A practical application of airborne LiDAR for forestry management in Scotland
|
|
|
- Dwight Nicholson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A practical application of airborne LiDAR for forestry management in Scotland Juan Suárez 1, Jacqueline Rosette 2, Bruce Nicoll 1 and Barry Gardiner 1 1 Forest Research Agency of the Forestry Commission, Northern Research Station, Roslin, Midlothian, EH25 9SY, UK. juan.suarez@forestry.gsi.gov.uk 2 Climate and Land-Surface Systems Interaction Centre, Geography Department, Swansea University, Swansea, SA2 8JP, UK. ggrosette@swansea.ac.uk Abstract This paper presents an assessment of the risk of windthrow for an area of ancient woodland of high environmental importance in Scotland, UK. ForestGALES (Geographical Analysis of the Losses and Effects of Storms in Forestry) is a process-based model, which identifies wind vulnerability. The collection of plot-level field data has previously permitted this model to be run for stand-level analysis. In this study, airborne LiDAR data were used to produce a normalised canopy height model (CHM). An algorithm was designed within Definiens Developer 7.0 object oriented analysis software in order to delineate individual tree crowns from the CHM. The results of this delineation were used to develop regression equations using individual tree height and crown width to estimate diameter at breast height. This aims to allow structural vegetation properties to be related to the spatial distribution of individuals. The spatial arrangement of individual tree heights and diameters at breast height were used to generate tree lists and use them as inputs to ForestGALES. This allowed the stability of individual trees to be mapped by modelling the critical wind speed at which they are predicted to be overturned. This offers a substantial improvement on previous model outputs and provides important data, which can inform forest management decisions. Keywords: Airborne LiDAR; high point density; canopy delineation; windthrow 1. Introduction Topographic exposure, the degree of exposure to Atlantic storms, shielding from adjacent vegetation together with individual tree dimensions are factors that need to be considered when modelling susceptibility to wind. Understanding these processes and site-specific risk will not only allow appropriate management of wind risk but also permit the optimum felling age of stands to be identified. Airborne LiDAR data enables the locations, heights and canopy dimensions of individual trees to be mapped and therefore addresses many of the data requirements for assessing vulnerability to wind (Suárez et al 2008). Glen Affric consists of an area of lochs, moorland and mountains in the Scottish Highlands. It contains one of the largest ancient Caledonian pinewoods in Scotland, consisting of species such as Scots pine, junipers, birches, willows and aspen. This diverse landscape provides habitats for a wide range of plant, animal and bird species. As a result, it has been designated a Caledonian Forest Reserve, National Scenic Area and National Nature Reserve. Since the 1960s, the core area of Glen Affric has been under conservation management by the Forestry Commission of Great Britain in recognition of its high environmental value (Forestry Commission 2008a, 2008b). 581
2 2. Aims Forest management plans contemplate a progressive transition from a traditional planting and clear-felling to a natural system characterised by a permanent presence of trees, selective cuttings and natural regeneration. The ultimate goal is the progressive substitution of non-native species for those ones that define a Caledonia forest. However, this area is regularly subjected to storm events coming from the North Atlantic added to permanent waterlogged conditions, which makes it vulnerable to wind damage during those storm events. This study was conducted as part of the EU-funded Interreg project StormRISK. The aim was to test the capabilities of LiDAR analysis to provide more accurate information than that routinely gathered in the field by the forest district. In particular, this work looked at mapping structural differences within the forest stands such as the spatial distribution of individual trees, distance between neighbours, individual tree heights and stem diameters. All this information has been used to generate tree lists that were subsequently input into the ForestGALES model (Geographical Analysis of the Losses and Effects of Storms in Forestry) to make predictions of the Critical Wind Speed required to overturn each tree. ForestGALES is a process-based model which enables risk of wind damage to be assessed for different management scenarios and with changing conditions due to stand growth (Gardiner et al 2004, Forestry Commission 2008b, Suárez et al 2008). Given local site characteristics, the model therefore identifies the wind speed at which windthrow will occur. Risk is expressed as the reoccurrence period of the critical wind speed calculated to overturn an average tree within a stand. These return times have been mapped for Britain using wind strength scores called DAMS (Detailed Aspect Method of Scoring). 3. Data Airborne LiDAR data were acquired for an area of 58 km 2 on 9 th, 11 th and 13 th June 2007 by The Environment Agency Science Enterprise Centre on behalf of Forest Research. The Optech ALTM 3100 LiDAR system was used recording up to four return echoes per laser shot at approximately 0.25m resolution. This resulted in an average pre-processed point density of approximately points/ m 2 producing good energy penetration throughout the canopy (Figure 1). Figure 1. LiDAR point cloud cross section of Glen Affric, Scotland. Image produced with Terrascan. 582
3 4. Methods A subset of airborne LiDAR data was used for a 1km x 2km area representing the range of surface and vegetative characteristics present within Glen Affric (Figure 2). This study area comprises stands of Scots Pine (Pinus sylvestris), Birch (Betula spp.), European Larch (Larix decidua), Douglas Fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii), mixed conifers, Sitka Spruce (Picea sitchensis), Norway Spruce (Picea abies) and Lodgepole Pine (Pinus contorta) in order of occurrence. Scots Pine formed the oldest and youngest stands of 208 and 8 years old respectively. For the purposes of this study, field measurements and models for stands of Scots Pine (Pinus sylvestris) are to be used for validation. The LiDAR data were processed as outlined below. Figure 2. (left) 0.5m resolution digital terrain model of a 1km x 1km area produced with Golden Software Surfer 8. (right) Canopy height model of the same area using ArcGIS 9.1 A ground return class was determined from last return echoes using Terrascan Software an extension application for Bentley Microstation V This ground class and all first return data were subsequently exported and converted into regular 0.5m resolution raster geotiffs using Delaunay triangulation with linear interpolation. A canopy height model (CHM) was calculated as the difference between the digital terrain model (DTM) created from the ground class and the digital surface model (DSM) from the first return data using ArcGIS 9.1. An algorithm was designed within Definiens Developer 7.0 to delineate individual tree canopies solely from the LiDAR-derived 0.5m resolution canopy height model. Firstly the CHM was smoothed with a kernel of 3x3 and local maxima were located and classified as tree tops. Areas of ground or understorey vegetation, plus canopy edges were identified and used as boundaries to prevent further canopy growth. Tree tops were subsequently extended radially until either meeting an adjacent canopy or designated boundaries and a mask was applied to limit irregularly shaped polygons. Tree top locations were then saved as point shapefiles and polygons representing individual canopies were also exported with associated maximum canopy height, area, maximum and minimum radii, width and polygon centroid co-ordinates. An allometric relationship between canopy width and height with diameter at breast height (DBH) was developed using the Forest Research Environmental Database (FRED) containing field measurements for more than 15,000 trees over the entire country. This model allowed the estimation of stem diameters for each individual tree. Thus, stand information obtained form the FC sub-compartment database was used to generate mean wind conditions inside the forest canopy for each stand in ForestGALES. Tree lists 583
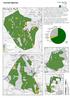
4 generated from LiDAR were used to calculate resistive factors at tree level. Finally, edge effects were estimated from the distance between each individual to its neighbours (Figures 3-5). Figure 3. Estimation of individual tree heights (in m). Figure 4. Estimation of individual DBH (in cm). Figure 5. Critical wind speed for overturning each tree (in ms -1 ). The most stable trees are depicted in green. 5. Results and Discussion The canopy delineation method produced a better description of the influence of stand structure on the risk of wind damage. This is a substantial improvement compared to the normal way of operating ForestGALES, with just mean stand parameters, because it allows the most vulnerable parts of the stand to be located. This is true for those individuals that are not properly sheltered by neighbours or present lower taper values. In Figure 5, the most vulnerable trees, depicted in red, are around the edges of the stand or inside the forest canopy if their taper relationships are below 80. On the contrary larger canopy dimensions, high taper values and sheltered trees are more stable and require higher critical wind speed values for overturning. Most of those trees, depicted in orange, require wind speeds between 10 and 20 ms
