International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences DIAGNOSIS OF EMERGING DISEASES IN COMMERCIALLY IMPORTANT SHRIMP ABSTRACT
|
|
|
- Rebecca Wade
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Research Article Biotechonology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN DIAGNOSIS OF EMERGING DISEASES IN COMMERCIALLY IMPORTANT SHRIMP R.CAROLINE JEBA*AND MARIA SHIRLEY Department of Bio-technology, Dr.M.G.R.Educational And Research Institute University, Chennai, India. ABSTRACT As emerging diseases are known to cause a serious setback in shrimp aquaculture due to production and economic losses, it is essential to screen for such diseases. Hence, this study was formulated with the objective to understand the prevalence of emerging diseases affecting commercially important cultured shrimp White spot syndrome virus (WSSV), Infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis (IHHNV), Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Diseases (AHPND)/ Early Mortality Syndrome(EMS), Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei (EHP), Hepatopancreatic parvovirus (HPV), Yellow head disease (YHV), Monodon baculovirus (MBV). KEYWORDS: Emerging diseases, PCR, Wet mount, Microscopy, Histopathology. R.CAROLINE JEBA Department of Bio-technology, Dr.M.G.R.Educational And Research Institute University, Chennai, India. *Corresponding author B - 937
2 INTRODUCTION Aquaculture is one of the fastest growing food production sectors in the world (Subasinghe et al., 1998). Shrimp aquaculture has emerged as a valuable foreign exchange earner for developing countries and as an alternative to meet the protein requirement of the increasing world population. Aquaculture shrimps have been the primary contributors to the seafood industry s growth, contributing 47 per cent of the total exports. Shrimp exports were $3.2 billion in , which was 64 per cent of total exports, of which aquaculture shrimp alone was worth $2.3 billion. Shrimp exports from capture fisheries contributed only 27 per cent of total exports with a value of $900 million 1. Shrimp is the largest single seafood commodity by value, accounting for 17% of all internationally traded fishery products. Approximately 75% of production is from aquaculture which is now almost entirely dominated by two species the black shrimp (Penaeus monodon) and the white Pacific shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) that represent the most important invertebrate food animals 2. India s Marine Products Exports Development Authority (MPEDA, 2013) reports that 22,715 hectares of ponds are dedicated to vannamei farming, but seafood exporters, some of whom are themselves involved in shrimp farming, estimate that there may at least be 50,000 hectares of vannamei ponds 3. The major causes of shrimp diseases include microbial pathogens, inadequate control of the culture environment leading to stress and susceptibility to disease. Diseases are caused by various factors of which pathogenic and non pathogenic factors forms the major cause. Pathogenic diseases include bacterial, viral and parasitic infection. Non pathogenic includes water quality and other factors during the maintenance of the shrimp farm 4. According to Snieszsko (1997), disease is an end result of an interaction of the shrimp, its environment and the pathogens itself Viral diseases are major threat to shrimp farming operation worldwide 5.Of all the known shrimp viruses, White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV), Yellow Head Virus (YHV) and Taura Syndrome Viruses (TSV) are the most important viral pathogens affecting the shrimp culture industry. Hence it is important for screening virus and other emerging diseases to avoid the production and economic loss 6. Of all the known shrimp viruses, White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV), Yellow Head Virus (YHV) and Taura Syndrome Viruses (TSV) are the most important viral pathogens affecting the shrimp culture industry. Hence it is important for screening virus and other emerging diseases to avoid the production and economic loss 7. MATERIALS AND METHODS MATERIALS (i) Samples and codes Shrimp samples were collected from various shrimp farms in and around Ponneri, Thiruvallur district, Tamilnadu. Samples were brought either in live condition or fixed live at the site in aerated bags to lab facilities at Shrimp Disease Diagnostic Laboratory of Tamilnadu Fisheries University. B - 938
3 Table 1 Details of the shrimp samples used in the study S.NO Sample Code Date Sample Source Organs used for DNA extraction 1. FRF FREC Farm, Chennai Gill, Whole head 2. FRF FREC Farm, Chennai HP 3. FRF FREC Farm,Chennai Gill, HP 4. MA Manoj-Thevampattu, Ponneri Gill 5. MA Manoj-Thevampattu, Ponneri Gill 6. MA Manoj-Thevampattu, Ponneri Gill 7. SK Kanish, Ponneri Gill 8. SE Shrimp aqua farm,sirkazhi Gill 9. CD Cheenu aqua farm, Ponneri Gill 10. SD Sudhakar aqua farm, Ponneri Gill 11. M Manikandan farm,ponneri Gill, HP 12. AD Sirkazhi farm Gill, HP 13. FRF FREC Farm,Chennai Gill, HP 14. FRF Shrimp farm,chennai Gill, Muscle 15. S Pulicat,Chennai Gill, HP (ii) Chemicals and molecular biologicals used in the study 1. Ethyl alcohol Fixing of samples was done either with ethyl alcohol or Davidson s fixative. DNA extraction kit was used with the samples fixed in 70% alcohol (70% ethyl alcohol, 30ml distilled water). 2. Davidson s fixative Davidson s fixative solution used for fixing the samples for histopathology can be prepared by mixing the following ingredients (total, 900 ml) in an appropriate size container and mixing well. a. 300 ml distilled water b. 200 ml formalin (37% formaldehyde) c. 100 ml acetic acid d. 300 ml 95% alcohol 2. Malachite green preparation Malachite green was used to stain the wet mounts of hepatopancreas tissues in screening for MBV, HPV, EH in Shrimp. Malachite Green: 0.1g Distilled Water: 1000ml Wet mount of squashed hepatopancreatic tissue were prepared in clean glass slides and stained with 0.05% malachite green (Lightner, 1996). The slides were observed under the microscopic for the histological changes specific to MBV, HPV or EH. 3. DNA Extraction chemicals Commercially available DNA extraction kit was used to perform the DNA extraction of required parts from the samples collected for the study (QIAGEN DNA extraction kit, USA). 4. PCR chemicals PCR Primers Primers used for the diagnosis of the diseases of Shrimp are listed in table 3. The primers included self designed and published primers. B - 939
4 Table 2 PCR Primers for emerging diseases used for screening the samples Virus WSSV EMS IHHNV HPV MBV EH YHV Primers WSS330F: 5 -TGG-TCC-CGT-CCT-CAT-CTC-AG-3 WSS330R: 5 -GCT-GCC-TTG-CCG-GAA-ATT-A-3 Product Size 330 AP3F:5 -ATGAGTAACAATATAAAACATGAAAC-3 AP3R:5 -GTGGTAATAGATTGTACAGAA IHHNV703F:5 -TTG-GGG-ATG-CAG-CAA-TAT-CT-3 IHHNV703R:5 -GTC-CAT-CCA-CTG-ATC-GGA-CT-3 441F:5 CTA-CTC-CAA-TGG-AAA-CTT-CTGAGC-3 441R:5 -GTG-GCG-TTG-GAA-GGC-ACT-TC-3 261F: 5 -AAT-CCT-AGG-CGA-TCT-TAC-CA-3 261R: 5 -CGT-TCG-TTG-ATG-AAC-ATC-TC-3 MF1: 5 -CCG GAG AGG GAG CCT GAGA-3 MR1: 5 -GAC GGG CGG TGT GTA CAA A-3 10F: 5 -CCG-CTA-ATT-TCA-AAA-ACT-ACG-3 144R: 5 -AAG-GTG-TTA-TGT-CGA-GGA-AGT-3 Reference SRFDLA Kallaya Sritunyalucksana et al., 703 SRFDLA 441 SRFDLA 261 SRFDLA 951 Flegel et al., SRFDLA PCR Reaction Mix (PCR master mix) Commercial PCR master mix with optimized concentration if bases, buffer and Mgcl2 was used in the study (GeNei master mix, Bangalore, India). DNA marker Commercially available 100bp molecular marker was also separated parallely to compare the PCR amplified product (medoxbio molecular marker, Chennai, India). Agarose Molecular biology grade Agarose gel was prepared in TBE buffer with 4 µl ethidium bromide for gel electrophoresis. Gel documentation The amplified product in gel were observed under UV and documented using a gel documentation unit (BioRad). METHODS (i) Collection and fixing of sample Shrimp samples were collected from different places like Minjur, Ponneri, Sirkazhi, Nagpattinam and from the farm facilities available in Tamilnadu Fisheries University Madhavaram campus. Shrimp sample were brought to the laboratory in live condition in aerated polythene bags or they were fixed in ethyl alcohol immediately after collection. The shrimp samples were selected based on the wet mount/pcr results, coded and stored in deep freezer (-70 C) to be used for the experiments. (ii) Maintenance of the sample Shrimp samples were maintained with good aeration; adequate feeding and maintenance of water quality parameters at ideal levels in the wet lab of state referral laboratory, Tamilnadu Fisheries university (TNFU), Madhavaram. (iii) Screening of shrimp samples for diseases The samples were screened for the presence of White spot syndrome (WSSV), Monodon baculovirus (MBV), Hepatopancreatic Parvovirus (HPV), Yellow Head Virus (YHV), Early mortality syndrome (EMS), Enterocytozoan hepatopenaei (EH). The following methodologies were followed for screening. B - 940
5 Table 3 Methodologies followed for screening of emerging diseases Disease White spot syndrome virus Infectious hypodermal and haematopoietic necrosis Acute Hepato pancreatic Necrosis Disease Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei Hepatopancreatic parvovirus Yellow head virus Monodon baculovirus Methodology followed Wet mount Histopathology PCR Microbiology a) Wet mount diagnosis of HPV, EH Wet mount of squashed hepatopancreatic tissue from the collected sample were prepared in clean glass slides and stained with 0.05% malachite green and observed under the microscope for disease specific changes. b) Histopathology diagnosis of samples for IHHNV, WSSV Samples are fixed with Davidson s fixative for carrying out the histopathological study for IHHNV, WSSV. The fixing of samples were done with Davidson s fixative processing of samples, sectioning and staining were carried out following standard methods utilizing the services of the Department of veterinary pathology, Madras Veterinary college, Chennai-7. The diseases were identified by histopathology and they were documented for the result analysis. c) PCR diagnosis for emerging diseases WSSV, IHHNV, EH, YHV, EMS, MBV, HPV Shrimp samples were screened by PCR using the primers. Primers were selected for the diagnosis of the diseases of shrimp listed in the study (table 4). The primers included were self designed and published primers. PCR standard protocols were followed in case of self designed primers and protocols based on the published papers in case of published primers. Specific primers were designed for the diagnosis of WSSV, IHHNV, YHV, MBV and HPV with the sequence information available in the Gen Bank, NCBI. DNA Extraction Organ such as Gill, hepato pancrease and whole head were exercised from the Shrimp sample were used for the extraction as the target organ of the pathogens of interest vary. The extracted DNA was coded and stored in a deep freezer (- 70 C) for the further study. Specific extracted DNA part was selected for each disease and the target organ varies for every disease. Preparation of PCR mixture Reagents Quantity/concentration required/reaction PCR master mix 22 µl(1x) Forward primer 1 µl(30 picomoles/reaction) Reverse primer 1 µl(30 picomoles/reaction) DNA of target organ 1 µl(50mg) Total 25 µl B - 941
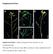
6 Agarose gel electrophoresis The amplified products from first step were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis. 2% agarose gel was prepared in 1X tris-borate EDTA buffer (TBE buffer) added with 4 µl ethidium bromide around 250ml was poured on the agarose gel electrophoresis apparatus.4 µl of PCR amplified product were loaded into performed wells of agarose gel.2 µl of 100bp molecular weight DNA ladder was also added in the gel comparing the size of the PCR products. Gel electrophoresis was carried out at 100 volts for 30min. After the run,the gel was viewed under UV gel documentation system. The results were documented, transferred and stored in the computer. RESULTS 1. Collection, fixing and maintenance of samples P.vannamei samples collected and maintained in the study is shown in Figure 1. Collection and maintenance of shrimp Figure 1 Collection and maintenance of shrimp samples used in the study with aeration in the wet lab during the study Shrimp samples were collected from various shrimp farms in and around Ponneri, Thiruvallur district, Tamilnadu. Samples were brought either in live condition or fixed live at the site in aerated bags to lab facilities at Shrimp Disease Diagnostic Laboratory of Tamilnadu Fisheries University. Fixing of samples is done either with 70% ethyl alcohol or Davidson s Fixative. Samples fixed with ethyl alcohol are used in DNA extraction and they are preserved for further study. Samples fixed with Davidson s Fixative are used in histopathological study. B - 942
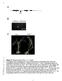
7 2. Isolation of Hepatopancreas Isolation of Hepatopancreas and gill Int J Pharm Bio Sci 2015 July; 6(3): (B) Figure 2 Hepatopancreas and gill of shrimp used for the extraction of DNA in molecular diagnosis by PCR 3. Wet mount squash preparation Monodon baculovirus Screening of the samples for MBV by wet mount squash method showed that none of the sample screened in this study showed characteristic occlusion bodies as shown in the Figure 3. Staining with malachite green revealed that the squash preparation contains occlusion bodies in the hepatopancreas of infected shrimp. Wet mount microscopic observation of hepatopancreas Figure 3 Hepatopancreas wet mount squash preparation showing MBV specific occlusion bodies The samples were showing HPV inclusion bodies when observed in the wet mount squash preparation in (100x magnification) of hepatopancreatic shrimp is shown in Figure 3.Hence the results of the squash preparation showed the presence of hepatopancreatic parvovirus in the cultured shrimp collected. B - 943
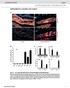
8 Wet mount microscopic observation of hepatopancreas Figure 4 HPV inclusion bodies observed in samples (100x magnification) compared with the results of previous study. Enterocytozoon Hepatopenaei The samples screened for E. hepatopenaei showed inclusion bodies observed in the hepatopancreas of shrimp in the wet mount preparation(100x magnification).the observed inclusion bodies were compared with the published literatures (Flegel et al.,) Wet mount microscopic observation of hepatopancreas Figure 5 E. hepatopenaei inclusion bodies observed in the hepatopancreas of shrimp (100x magnification) compared the results of previous study 4. Screening for diseases a) WSSV Shrimp samples showed white musculature which is being compared with the healthy shrimp is shown in (Figure 6 and 7) this shows that the white musculature is due to the shrimp affected by white spot syndrome. Shrimp samples were showing size variation which is due to the slow growth in the infected shrimps and mortality is shown in (Figure 8). B - 944
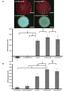
9 Shrimp showing mortality Figure 6 White musculature in WSSV infected P.vannamei compared to healthy shrimp which has a clear strature Figure 7 Shrimp showing mortality during the maintenance due to WSSV Infection. Shrimps showing size variation Figure 8 Size variation observed in the infected P.vannamei (slow growth) 5. Agarose gel electrophoresis WSSV PCR screening showed that the PCR amplified products of WSSV DNA. Presence of band formation relevant to the specific primers used 330 and 615 showed the presence of white spot syndrome in the cultured shrimps (Figure 9 and 10). B - 945
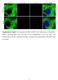
10 Agarose Gel Figure 9 Agarose gel shows the presence of Ethidium bromide dye (shown with an arrow) for WSSV 330 which is compared with the standard DNA marker run at the same time on the same gel cast (shown with an arrow M WSSV Figure 10 Agarose gel shows the presence of Ethidium bromide dye (shown with an arrow) for WSSV 615 which is compared with the standard DNA marker run at the same time on the same gel cast (shown with an arrow). WSSV M M WSSV IHHNV PCR screening for IHHNV showed amplification of IHHNV (703 bp) specific for IHHNV. B - 946
11 Figure 11 Agarose gel shows the presence of Ethidium bromide dye (shown with an arrow) for IHHNV 703 which is compared with the standard DNA marker run at the same time on the same gel cast (shown with an arrow). MBV, HPV IHHNV Although HPV inclusions were observed in a sample analysed by wet mount analysis, none of the samples screened for HPV/ MBV showed PCR amplification (Figure 12) which could be due to low level of infection or low detection limit of the PCR assay followed. M Figure 12 Agarose gel shows the absence of Ethidium bromide dye for MBV and HPV which is compared with the standard DNA marker run at the same time on the same gel cast (shown with an arrow). AHPND EMS was screened for the presence of vibrio bacteria on the TCBS plate is shown (Figure 13). B - 947
12 Figure 13 Formation of yellow and green colonies of vibrio species on TCBS agar plate due to the presence of parasite in P.vannamei showing AHPND infection. None of the samples screened for AHPND by PCR technique showed the PCR amplification of AHPND specific DNA hence showing the absence of the disease. Agarose Gel Figure 14 Agarose gel shows the absence of Ethidium bromide dye for AHPND which is compared with the standard DNA marker run at the same time on the same gel cast (shown with an arrow). 6. Histopathological studies Eosin - haematoxylin-counterstaining (blue) revealed distinct populations of stained cells with IHHNV showing absence of hemocyte aggregation and viral inclusions in the gills of shrimp. These staining of cells were completely absent for other formulation. The Blue staining (Haematoxylin) for the nuclei and the pink (Eosin) for the cytoplasm were clearly visualized for all the formulation under 100 X magnification. The eosin haematoxylin staining showed WSSV showing condensed B - 948
