Climate modification directed by control theory
|
|
|
- Garry Kelley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Climate modiication directed by control theory Wang Liang (Department o Control cience and Control Engineering, Huazhong University o cience and Technology, WuHan, 3007, P.R.China, wl@smail.hust.edu.cn) [bstract] Climate modiication measures to counteract global warming receive some more new attentions in these years. Most current researches only discuss the impact o these measures to climate, but how to design such a climate regulator is still unknown. This paper shows the control theory could give the systematic direction or climate modiication. But the control analyzing also reveals that climate modiications should only be regarded as a last-ditch measure. 1 Introduction IPCC (Intergovernmental panel on climate change) announce its Fourth ssessment Report in daptation and mitigation options are suggested to avoid all climate change impacts. Besides the mitigation method like aorestation in this report (1), some more ambitious measures are also reconsidered in these years, including putting up space shields that cover billions o square meters, using chemicals to relect sunlight or increase Earth s cloud cover, stimulating massive growth o phytoplankton in the oceans (2-7). ssessment o climate mitigation or manipulation has also been reviewed under various ramings including economics, risk, politics, and environmental ethics (8). But all these work still can t answer these questions: How to adjust the measures according to prediction or actual impact o active manipulation? Can the project be readily reversed i it goes awry? How to evaluate the eect o one measure in conjunction with other methods? Obviously, a systematic strategy to modiy the climate system is still absent. Here we will shows the control theory could meet this requirement. 2 Basic analyses or climate control design Control theory is an interdisciplinary branch o engineering and mathematics, which deals with inluencing the behavior o dynamical systems. The controller is designed to manipulate the inputs to a system to obtain the desired eect on the output o the system. electing the proper model is the irst step or control research. There are three kinds o climate models, simple climate model, earth models o intermediate complexity (EMICs) and global climate models (GCMs) (9). Their complexities increase in turn. Many research shows the results given by most complex GCM can also be captured by much simple model. o we use simple climate model to design the control law and then veriy this law in sophisticated GCM models. Here we select a simple climate model considering the atmosphere and the underlying surace (10,11,12):
2 C C dt dt dts dt = (1 α ) a[1 + (1 a) α ] Q + εδt = (1 α )(1 a)(1 α ) Q δt s 2εT + εδt 3 s + H ( T H ( T s T ) T ) (1) C =.6 10 Wm K C = Wm K = 32Wm 8 2 δ = Wm K, = H = 5.9Wm K. Here a, ε = , α = , α = , s Q, T, T is average air temperature and surace air temperature. The description o other parameters could be ound in (10). This model is zero-dimensional, representing global mean and vertically integrated conditions. In the model, energy is exchanged between the surace, atmosphere and space by short and long-wave radiation and by latent and sensible heat. Then we should determine the appropriate control input or said control measure. The overwhelming majority o climate manipulation proposals aim to alter radiative energy luxes, either by increasing the amount o outgoing inrared radiation through reduction o atmospheric CO2, or by decreasing the amount o absorbed solar radiation through an increase in albedo. Here we will consider this measure as control input. In principle, the use o space-based solar shields has signiicant advantages over other options (Fig.1). Because solar shields eect a clean alteration o the solar constant, their side eects would be both less signiicant and more predictable than or other albedo modiication schemes (13). Fig.1. pace-based albedo modiication (a picture rom Internet) Many current climate control proposals belong to open loop, which only consider the impact o measures. But how to regulate these measures according to the modiication eect is not mentioned, which may result in the system unstable. For example, erosols produced in the lower stratosphere can counteract some o the eects o global warming. But excessive aerosols may overly oset the warming and bring adverse impacts. To avoid the problems o the open-loop, most current controller uses eedback to control states or outputs o a dynamical system. The name close-loop eedback comes rom the inormation path in the system: process inputs have an eect on the process outputs, which is measured with sensors and processed by
3 the controller; the result (the control signal) is used as input to the process, closing the loop. For aerosols measures, the amount o aerosols injected in the air should be adjusted according to its impact to climate. o Here U denotes the control input. s a close-loop control system, it should be the unction T,. o mark it as U T, T ). s an albedo modiication control, it could be added in T ormula (1) as ollows: C C ( dt = (1 α ) a[1 + (1 a) α ] Q[1 U ( T, T )] + εδt 2εTs + H ( Ts T) dt dts = (1 α )(1 a)(1 αs) Q[1 U ( T, T )] δt + εδt H ( T T) dt 3 Here U is the percent o energy luxes that the control implementer could curtain o. particular issue is the requirement or a control system to perorm properly in the presence o input and state constraints. In the physical world every signal is limited. For example, the energy we can manipulate is very limited comparing with climate system. o the designed controller should avoid sending control signals that cannot be ollowed by the physical system. Here set the control constraint as: U [0,3%] (3) Then we need decide a main control aim. For climate system, most related researchers think that manipulations need not be aimed at changing the environment, but rather may aim to maintain a desired environmental state against perturbations either natural or anthropogenic. This aim could be regarded as state regulator problem and constant tracing problem in control theory. The ollowing parts will give the detailed discussion or these two control problems. (2) 3 Climate state regulator design The state regulator is an operator driving the system to equilibrium state by minimum cost. The cost unction could be the energy consumption, total time, etc. We could deine the climate regulator problem as ollows. For given system (1), its equilibrium state is: T = K, T = K Then or some temporary perturbations, the temperature raise to: T = 27K, T = 292K The system structure has no changes. We want to drive the climate system to original state as soon as possible. This problem could be deined as: Initial state: T ( t ), T ( t )] (270.2,288.0) [ 0 0 = Final state: [ T ( t ), T ( t )] = (27,292)
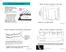
4 Cost unction: J t = t0 1 dt Control aims: J = min(j ) Many dierent design methods are available this problem. The risks posed by climate control are suiciently novel that, in general, the relevant biological and geophysical science is too uncertain to allow quantitative. In control engineering, typically a simpler mathematical model is chosen in order to simpliy calculations; otherwise the true system dynamics can be so complicated that a complete model is impossible, especially or climate system. But no real physical system truly behaves like the series o dierential equations used to represent it mathematically. o the climate control system must always have some robustness property. robust controller is such that its properties do not change much i applied to a system slightly dierent rom the mathematical one used or its synthesis. Now there are several robust design methods like H design. Here we select the cell mapping design method, which is simple, robust and easy to be understood (1-16). This method belongs to Bellman dynamic programming method. We can depict this method in an easy way: it divides the state space into small rectangle regions called cells. The control input is also discretized. Then a search algorithm is applied to assign only control input or each rectangle region/cell to meet the optimal requirement. The main operation o cell mapping design method is described as ollows: 1) elect interesting state region. T [268,276], T [286,29]. 2) Construct cell. We divide the T and T into 2 6 = 6 equal pieces, so there are 6 6 = 096 cells. 3) Determine the control input set U. The input set is divide into 8 equal pieces: U = {0,0.37%,0.75%,1.13%,1.5%,1.87%,2.25%,2.62%,3%}. ) Obtain Mappings rom every cell with the entire set o control inormation U. For each cell, we need calculate N = 9 number o cell transitions. Here select one quarter as the integral time. U The related cost is also obtained in this step. 5) Decide the only control inormation U or each cell. Dynamic programming is employed to identiy this inormation. The search algorithm associates each cell with a control action that maps the cell to a cell trajectory with the optimal cost. Discrete Optimal Control Table (DOC) is obtained to represent the discrete global optimal control solution. ll the optimum trajectories rom every possible initial condition in the cell state space can be generated once this database is built. The detailed algorithm could be ound in Hsu s original paper. In our instance, there are 3271 controllable cells. cell is said to be controllable i there exists a sequence o controls which could bring this cell to the target cell. The controllable region and DOC table or this example is shown in Fig.2:
5 29 Controllable region Uncontrollable region 29 B (K) T (K) T 0.02 U T (K) T (K) 0 Fig.2. () Controllable region, (B) Optimal control table, the control value or each cell/region is represented by dierent color. 6) The optimal sequence o control is readily obtainable rom DOC. Because DOC stores the singe control input or every cell, in operation process, the system only need read the input value rom DOC according to the eedback state. The cell optimal solution o our system is shown in ig.3: 27 ystem response without control C 273 T (K) 272 ystem response under control U B t (quarters) 292 ystem response without control ystem response under control t (quarters) T (K) t (quarters) Fig.3. (), (B) Response o system, (C) Control input In Fig.3., B, we could ind the system need about 60 quarters to resume to equilibrium state without any control. But i we add the control, it only needs about 20 quarters to resume. Global warming oset design Now the main topic or climate modiication is the compensation o CO2 emission. It s a tracing problem. Here assume the CO2 reach 560ppm in 2150, two times o concentration beore industrialization. Then CO2 will not increase anymore. We simulate this scene in a complex
6 GCM model GIⅡ(17,18). The global air surace temperature will increase rom ~286.88K to a new equilibrium ~.3K ater 2090, which is shown in Fig (K) T Fig.. Global temperature rom 2050 to 2150 The temperature in 2065 is ~288.2K, which is similar to current condition. o we use it as the reerence scene. The temperature changes between 2056 and 2100 are shown in Fig.5. Fig.5. Temperature changes between 2056 and 2100 Here the control aim could be deined as reducing the temperature rom equilibrium state ~.3k to the state o 2065 (~288.2K) using least time. We also design the control law by simple climate model (1), where the impact o CO2 is eatured by ε. We could adjust this parameter to simulate this climate system. I ε = , the new equilibrium state is: T = K, T =. 3K, this temperature is close to the equilibrium state o GCM models. Because there is no a corresponding air temperature in GCM model, we simply assume T T in GCM. We begin the control in 2100, its = s T =. 3K, T = K. This problem could be deined as:
7 Initial state: T ( t ), T ( t )] (271.8,.3) [ 0 0 = Final state: [ T ( t ), T ( t )] = (269.7,288.2) Cost unction: J t = t0 1 dt Control aims: J = min(j ) We still use the cell mapping method to design this control law. Here select the interesting area: T [269,273], T [287,291], integral time:1 year, other setting is similar to the operation in paragraph 3. The DOC table o this system is shown in Fig.6: (K) T U T (K) 0 Fig.6. Optimal control table or global warming oset Then we veriy this control law in GCM model. In every year, we choose the control input rom DOC table according to the average temperature o ormer year. The global average temperature reaches the control aim in 2105, which is shown in Fig.7:.5 T (K) Fig.7. Global temperature rom 2050 to 2150 I there is no a control strategy, we may not oset the warming so precisely. The control will end in Unlike the regulator problem, the temperature will rise again in o the control should continue according to the temperature o The DOC table should also be
8 adjusted i CO2 concentration markedly changes. I concentration gets back to a normal level, the control strategy could be converted to state regulator control. The temperature changes between reerence year 2065 and 2105 are shown in Fig.8: Fig.8. Temperature changes between 2056 and 2105 From Fig.8, we could ind the compensation is not very uniorm, though the dierence o averages temperatures between 2056 and 2105 is only 0.03K. To avoid this problem, multiple compensation measures or more precise simple climate model and more complex design method could be considered in the uture. 5 Conclusions The control theory could make the climate modiication more reliable and sae. But real climate system is a complex nonlinear, decentralized, strong coupling, distributed-parameters system, which still can t be well grasped by current control theory. The climate modiication provides a new big challenge or control research. Moreover, the eiciency o control design strongly relies on how well we know the controlled system. But our knowledge about climate is still very limited. o we d better test this technology in re-building the environment o Mars, but not on the Earth. Now the more reasonable and direct method may be still to curtail emissions o greenhouse gases. Reerence 1. IPCC report, Climate Change 2007:ynthesis Report 2. W. K. David, Geoengineering the Climate: history and prospect. nnual Review Energy Environ,25, (2000) 3. National cademy o ciences. Policy implications o greenhouse warming: Mitigation, adaptation and the science base. Washington, D.C: National cademy Press, 1992
9 . B. Govindasamy, K. Caldeira, P.B. Duy, Geoengineering Earth s radiation balance to mitigate climate change rom a quadrupling o CO2. Global and Planetary Change, 37, (2003) 5. Crutzen. P. J, lbedo enhancement by stratospheric sulur injections: a contribution to resolve a policy dilemma? Climatic Change, (2006), DOI: /s y 6. T. M. L. Wigley, Combined Mitigation/Geoengineering pproach to Climate tabilization. cience, 31, 52-5 (2006) 7. B. G. William, Climate control. IEEE pectrum, 5, (2007) 8. B. cott, The incredible Economics o Geoengineering. Environ Resource Econ, (2007),DOI /s K. Mcguie,. Henderson-ellers, Forty years o numerical climate modeling, International Journal o Climatology. 21, (2001) 10. K. zilder, E. P. Lozowski, G. W. Reuter, stochastic model o global atmospheric response to enhanced greenhouse warming with cloud eedback. tmospheric Research,7/8, (1998) 11. K. zilder, E. P. Lozowski. Cloud eedback examined using a two-components time - dependent climate model. Beitr. Phys. tmosph, 68, 3-57(1995) 12. K. zilder, E. P. Lozowski. The inluence o greenhouses warming o the atmospheric component o the hydrological cycle, Hydrological Processes, 10, (1996) 13. B. Peter,. Wolgang, M. Michael. Earth weather and climate control: can space technology contribute? pace Policy, 15, 27-32(1999) 1. C.. Hsu, generalized theory o cell-to-cell mapping or nonlinear dynamical systems. ME J. ppl. Mech, 8, 63-82(1981) 15. P. Mauricio, T. Heng-Ming,. ujeet, Cell mapping or controller design and evaluation. IEEE Control ystems,, 52-65(1997) 16.. Feijun,.M. mith, Cell state space based search. IEEE Control ystems Magazine, 8,2-56(2002) 17. J. Hansen, G. Russell, D. Rind, etc. Eicient three-dimensional global models or climate studies: Model 1 and 2. Monthly Weather Review,111, (1983) 18. EdGCM,
Radiative Forcing Components
 Radiative Forcing Components Content Definition of Radiative Forcing Radiation Balance Climate sensitivity Solar forcing Forcing due to atmospheric gas Definition of Radiative Forcing In climate science,
Radiative Forcing Components Content Definition of Radiative Forcing Radiation Balance Climate sensitivity Solar forcing Forcing due to atmospheric gas Definition of Radiative Forcing In climate science,
Winter 2009: ATMS/OCN/ESS 588 The Global Carbon Cycle and Greenhouse Gases. Course Goals
 PCC 588 - January 6 and 8 2009 Winter 2009: ATMS/OCN/ESS 588 The Global Carbon Cycle and Greenhouse Gases T,Th 12:00-1:20 pm OSB 25 Course Goals The course focuses on factors controlling the global cycle
PCC 588 - January 6 and 8 2009 Winter 2009: ATMS/OCN/ESS 588 The Global Carbon Cycle and Greenhouse Gases T,Th 12:00-1:20 pm OSB 25 Course Goals The course focuses on factors controlling the global cycle
CLIMATE MODELS: LARGE SCALE AND PREDICTABLE
 CCS 5-1 CLIMATE MODELS: LARGE SCALE AND PREDICTABLE 1. Print this file (and associated linked images if any). Also answer the "Concept of the Week" questions in the Weekly Climate News File. (Check for
CCS 5-1 CLIMATE MODELS: LARGE SCALE AND PREDICTABLE 1. Print this file (and associated linked images if any). Also answer the "Concept of the Week" questions in the Weekly Climate News File. (Check for
