Lecture/Demonstration on the History of Static Electricity in Medicine
|
|
|
- Oscar Oliver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture/Demonstration on the History of Static Electricity in Medicine Biography Joseph M. Chalovich was born in Pittsburgh, PA and attended St. Boniface grade school and North Catholic High School. His higher education was at the Pennsylvania State University (B.S.), Virginia Polytechnic Institute (M.S.) and University of Illinois School of Medicine (Ph.D., 1978). His Ph.D. was obtained in the laboratory of Dr. Michael Bárány. His postdoctoral training was done in the laboratory of Dr. Evan Eisenberg at the National Institutes of Health. There he studied the mechanism of regulation of muscle contraction by the actin binding complex of tropomyosin and troponin. He moved to East Carolina University in 1984 where he continued to study mechanisms of regulation of smooth, skeletal and cardiac muscles using biochemical and biophysical approaches. He also studies the protein fesselin (synaptopodin 2) and its role in organizing actin and myosin. He is currently a Distinguished Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at East Carolina University. Selected Publications according to topic I. Tribute to Michael and Kate Barany: Chalovich, J.M. (2012) Michael Bárány: a recollection. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. (In Press). PM: II. Regulation of Striated Muscle Contraction. Tropomyosin-troponin inhibits actin activation of myosin ATPase activity in solution without displacing myosin from actin. 7. Chalovich, J.M., Chock, P.B., and Eisenberg, E. (1981) Mechanism of action of troponintropomyosin. Inhibition of actomyosin ATPase activity without inhibition of myosin binding to actin. J. Biol. Chem. 256, PM: Hill, T.L., Eisenberg, E., and Chalovich, J.M. (1981) Theoretical models for cooperative steady-state ATPase activity of myosin subfragment-1 on regulated actin. Biophys. J. 35, PM:
2 9. Chalovich, J.M. and Eisenberg, E. (1982) Inhibition of actomyosin ATPase activity by troponin-tropomyosin without blocking the binding of myosin to actin. J. Biol. Chem. 257, PM: Brenner, B., Schoenberg, M., Chalovich, J.M., Greene, L.E., and Eisenberg, E. (1982) Possible crossbridge attachment in relaxed muscle at low ionic strength. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79, PM: Resetar, A.M. and Chalovich, J.M. (1995) Adenosine 5 -[thio]triphosphate: an ATP analog that should be used with caution in muscle contraction studies. Biochemistry, 34, PM: B. Brenner, T. Kraft, L. C. Yu, and J. M. Chalovich. (1999) Thin filament activation probed by fluorescence of N-((2-(iodoacetoxy)ethyl)-N-methyl)amino-7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazolelabeled troponin I incorporated into skinned fibers of rabbit psoas muscle. Biophys. J. 77, B. Brenner and J. M. Chalovich. (1999) Kinetics of thin filament activation probed by fluorescence of N-((2-iodoacetoxy)ethyl)-N-methyl)amino-7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazolelabeled troponin I incorporated into skinned fibers of rabbit psoas muscle: Implications for regulation of muscle contraction. Biophys J. 77, Resetar, A.M., Stephens, J.M., and Chalovich, J.M. (2002) Troponin-tropomyosin: an allosteric switch or a steric blocker? Biophys. J. 83: PM: Wang, H., Mao, S., Chalovich, J.M., Yan, Y., and Marriott, G. (2008) Analysis of tropomyosin dynamics in Ca2+-regulated cardiac thin filaments: Application of tethered donor probes for Foerster resonance energy transfer studies. Biophys. J. 94: Borrego-Diaz, E., and Chalovich, J.M. (2010) Kinetics of regulated actin transitions measured by probes on tropomyosin. Biophys. J. 98: PM: Varughese, J.F., Chalovich, J.M., and Li, Y. (2010) Molecular Dynamics Studies on Troponin (TnI-TnT-TnC) Complexes: Insight into the Regulation of Muscle Contraction. J. Biomolec. Struct. Dynam. 28: PM: Varughese, J., Baxley, T., Chalovich, J. and Li, Y. (2011) A Computational and Experimental Approach to investigate Bepridil binding with Cardiac Troponin. J. Phys. Chem.B. 115: PM: Wang, H., Chalovich, J.M. and Marriott, G. (2012) Structural dynamics of troponin I during Ca 2+ -activation of cardiac thin filaments: A multi-site Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) study. PLoS One, 7 (12).e Skowronsky, R.A., Schroeter, M., Baxley, T., Li, Y., Chalovich, J.M. and Spuches, A.M. (2012) Thermodynamics and molecular dynamics simulations of calcium binding to the regulatory site of human cardiac TnC: Evidence for communication with the structural
3 calcium binding sites, Journal of Biological Inorganic Chemistry. 18, DOI: /s III. Myosin-ATP binds to actin in relaxed muscle fibers over a range of ionic strengths ( mm) and temperatures. 28. Brenner, B., Yu, Leepo, C., and Chalovich, J.M. (1990) Parallel inhibition of active force and relaxed fiber stiffness in skeletal muscle by caldesmon: Implications for the pathway to force generation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 88, IV. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Evidence that disease causing mutations of troponin cause shifts in the distribution of actin-tropomyosintroponin states Inactive: Intermediate: Active (or blocked, closed/calcium, open/myosin). Depending on the mutant the active, intermediate or inactive states is favored. 75. Gafurov, B., Fredricksen, S., Cai, A., Brenner, B., Chase, P.B. and Chalovich, J.M. (2004) The Δ14 mutation of Troponin T enhances ATPase Activity and Alters the Cooperative Binding of S1-ADP to Regulated Actin Biochemistry 43: PM: Mathur, M.C., Kobayashi, T., and Chalovich, J.M. (2008) Negative Charges at Protein Kinase C Sites of Troponin I Stabilize the Inactive State of Actin. Biophys. J. 94: V. Evidence for a special role of the C-terminal region of troponin T in regulation. It seems to be critical for forming the inactive state. 95. Franklin, A.J., Baxley, T., Kobayashi, T., Chalovich, J.M. (2012) The C-terminus of troponin T is essential for maintaining the inactive state of regulated actin. Biophys. J. 102: PM: VI. Caldesmon and Regulation of Smooth Muscle Contraction. These papers show, among other things, that caldesmon binding to actintropomyosin displaces myosin-atp from binding. 22. Hemric, M.E., and Chalovich, J.M. (1988) Effect of caldesmon on smooth and skeletal heavy meromyosin ATP hydrolysis and binding to actin. J. Biol. Chem. 263,
