DIVERSION FOR SAFE SANITATION: A NEW APPROACH TO SANITATION IN INFORMAL SETTLEMENTS
|
|
|
- Dwain Chambers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DIVERSION FOR SAFE SANITATION: A NEW APPROACH TO SANITATION IN INFORMAL SETTLEMENTS Tove A. Larsen *, Heiko Gebauer *, Harald Gründl **, Rahel Künzle *, Christoph Lüthi *, Ulrike Messmer *, Eberhard Morgenroth *,***, Bernhard Ranner ** * Eawag, Switzerland, ** EOOS, Austria, *** ETH Zürich larsen@eawag.ch, Ueberlandstrasse 133, 8600 Dübendorf, tel ABSTRACT The project presented in this abstract is part of the Reinvent The Toilet Challenge (RTTC), a call from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF). Our project entry Diversion for safe sanitation is based on two main elements: diversion of urine and faeces at the source as basis for efficient resource recovery and linking different scales (household level and semi centralized resource recovery) allowing for rapid implementation of family toilets. Our objective was to develop an attractive grid free dry diversion toilet (separately diverting undiluted urine and faeces), which provides water for flushing, comfortable personal hygiene (for washers and for menstrual hygiene), and for hand washing. A service concept for linking the family scale to a community scale Resource Recovery Plant (RRP) as well as a business model with maximum profit for the local community was set up. The service including the entire sanitation value chain shall be provided as a profitable business with total fees of 5 ȼ/p/d. The toilet has been designed to fulfil all objectives, allowing for local rotational moulding of all parts. It can be installed as a shared toilet for 2 families in any available super structure or as an in house private toilet. The flush & wash water is recovered on site in a maintenance free ultrafiltration unit followed by on site electrolytic chlorine production. Total energy consumption is 4 8 W/toilet, provided by a small solar panel. The low energy consumption is only possible because at least 95 % of urine and faeces are diverted at source directly towards resource recovery not contaminating the wash & flush water. The Resource Recovery Plant is conceptually set up for 175 families and urine and faeces are collected from each toilet twice a week. Based on smart design and standardization, the service concept is hygienically safe and in densely populated informal settings, the collection service can be provided at around 1 ȼ/person/day. Resources can be recovered from urine and faeces by a large number of processes. We have set up a methodology for comparing different technologies, e.g. with respect to costs and energy consumption. For urine, we suggest nitrification followed by distillation, a favourable process developed within another BMGF project ( For faeces, the best technology still has to be chosen. A business model rent a toilet will make sure that landlords as well as tenants have access to the technology. Keywords: design, innovation, resource recovery, source separation, urban, wastewater treatment ABBREVIATIONS BMGF: Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation RRP: Resource Recovery Plant RTTC: Reinvent The Toilet Challenge TRL: Technology Readiness Level
2 Diversion for safe sanitation 2 INTRODUCTION The concept of diversion for safe sanitation has been developed in a project financed by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation within the program Reinvent The Toilet Challenge (RTTC). The requirements of the call were to provide a private or public toilet for dense urban areas, allowing for high personal comfort at a price of 5 US per person and day. Furthermore, valuable products should be extracted from the toilet waste, and no connection to running water, grid electricity, or sewers could be assumed. In the project diversion for safe sanitation, we decided to combine two different scales for solving this challenging problem (Figure 1): The toilet itself was developed as a shared private toilet for two families, whereas the resource recovery was set up at a small community scale for about people in a so called Resource Recovery Plant (RRP). This implies a logistics concept for transport of toilet waste from the toilet to the RRP. As the name indicates, the toilet is a diversion toilet, separating three streams: undiluted urine, dry faeces, and water. The water is used for flushing the dry (!) toilet, for hand washing and for personal hygiene (menstrual hygiene and anal cleansing, where required). It is recovered on site for re use for the same purposes within the toilet. Figure 1 Conceptual set up of the diversion for safe sanitation system ( EOOS) PROJECT STRUCTURE In order to make the project manageable, it was organized in five different objectives: Objective 1: Designing and constructing an attractive source separating toilet Objective 2: Demonstration of principle for on site wash & flush water recovery Objective 3: Transport logistic concept Objective 4: Evaluation of treatment technologies Objective 5: The diversion business model a market based sanitation approach PROJECT RESULTS Objective 1: Designing and constructing an attractive source separating toilet (Figure 2) A main goal of the project diversion for safe sanitation was to design an attractive source separating toilet that everybody wants to use, in high income as well as in low income countries. The toilet provides running water for hand washing and personal hygiene and a comfortable flush button for the cleansing of the pan. These well known functions are however translated into a next generation product, which works offgrid with a radical low cost innovation approach.
3 Diversion for safe sanitation 3 Figure 2 The diversion toilet ( EOOS) The toilet is designed for a setting of four families sharing two toilets. As a (re)movable piece of furniture it can be retrofitted into existing toilet superstructures (Figure 3), or in any other bathroom, and allows for setting up a rent a toilet system. This retrofitting concept as well as the toilet functions and aesthetics were tested in a reality check workshop in an informal settlement in Kampala, Uganda where it was well received. The toilet features an innovated dry source separating pan which can be cleaned with water from the on site water recovery without requiring mechanical parts for cleaning. By foot activation, the squatting pan transforms by rotation of 90 degrees into a washing pan (Figure 4). Figure 3 Photomontage of the retrofitting concept ( EOOS)
4 Diversion for safe sanitation 4 Figure 4 The squatting pan transforms by rotation of 90 degrees into a washing pan ( EOOS) The toilet s core is the back wall containing the compact water recovery technology. While faeces and urine are collected under the separating pan, the soiled water from hand washing, pan flushing, anal cleansing and menstrual hygiene is fully recycled on site. Important design features of the water recovery wall are the foot pump keeping the water recovery cycle activated, the water display tank indicating the amount of clean water available to the user, a hand wash basin with running water and a shower head, providing a comfortable cleansing device for menstrual hygiene or anal cleansing (Figure 1). Another important innovation is EOOS s design of a self sealing container which secures the safe removal and emptying of the faeces containers, even for the end user if the transport logistics break down temporarily (Figure 5). Figure 5 A self sealing container allows for safe removal and transportation of faeces Objective 2: Demonstration of principle for on site wash & flush water recovery The core principle of the on site water recovery technology is a gravity driven ultrafiltration (UF) unit, developed by Eawag researchers for drinking water production from polluted river water (Peter Varbanets et al. 2009). Due to the more heavily polluted wastewater to be recovered within the toilet (as compared to river water) and the recirculation of the treated water, aeration is introduced in order to keep the membrane biologically active and thus avoiding maintenance. The reactor is contained within the water recovery wall (Figure 6) and the design is based on several months of experiments in three parallel UF units. The experiments with simulate flush & wash water soiled with faeces, urine, soap, and blood showed that a stable flux could be obtained with the simplest possible reactor. Additionally, results show that technical design parameters of importance for sizing the reactor in the water recovery wall are water permeability and trans membrane pressure, which determine the water flux. In order to design the water recovery wall, a simple model implemented in the program Berkely Madonna was applied to simulate water availability at different reactor configurations, assuming a pattern of toilet visits modelled with a probabilistic approach. The results showed that in the chosen set up, around 75 Litres of water can be made available per day. With the assumed 50 toilet visits per day and toilet, this corresponds to an average of 1.5 Litres of water per toilet visit. Since the toilet can be comfortably flushed with half a Litre of water, 1 Litre of water per toilet visit is available for hygienic purposes.
