Unit 4: Revolutions of Democracy
|
|
|
- Lynn Georgina Owens
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit 4: Revolutions of Democracy
2 FOQ #1: Did the English Civil War help or hurt Democracy? Explain. FOQ #2: What were the causes of the American Revolutionary War? How did it end? FOQ #3: What were the main reasons for the French Revolution? FOQ #4: What Enlightenment ideas inspired the revolutions discussed this unit? FOQs
3 The textbook has a ton of stuff that can help you better understand the Unit 4 FOQs English Civil War, 17.3 on pages American Revolution, 18.4 on pages French Revolution, on pages Textbook Help
4 The Scientific Revolution in Europe started in 1500 During that time, many new and exciting discoveries were brought to the world. Besides science, the ideas of an organized universe and the scientific method of thinking inspired European philosophers. Philosophers such as John Locke, Baron de Montesquieu, Voltaire, and Mary Wollstonecraft wrote about government, human rights, and individual freedoms. These ideas led to huge changes in Europe Review
5 Throughout Europe, the most common type of government was a monarchy. A monarchy is another name for government led by a king or a queen. When a monarch (king or queen) has total control of his/her country, they re called an absolute monarch. When they share power with an elected group of men (like Parliament), they are called a limited monarch. When a limited monarch must obey a set of written laws, they are called a constitutional monarch. Governments in Europe
6 With a reading partner, read Setting the Scene on page 421. Next, Copy and answer the following prompt in your notes: Give your opinion why you think there will be conflict between parliament and King James I. Remember, it s your opinion. Activity #1
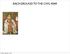
7 James I rising to the heavens as angels prepare to crown him king. A god chosen king is called a divine right king -Peter Paul Rubens
8 An absolute monarch in England named James I ruled England with very harsh rule. He believed that god chose him and that no man could question his right to rule. One area that James I couldn t control and that was the English treasury. A group of elected men controlled the treasury of England They were called Parliament. This situation caused a great deal of stress between James and Parliament. When James died, his son Charles I took over and was just like his dad. Problems with the King
9 Help!! Charles I needed money to raise an army to fight threatened invasions from Scotland and Ireland. He asked Parliament for new taxes to raise money for the fight and in return they wanted Charles to give up more of his power. Parliament wanted protections from random arrest and imprisonment as sometimes the king would lock up his enemies. It was called the Petition of Right. Charles I refused and decided to create taxes on his own, ignoring Parliament. This leads to war! More Problems with the King
10 The English Civil War was fought between Parliament (Round Heads) and Charles I (Cavaliers). The English Civil War saw increased use of firearms. FOQ #1:: Did the English Civil War help or hurt Democracy? Explain.
11 The English Civil War was between the English Parliament and King Charles I. Each side had an army. The Round Heads and Cavaliers They fought over how much power the king would have. Parliament won the war and for a while there was no king. Oliver Cromwell was the leader of England and was supported by Parliament. Oliver Cromwell was the hero of the English civil war
12 The Restoration of the monarchy When Cromwell died, the English people wanted a king back. Charles I son, Charles II was asked by Parliament to be the king and accept limited powers Charles II agreed This was called the Restoration. Charles II wasn t interested in absolute power. He loved parties, entertaining, and discussing science and Enlightenment philosophy. The power that Charles II gave up went to Parliament.
13 The Glorious Revolution When Charles II died, his brother James II came to power. James II wanted to get back the power that Charles II lost to Parliament. James II was a disaster, so Parliament called on Mary (James II s daughter) and her husband William of Orange to rule as constitutional monarchs. This gave most of the ruling power to Parliament. This was called the Glorious Revolution. Both William and Mary agreed to follow laws called the English Bill of Rights. All future monarchs and parliament agreed to follow those laws. The Magna Carta and the Bill of Rights became the English Constitution.
14 Work together in your reading pairs. Read all of The Struggle Between King and Parliament on page 425, studying all the parts. Copy the timeline into your notes Then copy and answer all the questions in the Skills Assessment box at the bottom of the page. Remember that this activity is all about understanding that England wanted a king to rule with limited powers. Finish as homework if needed. Homework #1
15 A political cartoon written by Ben Franklin The Bill of Rights and the Constitution FOQ #2: What were the causes of the American Revolutionary War? How did it end?
16 The original British colonies in North America first established in the 1600 s grew very successful and it people very rich. By the 1700 s the colonies had grown and were represented by a diverse religious and ethnic groups. The colonies were left alone and became very independent Things were good
17 After the French and Indian War, Britain and King George III demanded that its colonies help pay for the war cost through taxes. No taxation without representation. The colonial resentment caused many clashes between the colonies and Great Britain. See the Boston Massacre and Boston Tea Party. As anger and taxes increased, representatives from all 13 colonies met and declared their independence. Things were bad
18 The Declaration of Independence was inspired by John Locke s ideas. See page 461. A call for independence
19 The colonists joined with the French and fought against the British army. It was a difficult and bloody war, but the Continental Army won. The war for independence
20 A new government was formed and a constitution written. The United States of America was born. See A New Constitution on page to discover how else the Enlightenment philosophers inspired a new nation. The United States is born
21 FOQ #3: What were the main reasons for the French Revolution?
22 The French hated the English because they were powerful competitors. The French helped the colonists against the English during the Revolution. This cost France a lot of money. After the revolution, French soldiers went back to France and shared their stories. The American Revolution inspired many French people
23 The American Revolution cost France a lot of money. The Louis XVI and his wife Marie Antoinette spent tons of money of their lifestyle including their home. Bad weather destroyed crops which France needed to feed it people. France was in trouble!! The French economy was broke!
24 French society was divided into 3 parts called estates. The first and second estates were the very rich. The third was everyone else. The third estate were peasants, artisans, and professionals. To pay for everything, the third estate was the only part of society to pay taxes. When the king wanted to raise taxes even higher, members of the third estate had enough and wanted to make things fair. The majority of men and women in France were mad!
25 Work with your reading partner. Go to page and read about the Third Estate. Next look at the picture and chart on page 469. Choose (3) colored pens and copy the chart into your notes Lastly, copy and answer the question above the chart on page 469. Activity #2
26 At a meeting of the estates, representatives from the third estate walked out and decided that a constitution was needed. The their Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen, and the Constitution, the third estate wanted the rich to pay their fair share of taxes. The king rejected this at first and there was great violence in Paris and in the countryside. Finally the king agreed to a more fair system of taxes. Many of these angry French turned to violence!