4 23. Velaz, L., Hemric, M.E., Benson, C., and Chalovich, J.M. (1989) The binding of caldesmon to actin and its effect on the ATPase activity of soluble myosin subfragments in the presence and absence of tropomyosin. J. Biol. Chem. 264, Hemric, M.E., and Chalovich, J.M. (1990) Characterization of caldesmon binding to myosin. J. Biol. Chem. 265, Sen, A., Chen, Y.-D., Bo, Y. and Chalovich, J.M. (2001) Caldesmon reduces the apparent rate of binding of myosin S1 to actin-tropomyosin. Biochemistry 40: Crosbie, R., Adams, S., Chalovich, J.M. and Reisler, E. (1991) The interaction of caldesmon with the COOH terminus of actin. J.Biol.Chem. 266, Chen, Y.I., and Chalovich, J.M. (1992) Theory of cooperative binding of two n- mer ligands to a one-dimensional lattice and its application to a model for the binding of myosin subfragment-1 and caldesmon to actin. Biophys. J., 63, Pfitzer, G., Zeugner, C., Troschka, M. and Chalovich, J.M. (1993) Caldesmon and a 20-kDa actin-binding fragment of caldesmon inhibit tension development in skinned gizzard muscle fiber bundles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, Crosbie, R.H., Chalovich, J.M. and Reisler, E. (1995) Flexation of caldesmon: effect of conformation on the properties of caldesmon. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 16, Frisbie, M. C. Reedy, L. C. Yu, B. Brenner, J. M. Chalovich, and T. Kraft. (1999) Sarcomeric binding pattern of exogenously added intact caldesmon and its C-terminal 20-kDa fragment in skinned fibers of skeletal muscle. J.Muscle Res.Cell Motil. 20, Fredricksen,S., Cai, A., Gafurov, B., Resetar, A., and Chalovich, J.M. (2003) Influence of ionic strength, actin state, and caldesmon construct size on the number of actin monomers in a caldesmon binding site. Biochemistry 42: Hamden, S.S., Schroeter, M.M. and Chalovich, J.M. (2010) Phosphorylation of caldesmon at sites between residues 627 and 642 attenuates inhibitory activity and contributes to a reduction in Ca2+-calmodulin affinity. Biophys. J. 99: PM: Chalovich, J.M., Lutz, E., Baxley, T. and Schroeter, M.M. (2011) Acrylodan smooth muscle tropomyosin reports differences in effects of troponin and caldesmon in the transition from the active state to the inactive state. Biochemistry, 50, PM: VII. Calponin binds to actin and produces unique changes in the structure of actin filaments. 50. Lu, F.W.M., Freedman, M.V., and Chalovich, J.M. (1995) Characterization of calponin binding to actin. Biochemistry, 34,
5 64. Leinweber, B., Tang, J.X., Stafford, W.F. and Chalovich, J.M. (1999) Calponin interaction with α-actinin-actin: evidence for a structural role for calponin. Biophys. J. 77: PM: VIII. Smooth Muscle Myosin State Changes 81. Burgess, S.A., Yu, S., Walker, M.L., Chalovich, J.M. and Knight, P.L. (2007) Structures of smooth muscle myosin and heavy meromyosin in the folded, shutdown state. J. Miol. Biol. 372: Jung, H.S., Billington, N., Thirumurugan, K., Salzameda, B., Cremo, C.R., Chalovich, J.M., Chantler, P.D., and Knight, P.J. (2011) Role of the tail in the regulated state of myosin 2. J. Mol. Biol. 408, IX. Fesselin or avian Synaptopodin 2: Isolation, regulation of actin polymerization, binding to myosin and evidence that it is intrinsically disordered. 61. B. D. Leinweber, R. S. Fredricksen, D. R. Hoffman, and J. M. Chalovich. (1999) Fesselin: a novel synaptopodin-like actin binding protein from muscle tissue. J.Muscle Res.Cell Motil. 20, Beall, B. and Chalovich, J.M. (2001) Fesselin, a synaptopodin-like protein, stimulates actin nucleation and polymerization. Biochemistry 40: PM: Schroeter, M. and Chalovich, J.M. (2004) Ca ++ -Calmodulin Regulates Fesselin induced Actin Polymerization. Biochemistry 43: Schroeter, M.M. and Chalovich, J.M. (2005) Fesselin binds to actin and myosin and inhibits actin-activated ATPase activity. J. Muscle Research and Cell Motil. 26: Pham, M., and Chalovich, J.M. (2006) Smooth muscle α-actinin binds tightly to fesselin and attenuates its activity toward actin polymerization. J. Muscle Research and Cell Motil. 27: Khaymina, S.S., Kenney, J.M., Schroeter, M.M. and Chalovich, J.M. (2007) Fesselin is a natively unfolded protein. J. Proteome Res. 6: Renegar, R.H., Chalovich, J.M., Leinweber, B.D., Zary, J.T. and Schroeter, M.M. (2009) Localization of the actin-binding protein fesselin in chicken smooth muscle. Histochem. Cell Biol. 131:
6 X. General Reviews and How To s Chalovich, J.M. (1992) Actin Filament Based Regulation of Motility. In Pharmacology and Therapeutics 55, Chalovich, J.M. and Pfitzer, G. (1997) Structure and Function of the Thin Filament Proteins of Smooth Muscle. in: Cellular Aspects of Smooth Muscle Function; Cambridge University Press. Edited by C.Y. Kao and Mary E. Carsten. New York, NY Chalovich,J.M. (2002) Regulation of striated muscle contraction: a discussion. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 23: Chalovich, J.M. (2007) Equilibrium Binding of Proteins to F-Actin. Methods in Molecular Biology, A.O. Sperry Ed., Humana Press Inc., Totowa, NJ, 392: Chalovich, J.M. and Schroeter, M.M. (2010) Synaptopodin family of natively unfolded, actin binding proteins: physical properties and potential biological functions. Biophysical Reviews 2: Chalovich, J.M. (2012) Disease causing mutations of troponin alter regulated actin state distributions. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. (In Press). PM:
POSITION TITLE Professor
 NAME Joseph Michael Chalovich era COMMONS USER NAME chalovichj BIOGRAPHICAL SKETCH Provide the following information for the key personnel and other significant contributors. Follow this format for each
NAME Joseph Michael Chalovich era COMMONS USER NAME chalovichj BIOGRAPHICAL SKETCH Provide the following information for the key personnel and other significant contributors. Follow this format for each
Troponin-Tropomyosin: An Allosteric Switch or a Steric Blocker?
 Biophysical Journal Volume 83 August 2002 1039 1049 1039 Troponin-Tropomyosin: An Allosteric Switch or a Steric Blocker? Andrea M. Resetar, Jacqueline M. Stephens, and Joseph M. Chalovich Department of
Biophysical Journal Volume 83 August 2002 1039 1049 1039 Troponin-Tropomyosin: An Allosteric Switch or a Steric Blocker? Andrea M. Resetar, Jacqueline M. Stephens, and Joseph M. Chalovich Department of
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Biol Chem. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2005 October 21.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Biol Chem. 1995 April 28; 270(17): 9911 9916. Kinetics of Binding of Caldesmon to Actin * Joseph M. Chalovich,, Yi-der Chen, Ronald
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Biol Chem. 1995 April 28; 270(17): 9911 9916. Kinetics of Binding of Caldesmon to Actin * Joseph M. Chalovich,, Yi-der Chen, Ronald
The cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton, the motor proteins, the muscle and its regulation. The cytoskeleton. The cytoskeleton.
