Who Rules? STEP BY STEP
|
|
|
- Amberly Webster
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One Class Period Materials Needed: Student worksheets PowerPoint OR Transparency Copy Instructions: Student materials (double-sided, class set). Learning Objectives. Students will be able to: differentiate between the features of several forms of government using a semantic feature analysis map. compare and contrast forms of government in a sentence completion activity. STEP BY STEP PowerPoint Option ANTICIPATE the lesson by asking your students if they think that rules are more effective when developed by the class as a whole than simply decided by the teacher. Have them briefly share their responses, probing for reasoning. DISTRIBUTE the Who Rules? worksheets while you explain that you will be studying different forms of government and different ways that countries are run. RUN REVIEW PREVIEW INSTRUCT the Who Rules? PowerPoint, pausing after each form of government for the students to fill in a row on The Rules of Ruling chart (worksheet, pg 1). the completed chart when you reach the last slide of the PowerPoint, probing for reasoning by asking students to support their answers. worksheets pgs 2-3, reviewing instructions and expectations. students to complete the Who Rules? worksheets and circulate to assist. Non-PowerPoint Option DISTRIBUTE the Who Rules? reading. PREVIEW READ TELL REVIEW GUIDE REVIEW PREVIEW INSTRUCT the bold words with the class and ask after any prior knowledge of experiences with these worlds. the Who Rules? Reading, stopping to check for understanding and provide further explanation as needed. students that you will be comparing and contrasting these different forms of government while you distribute the Who Rules? Worksheets. the instructions with the students, guiding them as they fill in their government forms in the left-hand column of The Rules of Ruling (worksheet, pg 1). your students through the first 4 columns, gradually releasing responsibility as you move through columns You can make a transparency of the worksheet to make this easier. the completed chart and probe for reasoning by asking students to support their answers. worksheets pgs 2-3, reviewing instructions and expectations. students to complete the Who Rules? worksheets and circulate to assist. This lesson plan is part of the Foundations of Government series by icivics, Inc. a nonprofit organization dedicated to advancing civic education. For more resources, please visit where you can access the state standards aligned to this lesson plan. Provide feedback to feedback@icivics.org icivics, Inc. You may copy, distribute, or transmit this work for noncommercial purposes if you credit icivics. All other rights reserved.
2 Name: There are many different forms of government in our world. Each looks a little bit different. The major difference lies in who is in control, but there are subtle differences that exist as well. Let s explore different categories and forms of government Democracy Any form of government in which political power is exercised by all citizens, either directly or through their elected representatives. Have you ever been to vote with your parents? Direct Democracy In a direct democracy all citizens have a chance to participate. The people directly control and are responsible for the laws that govern their society. All citizens can take initiative to create public policy. An example of a direct democracy is ancient Athens where they held assemblies to pass laws. Representative Democracy Like direct democracy, representative democracy is a government by the people. Representative democracy is a form of government in which people elect leaders to write and manage laws for the country. These leaders are responsible for representing the will of the people and are elected at regular intervals. They are also often bound by a Constitution. Monarchy Kings, queens, princes, and princesses. We all pretend when we re little, but in a monarchy these roles are reality. Monarchy is rule by a king, or monarch, and he usually gains his power because his parents were rulers (monarchs) also. This applies to queens, too! Some modern monarchies like Spain and Japan have constitutions, while others do not. Dictatorship In a dictatorship power is not inherited, but usually is acquired by force. A dictator has absolute control over the lives of his citizens, like Kim Jong Il in North Korea. Because a dictator has absolute power, opposition is usually suppressed and people are prevented from voicing their opinions. Autocracy A form of government in which political power is controlled by one individual such as a monarch, dictator, emperor, etc. Theocracy The word theocracy contains the Greek root theo which means god. A theocracy is a rule by god or higher power. In a theocracy, religious leaders usually lead the society and religious law is used to settle disputes and rule the people. The Islamic Republic of Iran is an example of a modern theocracy. Oligarchy The philosopher Aristotle originally used the word oligarchy to refer to rule by the rich, but the literal definition of oligarchy is rule by the few. This means that a few people hold all the power based on military strength (known as a military junta), family power (an aristocracy), or religious force (a theocratic oligarchy). Oligarchies can often come from or lead to other forms of government like monarchies and dictatorships. Anarchy In this form of government no one is in charge! Sounds too good to be true? Think about all the possible outcomes of having no government at all. Reading p.1
3 Name: Enter the different forms of government in the left hand column. Then complete the following chart by placing a plus (+) under features that each form of government exhibits. Place a minus (-) under each feature not exhibited by each form of government. Use a question mark (?) if you re not sure. The Rules of Ruling Autocracy Democracy Forms of Government Rule by few Features Rule by one Rule by representatives Rule by none Controlled by citizens Ruled by god or higher power Power usually inherited Holds elections for leaders Constitutional government People have a say Worksheet p.1
4 Compare and contrast. Use the information you gathered on your chart on page 1 to complete the following graphic organizer with your analysis. Write your own for # Direct Democracy and Representative Democracy are alike because Oligarchy and Monarchy are different in that Analysis 3. Monarchy and Dictatorship share the characteristic 4. Monarchy and are similar, but Dictatorship 5. Autocracy and Democracy are different because 6. and Characteristics. For each form of government and its characteristics, circle the one that doesn t belong. 1. Direct democracy: rule by the people / lead by a monarch / regular voting 2. Anarchy: rule by the people / rule by no one / no laws 3. Monarchy: rule by one / power inherited from family / regular elections 4. Oligarchy: rule by few / military, religious, or family power / power always acquired by force 5. Autocracy: monarch or dictator / power always inherited from family / never a Constitution Worksheet p.2
5 Magic Square. After reading Who Rules? match the correct definition to each term by writing the number in the corresponding box below (ex. if the definition of A is number 1, write 1 in box A). Terms A.Democracy B.Dictatorship C.Direct Democracy D.Anarchy E.Monarchy F.Oligarchy G.Autocracy H.Representative Democracy I.Theocracy Definitions 1.Rule by god or higher power 2.Rule by none 3.Rule by a single person who gained power through force 4.Rule by a king or queen 5.Rule by the citizenry or public without representatives 6.Rule by one 7.Rule by the people 8.Rule by the people with elected representatives 9.Rule by the few A B C D E F To check your answers, add up the numbers in each row. Are they the same? Now add up the numbers in each column. They should be the same, too! What is the magic number? G H I If they don t add up to the same number, go back and check your answers! Your Opinion. Take this opportunity to voice your opinions about the forms of government covered today. Which form of government do you think is the best? List two reasons why you think that form of government is the best: Which form of government do you think is the worst? List two reasons why you think that form of government is the worst: Worksheet p.3
