HAZUS-MH: Earthquake Event Report
|
|
|
- Cornelius Harrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HAZUS-MH: Earthquake Event Report Region Name: Great Salt Lake Fault Earthquake Scenario: Great Salt Lake Fault Earthquake Mw 7.0 Print Date: December 22, 2009 Totals only reflect data for those census tracts/blocks included in the user s study region. Disclaimer: The estimates of social and economic impacts contained in this report were produced using HAZUS loss estimation methodology software which is based on current scientific and engineering knowledge. There are uncertainties inherent in any loss estimation technique. Therefore, there may be significant differences between the modeled results contained in this report and the actual social and economic losses following a specific earthquake. These results can be improved by using enhanced inventory, geotechnical, and observed ground motion data.
2 Table of Contents Section Page # General Description of the Region 3 Building and Lifeline Inventory 4 Building Inventory Critical Facility Inventory Transportation and Utility Lifeline Inventory Earthquake Scenario Parameters 6 Direct Earthquake Damage 7 Buildings Damage Critical Facilities Damage Transportation and Utility Lifeline Damage Induced Earthquake Damage 11 Fire Following Earthquake Debris Generation Social Impact 12 Shelter Requirements Casualties Economic Loss 13 Building Losses Transportation and Utility Lifeline Losses Long-term Indirect Economic Impacts Appendix A: County Listing for the Region Appendix B: Regional Population and Building Value Data Page 2 of 20
3 General Description of the Region HAZUS is a regional earthquake loss estimation model that was developed by the Federal Emergency Management Agency and the National Institute of Building Sciences. The primary purpose of HAZUS is to provide a methodology and software application to develop earthquake losses at a regional scale. These loss estimates would be used primarily by local, state and regional officials to plan and stimulate efforts to reduce risks from earthquakes and to prepare for emergency response and recovery. The earthquake loss estimates provided in this report was based on a region that includes 29 county(ies) from the following state(s): Utah Note: Appendix A contains a complete listing of the counties contained in the region. The geographical size of the region is 84, square miles and contains 496 census tracts. There are over 773 thousand households in the region and has a total population of 2,474,258 people (2000 Census Bureau data). The distribution of population by State and County is provided in Appendix B. There are an estimated 653 thousand buildings in the region with a total building replacement value (excluding contents) of 131,629 (millions of dollars). Approximately % of the buildings (and 0.00% of the building value) are associated with residential housing. The replacement value of the transportation and utility lifeline systems is estimated to be 54,677 and 9,370 dollars), respectively. (millions of Page 3 of 20
4 Building and Lifeline Inventory Building Inventory HAZUS estimates that there are 653 thousand buildings in the region which have an aggregate total replacement value of 131,629 (millions of dollars). Appendix B provides a general distribution of the building value by State and County. In terms of building construction types found in the region, wood frame construction makes up 46% of the building inventory. The remaining percentage is distributed between the other general building types. Critical Facility Inventory HAZUS breaks critical facilities into two (2) groups: essential facilities and high potential loss (HPL) facilities. Essential facilities include hospitals, medical clinics, schools, fire stations, police stations and emergency operations facilities. High potential loss facilities include dams, levees, military installations, nuclear power plants and hazardous material sites. For essential facilities, there are 56 hospitals in the region with a total bed capacity of 6,868 beds. There are 1,076 schools, 358 fire stations, 133 police stations and 7 emergency operation facilities. With respect to HPL facilities, there are 599 dams identified within the region. Of these, 212 of the dams are classified as high hazard. The inventory also includes 711 hazardous material sites, 0 military installations and 0 nuclear power plants. Transportation and Utility Lifeline Inventory Within HAZUS, the lifeline inventory is divided between transportation and utility lifeline systems. There are seven (7) transportation systems that include highways, railways, light rail, bus, ports, ferry and airports. There are six (6) utility systems that include potable water, wastewater, natural gas, crude & refined oil, electric power and communications. The lifeline inventory data are provided in Tables 1 and 2. The total value of the lifeline inventory is over 64, (millions of dollars). This inventory includes over 8,874 kilometers of highways, 3,009 bridges, 242,427 kilometers of pipes. Page 4 of 20
5 Table 1: Transportation System Lifeline Inventory System Component # locations/ # Segments Replacement value (millions of dollars) Highway Bridges 3,009 3, Segments 1,303 46, Tunnels Subtotal 49, Railways Bridges Facilities Segments 1,485 2, Tunnels Subtotal 2, Light Rail Bridges Facilities Segments Tunnels Subtotal Bus Ferry Port Airport Facilities Subtotal Facilities Subtotal 2.70 Facilities Subtotal 0.00 Facilities Runways 46 1, Subtotal Total 2, , Page 5 of 20
6 Table 2: Utility System Lifeline Inventory System Component # Locations / Segments Replacement value (millions of dollars) Potable Water Distribution Lines NA 2, Facilities Pipelines Subtotal 3, Waste Water Distribution Lines NA 1, Facilities 56 3, Pipelines Subtotal 5, Natural Gas Distribution Lines NA 1, Facilities Pipelines 957 2, Subtotal 3, Oil Systems Facilities Pipelines Subtotal Electrical Power Facilities 26 2, Subtotal 2, Communication Facilities Subtotal Total 15, Page 6 of 20
7 Earthquake Scenario HAZUS uses the following set of information to define the earthquake parameters used for the earthquake loss estimate provided in this report. Scenario Name Type of Earthquake Fault Name Historical Epicenter ID # Probabilistic Return Period Longitude of Epicenter Latitude of Epicenter Earthquake Magnitude Depth (Km) Rupture Length (Km) Rupture Orientation (degrees) Attenuation Function Great Salt Lake Fault Earthquake Mw 7.0 User-defined NA NA NA NA NA 7.00 NA NA NA NA Page 7 of 20
8 Building Damage Building Damage HAZUS estimates that about 19,782 buildings will be at least moderately damaged. This is over 3.00 % of the total number of buildings in the region. There are an estimated 103 buildings that will be damaged beyond repair. The definition of the damage states is provided in Volume 1: Chapter 5 of the HAZUS technical manual. Table 3 below summaries the expected damage by general occupancy for the buildings in the region. Table 4 summaries the expected damage by general building type. Table 3: Expected Building Damage by Occupancy None Slight Moderate Extensive Complete Count (%) Count (%) Count (%) Count (%) Count (%) Agriculture Commercial 18, , Education Government 1, Industrial 5, Other Residential 59, , , Religion 2, Single Family 480, , , , Total 569,786 63,655 18,010 1, Table 4: Expected Building Damage by Building Type (All Design Levels) None Slight Moderate Extensive Complete Count (%) Count (%) Count (%) Count (%) Count (%) Wood 284, Steel 5, Concrete 4, Precast 3, RM 114, , URM 133, , , MH 25, , Total 569,786 63,655 18,010 1, *Note: RM URM MH Reinforced Masonry Unreinforced Masonry Manufactured Housing Page 8 of 20
9 Essential Facility Damage Before the earthquake, the region had 6,868 hospital beds available for use. On the day of the earthquake, the model estimates that only 6,661 hospital beds (97.00%) are available for use by patients already in the hospital and those injured by the earthquake. After one week, % of the beds will be back in service. By 30 days, % will be operational. Table 5: Expected Damage to Essential Facilities # Facilities Classification Total At Least Moderate Complete With Functionality Damage > 50% Damage > 50% > 50% on day 1 Hospitals Schools 1, ,076 EOCs PoliceStations FireStations Page 9 of 20
10 Transportation and Utility Lifeline Damage Table 6 provides damage estimates for the transportation system. Table 6: Expected Damage to the Transportation Systems System Component Locations/ Segments With at Least Mod. Damage Number of Locations With Complete Damage With Functionality > 50 % After Day 1 After Day 7 Highway Segments 1, ,303 1,303 Bridges 3, ,995 2,999 Tunnels Railways Segments 1, ,485 1,485 Bridges Tunnels Facilities Light Rail Segments Bridges Tunnels Facilities Bus Facilities Ferry Facilities Port Facilities Airport Facilities Runways Note: Roadway segments, railroad tracks and light rail tracks are assumed to be damaged by ground failure only. If ground failure maps are not provided, damage estimates to these components will not be computed. Tables 7-9 provide information on the damage to the utility lifeline systems. Table 7 provides damage to the utility system facilities. Table 8 provides estimates on the number of leaks and breaks by the pipelines of the utility systems. For electric power and potable water, HAZUS performs a simplified system performance analysis. Table 9 provides a summary of the system performance information. Page 10 of 20
11 Table 7 : Expected Utility System Facility Damage # of Locations System Total # With at Least With Complete with Functionality > 50 % Moderate Damage Damage After Day 1 After Day 7 Potable Water Waste Water Natural Gas Oil Systems Electrical Power Communication Table 8 : Expected Utility System Pipeline Damage (Site Specific) System Total Pipelines Length (kms) Number of Leaks Number of Breaks Potable Water 147, Waste Water 88, Natural Gas 4, Oil 2, Table 9: Expected Potable Water and Electric Power System Performance Total # of Number of Households without Service Households At Day 1 At Day 3 At Day 7 At Day 30 At Day 90 Potable Water Electric Power 773,352 66,008 48,195 19, Page 11 of 20
12 Induced Earthquake Damage Fire Following Earthquake Fires often occur after an earthquake. Because of the number of fires and the lack of water to fight the fires, they can often burn out of control. HAZUS uses a Monte Carlo simulation model to estimate the number of ignitions and the amount of burnt area. For this scenario, the model estimates that there will be 57 ignitions that will burn about 1.76 sq. mi 0.00 % of the region s total area.) The model also estimates that the fires will displace about 6,279 people and burn about 295 (millions of dollars) of building value. Debris Generation HAZUS estimates the amount of debris that will be generated by the earthquake. The model breaks the debris into two general categories: a) Brick/Wood and b) Reinforced Concrete/Steel. This distinction is made because of the different types of material handling equipment required to handle the debris. The model estimates that a total of million tons of debris will be generated. Of the total amount, Brick/Wood comprises 68.00% of the total, with the remainder being Reinforced Concrete/Steel. If the debris tonnage is converted to an estimated number of truckloads, it will require 43,240,000 truckloads (@25 tons/truck) to remove the debris generated by the earthquake. Page 12 of 20
13 Social Impact Shelter Requirement HAZUS estimates the number of households that are expected to be displaced from their homes due to the earthquake and the number of displaced people that will require accommodations in temporary public shelters. The model estimates 660 households to be displaced due to the earthquake. Of these, 488 people (out of a total population of 2,474,258) will seek temporary shelter in public shelters. Casualties HAZUS estimates the number of people that will be injured and killed by the earthquake. The casualties are broken down into four (4) severity levels that describe the extent of the injuries. The levels are described as follows; Severity Level 1: Injuries will require medical attention but hospitalization is not needed. Severity Level 2: Injuries will require hospitalization but are not considered life-threatening Severity Level 3: Injuries will require hospitalization and can become life threatening if not promptly treated. Severity Level 4: Victims are killed by the earthquake. The casualty estimates are provided for three (3) times of day: 2:00 AM, 2:00 PM and 5:00 PM. These times represent the periods of the day that different sectors of the community are at their peak occupancy loads. The 2:00 AM estimate considers that the residential occupancy load is maximum, the 2:00 PM estimate considers that the educational, commercial and industrial sector loads are maximum and 5:00 PM represents peak commute time. Table 10 provides a summary of the casualties estimated for this earthquake Page 13 of 20
14 Table 10: Casualty Estimates Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 2 AM Commercial Commuting Educational Hotels Industrial Other-Residential Single Family Total PM Commercial Commuting Educational Hotels Industrial Other-Residential Single Family Total PM Commercial Commuting Educational Hotels Industrial Other-Residential Single Family Total Page 14 of 20
15 Economic Loss The total economic loss estimated for the earthquake is 1, (millions of dollars), which includes building and lifeline related losses based on the region's available inventory. The following three sections provide more detailed information about these losses. Building-Related Losses The building losses are broken into two categories: direct building losses and business interruption losses. The direct building losses are the estimated costs to repair or replace the damage caused to the building and its contents. The business interruption losses are the losses associated with inability to operate a business because of the damage sustained during the earthquake. Business interruption losses also include the temporary living expenses for those people displaced from their homes because of the earthquake. The total building-related losses were 1, (millions of dollars); 25 % of the estimated losses were related to the business interruption of the region. By far, the largest loss was sustained by the residential occupancies which made up over 45 % of the total loss. Table 11 below provides a summary of the losses associated with the building damage. Category Income Loses Area Capital Stock Loses Table 11: Building-Related Economic Loss Estimates Single Family Other Residential (Millions of dollars) Commercial Industrial Others Wage Capital-Related Rental Relocation Subtotal Structural Non_Structural Content Inventory Subtotal , Total , Total Page 15 of 20
16 Transportation and Utility Lifeline Losses For the transportation and utility lifeline systems, HAZUS computes the direct repair cost for each component only. There are no losses computed by HAZUS for business interruption due to lifeline outages. Tables 12 & 13 provide a detailed breakdown in the expected lifeline losses. HAZUS estimates the long-term economic impacts to the region for 15 years after the earthquake. The model quantifies this information in terms of income and employment changes within the region. Table 14 presents the results of the region for the given earthquake. Table 12: Transportation System Economic Losses (Millions of dollars) System Component Inventory Value Economic Loss Loss Ratio (%) Highway Segments 46, $ Bridges 3, $ Tunnels 1.96 $ Subtotal Railways Segments 2, $ Bridges 3.92 $ Tunnels 0.00 $ Facilities $ Subtotal Light Rail Segments $ Bridges 0.00 $ Tunnels 0.00 $ Facilities $ Subtotal Bus Facilities $ Subtotal Ferry Facilities 2.66 $ Subtotal Port Facilities 0.00 $ Subtotal Airport Facilities $ Runways 1, $ Subtotal Total Page 16 of 20
17 Table 13: Utility System Economic Losses (Millions of dollars) System Component Inventory Value Economic Loss Loss Ratio (%) Potable Water Pipelines 0.00 $ Facilities $ Distribution Lines 2, $ Subtotal 3, $8.45 Waste Water Pipelines 0.00 $ Facilities 3, $ Distribution Lines 1, $ Subtotal 5, $79.20 Natural Gas Pipelines 2, $ Facilities 8.50 $ Distribution Lines 1, $ Subtotal 3, $6.58 Oil Systems Pipelines $ Facilities 3.00 $ Subtotal $0.08 Electrical Power Facilities 2, $ Subtotal 2, $47.05 Communication Facilities $ Subtotal $0.37 Total 15, $ Page 17 of 20
18 Table 14. Indirect Economic Impact with outside aid (Employment as # of people and Income in millions of $) LOSS Total % First Year Employment Impact 32, Income Impact Second Year Employment Impact 13, Income Impact Third Year Employment Impact Income Impact (29) Fourth Year Employment Impact Income Impact (42) Fifth Year Employment Impact Income Impact (42) Years 6 to 15 Employment Impact Income Impact (42) Page 18 of 20
19 Appendix A: County Listing for the Region Beaver,UT Box Elder,UT Cache,UT Carbon,UT Daggett,UT Davis,UT Duchesne,UT Emery,UT Garfield,UT Grand,UT Iron,UT Juab,UT Kane,UT Millard,UT Morgan,UT Piute,UT Rich,UT Salt Lake,UT San Juan,UT Sanpete,UT Sevier,UT Summit,UT Tooele,UT Uintah,UT Utah,UT Wasatch,UT Washington,UT Wayne,UT Weber,UT Page 19 of 20
20 Appendix B: Regional Population and Building Value Data Building Value (millions of dollars) State County Name Population Residential Non-Residential Total Utah Beaver 6, Box Elder 45,659 1, ,346 Cache 100,585 3,382 1,703 5,085 Carbon 19, ,220 Daggett Davis 270,344 10,230 3,870 14,101 Duchesne 15, Emery 10, Garfield 4, Grand 8, Iron 37,498 1, ,065 Juab 9, Kane 6, Millard 12, Morgan 7, Piute 1, Rich 2, Salt Lake 962,837 39,526 18,636 58,162 San Juan 14, Sanpete 24, ,095 Sevier 19, ,013 Summit 35,804 2, ,307 Tooele 50,184 1, ,347 Uintah 26, ,312 Utah 429,727 9,780 6,285 16,065 Wasatch 18, Washington 113,489 3,900 1,839 5,739 Wayne 2, Weber 214,582 8,462 3,369 11,831 Total State 2,474,258 89,815 41, ,615 Total Region 2,474,258 89,815 41, ,615 Page 20 of 20
21 Direct Building Economic Loss - Earthquake Scenario: Great Salt Lake Segment, UT BOX ELDER WEBER M 7.0 Great Salt Lake Segment Earthquake DAVIS MORGAN PGA (% g's) < >0.18 1Dot= $1,000, TOOELE SALT LAKE Cost Cost Non- Total Loss Structural Structural (Including County Damage Damage Contents) Salt Lake 143, ,352 1,170,312 Juab Weber 19,837 61, ,990 Summit Cache ,837 Duchesne Morgan Rich Davis 42, , ,789 Millard Utah 1,383 7,922 16,608 Sanpete Wasatch Box Elder 440 1,527 3,298 Tooele 7,572 18,549 46,061 Total $216,039 $682,257 $1,684,629 * All values are thousands of dollars GreatSaltLakeFault Counties Interstate 15 UTAH WASATCH Miles FEMA & URS Corporation OR ID WY Ü NE Major Roads City Boundaries NV UT CO CA
22 Estimated Displaced Households & Short Term Public Shelter Needs - Earthquake Scenario: Great Salt Lake Segment, UT BOX ELDER WEBER M 7.0 Great Salt Lake Segment Earthquake DAVIS MORGAN Public Shelter Needs (Individuals) Displaced Households Total # Dot = 1 Public Shelter Need (Individuals)* 1 Dot = 1 Displaced Household* * delineated by census tract TOOELE SALT LAKE GreatSaltLakeFault Counties Interstate Major Roads City Boundaries 15 WASATCH Miles FEMA & URS Corporation Ü UTAH OR ID WY NE NV UT CO CA
23 Distribution of Elderly, Impaired Hospitals (Day 1) & Hospital Bed Availability - Earthquake Scenario: Great Salt Lake Segment, UT BOX ELDER WEBER M 7.0 Great Salt Lake Segment Earthquake Highway Damage Damage is expressed as the probability that a given bridge or highway segment will realize at least moderate damage. Highway Segment Impact Major Roadway Bridge Impact MORGAN Low Low DAVIS Moderate Moderate High High Impaired Hospitals (Day 1) Damage is expressed as Low the probablility that a given hospital will realize Moderate at least moderate damage. High TOOELE SALT LAKE County Total # Hospital Beds Hospital Beds Available Injuries Requiring Hospital Treatment 2pm Salt Lake 3,440 3, Juab Weber Cache Duchesne Davis Millard Utah 1,013 1,011 0 Sanpete Wasatch Box Elder Tooele Total 6,486 6, WASATCH Miles FEMA & URS Corporation Ü 1Dot=30 People Over 65 UTAH OR ID WY NE Nursing Home NV UT CO CA
24 Electrical, Natural Gas & Oil Facility Damage - Earthquake Scenario: Great Salt Lake Segment, UT BOX ELDER!? WEBER ë ë M 7.0 Great Salt Lake Segment Earthquake DAVIS MORGAN Utility Damage (at least moderate) Damage is expressed as the probability chance that a given utility system will realize at least moderate damage. Electric Power Facility!? Low!? Moderate ë ë Oil Facility Low Moderate 80 TOOELE ë ë!?!? ë!? ëë ë ë ë!?!?!? SALT LAKE!? o!? 80!? High PGA (% g's) < >0.18 Natural Gas Facility o o o Low ë Moderate High High Great Salt Lake Fault Counties Interstate Major Roads City Boundaries 15 UTAH ë WASATCH OR ID Miles FEMA & URS Corporation WY Ü NE ë NV UT CO CA
25 Estimated Building Inspection Needs - Earthquake Scenario: Great Salt Lake Segment, UT BOX ELDER WEBER M 7.0 Great Salt Lake Segment Earthquake DAVIS MORGAN Estimated # of Structures Estimated # of Inspectors Needed Red (Complete) Yellow (Extensive) 1, Light Green (Slight/ 81, Moderate) Total 83, *Estimated number of inspectors needed to complete inspections in 30 days. Red Tag (Complete Damage) 80 TOOELE SALT LAKE 80 Yellow Tag (Extensive Damage) Green Tag (Slight/Moderate Damage) *1 Dot = 10 (by census tract) 15 UTAH WASATCH Miles FEMA & URS Corporation OR ID WY Ü NE NV UT CO CA
26 Estimated Concrete, Steel Debris & Highway Damage - Earthquake Scenario: Great Salt Lake Segment, UT BOX ELDER WEBER M 7.0 Great Salt Lake Segment Earthquake Dot = 1 thousand tons of Concrete and Steel Debris (by census tract) MORGAN DAVIS County Brick and Wood (tons) Concrete and Steel (tons) *Estimated Truck Loads Box Elder 2, Cache 1, Davis 79,000 71,000 6,000 Salt Lake 576, ,000 32,640 Tooele 20,000 11,000 1,240 Utah 3,000 1, Weber 55,000 22,000 3,080 Total 736, ,000 43, SALT LAKE 80 Great Salt Lake Fault Counties Interstate TOOELE Major Roads City Boundaries 15 WASATCH Miles FEMA & URS Corporation Ü UTAH OR ID WY NE NV UT CO CA
27 Demographic Distribution & Highway Damage - Earthquake Scenario: Great Salt Lake Segment, UT BOX ELDER WEBER M 7.0 Great Salt Lake Segment Earthquake Highway Damage Damage is expressed as the probability that a given bridge or highway segment will realize at least moderate damage. Highway Segment Impact Major Roadway Bridge Impact MORGAN Low Low DAVIS Moderate Moderate High High Impaired Hospitals (Day 1) Low Damage is expressed as the probablility that a given hospital will realize Moderate at least moderate damage. High TOOELE SALT LAKE Demographics English Speaking Potentially Non-English Speaking *1 Dot = 500 People (by census tract) Counties City Boundaries WASATCH Miles FEMA & URS Corporation Ü UTAH OR ID WY NE NV UT CO CA
28 Estimated Highway Infrastructure Damage - Earthquake Scenario: Great Salt Lake Segment, UT BOX ELDER WEBER M 7.0 Great Salt Lake Segment Earthquake Highway Damage Damage is expressed as the probability that a given bridge or highway segment will realize at least moderate damage. DAVIS MORGAN Highway Segment Impact Low Major Roadway Bridge Impact Low Moderate Moderate High High County Total # of Bridges # Bridges Needing Priority Inspection *# of Bridge Engineers Needed TOOELE SALT LAKE Utah Box Elder Wasatch Tooele Salt Lake Weber Summit Morgan Davis Total 1, *Based on assuming that 2 engineers can inspect 5 bridges a day for 3 days. WASATCH Miles FEMA & URS Corporation Ü UTAH OR ID WY NE NV UT CO CA
29 Impaired Hospitals (Day 1), Hospital Availability & Highway Functionality - Earthquake Scenario: Great Salt Lake Segment, UT BOX ELDER WEBER M 7.0 Great Salt Lake Segment Earthquake Highway Damage Damage is expressed as the probability that a given bridge or highway segment will realize at least moderate damage. Highway Segment Impact Major Roadway Bridge Impact DAVIS MORGAN Low Moderate Low Moderate High High Impaired Hospitals (Day 1) Damage is expressed as Low the probablility that a given hospital will realize Moderate at least moderate damage. High TOOELE SALT LAKE County Total # Hospital Beds Hospital Beds Available Injuries Requiring Hospital Treatment 2pm Salt Lake 3,440 3, Juab Weber Cache Duchesne Davis Millard Utah 1,013 1,011 0 Sanpete Wasatch Box Elder Tooele Total 6,486 6, WASATCH Miles FEMA & URS Corporation Ü UTAH OR ID WY NE NV UT CO CA
30 Water Line, Sewage Treatment Facility Distribution and Liquefaction - Earthquake Scenario: Great Salt Lake Segment, UT BOX ELDER 80 TOOELE 3] DAVIS 3] 3] WEBER 3] 15 3] 3] 3] 3] 3] SALT LAKE 15 UTAH 3] 84 MORGAN 80 3] WASATCH M 7.0 Great Salt Lake Segment Earthquake Ü Miles FEMA & URS Corporation CA Liquefaction Susceptibility County OR NV Low Medium ID UT WY High Very High Dams 3] Sewage Treatment Facilities Counties Interstate Major Roads # Households without Potable Water (at Day 1) Daily Potable Water Needs Per Person (Gallons/day) Number of Truckloads needed Daily Utah Wasatch Tooele Salt Lake 64, , Weber Summit Morgan Davis 1,860 5,022 2 Total 66, , * Based on U.S. Army Corp Mission Guidebook (Daily water is based on an esimated 3 people per household at a gallon per day per person. One truck can transport an esimated 5000 gallons of water.) CO NE
31 Potential Search & Rescue Needs - Earthquake Scenario: Great Salt Lake Segment, UT BOX ELDER WEBER 15 M 7.0 Great Salt Lake Segment Earthquake 84 Impaired Hospitals (Day 1) Damage is expressed as Low the probablility that a given hospital will realize Moderate at least moderate damage. High DAVIS MORGAN PGA (% g's) < > Dot = 1 Life Threatening Injury (Severity Level 3) *Severity Level 3 is defined as injuries that require hospitalization and can become life threatening if not promptly treated. Structure Type Red (Complete) Collapse Rates for Complete Damage Total Collapse 80 SALT LAKE 80 Wood 24 3% 1 Steel 4 6% 0 Concrete 2 10% 0 Precast 1 13% 0 Reinforced 8 10% Masonry 1 Unreinforced 60 15% Masonry 9 Manufactured Housing 4 3% 0 Total TOOELE Requiring Hospital Treatment Immediate Life Threatening Injuries UTAH WASATCH Miles FEMA & URS Corporation OR ID WY Ü NE NV UT CO CA
32 Correctional and Daycare Facilities, Impaired Hospitals (Day 1) and Highway Functionality - Earthquake Scenario: Great Salt Lake Segment, UT BOX ELDER í WEBER í í í DAVIS í í í í MORGAN M 7.0 Great Salt Lake Segment Earthquake Highway Damage Damage is expressed as the probability that a given bridge or highway segment will realize at least moderate damage. Highway Segment Impact Low Moderate High Major Roadway Bridge Impact Low Moderate High TOOELE í í í í SALT LAKE í í UTAH WASATCH Impaired Hospitals (Day 1) Ü Miles FEMA & URS Corporation OR Daycare Facilities í Correctional Facilities ID Damage is expressed as Low the probablility that a given hospital will realize Moderate at least moderate damage. High WY NE CA NV UT CO
HAZUS-MH: Earthquake Event Report
 HAZUS-MH: Earthquake Event Report Region Name: Brigham City Earthquake Scenario: Brigham City Segment Mw 70 SM Scenario Print Date: February 19, 2010 Totals only reflect data for those census tracts/blocks
HAZUS-MH: Earthquake Event Report Region Name: Brigham City Earthquake Scenario: Brigham City Segment Mw 70 SM Scenario Print Date: February 19, 2010 Totals only reflect data for those census tracts/blocks
Hazus-MH: Earthquake Event Report
 Hazus-MH: Earthquake Event Report Region Name Earthquake Scenario: Print Date: Valmont M5 Valmont fault 5.0 June 07, 2013 Totals only reflect data for those census tracts/blocks included in the user s
Hazus-MH: Earthquake Event Report Region Name Earthquake Scenario: Print Date: Valmont M5 Valmont fault 5.0 June 07, 2013 Totals only reflect data for those census tracts/blocks included in the user s
+ Soil Maps + Building Inventory Maps
 Presentation Overview The Use of HAZUS for Earthquake Scenarios Hope A. Seligson MMI Engineering Very brief HAZUS overview Examples of HAZUS use in previous scenarios Strategies for improving HAZUS results
Presentation Overview The Use of HAZUS for Earthquake Scenarios Hope A. Seligson MMI Engineering Very brief HAZUS overview Examples of HAZUS use in previous scenarios Strategies for improving HAZUS results
Table 1. Study region population, households and building exposure by county
 Table 1. Study region population, households and building exposure by county County Population Households Building Exposure (dollars in millions) Residential Non-Residential Total Alameda 1,443,741 523,366
Table 1. Study region population, households and building exposure by county County Population Households Building Exposure (dollars in millions) Residential Non-Residential Total Alameda 1,443,741 523,366
EARTHQUAKE LOSS ESTIMATION AND RISK ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY FROM CONCEPT TO REAL APPLICATIONS YASIN M. FAHJAN
 Universidade do Minho Departamento de Engenharia Civil SEMINAR AND LUNCH ON EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING AND HISTORIC MASONRY July 12, 2010 EARTHQUAKE LOSS ESTIMATION AND RISK ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY FROM CONCEPT
Universidade do Minho Departamento de Engenharia Civil SEMINAR AND LUNCH ON EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING AND HISTORIC MASONRY July 12, 2010 EARTHQUAKE LOSS ESTIMATION AND RISK ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGY FROM CONCEPT
SPECIFIC SITUATION The potential conditions that the City of Oxnard may face in the earthquake include:
 MAJOR EARTHQUAKE GENERAL SITUATION The City of Oxnard is in the vicinity of several known active and potentially active earthquake faults including the San Andreas (42 miles), Oak Ridge (1 mile), Pitas
MAJOR EARTHQUAKE GENERAL SITUATION The City of Oxnard is in the vicinity of several known active and potentially active earthquake faults including the San Andreas (42 miles), Oak Ridge (1 mile), Pitas
Utah Pipeline Association Operator List
 Home Utah Pipeline Association Operator List Member Company Profiles Company Emergency Number Products Transported Anadarko 1-800-738-9816 Natural Gas Chevron Pipeline 1-800-762-3404 Crude Oil, Diesel
Home Utah Pipeline Association Operator List Member Company Profiles Company Emergency Number Products Transported Anadarko 1-800-738-9816 Natural Gas Chevron Pipeline 1-800-762-3404 Crude Oil, Diesel
Comparison Study of the 1985 CUSEC Six Cities Study Using HAZUS
 Comparison Study of the 1985 CUSEC Six Cities Study Using HAZUS Prepared by The Central United States Earthquake Consortium July 2003 Index I. HAZUS Comparison Study of 1985 CUSEPP Six Cities Study II.
Comparison Study of the 1985 CUSEC Six Cities Study Using HAZUS Prepared by The Central United States Earthquake Consortium July 2003 Index I. HAZUS Comparison Study of 1985 CUSEPP Six Cities Study II.
Rocky Hill. Challenges
 Rocky Hill Rocky Hill is located in the southern portion of the Capitol Region. Its land area covers 13.9 square miles with an estimated 2010 Census population of 19,703. Elevation in Rocky Hill ranges
Rocky Hill Rocky Hill is located in the southern portion of the Capitol Region. Its land area covers 13.9 square miles with an estimated 2010 Census population of 19,703. Elevation in Rocky Hill ranges
VULNERABILITY. A Presentation to the Global Earthquake Model Workshop Trinidad. By R. Clarke, Dept Civil & Environmental Engineering, UWI
 SEISMIC STRUCTURAL VULNERABILITY A Presentation to the Global Earthquake Model Workshop Trinidad By R. Clarke, UWI (3 May 2011) 1 PRESENTATION OUTLINE A. DEFINITION AND ASSOCIATED TERMINOLOGY B. HOW IS
SEISMIC STRUCTURAL VULNERABILITY A Presentation to the Global Earthquake Model Workshop Trinidad By R. Clarke, UWI (3 May 2011) 1 PRESENTATION OUTLINE A. DEFINITION AND ASSOCIATED TERMINOLOGY B. HOW IS
Natural Hazard Performance for Lifeline Systems: Natural Gas. Doug Honegger D.G. Honegger Consulting
 Natural Hazard Performance for Lifeline Systems: Natural Gas Doug Honegger D.G. Honegger Consulting 1 Topics Covered Overview of natural gas supply system Key performance issues for natural gas systems
Natural Hazard Performance for Lifeline Systems: Natural Gas Doug Honegger D.G. Honegger Consulting 1 Topics Covered Overview of natural gas supply system Key performance issues for natural gas systems
Earthquake-triggered accidents at industrial facilities: lessons learned from the Wenchuan earthquake
 Chengdu, 14 July, 2009 IDRC 2009 1 Earthquake-triggered accidents at industrial facilities: lessons learned from the Wenchuan earthquake E. Krausmann and A. M. Cruz European Commission, Joint Research
Chengdu, 14 July, 2009 IDRC 2009 1 Earthquake-triggered accidents at industrial facilities: lessons learned from the Wenchuan earthquake E. Krausmann and A. M. Cruz European Commission, Joint Research
Potential URMs in Nevada
 Potential URMs in Nevada Presentation for the Nevada Earthquake Safety Council 9 November 2011 by Jonathan G. Price, Craig M. depolo, and Gary L. Johnson Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology Nevada Public
Potential URMs in Nevada Presentation for the Nevada Earthquake Safety Council 9 November 2011 by Jonathan G. Price, Craig M. depolo, and Gary L. Johnson Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology Nevada Public
OREGON BENEFIT-COST ANALYSIS TOOL
 OREGON BENEFIT-COST ANALYSIS TOOL FOR EVALUATION OF SEISMIC REHABILITATION GRANT PROGRAM APPLICATIONS USER S GUIDE September 28, 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 WHAT IS BENEFIT-COST ANALYSIS?... 1 1.1 Overview...
OREGON BENEFIT-COST ANALYSIS TOOL FOR EVALUATION OF SEISMIC REHABILITATION GRANT PROGRAM APPLICATIONS USER S GUIDE September 28, 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1.0 WHAT IS BENEFIT-COST ANALYSIS?... 1 1.1 Overview...
Appendix D. Flood Specific Table Data Dictionary
 D-1 Appendix D. Flood Specific Data Dictionary of Contents Indexes List D-1 High Level List of Flood Specific s D-3 Data Dictionary for Flood Specific s D-3 s D.1 List D-3 D.2 Square Footage by General
D-1 Appendix D. Flood Specific Data Dictionary of Contents Indexes List D-1 High Level List of Flood Specific s D-3 Data Dictionary for Flood Specific s D-3 s D.1 List D-3 D.2 Square Footage by General
Data Documentation Template and Earthquake Checklist. Earthquake Data Analysis Methodology: Structural Retrofits of Buildings
 Data Documentation Template and Earthquake Checklist Earthquake Data Analysis Methodology: Structural Retrofits of s This data documentation template is designed to assist Benefit-Cost (BC) analysts in
Data Documentation Template and Earthquake Checklist Earthquake Data Analysis Methodology: Structural Retrofits of s This data documentation template is designed to assist Benefit-Cost (BC) analysts in
Scenario-based simulation of revenue loss at seismically damaged seaports
 2 nd International Conference on Urban Disaster Reduction November 27~29, 2007 Scenario-based simulation of revenue loss at seismically damaged seaports U. J. Na *, S. R. Chaudhuri, M. Shinozuka 1 Department
2 nd International Conference on Urban Disaster Reduction November 27~29, 2007 Scenario-based simulation of revenue loss at seismically damaged seaports U. J. Na *, S. R. Chaudhuri, M. Shinozuka 1 Department
Post-Disaster Safety Evaluations Using ATC-20/45
 Post-Disaster Safety Evaluations Using ATC-20/45 Presented by: Drew Martin, P.E., S.E. September 2, 2015 2015 APWA International Public Works Congress and Exposition Funded and Updated By: Office of Emergency
Post-Disaster Safety Evaluations Using ATC-20/45 Presented by: Drew Martin, P.E., S.E. September 2, 2015 2015 APWA International Public Works Congress and Exposition Funded and Updated By: Office of Emergency
Total fatal injuries (number) Total. Total Private industry Goods producing
 TABLE A-2. Fatal occupational resulting from transportation and homicides, South Carolina, 2015 Transportation 2 Homicides 2 fatal 117 54 37 4 9 13 13 Private industry 105 47 33 4 6 11 11 Goods producing
TABLE A-2. Fatal occupational resulting from transportation and homicides, South Carolina, 2015 Transportation 2 Homicides 2 fatal 117 54 37 4 9 13 13 Private industry 105 47 33 4 6 11 11 Goods producing
LAURIE JOHNSON CONSULTING Progress Report: CCSF Lifelines Council Interdependency Study
 LAURIE JOHNSON CONSULTING Progress Report: Urban Planning Risk Management Disaster Recovery CCSF Lifelines Council Interdependency Study Lifelines Council Meeting #9 September 6, 2012 (Source: JIIRC-UBC)
LAURIE JOHNSON CONSULTING Progress Report: Urban Planning Risk Management Disaster Recovery CCSF Lifelines Council Interdependency Study Lifelines Council Meeting #9 September 6, 2012 (Source: JIIRC-UBC)
SAN FRANCISCO S COMMUNITY ACTION PLAN FOR SEISMIC SAFETY
 SAN FRANCISCO S COMMUNITY ACTION PLAN FOR SEISMIC SAFETY Christopher Rojahn Applied Technology Council Redwood City, California USA Laurence Kornfield Department of Building Inspection San Francisco, California
SAN FRANCISCO S COMMUNITY ACTION PLAN FOR SEISMIC SAFETY Christopher Rojahn Applied Technology Council Redwood City, California USA Laurence Kornfield Department of Building Inspection San Francisco, California
DISASTER LOGISTICS: HOW TO ESTIMATE THE EMERGENCY GOODS TO SUPPORT EARTHQUAKE RELIEF OPERATIONS
 DISASTER LOGISTICS: HOW TO ESTIMATE THE EMERGENCY GOODS TO SUPPORT EARTHQUAKE RELIEF OPERATIONS by R. Oktarina 1,2, S. Nur Bahagia 3, L. Diawati 3, K. S. Pribadi 4, and K. Okazaki 5 1 PhD Student, Department
DISASTER LOGISTICS: HOW TO ESTIMATE THE EMERGENCY GOODS TO SUPPORT EARTHQUAKE RELIEF OPERATIONS by R. Oktarina 1,2, S. Nur Bahagia 3, L. Diawati 3, K. S. Pribadi 4, and K. Okazaki 5 1 PhD Student, Department
When the Big One Strikes Again Estimated Losses due to a Repeat of the 1906 San Francisco Earthquake
 When the Big One Strikes Again Estimated Losses due to a Repeat of the 1906 San Francisco Earthquake Charles A. Kircher, a M.EERI, Hope A. Seligson, b M.EERI, Jawhar Bouabid, c M.EERI, and Guy C. Morrow,
When the Big One Strikes Again Estimated Losses due to a Repeat of the 1906 San Francisco Earthquake Charles A. Kircher, a M.EERI, Hope A. Seligson, b M.EERI, Jawhar Bouabid, c M.EERI, and Guy C. Morrow,
Earthquake engineering is the science that studies the behavior of structures
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction Earthquake engineering is the science that studies the behavior of structures under earthquake excitation and provides the rules on how to design structures to survive seismic shocks.
CHAPTER 1 Introduction Earthquake engineering is the science that studies the behavior of structures under earthquake excitation and provides the rules on how to design structures to survive seismic shocks.
MONTE CARLO SIMULATION FOR THE SEISMIC RESPONSE ANALYSIS OF ELECTRIC POWER SYSTEM IN TAIWAN
 MONTE CARLO SIMULATION FOR THE SEISMIC RESPONSE ANALYSIS OF ELECTRIC POWER SYSTEM IN TAIWAN Gee-Yu Liu National Center for Research on Earthquake Engineering, Taipei, Taiwan karl@ncree.gov.tw C.-W. Liu
MONTE CARLO SIMULATION FOR THE SEISMIC RESPONSE ANALYSIS OF ELECTRIC POWER SYSTEM IN TAIWAN Gee-Yu Liu National Center for Research on Earthquake Engineering, Taipei, Taiwan karl@ncree.gov.tw C.-W. Liu
GIS and Database Tools for BART Seismic Upgrade. John Eidinger G&E Engineering Systems Inc.
 GIS and Database Tools for BART Seismic Upgrade John Eidinger G&E Engineering Systems Inc. eidinger@earthlink.net Agenda BART wants to do a comprehensive seismic evaluation and upgrade of its train system
GIS and Database Tools for BART Seismic Upgrade John Eidinger G&E Engineering Systems Inc. eidinger@earthlink.net Agenda BART wants to do a comprehensive seismic evaluation and upgrade of its train system
Stafford Capitol Region Natural Hazards Mitigation Plan Update - Page 384
 Stafford Stafford is a rural community of approximately 12,000 residents. Situated in the Willimantic River Valley between almost parallel ranges of hills, Stafford is located in the northern portion of
Stafford Stafford is a rural community of approximately 12,000 residents. Situated in the Willimantic River Valley between almost parallel ranges of hills, Stafford is located in the northern portion of
Sustainable development: Vulnerability functions for the evaluation of physical effects related to mountain hazard
 Sustainable development: Vulnerability functions for the evaluation of physical effects related to mountain hazard Sami Oguzhan Akbas, Ph.D. Supervisors: Dr. Sterlacchini (CNR), Dr. De Amicis & Prof. Giacomelli
Sustainable development: Vulnerability functions for the evaluation of physical effects related to mountain hazard Sami Oguzhan Akbas, Ph.D. Supervisors: Dr. Sterlacchini (CNR), Dr. De Amicis & Prof. Giacomelli
Risk Analysis and Assessment of Non-Ductile Concrete Buildings in Los Angeles County Using HAZUS-MH. Sarah Moreland
 Risk Analysis and Assessment of Non-Ductile Concrete Buildings in Los Angeles County Using HAZUS-MH by Sarah Moreland A Thesis Presented to the Faculty of the USC Graduate School University of Southern
Risk Analysis and Assessment of Non-Ductile Concrete Buildings in Los Angeles County Using HAZUS-MH by Sarah Moreland A Thesis Presented to the Faculty of the USC Graduate School University of Southern
Available at: Last Modified: December 2012
 6.3 Architectural Components 6.3.7 Chimneys and Stacks 6.3.7.1 Unreinforced Masonry Chimney Unreinforced masonry (URM) chimneys are extremely vulnerable to earthquake damage; their behavior has long been
6.3 Architectural Components 6.3.7 Chimneys and Stacks 6.3.7.1 Unreinforced Masonry Chimney Unreinforced masonry (URM) chimneys are extremely vulnerable to earthquake damage; their behavior has long been
FEMA 450 and 451. Acknowledgments. NEHRP Recommended Provisions: Instructional Materials (FEMA 451B) FEMA 451B Handouts Introduction 1
 NEHRP Recommended Provisions: Instructional Materials (FEMA 451B) These instructional materials complement FEMA 451, NEHRP Recommended Provisions: Design Examples Needed are copies of FEMA 451 and FEMA
NEHRP Recommended Provisions: Instructional Materials (FEMA 451B) These instructional materials complement FEMA 451, NEHRP Recommended Provisions: Design Examples Needed are copies of FEMA 451 and FEMA
Civil Engineering Courses
 Civil Engineering Courses CE 1000 - Civil Engineering CE 1001 - Sustainability and Civil Engineering Practice CE 3101 - Civil Engineering Materials CE 3202 - Structural Analysis CE 3331 - Professional
Civil Engineering Courses CE 1000 - Civil Engineering CE 1001 - Sustainability and Civil Engineering Practice CE 3101 - Civil Engineering Materials CE 3202 - Structural Analysis CE 3331 - Professional
Civil and Environmental Engineering at the University of Utah
 Civil and Environmental Engineering at the University of Utah Prof. Evert Lawton, Ph.D., P.E. Civil & Environmental Engineering Prepared for: Salt Lake Community College 2/2/2017 1 Civil & Environmental
Civil and Environmental Engineering at the University of Utah Prof. Evert Lawton, Ph.D., P.E. Civil & Environmental Engineering Prepared for: Salt Lake Community College 2/2/2017 1 Civil & Environmental
Regulation No July Engineering and Design REPORTING EARTHQUAKE EFFECTS TABLE OF CONTENTS
 DEPARTMENT OF THE ARMY *ER 1110-2-1802 U.S. Army Corps of Engineers CECW-EG Washington, DC 20314-1000 Regulation No. 1110-2-1802 28 July 2017 Engineering and Design REPORTING EARTHQUAKE EFFECTS Paragraph
DEPARTMENT OF THE ARMY *ER 1110-2-1802 U.S. Army Corps of Engineers CECW-EG Washington, DC 20314-1000 Regulation No. 1110-2-1802 28 July 2017 Engineering and Design REPORTING EARTHQUAKE EFFECTS Paragraph
Utah s Most Critical Surface Transportation Projects to Support Economic Growth and Quality of Life. March Washington, DC
 Utah s Most Critical Surface Transportation Projects to Support Economic Growth and Quality of Life March 2015 Washington, DC 202-466-6706 Founded in 1971, TRIP of Washington, DC, is a nonprofit organization
Utah s Most Critical Surface Transportation Projects to Support Economic Growth and Quality of Life March 2015 Washington, DC 202-466-6706 Founded in 1971, TRIP of Washington, DC, is a nonprofit organization
Mobility and System Reliability Goal
 Mobility and System Reliability Goal Provide surface transportation infrastructure and services that will advance the efficient and reliable movement of people and goods throughout the state. Background:
Mobility and System Reliability Goal Provide surface transportation infrastructure and services that will advance the efficient and reliable movement of people and goods throughout the state. Background:
POLICY EARTHQUAKE PRONE DANGEROUS & INSANITARY BUILDINGS
 POLICY EARTHQUAKE PRONE DANGEROUS & INSANITARY BUILDINGS Adopted: Council Meeting 30 June 2011 Review date: before 30 June 2016 Contents 1 Introduction and background... 1 2 Policy approach... 2 2.1 Policy
POLICY EARTHQUAKE PRONE DANGEROUS & INSANITARY BUILDINGS Adopted: Council Meeting 30 June 2011 Review date: before 30 June 2016 Contents 1 Introduction and background... 1 2 Policy approach... 2 2.1 Policy
F MI SUMMIT. Understanding the Trucking Labor Market. Dr. Kristen Monaco
 F MI SUMMIT 20 12 Understanding the Trucking Labor Market Dr. Kristen Monaco Agenda The Trucking Industry Deregulation s impact on industry structure Evolution of the labor market Labor Market Conditions
F MI SUMMIT 20 12 Understanding the Trucking Labor Market Dr. Kristen Monaco Agenda The Trucking Industry Deregulation s impact on industry structure Evolution of the labor market Labor Market Conditions
Seismic Safety of Schools. Washington Schools. Earthquake Performance Assessment Tool (EPAT) USER GUIDE. Kenneth A. Goettel Cale Ash Erica Fischer
 Seismic Safety of Schools Washington Schools Earthquake Performance Assessment Tool (EPAT) USER GUIDE Kenneth A. Goettel Cale Ash Erica Fischer August 10, 2017 Preface This User Guide provides detailed
Seismic Safety of Schools Washington Schools Earthquake Performance Assessment Tool (EPAT) USER GUIDE Kenneth A. Goettel Cale Ash Erica Fischer August 10, 2017 Preface This User Guide provides detailed
SEISMIC DESIGN CRITERIA FOR SAN FRACISCO WATER SYSTEM IMPROVEMENT PROGRAM
 SEISMIC DESIGN CRITERIA FOR SAN FRACISCO WATER SYSTEM IMPROVEMENT PROGRAM Luke Cheng 1 and Brian Sadden 2 1 Manager, Structural Design, Engineering Management Bureau, San Francisco Public Utilities Commission,
SEISMIC DESIGN CRITERIA FOR SAN FRACISCO WATER SYSTEM IMPROVEMENT PROGRAM Luke Cheng 1 and Brian Sadden 2 1 Manager, Structural Design, Engineering Management Bureau, San Francisco Public Utilities Commission,
Resilience Initiatives a Whole Community Approach. Program Overview
 City and County of San Francisco Resilience Initiatives a Whole Community Approach British Columbia Construction Round Table Vancouver, British Columbia Thursday, June 23, 2011 Program Overview Citywide
City and County of San Francisco Resilience Initiatives a Whole Community Approach British Columbia Construction Round Table Vancouver, British Columbia Thursday, June 23, 2011 Program Overview Citywide
Benchmarking FEMA P-58 performance predictions against observed earthquake data A preliminary evaluation for the Canterbury earthquake sequence
 Benchmarking FEMA P-58 performance predictions against observed earthquake data A preliminary evaluation for the Canterbury earthquake sequence J.W. Baker & G. Cremen Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering,
Benchmarking FEMA P-58 performance predictions against observed earthquake data A preliminary evaluation for the Canterbury earthquake sequence J.W. Baker & G. Cremen Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering,
Prepare60 s Guide to Securing Utah s Water Future
 Prepare60 s Guide to Securing Utah s Future Prepare60 Approach Utah s population is projected to double by 2060, and by 2030 our statewide demand for water will outpace supply. We need to act now to secure
Prepare60 s Guide to Securing Utah s Future Prepare60 Approach Utah s population is projected to double by 2060, and by 2030 our statewide demand for water will outpace supply. We need to act now to secure
Sustainable development: Vulnerability functions for the evaluation of physical effects related to mountain hazard
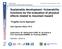 Sustainable development: Vulnerability functions for the evaluation of physical effects related to mountain hazard Fragility Curve Approach Sami Oguzhan Akbas, Ph.D. Supervisors: Dr. Sterlacchini (CNR),
Sustainable development: Vulnerability functions for the evaluation of physical effects related to mountain hazard Fragility Curve Approach Sami Oguzhan Akbas, Ph.D. Supervisors: Dr. Sterlacchini (CNR),
Developing Effective Local Government Programs in Earthquake Mitigation. JEANNE PERKINS ABAG Earthquake and Hazards Program Manager
 Developing Effective Local Government Programs in Earthquake Mitigation JEANNE PERKINS ABAG Earthquake and Hazards Program Manager Speakers JEANNE PERKINS ABAG Earthquake & Hazards Prog. Mgr. ARRIETTA
Developing Effective Local Government Programs in Earthquake Mitigation JEANNE PERKINS ABAG Earthquake and Hazards Program Manager Speakers JEANNE PERKINS ABAG Earthquake & Hazards Prog. Mgr. ARRIETTA
Final Conference Earthquake engineering Presentation of the book
 Final Conference Earthquake engineering Presentation of the book Strategies for reduction of the seismic risk Tunnel under seismic loading: a review of damage case histories and protection methods Giovanni
Final Conference Earthquake engineering Presentation of the book Strategies for reduction of the seismic risk Tunnel under seismic loading: a review of damage case histories and protection methods Giovanni
for a Better San Francisco Public Utilities Commission Pipe Users Group 2013 Seminar Form
 Rebuilding Today for a Better Tomorrow San Francisco Public Utilities Commission Pipe Users Group 2013 Seminar Form February 21 21, 2013 Water For the World Total World Population 6 Billion 1.1 Billion
Rebuilding Today for a Better Tomorrow San Francisco Public Utilities Commission Pipe Users Group 2013 Seminar Form February 21 21, 2013 Water For the World Total World Population 6 Billion 1.1 Billion
Pipe Replacement Strategies for Aging and Seismic Issues
 Pipe Replacement Strategies for Aging and Seismic Issues John Eidinger 1 and Jennifer Cioffi 2 1. G&E Engineering Systems Inc., PO Box 3592, Olympic Valley, CA 96146-3592; eidinger@geengineeringsystems.com
Pipe Replacement Strategies for Aging and Seismic Issues John Eidinger 1 and Jennifer Cioffi 2 1. G&E Engineering Systems Inc., PO Box 3592, Olympic Valley, CA 96146-3592; eidinger@geengineeringsystems.com
Damage to Building Structures Caused by the 1999 Chi-chi Earthquake in Taiwan
 Damage to Building Structures Caused by the 1999 Chi-chi Earthquake in Taiwan Koji YOSHIMURA* and Masayuki KUROKI** Based on the field investigation conducted in severely damaged areas in the central districts
Damage to Building Structures Caused by the 1999 Chi-chi Earthquake in Taiwan Koji YOSHIMURA* and Masayuki KUROKI** Based on the field investigation conducted in severely damaged areas in the central districts
Joshua Ritti. Professional Profile. Academic Credentials & Professional Honors
 Joshua Ritti Corporate Vice President, Principal & Practice Director Construction Consulting 475 14th Street, Suite 400 Oakland, CA 94612 (510) 268-5036 tel jritti@exponent.com Professional Profile Mr.
Joshua Ritti Corporate Vice President, Principal & Practice Director Construction Consulting 475 14th Street, Suite 400 Oakland, CA 94612 (510) 268-5036 tel jritti@exponent.com Professional Profile Mr.
Vehicle Miles Traveled Trends and Implications for the US Interstate Highway System
 Vehicle Miles Traveled Trends and Implications for the US Interstate Highway System The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine Transportation Research Board Future Interstate Study Steven
Vehicle Miles Traveled Trends and Implications for the US Interstate Highway System The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine Transportation Research Board Future Interstate Study Steven
New Madrid and Wabash Valley Seismic Study: Assessing the Impacts on Natural Gas Transmission Pipelines and Downstream Markets by Using NGFast
 New Madrid and Wabash Valley Seismic Study: Assessing the Impacts on Natural Gas Transmission Pipelines and Downstream Markets by Using NGFast Prepared for: FEMA Region V New Madrid Seismic Zone Planning
New Madrid and Wabash Valley Seismic Study: Assessing the Impacts on Natural Gas Transmission Pipelines and Downstream Markets by Using NGFast Prepared for: FEMA Region V New Madrid Seismic Zone Planning
Available at: Last Modified: December 2012
 6.4 Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing Components 6.4.5 Fluid Piping, not Fire Protection 6.4.5.1 Hazardous Materials Piping This category covers fluid piping, other than pressure piping or fire protection
6.4 Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing Components 6.4.5 Fluid Piping, not Fire Protection 6.4.5.1 Hazardous Materials Piping This category covers fluid piping, other than pressure piping or fire protection
Methodological Appendix Infrastructure Jobs Update
 Methodological Appendix Infrastructure Jobs Update Note: Methods used to classify infrastructure jobs, including specific occupations and industries, are described at greater length in Beyond Shovel-Ready:
Methodological Appendix Infrastructure Jobs Update Note: Methods used to classify infrastructure jobs, including specific occupations and industries, are described at greater length in Beyond Shovel-Ready:
FEMA s National Risk Index
 FEMA s National Risk Index Agenda National Risk Index (NRI) Background NRI Working Groups Calculating and NRI Hazard Data Resilience Score Social Vulnerability and Resilience Data Built Environment Data
FEMA s National Risk Index Agenda National Risk Index (NRI) Background NRI Working Groups Calculating and NRI Hazard Data Resilience Score Social Vulnerability and Resilience Data Built Environment Data
Importance Category and Seismic Restraint
 Ontario Association of Architects Practice Tip PT.35 Version 1.0 July 13, 2016 Importance Category and Seismic Restraint 2016 OAA, all rights reserved. Persons who are not members of the OAA must obtain
Ontario Association of Architects Practice Tip PT.35 Version 1.0 July 13, 2016 Importance Category and Seismic Restraint 2016 OAA, all rights reserved. Persons who are not members of the OAA must obtain
Selecting a Temporary Debris Management Site for Effective Debris Removal
 214 10 th International Conference of the International Institute for Infrastructure Resilience and Reconstruction (I3R2) 20 22 May 2014 Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA Selecting a Temporary
214 10 th International Conference of the International Institute for Infrastructure Resilience and Reconstruction (I3R2) 20 22 May 2014 Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana, USA Selecting a Temporary
SAFETY AND NOISE 9. Safety and Noise
 SAFETY AND NOISE 9 9 Safety and Noise Safety is a basic human need and is required for a community to thrive. The goals and policies in this element are designed to protect and enhance public health and
SAFETY AND NOISE 9 9 Safety and Noise Safety is a basic human need and is required for a community to thrive. The goals and policies in this element are designed to protect and enhance public health and
APPENDIX H: TRAVEL DEMAND MODEL VALIDATION AND ANALYSIS
 APPENDIX H: TRAVEL DEMAND MODEL VALIDATION AND ANALYSIS Travel demand models (TDM) simulate current travel conditions and forecast future travel patterns and conditions based on planned system improvements
APPENDIX H: TRAVEL DEMAND MODEL VALIDATION AND ANALYSIS Travel demand models (TDM) simulate current travel conditions and forecast future travel patterns and conditions based on planned system improvements
EXISTING AND FUTURE FREIGHT GOODS MOVEMENT ASSESSMENT
 Technical Memorandum EXISTING AND FUTURE FREIGHT GOODS MOVEMENT ASSESSMENT Prepared by: April 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction... 3 1.1 Study Purpose... 3 1.2 Data Reference List... 3 2. Data sources...
Technical Memorandum EXISTING AND FUTURE FREIGHT GOODS MOVEMENT ASSESSMENT Prepared by: April 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction... 3 1.1 Study Purpose... 3 1.2 Data Reference List... 3 2. Data sources...
Earthquake Risk of Kathmandu Valley. National Society for Earthquake Technology-Nepal (NSET)
 Earthquake Risk of Kathmandu Valley National Society for Earthquake Technology-Nepal (NSET) Seismic Hazard Bam (>40,000) Bhuj Kashmir (>80,000 ) Wenchuan (>70,000) Kathmandu k Acceleration Distribution
Earthquake Risk of Kathmandu Valley National Society for Earthquake Technology-Nepal (NSET) Seismic Hazard Bam (>40,000) Bhuj Kashmir (>80,000 ) Wenchuan (>70,000) Kathmandu k Acceleration Distribution
EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING FOR SEISMIC DISASTER MITIGATION IN THE 21 st CENTURY. Luis Esteva President, IAEE WORLD CONFERENCE ON DISASTER REDUCTION
 EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING FOR SEISMIC DISASTER MITIGATION IN THE 21 st CENTURY Luis Esteva President, IAEE WORLD CONFERENCE ON DISASTER REDUCTION Kobe, Japan January 2005 San Francisco, 1906 Taken from EERI
EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING FOR SEISMIC DISASTER MITIGATION IN THE 21 st CENTURY Luis Esteva President, IAEE WORLD CONFERENCE ON DISASTER REDUCTION Kobe, Japan January 2005 San Francisco, 1906 Taken from EERI
MASTERTON DISTRICT COUNCIL EARTHQUAKE PRONE BUILDINGS POLICY
 MASTERTON DISTRICT COUNCIL EARTHQUAKE PRONE BUILDINGS POLICY 2006 1. INTRODUCTION AND BACKGROUND 2 1.1 The Building Act 2004 requires territorial authorities to adopt a policy on earthquake prone buildings
MASTERTON DISTRICT COUNCIL EARTHQUAKE PRONE BUILDINGS POLICY 2006 1. INTRODUCTION AND BACKGROUND 2 1.1 The Building Act 2004 requires territorial authorities to adopt a policy on earthquake prone buildings
Community Resilience Evaluation including interdependencies
 Community Resilience Evaluation including interdependencies Vincenzo Arcidiacono & Gian Paolo Cimellaro Department of Structural, Geotechnical and Building Engineering (DISEG), Politecnico di Torino, Turin,
Community Resilience Evaluation including interdependencies Vincenzo Arcidiacono & Gian Paolo Cimellaro Department of Structural, Geotechnical and Building Engineering (DISEG), Politecnico di Torino, Turin,
The Northern Waterfront Seawall History and Earthquake Performance Waterfront Plan Working Group Meeting April 13, 2016
 The Northern Waterfront Seawall History and Earthquake Performance Waterfront Plan Working Group Meeting April 13, 2016 Steven Reel, PE - Project Manager, Engineering Division, Port 1 The Northern Waterfront
The Northern Waterfront Seawall History and Earthquake Performance Waterfront Plan Working Group Meeting April 13, 2016 Steven Reel, PE - Project Manager, Engineering Division, Port 1 The Northern Waterfront
2014 PUBLIC TRANSPORTATION FACT BOOK APPENDIX A: HISTORICAL TABLES. Revised September 2014
 2014 PUBLIC TRANSPORTATION FACT BOOK APPENDIX A: HISTORICAL TABLES Revised September 2014 American Public Transportation Association 1666 K Street, N.W. Suite 1100 Washington, DC 20006 (202) 496-4800 APTA
2014 PUBLIC TRANSPORTATION FACT BOOK APPENDIX A: HISTORICAL TABLES Revised September 2014 American Public Transportation Association 1666 K Street, N.W. Suite 1100 Washington, DC 20006 (202) 496-4800 APTA
Earthquake Damage Assessment System for New Taipei City
 Earthquake Damage Assessment System for New Taipei City * Chia-Chuan Hsu 1) and Yu-Chi Sung 2) 1) Bridge Division, NCREE, Taipei 10668, Taiwan 2) Department of Civil Engineering, NTUT, Taipei 10608, Taiwan
Earthquake Damage Assessment System for New Taipei City * Chia-Chuan Hsu 1) and Yu-Chi Sung 2) 1) Bridge Division, NCREE, Taipei 10668, Taiwan 2) Department of Civil Engineering, NTUT, Taipei 10608, Taiwan
Houston-Galveston Area Regional Hazard Mitigation Plan. Initial Planning Workshop
 Houston-Galveston Area Regional Hazard Mitigation Plan Initial Planning Workshop Overview Project Approach Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment Capability Assessment Policy Development and Project
Houston-Galveston Area Regional Hazard Mitigation Plan Initial Planning Workshop Overview Project Approach Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment Capability Assessment Policy Development and Project
RAPID STRUCTURAL ASSESSMENT REPORT
 Structure Type: SUPERSTRUCTURE Work Order: 5540 Facility Name: Pier 68 Warehouse FIN: 1680036 Building- Bldg. # 36 Asset Number: 1680-BLDG36 Facility Code: 3490 Asset Activity: STRUCTURE TWO YR Port Engineer:
Structure Type: SUPERSTRUCTURE Work Order: 5540 Facility Name: Pier 68 Warehouse FIN: 1680036 Building- Bldg. # 36 Asset Number: 1680-BLDG36 Facility Code: 3490 Asset Activity: STRUCTURE TWO YR Port Engineer:
EARTHQUAKE PRONE BUILDINGS POLICY
 EARTHQUAKE PRONE BUILDINGS POLICY 1. INTRODUCTION AND BACKGROUND 1.1 The Building Act 2004 requires territorial authorities to adopt a policy on earthquake prone buildings by 31 st May 2006. 1.2 This policy
EARTHQUAKE PRONE BUILDINGS POLICY 1. INTRODUCTION AND BACKGROUND 1.1 The Building Act 2004 requires territorial authorities to adopt a policy on earthquake prone buildings by 31 st May 2006. 1.2 This policy
An independent review of the current state of infrastructure needs, capability and funding in the State of Utah by the Utah
 An independent review of the current state of infrastructure needs, capability and funding in the State of Utah by the Utah 20XX REPORT CARD FOR STATE NAME(S) INFRASTRUCTURE I Section of the American Society
An independent review of the current state of infrastructure needs, capability and funding in the State of Utah by the Utah 20XX REPORT CARD FOR STATE NAME(S) INFRASTRUCTURE I Section of the American Society
OPERATIONAL SUPPORT FUNCTION Emergency Level Notifications. Office of Emergency Management
 City of Toronto Emergency Plan OPERATIONAL SUPPORT FUNCTION Emergency Level Notifications Office of Emergency Management Version 5.0 December 2013 Revision History Revision Number Name of Contributor Summary
City of Toronto Emergency Plan OPERATIONAL SUPPORT FUNCTION Emergency Level Notifications Office of Emergency Management Version 5.0 December 2013 Revision History Revision Number Name of Contributor Summary
The Central Utah Project
 The Central Utah Project Introduction The Central Utah Project ("CUP") has been in formal existence for over 3 decades and will provide part of the water supply for Salt Lake City's future needs. On May
The Central Utah Project Introduction The Central Utah Project ("CUP") has been in formal existence for over 3 decades and will provide part of the water supply for Salt Lake City's future needs. On May
INDUSTRIAL OUTPARCELS AVAILABLE WITH RAIL ACCESS BUILD TO SUIT OPTIONS. The Moser Group, Inc.
 INDUSTRIAL OUTPARCELS AVAILABLE WITH RAIL ACCESS BUILD TO SUIT OPTIONS Jan Ringeling Broker (704) 490-3872 jringeling@themosergroupinc.com The Moser Group, Inc. Indian Trail, North Carolina 28079 phone:
INDUSTRIAL OUTPARCELS AVAILABLE WITH RAIL ACCESS BUILD TO SUIT OPTIONS Jan Ringeling Broker (704) 490-3872 jringeling@themosergroupinc.com The Moser Group, Inc. Indian Trail, North Carolina 28079 phone:
3. CLASSIFICATION AND IMPLICATIONS OF DAMAGE
 3. CLASSIFICATION AND IMPLICATIONS OF DAMAGE 3.1 Summary of Earthquake Damage There are no modifications to the Guidelines or Commentary of Section 3.1 at this time. 3.2 Damage Types There are no modifications
3. CLASSIFICATION AND IMPLICATIONS OF DAMAGE 3.1 Summary of Earthquake Damage There are no modifications to the Guidelines or Commentary of Section 3.1 at this time. 3.2 Damage Types There are no modifications
Bridge Management. Developments in Short and Medium Span Bridge Engineering 94. Summary
 Developments in Short and Medium Span Bridge Engineering 94 Bridge Management Performance of Steel, Concrete, Prestressed Concrete, and Timber Bridges Kim Stantill-McMcillan Research General Engineer USDA
Developments in Short and Medium Span Bridge Engineering 94 Bridge Management Performance of Steel, Concrete, Prestressed Concrete, and Timber Bridges Kim Stantill-McMcillan Research General Engineer USDA
A MODAL COMPARISON OF DOMESTIC FREIGHT TRANSPORTATION EFFECTS ON THE GENERAL PUBLIC EXECUTIVE SUMMARY. November 2007
 A MODAL COMPARISON OF DOMESTIC FREIGHT TRANSPORTATION EFFECTS ON THE GENERAL PUBLIC EXECUTIVE SUMMARY November 2007 Prepared by CENTER FOR PORTS AND WATERWAYS TEXAS TRANSPORTATION INSTITUTE 701 NORTH POST
A MODAL COMPARISON OF DOMESTIC FREIGHT TRANSPORTATION EFFECTS ON THE GENERAL PUBLIC EXECUTIVE SUMMARY November 2007 Prepared by CENTER FOR PORTS AND WATERWAYS TEXAS TRANSPORTATION INSTITUTE 701 NORTH POST
SEISMIC RESPONSE, EVALUATION, AND RECONSTRUCTION OF THE DVA SEPULVEDA CAMPUS FOLLOWING THE 1994 NORTHRIDGE, CALIFORNIA, EARTHQUAKE
 SEISMIC RESPONSE, EVALUATION, AND RECONSTRUCTION OF THE DVA SEPULVEDA CAMPUS FOLLOWING THE 1994 NORTHRIDGE, CALIFORNIA, EARTHQUAKE Jeffrey R SOULAGES 1, James O MALLEY 2 and Raymond S PUGLIESI 3 SUMMARY
SEISMIC RESPONSE, EVALUATION, AND RECONSTRUCTION OF THE DVA SEPULVEDA CAMPUS FOLLOWING THE 1994 NORTHRIDGE, CALIFORNIA, EARTHQUAKE Jeffrey R SOULAGES 1, James O MALLEY 2 and Raymond S PUGLIESI 3 SUMMARY
Non-Ductile Concrete Buildings
 Non-Ductile Concrete Buildings How Many in LA City? Complexity of Task Preliminary Methods Used by LA City NEES Grand Challenge Additional Work Needed ``` NDC Presentation 1.28.9 Complexity of Task Challenges
Non-Ductile Concrete Buildings How Many in LA City? Complexity of Task Preliminary Methods Used by LA City NEES Grand Challenge Additional Work Needed ``` NDC Presentation 1.28.9 Complexity of Task Challenges
Potential benefits of strengthening earthquake-prone buildings
 Potential benefits of strengthening earthquake-prone buildings W.J. Cousins GNS Science, Lower Hutt, New Zealand. 2013 NZSEE Conference ABSTRACT: The New Zealand Department of Building and Housing was
Potential benefits of strengthening earthquake-prone buildings W.J. Cousins GNS Science, Lower Hutt, New Zealand. 2013 NZSEE Conference ABSTRACT: The New Zealand Department of Building and Housing was
APPENDIX B: SEISMIC ASSESSMENT GUIDELINES
 APPENDIX B: SEISMIC ASSESSMENT GUIDELINES PURPOSE Appendix B The following provide guidance for performing seismic assessments of stationary sources subject to the California Accidental Release Prevention
APPENDIX B: SEISMIC ASSESSMENT GUIDELINES PURPOSE Appendix B The following provide guidance for performing seismic assessments of stationary sources subject to the California Accidental Release Prevention
Railway-Related Cement Consumption Outlook
 Contact: Ed Sullivan, Senior VP & Chief Economist, (847) 972.9006, esullivan@cement.org Trevor Storck, Economist, (847) 972.9044, tstorck@cement.org May 2018 Railway-Related Cement Consumption Outlook
Contact: Ed Sullivan, Senior VP & Chief Economist, (847) 972.9006, esullivan@cement.org Trevor Storck, Economist, (847) 972.9044, tstorck@cement.org May 2018 Railway-Related Cement Consumption Outlook
Earthquake-Prone Buildings Policy
 Earthquake-Prone Buildings Policy Introduction and Purpose The purpose of this Policy is to balance out the need to address earthquake risk and other priorities, taking account of the social, cultural
Earthquake-Prone Buildings Policy Introduction and Purpose The purpose of this Policy is to balance out the need to address earthquake risk and other priorities, taking account of the social, cultural
Chapter 5 Direct Physical Damage - General Building Stock
 5.1 Introduction Chapter 5 Direct Physical Damage - General Building Stock This chapter describes methods for determining the probability of Slight, Moderate, Extensive and Complete damage to general building
5.1 Introduction Chapter 5 Direct Physical Damage - General Building Stock This chapter describes methods for determining the probability of Slight, Moderate, Extensive and Complete damage to general building
Seismic Design and Performance of Metal Buildings
 Seismic Design and Performance of Metal Buildings By W. Lee Shoemaker, P.E., Ph.D. March 31, 2006 The performance of metal building systems in earthquakes has been excellent over the years because they
Seismic Design and Performance of Metal Buildings By W. Lee Shoemaker, P.E., Ph.D. March 31, 2006 The performance of metal building systems in earthquakes has been excellent over the years because they
NJDOT: Asset Management Strategies and Tools
 NEW JERSEY DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION NJDOT: Asset Management Strategies and Tools Wednesday, October 1, 2014 Afternoon Session (1:45pm 2:30pm) Presenters Michael Castaldo New Jersey Department Of Transportation
NEW JERSEY DEPARTMENT OF TRANSPORTATION NJDOT: Asset Management Strategies and Tools Wednesday, October 1, 2014 Afternoon Session (1:45pm 2:30pm) Presenters Michael Castaldo New Jersey Department Of Transportation
PHMSA Update: Aging Infrastructure and Integrity Verification Process
 PHMSA Update: Aging Infrastructure and Integrity Verification Process NAPCA Workshop August 15, 2013 Houston, Texas Safety Administration (PHMSA) Steve Nanney 1 PHMSA Safety Update - Topics Performance
PHMSA Update: Aging Infrastructure and Integrity Verification Process NAPCA Workshop August 15, 2013 Houston, Texas Safety Administration (PHMSA) Steve Nanney 1 PHMSA Safety Update - Topics Performance
State of Idaho Profile
 Overview Of s 44 counties, 4 are within 20 miles of the Great Northern Corridor s (GNC) rail backbone. The GNC s multimodal corridor consisting of highways, rail and ports. It represents an east-west artery
Overview Of s 44 counties, 4 are within 20 miles of the Great Northern Corridor s (GNC) rail backbone. The GNC s multimodal corridor consisting of highways, rail and ports. It represents an east-west artery
5.D.1 HISTORIC, ARCHITECTURAL, ARCHEOLOGICAL, AND CULTURAL RESOURCES
 5.D.1 HISTORIC, ARCHITECTURAL, ARCHEOLOGICAL, AND CULTURAL RESOURCES Section 106 of the National Historic Preservation Act (NHPA) of 1966, as amended (16 U.S.C. Section 470(f)) protects properties that
5.D.1 HISTORIC, ARCHITECTURAL, ARCHEOLOGICAL, AND CULTURAL RESOURCES Section 106 of the National Historic Preservation Act (NHPA) of 1966, as amended (16 U.S.C. Section 470(f)) protects properties that
The Future of Trucking in Virginia: Interstate and Intermodal Strategies
 The Future of Trucking in Virginia: Interstate and Intermodal Strategies Randy Mullett Vice President - Government Relations & Public Affairs, Con-way Inc. Virginia Global Logistics Forum December 7, 2011
The Future of Trucking in Virginia: Interstate and Intermodal Strategies Randy Mullett Vice President - Government Relations & Public Affairs, Con-way Inc. Virginia Global Logistics Forum December 7, 2011
ESTIMATING SEISMIC DAMAGE AND REPAIR COSTS. Raymond Foltz The Citadel Texas A&M Advisor: Dr. Mary Beth Hueste
 ESTIMATING SEISMIC DAMAGE AND REPAIR COSTS Raymond Foltz The Citadel Texas A&M Advisor: Dr. Mary Beth Hueste August 2004 Abstract Since many structures in seismic regions are seismically vulnerable, building
ESTIMATING SEISMIC DAMAGE AND REPAIR COSTS Raymond Foltz The Citadel Texas A&M Advisor: Dr. Mary Beth Hueste August 2004 Abstract Since many structures in seismic regions are seismically vulnerable, building
Post-Earthquake Building Damage Assessment. John Osteraas, PhD, PE Exponent Failure Analysis Associates
 Post-Earthquake Building Damage Assessment John Osteraas, PhD, PE Exponent Failure Analysis Associates Agenda Introduction & Background Damage Assessment References ATC-43 Concrete & Masonry Wall Damage
Post-Earthquake Building Damage Assessment John Osteraas, PhD, PE Exponent Failure Analysis Associates Agenda Introduction & Background Damage Assessment References ATC-43 Concrete & Masonry Wall Damage
State Requirements for a S.E. to Design Structures
 State Requirements for a S.E. to Design Structures Structural Engineering Licensing Summit July 18, 2008 Reston, VA by Sam A. Rihani, PE, F.ASCE, SECB Oregon (Significant Structures) Essential Facilities:
State Requirements for a S.E. to Design Structures Structural Engineering Licensing Summit July 18, 2008 Reston, VA by Sam A. Rihani, PE, F.ASCE, SECB Oregon (Significant Structures) Essential Facilities:
PRELIMINARY STUDY ON THE FRAGILITY CURVES FOR HIGHWAY BRIDGES IN TAIWAN
 Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers, Vol. 27, No. 3, pp. 367-375 (2004) 367 PRELIMINARY STUDY ON THE FRAGILITY CURVES FOR HIGHWAY BRIDGES IN TAIWAN Wen-I Liao* and Ching-Hsiung Loh ABSTRACT This
Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers, Vol. 27, No. 3, pp. 367-375 (2004) 367 PRELIMINARY STUDY ON THE FRAGILITY CURVES FOR HIGHWAY BRIDGES IN TAIWAN Wen-I Liao* and Ching-Hsiung Loh ABSTRACT This
Seismic and Geotechnical Data Requirements in the 2010 California Building Code
 Seismic and Geotechnical Data Requirements in the 2010 California Building Code Jorge Meneses, PE, PhD San Diego, California May 21, 2010 Overview! Introduction! Chapter 16 (Soil lateral and eq. loads)!
Seismic and Geotechnical Data Requirements in the 2010 California Building Code Jorge Meneses, PE, PhD San Diego, California May 21, 2010 Overview! Introduction! Chapter 16 (Soil lateral and eq. loads)!
Developing Resilient Freight Systems
 Developing Resilient Freight Systems Barbara Ivanov Co-Director Freight Systems Division TRB 2011 Transportation Hazards and Security Summit August 23, 2011 How Can States Develop Resilient Freight Systems?
Developing Resilient Freight Systems Barbara Ivanov Co-Director Freight Systems Division TRB 2011 Transportation Hazards and Security Summit August 23, 2011 How Can States Develop Resilient Freight Systems?
PREPARE60 OVERVIEW 1
 PREPARE60 OVERVIEW 1 UTAH S WATER BUDGET Category Total precipitation 61,500,000 Used by vegetation & natural systems 53,789,000 Basin Yield 7,711,000 Compact decreases 535,000 Ground water mining increases
PREPARE60 OVERVIEW 1 UTAH S WATER BUDGET Category Total precipitation 61,500,000 Used by vegetation & natural systems 53,789,000 Basin Yield 7,711,000 Compact decreases 535,000 Ground water mining increases
TRANSPORTATION 101 Today and Tomorrow. Moving People and Goods
 TRANSPORTATION 101 Today and Tomorrow Moving People and Goods What is the Transportation Commission? An independent, seven-member body of citizens appointed by the Governor for six-year terms and representing
TRANSPORTATION 101 Today and Tomorrow Moving People and Goods What is the Transportation Commission? An independent, seven-member body of citizens appointed by the Governor for six-year terms and representing