 , the motor proteins, the muscle and its regulation Dept. of Biophysics, University of Pécs Zoltán Ujfalusi January-February 2012 Dynamic framework of the Eukaryotes Three main filament-class: 1. Intermedier
, the motor proteins, the muscle and its regulation Dept. of Biophysics, University of Pécs Zoltán Ujfalusi January-February 2012 Dynamic framework of the Eukaryotes Three main filament-class: 1. Intermedier
actin-tropomyosin-troponin Effect of Ca++ on the fluorescence transient
 Activation of skeletal S-1 ATPase activity by actin-tropomyosin-troponin ffect of Ca++ on the fluorescence transient Leonard A. Stein,* and Joseph M. Chalovicht *Departments of Medicine and Physiology,
Activation of skeletal S-1 ATPase activity by actin-tropomyosin-troponin ffect of Ca++ on the fluorescence transient Leonard A. Stein,* and Joseph M. Chalovicht *Departments of Medicine and Physiology,
Chapter 17. Molecular Motors. to accompany Biochemistry, 2/e by Reginald Garrett and Charles Grisham. Biochemistry 2/e - Garrett & Grisham
 Chapter 17 Molecular Motors to accompany Biochemistry, 2/e by Reginald Garrett and Charles Grisham All rights reserved. Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to:
Chapter 17 Molecular Motors to accompany Biochemistry, 2/e by Reginald Garrett and Charles Grisham All rights reserved. Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to:
Regulatory Proteins Alter Nucleotide Binding to Acto-Myosin of Sliding Filaments in Motility Assays
 1046 Biophysical Journal Volume 85 August 2003 1046 1052 Regulatory Proteins Alter Nucleotide Binding to Acto-Myosin of Sliding Filaments in Motility Assays E. Homsher, M. Nili, I. Y. Chen, and L. S. Tobacman*
1046 Biophysical Journal Volume 85 August 2003 1046 1052 Regulatory Proteins Alter Nucleotide Binding to Acto-Myosin of Sliding Filaments in Motility Assays E. Homsher, M. Nili, I. Y. Chen, and L. S. Tobacman*
Motifs of the caldesmon family
 Vol. 47 No. 4/2000 1019 1026 QUARTERLY Motifs of the caldesmon family Edward A. Czury³o Nencki Institute of Experimental Biology, Department of Muscle Biochemistry, Warszawa, Poland Received: 20 September,
Vol. 47 No. 4/2000 1019 1026 QUARTERLY Motifs of the caldesmon family Edward A. Czury³o Nencki Institute of Experimental Biology, Department of Muscle Biochemistry, Warszawa, Poland Received: 20 September,
INTRODUCTION. found that the index of retardation was (n 3) times that in the absence of P i
 Biochem. J. (2000) 350, 693 699 (Printed in Great Britain) 693 A simple method for measuring the relative force exerted by myosin on actin filaments in the in vitro motility assay: evidence that tropomyosin
Biochem. J. (2000) 350, 693 699 (Printed in Great Britain) 693 A simple method for measuring the relative force exerted by myosin on actin filaments in the in vitro motility assay: evidence that tropomyosin
Location and functional characterization of myosin contact sites in smoothmuscle
 Biochem. J. (1997) 328, 211 218 (Printed in Great Britain) 211 Location and functional characterization of myosin contact sites in smoothmuscle caldesmon Alexander V. VOROTNIKOV* 1, Steven B. MARSTON and
Biochem. J. (1997) 328, 211 218 (Printed in Great Britain) 211 Location and functional characterization of myosin contact sites in smoothmuscle caldesmon Alexander V. VOROTNIKOV* 1, Steven B. MARSTON and
Abstract. Fesselin and caldesmon: natively unfolded proteins in smooth muscle regulation. Svetlana Hamden. May 2010
 Abstract Fesselin and caldesmon: natively unfolded proteins in smooth muscle regulation by Svetlana Hamden May 2010 Committee chair: Joseph M. Chalovich Department: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Dysregulation
Abstract Fesselin and caldesmon: natively unfolded proteins in smooth muscle regulation by Svetlana Hamden May 2010 Committee chair: Joseph M. Chalovich Department: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Dysregulation
Role of Ca 2 and Cross-Bridges in Skeletal Muscle Thin Filament Activation Probed with Ca 2 Sensitizers
 2166 Biophysical Journal Volume 76 April 1999 2166 2176 Role of Ca 2 and Cross-Bridges in Skeletal Muscle Thin Filament Activation Probed with Ca 2 Sensitizers Philip A. Wahr and Joseph M. Metzger Department
2166 Biophysical Journal Volume 76 April 1999 2166 2176 Role of Ca 2 and Cross-Bridges in Skeletal Muscle Thin Filament Activation Probed with Ca 2 Sensitizers Philip A. Wahr and Joseph M. Metzger Department
FORMATION IN RELAXED MUSCLE FIBERS AT VARIOUS IONIC STRENGTHS
 X-RAY DIFFRACTION EVIDENCE FOR CROSS-BRIDGE FORMATION IN RELAXED MUSCLE FIBERS AT VARIOUS IONIC STRENGTHS BERNHARD BRENNER National Institute ofarthritis, Diabetes, and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National
X-RAY DIFFRACTION EVIDENCE FOR CROSS-BRIDGE FORMATION IN RELAXED MUSCLE FIBERS AT VARIOUS IONIC STRENGTHS BERNHARD BRENNER National Institute ofarthritis, Diabetes, and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National
states (in the presence of ATP), and the combined electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions for the strongly bound
 48 Biophysical Journal Volume 7 January 1996 48-56 Cross-Bridge Binding to Actin and Force Generation in Skinned Fibers of the Rabbit Psoas Muscle in the Presence of Antibody Fragments Against the N-Terminus
48 Biophysical Journal Volume 7 January 1996 48-56 Cross-Bridge Binding to Actin and Force Generation in Skinned Fibers of the Rabbit Psoas Muscle in the Presence of Antibody Fragments Against the N-Terminus
Dear members of the Council,
 Dear members of the Council, Thank you for awarding me the ESC First Contact Initiative Grant, which offered me the opportunity to travel to the University of Arizona to closely collaborate with Professor
Dear members of the Council, Thank you for awarding me the ESC First Contact Initiative Grant, which offered me the opportunity to travel to the University of Arizona to closely collaborate with Professor
ZE WANG*, HE JIANG, ZHI-QIONG YANG*, AND SAMUEL CHACKO*
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 94, pp. 11899 11904, October 1997 Biochemistry Both N-terminal myosin-binding and C-terminal actin-binding sites on smooth muscle caldesmon are required for caldesmonmediated
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 94, pp. 11899 11904, October 1997 Biochemistry Both N-terminal myosin-binding and C-terminal actin-binding sites on smooth muscle caldesmon are required for caldesmonmediated
CRISTINA IFTODE. Current position: Associate Professor, Rowan University, Dept. Biological Sciences. Research Interests. Education.
 CRISTINA IFTODE Work address Rowan University Dept. Biological Sciences 201 Mullica Hill Rd. Glassboro, NJ 08028 Phone: (856) 256-4500 ext.3586 E-mail: iftode@rowan.edu URL: http://www.rowan.edu/colleges/las/departments/biologicalsci/facultystaff/cristinaiftode.htm
CRISTINA IFTODE Work address Rowan University Dept. Biological Sciences 201 Mullica Hill Rd. Glassboro, NJ 08028 Phone: (856) 256-4500 ext.3586 E-mail: iftode@rowan.edu URL: http://www.rowan.edu/colleges/las/departments/biologicalsci/facultystaff/cristinaiftode.htm
BME Engineering Molecular Cell Biology. The Cytoskeleton (I): Actin The Cytoskeleton (II): Microtubule & Intermediate Filament
 BME 42-620 Engineering Molecular Cell Biology Lecture 09: The Cytoskeleton (I): Actin The Cytoskeleton (II): Microtubule & Intermediate Filament BME42-620 Lecture 09, September 27, 2011 1 Outline Overviewofcytoskeletal
BME 42-620 Engineering Molecular Cell Biology Lecture 09: The Cytoskeleton (I): Actin The Cytoskeleton (II): Microtubule & Intermediate Filament BME42-620 Lecture 09, September 27, 2011 1 Outline Overviewofcytoskeletal
A Model Based Analysis of Steady-State versus Dynamic Aspects of the Relationship between Calcium and Force
 A Model Based Analysis of Steady-State versus Dynamic Aspects of the Relationship between Calcium and Force Casey L. Overby Bioengineering and Bioinformatics Summer Institute 2007, University of Pittsburgh
A Model Based Analysis of Steady-State versus Dynamic Aspects of the Relationship between Calcium and Force Casey L. Overby Bioengineering and Bioinformatics Summer Institute 2007, University of Pittsburgh
ANAT Cell Biology Lecture 11 School of Medical Sciences The University of New South Wales. UNSW Copyright Notice
