Nitrogen absorption by Sparganium erectum L. and Typha domingensis (Pers.) Steudel grown as floaters
|
|
|
- Aileen Paul
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TÍTULO DEL TRABAJO Nitrogen absorption by Sparganium erectum L. and Typha domingensis (Pers.) Steudel grown as floaters TÍTULO RESUMIDO Nitrogen absorption by macrophytes grown as floaters NOMBRE DE AUTORES Mª Dolores Curt*, Pedro L. Aguado and Jesús Fernández NOMBRE Y DIRECCIÓN DE LAS INSTITUCIONES Dpto. Producción Vegetal: Botánica y Protección Vegetal. Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, Madrid (Spain) NÚMERO DE TELÉFONO, FAX Y Tfno: ; Fax: ; md.curt@upm.es FIGURAS Y TABLAS 3 tablas.
2 NITROGEN ABSORPTION BY Sparganium erectum L. AND Typha domingensis (Pers.) Steudel GROWN AS FLOATERS Mª Dolores Curt*, Pedro L. Aguado and Jesús Fernández Dpt. Producción Vegetal: Botánica y Protección Vegetal. Universidad Politécnica de Madrid. ABSTRACT The aim of this work was to study the uptake of nitrogen by young plants of Sparganium erectum L. y Typha domingensis (Pers.) Steudel in the period that follows their implantation in an induced floating system. The effect of the N-form was studied by isotopic tracers. Results showed that both species rapidly absorb N from the nutrient medium whether it is in the ammonia or nitric form. In the species studied, the rate of N absorption per unit of dry weight was similar for the two mineral N forms. S. erectum was revealed more efficient than T. domingensis in the removal of N. KEY-WORDS: Macrophytes, floaters, nitrogen, isotopes. ESTUDIO ISOTÓPICO DE LA ABSORCIÓN DE NITRÓGENO POR Sparganium erectum L. Y Typha domingensis (Pers.) Steudel DESARROLLADAS EN FLOTACIÓN RESUMEN En este trabajo se estudia mediante trazadores isotópicos la absorción de nitrógeno en forma amoniacal y nítrica por plantas jóvenes de Sparganium erectum L. y Typha domingensis (Pers.) Steudel durante el período inmediatamente posterior a su implantación en un sistema de flotación inducida. Los resultados mostraron que las dos especies absorbían rápidamente nitrógeno procedente de las dos formas aplicadas. En una misma especie, la tasa de absorción por unidad de peso seco fue similar para cualquiera de las dos formas aplicadas de nitrógeno. S. erectum resultó ser más eficiente que T. domingensis en la remoción del nitrógeno. PALABRAS CLAVE: Macrofitas, flotantes, nitrógeno, isótopos. 1. INTRODUCTION Constructed wetlands are wastewater treatment systems based on natural processes of depuration stimulated by plants. Physical, chemical and biological mechanisms interact in these systems resulting in the removal of water contaminants. Constructed wetlands are especially well suited for organic-type wastewater produced by small villages or by agricultural activities. One of the most common contaminant in this type of wastewater is the nitrogen, which can be in the organic nitrogen form (N org ) or in the mineralized nitrogen form (N-NH 4 and N-NO 3, mostly). The proportion of N org over total nitrogen can be high in municipal raw wastewaters and farming effluents, but it is transformed to ammonium nitrogen sooner or later as a result of organic matter degradation. Mineral nitrogen is one the prime contaminants causing eutrophication of water resources and, the same as other water contaminants, it has to be removed before the discharge of the wastewater to the environment. On the whole, three types of constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment are recognized: i) surface flow wetlands, also known as free water surface wetlands (FWS), ii) subsurface flow wetlands (SFW) or vegetated submerged beds, and iii) aquatic systems. Plant species used for wastewater treatment vary from one type to another. FWS and SFW are usually vegetated with emergent plants, like cattails (Typha spp), that are rooted in the bottom of the wetland. The third type of wastewater treatment system is vegetated with species exhibiting natural floating habit, like the water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes). More recently, a mixed system named Floating Macrophytes Filter has been proposed to treat wastewater. In that system, emergent plants are grown as floaters to join the advantages of the systems based on emergent plants and those based on aquatic plants. Knowledge of the
3 performance of emergent plants grown as floaters is a subject of growing interest for the development of this new system of wastewater treatment. This study is framed within the research and development line of the wastewater treatment system Floating Macrophytes Filter by the Polytechnic University of Madrid. Young plants of Sparganium erectum L. and Typha domingensis (Pers.) Steudel grown as floaters are studied for nitrogen absorption. Specific objectives of this work were i) to determine if just after the implantation these plants uptake nitrogen and ii) if nitrogen absorption is dependent on the mineralized nitrogen form. 2. MATERIAL AND METHODS 2.1. Experimental design and plant material The experiment was carried out using the stable nitrogen isotope 15 N as a tracer. In order to reproduce the same growing conditions in every trial, the nitrogen source formula was the same, NH 4 NO 3 and it was applied to the nutrient medium at a same dose. The experimental design was the following: 2 macrophytes species (Sparganium erectum L., Typha domingensis (Pers.) Steudel) x 3 treatments ( 15 NO 3 NH 4, 15 NH 4 NO 3, NH 4 NO 3 ) x 4 replications. Plants for this study came from the macrophytes nursery of the Agroenergy Group (GA) sited at the Polytechnic University of Madrid (Spain). T. domingensis plants were produced from seed in cell trays filled with a substrate 5 made up of 50% sand+50% peat. S. erectum plants were produced by vegetative propagation, given that the seeds produced from this species in the GA experimental conditions are not viable. At the phenological stage of 3-4 welldeveloped leaves -about cm plant length- the plants were taken off the cells in order to remove every substrate particulate. Then the plants were allowed to acclimatize in nutritive solution for 14 days. For that purpose the nutritive solution was prepared from a soluble fertilizer to the concentration of 50 ppm N, P 2 O 5 and K 2 O; micronutrients Fe, Mn, B, Cu, Zn, Mo were also included in the formulae of that fertilizer. At the end of the acclimatization period, a random sampling (n=4) was performed in order to characterize the plant biomass at the starting point of the experiment Experiment conditions The experiment was carried out in a controlled environment cabinet. Growing conditions were the following: 25ºC-20ºC light-dark temperature, light-dark cycle of 16 to 8 h, fluorescence light source (Gro-Lux 58 W lights; average PAR 53 µmol m -2 s -1 ). The trials were performed in square grass containers sizing 19 x 19 x 9 cm, in which 1 L nutritive solution without N had been poured in. Just before introducing the plants into the containers, 50 mg of the planned nitrogen source were added per litre of nutritive solution. The N- treatments were 15 NO 3 NH 4 with 9% 15 N (at%) as N- 15 NO 3 and 15 NH 4 NO 3 with 10 at% as N- 15 NH 4 ; besides, a control treatment with NH 4 NO 3 natural enrichment was performed. Just after adding the N-source, four young plants of the same species -previously acclimatized in the growth cabinet- were transferred per container. The container water surface was kept free and in order to compensate losses by evapotranspiration, N-free nutritive solution was periodically added as required. The N-free nutritive solution used for the trials was prepared at the laboratory, with MgSO 4 ( M), KH 2 PO 4 ( M), CaCl 2 ( M) and KCl ( M). A microelements solution was prepared from KCl (1.864 mg/l), H 3 BO 3 (773 mg/l), MnSO 4.H 2 O (423 mg/l), ZnSO 4.7H 2 O (288 mg/l), CuSO4.5H 2 O (63 mg/l), (NH 4 ) 6 Mo 7 O 44.4 H 2 O (9.2 mg/l) and
4 FeCl 3 (4.09 mg/l), which was added at a rate of 2 ml/l nutritive solution. Additionally, 1 ml algicide (CuSO 4.5H 2 O, 4 g/l) was added as well. Plants were allowed to grow under the abovementioned conditions for two weeks. On day 14 the whole plant material was harvested to proceed to the analytic determinations Analytic methods Each plant was separately evaluated and analysed. Shoot and roots were cut into pieces and dried at 105ºC in an air-fan oven; then, they were finely ground using an IKA analytic grinder mod. A10. Isotopic analysis were conducted following the ANCA/MS methodology. This involves interfacing an automatic nitrogen/carbon elemental analyser (ANCA) to a mass spectrometer (MS) for isotope ratio (Mulvaney 1993), operated by PC. Conveniently calibrated, the system provides data of nitrogen content (N% on dry weight basis, ANCA) and isotope ratio ( 15 N/N t as at %) from a single sample. In this experiment we used an elemental analyser model NA 2000 of FISON Inst., coupled to a mass spectrometer DELTA-plus of Finnigan MAT with an interface ConFlo II of Finnigan MAT. All the samples were analysed with 3 replications. Sampling size was about 2 mg dry weight, accurately determined to 0.01 mg precision. 3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Table 1 shows the results of plant characterization at the starting point of the experiment. The average dry weight of T. domingensis plants was about 75% higher than S. erectum in spite of the fact that the plant size was similar (? 15 cm shoot length); this is attributed to the lower biomass density of the latter. On the contrary, the N% of S. erectum was higher than that of T. domingensis. The results obtained after the complexion of the tracer trials are given in Table 2. In the experiment conditions, the plants grew more than 50% (dry weight basis) over the study period. The nitrogen content of S. erectum biomass was kept higher than that of T. domingensis. Non-significant differences were found between the N% of a same species; this result was expected from the fact that the nitrogen source and nitrogen dose was the same for every treatment (50 mg NH 4 NO 3 /L nutritive solution). The results of at% showed that both species took up 15 N from the nutritive solution; this indicating that the young plants of S. erectum and T. domingensis are able to uptake nitrogen immediately after they are implanted in a floating system. The higher at% of S. erectum suggested that the rate of N absorption of that species is higher than that of T. domingensis, consistent with the fact that the former has higher N content. From the results in Table 2, the average dry weight of plant biomass and the weighed values of total nitrogen content, the 15 N content in the plants of each treatment is calculated. The values are shown in Table 3. The effect of the N-form is given in the values of 15 N content (?g 15 N/g dm) respective to the control treatment. The performance of both species was similar in that, for a same species, the 15 N content for the two N-treatments ( 15 N-NO 3 and 15 N-NH 4 ) was similar. The values were few higher for the ammonia treatment. The fact that the tracer used for the N-NH 4 treatment were more enriched in 15 N (10 at% versus 9 at%) could explain the difference between the values of both treatments. S. erectum accumulated more 15 N per unit of dry weight than T. domingensis, this fact suggests that S. erectum is more efficient (>60%) in the removal of N. The recovery percentage of applied tracer in plant biomass is calculated from the results of biomass dry weight and 15 N content, respective to the amount of 15 N applied in each
5 treatment. Table 3 shows that Sparganium and Typha, grown as floaters, yield similar % recovery (60.5%) in the ammonia N treatment; therefore, the higher N-removal efficiency of Sparganium compensated the effect of the dry weight -lower figures- of Sparganium in this experiment. This was not the case for the 15 N-NO 3 treatment, in which T. domingensis recovered more nitrogen (76.5%) than S. erectum (67.8%). Lusby et al (1998), in a 15 N study of the fate of N-NH 4 in Typha orientalis, obtained 4.5 to 21% recovery for single plants (10-15 cm length) grown in sediment columns for 28 days, simulating a natural wetland. Isotope ratio analysis of the nutritive solution sampled at the end of the experiment clearly showed the presence of the 15 N tracer. Average values obtained for the trials with S. erectum were at% (N- 15 NO 3 treatment) y at% (N- 15 NH 4 ), and for T. domingensis at% (N- 15 NO 3 ) and at% (N- 15 NH 4 ). These figures showed that nitrogen was still available in the nutritive solution at the end of the experiment. Therefore, the possible nitrogen losses by volatilization or de-nitrification -nitrogen lost from the system- plus the nitrogen recovered in the plant biomass did not exhaust the amount of nitrogen applied to the nutrient medium. From the results of % recovery of the two N forms, the rate of N absorption is estimated. The young plants of S. erectum y T. domingensis grown as floaters in a solution containing 17.5 ppm N (50% N-NO % N-NH 4 ) absorbed and mg N/g dm/day respectively. These figures are equivalent to a N uptake of and mg N/plant/day for S. erectum y T. domingensis, respectively, given that the average biomass dry weight in the period was g/plant and g/plant, respectively. 4. CONCLUSIONS From the results obtained in this work, the following conclusions are drawn:??young plants of S. erectum y T. domingensis, grown as floaters, are able to uptake nitrogen in the nitric and ammonia form after they are implanted in the system.??for a same species, the rate of N absorption is similar when the nitrogen is supplied in the ammonia or nitric form; the treatment with N-NH 4 resulted in values very few higher than the treatment with N-NO 3.??The average rate of absorption of mineral N (N-NO 3 + N-NH 4 ) by young plants of S. erectum y T. domingensis, grown as floaters, is estimated at y mg N/g dm/day, respectively.?? S. erectum is more efficient in the removal of N than T. domingensis, no matter the mineral N form.??the advantage of S. erectum of being more efficient in the removal of N may be masked by differences in biomass dry weight. 5. REFERENCES EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (1988). Constructed wetlands and aquatic plant systems for municipal wastewater treatment. Design manual EPA/625/1-88/ pp. EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (1999). Constructed wetlands. Treatment of municipal wastewaters. Manual EPA/625/R-99/ pp.
6 Mulvaney, R.L., Mass spectrometry. In: Knowles R., Blackburn, T.H. (Eds.), Nitrogen Isotope Techniques. Academic Press, Inc., San Diego, CA, pp Lusby, F.E., Gibbs, M.M., Cooper, A.B., Thompson, K. (1998). The fate of groundwater ammonium in a lake edge wetland. J. Environ. Qual. 27, ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This work was partially funded by the Project LIFE-Environment of the EU New floating macrophytes green filters (FMF) for the Mediterranean region ( ).
7 7. TABLAS Y FIGURAS Table 1. Characterization of young plants of Sparganium erectum y Typha domingensis at the starting point of the experiment. DW, dry weight; N, content in total nitrogen (dry we ight basis); at, atomic isotope ratio 15 N/N total. (n=4) Species Shoot Roots DW (g) N (%) at (%) DW (g) N (%) at (%) S. erectum T. domingensis Table 2. Characterization of young plants of Sparganium erectum y Typha domingensis at the end of the experiment. DW, dry weight; N, content in total nitrogen (dry weight basis); at, atomic isotope ratio 15 N/N total. (n=4) Treatment Species Shoot Roots DW (g) N (%) at (%) DW (g) N (%) at (%) N- 15 NO 3 S. erectum T. domingensis N- 15 NH 4 S. erectum T. domingensis Control S. erectum T. domingensis Table 3. Balance of the experiment. DW, plant biomass dry weight; N, plant biomass content in nitrogen (weighed mean);? at, isotope ratio increment respective to control; %recovery, recovery of added 15 N in plant biomass; dm, dry matter. Treatment Species DW (g) N (%)? at (%) 15 N derived from tracer (µg 15 N/g dm) % recovery N- 15 NO 3 S. erectum T. domingensis N- 15 NH 4 S. erectum T. domingensis
STUDIES ON REMOVAL OF TOXIC HEAVY METALS FROM WATER BY Eichhornia crassipes
 Indian J.Sci.Res.3(2) : 99-103, 2012 STUDIES ON REMOVAL OF TOXIC HEAVY METALS FROM WATER BY Eichhornia crassipes a1 SUJATA GAHERWAR AND PRAGYA KULKARNI b a Department of Botany, Shri Shankaracharya Mahavidyalaya,
Indian J.Sci.Res.3(2) : 99-103, 2012 STUDIES ON REMOVAL OF TOXIC HEAVY METALS FROM WATER BY Eichhornia crassipes a1 SUJATA GAHERWAR AND PRAGYA KULKARNI b a Department of Botany, Shri Shankaracharya Mahavidyalaya,
Scientific registration n o : 2587 Symposium n o : 25 Presentation: poster. OLEK Jolanta, FILIPEK Tadeusz
 Scientific registration n o : 587 Symposium n o : 5 Presentation: poster Content and uptake of cadmium and lead by spring under conditions of sewage application Contenu et consommation de cadmium et plomb
Scientific registration n o : 587 Symposium n o : 5 Presentation: poster Content and uptake of cadmium and lead by spring under conditions of sewage application Contenu et consommation de cadmium et plomb
Wild Rice Juvenile Seedling Growth Test: Anoxic Conditions
 Wild Rice Juvenile Seedling Growth Test: Anoxic Conditions Experimental Method for Hydroponic Sulfide Toxicity Testing in Anoxic Conditions Using Zizania palustris (Wild Rice) as Test Organism 1.1 Scope
Wild Rice Juvenile Seedling Growth Test: Anoxic Conditions Experimental Method for Hydroponic Sulfide Toxicity Testing in Anoxic Conditions Using Zizania palustris (Wild Rice) as Test Organism 1.1 Scope
Can Sugar Beet Juice Effluent Be Used as a Biofertilizer?
 Can Sugar Beet Juice Effluent Be Used as a Biofertilizer? WRPI/USDA WATERSHED MANAGEMENT PROJECT REPORT Anna Allen USDA-ARS-SJVASC 9611 E. RIVERBEND AVE. PARLIER, CA 93648 1 Table of Contents Acknowledgements...
Can Sugar Beet Juice Effluent Be Used as a Biofertilizer? WRPI/USDA WATERSHED MANAGEMENT PROJECT REPORT Anna Allen USDA-ARS-SJVASC 9611 E. RIVERBEND AVE. PARLIER, CA 93648 1 Table of Contents Acknowledgements...
LECTURE 17 SOIL TESTING. Soil Testing, STL Functions. Soil Testing
 LECTURE 17 SOIL TESTING Soil Testing, STL Functions Soil Testing Soil testing is defined as a programme for procedural evaluation of soil fertility by Rapid chemical analysis particularly to assess the
LECTURE 17 SOIL TESTING Soil Testing, STL Functions Soil Testing Soil testing is defined as a programme for procedural evaluation of soil fertility by Rapid chemical analysis particularly to assess the
TR02-5. Technical Re.port. Application of Anaerobically Digested Biosolids to Dryland Winter Wheat
 Technical Re.port TR02-5 Agricultural - Department of Cooperative April 2002. Experiment Soil and Crop Extension Station Sciences i Application of Anaerobically Digested Biosolids to Dryland Winter Wheat
Technical Re.port TR02-5 Agricultural - Department of Cooperative April 2002. Experiment Soil and Crop Extension Station Sciences i Application of Anaerobically Digested Biosolids to Dryland Winter Wheat
Combination of biochar adsorption and struvite precipitation for nutrients removal from wastewater and its use as fertilizer
 Combination of biochar adsorption and struvite precipitation for nutrients removal from wastewater and its use as fertilizer Tao Xie, Krishna R. Reddy Department of Civil and Materials Engineering, University
Combination of biochar adsorption and struvite precipitation for nutrients removal from wastewater and its use as fertilizer Tao Xie, Krishna R. Reddy Department of Civil and Materials Engineering, University
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development ROOT ZONE METHOD FOR TREATMENT OF WASTE WATER
 Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.72 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 4, Issue 2, February -2017 e-issn (O): 2348-4470 p-issn (P): 2348-6406 ROOT
Scientific Journal of Impact Factor (SJIF): 4.72 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 4, Issue 2, February -2017 e-issn (O): 2348-4470 p-issn (P): 2348-6406 ROOT
Photochemical studies of Eichhornia crassipes (Water Hyacinth)
 International Letters of Chemistry, Physics and Astronomy Online: 2014-03-12 ISSN: 2299-3843, Vol. 30, pp 214-222 doi:10.18052/www.scipress.com/ilcpa.30.214 2014 SciPress Ltd., Switzerland Photochemical
International Letters of Chemistry, Physics and Astronomy Online: 2014-03-12 ISSN: 2299-3843, Vol. 30, pp 214-222 doi:10.18052/www.scipress.com/ilcpa.30.214 2014 SciPress Ltd., Switzerland Photochemical
The National Center for Agricultural Research and Extension
 The National Center for Agricultural Research and Extension Treatment and Reuse of Wastewater Using Surface and Subsurface Wetlands Dr. Luna Al-Hadidi 13th IWA Specialized Conference on Small Water and
The National Center for Agricultural Research and Extension Treatment and Reuse of Wastewater Using Surface and Subsurface Wetlands Dr. Luna Al-Hadidi 13th IWA Specialized Conference on Small Water and
Nitrogen Transformation within Constructed Wetlands Purifying Secondary Treated Sewage
 Nitrogen Transformation within Constructed Wetlands Purifying Secondary Treated Sewage T. Y. Yeh 1,*, C. M. Kao 2 1 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering National University of Kaohsiung Kaohsiung,
Nitrogen Transformation within Constructed Wetlands Purifying Secondary Treated Sewage T. Y. Yeh 1,*, C. M. Kao 2 1 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering National University of Kaohsiung Kaohsiung,
Algae & Water Hyacinth. Bioremediation potential for landfill leachate
 Algae & Water Hyacinth Bioremediation potential for landfill leachate Landfills Handle municipal solid waste (MSW), construction & demolition (C&D), and hazardous wastes. 1,754 reported US MSW landfills
Algae & Water Hyacinth Bioremediation potential for landfill leachate Landfills Handle municipal solid waste (MSW), construction & demolition (C&D), and hazardous wastes. 1,754 reported US MSW landfills
Removal of Heavy Metal from Landfill Leachate Using Vertical Flow Construction Wetland
 Removal of Heavy Metal from Landfill Leachate Using Vertical Flow Construction Wetland Mrs. Meenakshi A. Khapre 1 1 (Département of Civil Engineering, JSPM s, Rajarshi Shahu College of Engineering Pune-37,
Removal of Heavy Metal from Landfill Leachate Using Vertical Flow Construction Wetland Mrs. Meenakshi A. Khapre 1 1 (Département of Civil Engineering, JSPM s, Rajarshi Shahu College of Engineering Pune-37,
Loropetalum Screening for High Lime Induced Abnormalities
 Loropetalum Screening for High Lime Induced Abnormalities Nature of Work: Dr. James T. Midcap Department of Horticulture The University of Georgia Athens, GA 30602 Sizzling Pink Loropetalum has developed
Loropetalum Screening for High Lime Induced Abnormalities Nature of Work: Dr. James T. Midcap Department of Horticulture The University of Georgia Athens, GA 30602 Sizzling Pink Loropetalum has developed
Evaluation copy. Total Dissolved Solids. Computer INTRODUCTION
 Total Dissolved Solids Computer 12 INTRODUCTION Solids are found in streams in two forms, suspended and dissolved. Suspended solids include silt, stirred-up bottom sediment, decaying plant matter, or sewage-treatment
Total Dissolved Solids Computer 12 INTRODUCTION Solids are found in streams in two forms, suspended and dissolved. Suspended solids include silt, stirred-up bottom sediment, decaying plant matter, or sewage-treatment
TRANSFORMATION OF SOIL AND FERTILIZER NITROGEN IN PADDY SOIL AND THEIR AVAILABILITY TO RICE PLANTS
 Plant and Soil 47, 113-123 (1977) Ms. 3029 TRANSFORMATION OF SOIL AND FERTILIZER NITROGEN IN PADDY SOIL AND THEIR AVAILABILITY TO RICE PLANTS by TOMIO YOSHIDA* and BENJAMIN C. PADRE, JR. The International
Plant and Soil 47, 113-123 (1977) Ms. 3029 TRANSFORMATION OF SOIL AND FERTILIZER NITROGEN IN PADDY SOIL AND THEIR AVAILABILITY TO RICE PLANTS by TOMIO YOSHIDA* and BENJAMIN C. PADRE, JR. The International
Agronomic use of produced water on tomato plants (Solanum licopersicum L.)under greenhouse conditions.
 : Agronomic use of produced water on tomato plants (Solanum licopersicum L.)under greenhouse conditions. Universidad Autónoma Agraria Antonio Narro Saltillo, Coahuila, Mexico José Fernando Martel Valles
: Agronomic use of produced water on tomato plants (Solanum licopersicum L.)under greenhouse conditions. Universidad Autónoma Agraria Antonio Narro Saltillo, Coahuila, Mexico José Fernando Martel Valles
Improving Pomegranate Fertigation and Nitrogen Use Efficiency with Drip Irrigation Systems
 Improving Pomegranate Fertigation and Nitrogen Use Efficiency with Drip Irrigation Systems Project Leaders James E. Ayars, Ph.D., Research Agricultural Engineer, USDA-ARS, SJVASC, 9611 S. Riverbend Ave.,
Improving Pomegranate Fertigation and Nitrogen Use Efficiency with Drip Irrigation Systems Project Leaders James E. Ayars, Ph.D., Research Agricultural Engineer, USDA-ARS, SJVASC, 9611 S. Riverbend Ave.,
SUSTAINABILITY EFFECTS OF Crotalaria juncea L. AND Crotalaria spectabilis ROTH ON SOIL FERTILITY AND SOIL CONSERVATION
 Geophysical Research Abstracts Vol. 12, EGU2010-3271, 2010 EGU General Assembly 2010 Author(s) 2010 SUSTAINABILITY EFFECTS OF Crotalaria juncea L. AND Crotalaria spectabilis ROTH ON SOIL FERTILITY AND
Geophysical Research Abstracts Vol. 12, EGU2010-3271, 2010 EGU General Assembly 2010 Author(s) 2010 SUSTAINABILITY EFFECTS OF Crotalaria juncea L. AND Crotalaria spectabilis ROTH ON SOIL FERTILITY AND
Chris Kinsley, M.Eng., P.Eng. Anna Crolla, M.A.Sc., P.Eng. Sara Altimimi, B.A.Sc.
 From Brown Water to Blue Water Natural systems to recycle farm effluents Chris Kinsley, M.Eng., P.Eng. Anna Crolla, M.A.Sc., P.Eng. Sara Altimimi, B.A.Sc. Ontario Rural Wastewater Centre University of
From Brown Water to Blue Water Natural systems to recycle farm effluents Chris Kinsley, M.Eng., P.Eng. Anna Crolla, M.A.Sc., P.Eng. Sara Altimimi, B.A.Sc. Ontario Rural Wastewater Centre University of
Evaluating the Reuse of Swine Lagoon Effluent and Reclaimed Municipal Water for Agricultural Production Progress Report April 20, 2017
 Evaluating the Reuse of Swine Lagoon Effluent and Reclaimed Municipal Water for Agricultural Production Progress Report April 20, 2017 Hailin Zhang, Saleh Taghvaeian, Doug Hamilton, and Scott Carter This
Evaluating the Reuse of Swine Lagoon Effluent and Reclaimed Municipal Water for Agricultural Production Progress Report April 20, 2017 Hailin Zhang, Saleh Taghvaeian, Doug Hamilton, and Scott Carter This
Instituto de Ciencia y Tecnología Animal, Universidad Politécnica de Valencia, Camino de Vera s/n Valencia, Spain. *
 Air scrubbing techniques for the reduction of gaseous emissions from livestock farms. Actual knowledge in the Netherlands and possibilities for implementation on Spanish farms Estellés F.1)*, Melse R.W.2),
Air scrubbing techniques for the reduction of gaseous emissions from livestock farms. Actual knowledge in the Netherlands and possibilities for implementation on Spanish farms Estellés F.1)*, Melse R.W.2),
Process Monitoring for Biological and Chemical Nutrient Removal
 October 27, 2016 Process Monitoring for Biological and Chemical Nutrient Removal OWEA 2016 PLANT OPERATIONS & LABORATORY WORKSHOP Agenda Why Consider Nutrient Removal? Nitrogen Monitoring & Removal Phosphorus
October 27, 2016 Process Monitoring for Biological and Chemical Nutrient Removal OWEA 2016 PLANT OPERATIONS & LABORATORY WORKSHOP Agenda Why Consider Nutrient Removal? Nitrogen Monitoring & Removal Phosphorus
Nutrition & Lighting Requirements of Lettuce. Dr. Krishna Nemali
 Nutrition & Lighting Requirements of Lettuce Dr. Krishna Nemali Nutrients are supplied to lettuce plants in hydroponics by maintaining a target EC in the fertilizer solution Nutrient elements are taken
Nutrition & Lighting Requirements of Lettuce Dr. Krishna Nemali Nutrients are supplied to lettuce plants in hydroponics by maintaining a target EC in the fertilizer solution Nutrient elements are taken
Total Dissolved Solids
 Total Dissolved Solids LabQuest 12 INTRODUCTION Solids are found in streams in two forms, suspended and dissolved. Suspended solids include silt, stirred-up bottom sediment, decaying plant matter, or sewage-treatment
Total Dissolved Solids LabQuest 12 INTRODUCTION Solids are found in streams in two forms, suspended and dissolved. Suspended solids include silt, stirred-up bottom sediment, decaying plant matter, or sewage-treatment
APPLICATION OF VETIVER GRASS TECHNOLOGY IN OFF-SITE POLLUTION CONTROL II. TOLERANCE TO HERBICIDES UNDER SELECTED WETLAND CONDITIONS
 APPLICATION OF VETIVER GRASS TECHNOLOGY IN OFF-SITE POLLUTION CONTROL II. TOLERANCE TO HERBICIDES UNDER SELECTED WETLAND CONDITIONS Rachael Cull 1, Heather Hunter 1, Malcolm Hunter 2, Paul Truong 1 1 Queensland
APPLICATION OF VETIVER GRASS TECHNOLOGY IN OFF-SITE POLLUTION CONTROL II. TOLERANCE TO HERBICIDES UNDER SELECTED WETLAND CONDITIONS Rachael Cull 1, Heather Hunter 1, Malcolm Hunter 2, Paul Truong 1 1 Queensland
Available online at I-SEEC Proceeding - Science and Engineering (2013)
 Available online at www.iseec2012.com I-SEEC 2012 Proceeding - Science and Engineering (2013) 591 598 Proceeding Science and Engineering www.iseec2012.com Science and Engineering Symposium 4 th International
Available online at www.iseec2012.com I-SEEC 2012 Proceeding - Science and Engineering (2013) 591 598 Proceeding Science and Engineering www.iseec2012.com Science and Engineering Symposium 4 th International
PRODUCTION OF MEDIUM CHAIN LENGTH POLYHYDROXYALKANOATES BY Pseudomonas fluorescens AND UNRELATED CARBON SOURCE
 PRODUCTION OF MEDIUM CHAIN LENGTH POLYHYDROXYALKANOATES BY Pseudomonas fluorescens AND UNRELATED CARBON SOURCE DIANA MARCELA VANEGAS HERNÁNDEZ Ph.D, Chemical engineer MARGARITA ENID RAMÍREZ CARMONA Ph.D,
PRODUCTION OF MEDIUM CHAIN LENGTH POLYHYDROXYALKANOATES BY Pseudomonas fluorescens AND UNRELATED CARBON SOURCE DIANA MARCELA VANEGAS HERNÁNDEZ Ph.D, Chemical engineer MARGARITA ENID RAMÍREZ CARMONA Ph.D,
On-site wastewater treatment in Flanders, opportunities and threats for constructed wetlands
 Decentralized Water and Wastewater International Network(DEWSIN) Kathmandu Nepal 2009 On-site wastewater treatment in Flanders, opportunities and threats for constructed wetlands Mia Van Dyck, Rob Van
Decentralized Water and Wastewater International Network(DEWSIN) Kathmandu Nepal 2009 On-site wastewater treatment in Flanders, opportunities and threats for constructed wetlands Mia Van Dyck, Rob Van
Influence of Ironite and Phosphorus on Yield of Oats and Content of Lead and Arsenic at Different Stages of Growth
 Influence of Ironite and Phosphorus on Yield of Oats and Content of Lead and Arsenic at Different Stages of Growth Item type text; Article Authors Eberhardt, P. J.; Clark, L. J. Publisher Journal College
Influence of Ironite and Phosphorus on Yield of Oats and Content of Lead and Arsenic at Different Stages of Growth Item type text; Article Authors Eberhardt, P. J.; Clark, L. J. Publisher Journal College
Dieffenbachia Growth Responses and N Leaching from Container-Grown Plants Fertilized by Several Methods
 Dieffenbachia Growth Responses and N Leaching from Container-Grown Plants Fertilized by Several Methods M.L. Segura, J.M. Rodríguez, S. Jiménez and J. López Centro de Investigación y Formación Agraria.
Dieffenbachia Growth Responses and N Leaching from Container-Grown Plants Fertilized by Several Methods M.L. Segura, J.M. Rodríguez, S. Jiménez and J. López Centro de Investigación y Formación Agraria.
THE USE OF COVER CROPS AFTER A MAIZE CROP IN THE NORTH OF SPAIN. Dpto. Biología Vegetal y Ecología, UPV. Apdo. 644, Bilbao, Spain.
 ID # 04-03 THE USE OF COVER CROPS AFTER A MAIZE CROP IN THE NORTH OF SPAIN D. Báez 1, M. Pinto 1, M. Rodríguez 2, G. Besga 1 and J. M Estavillo 3 1 NEIKER, Berreaga 1,48160 Derio, Spain 2 Dpto. Sanidad.
ID # 04-03 THE USE OF COVER CROPS AFTER A MAIZE CROP IN THE NORTH OF SPAIN D. Báez 1, M. Pinto 1, M. Rodríguez 2, G. Besga 1 and J. M Estavillo 3 1 NEIKER, Berreaga 1,48160 Derio, Spain 2 Dpto. Sanidad.
Nutrient Cycling in an Aquatic Ecosystem
 Nutrient Cycling in an Aquatic Ecosystem 2.1 Productivity 2.2 Oxygen 2.3 Salinity 2.4 Carbon 2.5 Nitrogen 2.6 Phosphorous 2.7 Iron 2.8 Sulphur 2.9 Silica 2.3 Salinity of Inland Waters The salinity of freshwaters
Nutrient Cycling in an Aquatic Ecosystem 2.1 Productivity 2.2 Oxygen 2.3 Salinity 2.4 Carbon 2.5 Nitrogen 2.6 Phosphorous 2.7 Iron 2.8 Sulphur 2.9 Silica 2.3 Salinity of Inland Waters The salinity of freshwaters
Daw Nway Nway Khaing Assistant Lecturer Civil Engineering Department Yangon Technological University
 Daw Nway Nway Khaing Assistant Lecturer Civil Engineering Department Yangon Technological University Yangon Convention Center (YCC) 12 th October 2018 1 Outlines Introduction Objective Methodology Results
Daw Nway Nway Khaing Assistant Lecturer Civil Engineering Department Yangon Technological University Yangon Convention Center (YCC) 12 th October 2018 1 Outlines Introduction Objective Methodology Results
Wastewater Treatment Processes
 Wastewater Treatment Processes (Sep 27 th and 28 th, 2016) by Dr. Arun Kumar (arunku@civil.iitd.ac.in) Objective: To learn about processes used in tertiary treatment Courtesy: Dr. Irene Xagoraraki, MSU,
Wastewater Treatment Processes (Sep 27 th and 28 th, 2016) by Dr. Arun Kumar (arunku@civil.iitd.ac.in) Objective: To learn about processes used in tertiary treatment Courtesy: Dr. Irene Xagoraraki, MSU,
Hydrology and Water Quality. Water. Water 9/13/2016. Molecular Water a great solvent. Molecular Water
 Hydrology and Water Quality Water Molecular Water Exists as an equilibrium But equilibrium altered by what is dissolved in it Water Molecular Water a great solvent In reality, water in the environment
Hydrology and Water Quality Water Molecular Water Exists as an equilibrium But equilibrium altered by what is dissolved in it Water Molecular Water a great solvent In reality, water in the environment
Continuous bioremediation of phenol polluted air in an external loop airlift bioreactor with packed bed Hossein Nikakhtari 1 and Gordon A.
 CONTINUOUS BIOREMEDIATION OF PHENOL POLLUTED AIR IN AN EXTERNAL LOOP AIRLIFT BIOREACTOR 211 Continuous bioremediation of phenol polluted air in an external loop airlift bioreactor with packed bed Hossein
CONTINUOUS BIOREMEDIATION OF PHENOL POLLUTED AIR IN AN EXTERNAL LOOP AIRLIFT BIOREACTOR 211 Continuous bioremediation of phenol polluted air in an external loop airlift bioreactor with packed bed Hossein
Hydrology and Water Quality. Water. Water 9/11/2018. Molecular Water a great solvent. Molecular Water
 Hydrology and Water Quality Water Molecular Water Exists as an equilibrium But equilibrium altered by what is dissolved in it Water Molecular Water a great solvent In reality, water in the environment
Hydrology and Water Quality Water Molecular Water Exists as an equilibrium But equilibrium altered by what is dissolved in it Water Molecular Water a great solvent In reality, water in the environment
EUTROPHICATION. Student Lab Workbook
 EUTROPHICATION Student Lab Workbook THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD 1. Research Background literature research about a topic of interest 2. Identification of a problem Determine a problem (with regards to the topic)
EUTROPHICATION Student Lab Workbook THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD 1. Research Background literature research about a topic of interest 2. Identification of a problem Determine a problem (with regards to the topic)
Performance of upflow anoxic bioreactor for wastewater treatment
 Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4 (2): 247-252, 27 ISSN: 1735-1472 Spring 27, IRSEN, CEERS, IAU S.K., Behera, et al. Performance of upflow anoxic bioreactor for wastewater treatment 1* S. K. Behera, 2 E.
Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 4 (2): 247-252, 27 ISSN: 1735-1472 Spring 27, IRSEN, CEERS, IAU S.K., Behera, et al. Performance of upflow anoxic bioreactor for wastewater treatment 1* S. K. Behera, 2 E.
Improved Fertilizer use Efficiency with Controlled Release Sources on Sandy Soils in South Florida. FDACS Contract
 Improved Fertilizer use Efficiency with Controlled Release Sources on Sandy Soils in South Florida FDACS Contract 013960 Task 1: Field Evaluation of CRF Deliverable 1: Report N fertilizer Biomass Efficiency
Improved Fertilizer use Efficiency with Controlled Release Sources on Sandy Soils in South Florida FDACS Contract 013960 Task 1: Field Evaluation of CRF Deliverable 1: Report N fertilizer Biomass Efficiency
Chapter 4: Advanced Wastewater Treatment for Phosphorous Removal
 ENGI 9605 Advanced Wastewater Treatment Chapter 4: Advanced Wastewater Treatment for Phosphorous Removal Winter 2011 Faculty of Engineering & Applied Science 4.1 Phosphorous in wastewaters 1. Common forms
ENGI 9605 Advanced Wastewater Treatment Chapter 4: Advanced Wastewater Treatment for Phosphorous Removal Winter 2011 Faculty of Engineering & Applied Science 4.1 Phosphorous in wastewaters 1. Common forms
Coal Ash Concrete Blocks for Reduction of Algal Growth and Ammonia Toxicity
 2011 World of Coal Ash (WOCA) Conference May 9-12, 2011 in Denver, CO, USA http://www.flyash.info/ Coal Ash Concrete Blocks for Reduction of Algal Growth and Ammonia Toxicity Sangchul Hwang, Perla Torres,
2011 World of Coal Ash (WOCA) Conference May 9-12, 2011 in Denver, CO, USA http://www.flyash.info/ Coal Ash Concrete Blocks for Reduction of Algal Growth and Ammonia Toxicity Sangchul Hwang, Perla Torres,
Biogeochemistry of Wetlands
 Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences (IFAS) Biogeochemistry of Wetlands Si Science and da Applications Biogeochemical Properties of Wetlands Wetland Biogeochemistry Laboratory Soil and Water Science
Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences (IFAS) Biogeochemistry of Wetlands Si Science and da Applications Biogeochemical Properties of Wetlands Wetland Biogeochemistry Laboratory Soil and Water Science
THE INFLUENCE OF THE NUTRIENTS AND THE SOIL ph ON CADMIUM AND ZINC UPTAKE BY THE BRASSICA NAPUS
 LUCRĂRILE SEMINARULUI GEOGRAFIC DIMITRIE CANTEMIR NR. 36, 2013 THE INFLUENCE OF THE NUTRIENTS AND THE SOIL ph ON CADMIUM AND ZINC UPTAKE BY THE BRASSICA NAPUS Paula Cojocaru 1 Abstract. The paper presents
LUCRĂRILE SEMINARULUI GEOGRAFIC DIMITRIE CANTEMIR NR. 36, 2013 THE INFLUENCE OF THE NUTRIENTS AND THE SOIL ph ON CADMIUM AND ZINC UPTAKE BY THE BRASSICA NAPUS Paula Cojocaru 1 Abstract. The paper presents
Growth And Metals Accumulation In Guar (Cyamopsis Tetragonoloba) Irrigated With Treated Wastewater
 Growth And Metals Accumulation In (Cyamopsis Tetragonoloba) Irrigated With Treated Wastewater Hajo E. ElHassan, Eiman E. E. Diab, Gammaa A. M. Osman Abstract: The effect of different concentrations of
Growth And Metals Accumulation In (Cyamopsis Tetragonoloba) Irrigated With Treated Wastewater Hajo E. ElHassan, Eiman E. E. Diab, Gammaa A. M. Osman Abstract: The effect of different concentrations of
Management of Farmstead Area Runoff: Potential of Agricultural Filter Strips
 Management of Farmstead Area Runoff: Potential of Agricultural Filter Strips Becky Larson February 16, 2011 Department of Biological Systems Engineering University of Wisconsin-Madison Outline Background
Management of Farmstead Area Runoff: Potential of Agricultural Filter Strips Becky Larson February 16, 2011 Department of Biological Systems Engineering University of Wisconsin-Madison Outline Background
Nitrogen removal in constructed wetland treating wastewater from the seafood industry
 Nitrogen removal in constructed wetland treating wastewater from the seafood industry 1 2 U. Puetpaiboon & C. Yirong 1 Department of Civil Engineering, Prince of Songkla University, Thailand 2 Joint Graduate
Nitrogen removal in constructed wetland treating wastewater from the seafood industry 1 2 U. Puetpaiboon & C. Yirong 1 Department of Civil Engineering, Prince of Songkla University, Thailand 2 Joint Graduate
Nitrogen Removal Using Saturated Upflow Woody Fiber Media
 Nitrogen Removal Using Saturated Upflow Woody Fiber Media 2017 Onsite Wastewater Mega Conference October 24, 2017 Larry Stephens, P.E. Acknowledgement Some of this material comes from Stewart Oakley, Department
Nitrogen Removal Using Saturated Upflow Woody Fiber Media 2017 Onsite Wastewater Mega Conference October 24, 2017 Larry Stephens, P.E. Acknowledgement Some of this material comes from Stewart Oakley, Department
BIOLOGICAL WATER TREATMENT SYSTEMS. Sarah A. White, Ph.D. 25 Oct 2016
 BIOLOGICAL WATER TREATMENT SYSTEMS Sarah A. White, Ph.D. 25 Oct 2016 Water challenges & concerns Treatment technologies for runoff Sediment basins Filter strips Vegetative buffers Vegetative waterways
BIOLOGICAL WATER TREATMENT SYSTEMS Sarah A. White, Ph.D. 25 Oct 2016 Water challenges & concerns Treatment technologies for runoff Sediment basins Filter strips Vegetative buffers Vegetative waterways
Soil Tests for Predicting Nitrogen Supply for Grassland Under Controlled Environmental Conditions
 Soil Tests for Predicting Nitrogen Supply for Grassland Under Controlled Environmental Conditions Key Messages: Measuring mineralizable nitrogen (N) (MN) using the simple and robust Illinois Soil Nitrogen
Soil Tests for Predicting Nitrogen Supply for Grassland Under Controlled Environmental Conditions Key Messages: Measuring mineralizable nitrogen (N) (MN) using the simple and robust Illinois Soil Nitrogen
COMPARATIVE STUDY ON ACCUMULATION OF CADMIUM IN THREE AQUATIC PLANTS
 COMPARATIVE STUDY ON ACCUMULATION OF CADMIUM IN THREE AQUATIC PLANTS Ritusmita Goswami, Bhabani Devi and Kali Prasad Sarma* Department of Environmental Science, Tezpur University, Napaam, Tezpur-784028,
COMPARATIVE STUDY ON ACCUMULATION OF CADMIUM IN THREE AQUATIC PLANTS Ritusmita Goswami, Bhabani Devi and Kali Prasad Sarma* Department of Environmental Science, Tezpur University, Napaam, Tezpur-784028,
Mineral ammonium ion absorber as a fertilizer. DT conference 2012 Taina Laiho. University of Turku
 Mineral ammonium ion absorber as a fertilizer DT conference 2012 Taina Laiho Background Nano-modified silicate for ammonium absorption (GeoTrap) and fertilization (NGT) o Demand driven by more strict enforcement
Mineral ammonium ion absorber as a fertilizer DT conference 2012 Taina Laiho Background Nano-modified silicate for ammonium absorption (GeoTrap) and fertilization (NGT) o Demand driven by more strict enforcement
NUTRIENTS. Nitrogen (N) 15,000 Potassium (K) 10,000 Calcium (Ca) 5,000 Magnesium (Mg) 2,000 Phosphorus (P) 2,000 Sulfur (S) 1,000
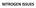 NITROGEN ISSUES NUTRIENTS Macro-nutrients mg/kg* Nitrogen (N) 15,000 Potassium (K) 10,000 Calcium (Ca) 5,000 Magnesium (Mg) 2,000 Phosphorus (P) 2,000 Sulfur (S) 1,000 * Based on Dry Weight of plant tissue
NITROGEN ISSUES NUTRIENTS Macro-nutrients mg/kg* Nitrogen (N) 15,000 Potassium (K) 10,000 Calcium (Ca) 5,000 Magnesium (Mg) 2,000 Phosphorus (P) 2,000 Sulfur (S) 1,000 * Based on Dry Weight of plant tissue
PO4 Sponge. Phosphorus Removal - Low & High Level Sources
 PO4 Sponge Phosphorus Removal - Low & High Level Sources Phosphorus (P) is a contaminant in streams and lakes that can degrade water bodies, especially when excessive. It contributes to growth of cyanobacteria
PO4 Sponge Phosphorus Removal - Low & High Level Sources Phosphorus (P) is a contaminant in streams and lakes that can degrade water bodies, especially when excessive. It contributes to growth of cyanobacteria
Are Constructed Wetlands a Cost-Effective Alternative to Activated Sludge Systems? Investigation of Plants in Germany and Mexico
 TÍTULO DEL TRABAJO Are Constructed Wetlands a Cost-Effective Alternative to Activated Sludge Systems? Investigation of Plants in Germany and Mexico TÍTULO RESUMIDO Economical Comparison of Constructed
TÍTULO DEL TRABAJO Are Constructed Wetlands a Cost-Effective Alternative to Activated Sludge Systems? Investigation of Plants in Germany and Mexico TÍTULO RESUMIDO Economical Comparison of Constructed
Constructed Wetlands
 Constructed Wetlands Constructed Wetlands Artificial wastewater treatment systems consisting of shallow ponds or channels which have been planted with aquatic plants to treat wastewater. Rely upon natural
Constructed Wetlands Constructed Wetlands Artificial wastewater treatment systems consisting of shallow ponds or channels which have been planted with aquatic plants to treat wastewater. Rely upon natural
Introduction. Wetland System. A Wetland Scene at Lorne C. Henderson Conservation Area near Petrolia
 Wetland Treatment of Wastewater This monograph, one in a series of single issue documents that deal with our local environment, has been prepared by the Sarnia-Lambton Environmental Association in co-operation
Wetland Treatment of Wastewater This monograph, one in a series of single issue documents that deal with our local environment, has been prepared by the Sarnia-Lambton Environmental Association in co-operation
Organic Fertilizer Calculator
 EM 8936-E September 2007 User guide Organic Fertilizer Calculator A tool for comparing the cost, nutrient value, and nitrogen availability of organic materials N. Andrews and J. Foster Choosing an organic
EM 8936-E September 2007 User guide Organic Fertilizer Calculator A tool for comparing the cost, nutrient value, and nitrogen availability of organic materials N. Andrews and J. Foster Choosing an organic
USE OF MICROALGAE FOR THE SIMULTANEOUS TREATMENT OF URBAN WASTEWATERS AND BIOENERGY PRODUCTION
 USE OF MICROALGAE FOR THE SIMULTANEOUS TREATMENT OF URBAN WASTEWATERS AND BIOENERGY PRODUCTION 2015 BioEnergy Symposium Technology Innovations Technical Session Catalina Dávila Aguer Department of Biology
USE OF MICROALGAE FOR THE SIMULTANEOUS TREATMENT OF URBAN WASTEWATERS AND BIOENERGY PRODUCTION 2015 BioEnergy Symposium Technology Innovations Technical Session Catalina Dávila Aguer Department of Biology
CHARACTERIZATION OF DYE INDUSTRY EFFLUENT AND ASSESSMENT OF ITS SUITABILITY FOR IRRIGATION PURPOSE
 CHARACTERIZATION OF DYE INDUSTRY EFFLUENT AND ASSESSMENT OF ITS SUITABILITY FOR IRRIGATION PURPOSE Y. N. JOLLY AND A. ISLAM * Chemistry Division, Atomic Energy Centre, P.O. Box 164 4, Kazi Nazrul Islam
CHARACTERIZATION OF DYE INDUSTRY EFFLUENT AND ASSESSMENT OF ITS SUITABILITY FOR IRRIGATION PURPOSE Y. N. JOLLY AND A. ISLAM * Chemistry Division, Atomic Energy Centre, P.O. Box 164 4, Kazi Nazrul Islam
WATER AND NUTRIENT BALANCES FOR THE TWIN FALLS IRRIGATION TRACT
 WATER AND NUTRIENT BALANCES FOR THE TWIN FALLS IRRIGATION TRACT D. Bjorneberg 1, D. Westermann 1 and N. Nelson 2 1 USDA ARS, Kimberly, ID 2 Kansas State University ABSTRACT Surface water return flow from
WATER AND NUTRIENT BALANCES FOR THE TWIN FALLS IRRIGATION TRACT D. Bjorneberg 1, D. Westermann 1 and N. Nelson 2 1 USDA ARS, Kimberly, ID 2 Kansas State University ABSTRACT Surface water return flow from
GENOTYPE X MINERAL NUTRIENT INTERACTIONS WITH FUSIFORM RUST RESISTANCE IN SLASH PINE. Charles A. Hollis, Joel E. Smith and Robert A.
 1/ GENOTYPE X MINERAL NUTRIENT INTERACTIONS WITH FUSIFORM RUST RESISTANCE IN SLASH PINE Charles A. Hollis, Joel E. Smith and Robert A. Schmidt/ Abstract.--The relationship of N, P and K availability to
1/ GENOTYPE X MINERAL NUTRIENT INTERACTIONS WITH FUSIFORM RUST RESISTANCE IN SLASH PINE Charles A. Hollis, Joel E. Smith and Robert A. Schmidt/ Abstract.--The relationship of N, P and K availability to
Application of biochar from coconut shells to different soils in Thua Thien Hue province, Vietnam
 Application of biochar from coconut shells to different soils in Thua Thien Hue province, Vietnam Tran Thi Tu 1), Morihiro Maeda 2), Le Van Thang 1), Nguyen Dang Hai 1), Tran Dang Bao Thuyen 1) 1) Institute
Application of biochar from coconut shells to different soils in Thua Thien Hue province, Vietnam Tran Thi Tu 1), Morihiro Maeda 2), Le Van Thang 1), Nguyen Dang Hai 1), Tran Dang Bao Thuyen 1) 1) Institute
CONSTRUCTED WETLANDS: A Critical Review of Wetland Treatment Processes
 CONSTRUCTED WETLANDS: A Critical Review of Wetland Treatment Processes Robert W. Seabloom, P.E. Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering University of Washington Adrian T. Hanson, PE Frank M. Tejeda
CONSTRUCTED WETLANDS: A Critical Review of Wetland Treatment Processes Robert W. Seabloom, P.E. Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering University of Washington Adrian T. Hanson, PE Frank M. Tejeda
EFFECT OF FERROUS SULPHATE ON THE SIMULTANEOUS ORGANIC MATTER AND NUTRIENT REMOVAL PERFORMANCE OF SEQUENCING BATCH REACTOR
 EFFECT OF FERROUS SULPHATE ON THE SIMULTANEOUS ORGANIC MATTER AND NUTRIENT REMOVAL PERFORMANCE OF SEQUENCING BATCH REACTOR Engin Gürtekin Department of Environmental Engineering, Firat University, Elazığ,
EFFECT OF FERROUS SULPHATE ON THE SIMULTANEOUS ORGANIC MATTER AND NUTRIENT REMOVAL PERFORMANCE OF SEQUENCING BATCH REACTOR Engin Gürtekin Department of Environmental Engineering, Firat University, Elazığ,
Modelling of nickel dynamics in vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands using a System Thinking Environment
 European Water 58: 159-164, 2017. 2017 E.W. Publications Modelling of nickel dynamics in vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands using a System Thinking Environment C. Defo 1,2* and R. Kaur 2 1 University
European Water 58: 159-164, 2017. 2017 E.W. Publications Modelling of nickel dynamics in vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands using a System Thinking Environment C. Defo 1,2* and R. Kaur 2 1 University
Effects of Sewage Sludge on Heavy Metal Accumulation in Soil and Plants, and on Crop Productivity in Aleppo Governorate
 Effects of Sewage Sludge on Heavy Metal Accumulation in Soil and Plants, and on Crop Productivity in Aleppo Governorate Abstract M.M. Al-Zoubi 1, A. Arslan 1,2, G. Abdelgawad 2, N. Pejon 1, M. Tabbaa 1
Effects of Sewage Sludge on Heavy Metal Accumulation in Soil and Plants, and on Crop Productivity in Aleppo Governorate Abstract M.M. Al-Zoubi 1, A. Arslan 1,2, G. Abdelgawad 2, N. Pejon 1, M. Tabbaa 1
Jorge A. Villa, William J. Mitsch. The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE GRADUATE PROGRAM
 Determining the role of different wetland plant communities on the export of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in the Florida Everglades - a mesocosm experiment Jorge A. Villa, William J. Mitsch The Ohio
Determining the role of different wetland plant communities on the export of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in the Florida Everglades - a mesocosm experiment Jorge A. Villa, William J. Mitsch The Ohio
Nitrogen dynamics of standard and enhanced urea in corn
 Nitrogen dynamics of standard and enhanced urea in corn James H. Houx III and Felix B. Fritschi INTRODUCTION: Concerns about illegal uses of anhydrous ammonia and ammonium nitrate may make urea a preferred
Nitrogen dynamics of standard and enhanced urea in corn James H. Houx III and Felix B. Fritschi INTRODUCTION: Concerns about illegal uses of anhydrous ammonia and ammonium nitrate may make urea a preferred
EU Water Analysis Using the Thermo Scientific icap 7400 ICP-OES Duo
 EU Water Analysis Using the Thermo Scientific icap 7400 ICP-OES Duo James Hannan, Applications Chemist, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Cambridge, UK Application Note 43171 Key Words Environmental, EU, waste,
EU Water Analysis Using the Thermo Scientific icap 7400 ICP-OES Duo James Hannan, Applications Chemist, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Cambridge, UK Application Note 43171 Key Words Environmental, EU, waste,
Constructed Wetland System for
 A Pilot Implementation of Constructed Wetland System for Domestic Wastewater Treatment and Reuse in a Green Village Ma. Cheryl F. Prudente Contributors: Amy M. Lecciones, Arch. Aaron Julius M. Lecciones,
A Pilot Implementation of Constructed Wetland System for Domestic Wastewater Treatment and Reuse in a Green Village Ma. Cheryl F. Prudente Contributors: Amy M. Lecciones, Arch. Aaron Julius M. Lecciones,
Organic Wastes As a Resource For Mediterranean Soils
 Workshop Biological Treatment of Biodegradable Waste Technical aspects Jointly co-organised by DG Environment and the JRC Organic Wastes As a Resource For Mediterranean Soils Brussels, 8-10 april 2002
Workshop Biological Treatment of Biodegradable Waste Technical aspects Jointly co-organised by DG Environment and the JRC Organic Wastes As a Resource For Mediterranean Soils Brussels, 8-10 april 2002
SZILI-KOVÁCS Tibor (1), GULYÁS Ferenc (1), ANTON Attila (1), FILIP Zdenek (2)
 Scientific registration n o : 2328 Symposium n o : 37 Presentation : poster An international approach to assess soil quality by biological methods: Experience from anthropogenically affected soils in Hungary
Scientific registration n o : 2328 Symposium n o : 37 Presentation : poster An international approach to assess soil quality by biological methods: Experience from anthropogenically affected soils in Hungary
Scientific Registration No. 168 Number of Symposium: 21 Presentation: Oral BRAR M.S., SINGH A.P., C.L. ARORA
 Scientific Registration No. 168 Number of Symposium: 1 Presentation: Oral Effect of effluent contaminated water on micro and potentially toxic elements in soils and potato plants Effets sur les sols et
Scientific Registration No. 168 Number of Symposium: 1 Presentation: Oral Effect of effluent contaminated water on micro and potentially toxic elements in soils and potato plants Effets sur les sols et
Control of Eurasian Watermilfoil in Mesocosms at Lake Tahoe
 Control of Eurasian Watermilfoil in Mesocosms at Lake Tahoe Robert J. DuVall, Graduate Group in Ecology, Lars W. J. Anderson, Weed Science Program Charles R. Goldman, Environmental Science and Policy and
Control of Eurasian Watermilfoil in Mesocosms at Lake Tahoe Robert J. DuVall, Graduate Group in Ecology, Lars W. J. Anderson, Weed Science Program Charles R. Goldman, Environmental Science and Policy and
Nutrient Management for Vegetable Production
 Nutrient Management for Vegetable Production Richard Smith, Farm Advisor Monterey County Farm Water Quality Planning Project UC Cooperative Extension/ USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service Fertilizers
Nutrient Management for Vegetable Production Richard Smith, Farm Advisor Monterey County Farm Water Quality Planning Project UC Cooperative Extension/ USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service Fertilizers
Anis Sholihah 1 & Agus Sugianto 2
 Journal of Agriculture and Environmental Sciences June 2015, Vol. 4, No. 1, pp. 21-25 ISSN: 2334-2404 (Print), 2334-2412 (Online) Copyright The Author(s). All Rights Reserved. Published by American Research
Journal of Agriculture and Environmental Sciences June 2015, Vol. 4, No. 1, pp. 21-25 ISSN: 2334-2404 (Print), 2334-2412 (Online) Copyright The Author(s). All Rights Reserved. Published by American Research
Do not oven-dry the soil
 Fertilizing Corn Fact Sheet No..38 Crop Series Soil by J.G. Davis and D.G. Westfall* Adequate soil fertility is one of the requirements for profitable corn production. Nitrogen (N) is the most yield-limiting
Fertilizing Corn Fact Sheet No..38 Crop Series Soil by J.G. Davis and D.G. Westfall* Adequate soil fertility is one of the requirements for profitable corn production. Nitrogen (N) is the most yield-limiting
Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals in Aqueous Solutions
 Leonardo Journal of Sciences ISSN 1583-0233 Issue 17, July-December 2010 p. 37-46 Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals in Aqueous Solutions Felix Aibuedefe AISIEN 1,*, Oluwole FALEYE 1 and Eki Tina AISIEN
Leonardo Journal of Sciences ISSN 1583-0233 Issue 17, July-December 2010 p. 37-46 Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals in Aqueous Solutions Felix Aibuedefe AISIEN 1,*, Oluwole FALEYE 1 and Eki Tina AISIEN
Application of the AGF (Anoxic Gas Flotation) Process
 Application of the AGF (Anoxic Gas Flotation) Process Dennis A. Burke Environmental Energy Company, 6007 Hill Road NE, Olympia, WA 98516 USA (E-mail: dennis@makingenergy.com http//www.makingenergy.com)
Application of the AGF (Anoxic Gas Flotation) Process Dennis A. Burke Environmental Energy Company, 6007 Hill Road NE, Olympia, WA 98516 USA (E-mail: dennis@makingenergy.com http//www.makingenergy.com)
Streamside Management. How the area around your pond effects the water.
 Streamside Management Zones and Water Quality How the area around your pond effects the water. Stream(pond)side Management Zone A streamside management zone (SMZ) is a strip of land immediately adjacent
Streamside Management Zones and Water Quality How the area around your pond effects the water. Stream(pond)side Management Zone A streamside management zone (SMZ) is a strip of land immediately adjacent
Zero-discharge of nutrients and water in a willow dominated constructed wetland
 Zero-discharge of nutrients and water in a willow dominated constructed wetland P. Gregersen* and H. Brix** * Centre of Recycling, Forsomho Skolevej 5, DK-6870 Ølgod, Denmark ** Department of Plant Ecology,
Zero-discharge of nutrients and water in a willow dominated constructed wetland P. Gregersen* and H. Brix** * Centre of Recycling, Forsomho Skolevej 5, DK-6870 Ølgod, Denmark ** Department of Plant Ecology,
AMMONIA VOLATILISATION IN WSP: A CASCADE OF MISINTERPRETATIONS?
 AMMONIA VOLATILISATION IN WSP: A CASCADE OF MISINTERPRETATIONS? Miller Alonso Camargo-Valero Universidad Nacional de Colombia University of Leeds Duncan Mara University of Leeds Outline Feasible mechanisms
AMMONIA VOLATILISATION IN WSP: A CASCADE OF MISINTERPRETATIONS? Miller Alonso Camargo-Valero Universidad Nacional de Colombia University of Leeds Duncan Mara University of Leeds Outline Feasible mechanisms
Understanding your EAL agricultural soil results
 Understanding your EAL agricultural soil results An EAL agricultural soil test report holds a wealth of information. To assist in its interpretation, please refer to the colour coded text below and within
Understanding your EAL agricultural soil results An EAL agricultural soil test report holds a wealth of information. To assist in its interpretation, please refer to the colour coded text below and within
Pomegranate Irrigation, Fertigation and Nitrogen Use Efficiency with Drip Irrigation
 Pomegranate Irrigation, Fertigation and Nitrogen Use Efficiency with Drip Irrigation Claude J. Phene, James A. Ayars, R. Scott Johnson, Gary S. Banuelos, Rebecca C. Phene, Dong Wang, Kevin Day & Rick Schoneman
Pomegranate Irrigation, Fertigation and Nitrogen Use Efficiency with Drip Irrigation Claude J. Phene, James A. Ayars, R. Scott Johnson, Gary S. Banuelos, Rebecca C. Phene, Dong Wang, Kevin Day & Rick Schoneman
Drawbacks & Opportunities of Electrocoagulation Technology in the Wastewater Treatment
 EMC 2007, June 11-14, Düsseldorf Germany Drawbacks & pportunities of Electrocoagulation Technology in the Wastewater Treatment J. Rodriguez, S. Stopić, B. Friedrich IME Process Metallurgy and Metal RWTH
EMC 2007, June 11-14, Düsseldorf Germany Drawbacks & pportunities of Electrocoagulation Technology in the Wastewater Treatment J. Rodriguez, S. Stopić, B. Friedrich IME Process Metallurgy and Metal RWTH
Removal Mechanisms in Constructed Wastewater Wetlands. Stephen Norton
 Removal Mechanisms in Constructed Wastewater Wetlands Stephen Norton ABSTRACT The use of constructed wetlands is a relatively new technology but the system is gaining popularity due to its low tech system
Removal Mechanisms in Constructed Wastewater Wetlands Stephen Norton ABSTRACT The use of constructed wetlands is a relatively new technology but the system is gaining popularity due to its low tech system
Bottom Ash Data Week 45
 Bottom Ash Data 2018 Week 45 The following analytical report was sent to the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy on November 21, 2018. The data represents bottom ash composite results for
Bottom Ash Data 2018 Week 45 The following analytical report was sent to the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy on November 21, 2018. The data represents bottom ash composite results for
The optimization of fermentation conditions particularly physical and chemical
 4.1 Preamble The optimization of fermentation conditions particularly physical and chemical parameters are of primary importance in the development of any fermentation process owing to their impact on
4.1 Preamble The optimization of fermentation conditions particularly physical and chemical parameters are of primary importance in the development of any fermentation process owing to their impact on
Struvia Technology for Phosphorus Recovery. o Re-Water Braunschweig November 2015
 Struvia Technology for Phosphorus Recovery o Re-Water Braunschweig 2.-3. November 2015 1 Resourcing the World o Vision of circular economy o Sous-titre o Waste and Waste Water are resources Veolia Water
Struvia Technology for Phosphorus Recovery o Re-Water Braunschweig 2.-3. November 2015 1 Resourcing the World o Vision of circular economy o Sous-titre o Waste and Waste Water are resources Veolia Water
Davie Kadyampakeni UF/IFAS CREC
 IMPROVED NUTRIENT MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES IN THE ERA OF HLB Davie Kadyampakeni UF/IFAS CREC Outline Status of HLB in FL: What we know now Strategies for managing HLB Nutrition studies for managing HLB: Highlights
IMPROVED NUTRIENT MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES IN THE ERA OF HLB Davie Kadyampakeni UF/IFAS CREC Outline Status of HLB in FL: What we know now Strategies for managing HLB Nutrition studies for managing HLB: Highlights
Bottom Ash Data Week 52
 Bottom Ash Data 2018 Week 52 The following analytical report was sent to the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy on January 10, 2019. The data represents bottom ash composite results for
Bottom Ash Data 2018 Week 52 The following analytical report was sent to the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy on January 10, 2019. The data represents bottom ash composite results for
Wetland Phosphorus Cycle
 Diffusion Sedimentation Diffusion allows dissolved forms of Phosphorus to be transferred from the incoming surface water into the soil and back again on occasion. A concentration gradient is what allows
Diffusion Sedimentation Diffusion allows dissolved forms of Phosphorus to be transferred from the incoming surface water into the soil and back again on occasion. A concentration gradient is what allows
We didn t plan to talk about it, but since quite a few of you asked... Source:
 We didn t plan to talk about it, but since quite a few of you asked... Source: Phytoremediation is the direct use of green plants and their associated microorganisms to stabilize or reduce contamination
We didn t plan to talk about it, but since quite a few of you asked... Source: Phytoremediation is the direct use of green plants and their associated microorganisms to stabilize or reduce contamination
Reed Canarygrass Response to Nitrogen and Chloride Fertilization
 Reed Canarygrass Response to Nitrogen and Chloride Fertilization William H. Miner Agricultural Research Institute P.O Box 90, Chazy, NY 12921 Everett D. Thomas Charlie J. Sniffen Carl J. Majewski Catherine
Reed Canarygrass Response to Nitrogen and Chloride Fertilization William H. Miner Agricultural Research Institute P.O Box 90, Chazy, NY 12921 Everett D. Thomas Charlie J. Sniffen Carl J. Majewski Catherine
Bottom Ash Data Week 47
 Bottom Ash Data 2018 Week 47 The following analytical report was sent to the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy on December 6, 2018. The data represents bottom ash composite results for
Bottom Ash Data 2018 Week 47 The following analytical report was sent to the Ministry of Environment and Climate Change Strategy on December 6, 2018. The data represents bottom ash composite results for
LAKE MANZALA ENGINEERED WETLAND A SUCCSSESFUL MODEL FOR THE METERRANIAN SEA PROTECTION
 LAKE MANZALA ENGINEERED WETLAND A SUCCSSESFUL MODEL FOR THE METERRANIAN SEA PROTECTION Prof. Dr. Ahmed Ali Rashed Drainage Research Institute National Water Research Center Ministry of Water Resources
LAKE MANZALA ENGINEERED WETLAND A SUCCSSESFUL MODEL FOR THE METERRANIAN SEA PROTECTION Prof. Dr. Ahmed Ali Rashed Drainage Research Institute National Water Research Center Ministry of Water Resources
EU water analysis using the Thermo Scientific icap 7400 ICP-OES Duo
 APPLICATION NOTE 43171 EU water analysis using the Thermo Scientific icap 7400 ICP-OES Duo Authors Introduction James Hannan, Application Specialist, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Hemel Hempstead, UK Within
APPLICATION NOTE 43171 EU water analysis using the Thermo Scientific icap 7400 ICP-OES Duo Authors Introduction James Hannan, Application Specialist, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Hemel Hempstead, UK Within
Implementation of Floating Aquatic Vegetative Tilling Technology in the Caloosahatchee River Watershed. Deliverable #19: Final Report.
 Implementation of Floating Aquatic Vegetative Tilling Technology in the Caloosahatchee River Watershed Deliverable #19: Final Report Site 1 Prepared for: Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer
Implementation of Floating Aquatic Vegetative Tilling Technology in the Caloosahatchee River Watershed Deliverable #19: Final Report Site 1 Prepared for: Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer
