Modelling of PFOS fate and transport
|
|
|
- Elmer Dixon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Modelling of PFOS fate and transport Thomas Franz, Adam Dawe, Lauren McDonald, Franz Environmental Inc. Chris>ne Levicki, Health Canada John Miller, Environment Canada
2 Conceptual model Par>>oning from soil to pore water (to soil gas) Transport of soil leachate through unsaturated zone Mixing of soil leachate into groundwater Transport in aquifer Leachate Groundwater flow PFOS source area (e.g. FFTA) Dissolved phase Drinking Water Surface Water
3 Model capabilities The model was designed to back- calculate soil concentra>on at PFOS source loca>on for a given concentra>on in groundwater or surface water Now also does forward calcula>ons by simula>ng PFOS transport from soil to groundwater to receptor within groundwater to receptor
4 CCME, 2006 SQG = DF1 x DF2 x DF3 x DF4 x DF5 x C MAC New: dilu%on at receptor (e.g. in wellbore or at groundwater - surface water interface) C MAC- DW C MAC- AW 10 m
5
6
7
8
9 CCME, 2006 SQG PW = DF1 x DF2 x DF3 x DF4 x DF5 x C MAC C MAC- DW C MAC- AW 10 m
10 CCME, 2006 ~7.3 ~2.4 to ~ SQG PW = DF1 x DF2 x DF3 x DF4 x DF5 x C MAC C MAC- DW C MAC- AW 10 m
11 Sorp%on PFOS- surface electrosta>c PFOS- PFOS electrosta>c repulsion Hydrophobic sorp>on Tang et al., 2010 Cs = Kd Cw Higgins & Luthy, 2006)
12 What affects sorption? Hydrophobic sorp%on Hydrophobic interac>on is the dominant mechanism of PFOS sorp>on to organic carbon, Strong hydrophobic nature of its perfluoroalkyl chain (Higgins and Luthy, 2006). Hydrophobic interac>on can also arise between the hydrophobic chains of different PFOS molecules. K oc and f oc (frac>on of organic carbon) are used to calculate adsorp>on coefficient (K d ) foc increases à Kd increases Higgins & Luthy, 2006)
13 What affects sorption? Hydrophobic sorp%on PFOS sorp>on increases in oil contaminated soil Oil contaminated soil à Kd increases Chen et al., 2009
14 What affects sorption? PFOS- surface electrosta%c interac%on due to ph. PFOS is nega>vely charged under all environmentally relevant ph values. A mineral surface becomes more posi>vely charged (or less nega>vely charged) at lower ph. Enhanced electrosta>c afrac>on force (or reduced electrosta>c repulsion force) results between the nega>vely charged PFOS molecules and the more posi>vely charged mineral surface at lower ph. ph decreases à Kd increases Higgins & Luthy, 2006)
15 What affects sorption? PFOS- PFOS electrosta%c interac%on. Two adjacent PFOS molecules on a surface will repel each other due to their nega>vely charged sulfonate head groups. A strong PFOS- PFOS repulsion tends to prevent these molecules gehng close to each other. Thus, a solu>on with high ionic strength has a tendency to promote PFOS adsorp>on as a result of the suppressed electrosta>c repulsive force.
16 What affects sorption? PFOS- surface electrosta%c interac%on due to ph. PFOS is nega>vely charged under all environmentally relevant ph values. A mineral surface becomes more posi>vely charged (or less nega>vely charged) at lower ph. Enhanced electrosta>c afrac>on force (or reduced electrosta>c repulsion force) results between the nega>vely charged PFOS molecules and the more posi>vely charged mineral surface at lower ph. ph decreases à Kd increases Higgins & Luthy, 2006)
17 What affects sorption? PFOS- surface electrosta%c interac%on due to ionic strength. Electrosta>c interac>on can be significantly weakened at higher ionic strength due to the double layer compression effect. For a posi>vely charged mineral surface, the amount of adsorbed PFOS tends to be reduced due to the weaker electrosta>c afrac>on. However, for a nega>vely charged surface, adsorp>on tends to increase as a result of weaker electrosta>c repulsion. e.g. Ca 2+ decreases à Kd increases (Higgins & Luthy, 2006; Chen et al., 2009; Pan and You, 2010; You et al., 2010)
18 Reviewed partitioning studies Method Selected studies with low dissolved PFOS concentra>ons Went to original papers Eliminated duplica>ons and copies Problem: many studies are for marine sediments (not soil) Results PFOS Koc ranges from 229 to 6310 (Kd from 0.08 to 250 L/kg) Median Koc 1441 L/kg (log Koc = 3.16 L/kg) Programmed spreadsheet to determine median Koc Can add data to this spreadsheet and/or manually override Koc Programmed pseudo- func>on to simulate ph dependency Typical Koc s (L/kg) Benzene = Toluene = 268 B(a)P = Naphthalene = 1837 TCE = 67.7 Acenaphthene = 6123 PFOS = > 6310
19 Authors Year Kd units Koc units Soil type / soil source Enevoldsen & Juhler L/kg 1500 L/kg Jyndevad (Denmark) soil, agricultural topsoil, A horizon, sandy soil Enevoldsen & Juhler L/kg 4048 L/kg Sj. Odde (Denmark) soil, agricultural topsoil, A horizon, clayey soil Ferry et al L/kg 3514 L/kg Minnesota aquifer material from landfill Ferry et al L/kg 229 L/kg same microcosm, but at end of 740 d study 3M L/kg 704 L/kg clay 3M L/kg 374 L/kg clay loam 3M L/kg 1260 L/kg sandy loam 3M L/kg 571 L/kg river sediment Chen et al., L/kg 2659 L/kg marine sediment, S1, from Dalian coastal area, China Chen et al., L/kg 2596 L/kg marine sediment, S2, from Dalian coastal area, China Chen et al., L/kg 3101 L/kg marine sediment, S3, from Dalian coastal area, China Chen et al., L/kg 2660 L/kg marine sediment, S4, from Dalian coastal area, China Chen et al., L/kg 3774 L/kg marine sediment, S5, from Dalian coastal area, China Chen et al L/kg 1349 L/kg soil from paddyfield in Panjin, China Higgins and Luthy L/kg 372 L/kg freshwater sediments (rivers and lakes) from USA Ahrens et al L/kg 5012 L/kg sandy river sediment from Kogaigawa, Japan Ahrens et al L/kg 3162 L/kg muddy river sediment from Sakuragawa, Japan Ahrens et al L/kg 2512 L/kg muddy marine sediment from Tokyo Bay Ahrens et al L/kg 6310 L/kg marine sediment cores from Tokyo Bay, Japan Kwadijk et al L/kg 1445 L/kg 19 sediment samples from rivers, lakes, canals in Netherlands Labadie & Chevreuil L/kg 5012 L/kg sediment from Orge River, France (near Paris) Johnson et al L/kg Ofawa sand Johnson et al L/kg L/kg kaolinite Johnson et al L/kg 376 L/kg Lake Michigan sediment Johnson et al L/kg goethite Johnson et al L/kg high iron sand Johnson et al L/kg 610 L/kg clay Johnson et al L/kg 324 L/kg clay loam Johnson et al L/kg 1177 L/kg sandy loam Johnson et al L/kg river sediment
20 Model limitations Equilibrium par>>oning between soil, water, vapour phases Assumes rela>vely low concentra>ons in soil / groundwater PFOS concentra>ons should be less than 10 mg/l Solubility = 500 to 600 mg/l (in freshwater), 12 mg/l (in seawater) Homogeneous geology However, can be different in unsaturated / saturated zones Uniform, unidirec>onal groundwater flow Constant source concentra>on
21 Primary data requirements Coordinates: x, y, z Geometry of PFOS source Frac>on of organic carbon (foc) Unsat zone thickness Average linear groundwater velocity Aquifer thickness Dispersivity
22 Model comparison of predicted vs measured ground water concentrations Four sites evaluated for transport modeling and empirical Kd calcula>ons: All at civilian or military airports 3 FFTAs 1 disposal site Koc, foc- unsat, m C=? Koc, foc- sat, b, v, n, alfa Dissolved phase
23 Disposal Site Soil and Ground Water Concentrations = Ground Water Concentra>on, units of ug/l = Soil Concentra>on, units of mg/kg Oil Disposal Pit
24 FFTA 1 Shallow Ground Water Contours Fire Training Area
25 FFTA 1 Soil and Ground Water Concentrations <0.02 = Ground Water Concentra>on, units of ug/l = Soil Concentra>on, units of mg/kg Fire Training Area
26 Model result with literature Koc (Koc = 1445 L/kg; Kd,sat = 2.17 L/kg) 5 Predicted vs Measured PFOS Concentra>ons in Ground Water Concentra>on (mg/l) Predicted Measured Distance from source (m)
27 Model calibration Match between observed and modelled PFOS concentra>ons was not very good using literature Koc (Kd) values Approach to improve model results: 1) Derived site- specific Kd values based on co- located soil and groundwater samples from the site(s) - > re- run model 2) Adjust Kd to obtain best fit - > brute force