 ANAT3231 - Cell Biology Lecture 11 School of Medical Sciences The University of New South Wales The actin cytoskeleton Prof Peter Gunning Oncology Research Unit Room 502A Wallace Wurth Building Email:
ANAT3231 - Cell Biology Lecture 11 School of Medical Sciences The University of New South Wales The actin cytoskeleton Prof Peter Gunning Oncology Research Unit Room 502A Wallace Wurth Building Email:
The length of cooperative units on the thin filament in rabbit psoas muscle fibres
 The length of cooperative units on the thin filament in rabbit psoas muscle fibres To elicit a biological function, multiple molecules of the same or similar kind are often assembled together, and they
The length of cooperative units on the thin filament in rabbit psoas muscle fibres To elicit a biological function, multiple molecules of the same or similar kind are often assembled together, and they
Altered Kinetics of Contraction in Skeletal Muscle Fibers Containing a Mutant Myosin Regulatory Light Chain with Reduced Divalent
 Biophysical Journal Volume 71 July 1996 341-350 341 Altered Kinetics of Contraction in Skeletal Muscle Fibers Containing a Mutant Myosin Regulatory Light Chain with Reduced Divalent Cation Binding Gary
Biophysical Journal Volume 71 July 1996 341-350 341 Altered Kinetics of Contraction in Skeletal Muscle Fibers Containing a Mutant Myosin Regulatory Light Chain with Reduced Divalent Cation Binding Gary
Spare the rod, spoil the regulation: Necessity for a myosin rod
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 94, pp. 48 52, January 1997 Biochemistry Spare the rod, spoil the regulation: Necessity for a myosin rod KATHLEEN M. TRYBUS*, YELENA FREYZON*, LYNN Z. FAUST, AND H. LEE
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 94, pp. 48 52, January 1997 Biochemistry Spare the rod, spoil the regulation: Necessity for a myosin rod KATHLEEN M. TRYBUS*, YELENA FREYZON*, LYNN Z. FAUST, AND H. LEE
cell fusion live and fixed imaging genetics biochemistry in vitro systems inhibitors of cellular processes (transcription, replication, microtubules)
 DISCUSSION SECTIONS BY STUDENT NUMBER ENDING IN ODD NUMBERS 2-3, EVEN 3-4 Methods for Studying the Cell Cycle cell fusion live and fixed imaging genetics biochemistry in vitro systems inhibitors of cellular
DISCUSSION SECTIONS BY STUDENT NUMBER ENDING IN ODD NUMBERS 2-3, EVEN 3-4 Methods for Studying the Cell Cycle cell fusion live and fixed imaging genetics biochemistry in vitro systems inhibitors of cellular
indicates that some of the disoriented heads are attached of head orientation. Mechanical (Brenner et al., 1982;
 Orientational disorder and motion of weakly attached cross-bridges Piotr G. Fajer,* Elizabeth A. Fajer,* Mark Schoenberg,' and David D. Thomas* *Department of Biochemistry, University of Minnesota Medical
Orientational disorder and motion of weakly attached cross-bridges Piotr G. Fajer,* Elizabeth A. Fajer,* Mark Schoenberg,' and David D. Thomas* *Department of Biochemistry, University of Minnesota Medical
THE MOLECULAR BASIS OF CROSS-BRIDGE FUNCTION
 THE MOLECULAR BASIS OF CROSS-BRIDGE FUNCTION Kenneth C. Holmes 1. INTRODUCTION Our understanding of the physiology of muscle depends critically on the resolution of the available anatomy. Early insight
THE MOLECULAR BASIS OF CROSS-BRIDGE FUNCTION Kenneth C. Holmes 1. INTRODUCTION Our understanding of the physiology of muscle depends critically on the resolution of the available anatomy. Early insight
Cross-Bridge versus Thin Filament Contributions to the Level and Rate of Force Development in Cardiac Muscle
 Biophysical Journal Volume 87 September 2004 1815 1824 1815 Cross-Bridge versus Thin Filament Contributions to the Level and Rate of Force Development in Cardiac Muscle M. Regnier,* H. Martin, y R. J.
Biophysical Journal Volume 87 September 2004 1815 1824 1815 Cross-Bridge versus Thin Filament Contributions to the Level and Rate of Force Development in Cardiac Muscle M. Regnier,* H. Martin, y R. J.
Molecular design principles underlying β-strand swapping. in the adhesive dimerization of cadherins
 Supplementary information for: Molecular design principles underlying β-strand swapping in the adhesive dimerization of cadherins Jeremie Vendome 1,2,3,5, Shoshana Posy 1,2,3,5,6, Xiangshu Jin, 1,3 Fabiana
Supplementary information for: Molecular design principles underlying β-strand swapping in the adhesive dimerization of cadherins Jeremie Vendome 1,2,3,5, Shoshana Posy 1,2,3,5,6, Xiangshu Jin, 1,3 Fabiana
Movement at the Molecular Level
 Movement at the Molecular Level Diffusion: = 6 D t (D 6 π µ a) Typical numbers: 10 nm protein in water D= 10-10 m 2 /s.in cells D= 10-12 m 2 /s (D= 10-14 m 2 /s lipids) [] 1/2 =1 µm, t ~0.2
Movement at the Molecular Level Diffusion: = 6 D t (D 6 π µ a) Typical numbers: 10 nm protein in water D= 10-10 m 2 /s.in cells D= 10-12 m 2 /s (D= 10-14 m 2 /s lipids) [] 1/2 =1 µm, t ~0.2
Regulation of force and unloaded sliding speed in single thin filaments: effects of regulatory proteins and calcium
 Keywords: 0196 Journal of Physiology (2000), 524.1, pp. 233 243 233 Regulation of force and unloaded sliding speed in single thin filaments: effects of regulatory proteins and calcium Earl Homsher, David
Keywords: 0196 Journal of Physiology (2000), 524.1, pp. 233 243 233 Regulation of force and unloaded sliding speed in single thin filaments: effects of regulatory proteins and calcium Earl Homsher, David
THE BIOCHEMICAL BASIS OF MUSCLE CONTRACTION 1
 THE BIOCHEMICAL BASIS OF MUSCLE CONTRACTION 1 Summary: Early microscopic data concerning the appearance of relaxed and contracted muscles is reviewed. This is correlated with modern biochemical studies
THE BIOCHEMICAL BASIS OF MUSCLE CONTRACTION 1 Summary: Early microscopic data concerning the appearance of relaxed and contracted muscles is reviewed. This is correlated with modern biochemical studies
Lecture 13. Motor Proteins I
 Lecture 13 Motor Proteins I Introduction: The study of motor proteins has become a major focus in cell and molecular biology. Motor proteins are very interesting because they do what no man-made engines
Lecture 13 Motor Proteins I Introduction: The study of motor proteins has become a major focus in cell and molecular biology. Motor proteins are very interesting because they do what no man-made engines
MCBII. Points this page
 1. What makes intermediate filaments (IFs) an inefficient track for motor proteins (4 pts)? A. The outer surface of IFs is hydrophobic. B. IFs are nonpolar structures. C. IFs contain coiled coil domains.
1. What makes intermediate filaments (IFs) an inefficient track for motor proteins (4 pts)? A. The outer surface of IFs is hydrophobic. B. IFs are nonpolar structures. C. IFs contain coiled coil domains.
Ca2'-dependent affinity of rapidly detaching zero-force
 Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 85, pp. 6716-672, September 1988 iophysics. Relaxation of muscle fibers with adenosine 5'-[y-thio]triphosphate (ATP[yS]) and by laser photolysis of caged ATPyS]: Evidence
Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 85, pp. 6716-672, September 1988 iophysics. Relaxation of muscle fibers with adenosine 5'-[y-thio]triphosphate (ATP[yS]) and by laser photolysis of caged ATPyS]: Evidence
Chemically modified nanopores as tools to detect single DNA and protein molecules. Overview
 Chemically modified nanopores as tools to detect single DNA and protein molecules Stefan Howorka Introduction Sensing principle Overview Single channel current recording Protein pore Nanopores detect individual
Chemically modified nanopores as tools to detect single DNA and protein molecules Stefan Howorka Introduction Sensing principle Overview Single channel current recording Protein pore Nanopores detect individual
6 pts. B) State two mechanisms to explain the effect shown in the figure.
 Question 1. (10 points) The rate of uptake of glucose into rat adipocytes is increased by addition of insulin to the medium. The increase reaches a maximum within 30 seconds at 37 C and is energy dependent.
Question 1. (10 points) The rate of uptake of glucose into rat adipocytes is increased by addition of insulin to the medium. The increase reaches a maximum within 30 seconds at 37 C and is energy dependent.