6 TEACHER S GUIDE Enter the different forms of government in the left hand column. Then complete the following chart by placing a plus (+) under features that each form of government exhibits. Place a minus (-) under each feature not exhibited by each form of government. Use a question mark (?) if you re not sure. The Rules of Ruling Anarchy Theocracy Oligarchy Autocracy Democracy Democracy Representative Democracy Monarchy Dictatorship Direct Forms of Government Features + Rule by few +/- + + Rule by one + Rule by representatives /- +/- +/- +/- +/- + +/ Rule by none Controlled by citizens Ruled by god or higher power Power usually inherited Holds elections for leaders Constitutional government People have a say Worksheet p.1
7 TEACHER S GUIDE Compare and contrast. Use the information you gathered on your chart on page 1 to complete the following graphic organizer with your analysis. Write your own for # Direct Democracy and Representative Democracy are alike because Sample Answer: they are both rule by the people and both hold voting. Oligarchy and Monarchy are different in that Sample Answer: one is rule by a few people and the other is rule by only one person. Monarchy and Dictatorship share the characteristic Sample Answer: that they are rule by a single person. Analysis Monarchy and Dictatorship are similar, but Sample Answer: in a monarchy power is inherited and in a dictatorship it is taken by force. Autocracy and Democracy are different because Sample Answer: because one is rule by a single person and the other is rule by the people. 6. and Characteristics. For each form of government and its characteristics, circle the one that doesn t belong. 1. Direct democracy: rule by the people / lead by a monarch / regular voting 2. Anarchy: rule by the people / rule by no one / no laws 3. Monarchy: rule by one / power inherited from family / regular elections 4. Oligarchy: rule by few / military, religious, or family power / power always acquired by force 5. Autocracy: monarch or dictator / power always inherited from family / never a Constitution Worksheet p.2
8 TEACHER S GUIDE Magic Square. After reading Who Rules? match the correct definition to each term by writing the number in the corresponding box below (ex. if the definition of A is number 1, write 1 in box A). Terms A.Democracy B.Dictatorship C.Direct Democracy D.Anarchy E.Monarchy F.Oligarchy G.Autocracy H.Representative Democracy I.Theocracy Definitions 1.Rule by god or higher power 2.Rule by none 3.Rule by a single person who gained power through force 4.Rule by a king or queen 5.Rule by the citizenry or public without representatives 6.Rule by one 7.Rule by the people 8.Rule by the people with elected representatives 9.Rule by the few A B C D E F To check your answers, add up the numbers in each row. Are they the same? Now add up the numbers in each column. They should be the same, too! What is the magic number? 15 G H I If they don t add up to the same number, go back and check your answers! Your Opinion. Take this opportunity to voice your opinions about the forms of government covered today. Which form of government do you think is the best? List two reasons why you think that form of government is the best: Which form of government do you think is the worst? List two reasons why you think that form of government is the worst: Worksheet p.3
Who Rules? STEP BY STEP
 Non-PowerPoint Option PowerPoint Option Teacher s Guide Time Needed: One Class Period Materials Needed: Student worksheets PowerPoint OR Transparency Copy Instructions: Student materials (double-sided,
Non-PowerPoint Option PowerPoint Option Teacher s Guide Time Needed: One Class Period Materials Needed: Student worksheets PowerPoint OR Transparency Copy Instructions: Student materials (double-sided,
Who Rules? STEP BY STEP
 Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector or Transparency Copy Instructions: Anticipation Mind Map (half page; class set) Reading (2 pages;
Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector or Transparency Copy Instructions: Anticipation Mind Map (half page; class set) Reading (2 pages;
Who Rules? STEP BY STEP
 Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector or Transparency Copy Instructions: Anticipation Mind Map (half page; class set) Reading (2 pages;
Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector or Transparency Copy Instructions: Anticipation Mind Map (half page; class set) Reading (2 pages;
Who Rules? STEP BY STEP
 Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector Transparency Copy Instructions: Anticipation Mind Map (half page; class set) Reading (2 pages; class
Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector Transparency Copy Instructions: Anticipation Mind Map (half page; class set) Reading (2 pages; class
GOVERNMENT ORGANIZATIONS, INSTITUTIONS, AND INDIVIDUALS THAT EXERCISE POLITICAL AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF A GROUP OF PEOPLE
 TYPES OF GOVERNMENT GOVERNMENT ORGANIZATIONS, INSTITUTIONS, AND INDIVIDUALS THAT EXERCISE POLITICAL AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF A GROUP OF PEOPLE CITIZEN A LEGAL MEMBER OF A COUNTRY CONSTITUTION A WRITTEN PLAN
TYPES OF GOVERNMENT GOVERNMENT ORGANIZATIONS, INSTITUTIONS, AND INDIVIDUALS THAT EXERCISE POLITICAL AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF A GROUP OF PEOPLE CITIZEN A LEGAL MEMBER OF A COUNTRY CONSTITUTION A WRITTEN PLAN
Wednesday March 22, 2017
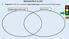 Wednesday March 22, 2017 1. Assignment 3. Open your workbook to page 8 (blank page), and draw the Venn Diagram below. dictatorship (autocracy) democracy What are you expected to do with these forms of
Wednesday March 22, 2017 1. Assignment 3. Open your workbook to page 8 (blank page), and draw the Venn Diagram below. dictatorship (autocracy) democracy What are you expected to do with these forms of
Question. What do you notice about the number of free vs. not free countries around the world?
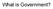 What is Government? Question 1) What do you notice about the number of free vs. not free countries around the world? 2) Where do you see most of the unfree countries in the world? I) What is Government?
What is Government? Question 1) What do you notice about the number of free vs. not free countries around the world? 2) Where do you see most of the unfree countries in the world? I) What is Government?
Different Democracies. EQ: How is a parliamentary democracy different from a presidential democracy?
 Different Democracies EQ: How is a parliamentary democracy different from a presidential democracy? What does the Legislative Branch do with law? They MAKE the laws! What does the Executive Branch do with
Different Democracies EQ: How is a parliamentary democracy different from a presidential democracy? What does the Legislative Branch do with law? They MAKE the laws! What does the Executive Branch do with
Unit Portfolio: Interpreting Visual Images
 Unit Portfolio: Interpreting Visual Images 1. What can you tell about this man based only on what you see in this picture? Make up a brief biography based on your perception of this photo. Use complete
Unit Portfolio: Interpreting Visual Images 1. What can you tell about this man based only on what you see in this picture? Make up a brief biography based on your perception of this photo. Use complete
4. Which noun below can also be used. 5. What is the meaning of the phrase
 Name: Date: WEEK 35 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. What kinds of rights do you think people should have? For example, you probably think that people have the right to be safe from burglars.
Name: Date: WEEK 35 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. What kinds of rights do you think people should have? For example, you probably think that people have the right to be safe from burglars.
SSCG1 Compare and contrast various systems of government.
 SSCG1 Compare and contrast various systems of government. 1a. Determine how governments differ in geographic distribution of power, particularly unitary, confederal, and federal types of government. Unitary
SSCG1 Compare and contrast various systems of government. 1a. Determine how governments differ in geographic distribution of power, particularly unitary, confederal, and federal types of government. Unitary
Government: Definition, Forms, and Purpose.
 Government: Definition, Forms, and Purpose. SS6CG4 The student will compare and contrast various forms of government. a. Describe the ways government systems distribute power: unitary, confederation, and
Government: Definition, Forms, and Purpose. SS6CG4 The student will compare and contrast various forms of government. a. Describe the ways government systems distribute power: unitary, confederation, and
AUTOCRACY. SS.7.C.3.1 Forms of Government
 AUTOCRACY An autocracy is a form of government where one person has unlimited power. One form of an autocracy is a dictatorship where a military leader secures power often through violent means. Another
AUTOCRACY An autocracy is a form of government where one person has unlimited power. One form of an autocracy is a dictatorship where a military leader secures power often through violent means. Another
CHAPTER 1: FOUNDATIONS OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: THE PURPOSE OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 2: FORMS OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 3: DEMOCRACY IN THE UNITED STATES
 CHAPTER 1: FOUNDATIONS OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: THE PURPOSE OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 2: FORMS OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 3: DEMOCRACY IN THE UNITED STATES SECTION 1: THE PURPOSES OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: FOCUS
CHAPTER 1: FOUNDATIONS OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: THE PURPOSE OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 2: FORMS OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 3: DEMOCRACY IN THE UNITED STATES SECTION 1: THE PURPOSES OF GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: FOCUS
LL Copy the chart below. Fill it in as we watch Types of Government game show.
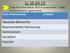 LL 10-24-13 Copy the chart below. Fill it in as we watch Types of Government game show. Form of Government 5 Details Absolute Monarchy Representative Democracy Communism Socialism Fascism The directions
LL 10-24-13 Copy the chart below. Fill it in as we watch Types of Government game show. Form of Government 5 Details Absolute Monarchy Representative Democracy Communism Socialism Fascism The directions
TABLE OF CONTENTS. SS.7.C.3.1 Updated 8/17 1
 COMPARING FORMS OF GOVERNMENT SS.7.C.3.1 Compare different forms of government (direct democracy, representative democracy, socialism, communism, monarchy, oligarchy, autocracy). TABLE OF CONTENTS Lesson
COMPARING FORMS OF GOVERNMENT SS.7.C.3.1 Compare different forms of government (direct democracy, representative democracy, socialism, communism, monarchy, oligarchy, autocracy). TABLE OF CONTENTS Lesson
State Power: Got a Reservation? STEP BY STEP
 Teacher s Guide Time Needed: One to two class periods Materials Needed: Student Worksheets Copy Instructions: Reading (2 pages; class set) Federal Power Cheat Sheet (1 page; class set) Strike-It Activity
Teacher s Guide Time Needed: One to two class periods Materials Needed: Student Worksheets Copy Instructions: Reading (2 pages; class set) Federal Power Cheat Sheet (1 page; class set) Strike-It Activity
Three Levels of Power Distribution Ø Unitary Ø Ø
 SS6CG4 The student will compare and contrast various forms of government. a. Describe the ways government systems distribute power: unitary, confederation, and federal. b. Explain how governments determine
SS6CG4 The student will compare and contrast various forms of government. a. Describe the ways government systems distribute power: unitary, confederation, and federal. b. Explain how governments determine
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1
 Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1 Basic Types of Government In a dictatorship, all powers are held by one person or group. In a democracy, authority lies with the people. The U.S. government
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1 Basic Types of Government In a dictatorship, all powers are held by one person or group. In a democracy, authority lies with the people. The U.S. government
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1
 Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Define government and the basic powers every government holds. 2. Describe the four defining characteristics of a state. 3. Identify four theories
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Define government and the basic powers every government holds. 2. Describe the four defining characteristics of a state. 3. Identify four theories
Writing the Constitution
 Writing the Constitution Backwards Planning Curriculum Units Michael Hutchison, Writer Dr. Aaron Willis, Project Coordinator Justin Coffey, Editor Kerry Gordonson, Editor Social Studies School Service
Writing the Constitution Backwards Planning Curriculum Units Michael Hutchison, Writer Dr. Aaron Willis, Project Coordinator Justin Coffey, Editor Kerry Gordonson, Editor Social Studies School Service
SS.7.C.2.1 Citizenship
 SS.7.C.2.1 Citizenship ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Define citizenship as stated in the 14 th Amendment Describe the process of becoming a naturalized citizen Evaluate
SS.7.C.2.1 Citizenship ****At the end of this lesson, I will be able to do the following: Define citizenship as stated in the 14 th Amendment Describe the process of becoming a naturalized citizen Evaluate
America: Republic vs. Democracy
 America: Republic vs. Democracy By Frank Li, Ph.D. Founder & President, West-East International, Inc. January 11, 2013 In my book Saving America, Chinese Style, I fundamentally questioned democracy as
America: Republic vs. Democracy By Frank Li, Ph.D. Founder & President, West-East International, Inc. January 11, 2013 In my book Saving America, Chinese Style, I fundamentally questioned democracy as
Watch the Preview for the lesson. Then write down examples of images that support the following statements or answer the questions below.
 P r e v i e w Watch the Preview for the lesson. Then write down examples of images that support the following statements or answer the questions below. 1. We live in a democracy. 2. We participate in our
P r e v i e w Watch the Preview for the lesson. Then write down examples of images that support the following statements or answer the questions below. 1. We live in a democracy. 2. We participate in our
A situation where there is no government. Anarchy. The provinces in Canada keep their power and the central government has limited power.