5 Diversion for safe sanitation 5 As the filtered water is slightly coloured it contains around mg COD/L and re growth of microorganisms will take place we recommend polishing of the effluent in order to minimize this risk and ensure colour removal. Preliminary results with electrolysis were successful, but still need to be optimized. Figure 6 Water recovery wall of the diversion toilet It can be concluded that safe water recovery through gravity driven ultrafiltration is feasible and maintenance free operation is stable. Polishing by electrolysis makes the water more appealing, increases the safety level, and minimizes the need for chlorination. Additional chlorination is possible if desired. Objective 3: Transport logistic concept The conceptual transport logistics comprise one collector per Resource Recovery Plant (RRP), collecting faeces and urine twice a week from the toilets and delivering both to the RRP. In order to obtain hygienic and aesthetic working conditions, faeces are removed in a self sealing container (Figure 5) and urine will be pumped. In objective 3 we explored whether a collection service system is feasible at a reasonable price, despite the labour intensive collection in rather complex contexts. Therefore, a numerical model was developed, allowing for evaluation and optimization of transport in a variety of spatial set ups (Schmitt 2012). We used GIS data of housing structures and road networks of 4 informal settlements in Africa and India. Regression techniques were used to analyse the spatial data (especially the influence of population density on travel distances). Moreover, bivariate regressions were applied in order to identify interdependencies of system parameters, e.g. of service time on costs and capacity. Analysing the spatial data, the results of the numerical model showed that travel distances are significantly related to user density. However, its influence on the system s performance is of minor importance as work productivity was identified as the key driver for overall system performance. This implies that the logistic system is suitable for a wide range of spatial setups from low to high population densities provided that work productivity is high. We conclude that one of the most important systems integration issues is the optimizing of collection of faeces containers, pumping of urine and discharging to the RRP. For the business model, an exact number of users per RRPs is required to calculate the business case for Kampala. We chose a user density of 150 persons per hectare, a service time per facility of 20 minutes, resulting in an RRP for 860 users and costs of $0.01 per user and day.
6 Diversion for safe sanitation 6 Objective 4: Evaluation of treatment technologies Objective 4 evaluates different treatment technologies for source separated urine and faeces, which can be operated in a Resource Recovery Plant (RRP). The result of Objective 4 is the identification of viable urine and faeces treatment combinations that fulfil the treatment requirements stipulated in the RTTC call (drinking water quality for liquid side products and solid organic matter only in stabilized forms). An excel tool for the evaluation of adequate urine and faeces treatment technology combinations was developed to support decision making. The technology combinations were compared using the following parameters: electrical energy consumption, weight of end product output, reactor volume, revenues from nutrients, total costs (investment, maintenance and running costs) and nutrient loss. We compared a number of technologies optimized for (a) low reactor volume, (b) high Technology Readiness Level (TRL) and (c) independence of solar energy (no solar panels and no solar evaporation). The main limitation for valid comparisons is the lack of reliable data on the still very young technologies. Furthermore, the choice of the optimal technology combination is subjective and depends on the preferences of the decision maker, which will be influenced by the local situation. Due to all these limitations, the results will be published separately with a thorough discussion of the uncertainties. We also categorized possible technology combinations including low, medium and high total costs. For the business case we selected anaerobic digestion of faeces and partial nitrification of urine combined with distillation (Udert & Wächter 2012) as a possible treatment technology combination, because both are already available at a high TRL and are classified as low total cost technologies. The cost evaluation for the technology combination low total costs showed that it is economically feasible within the total cost limit of $0.05 per user and day. Objective 5: The diversion business model a market based sanitation approach The diversion business model follows the marked based sanitation approach (Osterwalder & Pigneur 2010, London & Hart 2010). Sanitation entrepreneurs would generate sufficient revenues to cover the costs and create an attractive profit. The business model addresses two different customer groups: two families (average 5 persons) renting a single toilet and wholesalers buying end products. The value proposition for toilet users is about offering attractive and affordable rental toilets and a safe and reliable emptying. Such a value proposition would create a demand for toilets, which, in turn, generates revenue from service fees. In the diversion business model, the relationship with the toilet users is managed through mobile payments and twice a week visits of the collector to remove faeces and urine. Efficient treatment and resource recovery due to separated faeces and urine create another stream of revenue from the sales of endproducts. These two revenue streams make the business model robust and enable a positive cash flow while still allowing for the provision of attractive toilets at an affordable service fee. The corresponding revenue streams are, on one hand, the service fee of 5 per user and day, which covers toilet rent, emptying, and maintenance costs as well as most of the RRP costs. Sales of end products such as recovered water, nutrients and energy are estimated to reach about 2 per user and day. Such a value proposition means significant improvement compared to the existing situation (e.g. high emptying costs for the latrine ($ 30) or public toilet fees (7 )). The diversion business model enables the entrepreneur to develop a sanitation business. At full scale, the entrepreneur will manage a small firm with about 40 employees mostly collectors and RRP operators. At the RRPs, the urine and feces are treated to become valuable end products. The end products are sold to wholesalers at market price levels. The value proposition for wholesales refers to secure delivery of nutrients or fertilizers at a stable price (independent of marked fluctuations), low cost supply of distilled water because of the synergy with excreta management, stable supply of energy carrier, most probably in the form of bio char. Key competencies for executing the business model include logistic, operational, and management skills. Logistic skills ensure hygienic and safe removal of excreta, operational skills are necessary to convert urine
7 Diversion for safe sanitation 7 and feces at the RRPs into valuable end products, and management skills to promote and market the renta toilet service. Entrepreneurial skills to develop and scale up the business model are also a key concern. Necessary business partners are local toilet manufacturers, which produce the user interface, ultrafiltration membrane manufacturers, which produce the ultrafiltration membrane, treatment technology equipment providers, which provide the RRP equipment, and finally, local contractors, which assemble and retrofit the toilet into the existing superstructure and provide repairing of toilets and RRP machinery. Finally, to make the business model successful, the local community has to support the development of the sanitation business. DISCUSSION Within a relatively short time, we succeeded in setting up a concept for safe sanitation relying on the principle of diversion (source separation). We based the work on more than a decade of experience in the area of urine source separation (see for instance Larsen et al., 2009) and appropriate sanitation in lowincome areas of low and middle income countries (Lüthi et al., 2011). Furthermore, the work was highly interdisciplinary as well as transdisciplinary, involving not only a number of different disciplines, but also a design company (EOOS in Austria) and future users of the toilets (focus groups in an informal setting in Kampala, Uganda). The approach of the present project was to include technical aspects of the whole value chain as well as the personal preferences of the users. Whereas we are convinced that technical solutions are best obtained based on a dry urine diverting toilet (UDDT), experience in the field tells us that users are normally not very happy with such a toilet. Instead of trying to develop technology for a conventional flush toilet, however, we chose to develop a new type of UDDT, which would provide a maximum of comfort to the users. We identified the possibility of using water for flushing and personal hygiene as the most important deficits of the present UDDT technology and consequently set out to develop such a toilet. At the same time, we wanted to provide a toilet design, which would at the same time be attractive and affordable for the users. CONCLUSION Generally, we believe that it is productive to invest in the development of a superior toilet technology including the whole sanitation value chain in order to solve the problems of poor sanitation in dense informal urban settlements. This takes time, but granted that the right technologies are developed, this investment will allow for rapid dissemination of mass produced technology in a large number of informal settlements. The integration of designers in the technology development process already from the beginning is probably the most important single reason that we could come up with a design that seems promising for further development towards full scale implementation. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This project was financed by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. REFERENCES Larsen, T.A., Alder, A.C., Eggen, R.I.L, Maurer, M. & Lienert, J Source separation: Will we see a paradigm shift in wastewater handling? Environ. Sci. Technol. 43(16), : London, T. & Hart, S Next Generation Business Strategies for the Base of the Pyramid: New Approaches for Building Mutual Value. Financial Times Press, Upper Saddle River, NJ.
8 Diversion for safe sanitation 8 Lüthi, C., Panesar, A., Schütze, T., McConville, J., Parkinson, J. & Saywell, D Sustainable Sanitation in Cities: A Framework for Action. Papiroz Publishing, The Netherlands. Osterwalder, A. & Pigneur, Y Business Model Generation: A Handbook for Visionaries, Game Changers, and Challengers. Wiley, Ed. Tim Clark. Peter Varbanets, M. Zurbrügg, C., Swartz, C. & Pronk, W Decentralized systems for potable water and the potential of membrane technology. Water Res. 43(2), Schmitt, R. (2012) Reinvent the Toilet Challenge. Validation of the transport logistic concept. Final Report. Udert,K.M. & Wächter, M Complete nutrient recovery from source separated urine by nitrification and distillation. Water Res. 46(2),
Stress Test Report of the water recovery system in the Blue Diversion Toilet
 Stress Test Report of the water recovery system in the Blue Diversion Toilet Date: September 2 nd, 2013 Authors: Rahel Künzle, Susanne Scheidegger, Tove Larsen Eawag, Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic
Stress Test Report of the water recovery system in the Blue Diversion Toilet Date: September 2 nd, 2013 Authors: Rahel Künzle, Susanne Scheidegger, Tove Larsen Eawag, Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic
Chalmers Publication Library
 Chalmers Publication Library Decision Support for Redesigning Wastewater Treatment Technologies This document has been downloaded from Chalmers Publication Library (CPL). It is the author s version of
Chalmers Publication Library Decision Support for Redesigning Wastewater Treatment Technologies This document has been downloaded from Chalmers Publication Library (CPL). It is the author s version of
Wings Developing non-grid water and sanitation solutions for urban areas
 Wings Developing non-grid water and sanitation solutions for urban areas Dr. Sabine Hoffmann Team S. Hoffmann, B. Truffer H. Gebauer, J. Lienert U. Feldmann, J. Inauen C. Binz, M. Maurer, T. Larsen E.