28 Empirical Koc s Calculated empirical Kd by comparing co- located soil and groundwater sample concentra>ons Calculated Koc from Kd = Koc foc foc based on site- specific data Empirical Koc values range from 85 to 7619 (L/kg) Literature Koc values range from 229 to 6310 (L/Kg)
29 Model result with median empirical Kd (Kd = Koc foc = 1.6 L/kg ; Koc = 424 L/kg) 5 Predicted vs Measured PFOS Concentra>ons in Ground Water Concentra>on (mg/l) Predicted Measured Distance from source (m)
30 Brute Force best fit Excel SOLVER used to adjust Kd - > obtain best fit between observed and modelled PFOS concentra>ons
31 Model result with best fit Kd (Kd sat = 0.1 Kd unsat) (Kd,sat = L/kg; Koc = 342 L/kg) 5 Predicted vs Measured PFOS Concentra>ons in Ground Water Concentra>on (mg/l) Predicted Measured Distance from source (m)
32 Adjust other model parameters Koc alone is not the problem Modified transverse (horizontal) dispersivity to achieve befer match Likely unrealis>c dispersivity value
33 Adjust transverse dispersivity (transverse = longitudinal dispersivity) (Kd,sat = 1.2 L/kg) 5 Predicted vs Measured PFOS Concentra>ons in Ground Water Concentra>on (mg/l) Predicted Measured Distance from source (m)
34 Conclusions Simple mathema>cal model for PFOS fate & transport has been developed. Runs in Excel, easy to use, has a series of limita>ons. Limita>ons are similar to other models used for guideline development and risk assessment Use with cau>on for site specific applica>ons Primary afenua>on process for PFOS is par>>oning (sorp>on). Greatest uncertainty for modelling of PFOS stems from par>>oning coefficient Review of Koc s Empirical Koc s range from 85 to 7619 L/kg Literature Koc s range from 229 to 6310 L/kg Model results match field data befer for Koc s at the low end of the range (i.e. less sorp>on / more mobile)
35 Recommenda>ons For assessment of PFOS fate & transport, we need to collect foc data in unsaturated soil zone foc data in aquifer (groundwater transport) zone Collect data pairs of co- located soil and groundwater directly below source to determine site- specific Kd ph
36 Acknowledgments Sanya Petrovic, Health Canada Brian Asher, Health Canada Luigi Lorusso, Health Canada Jo- Ann Aldridge, Environment Canada Philippa Coureton, Environment Canada
37 Disposal Site Soil and Ground Water Concentrations = Ground Water Concentra>on, units of ug/l = Soil Concentra>on, units of mg/kg Oil Disposal Pit
38 Cold lake best solution, solve for unsat and sat Kd (0 <= unsat kd <= sat Kd Predicted vs Measured PFOS Concentra>ons in Ground Water Concentra>on (mg/l) Predicted Measured Distance from source (m)
TECHNICAL GUIDANCE. Groundwater Protection Model ON CONTAMINATED SITES
 Groundwater Protection Model 13 TECHNICAL GUIDANCE ON CONTAMINATED SITES Version 2.0 November 1, 2017 This document provides guidance to qualified professionals on using the ministry s Groundwater Protection
Groundwater Protection Model 13 TECHNICAL GUIDANCE ON CONTAMINATED SITES Version 2.0 November 1, 2017 This document provides guidance to qualified professionals on using the ministry s Groundwater Protection
Non-Aqueous Phase Liquids Young Environmental Professionals (YEPs) Presentation 23 February 2017
 Non-Aqueous Phase Liquids Young Environmental Professionals (YEPs) Presentation 23 February 2017 Gordon Binkhorst Senior Hydrogeologist at ALTA Environmental Corp. 1998 - Present Brown University, B.S.
Non-Aqueous Phase Liquids Young Environmental Professionals (YEPs) Presentation 23 February 2017 Gordon Binkhorst Senior Hydrogeologist at ALTA Environmental Corp. 1998 - Present Brown University, B.S.
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE AND TRANSPORT MODELING OF EXPLOSIVES IN THE UNSATURATED ZONE
 ENVIRONMENTAL FATE AND TRANSPORT MODELING OF EXPLOSIVES IN THE UNSATURATED ZONE Joseph Robb (AMEC) Jay Clausen (AMEC) Bill Gallagher (MAARNG) National Defense Industrial Association 29 th Environmental
ENVIRONMENTAL FATE AND TRANSPORT MODELING OF EXPLOSIVES IN THE UNSATURATED ZONE Joseph Robb (AMEC) Jay Clausen (AMEC) Bill Gallagher (MAARNG) National Defense Industrial Association 29 th Environmental
Groundwater Models and Modeling Considerations
 Groundwater Models and Modeling Considerations MPCA Industrial Landfill Guidance Workgroup April 30, 2009 Terry Johnson, P.G. Waste Management Inc., The Three Legs of the Stool 1. Engineering design and
Groundwater Models and Modeling Considerations MPCA Industrial Landfill Guidance Workgroup April 30, 2009 Terry Johnson, P.G. Waste Management Inc., The Three Legs of the Stool 1. Engineering design and
Geology 627, Hydrogeology Review questions for final exam h t 1/ 2
 Geology 67, Hydrogeology Review questions for final exam 004 Multiple choice and fill in the blank. There may be more than one correct choice for each question. 1. Which hydrogeologic quantities are represented
Geology 67, Hydrogeology Review questions for final exam 004 Multiple choice and fill in the blank. There may be more than one correct choice for each question. 1. Which hydrogeologic quantities are represented
Demonstrating Stormwater Infiltration to UICs is Protective of Groundwater Quality
 Demonstrating Stormwater Infiltration to UICs is Protective of Groundwater Quality GWPC Presentation September 28, 2010 Heidi Blischke, GSI Water Solutions, Inc. Barb Adkins, City of Portland, Oregon Rod
Demonstrating Stormwater Infiltration to UICs is Protective of Groundwater Quality GWPC Presentation September 28, 2010 Heidi Blischke, GSI Water Solutions, Inc. Barb Adkins, City of Portland, Oregon Rod
Development of Soil Cleanup Standards for Explosive Residues on Military Ranges
 Development of Soil Cleanup Standards for Explosive Residues on Military Ranges Jay Clausen AMEC Earth & Environmental Joe Robb AMEC Earth & Environmental Mahalingham Ravichandran AMEC Earth & Environmental
Development of Soil Cleanup Standards for Explosive Residues on Military Ranges Jay Clausen AMEC Earth & Environmental Joe Robb AMEC Earth & Environmental Mahalingham Ravichandran AMEC Earth & Environmental
DERIVATION OF HYDROCARBON SOIL ACCEPTANCE CRITERIA FOR THE PROTECTION OF SURFACE WATER QUALITY. Stephen Thomson URS New Zealand Limited
 DERIVATION OF HYDROCARBON SOIL ACCEPTANCE CRITERIA FOR THE PROTECTION OF SURFACE WATER QUALITY Stephen Thomson URS New Zealand Limited Players Born in Another Country (importers) 16 15 14 12 10 8 12 11
DERIVATION OF HYDROCARBON SOIL ACCEPTANCE CRITERIA FOR THE PROTECTION OF SURFACE WATER QUALITY Stephen Thomson URS New Zealand Limited Players Born in Another Country (importers) 16 15 14 12 10 8 12 11
Establishing Critical Protective Concentration Levels (PCLs) for Lead-Affected Soils
 Establishing Critical Protective Concentration Levels (PCLs) for Lead-Affected oils Introduction Effective Date: August 2, 2001 The purpose of this document is to describe the processes for establishing
Establishing Critical Protective Concentration Levels (PCLs) for Lead-Affected oils Introduction Effective Date: August 2, 2001 The purpose of this document is to describe the processes for establishing
6. Organic Compounds: Hydrocarbons. General Comments Borden, Canada, tracer test Laurens, SC, gasoline spill Bemidji, MN, crude oil spill
 6. Organic Compounds: Hydrocarbons General Comments Borden, Canada, tracer test Laurens, SC, gasoline spill Bemidji, MN, crude oil spill In the subsurface, biogeochemical processes that control contaminant
6. Organic Compounds: Hydrocarbons General Comments Borden, Canada, tracer test Laurens, SC, gasoline spill Bemidji, MN, crude oil spill In the subsurface, biogeochemical processes that control contaminant
The interactions between trichloroethylene (TCE) and clay
 Hydrvlogical, Œemicat and Bioh^calPmcess^ofTransformation and Transport of Contaminants inaquatic Environments (Proceedings of the Rostov-on-Don Symposium, May 1993). IAHS Publ. no. 219,1994. 99 The interactions
Hydrvlogical, Œemicat and Bioh^calPmcess^ofTransformation and Transport of Contaminants inaquatic Environments (Proceedings of the Rostov-on-Don Symposium, May 1993). IAHS Publ. no. 219,1994. 99 The interactions
Methodology for Establishing Cleanup Levels for Contaminated Sites
 Methodology for Establishing Cleanup Levels for Introduction: In Oklahoma, appropriate cleanup levels for a specific site are provided by the Department of Environmental Quality (DEQ). Achieving these
Methodology for Establishing Cleanup Levels for Introduction: In Oklahoma, appropriate cleanup levels for a specific site are provided by the Department of Environmental Quality (DEQ). Achieving these
PFAS in Sweden, a broad overview. ATV Vintermøde 2017 Fagsession 3, PFAS 8. marts 2017 Niklas Törneman, Sweco Environment
 PFAS in Sweden, a broad overview ATV Vintermøde 2017 Fagsession 3, PFAS 8. marts 2017 Niklas Törneman, Sweco Environment 1 Overall attention in Sweden Conclusions from a SEPA national assessment Sources
PFAS in Sweden, a broad overview ATV Vintermøde 2017 Fagsession 3, PFAS 8. marts 2017 Niklas Törneman, Sweco Environment 1 Overall attention in Sweden Conclusions from a SEPA national assessment Sources
Plume Area Treatment Example
 Page 1 of 5 H R C T E C H N I C A L B U L L E T I N # 2. 5. 1 Plume Area Treatment Example HRC injection grids are commonly employed at project sites where a localized plume of chlorinated solvent contamination
Page 1 of 5 H R C T E C H N I C A L B U L L E T I N # 2. 5. 1 Plume Area Treatment Example HRC injection grids are commonly employed at project sites where a localized plume of chlorinated solvent contamination
Groundwater Risk Assessment
 Groundwater Risk Assessment ELQF - 6 November 2012 Katy Baker Technical Director ARCADIS (UK) Limited Imagine the result Problem definition The importance of the CSM 2 The definition of the problem: 3
Groundwater Risk Assessment ELQF - 6 November 2012 Katy Baker Technical Director ARCADIS (UK) Limited Imagine the result Problem definition The importance of the CSM 2 The definition of the problem: 3
Groundwater Modeling Guidance
 Groundwater Modeling Guidance Richard J. Mandle Groundwater Modeling Program Michigan Department of Environmental Quality Draft 1.0 10/16/02 Executive Summary The use of groundwater models is prevalent
Groundwater Modeling Guidance Richard J. Mandle Groundwater Modeling Program Michigan Department of Environmental Quality Draft 1.0 10/16/02 Executive Summary The use of groundwater models is prevalent
(,,,) = ( )exp ( + C(x,y,z,t) = the concentration of the contaminant at location x, y, z from the source at time t.
 INTRODUCTION Quick Domenico.xls (QD) is a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet application of An Analytical Model For Multidimensional Transport of a Decaying Contaminant Species, by P.A. Domenico, Journal of Hydrology,
INTRODUCTION Quick Domenico.xls (QD) is a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet application of An Analytical Model For Multidimensional Transport of a Decaying Contaminant Species, by P.A. Domenico, Journal of Hydrology,
CSAP PD Webinar. SLRA and Groundwater Models - Nov.10th, 2016
 CSAP PD Webinar SLRA and Groundwater Models - Nov.10th, 2016 1 WEBINAR FORMAT: The Webinar consists of a Adobe Connect website portal which was supplied to you as a link and where the presentations can
CSAP PD Webinar SLRA and Groundwater Models - Nov.10th, 2016 1 WEBINAR FORMAT: The Webinar consists of a Adobe Connect website portal which was supplied to you as a link and where the presentations can
CONTAMINATED LAND FUNDAMENTALS
 CONTAMINATED LAND FUNDAMENTALS Hydrogeology Martin Robertson Z Energy Ltd HYDROGEOLOGY AND THE CSM. WATER CYCLE Groundwater is often a subdued replica of topography. Flow patterns are controlled by the
CONTAMINATED LAND FUNDAMENTALS Hydrogeology Martin Robertson Z Energy Ltd HYDROGEOLOGY AND THE CSM. WATER CYCLE Groundwater is often a subdued replica of topography. Flow patterns are controlled by the
Weikel 1. Actionable Science on Fate and Transport and Degradation and Remediation of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances
 Weikel 1 Actionable Science on Fate and Transport and Degradation and Remediation of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances 11/7/218 Ethan Weikel, PG Deputy Director USGS MD-DE- DC Water Science Center 5522
Weikel 1 Actionable Science on Fate and Transport and Degradation and Remediation of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances 11/7/218 Ethan Weikel, PG Deputy Director USGS MD-DE- DC Water Science Center 5522
Protocol Standards Derivation Methods Chapter 4. Derivation of Soil to Groundwater Protection Matrix Soil Quality Standards
 Protocol 28 2016 Standards Derivation Methods Chapter 4. Derivation of Soil to Groundwater Protection Matrix Soil Quality Standards 4.1 Definitions The following words, acronyms and expressions used in
Protocol 28 2016 Standards Derivation Methods Chapter 4. Derivation of Soil to Groundwater Protection Matrix Soil Quality Standards 4.1 Definitions The following words, acronyms and expressions used in
New insight into pesticide partition coefficient K d for modelling pesticide fluvial transport with the SWAT model
 New insight into pesticide partition coefficient K d for modelling pesticide fluvial transport with the SWAT model Laurie BOITHIAS, Sabine SAUVAGE, Raghavan SRINIVASAN, Jeff ARNOLD, José-Miguel SANCHEZ-PEREZ
New insight into pesticide partition coefficient K d for modelling pesticide fluvial transport with the SWAT model Laurie BOITHIAS, Sabine SAUVAGE, Raghavan SRINIVASAN, Jeff ARNOLD, José-Miguel SANCHEZ-PEREZ
Plume Cut-Off Treatment Example
 Page 1 of 5 H R C T E C H N I C A L B U L L E T I N # 2. 5. 2 Plume Cut-Off Treatment Example A biologically active barrier treatment zone can be constructed by applying HRC in rows of injection points.
Page 1 of 5 H R C T E C H N I C A L B U L L E T I N # 2. 5. 2 Plume Cut-Off Treatment Example A biologically active barrier treatment zone can be constructed by applying HRC in rows of injection points.
Vapor Intrusion - Site Characterization and Screening. NEWMOA Workshop on Vapor Intrusion Chelmsford, MA April 12, 2006
 Vapor Intrusion - Site Characterization and Screening NEWMOA Workshop on Vapor Intrusion Chelmsford, MA April 12, 2006 David J. Folkes P.E. 1 What is Vapor Intrusion?! Compounds of Concern " Volatile Organics
Vapor Intrusion - Site Characterization and Screening NEWMOA Workshop on Vapor Intrusion Chelmsford, MA April 12, 2006 David J. Folkes P.E. 1 What is Vapor Intrusion?! Compounds of Concern " Volatile Organics
Case Study: USEPA Benthic Invertebrate Risk Assessment for Endosulfan
 U.S. Environmental Protection Agency 1 Case Study: USEPA Benthic Invertebrate Risk Assessment for Endosulfan Presentation to: European Chemicals Agency Topical Scientific Workshop: Risk Assessment for
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency 1 Case Study: USEPA Benthic Invertebrate Risk Assessment for Endosulfan Presentation to: European Chemicals Agency Topical Scientific Workshop: Risk Assessment for
Waste Green Sands as Reactive Media for PRBs
 Waste Green Sands as Reactive Media for PRBs Craig H. Benson Geo Engineering, University of Wisconsin-Madison Taeyoon Lee Korean Research Institute and Industrial Science & Technology Gerald Eykholt Eykholt
Waste Green Sands as Reactive Media for PRBs Craig H. Benson Geo Engineering, University of Wisconsin-Madison Taeyoon Lee Korean Research Institute and Industrial Science & Technology Gerald Eykholt Eykholt
C = W/a a = Q + v s A + kv C=C o e -λt. 7. Lakes (reactors) in series (SS)
 What have we done to date? 1. Regulations 2. Hydrology (ΔS = Rivers + Precip. + Groundwater disch. Outflow Evap. GW out ) 3. Kinetics 4. Eutrophication description, model 5. Limnology (field trips) 6.
What have we done to date? 1. Regulations 2. Hydrology (ΔS = Rivers + Precip. + Groundwater disch. Outflow Evap. GW out ) 3. Kinetics 4. Eutrophication description, model 5. Limnology (field trips) 6.
PROTOCOL 27, SOIL LEACHING ASSESSMENT FOR USE IN DERIVING SITE SPECIFIC STANDARDS CSR STAGE 11 AMENDMENT WEBINAR #5 NOVEMBER 28, 2017
 PROTOCOL 27, SOIL LEACHING ASSESSMENT FOR USE IN DERIVING SITE SPECIFIC STANDARDS CSR STAGE 11 AMENDMENT WEBINAR #5 NOVEMBER 28, 2017 Lavinia Zanini, P.Geo. Contaminated Sites Officer This PowerPoint presentation
PROTOCOL 27, SOIL LEACHING ASSESSMENT FOR USE IN DERIVING SITE SPECIFIC STANDARDS CSR STAGE 11 AMENDMENT WEBINAR #5 NOVEMBER 28, 2017 Lavinia Zanini, P.Geo. Contaminated Sites Officer This PowerPoint presentation
GROUNDWATER CONTAMINATION ASSESSMENT IN THE VICINITY OF ABQAIQ LANDFILL, EASTERN SAUDI ARABIA-GIS APPROACH
 GROUNDWATER CONTAMINATION ASSESSMENT IN THE VICINITY OF ABQAIQ LANDFILL, EASTERN SAUDI ARABIA-GIS APPROACH By Salman F. Al-Khaldi Environmental Sciences Introduction Outline Landfill Classes and Methods
GROUNDWATER CONTAMINATION ASSESSMENT IN THE VICINITY OF ABQAIQ LANDFILL, EASTERN SAUDI ARABIA-GIS APPROACH By Salman F. Al-Khaldi Environmental Sciences Introduction Outline Landfill Classes and Methods
Cost-Effective, Accurate Environmental Investigations Using Passive Soil Gas Sampling
 Cost-Effective, Accurate Environmental Investigations Using Passive Soil Gas Sampling Jay W. Hodny, Ph.D. and George E. Shaw W. L. Gore & Associates, Inc. Intersol 2009 8 th International Conference-Exhibition
Cost-Effective, Accurate Environmental Investigations Using Passive Soil Gas Sampling Jay W. Hodny, Ph.D. and George E. Shaw W. L. Gore & Associates, Inc. Intersol 2009 8 th International Conference-Exhibition
April USING POLYETHYLENE PASSIVE SAMPLERS FOR THE DETERMINATION OF DISSOLVED PAHs IN GROUND WATER. Terry Obal, Ph.D., C.Chem.
 April 2012 USING POLYETHYLENE PASSIVE SAMPLERS FOR THE DETERMINATION OF DISSOLVED PAHs IN GROUND WATER Terry Obal, Ph.D., C.Chem. Acknowledgments Dillon Consulting Limited Ontario MOE Maxxam Analytics
April 2012 USING POLYETHYLENE PASSIVE SAMPLERS FOR THE DETERMINATION OF DISSOLVED PAHs IN GROUND WATER Terry Obal, Ph.D., C.Chem. Acknowledgments Dillon Consulting Limited Ontario MOE Maxxam Analytics
SoBRA Generic Assessment Criteria for Assessing Vapour Inhalation Risks from Groundwater Sources
 SoBRA Generic Assessment Criteria for Assessing Vapour Inhalation Risks from Groundwater Sources Eleanor Walker, Atkins Introduction Introduction to SoBRA Groundwater vapour sub-group work - objectives
SoBRA Generic Assessment Criteria for Assessing Vapour Inhalation Risks from Groundwater Sources Eleanor Walker, Atkins Introduction Introduction to SoBRA Groundwater vapour sub-group work - objectives
Determination of Local Background Concentrations in Groundwater at an Industrial Site. Dissolved Arsenic, Iron and Manganese
 Determination of Local Background Concentrations in Groundwater at an Industrial Site Dissolved Arsenic, Iron and Manganese October 15, 2016 About the Presenter Tyler Joyce, C.Tech Project Manager Stantec
Determination of Local Background Concentrations in Groundwater at an Industrial Site Dissolved Arsenic, Iron and Manganese October 15, 2016 About the Presenter Tyler Joyce, C.Tech Project Manager Stantec
8.1 Introduction 8.2 Summary 8.3 Conclusion. Contents
 Summary and Conclusion Contents Chapter 8 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION 8.1 Introduction 8.2 Summary 8.3 Conclusion 8.1 Introduction In landfills without liners between the waste and the underlying geology or
Summary and Conclusion Contents Chapter 8 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION 8.1 Introduction 8.2 Summary 8.3 Conclusion 8.1 Introduction In landfills without liners between the waste and the underlying geology or
VOLUME SECTION SUBSECTION PAGE 1 of 7
 1 of 7 This procedure replaces: Contaminated Sites Protocol 7: Regulation of Petroleum Hydrocarbons in Water under the Contaminated Sites and Special Waste Regulations, July 19, 1999. Staff, Organizations
1 of 7 This procedure replaces: Contaminated Sites Protocol 7: Regulation of Petroleum Hydrocarbons in Water under the Contaminated Sites and Special Waste Regulations, July 19, 1999. Staff, Organizations
Vadose Zone Profiling to Better Understand Processes
 Vapor Intrusion 2010 Sept. 29-30 Chicago Vadose Zone Profiling to Better Understand Processes Related to Vapor Intrusion Daniel B. Carr, P.E., P.G., Laurent C. Levy, Ph.D., P.E., Allan H. Horneman, D.E.S.
Vapor Intrusion 2010 Sept. 29-30 Chicago Vadose Zone Profiling to Better Understand Processes Related to Vapor Intrusion Daniel B. Carr, P.E., P.G., Laurent C. Levy, Ph.D., P.E., Allan H. Horneman, D.E.S.
GetIPM.com Children fall ill after pesticides sprayed -- 2,4-D applied to lawns near family's home Over-the-Counter Herbicides Pose a Significant Thre
 Environmental Fate of Herbicides: The Disappearing Act Adam Hixson BASF, The Chemical Company GetIPM.com Children fall ill after pesticides sprayed -- 2,4-D applied to lawns near family's home Over-the-Counter
Environmental Fate of Herbicides: The Disappearing Act Adam Hixson BASF, The Chemical Company GetIPM.com Children fall ill after pesticides sprayed -- 2,4-D applied to lawns near family's home Over-the-Counter
REPORT ON APPROACHES AND METHODS FOR EVALUATION VERTICAL TRANSPORT IN GROUNDWATER HYDROGEOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT TOOLS PROJECT.
 Ltd. 500 4260 Still Creek Drive Burnaby, British Columbia, Canada V5C 6C6 Telephone (604) 296-4200 Fax (604) 298-5253 REPORT ON APPROACHES AND METHODS FOR EVALUATION VERTICAL TRANSPORT IN GROUNDWATER HYDROGEOLOGICAL
Ltd. 500 4260 Still Creek Drive Burnaby, British Columbia, Canada V5C 6C6 Telephone (604) 296-4200 Fax (604) 298-5253 REPORT ON APPROACHES AND METHODS FOR EVALUATION VERTICAL TRANSPORT IN GROUNDWATER HYDROGEOLOGICAL
University of Arizona Department of Hydrology and Water Resources Dr. Marek Zreda
 University of Arizona Department of Hydrology and Water Resources Dr. Marek Zreda HWR431/531 - Hydrogeology Final exam - 12 May 1997 Open books and notes The test contains 8 problems on 7 pages. Read the
University of Arizona Department of Hydrology and Water Resources Dr. Marek Zreda HWR431/531 - Hydrogeology Final exam - 12 May 1997 Open books and notes The test contains 8 problems on 7 pages. Read the
Migration Behavior of Life Source Contaminants in a Landfill Site
 Migration Behavior of Life Source Contaminants in a Landfill Site Liwen CAO *, Dongmei WU, Yong WANG, Ke HAN, Xue QU and Pan HUO School of Resource and Earth Science, China University of Mining and Technology,
Migration Behavior of Life Source Contaminants in a Landfill Site Liwen CAO *, Dongmei WU, Yong WANG, Ke HAN, Xue QU and Pan HUO School of Resource and Earth Science, China University of Mining and Technology,
ENVIRONMENTAL GEOLOGY - GEOL 406/506
 ENVIRONMENTAL GEOLOGY - GEOL 406/506 Glossary of useful Terms: 1. Abiotic: not living. 2. A b s o r p t i o n: the penetration of atoms, ions, or molecules into the bulk mass of substrate. 3. Acclimation:
ENVIRONMENTAL GEOLOGY - GEOL 406/506 Glossary of useful Terms: 1. Abiotic: not living. 2. A b s o r p t i o n: the penetration of atoms, ions, or molecules into the bulk mass of substrate. 3. Acclimation:
A Comparison of Observed Pesticide Concentrations in Groundwater with Predictions by US Regulatory Models Used in Human Health Risk Assessments
 A Comparison of Observed Pesticide Concentrations in Groundwater with Predictions by US Regulatory Models Used in Human Health Risk Assessments Presented by: Michael Winchell 1, Tammara Estes 1, Scott
A Comparison of Observed Pesticide Concentrations in Groundwater with Predictions by US Regulatory Models Used in Human Health Risk Assessments Presented by: Michael Winchell 1, Tammara Estes 1, Scott
SCREENING LEVEL RISK ASSESSMENT (SLRA) UPDATE CSR STAGE 11 AMENDMENT WEBINAR #6 DECEMBER 5, 2017
 SCREENING LEVEL RISK ASSESSMENT (SLRA) UPDATE CSR STAGE 11 AMENDMENT WEBINAR #6 DECEMBER 5, 2017 GEORGE SZEFER Senior Contaminated Sites Officer This PowerPoint presentation and a recording of the audio
SCREENING LEVEL RISK ASSESSMENT (SLRA) UPDATE CSR STAGE 11 AMENDMENT WEBINAR #6 DECEMBER 5, 2017 GEORGE SZEFER Senior Contaminated Sites Officer This PowerPoint presentation and a recording of the audio
CHAPTER # 4. Fate of Pollutants in the Environment
 CHAPTER # 4 Fate of Pollutants in the Environment Once a pesticide is introduced into the environment, whether through an application, a disposal or a spill, it is influenced by many processes. These processes
CHAPTER # 4 Fate of Pollutants in the Environment Once a pesticide is introduced into the environment, whether through an application, a disposal or a spill, it is influenced by many processes. These processes
GROUNDWATER MODELING OF A PERMEABLE REACTIVE BARRIER TO ENHANCE SYSTEM PERFORMANCE
 GROUNDWATER MODELING OF A PERMEABLE REACTIVE BARRIER TO ENHANCE SYSTEM PERFORMANCE K.C. Scott, P.G., and D. J. Folkes, P.E. EnviroGroup Limited, 7208 South Tucson Way, Suite 125, Englewood, CO 80112; Phone:
GROUNDWATER MODELING OF A PERMEABLE REACTIVE BARRIER TO ENHANCE SYSTEM PERFORMANCE K.C. Scott, P.G., and D. J. Folkes, P.E. EnviroGroup Limited, 7208 South Tucson Way, Suite 125, Englewood, CO 80112; Phone:
In Situ, Low Temperature Thermal Remediation of LNAPL with Pesticides and Other Recalcitrant Compounds
 In Situ, Low Temperature Thermal Remediation of LNAPL with Pesticides and Other Recalcitrant Compounds RemTech 2017, Banff Springs Hotel and Conference Centre October 11, 2017 Presented by - Jay Dablow,
In Situ, Low Temperature Thermal Remediation of LNAPL with Pesticides and Other Recalcitrant Compounds RemTech 2017, Banff Springs Hotel and Conference Centre October 11, 2017 Presented by - Jay Dablow,
Evaluating Impoundment Closure Scenarios using Fate and Transport Modeling
 2017 World of Coal Ash (WOCA) Conference in Lexington, KY - May 9-11, 2017 http://www.flyash.info/ Evaluating Impoundment Closure Scenarios using Fate and Transport Modeling Jacob J. Walczak 1, Meng Wang
2017 World of Coal Ash (WOCA) Conference in Lexington, KY - May 9-11, 2017 http://www.flyash.info/ Evaluating Impoundment Closure Scenarios using Fate and Transport Modeling Jacob J. Walczak 1, Meng Wang
Processes that can be Modeled with RT3D
 Natural attenuation of contaminants in aquifer Advanced Environmental Technology Dragan Kaludjerovic PhD Hydrogeologist Email: advancedgwt@gmail.com Web site: www.advancegwt.com Mobile: +381-(0) (0)-62-965-1748
Natural attenuation of contaminants in aquifer Advanced Environmental Technology Dragan Kaludjerovic PhD Hydrogeologist Email: advancedgwt@gmail.com Web site: www.advancegwt.com Mobile: +381-(0) (0)-62-965-1748
Picture from USGS Scientific Investigations Report
 Picture from USGS Scientific Investigations Report 2008 5220 A Brief Summary of ArcNLET and Associated Tools for Estimation of Nitrate Load from Septic Systems to Surface Water Bodies Ming Ye (mye@fsu.edu),
Picture from USGS Scientific Investigations Report 2008 5220 A Brief Summary of ArcNLET and Associated Tools for Estimation of Nitrate Load from Septic Systems to Surface Water Bodies Ming Ye (mye@fsu.edu),
Fate and Transport of Sodium Chloride, Calcium Sulfate (Gypsum), Sodium Sulfate, and Boron in Soil: Implications for Guideline Development Work
 Fate and Transport of Sodium Chloride, Calcium Sulfate (Gypsum), Sodium Sulfate, and Boron in Soil: Implications for Guideline Development Work Presented at: PTAC Soil and Groundwater Forum Presentation
Fate and Transport of Sodium Chloride, Calcium Sulfate (Gypsum), Sodium Sulfate, and Boron in Soil: Implications for Guideline Development Work Presented at: PTAC Soil and Groundwater Forum Presentation
TREECS Overview, Validation, Example Applications M2S2 MC Seminar April 24, 2014
 TREECS Overview, Validation, Example Applications M2S2 MC Seminar April 24, 2014 Billy Johnson, ERDC Mark Dortch, LATA subcontractor Problem and Need! Military firing/training ranges contain munitions
TREECS Overview, Validation, Example Applications M2S2 MC Seminar April 24, 2014 Billy Johnson, ERDC Mark Dortch, LATA subcontractor Problem and Need! Military firing/training ranges contain munitions
Using Mass Balance to Assist in Determining Remedial Options. Stephen Thomson URS New Zealand Limited
 Using Mass Balance to Assist in Determining Remedial Options Stephen Thomson URS New Zealand Limited Presentation Outline Introduction. Example Site. Mass Balance. Calculations. Outcomes. Introduction
Using Mass Balance to Assist in Determining Remedial Options Stephen Thomson URS New Zealand Limited Presentation Outline Introduction. Example Site. Mass Balance. Calculations. Outcomes. Introduction
Surface Water and Seawater Interactions in the Coastal Environment of Biscayne Bay, Southeast Florida
 Surface Water and Seawater Interactions in the Coastal Environment of Biscayne Bay, Southeast Florida William C. Hutchings, MS, PG Nicholas Albergo, PE, DEE Paper No. 191-8 2005 Salt Lake City Annual Meeting
Surface Water and Seawater Interactions in the Coastal Environment of Biscayne Bay, Southeast Florida William C. Hutchings, MS, PG Nicholas Albergo, PE, DEE Paper No. 191-8 2005 Salt Lake City Annual Meeting
P in Groundwater and Groundwater dependent ecosystems
 P in Groundwater and Groundwater dependent ecosystems Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland Ministry of Energy, Utilities and Climate Lærke Thorling, Catharina Madsen and Bertel Nilsson Take home
P in Groundwater and Groundwater dependent ecosystems Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland Ministry of Energy, Utilities and Climate Lærke Thorling, Catharina Madsen and Bertel Nilsson Take home
Comparison of Various Extraction Methods for Petroleum Hydrocarbons (PHC) in Soils and in Drilling Waste
 Comparison of Various Extraction Methods for Petroleum Hydrocarbons (PHC) in Soils and in Drilling Waste John Ashworth 1 & Ron Minks 2 1. Director, Soil Science; ETL 2. Director of Calgary Operations;
Comparison of Various Extraction Methods for Petroleum Hydrocarbons (PHC) in Soils and in Drilling Waste John Ashworth 1 & Ron Minks 2 1. Director, Soil Science; ETL 2. Director of Calgary Operations;
Hydraulic containment landfills
 Assessing the risks from hydraulically contained landfill sites Dr Hugh Potter Environment Agency Hydraulic containment landfills h ~200 non-hazardous waste landfills are sub-water table h 40-50 of these
Assessing the risks from hydraulically contained landfill sites Dr Hugh Potter Environment Agency Hydraulic containment landfills h ~200 non-hazardous waste landfills are sub-water table h 40-50 of these
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY. 2. The effect of remediation on the distribution and mobility of both the LNAPL and water within the zone of interest.
