A NEW METHOD FOR CONTINUOUS EFFICIENCY MEASUREMENT FOR HYDRAULIC TURBINES
|
|
|
- Prosper Cameron
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A NEW METHOD FOR CONTINUOUS EFFICIENCY MEASUREMENT FOR HYDRAULIC TURBINES Jonathan Nicolle 1, Gilles Proulx 2 1- IREQ- Hydro-Québec Research Institute, 1800 boul. Lionel Boulet, Varennes, Canada, J3X 1S1 2- Hydro-Québec ESP (Essais Spéciaux de Production); 5655 de Marseille, Montréal, Canada, H1N 1J4 Corresponding author : nicolle.jonathan@ireq.ca ABTRACT Over the years, Hydro-Québec has developed solid expertise in efficiency measurements and computation fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations. These two fields were combined within a research project in order to design a new system for continuously monitor the efficiency of hydraulic turbines. With the use of CFD, the first part of the paper shows that the precision of usual index methods, like Winter-Kennedy (WK), is limited in semi-spiral casings as a result of sensitivity to inlet conditions and guide vane opening. The second part of the paper addresses the previously identified weaknesses by using a much larger pressure difference and calibrating it against the guide vane position. Experimental results confirm the validity of the proposed method. INTRO For a utility such as Hydro-Québec, the operation of low head plants, which are normally run-of-river, is somehow problematic since the optimal operating point can vary considerably depending on the flow conditions. Among the various factors involved, the main one is naturally head variation but there is also some effects related to trash rack clogging, operation of adjacent groups, air injection from the shaft, downstream levels fluctuations and degradation of the hydraulic profile. One obvious possibility to obtain all the required information is to do extensive measurements (absolute discharge) but it is often not feasible because of the time and money constraints. A more realistic approach to obtain the global picture is to continuously monitor the flow. In this context, a research project on efficiency monitoring was started in The project s objective was to maximize energy output and operational maintenance by improving the knowledge of the flow going trough the unit at all time. To be successful, the system had to be more accurate than what is currently available and to be deployable at low cost. PART I: Sensitivity of Winter-Kennedy index to flow conditions Because of their simplicity and low cost, pressure indices are often used during efficiency measurements to confirm the shape of the efficiency curve. Besides the well-known Winter-Kennedy index which uses the dynamic pressure in a spiral casing section, every hydraulic phenomenon that evolves as the square root of the flow rate (such as losses) can also be used as an index. Often the combined losses from the trash rack and intake channel can be successfully used to obtain a good index. However, since the rack clogging can vary quickly, this index is only valid for a limited period of time. As shown in Eq. 1, the principle of these relative methods is always to link the flow rate (Q) to the square root of the index ( P) via a constant (K). The exponent (b) is usually set at 0.5 but the IEC code [1] allows for some variation between 0.48 and 0.52 to obtain a better fit. However this is purely an empirical correction since there is no scientific reason that justifies it. Eq. 1 Q b = K * P Figure 1: Geometry and position of the WK probes 1
2 Under good conditions, the relative index will have an accuracy of about 1% while under the worst conditions, usually met in low-head plants, it may not work at all as in Kerkan [2]. The reasons why WK indices are useful in some plants and useless in others has never been explained before. One of the basic assumptions required for using those methods is that the flow in the region of interest remains similar under every condition. This came from the Bernouilli assumption that is only valid along a stream line. With the help of CFD simulation, this homology condition was investigated regarding the influence of guide vane opening and inlet conditions. The LG-1 power plant located in northern Québec was chosen for this investigation. One of the main reasons for this was the availability of tests results at various heads. Each of the plant s 12 propeller turbines can generate 110 MW under a normal head of 27.5 m. The semi-spiral casing has three inlet channels covering a width of 22 m and a height of 18 m. It has 24 guide vanes. The position of the WK probes is shown in Fig. 1. Numerical simulation setup Figure 2: Details of the spiral casing mesh The geometry of the semi-spiral casing was incorporated into CAD software using drawings. The inlet s upper surface was set at the normal operating level of the reservoir and the sides were modeled in the middle of the pier separating the units. A structured mesh was then created with IcemCFD for seven different guide vane openings covering a wide operating range. The mesh included 6.7 M hexahedral elements and was refined near the walls and in the distributor area to account for the velocity gradient. A close up view of the mesh is presented in Fig. 2. Part of the meridian channel up to the runner position was also represented to move the outlet boundary condition away from the region of interest. The turbine itself was not included in the simulation. CFX-11 was used to solve the steady flow. The measured flow rate was imposed at the inlet (in blue in Fig. 3) along with a 5% turbulence intensity. An average static pressure was used at the outlet (in green). When studying the influence of the guide vane position, the top and sides of the inlet area (in red) were considered as symmetry planes so no flow was allowed to cross them. The standard K-epsilon model with scalable wall functions was used to represent the flow turbulence. The walls were modeled as smooth. As a tradeoff between robustness and accuracy, the spatial resolution scheme was set to be 75% second order accurate by using a blending function with the upwind scheme. The solution was considered converged and the calculation stopped when the maximal residuals in the solution were below 1E-4 and the global engineering quantity such as losses and pressure differences were stable. Figure 3: Boundary conditions for CFD 2
3 Sensitivity of WK to guide vane position First, the flow distribution between the three inlet channels was used to check if the overall behaviour of the spiral casing was correctly predicted. As can be seen in Table 1, when compared with measurements previously done with current meters [3], the numerical results showed the proper distribution between channels. Flow [m3/s] % left channel % center % right channel CFD Exp [3] Table 1: Flow distribution at the inlet channels Next, the guide vane angular position was modified to determine its effects on the spiral casing flow and on the various indices. The impact of opening the guide vane is to align them with the flow thus lowering their losses. These losses, which can be assimilated to hydraulic resistance, tend to level the flow distribution between the different sectors. As can be seen in the left part of Fig. 4 which presents the normalized massflow through each sector, there is more flow passing trough the upstream sectors as the opening of the distributor increases. At full opening, the 6 th sector sees about 103% of the average flow. The fact that the flow is changing is a first sign that any flow measuring system based on the dynamic pressure monitoring should be used cautiously , deg 31.7 deg deg 45.6 deg deg 1 5 0, Right WK coefficient WK p1-p3 WK p2-p3 EXP 1997 EXP Left Opening angle [deg] Figure 4: Flow distribution and WK coefficient evolution with opening The right part of Fig. 4 presents the calculated and measured WK index coefficient based on the pressure difference and the measured flow rate. If the WK constant was independent of the opening, it would be an horizontal line on the plot. The slope clearly shows that the modifications in the flow distribution between the different sectors also impact the WK readings. Given the fact that no geometrical verification of the probe position and condition was done, they compare relatively well with the value determined experimentally with previous current meter measurements. Discrepancies between numerical and experimental coefficients were also obtained by Muntean [4]. Since its inner probe is located at a greater radius, the WK P1-P3 is less sensitive to the guide vane position than the WK P2-P3. However the latter is usually the one that is used because it sees a larger pressure difference which usually translates into more signal stability [2]. Assuming a constant value corresponding for the WK coefficient would introduce an error on the estimated flowrate that could reach ±1.5% at full load. This sensitivity compares wells with the 1.2% obtained after six months of following the WK index in one of the first attempts of online efficiency monitoring (see Streat [5]). Sensitivity of WK to adjacent unit operation To simulate the operation of adjacent units, the boundary conditions imposed on the inlet were modified while maintaining all other factors constant. For these tests, the inlet s sides could be included in the inlet or left as a symmetry plane. The basic assumption was that when the adjacent unit was in operation, the flow could not come from this side, therefor a symmetry plane was a reasonable approximation. In all situations, the upper 3
4 surface remained a symmetry plane. This allowed for four different inlet boundary conditions to be tested. The summary of those tests is presented in Fig. 5. Figure 5: impact of inflow conditions for WK index Although the inlet was probably too short to properly represent the incoming flow from the reservoir, this sensitivity test still gives a good indication of the validity of the chosen index. The two WKs are shown to have an average variation of 3% when modifying the inlet conditions. This is understandable since the measured pressure difference is only a few KPa (9.3K Pa for WK P2-P3 and 15.8 KPa for WK P1-P3 ), so it is easily affected when upstream condition changes. So here is the paradigm of the WK relative index method. It does not seem is not possible to have an index within the spiral casing that is at the same time independent of the opening and stable regarding adjacent unit operation. This is because the flow homology condition required is not fully observed. To be independent of the moving parts, the pressure probes must be positioned far enough of the guide vane. However to be stable regarding adjacent unit operation, they must also measure a significant pressure difference. This duality limits the accuracy of the WK system for continuous flow monitoring. PART II: New method for continuous efficiency measurement Numerical Results (reference) Q WKp1 p3 = -1,7 % Q WKp1 p3 = +3,3 % Q WKp1 p3 = +3,6 % Q WKp2 p3 = -0,2 % Q WKp2 p3 = +3,5 % Q WKp2 p3 = +5,4 % To improve relative measurement accuracy, a correction factor can be implemented for the guide vane position. As shown in Eq. 2, this means that the index constant K would no longer be universal but would vary with the opening. Since the guide vane position is usually known, it is important to understand that this system will still have only one degree of freedom i.e. one flow rate for a given pressure/opening combination. What is more interesting is the fact that, since there is already some correction for the moving parts, there is no reason to be away from the guide vane anymore. This allows for a large increase in the measured pressure difference, thus lowering the sensitivity to inflow conditions. Fig. 6 shows the static pressure distribution in the middle plane of the spiral casing. The WK indices are placed in the orange-to-yellow region. As one can see, the measured pressure difference would be much higher if the downstream probe was placed closer to the unit axis. As shown in Fig. 7, two different locations downstream of the guide vane were monitored on the meridian channel, one on the upper cover (P sup ) and one on the lower cover (P inf ). Coupling them with an upstream WK probe (WK P1 in this case) allowed three different indices to be monitored. Eq. 2 Q = K( op) * P As shown in Fig 8, the coefficient calibration curves obtained from the CFD simulation were smooth and very good correlations could easily obtained with low order polynomial functions. The exact positioning of the probes is not important since the calibration is done afterwards. It can also be seen that the coefficient increases with the opening. As expected, the WK coefficients are relatively constant given the plot scale. Since the sensitivity of the Figure 6: Pressure distribution in middle plane 4
5 index is related to the magnitude of the measured pressure difference, a good index would always have a coefficient that is as low as possible. In other words, to improve on the WK, the coefficient must always be lower. This is always the case when using the lower pressure probe (P inf ). 300 Coefficient WK p1-p3 WK p2-p3 Psup - p1 Pinf - p1 Psup - pinf R 2 = R 2 = Opening angle Figure 7: Pressure probe position for new index Figure 8: New calibrated index coefficient evolution The P WKp1 P inf index coefficient was estimated with a third order polynomial fit (Eq. 3) based on five of the previously calculated opening angles. To see how the method performs, the flow was then predicted for the remaining two openings (34.5 and 42.3 degrees). In a third test simulating a head change, the flow was increased by 10% at the nominal opening (36.7deg). As it can be seen in Table 3, by combining the polynomial function and pressure difference, the method was able to capture the flow variation quite well for the three points that were not included in the calibration process. 3 2 Eq. 3 K = x x X opening 29 deg 31.7 deg 36.7 deg 45.6 deg 50.5 deg 34.5 deg 42.3 deg 36.7 deg Q+10% Flow [m3/s] P WKp1-Pinf [KPa] K Coefficient Predicted flow [m3/s] (-0.16%) Table 2: Predicted flow rate for various openings and conditions (-0.23%) (-0.12%) To verify the sensitivity of the calibrated index to inflow conditions, the predicted flow rate was analysed in a similar way as for the WK. As shown in Fig. 9, the results were less affected than the WK probes, thanks to the large increase in pressure difference and the filtering effect of the guide vane. (reference) Q P1-Pinf = 0.5 % Q Psup-Pinf =0.1 % Q P1-Pinf = 0.4 % Q Psup-Pinf = 0.1 % Q P1-Pinf = 0.1 % Q Psup-Pinf = 0.2 -% Figure 9: Impact of inflow conditions for the new index 5
6 Experimental Results The numerical results were encouraging enough but the new method still had to pass the field test. In order to evaluate the sensitivity of the new index measurement as well as the classical Winter Kennedy index, the system performance was monitored on the Unit no. 5 over a six month period in Fig. 10 shows the measurement error over a period of two days when either of the adjacent units (no. 4 and no. 6) was started or stopped. Flow measurement was done by measuring the pressure difference between one of the pressure taps of the cover (P inf ) and one of the Winter Kennedy taps (WKP3 in this case). It shows that starting or stopping unit no 4 or 6 clearly affects the flow measurement given by the classical WK. The measurement error reaches 1% from the condition of the Unit no. 6 being stopped and Unit no. 4 running compared to the reverse. It is evident that the velocity profile in the WK taps section is immediately affected when one unit is stopped. In addition, the measurement error on the WK seems to evolve slowly while the adjacent units remain at rest. This has yet to be explained but could be related to the time constant of the upstream reservoir. As expected from the numerical simulations, the new index method is influenced by the operation of adjacent units to a far lesser extent Flow error (%) dq.qwkp1p3b dq.qpw k3pint Qgr Qgr5 50 Qgr Time (day) Discharge Units 4 to 6 (m³/s) Figure 10: Flow measurement error of the new index method and discharge of adjacent units Table 3 gives additional insight on the performance of the system by showing the standard deviation of the flow measurement over a period of 50 days. The operation during this period consisted mainly of a combination of optimal and peak loads in a context of high demand due to electric heating in the winter. The calibration of the various indices was done by setting the average error to zero for each method. The samples were taken as 5 minutes averages and were filtered to represent only steady operation. Two methods were used to obtain the flow rate from the WK index. The classical WK method used a fix coefficient and allowed for variation of the exponent (QWkP1P3b and QWkP2P3b) as in Eq. 1, while the alternative method (QWkP1P3 and QWkP2P3) used a variable coefficient and 0.5 for the exponent as suggested in this paper (Eq. 2). As often experimented, because of its higher pressure difference, the WK P2-P3 has the best performance of the two WK indices. However, it is interesting to note that applying a correction for the guide vane position can improve the performance of this index further. Also, the effect of the operation of Unit no. 4 is shown to be greater than that of Unit no. 6. This can be easily explained because Unit no. 4 is next to the left channel where the WK probes are located. With regards to the performance of the new index, one of the new index measurements ( Pwk1-Psup) shows an error of the same magnitude as the WK method. This is the measurement with the lowest pressure difference among the new index methods; in fact, it was about the order of magnitude of the WK pressure difference. Globally, when compared to the usual WK method (QWkP2P3b), the most representative index of the new method (QPwk3Pinf) cuts the error by half. This performance could probably be improved even more if, instead of using the WkP3, a pressure more representative of the upstream condition in the spiral casing could be used. 6
7 Index method All data Unit 4 Unit 6 Units 4 and 6 Units 4 and 6 stopped stopped stopped running QWkP1P QWkP1P3b QWkP2P QWkP2P3b QPwk1Pinf QPwk1Psup QPinfPsup QPwk3Pinf QPwk3Psup Occurrence (5 min ) WK New index method Table 3: Standard deviation of flow error for various index methods CONCLUSION While many papers mention the possibility of monitoring flow rate with the WK probes, many also reported experiences that were not so conclusive, especially in low-head plants. Frequently, different coefficients were found at various heads and exponents had to be modified accordingly to obtain a good fit. On the whole, those systems had limited range and were not very useful for predicting the flow under all conditions. By combining CFD and experimental expertises, a project was started to better understand what was going on with index testing and to develop a new system for monitoring the flow rate that could be installed in most plants. This paper demonstrated by numerical and experimental means that the sensitivity of the WK index measurement technique is limited because the flow homology condition is not always observed. By placing a pressure probe on the cover of the meridian channel behind the guide vane and calibrating the obtained index with the angular position of the distributor, a much better indication of the flow passing trough the turbine can be obtained. Since the calibration is mostly geometric, the suggested method theoretically allows for comparison between similar units. Moreover, as the calibration curve is valid at any head, it could save the time and money to measure at various head. The system works well for propeller units. Early results (not presented in this paper) show that it can also be used with similar success in Francis turbine. For Kaplan turbines, the system would need to be adapted to include the blade pitch because of the change in meridian channel flow distribution. This would turn the problem into determination of a calibration surface instead of a calibration curve. Unfortunately, this also means that such a method could not be used if the runner is replaced because a new calibration curve would then be necessary. The calibrated index method is one more tool available to field engineers to validate their results and a way to add some value to absolute efficiency testing since it can provide continuous information on unit performance after the measurement is done. This implementation could also potentially be used for maintenance purposes, in order to decide when to clean the trash rack, for instance. It is also important to mention that properly placed pressure probes behind the guide vane are often already available in more recent powerhouses. These were used during unit startup in order to monitor the rotor/stator interaction but were often abandoned afterwards. Many of the results presented in this paper were based on CFD simulations. These simulations are very useful for flow investigation and usually give the right trend and proper order of magnitude of a given phenomena. However, they also have many internal limits such as turbulence modeling, wall roughness representation, numerical dissipation and mesh sensitivity. Judgment must be used when dealing with theses aspects. The fact that the calculated calibration curve and WK constants did not match the measurements is to be borne in mind since the entire method is based on the link between the index coefficient and the guide vane opening. For the time being, the challenge will be to further investigate the accuracy and limits of the proposed method. The best way to obtain the calibration, either numerically, experimentally or with a combination of both, is also a subject of interest. Finally, and this may be the greatest challenge, the system will have to leave the research field to integrate operational practices in order to generate some added value. 7
8 REFERENCES [1] IEC 60041, Field Acceptance Tests to Determine the Hydraulic Performance of Hydraulic Turbines, Storage Pumps and Pump-Turbines, 3rd Edition, 1991 [2] Kercan, V.; Djelic, V.; Rus, T.; Vujanic V.; Experience with Kaplan turbine efficiency measurementscurrent meters and/or index test flow measurement, 1 st IGHEM conference, Montréal, Canada, 1996 [3] Cloutier, E.; Proulx G.; Bouhadji, L.; Lemon, D.; Comparison of discharge measurement by current meter and acoustic scientillation methods at La Grande-1 ; 4 th IGHEM conference, Lucerne, Switzerland, 2004 [4] Muntean, S.; Anton, L.E.; Baya, A.; Campian, V. Balint, D.; Susan-Resiga, R.; Validation of Numerical Results with In-situ Measurement for kaplan Turbine, 6 th IGHEM conference, Portland, USA, 2006 [5] Streat, N.; Macdonals J.A; Johnson R.E; Surveillance en ligne du rendement des génératrices hydroélectriques ; BC Hydro Report, Association Canadienne de l Électricité, Montréal, Canada, 1982 [6] Muciaccia, F. F.; Randall B.W.; Evalutation of the benefits of turbine refurbishment by means of Index Test Method; Reliability of results and Problems in Applications ; 3 rd IGHEM conference; Kempten, Germany, 2000 [7] Sheldon, L. H.; Modern Errors in Winter-Kennedy Piezometers, 2 nd IGHEM conference, Reno, USA, 1998 [8] Ansys CFX 11.0 reference manuals Jonathan Nicolle graduated in mechanical engineering from Université Laval in He obtained a master in aerospace engineering in Since then, he has been working at IREQ-Hydro-Québec s Research Institute where he specializes in CFD analyses of hydraulic turbines. Gilles Proulx, P. Eng., graduated in Mechanical Engineering from the École Polytechnique de Montréal in 1989 and has worked for Hydro-Québec s testing department since then. He has worked on the commissioning of Hydro-Québec's major power plants. He has performed many performance tests using different methods and is responsible for the R&D team of the testing department. He is the convenor of Maintenance Team 28 of the TC4 of IEC. 8
Flow simulation and efficiency hill chart prediction for a Propeller turbine
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science Flow simulation and efficiency hill chart prediction for a Propeller turbine To cite this article: T C Vu et al 2010 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ.
