Section 1 Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome
|
|
|
- Roberta Simmons
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Prologue
2 Section 1 Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome Main Idea The Greeks developed democracy, and the Romans added representative government. Why It Matters Now Representation and citizen participation are important features of democratic governments around the world.
3 Types of Government What is government? institution through which each state maintains social order, provides public services, and enforces decisions that are binding on all people living within the state System for exercising authority
4 Autocracy Rule by one person Autocracies are the oldest and one of the most common forms of government. Most autocrats have gained and maintained their power by inheritance or the ruthless use of military or police power. Several forms of autocracy exist, one of which is absolute or totalitarian dictatorship. monarchy, a king, queen, or emperor exercises the supreme powers of government
5 Oligarchy Rule by few persons Oligarchies derive their power from wealth, military power, social position, religion, or some combination of these elements Aristocracy Hereditary ruling class Both dictatorships and oligarchies sometimes claim they rule for the people, but they usually suppress all political opposition sometimes ruthlessly
6 Democracy Rule by many persons The key idea of a democracy is that the people hold sovereign power Abraham Lincoln described democracy as government of the people, by the people, and for the people There are two forms of democracy direct and indirect
7 Indirect Democracy In an indirect or representative democracy, the people elect representatives and give them the responsibility and power to make laws and conduct government.
8 Greece s Contribution Socrates Plato - In an ideal society the government should be controlled by a class of philosopher kings Aristotle Questioned world around them Students of the prior All used logic and reason to investigate the world, nature of the universe, society, and morality central to Western political thought today Natural law Individual achievement, dignity, and worth are of great importance Considered to be the birthplace of democracy
9 The following excerpt is from a speech known as The Funeral Oration, delivered by the Athenian general and politician Pericles in 431 BCE. Pericles was widely seen as the leader of Athens. He gave this speech during a funeral for Athenian soldiers that died in the first year of the brutal Peloponnesian War against Sparta, Athens s chief rival. The Athenian historian Thucydides included the speech in his book the History of the Peloponnesian War. Historians are not sure when Thucydides wrote down the speech or how close his version was to the original. Find a partner and discuss: 1. Based on what you know about Pericles and how this speech was recorded, what are the strengths and weaknesses of this document as a source about Athens s political system? Share out.
10 Our constitution favors the many instead of the few. This is why it is called a democracy. If we look to the laws, they give equal justice to all. Advancement in public life falls to one s reputation for good work. Social class is not allowed to interfere with someone s merit, and poverty does not block the way. If a man is able to serve the state, he is not stopped by the obscurity of his condition. The freedom which we enjoy in our government extends also to our ordinary life. There. Far from being jealous of each other, we do not feel called upon to be angry with our neighbor for doing what he likes. But all this ease in our private lives does not make us lawless as citizens. Fear is our chief protection against this, teaching us to obey the magistrates and the laws. Find a different partner and discuss. 2. According to Pericles, what were the characteristics of Athenian democracy? Share out.
11 But how many people were really voting?
12 Rome s Contribution Four Principles of Roman Law 1) All citizens had the right to equal treatment under law. 2) A person was considered innocent until proven guilty. 3) The burden of proof rested with the accuser rather than the accused. 4) Any law that seemed unreasonable or grossly unfair could be set aside. Written legal code (12 Tables) Applied equally and impartially to all citizens Republican form of government Used representatives in government
13 You will work in the groups that will eventually be your Jeopardy groups. With your group, you will imagine that you are a city-state of your own. You must decide what kind of government you will have and how you will run it.
14 1. Monarchy, Oligarchy, or Democracy? 2. Once you have decided how your government will distribute power, decide who is in charge. This will depend on what kind of government you chose. 3. Why did you choose this person or people to be in charge? 4. How will you create and enforce laws? 5. How will the next leader or leaders be chosen? 6. Why have you chosen this type of government? Answer on one sheet of paper for your group.
15 Answer in complete sentences on a half sheet of paper. 1. How does an aristocracy differ from an oligarchy? 2. Name one of the four basic principles of Roman law. 3. Which characteristic of the government under the Roman Republic had the greatest impact on the democratic tradition? 4. Why were the 12 Tables important? 5. Where can Rome s influence on the government of the United States be found?
16 Main Idea Section 2 Judeo Christian Tradition Judaism and Christianity taught individual worth, ethical values, and the need to fight injustice. Why It Matters Now These ideals continue to be important to democracy today.
17 Monotheism Belief in one god Christianity, Judaism, Islam Polytheism Belief in many gods Hinduism
18 Judaism Religion of the Hebrews Founded by Moses around 2000 B.C.E. Moses delivered the 10 Commandments Focused on morality and ethics
19 Buddhism Started 6 th century B.C. in India Based on the teachings of Siddhartha Gautama (Buddha or Enlightened One) Four Noble Truths with the Eightfold Path Escape suffering worldly desires Ashoka helped spread the religion with his rock pillars during his reign as ruler of the Mauryan Empire
20 Christianity Stressed importance of people s love for God, their neighbors, their enemies and themselves Used the Old Testament and teaching of Jesus and his disciples which became the New Testament Spread through the Roman Empire even though it was banned Became official religion of Roman Empire becoming Holy Roman Empire in 380
21 Based on Muhammad s teachings of the bond of community, unity of all people and charity Holy book is the Qu ran (Koran) Fastest growing religion in the world today Islam
22 Most powerful institution in Europe by the Middle Ages Catholic Church
23 Renaissance Starts in Italy Renewed interest in classical culture and rejected medieval view that life was only a preparation for the afterlife Technology helps make possible
24 Medieval Art (before the Renaissance) Middle Ages last from the 3 rd to 13 th century Learning is centered around the church and religion Artistic subjects are religious
25 What do you notice?
26 What do you notice? Most art has religious subjects. Figures always wear clothes. Saints have halos. Size of figures represents importance. Background is often gold, representing heaven. Figures are represented ideally, not as individuals. (They all look the same!)
27 Renaissance Art The Renaissance begins in the 14 th century. People begin to read the literature of Classical Greece and Rome. People begin to learn about the government, philosophy, and art from these writings. They begin to study the natural world, astronomy, math, and engineering. Artists created works outside the church, and begin to sign their own works.
28 What do you notice that is different from the Medieval paintings?
29 What do you notice that is different from the Medieval paintings?
30 What do you notice that was different from the Medieval paintings? Saints are depicted as more human. Saints are the same size as humans. Halos fade and eventually disappear. Natural landscape is the background. Perspective is used so the art looks more realistic.