27 The Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen demanded natural rights talked about by John Locke. The Constitution of 1791 protected those rights. French revolutionaries also demanded that the government change and that power be shared like in the writings of Montesquieu. Also, revolutionaries wanted freedom of speech like Voltaire talked about. These were the things that the French revolutionaries were fighting for. At first, Louis XVI agreed but then was called a traitor. Louis was executed in 1792 and the revolution continued. Check out to learn more. French revolutionaries were inspired by the philosophers
28 Locke Montesquieu Voltaire Wollstonecraft Homework #2: Review the entire unit PowerPoint and identify ideas of the philosophers that were part of the revolutions. Come up with as many examples as you can. FOQ #4: What Enlightenment ideas inspired the revolutions from this unit?
STANDARD WHII.6c The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth,
 STANDARD WHII.6c The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth, and eighteenth centuries by c) assessing the impacts
STANDARD WHII.6c The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth, and eighteenth centuries by c) assessing the impacts
The Age of Absolutism and Limited Government. Name: World History I + Mr. Horas
 The Age of Absolutism and Limited Government Name: World History I + Mr. Horas www.chshistory.net 1 World History I Mr. Horas Absolutism and Limited Government Reading #1 Reading #1: Europe in Crisis:
The Age of Absolutism and Limited Government Name: World History I + Mr. Horas www.chshistory.net 1 World History I Mr. Horas Absolutism and Limited Government Reading #1 Reading #1: Europe in Crisis:
English Civil War, the Restoration, and the Glorious Revolution
 English Civil War, the Restoration, and the Glorious Revolution Vocabulary Parliament Legislative, or law-making, body in government representing the interests of the people. (ex. England) Magna Carta
English Civil War, the Restoration, and the Glorious Revolution Vocabulary Parliament Legislative, or law-making, body in government representing the interests of the people. (ex. England) Magna Carta
The Commercial Revolution Most of Europe remained agricultural. Fastest growing part of the economy was trade of goods. Those manufactured in Europe
 13. The Old Regime: Absolutism and Enlightenment People to Know 1. Henry VIII 2. Thomas Hobbes 3. Louis XIV 4. John Locke 5. William Blackstone 6. Sir Isaac Newton 7. Robert Boyle 8. Thomas Jefferson 9.
13. The Old Regime: Absolutism and Enlightenment People to Know 1. Henry VIII 2. Thomas Hobbes 3. Louis XIV 4. John Locke 5. William Blackstone 6. Sir Isaac Newton 7. Robert Boyle 8. Thomas Jefferson 9.
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 1 Government in Colonial America ESSENTIAL QUESTION What influenced the development of our government institutions? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary establish to create or set up levy to charge
Lesson 1 Government in Colonial America ESSENTIAL QUESTION What influenced the development of our government institutions? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary establish to create or set up levy to charge
The Rise of Parliamentary Democracy in England. Student Handouts, Inc.
 The Rise of Parliamentary Democracy in England Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com James I James Stuart (James VI of Scotland) inherited the English throne from his cousin, Elizabeth I, in 1603
The Rise of Parliamentary Democracy in England Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com James I James Stuart (James VI of Scotland) inherited the English throne from his cousin, Elizabeth I, in 1603
The Rise of Parliamentary Democracy in England. Student Handouts, Inc.
 Slide 1 The Rise of Parliamentary Democracy in England Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com Slide 2 James I James Stuart (James VI of Scotland) inherited the English throne from his cousin, Elizabeth
Slide 1 The Rise of Parliamentary Democracy in England Student Handouts, Inc. www.studenthandouts.com Slide 2 James I James Stuart (James VI of Scotland) inherited the English throne from his cousin, Elizabeth
Section 5: Democratic Developments in England
 Chapter 1: Sources of the Democratic Tradition 2000 B.C.E. A.D. 1689 Section 5: Democratic Developments in England In medieval England, the Christian church, the nobility, and monarchy had all the power
Chapter 1: Sources of the Democratic Tradition 2000 B.C.E. A.D. 1689 Section 5: Democratic Developments in England In medieval England, the Christian church, the nobility, and monarchy had all the power
Makes civic virtue a necessity. Putting the common good (your country) before your own interests This is done through moral education
 Foundations of Government Greece (400 s BC): Democracy: rule by the people Rome (509-50 BC) Republic: Citizens govern, through elected representatives Focus on the common good Makes civic virtue a necessity
Foundations of Government Greece (400 s BC): Democracy: rule by the people Rome (509-50 BC) Republic: Citizens govern, through elected representatives Focus on the common good Makes civic virtue a necessity
Prologue Section 3 Democracy Develops in England
 Prologue Section 3 Democracy Develops in England Edward the Confessor Dies (one of the last Anglo-Saxon Kings of England) Some sources say that Edward had promised the throne to his cousin William. The
Prologue Section 3 Democracy Develops in England Edward the Confessor Dies (one of the last Anglo-Saxon Kings of England) Some sources say that Edward had promised the throne to his cousin William. The
The Origins of Early Government in the Colonies
 The Origins of Early Government in the Colonies Magna Carta, 1215 The Virginia House of Burgesses, 1619 The Mayflower Compact, 1620 General Court, 1629 Fundamental Orders of Connecticut, 1639 English Bill
The Origins of Early Government in the Colonies Magna Carta, 1215 The Virginia House of Burgesses, 1619 The Mayflower Compact, 1620 General Court, 1629 Fundamental Orders of Connecticut, 1639 English Bill
Life in the Colonies. Chapter 4, Section 1
 Life in the Colonies Chapter 4, Section 1 All English colonies shared a common English heritage, and that heritage included the idea that citizens had political rights. England also promoted the theory
Life in the Colonies Chapter 4, Section 1 All English colonies shared a common English heritage, and that heritage included the idea that citizens had political rights. England also promoted the theory
STANDARD 1.2 EARLY GOVERNMENTS AND ROAD TO REVOLUTION
 STANDARD 1.2 EARLY GOVERNMENTS AND ROAD TO REVOLUTION REPRESENTATIVE GOVERNMENT A form of government in which elected officials would vote on the laws for the good of the society. The American model is
STANDARD 1.2 EARLY GOVERNMENTS AND ROAD TO REVOLUTION REPRESENTATIVE GOVERNMENT A form of government in which elected officials would vote on the laws for the good of the society. The American model is
Louis XIV ( ) -Arguably the most powerful absolute monarch of all time. Louis learned at a young age that he wanted to be an absolute monarch.