Wings Developing non-grid water and sanitation solutions for urban areas Dr. Sabine Hoffmann Team S. Hoffmann, B. Truffer H. Gebauer, J. Lienert U. Feldmann, J. Inauen C. Binz, M. Maurer, T. Larsen E.
Water NEST: A Living Lab to Test Innovative Wastewater Treatment Solutions
 Water Hub @ NEST: A Living Lab to Test Innovative Wastewater Treatment Solutions B. Etter, A. Wittmer, B.J. Ward, K. M. Udert, L. Strande, T.A. Larsen, E. Morgenroth Eawag Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic
Water Hub @ NEST: A Living Lab to Test Innovative Wastewater Treatment Solutions B. Etter, A. Wittmer, B.J. Ward, K. M. Udert, L. Strande, T.A. Larsen, E. Morgenroth Eawag Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic
RWASH Information System Household Access Survey. Completion notes. H2: What is the main source of drinking water used by members of your household?
 RWASH Information System Household Access Survey Completion notes H2: What is the main source of drinking water used by members of your household? The question refers to the source of water used most commonly
RWASH Information System Household Access Survey Completion notes H2: What is the main source of drinking water used by members of your household? The question refers to the source of water used most commonly
Low-cost Innovation in Water and Sanitation at a Local Level
 ASSAf Leopoldina Technology Innovations for a Low Carbon Society Conference 8 9 October 2012 Low-cost Innovation in Water and Sanitation at a Local Level A set of creative and diverse research efforts
ASSAf Leopoldina Technology Innovations for a Low Carbon Society Conference 8 9 October 2012 Low-cost Innovation in Water and Sanitation at a Local Level A set of creative and diverse research efforts
Institutional and Collective Sanitation:
 Institutional and Collective Sanitation: Bottlenecks and Ways Forward National Sanitation Forum, Dushanbe, 26.11. 2015 Philippe Reymond philippe.reymond@eawag.ch Eawag: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic
Institutional and Collective Sanitation: Bottlenecks and Ways Forward National Sanitation Forum, Dushanbe, 26.11. 2015 Philippe Reymond philippe.reymond@eawag.ch Eawag: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic
User perspectives to direct water reuse from the Nano Membrane toilet
 38th WEDC International Conference, Loughborough University, UK, 2015 WATER, SANITATION AND HYGIENE SERVICES BEYOND 2015: IMPROVING ACCESS AND SUSTAINABILITY User perspectives to direct water reuse from
38th WEDC International Conference, Loughborough University, UK, 2015 WATER, SANITATION AND HYGIENE SERVICES BEYOND 2015: IMPROVING ACCESS AND SUSTAINABILITY User perspectives to direct water reuse from
Cleantech Innovation for Nutrient Recovery Dynamics within the Nexus Business Models Capital Attraction
 Cleantech Innovation for Nutrient Recovery Dynamics within the Nexus Business Models Capital Attraction R. Villarroel Walker & Bruce Beck University of Georgia IWA AND CLEANTECH BeCleantech Initiative
Cleantech Innovation for Nutrient Recovery Dynamics within the Nexus Business Models Capital Attraction R. Villarroel Walker & Bruce Beck University of Georgia IWA AND CLEANTECH BeCleantech Initiative
PROMOTING INNOVATIONS IN WASTEWATER MANAGEMENT IN ASIA AND THE PACIFIC
 PROMOTING INNOVATIONS IN WASTEWATER MANAGEMENT IN ASIA AND THE PACIFIC Regional Policy Workshop of Stakeholders on Decentralized Wastewater Treatment Systems (DEWATS) in Southeast Asia Bangkok Day 3 21
PROMOTING INNOVATIONS IN WASTEWATER MANAGEMENT IN ASIA AND THE PACIFIC Regional Policy Workshop of Stakeholders on Decentralized Wastewater Treatment Systems (DEWATS) in Southeast Asia Bangkok Day 3 21
The Economic Returns of Sanitation Interventions in Yunnan Province, People s Republic of China
 WATER AND SANITATION PROGRAM: RESEARCH BRIEF The Economic Returns of Sanitation Interventions in Yunnan Province, People s Republic of China August 2011 INTRODUCTION The (ESI) is a multi-country study
WATER AND SANITATION PROGRAM: RESEARCH BRIEF The Economic Returns of Sanitation Interventions in Yunnan Province, People s Republic of China August 2011 INTRODUCTION The (ESI) is a multi-country study
A Decentralised Urban Resource Recovery (DUR 2 ) System
 A Decentralised Urban Resource Recovery (DUR 2 ) System presented by J.Y. WANG School of Civil and Environmental Engineering Residues and Resource Reclamation Centre 24 October, 2012 In contrast, our
A Decentralised Urban Resource Recovery (DUR 2 ) System presented by J.Y. WANG School of Civil and Environmental Engineering Residues and Resource Reclamation Centre 24 October, 2012 In contrast, our
Water and sanitation challenges as opportunities a nexus approach Sustainable Urban Growth Workshop 8, September, 2015
 Water and sanitation challenges as opportunities a nexus approach Sustainable Urban Growth Workshop 8, September, 2015 Stockholm Environment Institute Jakob Granit, PhD Deputy Director Better Growth, Better
Water and sanitation challenges as opportunities a nexus approach Sustainable Urban Growth Workshop 8, September, 2015 Stockholm Environment Institute Jakob Granit, PhD Deputy Director Better Growth, Better
CITY OF YUMA WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANTS. Cactus Moon Education, LLC.
 CITY OF YUMA WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANTS Wastewater Purify Processes Environment Influent Landfill Bacterial Micro-organism Biological Clarification Residual Anaerobic Methane Bio-Solids Vocabulary All
CITY OF YUMA WASTEWATER TREATMENT PLANTS Wastewater Purify Processes Environment Influent Landfill Bacterial Micro-organism Biological Clarification Residual Anaerobic Methane Bio-Solids Vocabulary All
Sanitation Technology Options in Lesotho
 Technologies for Economic Development Polo Ground 49/3, PO BOX 14621, Maseru -100 Telephone: +266-22317795, Fax: +266 2232 5621, Email: info@ted-biogas.org web: www.ted-biogas.org; Reg. No.:2004/90 TED
Technologies for Economic Development Polo Ground 49/3, PO BOX 14621, Maseru -100 Telephone: +266-22317795, Fax: +266 2232 5621, Email: info@ted-biogas.org web: www.ted-biogas.org; Reg. No.:2004/90 TED
Review of on-site and communal water and sanitation systems for remote communities
 Environmental Economics and Investment Assessment II 275 Review of on-site and communal water and sanitation systems for remote communities A. Perks & T. Johnson R.V. Anderson Associates Limited, Ottawa,
Environmental Economics and Investment Assessment II 275 Review of on-site and communal water and sanitation systems for remote communities A. Perks & T. Johnson R.V. Anderson Associates Limited, Ottawa,
Transformative Sanitation Technologies. Carl Hensman, Ph.D. Program Officer Water, Sanitation & Hygiene (WSH)
 Transformative Sanitation Technologies Carl Hensman, Ph.D. Program Officer Water, Sanitation & Hygiene (WSH) THE SANITATION CRISIS ~2.5 billion people practice open defecation or lack adequate sanitation
Transformative Sanitation Technologies Carl Hensman, Ph.D. Program Officer Water, Sanitation & Hygiene (WSH) THE SANITATION CRISIS ~2.5 billion people practice open defecation or lack adequate sanitation
Green Solutions for Municipal Waste The Decentralized Way
 Green Solutions for Municipal Waste The Decentralized Way J. Y. Wang, Director, R3C 3 September 2013 R3C Residues and Resource Reclamation Centre 2 R3C was established on 1 May 2009 by EDB/EWI/ NTU and
Green Solutions for Municipal Waste The Decentralized Way J. Y. Wang, Director, R3C 3 September 2013 R3C Residues and Resource Reclamation Centre 2 R3C was established on 1 May 2009 by EDB/EWI/ NTU and
Greywater Recycle System. Optimising the re-use and recycling of waste water
 Greywater Recycle System Optimising the re-use and recycling of waste water SAVE up to 40% on your monthly water bill by installing an Filtration and Recycling System. ECO SMART Water Technologies CC developed
Greywater Recycle System Optimising the re-use and recycling of waste water SAVE up to 40% on your monthly water bill by installing an Filtration and Recycling System. ECO SMART Water Technologies CC developed
The Use of Urine as Fertilizer
 3 The Use of Urine as Fertilizer A Series of Educational Manuals on Ecological Sanitation and Hygiene The Use of Urine as Fertilizer Content What is Urine? Ecological Sanitation Technology Urine Diversion
3 The Use of Urine as Fertilizer A Series of Educational Manuals on Ecological Sanitation and Hygiene The Use of Urine as Fertilizer Content What is Urine? Ecological Sanitation Technology Urine Diversion
IWA Cities of the Future Workshop Istanbul, 7-11 February 2011
 Integrated Solutions for Fast Growing Urban Areas responsible reuse of water and energy IWA Cities of the Future Workshop Istanbul, 7-11 February 2011 Peter Cornel, Susanne Bieker, Martin Wagner Technische
Integrated Solutions for Fast Growing Urban Areas responsible reuse of water and energy IWA Cities of the Future Workshop Istanbul, 7-11 February 2011 Peter Cornel, Susanne Bieker, Martin Wagner Technische
Bio-Loo. The Water-borne Flushing Toilet
 Bio-Loo The Water-borne Flushing Toilet The improved hygienic and healthy sanitation solution for the people In support of Government and Municipalities in the delivery of sustainable sanitation systems
Bio-Loo The Water-borne Flushing Toilet The improved hygienic and healthy sanitation solution for the people In support of Government and Municipalities in the delivery of sustainable sanitation systems
Recycling wastewater yields multiple benefits. World Congress & Expo on Recycling, July 20-22, Barcelona, Spain
 Recycling wastewater yields multiple benefits World Congress & Expo on Recycling, July 20-22, Barcelona, Spain New approach, turning waste into wealth Worldwide, the new environmental paradigm is to eliminate
Recycling wastewater yields multiple benefits World Congress & Expo on Recycling, July 20-22, Barcelona, Spain New approach, turning waste into wealth Worldwide, the new environmental paradigm is to eliminate
Technical options in sanitation and reuse of toilet compost and urine in an African context. Peter Morgan
 Technical options in sanitation and reuse of toilet compost and urine in an African context. Peter Morgan 2009 The importance of improved sanitation throughout the developing world is currently being highlighted
Technical options in sanitation and reuse of toilet compost and urine in an African context. Peter Morgan 2009 The importance of improved sanitation throughout the developing world is currently being highlighted
W O C H H O L Z R E G I O N A L W A T E R R E C L A M A T I O N F A C I L I T Y O V E R V I E W
 Facility Overview The recently upgraded and expanded Henry N. Wochholz Regional Water Reclamation Facility (WRWRF) treats domestic wastewater generated from the Yucaipa-Calimesa service area. The WRWRF
Facility Overview The recently upgraded and expanded Henry N. Wochholz Regional Water Reclamation Facility (WRWRF) treats domestic wastewater generated from the Yucaipa-Calimesa service area. The WRWRF
ACEF Green Toilets Project at the Brainhouse School, Kenya
 ACEF Green Toilets Project at the Brainhouse School, Kenya The Challenge Brainhouse School is located in one of the world s largest slums in Kenya, and is home to over 800 students. Unfortunately, the
ACEF Green Toilets Project at the Brainhouse School, Kenya The Challenge Brainhouse School is located in one of the world s largest slums in Kenya, and is home to over 800 students. Unfortunately, the
Decentralized Rainwater Management Part of decentralized environmentally sound water and sanitation systems
 Decentralized Rainwater Management Part of decentralized environmentally sound water and sanitation systems T Schuetze Technical University Delft, Faculty of Architecture, Berlageweg 1, 2628 CR Delft,
Decentralized Rainwater Management Part of decentralized environmentally sound water and sanitation systems T Schuetze Technical University Delft, Faculty of Architecture, Berlageweg 1, 2628 CR Delft,
SOLAR PACKAGE SEWAGE TREATMENT PLANTS. ( Using NTS technology)
 SOLAR PACKAGE SEWAGE TREATMENT PLANTS ( Using NTS technology) Summary of Technology: (Anoxic Aerobic Absorption Separation Sewage Treatment Unit) The technology used to treat the sewage is a combination
SOLAR PACKAGE SEWAGE TREATMENT PLANTS ( Using NTS technology) Summary of Technology: (Anoxic Aerobic Absorption Separation Sewage Treatment Unit) The technology used to treat the sewage is a combination
Sanitation systems and technologies for developing countries
 Sanitation systems and technologies for developing countries Kai Udert and Elizabeth Tilley Eawag: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology The problem There is no urban wastewater management
Sanitation systems and technologies for developing countries Kai Udert and Elizabeth Tilley Eawag: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology The problem There is no urban wastewater management
Urine separation accomplished, what comes next? - Newest experiences of on-site treatment and transport by pipe or truck -
 Urine separation accomplished, what comes next? - Newest experiences of on-site treatment and transport by pipe or truck - Martina Winker 1* and Felix Tettenborn 2 1 German International Cooperation (GIZ)
Urine separation accomplished, what comes next? - Newest experiences of on-site treatment and transport by pipe or truck - Martina Winker 1* and Felix Tettenborn 2 1 German International Cooperation (GIZ)
Energy & Material Cycle of Waste-water
 Energy & Material Cycle of Waste-water Waste water to Energy Recycling of Grey water Innovative approaches for waste water management are needed adapted to the 21st Century with: global population growth
Energy & Material Cycle of Waste-water Waste water to Energy Recycling of Grey water Innovative approaches for waste water management are needed adapted to the 21st Century with: global population growth
THE STUDY OF ECOLOGICAL SANITATION SYSTEMS IN DAR-ES-SALAAM TANZANIA
 THE STUDY OF ECOLOGICAL SANITATION SYSTEMS IN DAR-ES-SALAAM (TANZANIA) By Anesi S. Mahenge Waste Stabilization Ponds and Constructed Wetlands Research Project, P.O Box 35131, COET, University of Dar-es-Salaam,
THE STUDY OF ECOLOGICAL SANITATION SYSTEMS IN DAR-ES-SALAAM (TANZANIA) By Anesi S. Mahenge Waste Stabilization Ponds and Constructed Wetlands Research Project, P.O Box 35131, COET, University of Dar-es-Salaam,
VUNA Nutrient Harvesting from Urine: Lessons from Field Studies
 VUNA Nutrient Harvesting from Urine: Lessons from Field Studies B. Etter 1, K. M. Udert 1, T. Gounden 2 1 Eawag: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology, Überlandstrasse 133, 8600 Dübendorf,
VUNA Nutrient Harvesting from Urine: Lessons from Field Studies B. Etter 1, K. M. Udert 1, T. Gounden 2 1 Eawag: Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology, Überlandstrasse 133, 8600 Dübendorf,
ecosan demonstration project within the GTZ headquarters main office building, Germany
 ecosan demonstration project within the GTZ headquarters main office building, Germany Arne Panesar, Christine Werner Deutsche Gesellschaft für Technische Zusammenarbeit (GTZ) GmbH ecosan program, division
ecosan demonstration project within the GTZ headquarters main office building, Germany Arne Panesar, Christine Werner Deutsche Gesellschaft für Technische Zusammenarbeit (GTZ) GmbH ecosan program, division
Sanitation Systems, Technology Options, Hygiene and Health
 Eawag/Sandec, SEI, BGR, TTZ, IWA, WSSCC, BOKU, UNESCO-IHE, AEE/INTEC, GTZ, IWWA, IWA-SG, UN- Habitat, UNDP, Ecosanlac, KfW Sanitation Systems, Technology Options, Hygiene and Health zurbrugg@eawag.ch Durban,
Eawag/Sandec, SEI, BGR, TTZ, IWA, WSSCC, BOKU, UNESCO-IHE, AEE/INTEC, GTZ, IWWA, IWA-SG, UN- Habitat, UNDP, Ecosanlac, KfW Sanitation Systems, Technology Options, Hygiene and Health zurbrugg@eawag.ch Durban,
Sustainable Sanitation in Eastern Europe and Germany. WECF (Women in Europe for a Common Future)
 www.wecf.eu Sustainable Sanitation in Eastern Europe and Germany Claudia Wendland Margriet Samwel WECF (Women in Europe for a Common Future) Gdynia 19/11/2009 www.wecf.eu 2 Contents Legal Framework in
www.wecf.eu Sustainable Sanitation in Eastern Europe and Germany Claudia Wendland Margriet Samwel WECF (Women in Europe for a Common Future) Gdynia 19/11/2009 www.wecf.eu 2 Contents Legal Framework in
Dry Sanitation, Urine Management, Containment Methods and Reuse Potential in Agriculture
 Dry Sanitation, Urine Management, Containment Methods and Reuse Potential in Agriculture Arno Rosemarin Stockholm Environment Institute International Symposium Coupling Sustainable Sanitation & Groundwater
Dry Sanitation, Urine Management, Containment Methods and Reuse Potential in Agriculture Arno Rosemarin Stockholm Environment Institute International Symposium Coupling Sustainable Sanitation & Groundwater
P.O Box Tel : (254) , , , Website:
 P.O Box 18187-00100 Tel : (254) 0721279699, 0726536565, 0722974812, 0723632853. Email: info@ecosavetech.co.ke Website: www.ecosavetech.co.ke Nairobi- Kenya. A leader in Waste Water Management focused on
P.O Box 18187-00100 Tel : (254) 0721279699, 0726536565, 0722974812, 0723632853. Email: info@ecosavetech.co.ke Website: www.ecosavetech.co.ke Nairobi- Kenya. A leader in Waste Water Management focused on
Biothane Anaerobic Technology Memthane 2.0
 Biothane Anaerobic Technology Memthane 2.0 WATER TECHNOLOGIES State-of-the-art solution Memthane is an Anaerobic Membrane Bio-Reactor (AnMBR) which maximizes renewable energy production while producing
Biothane Anaerobic Technology Memthane 2.0 WATER TECHNOLOGIES State-of-the-art solution Memthane is an Anaerobic Membrane Bio-Reactor (AnMBR) which maximizes renewable energy production while producing
Biothane Anaerobic Technology Memthane 2.0
 Biothane Anaerobic Technology Memthane 2.0 Memthane step-by-step Anaerobic digestion plus cross-flow membranes After equalization, highstrength wastewater is conditioned as needed. Influent is fed to the
Biothane Anaerobic Technology Memthane 2.0 Memthane step-by-step Anaerobic digestion plus cross-flow membranes After equalization, highstrength wastewater is conditioned as needed. Influent is fed to the
Ventilated Improved Pit (VIP)
 Ventilated Improved Pit (VIP) Item Qty Unit Rate Amount Cement (50 Kgs bags) 6 bags Material Estimate Pour-flush squatting pa 1 No Pipe 100mm or 150mm diameter 1 No Sliding bolt 1 No Tower bolt 1 No Handle
Ventilated Improved Pit (VIP) Item Qty Unit Rate Amount Cement (50 Kgs bags) 6 bags Material Estimate Pour-flush squatting pa 1 No Pipe 100mm or 150mm diameter 1 No Sliding bolt 1 No Tower bolt 1 No Handle
Management of EcoSan System in Urban Areas:" EcoSan_UE Project Case Study'' in four sectors of Ouagadougou, BF.
 Accra, Ghana, 10-12 November 2009 WEST AFRICA REGIONAL SANITATION AND HYGIENE SYMPOSIUM Management of EcoSan System in Urban Areas:" EcoSan_UE Project Case Study'' in four sectors of Ouagadougou, BF. Chiaka
Accra, Ghana, 10-12 November 2009 WEST AFRICA REGIONAL SANITATION AND HYGIENE SYMPOSIUM Management of EcoSan System in Urban Areas:" EcoSan_UE Project Case Study'' in four sectors of Ouagadougou, BF. Chiaka
ecosan principles, urban applications and challenges
 ecosan principles, urban applications and challenges Christine Werner, team leader, GTZ-ecosan-programme Deutsche Gesellschaft für Technische Zusammenarbeit (GTZ) GmbH, Germany UN-CSD-12 Commission --
ecosan principles, urban applications and challenges Christine Werner, team leader, GTZ-ecosan-programme Deutsche Gesellschaft für Technische Zusammenarbeit (GTZ) GmbH, Germany UN-CSD-12 Commission --
DEWATS. Decentralized Wastewater. Treatment Solutions. Demand-based technical solutions to reduce waterpollution
 Decentralized Wastewater Treatment Solutions DEWATS Decentralized Wastewater Treatment Solutions Demand-based technical solutions to reduce waterpollution by small and medium enterprises and settlements
Decentralized Wastewater Treatment Solutions DEWATS Decentralized Wastewater Treatment Solutions Demand-based technical solutions to reduce waterpollution by small and medium enterprises and settlements
Sanitation for the Rest of Us. Randal Samstag, P.E. Carollo Engineers
 Sanitation for the Rest of Us Randal Samstag, P.E. Carollo Engineers Global Sanitation Delivery: How big is the problem? 2.6 billion people are without access to any kind of improved sanitation. Singapore,
Sanitation for the Rest of Us Randal Samstag, P.E. Carollo Engineers Global Sanitation Delivery: How big is the problem? 2.6 billion people are without access to any kind of improved sanitation. Singapore,
Sortering ved kilden. Et globalt perspektiv på spildevandshåndtering
 Sortering ved kilden. Et globalt perspektiv på spildevandshåndtering Tove Larsen, Urban Water Management, Eawag Eawag: Das Wasserforschungsinstitut des ETH Bereichs Wastewater treatment: A never ending
Sortering ved kilden. Et globalt perspektiv på spildevandshåndtering Tove Larsen, Urban Water Management, Eawag Eawag: Das Wasserforschungsinstitut des ETH Bereichs Wastewater treatment: A never ending
CRUDDAS, PARKER & GORMLEY ENSURING AVAILABILITY AND SUSTAINABLE MANAGEMENT OF WATER AND SANITATION FOR ALL
 39 th WEDC International Conference, Kumasi, Ghana, 2016 ENSURING AVAILABILITY AND SUSTAINABLE MANAGEMENT OF WATER AND SANITATION FOR ALL User perceptions and practical considerations for implementation
39 th WEDC International Conference, Kumasi, Ghana, 2016 ENSURING AVAILABILITY AND SUSTAINABLE MANAGEMENT OF WATER AND SANITATION FOR ALL User perceptions and practical considerations for implementation
WHAT SYSTEM-WIDE INNOVATION IN PRO-POOR SANITATION COULD LOOK LIKE
 WHAT SYSTEM-WIDE INNOVATION IN PRO-POOR SANITATION COULD LOOK LIKE Presentation to WRI, November 16 th, 2016 Brian Arbogast Director, Water, Sanitation, Hygiene Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation MY TEAM
WHAT SYSTEM-WIDE INNOVATION IN PRO-POOR SANITATION COULD LOOK LIKE Presentation to WRI, November 16 th, 2016 Brian Arbogast Director, Water, Sanitation, Hygiene Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation MY TEAM
Innovative Mobile Payment and Metering Mechanism
 Innovative Mobile Payment and Metering Mechanism Anja Nina Kramer Senior Project Manager KfW Uganda 1 Current engagement of German Development Cooperation (GDC) for water and sanitation in Africa Largest
Innovative Mobile Payment and Metering Mechanism Anja Nina Kramer Senior Project Manager KfW Uganda 1 Current engagement of German Development Cooperation (GDC) for water and sanitation in Africa Largest
Innovative urine diverting dry toilet (UDDT) designs from East Africa
 Innovative urine diverting dry toilet (UDDT) designs from East Africa This paper presents different UDDT designs from East Africa, which are responding to their users preferences and needs. Author: Elke
Innovative urine diverting dry toilet (UDDT) designs from East Africa This paper presents different UDDT designs from East Africa, which are responding to their users preferences and needs. Author: Elke
Compendium of Sanitation Technologies in Emergencies How to best use this tool
 Compendium of Sanitation Technologies in Emergencies How to best use this tool This overview document is intended to serve as quick introduction into the structure, logic and application of the Compendium
Compendium of Sanitation Technologies in Emergencies How to best use this tool This overview document is intended to serve as quick introduction into the structure, logic and application of the Compendium
Managing wastewater in the city of the future. Decentralized wastewater and rainwater reclamation and use in Urban Agriculture
 Managing wastewater in the city of the future Decentralized wastewater and rainwater reclamation and use in Urban Agriculture Decentralized wastewater and rainwater reclamation and use in Urban Agriculture
Managing wastewater in the city of the future Decentralized wastewater and rainwater reclamation and use in Urban Agriculture Decentralized wastewater and rainwater reclamation and use in Urban Agriculture
East Asia Urban Sanitation Review
 EAP REGION URBAN SANITATION REVIEW East Asia Urban Sanitation Review Presentation prepared by Bank Team September 2013 Outline Sector Overview Issues Recommendations 1. Sector Overview PURPOSE OF THE STUDY
EAP REGION URBAN SANITATION REVIEW East Asia Urban Sanitation Review Presentation prepared by Bank Team September 2013 Outline Sector Overview Issues Recommendations 1. Sector Overview PURPOSE OF THE STUDY
Nutrients recovery of source separated urine by forward osmosis and a pilot scale resources-oriented sanitation system
 School of Environment, Tsinghua University Nutrients recovery of source separated urine by forward osmosis and a pilot scale resources-oriented sanitation system SWWS 2016, 15 September XU Yangyu, ZHOU
School of Environment, Tsinghua University Nutrients recovery of source separated urine by forward osmosis and a pilot scale resources-oriented sanitation system SWWS 2016, 15 September XU Yangyu, ZHOU
UDDT (ECOSAN) What is a sanitation system about?