5 The practical consequences for future management plans will contemplate the choice of thinning practices (normally ruling out thinning), the degree of exposure to certain parts of the stand when clearfelling neighbouring stands, the location of forest roads (normally avoiding the sudden exposure of vulnerable individuals), etc. The limitations of the ForestGALES method come from the modelling of the adaptation of trees to changing exposure conditions. In this case, most of the trees around the edges of the stands or those trees growing in open stands or in total isolation are already very well adapted to wind conditions. In particular, those individuals that form part of the remnants of the ancient Caledonian pinewood have been growing in isolation for more than 100 years without being affected by windthrow (top left of Figure 5). Therefore, this method seems to be more useful for new plantations (like the one than occupies most of the image) than for isolated individuals. More research will be required in the future for parameterising this adaptation to wind. Acknowledgements Many thanks to the Fort Augustus Forest District under whose responsibility Glen Affric lies and to the Interreg North Sea region StormRISK for funding this research. References Forestry Commission, 2008a, Glen Affric. Available online from: restglenaffric date accessed: May 2008 Forestry Commission, 2008b, Improving the ecological content of Forest Plans; A Case Study from Glen Affric, Forestry Commission Scotland, Forest Research, May 2008 Gardiner, B.A., Suárez, J.C., Achim, A., Hale, S. and Nicholl, B. 2004, ForestGALES 2.0; A PC-based wind risk model for British Forests. Forestry Commission Publications. Edinburgh. ISBN pp Suárez, J., Garcia, R., Gardiner, B. and Patenaude, G., 2008, The Estimation of Wind Risk in Forests Stands using Airborne Laser Scanning (ALS). Journal of Forest Planning, 13,
Object-based approach for mapping complex forest structure phases using LiDAR data
 Object-based approach for mapping complex forest structure phases using LiDAR data M. Petr* a, M. Smith a, J.C. Suaréz b a Centre for Human and Ecological Sciences, Forest Research, Northern Research Station,
Object-based approach for mapping complex forest structure phases using LiDAR data M. Petr* a, M. Smith a, J.C. Suaréz b a Centre for Human and Ecological Sciences, Forest Research, Northern Research Station,
FOREST PARAMETER EXTRACTION USING TERRESTRIAL LASER SCANNING
 FOREST PARAMETER EXTRACTION USING TERRESTRIAL LASER SCANNING P.J.Watt *, D.N.M. Donoghue and R.W. Dunford Department of Geography, University of Durham, Durham, DH1 3LE, United Kingdom *Corresponding author:
FOREST PARAMETER EXTRACTION USING TERRESTRIAL LASER SCANNING P.J.Watt *, D.N.M. Donoghue and R.W. Dunford Department of Geography, University of Durham, Durham, DH1 3LE, United Kingdom *Corresponding author:
The GB National Forest Inventory
 The GB National Forest Inventory NFI design 1. Forest Map 2. 15,000 one Ha Survey Squares 3. Map + Squares brought together in the NFI DB 4. Survey Square details multiplied up to the NFI map area X GB
The GB National Forest Inventory NFI design 1. Forest Map 2. 15,000 one Ha Survey Squares 3. Map + Squares brought together in the NFI DB 4. Survey Square details multiplied up to the NFI map area X GB
Airborne Laser Scanning (ALS) for forestry applications
 Airborne Laser Scanning (ALS) for forestry applications International School on Lidar Technology 2008 IIT Kanpur, India Norbert Pfeifer + I.P.F.-Team http://www.ipf.tuwien.ac.at/ Christian Doppler Laboratory
Airborne Laser Scanning (ALS) for forestry applications International School on Lidar Technology 2008 IIT Kanpur, India Norbert Pfeifer + I.P.F.-Team http://www.ipf.tuwien.ac.at/ Christian Doppler Laboratory
Habitat Management in Red Squirrel Reserves and Buffer Zones in Northern England
 Habitat Management in Red Squirrel Reserves and Buffer Zones in Northern England Red squirrel populations are suffering major decline in England. This is due to elements of habitat loss, and as a result
Habitat Management in Red Squirrel Reserves and Buffer Zones in Northern England Red squirrel populations are suffering major decline in England. This is due to elements of habitat loss, and as a result
ESTIMATION OF TREE SIZE DISTRIBUTIONS BY COMBINING VERTICAL AND HORIZONTAL DISTRIBUTION OF LASER MEASUREMENTS WITH EXTRACTION OF INDIVIDUAL TREES
 ESTIMATION OF TREE SIZE DISTRIBUTIONS BY COMBINING VERTICAL AND HORIZONTAL DISTRIBUTION OF LASER MEASUREMENTS WITH EXTRACTION OF INDIVIDUAL TREES Johan Holmgren and Jörgen Wallerman Swedish University
ESTIMATION OF TREE SIZE DISTRIBUTIONS BY COMBINING VERTICAL AND HORIZONTAL DISTRIBUTION OF LASER MEASUREMENTS WITH EXTRACTION OF INDIVIDUAL TREES Johan Holmgren and Jörgen Wallerman Swedish University
Terrestrial Laser Scanning in Forest Inventories
 ARTICLE TOWARD INTERNATIONAL BENCHMARKS Terrestrial Laser Scanning in Forest Inventories Measuring Tree Attributes Terrestrial laser scanning (TLS) is an effective technique for acquiring detailed tree
ARTICLE TOWARD INTERNATIONAL BENCHMARKS Terrestrial Laser Scanning in Forest Inventories Measuring Tree Attributes Terrestrial laser scanning (TLS) is an effective technique for acquiring detailed tree
Estimation of tree lists from airborne laser scanning data using a combination of analysis on single tree and raster cell level
 Estimation of tree lists from airborne laser scanning data using a combination of analysis on single tree and raster cell level Eva Lindberg 1, Johan Holmgren 1, Kenneth Olofsson 1, Håkan Olsson 1 and
Estimation of tree lists from airborne laser scanning data using a combination of analysis on single tree and raster cell level Eva Lindberg 1, Johan Holmgren 1, Kenneth Olofsson 1, Håkan Olsson 1 and
WILDING EXOTIC TREES. QLDC PROPOSED DISTRICT PLAN [PART FIVE] DECISIONS VERSION 34 Wilding Exotic Trees
![WILDING EXOTIC TREES. QLDC PROPOSED DISTRICT PLAN [PART FIVE] DECISIONS VERSION 34 Wilding Exotic Trees WILDING EXOTIC TREES. QLDC PROPOSED DISTRICT PLAN [PART FIVE] DECISIONS VERSION 34 Wilding Exotic Trees](/thumbs/84/89679179.jpg) 34 WILDING EXOTIC TREES 34.1 Purpose The purpose of these provisions is to prevent the spread of wilding exotic trees. Wilding is the term used for the natural regeneration or seedling spread of exotic
34 WILDING EXOTIC TREES 34.1 Purpose The purpose of these provisions is to prevent the spread of wilding exotic trees. Wilding is the term used for the natural regeneration or seedling spread of exotic
Epsilon Open Archive
 This is an author produced version of a paper published in International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Volume XXXIX-B8, 2012XXII ISPRS Congress, 25 August
This is an author produced version of a paper published in International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Volume XXXIX-B8, 2012XXII ISPRS Congress, 25 August
Forest and climate change
 Forest and climate change Seppo Kellomäki University of Eastern Finland School of Forest Sciences Joensuu Campus Finland 1 Contents Forests in the world Global climate change and impacts on forests Climate
Forest and climate change Seppo Kellomäki University of Eastern Finland School of Forest Sciences Joensuu Campus Finland 1 Contents Forests in the world Global climate change and impacts on forests Climate
Mapping Scotland with PALSAR: An Assessment of the Importance of L-Band Polarimetry
 Mapping Scotland with PALSAR: An Assessment of the Importance of L-Band Polarimetry Shane R. Cloude, AEL Consultants,Scotland, UK E-mail : aelc@mac.com Web :http://web.mac.com/aelc Iain H Woodhouse (2),
Mapping Scotland with PALSAR: An Assessment of the Importance of L-Band Polarimetry Shane R. Cloude, AEL Consultants,Scotland, UK E-mail : aelc@mac.com Web :http://web.mac.com/aelc Iain H Woodhouse (2),
Continuous Cover Forestry
 Silviculture / Management No. 8 Continuous cover forestry (CCF) is a management option in which canopy cover is maintained continuously, the soil is never exposed, and clearfelling is avoided for areas
Silviculture / Management No. 8 Continuous cover forestry (CCF) is a management option in which canopy cover is maintained continuously, the soil is never exposed, and clearfelling is avoided for areas
Farm Woodland Forum Annual Meeting, May , Organic Research Centre, Newbury
 Management of ash in Ireland in the light of ash dieback Dr Ian Short Jerry Campion Teagasc Forestry Development Dept. Ashtown Research Centre, Dublin 15 Overview of presentation Ash age profile Scenarios
Management of ash in Ireland in the light of ash dieback Dr Ian Short Jerry Campion Teagasc Forestry Development Dept. Ashtown Research Centre, Dublin 15 Overview of presentation Ash age profile Scenarios
Felling Decision Tool - Conifers
 Silviculture/Management No. 22 COFORD 2016 Estimates timber revenues for the main conifer species. User can select timber prices and rotation type. Estimates the revenue loss for felling earlier than rotation
Silviculture/Management No. 22 COFORD 2016 Estimates timber revenues for the main conifer species. User can select timber prices and rotation type. Estimates the revenue loss for felling earlier than rotation
Insect damage risk in continuous cover forests and forests managed in new ways.
