Longevity of untreated wood in use above ground
|
|
|
- Charlene Wilson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Longevity of untreated wood in use above ground Wallace E. Eslyn Terry L. Highley Frances F. Lombard Abstract Test crosses constructed from 12 different softwoods and 9 different hardwoods were exposed on a test fence for 9 to 12 years in both southern Mississippi and Wisconsin. Objectives of the test were to determine the aboveground longevity of these woods under varying climatic conditions and to identify the fungi associated with their deterioration. The woods tested in Mississippi were classified into aboveground decay resistance groups. The sapwood of lodgepole pine, basswood, balsam poplar, red alder, and sweetgum and the interior wood of sugar maple, yellow birch, and basswood decayed within an average of 7 years and were classified as nonresistant. Woods estimated to last over 20 years above ground, and thus classified as most resistant, included heartwood of Douglas-fir, redwood, western white pine, red and white oak, and sapwood of red oak. The remaining woods fell in between these classes. In Wisconsin most woods decayed too slowly for estimates to be made of their longevity. Gloeophyllum saepiarium, the white-rot fungus Unknown T, Schizophyllum commune, the brown-rot fungus Unknown U, and a Xylaria sp. were predominant in the Mississippi test units. Peniophora cinerea, Phanerochaete chrysosporium, Meruliopsis corium, Irpex lacteus, and Peniophora violaceo-livida predominated in Wisconsin. The present study was established to estimate, through actual field tests, the service life to be expected of these woods, also the heartwood of some, when exposed above ground in the form of cross-brace joints in highand moderate-decay hazard locales. In addition, we wished to determine the fungi associated with the decay. Materialsand methods Test units were constructed of boards, 1.9 by 7.62 by cm long (3/4 by 3 by 6 in.), nailed together at their centers to form a cross (Fig. 1). The intersection of the Numerous field studies have dealt with durability of untreated Wood in contact with soil (4,7-10,17-19). However, information is lacking on the comparative durability of American woods in aboveground exterior use. Recently, the relative decay resistance of the sapwood of 15 different American woods was determined, in the laboratory, using a test designed to simulate aboveground conditions (3). As a result of these tests, the woods were tentatively placed into sapwood decay-resistance groups. Figure 1. - Test crosses installed on fence. The authors are, respectively Supervisory Research Plant Pathologist, Research Plant Pathologist, and Botanist, USDA Forest Serv., Forest Prod. Lab., P.O. Box 5130, Madison, WI Financial support for this work was supplied, in part, by Naval Facilities Engineering Command, U.S. Navy. This paper was received for publication in June Forest Products Research Society Forest Prod. J. 35(5): MAY 1985
2 boards provided a water catchment area similar to joints where decay often originates in wood structures. Twenty units were constructed of wood from each tree species. Where both sapwood and heartwood were available from a given species an additional 20 units were constructed. Each series of units was then installed on test fences (Fig. 1) located near Gulfport, Miss., and near Madison, Wis., when sufficient number of units was available. The Gulfport climate promotes rapid decay in wood, while Madison s climate is only moderately favorable for promotion of decay (11). The test units (crosses) were constructed from sapwood (unless otherwise noted) of the following tree species: A. Coniferous woods Douglas-fir - Pseudotsuga menziesii (Mirb.) Franco 2. Douglas-fir heartwood 3. Engelmann spruce -Picea engelmannii Parry 4. Engelmann spruce heartwood 5. Sitka spruce -Picea sitchensis (Bong.) Carr. 6. White spruce - Picea glauca (Moench) Voss 7. Western hemlock -Tsuga heterophylla (Raf.) Sarg. 8. Western redcedar -Thuja plicata Donn. 9. Western redcedar heartwood 10. Redwood - Sequoia sempervirens (D. Don) Endl. 11. Redwood heartwood 12. Lodgepole pine - Pinus contorta Dougl. ex Loud. 13. Lodgepole pine heartwood 14. Ponderosa pine - Pinus ponderosa Dougl. ex Laws. 15. Ponderosa pine heartwood 16. Western white pine - Pinus monticola Dougl. ex D. Don 17. Western white pine heartwood 18. Red pine -Pinus resinosa Ait. 19. Southern yellow pine -Pinus sp. B. Hardwoods 1. Balsam poplar -Populus balsamifera L. 2. Basswood -Tilia americana L. 3. Basswood heartwood 4. Eucalyptus -Eucalyptus sp. 5. Eucalyptus heartwood 6. Red alder -Alnus rubra Bong. 7. Sugar maple -Acer saccharum Marsh. 8. Sugar maple interior wood-trueheartwood is not formed in this species (15), hence the term interior wood is used 9. Sweetgum -Liquidambar styraciflua L. 10. Red oak -Quercus sp. 11. Red oak heartwood 12. White oak - Quercus sp. 13. White oak heartwood 14. Yellow birch interior wood - Betula alleghaniensis Britton -see note under 8 above. Each summer the test units were examined for decay and fungal fruiting structures and isolations were attempted usually from two of the units within each group of tree species. In addition, units that had failed were brought back to the laboratory for dissection and intensive isolation work. Malt agar and Taylor s agar (16) were used for all isolations. Only the basidiomycetous isolates are discussed in this work. We considered separation of the cross components due to decay a failure of the unit. All Mississippi test units were removed to the laboratory for dissection, isolation, and decay rating in 1983, because decay was generally well established in most of the units. The decay ratings were No. 1, sound; No. 2, sound-appearing but infected with a Basidiomycete or a Xylaria spp.; No. 3, up to 25 percent decayed; No. 4, 26 to 50 percent decayed; and No. 5, 50 + percent decayed. The remaining units in the Wisconsin test were left for an indefinite period because little failure was evident. The condition of these units was assessed externally. Results and discussion Longevity of test units in Mississippi The time required for more than half of the test units of a given wood species to fail was termed the average service life (Table 1). In those cases in which failure of six or more units of one species occurred prior to final inspection, the average service life was readily discernible. For example, six of the southern pine units failed in 10 years, so the average service life of this pine was 10 years (Table 1). However, determination of the longevity of those wood species in which less than half of the test units had failed required extrapolation from data on related woods in this test and from the condition of the surviving units. The estimate of 20 + years service life for Douglas-fir heartwood was based upon the longevity reported by Scheffer and Eslyn (13,14) for untreated Douglas-fir cross braces and flooring boards stored above ground in Mississippi. Based upon their determined or estimated service life, the Mississippi-stored woods were rated as to aboveground decay resistance (Table 2.) Heartwood of Douglas-fir, western white pine, redwood, white and red oak, and red oak sapwood, each with an expected average service life of at least 20 years, were classified as most resistant. The sapwood of lodgepole pine, red alder, basswood, balsam poplar, and sweetgum and the heartwood or interior wood of basswood, yellow birch, and sugar maple, which could be expected to last 7 or fewer years, were classified as nonresistant. The remaining woods were moderately resistant or resistant based upon expected average service lives of 8 to 13 and 14 to 19 years, respectively. While the preceding resistance groupings may remain unaffected, the longevity spans now included within each group are likely to be determined by both board size and kind of structural joint. For example, 4-inch-thick planks of untreated Douglas-fir were estimated to have a service life of only 12 years (6), con- FOREST PRODUCTS JOURNAL Vol. 35, No. 5 29
3 TABLE 1. - Decay evaluation and longevity of test units composed of different woods and exposed above ground in Mississippi. Table continued on next page. 30 MAY 1985
