After meiosis, gametes have the amount of nuclear DNA as somatic cells. a. one-third b. twice c. half d. the same
|
|
|
- Elwin Fleming
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Concept 9.1 DNA Structure Reflects Its Role as the Genetic Material After meiosis, gametes have the amount of nuclear DNA as somatic cells. a. one-third b. twice c. half d. the same
2 Concept 9.1 DNA Structure Reflects Its Role as the Genetic Material Without looking at your notes: 1. Name the two purine nucleotides of DNA. 2. Name the two pyrimidine nucleotides of DNA. 3. Which nucleotides pair up with one another?
3 Concept 9.1 DNA Structure Reflects Its Role as the Genetic Material In DNA, the number of purines is equal to the number of pyrimidines. a. True b. False c. I don t know.
4 Concept 9.1 DNA Structure Reflects Its Role as the Genetic Material On a piece of paper, draw the two backbones of the DNA helix. Be sure to label: the 5 and 3 ends the direction of the strand the phosphate and hydroxyl groups at each end What do the 5 and 3 refer to?
5 Concept 9.2 DNA Replicates Semiconservatively Suppose a cell s DNA has all been labeled (for example, with radioactive atoms or some other marker). The cell is then provided with unlabelled nucleotides, and is allowed to grow, replicate its DNA, and divide. Which of the following correctly describes the DNA that is in the daughter cells? a. Both strands are labeled. b. One stand is labeled and the other strand is not. c. Both strands are unlabeled. d. I don t know.
6 Concept 9.2 DNA Replicates Semiconservatively Discuss with a partner: Nucleotides are added to the 5 end of the growing DNA strand. a. True b. False c. I don t know.
7 Concept 9.2 DNA Replicates Semiconservatively With a partner, discuss why eukaryotes have multiple origins of replication while prokaryotes have only one.
8 Concept 9.2 DNA Replicates Semiconservatively The leading strand grows continuously at its end. a. backward; 5 b. forward; 5 c. backward; 3 d. forward; 3
9 Concept 9.2 DNA Replicates Semiconservatively Recall the two mechanisms for repairing errors in DNA replication. Working in pairs: Have one partner name and describe the mechanism that takes place during replication. Then have the other partner name and describe the mechanism that takes place after replication.
10 Concept 9.2 DNA Replicates Semiconservatively Draw a sketch illustrating why the lagging strand must be synthesized in small pieces, while the leading strand can be synthesized in one continuous piece. Label the 5 and 3 ends of all the strands of DNA in your sketch. When you are finished, compare your sketch with that of your neighbors.
11 Concept 9.2 DNA Replicates Semiconservatively Review with a partner the functions of the following enzymes. What does each of these enzymes do? DNA ligase Telomerase DNA polymerase Primase In what sequence do these enzymes usually work? Which of these enzymes would you expect to find in stem cells? Why?
12 Concept 9.3 Mutations Are Heritable Changes in DNA Suppose you re setting up a PCR reaction that should give you the last bit of data that you need to complete your Ph.D. thesis. You want this reaction to go well, because this is your last chance to use the lab s thermocycler before your dissertation defense. You add the PCR ingredients, place everything in the thermocycler (the machine that will do repeated rounds of heating and cooling), press start on the thermocycler, and go home. Once you re home you suddenly realize that you forgot to add one of the primers. 1. Name all the other ingredients that you did add correctly. 2. If you let the reaction run overnight, what will the products be? Will any DNA be made at all? If so, will it be the piece that you wanted? [Hint: You may wish to sketch out a molecule of DNA as it proceeds through several rounds of replication.] 3. Do you need to go back to the lab and start over?
13 Concept 9.3 Mutations Are Heritable Changes in DNA Working in pairs, describe to your partner in your own words what the following phrases mean. Take turns one person define one phrase, then the other person define the next, etc. Point mutation Deletion Inversion Translocation Duplication Silent mutation Gain-of-function mutation Loss-of-function mutation
14 Concept 9.3 Mutations Are Heritable Changes in DNA A mutation that occurs in body cells (i.e., skin cells) and is passed on to the daughter cells during mitosis, but is not passed on to sexually produced offspring, is called a(n) mutation. a. germline b. meiotic c. asexual d. somatic
15 Concept 9.3 Mutations Are Heritable Changes in DNA In sickle-cell disease, the sickle allele differs from the normal allele by how many base pairs? a. 0 b. 1 c. 2 d. 3 What type of mutation is this?
Chapter 9 Preview - DNA
 Chapter 9 Preview - DNA Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. In order to show that DNA in cell extracts is responsible for genetic transformation
Chapter 9 Preview - DNA Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. In order to show that DNA in cell extracts is responsible for genetic transformation
DNA Replication and Repair
 DN Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif DN Replication genetic information is passed on to the next generation semi-conservative Parent molecule with
DN Replication and Repair http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/organic/imgorg/cendog.gif DN Replication genetic information is passed on to the next generation semi-conservative Parent molecule with
DNA vs. RNA DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid (double stranded) RNA: ribonucleic acid (single stranded) Both found in most bacterial and eukaryotic cells RNA
 DNA Replication DNA vs. RNA DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid (double stranded) RNA: ribonucleic acid (single stranded) Both found in most bacterial and eukaryotic cells RNA molecule can assume different structures
DNA Replication DNA vs. RNA DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid (double stranded) RNA: ribonucleic acid (single stranded) Both found in most bacterial and eukaryotic cells RNA molecule can assume different structures
I. DNA as Genetic Material Figure 1: Griffith s Experiment. Frederick Griffith:
 I. DNA as Genetic Material Figure 1: Griffith s Experiment Frederick Griffith: a) Frederick Griffith suspected that some component of the S strain was being passed along to the R strain, causing it to
I. DNA as Genetic Material Figure 1: Griffith s Experiment Frederick Griffith: a) Frederick Griffith suspected that some component of the S strain was being passed along to the R strain, causing it to
CH 4 - DNA. DNA = deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA is the hereditary substance that is found in the nucleus of cells
 CH 4 - DNA DNA is the hereditary substance that is found in the nucleus of cells DNA = deoxyribonucleic acid» its structure was determined in the 1950 s (not too long ago).» scientists were already investigating
CH 4 - DNA DNA is the hereditary substance that is found in the nucleus of cells DNA = deoxyribonucleic acid» its structure was determined in the 1950 s (not too long ago).» scientists were already investigating
DNA Replication * OpenStax
 OpenStax-CNX module: m45475 1 DNA Replication * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this section, you will be able
OpenStax-CNX module: m45475 1 DNA Replication * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this section, you will be able
DNA Replication * Robert Bear David Rintoul. Based on DNA Replication by OpenStax
 OpenStax-CNX module: m47204 1 DNA Replication * Robert Bear David Rintoul Based on DNA Replication by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
OpenStax-CNX module: m47204 1 DNA Replication * Robert Bear David Rintoul Based on DNA Replication by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
3.A.1 DNA and RNA: Structure and Replication
 3.A.1 DNA and RNA: Structure and Replication Each DNA polymer is made of Nucleotides (monomer) which are made of: a) Phosphate group: Negatively charged and polar b) Sugar: deoxyribose- a 5 carbon sugar
3.A.1 DNA and RNA: Structure and Replication Each DNA polymer is made of Nucleotides (monomer) which are made of: a) Phosphate group: Negatively charged and polar b) Sugar: deoxyribose- a 5 carbon sugar
The Structure of DNA
 The Structure of DNA Questions to Ponder 1) How is the genetic info copied? 2) How does DNA store the genetic information? 3) How is the genetic info passed from generation to generation? The Structure
The Structure of DNA Questions to Ponder 1) How is the genetic info copied? 2) How does DNA store the genetic information? 3) How is the genetic info passed from generation to generation? The Structure
Chapter 14: Genes in Action
 Chapter 14: Genes in Action Section 1: Mutation and Genetic Change Mutation: Nondisjuction: a failure of homologous chromosomes to separate during meiosis I or the failure of sister chromatids to separate
Chapter 14: Genes in Action Section 1: Mutation and Genetic Change Mutation: Nondisjuction: a failure of homologous chromosomes to separate during meiosis I or the failure of sister chromatids to separate
All This For Four Letters!?! DNA and Its Role in Heredity
 All This For Four Letters!?! DNA and Its Role in Heredity What Is the Evidence that the Gene Is DNA? By the 1920s, it was known that chromosomes consisted of DNA and proteins. A new dye stained DNA and
All This For Four Letters!?! DNA and Its Role in Heredity What Is the Evidence that the Gene Is DNA? By the 1920s, it was known that chromosomes consisted of DNA and proteins. A new dye stained DNA and
BIOLOGY 101. CHAPTER 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Life s Operating Instructions
 BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Life s Operating Instructions Life s Operating Instructions CONCEPTS: 16.1 DNA is the genetic material 16.2 Many proteins work together in DNA
BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance: Life s Operating Instructions Life s Operating Instructions CONCEPTS: 16.1 DNA is the genetic material 16.2 Many proteins work together in DNA
Genetic material must be able to:
 Genetic material must be able to: Contain the information necessary to construct an entire organism Pass from parent to offspring and from cell to cell during cell division Be accurately copied Account
Genetic material must be able to: Contain the information necessary to construct an entire organism Pass from parent to offspring and from cell to cell during cell division Be accurately copied Account
DNA Structure and Replication
 Name: DNA Structure and Replication 1. DNA: Deoxyribonucleic Acid a. Credit for discovery is given to Watson & Crick b. DNA stands for c. This chemical substance is present in the of all cells in all living
Name: DNA Structure and Replication 1. DNA: Deoxyribonucleic Acid a. Credit for discovery is given to Watson & Crick b. DNA stands for c. This chemical substance is present in the of all cells in all living
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.8 DNA REPLICATION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: SEMICONSERVATIVE REPLICATION Before replication was understood, there were three of how DNA is replicated Conservative replication states that after replication, there is
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: SEMICONSERVATIVE REPLICATION Before replication was understood, there were three of how DNA is replicated Conservative replication states that after replication, there is
Chapter 10. DNA: The Molecule of Heredity. Lectures by Gregory Ahearn. University of North Florida. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 DNA: The Molecule of Heredity Lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 10.1 What Is The Structure Of DNA? Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is
Chapter 10 DNA: The Molecule of Heredity Lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 10.1 What Is The Structure Of DNA? Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is
2. Structure and Replication of DNA. Higher Human Biology
 2. Structure and Replication of DNA Higher Human Biology Learning Intention Describe the structure of DNA Explain the base pairing rule using adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine Today we are moving
2. Structure and Replication of DNA Higher Human Biology Learning Intention Describe the structure of DNA Explain the base pairing rule using adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine Today we are moving
DNA. Discovery of the DNA double helix
 DNA Replication DNA Discovery of the DNA double helix A. 1950 s B. Rosalind Franklin - X-ray photo of DNA. C. Watson and Crick - described the DNA molecule from Franklin s X-ray. What is DNA? Question:
DNA Replication DNA Discovery of the DNA double helix A. 1950 s B. Rosalind Franklin - X-ray photo of DNA. C. Watson and Crick - described the DNA molecule from Franklin s X-ray. What is DNA? Question:
Covalently bonded sugar-phosphate backbone with relatively strong bonds keeps the nucleotides in the backbone connected in the correct sequence.
 Unit 14: DNA Replication Study Guide U7.1.1: DNA structure suggested a mechanism for DNA replication (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 347). 1. Outline the features of DNA structure that suggested
Unit 14: DNA Replication Study Guide U7.1.1: DNA structure suggested a mechanism for DNA replication (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 347). 1. Outline the features of DNA structure that suggested
DNA and Replication 1
 DNA and Replication 1 History of DNA 2 History of DNA Early scientists thought protein was the cell s hereditary material because it was more complex than DNA Proteins were composed of 20 different amino
DNA and Replication 1 History of DNA 2 History of DNA Early scientists thought protein was the cell s hereditary material because it was more complex than DNA Proteins were composed of 20 different amino
DNA & RNA. Chapter Twelve and Thirteen Biology One
 DNA & RNA Chapter Twelve and Thirteen Biology One I. DNA Structure A. DNA monomers = nucleotides *1. sugar bonded to PO4 & one of four possible nitrogen bases 2. bases = Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine
DNA & RNA Chapter Twelve and Thirteen Biology One I. DNA Structure A. DNA monomers = nucleotides *1. sugar bonded to PO4 & one of four possible nitrogen bases 2. bases = Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine
Chapter 16 DNA: The Genetic Material. The Nature of Genetic Material. Chemical Nature of Nucleic Acids. Chromosomes - DNA and protein
 Chapter 16 DNA: The Genetic Material The Nature of Genetic Material Chromosomes - DNA and protein Genes are subunits DNA = 4 similar nucleotides C(ytosine) A(denine) T(hymine) G(uanine) Proteins = 20 different
Chapter 16 DNA: The Genetic Material The Nature of Genetic Material Chromosomes - DNA and protein Genes are subunits DNA = 4 similar nucleotides C(ytosine) A(denine) T(hymine) G(uanine) Proteins = 20 different
Biology 30 DNA Review: Importance of Meiosis nucleus chromosomes Genes DNA
 Biology 30 DNA Review: Importance of Meiosis Every cell has a nucleus and every nucleus has chromosomes. The number of chromosomes depends on the species. o Examples: Chicken 78 Chimpanzee 48 Potato 48
Biology 30 DNA Review: Importance of Meiosis Every cell has a nucleus and every nucleus has chromosomes. The number of chromosomes depends on the species. o Examples: Chicken 78 Chimpanzee 48 Potato 48
C A T T A G C nitrogenous complimentary G T A A T C G to each other
 Name DNA RNA Review Worksheet Date 1. What does DNA stand for? Deoxyribonucleic acid 2. What is DNA s primary function? - Provides a pattern for protein manufacture - Provides a pattern for replication
Name DNA RNA Review Worksheet Date 1. What does DNA stand for? Deoxyribonucleic acid 2. What is DNA s primary function? - Provides a pattern for protein manufacture - Provides a pattern for replication
Active Learning Exercise 9. The Hereditary Material: DNA
 Name Biol 211 - Group Number Active Learning Exercise 9. The Hereditary Material: DNA Reference: Chapter 16 (Biology by Campbell/Reece, 8 th ed.) 1. a.) What is a nucleotide? b.) What is a nitrogen base?
Name Biol 211 - Group Number Active Learning Exercise 9. The Hereditary Material: DNA Reference: Chapter 16 (Biology by Campbell/Reece, 8 th ed.) 1. a.) What is a nucleotide? b.) What is a nitrogen base?
DNA Structure and Replication. Higher Human Biology
 DNA Structure and Replication Higher Human Biology Learning Intention Describe the structure of DNA Explain the base pairing rule using adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine 1 Division and differentiation
DNA Structure and Replication Higher Human Biology Learning Intention Describe the structure of DNA Explain the base pairing rule using adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine 1 Division and differentiation
copyright cmassengale 2
 1 copyright cmassengale 2 History of DNA Early scientists thought protein was the cell s hereditary material because it was more complex than DNA Proteins were composed of 20 different amino acids in long
1 copyright cmassengale 2 History of DNA Early scientists thought protein was the cell s hereditary material because it was more complex than DNA Proteins were composed of 20 different amino acids in long
CHAPTER 16 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE
 CHAPTER 16 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE DNA as genetic material? Deducted that DNA is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
CHAPTER 16 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE DNA as genetic material? Deducted that DNA is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
DNA Structure. DNA: The Genetic Material. Chapter 14
 DNA: The Genetic Material Chapter 14 DNA Structure DNA is a nucleic acid. The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides, each composed of: a 5-carbon sugar called deoxyribose a phosphate group (PO 4 ) a nitrogenous
DNA: The Genetic Material Chapter 14 DNA Structure DNA is a nucleic acid. The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides, each composed of: a 5-carbon sugar called deoxyribose a phosphate group (PO 4 ) a nitrogenous
What can you tell me about DNA? copyright cmassengale 1
 What can you tell me about DNA? copyright cmassengale 1 DNA and Replication copyright cmassengale 2 Credit for discovery of DNA is given to Watson & Crick 1 DNA DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid
What can you tell me about DNA? copyright cmassengale 1 DNA and Replication copyright cmassengale 2 Credit for discovery of DNA is given to Watson & Crick 1 DNA DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid
Fig. 16-7a. 5 end Hydrogen bond 3 end. 1 nm. 3.4 nm nm
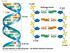 Fig. 16-7a end Hydrogen bond end 1 nm 3.4 nm 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure end (b) Partial chemical structure end Fig. 16-8 Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Concept 16.2: Many
Fig. 16-7a end Hydrogen bond end 1 nm 3.4 nm 0.34 nm (a) Key features of DNA structure end (b) Partial chemical structure end Fig. 16-8 Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) Concept 16.2: Many
DNA and Biotechnology
 DNA and Biotechnology What makes us human? Our DNA! It codes for our genes. (Gene = a piece of DNA that codes for a protein) What is DNA and why is it so important? DNA is the blueprint for an organism.
DNA and Biotechnology What makes us human? Our DNA! It codes for our genes. (Gene = a piece of DNA that codes for a protein) What is DNA and why is it so important? DNA is the blueprint for an organism.
Name Campbell Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 A.P. Biology Name Campbell Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance 305-310 Who are these dudes? A. B. What distinguishes DNA from all other molecules? What does the adage Like begets like mean? DNA
A.P. Biology Name Campbell Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance 305-310 Who are these dudes? A. B. What distinguishes DNA from all other molecules? What does the adage Like begets like mean? DNA
DNA is a functional genetic material as it:
 DNA DNA is a functional genetic material as it: varies between species and individuals can store information remains constant within a species Replicates undergoes mutations 1 `It has not escaped our notice
DNA DNA is a functional genetic material as it: varies between species and individuals can store information remains constant within a species Replicates undergoes mutations 1 `It has not escaped our notice
Chapter 16 Molecular Basis of. Chapter 16. Inheritance (DNA structure and Replication) Helicase Enzyme
 Chapter 16 Chapter 16 Molecular Basis of Inheritance (DNA structure and Replication) Helicase Enzyme The Amazing Race What is the genetic material? DNA or protein? 1928 Griffith transformation of pneumonia
Chapter 16 Chapter 16 Molecular Basis of Inheritance (DNA structure and Replication) Helicase Enzyme The Amazing Race What is the genetic material? DNA or protein? 1928 Griffith transformation of pneumonia
DNA is the genetic material. DNA structure. Chapter 7: DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation; Mutations & Ames test
 DNA is the genetic material Chapter 7: DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation; Mutations & Ames test Dr. Amy Rogers Bio 139 General Microbiology Hereditary information is carried by DNA Griffith/Avery
DNA is the genetic material Chapter 7: DNA Replication, Transcription & Translation; Mutations & Ames test Dr. Amy Rogers Bio 139 General Microbiology Hereditary information is carried by DNA Griffith/Avery
Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene
 Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene For Next Week Lab -Hand in questions from 4 and 5 by TUES in my mailbox (Biology Office) -Do questions for Lab 6 for next week -Lab practical next week Lecture Read
Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene For Next Week Lab -Hand in questions from 4 and 5 by TUES in my mailbox (Biology Office) -Do questions for Lab 6 for next week -Lab practical next week Lecture Read
DNA Replication semiconservative replication conservative replication dispersive replication DNA polymerase
 DNA Replication DNA Strands are templates for DNA synthesis: Watson and Crick suggested that the existing strands of DNA served as a template for the producing of new strands, with bases being added to
DNA Replication DNA Strands are templates for DNA synthesis: Watson and Crick suggested that the existing strands of DNA served as a template for the producing of new strands, with bases being added to
Chromosomes. Nucleosome. Chromosome. DNA double helix. Coils. Supercoils. Histones
 Chromosomes Chromosome Nucleosome DNA double helix Coils Supercoils Histones Evidence That DNA Can Transform Bacteria Frederick Griffith s experiment 1928 Griffith called the phenomenon transformation
Chromosomes Chromosome Nucleosome DNA double helix Coils Supercoils Histones Evidence That DNA Can Transform Bacteria Frederick Griffith s experiment 1928 Griffith called the phenomenon transformation
Name: - Bio A.P. DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis
 Name: - Bio A.P. DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis 1 ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE Big Idea 3: Living Systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information critical to living systems Enduring Understanding:
Name: - Bio A.P. DNA Replication & Protein Synthesis 1 ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE Big Idea 3: Living Systems store, retrieve, transmit and respond to information critical to living systems Enduring Understanding:
DNA Replication AP Biology
 DNA Replication 2007-2008 Watson and Crick 1953 1953 article in Nature Directionality of DNA You need to number the carbons! u it matters! u 3 refers to the 3 carbon on the sugar u 5 refers to the 5 carbon
DNA Replication 2007-2008 Watson and Crick 1953 1953 article in Nature Directionality of DNA You need to number the carbons! u it matters! u 3 refers to the 3 carbon on the sugar u 5 refers to the 5 carbon
Structure and Replication
 Structure and Replication 6.A: Students will identify components of DNA, and describe how information for specifying traits of an organism is carried in the DNA 6.B: Students will recognize that components
Structure and Replication 6.A: Students will identify components of DNA, and describe how information for specifying traits of an organism is carried in the DNA 6.B: Students will recognize that components
MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE
 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE C H A P T E R 1 6 as genetic material? Deducted that is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE C H A P T E R 1 6 as genetic material? Deducted that is the genetic material Initially worked by studying bacteria & the viruses that infected them 1928 Frederick Griffiths
A. Incorrect! This feature does help with it suitability as genetic material.
 College Biology - Problem Drill 08: Gene Structures and Functions No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the statements below is NOT true in explaining why DNA is a suitable genetic material? #01 (A) Its double helix
College Biology - Problem Drill 08: Gene Structures and Functions No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the statements below is NOT true in explaining why DNA is a suitable genetic material? #01 (A) Its double helix
A. Incorrect! Garrod s experiment linked genes to enzymes. It is important to be familiar with the milestone experiments in genetics.
 Genetics - Problem Drill 11: DNA - The Chemical Basis of Genetics No. 1 of 10 1. Which scientist first gave evidence that DNA is the genetic material? (A) Garrod, who postulated that Alcaptonuria, or black
Genetics - Problem Drill 11: DNA - The Chemical Basis of Genetics No. 1 of 10 1. Which scientist first gave evidence that DNA is the genetic material? (A) Garrod, who postulated that Alcaptonuria, or black
Rapid Learning Center Presents. Teach Yourself High School Biology in 24 Hours. and Functions
 Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presents Teach Yourself High School Biology in 24 Hours Gene e Structures and Functions High School Biology Rapid Learning
Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presents Teach Yourself High School Biology in 24 Hours Gene e Structures and Functions High School Biology Rapid Learning
DNA Replication. Packet #17 Chapter #16
 DNA Replication Packet #17 Chapter #16 1 HISTORICAL FACTS ABOUT DNA 2 Historical DNA Discoveries 1928 Frederick Griffith finds a substance in heat-killed bacteria that transforms living bacteria 1944 Oswald
DNA Replication Packet #17 Chapter #16 1 HISTORICAL FACTS ABOUT DNA 2 Historical DNA Discoveries 1928 Frederick Griffith finds a substance in heat-killed bacteria that transforms living bacteria 1944 Oswald
Chapter 4 The Transmission of DNA at Cell Division. DNA Replication Cell Division Mitosis Meiosis
 Chapter 4 The Transmission of DNA at Cell Division DNA Replication Cell Division Mitosis Meiosis The faithful transmission of genotype at cell division, illustrated by the behaviour of tumor cells Cell
Chapter 4 The Transmission of DNA at Cell Division DNA Replication Cell Division Mitosis Meiosis The faithful transmission of genotype at cell division, illustrated by the behaviour of tumor cells Cell
Essential Question. What is the structure of DNA, and how does it function in genetic inheritance?
 DNA Dr. Bertolotti Essential Question What is the structure of DNA, and how does it function in genetic inheritance? What is the role of DNA in hereditary? Transformation Transformation is the process
DNA Dr. Bertolotti Essential Question What is the structure of DNA, and how does it function in genetic inheritance? What is the role of DNA in hereditary? Transformation Transformation is the process
Molecular Genetics. The flow of genetic information from DNA. DNA Replication. Two kinds of nucleic acids in cells: DNA and RNA.
 Molecular Genetics DNA Replication Two kinds of nucleic acids in cells: DNA and RNA. DNA function 1: DNA transmits genetic information from parents to offspring. DNA function 2: DNA controls the functions
Molecular Genetics DNA Replication Two kinds of nucleic acids in cells: DNA and RNA. DNA function 1: DNA transmits genetic information from parents to offspring. DNA function 2: DNA controls the functions
Protein Synthesis
 HEBISD Student Expectations: Identify that RNA Is a nucleic acid with a single strand of nucleotides Contains the 5-carbon sugar ribose Contains the nitrogen bases A, G, C and U instead of T. The U is
HEBISD Student Expectations: Identify that RNA Is a nucleic acid with a single strand of nucleotides Contains the 5-carbon sugar ribose Contains the nitrogen bases A, G, C and U instead of T. The U is
Lecture Series 8 DNA and Its Role in Heredity
 Lecture Series 8 DNA and Its Role in Heredity DNA and Its Role in Heredity A. DNA: The Genetic Material B. The Structure of DNA C. DNA Replication D. The Mechanism of DNA Replication E. DNA Proofreading
Lecture Series 8 DNA and Its Role in Heredity DNA and Its Role in Heredity A. DNA: The Genetic Material B. The Structure of DNA C. DNA Replication D. The Mechanism of DNA Replication E. DNA Proofreading
DNA and Its Role in Heredity. DNA and Its Role in Heredity. A. DNA: The Genetic Material. A. DNA: The Genetic Material.
 DNA and Its Role in Heredity A. DNA: The Genetic Material Lecture Series 8 DNA and Its Role in Heredity B. The Structure of DNA C. DNA E. DNA Proofreading and Repair F. Practical Applications of DNA A.
DNA and Its Role in Heredity A. DNA: The Genetic Material Lecture Series 8 DNA and Its Role in Heredity B. The Structure of DNA C. DNA E. DNA Proofreading and Repair F. Practical Applications of DNA A.
DNA: Structure and Replication - 1
 DNA: Structure and Replication - 1 We have briefly discussed that DNA is the genetic molecule of life. In eukaryotic organisms DNA (along with its histone proteins) is found in chromosomes. All cell activities
DNA: Structure and Replication - 1 We have briefly discussed that DNA is the genetic molecule of life. In eukaryotic organisms DNA (along with its histone proteins) is found in chromosomes. All cell activities
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Chromosomes and DNA Morgan s experiments with Drosophila were able to link hereditary factors to specific locations on chromosomes. The double-helical model
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Chromosomes and DNA Morgan s experiments with Drosophila were able to link hereditary factors to specific locations on chromosomes. The double-helical model
Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 AP Biology Reading Guide Name Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Concept 16.1 DNA is the genetic material 1. What are the two chemical components of chromosomes? 2. The search for identifying
AP Biology Reading Guide Name Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Concept 16.1 DNA is the genetic material 1. What are the two chemical components of chromosomes? 2. The search for identifying
Chapter 9: DNA: The Molecule of Heredity
 Chapter 9: DNA: The Molecule of Heredity What is DNA? Answer: Molecule that carries the blueprint of life General Features: DNA is packages in chromosomes (DNA + Proteins) Gene = Functional segment of
Chapter 9: DNA: The Molecule of Heredity What is DNA? Answer: Molecule that carries the blueprint of life General Features: DNA is packages in chromosomes (DNA + Proteins) Gene = Functional segment of
Molecular Genetics I DNA
 Molecular Genetics I DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid is the molecule that encodes the characteristics of living things. It is the molecule that is passed from a mother cell to daughter cells, and the molecule
Molecular Genetics I DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid is the molecule that encodes the characteristics of living things. It is the molecule that is passed from a mother cell to daughter cells, and the molecule
The Molecule of Heredity. Chapter 12 (pg. 342)
 The Molecule of Heredity Chapter 12 (pg. 342) What is DNA? DNA contains instructions for assembling proteins. Proteins tell our cells how to function and act. The Roles of DNA DNA has three jobs in heredity:
The Molecule of Heredity Chapter 12 (pg. 342) What is DNA? DNA contains instructions for assembling proteins. Proteins tell our cells how to function and act. The Roles of DNA DNA has three jobs in heredity:
Lecture Overview. Overview of the Genetic Information. Chapter 3 DNA & RNA Lecture 6
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 3 DNA & RNA Lecture 6 Lecture Overview What is the cell s genetic information? How/where is the genetic information stored in eukaryotic
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 3 DNA & RNA Lecture 6 Lecture Overview What is the cell s genetic information? How/where is the genetic information stored in eukaryotic
AS Demonstrate understanding of life processes at the cellular level. DNA Replication
 AS 91156 Demonstrate understanding of life processes at the cellular level. DNA Replication (2017:3) Mitosis The table below shows how mitosis occurs at different rates in different types of human cells.
AS 91156 Demonstrate understanding of life processes at the cellular level. DNA Replication (2017:3) Mitosis The table below shows how mitosis occurs at different rates in different types of human cells.
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 1 Questions
 Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 1 Questions Multiple Choice Questions Question 1.1 In a DNA double helix each type of base forms a stable base pair with only one type of base. When bases on an
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 1 Questions Multiple Choice Questions Question 1.1 In a DNA double helix each type of base forms a stable base pair with only one type of base. When bases on an
DNA replication. Begins at specific sites on a double helix. Proceeds in both directions. Is initiated at many points in eukaryotic chromosomes.
 DNA replication Begins at specific sites on a double helix. Proceeds in both directions. Is initiated at many points in eukaryotic chromosomes. Figure 10.8 http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/media/ DNAi_replication_schematic-lg.mov
DNA replication Begins at specific sites on a double helix. Proceeds in both directions. Is initiated at many points in eukaryotic chromosomes. Figure 10.8 http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/media/ DNAi_replication_schematic-lg.mov
Purines vs. Pyrimidines
 Introduction to Genetics/DNA Replication The DNA molecule is found in the nucleus and is composed of nucleotides The DNA Molecule Composed of 2 polymers of nucleotides Polymers are oriented in antiparallel
Introduction to Genetics/DNA Replication The DNA molecule is found in the nucleus and is composed of nucleotides The DNA Molecule Composed of 2 polymers of nucleotides Polymers are oriented in antiparallel
Essential Questions. DNA: The Genetic Material. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education
 Essential Questions Which experiments led to the discovery of DNA as the genetic material? What is the basic structure of DNA? What is the basic structure of eukaryotic chromosomes? Vocabulary Review nucleic
Essential Questions Which experiments led to the discovery of DNA as the genetic material? What is the basic structure of DNA? What is the basic structure of eukaryotic chromosomes? Vocabulary Review nucleic
March 26, 2012 NUCLEIC ACIDS AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
 NUCLEIC ACIDS AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS MAIN MAIN TOPICS TOPICS TO TO BE BE COVERED COVERED THIS THIS UNIT: UNIT: I. I. EVIDENCE EVIDENCE OF OF DNA DNA AS AS THE THE GENETIC GENETIC CODE CODE II. II. DNA DNA
NUCLEIC ACIDS AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS MAIN MAIN TOPICS TOPICS TO TO BE BE COVERED COVERED THIS THIS UNIT: UNIT: I. I. EVIDENCE EVIDENCE OF OF DNA DNA AS AS THE THE GENETIC GENETIC CODE CODE II. II. DNA DNA
From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype
 12 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype 12.1 What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? The gene-enzyme relationship is one-gene, one-polypeptide relationship. Example: In hemoglobin, each
12 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype 12.1 What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? The gene-enzyme relationship is one-gene, one-polypeptide relationship. Example: In hemoglobin, each
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 1. Questions & Answers
 Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 1 Multiple Choice Questions Questions & Answers Question 1.1 In a DNA double helix each type of base forms a stable base pair with only one type of base. When
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 1 Multiple Choice Questions Questions & Answers Question 1.1 In a DNA double helix each type of base forms a stable base pair with only one type of base. When
Bundle 5 Test Review
 Bundle 5 Test Review DNA vs. RNA DNA Replication Gene Mutations- Protein Synthesis 1. Label the different components and complete the complimentary base pairing. What is this molecule called? _Nucleic
Bundle 5 Test Review DNA vs. RNA DNA Replication Gene Mutations- Protein Synthesis 1. Label the different components and complete the complimentary base pairing. What is this molecule called? _Nucleic
DNA replication: Enzymes link the aligned nucleotides by phosphodiester bonds to form a continuous strand.
 DNA replication: Copying genetic information for transmission to the next generation Occurs in S phase of cell cycle Process of DNA duplicating itself Begins with the unwinding of the double helix to expose
DNA replication: Copying genetic information for transmission to the next generation Occurs in S phase of cell cycle Process of DNA duplicating itself Begins with the unwinding of the double helix to expose
DNA Replication AP Biology
 DNA Replication 2007-2008 Watson and Crick 1953 article in Nature Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible
DNA Replication 2007-2008 Watson and Crick 1953 article in Nature Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible
Problem Set 2B Name and Lab Section:
 Problem Set 2B 9-26-06 Name and Lab Section: 1. Define each of the following rearrangements (mutations) (use one phrase or sentence for each). Then describe what kind of chromosomal structure you might
Problem Set 2B 9-26-06 Name and Lab Section: 1. Define each of the following rearrangements (mutations) (use one phrase or sentence for each). Then describe what kind of chromosomal structure you might
Outline. Structure of DNA DNA Functions Transcription Translation Mutation Cytogenetics Mendelian Genetics Quantitative Traits Linkage
 Genetics Outline Structure of DNA DNA Functions Transcription Translation Mutation Cytogenetics Mendelian Genetics Quantitative Traits Linkage Chromosomes are composed of chromatin, which is DNA and associated
Genetics Outline Structure of DNA DNA Functions Transcription Translation Mutation Cytogenetics Mendelian Genetics Quantitative Traits Linkage Chromosomes are composed of chromatin, which is DNA and associated
You Should Be Able To
 DNA Replica,on You Should Be Able To 1. Describe the func9on of: DNA POL1, DNA POL3, Sliding Clamp, SSBPs, Ligase, Topoisomerase, Helicase, Primase 2. Describe DNA synthesis on the leading and lagging
DNA Replica,on You Should Be Able To 1. Describe the func9on of: DNA POL1, DNA POL3, Sliding Clamp, SSBPs, Ligase, Topoisomerase, Helicase, Primase 2. Describe DNA synthesis on the leading and lagging
Genetic Information: DNA replication
 Genetic Information: DNA replication Umut Fahrioglu, PhD MSc DNA Replication Replication of DNA is vital to the transmission of genomes and the genes they contain from one cell generation to the other.
Genetic Information: DNA replication Umut Fahrioglu, PhD MSc DNA Replication Replication of DNA is vital to the transmission of genomes and the genes they contain from one cell generation to the other.
Transformation: change in genotype & phenotype due to assimilation of external DNA by a cell.
 DNA Replication Chapter 16: DNA as Genetic Material Genes are on Chromosomes T.H. Morgan o Working with Drosophila (fruit flies) o Genes are on chromosomes o But is it the protein or the DNA of the chromosomes
DNA Replication Chapter 16: DNA as Genetic Material Genes are on Chromosomes T.H. Morgan o Working with Drosophila (fruit flies) o Genes are on chromosomes o But is it the protein or the DNA of the chromosomes
Higher Human Biology Unit 1: Human Cells Pupils Learning Outcomes
 Higher Human Biology Unit 1: Human Cells Pupils Learning Outcomes 1.1 Division and Differentiation in Human Cells I can state that cellular differentiation is the process by which a cell develops more
Higher Human Biology Unit 1: Human Cells Pupils Learning Outcomes 1.1 Division and Differentiation in Human Cells I can state that cellular differentiation is the process by which a cell develops more
DNA REPLICATION. Anna Onofri Liceo «I.Versari»
 DNA REPLICATION Anna Onofri Liceo «I.Versari» Learning objectives 1. Understand the basic rules governing DNA replication 2. Understand the function of key proteins involved in a generalised replication
DNA REPLICATION Anna Onofri Liceo «I.Versari» Learning objectives 1. Understand the basic rules governing DNA replication 2. Understand the function of key proteins involved in a generalised replication
ADENINE, THYMINE,CYTOSINE, GUANINE
 MOLECULAR GENETICS Molecular Genetics - the branch of genetics concerned with the structure and activity of genetic material at the molecular level Genetic Material - chromatin (chromosomes) within the
MOLECULAR GENETICS Molecular Genetics - the branch of genetics concerned with the structure and activity of genetic material at the molecular level Genetic Material - chromatin (chromosomes) within the
Flow of Genetic Information
 Flow of Genetic Information DNA Replication Links to the Next Generation Standards Scientific and Engineering Practices: Asking Questions (for science) and Defining Problems (for engineering) Developing
Flow of Genetic Information DNA Replication Links to the Next Generation Standards Scientific and Engineering Practices: Asking Questions (for science) and Defining Problems (for engineering) Developing
Chapter 8 From DNA to Proteins. Chapter 8 From DNA to Proteins
 KEY CONCEPT Section 1 DNA was identified as the genetic material through a series of experiments. Griffith finds a transforming principle. Griffith experimented with the bacteria that cause pneumonia.
KEY CONCEPT Section 1 DNA was identified as the genetic material through a series of experiments. Griffith finds a transforming principle. Griffith experimented with the bacteria that cause pneumonia.