31 Humanism in Renaissance Art Changes in art reflect changes in the Renaissance view of people and their place in the world. With a partner, draw a Venn diagram on a half sheet of paper and compare and contrast Medieval Art and Renaissance Art. Medieval Renaissance Both
32 Protestants People who wanted to reform the Catholic Church during the Reformation Started by Martin Luther in the 16 th century Questions authority
33 Individuals Both the Renaissance and the Reformation stressed the importance of individual Turn to a partner and talk: How did they do this? People question authority and learn for themselves Helps lead to democracy and becomes rooted in Western culture
34 Answer in complete sentences in your notes. 1. How are the 10 Commandments different from the laws of other groups? 2. Which of the Christian teachings supports the central idea of democracy? 3. How did the Reformation indirectly contribute to the growth of democracy? 4. What ideas crucial to the shaping of democracy did Judaism and Christianity share? 5. How did the Reformation promote the idea of individualism? 6. How did the printing press help promote the ideas of democracy?
35 Religion Sourcing What are the similarities among Buddhism, Christianity, and Islam? Go to quia.com/web Login Go to the class page Find Religion Sourcing
36 What are the similarities among Buddhism, Christianity, and Islam? Read Buddhist Beliefs Discuss the questions below. Agree upon a response for each question. Write down the response to each question on one the back of the graphic organizer.
37 What are the similarities among Buddhism, Christianity, and Islam? Read the 10 Commandments Discuss the questions below.
38 What are the similarities among Buddhism, Christianity, and Islam? Read 5 Pillars Discuss the questions. Agree upon responses. Write down a response for each question for the two of you. Complete the Matrix/Chart. In at least one paragraph answer the main questions above.
39 What are the similarities among Buddhism, Christianity, and Islam? Complete the Matrix/Chart Measurable? Can you actually see this happening? Can you see someone going to Church? Can you observe someone praying? In at least one paragraph answer the main question above. There are many similarities between Buddhism, Christianity, and Islam. One similarity is that all three religions. Also, the religions all believe. Lastly, each religion states that.
40 Section 3 Democracy Develops in England Main Idea England began to develop democratic institutions that limited the power of the monarchy. Why It Matters Now Democratic traditions developed in England have influenced many countries, including the U.S.
41 Common Law English legal system that reflected the customs and principles established over time rather than the will of a ruler Look at precedence, past rulings Laws common to the country used throughout the country
42 Magna Carta Charter in 1215 that limited the power of the monarch Shows that rulers cannot rule any way they please No freeman could be punished without using the law of the land
43 Due Process Legal requirement in which the state must respect all of the legal rights owed to a person People have basic legal rights, such as trial by jury Does not allow monarchs to punish people without going through certain steps
44 Divine Right Chosen by god to rule Used by monarchs and emperors which are autocracies Hard to argue against
45 Parliament England s legislature that established the principle of representation and limited the power of the monarch by creating the House of Commons and House of Lords
46 Petition of Right Landmark in constitutional history, 1628 End of taxing without Parliament s consent, illegal imprisoning, housing troops, and military government during peacetime
47 Restoration 1660 Restoring of England s monarchy after a failed attempt of a military government by Oliver Cromwell
48 Glorious Revolution In order to take throne William and Mary had to agree to give up power Known as the Glorious Revolution Parliament could restrict power of the monarch and control succession to the throne
49 Constitutional Monarchy Prior events Magna Carta, Common Law, etc lead up to a limited monarchy Constitutional Monarchy Powers of a ruler/monarch are restricted by a written legal document known as a Constitution
50 English Bill of Rights 1689 Formal summary of English rights and liberties that include freedom of speech, suspension of laws, taxation without Parliament consent
51 Answer in complete sentences in your notes. 1. What was the Magna Carta s influence on history? 2. How are Mandate of Heaven and Divine Right the similar? 3. Why did Parliament invite William and Mary to rule England in 1689? 4. What impact did the English common law have on the United States? 5. Why was Oliver Cromwell s rule like that of an absolute monarch? 6. What were the main achievements of the Glorious Revolution? 7. Which country was the main influence on United States Constitution?
52 Section 4 Enlightenment and Democratic Main Idea Revolutions Enlightenment ideas helped bring about the American and French revolutions. Why It Matters Now These revolutions and the documents they produced have inspired other democratic movements.
53 Renaissance Although known as an artistic movement its individual nature helps inspire democracy with its independent thinking
54 Enlightenment Intellectual movement during the 17 th and 18 th centuries Apply reason and methods of science to all aspects of society Start to question reasoning for governments
55 Social Contract Thomas Hobbes in England was one of the first to theorize that people had a social contract with their leaders. Hobbes believed that people surrendered to the state the power needed to maintain order, in exchange for protection provided by the state.
56 Natural Rights John Locke took the social contract a step further when he wrote that the people could justly break the social contract when government failed to preserve the natural rights of the people to life, liberty, and property When the American colonies revolted against King George III, they declared their independence supported by the political philosophy of natural rights that Locke had written.
57 American Revolution Inspired by Enlightenment thinkers and the oppression of a ruler across the ocean British policies that go against British law but is permissible in the American colonies
58 United States Inspirations Locke Hobbes Rousseau Like Hobbes preached for a social contract but government comes from free individuals Voltaire Religious freedom and freedom of speech Montesquieu Separation of Power More than one branch government that has the ability to check the other to ensure one is not more powerful than another
59 United States of America First the Articles of Confederation fails Constitution Supreme law of the land Inspiration to other democracies Representative government Elect representatives to speak for the people Federal system Power of government divided between federal or central and states, or local governments
60 French Revolution Lots of underlying issues Inspired by Enlightenment ideals and success of American Revolution as well as American Democracy Much more bloody and radical
61 United Nations Democracy viewed as preferred form of government United Nations International peace keeping organization Although not all democracies basic liberties or freedoms are agreed upon by countries
62 Answer in complete sentences on a half-sheet of paper. 1. What were the natural rights? 2. What was Rousseau s idea of government? 3. What political rights are set forth in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights? 4. How did the writers of the U.S. Constitution adapt the political theories of the Enlightenment? 5. In what ways was the French Revolution similar to and different from the American Revolution? 6. Why has the idea of democracy survived wars and oppression?
The Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome
 Prologue 1 The Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome Essential Question: How did Greece and Rome contribute to the development of democracy in the United States? Athens Builds a Limited Democracy Changes In
Prologue 1 The Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome Essential Question: How did Greece and Rome contribute to the development of democracy in the United States? Athens Builds a Limited Democracy Changes In
Document A: Pericles (Modified)
 Document A: Pericles (Modified) The following excerpt is from a speech known as The Funeral Oration, delivered by the Athenian general and politician Pericles in 431 BCE. Pericles was widely seen as the
Document A: Pericles (Modified) The following excerpt is from a speech known as The Funeral Oration, delivered by the Athenian general and politician Pericles in 431 BCE. Pericles was widely seen as the
Document A: Pericles (Modified)
 Document A: Pericles (Modified) The following excerpt is from a speech known as The Funeral Oration, delivered by the Athenian general and politician Pericles in 431 BCE. Pericles was widely seen as the
Document A: Pericles (Modified) The following excerpt is from a speech known as The Funeral Oration, delivered by the Athenian general and politician Pericles in 431 BCE. Pericles was widely seen as the
Background. The background of Athenian Democracy. The definition of the term democracy. The three branches of Athenian government
 Name Period Page # Athenian Democracy Document Based Question: Was ancient Athens truly democratic? Background DIRECTIONS: As you view the PowerPoint presentation, take notes on The background of Athenian
Name Period Page # Athenian Democracy Document Based Question: Was ancient Athens truly democratic? Background DIRECTIONS: As you view the PowerPoint presentation, take notes on The background of Athenian
Legacy of Ancient Greece & Rome. World History Dr. Robbins
 Legacy of Ancient Greece & Rome World History Dr. Robbins Athens Builds a Limited Democracy First large democracy in ancient Greece democracy = rule of the people City-state was basic political unit Earliest
Legacy of Ancient Greece & Rome World History Dr. Robbins Athens Builds a Limited Democracy First large democracy in ancient Greece democracy = rule of the people City-state was basic political unit Earliest
Unit 4: Revolutions of Democracy
 Unit 4: Revolutions of Democracy FOQ #1: Did the English Civil War help or hurt Democracy? Explain. FOQ #2: What were the causes of the American Revolutionary War? How did it end? FOQ #3: What were the
Unit 4: Revolutions of Democracy FOQ #1: Did the English Civil War help or hurt Democracy? Explain. FOQ #2: What were the causes of the American Revolutionary War? How did it end? FOQ #3: What were the
The Athenian Constitution (Document A)
 The Athenian Constitution (Document A) Source: The following excerpt comes from The Athenian Constitution, written by the Greek philosopher Aristotle between 330 and 322 BC. Aristotle was the leading Greek
The Athenian Constitution (Document A) Source: The following excerpt comes from The Athenian Constitution, written by the Greek philosopher Aristotle between 330 and 322 BC. Aristotle was the leading Greek
STANDARD WHII.6c The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth,
 STANDARD WHII.6c The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth, and eighteenth centuries by c) assessing the impacts
STANDARD WHII.6c The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth, and eighteenth centuries by c) assessing the impacts
In framing a government which is to be administrated by men over men, the great difficulty lies in this: You must first enable the government to
 In framing a government which is to be administrated by men over men, the great difficulty lies in this: You must first enable the government to control the governed; and in the next place oblige it to
In framing a government which is to be administrated by men over men, the great difficulty lies in this: You must first enable the government to control the governed; and in the next place oblige it to
Prologue Section 3 Democracy Develops in England
 Prologue Section 3 Democracy Develops in England Edward the Confessor Dies (one of the last Anglo-Saxon Kings of England) Some sources say that Edward had promised the throne to his cousin William. The
Prologue Section 3 Democracy Develops in England Edward the Confessor Dies (one of the last Anglo-Saxon Kings of England) Some sources say that Edward had promised the throne to his cousin William. The
Life in the Colonies. Chapter 4, Section 1
 Life in the Colonies Chapter 4, Section 1 All English colonies shared a common English heritage, and that heritage included the idea that citizens had political rights. England also promoted the theory
Life in the Colonies Chapter 4, Section 1 All English colonies shared a common English heritage, and that heritage included the idea that citizens had political rights. England also promoted the theory
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1
 Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1 Basic Types of Government In a dictatorship, all powers are held by one person or group. In a democracy, authority lies with the people. The U.S. government
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1 Basic Types of Government In a dictatorship, all powers are held by one person or group. In a democracy, authority lies with the people. The U.S. government
Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1
 Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Identify the three concepts of government that influenced the American colonies. 2. Explain the influence of three landmark English documents.
Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Identify the three concepts of government that influenced the American colonies. 2. Explain the influence of three landmark English documents.
AUTOCRACY. SS.7.C.3.1 Forms of Government
 AUTOCRACY An autocracy is a form of government where one person has unlimited power. One form of an autocracy is a dictatorship where a military leader secures power often through violent means. Another
AUTOCRACY An autocracy is a form of government where one person has unlimited power. One form of an autocracy is a dictatorship where a military leader secures power often through violent means. Another
Look up the Triangular Trade on pg. 95 of your textbook and answer the following questions in complete sentences: 1. What was the triangular trade?
 Look up the Triangular Trade on pg. 95 of your textbook and answer the following questions in complete sentences: 1. What was the triangular trade? 2. Which 3 regions were involved in the triangular trade?
Look up the Triangular Trade on pg. 95 of your textbook and answer the following questions in complete sentences: 1. What was the triangular trade? 2. Which 3 regions were involved in the triangular trade?
The English Civil War and the Glorious Revolution
 The English Civil War and the Glorious Revolution Enduring Understanding: The relationship between citizens and their government is a fundamental component of political rule. To understand the role of
The English Civil War and the Glorious Revolution Enduring Understanding: The relationship between citizens and their government is a fundamental component of political rule. To understand the role of
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1
 Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Define government and the basic powers every government holds. 2. Describe the four defining characteristics of a state. 3. Identify four theories
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Define government and the basic powers every government holds. 2. Describe the four defining characteristics of a state. 3. Identify four theories
Writing the Constitution
 Writing the Constitution Backwards Planning Curriculum Units Michael Hutchison, Writer Dr. Aaron Willis, Project Coordinator Justin Coffey, Editor Kerry Gordonson, Editor Social Studies School Service
Writing the Constitution Backwards Planning Curriculum Units Michael Hutchison, Writer Dr. Aaron Willis, Project Coordinator Justin Coffey, Editor Kerry Gordonson, Editor Social Studies School Service
GOVERNMENT ORGANIZATIONS, INSTITUTIONS, AND INDIVIDUALS THAT EXERCISE POLITICAL AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF A GROUP OF PEOPLE
 TYPES OF GOVERNMENT GOVERNMENT ORGANIZATIONS, INSTITUTIONS, AND INDIVIDUALS THAT EXERCISE POLITICAL AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF A GROUP OF PEOPLE CITIZEN A LEGAL MEMBER OF A COUNTRY CONSTITUTION A WRITTEN PLAN
TYPES OF GOVERNMENT GOVERNMENT ORGANIZATIONS, INSTITUTIONS, AND INDIVIDUALS THAT EXERCISE POLITICAL AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF A GROUP OF PEOPLE CITIZEN A LEGAL MEMBER OF A COUNTRY CONSTITUTION A WRITTEN PLAN
Government in Athens
 SECTION 2 Government in Athens What You Will Learn Main Ideas 1. Aristocrats and tyrants ruled early Athens. 2. Athens created the world s first democracy. 3. Ancient democracy was different than modern
SECTION 2 Government in Athens What You Will Learn Main Ideas 1. Aristocrats and tyrants ruled early Athens. 2. Athens created the world s first democracy. 3. Ancient democracy was different than modern
SSCG1 Compare and contrast various systems of government.