ANAT Cell Biology Lecture 12 School of Medical Sciences The University of New South Wales
 ANAT3231 - Cell Biology Lecture 12 School of Medical Sciences The University of New South Wales Prof Peter Gunning Microfilaments, 2010 Sllide 1 UNSW Copyright Notice COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright
ANAT3231 - Cell Biology Lecture 12 School of Medical Sciences The University of New South Wales Prof Peter Gunning Microfilaments, 2010 Sllide 1 UNSW Copyright Notice COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright
Calponin Interaction with -Actinin-Actin: Evidence for a Structural Role for Calponin
 3208 Biophysical Journal Volume 77 December 1999 3208 3217 Calponin Interaction with -Actinin-Actin: Evidence for a Structural Role for Calponin Barbara Leinweber,* Jay X. Tang, # Walter F. Stafford, and
3208 Biophysical Journal Volume 77 December 1999 3208 3217 Calponin Interaction with -Actinin-Actin: Evidence for a Structural Role for Calponin Barbara Leinweber,* Jay X. Tang, # Walter F. Stafford, and
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information The cargo-binding domain regulates structure and activity of myosin 5 Kavitha Thirumurugan, Takeshi Sakamoto, John A Hammer III, James R. Sellers and Peter J. Knight This document
Supplementary Information The cargo-binding domain regulates structure and activity of myosin 5 Kavitha Thirumurugan, Takeshi Sakamoto, John A Hammer III, James R. Sellers and Peter J. Knight This document
MARCH 2, 2012 VOLUME 287 NUMBER 10 JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY 7661
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY VOL. 287, NO. 10, pp. 7661 7674, March 2, 2012 2012 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Published in the U.S.A. Structural Dynamics
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY VOL. 287, NO. 10, pp. 7661 7674, March 2, 2012 2012 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Published in the U.S.A. Structural Dynamics
me239 mechanics of the cell homework biopolymers - motivation 3.1 biopolymers - motivation 3. biopolymers biopolymers biopolymers
 3. biopolymers the inner life of a cell, viel & lue, harvard [2006] me239 mechanics of the cell 1 2 biopolymers Figure 3.1. Biopolymers. Characteristic length scales on the cellular and sucellular level..
3. biopolymers the inner life of a cell, viel & lue, harvard [2006] me239 mechanics of the cell 1 2 biopolymers Figure 3.1. Biopolymers. Characteristic length scales on the cellular and sucellular level..
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company. 5 Function of Globular Proteins
 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 5 Function of Globular Proteins CHAPTER 5: Function of Globular Proteins Key topics in protein function: Reversible binding of ligands is essential Specificity of ligands
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 5 Function of Globular Proteins CHAPTER 5: Function of Globular Proteins Key topics in protein function: Reversible binding of ligands is essential Specificity of ligands
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Equilibration and Exchange of Fluorescently Labeled Molecules in Skinned Skeletal Muscle Fibers Visualized by Confocal Microscopy
 1 246 Biophysical Journal Volume 69 October 1995 1246-1258 Equilibration and Exchange of Fluorescently Labeled Molecules in Skinned Skeletal Muscle Fibers Visualized by Confocal Microscopy T. Kraft,*j
1 246 Biophysical Journal Volume 69 October 1995 1246-1258 Equilibration and Exchange of Fluorescently Labeled Molecules in Skinned Skeletal Muscle Fibers Visualized by Confocal Microscopy T. Kraft,*j
Method for Folding of Recombinant Prion Protein to Soluble β-sheet Secondary Structure
 Chapter 2 Method for Folding of Recombinant Prion Protein to Soluble β-sheet Secondary Structure Laura J. Ellett Abstract A key event in the pathogenesis of prion diseases is the change in structure of
Chapter 2 Method for Folding of Recombinant Prion Protein to Soluble β-sheet Secondary Structure Laura J. Ellett Abstract A key event in the pathogenesis of prion diseases is the change in structure of
Role of Mutations in the Essential Light Chain (ELC) of Myosin in Familial Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (FHC)
 University of Miami Scholarly Repository Open Access Theses Electronic Theses and Dissertations 2011-05-09 Role of Mutations in the Essential Light Chain (ELC) of Myosin in Familial Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
University of Miami Scholarly Repository Open Access Theses Electronic Theses and Dissertations 2011-05-09 Role of Mutations in the Essential Light Chain (ELC) of Myosin in Familial Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Specificity: Induced Fit
 Specificity: Induced Fit Conformational changes may occur upon ligand binding (Daniel Koshland in 1958) This adaptation is called the induced fit Induced fit allows for tighter binding of the ligand Induced
Specificity: Induced Fit Conformational changes may occur upon ligand binding (Daniel Koshland in 1958) This adaptation is called the induced fit Induced fit allows for tighter binding of the ligand Induced
CYTOSKELETON, MOTORPROTEINS.
 CYTOSKELETON, MOTORPROTEINS. SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY Tamás Huber 15. 10. 2012. CYTOSKELETON: Dynamic scaffold in eukaryotic cells Three main filament systems: A. Intermediate filaments B. Microtubules C.
CYTOSKELETON, MOTORPROTEINS. SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY Tamás Huber 15. 10. 2012. CYTOSKELETON: Dynamic scaffold in eukaryotic cells Three main filament systems: A. Intermediate filaments B. Microtubules C.
Polymerization of G-actin by caldesmon
 Volume 184, number 1 FEBS 2538 May 1985 Polymerization of G-actin by caldesmon Barbara Galqzkiewicz, Malgorzata Mossakowska, Hanna Osiriska and Renata Dqbrowska* Nencki Institute of Experimental Biology,
Volume 184, number 1 FEBS 2538 May 1985 Polymerization of G-actin by caldesmon Barbara Galqzkiewicz, Malgorzata Mossakowska, Hanna Osiriska and Renata Dqbrowska* Nencki Institute of Experimental Biology,
Modulation of Thin Filament Activation of Myosin ATP Hydrolysis by N Terminal Domains of Cardiac Myosin Binding Protein C
 pubs.acs.org/biochemistry Terms of Use Modulation of Thin Filament Activation of Myosin ATP Hydrolysis by N Terminal Domains of Cardiac Myosin Binding Protein C Betty Belknap, Samantha P. Harris, and Howard
pubs.acs.org/biochemistry Terms of Use Modulation of Thin Filament Activation of Myosin ATP Hydrolysis by N Terminal Domains of Cardiac Myosin Binding Protein C Betty Belknap, Samantha P. Harris, and Howard
The mechanism(s) of protein folding. What is meant by mechanism. Experimental approaches
 The mechanism(s) of protein folding What is meant by mechanism Computational approaches Experimental approaches Questions: What events occur and in what time sequence when a protein folds Is there a specified
The mechanism(s) of protein folding What is meant by mechanism Computational approaches Experimental approaches Questions: What events occur and in what time sequence when a protein folds Is there a specified
Modulation of Thin Filament Activation of Myosin ATP Hydrolysis by N Terminal Domains of Cardiac Myosin Binding Protein C
 This is an open access article published under an ACS AuthorChoice License, which permits copying and redistribution of the article or any adaptations for non-commercial purposes. pubs.acs.org/biochemistry
This is an open access article published under an ACS AuthorChoice License, which permits copying and redistribution of the article or any adaptations for non-commercial purposes. pubs.acs.org/biochemistry