13 chromatin in the gills of shrimp blue large sized granular shaped structures which are a clear evident for the presence of Evans blue dye. Histology slides Figure 15 IHHNV showing absence of hemocyte aggregation and viral inclusions in the gills of shrimp (100x magnification) compared with the previous study. Figure 16 WSSV showing condensed chromatin in the gills of shrimp (100x magnification) compared with the previous study. DISCUSSION The results from the wet mount squash preparation showed that the hepatopancreas of none of the sample screened in this study showed characteristic occlusion bodies. Staining with malachite green revealed that the squash preparation contains occlusion bodies in the hepatopancreas of infected shrimp. The shrimp samples were showing HPV inclusion bodies when observed in the wet mount squash preparation in (100x magnification) of hepatopancreatic shrimp. Hence the results of the squash preparation showed the presence of hepatopancreatic parvovirus in the cultured shrimp collected.shrimp samples showed white musculature which is being compared with the healthy shrimp is shown in (Figure 6 and 7) this shows that the white musculature is due to the shrimp affected by white spot syndrome. Shrimp samples were showing size variation which is due to the slow growth in the infected shrimps and mortality is shown in (Figure 8). PCR screening showed that the PCR amplified products of WSSV DNA. Presence of band B - 949
14 formation relevant to the specific primers used 330 and 615 showed the presence of white spot syndrome in the cultured shrimps (Figure 9 and 10). PCR screening for IHHNV showed amplification of IHHNV (703 bp) specific for IHHNV. Although HPV inclusions were observed in a sample analysed by wet mount analysis, none of the samples screened for HPV/ MBV showed PCR amplification (Figure 12) which could be due to low level of infection or low detection limit of the PCR assay followed. EMS was screened for the presence of vibrio bacteria on the TCBS plate is shown (Figure 13). Eosin - haematoxylin-counterstaining (blue) revealed distinct populations of stained cells with IHHNV showing absence of hemocyte aggregation and viral inclusions in the gills of shrimp. These staining of cells was completely absent for other formulation. The Blue staining (Haematoxylin) for the nuclei and the pink (Eosin) for the cytoplasm were clearly visualized for all the formulation under 100 X magnification.the eosin haematoxylin staining showed WSSV showing condensed chromatin in the gills of shrimp blue large sized granular shaped structures which are a clear evident for the presence of Evans blue dye (Figure 15 and 16). CONCLUSION Thus, the shrimp aquaculture is facing a serious threat due to the emerging diseases which causes huge economic losses. Though the brooders which are transported stating viral free brooders may also contain a certain silent pathogen which emerges out once they attain maturity. Diseases in shrimp are mainly caused due to the stress which is caused during the maintenance of the shrimp culture. Hence it is very much important to screen the diseases which are more prevalently found and also the uncommon viral emerging diseases which bring about the major mortality range which causes a drastic loss both economically and commercially. REFERENCES 1. Lightner D.V, Biosecurity in shrimp farming: Pathogen exclusion through the use of SPF stock and routine surveillance. Shrimp aquaculture, 13 (12): , (2005). 2. Phromjai J, Sukhumsirichart W, Pantoja C, Lightner D.V. & Flegel T.W, Different reactions obtained using the same DNA detection reagents for Thai and Korean hepatopancreatic parvovirus of penaeid shrimp. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 46, , (2001). 3. Bondad-Reantaso M.G, Mcgladdery S.E, East.I & Subasinghe R.P, Asia Diagnostic Guide to Aquatic Animal Diseases. FAO Fisheries Technical Paper 402,(2001). 4. Bonnichon V, Bonami J.R.& Lightner D.V, Viral interference between infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV) and white spot syndrome virus in Litopenaeus vannamei. Dis. Aquat. Org., 72, , (2006). 5. Bray W.A., Lawrence A.L. & Leung-Trujillo J.R, The effect of salinity on growth and survival of Penaeus vannamei, with observations on the interaction of IHHN virus and salinity. Aquaculture, 122, , (1998). 6. Brock J.A. & Lightner D.V, Diseases of Crustaceans. Diseases Caused by Microorganisms. In: Diseases of Marine Animals, Vol. III, Kinne O., ed. Biologische Anstalt Helgoland, Hamburg, Germany, , (2006). 7. Brock J.A., Lightner D.V. & Bell T.A, A review of four virus (BP, MBV, BMN, and IHHNV) diseases of penaeid shrimp with particular reference to clinical significance, diagnosis and control in shrimp aquaculture, C.M. 1983/Gen:10/1 18, (2008). 8. Paynter, Bondad-Reantaso, Tourtip mari, Poultes, International journal of pharma and Bio sciences, Soc. 36, (2011). B - 950
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Dissecting binding of a β-barrel outer membrane
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Dissecting binding of a β-barrel outer membrane
Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC
 Supplementary Appendixes Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC ACG TAG CTC CGG CTG GA-3 for vimentin, /5AmMC6/TCC CTC GCG CGT GGC TTC CGC
Supplementary Appendixes Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC ACG TAG CTC CGG CTG GA-3 for vimentin, /5AmMC6/TCC CTC GCG CGT GGC TTC CGC
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1.
 Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
Supplementary. Table 1: Oligonucleotides and Plasmids. complementary to positions from 77 of the SRα '- GCT CTA GAG AAC TTG AAG TAC AGA CTG C
 Supplementary Table 1: Oligonucleotides and Plasmids 913954 5'- GCT CTA GAG AAC TTG AAG TAC AGA CTG C 913955 5'- CCC AAG CTT ACA GTG TGG CCA TTC TGC TG 223396 5'- CGA CGC GTA CAG TGT GGC CAT TCT GCT G
Supplementary Table 1: Oligonucleotides and Plasmids 913954 5'- GCT CTA GAG AAC TTG AAG TAC AGA CTG C 913955 5'- CCC AAG CTT ACA GTG TGG CCA TTC TGC TG 223396 5'- CGA CGC GTA CAG TGT GGC CAT TCT GCT G
Cat. # Product Size DS130 DynaExpress TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) 20 reactions Box 1 (-20 ) ptakn-2 Vector, linearized 20 µl (50 ng/µl) 1
 Product Name: Kit Component TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) Cat. # Product Size DS130 TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) 20 reactions Box 1 (-20 ) ptakn-2 Vector, linearized 20 µl (50 ng/µl) 1 2 Ligation Buffer
Product Name: Kit Component TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) Cat. # Product Size DS130 TA PCR Cloning Kit (ptakn-2) 20 reactions Box 1 (-20 ) ptakn-2 Vector, linearized 20 µl (50 ng/µl) 1 2 Ligation Buffer
strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular
![strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular](/thumbs/72/66361212.jpg) Additional file 2 Identification of AOX1 in P. pastoris GS115 with a Mut s phenotype Results and Discussion The HBsAg producing strain was originally identified as a Mut s (methanol utilization slow) strain
Additional file 2 Identification of AOX1 in P. pastoris GS115 with a Mut s phenotype Results and Discussion The HBsAg producing strain was originally identified as a Mut s (methanol utilization slow) strain
Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis Information Research). Exons
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis Information Research). Exons
Y-chromosomal haplogroup typing Using SBE reaction
 Schematic of multiplex PCR followed by SBE reaction Multiplex PCR Exo SAP purification SBE reaction 5 A 3 ddatp ddgtp 3 T 5 A G 3 T 5 3 5 G C 5 3 3 C 5 ddttp ddctp 5 T 3 T C 3 A 5 3 A 5 5 C 3 3 G 5 3 G
Schematic of multiplex PCR followed by SBE reaction Multiplex PCR Exo SAP purification SBE reaction 5 A 3 ddatp ddgtp 3 T 5 A G 3 T 5 3 5 G C 5 3 3 C 5 ddttp ddctp 5 T 3 T C 3 A 5 3 A 5 5 C 3 3 G 5 3 G
ABSTRACT. Department of Fishery Biology, Faculty of Fisheries, Kasetsart University, Bangkok 10900, Thailand.
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 38 : 236-240 (2004) Effect of Infectious Hypodermal and Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus (IHHNV) on Growth, Survival Rate and Histopathological Changes of Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 38 : 236-240 (2004) Effect of Infectious Hypodermal and Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus (IHHNV) on Growth, Survival Rate and Histopathological Changes of Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus
Lecture 10, 20/2/2002: The process of solution development - The CODEHOP strategy for automatic design of consensus-degenerate primers for PCR
 Lecture 10, 20/2/2002: The process of solution development - The CODEHOP strategy for automatic design of consensus-degenerate primers for PCR 1 The problem We wish to clone a yet unknown gene from a known
Lecture 10, 20/2/2002: The process of solution development - The CODEHOP strategy for automatic design of consensus-degenerate primers for PCR 1 The problem We wish to clone a yet unknown gene from a known
Legends for supplementary figures 1-3
 High throughput resistance profiling of Plasmodium falciparum infections based on custom dual indexing and Illumina next generation sequencing-technology Sidsel Nag 1,2 *, Marlene D. Dalgaard 3, Poul-Erik
High throughput resistance profiling of Plasmodium falciparum infections based on custom dual indexing and Illumina next generation sequencing-technology Sidsel Nag 1,2 *, Marlene D. Dalgaard 3, Poul-Erik
Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH).
 Bisulfite Treatment of DNA Dilute DNA sample to 2µg DNA in 50µl ddh 2 O. Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH). Incubate in a 37ºC water bath for 30 minutes. To 55µl samples
Bisulfite Treatment of DNA Dilute DNA sample to 2µg DNA in 50µl ddh 2 O. Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH). Incubate in a 37ºC water bath for 30 minutes. To 55µl samples
Supplementary Figure 1A A404 Cells +/- Retinoic Acid
 Supplementary Figure 1A A44 Cells +/- Retinoic Acid 1 1 H3 Lys4 di-methylation SM-actin VEC cfos (-) RA (+) RA 14 1 1 8 6 4 H3 Lys79 di-methylation SM-actin VEC cfos (-) RA (+) RA Supplementary Figure
Supplementary Figure 1A A44 Cells +/- Retinoic Acid 1 1 H3 Lys4 di-methylation SM-actin VEC cfos (-) RA (+) RA 14 1 1 8 6 4 H3 Lys79 di-methylation SM-actin VEC cfos (-) RA (+) RA Supplementary Figure
Hes6. PPARα. PPARγ HNF4 CD36
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Table Positions and Sequences of ChIP primers -63 AGGTCACTGCCA -79 AGGTCTGCTGTG Hes6-0067 GGGCAaAGTTCA ACOT -395 GGGGCAgAGTTCA PPARα -309 GGCTCAaAGTTCAaGTTCA CPTa
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Table Positions and Sequences of ChIP primers -63 AGGTCACTGCCA -79 AGGTCTGCTGTG Hes6-0067 GGGCAaAGTTCA ACOT -395 GGGGCAgAGTTCA PPARα -309 GGCTCAaAGTTCAaGTTCA CPTa
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. 1 Characterization of GSCs. a. Immunostaining of primary GSC spheres from GSC lines. Nestin (neural progenitor marker, red), TLX (green). Merged images of nestin,
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig. 1 Characterization of GSCs. a. Immunostaining of primary GSC spheres from GSC lines. Nestin (neural progenitor marker, red), TLX (green). Merged images of nestin,
MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kit Manual
 MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kit Manual Shipping and Storage MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kits are shipped on dry ice. Each kit contains a box with cloning reagents and an attached bag with Eco-Blue Competent Cells (optional).
MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kit Manual Shipping and Storage MacBlunt PCR Cloning Kits are shipped on dry ice. Each kit contains a box with cloning reagents and an attached bag with Eco-Blue Competent Cells (optional).
Announcement regarding free release of primers for specific detection of bacterial isolates that cause acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND)
 Announcement regarding free release of primers for specific detection of bacterial isolates that cause acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) From: Prof. T.W. Flegel Center of Excellence for Shrimp
Announcement regarding free release of primers for specific detection of bacterial isolates that cause acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) From: Prof. T.W. Flegel Center of Excellence for Shrimp
Materials Protein synthesis kit. This kit consists of 24 amino acids, 24 transfer RNAs, four messenger RNAs and one ribosome (see below).
 Protein Synthesis Instructions The purpose of today s lab is to: Understand how a cell manufactures proteins from amino acids, using information stored in the genetic code. Assemble models of four very
Protein Synthesis Instructions The purpose of today s lab is to: Understand how a cell manufactures proteins from amino acids, using information stored in the genetic code. Assemble models of four very
PCR-based Markers and Cut Flower Longevity in Carnation
 PCRbased Markers and Cut Flower Longevity in Carnation Laura De Benedetti, Luca Braglia, Simona Bruna, Gianluca Burchi *, Antonio Mercuri and Tito Schiva Istituto Sperimentale per la Floricoltura, Corso
PCRbased Markers and Cut Flower Longevity in Carnation Laura De Benedetti, Luca Braglia, Simona Bruna, Gianluca Burchi *, Antonio Mercuri and Tito Schiva Istituto Sperimentale per la Floricoltura, Corso
Dierks Supplementary Fig. S1
 Dierks Supplementary Fig. S1 ITK SYK PH TH K42R wt K42R (kinase deficient) R29C E42K Y323F R29C E42K Y323F (reduced phospholipid binding) (enhanced phospholipid binding) (reduced Cbl binding) E42K Y323F
Dierks Supplementary Fig. S1 ITK SYK PH TH K42R wt K42R (kinase deficient) R29C E42K Y323F R29C E42K Y323F (reduced phospholipid binding) (enhanced phospholipid binding) (reduced Cbl binding) E42K Y323F
Quantitative reverse-transcription PCR. Transcript levels of flgs, flgr, flia and flha were
 1 Supplemental methods 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 Quantitative reverse-transcription PCR. Transcript levels of flgs, flgr, flia and flha were monitored by quantitative reverse-transcription
1 Supplemental methods 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 Quantitative reverse-transcription PCR. Transcript levels of flgs, flgr, flia and flha were monitored by quantitative reverse-transcription
Supplemental Data. mir156-regulated SPL Transcription. Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering. Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana
 Cell, Volume 138 Supplemental Data mir156-regulated SPL Transcription Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana Jia-Wei Wang, Benjamin Czech, and Detlef Weigel Table S1. Interaction
Cell, Volume 138 Supplemental Data mir156-regulated SPL Transcription Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana Jia-Wei Wang, Benjamin Czech, and Detlef Weigel Table S1. Interaction
PGRP negatively regulates NOD-mediated cytokine production in rainbow trout liver cells
 Supplementary Information for: PGRP negatively regulates NOD-mediated cytokine production in rainbow trout liver cells Ju Hye Jang 1, Hyun Kim 2, Mi Jung Jang 2, Ju Hyun Cho 1,2,* 1 Research Institute
Supplementary Information for: PGRP negatively regulates NOD-mediated cytokine production in rainbow trout liver cells Ju Hye Jang 1, Hyun Kim 2, Mi Jung Jang 2, Ju Hyun Cho 1,2,* 1 Research Institute
ΔPDD1 x ΔPDD1. ΔPDD1 x wild type. 70 kd Pdd1. Pdd3
 Supplemental Fig. S1 ΔPDD1 x wild type ΔPDD1 x ΔPDD1 70 kd Pdd1 50 kd 37 kd Pdd3 Supplemental Fig. S1. ΔPDD1 strains express no detectable Pdd1 protein. Western blot analysis of whole-protein extracts
Supplemental Fig. S1 ΔPDD1 x wild type ΔPDD1 x ΔPDD1 70 kd Pdd1 50 kd 37 kd Pdd3 Supplemental Fig. S1. ΔPDD1 strains express no detectable Pdd1 protein. Western blot analysis of whole-protein extracts
Arabidopsis actin depolymerizing factor AtADF4 mediates defense signal transduction triggered by the Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrPphB
 Arabidopsis actin depolymerizing factor mediates defense signal transduction triggered by the Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrPphB Files in this Data Supplement: Supplemental Table S1 Supplemental Table
Arabidopsis actin depolymerizing factor mediates defense signal transduction triggered by the Pseudomonas syringae effector AvrPphB Files in this Data Supplement: Supplemental Table S1 Supplemental Table
Detection by PCR of hepatopancreatic parvovirus (HPV) and other viruses in hatchery-reared Penaeus monodon postlarvae
 DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Vol. 57: 141 146, 2003 Published December 3 Dis Aquat Org NOTE Detection by PCR of hepatopancreatic parvovirus (HPV) and other viruses in hatchery-reared Penaeus monodon postlarvae
DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Vol. 57: 141 146, 2003 Published December 3 Dis Aquat Org NOTE Detection by PCR of hepatopancreatic parvovirus (HPV) and other viruses in hatchery-reared Penaeus monodon postlarvae
Converting rabbit hybridoma into recombinant antibodies with effective transient production in an optimized human expression system
 Converting rabbit hybridoma into recombinant antibodies with effective transient production in an optimized human expression system Dr. Tim Welsink Molecular Biology Transient Gene Expression OUTLINE Short
Converting rabbit hybridoma into recombinant antibodies with effective transient production in an optimized human expression system Dr. Tim Welsink Molecular Biology Transient Gene Expression OUTLINE Short
Supporting Information. Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, 2006
 Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Supporting Information for Expanding the Genetic
Supporting Information Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Copyright Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69451 Weinheim, 2006 Supporting Information for Expanding the Genetic
11th Meeting of the Science Working Group. Lima, Peru, October 2012 SWG-11-JM-11
 11th Meeting of the Science Working Group Lima, Peru, 15-19 October 2012 Russian population genetics studies of jack mackerel in the South Pacific P.K.Afanasiev M.A.Rabchun A.I.Glubokov Introduction. In
11th Meeting of the Science Working Group Lima, Peru, 15-19 October 2012 Russian population genetics studies of jack mackerel in the South Pacific P.K.Afanasiev M.A.Rabchun A.I.Glubokov Introduction. In
Supporting information for Biochemistry, 1995, 34(34), , DOI: /bi00034a013
 Supporting information for Biochemistry, 1995, 34(34), 10807 10815, DOI: 10.1021/bi00034a013 LESNIK 10807-1081 Terms & Conditions Electronic Supporting Information files are available without a subscription
Supporting information for Biochemistry, 1995, 34(34), 10807 10815, DOI: 10.1021/bi00034a013 LESNIK 10807-1081 Terms & Conditions Electronic Supporting Information files are available without a subscription
ORFs and genes. Please sit in row K or forward
 ORFs and genes Please sit in row K or forward https://www.flickr.com/photos/teseum/3231682806/in/photostream/ Question: why do some strains of Vibrio cause cholera and others don t? Methods Mechanisms
ORFs and genes Please sit in row K or forward https://www.flickr.com/photos/teseum/3231682806/in/photostream/ Question: why do some strains of Vibrio cause cholera and others don t? Methods Mechanisms
Disease and selection in the human genome 3
 Disease and selection in the human genome 3 Ka/Ks revisited Please sit in row K or forward RBFD: human populations, adaptation and immunity Neandertal Museum, Mettman Germany Sequence genome Measure expression
Disease and selection in the human genome 3 Ka/Ks revisited Please sit in row K or forward RBFD: human populations, adaptation and immunity Neandertal Museum, Mettman Germany Sequence genome Measure expression
PCR analysis was performed to show the presence and the integrity of the var1csa and var-
 Supplementary information: Methods: Table S1: Primer Name Nucleotide sequence (5-3 ) DBL3-F tcc ccg cgg agt gaa aca tca tgt gac tg DBL3-R gac tag ttt ctt tca ata aat cac tcg c DBL5-F cgc cct agg tgc ttc
Supplementary information: Methods: Table S1: Primer Name Nucleotide sequence (5-3 ) DBL3-F tcc ccg cgg agt gaa aca tca tgt gac tg DBL3-R gac tag ttt ctt tca ata aat cac tcg c DBL5-F cgc cct agg tgc ttc
Putth Songsangjinda Senior Expert on Marine Shrimp Culture Department of Fisheries, Thailand
 Putth Songsangjinda Senior Expert on Marine Shrimp Culture Department of Fisheries, Thailand 2700 km of coastal line Located at the tropical climate, Ideal for coastal aquaculture Basic biophysical of
Putth Songsangjinda Senior Expert on Marine Shrimp Culture Department of Fisheries, Thailand 2700 km of coastal line Located at the tropical climate, Ideal for coastal aquaculture Basic biophysical of
Supplemental Table 1. Mutant ADAMTS3 alleles detected in HEK293T clone 4C2. WT CCTGTCACTTTGGTTGATAGC MVLLSLWLIAAALVEVR
 Supplemental Dataset Supplemental Table 1. Mutant ADAMTS3 alleles detected in HEK293T clone 4C2. DNA sequence Amino acid sequence WT CCTGTCACTTTGGTTGATAGC MVLLSLWLIAAALVEVR Allele 1 CCTGTC------------------GATAGC
Supplemental Dataset Supplemental Table 1. Mutant ADAMTS3 alleles detected in HEK293T clone 4C2. DNA sequence Amino acid sequence WT CCTGTCACTTTGGTTGATAGC MVLLSLWLIAAALVEVR Allele 1 CCTGTC------------------GATAGC
RPA-AB RPA-C Supplemental Figure S1: SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie Blue after protein purification.
 RPA-AB RPA-C (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) Supplemental Figure S: SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie Blue after protein purification. (a) RPA; (b) RPA-AB; (c) RPA-CDE; (d) RPA-CDE core; (e) RPA-DE; and (f) RPA-C
RPA-AB RPA-C (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) Supplemental Figure S: SDS-PAGE stained with Coomassie Blue after protein purification. (a) RPA; (b) RPA-AB; (c) RPA-CDE; (d) RPA-CDE core; (e) RPA-DE; and (f) RPA-C
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Transfection of DNA Cages into Mammalian Cells Email: a.turberfield@physics.ox.ac.uk Table of Contents Supporting Figure 1 DNA tetrahedra used in transfection experiments 2 Supporting
Supporting Information Transfection of DNA Cages into Mammalian Cells Email: a.turberfield@physics.ox.ac.uk Table of Contents Supporting Figure 1 DNA tetrahedra used in transfection experiments 2 Supporting
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/10/494/eaan6284/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Activation of master virulence regulator PhoP in acidic ph requires the Salmonella-specific protein UgtL Jeongjoon
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/10/494/eaan6284/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Activation of master virulence regulator PhoP in acidic ph requires the Salmonella-specific protein UgtL Jeongjoon
hcd1tg/hj1tg/ ApoE-/- hcd1tg/hj1tg/ ApoE+/+
 ApoE+/+ ApoE-/- ApoE-/- H&E (1x) Supplementary Figure 1. No obvious pathology is observed in the colon of diseased ApoE-/me. Colon samples were fixed in 1% formalin and laid out in Swiss rolls for paraffin
ApoE+/+ ApoE-/- ApoE-/- H&E (1x) Supplementary Figure 1. No obvious pathology is observed in the colon of diseased ApoE-/me. Colon samples were fixed in 1% formalin and laid out in Swiss rolls for paraffin
Supplementary Information. Construction of Lasso Peptide Fusion Proteins
 Supplementary Information Construction of Lasso Peptide Fusion Proteins Chuhan Zong 1, Mikhail O. Maksimov 2, A. James Link 2,3 * Departments of 1 Chemistry, 2 Chemical and Biological Engineering, and
Supplementary Information Construction of Lasso Peptide Fusion Proteins Chuhan Zong 1, Mikhail O. Maksimov 2, A. James Link 2,3 * Departments of 1 Chemistry, 2 Chemical and Biological Engineering, and
Supplemental material
 Supplemental material Diversity of O-antigen repeat-unit structures can account for the substantial sequence variation of Wzx translocases Yaoqin Hong and Peter R. Reeves School of Molecular Bioscience,
Supplemental material Diversity of O-antigen repeat-unit structures can account for the substantial sequence variation of Wzx translocases Yaoqin Hong and Peter R. Reeves School of Molecular Bioscience,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Table S1. Oligonucleotide sequences used in this work Oligo DNA A B C D CpG-A CpG-B CpG-C CpG-D Sequence 5 ACA TTC CTA AGT CTG AAA CAT TAC AGC TTG CTA CAC GAG AAG AGC CGC CAT AGT
Supporting Information Table S1. Oligonucleotide sequences used in this work Oligo DNA A B C D CpG-A CpG-B CpG-C CpG-D Sequence 5 ACA TTC CTA AGT CTG AAA CAT TAC AGC TTG CTA CAC GAG AAG AGC CGC CAT AGT
Occurrence of Multiple Viruses in Penaeus monodon Shrimp Ponds and Their Effect on Shrimp Production
 Occurrence of Multiple Viruses in Penaeus monodon Shrimp Ponds and Their Effect on Shrimp Production UMESHA KANASINAKATTE RUDRAPPA, ANIRBAN CHAKRABORTY, VENUGOPAL, M. NAGARAJAPPA, INDRANI KARUNASAGAR and
Occurrence of Multiple Viruses in Penaeus monodon Shrimp Ponds and Their Effect on Shrimp Production UMESHA KANASINAKATTE RUDRAPPA, ANIRBAN CHAKRABORTY, VENUGOPAL, M. NAGARAJAPPA, INDRANI KARUNASAGAR and
Supplemental Data. Bennett et al. (2010). Plant Cell /tpc
 BRN1 ---------MSSSNGGVPPGFRFHPTDEELLHYYLKKKISYEKFEMEVIKEVDLNKIEPWDLQDRCKIGSTPQNEWYFFSHKDRKYPTGS 81 BRN2 --------MGSSSNGGVPPGFRFHPTDEELLHYYLKKKISYQKFEMEVIREVDLNKLEPWDLQERCKIGSTPQNEWYFFSHKDRKYPTGS 82 SMB
BRN1 ---------MSSSNGGVPPGFRFHPTDEELLHYYLKKKISYEKFEMEVIKEVDLNKIEPWDLQDRCKIGSTPQNEWYFFSHKDRKYPTGS 81 BRN2 --------MGSSSNGGVPPGFRFHPTDEELLHYYLKKKISYQKFEMEVIREVDLNKLEPWDLQERCKIGSTPQNEWYFFSHKDRKYPTGS 82 SMB
Gene synthesis by circular assembly amplification
 Gene synthesis by circular assembly amplification Duhee Bang & George M Church Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Dpo4 gene (1.05kb) construction by various methods. Supplementary
Gene synthesis by circular assembly amplification Duhee Bang & George M Church Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Dpo4 gene (1.05kb) construction by various methods. Supplementary
Supplemental Information. Human Senataxin Resolves RNA/DNA Hybrids. Formed at Transcriptional Pause Sites. to Promote Xrn2-Dependent Termination
 Supplemental Information Molecular Cell, Volume 42 Human Senataxin Resolves RNA/DNA Hybrids Formed at Transcriptional Pause Sites to Promote Xrn2-Dependent Termination Konstantina Skourti-Stathaki, Nicholas
Supplemental Information Molecular Cell, Volume 42 Human Senataxin Resolves RNA/DNA Hybrids Formed at Transcriptional Pause Sites to Promote Xrn2-Dependent Termination Konstantina Skourti-Stathaki, Nicholas
II 0.95 DM2 (RPP1) DM3 (At3g61540) b
 Table S2. F 2 Segregation Ratios at 16 C, Related to Figure 2 Cross n c Phenotype Model e 2 Locus A Locus B Normal F 1 -like Enhanced d Uk-1/Uk-3 149 64 36 49 DM2 (RPP1) DM1 (SSI4) a Bla-1/Hh-0 F 3 111
Table S2. F 2 Segregation Ratios at 16 C, Related to Figure 2 Cross n c Phenotype Model e 2 Locus A Locus B Normal F 1 -like Enhanced d Uk-1/Uk-3 149 64 36 49 DM2 (RPP1) DM1 (SSI4) a Bla-1/Hh-0 F 3 111
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for PCR.
 Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for PCR. Gene Type Primer Sequence Genotyping and semi-quantitative RT-PCR F 5 -TTG CCC GAT CAC CAT CTG TA-3 rwa1-1 R 5 -TGT AGC GAT CAA GGC CTG ATC TAA-3 LB 5 -TAG CAT
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for PCR. Gene Type Primer Sequence Genotyping and semi-quantitative RT-PCR F 5 -TTG CCC GAT CAC CAT CTG TA-3 rwa1-1 R 5 -TGT AGC GAT CAA GGC CTG ATC TAA-3 LB 5 -TAG CAT
Anti-White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) monoclonal antibody. Product no: P13
 Anti-White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) monoclonal antibody Product no: P13 Product Description The monoclonal antibody (Mab) against the Vp28 protein of White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) is specific for
Anti-White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) monoclonal antibody Product no: P13 Product Description The monoclonal antibody (Mab) against the Vp28 protein of White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) is specific for
Project 07/111 Final Report October 31, Project Title: Cloning and expression of porcine complement C3d for enhanced vaccines
 Project 07/111 Final Report October 31, 2007. Project Title: Cloning and expression of porcine complement C3d for enhanced vaccines Project Leader: Dr Douglas C. Hodgins (519-824-4120 Ex 54758, fax 519-824-5930)
Project 07/111 Final Report October 31, 2007. Project Title: Cloning and expression of porcine complement C3d for enhanced vaccines Project Leader: Dr Douglas C. Hodgins (519-824-4120 Ex 54758, fax 519-824-5930)
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS Supplementary Table S1: Water sampling sites in Brisbane River and their characteristics Sampling sites GPS coordinates Site characteristics Suspected source of fecal pollution
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS Supplementary Table S1: Water sampling sites in Brisbane River and their characteristics Sampling sites GPS coordinates Site characteristics Suspected source of fecal pollution
Supporting Online Information
 Supporting Online Information Isolation of Human Genomic DNA Sequences with Expanded Nucleobase Selectivity Preeti Rathi, Sara Maurer, Grzegorz Kubik and Daniel Summerer* Department of Chemistry and Chemical
Supporting Online Information Isolation of Human Genomic DNA Sequences with Expanded Nucleobase Selectivity Preeti Rathi, Sara Maurer, Grzegorz Kubik and Daniel Summerer* Department of Chemistry and Chemical
Overexpression Normal expression Overexpression Normal expression. 26 (21.1%) N (%) P-value a N (%)
 SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Table S1. Alteration of ZNF322A protein expression levels in relation to clinicopathological parameters in 123 Asian and 74 Caucasian lung cancer patients. Asian patients Caucasian
SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Table S1. Alteration of ZNF322A protein expression levels in relation to clinicopathological parameters in 123 Asian and 74 Caucasian lung cancer patients. Asian patients Caucasian
Occurrence of viruses in apple and pear orchards in Latvia.
 INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE Sustainable Fruit Growing: From Plant to Product Occurrence of viruses in apple and pear orchards in Latvia. Neda P pola, Anna K le, Inga Moro ko Bi evska. The economically
INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE Sustainable Fruit Growing: From Plant to Product Occurrence of viruses in apple and pear orchards in Latvia. Neda P pola, Anna K le, Inga Moro ko Bi evska. The economically
S4B fluorescence (AU)
 A S4B fluorescence (AU) S4B fluorescence (AU) dsbb csgba csgd dsbb csgba bcsa 5000 * NS NS 4000 * 3000 2000 1000 0 ΔcsgBAΔbcsA ΔcsgDΔdsbBΔbcsA ΔcsgBA ΔdsbBΔcsgBA ΔcsgDΔdsbB B -1000 4000 * * NS 3500 * 3000
A S4B fluorescence (AU) S4B fluorescence (AU) dsbb csgba csgd dsbb csgba bcsa 5000 * NS NS 4000 * 3000 2000 1000 0 ΔcsgBAΔbcsA ΔcsgDΔdsbBΔbcsA ΔcsgBA ΔdsbBΔcsgBA ΔcsgDΔdsbB B -1000 4000 * * NS 3500 * 3000
NAME:... MODEL ANSWER... STUDENT NUMBER:... Maximum marks: 50. Internal Examiner: Hugh Murrell, Computer Science, UKZN
 COMP710, Bioinformatics with Julia, Test One, Thursday the 20 th of April, 2017, 09h30-11h30 1 NAME:...... MODEL ANSWER... STUDENT NUMBER:...... Maximum marks: 50 Internal Examiner: Hugh Murrell, Computer
COMP710, Bioinformatics with Julia, Test One, Thursday the 20 th of April, 2017, 09h30-11h30 1 NAME:...... MODEL ANSWER... STUDENT NUMBER:...... Maximum marks: 50 Internal Examiner: Hugh Murrell, Computer
Multiplexing Genome-scale Engineering
 Multiplexing Genome-scale Engineering Harris Wang, Ph.D. Department of Systems Biology Department of Pathology & Cell Biology http://wanglab.c2b2.columbia.edu Rise of Genomics An Expanding Toolbox Esvelt
Multiplexing Genome-scale Engineering Harris Wang, Ph.D. Department of Systems Biology Department of Pathology & Cell Biology http://wanglab.c2b2.columbia.edu Rise of Genomics An Expanding Toolbox Esvelt
Table S1. Bacterial strains (Related to Results and Experimental Procedures)
 Table S1. Bacterial strains (Related to Results and Experimental Procedures) Strain number Relevant genotype Source or reference 1045 AB1157 Graham Walker (Donnelly and Walker, 1989) 2458 3084 (MG1655)
Table S1. Bacterial strains (Related to Results and Experimental Procedures) Strain number Relevant genotype Source or reference 1045 AB1157 Graham Walker (Donnelly and Walker, 1989) 2458 3084 (MG1655)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature07182 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES AND TABLES Fig. S1. myf5-expressing cells give rise to brown fat depots and skeletal muscle (a) Perirenal BAT from control (cre negative) and myf5-cre:r26r3-yfp
doi: 10.1038/nature07182 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURES AND TABLES Fig. S1. myf5-expressing cells give rise to brown fat depots and skeletal muscle (a) Perirenal BAT from control (cre negative) and myf5-cre:r26r3-yfp
UNOFFICIAL TRANSLATION
 UNOFFICIAL TRANSLATION MINISTERIAL REGULATION ON THE ESTABLISHMENT OF THAI AGRICULTURAL STANDARD ON GOOD AQUACULTURE PRACTICES FOR HATCHERY OF DISEASE FREE PACIFIC WHITE SHRIMP (Litopenaeus vannamei) AS
UNOFFICIAL TRANSLATION MINISTERIAL REGULATION ON THE ESTABLISHMENT OF THAI AGRICULTURAL STANDARD ON GOOD AQUACULTURE PRACTICES FOR HATCHERY OF DISEASE FREE PACIFIC WHITE SHRIMP (Litopenaeus vannamei) AS
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Investigation of the Biosynthesis of the Lasso Peptide Chaxapeptin Using an E. coli-based Production System Helena Martin-Gómez, Uwe Linne, Fernando Albericio, Judit Tulla-Puche,*
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Investigation of the Biosynthesis of the Lasso Peptide Chaxapeptin Using an E. coli-based Production System Helena Martin-Gómez, Uwe Linne, Fernando Albericio, Judit Tulla-Puche,*
SAY IT WITH DNA: Protein Synthesis Activity by Larry Flammer
 TEACHER S GUIDE SAY IT WITH DNA: Protein Synthesis Activity by Larry Flammer SYNOPSIS This activity uses the metaphor of decoding a secret message for the Protein Synthesis process. Students teach themselves
TEACHER S GUIDE SAY IT WITH DNA: Protein Synthesis Activity by Larry Flammer SYNOPSIS This activity uses the metaphor of decoding a secret message for the Protein Synthesis process. Students teach themselves
Sequencing of DNA lesions facilitated by site-specific excision via base. excision repair DNA glycosylases yielding ligatable gaps
 Supporting information Sequencing of DNA lesions facilitated by site-specific excision via base excision repair DNA glycosylases yielding ligatable gaps Jan Riedl, Aaron M. Fleming, and Cynthia J. Burrows*
Supporting information Sequencing of DNA lesions facilitated by site-specific excision via base excision repair DNA glycosylases yielding ligatable gaps Jan Riedl, Aaron M. Fleming, and Cynthia J. Burrows*
Supporting Information. Trifluoroacetophenone-Linked Nucleotides and DNA for Studying of DNA-protein Interactions by 19 F NMR Spectroscopy
 Supporting Information Trifluoroacetophenone-Linked Nucleotides and DNA for Studying of DNA-protein Interactions by 19 F NMR Spectroscopy Agata Olszewska, Radek Pohl and Michal Hocek # * Institute of Organic
Supporting Information Trifluoroacetophenone-Linked Nucleotides and DNA for Studying of DNA-protein Interactions by 19 F NMR Spectroscopy Agata Olszewska, Radek Pohl and Michal Hocek # * Institute of Organic
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Barderas et al. 10.1073/pnas.0801221105 SI Text: Docking of gastrin to Constructed scfv Models Interactive predocking of the 4-WL-5 motif into the central pocket observed in the
Supporting Information Barderas et al. 10.1073/pnas.0801221105 SI Text: Docking of gastrin to Constructed scfv Models Interactive predocking of the 4-WL-5 motif into the central pocket observed in the
Search for and Analysis of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) in Rice (Oryza sativa, Oryza rufipogon) and Establishment of SNP Markers
 DNA Research 9, 163 171 (2002) Search for and Analysis of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) in Rice (Oryza sativa, Oryza rufipogon) and Establishment of SNP Markers Shinobu Nasu, Junko Suzuki, Rieko
DNA Research 9, 163 171 (2002) Search for and Analysis of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) in Rice (Oryza sativa, Oryza rufipogon) and Establishment of SNP Markers Shinobu Nasu, Junko Suzuki, Rieko
Lecture 11: Gene Prediction
 Lecture 11: Gene Prediction Study Chapter 6.11-6.14 1 Gene: A sequence of nucleotides coding for protein Gene Prediction Problem: Determine the beginning and end positions of genes in a genome Where are
Lecture 11: Gene Prediction Study Chapter 6.11-6.14 1 Gene: A sequence of nucleotides coding for protein Gene Prediction Problem: Determine the beginning and end positions of genes in a genome Where are
Anti-Pim-1 (Cat#3247), anti-met (Cat#3127), anti-ron (Cat#2654), Anti-EGFR
 Supplementary Methods Antibodies Anti-Pim-1 (Cat#3247), anti-met (Cat#3127), anti-ron (Cat#2654), Anti-EGFR (Cat#2646), anti-igf1r (Cat#3018), anti-insr (Cat#3020), anti-akt (pan, Cat#4691), anti-phospho-akt
Supplementary Methods Antibodies Anti-Pim-1 (Cat#3247), anti-met (Cat#3127), anti-ron (Cat#2654), Anti-EGFR (Cat#2646), anti-igf1r (Cat#3018), anti-insr (Cat#3020), anti-akt (pan, Cat#4691), anti-phospho-akt
Expression of Recombinant Proteins
 Expression of Recombinant Proteins Uses of Cloned Genes sequencing reagents (eg, probes) protein production insufficient natural quantities modify/mutagenesis library screening Expression Vector Features
Expression of Recombinant Proteins Uses of Cloned Genes sequencing reagents (eg, probes) protein production insufficient natural quantities modify/mutagenesis library screening Expression Vector Features
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature11496 Cl. 8 Cl. E93 Rag1 -/- 3H9 + BM Rag1 -/- BM CD CD c-kit c-kit c-kit wt Spleen c-kit B22 B22 IgM IgM IgM Supplementary Figure 1. FACS analysis of single-cell-derived pre-b cell clones.
doi:1.138/nature11496 Cl. 8 Cl. E93 Rag1 -/- 3H9 + BM Rag1 -/- BM CD CD c-kit c-kit c-kit wt Spleen c-kit B22 B22 IgM IgM IgM Supplementary Figure 1. FACS analysis of single-cell-derived pre-b cell clones.
SUPPORTING INFORMATION FILE
 Intrinsic and extrinsic connections of Tet3 dioxygenase with CXXC zinc finger modules Nan Liu, Mengxi Wang, Wen Deng, Christine S. Schmidt, Weihua Qin, Heinrich Leonhardt and Fabio Spada Department of
Intrinsic and extrinsic connections of Tet3 dioxygenase with CXXC zinc finger modules Nan Liu, Mengxi Wang, Wen Deng, Christine S. Schmidt, Weihua Qin, Heinrich Leonhardt and Fabio Spada Department of
2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Supplemental Table 1. Magnaporthe oryzae strains generated in this study. Strain background Genotype Strain name Description Guy-11 H1:RFP H1:RFP Strain expressing Histone H1- encoding gene
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Supplemental Table 1. Magnaporthe oryzae strains generated in this study. Strain background Genotype Strain name Description Guy-11 H1:RFP H1:RFP Strain expressing Histone H1- encoding gene
Anil Kumar Moola. Index Terms Exotic species, internal mortality syndrome, shrimp diseases, Histological studies, Non-biological agents.
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 1, January-2015 756 STUDY ON NEW SHRIMP DISEASE Internal mortality syndrome OF EXOTIC SPECIES litopenaeus vannamei Anil Kumar
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 6, Issue 1, January-2015 756 STUDY ON NEW SHRIMP DISEASE Internal mortality syndrome OF EXOTIC SPECIES litopenaeus vannamei Anil Kumar
Emerging Diseases of Concerns in Shrimp Aquaculture: Biology, Genomics and Management Practices
 Emerging Diseases of Concerns in Shrimp Aquaculture: Biology, Genomics and Management Practices Arun K. Dhar, PhD Aquaculture Pathology Laboratory The University of Arizona Tucson, Arizona, USA Agenda
Emerging Diseases of Concerns in Shrimp Aquaculture: Biology, Genomics and Management Practices Arun K. Dhar, PhD Aquaculture Pathology Laboratory The University of Arizona Tucson, Arizona, USA Agenda
OIE Reference Laboratory Reports Activities
 OIE Reference Laboratory Reports Activities Activities in 2014 This report has been submitted : 2015-01-12 14:55:35 Name of disease (or topic) for which you are a designated OIE Reference Laboratory: White
OIE Reference Laboratory Reports Activities Activities in 2014 This report has been submitted : 2015-01-12 14:55:35 Name of disease (or topic) for which you are a designated OIE Reference Laboratory: White
Table S1. Sequences of mutagenesis primers used to create altered rdpa- and sdpa genes
 Supplementary Table and Figures for Structural Basis for the Enantiospecificities of R- and S-Specific Phenoxypropionate/α-Ketoglutarate Dioxygenases by Tina A. Müller, Maria I. Zavodszky, Michael Feig,
Supplementary Table and Figures for Structural Basis for the Enantiospecificities of R- and S-Specific Phenoxypropionate/α-Ketoglutarate Dioxygenases by Tina A. Müller, Maria I. Zavodszky, Michael Feig,
Supplementary Methods Quantitative RT-PCR. For mrna, total RNA was prepared using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen) and genomic DNA was eliminated with TURB
 Supplementary Methods Quantitative RT-PCR. For mrna, total RNA was prepared using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen) and genomic DNA was eliminated with TURBO DNA-free Kit (Ambion). One µg of total RNA was reverse
Supplementary Methods Quantitative RT-PCR. For mrna, total RNA was prepared using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen) and genomic DNA was eliminated with TURBO DNA-free Kit (Ambion). One µg of total RNA was reverse
Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of MST1 in RPE cells. Proliferating or ciliated HA- MST1 expressing RPE cells (see Fig. 5b for establishment of
 Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of MST1 in RPE cells. Proliferating or ciliated HA- MST1 expressing RPE cells (see Fig. 5b for establishment of the cell line) were immunostained for HA, acetylated
Supplementary Figure 1. Localization of MST1 in RPE cells. Proliferating or ciliated HA- MST1 expressing RPE cells (see Fig. 5b for establishment of the cell line) were immunostained for HA, acetylated
The B1 Protein Guides the Biosynthesis of a Lasso Peptide
 The B1 Protein Guides the Biosynthesis of a Lasso Peptide Shaozhou Zhu 1,2, Christopher D. Fage 1, Julian D. Hegemann 1, Andreas Mielcarek 1, Dushan Yan 1, Uwe Linne 1 & Mohamed A. Marahiel*,1 1 Department
The B1 Protein Guides the Biosynthesis of a Lasso Peptide Shaozhou Zhu 1,2, Christopher D. Fage 1, Julian D. Hegemann 1, Andreas Mielcarek 1, Dushan Yan 1, Uwe Linne 1 & Mohamed A. Marahiel*,1 1 Department
Norhaziyah Halim Aquatic Animal Health Services Centre Department of Fisheries
 ASEAN Regional Technical Consultation on Aquatic Emergency Preparedness and Response Systems for Effective Management of Transboundary Disease Outbreaks in Southeast Asia Country Report: Brunei Darussalam
ASEAN Regional Technical Consultation on Aquatic Emergency Preparedness and Response Systems for Effective Management of Transboundary Disease Outbreaks in Southeast Asia Country Report: Brunei Darussalam
NESTED Sequence-based Typing (SBT) protocol for epidemiological typing of Legionella pneumophila directly from clinical samples
 NESTED Sequence-based Typing (SBT) protocol for epidemiological typing of Legionella pneumophila directly from clinical samples VERSION 2.0 SUMMARY This procedure describes the use of nested Sequence-Based
NESTED Sequence-based Typing (SBT) protocol for epidemiological typing of Legionella pneumophila directly from clinical samples VERSION 2.0 SUMMARY This procedure describes the use of nested Sequence-Based
PILRα Is a Herpes Simplex Virus-1 Entry Coreceptor That Associates with Glycoprotein B
 Satoh et al. Page S1 Cell, Volume 132 PILRα Is a Herpes Simplex Virus-1 Entry Coreceptor That Associates with Glycoprotein B Takeshi Satoh, Jun Arii, Tadahiro Suenaga, Jing Wang, Amane Kogure, Junji Uehori,
Satoh et al. Page S1 Cell, Volume 132 PILRα Is a Herpes Simplex Virus-1 Entry Coreceptor That Associates with Glycoprotein B Takeshi Satoh, Jun Arii, Tadahiro Suenaga, Jing Wang, Amane Kogure, Junji Uehori,
-15 diopter negative lenses in wild-type and homozygous CHRM2-deleted mice, and
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure 1: Myopia induction was performed using uniocular -10 and -15 diopter negative lenses in wild-type and homozygous CHRM2-deleted mice, and results at 2, 4 and
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure 1: Myopia induction was performed using uniocular -10 and -15 diopter negative lenses in wild-type and homozygous CHRM2-deleted mice, and results at 2, 4 and
G+C content. 1 Introduction. 2 Chromosomes Topology & Counts. 3 Genome size. 4 Replichores and gene orientation. 5 Chirochores.
 1 Introduction 2 Chromosomes Topology & Counts 3 Genome size 4 Replichores and gene orientation 5 Chirochores 6 7 Codon usage 121 marc.bailly-bechet@univ-lyon1.fr Bacterial genome structures Introduction
1 Introduction 2 Chromosomes Topology & Counts 3 Genome size 4 Replichores and gene orientation 5 Chirochores 6 7 Codon usage 121 marc.bailly-bechet@univ-lyon1.fr Bacterial genome structures Introduction
Fig. S1: Nkx2.2 is specifically deleted in the intestinal epithelium.
 Fig. S1: Nkx2.2 is specifically deleted in the intestinal epithelium. PCR of representative tissues with oligonucleotides to identify recombination of the Nkx2.2flox allele. Nkx2.2 is specifically deleted
Fig. S1: Nkx2.2 is specifically deleted in the intestinal epithelium. PCR of representative tissues with oligonucleotides to identify recombination of the Nkx2.2flox allele. Nkx2.2 is specifically deleted
Homework. A bit about the nature of the atoms of interest. Project. The role of electronega<vity
 Homework Why cited articles are especially useful. citeulike science citation index When cutting and pasting less is more. Project Your protein: I will mail these out this weekend If you haven t gotten
Homework Why cited articles are especially useful. citeulike science citation index When cutting and pasting less is more. Project Your protein: I will mail these out this weekend If you haven t gotten
National PHL TB DST Reference Center PSQ Reporting Language Table of Contents
 PSQ Reporting Language Table of Contents Document Page Number PSQ for Rifampin 2-6 Comparison table for rpob Codon Numbering 2 rpob mutation list (new numbering system) 3-5 rpob interpretations 6 PSQ for
PSQ Reporting Language Table of Contents Document Page Number PSQ for Rifampin 2-6 Comparison table for rpob Codon Numbering 2 rpob mutation list (new numbering system) 3-5 rpob interpretations 6 PSQ for
evaluated with UAS CLB eliciting UAS CIT -N Libraries increase in the
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Promoter scaffold library assemblies. Many ensembless of libraries were evaluated in this work. As a legend, the box outline color in top half of the figure
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Promoter scaffold library assemblies. Many ensembless of libraries were evaluated in this work. As a legend, the box outline color in top half of the figure
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information A general solution for opening double-stranded DNA for isothermal amplification Gangyi Chen, Juan Dong, Yi Yuan, Na Li, Xin Huang, Xin Cui* and Zhuo Tang* Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Information A general solution for opening double-stranded DNA for isothermal amplification Gangyi Chen, Juan Dong, Yi Yuan, Na Li, Xin Huang, Xin Cui* and Zhuo Tang* Supplementary Materials
Lecture 19A. DNA computing
 Lecture 19A. DNA computing What exactly is DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)? DNA is the material that contains codes for the many physical characteristics of every living creature. Your cells use different
Lecture 19A. DNA computing What exactly is DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)? DNA is the material that contains codes for the many physical characteristics of every living creature. Your cells use different
Second Interregional Workshop of FAO TCP/INT/3501. Diagnostic Methods for the Detection of IMNV: Gross signs, RT-PCR, RTqPCR
 Second Interregional Workshop of FAO TCP/INT/3501 Diagnostic Methods for the Detection of IMNV: Gross signs, RT-PCR, RTqPCR Gross signs for IMNV (A) Farmed P. vannamei from an outbreak in Brazil, exhibiting
Second Interregional Workshop of FAO TCP/INT/3501 Diagnostic Methods for the Detection of IMNV: Gross signs, RT-PCR, RTqPCR Gross signs for IMNV (A) Farmed P. vannamei from an outbreak in Brazil, exhibiting
Complexity of the Ruminococcus flavefaciens FD-1 cellulosome reflects an expansion of family-related protein-protein interactions
 Complexity of the Ruminococcus flavefaciens FD-1 cellulosome reflects an expansion of family-related protein-protein interactions Vered Israeli-Ruimy 1,*, Pedro Bule 2,*, Sadanari Jindou 3, Bareket Dassa
Complexity of the Ruminococcus flavefaciens FD-1 cellulosome reflects an expansion of family-related protein-protein interactions Vered Israeli-Ruimy 1,*, Pedro Bule 2,*, Sadanari Jindou 3, Bareket Dassa
Chapter 13 Chromatin Structure and its Effects on Transcription
 Chapter 13 Chromatin Structure and its Effects on Transcription Students must be positive that they understand standard PCR. There is a resource on the web for this purpose. Warn them before this class.
Chapter 13 Chromatin Structure and its Effects on Transcription Students must be positive that they understand standard PCR. There is a resource on the web for this purpose. Warn them before this class.
Primer Design Workshop. École d'été en géné-que des champignons 2012 Dr. Will Hintz University of Victoria
 Primer Design Workshop École d'été en géné-que des champignons 2012 Dr. Will Hintz University of Victoria Scenario You have discovered the presence of a novel endophy5c organism living inside the cells
Primer Design Workshop École d'été en géné-que des champignons 2012 Dr. Will Hintz University of Victoria Scenario You have discovered the presence of a novel endophy5c organism living inside the cells
Introduction Use of quality planting materials - prerequisite for increasing production and productivity of banana
 A novel molecular technique for mass indexing of tissue cultured banana plants for Banana Bunchy Top Virus (BBTV) W.A.R.T. Wickramaarachchi, K.T. Ragnaswamy and K.S. Shankaraappa Horticultural Crops Research
A novel molecular technique for mass indexing of tissue cultured banana plants for Banana Bunchy Top Virus (BBTV) W.A.R.T. Wickramaarachchi, K.T. Ragnaswamy and K.S. Shankaraappa Horticultural Crops Research
A netlike rolling circle nucleic acid amplification technique
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information A netlike rolling circle nucleic acid amplification technique Xiaoli Zhu,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Analyst. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information A netlike rolling circle nucleic acid amplification technique Xiaoli Zhu,
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL GENOTYPING WITH MULTIPLEXING TARGETED RESEQUENCING
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL GENOTYPING WITH MULTIPLEXING TARGETED RESEQUENCING All of the patients and control subjects were sequenced and genotyped in the same way. Shotgun libraries of approximately 250 bp
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL GENOTYPING WITH MULTIPLEXING TARGETED RESEQUENCING All of the patients and control subjects were sequenced and genotyped in the same way. Shotgun libraries of approximately 250 bp
Luo et al. Supplemental Figures and Materials and Methods
 Luo et al. Supplemental Figures and Materials and Methods The supplemental figures demonstrate that nuclear NFAT is situated at PODs, overexpressed PML does not increase NFAT nuclear localization, and
Luo et al. Supplemental Figures and Materials and Methods The supplemental figures demonstrate that nuclear NFAT is situated at PODs, overexpressed PML does not increase NFAT nuclear localization, and
Supplemental Data. Jones et al. Plant Cell. (2010) /tpc
 IAA synthesis rate Supplemental Data. Jones et al. Plant Cell. ()..5/tpc..7856 Supplemental Figure. Root tip specific IAA biosynthesis after induction of the CKX gene. 6 DAG pmdc7:atckx seedling roots
IAA synthesis rate Supplemental Data. Jones et al. Plant Cell. ()..5/tpc..7856 Supplemental Figure. Root tip specific IAA biosynthesis after induction of the CKX gene. 6 DAG pmdc7:atckx seedling roots
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS AND METHODS. E. coli strains, plasmids, and growth conditions. Escherichia coli strain P90C (1)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS AND METHODS E. coli strains, plasmids, and growth conditions. Escherichia coli strain P90C (1) dinb::kan (lab stock) derivative was used as wild-type. MG1655 alka tag dinb (2) is
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS AND METHODS E. coli strains, plasmids, and growth conditions. Escherichia coli strain P90C (1) dinb::kan (lab stock) derivative was used as wild-type. MG1655 alka tag dinb (2) is