 SSCG1 Compare and contrast various systems of government. 1a. Determine how governments differ in geographic distribution of power, particularly unitary, confederal, and federal types of government. Unitary
SSCG1 Compare and contrast various systems of government. 1a. Determine how governments differ in geographic distribution of power, particularly unitary, confederal, and federal types of government. Unitary
Unit Portfolio: Interpreting Visual Images
 Unit Portfolio: Interpreting Visual Images 1. What can you tell about this man based only on what you see in this picture? Make up a brief biography based on your perception of this photo. Use complete
Unit Portfolio: Interpreting Visual Images 1. What can you tell about this man based only on what you see in this picture? Make up a brief biography based on your perception of this photo. Use complete
Monday, January 23 rd
 Monday, January 23 rd For help with lecture, readings, help with essays, and test preparation, visit 173A SWKT (The American Heritage Review Room. It is open from 9:00 am to 4:00 pm, Monday through Friday.
Monday, January 23 rd For help with lecture, readings, help with essays, and test preparation, visit 173A SWKT (The American Heritage Review Room. It is open from 9:00 am to 4:00 pm, Monday through Friday.
We the People Lesson 1
 We the People Lesson 1 1. What is the purpose of government according to the natural rights philosophers? The main purpose of government should be to protect people s natural rights. 2. Where does government
We the People Lesson 1 1. What is the purpose of government according to the natural rights philosophers? The main purpose of government should be to protect people s natural rights. 2. Where does government
Who Rules? STEP BY STEP
 Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector or Transparency Copy Instructions: Anticipation Mind Map (half page; class set) Reading (2 pages;
Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector or Transparency Copy Instructions: Anticipation Mind Map (half page; class set) Reading (2 pages;
The History of Government The Origins of Government Ancient Civilizations The First Set of Laws
 The History of Government The Origins of Government Government is one of humanity's oldest and most important institutions. From earliest times, some kind of government has been a vital part of every society.
The History of Government The Origins of Government Government is one of humanity's oldest and most important institutions. From earliest times, some kind of government has been a vital part of every society.
The French Revolution
 The French Revolution Using your notes, complete the following paragraph. The Enlightenment is also known as the. During this time, people began to reject the teachings of the and the and question traditional
The French Revolution Using your notes, complete the following paragraph. The Enlightenment is also known as the. During this time, people began to reject the teachings of the and the and question traditional
Who Rules? STEP BY STEP
 Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector or Transparency Copy Instructions: Anticipation Mind Map (half page; class set) Reading (2 pages;
Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector or Transparency Copy Instructions: Anticipation Mind Map (half page; class set) Reading (2 pages;
The Rise of Parliamentary Democracy in England. Student Handouts, Inc.
 Slide 1 The Rise of Parliamentary Democracy in England Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com Slide 2 James I James Stuart (James VI of Scotland) inherited the English throne from his cousin, Elizabeth
Slide 1 The Rise of Parliamentary Democracy in England Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com Slide 2 James I James Stuart (James VI of Scotland) inherited the English throne from his cousin, Elizabeth
Who Rules? STEP BY STEP
 Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector Transparency Copy Instructions: Anticipation Mind Map (half page; class set) Reading (2 pages; class
Teacher s Guide Who Rules? Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector Transparency Copy Instructions: Anticipation Mind Map (half page; class set) Reading (2 pages; class
1. Constitutional Law Based on the constitution Sets out how power is divided between governments Limits the powers of government Any other law that
 Where do laws come from? There are three sources of law: 1. Canadian Constitution (constitutional law, over-rides all other laws) 2. Statute Law - passed by governments (over-rides common law) 3. Common
Where do laws come from? There are three sources of law: 1. Canadian Constitution (constitutional law, over-rides all other laws) 2. Statute Law - passed by governments (over-rides common law) 3. Common
The$Rise$of$Absolu.sm$&$ Cons.tu.onalism$ Part$1$88$As$Poli.cal$Systems$ Part$2$88$Within$England$and$France$
 The$Rise$of$Absolu.sm$&$ Cons.tu.onalism$ Part$1$88$As$Poli.cal$Systems$ Part$2$88$Within$England$and$France$ Part 1: Absolutism and Constitutionalism as political systems Essential Question: 1) What are
The$Rise$of$Absolu.sm$&$ Cons.tu.onalism$ Part$1$88$As$Poli.cal$Systems$ Part$2$88$Within$England$and$France$ Part 1: Absolutism and Constitutionalism as political systems Essential Question: 1) What are
MODELS OF GOVERNANCE: PALEOLITHIC ANCIENT ERA
 Students should explain how and why models of governance evolved between the Paleolithic and Ancient eras Section Overview: What is Government? : a system for controlling society Throughout history people
Students should explain how and why models of governance evolved between the Paleolithic and Ancient eras Section Overview: What is Government? : a system for controlling society Throughout history people
The French Revolution CH
 The French Revolution CH. 7.2-5 The Assembly Reforms France National Assembly, declared: 1. All citizens (men) of France EQUAL. 2. Declaration of the Rights of Man Copied from US Dec. of Ind. *Protect
The French Revolution CH. 7.2-5 The Assembly Reforms France National Assembly, declared: 1. All citizens (men) of France EQUAL. 2. Declaration of the Rights of Man Copied from US Dec. of Ind. *Protect
ABSOLUTISM IN EASTERN EUROPE: Austria
 CC8.RH.2: Determine the central ideas of a primary source ABSOLUTISM IN EASTERN EUROPE: Austria In many respects the rise of absolutism was a natural response to the chaos of the religious wars. Absolute
CC8.RH.2: Determine the central ideas of a primary source ABSOLUTISM IN EASTERN EUROPE: Austria In many respects the rise of absolutism was a natural response to the chaos of the religious wars. Absolute
HISTORY CURRICULUM KEY STAGE 3. Mr A. Chan (AHT for Teaching and Learning) Mr E. McHugh (AHT for KS5) Mr D. West Mr L. Martin
 HISTORY CURRICULUM Mr A. Chan (AHT for Teaching and Learning) Mr E. McHugh (AHT for KS5) Mr D. West Mr L. Martin KEY STAGE 3 YEAR 7: Britain 1066-1603 Term 1: The Norman Conquest & William s Consolidation
HISTORY CURRICULUM Mr A. Chan (AHT for Teaching and Learning) Mr E. McHugh (AHT for KS5) Mr D. West Mr L. Martin KEY STAGE 3 YEAR 7: Britain 1066-1603 Term 1: The Norman Conquest & William s Consolidation
Who Rules? STEP BY STEP
 Non-PowerPoint Option PowerPoint Option Teacher s Guide Time Needed: One Class Period Materials Needed: Student worksheets PowerPoint OR Transparency Copy Instructions: Student materials (double-sided,
Non-PowerPoint Option PowerPoint Option Teacher s Guide Time Needed: One Class Period Materials Needed: Student worksheets PowerPoint OR Transparency Copy Instructions: Student materials (double-sided,
THE MIDDLE AGES. The Feudal System. The Feudal System. The Medieval Manor. The Early Ages (The Dark Ages)
 The Early Ages 500 1000 (The Dark Ages) THE MIDDLE AGES 500 1500 A.D. Medieval Europe Barbarian invaders destroy Roman Empire Robbers and Bandits stop commerce & travel Reading, writing, arts, science
The Early Ages 500 1000 (The Dark Ages) THE MIDDLE AGES 500 1500 A.D. Medieval Europe Barbarian invaders destroy Roman Empire Robbers and Bandits stop commerce & travel Reading, writing, arts, science
DRAFT SOCIAL SCIENCES STANDARDS: CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT
 DRAFT SOCIAL SCIENCES STANDARDS: CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT CORE STANDARDS Civics and Government 10. Examine the relationship between government and citizens to distinguish and evaluate the ways that civic
DRAFT SOCIAL SCIENCES STANDARDS: CIVICS AND GOVERNMENT CORE STANDARDS Civics and Government 10. Examine the relationship between government and citizens to distinguish and evaluate the ways that civic
Austria-Hungary and the Ottoman Empire
 Austria-Hungary and the Ottoman Empire Learning Goals: Analyze and Explain the impact of nationalism in Austro-Hungarian Empire and Ottoman Empire. Explain how Nationalism leads to WWI. Nationalism in
Austria-Hungary and the Ottoman Empire Learning Goals: Analyze and Explain the impact of nationalism in Austro-Hungarian Empire and Ottoman Empire. Explain how Nationalism leads to WWI. Nationalism in
TABLE OF CONTENTS. SS.7.C.3.1 Updated 8/17 1
 COMPARING FORMS OF GOVERNMENT SS.7.C.3.1 Compare different forms of government (direct democracy, representative democracy, socialism, communism, monarchy, oligarchy, autocracy). TABLE OF CONTENTS Lesson
COMPARING FORMS OF GOVERNMENT SS.7.C.3.1 Compare different forms of government (direct democracy, representative democracy, socialism, communism, monarchy, oligarchy, autocracy). TABLE OF CONTENTS Lesson
THE STRENGTH OF AMERICAN FEDERAL DEMOCRACY by Roger Myerson
 THE STRENGTH OF AMERICAN FEDERAL DEMOCRACY by Roger Myerson http://home.uchicago.edu/~rmyerson/research/amerfed.pdf The institutions received from England were admirably calculated to lay the foundation
THE STRENGTH OF AMERICAN FEDERAL DEMOCRACY by Roger Myerson http://home.uchicago.edu/~rmyerson/research/amerfed.pdf The institutions received from England were admirably calculated to lay the foundation
America: Republic vs. Democracy
 America: Republic vs. Democracy By Frank Li, Ph.D. Founder & President, West-East International, Inc. January 11, 2013 In my book Saving America, Chinese Style, I fundamentally questioned democracy as
America: Republic vs. Democracy By Frank Li, Ph.D. Founder & President, West-East International, Inc. January 11, 2013 In my book Saving America, Chinese Style, I fundamentally questioned democracy as
The Attempted Revival of Empire
 Ironically, most monarchs in Europe benefited from religious strife. Established monarchs consolidated their power while ambitious opportunists used the chaos to gain power. The Holy Roman Empire remained
Ironically, most monarchs in Europe benefited from religious strife. Established monarchs consolidated their power while ambitious opportunists used the chaos to gain power. The Holy Roman Empire remained
feb 6 10:27 VISUAL VOCABULARY AND EXERCISES ws.
 THE MONARCHY VOCABULARY AND STRUCTURES feb 6 10:27 VISUAL VOCABULARY AND EXERCISES http://www.languageguide.org/english/vocabulary/history/ http://www.surfnetkids.com/games/monarchy ws.htm http://quizlet.com/5913312/revolutions
THE MONARCHY VOCABULARY AND STRUCTURES feb 6 10:27 VISUAL VOCABULARY AND EXERCISES http://www.languageguide.org/english/vocabulary/history/ http://www.surfnetkids.com/games/monarchy ws.htm http://quizlet.com/5913312/revolutions
Main Idea: The Ottomans established a Muslim empire that combined many cultures and lasted for more than 600 years.
 Absolute Monarchs in the Middle East & Europe (1500 1800) Pondering the Entire Unit What might be a benefit as well as a drawback having one person with complete control (Absolutism) in charge of a country?
Absolute Monarchs in the Middle East & Europe (1500 1800) Pondering the Entire Unit What might be a benefit as well as a drawback having one person with complete control (Absolutism) in charge of a country?
Georgia Milestones Grade 6 EOG Study/Resource Guide for Students and Parents Page 201 of 218
 Unit 8: Canada Today In this unit, you will examine our neighbor to the north, Canada. You will learn about its forms of government, including presidential, unitary, monarchy, and parliamentary systems
Unit 8: Canada Today In this unit, you will examine our neighbor to the north, Canada. You will learn about its forms of government, including presidential, unitary, monarchy, and parliamentary systems
Standard 7-3: The student will demonstrate an understanding of independence movements that occurred throughout the world from 1770 through 1900.
 Standard 7-3: The student will demonstrate an understanding of independence movements that occurred throughout the world from 1770 through 1900. 7-3.2 Analyze the effects of the Napoleonic Wars on the
Standard 7-3: The student will demonstrate an understanding of independence movements that occurred throughout the world from 1770 through 1900. 7-3.2 Analyze the effects of the Napoleonic Wars on the
LL Copy the chart below. Fill it in as we watch Types of Government game show.
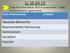 LL 10-24-13 Copy the chart below. Fill it in as we watch Types of Government game show. Form of Government 5 Details Absolute Monarchy Representative Democracy Communism Socialism Fascism The directions
LL 10-24-13 Copy the chart below. Fill it in as we watch Types of Government game show. Form of Government 5 Details Absolute Monarchy Representative Democracy Communism Socialism Fascism The directions
Impossible demands made of government, which, if granted, would mean its end. Unsuccessful gov t attempts to suppress the revolutionaries
 Stages of Crane Brinton Impossible demands made of government, which, if granted, would mean its end Unsuccessful gov t attempts to suppress the revolutionaries Revolutions gain power and seem united.
Stages of Crane Brinton Impossible demands made of government, which, if granted, would mean its end Unsuccessful gov t attempts to suppress the revolutionaries Revolutions gain power and seem united.
The Decline of Feudalism (7.6.5)
 The Decline of Feudalism (7.6.5) LIMITING POWER OF MONARCHS Monarchs gain power Charlemagne uses during Crusades system of rewards Emperor Henry IV excommunicated FEUDALISM Magna Carta limits power of
The Decline of Feudalism (7.6.5) LIMITING POWER OF MONARCHS Monarchs gain power Charlemagne uses during Crusades system of rewards Emperor Henry IV excommunicated FEUDALISM Magna Carta limits power of
Three Levels of Power Distribution Ø Unitary Ø Ø
 SS6CG4 The student will compare and contrast various forms of government. a. Describe the ways government systems distribute power: unitary, confederation, and federal. b. Explain how governments determine
SS6CG4 The student will compare and contrast various forms of government. a. Describe the ways government systems distribute power: unitary, confederation, and federal. b. Explain how governments determine
Handout D: The Bill of Rights 1 per student. Unit IV: Rights and Responsibilities LESSON 2: MR. MADISON NEEDS SOME HELP. Overview
 Unit IV: Rights and Responsibilities LESSON 2: MR. MADISON NEEDS SOME HELP OBJECTIVES Students will be able to: Explain why the Bill of Rights was added to the Constitution. Identify rights they have learned
Unit IV: Rights and Responsibilities LESSON 2: MR. MADISON NEEDS SOME HELP OBJECTIVES Students will be able to: Explain why the Bill of Rights was added to the Constitution. Identify rights they have learned
Civics EOC Review 1. Enlightenment SS.7.C.1.1 Founding Documents SS.7.C.1.2 Rule of Law SS.7.C.1.9 Citizenship SS.7.C.2.1 and 2.2
 Civics EOC Review 1 Enlightenment SS.7.C.1.1 Founding Documents SS.7.C.1.2 Rule of Law SS.7.C.1.9 Citizenship SS.7.C.2.1 and 2.2 Enlightenment SS.7.C.1.1 Recognize how Enlightenment ideas including Montesquieu
Civics EOC Review 1 Enlightenment SS.7.C.1.1 Founding Documents SS.7.C.1.2 Rule of Law SS.7.C.1.9 Citizenship SS.7.C.2.1 and 2.2 Enlightenment SS.7.C.1.1 Recognize how Enlightenment ideas including Montesquieu
The Age of Absolutism
 The Age of Absolutism Chapter 17 Ms. Rosenberg Europe s Absolute Monarchies Russia England Prussia France Austria Spain Chapter 17, Section 1 Extending Spanish Power Charles V & the Hapsburgs Spain was
The Age of Absolutism Chapter 17 Ms. Rosenberg Europe s Absolute Monarchies Russia England Prussia France Austria Spain Chapter 17, Section 1 Extending Spanish Power Charles V & the Hapsburgs Spain was
Primary Sources: Declaration of the Rights of Man
 Primary Sources: Declaration of the Rights of Man By Original document from the public domain, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.28.16 Word Count 886 This representation of the Declaration of the Rights of
Primary Sources: Declaration of the Rights of Man By Original document from the public domain, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.28.16 Word Count 886 This representation of the Declaration of the Rights of
Chapter 21. Absolute Monarchs in Europe,
 Chapter 21 Absolute Monarchs in Europe, 1500-1800 Section 1: Spain s Empire and European Absolutism During a time of religious and economic instability, Philip II rules Spain with a strong hand. A Powerful
Chapter 21 Absolute Monarchs in Europe, 1500-1800 Section 1: Spain s Empire and European Absolutism During a time of religious and economic instability, Philip II rules Spain with a strong hand. A Powerful
Part I. The Evolution of English Constitutional Government
 Part I The Evolution of English Constitutional Government Preface Why Begin a Study of Christianity in America With an Overview of English Political and Religious History? (1)We cannot learn history in
Part I The Evolution of English Constitutional Government Preface Why Begin a Study of Christianity in America With an Overview of English Political and Religious History? (1)We cannot learn history in
THE GLORIOUS REVOLUTION AND THE IMPACT ON AUSTRALIAN CONSTITUTIONAL LAW
 Vol 8 The Western Australian Jurist 427 THE GLORIOUS REVOLUTION AND THE IMPACT ON AUSTRALIAN CONSTITUTIONAL LAW LAURA JACKSON* I INTRODUCTION It has been proposed that The Glorious Revolution is irrelevant
Vol 8 The Western Australian Jurist 427 THE GLORIOUS REVOLUTION AND THE IMPACT ON AUSTRALIAN CONSTITUTIONAL LAW LAURA JACKSON* I INTRODUCTION It has been proposed that The Glorious Revolution is irrelevant
German Unification. Nationalism in Europe Section 2. Preview
 Preview German Unification Main Idea / Reading Focus Steps Toward Unification Bismarck s Plan for Germany Quick Facts: Steps to Unification in Germany Faces of History: Otto von Bismarck Unification and
Preview German Unification Main Idea / Reading Focus Steps Toward Unification Bismarck s Plan for Germany Quick Facts: Steps to Unification in Germany Faces of History: Otto von Bismarck Unification and
English Constitutional Monarchy. A slightly more effeminate version of the US move to Constitutionalism
 English Constitutional Monarchy A slightly more effeminate version of the US move to Constitutionalism Background (1215-1603) Magna Carta, 1215 a a A list of demands made by the nobility.. Established
English Constitutional Monarchy A slightly more effeminate version of the US move to Constitutionalism Background (1215-1603) Magna Carta, 1215 a a A list of demands made by the nobility.. Established
Chapter 1 Constitutional Democracy. Constitutional Democracy. Constitutional Democracy. The peaceful transfer of political power through elections
 Chapter 1 A student from Chicago casts an early vote in the 2008 Illinois presidential primary. The peaceful transfer of political power through elections In 2000, Democrat Al Gore won the popular vote,
Chapter 1 A student from Chicago casts an early vote in the 2008 Illinois presidential primary. The peaceful transfer of political power through elections In 2000, Democrat Al Gore won the popular vote,
12 December 2005 Final Draft of DBQ on the Glorious Revolution
 Andrew Gwyn Mr. Meng Final DBQ 12 December 2005 Final Draft of DBQ on the Glorious Revolution EUROPEAN HISTORY SECTION II Part A (Suggested writing time---45 minutes) Percent of Section II score---45 Directions:
Andrew Gwyn Mr. Meng Final DBQ 12 December 2005 Final Draft of DBQ on the Glorious Revolution EUROPEAN HISTORY SECTION II Part A (Suggested writing time---45 minutes) Percent of Section II score---45 Directions:
Government in Athens
 Government in Athens Aristocrats Democracy was born in Ancient Greece in the city of Athens. Democracy is a form of a government in which people rule themselves. However, Athens was ruled first by kings,
Government in Athens Aristocrats Democracy was born in Ancient Greece in the city of Athens. Democracy is a form of a government in which people rule themselves. However, Athens was ruled first by kings,
Chapter 22: Comparative Political Systems Section 4
 Chapter 22: Comparative Political Systems Section 4 Objectives 1. Examine elements of the United Kingdom s parliamentary democracy. 2. Describe regional and local government in the United Kingdom. 3. Analyze
Chapter 22: Comparative Political Systems Section 4 Objectives 1. Examine elements of the United Kingdom s parliamentary democracy. 2. Describe regional and local government in the United Kingdom. 3. Analyze
Huntsville City Schools Pacing Guide Course: Civics Grade: 7 First 9 Weeks
 Huntsville City Schools 2017-18 Pacing Guide Course: Civics Grade: 7 First 9 Weeks Civics Fall 2017 General Resources The State of Alabama is now requiring that all students pass a Civics test to receive
Huntsville City Schools 2017-18 Pacing Guide Course: Civics Grade: 7 First 9 Weeks Civics Fall 2017 General Resources The State of Alabama is now requiring that all students pass a Civics test to receive
UNIT Y108 THE EARLY STUARTS AND THE ORIGINS OF THE CIVIL WAR
 UNIT Y108 THE EARLY STUARTS AND THE ORIGINS OF THE CIVIL WAR NOTE: BASED ON 3X 50 MINUTE LESSONS PER WEEK TERMS BASED ON 6 TERM YEAR. Key Topic Term Week Number Indicative Content Extended Content Resources
UNIT Y108 THE EARLY STUARTS AND THE ORIGINS OF THE CIVIL WAR NOTE: BASED ON 3X 50 MINUTE LESSONS PER WEEK TERMS BASED ON 6 TERM YEAR. Key Topic Term Week Number Indicative Content Extended Content Resources
Breaking with Britain. Part I
 Breaking with Britain Part I Monday, February 6 th COMING SOON: Open Lab Test Review on Saturday, February 11 th from 10:00 am to 2:00 pm in 173A, 240, and 270 SWKT Midterm #1: February 14th 17th Tuesday,
Breaking with Britain Part I Monday, February 6 th COMING SOON: Open Lab Test Review on Saturday, February 11 th from 10:00 am to 2:00 pm in 173A, 240, and 270 SWKT Midterm #1: February 14th 17th Tuesday,
Louis XIV Absolutism and Wars
 Louis XIV Absolutism and Wars Key Concept 2.1 Different models of political sovereignty affected the relationship among states and between states and individuals. Key Concept 2.1.I In much of Europe, absolute
Louis XIV Absolutism and Wars Key Concept 2.1 Different models of political sovereignty affected the relationship among states and between states and individuals. Key Concept 2.1.I In much of Europe, absolute
What is nationalism? What impact can it have?
 What is nationalism? What impact can it have? Nation - a group of people who share a common history, culture, or language and who live in the same area Nationalism- strong feelings of support for one s
What is nationalism? What impact can it have? Nation - a group of people who share a common history, culture, or language and who live in the same area Nationalism- strong feelings of support for one s
The European Constitution
 The European Constitution What is the position in 2011? History of constitutions Does Britain have a constitution? Where do we stand now? What is it? Is it necessary? Robert Jones robert.jones@anglia.ac.uk
The European Constitution What is the position in 2011? History of constitutions Does Britain have a constitution? Where do we stand now? What is it? Is it necessary? Robert Jones robert.jones@anglia.ac.uk
10/6/2015. Federal (Ottawa)
 Federal (Ottawa) 1 2 3 The Parliament of Canada 4 When Canada became a nation, the British North America (BNA) Act guaranteed that Canada would be under a parliamentary democracy. The ruling party in the
Federal (Ottawa) 1 2 3 The Parliament of Canada 4 When Canada became a nation, the British North America (BNA) Act guaranteed that Canada would be under a parliamentary democracy. The ruling party in the
The Glorious Revolution and the English Bill of Rights
 The Glorious Revolution and the English Bill of Rights With a Protestant majority and a developing democratic tradition, England did not take kindly the rule of James II. The king s absolutist tendencies
The Glorious Revolution and the English Bill of Rights With a Protestant majority and a developing democratic tradition, England did not take kindly the rule of James II. The king s absolutist tendencies
Democratic Developments in England
 SECTION 5 Standards-Based Instruction Standards-at-a-Glance History-Social Science Students have learned about ideas on the law in Greece and Rome, and in Judaism and Christianity. Now they will learn
SECTION 5 Standards-Based Instruction Standards-at-a-Glance History-Social Science Students have learned about ideas on the law in Greece and Rome, and in Judaism and Christianity. Now they will learn
Different Democracies. EQ: How is a parliamentary democracy different from a presidential democracy?
 Different Democracies EQ: How is a parliamentary democracy different from a presidential democracy? What does the Legislative Branch do with law? They MAKE the laws! What does the Executive Branch do with
Different Democracies EQ: How is a parliamentary democracy different from a presidential democracy? What does the Legislative Branch do with law? They MAKE the laws! What does the Executive Branch do with
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. France Under Louis XIV
 France Under Louis XIV Objectives Understand how Henry IV rebuilt France after the wars of religion. Explain how Louis XIV became an absolute monarch. Describe how Versailles was a symbol of royal power.
France Under Louis XIV Objectives Understand how Henry IV rebuilt France after the wars of religion. Explain how Louis XIV became an absolute monarch. Describe how Versailles was a symbol of royal power.
POLITICAL SYSTEMS IN EUROPE
 POLITICAL SYSTEMS IN EUROPE In the Modern Erathe political ideas of the Middle Ages began to change. There no longer existed the ideal of a Christian Empire, becouse the Reformation diminished the power
POLITICAL SYSTEMS IN EUROPE In the Modern Erathe political ideas of the Middle Ages began to change. There no longer existed the ideal of a Christian Empire, becouse the Reformation diminished the power
Government & Economy of South East Asia. EQ: How do the governments and economies of India, China, Japan, and North Korea compare and contrast?
 Government & Economy of South East Asia EQ: How do the governments and economies of India, China, Japan, and North Korea compare and contrast? Directions: As we discuss the governments of Southeast Asia,
Government & Economy of South East Asia EQ: How do the governments and economies of India, China, Japan, and North Korea compare and contrast? Directions: As we discuss the governments of Southeast Asia,
ORIGIN OF MONARCHY IN ENGLAND
 ORIGIN OF MONARCHY IN ENGLAND Around 600 A.D.,Anglo-Saxon people of Denmark occupied most of England and established Monarchy in England. Later, Norman king William occupied England in 1066 and established
ORIGIN OF MONARCHY IN ENGLAND Around 600 A.D.,Anglo-Saxon people of Denmark occupied most of England and established Monarchy in England. Later, Norman king William occupied England in 1066 and established
Section 2. Objectives
 Objectives Understand how Henry IV rebuilt France after the wars of religion. Explain how Louis XIV became an absolute monarch. Describe how Versailles was a symbol of royal power. Identify Louis XIV s
Objectives Understand how Henry IV rebuilt France after the wars of religion. Explain how Louis XIV became an absolute monarch. Describe how Versailles was a symbol of royal power. Identify Louis XIV s
Th F e rench Revolution
 The French Revolution 1789-1799 The Old Regime (Ancien Regime) Old Regime social & political system which existed in most of Europe during the 18 th century Countries were ruled by absolutism Divine Right
The French Revolution 1789-1799 The Old Regime (Ancien Regime) Old Regime social & political system which existed in most of Europe during the 18 th century Countries were ruled by absolutism Divine Right
2014 Brain Wrinkles. A Federal Parliamentary Democracy
 A Federal Parliamentary Democracy Standards SS6CG6 The student will compare and contrast various forms of government. a. Describe the ways government systems distribute power: unitary, confederation, and
A Federal Parliamentary Democracy Standards SS6CG6 The student will compare and contrast various forms of government. a. Describe the ways government systems distribute power: unitary, confederation, and
The British, recognizing that Newfoundland was no longer a collection of work camps, appointed a year-round governor in TOPIC 3.
 TOPIC 3.7 The first general election for representative government was held in 1832. How do you think candidates campaigned for the election? Why is representative government important? Introduction In
TOPIC 3.7 The first general election for representative government was held in 1832. How do you think candidates campaigned for the election? Why is representative government important? Introduction In
It is envisaged that students will have a better-than-basic knowledge of their own country s legal and constitutional system.
 The English Constitution teacher s notes By Nigel Haines As most countries have a written constitution, the English example is usually particularly curious to foreign students. This lesson explores the
The English Constitution teacher s notes By Nigel Haines As most countries have a written constitution, the English example is usually particularly curious to foreign students. This lesson explores the
UNIT Y106: THE EARLY TUDORS
 UNIT Y106: THE EARLY TUDORS NOTE: BASED ON 3X 50 MINUTE LESSONS PER WEEK TERMS BASED ON 6 TERM YEAR. Key Topic Term Week Number Indicative Content Extended Content Resources The government of Henry VII
UNIT Y106: THE EARLY TUDORS NOTE: BASED ON 3X 50 MINUTE LESSONS PER WEEK TERMS BASED ON 6 TERM YEAR. Key Topic Term Week Number Indicative Content Extended Content Resources The government of Henry VII
In the early 1800s, German speaking people lived in a number of small and medium-sized states as well and in Prussia and Austrian Hapsburg empire.
 German Unification In the early 1800s, German speaking people lived in a number of small and medium-sized states as well and in Prussia and Austrian Hapsburg empire. Between 1806 and 1812 Napoleon made
German Unification In the early 1800s, German speaking people lived in a number of small and medium-sized states as well and in Prussia and Austrian Hapsburg empire. Between 1806 and 1812 Napoleon made
Student s Name: Period: ABSOLUTE MONARCHS. 1. What helped Absolute Monarchs initially gain power during the Middle Ages?
 Lesson Summary Questions Using your textbook, notes, and graphic organizers, complete the critical thinking questions below. 1. What helped Absolute Monarchs initially gain power during the Middle Ages?
Lesson Summary Questions Using your textbook, notes, and graphic organizers, complete the critical thinking questions below. 1. What helped Absolute Monarchs initially gain power during the Middle Ages?
An Introduction to British History S. L. Rosen
 An Introduction to British History S. L. Rosen Kings and Queens of England from Norman Times 1 William I (-) William II (-10) Henry I ( 10-) Stephen (-) Henry II (-1) Richard I (1-1) Richard the Lion Heart
An Introduction to British History S. L. Rosen Kings and Queens of England from Norman Times 1 William I (-) William II (-10) Henry I ( 10-) Stephen (-) Henry II (-1) Richard I (1-1) Richard the Lion Heart
The Unification of Italy
 The Unification of Italy The beginning of Italian Independence starts with the French Revolution and the Napoleonic Era Prior to this time period the Italian peninsula did not wish to be unified Elimination
The Unification of Italy The beginning of Italian Independence starts with the French Revolution and the Napoleonic Era Prior to this time period the Italian peninsula did not wish to be unified Elimination
Before the Revolution
 Before the Revolution Growing Financial Crisis 1763 End of the Seven Years War 1780s Aid to the American Revolution 1788 Call for the Estates General when King wants to tax nobles Desperate times in the
Before the Revolution Growing Financial Crisis 1763 End of the Seven Years War 1780s Aid to the American Revolution 1788 Call for the Estates General when King wants to tax nobles Desperate times in the
Western Europe and Political Democracy
 Western Europe and Political Democracy Growing prosperity after 1850 contributed to the expansion of democracy in Western Europe. Western Europe and Political Democracy In the late 1800s, political democracy
Western Europe and Political Democracy Growing prosperity after 1850 contributed to the expansion of democracy in Western Europe. Western Europe and Political Democracy In the late 1800s, political democracy
Unit 6: Absolutism and Constitutionalism in Western Europe (ca )
 Unit 6: Absolutism and Constitutionalism in Western Europe (ca 1589-1715) Learning Objectives Understand the contrasts between absolutism and constitutionalism. Describe the strategies employed by Louis
Unit 6: Absolutism and Constitutionalism in Western Europe (ca 1589-1715) Learning Objectives Understand the contrasts between absolutism and constitutionalism. Describe the strategies employed by Louis
The Sacrament of Language: An Archaeology of the Oath by Giorgio Agamben
 The Sacrament of Language: An Archaeology of the Oath by Giorgio Agamben Cambridge: Stanford University Press and Polity Press, 2010 (ISBN 978-0-7456-4972-6). 79pp. Henry King (University of Glasgow) The
The Sacrament of Language: An Archaeology of the Oath by Giorgio Agamben Cambridge: Stanford University Press and Polity Press, 2010 (ISBN 978-0-7456-4972-6). 79pp. Henry King (University of Glasgow) The
FAITH, FAMILY, AND PENNSYLVANIA VALUES AN AGENDA TO STRENGTHEN THE FABRIC OF OUR COMMUNITIES
 FAITH, FAMILY, AND PENNSYLVANIA VALUES AN AGENDA TO STRENGTHEN THE FABRIC OF OUR COMMUNITIES Paul Mango, Republican Candidate for Governor of Pennsylvania For My God will make it a seed of a nation, a
FAITH, FAMILY, AND PENNSYLVANIA VALUES AN AGENDA TO STRENGTHEN THE FABRIC OF OUR COMMUNITIES Paul Mango, Republican Candidate for Governor of Pennsylvania For My God will make it a seed of a nation, a
Athenian Democracy. To what extent was Athenian democracy an incomplete and restricted form of political suffrage? DISSECTING DEMOCRACY PLII001
 Athenian Democracy To what extent was Athenian democracy an incomplete and restricted form of political suffrage? DISSECTING DEMOCRACY PLII001 1 To what extent was Athenian democracy an incomplete and
Athenian Democracy To what extent was Athenian democracy an incomplete and restricted form of political suffrage? DISSECTING DEMOCRACY PLII001 1 To what extent was Athenian democracy an incomplete and
Option 1C: Britain, : conflict, revolution and settlement
 Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2016 Pearson Edexcel GCE in History (8HI0) Paper 1C Paper 1: Breadth study with interpretations Option 1C: Britain, 1625-1701: conflict, revolution and settlement Edexcel and
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2016 Pearson Edexcel GCE in History (8HI0) Paper 1C Paper 1: Breadth study with interpretations Option 1C: Britain, 1625-1701: conflict, revolution and settlement Edexcel and
Honors Western Civilization I (to 1500) History 112HN, 3 Credit Hours John E. Moser Ashland University Honors Program Christopher Swanson, Director
 Honors Western Civilization I (to 1500) History 112HN, 3 Credit Hours John E. Moser Ashland University Honors Program Christopher Swanson, Director General Description: This course is a study of the history
Honors Western Civilization I (to 1500) History 112HN, 3 Credit Hours John E. Moser Ashland University Honors Program Christopher Swanson, Director General Description: This course is a study of the history