4 TABLE 1. - Continued. TABLE 2. - Grouping of test woods for aboveground decay resistance and service life in a climate such as that of southern Mississippi. siderably less than the 20 + life determined for the thin test crosses of the same species used in the present test. The shorter longevity of the larger units may be due to longer moisture retention, particularly if checking is involved, increasing the period during which invading fungi can grow and deteriorate the wood. Similar planks of southern pine were heavily decayed after 5 years in aboveground tests (5). Hence, longevity spans derived herein will apply only to structural components similar in cross-sectional size to the test units used in this study. Millwork and fencing components may fit into this category. Longevity span will also be affected by variability within species. For example, Scheffer et al. (12) concluded that use of white oak will provide superior decay resistance in general, but some individual trees of this species may have only moderate resistance. Furthermore, they report variability in decay resistance with locality, tree size, and position of the wood in the tree. Longevity of test units in Wisconsin The average service life was determinable for only five of the woods stored in Wisconsin (Table 3). These woods, whose longevity ranged from 8 to 11 years, are sapwood of lodgepole pine, red pine, sweetgum, basswood, and basswood heartwood. All except red pine were in the nonresistant group (< 7 years) in the Mississippi test (Table 2). We did not attempt to estimate the longevity of the woods remaining in test in Wisconsin (Table 3) because of the few failures. These estimates will be made in the future. Fungi associated with decay of test units in Mississippi Over 22 species of Hymenomycetes and wooddecaying members of the Xylariaceae were isolated from or found fruiting on test units exposed in Mississippi (Table 4). Gloeophyllum saepiarium, Unknown T, Schizophyllum commune, Unknown U, and Xylaria spp. predominated, in that order. The other fungi we found were each isolated from fewer than five test units (Table 4). The hyphae of both Unknown T and Unknown U contain clamp connections and are considered to be Basidiomycetes. The positive Bavendamm reaction (1) of Unknown T indicates it is a white-rot fungus while the negative reaction of Unknown U indicates it is a brown-rot fungus. Gloeophyllum saepiarium was found fruiting on southern pine units as early as 1 year after installation in Mississippi (Table 4), but first failure of these units did not occur until the 9th year of test (Table 1). Interestingly, at time of failure or conclusion of the test, we could not isolate G. saepiarium from the units on which it had fruited years earlier. Apparently this fungus, or specific strains of this fungus, were dying out or not successfully competing with other wood-inhabiting FOREST PRODUCTS JOURNAL Vol. 35, No. 5 31
5 TABLE 3. - Decay evaluation and longevity of test units composed of different woods and exposed above ground in Wisconsin. fungi in some of the test units. We also found S. commune, the Peniophora spp., Phanerochaete sordida, and Corticium C fruiting on, or isolated them from, test units shortly after installation only (Table 4). These early colonizers may be poor wood decayers, e.g. S. commune is, and unable to compete with later, more vigorous fungal competitors. Fungi associated with decay of test units in Wisconsin Half the number of species of Hymenomycetes encountered in test units in Mississippi (Table 4) were found in Wisconsin (Table 5). Only Phanerochaete chrysosporium and Phlebia subserialis were found in common. In the Wisconsin test units Peniophora cinerea, Phanerochaete chrysosporium, Meruliopsis corium, Irpex lacteus, and Peniophora violaceo-livida predominated (Table 5). Surprisingly, Gloeophyllum trabeum most often associated with decay in aboveground building components (2), was expected to be strongly represented in these isolations but was not obtained. Conclusions In the aboveground test in Mississippi, the longevity of both the sapwood and heartwood of different wood species varied significantly. The variance encountered in sapwood decay susceptibility supported earlier laboratory findings (3) and, together with the heartwood test data, formed the basis for establishment of both aboveground decay resistance classes and length of service estimates for the woods in test. Unlike a decay-resistance class, however, length of service of a given wood is influenced by its cross-sectional size and by its surrounding climatic conditions. For example, 32 MAY 1985
6 TABLE 4. - Hymenomycetes and Xylariaceae associated with test units constructed of different woods and exposed above ground in Mississippi. Table continued on next page. FOREST PRODUCTS JOURNAL Vol. 35, No. 5 33
7 TABLE 4. - Continued. TABLE 5. - Hymenomycetes associated with test units constructed of different woods and exposed above ground in Wisconsin. Table continued on next page. 34 MAY 1985
8 TABLE 5. - Continued. large wood pieces subject to extensive splitting, and thus to increased water retention, may fail sooner than thinner pieces in aboveground use. Also, wood in test in northern, moderate-decay hazard climates (11) may be expected to outlast similar wood installed in southern, high-decay hazard zones. This has proven true in the present test where far fewer wood failures occurred in Wisconsin than in Mississippi; the paucity of failures in the former prevents the assemblage of wood species into service life groupings for that area. Climate appeared to exert great influence upon the fungi associated with test units in Mississippi and Wisconsin as only 2 of the more than 23 Basidiomycetes identified in this study were obtained from both areas. Literature cited FOREST PRODUCTS JOURNAL Vol. 35, No. 5 35
Disclaimers. Authors
 Disclaimers Canada The exclusion of certain manufactured products does not necessarily imply disapproval nor does the mention of other products necessarily imply endorsement by the Canadian Forest Service.
Disclaimers Canada The exclusion of certain manufactured products does not necessarily imply disapproval nor does the mention of other products necessarily imply endorsement by the Canadian Forest Service.
U.S.D.A. FOREST SERVICE RESEARCH PAPER FPL 124 OCTOBER 1969 SAPWOOD THICKNESS. of douglas-fir and five other western softwoods
 U.S.D.A. FOREST SERVICE RESEARCH PAPER FPL 124 OCTOBER 1969 SAPWOOD THICKNESS of douglas-fir and five other western softwoods U.S. Department of Agriculture Forest Service Forest Products Laboratory Madison,
U.S.D.A. FOREST SERVICE RESEARCH PAPER FPL 124 OCTOBER 1969 SAPWOOD THICKNESS of douglas-fir and five other western softwoods U.S. Department of Agriculture Forest Service Forest Products Laboratory Madison,
Productivity of red alder in western Oregon and Washington
 From Biology of Alder Proceedings of Northwest Scientific Association Annual Meeting April 14-15, 1967 Published 1966 Productivity of red alder in western Oregon and Washington Red alder in western Oregon
From Biology of Alder Proceedings of Northwest Scientific Association Annual Meeting April 14-15, 1967 Published 1966 Productivity of red alder in western Oregon and Washington Red alder in western Oregon
Site Index Adjustments for Old-growth Stands Based on Veteran Trees
 WORKING PAPER 36 Site Index Adjustments for Old-growth Stands Based on Veteran Trees 1 9 9 8 Ministry of Forests Research Program Site Index Adjustments for Old-growth Stands Based on Veteran Trees Gordon
WORKING PAPER 36 Site Index Adjustments for Old-growth Stands Based on Veteran Trees 1 9 9 8 Ministry of Forests Research Program Site Index Adjustments for Old-growth Stands Based on Veteran Trees Gordon
Daniel Omdal Forest Pathologist
 Daniel Omdal Forest Pathologist Dan.omdal@dnr.wa.gov Conifer Root Diseases and Heart Rots Distribution of Laminated Root Rot in western North America Root diseases among the greatest mortality risks to
Daniel Omdal Forest Pathologist Dan.omdal@dnr.wa.gov Conifer Root Diseases and Heart Rots Distribution of Laminated Root Rot in western North America Root diseases among the greatest mortality risks to
Willow and Cottonwood
 VOL. 16, NO. 11 FOREST PRODUCTS JOURNAL NOVEMBER 1966 Deterioration Rates of Willow and Cottonwood during Storage in Georgia By P. J. Bois 1 Southeastern Forest Experiment Station Asheville, N. C. W. E.
VOL. 16, NO. 11 FOREST PRODUCTS JOURNAL NOVEMBER 1966 Deterioration Rates of Willow and Cottonwood during Storage in Georgia By P. J. Bois 1 Southeastern Forest Experiment Station Asheville, N. C. W. E.
Managing the Stands of the Future Based on the Lessons of the Past:
 United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service Pacific Northwest Research Station Research Note PNW-RN-528 September 2000 Managing the Stands of the Future Based on the Lessons of the Past: Estimating
United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service Pacific Northwest Research Station Research Note PNW-RN-528 September 2000 Managing the Stands of the Future Based on the Lessons of the Past: Estimating
Tree Identification Topics: Original Bearing and Line Trees
 Tree Identification Topics: Original Bearing and Line Trees Staples http://files.dnr.state.mn.us/eco/nhnrp/brgtree.pdf https://gisdata.mn.gov/dataset/biota-original-pls-bearing-trees Common Original Bearing
Tree Identification Topics: Original Bearing and Line Trees Staples http://files.dnr.state.mn.us/eco/nhnrp/brgtree.pdf https://gisdata.mn.gov/dataset/biota-original-pls-bearing-trees Common Original Bearing
ORNAMENTALS NORTHWEST ARCHIVES
 ORNAMENTALS NORTHWEST ARCHIVES July-August 1989 Vol.13, Issue 4 Pages 5-8 Sally J. Campbell and Philip B. Hamm Plant Pathologist, USDA Forest Service, Pacific Northwest Region, Portland, OR and Senior
ORNAMENTALS NORTHWEST ARCHIVES July-August 1989 Vol.13, Issue 4 Pages 5-8 Sally J. Campbell and Philip B. Hamm Plant Pathologist, USDA Forest Service, Pacific Northwest Region, Portland, OR and Senior
Ten-Year Performance of Treated Northeastern Softwoods in Aboveground and Ground-Contact Exposures
 United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service Forest Products Laboratory Research Paper FPL RP 578 Ten-Year Performance of Treated Northeastern Softwoods in Aboveground and Ground-Contact Exposures
United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service Forest Products Laboratory Research Paper FPL RP 578 Ten-Year Performance of Treated Northeastern Softwoods in Aboveground and Ground-Contact Exposures
Finnish Wood Species. How much wood do we have in Finland?
 Finnish Wood Species How much wood do we have in Finland? How much of Finland is forest? How many trees are there in Finland? 24,622,888,500 Trees per person in Finland Source: Mapping tree density at
Finnish Wood Species How much wood do we have in Finland? How much of Finland is forest? How many trees are there in Finland? 24,622,888,500 Trees per person in Finland Source: Mapping tree density at
FOREST ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
 FOREST ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION USDA FOREST SERVICE NORTHERN REGION State & Private Forestry Missoula, MT 59801 PRONG BINDER 5200 Report No. 75-19 December 1975 SURVEY AND EVALUATION OF PARK, CEMETERY,
FOREST ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION USDA FOREST SERVICE NORTHERN REGION State & Private Forestry Missoula, MT 59801 PRONG BINDER 5200 Report No. 75-19 December 1975 SURVEY AND EVALUATION OF PARK, CEMETERY,
MANAGEMENT NOTES Number 8
 MANAGEMENT NOTES Number 8 PLANTING WHITE PINE AND RED SPRUCE WITH SHELTER/SHADE Preliminary results by William M. Glen, 1993 INTRODUCTION The forests of Prince Edward Island have been subject to selective
MANAGEMENT NOTES Number 8 PLANTING WHITE PINE AND RED SPRUCE WITH SHELTER/SHADE Preliminary results by William M. Glen, 1993 INTRODUCTION The forests of Prince Edward Island have been subject to selective
CLIMATE CHANGE AND FOREST BIODIVERSITY: A VULNERABILITY ASSESSMENT AND ACTION PLAN FOR NATIONAL FORESTS IN WASHINGTON
 CLIMATE CHANGE AND FOREST BIODIVERSITY: A VULNERABILITY ASSESSMENT AND ACTION PLAN FOR NATIONAL FORESTS IN WASHINGTON USDA Forest Service, Pacific Northwest Region Carol Aubry, Forest Geneticist, Olympic
CLIMATE CHANGE AND FOREST BIODIVERSITY: A VULNERABILITY ASSESSMENT AND ACTION PLAN FOR NATIONAL FORESTS IN WASHINGTON USDA Forest Service, Pacific Northwest Region Carol Aubry, Forest Geneticist, Olympic
LOCAL VOLUME TABLES, TOTAL VOLUME, MERCHANTABLE VOLUME AND TREE BIOMASS, FOR THE COMMERCIAL TREE SPECIES OF PRINCE EDWARD ISLAND PRINCE EDWARD ISLAND
 LOCAL VOLUME TABLES, TOTAL VOLUME, MERCHANTABLE VOLUME AND TREE BIOMASS, FOR THE COMMERCIAL TREE SPECIES OF PRINCE EDWARD ISLAND PRINCE EDWARD ISLAND DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY AND FORESTRY FORESTRY BRANCH SILVICULTURE
LOCAL VOLUME TABLES, TOTAL VOLUME, MERCHANTABLE VOLUME AND TREE BIOMASS, FOR THE COMMERCIAL TREE SPECIES OF PRINCE EDWARD ISLAND PRINCE EDWARD ISLAND DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY AND FORESTRY FORESTRY BRANCH SILVICULTURE
EFFECT OF LIGNIN CONTENT AND EXTRACTIVES ON THE HIGHER HEATING VALUE OF WOOD. Robert H. White
 EFFECT OF LIGNIN CONTENT AND EXTRACTIVES ON THE HIGHER HEATING VALUE OF WOOD Robert H. White Research Forest Products Technologist Forest Products Laboratory, Madison, WI 53705-2398' (Received December
EFFECT OF LIGNIN CONTENT AND EXTRACTIVES ON THE HIGHER HEATING VALUE OF WOOD Robert H. White Research Forest Products Technologist Forest Products Laboratory, Madison, WI 53705-2398' (Received December
Defining Forests. forestry hardwood log native forest old-growth forest. E-unit: Defining Forests Page 1
 Defining Forests W HEN WE use the tree respectfully and economically, we have one of the greatest resources on the earth, said Frank Lloyd Wright. Clearly Mr. Wright placed value on trees and had sustainability
Defining Forests W HEN WE use the tree respectfully and economically, we have one of the greatest resources on the earth, said Frank Lloyd Wright. Clearly Mr. Wright placed value on trees and had sustainability
Table 2 Green specific gravity and oven-dry density for 14 tree species commonly piled and burned in the Western United States
 Figure 6 The nomagram assists in determining net mass of the wood (X-axis at right) by using gross pile volume (X-axis at left), packing ratio (diagonal lines at left), net wood volume (Y-axis), and wood
Figure 6 The nomagram assists in determining net mass of the wood (X-axis at right) by using gross pile volume (X-axis at left), packing ratio (diagonal lines at left), net wood volume (Y-axis), and wood
Specifically you have requested that we provide you with comment regarding:
 16 February 2011 Our Ref. 269-201 Properties of Medite Tricoya and its possible application for use We understand that you are conducting technical due diligence on the in-development product Medite Tricoya
16 February 2011 Our Ref. 269-201 Properties of Medite Tricoya and its possible application for use We understand that you are conducting technical due diligence on the in-development product Medite Tricoya
Using the Air-Drying Estimator to Predict the Air-Drying Time for Lumber. By Phil Mitchell North Carolina State University INTRODUCTION
 Department of Forest Biomaterials Campus Box 8003 North Carolina State University Raleigh, North Carolina 27695-8003 Summary: Lumber is often air-dried for months prior to being kiln dried. The airdrying
Department of Forest Biomaterials Campus Box 8003 North Carolina State University Raleigh, North Carolina 27695-8003 Summary: Lumber is often air-dried for months prior to being kiln dried. The airdrying
RESEARCH NOTES. Oregon State Board of Forestry Salem, Oregon 1951 CONE CROP SURVEY REPORT. Wilbur H. Engstrom. Research Forester
 AGRICULTURE ROOM RESEARCH NOTES Oregon State Board of Forestry Salem, Oregon No. 4 August 1951 1951 CONE CROP SURVEY REPORT Wilbur H. Engstrom Research Forester The following report on the status of the
AGRICULTURE ROOM RESEARCH NOTES Oregon State Board of Forestry Salem, Oregon No. 4 August 1951 1951 CONE CROP SURVEY REPORT Wilbur H. Engstrom Research Forester The following report on the status of the
Volume and Average Stumpage Price of Selected Species on the National Forests of the Pacific Northwest Region, 1973 to 1984
 United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service Pacific Northwest Research Station Research Note PNW-446 July 1986 Volume and Average Stumpage Price of Selected Species on the National Forests of
United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service Pacific Northwest Research Station Research Note PNW-446 July 1986 Volume and Average Stumpage Price of Selected Species on the National Forests of
2017 SPECIES USED BY MILL FOR VIRGIN RAW MATERIAL
 2017 SPECIES USED BY MILL FOR VIRGIN RAW MATERIAL ASHDOWN MILL Hardwood Ash Green Fraxinus pennsylvanica Hardwood Beech American Fagus grandifolia Hardwood Birch River Betula nigra Hardwood Cottonwood
2017 SPECIES USED BY MILL FOR VIRGIN RAW MATERIAL ASHDOWN MILL Hardwood Ash Green Fraxinus pennsylvanica Hardwood Beech American Fagus grandifolia Hardwood Birch River Betula nigra Hardwood Cottonwood
Mechanical Properties of Salvaged Dead Yellow-Cedar in Southeast Alaska
 United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service Forest Products Laboratory Research Paper FPL RP 565 Mechanical Properties of Salvaged Dead Yellow-Cedar in Southeast Alaska Phase I Kent A. McDonald
United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service Forest Products Laboratory Research Paper FPL RP 565 Mechanical Properties of Salvaged Dead Yellow-Cedar in Southeast Alaska Phase I Kent A. McDonald
DATA SIZE * S O L D * C U T * CLASS CLASS DESCRIPTION SALES VOLUME-MBF VALUE VOLUME-MBF VALUE
 DATE: 02/11/04 TCS004 TIMBER CUT AND SOLD ON NATIONAL FORESTS SERVICE-WIDE PAGE 1 DATA SIZE * S O L D * C U T * CLASS CLASS DESCRIPTION SALES VOLUME-MBF VALUE VOLUME-MBF VALUE 2 1 NON-CONVERTIBLE 183,360.00
DATE: 02/11/04 TCS004 TIMBER CUT AND SOLD ON NATIONAL FORESTS SERVICE-WIDE PAGE 1 DATA SIZE * S O L D * C U T * CLASS CLASS DESCRIPTION SALES VOLUME-MBF VALUE VOLUME-MBF VALUE 2 1 NON-CONVERTIBLE 183,360.00
Salem Street Trees: Sample Inventory
 Salem Street Trees: Sample Inventory November 2018 Salem Street Trees: Sample Inventory City of Salem November 2018 Prepared by: Olivia Poblacion, Seasonal Planner I CONTENTS 2 Key Findings 2 Background
Salem Street Trees: Sample Inventory November 2018 Salem Street Trees: Sample Inventory City of Salem November 2018 Prepared by: Olivia Poblacion, Seasonal Planner I CONTENTS 2 Key Findings 2 Background
Treatability of Native Softwood Species of the Northeastern United States
 United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service Forest Products Laboratory Research Paper FPL-RP-8 Treatability of Native Softwood Species of the Northeastern United States Lee R. Gjovik David R.
United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service Forest Products Laboratory Research Paper FPL-RP-8 Treatability of Native Softwood Species of the Northeastern United States Lee R. Gjovik David R.
SCHIRP: Second Broadcast Fertilization Application.
 INNOVATIVE PROJECT FIA LBIP Project 6218029 Report: SCHIRP: Second Broadcast Fertilization Application. March, 2004 Annette van Niejenhuis, RPF Tree Improvement and Research Coordinator Western Forest
INNOVATIVE PROJECT FIA LBIP Project 6218029 Report: SCHIRP: Second Broadcast Fertilization Application. March, 2004 Annette van Niejenhuis, RPF Tree Improvement and Research Coordinator Western Forest
Timber Cladding for Wales An Introduction. Dennis Jones (WKW)
 Timber Cladding for Wales An Introduction Dennis Jones (WKW) How to increase timber cladding Understanding material Timber selection Timber Quality Performance Stability Marketing Environmental benefits
Timber Cladding for Wales An Introduction Dennis Jones (WKW) How to increase timber cladding Understanding material Timber selection Timber Quality Performance Stability Marketing Environmental benefits
EFFECT OF SPECIFIC GRAVITY AND SPECIES ON A CAPACITANCE-TYPE MOISTURE METER
 EFFECT OF SPECIFIC GRAVITY AND SPECIES ON A CAPACITANCE-TYPE MOISTURE METER Michael R. Milota Oregon State University Corvallis, OR INTRODUCTION Correct estimation of kiln-dry moisture content is important
EFFECT OF SPECIFIC GRAVITY AND SPECIES ON A CAPACITANCE-TYPE MOISTURE METER Michael R. Milota Oregon State University Corvallis, OR INTRODUCTION Correct estimation of kiln-dry moisture content is important
Persistence of Western Hemlock and Western Redcedar Trees 38 Years After Girdling at Cat Island in Southeast Alaska
 United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service Pacific Northwest Research Station Research Note PNW-RN-507 November 1991 Persistence of Western Hemlock and Western Redcedar Trees 38 Years After
United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service Pacific Northwest Research Station Research Note PNW-RN-507 November 1991 Persistence of Western Hemlock and Western Redcedar Trees 38 Years After
APPENDIX 2 -- EASTERN U.S. SITE-TREE SELECTION CRITERIA AND FIA FOREST TYPE ALGORITHM FOR THE U.S. EASTERN U.S. SITE-TREE SELECTION CRITERIA
 rtheast Field Guide, Version 1.7 APPENDIX 2 -- EASTERN U.S. SITE-TREE SELECTION CRITERIA AND FIA FOREST TYPE ALGORITHM FOR THE U.S. EASTERN U.S. SITE-TREE SELECTION CRITERIA Ideally, site trees in the
rtheast Field Guide, Version 1.7 APPENDIX 2 -- EASTERN U.S. SITE-TREE SELECTION CRITERIA AND FIA FOREST TYPE ALGORITHM FOR THE U.S. EASTERN U.S. SITE-TREE SELECTION CRITERIA Ideally, site trees in the
SURVEY OF SPECIFIC GRAVITY OF EIGHT MAINE CONIFERS
 U.S.D.A. FOREST SERVICE RESEARCH PAPER FPL 95 JULY 1968 U.S. DEPARTMEMENT OF AGRICULTURE FOREST SERVICE FOREST PRODUCTS LABORATORY MADISON, WIS. SURVEY OF SPECIFIC GRAVITY OF EIGHT MAINE CONIFERS Abstract
U.S.D.A. FOREST SERVICE RESEARCH PAPER FPL 95 JULY 1968 U.S. DEPARTMEMENT OF AGRICULTURE FOREST SERVICE FOREST PRODUCTS LABORATORY MADISON, WIS. SURVEY OF SPECIFIC GRAVITY OF EIGHT MAINE CONIFERS Abstract
UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE FOREST PRODUCTS LABORATORY FOREST SERVICE MADISON 5, WISCONSIN
 SECOND GROWTH IS GOOD No. 2083 May 1957 INFORMATION REVIEVVEIN AND REAFFIRMED 1963 r,.0001111111i11110111111it 141 11111111Wririlmor FPUR FILE COPY DO MT REMOVE FROM UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE
SECOND GROWTH IS GOOD No. 2083 May 1957 INFORMATION REVIEVVEIN AND REAFFIRMED 1963 r,.0001111111i11110111111it 141 11111111Wririlmor FPUR FILE COPY DO MT REMOVE FROM UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE
THE CORPORATION OF THE DISTRICT OF COLDSTREAM A BYLAW TO REGULATE AND PROHIBIT THE CUTTING DOWN AND REMOVAL OF TREES
 THE CORPORATION OF THE DISTRICT OF COLDSTREAM BYLAW NO. 1198 A BYLAW TO REGULATE AND PROHIBIT THE CUTTING DOWN AND REMOVAL OF TREES WHEREAS pursuant to Part 28, Division 4.1 of the Municipal Act, Council
THE CORPORATION OF THE DISTRICT OF COLDSTREAM BYLAW NO. 1198 A BYLAW TO REGULATE AND PROHIBIT THE CUTTING DOWN AND REMOVAL OF TREES WHEREAS pursuant to Part 28, Division 4.1 of the Municipal Act, Council
7 COARSE WOODY DEBRIS
 Contents 7 COARSE WOODY DEBRIS Page Coarse Woody Debris Form... 2 Field Procedure... 3 Definition of Coarse Woody Debris... 4 Sampling Methods... 4 Rules for Sampling... 5 Completing the form... 8 1. Plot
Contents 7 COARSE WOODY DEBRIS Page Coarse Woody Debris Form... 2 Field Procedure... 3 Definition of Coarse Woody Debris... 4 Sampling Methods... 4 Rules for Sampling... 5 Completing the form... 8 1. Plot
2018 Career Development Event Rules and Regulations. Forestry
 Forestry Maximum Number of Team Members 4 Number of Team Members Scored 4 Scantron Forestry Form # 530-3 Committee: Kelsey Flinn Scott Garber Julie Sions John Smith John Workman All participants in the
Forestry Maximum Number of Team Members 4 Number of Team Members Scored 4 Scantron Forestry Form # 530-3 Committee: Kelsey Flinn Scott Garber Julie Sions John Smith John Workman All participants in the
Effect of Heating in Water on the Strength Properties of Wood 1
 AMERICAN WOOD-PRESERVERS ASSOCIATION 1954 Effect of Heating in Water on the Strength Properties of Wood 1 Engineer Emeritus, Forest Products Laboratory, 2 J. D. MacLean Forest Service, U. S. Department
AMERICAN WOOD-PRESERVERS ASSOCIATION 1954 Effect of Heating in Water on the Strength Properties of Wood 1 Engineer Emeritus, Forest Products Laboratory, 2 J. D. MacLean Forest Service, U. S. Department
Biological Control of Wood-Attacking Fungi Using Bacteria
 BIODETERIORATION RESEARCH 3: 327-332 Plenum Press, New York, 1990 In: Llewellyn, Gerald C.; O Rear, Charles E., eds. Biodeterioration Research 3: Proceedings of the 3d meeting of the Pan American Biodeterioration
BIODETERIORATION RESEARCH 3: 327-332 Plenum Press, New York, 1990 In: Llewellyn, Gerald C.; O Rear, Charles E., eds. Biodeterioration Research 3: Proceedings of the 3d meeting of the Pan American Biodeterioration
DETERMINING LOSS OF WOOD SUBSTANCE A COMPARISON OF TWO METHODS IN OUTSIDE CHIP STORAGE:
 DETERMINING LOSS OF WOOD SUBSTANCE IN OUTSIDE CHIP STORAGE: A COMPARISON OF TWO METHODS U.S.D.A., FOREST SERVICE RESEARCH PAPER FPL 189 1972 U.S. Department of Agriculture Forest Service Forest Products
DETERMINING LOSS OF WOOD SUBSTANCE IN OUTSIDE CHIP STORAGE: A COMPARISON OF TWO METHODS U.S.D.A., FOREST SERVICE RESEARCH PAPER FPL 189 1972 U.S. Department of Agriculture Forest Service Forest Products
A KEY TO THE LITERATURE PRESENTING SITE-INDEX AND DOMINANT-HEIGHT- GROWTH CURVES AND EQUATIONS FOR SPECIES IN THE PACIFIC NORTHWEST AND CALIFORNIA
 Research Contribution 7 March 1995 A KEY TO THE LITERATURE PRESENTING SITE-INDEX AND DOMINANT-HEIGHT- GROWTH CURVES AND EQUATIONS FOR SPECIES IN THE PACIFIC NORTHWEST AND CALIFORNIA by David W. Hann College
Research Contribution 7 March 1995 A KEY TO THE LITERATURE PRESENTING SITE-INDEX AND DOMINANT-HEIGHT- GROWTH CURVES AND EQUATIONS FOR SPECIES IN THE PACIFIC NORTHWEST AND CALIFORNIA by David W. Hann College
NATIVE INSECTS AND DISEASES PLAY AN IMPORTANT ROLE IN WESTERN OREGON
 What Insects and Diseases Are in Western Oregon Forests? NATIVE INSECTS AND DISEASES PLAY AN IMPORTANT ROLE IN WESTERN OREGON forests both beneficial and detrimental, depending on your point of view.they
What Insects and Diseases Are in Western Oregon Forests? NATIVE INSECTS AND DISEASES PLAY AN IMPORTANT ROLE IN WESTERN OREGON forests both beneficial and detrimental, depending on your point of view.they
Role of nondestructive evaluation in the inspection and repair of the USS Constitution
 Eleventh International Symposium on Nondestructive Testing of Wood Role of nondestructive evaluation in the inspection and repair of the USS Constitution Robert J. Ross Lawrence A. Soltis Patrick Otton
Eleventh International Symposium on Nondestructive Testing of Wood Role of nondestructive evaluation in the inspection and repair of the USS Constitution Robert J. Ross Lawrence A. Soltis Patrick Otton
DECOMPOSITION OF ORGANIC MATTER IN SOIL
 DECOMPOSITION OF ORGANIC MATTER IN SOIL The rapidity with which a given organic amendment is decomposed depends on temperature, the supply of oxygen, moisture, and available minerals, the C/N ratio of
DECOMPOSITION OF ORGANIC MATTER IN SOIL The rapidity with which a given organic amendment is decomposed depends on temperature, the supply of oxygen, moisture, and available minerals, the C/N ratio of
This event will provide the participant with the ability to:
 12.013 The New Jersey FFA Forestry Career Development Event is designed to stimulate student interest and to promote the forestry industry as a career choice. It also provides recognition for those who
12.013 The New Jersey FFA Forestry Career Development Event is designed to stimulate student interest and to promote the forestry industry as a career choice. It also provides recognition for those who
NECTRIA FUCKELIANA INFECTION OF PINUS RADIATA IN NEW ZEALAND: RESEARCH APPROACH AND INTERIM RESULTS
 NECTRIA FUCKELIANA INFECTION OF PINUS RADIATA IN NEW ZEALAND: RESEARCH APPROACH AND INTERIM RESULTS MARGARET DICK, LINDSAY BULMAN AND PATRICIA CRANE * Abstract Stem malformation, typically developing after
NECTRIA FUCKELIANA INFECTION OF PINUS RADIATA IN NEW ZEALAND: RESEARCH APPROACH AND INTERIM RESULTS MARGARET DICK, LINDSAY BULMAN AND PATRICIA CRANE * Abstract Stem malformation, typically developing after
DETERIORATION OF FIRE-KILLED TIMBER AT TAYLOR RIVER VANCOUVER ISLAND, BRITISH COLUMBIA
 L I I DETERIORATION OF FIRE-KILLED TIMBER AT TAYLOR RIVER VANCOUVER ISLAND, BRITISH COLUMBIA.. by G. W. Wa1li8, H. A. Richmond J. N. Godfrey and H. M. Craig FOREST RESEARCH LABORATORY CANADIAN FORESTRY
L I I DETERIORATION OF FIRE-KILLED TIMBER AT TAYLOR RIVER VANCOUVER ISLAND, BRITISH COLUMBIA.. by G. W. Wa1li8, H. A. Richmond J. N. Godfrey and H. M. Craig FOREST RESEARCH LABORATORY CANADIAN FORESTRY
Landscaping Requirements McConachie
 Landscaping Requirements McConachie In accordance with the Architectural Guidelines: Landscaping A $2000.00 deposit is required from the homeowner at the time of closing in the event that the builder has
Landscaping Requirements McConachie In accordance with the Architectural Guidelines: Landscaping A $2000.00 deposit is required from the homeowner at the time of closing in the event that the builder has
December 10, Gino J. Aiello, Landscape Architect 50 Camelot Drive Ottawa, ON K2G 5X8 RE: TREE CONSERVATION REPORT LES TERRASSES FRANCESCA
 P.O. Box 13593, Ottawa, ON K2K 1X6 Telephone: (613) 838-5717 Fax: (613) 839-0114 Website: www.ifsassociates.ca Urban Forestry & Forest Management Consulting December 10, 2012 Gino J. Aiello, Landscape
P.O. Box 13593, Ottawa, ON K2K 1X6 Telephone: (613) 838-5717 Fax: (613) 839-0114 Website: www.ifsassociates.ca Urban Forestry & Forest Management Consulting December 10, 2012 Gino J. Aiello, Landscape
Land Capability and Site Index Curves for Nova Scotia Hardwoods
 Contents Introduction 1 Methods..... 2 Results... 2 How To Use LC/SI Curves.... 3 LC/SI Curves 4 References 7 SI Equations. 8 March, 2011 Report FOR 2011-4 No. 92 Land Capability and Site Index Curves
Contents Introduction 1 Methods..... 2 Results... 2 How To Use LC/SI Curves.... 3 LC/SI Curves 4 References 7 SI Equations. 8 March, 2011 Report FOR 2011-4 No. 92 Land Capability and Site Index Curves
LABORATORY DECAY RESISTANCE OF PALMYRA PALM WOOD
 ISSN impresa 0717-3644 ISSN online 0718-221X Maderas. Ciencia y tecnología 20(3): 353-358, 2018 DOI: 10.4067/S0718-221X2018005003601 LABORATORY DECAY RESISTANCE OF PALMYRA PALM WOOD Xiaoping Li 1, Scott
ISSN impresa 0717-3644 ISSN online 0718-221X Maderas. Ciencia y tecnología 20(3): 353-358, 2018 DOI: 10.4067/S0718-221X2018005003601 LABORATORY DECAY RESISTANCE OF PALMYRA PALM WOOD Xiaoping Li 1, Scott
Tie Dual Treatments with TimBor and Creosote or Copper Naphthenate 20 Years of Exposure in AWPA Hazard Zone 4
 Tie Dual Treatments with TimBor and Creosote or Copper Naphthenate 20 Years of Exposure in AWPA Hazard Zone 4 Terry L. Amburgey, TASKpro, LLC Michael G. Sanders, Forest Products Department, Mississippi
Tie Dual Treatments with TimBor and Creosote or Copper Naphthenate 20 Years of Exposure in AWPA Hazard Zone 4 Terry L. Amburgey, TASKpro, LLC Michael G. Sanders, Forest Products Department, Mississippi
Plant Propagation Protocol for Larix occidentalis. Picture taken by Dylan Holm (Western Larch in the fall)
 Plant Propagation Protocol for Larix occidentalis Picture taken by Dylan Holm (Western Larch in the fall) Picture acquired from www.dkimages.com ESRM 412 Native Plant Production Spring 2008 Family Names
Plant Propagation Protocol for Larix occidentalis Picture taken by Dylan Holm (Western Larch in the fall) Picture acquired from www.dkimages.com ESRM 412 Native Plant Production Spring 2008 Family Names
SSAFR Field Tour to the Olympic Peninsula
 SSAFR 2017 Field Tour to the Olympic Peninsula Examples of Forest Management on State Lands and Hike to Old-Growth Forest August 27, 2017 (Sunday) Meet at 09.00 Return time 17.00 1 Field Tour Itinerary
SSAFR 2017 Field Tour to the Olympic Peninsula Examples of Forest Management on State Lands and Hike to Old-Growth Forest August 27, 2017 (Sunday) Meet at 09.00 Return time 17.00 1 Field Tour Itinerary
Redwood. Redwood Empire. The Environmental Advice A Division of Pacific States Industries, Inc.
 Redwood The Environmental Advice Redwood Empire A Division of Pacific States Industries, Inc. 1-800-862-4657 www.buyredwood.com Dimensional Stability of California Redwood Redwood is much less subject
Redwood The Environmental Advice Redwood Empire A Division of Pacific States Industries, Inc. 1-800-862-4657 www.buyredwood.com Dimensional Stability of California Redwood Redwood is much less subject
SAJUAN) Ç(ISLA D, À/KITSA o ties J4A \131 U. S. DEPT. OF AGRICULTURE.FOREST SERVICE
 SAJUAN) Ç(ISLA D, À/KITSA o ties J4A d c1 \131 Ø' 196 U. S. DEPT. OF AGRICULTURE.FOREST SERVICE PREPARED BY THE DIVISION OF FOREST ECONOMICS RESEARCH Carl A. Newport, Chief FOREST SURVEY Melvin E. Metcalf,
SAJUAN) Ç(ISLA D, À/KITSA o ties J4A d c1 \131 Ø' 196 U. S. DEPT. OF AGRICULTURE.FOREST SERVICE PREPARED BY THE DIVISION OF FOREST ECONOMICS RESEARCH Carl A. Newport, Chief FOREST SURVEY Melvin E. Metcalf,
UNDERSTANDING WOOD DISCOLORATION HELPS MAXIMIZE WOOD PROFITS
 UNDERSTANDING WOOD DISCOLORATION HELPS MAXIMIZE WOOD PROFITS Bernhard Kreber Forintek Canada Corp. Vancouver, B.C. Wood discolorations are an old problem and they can be defined as abnormal color patterns.
UNDERSTANDING WOOD DISCOLORATION HELPS MAXIMIZE WOOD PROFITS Bernhard Kreber Forintek Canada Corp. Vancouver, B.C. Wood discolorations are an old problem and they can be defined as abnormal color patterns.
2/24/2009. The factors that determine what type of forest will grow in a region are temperature precipitation growing season soil land forms
 FOREST FACTS Forestry 37% of Canada's land area covered by forests. Stretches in a continuous band from BC to NL. Commercial forests are forests that could be easily be harvested for timber. Non-commercial
FOREST FACTS Forestry 37% of Canada's land area covered by forests. Stretches in a continuous band from BC to NL. Commercial forests are forests that could be easily be harvested for timber. Non-commercial
PACIFIC NORTHWEST: '1910-'198'1
 RESEARCH BULLETIN 39 NOVEMBER 1982 144 7 A45 no$39. op.2 COMPACT A KEY TO THE LITERATURE ON FOREST GROWTH AND YIELD IN THE PACIFIC NORTHWEST: '1910-'198'1 D.W. HANN K. RIITTERS SCHOOL OF FORESTRY OREGON
RESEARCH BULLETIN 39 NOVEMBER 1982 144 7 A45 no$39. op.2 COMPACT A KEY TO THE LITERATURE ON FOREST GROWTH AND YIELD IN THE PACIFIC NORTHWEST: '1910-'198'1 D.W. HANN K. RIITTERS SCHOOL OF FORESTRY OREGON
IR-4 Ornamental Horticulture Program Imazamox Crop Safety
 http://www.ir4project.org/about-environmental-horticulture/environmental-horticulture-researchsummaries IR-4 Ornamental Horticulture Program Imazamox Crop Safety Authors: Ely Vea and Cristi L. Palmer Date:
http://www.ir4project.org/about-environmental-horticulture/environmental-horticulture-researchsummaries IR-4 Ornamental Horticulture Program Imazamox Crop Safety Authors: Ely Vea and Cristi L. Palmer Date:
Guidelines for Estimating Volume, Biomass, and Smoke Production for Piled Slash
 United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service Pacific Northwest Research Station General Technical Report PNW-GTR-364 February 1996 Guidelines for Estimating Volume, Biomass, and Smoke Production
United States Department of Agriculture Forest Service Pacific Northwest Research Station General Technical Report PNW-GTR-364 February 1996 Guidelines for Estimating Volume, Biomass, and Smoke Production
TREATMENT OF PINUS SYLVESTRIS POSTS WITH A CCA PRESERVATIVE
 96 TREATMENT OF PINUS SYLVESTRIS POSTS WITH A CCA PRESERVATIVE R. K. BAGNALL New Zealand Forest Service, P.O. Box 140, Nelson, New Zealand (Received for publication 18 December 1981; revision 3 March 1982)
96 TREATMENT OF PINUS SYLVESTRIS POSTS WITH A CCA PRESERVATIVE R. K. BAGNALL New Zealand Forest Service, P.O. Box 140, Nelson, New Zealand (Received for publication 18 December 1981; revision 3 March 1982)
Laboratory Tests on Fungal Resistance of Wood Filled Polyethylene Composites
 Laboratory Tests on Fungal Resistance of Wood Filled Polyethylene Composites Craig M. Clemons, USDA ForestService, ForestProducts Laboratory Rebecca E. Ibach, USDA ForestService, ForestProducts Laboratory
Laboratory Tests on Fungal Resistance of Wood Filled Polyethylene Composites Craig M. Clemons, USDA ForestService, ForestProducts Laboratory Rebecca E. Ibach, USDA ForestService, ForestProducts Laboratory
Timber Properties of Minor Conifer Species A report to the Forestry Commission. James Ramsay and Elspeth Macdonald
 Timber Properties of Minor Conifer Species A report to the Forestry Commission James Ramsay and Elspeth Macdonald Forest Research is the Research Agency of the Forestry Commission and is the leading UK
Timber Properties of Minor Conifer Species A report to the Forestry Commission James Ramsay and Elspeth Macdonald Forest Research is the Research Agency of the Forestry Commission and is the leading UK
DECOMPOSITION OF METHAM SODIUM TO METHYLISOTHIOCYANATE AS AFFECTED BY WOOD SPECIES, TEMPERATURE, AND MOISTURE CONTENT1 Jefrey J.
 DECOMPOSITION OF METHAM SODIUM TO METHYLISOTHIOCYANATE AS AFFECTED BY WOOD SPECIES, TEMPERATURE, AND MOISTURE CONTENT1 Jefrey J. Morrell Assistant Professor Department of Forest Products Oregon State University
DECOMPOSITION OF METHAM SODIUM TO METHYLISOTHIOCYANATE AS AFFECTED BY WOOD SPECIES, TEMPERATURE, AND MOISTURE CONTENT1 Jefrey J. Morrell Assistant Professor Department of Forest Products Oregon State University
EVALUATION OF DISEASES WITHIN SELECTED STANDS ON THE PRIEST RIVER EXPERIMENTAL FOREST, IDAHO
 EVALUATIN F DISEASES WITIN SELECTED STANDS N TE PRIEST RIVER EXPERIMENTAL FREST, IDA by R. L. James, Plant Pathologist S.. Dubreuil, Plant Pathologist W. E. Bousfield, Impact Specialist J. W. Byler, Supervisory
EVALUATIN F DISEASES WITIN SELECTED STANDS N TE PRIEST RIVER EXPERIMENTAL FREST, IDA by R. L. James, Plant Pathologist S.. Dubreuil, Plant Pathologist W. E. Bousfield, Impact Specialist J. W. Byler, Supervisory
TREATMENT OF ALASKAN SPECIES BY DOUBLE-DIFFUSION AND MODIFIED DOUBLE-DIFFUSION METHODS
 TREATMENT OF ALASKAN SPECIES BY DOUBLE-DIFFUSION AND MODIFIED DOUBLE-DIFFUSION METHODS U.S.D.A., FOREST SERVICE RESEARCH PA PER FPL 182 1972 U.S. DEPARTMENT OF AGRlCULTURE FOREST SERVICE FOREST PRODUCTS
TREATMENT OF ALASKAN SPECIES BY DOUBLE-DIFFUSION AND MODIFIED DOUBLE-DIFFUSION METHODS U.S.D.A., FOREST SERVICE RESEARCH PA PER FPL 182 1972 U.S. DEPARTMENT OF AGRlCULTURE FOREST SERVICE FOREST PRODUCTS
THE INTERNATION RESEARCH GROUP ON WOOD PRESERVATION. Vina W. Yang and Barbara L. Illman
 IRG/WP 99-50142 THE INTERNATION RESEARCH GROUP ON WOOD PRESERVATION SECTION 5 ENVIRONMENTAL ASPECTS Optimum Growth Conditions for the Metal-Tolerant Wood Decay Fungus, Meruliporia incrassata TFFH 294 By
IRG/WP 99-50142 THE INTERNATION RESEARCH GROUP ON WOOD PRESERVATION SECTION 5 ENVIRONMENTAL ASPECTS Optimum Growth Conditions for the Metal-Tolerant Wood Decay Fungus, Meruliporia incrassata TFFH 294 By
HOW DOES WESTERN SPRUCE BUDWORM FEEDING AFFECT WESTERN LARCH?
 This file was created by scanning the printed publication. Errors identified by the software have been corrected; however, some errors may remain. HOW DOES WESTERN SPRUCE BUDWORM FEEDING AFFECT WESTERN
This file was created by scanning the printed publication. Errors identified by the software have been corrected; however, some errors may remain. HOW DOES WESTERN SPRUCE BUDWORM FEEDING AFFECT WESTERN
Forest Health Protection Pacific Southwest Region
 Forest Health Protection Pacific Southwest Region Report No. R06-01 3420 Evaluation March, 2006 Efficacy of Treating Live vs. Dead Stumps With Sporax to Prevent Annosus Root Disease John Kliejunas and
Forest Health Protection Pacific Southwest Region Report No. R06-01 3420 Evaluation March, 2006 Efficacy of Treating Live vs. Dead Stumps With Sporax to Prevent Annosus Root Disease John Kliejunas and
Abstract. OSB Structural Panels. by pre-infection of the panels during the construction process due to deficient weather protection.
 Abstract At many construction projects, the exterior wall and roof sheathing are comprised of oriented strandboard (OSB) panels produced by more than one manufacturer or produced by one manufacturer from
Abstract At many construction projects, the exterior wall and roof sheathing are comprised of oriented strandboard (OSB) panels produced by more than one manufacturer or produced by one manufacturer from
Western Larch. An American Wood. United States Department of Agriculture. Forest Service
 Forest Service United States Department of Agriculture FS-243 The spectacular western larch, which is the largest of the American larches, occurs throughout the forests of western Montana, northern Idaho,
Forest Service United States Department of Agriculture FS-243 The spectacular western larch, which is the largest of the American larches, occurs throughout the forests of western Montana, northern Idaho,
The First Separation of Softwood Species
 University of Kentucky College of Agriculture, Food and Environment FOR-127 Cooperative Extension Service PART IDENTIFYING WOOD A Primer for Everyone 5 The First Separation of Softwood Species Terry Conners,
University of Kentucky College of Agriculture, Food and Environment FOR-127 Cooperative Extension Service PART IDENTIFYING WOOD A Primer for Everyone 5 The First Separation of Softwood Species Terry Conners,
SELECTIONS OF MAPLE AND BIRCH TREES WITH HIGH RESISTANCE TO SPREAD OF DECAY ASSOCIATED WITH WOUNDS
 SELECTIONS OF MAPLE AND BIRCH TREES WITH HIGH RESISTANCE TO SPREAD OF DECAY ASSOCIATED WITH WOUNDS by Alex L. Shigo, Donald Dorn, and Herbert C. Lee Authors are Chief Scientist, Northeastern Forest Experiment
SELECTIONS OF MAPLE AND BIRCH TREES WITH HIGH RESISTANCE TO SPREAD OF DECAY ASSOCIATED WITH WOUNDS by Alex L. Shigo, Donald Dorn, and Herbert C. Lee Authors are Chief Scientist, Northeastern Forest Experiment
Flame Spread Performance of Wood Products Used for Interior Finish
 Performance of Wood Products Used for Interior Finish Wood and wood-based products are widely used as interior wall, ceiling, and floor surfaces in all types of buildings. Appearance, acoustical qualities,
Performance of Wood Products Used for Interior Finish Wood and wood-based products are widely used as interior wall, ceiling, and floor surfaces in all types of buildings. Appearance, acoustical qualities,
THE INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH GROUP ON WOOD PRESERVATION ENVIRONMENTAL ASPECTS. Bioprocessing Preservative-Treated Waste Wood
 IRG/WP 00-50145 THE INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH GROUP ON WOOD PRESERVATION SECTION 5 ENVIRONMENTAL ASPECTS Bioprocessing Preservative-Treated Waste Wood By Barbara L. Illman, Vina W. Yang and Les Ferge USDA
IRG/WP 00-50145 THE INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH GROUP ON WOOD PRESERVATION SECTION 5 ENVIRONMENTAL ASPECTS Bioprocessing Preservative-Treated Waste Wood By Barbara L. Illman, Vina W. Yang and Les Ferge USDA
WOOD ANALYS~S OF four COFFIN SAMPLES, CHARLESTON COUNTY, SOUTH CAROLINA
 WOOD ANALYS~S OF four COFFIN SAMPLES, CHARLESTON COUNTY, SOUTH CAROLINA RESEARCH CONTRIBUTION 1 2001 by Chicora Foundation, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored
WOOD ANALYS~S OF four COFFIN SAMPLES, CHARLESTON COUNTY, SOUTH CAROLINA RESEARCH CONTRIBUTION 1 2001 by Chicora Foundation, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored
Cursory Tree Evaluation Report:
 Cursory Tree Evaluation Report: Grandview Heights Area #2 Neighbourhood Concept Plan PREPARED FOR: City of Surrey, Planning and Development Department PREPARED BY: Mike Fadum ISA Certified Arborist: PN-705A,
Cursory Tree Evaluation Report: Grandview Heights Area #2 Neighbourhood Concept Plan PREPARED FOR: City of Surrey, Planning and Development Department PREPARED BY: Mike Fadum ISA Certified Arborist: PN-705A,
A Clear cutting History Survey of the UNDERC Property. Brian Mahon BIOS 569 Advisor: Dr. Botkin
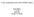 A Clear cutting History Survey of the UNDERC Property Brian Mahon 7 22 03 BIOS 569 Advisor: Dr. Botkin Abstract: From the time of the logging industry boom in the upper midwest until 1968, the land that
A Clear cutting History Survey of the UNDERC Property Brian Mahon 7 22 03 BIOS 569 Advisor: Dr. Botkin Abstract: From the time of the logging industry boom in the upper midwest until 1968, the land that
Preservative-Treated Yellow Poplar for Above-Ground Use
 Preservative-Treated Yellow Poplar for Above-Ground Use Michael O. Hunt * Professor emeritus of Wood Science Terry Amburgey Giles Distinguished Professor emeritus of Forest Products Department of Forest
Preservative-Treated Yellow Poplar for Above-Ground Use Michael O. Hunt * Professor emeritus of Wood Science Terry Amburgey Giles Distinguished Professor emeritus of Forest Products Department of Forest
Western redcedar (Cw)- Thuja plicata
 Western redcedar (Cw)- Thuja plicata Tree Species > Western redcedar Page Index Distribution Range and Amplitiudes Tolerances and Damaging Agents Silvical Characteristics Genetics and Notes BC Distribution
Western redcedar (Cw)- Thuja plicata Tree Species > Western redcedar Page Index Distribution Range and Amplitiudes Tolerances and Damaging Agents Silvical Characteristics Genetics and Notes BC Distribution
Observed Relationships between Wood Density and Solution Uptake during Pressure Treatment
 Observed Relationships between Wood Density and Solution Uptake during Pressure Treatment Steve Halverson Stan Lebow USDA Forest Service, Forest Products Laboratory Madison, Wisconsin ABSTRACT A better
Observed Relationships between Wood Density and Solution Uptake during Pressure Treatment Steve Halverson Stan Lebow USDA Forest Service, Forest Products Laboratory Madison, Wisconsin ABSTRACT A better
N 2 Fixation in Brown-Rotted Soil Wood in an lntermountain Cedar-Hemlock Ecosystem
 Forest Sci., Vol., 28, No. 2, 1982, pp. 292-296 1982, by the Society of American Foresters N 2 Fixation in Brown-Rotted Soil Wood in an lntermountain Cedar-Hemlock Ecosystem Michael J. Larsen, Martin F.
Forest Sci., Vol., 28, No. 2, 1982, pp. 292-296 1982, by the Society of American Foresters N 2 Fixation in Brown-Rotted Soil Wood in an lntermountain Cedar-Hemlock Ecosystem Michael J. Larsen, Martin F.
U.S. Census Bureau Lumber Production and Mill Stocks MA321T(07) Issued May 2008
 U.S. Census Bureau Lumber Production and Mill Stocks - 2007 MA321T(07) Issued May 2008 Address inquiries concerning these data to Primary Goods Industries Branch, U.S. Department of Commerce, Census Bureau,
U.S. Census Bureau Lumber Production and Mill Stocks - 2007 MA321T(07) Issued May 2008 Address inquiries concerning these data to Primary Goods Industries Branch, U.S. Department of Commerce, Census Bureau,
An Evaluation of Used Wood Crossties
 An Evaluation of Used Wood Crossties David A. Webb Administrative Director Creosote Council Creosote has proven to be an effective preservative for sawn and peeled timber products. It has been used for
An Evaluation of Used Wood Crossties David A. Webb Administrative Director Creosote Council Creosote has proven to be an effective preservative for sawn and peeled timber products. It has been used for
EFFECT OF ph AND BUFFERING CAPACITY OF WOOD ON THE GELATION TIME OF UREA-FORMALDEHYDE RESIN1 William E. Johns. Khan A. Niazi
 EFFECT OF ph AND BUFFERING CAPACITY OF WOOD ON THE GELATION TIME OF UREA-FORMALDEHYDE RESIN1 William E. Johns Assistant Professor and Khan A. Niazi Graduate Research Assistant Wood Technology Section,
EFFECT OF ph AND BUFFERING CAPACITY OF WOOD ON THE GELATION TIME OF UREA-FORMALDEHYDE RESIN1 William E. Johns Assistant Professor and Khan A. Niazi Graduate Research Assistant Wood Technology Section,
Western Oregon Forest Ecology. Michael Ahr, Forest Conservationist
 Western Oregon Forest Ecology Michael Ahr, Forest Conservationist Outline Geology Forest Types Common NW Tree Species Successional Stand Types Brief History of Forest Management Effects on NW Ecosystems
Western Oregon Forest Ecology Michael Ahr, Forest Conservationist Outline Geology Forest Types Common NW Tree Species Successional Stand Types Brief History of Forest Management Effects on NW Ecosystems
Stem Decays. Identification, Biology, & Management. Brennan Ferguson USDA Forest Service Forest Health Protection
 Stem Decays Identification, Biology, & Management Brennan Ferguson USDA Forest Service Forest Health Protection Photo credits Idaho Department of Lands USFS PNW Research Station USFS Region 1 & 6 Forest
Stem Decays Identification, Biology, & Management Brennan Ferguson USDA Forest Service Forest Health Protection Photo credits Idaho Department of Lands USFS PNW Research Station USFS Region 1 & 6 Forest
High-temperature kiln-drying of 4/4 lumber from 12 hardwood species
 High-temperature kiln-drying of 4/4 lumber from 12 hardwood species R. Sidney Boone Abstract One-inch lumber of 12 hardwood species was kilndried by two schedules: 1) 230 F on stock green from the saw
High-temperature kiln-drying of 4/4 lumber from 12 hardwood species R. Sidney Boone Abstract One-inch lumber of 12 hardwood species was kilndried by two schedules: 1) 230 F on stock green from the saw
Forestry CDE. Purpose. Eligibility. Event Format. Event Procedures. (rev. Oct. 2017)
 Forestry CDE Purpose (rev. Oct. 2017) The Forestry Career Development Event is designed to stimulate student interest and to promote forestry instruction in the agricultural education curriculum and to
Forestry CDE Purpose (rev. Oct. 2017) The Forestry Career Development Event is designed to stimulate student interest and to promote forestry instruction in the agricultural education curriculum and to
tunity to rate their regions and tree
 FIRE RESISTANCE IN THE FOREST Bxr T..J. STARKER Pro/essor o/ Forest, ry, Oregon State College A rating scale of the resistance to fire would be helpful knowledge in the management of a forest in any region.
FIRE RESISTANCE IN THE FOREST Bxr T..J. STARKER Pro/essor o/ Forest, ry, Oregon State College A rating scale of the resistance to fire would be helpful knowledge in the management of a forest in any region.
FIRE PERFORMANCE OF WOOD: TEST METHODS AND FIRE RETARDANT TREATMENTS. Abstract
 FIRE PERFORMANCE OF WOOD: TEST METHODS AND FIRE RETARDANT TREATMENTS Mitchell S. Sweet Fire Safety of Wood Products, USDA Forest Service Forest Products Laboratory 1 One Gifford Pinchot Drive Madison,
FIRE PERFORMANCE OF WOOD: TEST METHODS AND FIRE RETARDANT TREATMENTS Mitchell S. Sweet Fire Safety of Wood Products, USDA Forest Service Forest Products Laboratory 1 One Gifford Pinchot Drive Madison,
The importance of plant size for successful forest plantation establishment Conor O Reilly 1, Michael Keane 2 and Ned Morrissey 3
 Reproductive Material No. 5 The importance of plant size for successful forest plantation establishment Conor O Reilly 1, Michael Keane 2 and Ned Morrissey 3 Bare-root stock is grown in nursery beds, then
Reproductive Material No. 5 The importance of plant size for successful forest plantation establishment Conor O Reilly 1, Michael Keane 2 and Ned Morrissey 3 Bare-root stock is grown in nursery beds, then
RESEARCHES CONCERNING THE CHEMICAL PRESERVATION OF WOOD USED IN CONDITIONS OF HAZARD CLASS 4
 RESEARCHES CONCERNING THE CHEMICAL PRESERVATION OF WOOD USED IN CONDITIONS OF HAZARD CLASS 4 OCTAVIA ZELENIUC, LUMINIŢA ENESCU, MARIANA PRUNĂ National Institute of Wood - I.N.L., Bucharest, Romania ABSTRACT
RESEARCHES CONCERNING THE CHEMICAL PRESERVATION OF WOOD USED IN CONDITIONS OF HAZARD CLASS 4 OCTAVIA ZELENIUC, LUMINIŢA ENESCU, MARIANA PRUNĂ National Institute of Wood - I.N.L., Bucharest, Romania ABSTRACT
BIOL 462 Dendrology Study Guide, Exam 3
 BIOL 462 Dendrology Study Guide, Exam 3 Plant Anatomy & Physiology: 1. What are the functions of the stem, leaves, and roots (i.e., support, transport, storage, photosynthesis, transpiration, anchorage,
BIOL 462 Dendrology Study Guide, Exam 3 Plant Anatomy & Physiology: 1. What are the functions of the stem, leaves, and roots (i.e., support, transport, storage, photosynthesis, transpiration, anchorage,
1992 EXTENSION DEMONSTRATION AND RESEARCH REPORT COOPERATIVE EXTENSION SERVICE UNIVERSITY OF ALASKA FAIRBANKS FAIRBANKS, ALASKA
 1992 EXTENSION DEMONSTRATION AND RESEARCH REPORT COOPERATIVE EXTENSION SERVICE UNIVERSITY OF ALASKA FAIRBANKS FAIRBANKS, ALASKA Ken Krieg Editor February, 1993 SERVICE LIFE OF PRESERVATIVE TREATED POSTS
1992 EXTENSION DEMONSTRATION AND RESEARCH REPORT COOPERATIVE EXTENSION SERVICE UNIVERSITY OF ALASKA FAIRBANKS FAIRBANKS, ALASKA Ken Krieg Editor February, 1993 SERVICE LIFE OF PRESERVATIVE TREATED POSTS
Chapter 7 I-Joists and Headers. Brian K. Brashaw Program Director, Natural Resources Research Institute, University of Minnesota Duluth
 Chapter 7 I-Joists and Headers Brian K. Brashaw Program Director, Natural Resources Research Institute, University of Minnesota Duluth Robert J. Ross Project Leader, USDA Forest Products Laboratory P refabricated
Chapter 7 I-Joists and Headers Brian K. Brashaw Program Director, Natural Resources Research Institute, University of Minnesota Duluth Robert J. Ross Project Leader, USDA Forest Products Laboratory P refabricated
ROOT SPREAD CAN BE ESTIMATED FROM CROWN WIDTH OF DOUGLAS FIR, LODGEPOLE PINE, AND OTHER BWllTlSH COLUFABiA TREE SPECIES '
 ROOT SPREAD CAN BE ESTIMATED FROM CROWN WIDTH OF DOUGLAS FIR, LODGEPOLE PINE, AND OTHER BWllTlSH COLUFABiA TREE SPECIES ' By J. HARRY G. SMITH ABSTRACT Knowledge of the relationships between lateral root
ROOT SPREAD CAN BE ESTIMATED FROM CROWN WIDTH OF DOUGLAS FIR, LODGEPOLE PINE, AND OTHER BWllTlSH COLUFABiA TREE SPECIES ' By J. HARRY G. SMITH ABSTRACT Knowledge of the relationships between lateral root
Forest Health Protection
 Forest Health Protection Pacific Southwest Region Date: January 27, 1012 File Code: 3420 To: Subject: Lee Johnson, Acting Forest Supervisor, Mendocino National Forest Biological Evaluation of, Grindstone
Forest Health Protection Pacific Southwest Region Date: January 27, 1012 File Code: 3420 To: Subject: Lee Johnson, Acting Forest Supervisor, Mendocino National Forest Biological Evaluation of, Grindstone
2.4 MANAGING FOR HIGH-VALUE TREES
 2.4 MANAGING FOR HIGH-VALUE TREES BACKGROUND Quality timber trees are important to the region s wood products industry. Quality is determined by tree size and the amount of clear, knot-free lumber the
2.4 MANAGING FOR HIGH-VALUE TREES BACKGROUND Quality timber trees are important to the region s wood products industry. Quality is determined by tree size and the amount of clear, knot-free lumber the