 Anarchy A situation where there is no government. Canada The provinces in Canada keep their power and the central government has limited power. Confederation a political system in which the central government
Anarchy A situation where there is no government. Canada The provinces in Canada keep their power and the central government has limited power. Confederation a political system in which the central government
The Rise of Democracy
 The Rise of Democracy Chapter 26 1 The Rise of Democracy Chapter 26 2 26.1 Last chapter we talked about the fact that mountains and seas isolated Greek communities. As a result Greek communities developed
The Rise of Democracy Chapter 26 1 The Rise of Democracy Chapter 26 2 26.1 Last chapter we talked about the fact that mountains and seas isolated Greek communities. As a result Greek communities developed
MODELS OF GOVERNANCE: PALEOLITHIC ANCIENT ERA
 Students should explain how and why models of governance evolved between the Paleolithic and Ancient eras Section Overview: What is Government? : a system for controlling society Throughout history people
Students should explain how and why models of governance evolved between the Paleolithic and Ancient eras Section Overview: What is Government? : a system for controlling society Throughout history people
In framing a government which is to be administrated by men over men, the great difficulty lies in this: You must first enable the government to
 In framing a government which is to be administrated by men over men, the great difficulty lies in this: You must first enable the government to control the governed; and in the next place oblige it to
In framing a government which is to be administrated by men over men, the great difficulty lies in this: You must first enable the government to control the governed; and in the next place oblige it to
What level of government has the most amount of the power?
 Governments Form of Government Confederation What level of government has the most amount of the power? What level of government has the least amount of power? Example Unitary System Federal System Confederation
Governments Form of Government Confederation What level of government has the most amount of the power? What level of government has the least amount of power? Example Unitary System Federal System Confederation
Suppose you are on a sports team that is one play away from winning a game. Which is the best way to choose the final play of the game?
 Warm Up: Suppose you are on a sports team that is one play away from winning a game. Which is the best way to choose the final play of the game? A. Have the coach or the assistant coach choose. B. Have
Warm Up: Suppose you are on a sports team that is one play away from winning a game. Which is the best way to choose the final play of the game? A. Have the coach or the assistant coach choose. B. Have
Government & Economy of South East Asia. EQ: How do the governments and economies of India, China, Japan, and North Korea compare and contrast?
 Government & Economy of South East Asia EQ: How do the governments and economies of India, China, Japan, and North Korea compare and contrast? Directions: As we discuss the governments of Southeast Asia,
Government & Economy of South East Asia EQ: How do the governments and economies of India, China, Japan, and North Korea compare and contrast? Directions: As we discuss the governments of Southeast Asia,
The Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome
 Prologue 1 The Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome Essential Question: How did Greece and Rome contribute to the development of democracy in the United States? Athens Builds a Limited Democracy Changes In
Prologue 1 The Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome Essential Question: How did Greece and Rome contribute to the development of democracy in the United States? Athens Builds a Limited Democracy Changes In
2014 Brain Wrinkles. A Federal Parliamentary Democracy
 A Federal Parliamentary Democracy Standards SS6CG6 The student will compare and contrast various forms of government. a. Describe the ways government systems distribute power: unitary, confederation, and
A Federal Parliamentary Democracy Standards SS6CG6 The student will compare and contrast various forms of government. a. Describe the ways government systems distribute power: unitary, confederation, and
Section 1 Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome
 Prologue Section 1 Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome Main Idea The Greeks developed democracy, and the Romans added representative government. Why It Matters Now Representation and citizen participation
Prologue Section 1 Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome Main Idea The Greeks developed democracy, and the Romans added representative government. Why It Matters Now Representation and citizen participation
Public affairs overseas
 Basic Public Affairs Specialist Course Public affairs overseas What do you think are the chances of you being stationed overseas at some point in your career, whether permanently assigned or deployed to
Basic Public Affairs Specialist Course Public affairs overseas What do you think are the chances of you being stationed overseas at some point in your career, whether permanently assigned or deployed to
132. What type of government exists in Brazil? A. communist B. monarchy C. presidential democracy D. parliamentary democracy
 SS6CG2 The student will explain the structures of national governments in Latin America and the Caribbean. a. Compare the federal-republican systems of the Federative Republic of Brazil (Brazil) and the
SS6CG2 The student will explain the structures of national governments in Latin America and the Caribbean. a. Compare the federal-republican systems of the Federative Republic of Brazil (Brazil) and the
A tyranny is a form of government in which the ruling power is in the hands of an individual who has seized control, often by illegal means.
 A monarchy is a form of government in which the ruling power is in the hands of a single person. Most monarchies have been ruled by kings, usually with the help of a council of advisors. The word monarchy
A monarchy is a form of government in which the ruling power is in the hands of a single person. Most monarchies have been ruled by kings, usually with the help of a council of advisors. The word monarchy
DEMOCRACY DOWN UNDER. Student facts. How should a nation be ruled? 1. Absolute monarchy. 2. Direct democracy.
 Student facts How should a nation be ruled? Have you ever thought about how Australia is ruled? What about other countries around the world? Are they all ruled in the same way? Australia is a democracy,
Student facts How should a nation be ruled? Have you ever thought about how Australia is ruled? What about other countries around the world? Are they all ruled in the same way? Australia is a democracy,
Student s Name: Period: ABSOLUTE MONARCHS. 1. What helped Absolute Monarchs initially gain power during the Middle Ages?
 Lesson Summary Questions Using your textbook, notes, and graphic organizers, complete the critical thinking questions below. 1. What helped Absolute Monarchs initially gain power during the Middle Ages?
Lesson Summary Questions Using your textbook, notes, and graphic organizers, complete the critical thinking questions below. 1. What helped Absolute Monarchs initially gain power during the Middle Ages?
Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1
 Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Identify the three concepts of government that influenced the American colonies. 2. Explain the influence of three landmark English documents.
Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Identify the three concepts of government that influenced the American colonies. 2. Explain the influence of three landmark English documents.
