,
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 25:1288 1292 (2007) Clinical Note High-Speed 3T MR Spectroscopic Imaging of Prostate With Flyback Echo-Planar Encoding Albert P. Chen, PhD, 1,2 Charles H. Cunningham,
MRI Protocols in Experimental Stroke. Xenios Milidonis Centre for Clinical Brain Sciences The University of Edinburgh
 MRI Protocols in Experimental Stroke Xenios Milidonis Centre for Clinical Brain Sciences The University of Edinburgh MultiPART Meeting, Barcelona, 2 October 204 Objective In MultiPART magnetic resonance
MRI Protocols in Experimental Stroke Xenios Milidonis Centre for Clinical Brain Sciences The University of Edinburgh MultiPART Meeting, Barcelona, 2 October 204 Objective In MultiPART magnetic resonance
High quality and fast scanning with Compressed SENSE at KCH
 FieldStrength MRI articles High quality and fast scanning with at KCH FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - November 2018 www.philips.com/fieldstrength At Kurashiki Central Hospital, use of resulted
FieldStrength MRI articles High quality and fast scanning with at KCH FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - November 2018 www.philips.com/fieldstrength At Kurashiki Central Hospital, use of resulted
Simple, intuitive and accessible MRI solution for preclinical research. M-Series Compact MRI Systems
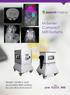 Simple, intuitive and accessible MRI solution for preclinical research M-Series Compact MRI Systems Application Oriented Imaging Anatomy and Morphology In vivo soft tissue imaging for morphological characterization.
Simple, intuitive and accessible MRI solution for preclinical research M-Series Compact MRI Systems Application Oriented Imaging Anatomy and Morphology In vivo soft tissue imaging for morphological characterization.
Metabolomics. Primary Molecules. Secondary Molecules TMAO. creatinine citrate. hippurate. allantoin creatinine taurine. urea water.
 Metabolomics Nature Reviews: Drug Discovery Nicholson et al. (22) Efficacy Toxicity Primary Molecules Secondary Molecules Filtration Resorption Dilution Concentration TMAO hippurate allantoin creatinine
Metabolomics Nature Reviews: Drug Discovery Nicholson et al. (22) Efficacy Toxicity Primary Molecules Secondary Molecules Filtration Resorption Dilution Concentration TMAO hippurate allantoin creatinine
Simple, intuitive and accessible MRI solution for preclinical research. M-Series Compact MRI Systems
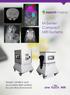 Simple, intuitive and accessible MRI solution for preclinical research M-Series Compact MRI Systems Application Oriented Imaging Molecular Imaging Using Contrast Agents Detection and quantification of
Simple, intuitive and accessible MRI solution for preclinical research M-Series Compact MRI Systems Application Oriented Imaging Molecular Imaging Using Contrast Agents Detection and quantification of
Comparing different analysis methods for quantifying the MRI amide proton transfer (APT) effect in hyperacute stroke patients
 Research article Received: 20 December 2013, Revised: 6 May 2014, Accepted: 7 May 2014, Published online in Wiley Online Library: 10 June 2014 (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI: 10.1002/nbm.3147 Comparing different
Research article Received: 20 December 2013, Revised: 6 May 2014, Accepted: 7 May 2014, Published online in Wiley Online Library: 10 June 2014 (wileyonlinelibrary.com) DOI: 10.1002/nbm.3147 Comparing different
Considerations in applying 3D PRESS H-1 brain MRSI with an eight-channel phased-array coil at 3 T
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging 24 (2006) 1295 1302 Considerations in applying 3D PRESS H-1 brain MRSI with an eight-channel phased-array coil at 3 T Yan Li a,b, Joseph A. Osorio a,b, Esin Ozturk-Isik a,b,
Magnetic Resonance Imaging 24 (2006) 1295 1302 Considerations in applying 3D PRESS H-1 brain MRSI with an eight-channel phased-array coil at 3 T Yan Li a,b, Joseph A. Osorio a,b, Esin Ozturk-Isik a,b,
Time-resolved Measurements Using the Agilent Cary Eclipse Fluorescence Spectrophotometer A Versatile Instrument for Accurate Measurements
 Time-resolved Measurements Using the Agilent Cary Eclipse Fluorescence Spectrophotometer A Versatile Instrument for Accurate Measurements Technical Overview Authors Dr. Fabian Zieschang, Katherine MacNamara,
Time-resolved Measurements Using the Agilent Cary Eclipse Fluorescence Spectrophotometer A Versatile Instrument for Accurate Measurements Technical Overview Authors Dr. Fabian Zieschang, Katherine MacNamara,
Propel your imaging abilities into the future.
 GE Healthcare Propel your imaging abilities into the future. SIGNA CREATOR Imagine what MR can be. Leap ahead and create your future in imaging. Meet SIGNA Creator, named for its ability to help you create
GE Healthcare Propel your imaging abilities into the future. SIGNA CREATOR Imagine what MR can be. Leap ahead and create your future in imaging. Meet SIGNA Creator, named for its ability to help you create
Imaging Considerations for In Vivo 13 C Metabolic Mapping Using Hyperpolarized 13 C-Pyruvate
 FULL PAPERS Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 62:1 10 (2009) Imaging Considerations for In Vivo 13 C Metabolic Mapping Using Hyperpolarized 13 C-Pyruvate Y-F. Yen, 1 * S.J. Kohler, 2 A.P. Chen, 3 J. Tropp,
FULL PAPERS Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 62:1 10 (2009) Imaging Considerations for In Vivo 13 C Metabolic Mapping Using Hyperpolarized 13 C-Pyruvate Y-F. Yen, 1 * S.J. Kohler, 2 A.P. Chen, 3 J. Tropp,
Basic principles of NMR-based metabolomics
 Basic principles of NMR-based metabolomics Professor Dan Stærk Bioanalytical Chemistry and Metabolomics research group Natural Products and Peptides research section Department of Drug Design and Pharmacology
Basic principles of NMR-based metabolomics Professor Dan Stærk Bioanalytical Chemistry and Metabolomics research group Natural Products and Peptides research section Department of Drug Design and Pharmacology
8/1/2018. Optimization Strategies for Pediatric CT Imaging. Educational Objectives. Brain CT
 Image Quality Radiation Dose Contrast Dose Sedation Optimization Strategies for Pediatric CT Imaging Samuel Brady, M.S. Ph.D. DABR samuel.brady@cchmc.org 8-1-218 @CincyKidsRad facebook.com/cincykidsrad
Image Quality Radiation Dose Contrast Dose Sedation Optimization Strategies for Pediatric CT Imaging Samuel Brady, M.S. Ph.D. DABR samuel.brady@cchmc.org 8-1-218 @CincyKidsRad facebook.com/cincykidsrad
Table 1 Sensitivity elative to 1 H
 Cellular and Molecular Imaging: non-proton MRI Andrew Webb. C.J.Gorter Centre for High Field MRI, Department of Radiology, Leiden University Medical Centre, Albinusdreef 2, 2333 ZA Leiden, The Netherlands.
Cellular and Molecular Imaging: non-proton MRI Andrew Webb. C.J.Gorter Centre for High Field MRI, Department of Radiology, Leiden University Medical Centre, Albinusdreef 2, 2333 ZA Leiden, The Netherlands.
Reduced Field-of-View MRI Using Outer Volume Suppression for Spinal Cord Diffusion Imaging
 Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 57:625 630 (2007) Reduced Field-of-View MRI Using Outer Volume Suppression for Spinal Cord Diffusion Imaging B.J. Wilm, 1,2 * J. Svensson, 1,3 A. Henning, 2 K.P. Pruessmann,
Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 57:625 630 (2007) Reduced Field-of-View MRI Using Outer Volume Suppression for Spinal Cord Diffusion Imaging B.J. Wilm, 1,2 * J. Svensson, 1,3 A. Henning, 2 K.P. Pruessmann,
CQIE PET PROCEDURES. American College of Radiology Clinical Research Center. Centers for Quantitative Imaging Excellence LEARNING MODULE
 Centers for Quantitative Imaging Excellence LEARNING MODULE CQIE PET PROCEDURES American College of Radiology Clinical Research Center Imaging Core Laboratory v2.1 Centers for Quantitative Imaging Excellence
Centers for Quantitative Imaging Excellence LEARNING MODULE CQIE PET PROCEDURES American College of Radiology Clinical Research Center Imaging Core Laboratory v2.1 Centers for Quantitative Imaging Excellence
Intelligent and automatic in vivo detection and quantification of transplanted cells in MRI (Supporting Material)
 Intelligent and automatic in vivo detection and quantification of transplanted cells in MRI (Supporting Material) Muhammad Jamal Afridi 1, Arun Ross 1, Xiaoming Liu 1, Margaret F. Bennewitz 2, Dorela D.
Intelligent and automatic in vivo detection and quantification of transplanted cells in MRI (Supporting Material) Muhammad Jamal Afridi 1, Arun Ross 1, Xiaoming Liu 1, Margaret F. Bennewitz 2, Dorela D.
CQIE MRI PROCEDURES. American College of Radiology Clinical Research Center. Centers for Quantitative Imaging Excellence LEARNING MODULE
 Centers for Quantitative Imaging Excellence LEARNING MODULE CQIE MRI PROCEDURES American College of Radiology Clinical Research Center Imaging Core Laboratory v.2 Centers for Quantitative Imaging Excellence
Centers for Quantitative Imaging Excellence LEARNING MODULE CQIE MRI PROCEDURES American College of Radiology Clinical Research Center Imaging Core Laboratory v.2 Centers for Quantitative Imaging Excellence
Disclaimer. Fat in the body. Outline. Managing fat in MRI: a technical perspective
 Managing fat in MRI: a technical perspective Jingfei Ma, PhD, DABR Department of Imaging Physics Disclaimer The speaker is an inventor of US patents or patent applications that are licensed to GE Healthcare
Managing fat in MRI: a technical perspective Jingfei Ma, PhD, DABR Department of Imaging Physics Disclaimer The speaker is an inventor of US patents or patent applications that are licensed to GE Healthcare
Study of Laser Ablation in the In Vivo Rabbit Brain With MR Thermometry
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 16:147 152 (2002) Original Research Study of Laser Ablation in the In Vivo Rabbit Brain With MR Thermometry Lili Chen, PhD, 1 Janaka P. Wansapura, PhD, 1 Gary Heit,
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 16:147 152 (2002) Original Research Study of Laser Ablation in the In Vivo Rabbit Brain With MR Thermometry Lili Chen, PhD, 1 Janaka P. Wansapura, PhD, 1 Gary Heit,
Vevo The Ultimate Preclinical Imaging Experience
 The Ultimate Preclinical Imaging Experience 2 Introducing The World s First One-Touch Preclinical Imaging Platform The is a new and innovative platform created for the future of imaging. It combines ultra
The Ultimate Preclinical Imaging Experience 2 Introducing The World s First One-Touch Preclinical Imaging Platform The is a new and innovative platform created for the future of imaging. It combines ultra
Low-dose and High-resolution Cardiovascular Imaging with Revolution* CT
 GE Healthcare Case study Low-dose and High-resolution Cardiovascular Imaging with Revolution* CT Jean-Louis Sablayrolles, M.D. Laurent Macron, M.D. Jacques Feignoux, M.D. Centre Cardiologique du Nord,
GE Healthcare Case study Low-dose and High-resolution Cardiovascular Imaging with Revolution* CT Jean-Louis Sablayrolles, M.D. Laurent Macron, M.D. Jacques Feignoux, M.D. Centre Cardiologique du Nord,
DEVELOPMENT OF QUANTITATIVE FAST IMAGING WITH STEADY-STATE FREE PRECESSION (FISP) TECHNIQUES FOR HIGH FIELD PRECLINICAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING
 DEVELOPMENT OF QUANTITATIVE FAST IMAGING WITH STEADY-STATE FREE PRECESSION (FISP) TECHNIQUES FOR HIGH FIELD PRECLINICAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING by YING GAO Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements
DEVELOPMENT OF QUANTITATIVE FAST IMAGING WITH STEADY-STATE FREE PRECESSION (FISP) TECHNIQUES FOR HIGH FIELD PRECLINICAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING by YING GAO Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0231 TITLE: Spectroscopic Photoacoustic Tomography of Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Xueding Wang CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University Of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI 48109-1274
AD Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0231 TITLE: Spectroscopic Photoacoustic Tomography of Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Xueding Wang CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University Of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI 48109-1274
Product Brief: VevoCQ Advanced Contrast Quantification Software Analysis Tools for the Vevo 2100 System
 Product Brief: VevoCQ Advanced Contrast Quantification Software Analysis Tools for the Vevo 2100 System Introduction Microbubble contrast agents have been used as a method of assessing in vivo microvascular
Product Brief: VevoCQ Advanced Contrast Quantification Software Analysis Tools for the Vevo 2100 System Introduction Microbubble contrast agents have been used as a method of assessing in vivo microvascular
The time has come. Philips GEMINI TF PET/CT with TruFlight technology
 The time has come Philips GEMINI TF PET/CT with TruFlight technology TruFlight has arrived Time-of-flight technology has always held the promise of better PET imaging. But it took Philips to harness its
The time has come Philips GEMINI TF PET/CT with TruFlight technology TruFlight has arrived Time-of-flight technology has always held the promise of better PET imaging. But it took Philips to harness its
Advances in Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agents for Biomarker Detection
 AUAL REVIEWS Further Click here to view this article's online features: Download figures as PPT slides avigate linked references Download citations Explore related articles Search keywords Annu. Rev. Anal.
AUAL REVIEWS Further Click here to view this article's online features: Download figures as PPT slides avigate linked references Download citations Explore related articles Search keywords Annu. Rev. Anal.
VisualSonics Application Protocol Gene Delivery Applications into Subcutaneous Tumors
 VisualSonics Application Protocol Gene Delivery Applications into Subcutaneous Tumors 1 Objective The objective of the Delivery of Genetic Material for Gene Therapy Applications into Subcutaneous Tumors
VisualSonics Application Protocol Gene Delivery Applications into Subcutaneous Tumors 1 Objective The objective of the Delivery of Genetic Material for Gene Therapy Applications into Subcutaneous Tumors
Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
 Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Itamar Ronen 1 & Julien Valette 2 1 Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, The Netherlands 2 Molecular Imaging Research Center, Commissariat àl énergie
Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Itamar Ronen 1 & Julien Valette 2 1 Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, The Netherlands 2 Molecular Imaging Research Center, Commissariat àl énergie
Time-resolved 4D TWIST MR angiography of congenital heart and vessel anomalies: image quality and added diagnostic value compared to 3D MRA
 Time-resolved 4D TWIST MR angiography of congenital heart and vessel anomalies: image quality and added diagnostic value compared to 3D MRA Poster No.: C-1663 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper
Time-resolved 4D TWIST MR angiography of congenital heart and vessel anomalies: image quality and added diagnostic value compared to 3D MRA Poster No.: C-1663 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper
The technique for increase in signal-to-noise ratio of 10,000
 Real-time metabolic imaging Klaes Golman*, René in t Zandt, and Mikkel Thaning Amersham Health R&D AB, GE Healthcare, Medeon, SE-205 12 Malmö, Sweden Communicated by Alexander Pines, University of California,
Real-time metabolic imaging Klaes Golman*, René in t Zandt, and Mikkel Thaning Amersham Health R&D AB, GE Healthcare, Medeon, SE-205 12 Malmö, Sweden Communicated by Alexander Pines, University of California,
BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING (BME)
 Biomedical Engineering (BME) 1 BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING (BME) BME 500 Introduction to Biomedical Engineering Introduction to the concepts and research in biomedical engineering. Provides an overview of current
Biomedical Engineering (BME) 1 BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING (BME) BME 500 Introduction to Biomedical Engineering Introduction to the concepts and research in biomedical engineering. Provides an overview of current
Insight Through In Vivo Imaging
 Insight Through In Vivo Imaging Resolution Revolution in Realtime The Vevo 770 provides anatomical, functional and molecular data in realtime, on an affordable, easy to use and translational platform.
Insight Through In Vivo Imaging Resolution Revolution in Realtime The Vevo 770 provides anatomical, functional and molecular data in realtime, on an affordable, easy to use and translational platform.
Human Cardiac 31 P Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy at 7 Tesla
 SPECTROSCOPIC METHODOLOGY - Full Paper Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 72:304 315 (2014) Human Cardiac 31 P Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy at 7 Tesla Christopher T. Rodgers, 1 * William T. Clarke, 1 Carl
SPECTROSCOPIC METHODOLOGY - Full Paper Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 72:304 315 (2014) Human Cardiac 31 P Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy at 7 Tesla Christopher T. Rodgers, 1 * William T. Clarke, 1 Carl
Nature Reviews: Drug Discovery Nicholson et al. (2002)
 Metabolomics Nature Reviews: Drug Discovery Nicholson et al. (2002) Efficacy Toxicity Primary Molecules Secondary Molecules Filtration Resorption Dilution Concentration TMAO hippurate allantoin creatinine
Metabolomics Nature Reviews: Drug Discovery Nicholson et al. (2002) Efficacy Toxicity Primary Molecules Secondary Molecules Filtration Resorption Dilution Concentration TMAO hippurate allantoin creatinine
Award Number: W81XWH TITLE: Magnetic Resonance Characterization of Axonal Response to Spinal Cord Injury
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0713 TITLE: Magnetic Resonance Characterization of Axonal Response to Spinal Cord Injury PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: David B Hackney CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Beth Israel Deaconess
AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0713 TITLE: Magnetic Resonance Characterization of Axonal Response to Spinal Cord Injury PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: David B Hackney CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Beth Israel Deaconess
Magnetic resonance (MR) has historically been characterized
 This is an open access article published under an ACS AuthorChoice License, which permits copying and redistribution of the article or any adaptations for non-commercial purposes. pubs.acs.org/biochemistry
This is an open access article published under an ACS AuthorChoice License, which permits copying and redistribution of the article or any adaptations for non-commercial purposes. pubs.acs.org/biochemistry
Angio PL.U.S. PLaneWave UltraSensitive TM ultrasound imaging. White Paper
 White Paper Angio PL.U.S. PLaneWave UltraSensitive TM ultrasound imaging Jeremy Bercoff, Vice President of Product Management & Ultrasound Engineering Thomas Frappart, R&D Ultrasound Engineer Introduction
White Paper Angio PL.U.S. PLaneWave UltraSensitive TM ultrasound imaging Jeremy Bercoff, Vice President of Product Management & Ultrasound Engineering Thomas Frappart, R&D Ultrasound Engineer Introduction
TITLE: Hyperpolarized 13C MR markers of renal tumor aggressiveness. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of California, San Francisco
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0328 TITLE: Hyperpolarized 13C MR markers of renal tumor aggressiveness PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Renuka Sriram CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of California, San Francisco
AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0328 TITLE: Hyperpolarized 13C MR markers of renal tumor aggressiveness PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Renuka Sriram CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of California, San Francisco
Powerful MRI, Simplified. Innovation with Integrity. ICON, compact MRI system. Compact MRI
 Powerful MRI, Simplified ICON, compact MRI system Innovation with Integrity Compact MRI Preclinical MRI with the ICON : Powerful insights, simplicity in operation Traditionally MRI technology has been
Powerful MRI, Simplified ICON, compact MRI system Innovation with Integrity Compact MRI Preclinical MRI with the ICON : Powerful insights, simplicity in operation Traditionally MRI technology has been
Quantification in emission tomography: challenges, solutions, performance and impact
 EuroMedIm 2006 Quantification in emission tomography: challenges, solutions, performance and impact Irène Buvat U678 INSERM, Paris buvat@imed.jussieu.fr http://www.guillemet.org/irene EuroMedIm 2006 -
EuroMedIm 2006 Quantification in emission tomography: challenges, solutions, performance and impact Irène Buvat U678 INSERM, Paris buvat@imed.jussieu.fr http://www.guillemet.org/irene EuroMedIm 2006 -
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Membrane Fouling Dr Einar Fridjonsson
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Membrane Fouling Dr Einar Fridjonsson Fluid Science & Resources School of Mechanical and Chemical Engineering University of Western Australia Mobile NMR technology Research
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Membrane Fouling Dr Einar Fridjonsson Fluid Science & Resources School of Mechanical and Chemical Engineering University of Western Australia Mobile NMR technology Research
An automated image processing routine for segmentation of cell cytoplasms in high-resolution autofluorescence images
 An automated image processing routine for segmentation of cell cytoplasms in high-resolution autofluorescence images Alex J. Walsh a, Melissa C. Skala *a a Department of Biomedical Engineering, Vanderbilt
An automated image processing routine for segmentation of cell cytoplasms in high-resolution autofluorescence images Alex J. Walsh a, Melissa C. Skala *a a Department of Biomedical Engineering, Vanderbilt
Implementation of fast macromolecular proton fraction mapping on 1.5 and 3 Tesla clinical MRI scanners: preliminary experience
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Implementation of fast macromolecular proton fraction mapping on 1.5 and 3 Tesla clinical MRI scanners: preliminary experience To cite this article:
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Implementation of fast macromolecular proton fraction mapping on 1.5 and 3 Tesla clinical MRI scanners: preliminary experience To cite this article:
Examples of component location and routing are shown on the next page:
 The Cleveland FES Center MetroHealth Medical Center Hamann Building Room 601 2500 MetroHealth Drive Cleveland, Ohio 44109 (216) 778-3480 (216) 778-4259 (fax) www.fescenter.org Memo To: Re: Whom it may
The Cleveland FES Center MetroHealth Medical Center Hamann Building Room 601 2500 MetroHealth Drive Cleveland, Ohio 44109 (216) 778-3480 (216) 778-4259 (fax) www.fescenter.org Memo To: Re: Whom it may
Data Analysis in Metabolomics. Tim Ebbels Imperial College London
 Data Analysis in Metabolomics Tim Ebbels Imperial College London Themes Overview of metabolomics data processing workflow Differences between metabolomics and transcriptomics data Approaches to improving
Data Analysis in Metabolomics Tim Ebbels Imperial College London Themes Overview of metabolomics data processing workflow Differences between metabolomics and transcriptomics data Approaches to improving
CONTENTS 1 BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING: A HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE 1 2 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY 29. FOREWORD xiii. CONTRIBUTORS xv
 CONTENTS FOREWORD xiii CONTRIBUTORS xv 1 BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING: A HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE 1 1.1 Evolution of the Modern Health Care System 2 1.2 The Modern Health Care System 8 1.3 What Is Biomedical Engineering?
CONTENTS FOREWORD xiii CONTRIBUTORS xv 1 BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING: A HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE 1 1.1 Evolution of the Modern Health Care System 2 1.2 The Modern Health Care System 8 1.3 What Is Biomedical Engineering?
Advances in arterial spin labelling MRI methods for measuring perfusion and collateral flow
 Review Article Advances in arterial spin labelling MRI methods for measuring perfusion and collateral flow Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism 0(00) 1 20! Author(s) 2017 Reprints and permissions:
Review Article Advances in arterial spin labelling MRI methods for measuring perfusion and collateral flow Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism 0(00) 1 20! Author(s) 2017 Reprints and permissions:
Construction and evaluation of a quantitative arterial spin labeling brain perfusion template at 3T
 Construction and evaluation of a quantitative arterial spin labeling brain perfusion template at 3T Jan Petr, Jean-Christophe Ferré, Elise Bannier, Hélène Raoult, Jean-Yves Gauvrit, Christian Barillot
Construction and evaluation of a quantitative arterial spin labeling brain perfusion template at 3T Jan Petr, Jean-Christophe Ferré, Elise Bannier, Hélène Raoult, Jean-Yves Gauvrit, Christian Barillot
Supplementary Material Cohort Description
 Supplementary Material Cohort Description The following longitudinal twin cohorts were included: BrainSCALE: Brain Structure and Cognition: an Adolescent Longitudinal Twin Study into genetic etiology University
Supplementary Material Cohort Description The following longitudinal twin cohorts were included: BrainSCALE: Brain Structure and Cognition: an Adolescent Longitudinal Twin Study into genetic etiology University
Face detection method based on photoplethysmography
 Workshop on Low-Resolution Face Analysis (LRFA) in conjunction with 2013 10th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance Face detection method based on photoplethysmography
Workshop on Low-Resolution Face Analysis (LRFA) in conjunction with 2013 10th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance Face detection method based on photoplethysmography
실험동물을이용한분자영상 (In Vivo Molecular Imaging)
 실험동물을이용한분자영상 (In Vivo Molecular Imaging) May. 23. 2012. Jehoon Yang Contents Tissue sampling & fixation What s the molecular imaging? In vivo molecular imaging modalities MRI/MRS/fMRI In vivo molecular
실험동물을이용한분자영상 (In Vivo Molecular Imaging) May. 23. 2012. Jehoon Yang Contents Tissue sampling & fixation What s the molecular imaging? In vivo molecular imaging modalities MRI/MRS/fMRI In vivo molecular
Balancing versatility and value Introducing Optima MR T
 GE Healthcare Balancing versatility and value Introducing Optima MR360 1.5T Optima MR360 1.5T Providing an innovative balance in MR You know what you need from an MR scanner. The new Optima MR360 is engineered
GE Healthcare Balancing versatility and value Introducing Optima MR360 1.5T Optima MR360 1.5T Providing an innovative balance in MR You know what you need from an MR scanner. The new Optima MR360 is engineered
Press Presse Press Presse
 Press Presse Press Presse Healthcare Sector Imaging & IT Division Erlangen, November 30, 2009 Siemens Introduces its New Power Couple at RSNA 2009 Tim and Dot* redefine productivity in MRI up to 30 percent
Press Presse Press Presse Healthcare Sector Imaging & IT Division Erlangen, November 30, 2009 Siemens Introduces its New Power Couple at RSNA 2009 Tim and Dot* redefine productivity in MRI up to 30 percent
The Unique, New MRI Philips Ingenia 3 Tesla is now in Ayios Therissos! The first-ever digital broadband MR system has been installed in Ayios
 The Unique, New MRI Philips Ingenia 3 Tesla is now in Ayios Therissos! The first-ever digital broadband MR system has been installed in Ayios Therissos-Nicosia that delivers crystal clear images, remarkable
The Unique, New MRI Philips Ingenia 3 Tesla is now in Ayios Therissos! The first-ever digital broadband MR system has been installed in Ayios Therissos-Nicosia that delivers crystal clear images, remarkable
HEPARIN CALCIUM. Heparinum calcicum
 Pharmeuropa 25.1 1 Reference: PA/PH/Exp. 6/T (12) 38 ANP NOTE ON THE MONOGRAPH Definition. It is proposed to restrict the scope to heparin material of porcine origin since some of the latest requirements
Pharmeuropa 25.1 1 Reference: PA/PH/Exp. 6/T (12) 38 ANP NOTE ON THE MONOGRAPH Definition. It is proposed to restrict the scope to heparin material of porcine origin since some of the latest requirements
Revised Examination Guidelines for Industrially Applicable Inventions (Provisional Translation)
 Revised Examination Guidelines for Industrially Applicable Inventions (Provisional Translation) Examination Guidelines for Patent and Utility Model Part II: REQUIREMENTS FOR PATENTABILITY Chapter 1 Industrially
Revised Examination Guidelines for Industrially Applicable Inventions (Provisional Translation) Examination Guidelines for Patent and Utility Model Part II: REQUIREMENTS FOR PATENTABILITY Chapter 1 Industrially
Application Note 6: On-line Reaction Monitoring of Alcoholic Fermentation
 Application Note 6: On-line Reaction Monitoring of Alcoholic Fermentation NMR spectroscopy is an excellent technique for monitoring organic reactions due to its high degree of functional group specificity.
Application Note 6: On-line Reaction Monitoring of Alcoholic Fermentation NMR spectroscopy is an excellent technique for monitoring organic reactions due to its high degree of functional group specificity.
MEDICAL EQUIPMENT (1) TOPIC 1: RECORDING AND PROCESSING OF BIOSIGNALS
 MEDICAL EQUIPMENT (1) TOPIC 1: RECORDING AND PROCESSING OF BIOSIGNALS Term 1 2013/14 Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah www.k-space.org Measurement Basics Measuring is the experimental determination of a measured
MEDICAL EQUIPMENT (1) TOPIC 1: RECORDING AND PROCESSING OF BIOSIGNALS Term 1 2013/14 Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah www.k-space.org Measurement Basics Measuring is the experimental determination of a measured
Our web collection on statistics for biologists may be useful.
 Reporting Summary Corresponding author(s): Charles E. Murry Nature Research wishes to improve the reproducibility of the work that we publish. This form provides structure for consistency and transparency
Reporting Summary Corresponding author(s): Charles E. Murry Nature Research wishes to improve the reproducibility of the work that we publish. This form provides structure for consistency and transparency
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Maryland, Baltimore Baltimore, MD 21201
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0098 TITLE: Evaluation of Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging in Traumatic Brain Injury PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Rao P Gullapalli CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Maryland, Baltimore
AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0098 TITLE: Evaluation of Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging in Traumatic Brain Injury PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Rao P Gullapalli CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Maryland, Baltimore
ProMass HR Applications!
 ProMass HR Applications! ProMass HR Features Ø ProMass HR includes features for high resolution data processing. Ø ProMass HR includes the standard ProMass deconvolution algorithm as well as the full Positive
ProMass HR Applications! ProMass HR Features Ø ProMass HR includes features for high resolution data processing. Ø ProMass HR includes the standard ProMass deconvolution algorithm as well as the full Positive
Date: May 26, 2015 Page 1
 Part I. Answer these questions by marking the best answer among the choices given: [2 points each] 1. Ethics and morals differ in that a. Only one of them should be followed b. Ethics are for professionals
Part I. Answer these questions by marking the best answer among the choices given: [2 points each] 1. Ethics and morals differ in that a. Only one of them should be followed b. Ethics are for professionals
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0231 TITLE: Spectroscopic Photoacoustic Tomography of Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Xueding Wang CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University Of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI 48109-1274
AD Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0231 TITLE: Spectroscopic Photoacoustic Tomography of Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Xueding Wang CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University Of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI 48109-1274