Uncertainty Analysis and Application of Construction Diversion Tunnel Discharge Capacity
 International Conerence on Mechatronics, Electronic, Industrial and Control Engineering (MEIC 2014) Uncertainty Analysis and Application o Construction Diversion Tunnel Discharge Capacity Wang Changhong*
International Conerence on Mechatronics, Electronic, Industrial and Control Engineering (MEIC 2014) Uncertainty Analysis and Application o Construction Diversion Tunnel Discharge Capacity Wang Changhong*
Module 3. Process Control. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 3 Process Control Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 15 Special Control Structures: Feedorward and Ratio Control Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives At the end o this lesson,
Module 3 Process Control Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 15 Special Control Structures: Feedorward and Ratio Control Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives At the end o this lesson,
Module 3. Process Control. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 3 Process Control Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 15 Special Control Structures: Feedorward and Ratio Control Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives At the end o this lesson,
Module 3 Process Control Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 Lesson 15 Special Control Structures: Feedorward and Ratio Control Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives At the end o this lesson,
Technological processes optimisation according to MSTP procedure
 o Achievements in Materials and Manuacturing Engineering VOLUME 31 ISSUE 2 December 2008 Technological es optimisation according to MSTP procedure R. Nowosielski, A. Kania, M. Spilka Division o Nanocrystalline
o Achievements in Materials and Manuacturing Engineering VOLUME 31 ISSUE 2 December 2008 Technological es optimisation according to MSTP procedure R. Nowosielski, A. Kania, M. Spilka Division o Nanocrystalline
Core Drying Simulation and Validation
 Paper 11-028.pd, Page 1 o 5 Core Drying Simulation and Validation A. Starobin and C.W. Hirt Flow Science, Inc., Santa Fe, NM H. Lang BMW Group, Landshut, Germany M. Todte CFD Consultants GmbH, Rottenburg,
Paper 11-028.pd, Page 1 o 5 Core Drying Simulation and Validation A. Starobin and C.W. Hirt Flow Science, Inc., Santa Fe, NM H. Lang BMW Group, Landshut, Germany M. Todte CFD Consultants GmbH, Rottenburg,
Utilizing Model to Optimize Crop Plant Density: A Case Study on Tomato
 Utilizing Model to Optimize Crop Plant Density: A Case Study on Tomato LiLi Yang, QiaoXue Dong, and Daoliang Li * College o Inormation and Electrical Engineering, China Agricultural University, Beijing,
Utilizing Model to Optimize Crop Plant Density: A Case Study on Tomato LiLi Yang, QiaoXue Dong, and Daoliang Li * College o Inormation and Electrical Engineering, China Agricultural University, Beijing,
Radiative forcing of climate change
 Radiative forcing of climate change Joanna D. Haigh Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, London Radiative forcing concept, definition and applications On a global and annual average, and
Radiative forcing of climate change Joanna D. Haigh Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, London Radiative forcing concept, definition and applications On a global and annual average, and
Utilizing model to optimize crop plant density: a case study on tomato
 Utilizing model to optimize crop plant density: a case study on tomato LiLi Yang 1 QiaoXue Dong 1 Daoliang Li 1 * College o Inormation and Electrical Engineering, China Agricultural University, Beijing,
Utilizing model to optimize crop plant density: a case study on tomato LiLi Yang 1 QiaoXue Dong 1 Daoliang Li 1 * College o Inormation and Electrical Engineering, China Agricultural University, Beijing,
Understanding Global Warming
 Math 483 Spring Semester, 2013 California State University, Northridge Understanding Global Warming Global Warming is Real December 2012 is 334th consecutive Month with global temperatures above the 20th
Math 483 Spring Semester, 2013 California State University, Northridge Understanding Global Warming Global Warming is Real December 2012 is 334th consecutive Month with global temperatures above the 20th
Radiative Forcing and
 Radiative Forcing and Feedbacks in Climate Change Júlio C. S. Chagas Entrenamiento en Modelado Numérico de Escenarios de Cambios Climáticos Cachoeira Paulista, 30 de Agosto 4 de Septiembre de 2009. Definitions
Radiative Forcing and Feedbacks in Climate Change Júlio C. S. Chagas Entrenamiento en Modelado Numérico de Escenarios de Cambios Climáticos Cachoeira Paulista, 30 de Agosto 4 de Septiembre de 2009. Definitions
Some resources (more websites later)
 Some resources (more websites later) Intergovernmental Panel Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis at http://www.ipcc.ch/pub/reports.htm John Houghton Global Warming - the complete briefing Cambridge
Some resources (more websites later) Intergovernmental Panel Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis at http://www.ipcc.ch/pub/reports.htm John Houghton Global Warming - the complete briefing Cambridge
Lecture 8: Anthropogenic Climate Change. Instructor: Prof. Johnny Luo. Acknowledge: IPCC
 Lecture 8: Anthropogenic Climate Change Instructor: Prof. Johnny Luo Acknowledge: IPCC Energy Budget Fluid (atmosphere/ ocean) motions to redistribute energy Energy imbalance (forcing) and climate change
Lecture 8: Anthropogenic Climate Change Instructor: Prof. Johnny Luo Acknowledge: IPCC Energy Budget Fluid (atmosphere/ ocean) motions to redistribute energy Energy imbalance (forcing) and climate change
Klimaänderung. Robert Sausen Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Oberpfaffenhofen
 Klimaänderung Robert Sausen Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Oberpfaffenhofen Vorlesung WS 2017/18 LMU München 8. Anthropogener und natürlicher Strahlungsantrieb
Klimaänderung Robert Sausen Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Oberpfaffenhofen Vorlesung WS 2017/18 LMU München 8. Anthropogener und natürlicher Strahlungsantrieb
Unstable behaviour of RPT when testing turbine characteristics in the laboratory
 IOP Conerence Series: Earth and Environmental Science OPEN ACCESS Unstable behaviour o RPT when testing turbine characteristics in the laboratory To cite this article: T K Nielsen and M Fjørtot Svarstad
IOP Conerence Series: Earth and Environmental Science OPEN ACCESS Unstable behaviour o RPT when testing turbine characteristics in the laboratory To cite this article: T K Nielsen and M Fjørtot Svarstad
A simultaneous heat and water transfer model in frozen and thawed soil
 A simultaneous heat and water transer model in roen and thawed soil Zhenghui Xie Liye Song Aiwen Wang ICCES/LASG Institute o Atmospheric Physics Chinese Academy o Sciences (xie@lasg.iap.ac.cn) Xiaobing
A simultaneous heat and water transer model in roen and thawed soil Zhenghui Xie Liye Song Aiwen Wang ICCES/LASG Institute o Atmospheric Physics Chinese Academy o Sciences (xie@lasg.iap.ac.cn) Xiaobing
APPLICATION OF ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK TECHNOLOGY IN WATER COLOR REMOTE SENSING INVERSION OF INLAND WATER BODY USING TM DATA
 APPLICATION OF ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK TECHNOLOGY IN WATER COLOR REMOTE SENSING INVERSION OF INLAND WATER BODY USING TM DATA J. P. Wang *, S. T. Cheng, H. F. Jia The Department o Environmental Science
APPLICATION OF ARTIFICIAL NEURAL NETWORK TECHNOLOGY IN WATER COLOR REMOTE SENSING INVERSION OF INLAND WATER BODY USING TM DATA J. P. Wang *, S. T. Cheng, H. F. Jia The Department o Environmental Science
TOPIC # 15 GLOBAL WARMING & ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING
 TOPIC # 15 GLOBAL WARMING & ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING Part B The Key To It All: SORTING OUT THE RADIATIVE FORCINGS OF CLIMATE Class Notes p 83 Greenhouse Gas emissions from Forestry (Deforestation, biomass
TOPIC # 15 GLOBAL WARMING & ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING Part B The Key To It All: SORTING OUT THE RADIATIVE FORCINGS OF CLIMATE Class Notes p 83 Greenhouse Gas emissions from Forestry (Deforestation, biomass
WRAP- UP of TOPIC #14 on ANTHROPOGENIC GLOBAL WARMING
 WRAP- UP of TOPIC #14 on ANTHROPOGENIC GLOBAL WARMING p 77 Energy Buildings Transport Industry Forestry Agriculture Waste TOPIC # 14, PART B: Evidence from Natural Archives Class Notes pp 78 KEY GRAPH!
WRAP- UP of TOPIC #14 on ANTHROPOGENIC GLOBAL WARMING p 77 Energy Buildings Transport Industry Forestry Agriculture Waste TOPIC # 14, PART B: Evidence from Natural Archives Class Notes pp 78 KEY GRAPH!
Earth s Climate from Space. Richard Allan Department of Meteorology University of Reading
 Earth s Climate from Space Richard Allan Department of Meteorology University of Reading Earth s energy balance in space S πr 2 4πr 2 Outgoing Thermal Radiative Energy Absorbed Solar Radiative Energy
Earth s Climate from Space Richard Allan Department of Meteorology University of Reading Earth s energy balance in space S πr 2 4πr 2 Outgoing Thermal Radiative Energy Absorbed Solar Radiative Energy
HEAT TRANSFER ANALYSIS OF GEOTHERMAL HEAT EXCHANGERS IN GROUND-COUPLED HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS. Abstract. 1. Introduction
 HEX-01 HEAT TRANSFER ANALYSIS OF GEOTHERMAL HEAT EXCHANGERS IN GROUND-COUPLED HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS Z Fang, N Diao, M Yu, P Cui The Ground Source Heat Pump Research Center Shandong Institute o Architecture
HEX-01 HEAT TRANSFER ANALYSIS OF GEOTHERMAL HEAT EXCHANGERS IN GROUND-COUPLED HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS Z Fang, N Diao, M Yu, P Cui The Ground Source Heat Pump Research Center Shandong Institute o Architecture
2013 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. Permission from IEEE must be obtained for all other uses, in any current or future media,
 213 IEEE. Personal use o this material is permitted. Permission rom IEEE must be obtained or all other uses, in any current or uture media, including reprinting/republishing this material or advertising
213 IEEE. Personal use o this material is permitted. Permission rom IEEE must be obtained or all other uses, in any current or uture media, including reprinting/republishing this material or advertising
CFD Analysis of a Cross-flow Heat Exchanger with Different fin thickness
 International Journal o Dynamics o Fluids. ISSN 0973-1784 Volume 13, Number 2 (2017), pp. 345-362 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com CFD Analysis o a Cross-low Heat Exchanger with
International Journal o Dynamics o Fluids. ISSN 0973-1784 Volume 13, Number 2 (2017), pp. 345-362 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com CFD Analysis o a Cross-low Heat Exchanger with
THE PHYSICAL BASIS FOR EARTH S CLIMATE SYSTEM
 CCS 1-1 THE PHYSICAL BASIS FOR EARTH S CLIMATE SYSTEM Do Now: 1. Print this file. 2. Print the Weekly Climate News file and answer the two Concept of the Week questions in the Weekly Climate News File.
CCS 1-1 THE PHYSICAL BASIS FOR EARTH S CLIMATE SYSTEM Do Now: 1. Print this file. 2. Print the Weekly Climate News file and answer the two Concept of the Week questions in the Weekly Climate News File.
1 Background and Motivation
 Type of activity: Standard study (25 k ) Study Description: Assessment of the Impact of the Release of Greenhouse Gases into the Martian Atmosphere using Numerical Evaluations Derived from Martian GCMs
Type of activity: Standard study (25 k ) Study Description: Assessment of the Impact of the Release of Greenhouse Gases into the Martian Atmosphere using Numerical Evaluations Derived from Martian GCMs
INTEGRATED TIMETABLE AND SCHEDULING OPTIMIZATION WITH MULTIOBJECTIVE EVOLUTIONARY ALGORITHM. Michal Weiszer 1
 The International Journal o TRANSPORT & LOGISTICS Medzinárodný časopis DOPRAVA A LOGISTIKA ISSN 45-07X INTEGRATED TIMETABLE AND SCHEDULING OPTIMIZATION WITH MULTIOBJECTIVE EVOLUTIONARY ALGORITHM Michal
The International Journal o TRANSPORT & LOGISTICS Medzinárodný časopis DOPRAVA A LOGISTIKA ISSN 45-07X INTEGRATED TIMETABLE AND SCHEDULING OPTIMIZATION WITH MULTIOBJECTIVE EVOLUTIONARY ALGORITHM Michal
Robust increase in effective climate sensitivity with transient warming
 Robust increase in effective climate sensitivity with transient warming Kyle C Armour Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences Massachusetts Institute of Technology Ringberg 5 Courtesy of NASA s Earth
Robust increase in effective climate sensitivity with transient warming Kyle C Armour Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences Massachusetts Institute of Technology Ringberg 5 Courtesy of NASA s Earth
NSTA Web Seminar: Earth Then, Earth Now: Our Changing Climate Climate Change Jeopardy
 LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP NSTA Web Seminar: Earth Then, Earth Now: Our Changing Climate Climate Change Jeopardy Presented by Dr. Mike Winton, NOAA Tuesday, March 31, 2009 Climate Change
LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP NSTA Web Seminar: Earth Then, Earth Now: Our Changing Climate Climate Change Jeopardy Presented by Dr. Mike Winton, NOAA Tuesday, March 31, 2009 Climate Change
PERFORMANCE-BASED SEISMIC DESIGN OF REINFORCED CONCRETE BRIDGE COLUMNS
 PERFORMANCE-BASED SEISMIC DESIGN OF REINFORCED CONCRETE BRIDGE COLUMNS Dawn E LEHMAN 1 And Jack P MOEHLE 2 SUMMARY There is a new ocus in seismic design on the perormance o reinorced concrete bridges.
PERFORMANCE-BASED SEISMIC DESIGN OF REINFORCED CONCRETE BRIDGE COLUMNS Dawn E LEHMAN 1 And Jack P MOEHLE 2 SUMMARY There is a new ocus in seismic design on the perormance o reinorced concrete bridges.
TOPIC # 16 GLOBAL WARMING & ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING
 TOPIC # 16 GLOBAL WARMING & ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING TODAY s 3 KEY CONCEPTS: Carbon / Forests / Deforestation Computer Model Evidence for Anthropogenic GW Forcing Tying it all together w/ RADIATIVE FORCING
TOPIC # 16 GLOBAL WARMING & ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING TODAY s 3 KEY CONCEPTS: Carbon / Forests / Deforestation Computer Model Evidence for Anthropogenic GW Forcing Tying it all together w/ RADIATIVE FORCING
FUZZY RELIABILITY ANALYSIS FOR THE EVALUATION OF WATER RESOURCE SYSTEMS PERFORMANCE
 FUZZY RELIABILITY ANALYSIS FOR THE EVALUATION OF WATER RESOURCE SYSTEMS PERFORMANCE Ibrahim El-Baroudy, Shohan Ahmad and Slobodan P. Simonovic Department o Civil and Environmental Engineering, Institute
FUZZY RELIABILITY ANALYSIS FOR THE EVALUATION OF WATER RESOURCE SYSTEMS PERFORMANCE Ibrahim El-Baroudy, Shohan Ahmad and Slobodan P. Simonovic Department o Civil and Environmental Engineering, Institute
Radiative forcing of gases, aerosols and, clouds.
 Lecture 23. Radiative forcing of gases, aerosols and, clouds. 1. Concepts of radiative forcing, climate sensitivity, and radiation feedbacks. 2. Radiative forcing of anthropogenic greenhouse gases. 3.
Lecture 23. Radiative forcing of gases, aerosols and, clouds. 1. Concepts of radiative forcing, climate sensitivity, and radiation feedbacks. 2. Radiative forcing of anthropogenic greenhouse gases. 3.
Climate Change, Greenhouse Gases and Aerosols
 Climate Change, Greenhouse Gases and Aerosols J Srinivasan J Srinivasan is a Professor at the Centre for Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences at Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. He was a lead author
Climate Change, Greenhouse Gases and Aerosols J Srinivasan J Srinivasan is a Professor at the Centre for Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences at Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. He was a lead author
Into the Great Wide Open?: The Potential Promise and Perils of Climate Geoengineering
 Into the Great Wide Open?: The Potential Promise and Perils of Climate Geoengineering Dr. Wil Burns, Forum for Climate Engineering Assessment Dominican University September 14, 2015 Geoengineering [O]ptions
Into the Great Wide Open?: The Potential Promise and Perils of Climate Geoengineering Dr. Wil Burns, Forum for Climate Engineering Assessment Dominican University September 14, 2015 Geoengineering [O]ptions
This is a repository copy of Precipitation, radiative forcing and global temperature change.
 This is a repository copy of Precipitation, radiative forcing and global temperature change. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/43204/ Article: Andrews, T, Forster,
This is a repository copy of Precipitation, radiative forcing and global temperature change. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/43204/ Article: Andrews, T, Forster,
Lecture 29: Detection of Climate Change and Attribution of Causes
 Lecture 29: Detection of Climate Change and Attribution of Causes 1. The Meaning of Detection and Attribution The response to anthropogenic changes in climate forcing occurs against a backdrop of natural
Lecture 29: Detection of Climate Change and Attribution of Causes 1. The Meaning of Detection and Attribution The response to anthropogenic changes in climate forcing occurs against a backdrop of natural
Energy Tutorial: Geoengineering 101
 GLOBAL CLIMATE AND ENERGY PROJECT STANFORD UNIVERSITY Energy Tutorial: Geoengineering 101 GCEP RESEARCH SYMPOSIUM 2012 STANFORD, CA Ken Caldeira Staff Scientist Carnegie Institution Professor (by courtesy)
GLOBAL CLIMATE AND ENERGY PROJECT STANFORD UNIVERSITY Energy Tutorial: Geoengineering 101 GCEP RESEARCH SYMPOSIUM 2012 STANFORD, CA Ken Caldeira Staff Scientist Carnegie Institution Professor (by courtesy)
Risks from Geoengineering
 Risks from Geoengineering (Solar Radiation Management) Alan Robock Rutgers University, New Brunswick, New Jersey robock@envsci.rutgers.edu http://envsci.rutgers.edu/~robock Geoengineering is defined as
Risks from Geoengineering (Solar Radiation Management) Alan Robock Rutgers University, New Brunswick, New Jersey robock@envsci.rutgers.edu http://envsci.rutgers.edu/~robock Geoengineering is defined as
BAYESIAN MODELS AND STOCHASTIC PROCESSES APPLIED TO CSP SAMPLING PLANS FOR QUALITY CONTROL IN PRODUCTION IN SERIES AND BY LOTS
 Proceedings o the 2009 Winter Simulation Conerence M. D. Rossetti, R. R. Hill, B. Johansson, A. Dunkin and R. G. Ingalls, eds. BAYESIAN MODELS AND STOCHASTIC PROCESSES APPLIED TO CSP SAMPLING PLANS FOR
Proceedings o the 2009 Winter Simulation Conerence M. D. Rossetti, R. R. Hill, B. Johansson, A. Dunkin and R. G. Ingalls, eds. BAYESIAN MODELS AND STOCHASTIC PROCESSES APPLIED TO CSP SAMPLING PLANS FOR
Serration characteristic of shaving cutters
 Serration characteristic o shaving cutters The cutting edges o the shaving cutters are perormed along the lank o every tooth through a slotting process which uses tools as per type o igure N 1. Fig.N 1-
Serration characteristic o shaving cutters The cutting edges o the shaving cutters are perormed along the lank o every tooth through a slotting process which uses tools as per type o igure N 1. Fig.N 1-
The Use of Climate Engineering and Climate Change Law
 The Use of Climate Engineering and Climate Change Law Prof. Tracy Hester University of Houston Law Center Houston, Texas Nov. 13, 2017 Geoengineering trials get under way Updated 17:10 14 September 2011
The Use of Climate Engineering and Climate Change Law Prof. Tracy Hester University of Houston Law Center Houston, Texas Nov. 13, 2017 Geoengineering trials get under way Updated 17:10 14 September 2011
Greenhouse gases. A snow-covered surface refl ects massive amounts of sunlight and therefore has a cooling effect on the climate.
 A k t u e l N a t u r v i d e n s k a b 2 0 0 9 G R E E N H O U S E G A S E S 13 Greenhouse gases - and their impact on the climate The greenhouse effect is the best understood and well mapped of the mechanisms
A k t u e l N a t u r v i d e n s k a b 2 0 0 9 G R E E N H O U S E G A S E S 13 Greenhouse gases - and their impact on the climate The greenhouse effect is the best understood and well mapped of the mechanisms
Theoretical Investigation of Hollow Fibres Structure: Relations between Fibre Inner Diameter, Wall Thickness, and Conventional Structural Indices
 ISSN 139 130 MATERIALS SCIENCE (MEDŽIAGOTYRA). Vol. 9, No.. 003 Theoretical Investigation o Hollow Fibres Structure: Relations between Fibre Inner Diameter, Wall Thickness, and Conventional Structural
ISSN 139 130 MATERIALS SCIENCE (MEDŽIAGOTYRA). Vol. 9, No.. 003 Theoretical Investigation o Hollow Fibres Structure: Relations between Fibre Inner Diameter, Wall Thickness, and Conventional Structural
Local and Global Impacts of Climate Change: Predictions of the 5th IPCC Report
 Local and Global Impacts of Climate Change: Predictions of the 5th IPCC Report Peter Schlosser Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences and Department of Earth and Environmental Engineering The Earth
Local and Global Impacts of Climate Change: Predictions of the 5th IPCC Report Peter Schlosser Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences and Department of Earth and Environmental Engineering The Earth
STRUCTURAL, THERMOPHYSICAL AND MECHANICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF METAL FELT WICKS OF MODERN HEAT PIPES
 7th International Heat Pipe Conerence (7 th IHPC) Kanpur, India, October 3-7, 3 STRUCTURAL, THERMOPHYSICAL AND MECHANICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF METAL FELT WICKS OF MODERN HEAT PIPES Gershuni A, Zaripov V
7th International Heat Pipe Conerence (7 th IHPC) Kanpur, India, October 3-7, 3 STRUCTURAL, THERMOPHYSICAL AND MECHANICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF METAL FELT WICKS OF MODERN HEAT PIPES Gershuni A, Zaripov V
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Climate Forcings
 Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Climate Forcings DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES DAY 7: 10-16-13 Outline of This Topic Climate forcings Things that directly
Climate Dynamics (PCC 587): Climate Forcings DARGAN M. W. FRIERSON UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON, DEPARTMENT OF ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES DAY 7: 10-16-13 Outline of This Topic Climate forcings Things that directly
THERMOMECHANICAL FATIGUE MADE EASY
 THERMOMECHANICAL FATIGUE MADE EASY Darrell Socie * and Benjamin Socie + Thermo Mechanical Fatigue ( TMF ) is a complex subject because o the interaction o several ailure modes including atigue, oxidation
THERMOMECHANICAL FATIGUE MADE EASY Darrell Socie * and Benjamin Socie + Thermo Mechanical Fatigue ( TMF ) is a complex subject because o the interaction o several ailure modes including atigue, oxidation
PHY392S Physics of Climate. Lecture 1. Introduction
 PHY392S Physics of Climate Lecture 1 Introduction Slides based on material from Prof. K. Strong PHY392S - Physics of Climate Lecture 1, Page 1 Some Definitions Weather the fluctuating state of the atmosphere
PHY392S Physics of Climate Lecture 1 Introduction Slides based on material from Prof. K. Strong PHY392S - Physics of Climate Lecture 1, Page 1 Some Definitions Weather the fluctuating state of the atmosphere
Using Models to Make Predictions
 Activity APPLY For Educator 45 Minutes Grades 7-12+ Ages 12+ Using Models to Make Predictions How much do humans have to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to prevent major warming? For the complete activity
Activity APPLY For Educator 45 Minutes Grades 7-12+ Ages 12+ Using Models to Make Predictions How much do humans have to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to prevent major warming? For the complete activity
Sensitivity of ocean acidification to geoengineered climate stabilization
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36,, doi:10.1029/2009gl037488, 2009 Sensitivity of ocean acidification to geoengineered climate stabilization H. Damon Matthews, 1 Long Cao,
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36,, doi:10.1029/2009gl037488, 2009 Sensitivity of ocean acidification to geoengineered climate stabilization H. Damon Matthews, 1 Long Cao,
Article Inverse Modeling of Nitrogen Oxides Emissions from the 2010 Russian Wildfires by Using Satellite Measurements of Nitrogen Dioxide
 Article Inverse Modeling o Nitrogen Oides Emissions rom the 2010 Russian Wildires by Using Satellite Measurements o Nitrogen Dioide Evgeny V. Berezin 1, Igor B. Konovalov 1, * and Yulia Y. Romanova 2,
Article Inverse Modeling o Nitrogen Oides Emissions rom the 2010 Russian Wildires by Using Satellite Measurements o Nitrogen Dioide Evgeny V. Berezin 1, Igor B. Konovalov 1, * and Yulia Y. Romanova 2,
EXPERIMENTAL VERIFICATION OF THE CONCRETE SHRINKAGE STRAINS COURSE ACCORDING TO EN STANDARD
 DOI: 10.1515/adms-2015-0009 W. Raczkiewicz, M. Bacharz, K. Bacharz Kielce University o Technology, Faculty o Civil Engineering and Architecture, Department o Strength o Materials and Concrete Structures,
DOI: 10.1515/adms-2015-0009 W. Raczkiewicz, M. Bacharz, K. Bacharz Kielce University o Technology, Faculty o Civil Engineering and Architecture, Department o Strength o Materials and Concrete Structures,
Fitness Uniform Optimization
 Technical Report IDSIA-6-06 Fitness Uniorm Optimization arxiv:cs/06026v [cs.ne] 20 Oct 2006 Abstract Marcus Hutter IDSIA, Galleria 2, CH-6928 Manno-Lugano, Switzerland marcus@idsia.ch In evolutionary algorithms,
Technical Report IDSIA-6-06 Fitness Uniorm Optimization arxiv:cs/06026v [cs.ne] 20 Oct 2006 Abstract Marcus Hutter IDSIA, Galleria 2, CH-6928 Manno-Lugano, Switzerland marcus@idsia.ch In evolutionary algorithms,
Keyur C. Patel a *, Vikas J. Lakhera b, Dilip Sarda c
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 51 ( 013 ) 650 654 Chemical, Civil and Mechanical Engineering Tracks o 3 rd Nirma University International Conerence (NUiCONE 01) Thermal
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 51 ( 013 ) 650 654 Chemical, Civil and Mechanical Engineering Tracks o 3 rd Nirma University International Conerence (NUiCONE 01) Thermal
Pumping optimization in coastal aquifers: Comparison of sharp interface and density dependent models
 European Water 57: 443-449, 2017. 2017 E.W. Publications Pumping optimization in coastal aquiers: Comparison o sharp interace and density dependent models G. Kopsiatis *, V. Christelis and A. Mantoglou
European Water 57: 443-449, 2017. 2017 E.W. Publications Pumping optimization in coastal aquiers: Comparison o sharp interace and density dependent models G. Kopsiatis *, V. Christelis and A. Mantoglou
US climate change impacts from the PAGE2002 integrated assessment model used in the Stern report
 Page 1 of 54 16 November 27 US climate change impacts from the PAGE22 integrated assessment model used in the Stern report Chris Hope & Stephan Alberth Judge Business School, University of Cambridge, UK
Page 1 of 54 16 November 27 US climate change impacts from the PAGE22 integrated assessment model used in the Stern report Chris Hope & Stephan Alberth Judge Business School, University of Cambridge, UK
- geographic patterns of energy balance
 (1 of 10) Further Reading: Chapter 04 of the text book Outline - geographic patterns of energy balance - net radiation - meridional transport (2 of 10) Introduction Previously, we discussed the energy
(1 of 10) Further Reading: Chapter 04 of the text book Outline - geographic patterns of energy balance - net radiation - meridional transport (2 of 10) Introduction Previously, we discussed the energy
Why More Carbon Dioxide Makes Little Difference
 Why More Carbon Dioxide Makes Little Difference A mistake in the climate model architecture changes everything ; trapped energy just reroutes to space on another path Dr David Evans, sciencespeak.com 26
Why More Carbon Dioxide Makes Little Difference A mistake in the climate model architecture changes everything ; trapped energy just reroutes to space on another path Dr David Evans, sciencespeak.com 26
SIMPLE THEORETICAL FORMULA TO ADJUST AMOUNT OF REINFORCEMENT
 SIMPLE THEORETICAL FORMULA TO ADJUST AMOUNT OF REINFORCEMENT Kanaan Sliwo Youkhanna College o Engineering, Universit o Duhok, IRAQ Abstract In construction industr, it is common practice that sometimes
SIMPLE THEORETICAL FORMULA TO ADJUST AMOUNT OF REINFORCEMENT Kanaan Sliwo Youkhanna College o Engineering, Universit o Duhok, IRAQ Abstract In construction industr, it is common practice that sometimes
Global Warming: What is the role of aerosol?
 Global Warming: What is the role of aerosol? Barbara Wyslouzil, Sept. 10 2007 Outline Aerosols 101 The greenhouse effect Global temperature records The global warming problem How do aerosols play a role
Global Warming: What is the role of aerosol? Barbara Wyslouzil, Sept. 10 2007 Outline Aerosols 101 The greenhouse effect Global temperature records The global warming problem How do aerosols play a role
11/16/10. Why do climates change? Take away ideas and understandings. Our first climate model. Climate changes over the last millennium
 Why do climates change? Climate changes over the last millennium Take away ideas and understandings What factors influence climate change over decadal to century timescales? Solar variability, volcanic
Why do climates change? Climate changes over the last millennium Take away ideas and understandings What factors influence climate change over decadal to century timescales? Solar variability, volcanic
Ahlvik, L.; et al. (2018): Optimal geoengineering experiments
 20.09.2018 # New Publications Ahlvik, L.; et al. (2018): Optimal geoengineering experiments Ahlvik, L.; Iho, A. (2018): Optimal geoengineering experiments. In: Journal of Environmental Economics and Management.
20.09.2018 # New Publications Ahlvik, L.; et al. (2018): Optimal geoengineering experiments Ahlvik, L.; Iho, A. (2018): Optimal geoengineering experiments. In: Journal of Environmental Economics and Management.
ATS 421/521. Climate Modeling. Spring Lecture 3 HW1 due. Radiative Forcing Feedbacks Climate Sensitivity. Monday, April 8, 13
 ATS 421/521 Climate Modeling Spring 2013 Lecture 3 HW1 due Radiative Forcing Feedbacks Climate Sensitivity Special lecture at the LaSells Stewart Center: Title: Air Bubbles in Ice, Salt in the Sea Speakers:
ATS 421/521 Climate Modeling Spring 2013 Lecture 3 HW1 due Radiative Forcing Feedbacks Climate Sensitivity Special lecture at the LaSells Stewart Center: Title: Air Bubbles in Ice, Salt in the Sea Speakers:
Global Warming and the Hydrological Cycle
 Global Warming and the Hydrological Cycle Climate Change Projections Wet regions will become wetter Dry regions will become drier Precipitation will occur less frequently Precipitation will be more intense
Global Warming and the Hydrological Cycle Climate Change Projections Wet regions will become wetter Dry regions will become drier Precipitation will occur less frequently Precipitation will be more intense
Will Geoengineering With Solar Radiation Management Ever Be Used? Department of Environmental Sciences, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, New Jersey
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 Will Geoengineering With Solar Radiation Management Ever Be Used? Alan Robock
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 Will Geoengineering With Solar Radiation Management Ever Be Used? Alan Robock
Numerical Simulation of Airflow Temperature Field in Rotary Kiln
 Sensors & Transducers, Vol. 6, Issue, December 03, pp. 7-76 Sensors & Transducers 03 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.com Numerical Simulation o Airlow Temperature Field in Rotary Kiln, Gonga Li, Jia Liu,
Sensors & Transducers, Vol. 6, Issue, December 03, pp. 7-76 Sensors & Transducers 03 by IFSA http://www.sensorsportal.com Numerical Simulation o Airlow Temperature Field in Rotary Kiln, Gonga Li, Jia Liu,
Solutions to Global Warming. World Population Growth
 Solutions to Global Warming World Population Growth Growing Energy Demands World Energy Demand increased by 87% between 1971 and 2002 projected to increase by 60% between 2002 and 2030 U.S. 186.1 Mexico
Solutions to Global Warming World Population Growth Growing Energy Demands World Energy Demand increased by 87% between 1971 and 2002 projected to increase by 60% between 2002 and 2030 U.S. 186.1 Mexico
ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007
 ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007 Name This examination consists of a total of 100 points. In each of the first two sections, you have a choice of which questions to answer. Please note that you
ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007 Name This examination consists of a total of 100 points. In each of the first two sections, you have a choice of which questions to answer. Please note that you
Case 3:17-cv WHA Document Filed 03/23/18 Page 1 of 71 EXHIBIT 5
 Case 3:17-cv-06011-WHA Document 183-5 Filed 03/23/18 Page 1 of 71 EXHIBIT 5 Case 3:17-cv-06011-WHA Document 183-5 Filed 03/23/18 Page 2 of 71 Understanding how carbon dioxide emissions from human activity
Case 3:17-cv-06011-WHA Document 183-5 Filed 03/23/18 Page 1 of 71 EXHIBIT 5 Case 3:17-cv-06011-WHA Document 183-5 Filed 03/23/18 Page 2 of 71 Understanding how carbon dioxide emissions from human activity
An introduction to climate change
 Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications 2012 2012 An introduction to climate change Geoffrey Swan Edith Cowan University This article was originally published as: Swan, G. I. (2012). An
Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications 2012 2012 An introduction to climate change Geoffrey Swan Edith Cowan University This article was originally published as: Swan, G. I. (2012). An
Announcements. Homework 8 - paper 2 topics, questions and sources due Tuesday, Nov. 13 Midterm Paper 2 - due Tuesday, Nov. 20
 Thursday, November 6th. Announcements. Homework 8 - paper 2 topics, questions and sources due Tuesday, Nov. 13 Midterm Paper 2 - due Tuesday, Nov. 20 Lecture #18-1 Lecture #18-2 http://dotearth.blogs.nytimes.com/2007/11/06/project-to-harness-plankton-puts-to-sea/index.html
Thursday, November 6th. Announcements. Homework 8 - paper 2 topics, questions and sources due Tuesday, Nov. 13 Midterm Paper 2 - due Tuesday, Nov. 20 Lecture #18-1 Lecture #18-2 http://dotearth.blogs.nytimes.com/2007/11/06/project-to-harness-plankton-puts-to-sea/index.html
Climate Engineering and Environmental Law
 Climate Engineering and Environmental Law Prof. Tracy Hester Director of Environment, Energy & Natural Resource Center University of Houston Law Center Houston, Texas Sept. 16, 2013 Geoengineering trials
Climate Engineering and Environmental Law Prof. Tracy Hester Director of Environment, Energy & Natural Resource Center University of Houston Law Center Houston, Texas Sept. 16, 2013 Geoengineering trials
Environmental Engineering Atmosphere & pollution 2
 Environmental Engineering Atmosphere & pollution 2 Global radiation Greenhouse effect Kyoto protocol David Zumr Dpt. of Drainage, Irrigation and Landscape Eng. 1/ insolation from the Sun Electromagnetic
Environmental Engineering Atmosphere & pollution 2 Global radiation Greenhouse effect Kyoto protocol David Zumr Dpt. of Drainage, Irrigation and Landscape Eng. 1/ insolation from the Sun Electromagnetic
Evaluating the impact of standards and fiscal policies on CO 2 emissions of cars in Europe. Abstract. Introduction
 Evaluating the impact o standards and iscal policies on CO 2 emissions o cars in Europe Amela Ajanovic, Vienna University o Technology, Ailiation, Vienna, Austria Reinhard Haas, Vienna University o Technology,
Evaluating the impact o standards and iscal policies on CO 2 emissions o cars in Europe Amela Ajanovic, Vienna University o Technology, Ailiation, Vienna, Austria Reinhard Haas, Vienna University o Technology,
On Evaluating Optimality Losses of Greenhouse Climate Controllers
 Proceedings o the 7th World Congress he International Federation o Automatic Control On Evaluating Optimality Losses o Greenhouse Climate Controllers G. van Straten and L.G. van Willigenburg * Wageningen
Proceedings o the 7th World Congress he International Federation o Automatic Control On Evaluating Optimality Losses o Greenhouse Climate Controllers G. van Straten and L.G. van Willigenburg * Wageningen
Adequacy of the U10 & L11 Gusset Plate Designs for the Minnesota Bridge No (I-35W over the Mississippi River) INTERIM REPORT
 FEDERAL HIGHWAY ADMINISTRATION TURNER-FAIRBANK HIGHWAY RESEARCH CENTER REPORT Adequacy o the U10 & L11 Gusset Plate Designs or the Minnesota Bridge No. 9340 (I-35W over the Mississippi River) INTERIM REPORT
FEDERAL HIGHWAY ADMINISTRATION TURNER-FAIRBANK HIGHWAY RESEARCH CENTER REPORT Adequacy o the U10 & L11 Gusset Plate Designs or the Minnesota Bridge No. 9340 (I-35W over the Mississippi River) INTERIM REPORT
MODEL FOR CALCULATION OF CREEP AND SHRINKAGE OF FIBER REINFORCED CONCRETE
 MODEL FOR CALCULATION OF CREEP AND SHRINKAGE OF FIBER REINFORCED CONCRETE Dusan Spura, Jan Vodicka, Jiri Kratky Czech Technical University, Faculty o Civil Engineering, Prague, Czech Republic Abstract
MODEL FOR CALCULATION OF CREEP AND SHRINKAGE OF FIBER REINFORCED CONCRETE Dusan Spura, Jan Vodicka, Jiri Kratky Czech Technical University, Faculty o Civil Engineering, Prague, Czech Republic Abstract
Understanding how carbon dioxide emissions from human activity contribute to global climate change MYLES ALLEN Environmental Change Institute, School
 Understanding how carbon dioxide emissions from human activity contribute to global climate change MYLES ALLEN Environmental Change Institute, School of Geography and the Environment & Department of Physics
Understanding how carbon dioxide emissions from human activity contribute to global climate change MYLES ALLEN Environmental Change Institute, School of Geography and the Environment & Department of Physics
Outline. should believe in global warming. prediction of climate change Is it us and what will it mean? extreme weather Barriers to progress?
 Outline What s happening to our climate and why we should believe in global warming Climate modelling and the attribution and prediction of climate change Is it us and what will it mean? Big issues and
Outline What s happening to our climate and why we should believe in global warming Climate modelling and the attribution and prediction of climate change Is it us and what will it mean? Big issues and
Advanced Control Strategies for a Bioreactor Based on an Alternative Structured Kinetic Model
 Advanced Control Strategies or a Bioreactor Based on an Alternative Structured Kinetic Model Dile Pontarolo Stremel 1, Eduardo Coselli Vasco de Toledo 2* and Rubens Maciel Filho 2 1 ENGEPRO Universidade
Advanced Control Strategies or a Bioreactor Based on an Alternative Structured Kinetic Model Dile Pontarolo Stremel 1, Eduardo Coselli Vasco de Toledo 2* and Rubens Maciel Filho 2 1 ENGEPRO Universidade
Use of a spatial process-based model to quantify forest plantation productivity and water use efficiency under climate change scenarios
 18 th World IMACS / MODSIM Congress, Cairns, Australia 1-1 July 29 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim9 Use o a spatial process-based model to quantiy orest plantation productivity and water use eiciency under
18 th World IMACS / MODSIM Congress, Cairns, Australia 1-1 July 29 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim9 Use o a spatial process-based model to quantiy orest plantation productivity and water use eiciency under
An Unsettling Look at the Settled Science of Global Warming Part 2: Layman s Discussion John Eggert P.Eng.
 An Unsettling Look at the Settled Science of Global Warming Part 2: Layman s Discussion John Eggert P.Eng. Introduction This is the second of three papers on the impact of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) on climate.
An Unsettling Look at the Settled Science of Global Warming Part 2: Layman s Discussion John Eggert P.Eng. Introduction This is the second of three papers on the impact of Carbon Dioxide (CO2) on climate.
2. Climate Change: Projections of Climate Change: 2100 and beyond
 Global Warming: Science, Projections and Uncertainties Global Warming: Science, Projections and Uncertainties An overview of the basic science An overview of the basic science 1. A Brief History of Global
Global Warming: Science, Projections and Uncertainties Global Warming: Science, Projections and Uncertainties An overview of the basic science An overview of the basic science 1. A Brief History of Global
Existing Gravity System
 Existing Gravity System Duquesne University s Multipurpose Athletic Facility is supported by a steel superstructure, including a composite steel loor system. Each o the irst three loors is ramed in rectangular
Existing Gravity System Duquesne University s Multipurpose Athletic Facility is supported by a steel superstructure, including a composite steel loor system. Each o the irst three loors is ramed in rectangular
Investigation Into The Floor Diaphragm Flexibility In Rectangular Reinforced Concrete Buildings And Error Formula
 The th World Conerence on Earthquake Engineering October 7, 008, Beijing, China Investigation Into The Floor Diaphragm Flexibility In Rectangular Reinorced Concrete Buildings And Error Formula M. Moeini,
The th World Conerence on Earthquake Engineering October 7, 008, Beijing, China Investigation Into The Floor Diaphragm Flexibility In Rectangular Reinorced Concrete Buildings And Error Formula M. Moeini,
ESS 312 Geochemistry. Simulating Steady State: The Carbon Cycle and the Effect of Burning Fossil Fuels
 ESS 312 Geochemistry Simulating Steady State: The Carbon Cycle and the Effect of Burning Fossil Fuels Objectives: Many problems in earth sciences involve understanding how mass is transferred among different
ESS 312 Geochemistry Simulating Steady State: The Carbon Cycle and the Effect of Burning Fossil Fuels Objectives: Many problems in earth sciences involve understanding how mass is transferred among different
Combating Climate Change with Geoengineering Daniel Callies
 Policy Brief Environment Outlooks May 2016 Combating Climate Change with Geoengineering Daniel Callies Summary This series of policy briefs provides an independent commentary on current themes associated
Policy Brief Environment Outlooks May 2016 Combating Climate Change with Geoengineering Daniel Callies Summary This series of policy briefs provides an independent commentary on current themes associated
SHEAR AND DIAGONAL TENSION IN BEAMS
 CHAPTER REINFORCED CONCRETE Reinorced Concrete Design Fith Edition A Fundamental Approach - Fith Edition SHEAR AND DIAGONAL TENSION IN BEAMS A. J. Clark School o Engineering Department o Civil and Environmental
CHAPTER REINFORCED CONCRETE Reinorced Concrete Design Fith Edition A Fundamental Approach - Fith Edition SHEAR AND DIAGONAL TENSION IN BEAMS A. J. Clark School o Engineering Department o Civil and Environmental
The Chemistry of Climate Change. Reading: Chapter 8 Environmental Chemistry, G. W. vanloon. S. J. Duffy
 The Chemistry of Climate Change Reading: Chapter 8 Environmental Chemistry, G. W. vanloon. S. J. Duffy The Science of Global Climate There's a lot of differing data, but as far as I can gather, over the
The Chemistry of Climate Change Reading: Chapter 8 Environmental Chemistry, G. W. vanloon. S. J. Duffy The Science of Global Climate There's a lot of differing data, but as far as I can gather, over the
EFFECT OF DIFFERENT MICRO STRUCTURES ON HEAT DISSIPATION OF CPU SURFACE HEAT SINK
 SCIENTIFIC PAPERS EFFECT OF DIFFERENT MICRO STRUCTURES ON HEAT DISSIPATION OF CPU SURFACE HEAT SINK Yan WANG 1,a ABSTRACT: In order to discuss the heat dissipation perormance o CPU heat sink, based on
SCIENTIFIC PAPERS EFFECT OF DIFFERENT MICRO STRUCTURES ON HEAT DISSIPATION OF CPU SURFACE HEAT SINK Yan WANG 1,a ABSTRACT: In order to discuss the heat dissipation perormance o CPU heat sink, based on
Feedbacks of Ice and Clouds
 Activity DEVELOP For Educator 45 Minutes Grades 7-12+ Ages 12+ Feedbacks of Ice and Clouds How do ice and clouds cool the Earth? For the complete activity with media resources, visit: http://education.nationalgeographic.com/education/activity/feedbacks-ice-and-clouds/
Activity DEVELOP For Educator 45 Minutes Grades 7-12+ Ages 12+ Feedbacks of Ice and Clouds How do ice and clouds cool the Earth? For the complete activity with media resources, visit: http://education.nationalgeographic.com/education/activity/feedbacks-ice-and-clouds/
Radiation and Climate Change
 Radiation and Climate Change Earth s Energy Balance Forcing and Feedback Implications for climate change including the global water cycle Introduction / Motivations Past societies e.g. Jared Diamond: Collapse
Radiation and Climate Change Earth s Energy Balance Forcing and Feedback Implications for climate change including the global water cycle Introduction / Motivations Past societies e.g. Jared Diamond: Collapse
The Earth s Global Energy Balance
 The Earth s Global Energy Balance Electromagnetic Radiation Insolation over the Globe World Latitude Zones Composition of the Atmosphere Sensible Heat and Latent Heat Transfer The Global Energy System
The Earth s Global Energy Balance Electromagnetic Radiation Insolation over the Globe World Latitude Zones Composition of the Atmosphere Sensible Heat and Latent Heat Transfer The Global Energy System
Major Volcanic Eruptions in the past. Major Volcanic Eruptions in the past. Volcanic Eruptions and Global Temperature
 Mechanism of Volcanic Perturbation Amount of sunlight scattered depends greatly on size and amount of aerosol particles The global monitoring of aerosols began in ~1980 Hence, the history of the amplitude
Mechanism of Volcanic Perturbation Amount of sunlight scattered depends greatly on size and amount of aerosol particles The global monitoring of aerosols began in ~1980 Hence, the history of the amplitude
Multiple Fires in a Mine Drift with Longitudinal Ventilation
 Multiple Fires in a Mine Drit with Longitudinal Ventilation Analysis o ire behaviour o perormed ire experiments in a model scale mine drit Rickard Hansen Table o Contents Abstract... 3 Nomenclature...
Multiple Fires in a Mine Drit with Longitudinal Ventilation Analysis o ire behaviour o perormed ire experiments in a model scale mine drit Rickard Hansen Table o Contents Abstract... 3 Nomenclature...
TORSIONAL STRENGTHENING OF SPANDREL BEAMS WITH COMPOSITE LAMINATES. Abstract
 TORSIONAL STRENGTHENING OF SPANDREL BEAMS WITH COMPOSITE LAMINATES Pedro Salom, Zapata Engineering, Charlotte, NC Janos Gergely, UNC Charlotte, Charlotte, NC David T. Young, UNC Charlotte, Charlotte, NC
TORSIONAL STRENGTHENING OF SPANDREL BEAMS WITH COMPOSITE LAMINATES Pedro Salom, Zapata Engineering, Charlotte, NC Janos Gergely, UNC Charlotte, Charlotte, NC David T. Young, UNC Charlotte, Charlotte, NC
Climate Change: What do we know and what do we guess?
 What do we know and what do we guess? Manfred Grasserbauer * Vienna University of Technology * Director Institute for Environment and Sustainability, Joint Research Centre, European Commission (Ispra)
What do we know and what do we guess? Manfred Grasserbauer * Vienna University of Technology * Director Institute for Environment and Sustainability, Joint Research Centre, European Commission (Ispra)
THE IMPORTANCE OF THE TROPICAL HOT SPOT TO EPA S ENDANGERMENT FINDING
 THE IMPORTANCE OF THE TROPICAL HOT SPOT TO EPA S ENDANGERMENT FINDING On September 21, 2016, a new Research Report by James P. Wallace, III, John R. Christy and Joseph S. D Aleo, On the Existence of a
THE IMPORTANCE OF THE TROPICAL HOT SPOT TO EPA S ENDANGERMENT FINDING On September 21, 2016, a new Research Report by James P. Wallace, III, John R. Christy and Joseph S. D Aleo, On the Existence of a