Huntsville City Schools Pacing Guide Course: Civics Grade: 7 First 9 Weeks
 Huntsville City Schools 2017-18 Pacing Guide Course: Civics Grade: 7 First 9 Weeks Civics Fall 2017 General Resources The State of Alabama is now requiring that all students pass a Civics test to receive
Huntsville City Schools 2017-18 Pacing Guide Course: Civics Grade: 7 First 9 Weeks Civics Fall 2017 General Resources The State of Alabama is now requiring that all students pass a Civics test to receive
The Athenian Constitution (Document A)
 The Athenian Constitution (Document A) Source: The following excerpt comes from The Athenian Constitution, written by the Greek philosopher Aristotle between 330 and 322 BC. Aristotle was the leading Greek
The Athenian Constitution (Document A) Source: The following excerpt comes from The Athenian Constitution, written by the Greek philosopher Aristotle between 330 and 322 BC. Aristotle was the leading Greek
Background. The background of Athenian Democracy. The definition of the term democracy. The three branches of Athenian government
 Name Period Page # Athenian Democracy Document Based Question: Was ancient Athens truly democratic? Background DIRECTIONS: As you view the PowerPoint presentation, take notes on The background of Athenian
Name Period Page # Athenian Democracy Document Based Question: Was ancient Athens truly democratic? Background DIRECTIONS: As you view the PowerPoint presentation, take notes on The background of Athenian
Government in Athens
 SECTION 2 Government in Athens What You Will Learn Main Ideas 1. Aristocrats and tyrants ruled early Athens. 2. Athens created the world s first democracy. 3. Ancient democracy was different than modern
SECTION 2 Government in Athens What You Will Learn Main Ideas 1. Aristocrats and tyrants ruled early Athens. 2. Athens created the world s first democracy. 3. Ancient democracy was different than modern
Legacy of Ancient Greece & Rome. World History Dr. Robbins
 Legacy of Ancient Greece & Rome World History Dr. Robbins Athens Builds a Limited Democracy First large democracy in ancient Greece democracy = rule of the people City-state was basic political unit Earliest
Legacy of Ancient Greece & Rome World History Dr. Robbins Athens Builds a Limited Democracy First large democracy in ancient Greece democracy = rule of the people City-state was basic political unit Earliest
The cradle of democracy.
 The cradle of democracy. Democracy derives from the ancient Greek, demokratia. : Demos = The people Kratien = To rule Quick Notes - The stuff you should write down. Greek word - Democracy Demos = The people
The cradle of democracy. Democracy derives from the ancient Greek, demokratia. : Demos = The people Kratien = To rule Quick Notes - The stuff you should write down. Greek word - Democracy Demos = The people
Civilization in Sumer
 Civilization in Sumer Vocabulary Words innovation division of labor surplus monarchy absolute authority bureaucracy pictograph cuneiform social class merchant INNOVATION A new way of doing things. Division
Civilization in Sumer Vocabulary Words innovation division of labor surplus monarchy absolute authority bureaucracy pictograph cuneiform social class merchant INNOVATION A new way of doing things. Division
What is Government? Chapter 3
 Chapter 3 What is Government? You must have heard the word 'government' mentioned several times. In this chapter you will learn about what a government is and the important role it plays in our lives.
Chapter 3 What is Government? You must have heard the word 'government' mentioned several times. In this chapter you will learn about what a government is and the important role it plays in our lives.
Document A: Pericles (Modified)
 Document A: Pericles (Modified) The following excerpt is from a speech known as The Funeral Oration, delivered by the Athenian general and politician Pericles in 431 BCE. Pericles was widely seen as the
Document A: Pericles (Modified) The following excerpt is from a speech known as The Funeral Oration, delivered by the Athenian general and politician Pericles in 431 BCE. Pericles was widely seen as the
Australian Capital Territory
 Australian Capital Territory Every chance to learn: Curriculum framework for ACT schools, Preschool to year 10, Phase 2 Trial Draft 2006 Investigation: What do we mean by democracy? the three levels of
Australian Capital Territory Every chance to learn: Curriculum framework for ACT schools, Preschool to year 10, Phase 2 Trial Draft 2006 Investigation: What do we mean by democracy? the three levels of
Document A: Pericles (Modified)
 Document A: Pericles (Modified) The following excerpt is from a speech known as The Funeral Oration, delivered by the Athenian general and politician Pericles in 431 BCE. Pericles was widely seen as the
Document A: Pericles (Modified) The following excerpt is from a speech known as The Funeral Oration, delivered by the Athenian general and politician Pericles in 431 BCE. Pericles was widely seen as the
It is envisaged that students will have a better-than-basic knowledge of their own country s legal and constitutional system.
 The English Constitution teacher s notes By Nigel Haines As most countries have a written constitution, the English example is usually particularly curious to foreign students. This lesson explores the
The English Constitution teacher s notes By Nigel Haines As most countries have a written constitution, the English example is usually particularly curious to foreign students. This lesson explores the
Poll verdict on the future King Charles: "unpopular and untrusted even at home"
 MEDIA RELEASE Poll verdict on the future King Charles: "unpopular and untrusted even at home" EMBARGOED UNTIL MONDAY 25 SEPTEMBER 2017 A new poll of public opinion in the UK is bad news for Prince Charles.
MEDIA RELEASE Poll verdict on the future King Charles: "unpopular and untrusted even at home" EMBARGOED UNTIL MONDAY 25 SEPTEMBER 2017 A new poll of public opinion in the UK is bad news for Prince Charles.
Bell Work. Compact. Elongated. Fragmented. Perforated. Prorupted. Enclave. Exclave
 Bell Work Shape Compact Elongated Fragmented Perforated Prorupted Enclave Exclave Definition Example Political Geography Comparative Pol/Econ The Two Categories of Gov t Unitary highly centralized government
Bell Work Shape Compact Elongated Fragmented Perforated Prorupted Enclave Exclave Definition Example Political Geography Comparative Pol/Econ The Two Categories of Gov t Unitary highly centralized government
Government in Athens
 Government in Athens Aristocrats Democracy was born in Ancient Greece in the city of Athens. Democracy is a form of a government in which people rule themselves. However, Athens was ruled first by kings,
Government in Athens Aristocrats Democracy was born in Ancient Greece in the city of Athens. Democracy is a form of a government in which people rule themselves. However, Athens was ruled first by kings,
Monday, January 23 rd
 Monday, January 23 rd For help with lecture, readings, help with essays, and test preparation, visit 173A SWKT (The American Heritage Review Room. It is open from 9:00 am to 4:00 pm, Monday through Friday.
Monday, January 23 rd For help with lecture, readings, help with essays, and test preparation, visit 173A SWKT (The American Heritage Review Room. It is open from 9:00 am to 4:00 pm, Monday through Friday.
Social Studies Review. Geography & Early Man
 Geography & Early Man Word Bank: Barter Latitude Basic needs Fresh water Culture Primary source Peninsula Good soil (fertile land) Longitude Directions: Fill in the blanks using the word bank above. 1.
Geography & Early Man Word Bank: Barter Latitude Basic needs Fresh water Culture Primary source Peninsula Good soil (fertile land) Longitude Directions: Fill in the blanks using the word bank above. 1.
STANDARD WHII.6c The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth,
 STANDARD WHII.6c The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth, and eighteenth centuries by c) assessing the impacts
STANDARD WHII.6c The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth, and eighteenth centuries by c) assessing the impacts
Standard 7-3: The student will demonstrate an understanding of independence movements that occurred throughout the world from 1770 through 1900.
 Standard 7-3: The student will demonstrate an understanding of independence movements that occurred throughout the world from 1770 through 1900. 7-3.2 Analyze the effects of the Napoleonic Wars on the
Standard 7-3: The student will demonstrate an understanding of independence movements that occurred throughout the world from 1770 through 1900. 7-3.2 Analyze the effects of the Napoleonic Wars on the
Life in the Colonies. Chapter 4, Section 1
 Life in the Colonies Chapter 4, Section 1 All English colonies shared a common English heritage, and that heritage included the idea that citizens had political rights. England also promoted the theory
Life in the Colonies Chapter 4, Section 1 All English colonies shared a common English heritage, and that heritage included the idea that citizens had political rights. England also promoted the theory
News Literacy Teacher Guide Mini-Lesson A: Monetization. Step by Step
 News Literacy Teacher Guide Time Needed: 1-2 class periods Materials: Web Activity link found on the teacher web page for this lesson Student internet access -OR- a classroom computer and projector with
News Literacy Teacher Guide Time Needed: 1-2 class periods Materials: Web Activity link found on the teacher web page for this lesson Student internet access -OR- a classroom computer and projector with
Map of North and South America
 PASS Social Studies Grade 7 Test 1 Map of North and South America (drawn around the year 1700) SC07SS070101 1. Judging from the above map, it is clear that Europeans in the year 1700 knew the least about
PASS Social Studies Grade 7 Test 1 Map of North and South America (drawn around the year 1700) SC07SS070101 1. Judging from the above map, it is clear that Europeans in the year 1700 knew the least about
Marginal Costing Q.8
 Marginal Costing. 2008 Q.8 Break-Even Point. Before tackling a marginal costing question, it s first of all crucial that you understand what is meant by break-even point. What this means is that a firm
Marginal Costing. 2008 Q.8 Break-Even Point. Before tackling a marginal costing question, it s first of all crucial that you understand what is meant by break-even point. What this means is that a firm
Reading to Learn. Summative Assessment #2 For the Unit, We The People (Reading) Table of Contents
 Reading to Learn Summative Assessment #2 For the Unit, We The People (Reading) Table of Contents Item Page Number Reading to Learn - Instructions Page 2 Reading to Learn - Assessment Tool Pages 3-5 Reading
Reading to Learn Summative Assessment #2 For the Unit, We The People (Reading) Table of Contents Item Page Number Reading to Learn - Instructions Page 2 Reading to Learn - Assessment Tool Pages 3-5 Reading
Communications Plan. Registered Electors. Number. Number
 Communications Plan SUBJECT: Registration of 16-17 year old students The Register of Electors is a database of Nova Scotians who are qualified to vote in provincial elections. It includes the name, date
Communications Plan SUBJECT: Registration of 16-17 year old students The Register of Electors is a database of Nova Scotians who are qualified to vote in provincial elections. It includes the name, date
Starting Your Own Business
 Grade Five Starting Your Own Business Overview Students listen to several chapters from The Toothpaste Millionaire, by Jean Merrill, to learn about starting a business and earning a profit. They complete
Grade Five Starting Your Own Business Overview Students listen to several chapters from The Toothpaste Millionaire, by Jean Merrill, to learn about starting a business and earning a profit. They complete
11/26/2009. Parliament: The legislative (law-making) part of the government, made up of: Monarch Senate House of Commons
 The Parliament of Canada Federal (Ottawa) When Canada became a nation, the British North America (BNA) Act guaranteed that Canada would be under a parliamentary democracy. The ruling party in the House
The Parliament of Canada Federal (Ottawa) When Canada became a nation, the British North America (BNA) Act guaranteed that Canada would be under a parliamentary democracy. The ruling party in the House
Lesson Plan Promotion Involves Communication
 Lesson Plan Promotion Involves Communication Course Title: Marketing Session Title: Promotion Involves Communication Performance Objective: Upon completion of this lesson, the student will be able to explain
Lesson Plan Promotion Involves Communication Course Title: Marketing Session Title: Promotion Involves Communication Performance Objective: Upon completion of this lesson, the student will be able to explain
How do my values influence my career choice? Which career am I most passionate about and why?
 Choosing a Career 6 CAREERS The BIG Idea How do my values influence my career choice? Which career am I most passionate about and why? AGENDA Approx. 45 minutes I. Warm Up: Values (5 minutes) II. Comparing
Choosing a Career 6 CAREERS The BIG Idea How do my values influence my career choice? Which career am I most passionate about and why? AGENDA Approx. 45 minutes I. Warm Up: Values (5 minutes) II. Comparing
DRAFT SOCIAL SCIENCES STANDARDS: CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT
 DRAFT SOCIAL SCIENCES STANDARDS: CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT CORE STANDARDS Civics and Government 10. Examine the relationship between government and citizens to distinguish and evaluate the ways that civic
DRAFT SOCIAL SCIENCES STANDARDS: CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT CORE STANDARDS Civics and Government 10. Examine the relationship between government and citizens to distinguish and evaluate the ways that civic
Collective-Action Problems and Other Types of Collective Dilemmas
 Collective-Action Problems and Other Types of Collective Dilemmas Ryan D. Williamson University of Georgia Ryan D. Williamson Collective Dilemmas 1 / 26 Agenda Attendance Discuss Collective Dilemmas Readings
Collective-Action Problems and Other Types of Collective Dilemmas Ryan D. Williamson University of Georgia Ryan D. Williamson Collective Dilemmas 1 / 26 Agenda Attendance Discuss Collective Dilemmas Readings
Sawtooth Software. Sample Size Issues for Conjoint Analysis Studies RESEARCH PAPER SERIES. Bryan Orme, Sawtooth Software, Inc.
 Sawtooth Software RESEARCH PAPER SERIES Sample Size Issues for Conjoint Analysis Studies Bryan Orme, Sawtooth Software, Inc. 1998 Copyright 1998-2001, Sawtooth Software, Inc. 530 W. Fir St. Sequim, WA
Sawtooth Software RESEARCH PAPER SERIES Sample Size Issues for Conjoint Analysis Studies Bryan Orme, Sawtooth Software, Inc. 1998 Copyright 1998-2001, Sawtooth Software, Inc. 530 W. Fir St. Sequim, WA
U.S. Presidents...79
 Table of Contents Introduction... 4 The Basics of Government Government in Your Life...5 What Is Government?...6 Authority vs. Power...7 Why Do We Need Government?...8 What Does Government Do?...9 Limited
Table of Contents Introduction... 4 The Basics of Government Government in Your Life...5 What Is Government?...6 Authority vs. Power...7 Why Do We Need Government?...8 What Does Government Do?...9 Limited
Unit 4: Revolutions of Democracy
 Unit 4: Revolutions of Democracy FOQ #1: Did the English Civil War help or hurt Democracy? Explain. FOQ #2: What were the causes of the American Revolutionary War? How did it end? FOQ #3: What were the
Unit 4: Revolutions of Democracy FOQ #1: Did the English Civil War help or hurt Democracy? Explain. FOQ #2: What were the causes of the American Revolutionary War? How did it end? FOQ #3: What were the
HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY STUDENT BOOK. 12th Grade Unit 4
 HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 4 HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY 1204 HISTORY OF GOVERNMENTS Unit 4 HISTORY OF GOVERNMENTS INTRODUCTION 3 1. ANCIENT GOVERNMENTS 5 A PRIMITIVE GOVERNMENT PRIMER 6
HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 4 HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY 1204 HISTORY OF GOVERNMENTS Unit 4 HISTORY OF GOVERNMENTS INTRODUCTION 3 1. ANCIENT GOVERNMENTS 5 A PRIMITIVE GOVERNMENT PRIMER 6
JOB INSTRUCTION. Instructors Guide Session 3
 JOB INSTRUCTION Instructors Guide Session 3 SESSION 3 - INSTRUCTIONS It is important to read this manual and have a clear understanding of the contents, prior to the start of training. Before the session
JOB INSTRUCTION Instructors Guide Session 3 SESSION 3 - INSTRUCTIONS It is important to read this manual and have a clear understanding of the contents, prior to the start of training. Before the session
10/6/2015. Federal (Ottawa)
 Federal (Ottawa) 1 2 3 The Parliament of Canada 4 When Canada became a nation, the British North America (BNA) Act guaranteed that Canada would be under a parliamentary democracy. The ruling party in the
Federal (Ottawa) 1 2 3 The Parliament of Canada 4 When Canada became a nation, the British North America (BNA) Act guaranteed that Canada would be under a parliamentary democracy. The ruling party in the
Georgia Milestones Grade 6 EOG Study/Resource Guide for Students and Parents Page 201 of 218
 Unit 8: Canada Today In this unit, you will examine our neighbor to the north, Canada. You will learn about its forms of government, including presidential, unitary, monarchy, and parliamentary systems
Unit 8: Canada Today In this unit, you will examine our neighbor to the north, Canada. You will learn about its forms of government, including presidential, unitary, monarchy, and parliamentary systems
Look up the Triangular Trade on pg. 95 of your textbook and answer the following questions in complete sentences: 1. What was the triangular trade?
 Look up the Triangular Trade on pg. 95 of your textbook and answer the following questions in complete sentences: 1. What was the triangular trade? 2. Which 3 regions were involved in the triangular trade?
Look up the Triangular Trade on pg. 95 of your textbook and answer the following questions in complete sentences: 1. What was the triangular trade? 2. Which 3 regions were involved in the triangular trade?
Which careers are expected to have the most job openings in the future, and how will this affect my plans?
 Career Outlook 2 CAREERS The BIG Idea Which careers are expected to have the most job openings in the future, and how will this affect my plans? AGENDA Approx. 45 minutes I. Warm Up: What s a Career Outlook?
Career Outlook 2 CAREERS The BIG Idea Which careers are expected to have the most job openings in the future, and how will this affect my plans? AGENDA Approx. 45 minutes I. Warm Up: What s a Career Outlook?
IN THE ABSENCE OF GOOD DATA ONE CANNOT MAKE GOOD BUSINESS DECISIONS
 ONE CANNOT MAKE GOOD BUSINESS DECISIONS Ellen Freedman, CLM Law Practice Management Coordinator Pennsylvania Bar Association Please indulge me for a minute: reread the title of this article. OK, now one
ONE CANNOT MAKE GOOD BUSINESS DECISIONS Ellen Freedman, CLM Law Practice Management Coordinator Pennsylvania Bar Association Please indulge me for a minute: reread the title of this article. OK, now one
Philanthropy Center Manufacturing Center
 Volunteer Manual JA BizTown Philanthropy Center Manufacturing Center ROLE OF THE VOLUNTEER IMPORTANT POINTS TO REMEMBER Provide guidance and assistance to students Conduct scheduled staff meetings Use
Volunteer Manual JA BizTown Philanthropy Center Manufacturing Center ROLE OF THE VOLUNTEER IMPORTANT POINTS TO REMEMBER Provide guidance and assistance to students Conduct scheduled staff meetings Use
Passwords. Social Studies Vocabulary. Louisiana: Grade 8
 Passwords Social Studies Vocabulary Louisiana: Grade 8 To the Student What does bicameral mean? What is the difference between coniferous and deciduous? What is mercantilism? Passwords: Social Studies
Passwords Social Studies Vocabulary Louisiana: Grade 8 To the Student What does bicameral mean? What is the difference between coniferous and deciduous? What is mercantilism? Passwords: Social Studies
Debate. Introduction page 2 Lesson Plan page 3-4 For and Against Worksheet page 5 Presiding Officer page 6 Duties page 7 Voting Cards page 8-9
 Debate Curriculum Guide: Social Studies, Religious and Moral Education, Language, Literacy, Expressive Arts eaching Levels: 1, 2, 3 and 4 (P4 - S4) Citizenship hemes: litical Awareness, Peace Education
Debate Curriculum Guide: Social Studies, Religious and Moral Education, Language, Literacy, Expressive Arts eaching Levels: 1, 2, 3 and 4 (P4 - S4) Citizenship hemes: litical Awareness, Peace Education
Bell Ringer: September (5)6, 2017
 Announcements: 1: Check your grades! You need: 1: Spiral/blank sheet of paper 2: River Valley Civilizations Map/Anchor Chart Assignment Bell Ringer: September (5)6, 2017 1. Get out your notes from last
Announcements: 1: Check your grades! You need: 1: Spiral/blank sheet of paper 2: River Valley Civilizations Map/Anchor Chart Assignment Bell Ringer: September (5)6, 2017 1. Get out your notes from last
Glossary Capitalist markets Capitalist Trade Civil association
 Glossary Capitalist markets Capitalist markets are systems of exchange that emphasize economic values. An ideal type that explains them would include certain attributes such as efficiency, productivity,
Glossary Capitalist markets Capitalist markets are systems of exchange that emphasize economic values. An ideal type that explains them would include certain attributes such as efficiency, productivity,
Scottish Rugby Marketing Guide for Clubs
 Scottish Rugby Marketing Guide for Clubs First things first, what is marketing? Here is a very basic definition: The action or business of promoting and selling products or services, including market research
Scottish Rugby Marketing Guide for Clubs First things first, what is marketing? Here is a very basic definition: The action or business of promoting and selling products or services, including market research
We the People Lesson 1
 We the People Lesson 1 1. What is the purpose of government according to the natural rights philosophers? The main purpose of government should be to protect people s natural rights. 2. Where does government
We the People Lesson 1 1. What is the purpose of government according to the natural rights philosophers? The main purpose of government should be to protect people s natural rights. 2. Where does government
Sociocracy. A brief introduction :03 1
 Sociocracy A brief introduction. 2014-12-23 22:03 1 Opening (Option 1) (Select the option that best suits the audience) What brought you here and what is your biggest need for your organization? Facilitate
Sociocracy A brief introduction. 2014-12-23 22:03 1 Opening (Option 1) (Select the option that best suits the audience) What brought you here and what is your biggest need for your organization? Facilitate
Debate a bill Level 2
 Debate a bill Level 2 Making laws In this activity your students will have a go at scrutinising a bill for themselves before moving on to the final vote in the House of Commons or House of Lords. The activities
Debate a bill Level 2 Making laws In this activity your students will have a go at scrutinising a bill for themselves before moving on to the final vote in the House of Commons or House of Lords. The activities
Curriculum Catalog
 2017-2018 Curriculum Catalog 2017 Glynlyon, Inc. Table of Contents GOVERNMENT AND ECONOMICS COURSE OVERVIEW... 1 UNIT 1: INTERNATIONAL GOVERNMENTS... 1 UNIT 2: UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT... 1 UNIT 3: THE
2017-2018 Curriculum Catalog 2017 Glynlyon, Inc. Table of Contents GOVERNMENT AND ECONOMICS COURSE OVERVIEW... 1 UNIT 1: INTERNATIONAL GOVERNMENTS... 1 UNIT 2: UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT... 1 UNIT 3: THE
Social Studies Lesson Plan- SS.3.C.1.2: How the government gains its powers from the people
 Teacher s Name: Employee Number: School: Social Studies Lesson Plan- SS.3.C.1.2: How the government gains its powers 1. Title: How Government Gains its Powers 2. Overview - Big Ideas: Enduring Understandings
Teacher s Name: Employee Number: School: Social Studies Lesson Plan- SS.3.C.1.2: How the government gains its powers 1. Title: How Government Gains its Powers 2. Overview - Big Ideas: Enduring Understandings
YOUR KEY KNOWLEDGE THIS IS WHAT THE EXAMINER CAN TEST YOU ON
 YOUR KEY KNOWLEDGE THIS IS WHAT THE EXAMINER CAN TEST YOU ON CASE STUDY OCCUPY MELBOURNE On 15 October 2011, a group of protesters moved into Melbourne's City Square in Swanston Street. This action was
YOUR KEY KNOWLEDGE THIS IS WHAT THE EXAMINER CAN TEST YOU ON CASE STUDY OCCUPY MELBOURNE On 15 October 2011, a group of protesters moved into Melbourne's City Square in Swanston Street. This action was
Succession Planning Who Is Going to Take My Place?
 2/24/2015 Who Is Going to Take My Place? Chuck Wunder MSL, EFO, CFO Fire Chief Green Valley Fire District 1 Objectives Define Understand Why We Need Identify The Opportunities and Challenges Of Discuss
2/24/2015 Who Is Going to Take My Place? Chuck Wunder MSL, EFO, CFO Fire Chief Green Valley Fire District 1 Objectives Define Understand Why We Need Identify The Opportunities and Challenges Of Discuss
People and Environments: The Role of Government and. Responsible Citizenship
 People and Environments: The Role of Government and Responsible Citizenship Name: (Please have this booklet at school every day.) Table Of Contents What is government? p.1 Elections p.2 Election day p.3
People and Environments: The Role of Government and Responsible Citizenship Name: (Please have this booklet at school every day.) Table Of Contents What is government? p.1 Elections p.2 Election day p.3
5. Revolutions A: English Civil War, Absolutism, Scientific Rev and Enlightenment
 5. Revolutions A: English Civil War, Absolutism, Scientific Rev and Enlightenment Study online at quizlet.com/_2rq93a 1. Absolutism 5. Cardinal Richelieu When kings and queens have complete control over
5. Revolutions A: English Civil War, Absolutism, Scientific Rev and Enlightenment Study online at quizlet.com/_2rq93a 1. Absolutism 5. Cardinal Richelieu When kings and queens have complete control over
I. Survey Methodology
 I. Survey Methodology The Elon University Poll is conducted using a stratified random sample of households with telephones and wireless telephone numbers in the population of interest in this case, citizens
I. Survey Methodology The Elon University Poll is conducted using a stratified random sample of households with telephones and wireless telephone numbers in the population of interest in this case, citizens
HOW YOUR CAREER BACKGROUND CAN HELP YOU BECOME A BUSINESS ANALYST
 By Laura Brandenburg Lesson Objective: After completing this lesson, you ll be able to identify strengths from your career background that will directly support your transition into business analysis.
By Laura Brandenburg Lesson Objective: After completing this lesson, you ll be able to identify strengths from your career background that will directly support your transition into business analysis.
Housing Authority of the City of Raleigh 900 Haynes Street, Raleigh, NC GENERAL APPLICATION FOR EMPLOYMENT (Administrative) o Part-time
 An Equal Opportunity Employer Housing Authority of the City of Raleigh 900 Haynes Street, Raleigh, NC 27604 GENERAL APPLICATION FOR EMPLOYMENT (Administrative) To be considered for employment, applicants
An Equal Opportunity Employer Housing Authority of the City of Raleigh 900 Haynes Street, Raleigh, NC 27604 GENERAL APPLICATION FOR EMPLOYMENT (Administrative) To be considered for employment, applicants
Data Collection Instrument. By Temtim Assefa
 Data Collection Instrument Design By Temtim Assefa Instruments Instruments are tools that are used to measure variables There are different types of instruments Questionnaire Structured interview Observation
Data Collection Instrument Design By Temtim Assefa Instruments Instruments are tools that are used to measure variables There are different types of instruments Questionnaire Structured interview Observation