 UDDT (ECOSAN) What is a sanitation system about? What is Ecosan? What is UDDT? Why UDDT? How it differs? What are the advantages? What are the disadvantages What is urine, apart from being a waste product?
UDDT (ECOSAN) What is a sanitation system about? What is Ecosan? What is UDDT? Why UDDT? How it differs? What are the advantages? What are the disadvantages What is urine, apart from being a waste product?
Product Scan Findings from Benin, Côte d Ivoire, and Ghana
 Product Scan Findings from Benin, Côte d Ivoire, and Ghana A summary of gaps identified along the sanitation service chain BACKGROUND The Sanitation Service Delivery (SSD) Program in West Africa is a USAID-funded
Product Scan Findings from Benin, Côte d Ivoire, and Ghana A summary of gaps identified along the sanitation service chain BACKGROUND The Sanitation Service Delivery (SSD) Program in West Africa is a USAID-funded
40 The Double Pit Latrine
 40 - Recycling - The Double Pit Latrine 105 40 The Double Pit Latrine A double pit latrine is a sanitation system specifically constructed to produce valuable fertilizer for gardens. It consists of two
40 - Recycling - The Double Pit Latrine 105 40 The Double Pit Latrine A double pit latrine is a sanitation system specifically constructed to produce valuable fertilizer for gardens. It consists of two
Compendium of. Sanitation Technologies in Emergencies. Stockholm World Water Week 2017 I August 30, Compendium of
 Compendium of Compendium of Sanitation Technologies in Emergencies Sanitation Technologies in Emergencies Stockholm World Water Week 2017 I August 30, 2017 Agenda 09:00 Existing Sanitation Challenges:
Compendium of Compendium of Sanitation Technologies in Emergencies Sanitation Technologies in Emergencies Stockholm World Water Week 2017 I August 30, 2017 Agenda 09:00 Existing Sanitation Challenges:
URBAN WORKSHOP BLACK WATER TREATMENT COMMISSIONING REPORT JANUARY 2007
 URBAN WORKSHOP BLACK WATER TREATMENT COMMISSIONING REPORT JANUARY 2007 The Urban Workshop 50 Lonsdale Street Melbourne, VIC 3000 The Urban Workshop is a 34 storey commercial office building with adjacent
URBAN WORKSHOP BLACK WATER TREATMENT COMMISSIONING REPORT JANUARY 2007 The Urban Workshop 50 Lonsdale Street Melbourne, VIC 3000 The Urban Workshop is a 34 storey commercial office building with adjacent
Your Guide to the. Budd Inlet Treatment Plant
 Your Guide to the Budd Inlet Treatment Plant How does LOTT know the plant is working correctly? All activity within the treatment plant is monitored 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. A highly trained team
Your Guide to the Budd Inlet Treatment Plant How does LOTT know the plant is working correctly? All activity within the treatment plant is monitored 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. A highly trained team
UNIVERSITà DEGLI STUDI DI NAPOLI FEDERICO II
 UNIVERSITà DEGLI STUDI DI NAPOLI FEDERICO II FACOLTÀ DI INGEGNERIA CORSO DI LAUREA IN INGEGNERIA PER L AMBIENTE E IL TERRITORIO (CLASSE DELLE LAUREE IN INGEGNERIA CIVILE E AMBIENTALE) DIPARTIMENTO DI INGEGNERIA
UNIVERSITà DEGLI STUDI DI NAPOLI FEDERICO II FACOLTÀ DI INGEGNERIA CORSO DI LAUREA IN INGEGNERIA PER L AMBIENTE E IL TERRITORIO (CLASSE DELLE LAUREE IN INGEGNERIA CIVILE E AMBIENTALE) DIPARTIMENTO DI INGEGNERIA
Wastewater: Moving Towards Low Carbon and Energy-generating Technologies. Jingmin Huang Senior Urban Development Specialist RSAS
 Wastewater: Moving Towards Low Carbon and Energy-generating Technologies Jingmin Huang Senior Urban Development Specialist RSAS Impacts of Climate Change Global climate change impacts will be on water
Wastewater: Moving Towards Low Carbon and Energy-generating Technologies Jingmin Huang Senior Urban Development Specialist RSAS Impacts of Climate Change Global climate change impacts will be on water
Experience with the introduction of dry, urine diverting sanitation systems in Ethiopia
 34th WEDC International Conference, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2009 WATER, SANITATION AND HYGIENE: SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT AND MULTISECTORAL APPROACHES Experience with the introduction of dry, urine diverting
34th WEDC International Conference, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2009 WATER, SANITATION AND HYGIENE: SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT AND MULTISECTORAL APPROACHES Experience with the introduction of dry, urine diverting
Turbo4bio System For the Treatment of Sewage & Organic Effluents
 Turbo4bio System For the Treatment of Sewage & Organic Effluents Dr.Hans. H.Badreddine President Turbo4bio Page 1 Executive Summary The Turbo4bio system has been patented in the UK and Europe by Hans Bioshaft
Turbo4bio System For the Treatment of Sewage & Organic Effluents Dr.Hans. H.Badreddine President Turbo4bio Page 1 Executive Summary The Turbo4bio system has been patented in the UK and Europe by Hans Bioshaft
Ecological Sanitation in Southern Africa Many approaches to a varied need
 Ecological Sanitation in Southern Africa Many approaches to a varied need Peter Morgan Aquamor,, Harare Southern Africa is a huge territory with a diverse range of well established sanitary options available
Ecological Sanitation in Southern Africa Many approaches to a varied need Peter Morgan Aquamor,, Harare Southern Africa is a huge territory with a diverse range of well established sanitary options available
ECOLOO Group facebook.com/ecoloogroup
 Flowchart of ECOLOO 1 ECOLOO COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGES 1 Flushing Toilet Vs ECOLOO Some people are so used to the flush-toilet and its problems that they can't imagine anything better until they try ECOLOO.
Flowchart of ECOLOO 1 ECOLOO COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGES 1 Flushing Toilet Vs ECOLOO Some people are so used to the flush-toilet and its problems that they can't imagine anything better until they try ECOLOO.
A SUSTAINABLE TOILET SOLUTION TO FIGHT THE GLOBAL SANITATION CRISIS
 A SUSTAINABLE TOILET SOLUTION TO FIGHT THE GLOBAL SANITATION CRISIS Australian Centre for Education and Training Global (ACET-Global), Melbourne, VIC, Australia INTRODUCTION Globally, limited access to
A SUSTAINABLE TOILET SOLUTION TO FIGHT THE GLOBAL SANITATION CRISIS Australian Centre for Education and Training Global (ACET-Global), Melbourne, VIC, Australia INTRODUCTION Globally, limited access to
MEMBRANE BIO-REACTOR. Prashanth N 1 1. INTRODUCION
 International Journal of Latest Trends in Engineering and Technology Vol.(7)Issue(3), pp. 296 301 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.21172/1.73.540 e ISSN:2278 621X MEMBRANE BIO-REACTOR Prashanth N 1 ABSTRACT:
International Journal of Latest Trends in Engineering and Technology Vol.(7)Issue(3), pp. 296 301 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.21172/1.73.540 e ISSN:2278 621X MEMBRANE BIO-REACTOR Prashanth N 1 ABSTRACT:
OVERVIEW SOCIAL ACCEPTABILITY ENVIRONMENTAL SUSTAINABILITY
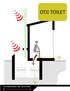 OTJI TOILET OVERVIEW A Otji toilet is a dry toilet system which collects humanure in a large perforated bucket in a chamber beneath the toilet. A specially designed urine diversion toilet is used to divert
OTJI TOILET OVERVIEW A Otji toilet is a dry toilet system which collects humanure in a large perforated bucket in a chamber beneath the toilet. A specially designed urine diversion toilet is used to divert
Investing in Sustainable cities. Water Management in urban areas: Yangon s case
 Investing in Sustainable cities Water Management in urban areas: Yangon s case I. Water management: general perspective The main goals of urban water and waste water management are : provide clean water
Investing in Sustainable cities Water Management in urban areas: Yangon s case I. Water management: general perspective The main goals of urban water and waste water management are : provide clean water
Using tariff structures as a demand management instrument: The case of Kampala
 34th WEDC International Conference, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2009 WATER, SANITATION AND HYGIENE: SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT AND MULTISECTORAL APPROACHES Using tariff structures as a demand management instrument:
34th WEDC International Conference, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2009 WATER, SANITATION AND HYGIENE: SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT AND MULTISECTORAL APPROACHES Using tariff structures as a demand management instrument:
Water Reuse Terminology
 Water Reuse Terminology Produced by the ACWA Communications Committee Recycled Water Work Group June 2016 With water reuse playing an increasingly important role in California s water supply portfolio,
Water Reuse Terminology Produced by the ACWA Communications Committee Recycled Water Work Group June 2016 With water reuse playing an increasingly important role in California s water supply portfolio,
Innovatieve nieuwe sanitatie ontwikkelingen in North and South
 Innovatieve nieuwe sanitatie ontwikkelingen in North and South * + Grietje Zeeman, * + Katarzyna Kujawa-Roeleveld, # Brendo Meulman, @ Lucia-Hernandez *WUR-ETE, + LeAF, @ WETSUS, # DeSaH BV Presentation
Innovatieve nieuwe sanitatie ontwikkelingen in North and South * + Grietje Zeeman, * + Katarzyna Kujawa-Roeleveld, # Brendo Meulman, @ Lucia-Hernandez *WUR-ETE, + LeAF, @ WETSUS, # DeSaH BV Presentation
European Water and Sanitation Services vs. Sustainable Development Example Germany. ATHENS European Week, Autumn 2013 Paris, November 19 th, 2013
 1G e r m a n I n s t i t u t e o f U r b a n A f f a i r s European Water and Sanitation Services vs. Sustainable Development Example Germany ATHENS European Week, Autumn 2013 Paris, November 19 th, 2013
1G e r m a n I n s t i t u t e o f U r b a n A f f a i r s European Water and Sanitation Services vs. Sustainable Development Example Germany ATHENS European Week, Autumn 2013 Paris, November 19 th, 2013
THE BIOFIL TOILET SYSTEM
 THE BIOFIL TOILET SYSTEM The Toilet Facility that Makes Good Sanitation Sense The Biofil Digester is a simple compact on-site organic waste treatment system that uniquely combines the benefits of the flush
THE BIOFIL TOILET SYSTEM The Toilet Facility that Makes Good Sanitation Sense The Biofil Digester is a simple compact on-site organic waste treatment system that uniquely combines the benefits of the flush
Turn waste into value. Industrial water and waste treatment solutions
 Turn waste into value Industrial water and waste treatment solutions Turn waste into value Most industrial processes consume lots of water and generate waste that needs to be treated to meet tough legislation
Turn waste into value Industrial water and waste treatment solutions Turn waste into value Most industrial processes consume lots of water and generate waste that needs to be treated to meet tough legislation
Best Practice in Sewage and Effluent Treatment Technologies
 Best Practice in Sewage and Effluent Treatment Technologies Contents 1 Wastewater - Introduction 1 1.1 Earth s ecological system 1 1.1.1 Water effect on ecology 2 1.1.2 Wastewater generation 3 1.2 Wastewater
Best Practice in Sewage and Effluent Treatment Technologies Contents 1 Wastewater - Introduction 1 1.1 Earth s ecological system 1 1.1.1 Water effect on ecology 2 1.1.2 Wastewater generation 3 1.2 Wastewater
Waterharmonica THE POTENTIAL OF WATERHARMONICA CONCEPT IN TANZANIA. The bridge between treated wastewater and surface water. a Dutch initiative
 THE POTENTIAL OF WATERHARMONICA CONCEPT IN TANZANIA The bridge between treated wastewater and surface water Presented by: Hamidar Chanzi IBP 2004/5 - Environmental Science, Saxion University Deventer Waterboard
THE POTENTIAL OF WATERHARMONICA CONCEPT IN TANZANIA The bridge between treated wastewater and surface water Presented by: Hamidar Chanzi IBP 2004/5 - Environmental Science, Saxion University Deventer Waterboard
JOELEX UGANDA LIMITED PLOT 65 P.O BOX KAMPALA, UGANDA
 JOELEX UGANDA LIMITED PLOT 65 P.O BOX 35572 KAMPALA, UGANDA joel.ssimbwa@gmail.com +256774484110 Mr.Mukasa Joel Sssimbwa Dr.James NOW LETS Akampumuza INNOVATE Miss Dorothy Atukunda 1 PROBLEM Our bio-toilet
JOELEX UGANDA LIMITED PLOT 65 P.O BOX 35572 KAMPALA, UGANDA joel.ssimbwa@gmail.com +256774484110 Mr.Mukasa Joel Sssimbwa Dr.James NOW LETS Akampumuza INNOVATE Miss Dorothy Atukunda 1 PROBLEM Our bio-toilet
ENERGY AND CARBON FOOTPRINT: A COMPARISON OF NON-POTABLE WATER AND WASTEWATER SERVICING APPROACHES
 ENERGY AND CARBON FOOTPRINT: A COMPARISON OF NON-POTABLE WATER AND WASTEWATER SERVICING APPROACHES Django Seccombe 1, Matthew Ferguson 1, Andrew Bovis 1 1. Sydney Water Corporation, Sydney, NSW ABSTRACT
ENERGY AND CARBON FOOTPRINT: A COMPARISON OF NON-POTABLE WATER AND WASTEWATER SERVICING APPROACHES Django Seccombe 1, Matthew Ferguson 1, Andrew Bovis 1 1. Sydney Water Corporation, Sydney, NSW ABSTRACT
Dealing with Glenorchy s faeces urine and greywater - grasping the potential by thinking differently
 Dealing with Glenorchy s faeces urine and greywater - grasping the potential by thinking differently The Glenorchy sewerage debate so far has avoided attempting to grasp the potential that is available
Dealing with Glenorchy s faeces urine and greywater - grasping the potential by thinking differently The Glenorchy sewerage debate so far has avoided attempting to grasp the potential that is available
Water Conservation Tips for TNRD Residents SPENCES BRIDGE
 Water Conservation Tips for TNRD Residents SPENCES BRIDGE Do You Know Your Drinking Water Source? Before: Murray Creek Now: Well Source on Cook s Ferry IB Do You Know What Costs Are Associated to Supplying
Water Conservation Tips for TNRD Residents SPENCES BRIDGE Do You Know Your Drinking Water Source? Before: Murray Creek Now: Well Source on Cook s Ferry IB Do You Know What Costs Are Associated to Supplying
Ultrafiltration of Desizing Effluents. Lecture 24
 Ultrafiltration of Desizing Effluents Lecture 24 Ultrafiltration of Desizing Effluents Textile sizes can be removed from the fabric in the same form as they were applied to the warp and the recovery of
Ultrafiltration of Desizing Effluents Lecture 24 Ultrafiltration of Desizing Effluents Textile sizes can be removed from the fabric in the same form as they were applied to the warp and the recovery of
Water Supply and Sanitation Infrastructure
 Water Supply and Sanitation Infrastructure WHO-UNICEF Joint Monitoring Program, 2010 WHO-UNICEF Joint Monitoring Program, 2010 General Sanitation Overview... JMP s definition of basic sanitation Add WATER
Water Supply and Sanitation Infrastructure WHO-UNICEF Joint Monitoring Program, 2010 WHO-UNICEF Joint Monitoring Program, 2010 General Sanitation Overview... JMP s definition of basic sanitation Add WATER
Evaluation of distribution models for household water treatment products in Kenya
 37th WEDC International Conference, Hanoi, Vietnam, 2014 SUSTAINABLE WATER AND SANITATION SERVICES FOR ALL IN A FAST CHANGING WORLD Evaluation of distribution models for household water treatment products
37th WEDC International Conference, Hanoi, Vietnam, 2014 SUSTAINABLE WATER AND SANITATION SERVICES FOR ALL IN A FAST CHANGING WORLD Evaluation of distribution models for household water treatment products
WATER AND WASTEWATER FACILITY CLASSIFICATION APPLICATION FORM
 WATER AND WASTEWATER FACILITY CLASSIFICATION APPLICATION FORM APPLICATION INSTRUCTIONS Please print or type. In keeping with the privacy provisions of the Nova Scotia Freedom of Information & Protection
WATER AND WASTEWATER FACILITY CLASSIFICATION APPLICATION FORM APPLICATION INSTRUCTIONS Please print or type. In keeping with the privacy provisions of the Nova Scotia Freedom of Information & Protection
An innovative, locally adapted, dry sanitation system for arid regions
 1 An innovative, locally adapted, dry sanitation system for arid regions Identifying suitable sanitation facilities specifically adapted to the local context is central to ensuring long term sustainability.
1 An innovative, locally adapted, dry sanitation system for arid regions Identifying suitable sanitation facilities specifically adapted to the local context is central to ensuring long term sustainability.
Greywater recovery system.
 Greywater recovery system www.redi.it Products Water a precious good With REDI greywater recovery system it is possible to reduce drinking water consumption in a building up to 50% Redi has developed a
Greywater recovery system www.redi.it Products Water a precious good With REDI greywater recovery system it is possible to reduce drinking water consumption in a building up to 50% Redi has developed a
BIOGAS and DEWATS, a perfect match? Summary. Susmita Sinha & Alex Kazaglis
 BIOGAS and DEWATS, a perfect match? Susmita Sinha & Alex Kazaglis Summary BORDA s approach to DECENTRALISED WASTEWATER TREATMENT (DEWATS) foresees BIOGAS digesters as one treatment module. DEWATS linked
BIOGAS and DEWATS, a perfect match? Susmita Sinha & Alex Kazaglis Summary BORDA s approach to DECENTRALISED WASTEWATER TREATMENT (DEWATS) foresees BIOGAS digesters as one treatment module. DEWATS linked
PHOSPHORUS RECOVERY - LABORATORY SCALE EXPERIMENTS
 PHOSPHORUS RECOVERY - LABORATORY SCALE EXPERIMENTS Jan Suschka and S. Popławski Technical University of Łódź, Filial Bielsko-Biała, Poland, ul. Willowa 2, 43-39 Bielsko-Biała. ABSTARCT Laboratory scale
PHOSPHORUS RECOVERY - LABORATORY SCALE EXPERIMENTS Jan Suschka and S. Popławski Technical University of Łódź, Filial Bielsko-Biała, Poland, ul. Willowa 2, 43-39 Bielsko-Biała. ABSTARCT Laboratory scale
Progressing towards the millennium development goals for sanitation through CLTS. The Experience of Mali
 Progressing towards the millennium development goals for sanitation through CLTS The Experience of Mali By Modibo Diallo, National Directorate of Sanitation Ministry of Environment and Sanitation, Government
Progressing towards the millennium development goals for sanitation through CLTS The Experience of Mali By Modibo Diallo, National Directorate of Sanitation Ministry of Environment and Sanitation, Government
CIE4485 Wastewater Treatment
 CIE4485 Wastewater Treatment Dr.ir. M.K. de Kreuk 15. WWTP 2030 and Resource Factory 1 CT4485 Wastewater Treatment WWTP 2030 and Resource Factory Dr. Ir. M.K. de Kreuk 10 January 2013 Delft University
CIE4485 Wastewater Treatment Dr.ir. M.K. de Kreuk 15. WWTP 2030 and Resource Factory 1 CT4485 Wastewater Treatment WWTP 2030 and Resource Factory Dr. Ir. M.K. de Kreuk 10 January 2013 Delft University
Use and Maintenance of Urine Diversion Dry Toilets (UDDTs) and Composting Toilets
 4 Use and Maintenance of Urine Diversion Dry Toilets (UDDTs) and Composting Toilets A Series of Educational Manuals on Ecological Sanitation and Hygiene Use and Maintenance of Urine Diversion Dry Toilets
4 Use and Maintenance of Urine Diversion Dry Toilets (UDDTs) and Composting Toilets A Series of Educational Manuals on Ecological Sanitation and Hygiene Use and Maintenance of Urine Diversion Dry Toilets
Use and Maintenance of Urine Diversion Dry Toilets (UDDTs) and Composting Toilets
 4 Use and Maintenance of Urine Diversion Dry Toilets (UDDTs) and Composting Toilets A Series of Educational Manuals on Ecological Sanitation and Hygiene Use and Maintenance of Urine Diversion Dry Toilets
4 Use and Maintenance of Urine Diversion Dry Toilets (UDDTs) and Composting Toilets A Series of Educational Manuals on Ecological Sanitation and Hygiene Use and Maintenance of Urine Diversion Dry Toilets
5.3.1 Water seal Positioning the toilet pan 12
 Table of contents 5.0 Introduction 5 5.1 The toilet and its components 6 5.1.1 Purpose and importance of the toilet 6 5.1.2 General types and designs of toilets in rural areas 6 5.1.3 Important features
Table of contents 5.0 Introduction 5 5.1 The toilet and its components 6 5.1.1 Purpose and importance of the toilet 6 5.1.2 General types and designs of toilets in rural areas 6 5.1.3 Important features
Chapter 2 Screening Approach and Criteria
 Chapter 2 Screening Approach and Criteria CHAPTER 2 SCREENING APPROACH AND CRITERIA 2.1 INTRODUCTION As discussed in Chapter 1, the purpose of this report is to identify and screen alternative technologies,
Chapter 2 Screening Approach and Criteria CHAPTER 2 SCREENING APPROACH AND CRITERIA 2.1 INTRODUCTION As discussed in Chapter 1, the purpose of this report is to identify and screen alternative technologies,
Blue Responsibility Award: Manufacturing for a Sustainable Terra Preta Sanitation System
 12th Conference on Sustainable Manufacturing (GCSM) Johor Bahru, Malaysia, September 22 nd -24 th 2014 Blue Responsibility Award: Manufacturing for a Sustainable Terra Preta Sanitation System Innovative
12th Conference on Sustainable Manufacturing (GCSM) Johor Bahru, Malaysia, September 22 nd -24 th 2014 Blue Responsibility Award: Manufacturing for a Sustainable Terra Preta Sanitation System Innovative
Lesson W9 Wastewater and CSOs
 Lesson W9 Wastewater and CSOs Where Does our Water Go When We Flush it Down the Drain? When you flush your toilet or wash your dishes, where does the water go? We learned that only 2-3% of the water used
Lesson W9 Wastewater and CSOs Where Does our Water Go When We Flush it Down the Drain? When you flush your toilet or wash your dishes, where does the water go? We learned that only 2-3% of the water used
Enhancing Sanitation in Vietnam through Decentralized Wastewater Treatment Technology Transfer
 Consultative Meeting on Water and Wastewater Management 19-20 April 2010, Shiga, Japan Enhancing Sanitation in Vietnam through Decentralized Wastewater Treatment Technology Transfer Assoc. Prof. Dr. Nguyen
Consultative Meeting on Water and Wastewater Management 19-20 April 2010, Shiga, Japan Enhancing Sanitation in Vietnam through Decentralized Wastewater Treatment Technology Transfer Assoc. Prof. Dr. Nguyen
Experience with the introduction of dry, urine-diverting sanitation systems in Ethiopia
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Experience with the introduction of dry, urine-diverting sanitation systems in Ethiopia This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Experience with the introduction of dry, urine-diverting sanitation systems in Ethiopia This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional