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science Flow simulation and efficiency hill chart prediction for a Propeller turbine To cite this article: T C Vu et al 2010 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Environ.
PERFORMANCE MEASUREMENTS ON REFURBISHED TURBINES OF 770,000 kw AT GURI HYDROELECTRIC COMPLEX
 5 th IGHEM International Conference 1 (10) PERFORMANCE MEASUREMENTS ON REFURBISHED TURBINES OF 770,000 kw AT GURI HYDROELECTRIC COMPLEX N. CARON, F. ARZOLA Essais Spéciaux de Production, Hydro-Québec,
5 th IGHEM International Conference 1 (10) PERFORMANCE MEASUREMENTS ON REFURBISHED TURBINES OF 770,000 kw AT GURI HYDROELECTRIC COMPLEX N. CARON, F. ARZOLA Essais Spéciaux de Production, Hydro-Québec,
CFD Analysis of a Low Head Propeller Turbine with Comparison to Experimental Data By: Artem Ivashchenko, Mechanical Solutions, Inc.
 CFD Analysis of a Low Head Propeller Turbine with Comparison to Experimental Data By: Artem Ivashchenko, Mechanical Solutions, Inc. Edward Bennett, Mechanical Solutions, Inc. CFD Analysis of a Low Head
CFD Analysis of a Low Head Propeller Turbine with Comparison to Experimental Data By: Artem Ivashchenko, Mechanical Solutions, Inc. Edward Bennett, Mechanical Solutions, Inc. CFD Analysis of a Low Head
CFD analysis of high speed Francis hydraulic turbines
 TRANSACTIONS OF THE INSTITUTE OF FLUID-FLOW MACHINERY No. 131, 2016, 111 120 Maciej Kaniecki a, Zbigniew Krzemianowski b CFD analysis of high speed Francis hydraulic turbines a Research and Development
TRANSACTIONS OF THE INSTITUTE OF FLUID-FLOW MACHINERY No. 131, 2016, 111 120 Maciej Kaniecki a, Zbigniew Krzemianowski b CFD analysis of high speed Francis hydraulic turbines a Research and Development
Task 1 For Task 1, the outlet was set as a zero-gauge pressure outlet, which is the same outlet condition as the five smaller pipes.
 Jacob Schichtel Project 2 Page 1 of 9 Setup The geometry was created in ANSYS Design modeler as specified in the report instructions. A plane of symmetry was used to reduce the computation time and to
Jacob Schichtel Project 2 Page 1 of 9 Setup The geometry was created in ANSYS Design modeler as specified in the report instructions. A plane of symmetry was used to reduce the computation time and to
CFD Analysis of Pelton Runner
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 4, Issue 8, August 2014 1 CFD Analysis of Pelton Runner Amod Panthee *, Hari Prasad Neopane **, Bhola Thapa ** * Turbine Testing Lab,
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 4, Issue 8, August 2014 1 CFD Analysis of Pelton Runner Amod Panthee *, Hari Prasad Neopane **, Bhola Thapa ** * Turbine Testing Lab,
Design and Simulation of Very Low Head Axial Hydraulic Turbine with Variation of Swirl Velocity Criterion
 International Journal of Fluid Machinery and Systems DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.5293/ijfms.2014.7.2.068 Vol. 7, No. 2, April-June 2014 ISSN (Online): 1882-9554 Original Paper (Invited) Design and Simulation
International Journal of Fluid Machinery and Systems DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.5293/ijfms.2014.7.2.068 Vol. 7, No. 2, April-June 2014 ISSN (Online): 1882-9554 Original Paper (Invited) Design and Simulation
CRHT VII. Design and CFD analysis of Pico- hydro Turgo turbine. Paper no. CRHT17-11
 Proceedings of the International Symposium on Current Research in Hydraulic Turbines CRHT VII April 04, 2016, Turbine Testing Lab, Kathmandu University, Dhulikhel, Nepal Paper no. CRHT17-11 Design and
Proceedings of the International Symposium on Current Research in Hydraulic Turbines CRHT VII April 04, 2016, Turbine Testing Lab, Kathmandu University, Dhulikhel, Nepal Paper no. CRHT17-11 Design and
Pressure Pulsations and Vibration Measurements in Francis Turbines with and without Freely Rotating Runner Cone Extension
 Proceedings of the International Symposium on Current Research in Hydraulic Turbines CRHT VI March 14, 2016, Turbine Testing Lab, Kathmandu University, Dhulikhel, Nepal Paper no. CRHT2016-15 Pressure Pulsations
Proceedings of the International Symposium on Current Research in Hydraulic Turbines CRHT VI March 14, 2016, Turbine Testing Lab, Kathmandu University, Dhulikhel, Nepal Paper no. CRHT2016-15 Pressure Pulsations
WATER JET CONTROL TECHNIQUE FOR SWIRLING FLOWS IN FRANCIS TURBINES DIFFUSER
 3 rd International Conference on Energy and Environment CIEM2007, Bucharest, 22-23 November WATER JET CONTROL TECHNIQUE FOR SWIRLING FLOWS IN FRANCIS TURBINES DIFFUSER Sebastian MUNTEAN 1*, Romeo SUSAN-RESIGA
3 rd International Conference on Energy and Environment CIEM2007, Bucharest, 22-23 November WATER JET CONTROL TECHNIQUE FOR SWIRLING FLOWS IN FRANCIS TURBINES DIFFUSER Sebastian MUNTEAN 1*, Romeo SUSAN-RESIGA
Volumetric gauging method vs Gibson method - comparative analysis of the measurement results of discharge through pomp-turbine in both operation modes
 Volumetric gauging method vs Gibson method - comparative analysis of the measurement results of discharge through pomp-turbine in both operation modes dam damkowski, Waldemar Janicki, Zbigniew Krzemianowski,
Volumetric gauging method vs Gibson method - comparative analysis of the measurement results of discharge through pomp-turbine in both operation modes dam damkowski, Waldemar Janicki, Zbigniew Krzemianowski,
Impellers of low specific speed centrifugal pump based on the draughting technology
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science Impellers of low specific speed centrifugal pump based on the draughting technology To cite this article: C Hongxun et al 2010 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science Impellers of low specific speed centrifugal pump based on the draughting technology To cite this article: C Hongxun et al 2010 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth
Derivation of Global Parametric Performance of Mixed Flow Hydraulic Turbine Using CFD. Ruchi Khare, Vishnu Prasad and Sushil Kumar
 Derivation of Global Parametric Performance of Mixed Flow Hydraulic Turbine Using CFD Ruchi Khare, Vishnu Prasad and Sushil Kumar Ruchi Khare Vishnu Prasad Sushil Kumar Abstract: The testing of physical
Derivation of Global Parametric Performance of Mixed Flow Hydraulic Turbine Using CFD Ruchi Khare, Vishnu Prasad and Sushil Kumar Ruchi Khare Vishnu Prasad Sushil Kumar Abstract: The testing of physical
Comparison between 2D and 3D Hydraulic Modelling Approaches for Simulation of Vertical Slot Fishways
 5 th International Symposium on Hydraulic Structures Brisbane, Australia, 25-27 June 2014 Hydraulic Structures and Society: Engineering Challenges and Extremes ISBN 9781742721156 - DOI: 10.14264/uql.2014.49
5 th International Symposium on Hydraulic Structures Brisbane, Australia, 25-27 June 2014 Hydraulic Structures and Society: Engineering Challenges and Extremes ISBN 9781742721156 - DOI: 10.14264/uql.2014.49
Measuring discharge. Climatological and hydrological field work
 Measuring discharge Climatological and hydrological field work 1. Background Discharge (or surface runoff Q s) refers to the horizontal water flow occurring at the surface in rivers and streams. It does
Measuring discharge Climatological and hydrological field work 1. Background Discharge (or surface runoff Q s) refers to the horizontal water flow occurring at the surface in rivers and streams. It does
3- Hydropower. Energy conversion and hydropower principles
 3- Hydropower The hydraulic power is one of the oldest energy sources of the mankind, namely for irrigation and industry. Nowadays, small hydro is one of the most valuable answers to the question of how
3- Hydropower The hydraulic power is one of the oldest energy sources of the mankind, namely for irrigation and industry. Nowadays, small hydro is one of the most valuable answers to the question of how
Turbine hydraulic assessment and optimization in rehabilitation projects
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science OPEN ACCESS Turbine hydraulic assessment and optimization in rehabilitation projects To cite this article: L Bornard et al 2014 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science OPEN ACCESS Turbine hydraulic assessment and optimization in rehabilitation projects To cite this article: L Bornard et al 2014 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth
CFD on Small Flow Injection of Advanced Accumulator in APWR
 54 CFD on Small Flow Injection of Advanced Accumulator in APWR TOMOSHIGE TAKATA TAKAFUMI OGINO TAKASHI ISHIBASHI TADASHI SHIRAISHI The advanced accumulator in the advanced pressurized-water reactor is
54 CFD on Small Flow Injection of Advanced Accumulator in APWR TOMOSHIGE TAKATA TAKAFUMI OGINO TAKASHI ISHIBASHI TADASHI SHIRAISHI The advanced accumulator in the advanced pressurized-water reactor is
Swansea Bay tidal powerplant: Bi-directional bulb pump-turbine with variable speed
 Swansea Bay tidal powerplant: Bi-directional bulb pump-turbine with variable speed M. Kragl, E. Kontoleontos, J. Michelcic, M. Case S. Weissenberger and B. Benz Tidal Lagoon Power Research and Development
Swansea Bay tidal powerplant: Bi-directional bulb pump-turbine with variable speed M. Kragl, E. Kontoleontos, J. Michelcic, M. Case S. Weissenberger and B. Benz Tidal Lagoon Power Research and Development
Lateral Outflow from Supercritical Channels
 Lateral Outflow from Supercritical Channels J. Coonrod 1, J. Ho 2 and N. Bernardo 3 1 Associate Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM 87131; PH (505) 277-3233;
Lateral Outflow from Supercritical Channels J. Coonrod 1, J. Ho 2 and N. Bernardo 3 1 Associate Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM 87131; PH (505) 277-3233;
Pumps, Turbines, and Pipe Networks, part 2. Ch 11 Young
 Pumps, Turbines, and Pipe Networks, part 2 Ch 11 Young Pump and Turbine Dimensional Analysis (11.5 Young) Say we want to replace turbines on the Hoover Dam Want to have a good design Essentially impossible
Pumps, Turbines, and Pipe Networks, part 2 Ch 11 Young Pump and Turbine Dimensional Analysis (11.5 Young) Say we want to replace turbines on the Hoover Dam Want to have a good design Essentially impossible
Preliminary Study for Design Core of Nuclear Research Reactor of TRIGA Bandung Using Fuel Element Plate MTR
 Article Preliminary Study for Design Core of Nuclear Research Reactor of TRIGA Bandung Using Fuel Element Plate MTR Anwar Ilmar Ramadhan 1,3, *, Aryadi Suwono 1, Efrizon Umar 2, and Nathanael Panagung
Article Preliminary Study for Design Core of Nuclear Research Reactor of TRIGA Bandung Using Fuel Element Plate MTR Anwar Ilmar Ramadhan 1,3, *, Aryadi Suwono 1, Efrizon Umar 2, and Nathanael Panagung
Aerodynamic Design of 2.5 MW Horizontal Wind Turbine Blade in Combination with CFD Analysis
 Aerodynamic Design of 2.5 MW Horizontal Wind Turbine Blade in Combination with CFD Analysis Seul-Ki Yeom *, Tae-Jin Kang *, Warn-Gyu Park 1) School of Mechanical Engineering, Pusan National University,
Aerodynamic Design of 2.5 MW Horizontal Wind Turbine Blade in Combination with CFD Analysis Seul-Ki Yeom *, Tae-Jin Kang *, Warn-Gyu Park 1) School of Mechanical Engineering, Pusan National University,
Computational and Experimental Study of an Ultra Low Head Turbine
 Kathmandu University Computational and Experimental Study of an Ultra Low Head Turbine Group members: Nischal Pokharel(loyalnp18@gmail.com) Pradeep Parajuli Pratik Koirala Under the Supervision of: Prof.
Kathmandu University Computational and Experimental Study of an Ultra Low Head Turbine Group members: Nischal Pokharel(loyalnp18@gmail.com) Pradeep Parajuli Pratik Koirala Under the Supervision of: Prof.
Optimizing a cooling water outfall inside the Maasvlakte 2 port extension - dealing with conflicting requirements
 Optimizing a cooling water outfall inside the Maasvlakte 2 port extension - dealing with conflicting requirements Martijn P.C. de Jong 1,2, Arnout C. Bijlsma 1, and Aron Ament 3 1 Deltares, P.O. Box 177,
Optimizing a cooling water outfall inside the Maasvlakte 2 port extension - dealing with conflicting requirements Martijn P.C. de Jong 1,2, Arnout C. Bijlsma 1, and Aron Ament 3 1 Deltares, P.O. Box 177,
CFD/FEM Based Analysis Framework for Wind Effects on Tall Buildings in Urban Areas
 2017 2nd International Conference on Industrial Aerodynamics (ICIA 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-481-3 CFD/FEM Based Analysis Framework for Wind Effects on Tall Buildings in Urban Areas Qiao Yan, Dalong Li,
2017 2nd International Conference on Industrial Aerodynamics (ICIA 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-481-3 CFD/FEM Based Analysis Framework for Wind Effects on Tall Buildings in Urban Areas Qiao Yan, Dalong Li,
Discharge measurements at SLAPY HPP Comparison between acoustic scintillation and pressure-time methods
 Discharge measurements at SLAPY HPP Comparison between acoustic scintillation and pressure-time methods Presented at Hydro 2013 Petr SEVCIK, Dipl. Eng., OSC, Brno, Czech Republic Bertrand REEB, Dipl. Eng.,
Discharge measurements at SLAPY HPP Comparison between acoustic scintillation and pressure-time methods Presented at Hydro 2013 Petr SEVCIK, Dipl. Eng., OSC, Brno, Czech Republic Bertrand REEB, Dipl. Eng.,
International Symposium on Current Research in HydraulicTurbines DESIGN AND CFD ANALYSIS OF PICO HYDRO TURGO TURBINE
 Kathmandu University International Symposium on Current Research in HydraulicTurbines (CRHT-VII) DESIGN AND CFD ANALYSIS OF PICO HYDRO TURGO TURBINE Sudish Gyanwali 1*, Kush Kuikel 1 and Abinath Thapa
Kathmandu University International Symposium on Current Research in HydraulicTurbines (CRHT-VII) DESIGN AND CFD ANALYSIS OF PICO HYDRO TURGO TURBINE Sudish Gyanwali 1*, Kush Kuikel 1 and Abinath Thapa
ELBE RIVER MODEL: UVP FLOW MAPPING
 ELBE RIVER MODEL: UVP FLOW MAPPING Vojtech Bares 1 and Prof. Vojtech Broza 2 1 Doctorand, Czech Technical University in Prague, Faculty of Civil Engineering, Laboratory of Ecological Risks in Urban Drainage,
ELBE RIVER MODEL: UVP FLOW MAPPING Vojtech Bares 1 and Prof. Vojtech Broza 2 1 Doctorand, Czech Technical University in Prague, Faculty of Civil Engineering, Laboratory of Ecological Risks in Urban Drainage,
Interference of Wind Turbines with Different Yaw Angles of the Upstream Wind Turbine
 42nd AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference and Exhibit 25-28 June 2012, New Orleans, Louisiana AIAA 2012-2719 Interference of Wind Turbines with Different Yaw Angles of the Upstream Wind Turbine Ahmet Ozbay 1,
42nd AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference and Exhibit 25-28 June 2012, New Orleans, Louisiana AIAA 2012-2719 Interference of Wind Turbines with Different Yaw Angles of the Upstream Wind Turbine Ahmet Ozbay 1,
The Technical Challenges of Dissolved Oxygen Enhancement
 The Technical Challenges of Dissolved Oxygen Enhancement B.Papillon EPRI-DOE Conference on Environmentally-Enhanced Hydro Turbines Washington DC May 19, 2011 Agenda 1st topic 2nd topic 3nd topic 4nd topic
The Technical Challenges of Dissolved Oxygen Enhancement B.Papillon EPRI-DOE Conference on Environmentally-Enhanced Hydro Turbines Washington DC May 19, 2011 Agenda 1st topic 2nd topic 3nd topic 4nd topic
A STUDY OF CROSS CONTAMINATION OF IN-SUITE VENTILATION SYSTEMS USED IN MULTI-UNIT RESIDENTIAL BUILDINGS
 A STUDY OF CROSS CONTAMINATION OF IN-SUITE VENTILATION SYSTEMS USED IN MULTI-UNIT RESIDENTIAL BUILDINGS C.A. Parker, K.D. Pressnail, M.F. Touchie, D. DeRose, and S. Dedesko ABSTRACT Complaints of cross
A STUDY OF CROSS CONTAMINATION OF IN-SUITE VENTILATION SYSTEMS USED IN MULTI-UNIT RESIDENTIAL BUILDINGS C.A. Parker, K.D. Pressnail, M.F. Touchie, D. DeRose, and S. Dedesko ABSTRACT Complaints of cross
Numerical Modelling of Air Distribution in the Natatorium Supported by the Experiment
 Proceedings of the World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM 2015) Barcelona, Spain July 20-21, 2015 Paper No. 277 Numerical Modelling of Air Distribution in the Natatorium
Proceedings of the World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM 2015) Barcelona, Spain July 20-21, 2015 Paper No. 277 Numerical Modelling of Air Distribution in the Natatorium
Discharge Measurement in Small Hydropower Stations using Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler
 Discharge Measurement in Small Hydropower Stations using Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler B.K. Gandhi 1, H.K. Verma 2 and S.S. Patnaik 3 1) Department of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering, Indian Institute
Discharge Measurement in Small Hydropower Stations using Acoustic Doppler Current Profiler B.K. Gandhi 1, H.K. Verma 2 and S.S. Patnaik 3 1) Department of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering, Indian Institute
Performance improvement of headworks: a case of Kalignadaki A Hydropweor Project through physical hydraulic modelling
 Performance improvement of headworks: a case of Kalignadaki A Hydropweor Project through physical hydraulic modelling Dr. Ing. Meg B. Bishwakarma General Manager, Hydro Lab Pvt. Ltd., Nepal ABSTRACT: The
Performance improvement of headworks: a case of Kalignadaki A Hydropweor Project through physical hydraulic modelling Dr. Ing. Meg B. Bishwakarma General Manager, Hydro Lab Pvt. Ltd., Nepal ABSTRACT: The
ORCHID Turbine. Fluid-dynamic design and characterization of a mini-orc turbine for laboratory experiments
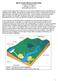
 Prof. ORCHID Turbine Fluid-dynamic design and characterization of a mini-orc turbine for laboratory experiments M. Pini, C. De Servi, M. Burigana, S. Bahamonde, A. Rubino, S. Vitale, P. Colonna ORC2017-14/09/2017
Prof. ORCHID Turbine Fluid-dynamic design and characterization of a mini-orc turbine for laboratory experiments M. Pini, C. De Servi, M. Burigana, S. Bahamonde, A. Rubino, S. Vitale, P. Colonna ORC2017-14/09/2017
Numerical Investigation of the Flow Structure in a Kaplan Draft Tube at Part Load
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Numerical Investigation of the Flow Structure in a Kaplan Draft Tube at Part Load To cite this article: R Maddahian et al 2016 IOP
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Numerical Investigation of the Flow Structure in a Kaplan Draft Tube at Part Load To cite this article: R Maddahian et al 2016 IOP
Design of Experiment Pressure Measurements Inside the Tokke Runner. * Corresponding author
 Proceedings of the International Symposium on Current Research in Hydraulic Turbines CRHT VI March 14, 2016, Turbine Testing Lab, Kathmandu University, Dhulikhel, Nepal Paper no. CRHT2016-16 Design of
Proceedings of the International Symposium on Current Research in Hydraulic Turbines CRHT VI March 14, 2016, Turbine Testing Lab, Kathmandu University, Dhulikhel, Nepal Paper no. CRHT2016-16 Design of
Performance of an Open Ducted Type Very Low Head Cross- Flow Turbine
 Performance of an Open Ducted Type Very Low Head Cross- Flow Turbine Zhenmu Chen, Van Thanh Tien Nguyen, Morihito Inagaki, and Young-Do Choi * Abstract Cross Flow Turbine (CFT) known as a Banki turbine
Performance of an Open Ducted Type Very Low Head Cross- Flow Turbine Zhenmu Chen, Van Thanh Tien Nguyen, Morihito Inagaki, and Young-Do Choi * Abstract Cross Flow Turbine (CFT) known as a Banki turbine
ISSN No MIT Publications
 MIT International Journal of Mechanical Engineering Vol. 1 No. 2 Aug 2011, pp 93-100 93 CFD Analysis of 3-D Flow for Francis Turbine Manoj Kumar Shukla Lecturer, KNPC, Jabalpur (MP), India (Email: mksmact@gmail.com)
MIT International Journal of Mechanical Engineering Vol. 1 No. 2 Aug 2011, pp 93-100 93 CFD Analysis of 3-D Flow for Francis Turbine Manoj Kumar Shukla Lecturer, KNPC, Jabalpur (MP), India (Email: mksmact@gmail.com)
Transient and Succession-of-Steady-States Pipeline Flow Models
 Transient and Succession-of-Steady-States Pipeline Flow Models Jerry L. Modisette, PhD, Consultant Jason P. Modisette, PhD, Energy Solutions International This paper is copyrighted to the Pipeline Simulation
Transient and Succession-of-Steady-States Pipeline Flow Models Jerry L. Modisette, PhD, Consultant Jason P. Modisette, PhD, Energy Solutions International This paper is copyrighted to the Pipeline Simulation
O. Capron *1, A. Samba 1,2, N. Omar 1, H. Gualous 2, P. Van den Bossche 1, J. Van Mierlo 1. Brussel, Brussels, BELGIUM. 1.
 Large and High Power Cylindrical Batteries Analysis of the Battery Packs Temperature Distributions Using COMSOL Multiphysics and MATLAB Simulation Softwares O. Capron *1, A. Samba 1,2, N. Omar 1, H. Gualous
Large and High Power Cylindrical Batteries Analysis of the Battery Packs Temperature Distributions Using COMSOL Multiphysics and MATLAB Simulation Softwares O. Capron *1, A. Samba 1,2, N. Omar 1, H. Gualous
Urban Physics: towards sustainable buildings and cities
 Inauguration Event & Mini-Symposium for Prof.dr. Alexey Voinov: SYSTEMS AND SUSTAINABILITY IN TIME AND SPACE Urban Physics: towards sustainable buildings and cities Prof.dr.ir. Bert Blocken Eindhoven University
Inauguration Event & Mini-Symposium for Prof.dr. Alexey Voinov: SYSTEMS AND SUSTAINABILITY IN TIME AND SPACE Urban Physics: towards sustainable buildings and cities Prof.dr.ir. Bert Blocken Eindhoven University
Chapter Six{ TC "Chapter Six" \l 1 } System Simulation
 Chapter Six{ TC "Chapter Six" \l 1 } System Simulation In the previous chapters models of the components of the cooling cycle and of the power plant were introduced. The TRNSYS model of the power plant
Chapter Six{ TC "Chapter Six" \l 1 } System Simulation In the previous chapters models of the components of the cooling cycle and of the power plant were introduced. The TRNSYS model of the power plant
NUMERICAL SIMULATION DOWNSTREAM ATTRACTION FLOW AT DANUBE WEIR DONAUWÖRTH
 9 th ISE 2012, Vienna NUMERICAL SIMULATION DOWNSTREAM ATTRACTION FLOW AT DANUBE WEIR DONAUWÖRTH MARKUS GRÜNZNER TECHNISCHE UNIVERSITÄT MÜNCHEN DEPARTMENT OF HYDRAULIC ENGINEERING 80333 MUNICH, BAVARIA,
9 th ISE 2012, Vienna NUMERICAL SIMULATION DOWNSTREAM ATTRACTION FLOW AT DANUBE WEIR DONAUWÖRTH MARKUS GRÜNZNER TECHNISCHE UNIVERSITÄT MÜNCHEN DEPARTMENT OF HYDRAULIC ENGINEERING 80333 MUNICH, BAVARIA,
Agenda. Background Validation studies. 3D application. Co-simulation. Summary. Espedal stratified flow. StatOil wavy-slug flow.
 www.cd-adapco.com Computational Flow Assurance Recent progress in modelling of multiphase flows in long pipelines Simon Lo, Abderrahmane Fiala (presented by Demetris Clerides) Subsea Asia 2010 Agenda Background
www.cd-adapco.com Computational Flow Assurance Recent progress in modelling of multiphase flows in long pipelines Simon Lo, Abderrahmane Fiala (presented by Demetris Clerides) Subsea Asia 2010 Agenda Background
Types of Hydropower Facilities
 Types of Hydropower Facilities 1 Impoundment Hydropower- uses a dam to store water. Water may be released either to meet changing electricity needs or to maintain a constant water level. 2 Run-of-River
Types of Hydropower Facilities 1 Impoundment Hydropower- uses a dam to store water. Water may be released either to meet changing electricity needs or to maintain a constant water level. 2 Run-of-River
Hydraulic performance of a low specific speed centrifugal pump with Spanwise-Slotted Blades
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Hydraulic performance of a low specific speed centrifugal pump with Spanwise-Slotted Blades To cite this article: D X Ye et al 2013
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Hydraulic performance of a low specific speed centrifugal pump with Spanwise-Slotted Blades To cite this article: D X Ye et al 2013
A CFD ANALYSIS OF CENTRIFUGAL PUMP TO IMPROVE DISCHARGE BY VARYING BLADE GEOMETRY
 A CFD ANALYSIS OF CENTRIFUGAL PUMP TO IMPROVE DISCHARGE BY VARYING BLADE GEOMETRY 1 ANJANI KUMAR SINHA, 2 A. JOHN RAJAN, 3 ERIKI ANANDA KUMAR 1,3 Senior Lecturer, Dept. of Mech. Eng., Nilai University,
A CFD ANALYSIS OF CENTRIFUGAL PUMP TO IMPROVE DISCHARGE BY VARYING BLADE GEOMETRY 1 ANJANI KUMAR SINHA, 2 A. JOHN RAJAN, 3 ERIKI ANANDA KUMAR 1,3 Senior Lecturer, Dept. of Mech. Eng., Nilai University,
Combustion in anode baking furnaces: Comparison of two modeling approaches to predict variability
 338 Proceedings of Combustion Institute Canadian Section Spring Technical Meeting Université Laval May 13-16, 2013 Combustion in anode baking furnaces: Comparison of two modeling approaches to predict
338 Proceedings of Combustion Institute Canadian Section Spring Technical Meeting Université Laval May 13-16, 2013 Combustion in anode baking furnaces: Comparison of two modeling approaches to predict
The influence of the lengths of turbine blades on the power produced by miniature wind turbines that operate in non-uniform flow fields
 World Transactions on Engineering and Technology Education Vol.10, No.2, 2012 2012 WIETE The influence of the lengths of turbine blades on the power produced by miniature wind turbines that operate in
World Transactions on Engineering and Technology Education Vol.10, No.2, 2012 2012 WIETE The influence of the lengths of turbine blades on the power produced by miniature wind turbines that operate in
Hydro Electric Power (Hydel Power)
 Operating Principle Hydro Electric Power (Hydel Power) Hydro-electric power is generated by the flow of water through turbine, turning the blades of the turbine. A generator shaft connected to this turbine
Operating Principle Hydro Electric Power (Hydel Power) Hydro-electric power is generated by the flow of water through turbine, turning the blades of the turbine. A generator shaft connected to this turbine
An Investigation of Oxide Layer Impact on Heat Transfer in a Fuel Element of the MARIA Reactor
 Open Access Journal Journal of Power Technologies 93 (4) (2013) 247 256 journal homepage:papers.itc.pw.edu.pl An Investigation of Oxide Layer Impact on Heat Transfer in a Fuel Element of the MARIA Reactor
Open Access Journal Journal of Power Technologies 93 (4) (2013) 247 256 journal homepage:papers.itc.pw.edu.pl An Investigation of Oxide Layer Impact on Heat Transfer in a Fuel Element of the MARIA Reactor
SMALL HYDRO BIG CHALLENGES Renewable Energy World Asia 2016 Martin P. Bieri. September 21, 2016
 SMALL HYDRO BIG CHALLENGES Renewable Energy World Asia 2016 Martin P. Bieri September 21, 2016 CONTENT Introduction Potential in Southeast Asia Challenges in Small Hydro Main Design Steps (Bad) Examples
SMALL HYDRO BIG CHALLENGES Renewable Energy World Asia 2016 Martin P. Bieri September 21, 2016 CONTENT Introduction Potential in Southeast Asia Challenges in Small Hydro Main Design Steps (Bad) Examples
ASME PTC Flow Measurement
 ASME PTC 19.5-2004 Flow Measurement Performance Test Codes A N A M E R I C A N N A T I O N A L S T A N D A R D ASME PTC 19.5-2004 Flow Measurement Performance Test Codes AN AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD Three
ASME PTC 19.5-2004 Flow Measurement Performance Test Codes A N A M E R I C A N N A T I O N A L S T A N D A R D ASME PTC 19.5-2004 Flow Measurement Performance Test Codes AN AMERICAN NATIONAL STANDARD Three
Latest Simulation Technologies for Improving Reliability of Electric Power Systems
 Latest Simulation Technologies for Improving Reliability of Electric Power Systems 386 Latest Simulation Technologies for Improving Reliability of Electric Power Systems Kiyoshi Segawa Yasuo Takahashi
Latest Simulation Technologies for Improving Reliability of Electric Power Systems 386 Latest Simulation Technologies for Improving Reliability of Electric Power Systems Kiyoshi Segawa Yasuo Takahashi
Heat Transfer Augmentation of Air Cooled Internal Combustion Engine Using Fins through Numerical Techniques
 Research Journal of Engineering Sciences ISSN 2278 9472 Heat Transfer Augmentation of Air Cooled Internal Combustion Engine Using Fins through Numerical Techniques Abstract Mishra A.K., Nawal S. and Thundil
Research Journal of Engineering Sciences ISSN 2278 9472 Heat Transfer Augmentation of Air Cooled Internal Combustion Engine Using Fins through Numerical Techniques Abstract Mishra A.K., Nawal S. and Thundil
Created by Simpo PDF Creator Pro (unregistered version) Asst.Prof.Dr. Jaafar S. Maatooq
 Lect.No.9 2 nd Semester Barrages, Regulators, Dams 1 of 15 In order to harness the water potential of a river optimally, it is necessary to construct two types of hydraulic structures, as shown in Figure
Lect.No.9 2 nd Semester Barrages, Regulators, Dams 1 of 15 In order to harness the water potential of a river optimally, it is necessary to construct two types of hydraulic structures, as shown in Figure
Potential effects evaluation of dewatering an underground mine on surface water and groundwater located in a rural area
 Potential effects evaluation of dewatering an underground mine on surface water and groundwater located in a rural area ITRODUCTIO Michel Mailloux* Eng. M.Sc, Vincent Boisvert, M.Sc, Denis Millette, Eng.,
Potential effects evaluation of dewatering an underground mine on surface water and groundwater located in a rural area ITRODUCTIO Michel Mailloux* Eng. M.Sc, Vincent Boisvert, M.Sc, Denis Millette, Eng.,
Chapter 7 : Conclusions and recommendations
 Chapter 7 : Conclusions and recommendations 7.1 Conclusions The main goal of this research was to investigate the modelling and rainfall data requirements for the design of combined sewer systems and the
Chapter 7 : Conclusions and recommendations 7.1 Conclusions The main goal of this research was to investigate the modelling and rainfall data requirements for the design of combined sewer systems and the
nhc EARTH TECH CANADA INC. CITY OF WINNIPEG NORTH END WATER POLLUTION CONTROL CENTRE PUMP STATION MODEL TEST FINAL REPORT JANUARY 2005
 EARTH TECH CANADA INC. CITY OF WINNIPEG NORTH END WATER POLLUTION CONTROL CENTRE PUMP STATION MODEL TEST FINAL REPORT JANUARY 2005 nhc northwest hydraulic consultants CITY OF WINNIPEG NORTH END WATER POLLUTION
EARTH TECH CANADA INC. CITY OF WINNIPEG NORTH END WATER POLLUTION CONTROL CENTRE PUMP STATION MODEL TEST FINAL REPORT JANUARY 2005 nhc northwest hydraulic consultants CITY OF WINNIPEG NORTH END WATER POLLUTION
Design and Testing of a Rotating Detonation Engine for Open-Loop Gas Turbine Integration
 25 th ICDERS August 2 7, 2015 Leeds, UK Design and Testing of a Rotating Detonation Engine for Open-Loop Gas Turbine Integration Andrew Naples 1, Matt Fotia 2, Scott Theuerkauf 2, John L. Hoke 1, Fred
25 th ICDERS August 2 7, 2015 Leeds, UK Design and Testing of a Rotating Detonation Engine for Open-Loop Gas Turbine Integration Andrew Naples 1, Matt Fotia 2, Scott Theuerkauf 2, John L. Hoke 1, Fred
Lubricating grease shear flow and boundary layers in a concentric. cylinder configuration
 45 3rd International Tribology Symposium of IFToMM, March in 2013, Luleå Lubricating grease shear flow and boundary layers in a concentric cylinder configuration J. X. LI 1, LARS G. WESTERBERG 2, E. HÖGLUND
45 3rd International Tribology Symposium of IFToMM, March in 2013, Luleå Lubricating grease shear flow and boundary layers in a concentric cylinder configuration J. X. LI 1, LARS G. WESTERBERG 2, E. HÖGLUND
ISO INTERNATIONAL STANDARD
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 10816-2 Third edition 2009-10-01 Mechanical vibration Evaluation of machine vibration by measurements on non-rotating parts Part 2: Land-based steam turbines and generators in
INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 10816-2 Third edition 2009-10-01 Mechanical vibration Evaluation of machine vibration by measurements on non-rotating parts Part 2: Land-based steam turbines and generators in
ENHANCEMENT OF COEFFICIENT OF PERFORMANCE IN VAPOUR COMPRESSION REFRIGERATION CYCLE
 ENHANCEMENT OF COEFFICIENT OF PERFORMANCE IN VAPOUR COMPRESSION REFRIGERATION CYCLE Dr Venkata Ramana Reddy Mula 1, H.V.Harish 2 1 Professor and Head, Department of Aeronautical Engineering NMIT BANGALORE
ENHANCEMENT OF COEFFICIENT OF PERFORMANCE IN VAPOUR COMPRESSION REFRIGERATION CYCLE Dr Venkata Ramana Reddy Mula 1, H.V.Harish 2 1 Professor and Head, Department of Aeronautical Engineering NMIT BANGALORE
A simple model for low flow forecasting in Mediterranean streams
 European Water 57: 337-343, 2017. 2017 E.W. Publications A simple model for low flow forecasting in Mediterranean streams K. Risva 1, D. Nikolopoulos 2, A. Efstratiadis 2 and I. Nalbantis 1* 1 School of
European Water 57: 337-343, 2017. 2017 E.W. Publications A simple model for low flow forecasting in Mediterranean streams K. Risva 1, D. Nikolopoulos 2, A. Efstratiadis 2 and I. Nalbantis 1* 1 School of
SIMULATION AND PIV EXPERIMENT OF THE DUCTED WATER CURRENT TURBINE AND EXTREMELY LOW HEAD HELICAL TURBINE
 SIMULATION AND PIV EXPERIMENT OF THE DUCTED WATER CURRENT TURBINE AND EXTREMELY LOW HEAD HELICAL TURBINE Sounthisack Phommachanh 1, Shinnosuke Obi 2, Priyono Sutikno 3, Aryadi Soewono 4 1,3,4 Mechanical
SIMULATION AND PIV EXPERIMENT OF THE DUCTED WATER CURRENT TURBINE AND EXTREMELY LOW HEAD HELICAL TURBINE Sounthisack Phommachanh 1, Shinnosuke Obi 2, Priyono Sutikno 3, Aryadi Soewono 4 1,3,4 Mechanical
A Guide to Design Load Validation
 A Guide to Design Load Validation Holger Söker, Martina Damaschke, Deutsches Windenergie-Institut GmbH, Ebertstr. 96, D-26382 Wilhelmshaven, Germany, Tel. : +49-4421-4808 0, Fax: +49-4421-4808-43, h.soeker@dewi.de
A Guide to Design Load Validation Holger Söker, Martina Damaschke, Deutsches Windenergie-Institut GmbH, Ebertstr. 96, D-26382 Wilhelmshaven, Germany, Tel. : +49-4421-4808 0, Fax: +49-4421-4808-43, h.soeker@dewi.de
Computational Fluid Dynamic Analysis of Cross Flow Turbine
 Computational Fluid Dynamic Analysis of Cross Flow Turbine Mrudang Patel, Nirav Oza, Karna Patel U.G. Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, NIRMA University, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India ABSTRACT:
Computational Fluid Dynamic Analysis of Cross Flow Turbine Mrudang Patel, Nirav Oza, Karna Patel U.G. Student, Department of Mechanical Engineering, NIRMA University, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India ABSTRACT:
Heat transfer modelling of slot jet impinging on an inclined plate
 Heat transfer modelling of slot jet impinging on an inclined plate A. Ramezanpour 1, H. Shirvani 1 & I. Mirzaee 2 1 School of Design and Communication Systems, APU University, UK 2 CFD Research Centre,
Heat transfer modelling of slot jet impinging on an inclined plate A. Ramezanpour 1, H. Shirvani 1 & I. Mirzaee 2 1 School of Design and Communication Systems, APU University, UK 2 CFD Research Centre,
Optimization Of Pattern Factor Of The Annular Gas Turbine Combustor For Better Turbine Life
 Optimization Of Pattern Factor Of he Annular Gas urbine Combustor For Better urbine Life 1 Ambrish babu D, 2 K.K.Arun, 3 Anandanarayanan R 1, 2 (Mechanical Engineering, Kumaraguru College of echnology/anna
Optimization Of Pattern Factor Of he Annular Gas urbine Combustor For Better urbine Life 1 Ambrish babu D, 2 K.K.Arun, 3 Anandanarayanan R 1, 2 (Mechanical Engineering, Kumaraguru College of echnology/anna
Investigation of Rotating Instability in the Last Stage of Low Pressure Turbine during Low volume flow Operation
 Investigation of Rotating Instability in the Last Stage of Low Pressure Turbine during Low volume flow Operation Dilip Kumar Garg 1, Shrinivas Chambalwar 2, Jayant Sarode 3, Ajay Dhanopia 4 1 Department
Investigation of Rotating Instability in the Last Stage of Low Pressure Turbine during Low volume flow Operation Dilip Kumar Garg 1, Shrinivas Chambalwar 2, Jayant Sarode 3, Ajay Dhanopia 4 1 Department
HYDROLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF FLOW VARIATIONS ON SHPP SITE
 13 th International Symposium on Water Management and Hydraulic Engineering, September 9-12, 2013 Bratislava, Slovakia HYDROLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF FLOW VARIATIONS ON SHPP SITE Gordon Gilja 1, Eva Ocvirk 2
13 th International Symposium on Water Management and Hydraulic Engineering, September 9-12, 2013 Bratislava, Slovakia HYDROLOGICAL ANALYSIS OF FLOW VARIATIONS ON SHPP SITE Gordon Gilja 1, Eva Ocvirk 2
Numerical Investigation of the Integration of Heat Transfer Devices into Wind Towers
 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 34, 2013 Guest Editors: Neven Duić, Petar Sabev Varbanov Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-25-9; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 34, 2013 Guest Editors: Neven Duić, Petar Sabev Varbanov Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-25-9; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
Parametric Study for Evaluation of Design Parameters of Standing Column Well
 Proceedings World Geothermal Congress Bali, Indonesia, 5-9 April Parametric Study for Evaluation of Design Parameters of Standing Column Well Dong-Yeop Kwak 1, Duhee Park 1, Jae-Hoon Chang 1, Sang-Min
Proceedings World Geothermal Congress Bali, Indonesia, 5-9 April Parametric Study for Evaluation of Design Parameters of Standing Column Well Dong-Yeop Kwak 1, Duhee Park 1, Jae-Hoon Chang 1, Sang-Min
Thermodynamic Considerations for Large Steam Turbine Upgrades and Retrofits
 POWER-GEN Asia 2011 Kuala-Lumpur, Malaysia September 27-29, 2011 Thermodynamic Considerations for Large Steam Turbine Upgrades and Retrofits Leonid Moroz, Kirill Grebennik 15 New England Executive Park,
POWER-GEN Asia 2011 Kuala-Lumpur, Malaysia September 27-29, 2011 Thermodynamic Considerations for Large Steam Turbine Upgrades and Retrofits Leonid Moroz, Kirill Grebennik 15 New England Executive Park,
Cavitation measurements on a pump-turbine model
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Cavitation measurements on a pump-turbine model To cite this article: H Schmidt et al 2015 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 656 012071 Related content - Nucleation
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Cavitation measurements on a pump-turbine model To cite this article: H Schmidt et al 2015 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 656 012071 Related content - Nucleation
Design of a Small Scale CFB Boiler Combustion Chamber for Laboratory Purposes
 International Journal of Emerging Engineering Research and Technology Volume 3, Issue 9, September, 2015, PP 1-7 ISSN 2349-4395 (Print) & ISSN 2349-4409 (Online) Design of a Small Scale CFB Boiler Combustion
International Journal of Emerging Engineering Research and Technology Volume 3, Issue 9, September, 2015, PP 1-7 ISSN 2349-4395 (Print) & ISSN 2349-4409 (Online) Design of a Small Scale CFB Boiler Combustion
FLOW VISUALIZATION IN A SWIRLING FLUIDIZED BED Sulastri Sabudin 1*, Shahzada Khan Nawab Khan 1 and Mohd Faizal Mohideen Batcha 1
 International Conference on Mechanical Engineering Research (ICMER2013), 1-3 July 2013 Bukit Gambang Resort City, Kuantan, Pahang, Malaysia Organized by Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti Malaysia
International Conference on Mechanical Engineering Research (ICMER2013), 1-3 July 2013 Bukit Gambang Resort City, Kuantan, Pahang, Malaysia Organized by Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti Malaysia
Pumps, Turbines, and Pipe Networks. Ch 11 Young
 Pumps, Turbines, and Pipe Networks Ch 11 Young Chapter Topics Types of pumps and turbines Moment of momentum review Pump and turbine theory Energy and power Pump selection Pump-pipe networks Use of pipe
Pumps, Turbines, and Pipe Networks Ch 11 Young Chapter Topics Types of pumps and turbines Moment of momentum review Pump and turbine theory Energy and power Pump selection Pump-pipe networks Use of pipe
Aerodynamic Performance Sensitivity Analysis of Blade Design for a 100 kw HAWT
 Aerodynamic Performance Sensitivity Analysis of Blade Design for a 100 kw HAWT Hassan Dogan 1 and Mahmut Faruk Aksit 2 1 PhD Candidate, 2 Associate Professor Mechatronics Program, Faculty of Engineering
Aerodynamic Performance Sensitivity Analysis of Blade Design for a 100 kw HAWT Hassan Dogan 1 and Mahmut Faruk Aksit 2 1 PhD Candidate, 2 Associate Professor Mechatronics Program, Faculty of Engineering
Tutorial letter 101/0/2016
 Tutorial letter 101/0/2016 Hydraulic Machines III (Theory) FMA3602 Year Module Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering IMPORTANT INFORMATION: This tutorial letter contains important information
Tutorial letter 101/0/2016 Hydraulic Machines III (Theory) FMA3602 Year Module Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering IMPORTANT INFORMATION: This tutorial letter contains important information
Field and CFD Analysis of Jet Aeration and Mixing
 Field and CFD Analysis of Jet Aeration and Mixing Randal W. Samstag 1 *, Edward A. Wicklein 1, Roderick D. Reardon 2, Robert J. Leetch 3, R. (Robbie) M. Parks 3, and Colin D. Groff 3 1 Carollo Engineers,
Field and CFD Analysis of Jet Aeration and Mixing Randal W. Samstag 1 *, Edward A. Wicklein 1, Roderick D. Reardon 2, Robert J. Leetch 3, R. (Robbie) M. Parks 3, and Colin D. Groff 3 1 Carollo Engineers,
NUMERICAL SIMULATION AND CFD ANALYSIS FOR ENERGY LOSS COMPUTATION IN FULLY OPEN GEOMETRY OF PELTON TURBINE NOZZLE
 International Journal of Latest Research in Science and Technology Volume2,Issue 1 :Page No.586-593,January-February (2013) http://www.mnkjournals.com/ijlrst.htm ISSN (Online):2278-5299 NUMERICAL SIMULATION
International Journal of Latest Research in Science and Technology Volume2,Issue 1 :Page No.586-593,January-February (2013) http://www.mnkjournals.com/ijlrst.htm ISSN (Online):2278-5299 NUMERICAL SIMULATION
Modeling for Wind Farm Control
 Modeling for Wind Farm Control A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Jennifer Annoni IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER
Modeling for Wind Farm Control A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Jennifer Annoni IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER
River Current Resource Assessment and Characterization Considering Ice Conditions
 River Current Resource Assessment and Characterization Considering Ice Conditions Marie-Hélène Briand, Eng., Ph.D. Gilles Boesch, M.Eng., ing Vadim Belotserkovsky Marine Renewables Canada 2013 Annual Conference
River Current Resource Assessment and Characterization Considering Ice Conditions Marie-Hélène Briand, Eng., Ph.D. Gilles Boesch, M.Eng., ing Vadim Belotserkovsky Marine Renewables Canada 2013 Annual Conference
Screening, Definition: The unit involved is called a screen.
 Screening, Definition: Screening is a unit operation that separates materials in and/or on water (found in different sizes) from water and from entering water treatment facilities and mains. The unit involved
Screening, Definition: Screening is a unit operation that separates materials in and/or on water (found in different sizes) from water and from entering water treatment facilities and mains. The unit involved
MICRO-HYDRO INSTALLATION SIZING Jacques Chaurette eng. January 17, 2008
 MICRO-HYDRO INSTALLATION SIZING Jacques Chaurette eng. January 17, 2008 www.lightmypump.com A friend of mine asked me to help size a micro-hydro installation that he was thinking of installing at his cottage.
MICRO-HYDRO INSTALLATION SIZING Jacques Chaurette eng. January 17, 2008 www.lightmypump.com A friend of mine asked me to help size a micro-hydro installation that he was thinking of installing at his cottage.
INFLUENCE OF HEAT SOURCE LOCATION ON AIR TEMPERATURES IN SEALED MV SWITCHGEAR
 INFLUENCE OF HEAT SOURCE LOCATION ON AIR TEMPERATURES IN SEALED MV SWITCHGEAR Elin FJELD Wilhelm RONDEEL Knut VAAGSAETHER Univ.Coll. of Southeast Norway USN Norway USN - Norway elin.fjeld@usn.no wilhelm.rondeel@usn.no
INFLUENCE OF HEAT SOURCE LOCATION ON AIR TEMPERATURES IN SEALED MV SWITCHGEAR Elin FJELD Wilhelm RONDEEL Knut VAAGSAETHER Univ.Coll. of Southeast Norway USN Norway USN - Norway elin.fjeld@usn.no wilhelm.rondeel@usn.no
Introduction To Computational Fluid Dynamics. Presented by Marc Laing CFD Team Manager
 Introduction To Computational Fluid Dynamics Presented by Marc Laing CFD Team Manager Slide 1 50 years research in fluid and thermodynamics Flow meter calibration and development testing State-of-the-art
Introduction To Computational Fluid Dynamics Presented by Marc Laing CFD Team Manager Slide 1 50 years research in fluid and thermodynamics Flow meter calibration and development testing State-of-the-art
Three-Dimensional Numerical Simulation of a Model Wind Turbine
 Three-Dimensional Numerical Simulation of a Model Wind Turbine N. Tabatabaei 1, M.J. Cervantes 1,2, C. Trivedi 2, J-O Aidanpää 1 1 Luleå University of Technology, Sweden 2 Norwegian University of Science
Three-Dimensional Numerical Simulation of a Model Wind Turbine N. Tabatabaei 1, M.J. Cervantes 1,2, C. Trivedi 2, J-O Aidanpää 1 1 Luleå University of Technology, Sweden 2 Norwegian University of Science
Solution for the conclusion of the Mackenzie access in Sao Paulo Line 4 Subway.
 Solution for the conclusion of the Mackenzie access in Sao Paulo Line 4 Subway. B. Celada, F. Abamonte and P. Varona Geocontrol do Brasil, Sao Paulo, Brasil. R. Martinati Nucleo de Projetos e Engenheria,
Solution for the conclusion of the Mackenzie access in Sao Paulo Line 4 Subway. B. Celada, F. Abamonte and P. Varona Geocontrol do Brasil, Sao Paulo, Brasil. R. Martinati Nucleo de Projetos e Engenheria,
Performance Test and Structural Analysis of Cross-Flow Turbine
 American Scientific Research Journal for Engineering, Technology, and Sciences (ASRJETS) ISSN (Print) 2313-4410, ISSN (Online) 2313-4402 Global Society of Scientific Research and Researchers http://asrjetsjournal.org/
American Scientific Research Journal for Engineering, Technology, and Sciences (ASRJETS) ISSN (Print) 2313-4410, ISSN (Online) 2313-4402 Global Society of Scientific Research and Researchers http://asrjetsjournal.org/
Microfluidic Systems for Cell Growth and Cell Migration Studies
 Microfluidic Systems for Cell Growth and Cell Migration Studies Maria Dimaki 1, Pranjul Shah 1, Dorota Kwasny 1, Jacob Moresco 2 and Winnie E. Svendsen 1 1 DTU Nanotech Department of Micro- and Nanotechnology,
Microfluidic Systems for Cell Growth and Cell Migration Studies Maria Dimaki 1, Pranjul Shah 1, Dorota Kwasny 1, Jacob Moresco 2 and Winnie E. Svendsen 1 1 DTU Nanotech Department of Micro- and Nanotechnology,
Range of utilization. Envelope
 Kaplan Turbines Development Based on the principles of a Francis Turbine the Kaplan Turbine was developed by the Austrian engineer Victor Kaplan towards the beginning of the 20th century. Due to its adjustable
Kaplan Turbines Development Based on the principles of a Francis Turbine the Kaplan Turbine was developed by the Austrian engineer Victor Kaplan towards the beginning of the 20th century. Due to its adjustable
Manual of Petroleum Measurement Standards Chapter 5 Metering
 Addendum 1 July 2009 Manual of Petroleum Measurement Standards Chapter 5 Metering Section 3 Measurement of Liquid Hydrocarbons by Turbine Meters FIFTH EDITION, SEPTEMBER 2005 Addendum to MPMS Chapter
Addendum 1 July 2009 Manual of Petroleum Measurement Standards Chapter 5 Metering Section 3 Measurement of Liquid Hydrocarbons by Turbine Meters FIFTH EDITION, SEPTEMBER 2005 Addendum to MPMS Chapter
EARTHQUAKE-RESISTANT BRIDGE COMPETITION STUDENT GUIDELINES
 EARTHQUAKE-RESISTANT BRIDGE COMPETITION STUDENT GUIDELINES A PROJECT DEVELOPED FOR THE UNIVERSITY CONSORTIUM ON INSTRUCTIONAL SHAKE TABLES Developed by: Kurt McMullin Assistant Professor Department of
EARTHQUAKE-RESISTANT BRIDGE COMPETITION STUDENT GUIDELINES A PROJECT DEVELOPED FOR THE UNIVERSITY CONSORTIUM ON INSTRUCTIONAL SHAKE TABLES Developed by: Kurt McMullin Assistant Professor Department of
NEW ANALYZER FOR VISCOSITY MEASUREMENT AT REFERENCE TEMPERATURE
 NEW ANALYZER FOR VISCOSITY MEASUREMENT AT REFERENCE TEMPERATURE Dr. Luc K. Bellière, Dr. Valerie Lefèvre Sofraser Villemandeur, France Corentin Thierry Sofraser USA Houston, TX, USA KEYWORDS VISCOSITY,
NEW ANALYZER FOR VISCOSITY MEASUREMENT AT REFERENCE TEMPERATURE Dr. Luc K. Bellière, Dr. Valerie Lefèvre Sofraser Villemandeur, France Corentin Thierry Sofraser USA Houston, TX, USA KEYWORDS VISCOSITY,
Outlet Flow Velocity in Circular Culvert
 Archives of Hydro-Engineering and Environmental Mechanics Vol. 61 (2014), No. 3 4, pp. 193 203 DOI: 10.1515/heem-2015-0013 IBW PAN, ISSN 1231 3726 Outlet Flow Velocity in Circular Culvert Wojciech Szpakowski
Archives of Hydro-Engineering and Environmental Mechanics Vol. 61 (2014), No. 3 4, pp. 193 203 DOI: 10.1515/heem-2015-0013 IBW PAN, ISSN 1231 3726 Outlet Flow Velocity in Circular Culvert Wojciech Szpakowski
CFD Analysis of Clarifier Performance With and Without Energy Dissipating Inlet
 CFD Analysis of Clarifier Performance With and Without Energy Dissipating Inlet Figure 1: Energy Dissipating Inlet (LA-EDI) Introduction To estimate performance enhancements resulting from the use of an
CFD Analysis of Clarifier Performance With and Without Energy Dissipating Inlet Figure 1: Energy Dissipating Inlet (LA-EDI) Introduction To estimate performance enhancements resulting from the use of an