DNA Model Building and Replica3on
 DNA Model Building and Replica3on DNA Replication S phase Origins of replication in E. coli and eukaryotes (a) Origin of replication in an E. coli cell Origin of replication Bacterial chromosome Doublestranded
DNA Model Building and Replica3on DNA Replication S phase Origins of replication in E. coli and eukaryotes (a) Origin of replication in an E. coli cell Origin of replication Bacterial chromosome Doublestranded
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
 Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Question? Traits are inherited on chromosomes, but what in the chromosomes is the genetic material? Two possibilities: Protein DNA Qualifications Protein:
Chapter 16 The Molecular Basis of Inheritance Question? Traits are inherited on chromosomes, but what in the chromosomes is the genetic material? Two possibilities: Protein DNA Qualifications Protein:
The Genetic Material. The Genetic Material. The Genetic Material. DNA: The Genetic Material. Chapter 14
 DNA: Chapter 14 Frederick Griffith, 1928 studied Streptococcus pneumoniae, a pathogenic bacterium causing pneumonia there are 2 strains of Streptococcus: - S strain is virulent - R strain is nonvirulent
DNA: Chapter 14 Frederick Griffith, 1928 studied Streptococcus pneumoniae, a pathogenic bacterium causing pneumonia there are 2 strains of Streptococcus: - S strain is virulent - R strain is nonvirulent
Winter Quarter Midterm Exam
 1. For a science fair project, two students decided to repeat the Hershey and Chase experiment, with modifications. They decided to label the nitrogen of the DNA, rather than the phosphate. They reasoned
1. For a science fair project, two students decided to repeat the Hershey and Chase experiment, with modifications. They decided to label the nitrogen of the DNA, rather than the phosphate. They reasoned
DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid
 DNA DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid This chemical substance is present in the nucleus of all cells in all living organisms DNA controls all the chemical changes which take place in cells DNA Structure
DNA DNA stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid This chemical substance is present in the nucleus of all cells in all living organisms DNA controls all the chemical changes which take place in cells DNA Structure
DNA REPLICATION. Third Stage. Lec. 12 DNA Replication. Lecture No.: 12. A. Watson & Crick (1952) C. Cairns (1963) autoradiographic experiment
 Lec. 12 DNA Replication A. Watson & Crick (1952) Proposed a model where hydrogen bonds break, the two strands separate, and DNA synthesis occurs semi-conservatively in the same net direction. While a straightforward
Lec. 12 DNA Replication A. Watson & Crick (1952) Proposed a model where hydrogen bonds break, the two strands separate, and DNA synthesis occurs semi-conservatively in the same net direction. While a straightforward
1. True or False? At the DNA level, recombination is initiated by a single stranded break in a DNA molecule.
 1. True or False? At the DNA level, recombination is initiated by a single stranded break in a DNA molecule. 2. True or False? Dideoxy sequencing is a chain initiation method of DNA sequencing. 3. True
1. True or False? At the DNA level, recombination is initiated by a single stranded break in a DNA molecule. 2. True or False? Dideoxy sequencing is a chain initiation method of DNA sequencing. 3. True
DNA: Structure and Replication - 1
 DNA: Structure and Replication - 1 We have briefly discussed that DNA is the genetic molecule of life. In eukaryotic organisms DNA (along with its histone proteins) is found in chromosomes. We have also
DNA: Structure and Replication - 1 We have briefly discussed that DNA is the genetic molecule of life. In eukaryotic organisms DNA (along with its histone proteins) is found in chromosomes. We have also
DNA Replication. The Organization of DNA. Recall:
 Recall: The Organization of DNA DNA Replication Chromosomal form appears only during mitosis, and is used in karyotypes. folded back upon itself (chromosomes) coiled around itself (chromatin) wrapped around
Recall: The Organization of DNA DNA Replication Chromosomal form appears only during mitosis, and is used in karyotypes. folded back upon itself (chromosomes) coiled around itself (chromatin) wrapped around
DNA Replication AP Biology
 DNA Replication 2007-2008 Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material.
DNA Replication 2007-2008 Double helix structure of DNA It has not escaped our notice that the specific pairing we have postulated immediately suggests a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material.
4) separates the DNA strands during replication a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E. 5) covalently connects segments of DNA a. A b. B c. C d. D e.
 1) Chargaff's analysis of the relative base composition of DNA was significant because he was able to show that a. the relative proportion of each of the four bases differs from species to species. b.
1) Chargaff's analysis of the relative base composition of DNA was significant because he was able to show that a. the relative proportion of each of the four bases differs from species to species. b.
IB BIO I Replication/Transcription/Translation Van Roekel/Madden. Name Date Period. D. It separates DNA strands. (Total 1 mark)
 Name Date Period 1. What is the function of helicase? A. It forms bonds between DNA nucleotides. B. It adds new nucleotides to the DNA helix. C. It forms the DNA helix. D. It separates DNA strands. 2.
Name Date Period 1. What is the function of helicase? A. It forms bonds between DNA nucleotides. B. It adds new nucleotides to the DNA helix. C. It forms the DNA helix. D. It separates DNA strands. 2.
* NOTE: If Lesson 2 has been performed, the DNA model should be uncoiled (and taken off its stand or tubing) to perform the steps on Pages
 OBJECTIVES Students will be able to: 1. Understand the DNA replication process. 2. Identify reasons for replication of DNA. 3. Understand the need for an exact copy of DNA. 4. Understand the function of
OBJECTIVES Students will be able to: 1. Understand the DNA replication process. 2. Identify reasons for replication of DNA. 3. Understand the need for an exact copy of DNA. 4. Understand the function of
Friday, April 17 th. Crash Course: DNA, Transcription and Translation. AP Biology
 Friday, April 17 th Crash Course: DNA, Transcription and Translation Today I will 1. Review the component parts of a DNA molecule. 2. Describe the process of transformation. 3. Explain what is meant by
Friday, April 17 th Crash Course: DNA, Transcription and Translation Today I will 1. Review the component parts of a DNA molecule. 2. Describe the process of transformation. 3. Explain what is meant by
Semester 2: Unit 1: Molecular Genetics
 Semester 2: Unit 1: Molecular Genetics Information Overload : Cells store information in DNA. Information is used to build molecules needed for cell growth. As cell size increases, the demands on that
Semester 2: Unit 1: Molecular Genetics Information Overload : Cells store information in DNA. Information is used to build molecules needed for cell growth. As cell size increases, the demands on that
DNA: The Primary Source of Heritable Information. Genetic information is transmitted from one generation to the next through DNA or RNA
 DNA and Replication DNA: The Primary Source of Heritable Information Genetic information is transmitted from one generation to the next through DNA or RNA Chromosomes Non-eukaryotic (bacteria) organisms
DNA and Replication DNA: The Primary Source of Heritable Information Genetic information is transmitted from one generation to the next through DNA or RNA Chromosomes Non-eukaryotic (bacteria) organisms
