Extinction Rate and Consequences
|
|
|
- Alan Harris
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Are communities saturated? Extinction Rate and Consequences Species area relationships appear driven by extinction-colonization equilibrium. Thus, there are predictable relationships between regional (gamma) diversity and local (alpha) Saturation there is a maximum alpha diversity regardless of gamma Alternatively, there may be no limit to alpha diversity and it could increase linearly with gamma Extinction rates are known to be variable through time (mass extinctions in the fossil record) Data suggests we are in or approaching a mass extinction period So? Community Emergent Properties Diversity - # species, relative abundances, other measures of Trophic structure number of trophic levels, food web structure Species composition What species occur in a region and why? Productivity Primary productivity and energy transfer through ecosystem Nutrient cycling and/or use Stability Resistance, Resilience response to environmental change Is the community resistant to change (do we observe the same species through time)? Is the community resilient (if disturbed, does the community return to pre-disturbance conditions)? Patterns of colonization and extinction What species persist or disappear from a community? How Will Emergent Properties Change With Diversity? For most metrics, ecosystem function (emergent properties) seems to be correlated with Field experiments demonstrate drought resistance (loss of biomass during drought compared to normal conditions) increases with Why?
2 Diversity and Productivity We talked before about productivity explaining (to some degree) latitudinal diversity gradients. So, no surprise that diversity and productivity are related. But, how might diversity increase productivity? Within a site, or among sites, diversity and productivity related. Coexisting species expected to have low niche overlap (Gause s Principle). Experimental Food webs demonstrate higher diversity yields greater plant biomass. Diversity Productivity Mechanisms Niche Complimentarity Species complement each other by all utilizing different resources. The more species, the greater proportion of resources used. Diversity Productivity Mechanisms If more diverse communities feature species with complimentary niches, we expect more efficient resource use at higher More available niche space is filled, more efficient use. Species Selection (Sampling Effect) Diverse communities are more likely to contain productive species. Some support for both, patterns change over time:
3 Stability How do emergent properties of communities respond to disturbance? Resistance Resilience Local and global stability Diversity Stability Relationships (Tillman 994) Stability in any community emergent property increases with diversity Individual species stability decreases Insurance hypothesis (aka. Portfolio effect) Overall community stability (total plant biomass/variance) increases with Dynamically fragile Dynamically robust How does diversity relate to stability? Individual species stability decreases with Evidence for diversity-stability Diversity itself may not be as important as the number of species interactions. Evidence Mathematical models predict low S = low stability Small island (low S) habitats are more susceptible to invasion Cultivated or monoculture habitat is more susceptible to invasion or disturbance Diverse tropical systems less invasible and/or more stable Pesticide use (reducing diversity or links among species) increases variation in pest populations. Still somewhat controversial 3
4 Models of stability (May 97) Constructed model food webs, varying diversity and complexity and measuring stability. Found that stability only occurred if: B( SC) β = strength of species interactions, assumed a constant, impossible to measure. S = # species C = connectance proportion of total number of possible species connections. ( SC) For a stable community, as S increases, C must decrease and vice versa. Models of stability (May 97) Connectance ( SC) stable unstable S Increased diversity and/or complexity decrease stability. More diversity communities are only stable if connectance is low. Low diversity systems require high connectance to be stable. Criticism of May (97) Constructed food webs at random Resulted in some unrealistic links Assumed all species linked similarly (no strong interactors) Criticisms of diversity-stability Monocultures and human altered ecosystems are not in equilibrium. Low diversity equilibrium systems are not invasible. High diversity tropical systems may be less stable than assumed, large fluctuations may go unnoticed. Islands are a special case. Diversity-stability relationships may be a mathematical inevitability. Are strong interactors more important than weak ones? 4
5 Functional Diversity The focus should not be on taxonomic diversity but on the functional roles played by species. Functional redundancy two species can play the same role, loss of one does not change ecosystem function (stabilizing) Functional insurance differences in species response (ie. Functional diversity) to disturbance buffer ecosystems against change (stabilizing effect). Phylogenetic diversity may be more important than species More distantly related taxa more likely to provide functional insurance. Diminishing returns of ecosystem function with increased Suggests functional redundancy and that species are not complementary 5
Patterns of Biological Diversity
 Patterns of Biological Diversity 1. What is biodiversity? 2. Measuring and estimating biodiversity 3. Biodiversity patterns across spatial scales 4. What explains the most prevalent biodiversity pattern,
Patterns of Biological Diversity 1. What is biodiversity? 2. Measuring and estimating biodiversity 3. Biodiversity patterns across spatial scales 4. What explains the most prevalent biodiversity pattern,
FOOD WEBS. Based on--food webs: Reconciling the structure and function of biodiversity (Thompson et al., 2012). By Jessica and Marina
 FOOD WEBS Based on--food webs: Reconciling the structure and function of biodiversity (Thompson et al., 2012). By Jessica and Marina Outline 1. Food Web Attributes 2. Food Web Ecology 3. Characteristics
FOOD WEBS Based on--food webs: Reconciling the structure and function of biodiversity (Thompson et al., 2012). By Jessica and Marina Outline 1. Food Web Attributes 2. Food Web Ecology 3. Characteristics
Chapter 19: Community Structure in Space Biodiversity
 Chapter 19: Community Structure in Space Biodiversity Measurement of biodiversity Commonness, rarity and dominance Preston s log normal distribution model a few common species with high abundances many
Chapter 19: Community Structure in Space Biodiversity Measurement of biodiversity Commonness, rarity and dominance Preston s log normal distribution model a few common species with high abundances many
Ecology Review A: Top Ten
 Ecology Review A: Top Ten 1. Populations Group of individuals of same species living in the same area at the same time Habitat vs. niche Competition a. Survivorship curves Type 1 = most live long life
Ecology Review A: Top Ten 1. Populations Group of individuals of same species living in the same area at the same time Habitat vs. niche Competition a. Survivorship curves Type 1 = most live long life
Some of the material in this sample old exam may not have been covered for you.
 SAMPLE EXAM 3 FOR BIO213 Some of the material in this sample old exam may not have been covered for you. Upon request from some students, answers are not highlighted. They will be provided and discussed
SAMPLE EXAM 3 FOR BIO213 Some of the material in this sample old exam may not have been covered for you. Upon request from some students, answers are not highlighted. They will be provided and discussed
Dynamics of Ecosystems. Chapter 57
 Dynamics of Ecosystems Chapter 57 1 The Water Cycle Nutrient Cycles Trophic Levels Primary Productivity Outline The Energy in Food Chains Ecological Pyramids Interactions Among Trophic Levels Species Richness
Dynamics of Ecosystems Chapter 57 1 The Water Cycle Nutrient Cycles Trophic Levels Primary Productivity Outline The Energy in Food Chains Ecological Pyramids Interactions Among Trophic Levels Species Richness
Restoration Ecology & Invasive Species
 Objectives: Ecology and management of invasive species in a restoration context In most cases, impossible to talk about restoration ecology without explicitly considering invasive species What is an invasive
Objectives: Ecology and management of invasive species in a restoration context In most cases, impossible to talk about restoration ecology without explicitly considering invasive species What is an invasive
CHAPTER 55: Community Ecology
 CHAPTER 55: Community Ecology 1) How is co-evolution significant in community ecology? 2) What is meant by the trophic structure of a community? 3) What does a food web show that isn t indicated by a food
CHAPTER 55: Community Ecology 1) How is co-evolution significant in community ecology? 2) What is meant by the trophic structure of a community? 3) What does a food web show that isn t indicated by a food
79. Cone- bearing trees are characteristic of the a) taiga. b) tropical rain forest. c) temperate deciduous forest. d) savanna.
 73. The portion of a species resource (biological, chemical, and physical) which a particular species actually utilizes is known as the: a) Reserve niche b) Conservation niche c) Basic niche d) Fundamental
73. The portion of a species resource (biological, chemical, and physical) which a particular species actually utilizes is known as the: a) Reserve niche b) Conservation niche c) Basic niche d) Fundamental
Community Ecology. A) Five fundamental types of species interactions: But populations and species do not exist in a vacuum. Species interactions
 ut populations and species do not exist in a vacuum Species interactions Community Ecology ) Five fundamental types of species interactions: Effect on species Competition Predation Mutualism Commensalism
ut populations and species do not exist in a vacuum Species interactions Community Ecology ) Five fundamental types of species interactions: Effect on species Competition Predation Mutualism Commensalism
Biomass. primary productivity. Read Discovery: Ecology: Online reading on last slide Prentice Hall chapters 3&4. Ecosystems
 How are detritivores different from decomposers? (please add this to your study guide) Detritivores take in dead material and it digest internally. They are all multicellular and eukaryotic (animals).
How are detritivores different from decomposers? (please add this to your study guide) Detritivores take in dead material and it digest internally. They are all multicellular and eukaryotic (animals).
Integration of climate change adaptation : site and landscape responses. Simon Duffield Natural England
 Integration of climate change adaptation : site and landscape responses Simon Duffield Natural England Present more in detail the topics on which the Convention should work, explaining why it would be
Integration of climate change adaptation : site and landscape responses Simon Duffield Natural England Present more in detail the topics on which the Convention should work, explaining why it would be
Control of Eurasian Water Milfoil & Large-scale Aquatic Herbicide Use Updated July 2006 Prepared by WDNR Lakes and Aquatic Plant Management Staff
 Control of Eurasian Water Milfoil & Large-scale Aquatic Herbicide Use Updated July 2006 Prepared by WDNR Lakes and Aquatic Plant Management Staff Introduction The spread of aquatic invasive plants is a
Control of Eurasian Water Milfoil & Large-scale Aquatic Herbicide Use Updated July 2006 Prepared by WDNR Lakes and Aquatic Plant Management Staff Introduction The spread of aquatic invasive plants is a
Patterns of Species Richness Among Biomes
 Patterns of Species Richness Among Biomes Topics and approach What is biodiversity and why is it important? What are the major drivers of species richness? Habitat heterogeneity Disturbance Species energy
Patterns of Species Richness Among Biomes Topics and approach What is biodiversity and why is it important? What are the major drivers of species richness? Habitat heterogeneity Disturbance Species energy
1. Larval production 4. Post-settlement
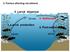 V. Factors affecting recruitment 2. Larval dispersal 3. Settlement 1. Larval production 4. Post-settlement V) Factors affecting recruitment C) Processes affecting settlement 1) Physical processes (e.g.,
V. Factors affecting recruitment 2. Larval dispersal 3. Settlement 1. Larval production 4. Post-settlement V) Factors affecting recruitment C) Processes affecting settlement 1) Physical processes (e.g.,
Grazing Land Management and Water Quality
 Grazing Land Management and Water Quality In generally management of grazing lands requires fewer chemical inputs such as fertilizers and herbicides. However, grazing lands account for a larger land surface
Grazing Land Management and Water Quality In generally management of grazing lands requires fewer chemical inputs such as fertilizers and herbicides. However, grazing lands account for a larger land surface
h p://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/biodiversity Biodiversity defined
 Biodiversity h p://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/biodiversity Biodiversity defined Typically defined as species diversity (species richness) the number of species within a given area. (many other defini ons exist)
Biodiversity h p://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/biodiversity Biodiversity defined Typically defined as species diversity (species richness) the number of species within a given area. (many other defini ons exist)
5-2 Limits to Growth Slide 1 of 21
 1 of 21 Limiting Factors Limiting Factors The primary productivity of an ecosystem can be reduced when there is an insufficient supply of a particular nutrient. Ecologists call such substances limiting
1 of 21 Limiting Factors Limiting Factors The primary productivity of an ecosystem can be reduced when there is an insufficient supply of a particular nutrient. Ecologists call such substances limiting
AP BIOLOGY 2011 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B)
 AP BIOLOGY 2011 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 3 Invasive species, such as red fire ants, introduced into an ecosystem often threaten native plants and animals. (a) Describe THREE different factors
AP BIOLOGY 2011 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 3 Invasive species, such as red fire ants, introduced into an ecosystem often threaten native plants and animals. (a) Describe THREE different factors
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology. Tuesday, September 19, 17
 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Reversing Deforestation in Haiti Answers the following: Why is deforestation in Haiti so common? What the negative impacts of deforestation? Name three actions intended counteract
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Reversing Deforestation in Haiti Answers the following: Why is deforestation in Haiti so common? What the negative impacts of deforestation? Name three actions intended counteract
Core Case Study: Southern Sea Otters: Are They Back from the Brink of Extinction?
 Core Case Study: Southern Sea Otters: Are They Back from the Brink of Extinction? Habitat Hunted: early 1900s Partial recovery Why care about sea otters? Ethics Keystone species Tourism dollars Just last
Core Case Study: Southern Sea Otters: Are They Back from the Brink of Extinction? Habitat Hunted: early 1900s Partial recovery Why care about sea otters? Ethics Keystone species Tourism dollars Just last
by 2010 or beyond and what are the implications for the Convention on Biological Diversity?
 6. What are the prospects for reducing the rate of loss of biodiversity by 2010 or beyond and what are the implications for the Convention on Biological Diversity? Biodiversity will continue to decline
6. What are the prospects for reducing the rate of loss of biodiversity by 2010 or beyond and what are the implications for the Convention on Biological Diversity? Biodiversity will continue to decline
 Chapter-15: BIODIVERSITY AND CONSERVATION Biodiversity is defined as the totality of genes, species and ecosystems of a given region, It is the variety and variability of life form (all animals, plants
Chapter-15: BIODIVERSITY AND CONSERVATION Biodiversity is defined as the totality of genes, species and ecosystems of a given region, It is the variety and variability of life form (all animals, plants
IB Environmental Systems & Societies
 IB Environmental Systems & Societies YEAR 1 Syllabus Content: Topics and Assessment Statements Mr. Rees Topic 7: Environmental Value Systems 7.1.1 State what it is meant by an environmental value system.
IB Environmental Systems & Societies YEAR 1 Syllabus Content: Topics and Assessment Statements Mr. Rees Topic 7: Environmental Value Systems 7.1.1 State what it is meant by an environmental value system.
Chapter 30. Conserving Earth s Biodiversity
 Chapter 30 Conserving Earth s Biodiversity Chapter 30 At a Glance What Is Conservation Biology? Why Is Biodiversity Important? Is Earth s Biodiversity Diminishing? What Are the Major Threats to Biodiversity?
Chapter 30 Conserving Earth s Biodiversity Chapter 30 At a Glance What Is Conservation Biology? Why Is Biodiversity Important? Is Earth s Biodiversity Diminishing? What Are the Major Threats to Biodiversity?
PLANT AND ANIMAL DIVERSITY
 by the planning rule team as of. These ideas are for discussion purposes and do not What we want to achieve PLANT AND ANIMAL DIVERSITY The Forest Service is committed to protecting species and sustaining
by the planning rule team as of. These ideas are for discussion purposes and do not What we want to achieve PLANT AND ANIMAL DIVERSITY The Forest Service is committed to protecting species and sustaining
Alien species and food webs in the Marine Strategy Framework Directive: What is expected from scientists?
 Alien species and food webs in the Marine Strategy Framework Directive: What is expected from scientists? Samuli Korpinen HELCOM Secretariat 28 August 2012, Helsinki Why MSFD is challenging for Europe?
Alien species and food webs in the Marine Strategy Framework Directive: What is expected from scientists? Samuli Korpinen HELCOM Secretariat 28 August 2012, Helsinki Why MSFD is challenging for Europe?
BREN 201: ECOLOGY OF MANAGED ECOSYSTEMS Dr. David Tilman Course Syllabus, Winter 2013
 BREN 201: ECOLOGY OF MANAGED ECOSYSTEMS Dr. David Tilman Course Syllabus, Winter 2013 Lectures: 8:30-9:45 AM, Tuesday/Thursday, 1414 Bren Hall, by Dr. David Tilman Email: tilman@bren.ucsb.edu Office Hours:
BREN 201: ECOLOGY OF MANAGED ECOSYSTEMS Dr. David Tilman Course Syllabus, Winter 2013 Lectures: 8:30-9:45 AM, Tuesday/Thursday, 1414 Bren Hall, by Dr. David Tilman Email: tilman@bren.ucsb.edu Office Hours:
Biodiversity and Sustainable Agriculture
 Biodiversity and Sustainable Agriculture FAB-465 (Lecture 6) This Lecture Definitions of sustainable development and sustainable agriculture Significance of biodiversity in the ecosystem Significance of
Biodiversity and Sustainable Agriculture FAB-465 (Lecture 6) This Lecture Definitions of sustainable development and sustainable agriculture Significance of biodiversity in the ecosystem Significance of
Ecosystems: Human Impacts and Conservation (+ Internal Assessment. IB Diploma Environmental Systems and Societies. Skills and Opportunities) 6 days
 IB Diploma Environmental Systems and Societies Ecosystems: Human Impacts and Conservation (+ Internal Assessment Skills and Opportunities) This is a packed six day course for IB Diploma ESS students giving
IB Diploma Environmental Systems and Societies Ecosystems: Human Impacts and Conservation (+ Internal Assessment Skills and Opportunities) This is a packed six day course for IB Diploma ESS students giving
CARIBBEAN FOOD CROPS SOCIETY
 CARIBBEAN FOOD CROPS SOCIETY SERVING THE CARIBBEAN SINCE 1963 CARIBBEAN FOOD CROPS SOCIETY 47 Forty-Seventh Annual Meeting 2011 Bridgetown, Barbados Volume XLVII - Number 1 T-STAR Invasive Species Symposium
CARIBBEAN FOOD CROPS SOCIETY SERVING THE CARIBBEAN SINCE 1963 CARIBBEAN FOOD CROPS SOCIETY 47 Forty-Seventh Annual Meeting 2011 Bridgetown, Barbados Volume XLVII - Number 1 T-STAR Invasive Species Symposium
Experiments by Gause with Paramecium species in lab culture: With constant environment and constant input of food, P. aurelia always displaces P.
 1 Experiments by Gause with Paramecium species in lab culture: With constant environment and constant input of food, P. aurelia always displaces P. caudatum when grown in mixed culture. Gause formulated
1 Experiments by Gause with Paramecium species in lab culture: With constant environment and constant input of food, P. aurelia always displaces P. caudatum when grown in mixed culture. Gause formulated
Draw disruptive, stabilizing, and directional selection on the board. Explain disruptive selection using an example. What effects speciation most?
 Draw disruptive, stabilizing, and directional selection on the board. disruptive selection using an Disruptive selection is when the average physical characteristic of a population is not beneficial. Example:
Draw disruptive, stabilizing, and directional selection on the board. disruptive selection using an Disruptive selection is when the average physical characteristic of a population is not beneficial. Example:
Pesticides & Pest Control. Chapter 20
 Pesticides & Pest Control Chapter 20 Rachael Carson In 1962 wrote Silent Spring This book warned against the use of synthetic chemicals to kill insects and other pests. Pests Any species that competes
Pesticides & Pest Control Chapter 20 Rachael Carson In 1962 wrote Silent Spring This book warned against the use of synthetic chemicals to kill insects and other pests. Pests Any species that competes
Climate Change Adaptation Measures for Forest Ecosystems
 Climate Change Adaptation Measures for Forest Ecosystems Abdul Rahim Nik Presentation Outline Introduction the latest global GHG emission GHG Emissions in Malaysia Framework for Adaptation Measures Climate
Climate Change Adaptation Measures for Forest Ecosystems Abdul Rahim Nik Presentation Outline Introduction the latest global GHG emission GHG Emissions in Malaysia Framework for Adaptation Measures Climate
GM Crops and Biodiversity is this solely a GM issue?
 GM Crops and Biodiversity is this solely a GM issue? Brian Johnson Former Head of Biotechnology Unit English Nature Why does farmland biodiversity matter? A high proportion of our natural biodiversity
GM Crops and Biodiversity is this solely a GM issue? Brian Johnson Former Head of Biotechnology Unit English Nature Why does farmland biodiversity matter? A high proportion of our natural biodiversity
River Wars: Influx of Zebra Mussels in the Hudson River Watershed By: Jason Aguirre and Soon il Higashino Ossining High School
 River Wars: Influx of Zebra Mussels in the Hudson River Watershed By: Jason Aguirre and Soon il Higashino Ossining High School http://www.biodrawversity.com/images/photos/zebramussel.jpg http://www.fws.
River Wars: Influx of Zebra Mussels in the Hudson River Watershed By: Jason Aguirre and Soon il Higashino Ossining High School http://www.biodrawversity.com/images/photos/zebramussel.jpg http://www.fws.
Human-microbe mutualism: stability and resilience in health and disease
 Human-microbe mutualism: stability and resilience in health and disease David A. Relman, Stanford University IOM Forum on Microbial Threats March 7, 2012 Our extended self : human-microbe mutualism (Based
Human-microbe mutualism: stability and resilience in health and disease David A. Relman, Stanford University IOM Forum on Microbial Threats March 7, 2012 Our extended self : human-microbe mutualism (Based
1 Introduction: agricultural ecosystems and conservation
 1 Introduction: agricultural ecosystems and conservation Development of agriculture has had profound effects on natural communities and has involved changes in land-use patterns over much of the world.
1 Introduction: agricultural ecosystems and conservation Development of agriculture has had profound effects on natural communities and has involved changes in land-use patterns over much of the world.
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology
 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Ecosystem Ecology Examines Interactions Between the Living and Non-Living World Ecosystem- A particular location on Earth distinguished by its particular mix of interacting
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Ecosystem Ecology Examines Interactions Between the Living and Non-Living World Ecosystem- A particular location on Earth distinguished by its particular mix of interacting
Biodiversity, Species Interactions, and Population Control. Chapter 5
 Biodiversity, Species Interactions, and Population Control Chapter 5 Core Case Study: Southern Sea Otters: Are They Back from the Brink of Extinction? Habitat Hunted: early 1900s Partial recovery Why care
Biodiversity, Species Interactions, and Population Control Chapter 5 Core Case Study: Southern Sea Otters: Are They Back from the Brink of Extinction? Habitat Hunted: early 1900s Partial recovery Why care
ADAPTING URBAN FORESTS TO CLIMATE CHANGE: APPROACHES FOR ACTION. Leslie Brandt
 ADAPTING URBAN FORESTS TO CLIMATE CHANGE: APPROACHES FOR ACTION Leslie Brandt ACTIONS FOR ADAPTATION Adaptation actions are designed to specifically address climate change impacts & vulnerabilities in
ADAPTING URBAN FORESTS TO CLIMATE CHANGE: APPROACHES FOR ACTION Leslie Brandt ACTIONS FOR ADAPTATION Adaptation actions are designed to specifically address climate change impacts & vulnerabilities in
Unifying concepts in ecology
 Unifying concepts in ecology UNIFYING CONCEPTS IN ECOLOGY Report of the plenary sessions of the First international congress of ecology, The Hague, the Netherlands, September 8-14, 1974 Editors: W. H.
Unifying concepts in ecology UNIFYING CONCEPTS IN ECOLOGY Report of the plenary sessions of the First international congress of ecology, The Hague, the Netherlands, September 8-14, 1974 Editors: W. H.
Crop Science Society of America
 Crop Science Society of America Grand Challenge Statements Crop science is a highly integrative science employing the disciplines of conventional plant breeding, transgenic crop improvement, plant physiology,
Crop Science Society of America Grand Challenge Statements Crop science is a highly integrative science employing the disciplines of conventional plant breeding, transgenic crop improvement, plant physiology,
Chapter 05 A Study in Biodiversity: Rain Forest Tree Species Richness
 Chapter 05 A Study in Biodiversity: Rain Forest Tree Species Richness PLATE 5-1 PASOH FOREST, MALAYSIA PLATE 5-2 The extreme high species richness of trees in many tropical forests such as this one in
Chapter 05 A Study in Biodiversity: Rain Forest Tree Species Richness PLATE 5-1 PASOH FOREST, MALAYSIA PLATE 5-2 The extreme high species richness of trees in many tropical forests such as this one in
Sustaining Terrestrial Biodiversity: Saving Ecosystems and Ecosystem Services
 LIVING IN THE ENVIRONMENT, 18e G. TYLER MILLER SCOTT E. SPOOLMAN 10 Sustaining Terrestrial Biodiversity: Saving Ecosystems and Ecosystem Services Core Case Study: Costa Rica A Global Conservation Leader
LIVING IN THE ENVIRONMENT, 18e G. TYLER MILLER SCOTT E. SPOOLMAN 10 Sustaining Terrestrial Biodiversity: Saving Ecosystems and Ecosystem Services Core Case Study: Costa Rica A Global Conservation Leader
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology
 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Ecosystem Ecology Examines Interactions Between the Living and Non-Living World Ecosystem- A particular location on Earth distinguished by its particular mix of interacting
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Ecosystem Ecology Examines Interactions Between the Living and Non-Living World Ecosystem- A particular location on Earth distinguished by its particular mix of interacting
Restoration Ecology, Part 2 Lecture 19 Spring 2014
 Restoration Ecology, Part 2 Lecture 19 Spring 2014 Restoration Ecology 1 Major questions: Will an ecosystem return to the same ecosystem after disturbance? Succession How is balance maintained in food
Restoration Ecology, Part 2 Lecture 19 Spring 2014 Restoration Ecology 1 Major questions: Will an ecosystem return to the same ecosystem after disturbance? Succession How is balance maintained in food
REINTRODUCING NATIVE PLANTS INTO THE WILD
 REINTRODUCING NATIVE PLANTS INTO THE WILD Written for the New England Plant Conservation Program (NEPCoP) by Mary Parkin, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Every year more rare plant populations and habitats
REINTRODUCING NATIVE PLANTS INTO THE WILD Written for the New England Plant Conservation Program (NEPCoP) by Mary Parkin, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Every year more rare plant populations and habitats
A NOTE ON THE BIO-DIVERSITY CONSERVATION, CAUSES AND EFFECTS
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 1, No 1, 29-35, 2012 A NOTE ON THE BIO-DIVERSITY CONSERVATION, CAUSES AND EFFECTS D. Lalsangzuala Aizawl, Mizoram Abstract: The different
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 1, No 1, 29-35, 2012 A NOTE ON THE BIO-DIVERSITY CONSERVATION, CAUSES AND EFFECTS D. Lalsangzuala Aizawl, Mizoram Abstract: The different
Bioe 515 Lec 4: Environmental gradients, landscape pattern, ecological function
 Bioe 515 Lec 4: Environmental gradients, landscape pattern, ecological function Physical Factors that Pattern Landscapes: climate, landform, soils, water, nutrients. Conceptual Framework The framework
Bioe 515 Lec 4: Environmental gradients, landscape pattern, ecological function Physical Factors that Pattern Landscapes: climate, landform, soils, water, nutrients. Conceptual Framework The framework
Habitat Restoration, Longleaf Pine Forests, and the Flatwoods Salamander. Goals of Today s Talk. Habitat Restoration. Habitat Restoration
 Habitat Restoration, Longleaf Pine Forests, and the Flatwoods Salamander Kenny Wray Goals of Today s Talk Introduce you to the science of Restoration Ecology. Give you examples of the theory and processes
Habitat Restoration, Longleaf Pine Forests, and the Flatwoods Salamander Kenny Wray Goals of Today s Talk Introduce you to the science of Restoration Ecology. Give you examples of the theory and processes
The idea of reserves is ancient. There are some nice examples of reserves from ancient China in the text.
 Reserves. What we re interested in here is in how to design reserves. Unfortunately, theory and practice are often two different things. We ll start with the theoretical approach and see how it s actually
Reserves. What we re interested in here is in how to design reserves. Unfortunately, theory and practice are often two different things. We ll start with the theoretical approach and see how it s actually
Why Every Farmer Needs a Microscope. by Dr. Mary Lucero Systems Biologist, CEO End-O-Fite Enterprises, LLC
 Why Every Farmer Needs a Microscope by Dr. Mary Lucero Systems Biologist, CEO End-O-Fite Enterprises, LLC In the 20 th Century, society launched a collective experiment: What would happen if we grew more
Why Every Farmer Needs a Microscope by Dr. Mary Lucero Systems Biologist, CEO End-O-Fite Enterprises, LLC In the 20 th Century, society launched a collective experiment: What would happen if we grew more
Chapter Biodiversity
 Chapter 6 6.3 Biodiversity Key Questions: 1) Why is biodiversity important? 2) What are the most significant threats to biodiversity? 3) How do we preserve biodiversity? Types of Biodiversity Biological
Chapter 6 6.3 Biodiversity Key Questions: 1) Why is biodiversity important? 2) What are the most significant threats to biodiversity? 3) How do we preserve biodiversity? Types of Biodiversity Biological
New Mexico Forest Restoration Principles
 New Mexico Forest Restoration Principles Preamble These principles were collaboratively developed by a team of dedicated professionals representing industry, conservation organizations, land management
New Mexico Forest Restoration Principles Preamble These principles were collaboratively developed by a team of dedicated professionals representing industry, conservation organizations, land management
Managing Climate Risk to NC Farms and Forests
 Managing Climate Risk to NC Farms and Forests Understanding Exposure, Sensitivity, and Adaptive Capacity Laura Lengnick Fernleaf Solutions Asheville, NC Agricultural Risks Climate Production Financial
Managing Climate Risk to NC Farms and Forests Understanding Exposure, Sensitivity, and Adaptive Capacity Laura Lengnick Fernleaf Solutions Asheville, NC Agricultural Risks Climate Production Financial
A Case Study on Ocean Acidification By Sindia M. Rivera-Jiménez, Ph.D. Department of Natural Science, Santa Fe College, Gainesville Fl
 A Case Study on Ocean Acidification By Sindia M. Rivera-Jiménez, Ph.D. Department of Natural Science, Santa Fe College, Gainesville Fl Please read the following abstract of an article from the journal
A Case Study on Ocean Acidification By Sindia M. Rivera-Jiménez, Ph.D. Department of Natural Science, Santa Fe College, Gainesville Fl Please read the following abstract of an article from the journal
Section Objectives: Explain biodiversity and its importance. Relate various threats to the loss of biodiversity.
 Section Objectives: Explain biodiversity and its importance. Relate various threats to the loss of biodiversity. Biological Diversity Biodiversity refers to the variety of species in a specific area. The
Section Objectives: Explain biodiversity and its importance. Relate various threats to the loss of biodiversity. Biological Diversity Biodiversity refers to the variety of species in a specific area. The
Ecosystem, Biodiversity. Lecture 4: Introduction to Civil and Environmental Engineering
 Ecosystem, Biodiversity Lecture 4: Introduction to Civil and Environmental Engineering What are Ecosystems? Ecosystems are the biotic and abiotic factors in a specified area that interact with one another.
Ecosystem, Biodiversity Lecture 4: Introduction to Civil and Environmental Engineering What are Ecosystems? Ecosystems are the biotic and abiotic factors in a specified area that interact with one another.
Unlocking the potential of agrobiodiversity conservation for food and nutrition security and mitigating the effects of climate change
 Unlocking the potential of agrobiodiversity conservation for food and nutrition security and mitigating the effects of climate change SIMON MBURU KENYATTA UNIVERSITY Quantitative methods for integrated
Unlocking the potential of agrobiodiversity conservation for food and nutrition security and mitigating the effects of climate change SIMON MBURU KENYATTA UNIVERSITY Quantitative methods for integrated
Predicting the unpredictable - a macroecological approach towards future ecosystem scenarios
 Predicting the unpredictable - a macroecological approach towards future ecosystem scenarios Thomas Brey, AWI Natasha Del Cid 2011 1 Predicting the unpredictable - a macroecological approach towards future
Predicting the unpredictable - a macroecological approach towards future ecosystem scenarios Thomas Brey, AWI Natasha Del Cid 2011 1 Predicting the unpredictable - a macroecological approach towards future
Crosswalk of Georgia Performance Standards & Georgia Standards of Excellence GSE Implementation in Environmental Science
 SEV1. Students will investigate the flow of energy and cycling of matter within an ecosystem and relate these phenomena to human society. a. Interpret biogeochemical cycles including hydrologic, nitrogen,
SEV1. Students will investigate the flow of energy and cycling of matter within an ecosystem and relate these phenomena to human society. a. Interpret biogeochemical cycles including hydrologic, nitrogen,
Chapter 36: Population Growth
 Chapter 36: Population Growth Population: Population Concepts interbreeding group of same species Carrying Capacity: maximum population size an ecosystem can sustainably support Critical Number: minimum
Chapter 36: Population Growth Population: Population Concepts interbreeding group of same species Carrying Capacity: maximum population size an ecosystem can sustainably support Critical Number: minimum
Effects of Herbivory on woody plant functional traits, structural diversity and ecosystem services in a semiarid. Staline Kibet
 Effects of Herbivory on woody plant functional traits, structural diversity and ecosystem services in a semiarid savanna Staline Kibet Background 3000 yrs BP 1790 1880 1890 1895 1904 & 1911 1960 1970
Effects of Herbivory on woody plant functional traits, structural diversity and ecosystem services in a semiarid savanna Staline Kibet Background 3000 yrs BP 1790 1880 1890 1895 1904 & 1911 1960 1970
Exactly how resilient are ecosystems?
 Exactly how resilient are ecosystems? Beth Fulton Head of marine ecosystem modelling, CSIRO Australia 2014 CSIRO WEALTH FROM OCEANS FLAGSHIP Competing use of space & pressures Planetary Boundaries Natural
Exactly how resilient are ecosystems? Beth Fulton Head of marine ecosystem modelling, CSIRO Australia 2014 CSIRO WEALTH FROM OCEANS FLAGSHIP Competing use of space & pressures Planetary Boundaries Natural
GUEST ESSAY The Scientific Consensus About Global Warming John Harte
 GUEST ESSAY The Scientific Consensus About Global Warming John Harte John Harte is Professor of Energy and Resources at the University of California, Berkeley. He is a Phi Beta Kappa distinguished Visiting
GUEST ESSAY The Scientific Consensus About Global Warming John Harte John Harte is Professor of Energy and Resources at the University of California, Berkeley. He is a Phi Beta Kappa distinguished Visiting
Managing Soil Biology to Increase Agricultural Production and Sustainability
 Managing Soil Biology to Increase Agricultural Production and Sustainability Kate Scow Dept. of Land, Air & Water Resources Agricultural Sustainability Institute Soil biodiversity: like an iceberg... most
Managing Soil Biology to Increase Agricultural Production and Sustainability Kate Scow Dept. of Land, Air & Water Resources Agricultural Sustainability Institute Soil biodiversity: like an iceberg... most
Nourish Scotland s response to the Scottish Governments consultation on the National Plan for Adaptation to Climate Change
 September 2013 Nourish Scotland s response to the Scottish Governments consultation on the National Plan for Adaptation to Climate Change Nourish Scotland welcomes the opportunity to respond to the Scottish
September 2013 Nourish Scotland s response to the Scottish Governments consultation on the National Plan for Adaptation to Climate Change Nourish Scotland welcomes the opportunity to respond to the Scottish
Sustaining Ecological Networks and their Services: Network theory of biodiversity and ecosystem function
 Sustaining Ecological Networks and their Services: Network theory of biodiversity and ecosystem function Neo D. Martinez Pacific Ecoinformatics and Computational Ecology Lab www.foodwebs.org 00 www.foodwebs.org
Sustaining Ecological Networks and their Services: Network theory of biodiversity and ecosystem function Neo D. Martinez Pacific Ecoinformatics and Computational Ecology Lab www.foodwebs.org 00 www.foodwebs.org
Adaptation Options for Managing Ecosystems; Coping with Climate Change Forest Service Research and Development Support for Management of Wildlands
 Adaptation Options for Managing Ecosystems; Coping with Climate Change Forest Service Research and Development Support for Management of Wildlands Peter A. Stine, Ph.D. Sierra Nevada Research Center Pacific
Adaptation Options for Managing Ecosystems; Coping with Climate Change Forest Service Research and Development Support for Management of Wildlands Peter A. Stine, Ph.D. Sierra Nevada Research Center Pacific
Lecture 10. Chapter 7: Species Interactions/Competition Chapter 8: Mutualisms
 Lecture 10 Chapter 7: Species Interactions/Competition Chapter 8: Mutualisms Terminology -/- Competition -/+ Predation and other associations where one species benefits and the other is harmed +/0 Commensalism
Lecture 10 Chapter 7: Species Interactions/Competition Chapter 8: Mutualisms Terminology -/- Competition -/+ Predation and other associations where one species benefits and the other is harmed +/0 Commensalism
Centerville Sr. High School Curriculum Mapping Environmental Science, Advanced (submitted by Matt Osborne) 1 st Nine Weeks
 Days Unit 1, Unit 1, Unit 1, Indiana Standard(s) Env 1.22 Env 2.2 Env 1.17 Env 1.10 Centerville Sr. High School Curriculum Mapping Environmental Science, Advanced (submitted by Matt Osborne) 1 st Nine
Days Unit 1, Unit 1, Unit 1, Indiana Standard(s) Env 1.22 Env 2.2 Env 1.17 Env 1.10 Centerville Sr. High School Curriculum Mapping Environmental Science, Advanced (submitted by Matt Osborne) 1 st Nine
Ecology, the Environment, and Us
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 23 Ecology, the Environment, and Us Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 23 Ecology, the Environment, and Us Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University
Field 009: Career and Technical Education Agriculture Assessment Blueprint
 Field 009: Career and Technical Education Agriculture Assessment Blueprint Domain I Agribusiness 0001 Agricultural Business, Economics, Finance, and Marketing (Standard 1) Domain II Animal Science 0002
Field 009: Career and Technical Education Agriculture Assessment Blueprint Domain I Agribusiness 0001 Agricultural Business, Economics, Finance, and Marketing (Standard 1) Domain II Animal Science 0002
The Introduction of Non-Native Species
 http://www.invasivespeciesscotland.org.uk/filelibrary/images/profiles/zebra_mussel_glerl_3.jpg The Introduction of Non-Native Species Introduced Species Food webs are complex interactions among species
http://www.invasivespeciesscotland.org.uk/filelibrary/images/profiles/zebra_mussel_glerl_3.jpg The Introduction of Non-Native Species Introduced Species Food webs are complex interactions among species
Elasticity of Demand
 Elasticity of Demand Elasticity of Demand The law of demand states that an increase in price causes a decrease in quantity demanded (and vice-versa) Question: How much quantity demanded changes in response
Elasticity of Demand Elasticity of Demand The law of demand states that an increase in price causes a decrease in quantity demanded (and vice-versa) Question: How much quantity demanded changes in response
Wales Natural Resources: Resilience of Ecosystems and Biodiversity. Prof Jack Cosby NERC s Centre for Ecology and Hydrology Bangor
 Wales Natural Resources: Resilience of Ecosystems and Biodiversity Prof Jack Cosby NERC s Centre for Ecology and Hydrology Bangor A substantial challenge!! Overview Improving resilience of ecosystems and
Wales Natural Resources: Resilience of Ecosystems and Biodiversity Prof Jack Cosby NERC s Centre for Ecology and Hydrology Bangor A substantial challenge!! Overview Improving resilience of ecosystems and
Insect Response to the 1988 Fires in Yellowstone National Park
 University of Wyoming National Park Service Research Center Annual Report Volume 13 13th Annual Report, 1989 Article 34 1-1-1989 Insect Response to the 1988 Fires in Yellowstone National Park Robert J.
University of Wyoming National Park Service Research Center Annual Report Volume 13 13th Annual Report, 1989 Article 34 1-1-1989 Insect Response to the 1988 Fires in Yellowstone National Park Robert J.
UNIT 1 SUSTAINING ECOSYSTEMS
 UNIT 1 SUSTAINING ECOSYSTEMS Chapter 1 Diversity in Ecosystems Science 1206 / 2200 What is a Paradigm? (para-dime) Definition A philosophical and theoretical framework of a scientific school or discipline
UNIT 1 SUSTAINING ECOSYSTEMS Chapter 1 Diversity in Ecosystems Science 1206 / 2200 What is a Paradigm? (para-dime) Definition A philosophical and theoretical framework of a scientific school or discipline
Foundation Course. Semester 3 THREATS TO THE ENVIRONMENT
 Foundation Course Semester 3 THREATS TO THE ENVIRONMENT INTRODUCTION Atmosphere, water and soil are the most important components of environment in which we live. Atmospheric factors like rainfall, humidity,
Foundation Course Semester 3 THREATS TO THE ENVIRONMENT INTRODUCTION Atmosphere, water and soil are the most important components of environment in which we live. Atmospheric factors like rainfall, humidity,
Development of Guidance for the. Environmental Risk Assessment (ERA) Environmental risk assessment of plant pests by
 Development of Guidance for the Environmental Risk Assessment (ERA) Environmental risk assessment of plant pests integrating analysis of by impacts on biodiversity and EFSA on Panel ecosystem on Plant
Development of Guidance for the Environmental Risk Assessment (ERA) Environmental risk assessment of plant pests integrating analysis of by impacts on biodiversity and EFSA on Panel ecosystem on Plant
Cover Crops for Soil Health and Water Quality
 Cover Crops for Soil Health and Water Quality 2014 SURFACE WATER FORUM - NOVEMBER 12, 2014 JILL L. SACKETT EXTENSION EDUCATOR 1 BACKGROUND University of Minnesota Extension Local Extension Educator, Ag
Cover Crops for Soil Health and Water Quality 2014 SURFACE WATER FORUM - NOVEMBER 12, 2014 JILL L. SACKETT EXTENSION EDUCATOR 1 BACKGROUND University of Minnesota Extension Local Extension Educator, Ag
Biodiversity and Biomes Power Point Notes
 Name Date Period 1. One teacher is to as all teachers is to. 2. Teachers and students are to as George West is to. 3. Vocabulary: fill in the correct definition habitat species population ecosystem biome
Name Date Period 1. One teacher is to as all teachers is to. 2. Teachers and students are to as George West is to. 3. Vocabulary: fill in the correct definition habitat species population ecosystem biome
Chapter 5: How Ecosystems Work Section 1, Energy Flow in Ecosystems
 Life Depends on the Sun Chapter 5: How Ecosystems Work Section 1, Energy Flow in Ecosystems Energy from the sun enters an ecosystem when plants use sunlight to make sugar molecules. This happens through
Life Depends on the Sun Chapter 5: How Ecosystems Work Section 1, Energy Flow in Ecosystems Energy from the sun enters an ecosystem when plants use sunlight to make sugar molecules. This happens through
Ecosystems Section 1 What Is an Ecosystem? Objectives Distinguish Describe Sequence Interactions of Organisms and Their Environment Ecology Habitat
 Name Period Ecosystems Section 1 What Is an Ecosystem? Objectives Distinguish an ecosystem from a community. Describe the diversity of a representative ecosystem. Sequence the process of succession. Interactions
Name Period Ecosystems Section 1 What Is an Ecosystem? Objectives Distinguish an ecosystem from a community. Describe the diversity of a representative ecosystem. Sequence the process of succession. Interactions
*Endangered Species project due Wednesday December 11th (not the 9th)
 *Endangered Species project due Wednesday December 11th (not the 9th) *If you scored below 30 on the multiple choice section for the Unit 3 test, you should come in during 7th and figure out why you are
*Endangered Species project due Wednesday December 11th (not the 9th) *If you scored below 30 on the multiple choice section for the Unit 3 test, you should come in during 7th and figure out why you are
Understanding and Managing the Range of Phosphorus Forms Contributing to Eutrophication
 Understanding and Managing the Range of Phosphorus Forms Contributing to Eutrophication Marc Stutter, Benoit Demars The Macaulay Land Use Research Institute, Aberdeen, UK Session 3: Monitoring and evaluation
Understanding and Managing the Range of Phosphorus Forms Contributing to Eutrophication Marc Stutter, Benoit Demars The Macaulay Land Use Research Institute, Aberdeen, UK Session 3: Monitoring and evaluation
BIOLOGY 215 PRINCIPLES OF ECOLOGY (10262) Sept t2015
 BIOLOGY 215 PRINCIPLES OF ECOLOGY (10262) Sept t2015 INSTRUCTOR: Dr. T. E. Reimchen Office: Cunn 056, Ph 721 71017101 SENIOR LAB COORDINATOR: Dr. Neville Winchester Office : Cun 232b Ph. 721 7099, winchest@uvic.ca
BIOLOGY 215 PRINCIPLES OF ECOLOGY (10262) Sept t2015 INSTRUCTOR: Dr. T. E. Reimchen Office: Cunn 056, Ph 721 71017101 SENIOR LAB COORDINATOR: Dr. Neville Winchester Office : Cun 232b Ph. 721 7099, winchest@uvic.ca
Agriculture, Diet and the Environment. by David Tilman University of Minnesota, and University of California Santa Barbara
 Agriculture, Diet and the Environment by David Tilman University of Minnesota, and University of California Santa Barbara Environmental Impacts of Agriculture N, P, Pesticides Biodiversity Loss; GHG Water
Agriculture, Diet and the Environment by David Tilman University of Minnesota, and University of California Santa Barbara Environmental Impacts of Agriculture N, P, Pesticides Biodiversity Loss; GHG Water
Habitat Loss and Fragmentation
 Habitat Loss and Fragmentation 83% of Earth s Land Surface Transformed by Human Activity Temperate Grasslands, Savannas, Shrublands: > 80% Loss Mediterranean Habitats: 72% Loss Coral Reefs: 20% Destroyed
Habitat Loss and Fragmentation 83% of Earth s Land Surface Transformed by Human Activity Temperate Grasslands, Savannas, Shrublands: > 80% Loss Mediterranean Habitats: 72% Loss Coral Reefs: 20% Destroyed
IB Environmental Systems and Societies
 IB Environmental Systems and Societies Unit 1 Systems and Models Nautre Does nothing uselessly Aristotle (384 322 BC) Assessment statement 1.1.1 Outline the concept and characteristics of systems. 1.1.2
IB Environmental Systems and Societies Unit 1 Systems and Models Nautre Does nothing uselessly Aristotle (384 322 BC) Assessment statement 1.1.1 Outline the concept and characteristics of systems. 1.1.2
Community: an assemblage of species living close enough together for potential interactions How do organisms of different species interact?
 1 BIO 1101 Lecture 17 (Guided Notes) Chapter 20: Community Ecology 2 Community: an assemblage of species living close enough together for potential interactions How do organisms of different species interact?
1 BIO 1101 Lecture 17 (Guided Notes) Chapter 20: Community Ecology 2 Community: an assemblage of species living close enough together for potential interactions How do organisms of different species interact?
Next Generation Science Standards
 Pearson Environmental Science Your World, Your Turn 2011 To the Next Generation Science Standards Life Science Standards Earth & Space Science Standards DRAFT, MAY 2012 Dear Educator, As we embark upon
Pearson Environmental Science Your World, Your Turn 2011 To the Next Generation Science Standards Life Science Standards Earth & Space Science Standards DRAFT, MAY 2012 Dear Educator, As we embark upon
Biomes and Biodiversity Power Point Notes
 Name period date assigned date due date returned Biomes and Biodiversity Power Point Notes 1. One teacher is to as all teachers is to. 2. Teachers and students are to as George West is to. Vocabulary Word
Name period date assigned date due date returned Biomes and Biodiversity Power Point Notes 1. One teacher is to as all teachers is to. 2. Teachers and students are to as George West is to. Vocabulary Word
Think CARPATHIAN, act locally and regionally Fourth Meeting of the Conference of the Parties September 2014, Mikulov
 Think CARPATHIAN, act locally and regionally Fourth Meeting of the Conference of the Parties 23 26 September 2014, Mikulov Pictures: Mircea Verghelet Welcome to COP4 Since COP3 1. Success 2. Challenges
Think CARPATHIAN, act locally and regionally Fourth Meeting of the Conference of the Parties 23 26 September 2014, Mikulov Pictures: Mircea Verghelet Welcome to COP4 Since COP3 1. Success 2. Challenges
ECOLOGICAL RESTORATION: AN OVERVIEW
 ECOLOGICAL RESTORATION: AN OVERVIEW AAN N A FAQ document intended to give a broad overview of the concept and practice of ecological restoration to the reader. Humankind has not woven the web of life.
ECOLOGICAL RESTORATION: AN OVERVIEW AAN N A FAQ document intended to give a broad overview of the concept and practice of ecological restoration to the reader. Humankind has not woven the web of life.
Ecology Part 2: How Ecosystems Work
 Ecology Part 2: How Ecosystems Work Name: Unit 2 1 In this second part of Unit 2, our big idea questions are: SECTION 1 How is energy transferred from the Sun to producers and then to consumers? Why do
Ecology Part 2: How Ecosystems Work Name: Unit 2 1 In this second part of Unit 2, our big idea questions are: SECTION 1 How is energy transferred from the Sun to producers and then to consumers? Why do
Simpson's Diversity Index
 Simpson's Diversity Index Simpson's Diversity Index is a measure of diversity. In ecology, it is often used to quantify the biodiversity of a habitat. It takes into account the number of species present,
Simpson's Diversity Index Simpson's Diversity Index is a measure of diversity. In ecology, it is often used to quantify the biodiversity of a habitat. It takes into account the number of species present,
Ecology the scientific study of interactions between different organisms and between organisms and their environment or surroundings
 Ecology the scientific study of interactions between different organisms and between organisms and their environment or surroundings Biotic living factors that influence an ecosystem Abiotic non-living
Ecology the scientific study of interactions between different organisms and between organisms and their environment or surroundings Biotic living factors that influence an ecosystem Abiotic non-living