 Absolutism in seventeenth century Europe was tied to: the divine right of kings. The divine right of kings is a belief that rulers get their power to rule from God and were responsible to no one but God.
Absolutism in seventeenth century Europe was tied to: the divine right of kings. The divine right of kings is a belief that rulers get their power to rule from God and were responsible to no one but God.
Warm Up. Explain the economic concept of mercantilism:
 Warm Up 1 Explain the economic concept of mercantilism: 2 What laws did British Parliament pass to designed to enforce the economic concept of mercantilism 3 Explain the colonial reaction to the Navigation
Warm Up 1 Explain the economic concept of mercantilism: 2 What laws did British Parliament pass to designed to enforce the economic concept of mercantilism 3 Explain the colonial reaction to the Navigation
How were the Americans in'fluenced by their English background?
 - - - - --- Lesson 5 How were the Americans in'fluenced by their English background? Americans' knowledge of British government The American colonies had been ruled by the British government for over 150
- - - - --- Lesson 5 How were the Americans in'fluenced by their English background? Americans' knowledge of British government The American colonies had been ruled by the British government for over 150
The English Civil War and the Glorious Revolution
 The English Civil War and the Glorious Revolution Enduring Understanding: The relationship between citizens and their government is a fundamental component of political rule. To understand the role of
The English Civil War and the Glorious Revolution Enduring Understanding: The relationship between citizens and their government is a fundamental component of political rule. To understand the role of
ENGLAND & THE COLONIES
 WARM UP 1 2 Create a triple Venn-Diagram that compares the New England, Middle and Southern colonies Include economic, political and social differences... ENGLAND & THE COLONIES Colonial Mercantilism Colonies
WARM UP 1 2 Create a triple Venn-Diagram that compares the New England, Middle and Southern colonies Include economic, political and social differences... ENGLAND & THE COLONIES Colonial Mercantilism Colonies
Chapter 6 Study Guide
 Chapter 6 Study Guide assembly boycott delegate independence Loyalist militia minutemen Patriot rebel repeal representation revolution self government Sons of Liberty traitor treason a law-making body
Chapter 6 Study Guide assembly boycott delegate independence Loyalist militia minutemen Patriot rebel repeal representation revolution self government Sons of Liberty traitor treason a law-making body
Terms, People, and Places
 Terms, People, and Places James I dissenters Puritans Charles I Petition of Right Oliver Cromwell Commonwealth The Restoration The Glorious Revolution English Bill of Rights limited monarchy constitutional
Terms, People, and Places James I dissenters Puritans Charles I Petition of Right Oliver Cromwell Commonwealth The Restoration The Glorious Revolution English Bill of Rights limited monarchy constitutional
Origins of American Government Chapter 2:1:
 Origins of American Government Chapter 2:1: Objectives: 2:1 Our Political Beginnings o Students will identify the three concepts of government that influenced the American colonies. o Students will explain
Origins of American Government Chapter 2:1: Objectives: 2:1 Our Political Beginnings o Students will identify the three concepts of government that influenced the American colonies. o Students will explain
Spain s Empire Philip II - son of V - seized control of - empire of vast Defender of Spanish destroyed by Protestant England
 Module 11 Absolute Monarchs in Europe Absolutism A decline in feudalism led to a rise of strong national kingdoms with more authority Absolute rulers wanted to control every of society Believed in Right
Module 11 Absolute Monarchs in Europe Absolutism A decline in feudalism led to a rise of strong national kingdoms with more authority Absolute rulers wanted to control every of society Believed in Right
Section 3. Objectives
 Objectives Describe the Tudor monarchs relations with Parliament. Analyze how clashes between the Stuarts and Parliament ushered in a century of revolution. Understand how the English Civil War and the
Objectives Describe the Tudor monarchs relations with Parliament. Analyze how clashes between the Stuarts and Parliament ushered in a century of revolution. Understand how the English Civil War and the
The French Monarchy. Pg
 The French Monarchy Pg.452-457 After the Reformation Catholics and Protestants (aka-huguenots) are fighting They arrange a marriage to stop the fighting Catherine de Medici convinces her son (brother of
The French Monarchy Pg.452-457 After the Reformation Catholics and Protestants (aka-huguenots) are fighting They arrange a marriage to stop the fighting Catherine de Medici convinces her son (brother of
The French Revolution Begins!
 The French Revolution Begins! France - The Old Regime Social System: pre-1789 Monarch Three Estates Clergy Rich Nobles Commoners Bourgeoisie: Middle Class (Doctors, Lawyers, Merchants, skilled artisans)
The French Revolution Begins! France - The Old Regime Social System: pre-1789 Monarch Three Estates Clergy Rich Nobles Commoners Bourgeoisie: Middle Class (Doctors, Lawyers, Merchants, skilled artisans)
APUSH. PowerPoint #2.1(Part1 of 4) Uni#1 Transformations of North America Unit #2 - British North America & the Atlantic World
 APUSH PowerPoint #2.1(Part1 of 4) Uni#1 Transformations of North America Unit #2 - British North America & the Atlantic World Chapters 1-3 BFW Textbook Topic 2.1 British North America English Background
APUSH PowerPoint #2.1(Part1 of 4) Uni#1 Transformations of North America Unit #2 - British North America & the Atlantic World Chapters 1-3 BFW Textbook Topic 2.1 British North America English Background
The French Revolution
 The French Revolution Using your notes, complete the following paragraph. The Enlightenment is also known as the. During this time, people began to reject the teachings of the and the and question traditional
The French Revolution Using your notes, complete the following paragraph. The Enlightenment is also known as the. During this time, people began to reject the teachings of the and the and question traditional
Major transformation of the society and a political system of France, which lasted from 1789 to 1799.
 Major transformation of the society and a political system of France, which lasted from 1789 to 1799. Phases of the Revolution Chain of Events First Phase Second Phase Third Phase Outcome: Effects of the
Major transformation of the society and a political system of France, which lasted from 1789 to 1799. Phases of the Revolution Chain of Events First Phase Second Phase Third Phase Outcome: Effects of the
Essential Question: To what extent are Louis XIV (France), Peter the Great (Russia), & Elizabeth I (England) examples of absolute monarchs?
 Essential Question: To what extent are Louis XIV (France), Peter the Great (Russia), & Elizabeth I (England) examples of absolute monarchs? Warm-Up Question: What is a monarch? What is mercantilism? What
Essential Question: To what extent are Louis XIV (France), Peter the Great (Russia), & Elizabeth I (England) examples of absolute monarchs? Warm-Up Question: What is a monarch? What is mercantilism? What
Thursday, December 12, 2013 BACKGROUND TO THE CIVIL WAR
 BACKGROUND TO THE CIVIL WAR BACKGROUND TO THE CIVIL WAR ELIZABETH - childless, succeeded by James VI, son of Mary Stuart, king of Scotland BACKGROUND TO THE CIVIL WAR ELIZABETH - childless, succeeded by
BACKGROUND TO THE CIVIL WAR BACKGROUND TO THE CIVIL WAR ELIZABETH - childless, succeeded by James VI, son of Mary Stuart, king of Scotland BACKGROUND TO THE CIVIL WAR ELIZABETH - childless, succeeded by
The French Revolution
 VISIT WWW.STUDENTHANDOUTS.COM FOR FREE INTERACTIVE TEST-PREP GAMES NO LOG-IN REQUIRED! The French Revolution Student Workbook Student Handouts, Inc. 2011 Name: Page2 Name: Date: Class: The Old Regime The
VISIT WWW.STUDENTHANDOUTS.COM FOR FREE INTERACTIVE TEST-PREP GAMES NO LOG-IN REQUIRED! The French Revolution Student Workbook Student Handouts, Inc. 2011 Name: Page2 Name: Date: Class: The Old Regime The
Key areas to pay attention to for the CBA 2
 Sequencing Key areas to pay attention to for the CBA 2 There are four fundamental documents that are created in America and that lead to our system of government now. In sequential order they are Fundamental
Sequencing Key areas to pay attention to for the CBA 2 There are four fundamental documents that are created in America and that lead to our system of government now. In sequential order they are Fundamental
Analyze the ideological, military, social, and diplomatic aspects of the American Revolution.
 Analyze the ideological, military, social, and diplomatic aspects of the American Revolution. The Proclamation of 1763 When the French and Indian War ended, the French LEFT But the Indians remained And
Analyze the ideological, military, social, and diplomatic aspects of the American Revolution. The Proclamation of 1763 When the French and Indian War ended, the French LEFT But the Indians remained And
Look up the Triangular Trade on pg. 95 of your textbook and answer the following questions in complete sentences: 1. What was the triangular trade?
 Look up the Triangular Trade on pg. 95 of your textbook and answer the following questions in complete sentences: 1. What was the triangular trade? 2. Which 3 regions were involved in the triangular trade?
Look up the Triangular Trade on pg. 95 of your textbook and answer the following questions in complete sentences: 1. What was the triangular trade? 2. Which 3 regions were involved in the triangular trade?
Political Systems (Forms of Government) Autocracy: Any form of government where one person (auto) holds all the power
 Name Political Systems (Forms of Government) Democracy: Any form of government where citizens control their government through voting in elections o Direct Democracy: All citizens have a chance to participate.
Name Political Systems (Forms of Government) Democracy: Any form of government where citizens control their government through voting in elections o Direct Democracy: All citizens have a chance to participate.
The American Revolution
 The American Revolution 1765-1783 http://www.history.com/topics/american-revolution/american-revolution-history/videos/american-revolution The American Revolution in relation to... the English Civil War
The American Revolution 1765-1783 http://www.history.com/topics/american-revolution/american-revolution-history/videos/american-revolution The American Revolution in relation to... the English Civil War
Where is this in my book? It s in there, how about using the Index? But that s hard!
 Prologue Where is this in my book? It s in there, how about using the Index? But that s hard! Section 1 Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome Main Idea The Greeks developed democracy, and the Romans added
Prologue Where is this in my book? It s in there, how about using the Index? But that s hard! Section 1 Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome Main Idea The Greeks developed democracy, and the Romans added
WHEN THE U.S. WAS NEW
 WHEN THE U.S. WAS NEW When America was new, every state had its own rules. Money was not the same in all states. Each state had a leader. No one was the leader of all the people. This was not working!
WHEN THE U.S. WAS NEW When America was new, every state had its own rules. Money was not the same in all states. Each state had a leader. No one was the leader of all the people. This was not working!
Complete the associated worksheet using this article with your partners.
 Complete the associated worksheet using this article with your partners. Section # 5 England (1603 1714) Tudor Legacy: The Tudor monarchy produced some of the greatest, most well known, and most controversial
Complete the associated worksheet using this article with your partners. Section # 5 England (1603 1714) Tudor Legacy: The Tudor monarchy produced some of the greatest, most well known, and most controversial
The Age of Absolutism. Chapter 16
 The Age of Absolutism Chapter 16 Philip II Absolute Monarchy: reigned with complete authority over the government Divine Right: rule came directly from God Guardian of the Roman Catholic Church Inquisition
The Age of Absolutism Chapter 16 Philip II Absolute Monarchy: reigned with complete authority over the government Divine Right: rule came directly from God Guardian of the Roman Catholic Church Inquisition
Roots of Representative Government
 2 Roots of Representative Government MAIN IDEA Colonists expected their government to preserve their basic rights as English subjects. WHY IT MATTERS NOW U.S. citizens expect these same rights, such as
2 Roots of Representative Government MAIN IDEA Colonists expected their government to preserve their basic rights as English subjects. WHY IT MATTERS NOW U.S. citizens expect these same rights, such as
Monday, January 23 rd
 Monday, January 23 rd For help with lecture, readings, help with essays, and test preparation, visit 173A SWKT (The American Heritage Review Room. It is open from 9:00 am to 4:00 pm, Monday through Friday.
Monday, January 23 rd For help with lecture, readings, help with essays, and test preparation, visit 173A SWKT (The American Heritage Review Room. It is open from 9:00 am to 4:00 pm, Monday through Friday.
Plato s Government Categories
 KNOW both PREAMBLES (U.S. Constitution and the Declaration of Independence - for the Declaration of Independence, make sure you can explain any or all parts) Ba able to define civics, polis and society
KNOW both PREAMBLES (U.S. Constitution and the Declaration of Independence - for the Declaration of Independence, make sure you can explain any or all parts) Ba able to define civics, polis and society
Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1
 Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Identify the three concepts of government that influenced the American colonies. 2. Explain the influence of three landmark English documents.
Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Identify the three concepts of government that influenced the American colonies. 2. Explain the influence of three landmark English documents.
The French and Indian War
 The French and Indian War British/French Rivalry 1689: Glorious Revolution; England becomes a constitutional monarchy France ruled by Louis XIV; L état c est moi ; absolute monarchy France and England
The French and Indian War British/French Rivalry 1689: Glorious Revolution; England becomes a constitutional monarchy France ruled by Louis XIV; L état c est moi ; absolute monarchy France and England
Chapter 2.1 Our English Heritage P28-30
 Chapter 2.1 Our English Heritage P28-30 Influences from England s Early Government The English brought with them a history of limited and representative government. England was ruled by a monarch a king
Chapter 2.1 Our English Heritage P28-30 Influences from England s Early Government The English brought with them a history of limited and representative government. England was ruled by a monarch a king
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 4 The American Revolution ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Why do new ideas often spark change? How do new ways of thinking affect the way people respond to their surroundings? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary
Lesson 4 The American Revolution ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Why do new ideas often spark change? How do new ways of thinking affect the way people respond to their surroundings? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary
Foundations of American Government
 Foundations of American Government Why Do We Need Government? Maintain social order Ensure domestic tranquility Establish justice Provide for the common defense Promote the general welfare Secure liberty
Foundations of American Government Why Do We Need Government? Maintain social order Ensure domestic tranquility Establish justice Provide for the common defense Promote the general welfare Secure liberty
Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1
 Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Identify the three concepts of government that influenced the American colonies. 2. Explain the influence of three landmark English documents.
Chapter 2: Origins of American Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Identify the three concepts of government that influenced the American colonies. 2. Explain the influence of three landmark English documents.
Handout D: The Bill of Rights 1 per student. Unit IV: Rights and Responsibilities LESSON 2: MR. MADISON NEEDS SOME HELP. Overview
 Unit IV: Rights and Responsibilities LESSON 2: MR. MADISON NEEDS SOME HELP OBJECTIVES Students will be able to: Explain why the Bill of Rights was added to the Constitution. Identify rights they have learned
Unit IV: Rights and Responsibilities LESSON 2: MR. MADISON NEEDS SOME HELP OBJECTIVES Students will be able to: Explain why the Bill of Rights was added to the Constitution. Identify rights they have learned
World History (Survey)
 World History (Survey) Chapter 21: Absolute Monarchs in Europe, 1500 1800 Section 1: Spain s Empire and European Absolutism Charles V ruled the Holy Roman Empire and various other European countries. In
World History (Survey) Chapter 21: Absolute Monarchs in Europe, 1500 1800 Section 1: Spain s Empire and European Absolutism Charles V ruled the Holy Roman Empire and various other European countries. In
Announcements: 1: Test 1/31(2/1)! Review is on the Weebly!
 Announcements: 1: Test 1/31(2/1)! Review is on the Weebly! Materials: 1: Spiral/blank sheet of paper 2: Copy of the Comparing the French and American Revolutions worksheet Bell Ringer: January 24(25),
Announcements: 1: Test 1/31(2/1)! Review is on the Weebly! Materials: 1: Spiral/blank sheet of paper 2: Copy of the Comparing the French and American Revolutions worksheet Bell Ringer: January 24(25),
5. Revolutions A: English Civil War, Absolutism, Scientific Rev and Enlightenment
 5. Revolutions A: English Civil War, Absolutism, Scientific Rev and Enlightenment Study online at quizlet.com/_2rq93a 1. Absolutism 5. Cardinal Richelieu When kings and queens have complete control over
5. Revolutions A: English Civil War, Absolutism, Scientific Rev and Enlightenment Study online at quizlet.com/_2rq93a 1. Absolutism 5. Cardinal Richelieu When kings and queens have complete control over
Unit Portfolio: Interpreting Visual Images
 Unit Portfolio: Interpreting Visual Images 1. What can you tell about this man based only on what you see in this picture? Make up a brief biography based on your perception of this photo. Use complete
Unit Portfolio: Interpreting Visual Images 1. What can you tell about this man based only on what you see in this picture? Make up a brief biography based on your perception of this photo. Use complete
Year 7 The Civil War and Restoration knowledge organiser
 Year 7 The Civil War and Restoration knowledge organiser Charles I Charles II James II Civil war battles Oliver Cromwell Roundheads & cavaliers William&Mary - Glorious Revolution Key people James I King
Year 7 The Civil War and Restoration knowledge organiser Charles I Charles II James II Civil war battles Oliver Cromwell Roundheads & cavaliers William&Mary - Glorious Revolution Key people James I King
France before the Revolution
 France before the Revolution Unit 1, Part 5 1 Objectives: To understand the class (estate) system in France To know what privileges existed in society and who enjoyed them To see the power, privilege and
France before the Revolution Unit 1, Part 5 1 Objectives: To understand the class (estate) system in France To know what privileges existed in society and who enjoyed them To see the power, privilege and
Makes civic virtue a necessity. Putting the common good (your country) before your own interests This is done through moral education
 Foundations of Government Greece (400 s BC): Democracy: rule by the people Rome (509-50 BC) Republic: Citizens govern, through elected representatives Focus on the common good Makes civic virtue a necessity
Foundations of Government Greece (400 s BC): Democracy: rule by the people Rome (509-50 BC) Republic: Citizens govern, through elected representatives Focus on the common good Makes civic virtue a necessity
The French Revolution CH
 The French Revolution CH. 7.2-5 The Assembly Reforms France National Assembly, declared: 1. All citizens (men) of France EQUAL. 2. Declaration of the Rights of Man Copied from US Dec. of Ind. *Protect
The French Revolution CH. 7.2-5 The Assembly Reforms France National Assembly, declared: 1. All citizens (men) of France EQUAL. 2. Declaration of the Rights of Man Copied from US Dec. of Ind. *Protect
In the 1600s and 1700s, French kings still ruled by divine right with absolute power. And they lived more luxuriously than perhaps anyone, anywhere
 1789-1815 In the 1600s and 1700s, French kings still ruled by divine right with absolute power. And they lived more luxuriously than perhaps anyone, anywhere in the history of the world. Louis XIV, King
1789-1815 In the 1600s and 1700s, French kings still ruled by divine right with absolute power. And they lived more luxuriously than perhaps anyone, anywhere in the history of the world. Louis XIV, King
2. According to the principles included in the Declaration of. Independence, what is the main purpose of government?
 1. According to the principles included in the Declaration of Independence, what is the main purpose of government? To control dangerous people through harsh punishment. To ensure that everyone has enough
1. According to the principles included in the Declaration of Independence, what is the main purpose of government? To control dangerous people through harsh punishment. To ensure that everyone has enough
US History, Ms. Brown Website: dph7history.weebly.com
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #40 Aims: SWBAT identify the three geographic areas of the 13 colonies SWBAT identify and explain mercantilism DO NOW Directions:
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #40 Aims: SWBAT identify the three geographic areas of the 13 colonies SWBAT identify and explain mercantilism DO NOW Directions:
9. How did the Protestant Reformation cause the Monarchical Revolution?
 Week 1 Absolutism- The Monarch s Revolution 1. What was Barzun s name for the second revolution, the one that came right after the 16th-century religious revolution (the Protestant Reformation)? 2. What
Week 1 Absolutism- The Monarch s Revolution 1. What was Barzun s name for the second revolution, the one that came right after the 16th-century religious revolution (the Protestant Reformation)? 2. What
The$Rise$of$Absolu.sm$&$ Cons.tu.onalism$ Part$1$88$As$Poli.cal$Systems$ Part$2$88$Within$England$and$France$
 The$Rise$of$Absolu.sm$&$ Cons.tu.onalism$ Part$1$88$As$Poli.cal$Systems$ Part$2$88$Within$England$and$France$ Part 1: Absolutism and Constitutionalism as political systems Essential Question: 1) What are
The$Rise$of$Absolu.sm$&$ Cons.tu.onalism$ Part$1$88$As$Poli.cal$Systems$ Part$2$88$Within$England$and$France$ Part 1: Absolutism and Constitutionalism as political systems Essential Question: 1) What are
Absolutism in Europe: Part 1 the 1500s - Spain v. England Page 1
 Absolutism in Europe: Part 1 the 1500s - Spain v. England Page 1 Catholic Spain King Philip II 1556 1598 In 1556 Philip II inherited Spain, the Spanish Netherlands, & the American colonies from his father
Absolutism in Europe: Part 1 the 1500s - Spain v. England Page 1 Catholic Spain King Philip II 1556 1598 In 1556 Philip II inherited Spain, the Spanish Netherlands, & the American colonies from his father
feb 6 10:27 VISUAL VOCABULARY AND EXERCISES ws.
 THE MONARCHY VOCABULARY AND STRUCTURES feb 6 10:27 VISUAL VOCABULARY AND EXERCISES http://www.languageguide.org/english/vocabulary/history/ http://www.surfnetkids.com/games/monarchy ws.htm http://quizlet.com/5913312/revolutions
THE MONARCHY VOCABULARY AND STRUCTURES feb 6 10:27 VISUAL VOCABULARY AND EXERCISES http://www.languageguide.org/english/vocabulary/history/ http://www.surfnetkids.com/games/monarchy ws.htm http://quizlet.com/5913312/revolutions
Lesson Two. Aims. Context. In this lesson we are going to find out about: what impact the civil war had on families
 Lesson Two England and the civil wars Aims In this lesson we are going to find out about: what impact the civil war had on families how Parliament was able to win the war what happened after the execution
Lesson Two England and the civil wars Aims In this lesson we are going to find out about: what impact the civil war had on families how Parliament was able to win the war what happened after the execution
What is a REVOLUTION? How does the spirit of the Enlightenment encourage revolution? How did the American Revolution ( ) encourage the French
 What is a REVOLUTION? How does the spirit of the Enlightenment encourage revolution? How did the American Revolution (1775 83) encourage the French Revolution? What are the causes of the French Revolution?
What is a REVOLUTION? How does the spirit of the Enlightenment encourage revolution? How did the American Revolution (1775 83) encourage the French Revolution? What are the causes of the French Revolution?
Napoleon Bonaparte. Ambition is never content even on the summit of greatness.
 Napoleon Bonaparte Ambition is never content even on the summit of greatness. Born in Corsica as an Italian- Became a French citizen at the age of 1 Home in which Napoleon was born Corsica Became dictator
Napoleon Bonaparte Ambition is never content even on the summit of greatness. Born in Corsica as an Italian- Became a French citizen at the age of 1 Home in which Napoleon was born Corsica Became dictator
Napoleon s Rise and Fall. AP Euro SAHS 2017
 Napoleon s Rise and Fall AP Euro SAHS 2017 Napoleon Gains Power Napoleon became a hero when he saved the National Assembly from the Royalist Napoleon was a fairly successful military leader He was able
Napoleon s Rise and Fall AP Euro SAHS 2017 Napoleon Gains Power Napoleon became a hero when he saved the National Assembly from the Royalist Napoleon was a fairly successful military leader He was able
Creating the Constitution
 Creating the Constitution What is a government? A government is a person, or group, who has the power to provide law, order, services, and security within a country. Government gives organization and structure
Creating the Constitution What is a government? A government is a person, or group, who has the power to provide law, order, services, and security within a country. Government gives organization and structure
Foundations of Government. Section 1: Page 24
 Foundations of Government Section 1: Page 24 Types of governments: Govern means rule A government is any organization set up to make and enforce laws Every country in the world has their own form and system
Foundations of Government Section 1: Page 24 Types of governments: Govern means rule A government is any organization set up to make and enforce laws Every country in the world has their own form and system
Unit One: Foundations of American Government
 Unit One: Foundations of American Government Intro Unit Lesson 1 1. Define demographics. Based on the pie charts below, compare the demographics of Durham to those of the United States as a whole. 2. We
Unit One: Foundations of American Government Intro Unit Lesson 1 1. Define demographics. Based on the pie charts below, compare the demographics of Durham to those of the United States as a whole. 2. We
The Attempted Revival of Empire
 Ironically, most monarchs in Europe benefited from religious strife. Established monarchs consolidated their power while ambitious opportunists used the chaos to gain power. The Holy Roman Empire remained
Ironically, most monarchs in Europe benefited from religious strife. Established monarchs consolidated their power while ambitious opportunists used the chaos to gain power. The Holy Roman Empire remained
Hapsburg Absolute monarch Divine right
 Absolutism Spain Objective: Discuss and analyze the golden age and decline of Spain as a power. Key Terms and People: Hapsburg, absolute monarch, divine right, Charles V, Peace of Augsburg, Philip II,
Absolutism Spain Objective: Discuss and analyze the golden age and decline of Spain as a power. Key Terms and People: Hapsburg, absolute monarch, divine right, Charles V, Peace of Augsburg, Philip II,
Birth of the Republic
 Birth of the Republic 1 2 The American Colonists Mainly of English descent Scotch-Irish / Germans --> Pennsylvania Black Africans --> the South Believed they were preserving the true traditions of English
Birth of the Republic 1 2 The American Colonists Mainly of English descent Scotch-Irish / Germans --> Pennsylvania Black Africans --> the South Believed they were preserving the true traditions of English
United States Government
 United States Government I. Early Governments (Intro) 100 years ago governments were led by rulers, who ruled by force Direct democracy- Greeks invented this government, government run by the people to
United States Government I. Early Governments (Intro) 100 years ago governments were led by rulers, who ruled by force Direct democracy- Greeks invented this government, government run by the people to
THE GLORIOUS REVOLUTION AND THE IMPACT ON AUSTRALIAN CONSTITUTIONAL LAW
 Vol 8 The Western Australian Jurist 427 THE GLORIOUS REVOLUTION AND THE IMPACT ON AUSTRALIAN CONSTITUTIONAL LAW LAURA JACKSON* I INTRODUCTION It has been proposed that The Glorious Revolution is irrelevant
Vol 8 The Western Australian Jurist 427 THE GLORIOUS REVOLUTION AND THE IMPACT ON AUSTRALIAN CONSTITUTIONAL LAW LAURA JACKSON* I INTRODUCTION It has been proposed that The Glorious Revolution is irrelevant
THE GLORIOUS REVOLUTION AND THE IMPACT ON AUSTRALIAN CONSTITUTIONAL LAW
 Vol 8 The Western Australian Jurist 427 THE GLORIOUS REVOLUTION AND THE IMPACT ON AUSTRALIAN CONSTITUTIONAL LAW LAURA JACKSON* I INTRODUCTION It has been proposed that The Glorious Revolution is irrelevant
Vol 8 The Western Australian Jurist 427 THE GLORIOUS REVOLUTION AND THE IMPACT ON AUSTRALIAN CONSTITUTIONAL LAW LAURA JACKSON* I INTRODUCTION It has been proposed that The Glorious Revolution is irrelevant
2. THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE FRENCH REVOLUTION
 2. THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE FRENCH REVOLUTION 2.1. PHASES OF THE REVOLUTION A) Constitutional Monarchy (1789-1792): First liberal government with a constitutional monarchy. B) Social Republic (1792-1794):
2. THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE FRENCH REVOLUTION 2.1. PHASES OF THE REVOLUTION A) Constitutional Monarchy (1789-1792): First liberal government with a constitutional monarchy. B) Social Republic (1792-1794):
GOVERNMENT ORGANIZATIONS, INSTITUTIONS, AND INDIVIDUALS THAT EXERCISE POLITICAL AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF A GROUP OF PEOPLE
 TYPES OF GOVERNMENT GOVERNMENT ORGANIZATIONS, INSTITUTIONS, AND INDIVIDUALS THAT EXERCISE POLITICAL AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF A GROUP OF PEOPLE CITIZEN A LEGAL MEMBER OF A COUNTRY CONSTITUTION A WRITTEN PLAN
TYPES OF GOVERNMENT GOVERNMENT ORGANIZATIONS, INSTITUTIONS, AND INDIVIDUALS THAT EXERCISE POLITICAL AUTHORITY ON BEHALF OF A GROUP OF PEOPLE CITIZEN A LEGAL MEMBER OF A COUNTRY CONSTITUTION A WRITTEN PLAN
Main Idea: The Ottomans established a Muslim empire that combined many cultures and lasted for more than 600 years.
 Absolute Monarchs in the Middle East & Europe (1500 1800) Pondering the Entire Unit What might be a benefit as well as a drawback having one person with complete control (Absolutism) in charge of a country?
Absolute Monarchs in the Middle East & Europe (1500 1800) Pondering the Entire Unit What might be a benefit as well as a drawback having one person with complete control (Absolutism) in charge of a country?
A Children s Book for the Declaration of Independence
 A Children s Book for the Declaration of Independence 1. Create a Children s Book to help explain the importance of the Declaration of Independence. 2. Your Children s Book will have a 7 pages in total:
A Children s Book for the Declaration of Independence 1. Create a Children s Book to help explain the importance of the Declaration of Independence. 2. Your Children s Book will have a 7 pages in total:
English Constitutional Monarchy. A slightly more effeminate version of the US move to Constitutionalism
 English Constitutional Monarchy A slightly more effeminate version of the US move to Constitutionalism Background (1215-1603) Magna Carta, 1215 a a A list of demands made by the nobility.. Established
English Constitutional Monarchy A slightly more effeminate version of the US move to Constitutionalism Background (1215-1603) Magna Carta, 1215 a a A list of demands made by the nobility.. Established
AP European History Chapter 15 Study Guide: State Building and the Search for Order in the Seventeenth Century
 AP European History Name: Chapter 15 Study Guide: State Building and the Search for Order in the Seventeenth Century Identifications: On index cards, identify the following. 1. Thirty Years War 19. Bourbon
AP European History Name: Chapter 15 Study Guide: State Building and the Search for Order in the Seventeenth Century Identifications: On index cards, identify the following. 1. Thirty Years War 19. Bourbon
Chapter 19 Vocabulary. Section 1 France in the Age of Absolutism
 Intendant Divine Rights of Kings Balance of Power Czar Pragmatic Sanction Diplomatic Revolution Spanish Armada Puritans Chapter 19 Vocabulary Section 1 France in the Age of Absolutism Henry IV Comes to
Intendant Divine Rights of Kings Balance of Power Czar Pragmatic Sanction Diplomatic Revolution Spanish Armada Puritans Chapter 19 Vocabulary Section 1 France in the Age of Absolutism Henry IV Comes to
2/16/2015. Outcome: Absolutism & Absolute Monarchs. French Absolutism, Enlightenment, & Revolution
 Outcome: Absolutism & Absolute Monarchs French Absolutism, Enlightenment, & Revolution 1 Constructive Response Questions 1. Describe what an absolute monarch is and provide two examples: 2 What Will We
Outcome: Absolutism & Absolute Monarchs French Absolutism, Enlightenment, & Revolution 1 Constructive Response Questions 1. Describe what an absolute monarch is and provide two examples: 2 What Will We
Slide 1. Slide 2. Before the Revolution Begins. Slide 3. BELLRINGER What determines a person s class (upper, middle, lower)in the United States today?
 Slide 1 BELLRINGER What determines a person s class (upper, middle, lower)in the United States today? Slide 2 Before the Revolution Begins Slide 3 The Old Regime Old Regime social and political system
Slide 1 BELLRINGER What determines a person s class (upper, middle, lower)in the United States today? Slide 2 Before the Revolution Begins Slide 3 The Old Regime Old Regime social and political system
Trouble Brewing. Colonies
 Trouble Brewing in the Colonies French and Indian War Aftermath Colonists began to become disenchanted with British rule after the French and Indian War Treatment of colonial militias during war Proclamation
Trouble Brewing in the Colonies French and Indian War Aftermath Colonists began to become disenchanted with British rule after the French and Indian War Treatment of colonial militias during war Proclamation
A Children s Book for the Declaration of Independence
 A Children s Book for the Declaration of Independence 1. Create a Children s Book to help explain the importance of the Declaration of Independence. 2. Your Children s Book will have 6 pages in total:
A Children s Book for the Declaration of Independence 1. Create a Children s Book to help explain the importance of the Declaration of Independence. 2. Your Children s Book will have 6 pages in total:
Chapter 4. Anglo Saxon: A.D. mixed with the natives of the island Native Brits + Germans = rule the Island of England
 English History Chapter 4 Anglo Saxon: 450 1066 A.D. mixed with the natives of the island Native Brits + Germans = rule the Island of England 1066 A.D. Norman Conquest: William of Normandy France conquers
English History Chapter 4 Anglo Saxon: 450 1066 A.D. mixed with the natives of the island Native Brits + Germans = rule the Island of England 1066 A.D. Norman Conquest: William of Normandy France conquers
Ms. Susan M. Pojer Horace Greeley HS Chappaqua, NY
 Ms. Susan M. Pojer Horace Greeley HS Chappaqua, NY 1. Controversy Over Succession The French nobility selected Philip of Valois, a cousin of the last king through the male line. He founded a new French
Ms. Susan M. Pojer Horace Greeley HS Chappaqua, NY 1. Controversy Over Succession The French nobility selected Philip of Valois, a cousin of the last king through the male line. He founded a new French
Section 1. Objectives
 Objectives Learn how monarchs gained power over nobles and the Church. Describe how William the Conqueror and Henry II strengthened English royal power. Analyze the traditions of government that developed
Objectives Learn how monarchs gained power over nobles and the Church. Describe how William the Conqueror and Henry II strengthened English royal power. Analyze the traditions of government that developed
CHAPTER 2. Roots of American Democracy
 CHAPTER 2 Roots of American Democracy Section 1 Our English Heritage Influences from England s Early Government The English brought with them a history of LIMITED and REPRESENTATIVE government. England
CHAPTER 2 Roots of American Democracy Section 1 Our English Heritage Influences from England s Early Government The English brought with them a history of LIMITED and REPRESENTATIVE government. England
AUTOCRACY. SS.7.C.3.1 Forms of Government
 AUTOCRACY An autocracy is a form of government where one person has unlimited power. One form of an autocracy is a dictatorship where a military leader secures power often through violent means. Another
AUTOCRACY An autocracy is a form of government where one person has unlimited power. One form of an autocracy is a dictatorship where a military leader secures power often through violent means. Another
Section 1 Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome
 Prologue Section 1 Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome Main Idea The Greeks developed democracy, and the Romans added representative government. Why It Matters Now Representation and citizen participation
Prologue Section 1 Legacy of Ancient Greece and Rome Main Idea The Greeks developed democracy, and the Romans added representative government. Why It Matters Now Representation and citizen participation
Map of North and South America
 PASS Social Studies Grade 7 Test 1 Map of North and South America (drawn around the year 1700) SC07SS070101 1. Judging from the above map, it is clear that Europeans in the year 1700 knew the least about
PASS Social Studies Grade 7 Test 1 Map of North and South America (drawn around the year 1700) SC07SS070101 1. Judging from the above map, it is clear that Europeans in the year 1700 knew the least about
England: The Growth of Limited Government
 England: The Growth of Limited Government Foundations for the Growth of Limited Government and Democracy 1. Magna Carta 1215 King John, who demanded increased funds from his feudal nobles, was accused
England: The Growth of Limited Government Foundations for the Growth of Limited Government and Democracy 1. Magna Carta 1215 King John, who demanded increased funds from his feudal nobles, was accused
Unit 1. The learner will investigate the foundations of the American political system and explore basic values and principles of American democracy.
 Unit 1 The learner will investigate the foundations of the American political system and explore basic values and principles of American democracy. 1.02 Which documents and people influenced the colonists
Unit 1 The learner will investigate the foundations of the American political system and explore basic values and principles of American democracy. 1.02 Which documents and people influenced the colonists
Foundations of Western Civilization. World History Chapter 1
 Foundations of Western Civilization World History Chapter 1 The Basics of History What does history mean to you? How can we approach history? (People? Places?) What is meaningful in our study of history?
Foundations of Western Civilization World History Chapter 1 The Basics of History What does history mean to you? How can we approach history? (People? Places?) What is meaningful in our study of history?
What is the advantage of having a common law system?
 What is the advantage of having a common law system? 1) English Heritage Info Sheet 2) All side notes 3) One page summary (14 s.) 4) No title issues Renaissance and Reformation Renaissance and Reformation
What is the advantage of having a common law system? 1) English Heritage Info Sheet 2) All side notes 3) One page summary (14 s.) 4) No title issues Renaissance and Reformation Renaissance and Reformation