 Insect damage risk in continuous cover forests and forests managed in new ways. Helena Bylund Dept. of Ecology, Unit of Forest Entomology Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Based on a book chapter
Insect damage risk in continuous cover forests and forests managed in new ways. Helena Bylund Dept. of Ecology, Unit of Forest Entomology Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences Based on a book chapter
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
 GLOBAL FOREST RESOURCES ASSESSMENT 2015 COUNTRY REPORT United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland Rome, 2014 FAO, at the request of its member countries, regularly monitors the world s forests
GLOBAL FOREST RESOURCES ASSESSMENT 2015 COUNTRY REPORT United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland Rome, 2014 FAO, at the request of its member countries, regularly monitors the world s forests
forests ISSN
 Forests 2015, 6, 879-902; doi:10.3390/f6040879 Review OPEN ACCESS forests ISSN 1999-4907 www.mdpi.com/journal/forests Implementing Continuous Cover Forestry in Planted Forests: Experience with Sitka Spruce
Forests 2015, 6, 879-902; doi:10.3390/f6040879 Review OPEN ACCESS forests ISSN 1999-4907 www.mdpi.com/journal/forests Implementing Continuous Cover Forestry in Planted Forests: Experience with Sitka Spruce
PREDICTING DIAMETER AT BREAST HEIGHT FROM TOTAL HEIGHT AND CROWN LENGTH
 PREDICTING DIAMETER AT BREAST HEIGHT FROM TOTAL HEIGHT AND CROWN LENGTH Quang V. Cao and Thomas J. Dean Abstract Tree diameter at breast height (d.b.h.) is often predicted from total height (model a) or
PREDICTING DIAMETER AT BREAST HEIGHT FROM TOTAL HEIGHT AND CROWN LENGTH Quang V. Cao and Thomas J. Dean Abstract Tree diameter at breast height (d.b.h.) is often predicted from total height (model a) or
Development of Measurement System for Evaluating Forest Ecosystems: Measurement Method of Aboveground Biomass Growth by Using Airborne Laser Survey
 Phyton (Austria) Special issue: "APGC 2004" Vol. 45 Fasc. 4 (517M524) 1.10.2005 Development of Measurement System for Evaluating Forest Ecosystems: Measurement Method of Aboveground Biomass Growth by Using
Phyton (Austria) Special issue: "APGC 2004" Vol. 45 Fasc. 4 (517M524) 1.10.2005 Development of Measurement System for Evaluating Forest Ecosystems: Measurement Method of Aboveground Biomass Growth by Using
Estimation of forest above-ground biomass rate using airborne LiDAR data
 Popov M., Semko I., Kozak I., 2014. Estimation of forest above-ground biomass rate using airborne LiDAR data. PEK, T. XXXVIII, 33-40. Estimation of forest above-ground biomass rate using airborne LiDAR
Popov M., Semko I., Kozak I., 2014. Estimation of forest above-ground biomass rate using airborne LiDAR data. PEK, T. XXXVIII, 33-40. Estimation of forest above-ground biomass rate using airborne LiDAR
Table of Contents. Page 1 of 15
 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Steps of Lidar Tree Crown Identification Accuracy Analysis... 4 2.1 Ground Truthing Field Work... 4 2.2 Lidar Tree Crown Identification Accuracy Analysis and Algorithm
Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Steps of Lidar Tree Crown Identification Accuracy Analysis... 4 2.1 Ground Truthing Field Work... 4 2.2 Lidar Tree Crown Identification Accuracy Analysis and Algorithm
Current Age Class. Legend
 Current Species Page 14 The species composition of the Dartmoor forests is predominantly made up of Sitka spruce, 65% (904ha) of the Plan Area. The minor species are primarily made up of other conifers
Current Species Page 14 The species composition of the Dartmoor forests is predominantly made up of Sitka spruce, 65% (904ha) of the Plan Area. The minor species are primarily made up of other conifers
Evaluation of forest function using GIS data generated by LiDAR data UC th July 2014 ASIA AIR SURVEY Katsumasa OONO
 Evaluation of forest function using GIS data generated by LiDAR data UC644 15 th July 2014 ASIA AIR SURVEY Katsumasa OONO Back Ground & purpose In Japan, the Regional Forest Plan is planed every five year.
Evaluation of forest function using GIS data generated by LiDAR data UC644 15 th July 2014 ASIA AIR SURVEY Katsumasa OONO Back Ground & purpose In Japan, the Regional Forest Plan is planed every five year.
ESTIMATION OF GROWTH RATES AT KIELDER FOREST USING AIRBORNE LASER SCANNING
 ESTIMATION OF GROWTH RATES AT KIELDER FOREST USING AIRBORNE LASER SCANNING A.S. Woodget*, D.M.N. Donoghue and P.E. Carbonneau. Department of Geography, University of Durham, Science Laboratories, South
ESTIMATION OF GROWTH RATES AT KIELDER FOREST USING AIRBORNE LASER SCANNING A.S. Woodget*, D.M.N. Donoghue and P.E. Carbonneau. Department of Geography, University of Durham, Science Laboratories, South
North West Geography
 ISSN 1476-1580 North West Geography Volume 11, Number 1, 2011 North West Geography, Volume 11, 2011 7 Characterising phenological changes in North West forests using terrestrial laser scanning: some preliminary
ISSN 1476-1580 North West Geography Volume 11, Number 1, 2011 North West Geography, Volume 11, 2011 7 Characterising phenological changes in North West forests using terrestrial laser scanning: some preliminary
Stability of LiDAR-derived raster canopy attributes with changing pulse repetition frequency
 Stability of LiDAR-derived raster canopy attributes with changing pulse repetition frequency Allyson Fox 1,2, Chris Hopkinson 2,1 Laura Chasmer 3 & Ashley Wile 2 1Acadia University, Wolfville, Nova Scotia,
Stability of LiDAR-derived raster canopy attributes with changing pulse repetition frequency Allyson Fox 1,2, Chris Hopkinson 2,1 Laura Chasmer 3 & Ashley Wile 2 1Acadia University, Wolfville, Nova Scotia,
2009 Council on Forest Engineering (COFE) Conference Proceedings: Environmentally Sound Forest Operations. Lake Tahoe, June 15-18, 2009
 2009 Council on Forest Engineering (COFE) Conference Proceedings: Environmentally Sound Forest Operations. Lake Tahoe, June 15-18, 2009 Determining Radiata pine tree value and log product yields using
2009 Council on Forest Engineering (COFE) Conference Proceedings: Environmentally Sound Forest Operations. Lake Tahoe, June 15-18, 2009 Determining Radiata pine tree value and log product yields using
LiDAR based sampling for subtle change, developments, and status
 LiDAR based sampling for subtle change, developments, and status Erik Næsset Norwegian University of Life Sciences, Norway 2111 2005 Conclusions: 1. LiDAR is an extremely precise tool for measuring forest
LiDAR based sampling for subtle change, developments, and status Erik Næsset Norwegian University of Life Sciences, Norway 2111 2005 Conclusions: 1. LiDAR is an extremely precise tool for measuring forest
Cross correlation of diameter measures for the co registration of forest inventory plots with airborne laser scanning data
 Cross correlation of diameter measures for the co registration of forest inventory plots with airborne laser scanning data J.M. Monnet, E. Mermin To cite this version: J.M. Monnet, E. Mermin. Cross correlation
Cross correlation of diameter measures for the co registration of forest inventory plots with airborne laser scanning data J.M. Monnet, E. Mermin To cite this version: J.M. Monnet, E. Mermin. Cross correlation
Fig. 1. Location of the study area in southern Finland (61 15 N; E; left) and study area (encircled) with the locations of natural (bolded
 Fig. 1. Location of the study area in southern Finland (61 15 N; 25 03 E; left) and study area (encircled) with the locations of natural (bolded circle), managed core (filled circle) and other managed
Fig. 1. Location of the study area in southern Finland (61 15 N; 25 03 E; left) and study area (encircled) with the locations of natural (bolded circle), managed core (filled circle) and other managed
Forest Assessments with LiDAR: from Research to Operational Programs
 Forest Assessments with LiDAR: from Research to Operational Programs David L. Evans Department of Forestry Forest and Wildlife Research Center Mississippi State University Forest Remote Sensing: Then and
Forest Assessments with LiDAR: from Research to Operational Programs David L. Evans Department of Forestry Forest and Wildlife Research Center Mississippi State University Forest Remote Sensing: Then and
Determining the Disturbance Effect on Forest Development for Use in Park Management Plans
 Determining the Disturbance Effect on Forest Development for Use in Park Management Plans Bruce Larson, Faculty of Forestry, University of British Columbia, 2329 West Mall, Vancouver, BC V6T 1Z4, Canada;
Determining the Disturbance Effect on Forest Development for Use in Park Management Plans Bruce Larson, Faculty of Forestry, University of British Columbia, 2329 West Mall, Vancouver, BC V6T 1Z4, Canada;
Comparison of Current and Future Boreal Fire Regimes in Canada and Russia
 Comparison of Current and Future Boreal Fire Regimes in Canada and Russia WJ de Groot MD Flannigan BJ Stocks DR Cahoon AJ Soja E Kukavskaya G Ivanova AS Cantin N Jurko SG Conard 1 Outline General fuel,
Comparison of Current and Future Boreal Fire Regimes in Canada and Russia WJ de Groot MD Flannigan BJ Stocks DR Cahoon AJ Soja E Kukavskaya G Ivanova AS Cantin N Jurko SG Conard 1 Outline General fuel,
Teton County Flammulated Owl Survey
 Teton County Flammulated Owl Survey 2016 Teton Raptor Center Report Teton Raptor Center, funded by Teton Conservation District, initiated Flammulated Owl (Psiloscops flammeolus) surveys in a portion of
Teton County Flammulated Owl Survey 2016 Teton Raptor Center Report Teton Raptor Center, funded by Teton Conservation District, initiated Flammulated Owl (Psiloscops flammeolus) surveys in a portion of
Bending and compression properties of small diameter round timber
 Bending and compression properties of small diameter round timber Ranta-Maunus, Alpo ABSTRACT Objective of the completed European project was to find new uses for small diameter round timber harvested
Bending and compression properties of small diameter round timber Ranta-Maunus, Alpo ABSTRACT Objective of the completed European project was to find new uses for small diameter round timber harvested
CHURN CREEK BIGHORN SHEEP MIGRATION CORRIDOR RESTORATION TREATMENTS. INTRODUCTION. Progress Report, prepared by. Ken MacKenzie, R. P. Bio.
 CHURN CREEK BIGHORN SHEEP MIGRATION CORRIDOR RESTORATION TREATMENTS. Progress Report, 2008 prepared by Ken MacKenzie, R. P. Bio. For Becky Bings, Ministry of Environment, Williams Lake INTRODUCTION The
CHURN CREEK BIGHORN SHEEP MIGRATION CORRIDOR RESTORATION TREATMENTS. Progress Report, 2008 prepared by Ken MacKenzie, R. P. Bio. For Becky Bings, Ministry of Environment, Williams Lake INTRODUCTION The
AUTOMATIC DELINEATION OF FOREST STANDS FROM LIDAR DATA
 AUTOMATIC DELINEATION OF FOREST STANDS FROM LIDAR DATA V. J. Leppänen a, *, T. Tokola a, M. Maltamo a, L. Mehtätalo a, T. Pusa b, J. Mustonen c a University of Joensuu, Faculty of Forest Sciences PL111,
AUTOMATIC DELINEATION OF FOREST STANDS FROM LIDAR DATA V. J. Leppänen a, *, T. Tokola a, M. Maltamo a, L. Mehtätalo a, T. Pusa b, J. Mustonen c a University of Joensuu, Faculty of Forest Sciences PL111,
SAR forest canopy penetration depth as an indicator for forest health monitoring based on leaf area index (LAI)
 SAR forest canopy penetration depth as an indicator for forest health monitoring based on leaf area index (LAI) Svein Solberg 1, Dan Johan Weydahl 2, Erik Næsset 3 1 Norwegian Forest and Landscape Institute,
SAR forest canopy penetration depth as an indicator for forest health monitoring based on leaf area index (LAI) Svein Solberg 1, Dan Johan Weydahl 2, Erik Næsset 3 1 Norwegian Forest and Landscape Institute,
Environmental Modelling & Software
 Environmental Modelling & Software 68 (205) 27e4 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Environmental Modelling & Software journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/envsoft Comparison and validation