1. The microtubule wall is composed of globular proteins arranged in longitudinal rows called.
 Name: Quiz name: Quiz 7 ate: 1. The microtubule wall is composed of globular proteins arranged in longitudinal rows called. microfilaments protofilaments prototubules microtubular subunits 2. Which of
Name: Quiz name: Quiz 7 ate: 1. The microtubule wall is composed of globular proteins arranged in longitudinal rows called. microfilaments protofilaments prototubules microtubular subunits 2. Which of
Supplementary Note 1. Enzymatic properties of the purified Syn BVR
 Supplementary Note 1. Enzymatic properties of the purified Syn BVR The expression vector pet15b-syn bvr allowed us to routinely prepare 15 mg of electrophoretically homogenous Syn BVR from 2.5 L of TB-medium
Supplementary Note 1. Enzymatic properties of the purified Syn BVR The expression vector pet15b-syn bvr allowed us to routinely prepare 15 mg of electrophoretically homogenous Syn BVR from 2.5 L of TB-medium
Supplemental Information. A Computational Model of YAP/TAZ Mechanosensing. Meng Sun, Fabian Spill, and Muhammad H. Zaman
 Biophysical Journal, Volume 110 Supplemental Information A Computational Model of YAP/TAZ Mechanosensing Meng Sun, Fabian Spill, and Muhammad H. Zaman Supporting Methods Molecular intervention When latrunculin
Biophysical Journal, Volume 110 Supplemental Information A Computational Model of YAP/TAZ Mechanosensing Meng Sun, Fabian Spill, and Muhammad H. Zaman Supporting Methods Molecular intervention When latrunculin
Tropomyosin Exon 6b Is Troponin-specific and Required for Correct Acto-myosin Regulation*
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 279, No. 18, Issue of April 30, pp. 18203 18209, 2004 2004 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. Tropomyosin Exon
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY Vol. 279, No. 18, Issue of April 30, pp. 18203 18209, 2004 2004 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in U.S.A. Tropomyosin Exon
Time-resolved low-angle X-ray diffraction of muscle reveals temporal relationship between crossbridge movements and tension development
 TIMELINE The myosin swinging cross-bridge model James A. Spudich No biological system has been studied by more diverse approaches than the actinbased molecular motor myosin. Biophysics, biochemistry, physiology,
TIMELINE The myosin swinging cross-bridge model James A. Spudich No biological system has been studied by more diverse approaches than the actinbased molecular motor myosin. Biophysics, biochemistry, physiology,
20 years of splines and biomedical imaging: The prehistory
 20 years of splines and biomedical imaging: The prehistory Michael Unser Biomedical Imaging Group EPFL, Lausanne Switzerland BIG's 20th Birthday, March 23, 2018, EPFL, Switzerland 1981: Master in EE 1984:
20 years of splines and biomedical imaging: The prehistory Michael Unser Biomedical Imaging Group EPFL, Lausanne Switzerland BIG's 20th Birthday, March 23, 2018, EPFL, Switzerland 1981: Master in EE 1984:
An actin-dependent conformational change in myosin
 An actin-dependent conformational change in myosin Ming Xiao 1,2, Jeff G. Reifenberger 1, Amber L. Wells 3, Corry Baldacchino 3, Li-Qiong Chen 3, Pinghua Ge 1, H. Lee Sweeney 3 and Paul R. Selvin 1,4 Published
An actin-dependent conformational change in myosin Ming Xiao 1,2, Jeff G. Reifenberger 1, Amber L. Wells 3, Corry Baldacchino 3, Li-Qiong Chen 3, Pinghua Ge 1, H. Lee Sweeney 3 and Paul R. Selvin 1,4 Published
Tropomyosin Positions in Regulated Thin Filaments Revealed by Cryoelectron Microscopy
 Biophysical Journal Volume 77 August 1999 985 992 985 Tropomyosin Positions in Regulated Thin Filaments Revealed by Cryoelectron Microscopy C. Xu*, R. Craig, # L. Tobacman, R. Horowitz, # and W. Lehman*
Biophysical Journal Volume 77 August 1999 985 992 985 Tropomyosin Positions in Regulated Thin Filaments Revealed by Cryoelectron Microscopy C. Xu*, R. Craig, # L. Tobacman, R. Horowitz, # and W. Lehman*
Research Profile. Modeling on Tropomyosin/Actin complex
 Research Profile Through my long interdisciplinary education in Computational Science Computation Chemistry, and Computer Science, you can be certain I can make a big contribution to your institution.
Research Profile Through my long interdisciplinary education in Computational Science Computation Chemistry, and Computer Science, you can be certain I can make a big contribution to your institution.
Practice Exam 3 MCBII
 1. Which is not a feature of lamin intermediate filaments (IFs)? (4 pts) A. They are protein polymers. B. They are used by motor proteins to traffic cargo. C. They contain coiled coil domains. D. They
1. Which is not a feature of lamin intermediate filaments (IFs)? (4 pts) A. They are protein polymers. B. They are used by motor proteins to traffic cargo. C. They contain coiled coil domains. D. They
Paramagnetic probes attached to a light chain on the myosin head
 Paramagnetic probes attached to a light chain on the myosin head are highly disordered in active muscle fibers Brett Hambly, * Kathleen Franks,t and Roger Cooket *Department of Pathology, The University
Paramagnetic probes attached to a light chain on the myosin head are highly disordered in active muscle fibers Brett Hambly, * Kathleen Franks,t and Roger Cooket *Department of Pathology, The University
Differential regulation of the actomyosin interaction by skeletal and cardiac troponin isoforms
 JBC Papers in Press. Published on December 9, 2002 as Manuscript M210690200 Differential regulation of the actomyosin interaction by skeletal and cardiac troponin isoforms Robin Maytum *, Barbara Westerdorf,
JBC Papers in Press. Published on December 9, 2002 as Manuscript M210690200 Differential regulation of the actomyosin interaction by skeletal and cardiac troponin isoforms Robin Maytum *, Barbara Westerdorf,
Muscle contraction on the molecular level. Actin-myosin interaction studied in an in vitro motility assay Hamelink, W.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Muscle contraction on the molecular level. Actin-myosin interaction studied in an in vitro motility assay Hamelink, W. Link to publication Citation for published
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Muscle contraction on the molecular level. Actin-myosin interaction studied in an in vitro motility assay Hamelink, W. Link to publication Citation for published
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH CYTOSKELETON AND CELL MOVEMENT.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF THE CYTOSKELETON The cytoskeleton is an intricate of protein filaments that extend throughout the cytoplasm It is a highly organized and dynamic structure (constantly
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF THE CYTOSKELETON The cytoskeleton is an intricate of protein filaments that extend throughout the cytoplasm It is a highly organized and dynamic structure (constantly
m a n u e l f r a n c i s c o m o r a l e s
 n a t i o n a l a c a d e m y o f s c i e n c e s m a n u e l f r a n c i s c o m o r a l e s 1 9 1 9 2 0 0 9 A Biographical Memoir by r o g e r c o o k e a n d s t e f a n h i g h s m i t h Any opinions
n a t i o n a l a c a d e m y o f s c i e n c e s m a n u e l f r a n c i s c o m o r a l e s 1 9 1 9 2 0 0 9 A Biographical Memoir by r o g e r c o o k e a n d s t e f a n h i g h s m i t h Any opinions
Biophysics of Molecules
 Biophysics of Molecules Cytoskeletal filaments, Actin polymerization and Actin Treadmilling Part 2 (26.11.2012) Dr. Carsten Grashoff MPI of Biochemistry E-mail: cgrasho@biochem.mpg.de Lecture Outline The
Biophysics of Molecules Cytoskeletal filaments, Actin polymerization and Actin Treadmilling Part 2 (26.11.2012) Dr. Carsten Grashoff MPI of Biochemistry E-mail: cgrasho@biochem.mpg.de Lecture Outline The
Protein-Protein Interactions II
 Biochemistry 412 Protein-Protein Interactions II March 28, 2008 Delano (2002) Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 12, 14. Some ways that mutations can destabilize protein-protein interactions Delano (2002) Curr.
Biochemistry 412 Protein-Protein Interactions II March 28, 2008 Delano (2002) Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 12, 14. Some ways that mutations can destabilize protein-protein interactions Delano (2002) Curr.
MICB688L/MOCB639 Advanced Cell Biology Exam II
 MICB688L/MOCB639 Advanced Cell Biology Exam II May 10, 2001 Name: 1. Briefly describe the four major classes of cell surface receptors and their modes of action (immediate downstream only) (8) 2. Please
MICB688L/MOCB639 Advanced Cell Biology Exam II May 10, 2001 Name: 1. Briefly describe the four major classes of cell surface receptors and their modes of action (immediate downstream only) (8) 2. Please
Protein Folding Problem I400: Introduction to Bioinformatics
 Protein Folding Problem I400: Introduction to Bioinformatics November 29, 2004 Protein biomolecule, macromolecule more than 50% of the dry weight of cells is proteins polymer of amino acids connected into
Protein Folding Problem I400: Introduction to Bioinformatics November 29, 2004 Protein biomolecule, macromolecule more than 50% of the dry weight of cells is proteins polymer of amino acids connected into
STIFFNESS OF SKINNED RABBIT PSOAS FIBERS IN
 STIFFNSS OF SKINND RABBIT PSOAS FIBRS IN MgATP AND MgPPi SOLUTION B. BRNNR, J. M. HALOVIH, t L.. GRN, *. ISNBRG, t AND M. SHONBRG' *Laboratory ofphysical Biology, National Institute ofarthritis, Diabetes,
STIFFNSS OF SKINND RABBIT PSOAS FIBRS IN MgATP AND MgPPi SOLUTION B. BRNNR, J. M. HALOVIH, t L.. GRN, *. ISNBRG, t AND M. SHONBRG' *Laboratory ofphysical Biology, National Institute ofarthritis, Diabetes,
Boston, Massachusetts USA; and glmperial College School. studies where thin filaments were reconstituted with physiological
 1920 Affinity and Structure of Complexes of Tropomyosin and Caldesmon Domains Biophysical Journal Volume 71 October 1996 1920-1933 Eric J. Hnath,* C.-L. Albert Wang,# Pia A. J. Huber,5 Steve B. Marston,5
1920 Affinity and Structure of Complexes of Tropomyosin and Caldesmon Domains Biophysical Journal Volume 71 October 1996 1920-1933 Eric J. Hnath,* C.-L. Albert Wang,# Pia A. J. Huber,5 Steve B. Marston,5
System of protein filaments in the cytoplasm of. eukaryotic cell that gives the cell shape and capacity for
 Cytoskeleton System of protein filaments in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cell that gives the cell shape and capacity for directed movement. The protein filaments are responsible for the shaping, moving,
Cytoskeleton System of protein filaments in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cell that gives the cell shape and capacity for directed movement. The protein filaments are responsible for the shaping, moving,
Myosin Light Chain Phosphorylation Affects the Structure of Rabbit
 898 Biophysical Journal Volume 71 August 1996 898-907 Myosin Light Chain Phosphorylation Affects the Structure of Rabbit Skeletal Muscle Thick Filaments Rhea J. C. Levine,* Robert W. Kensler,# Zhaohui
898 Biophysical Journal Volume 71 August 1996 898-907 Myosin Light Chain Phosphorylation Affects the Structure of Rabbit Skeletal Muscle Thick Filaments Rhea J. C. Levine,* Robert W. Kensler,# Zhaohui
Slow cycling of unphosphorylated myosin is inhibited by calponin, thus keeping smooth muscle relaxed
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 94, pp. 7655 7660, July 1997 Physiology Slow cycling of unphosphorylated myosin is inhibited by calponin, thus keeping smooth muscle relaxed ULF MALMQVIST*, KATHLEEN M.
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 94, pp. 7655 7660, July 1997 Physiology Slow cycling of unphosphorylated myosin is inhibited by calponin, thus keeping smooth muscle relaxed ULF MALMQVIST*, KATHLEEN M.
COMPUTER AIDED DRUG DESIGN: AN OVERVIEW
 Available online on 19.09.2018 at http://jddtonline.info Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics Open Access to Pharmaceutical and Medical Research 2011-18, publisher and licensee JDDT, This is an Open
Available online on 19.09.2018 at http://jddtonline.info Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics Open Access to Pharmaceutical and Medical Research 2011-18, publisher and licensee JDDT, This is an Open
Buffer NaCl concentration regulates Renilla luciferase activity and ligand-induced conformational changes in the BRET-based PDE5 sensor
 Correspondence mbikhb@nus.edu.sg sandhya@mrdg.iisc.ernet.in Disciplines Biochemistry Biophysics Keywords Luciferase Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer (BRET) Type of Observation Standalone Type
Correspondence mbikhb@nus.edu.sg sandhya@mrdg.iisc.ernet.in Disciplines Biochemistry Biophysics Keywords Luciferase Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer (BRET) Type of Observation Standalone Type
Calponin binds G-actin and F-actin with similar affinity
 Calponin binds G-actin and F-actin with similar affinity Imen Ferjani a,d, Abdellatif Fattoum c, Sutherland K. Maciver b, Mohamed Manai d, Yves Benyamin a, Claude Roustan a, * a UMR 5539 (CNRS) Laboratoire
Calponin binds G-actin and F-actin with similar affinity Imen Ferjani a,d, Abdellatif Fattoum c, Sutherland K. Maciver b, Mohamed Manai d, Yves Benyamin a, Claude Roustan a, * a UMR 5539 (CNRS) Laboratoire
Temperature-induced Structural Changes in the Myosin Thick Filament of
 2304 Biophysical Journal Volume 73 November 1997 2304-2312 Temperature-induced Structural Changes in the Myosin Thick Filament of Skinned Rabbit Psoas Muscle S. Malinchik, S. Xu, and L. C. Yu Laboratory
2304 Biophysical Journal Volume 73 November 1997 2304-2312 Temperature-induced Structural Changes in the Myosin Thick Filament of Skinned Rabbit Psoas Muscle S. Malinchik, S. Xu, and L. C. Yu Laboratory
Richard H. Ebright Board of Governors Professor of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Rutgers University
 Chemistry 01:160:480, Chemistry 16:160:580, Quantitative Biomedicine 16:118:617:05 Structural Biology, Structural Biophysics, and Chemical Biology of Transcription Instructor Richard H. Ebright Board of
Chemistry 01:160:480, Chemistry 16:160:580, Quantitative Biomedicine 16:118:617:05 Structural Biology, Structural Biophysics, and Chemical Biology of Transcription Instructor Richard H. Ebright Board of
The Ca 2þ -based control of cardiac muscle function has long. A Model of Calcium Activation of the Cardiac Thin Filament
 pubs.acs.org/biochemistry A Model of Calcium Activation of the Cardiac Thin Filament Edward P. Manning, Jil C. Tardiff, and Steven D. Schwartz*,,, Department of Biophysics, Albert Einstein College of Medicine,
pubs.acs.org/biochemistry A Model of Calcium Activation of the Cardiac Thin Filament Edward P. Manning, Jil C. Tardiff, and Steven D. Schwartz*,,, Department of Biophysics, Albert Einstein College of Medicine,
Florida State University Libraries
 Florida State University Libraries Electronic Theses, Treatises and Dissertations The Graduate School 2014 The Thick Filament Origins of Cross- Bridges in Rigor Insect Flight Muscle Claudia Arakelian Follow
Florida State University Libraries Electronic Theses, Treatises and Dissertations The Graduate School 2014 The Thick Filament Origins of Cross- Bridges in Rigor Insect Flight Muscle Claudia Arakelian Follow
Of the 15 types of myosin in the myosin superfamily, only
 Three-dimensional image reconstruction of dephosphorylated smooth muscle heavy meromyosin reveals asymmetry in the interaction between myosin heads and placement of subfragment 2 Thomas Wendt*, Dianne
Three-dimensional image reconstruction of dephosphorylated smooth muscle heavy meromyosin reveals asymmetry in the interaction between myosin heads and placement of subfragment 2 Thomas Wendt*, Dianne
Universities of Leeds, Sheffield and York
 promoting access to White Rose research papers Universities of Leeds, Sheffield and York http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/ This is an author produced version of a paper published in Journal of Molecular
promoting access to White Rose research papers Universities of Leeds, Sheffield and York http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/ This is an author produced version of a paper published in Journal of Molecular