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY For many decades, the oil production industry has recognized that significant limitations exist to complete extraction of oil from geologic formations. Attempts to recover fuels and crude
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY For many decades, the oil production industry has recognized that significant limitations exist to complete extraction of oil from geologic formations. Attempts to recover fuels and crude
Groundwater Mounding Causes, Issues and Prevention
 Groundwater Mounding Causes, Issues and Prevention WCOWMA - Onsite Wastewater Association of BC 2017 Annual Convention and Tradeshow March 11, 2017 Presented by Daniel Watterson, P.Geo., LHG Watterson
Groundwater Mounding Causes, Issues and Prevention WCOWMA - Onsite Wastewater Association of BC 2017 Annual Convention and Tradeshow March 11, 2017 Presented by Daniel Watterson, P.Geo., LHG Watterson
IN-SITU BIOREMEDIATION EVALUATION USING THE WATERLOO EMITTER
 IN-SITU BIOREMEDIATION EVALUATION USING THE WATERLOO EMITTER Douglas A. Sweeney, M.Sc., P.Eng. and Ian Mitchell, M.Sc., P.Geo. October 2004 PRESENTATION OUTLINE Introduction Case Study Waterloo Emitter
IN-SITU BIOREMEDIATION EVALUATION USING THE WATERLOO EMITTER Douglas A. Sweeney, M.Sc., P.Eng. and Ian Mitchell, M.Sc., P.Geo. October 2004 PRESENTATION OUTLINE Introduction Case Study Waterloo Emitter
2005 Review of Canada-Wide Standards for Petroleum Hydrocarbons in Soil: Report of the Model Parameter Advisory (MPA) Sub Group
 2005 Review of Canada-Wide Standards for Petroleum Hydrocarbons in Soil: Report of the Model Parameter Advisory (MPA) Sub Group March 2006 1 Acknowledgement We would like to thank all the members of the
2005 Review of Canada-Wide Standards for Petroleum Hydrocarbons in Soil: Report of the Model Parameter Advisory (MPA) Sub Group March 2006 1 Acknowledgement We would like to thank all the members of the
THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY AND MINERAL ENGINEERING GEOEE 408 CONTAMINANT HYDROLOGY
 THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY AND MINERAL ENGINEERING GEOEE 408 CONTAMINANT HYDROLOGY Mid-term Examination Tuesday March 4 th, 2008 75 minutes Answer all three questions. For water
THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY AND MINERAL ENGINEERING GEOEE 408 CONTAMINANT HYDROLOGY Mid-term Examination Tuesday March 4 th, 2008 75 minutes Answer all three questions. For water
Groundwater Modeling in Mining: A Case Study. FIDS Water Resources Symposium
 Groundwater Modeling in Mining: A Case Study Mundzir H. Basri London May 11-12, 2014 FIDS Water Resources Symposium Outline INTRODUCTION GUIDELINES AND OBJECTIVE MODEL CONSTRUCTION AND CALIBRATION SIMULATED
Groundwater Modeling in Mining: A Case Study Mundzir H. Basri London May 11-12, 2014 FIDS Water Resources Symposium Outline INTRODUCTION GUIDELINES AND OBJECTIVE MODEL CONSTRUCTION AND CALIBRATION SIMULATED
Petroleum Hydrocarbon Sediment Quality Guidelines
 Petroleum Hydrocarbon Sediment Quality Guidelines Rita Mroz, Environment Canada Ulysses Klee, Stantec Rob Willis, Dillon Consulting Real Property Institute of Canada Federal Contaminated Sites National
Petroleum Hydrocarbon Sediment Quality Guidelines Rita Mroz, Environment Canada Ulysses Klee, Stantec Rob Willis, Dillon Consulting Real Property Institute of Canada Federal Contaminated Sites National
Variations on a Theme, Groundwater Sensitivity
 Variations on a Theme, Groundwater Sensitivity Amy Ritter, Waterborne Environmental, Inc. Mark Cheplick, Waterborne Environmental, Inc. Isha Khanijo, Waterborne Environmental, Inc. American Chemical Society,
Variations on a Theme, Groundwater Sensitivity Amy Ritter, Waterborne Environmental, Inc. Mark Cheplick, Waterborne Environmental, Inc. Isha Khanijo, Waterborne Environmental, Inc. American Chemical Society,
1. Apply knowledge of the controlling variables for groundwater flow. 2. Demonstrate groundwater flow direction based on hydraulic head observations.
 .9-12 HYDRAULIC HEAD SUBJECTS: TIME: Science (Physical Science, Physics), Math 1 class period MATERIALS: Copies of student sheets and background information OBJECTIVES The student will do the following:
.9-12 HYDRAULIC HEAD SUBJECTS: TIME: Science (Physical Science, Physics), Math 1 class period MATERIALS: Copies of student sheets and background information OBJECTIVES The student will do the following:
APPENDIX I A SITE-SPECIFIC RECAP EVALUATION FOR TYPICAL UST SITES
 APPENDIX I A SITE-SPECIFIC RECAP EVALUATION FOR TYPICAL UST SITES LDEQ RECAP 2003 TABLE OF CONTENTS List of Figures List of Tables List of Worksheets Page... i... i... ii I1.0 APPENDIX I UNDERGROUND STORAGE
APPENDIX I A SITE-SPECIFIC RECAP EVALUATION FOR TYPICAL UST SITES LDEQ RECAP 2003 TABLE OF CONTENTS List of Figures List of Tables List of Worksheets Page... i... i... ii I1.0 APPENDIX I UNDERGROUND STORAGE
Site Specific Remediation Objectives for Soil Vapour in Alberta (Draft) Norman Sawatsky
 Site Specific Remediation Objectives for Soil Vapour in Alberta (Draft) Norman Sawatsky Outline Contaminated Site Management Policy General Principles of Risk Assessment Tiered Risk Assessment Framework
Site Specific Remediation Objectives for Soil Vapour in Alberta (Draft) Norman Sawatsky Outline Contaminated Site Management Policy General Principles of Risk Assessment Tiered Risk Assessment Framework
Lessons Learned from the Installation and Monitoring of a Permeable Reactive Barrier at the Lake City Army Ammunition Plant, Independence, MO
 Lessons Learned from the Installation and Monitoring of a Permeable Reactive Barrier at the Lake City Army Ammunition Plant, Independence, MO Presented by Kevin Keller, PG, CGWP - Shaw E&I, Inc. Thomas
Lessons Learned from the Installation and Monitoring of a Permeable Reactive Barrier at the Lake City Army Ammunition Plant, Independence, MO Presented by Kevin Keller, PG, CGWP - Shaw E&I, Inc. Thomas
East Maui Watershed Partnership Adapted from Utah State University and University of Wisconsin Ground Water Project Ages 7 th -Adult
 INTRODUCTION What is groundwater? Water contained in saturated soil and rock materials below the surface of the earth. It is not NEW water, but is recycled water through the hydraulic cycle. The source
INTRODUCTION What is groundwater? Water contained in saturated soil and rock materials below the surface of the earth. It is not NEW water, but is recycled water through the hydraulic cycle. The source
New Tier 1 Boron Guideline for Alberta
 Equilibrium Environmental Inc. New Tier 1 Boron Guideline for Alberta Greg Huber, M.Sc., P.Eng., PMP (Equilibrium) Anthony Knafla, M.Sc., DABT (Equilibrium) Ian McIvor, M.Sc., P.Biol (Equilibrium) Holly
Equilibrium Environmental Inc. New Tier 1 Boron Guideline for Alberta Greg Huber, M.Sc., P.Eng., PMP (Equilibrium) Anthony Knafla, M.Sc., DABT (Equilibrium) Ian McIvor, M.Sc., P.Biol (Equilibrium) Holly
Evolution of Dissolved Arsenic in Groundwater Downgradient of a Coal Ash Impoundment
 2007 World of Coal Ash (WOCA), May 7-10, 2007, Northern Kentucky, USA http://www.flyash.info Evolution of Dissolved Arsenic in Groundwater Downgradient of a Coal Ash Impoundment Bruce R. Hensel 1 and Eric
2007 World of Coal Ash (WOCA), May 7-10, 2007, Northern Kentucky, USA http://www.flyash.info Evolution of Dissolved Arsenic in Groundwater Downgradient of a Coal Ash Impoundment Bruce R. Hensel 1 and Eric
4.0 ENVIRONMENTAL TRANSPORT AND FATE PRINCIPAL FINDINGS
 4.0 ENVIRONMENTAL TRANSPORT AND FATE PRINCIPAL FINDINGS Both EDB and EDC: o Have low to moderate sorptive affinity for aquifer solids o Are relatively mobile in groundwater o Can volatilize from solution
4.0 ENVIRONMENTAL TRANSPORT AND FATE PRINCIPAL FINDINGS Both EDB and EDC: o Have low to moderate sorptive affinity for aquifer solids o Are relatively mobile in groundwater o Can volatilize from solution
MTBE Fact Sheet #2 Remediation Of MTBE Contaminated Soil And Groundwater Background
 United States Office Of Solid Waste And EPA 510-F-98-002 Environmental Protection Emergency Response Agency (5401G) www.epa.gov/oust/mtbe/ Office Of Underground Storage Tanks MTBE Fact Sheet #2 Remediation
United States Office Of Solid Waste And EPA 510-F-98-002 Environmental Protection Emergency Response Agency (5401G) www.epa.gov/oust/mtbe/ Office Of Underground Storage Tanks MTBE Fact Sheet #2 Remediation
Evaluating the Petroleum Vapor Intrusion Pathway
 Evaluating the Petroleum Vapor Intrusion Pathway Studies of Natural Attenuation of Subsurface Petroleum Hydrocarbons & Recommended Screening Criteria NEIWPCC Webinar on Petroleum Vapor Intrusion June 26,
Evaluating the Petroleum Vapor Intrusion Pathway Studies of Natural Attenuation of Subsurface Petroleum Hydrocarbons & Recommended Screening Criteria NEIWPCC Webinar on Petroleum Vapor Intrusion June 26,
Criteria for mapping brackish groundwater
 Criteria for mapping brackish groundwater Texas Desal 2018 John Meyer, P.G. Innovative Water Technologies Texas Water Development Board Unless specifically noted, this presentation does not necessarily
Criteria for mapping brackish groundwater Texas Desal 2018 John Meyer, P.G. Innovative Water Technologies Texas Water Development Board Unless specifically noted, this presentation does not necessarily
COMSOL Modeling of Groundwater Flow and Contaminant Transport in Two-Dimensional Geometries With Heterogeneities
 COMSOL Modeling of Groundwater Flow and Contaminant Transport in Two-Dimensional Geometries With Heterogeneities M. K. B. Whitmore 1, D. W. Trott 1, B. E. Peercy 1, M. E. Baker 2, and M. K. Gobbert 1 1
COMSOL Modeling of Groundwater Flow and Contaminant Transport in Two-Dimensional Geometries With Heterogeneities M. K. B. Whitmore 1, D. W. Trott 1, B. E. Peercy 1, M. E. Baker 2, and M. K. Gobbert 1 1
The FACT-FLUTe technology A modeling tool for interpreting field data
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Nov 01, 2018 The FACT-FLUTe technology A modeling tool for interpreting field data Mosthaf, Klaus; Broholm, Mette Martina; Binning, Philip John Publication date: 2014 Document
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Nov 01, 2018 The FACT-FLUTe technology A modeling tool for interpreting field data Mosthaf, Klaus; Broholm, Mette Martina; Binning, Philip John Publication date: 2014 Document
Session 3: Emerging Contaminants. Emerging Contaminants: National Guidance for Australia
 Session 3: Emerging Contaminants Emerging Contaminants: National Guidance for Australia Dr Bruce Kennedy Executive Policy Adviser CRC CARE 11 September 2015 Outline CRC CARE CRC CARE and guidance development
Session 3: Emerging Contaminants Emerging Contaminants: National Guidance for Australia Dr Bruce Kennedy Executive Policy Adviser CRC CARE 11 September 2015 Outline CRC CARE CRC CARE and guidance development
INTRODUCTION: ENVIRONMENTAL DISTRIBUTION
 5/26/26 SUBSURFACE FATE AND TRANSPORT OF POLY- AND PERFLUOROALKYL SUBSTANCES (PFAS) Jennifer Guelfo, PhD State Agencies Liaison, Brown SRP May 23, 26 5/26/26 INTRODUCTION: ENVIRONMENTAL DISTRIBUTION Consumer/
5/26/26 SUBSURFACE FATE AND TRANSPORT OF POLY- AND PERFLUOROALKYL SUBSTANCES (PFAS) Jennifer Guelfo, PhD State Agencies Liaison, Brown SRP May 23, 26 5/26/26 INTRODUCTION: ENVIRONMENTAL DISTRIBUTION Consumer/
Annual P Loss Estimator (APLE)
 Annual P Loss Estimator (APLE) User-friendly Model for Annual, Field-Scale Phosphorus Loss Peter Vadas USDA-ARS Madison, WI Phosphorus input to water bodies continues to be an issue Agriculture continues
Annual P Loss Estimator (APLE) User-friendly Model for Annual, Field-Scale Phosphorus Loss Peter Vadas USDA-ARS Madison, WI Phosphorus input to water bodies continues to be an issue Agriculture continues
Florida Aquifer Geology
 Florida Aquifer Geology September 2016 Sampler Training Workshop Thomas Seal, ES III Watershed Monitoring Section (WMS) Water Quality Assessment Program DEAR Tallahassee Aquifer Basics Essential Definitions
Florida Aquifer Geology September 2016 Sampler Training Workshop Thomas Seal, ES III Watershed Monitoring Section (WMS) Water Quality Assessment Program DEAR Tallahassee Aquifer Basics Essential Definitions
Synopsis. Geoffrey R. Tick Dorina Murgulet Hydrogeology Group The University of Alabama UA Project Number Grant # 09-EI UAT-2
 Assessment of Groundwater Flow Paths and Discharge to the Coastal Region of Baldwin County, Alabama to Understand Contaminant Transport using a Cross- Sectional Groundwater Flow and Transport Synopsis
Assessment of Groundwater Flow Paths and Discharge to the Coastal Region of Baldwin County, Alabama to Understand Contaminant Transport using a Cross- Sectional Groundwater Flow and Transport Synopsis
Remediation of 1, 4-Dioxane
 Do it Right, Do it once Remediation of 1, 4-Dioxane Presented by Mike Marley February 12, 2016 Agenda Basic properties of 1,4-dioxane with respect to remediation A discussion of applicable reliable remedial
Do it Right, Do it once Remediation of 1, 4-Dioxane Presented by Mike Marley February 12, 2016 Agenda Basic properties of 1,4-dioxane with respect to remediation A discussion of applicable reliable remedial
Conceptual Site Models for Environmental Investigations and Remediation
 Remediation Technology Symposium (RemTech) 2012 Conceptual Site Models for Environmental Investigations and Remediation October 18, 2012 Tai T. Wong, P.Eng. Authors and Presenter Authors: James Carss,
Remediation Technology Symposium (RemTech) 2012 Conceptual Site Models for Environmental Investigations and Remediation October 18, 2012 Tai T. Wong, P.Eng. Authors and Presenter Authors: James Carss,
On-site Systems and Groundwater Washington State Department of Health February 6, 2014
 On-site Systems and Groundwater Washington State Department of Health February 6, 2014 1 Nancy Darling, LHG, CPSS Office of Shellfish and Water Protection Key Groundwater Considerations Type and strength
On-site Systems and Groundwater Washington State Department of Health February 6, 2014 1 Nancy Darling, LHG, CPSS Office of Shellfish and Water Protection Key Groundwater Considerations Type and strength
Florida Aquifer Geology
 Florida Aquifer Geology February 2017 Sampler Training Workshop Thomas Seal, ES III Watershed Monitoring Section (WMS) Water Quality Assessment Program DEAR Tallahassee Aquifer Basics Essential Definitions
Florida Aquifer Geology February 2017 Sampler Training Workshop Thomas Seal, ES III Watershed Monitoring Section (WMS) Water Quality Assessment Program DEAR Tallahassee Aquifer Basics Essential Definitions
Stylistic Modeling of Vadose Zone Transport Insight into Vapor Intrusion Processes
 March 15, 2011 Workshop, Addressing Regulatory Challenges In Vapor Intrusion, A State of the Science Update Stylistic Modeling of Vadose Zone Transport Insight into Vapor Intrusion Processes Daniel B.
March 15, 2011 Workshop, Addressing Regulatory Challenges In Vapor Intrusion, A State of the Science Update Stylistic Modeling of Vadose Zone Transport Insight into Vapor Intrusion Processes Daniel B.
API SOIL & GROUNDWATER RESEARCH BULLETIN
 American Petroleum Institute API SOIL & GROUNDWATER RESEARC BULLETIN A summary of research results from APIÕs Soil and Groundwater Technical Task Force. August 998 No. 7 DAFfy Graphs An Innovative Approach
American Petroleum Institute API SOIL & GROUNDWATER RESEARC BULLETIN A summary of research results from APIÕs Soil and Groundwater Technical Task Force. August 998 No. 7 DAFfy Graphs An Innovative Approach
Ground Water Assessment. Investigating Ground Water: Discussion Topics. Leaching. Soil Impacts to Ground Water
 Ground Water Assessment Investigation, Protection, Classification, and Response Requirements OAC 3745-300-10 and parts of 3745-300-07 Certified Professional 8-Hour Training Investigating Ground Water:
Ground Water Assessment Investigation, Protection, Classification, and Response Requirements OAC 3745-300-10 and parts of 3745-300-07 Certified Professional 8-Hour Training Investigating Ground Water:
Modelling Groundwater Flow and Transport in Peat with Focus on Northern Alberta. Ranjeet M. Nagare, PhD WorleyParsons Canada Services Ltd.
 Modelling Groundwater Flow and Transport in Peat with Focus on Northern Alberta Ranjeet M. Nagare, PhD WorleyParsons Canada Services Ltd. 1 Outline Background Problem Statement Case Study 2 Northern Alberta
Modelling Groundwater Flow and Transport in Peat with Focus on Northern Alberta Ranjeet M. Nagare, PhD WorleyParsons Canada Services Ltd. 1 Outline Background Problem Statement Case Study 2 Northern Alberta
Florida Aquifer Geology
 Florida Aquifer Geology September 2017 Sampler Training Workshop Thomas Seal, ES III Watershed Monitoring Section (WMS) Water Quality Assessment Program DEAR Tallahassee Aquifer Basics Essential Definitions
Florida Aquifer Geology September 2017 Sampler Training Workshop Thomas Seal, ES III Watershed Monitoring Section (WMS) Water Quality Assessment Program DEAR Tallahassee Aquifer Basics Essential Definitions
A case study for demonstrating the application of U.S. EPA s monitored natural attenuation screening protocol at a hazardous waste site
 Journal of Contaminant Hydrology 59 (2002) 133 162 www.elsevier.com/locate/jconhyd A case study for demonstrating the application of U.S. EPA s monitored natural attenuation screening protocol at a hazardous
Journal of Contaminant Hydrology 59 (2002) 133 162 www.elsevier.com/locate/jconhyd A case study for demonstrating the application of U.S. EPA s monitored natural attenuation screening protocol at a hazardous
Figure 3: Refined Interpolated Groundwater Level Contours Based on Information from the MOE Water Well Information System (WWIS)
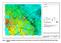 Figure 3: Refined Interpolated Groundwater Level Contours Based on Information from the MOE Water Well Information System (WWIS) Figure 4: Strahler Classes 1 through 4 Defined as Drains and Rivers Figure
Figure 3: Refined Interpolated Groundwater Level Contours Based on Information from the MOE Water Well Information System (WWIS) Figure 4: Strahler Classes 1 through 4 Defined as Drains and Rivers Figure
Henry Saltwater Intrusion Problem
 Introduction Henry Saltwater Intrusion Problem The Henry saltwater intrusion problem is considered the benchmark analysis for testing densitydependent groundwater flow models. The problem considers a vertical
Introduction Henry Saltwater Intrusion Problem The Henry saltwater intrusion problem is considered the benchmark analysis for testing densitydependent groundwater flow models. The problem considers a vertical
CEE 370 Environmental Engineering Principles
 Updated: 25 October 2015 Print version CEE 370 Environmental Engineering Principles Lecture #22 Water Resources & Hydrology II: Wells, Withdrawals and Contaminant Transport Reading: Mihelcic & Zimmerman,
Updated: 25 October 2015 Print version CEE 370 Environmental Engineering Principles Lecture #22 Water Resources & Hydrology II: Wells, Withdrawals and Contaminant Transport Reading: Mihelcic & Zimmerman,
Kerdiffstown Landfill Remediation Project
 Envir onmental Impact Assessment Report (EIAR) Vol ume 4 of 4: Appendices ( Part 4) Kildare C ounty Council Kerdiffstown Landfill Remediation Project Kildare County Council Environmental Impact Assessment
Envir onmental Impact Assessment Report (EIAR) Vol ume 4 of 4: Appendices ( Part 4) Kildare C ounty Council Kerdiffstown Landfill Remediation Project Kildare County Council Environmental Impact Assessment
22015 International SWAT Conference
 22015 International SWAT Conference A Heavy Metal Module Coupled in SWAT Model and Its Application in Liuyang River Upstream Basin in China Lingfeng Zhou* Yaobin Meng* Shouliang He* Chao Lu* Peixi Ji*
22015 International SWAT Conference A Heavy Metal Module Coupled in SWAT Model and Its Application in Liuyang River Upstream Basin in China Lingfeng Zhou* Yaobin Meng* Shouliang He* Chao Lu* Peixi Ji*
Viruses from septic systems. Ian Ralston and Michael Payne
 Viruses from septic systems Ian Ralston and Michael Payne Research summary Viruses, what and why? Literature review Risk management objectives Virus removal from sewage to water source Factors for improved
Viruses from septic systems Ian Ralston and Michael Payne Research summary Viruses, what and why? Literature review Risk management objectives Virus removal from sewage to water source Factors for improved
A MODEL OF SEAWATER INTRUSION IN SURFICIAL AND CONFINED AQUIFERS OF NORTHEAST FLORIDA
 The Second International Conference on Saltwater Intrusion and Coastal Aquifers - Monitoring, Modeling, and Management. Mérida, Yucatán, México, March 30 - April 2, 2003 A MODEL OF SEAWATER INTRUSION IN
The Second International Conference on Saltwater Intrusion and Coastal Aquifers - Monitoring, Modeling, and Management. Mérida, Yucatán, México, March 30 - April 2, 2003 A MODEL OF SEAWATER INTRUSION IN
Guidance for Industrial Waste Management Evaluation Model (IWEM) Waste/Solid Waste #5.03, October 2005
 Solid Waste Program Guidance for Industrial Waste Management Evaluation Model (IWEM), October 2005 Contents: Introduction... 1 Background... 1 IWEM... 2 Tier 1 Evaluation... 2 Tier 2 Evaluation... 3 Infiltration
Solid Waste Program Guidance for Industrial Waste Management Evaluation Model (IWEM), October 2005 Contents: Introduction... 1 Background... 1 IWEM... 2 Tier 1 Evaluation... 2 Tier 2 Evaluation... 3 Infiltration