Environmental Modelling & Software 68 (205) 27e4 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Environmental Modelling & Software journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/envsoft Comparison and validation
Airborne LiDAR and SAR estimation of forest top height
 Airborne LiDAR and SAR estimation of forest top height E. D. Wallington 1* and J.C. Suárez 2 1 Forestry Commission, Silvan House, 231 Corstorphine Road, Edinburgh, EH12 7AT, UK. *e-mail: edward.wallington@forestry.gsi.gov.uk
Airborne LiDAR and SAR estimation of forest top height E. D. Wallington 1* and J.C. Suárez 2 1 Forestry Commission, Silvan House, 231 Corstorphine Road, Edinburgh, EH12 7AT, UK. *e-mail: edward.wallington@forestry.gsi.gov.uk
Features of the Forest Canopy at Sierra Sooty Grouse Courtship Sites
 Features of the Forest Canopy at Sierra Sooty Grouse Courtship Sites CDFG Contract No. S0680003 James D. Bland 705 Birch Court, Herndon, VA 20170 Basic features of the forest canopy were recorded at ten
Features of the Forest Canopy at Sierra Sooty Grouse Courtship Sites CDFG Contract No. S0680003 James D. Bland 705 Birch Court, Herndon, VA 20170 Basic features of the forest canopy were recorded at ten
State of the Forests and Management Trends in the Forests of Northwest Russia
 State of the Forests and Management Trends in the Forests of Northwest Russia Prof. Dr. Alexander Alekseev Head of the Dept. of Forest Inventory, Management and GIS of Saint- Petersburg State Forest Technical
State of the Forests and Management Trends in the Forests of Northwest Russia Prof. Dr. Alexander Alekseev Head of the Dept. of Forest Inventory, Management and GIS of Saint- Petersburg State Forest Technical
FORESTRY IN UKRAINE: CURRENT STATE AND DEVELOPMENT TRENDS
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series II: Forestry Wood Industry Agricultural Food Engineering Vol. 9 (58) No.2-2016 FORESTRY IN UKRAINE: CURRENT STATE AND DEVELOPMENT TRENDS H. T. KRYNYTSKYY
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series II: Forestry Wood Industry Agricultural Food Engineering Vol. 9 (58) No.2-2016 FORESTRY IN UKRAINE: CURRENT STATE AND DEVELOPMENT TRENDS H. T. KRYNYTSKYY
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR BEST PRACTICE
 PRODUCED BY THE COMMITTEE ON PLANT SUPPLY AND ESTABLISHMENT SPECIFYING SEED SOURCES FOR TREES FOR LARGE SCALE AMENITY AND FORESTRY PLANTING RECOMMENDATIONS FOR BEST PRACTICE ON BEHALF OF THE JOINT COUNCIL
PRODUCED BY THE COMMITTEE ON PLANT SUPPLY AND ESTABLISHMENT SPECIFYING SEED SOURCES FOR TREES FOR LARGE SCALE AMENITY AND FORESTRY PLANTING RECOMMENDATIONS FOR BEST PRACTICE ON BEHALF OF THE JOINT COUNCIL
Monitoring and Managing CCF in Ireland. Áine Ní Dhubháin and Lucie Vítková. A presentation from the CCFG National Conference 2014
 Monitoring and Managing CCF in Ireland Áine Ní Dhubháin and Lucie Vítková A presentation from the CCFG National Conference 214 Continuous Cover Forestry: Delivering sustainable and resilient woodlands
Monitoring and Managing CCF in Ireland Áine Ní Dhubháin and Lucie Vítková A presentation from the CCFG National Conference 214 Continuous Cover Forestry: Delivering sustainable and resilient woodlands
Forest tree breeding and Gene conservation in Denmark
 Forest tree breeding and Gene conservation in Denmark NordGen Akureyri, April 2018 Gunnar Friis Proschowsky Introduction: - The Nature Agency - Danish Forest area - Institutions Breeding programmes: -
Forest tree breeding and Gene conservation in Denmark NordGen Akureyri, April 2018 Gunnar Friis Proschowsky Introduction: - The Nature Agency - Danish Forest area - Institutions Breeding programmes: -
Introduced or native tree species to maintain forest ecosystem services in a hotter and drier future?
 Introduced or native tree species to maintain forest ecosystem services in a hotter and drier future? A. Rigling, A. Gessler, L. Feichtinger, V. Queloz, T. Wohlgemuth Drought and tree mortality Global
Introduced or native tree species to maintain forest ecosystem services in a hotter and drier future? A. Rigling, A. Gessler, L. Feichtinger, V. Queloz, T. Wohlgemuth Drought and tree mortality Global
Access to the published version may require journal subscription. Published with permission from: Taylor & Francis.
 This is an author produced version of a paper published in International Journal of Remote Sensing. This paper has been peer-reviewed and is proof-corrected, but does not include the journal pagination.
This is an author produced version of a paper published in International Journal of Remote Sensing. This paper has been peer-reviewed and is proof-corrected, but does not include the journal pagination.
rufa group): their contribution to soil C and N pools and CO 2 emissions in subalpine conifer forests
 Red wood ants (Formica( rufa group): their contribution to soil C and N pools and CO 2 emissions in subalpine conifer forests Anita C. Risch (Syracuse University,USA) Martin F. Jurgensen (Michigan Technological
Red wood ants (Formica( rufa group): their contribution to soil C and N pools and CO 2 emissions in subalpine conifer forests Anita C. Risch (Syracuse University,USA) Martin F. Jurgensen (Michigan Technological
ASSESSING THE STRUCTURE OF DEGRADED FOREST USING UAV
 ASSESSING THE STRUCTURE OF DEGRADED FOREST USING UAV STUDY CASE IN YUNGAS CLOUD FOREST, NORTH ARGENTINA Fernando Rossi 1, Andreas Fritz 2, Gero Becker 1, Barbara Koch 2 Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg
ASSESSING THE STRUCTURE OF DEGRADED FOREST USING UAV STUDY CASE IN YUNGAS CLOUD FOREST, NORTH ARGENTINA Fernando Rossi 1, Andreas Fritz 2, Gero Becker 1, Barbara Koch 2 Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg
ForeSTClim Outline of proposed forest modelling work by Forest Research in Group C + D. Duncan Ray Bill Mason Bruce Nicoll Georgios Xenakis
 ForeSTClim Outline of proposed forest modelling work by Forest Research in Group C + D Duncan Ray Bill Mason Bruce Nicoll Georgios Xenakis Topic areas Assessment of UKCIP08 probabilistic simulations for
ForeSTClim Outline of proposed forest modelling work by Forest Research in Group C + D Duncan Ray Bill Mason Bruce Nicoll Georgios Xenakis Topic areas Assessment of UKCIP08 probabilistic simulations for
Comparing the provision of ecosystem services in plantation forests under alternative climate change adaptation management options in Wales
 Reg Environ Change (2015) 15:1501 1513 DOI 10.1007/s10113-014-0644-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparing the provision of ecosystem services in plantation forests under alternative climate change adaptation management
Reg Environ Change (2015) 15:1501 1513 DOI 10.1007/s10113-014-0644-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparing the provision of ecosystem services in plantation forests under alternative climate change adaptation management
INVENTORY? - MEASUREMENTS & - BASIC STATISTICS ARE IMPORTANT FOR PRUDENT FOREST MANAGEMENT
 INVENTORY? - MEASUREMENTS & - BASIC STATISTICS ARE IMPORTANT FOR PRUDENT FOREST MANAGEMENT BY BALOZI AND JARNO Contents What is ArboLiDAR? Input data Sampling and field work Automatic stand segmentation
INVENTORY? - MEASUREMENTS & - BASIC STATISTICS ARE IMPORTANT FOR PRUDENT FOREST MANAGEMENT BY BALOZI AND JARNO Contents What is ArboLiDAR? Input data Sampling and field work Automatic stand segmentation
Predicting productivity using combinations of LiDAR, satellite imagery and environmental data
 Date: June Reference: GCFF TN - 007 Predicting productivity using combinations of LiDAR, satellite imagery and environmental data Author/s: Michael S. Watt, Jonathan P. Dash, Pete Watt, Santosh Bhandari
Date: June Reference: GCFF TN - 007 Predicting productivity using combinations of LiDAR, satellite imagery and environmental data Author/s: Michael S. Watt, Jonathan P. Dash, Pete Watt, Santosh Bhandari
Mapping Hemlocks to Estimate Potential Canopy Gaps Following Hemlock Woolly Adelgid Infestations in the Southern Appalachian Mountains
 Mapping Hemlocks to Estimate Potential Canopy Gaps Following Hemlock Woolly Adelgid Infestations in the Southern Appalachian Mountains Tuula Kantola, Maria Tchakerian, Päivi Lyytikäinen-Saarenmaa, Robert
Mapping Hemlocks to Estimate Potential Canopy Gaps Following Hemlock Woolly Adelgid Infestations in the Southern Appalachian Mountains Tuula Kantola, Maria Tchakerian, Päivi Lyytikäinen-Saarenmaa, Robert
A preliminary evaluation of the application of multi-return LiDAR for forestry in Ireland
 Silviculture / Management No. 18 COFORD 2010 This study is a preliminary examination of the potential of LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) for forest resource assessment in Ireland. LiDAR allows the
Silviculture / Management No. 18 COFORD 2010 This study is a preliminary examination of the potential of LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) for forest resource assessment in Ireland. LiDAR allows the
Effect of growth rate on wood properties of genetically improved Sitka spruce
 Effect of growth rate on wood properties of genetically improved Sitka spruce A.K. LIVINGSTON 1, A.D. CAMERON 1 *, J.A. PETTY 1 AND S.L. LEE 2 1 School of Biological Sciences, University of Aberdeen, MacRobert
Effect of growth rate on wood properties of genetically improved Sitka spruce A.K. LIVINGSTON 1, A.D. CAMERON 1 *, J.A. PETTY 1 AND S.L. LEE 2 1 School of Biological Sciences, University of Aberdeen, MacRobert
Joint Research Centre (JRC)
 11 th European Forum on Urban Forestry. May 2008, Hämeenlinna, Finland - stefano.casalegno@jrc.it 1 Joint Research Centre (JRC) The European Commission s Research-Based Policy Support Organisation URBAN
11 th European Forum on Urban Forestry. May 2008, Hämeenlinna, Finland - stefano.casalegno@jrc.it 1 Joint Research Centre (JRC) The European Commission s Research-Based Policy Support Organisation URBAN
A guide for increasing tree species diversity in Wales
 A guide for increasing tree species diversity in Wales Contents 1. Introduction...3 2. The changing climate...4 3. The need for diversification...5 3.1 What is diversification?...5 3.2 Targeting diversification...6
A guide for increasing tree species diversity in Wales Contents 1. Introduction...3 2. The changing climate...4 3. The need for diversification...5 3.1 What is diversification?...5 3.2 Targeting diversification...6
Development of an energy balance model to estimate stomatal conductance as an indicator of plant stress
 Development of an energy balance model to estimate stomatal conductance as an indicator of plant stress Juan C. Suárez 1, Georgios Xenakis 1, Magdalena Smigaj 2, Roberto Antolín 1,3 1. Centre for Sustainable
Development of an energy balance model to estimate stomatal conductance as an indicator of plant stress Juan C. Suárez 1, Georgios Xenakis 1, Magdalena Smigaj 2, Roberto Antolín 1,3 1. Centre for Sustainable
Precision forestry in Finland
 Precision forestry in Finland ICT Smart Precision Forestry with Laser Scanning, Finland Japan Joint Symposium (3 rd edition), Tokyo Associate Professor Mikko Vastaranta, School of Forest Sciences, Faculty
Precision forestry in Finland ICT Smart Precision Forestry with Laser Scanning, Finland Japan Joint Symposium (3 rd edition), Tokyo Associate Professor Mikko Vastaranta, School of Forest Sciences, Faculty
Forecasting Timber, Biomass, and Tree Carbon Pools with the Output of State and Transition Models
 Proceedings of the First Landscape State-and-Transition Simulation Modeling Conference, June 14 16, 2011 Forecasting Timber, Biomass, and Tree Carbon Pools with the Output of State and Transition Models
Proceedings of the First Landscape State-and-Transition Simulation Modeling Conference, June 14 16, 2011 Forecasting Timber, Biomass, and Tree Carbon Pools with the Output of State and Transition Models
The stability of different silvicultural systems: a wind-tunnel investigation
 The stability of different silvicultural systems: a wind-tunnel investigation BARRY GARDINER 1 *, BRYAN MARSHALL,3, ALEXIS ACHIM 1, REX BELCHER and COLIN WOOD 1 Forestry Research, Northern Research Station,
The stability of different silvicultural systems: a wind-tunnel investigation BARRY GARDINER 1 *, BRYAN MARSHALL,3, ALEXIS ACHIM 1, REX BELCHER and COLIN WOOD 1 Forestry Research, Northern Research Station,
Dead wood modelling at stand-level
 Dead wood modelling at stand-level Jari Hynynen & Harri Mäkinen Finnish Forest Research Institute Vantaa Research Unit MOTTI stand simulator Salminen et al. (2005), Hynynen et al. (2005) A stand-level
Dead wood modelling at stand-level Jari Hynynen & Harri Mäkinen Finnish Forest Research Institute Vantaa Research Unit MOTTI stand simulator Salminen et al. (2005), Hynynen et al. (2005) A stand-level
Executive Summary. FIA-FSP Project Number: Project Title: Project Purpose: Management Implications:
 Executive Summary FIA-FSP Project Number: Project Title: Project Purpose: Management Implications: Y081171 Equivalent clear cut area thresholds in large-scale disturbed forests The purpose of this project
Executive Summary FIA-FSP Project Number: Project Title: Project Purpose: Management Implications: Y081171 Equivalent clear cut area thresholds in large-scale disturbed forests The purpose of this project
0 10 felled total (2008) W 6 7 HAW 5 3
 Carnoustie Golf Links Woodland compartment records Fell Replant Planting Number Compartment No. Grid Ref. Species Top height Area areas Year of trees Planned management Description Clear fell under felling
Carnoustie Golf Links Woodland compartment records Fell Replant Planting Number Compartment No. Grid Ref. Species Top height Area areas Year of trees Planned management Description Clear fell under felling
Regeneration / Young Stand Models
 Many of the standard growth and yield models that are currently in use start with stands that have passed the regeneration phase of development (i.e., they start with stands with ages of 15 or 20 years
Many of the standard growth and yield models that are currently in use start with stands that have passed the regeneration phase of development (i.e., they start with stands with ages of 15 or 20 years
SPECIES CHOICE FOR TIMBER AND BIOMASS
 SPECIES CHOICE FOR TIMBER AND BIOMASS Elspeth Macdonald Scottish School of Forestry Inverness College UHI With thanks to colleagues in Forest Research and Edinburgh Napier University Species choice in
SPECIES CHOICE FOR TIMBER AND BIOMASS Elspeth Macdonald Scottish School of Forestry Inverness College UHI With thanks to colleagues in Forest Research and Edinburgh Napier University Species choice in
7.39 Wilding conifers
 7.39 Wilding Definition Wilding are any introduced conifer tree, including (but not limited to) any of the species listed in Table 13, established by natural means, unless it is located within a forest
7.39 Wilding Definition Wilding are any introduced conifer tree, including (but not limited to) any of the species listed in Table 13, established by natural means, unless it is located within a forest
BALNABEERAN FOREST. Near Errogie, Inverness-shire Hectares / Acres
 BALNABEERAN FOREST Near Errogie, Inverness-shire 91.50 Hectares / 226.10 Acres BALNABEERAN FOREST Inverness 16 miles Nairn 36 miles Perth 122 miles (Distances are approximate) Fort William 50 miles BALNABEERAN
BALNABEERAN FOREST Near Errogie, Inverness-shire 91.50 Hectares / 226.10 Acres BALNABEERAN FOREST Inverness 16 miles Nairn 36 miles Perth 122 miles (Distances are approximate) Fort William 50 miles BALNABEERAN
Agroforestry and the Afforestation Programme in The Republic of Ireland
 Agroforestry and the Afforestation Programme in The Republic of Ireland Farm Woodland Forum Elm Farm, Newbury. 18 th 19 th May 2015 Mr. Eugene Curran, Forest Service, Department of Agriculture, Food and
Agroforestry and the Afforestation Programme in The Republic of Ireland Farm Woodland Forum Elm Farm, Newbury. 18 th 19 th May 2015 Mr. Eugene Curran, Forest Service, Department of Agriculture, Food and
Refinement of the FVS-NE predictions of
 Refinement of the FVS-NE predictions of individual tree growth response to thinning PI: Aaron Weiskittel University of Maine, School of Forest Resources Co-PIs: John Kershaw University of New Brunswick
Refinement of the FVS-NE predictions of individual tree growth response to thinning PI: Aaron Weiskittel University of Maine, School of Forest Resources Co-PIs: John Kershaw University of New Brunswick
DAVIOT WOOD. Near Inverness, Inverness-shire Hectares / Acres
 DAVIOT WOOD Near Inverness, Inverness-shire 136.60 Hectares / 337.53 Acres DAVIOT WOOD Inverness 3.5 miles Nairn 17 miles Perth 110 miles Edinburgh 155 miles (Distances are approximate) DAVIOT WOOD 136.60
DAVIOT WOOD Near Inverness, Inverness-shire 136.60 Hectares / 337.53 Acres DAVIOT WOOD Inverness 3.5 miles Nairn 17 miles Perth 110 miles Edinburgh 155 miles (Distances are approximate) DAVIOT WOOD 136.60
LIFE 14ENV/IT/ Demonstrating Remote Sensing integration in sustainable forest management FRESh Life ACTION B3 Mapping SFM indicators
 LIFE 14ENV/IT/000414 Demonstrating Remote Sensing integration in sustainable forest management FRESh Life ACTION B3 Mapping SFM indicators Deliverable Maps of SFM indicators Defoliation (# 2.3), Forest
LIFE 14ENV/IT/000414 Demonstrating Remote Sensing integration in sustainable forest management FRESh Life ACTION B3 Mapping SFM indicators Deliverable Maps of SFM indicators Defoliation (# 2.3), Forest
Vegetation height and cover fraction between 60 S and 60 N from ICESat GLAS data
 Geosci. Model Dev., 5, 413 432, 2012 doi:10.5194/gmd-5-413-2012 Author(s) 2012. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Geoscientific Model Development Vegetation height and cover fraction between 60 S and 60 N from
Geosci. Model Dev., 5, 413 432, 2012 doi:10.5194/gmd-5-413-2012 Author(s) 2012. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Geoscientific Model Development Vegetation height and cover fraction between 60 S and 60 N from
ERCHLESS FOREST EAST. Nr Beauly, Inverness-shire Hectares / 1, Acres. John Clegg & Co CHARTERED SURVEYORS & FORESTRY AGENTS
 ERCHLESS FOREST EAST Nr Beauly, Inverness-shire 450.65 Hectares / 1,113.55 Acres John Clegg & Co CHARTERED SURVEYORS & FORESTRY AGENTS ERCHLESS FOREST EAST Beauly 10 miles Dingwall 19 miles Inverness 20
ERCHLESS FOREST EAST Nr Beauly, Inverness-shire 450.65 Hectares / 1,113.55 Acres John Clegg & Co CHARTERED SURVEYORS & FORESTRY AGENTS ERCHLESS FOREST EAST Beauly 10 miles Dingwall 19 miles Inverness 20
CLIMATE CHANGE INDUCED VEGETATION SHIFTS IN EUROPE
 CLIMATE CHANGE INDUCED VEGETATION SHIFTS IN EUROPE ÁGNES GARAMVÖLGYI Corvinus University of Budapest, Department of Mathematics and Informatics H-1118 Budapest, Villányi út 29-43. e-mail: garamvolgyiagi@gmail.com
CLIMATE CHANGE INDUCED VEGETATION SHIFTS IN EUROPE ÁGNES GARAMVÖLGYI Corvinus University of Budapest, Department of Mathematics and Informatics H-1118 Budapest, Villányi út 29-43. e-mail: garamvolgyiagi@gmail.com
The Alex Fraser Research Forest
 The Alex Fraser Research Forest What s New in Research? October 2, 2010 Cathy Koot R.P. Bio, Research Coordinator Situated on ~ 10 000 hectares of Crown land Managed since 1987 to provide an optimal environment
The Alex Fraser Research Forest What s New in Research? October 2, 2010 Cathy Koot R.P. Bio, Research Coordinator Situated on ~ 10 000 hectares of Crown land Managed since 1987 to provide an optimal environment
Establishment of mixed species stands. Magnus Löf, Sweden
 Establishment of mixed species stands Magnus Löf, Sweden Outline 1. Forest history 2. Present situation and drivers for change 3. Mixed forests in Europe 4. From conifers to broadleaves 5. New types of
Establishment of mixed species stands Magnus Löf, Sweden Outline 1. Forest history 2. Present situation and drivers for change 3. Mixed forests in Europe 4. From conifers to broadleaves 5. New types of
Estimating poplar plantation stand value and log product yields using terrestrial laser scanning and optimal bucking
 Estimating poplar plantation stand value and log product yields using terrestrial laser scanning and optimal bucking Glen Murphy & Jennifer Barnett Oregon State University Bruce Summers Greenwood Resources
Estimating poplar plantation stand value and log product yields using terrestrial laser scanning and optimal bucking Glen Murphy & Jennifer Barnett Oregon State University Bruce Summers Greenwood Resources
Effects of starting conditions of SORTIE-ND model growth predictions: tree spatial coordinate randomization
 Effects of starting conditions of SORTIE-ND model growth predictions: tree spatial coordinate randomization Marie-Lou Lefrancois 1, K. David Coates 2, and Rasmus Astrup 1, 3 (1) Bulkley Valley Centre for
Effects of starting conditions of SORTIE-ND model growth predictions: tree spatial coordinate randomization Marie-Lou Lefrancois 1, K. David Coates 2, and Rasmus Astrup 1, 3 (1) Bulkley Valley Centre for
NORWAY. 21 March Submission to the Ad-Hoc Working Group on Further Commitments for Annex I Parties under the Kyoto Protocol (AWG-KP)
 NORWAY 21 March 2011 Submission to the Ad-Hoc Working Group on Further Commitments for Annex I Parties under the Kyoto Protocol (AWG-KP) Information on forest management reference level Summary According
NORWAY 21 March 2011 Submission to the Ad-Hoc Working Group on Further Commitments for Annex I Parties under the Kyoto Protocol (AWG-KP) Information on forest management reference level Summary According
Mediterranean Forests in Transition (MEDIT): Deliverable No1
 Mediterranean Forests in Transition (MEDIT): Deliverable No1 Title: Report on the results of the tree-rings meta-analysis Due to Project Month 6, Date: 30/09/2012 Introduction This manuscript summarises
Mediterranean Forests in Transition (MEDIT): Deliverable No1 Title: Report on the results of the tree-rings meta-analysis Due to Project Month 6, Date: 30/09/2012 Introduction This manuscript summarises
Forest data services of the Finnish Forest Centre. Juho Heikkilä, Chief Forest Data Specialist, Lic.Sc. (For.) Lahti, Finland, May 31, 2017
 Forest data services of the Finnish Forest Centre Juho Heikkilä, Chief Forest Data Specialist, Lic.Sc. (For.) Lahti, Finland, May 31, 2017 Finland - the most forested land in Europe The population of Finland
Forest data services of the Finnish Forest Centre Juho Heikkilä, Chief Forest Data Specialist, Lic.Sc. (For.) Lahti, Finland, May 31, 2017 Finland - the most forested land in Europe The population of Finland
Quantification of understory fuels in Superior National Forest using LiDAR Data
 2017-2018 Webinar Series February 15, 2018 Quantification of understory fuels in Superior National Forest using LiDAR Data Jeff Irwin USGS Earth Resources Observation and Science Center Audio will start
2017-2018 Webinar Series February 15, 2018 Quantification of understory fuels in Superior National Forest using LiDAR Data Jeff Irwin USGS Earth Resources Observation and Science Center Audio will start
5.2 Douglas fir in Freiburg City Forest: an introduced tree species in the light of multifunctional management objectives
 5.2 Douglas fir in Freiburg City Forest: an introduced tree species in the light of multifunctional management objectives Nicole Schmalfuss and Lucie Vítková Freiburg City Forest is located in the southwestern
5.2 Douglas fir in Freiburg City Forest: an introduced tree species in the light of multifunctional management objectives Nicole Schmalfuss and Lucie Vítková Freiburg City Forest is located in the southwestern
TOMCHRASKY WOOD, GLENMORISTON, INVERNESS-SHIRE
 TOMCHRASKY WOOD, GLENMORISTON, INVERNESS-SHIRE TOMCHRASKY WOOD GLENMORISTON, INVERNESS-SHIRE A block of mature commercial woodland with potential for an early income stream Well located to timber markets
TOMCHRASKY WOOD, GLENMORISTON, INVERNESS-SHIRE TOMCHRASKY WOOD GLENMORISTON, INVERNESS-SHIRE A block of mature commercial woodland with potential for an early income stream Well located to timber markets
Forestry Applications of LiDAR Data Funded by the Minnesota Environment and Natural Resources Trust Fund
 Conservation Applications of LiDAR Data Workshops funded by the Minnesota Environment and Natural Resources Trust Fund Conservation Applications of LiDAR Data Workshops funded by: Minnesota Environment
Conservation Applications of LiDAR Data Workshops funded by the Minnesota Environment and Natural Resources Trust Fund Conservation Applications of LiDAR Data Workshops funded by: Minnesota Environment
Nest tree characteristics of the old-growth specialist Three-toed Woodpecker Picoides tridactylus
 https://helda.helsinki.fi Nest tree characteristics of the old-growth specialist Three-toed Woodpecker Picoides tridactylus Pakkala, Timo 2018 Pakkala, T, Tiainen, J, Piha, M & Kouki, J 2018, ' Nest tree
https://helda.helsinki.fi Nest tree characteristics of the old-growth specialist Three-toed Woodpecker Picoides tridactylus Pakkala, Timo 2018 Pakkala, T, Tiainen, J, Piha, M & Kouki, J 2018, ' Nest tree
INTERNAL REPORT 98 STAND STRUCTURE SIMULATION. Peter Farnum. University of Washington ABSTRACT
 INTERNAL REPORT 98 STAND STRUCTURE SIMULATION BASED ON INDIVIDUAL TREE UNITS Peter Farnum University of Washington ABSTRACT A model is developed to simulate basal area growth and mortality for forest stands
INTERNAL REPORT 98 STAND STRUCTURE SIMULATION BASED ON INDIVIDUAL TREE UNITS Peter Farnum University of Washington ABSTRACT A model is developed to simulate basal area growth and mortality for forest stands
Fax: (613) June 1, Ottawa, ON K2G 5X8. Dear Gino, property. by the City. construction. the. status of the. findings of. property.
 P.O. Box 13593, Ottawa, ON K2KK 1X6 Telephone: (613) 839-0101 Fax: (613) 839-0114 Website: www.ifsassociates.ca Urban Forestry & Forest Management Consulting June 1, 2015 Gino J. Aiello, Landscape Architect
P.O. Box 13593, Ottawa, ON K2KK 1X6 Telephone: (613) 839-0101 Fax: (613) 839-0114 Website: www.ifsassociates.ca Urban Forestry & Forest Management Consulting June 1, 2015 Gino J. Aiello, Landscape Architect
ARDTEATLE FOREST. Loch Awe, Argyll Hectares / Acres
 ARDTEATLE FOREST Loch Awe, Argyll 144.10 Hectares / 356.07Acres ARDTEATLE FOREST Dalmally 3 miles Fort William 61 miles Perth 73 miles (Distances are approximate) Glasgow 75 miles ARDTEATLE FOREST 144.10
ARDTEATLE FOREST Loch Awe, Argyll 144.10 Hectares / 356.07Acres ARDTEATLE FOREST Dalmally 3 miles Fort William 61 miles Perth 73 miles (Distances are approximate) Glasgow 75 miles ARDTEATLE FOREST 144.10
U.S.D.A. FOREST SERVICE RESEARCH PAPER FPL 124 OCTOBER 1969 SAPWOOD THICKNESS. of douglas-fir and five other western softwoods
 U.S.D.A. FOREST SERVICE RESEARCH PAPER FPL 124 OCTOBER 1969 SAPWOOD THICKNESS of douglas-fir and five other western softwoods U.S. Department of Agriculture Forest Service Forest Products Laboratory Madison,
U.S.D.A. FOREST SERVICE RESEARCH PAPER FPL 124 OCTOBER 1969 SAPWOOD THICKNESS of douglas-fir and five other western softwoods U.S. Department of Agriculture Forest Service Forest Products Laboratory Madison,
IDENTIFICATION OF WOOD SPECIES BY USING COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY
 9th International Scientific Conference on Production Engineering DEVELOPMENT AND MODERNIZATION OF PRODUCTION IDENTIFICATION OF WOOD SPECIES BY USING COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Bakhshieva Maria, 2Fleur Longuetaud,
9th International Scientific Conference on Production Engineering DEVELOPMENT AND MODERNIZATION OF PRODUCTION IDENTIFICATION OF WOOD SPECIES BY USING COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Bakhshieva Maria, 2Fleur Longuetaud,
Digital Restoration Guide for Increasing Efficiency in Planning and Implementation of the Four Forest Restoration Initiative. Challenge and Need
 To succeed at forest restoration, the core strategy of The Nature Conservancy in Arizona helps resolve two challenges: the low value of small-diameter wood and associated biomass; and the tentative social
To succeed at forest restoration, the core strategy of The Nature Conservancy in Arizona helps resolve two challenges: the low value of small-diameter wood and associated biomass; and the tentative social
Defining Forests. forestry hardwood log native forest old-growth forest. E-unit: Defining Forests Page 1
 Defining Forests W HEN WE use the tree respectfully and economically, we have one of the greatest resources on the earth, said Frank Lloyd Wright. Clearly Mr. Wright placed value on trees and had sustainability
Defining Forests W HEN WE use the tree respectfully and economically, we have one of the greatest resources on the earth, said Frank Lloyd Wright. Clearly Mr. Wright placed value on trees and had sustainability
TREATMENT OF PINUS SYLVESTRIS POSTS WITH A CCA PRESERVATIVE
 96 TREATMENT OF PINUS SYLVESTRIS POSTS WITH A CCA PRESERVATIVE R. K. BAGNALL New Zealand Forest Service, P.O. Box 140, Nelson, New Zealand (Received for publication 18 December 1981; revision 3 March 1982)
96 TREATMENT OF PINUS SYLVESTRIS POSTS WITH A CCA PRESERVATIVE R. K. BAGNALL New Zealand Forest Service, P.O. Box 140, Nelson, New Zealand (Received for publication 18 December 1981; revision 3 March 1982)
The Use of Terrestrial LiDAR to Characterize Single Trees Jean-François Côté (CWFC) Chhun-Huor Ung (CWFC) Joan Luther (CFS)
 The Use of Terrestrial LiDAR to Characterize Single Trees Jean-François Côté (CWFC) Chhun-Huor Ung (CWFC) Joan Luther (CFS) Canadian Woodlands Forum 2013 Fall Meeting Inventory Inventory information essential
The Use of Terrestrial LiDAR to Characterize Single Trees Jean-François Côté (CWFC) Chhun-Huor Ung (CWFC) Joan Luther (CFS) Canadian Woodlands Forum 2013 Fall Meeting Inventory Inventory information essential
REMOTE SENSING APPLICATION IN FOREST ASSESSMENT
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series II: Forestry Wood Industry Agricultural Food Engineering Vol. 4 (53) No. 2-2011 REMOTE SENSING APPLICATION IN FOREST ASSESSMENT A. PINEDO 1 C. WEHENKEL
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Series II: Forestry Wood Industry Agricultural Food Engineering Vol. 4 (53) No. 2-2011 REMOTE SENSING APPLICATION IN FOREST ASSESSMENT A. PINEDO 1 C. WEHENKEL