Biosensors. DNA Microarrays (for chemical analysis) Protein Sensors (for identifying viruses)
 Biosensors DNA Microarrays (for chemical analysis) Protein Sensors (for identifying viruses) DNA Microarrays 40 000 detectors in parallel, each detecting a specific DNA sequence. Combinatorial Chemistry
Biosensors DNA Microarrays (for chemical analysis) Protein Sensors (for identifying viruses) DNA Microarrays 40 000 detectors in parallel, each detecting a specific DNA sequence. Combinatorial Chemistry
Andrew D. Hollenbach, PhD Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Genetics 533 Bolivar St. New Orleans, LA 70112
 Andrew D. Hollenbach, PhD Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Genetics 533 Bolivar St. New Orleans, LA 70112 Phone: (504)568-2431 e-mail: aholle@lsuhsc.edu EDUCATION Research
Andrew D. Hollenbach, PhD Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Genetics 533 Bolivar St. New Orleans, LA 70112 Phone: (504)568-2431 e-mail: aholle@lsuhsc.edu EDUCATION Research
INTERACTION OF AMINOGLYCOSIDES AND OTHER ANTIBIOTICS. AKIRA SOMEYA and NoBuo TANAKA
 156 THE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS FEB. 1979 INTERACTION OF AMINOGLYCOSIDES AND OTHER ANTIBIOTICS WITH ACTIN AKIRA SOMEYA and NoBuo TANAKA Institute of Applied Microbiology, University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
156 THE JOURNAL OF ANTIBIOTICS FEB. 1979 INTERACTION OF AMINOGLYCOSIDES AND OTHER ANTIBIOTICS WITH ACTIN AKIRA SOMEYA and NoBuo TANAKA Institute of Applied Microbiology, University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan
Single Molecule Force Spectroscopy
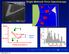 Single Molecule Force Spectroscopy force 0 250 pn rupture force counts cantilever-position x rupture force [pn] E.-L. Florin, V. T. Moy, H. E. Gaub, Science 264, 415 (1994) 1 Streptavidin/Biotin Unbinding
Single Molecule Force Spectroscopy force 0 250 pn rupture force counts cantilever-position x rupture force [pn] E.-L. Florin, V. T. Moy, H. E. Gaub, Science 264, 415 (1994) 1 Streptavidin/Biotin Unbinding
CURRICULUM VITAE FREDERICK S. GIMBLE ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF BIOCHEMISTRY
 CURRICULUM VITAE FREDERICK S. GIMBLE ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF BIOCHEMISTRY ADDRESS: Department of Biochemistry Purdue University 175 S. University St. West Lafayette, IN 47907-1153 Phone: (765) 494-1653
CURRICULUM VITAE FREDERICK S. GIMBLE ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR OF BIOCHEMISTRY ADDRESS: Department of Biochemistry Purdue University 175 S. University St. West Lafayette, IN 47907-1153 Phone: (765) 494-1653
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Drugs Modulate Interactions Between the First Nucleotide-Binding Domain and the Fourth Cytoplasmic Loop of Human P-glycoprotein Tip W. Loo and David M. Clarke Department of Medicine
Supporting Information Drugs Modulate Interactions Between the First Nucleotide-Binding Domain and the Fourth Cytoplasmic Loop of Human P-glycoprotein Tip W. Loo and David M. Clarke Department of Medicine
Challenges to measuring intracellular Ca 2+ Calmodulin: nature s Ca 2+ sensor
 Calcium Signals in Biological Systems Lecture 3 (2/9/0) Measuring intracellular Ca 2+ signals II: Genetically encoded Ca 2+ sensors Henry M. Colecraft, Ph.D. Challenges to measuring intracellular Ca 2+
Calcium Signals in Biological Systems Lecture 3 (2/9/0) Measuring intracellular Ca 2+ signals II: Genetically encoded Ca 2+ sensors Henry M. Colecraft, Ph.D. Challenges to measuring intracellular Ca 2+
Research Papers (EGFR) PCR (MIF) EcoR Not Bgl. Pyrobest Taq. (scfv) Progress in Biochemistry and Biophysics 2009, 36(3): 305~310
 Research Papers Progress in Biochemistry and Biophysics 29, 36(3): 35~31 wwwpibbaccn * 1, 2) 1) 1)** ( 1) 111 2) 139) (macrophage migration inhibitory factor MIF) 3 1C3 2A12 4E1 MIF 3 MIF Q5 R392 DOI:
Research Papers Progress in Biochemistry and Biophysics 29, 36(3): 35~31 wwwpibbaccn * 1, 2) 1) 1)** ( 1) 111 2) 139) (macrophage migration inhibitory factor MIF) 3 1C3 2A12 4E1 MIF 3 MIF Q5 R392 DOI:
Culture and Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cells to Form Specific, Functional Cell Types. NAS June 3, 2010
 Culture and Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cells to Form Specific, Functional Cell Types NAS June 3, 2010 hescs: Specific Cell Types Available On Demand for Numerous Applications Human Embryonic
Culture and Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cells to Form Specific, Functional Cell Types NAS June 3, 2010 hescs: Specific Cell Types Available On Demand for Numerous Applications Human Embryonic
Myosin II is involved in muscle contraction and cellular and
 Holding two heads together: Stability of the myosin II rod measured by resonance energy transfer between the heads Tania Chakrabarty*, Ming Xiao*, Roger Cooke, and Paul R. Selvin* *Physics Department and
Holding two heads together: Stability of the myosin II rod measured by resonance energy transfer between the heads Tania Chakrabarty*, Ming Xiao*, Roger Cooke, and Paul R. Selvin* *Physics Department and
7llffllIf. *b-ft FORMATION AND REMODELING OF THE EARLY MOUND MMTRIX(U) 1
 I *b-ft93 655 FORMATION AND REMODELING OF THE EARLY MOUND MMTRIX(U) 1 7llffllIf TEXAS IMIY MEDICAL DRAWNH AT GALVESTON DEPT OF WAUM BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY AMD GENETICS P N WEIGEL 11 MA SE UL SSIFIEO N@9014-S2-K-S2?9
I *b-ft93 655 FORMATION AND REMODELING OF THE EARLY MOUND MMTRIX(U) 1 7llffllIf TEXAS IMIY MEDICAL DRAWNH AT GALVESTON DEPT OF WAUM BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY AMD GENETICS P N WEIGEL 11 MA SE UL SSIFIEO N@9014-S2-K-S2?9
Phosphorylation of cardiac myosin binding protein C releases myosin heads from the surface of cardiac thick filaments
 Phosphorylation of cardiac myosin binding protein C releases myosin heads from the surface of cardiac thick filaments Robert W. Kensler a,1, Roger Craig b, and Richard L. Moss c a Department of Anatomy
Phosphorylation of cardiac myosin binding protein C releases myosin heads from the surface of cardiac thick filaments Robert W. Kensler a,1, Roger Craig b, and Richard L. Moss c a Department of Anatomy
5-Formyl- and 5-carboxyl-cytosine reduce the rate and substrate specificity. of RNA polymerase II transcription
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR 5-Formyl- and 5-carboxyl-cytosine reduce the rate and substrate specificity of RNA polymerase II transcription Matthew W. Kellinger 1, Chunxiao Song 2, Jenny Chong 1, Xingyu
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR 5-Formyl- and 5-carboxyl-cytosine reduce the rate and substrate specificity of RNA polymerase II transcription Matthew W. Kellinger 1, Chunxiao Song 2, Jenny Chong 1, Xingyu
Troponin T Isoform Regulation and Structure-Function Relationships. Jian-Ping Jin, Qi-Quan Huang, Ozgur Ogut, Aihua Chen and Jennifer Wang
 Troponin T Isoform Regulation and Structure-Function Relationships Jian-Ping Jin, Qi-Quan Huang, Ozgur Ogut, Aihua Chen and Jennifer Wang Department of Physiology and Biophysics, Case Western Reserve University
Troponin T Isoform Regulation and Structure-Function Relationships Jian-Ping Jin, Qi-Quan Huang, Ozgur Ogut, Aihua Chen and Jennifer Wang Department of Physiology and Biophysics, Case Western Reserve University
Topics in Fluorescence Spectroscopy. Volume 2 Principles
 Topics in Fluorescence Spectroscopy Volume 2 Principles Topics in Fluorescence Spectroscopy Edited by JOSEPH R. LAKOWICZ Volume 1: Techniques Volume 2: Principles Volume 3: Biochemical Applications Topics
Topics in Fluorescence Spectroscopy Volume 2 Principles Topics in Fluorescence Spectroscopy Edited by JOSEPH R. LAKOWICZ Volume 1: Techniques Volume 2: Principles Volume 3: Biochemical Applications Topics
