H CALL SELECTION SC3 DRAFT WP
|
|
|
- Noel Snow
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TOTAL CALLS CODE TOPIC/NAME H CALL SELECTION SC3 DRAFT WP TYPE OF ACTION 26 FROM TO LC-SC3-EE-6 LC-SC3-EE-13 LC-SC3-EE-16 LC-SC3-RES-5 LC-SC3-RES-8 LC-SC3-SCC-1 LC-SC3-EE-1 LC-SC3-EE-4 Business case for industrial waste heat/cold recovery Enabling next generation of smart energy services valorising energy efficiency as energy resource Supporting public authorities to implement the Energy Union Increased performance of technologies for local heating and cooling solutions Combining Renewable Technologies for a Renewable District Heating System Smart Cities and Communities Decarbonisation of the EU building stock: innovative approaches and affordable solutions changing the market for buildings renovation. Upgrading smartness of existing buildings through innovations for legacy equipment. IA TRL BUDGET OF CALL SUGGESTED PROJECT BUDGET STAGE OPENING DATE Nov 2017 CSA CSA IA To be defined Nov 2017 CSA Nov 2017 CSA To be define DEADLINE IA Single 2 Nov Feb 2018 IA Single 05 Sep Dec 2018 IA Single 05 Dec Apr 2018 IA Nov 2017 IA To be defined
2 LC-SC3-EE-5 LC-SC3-EE-11 LC-SC3-EE-12 LC-SC3-EE-14 LC-SC3-RES-1 LC-SC3-RES-4 LC-SC3-RES-7 LC-SC3-RES-11 LC-SC3-RES-13 LC-SC3-RES-14 Next-generation of Energy Performance Assessment and Certification. Aggregation - Project Development Assistance Innovation procurement for energy efficiency Socio-economic research conceptualising and modelling energy efficiency and energy demand Developing the next generation of renewable energy technologies Renewable energy system integrated at the building scale Solar Energy in Industrial Processes Developing solutions to reduce the cost and increase performance of renewable technologies Demonstrate solutions that significantly reduce the cost of renewable power generation Optimising manufacturing and system operation CSA IA CSA CSA PPI RIA RIA RIA Nov 2017 To be defined Nov 2017 To be defined To be defined Nov 2017 Double 3 Jul 2018 RIA Double 2 Nov Oct 2019 (First Stage) 30 Apr 2019 (Second Satge) 31/01/2018 (First Stage) 23/08/2018 (Second Stage) RIA Single 05 Sep Dec 2018 RIA Double 2 Nov /01/2018 (First Stage) 23/08/2018 (Second Stage) IA single 2 Nov /02/2018 RIA Double 03 Jul Oct (First Stage) 30 Apr 2019 (second Stage)
3 LC-SC3-RES-16 LC-SC3-RES-17 Development of solutions based on renewable sources that provide flexibility to the energy system Demonstration of solutions based on renewable sources that provide flexibility to the energy system IA Single IA Single 05 Sept Sept Dec Dec 2018 LC-SC3-RES-28 Market Uptake support CSA Single 02 Nov Feb 2018 LC-SC3-EC-1- The role of consumers in CSA Nov 2017 changing the market with informed decision or To be CSA collective actions defined LC-SC3-EC-2 Mitigating household CSA Nov 2017 energy poverty CSA LC-SC3-EC-3 Consumer engagement and demand response IA Single 05 Dec Apr 2018 LC-SC3-ES-3 Integrated local energy systems (Energy islands) IA single 05 Dec Apr 2018 LC-SC3-NZE-1 Advanced capture technologies RIA Single 02 Mat Sep 2018
4 LC-SC3-EE : BUSINESS CASE FOR INDUSTRIAL WASTE HEAT/COLD RECOVERY Scope: 2018: Cost-benefit models for industrial waste heat/cold recovery: Proposals should develop integrated cost-benefit simulation tools that, based on the characterization of processes, heat/cold streams and other relevant variables, can determine the best utilisation options of recovered waste heat/cold and/ or surplus renewable energy from industrial and eventual other sources (when available). Proposals should also consider the possibility to contribute to efficient use/system integration of renewable energy sources through e.g. heat/cold storage and flexible production. The proposals are expected to put forward simulation tools that would allow industrial sites/parks to determine the most financial attractive option for using their recovered waste heat/cold and/or surplus renewable energy. This should be based on, inter-alia, waste heat/cold recovery (and storage if necessary) costs (including equipment and process adaptation), retail and/ or whole sale energy prices, (new contracts) administrative and legal costs, (external connecting) infrastructure costs, internal and external demand, waste heat/cold as source of flexibility in electricity system. Other relevant variables should also be included, inter-alia, characterisation of barriers and opportunities on the DHC side (e.g. competition with other heat/cold sources, thermal storage, regulatory conditions). The simulation tools are expected to be flexible enough to allow a large number of different types of industrial sites/ parks to use it, i.e. should allow many energy intensive process characterizations irrespective of the industrial sector and geographic location, and should also take into account supply demand dynamics. The simulation tools should be validated through demonstration in real operating conditions in industrial facilities. 2019: Symbiosis in industrial parks and clusters- non-technological barriers Proposals should improve the energy efficiency of industrial parks districts and clusters by unlocking the market potential and supporting the demand and offer of high-quality energy services by addressing at least one of the following: The development and testing of instruments facilitating, at customer/ business level, the actual implementation of energy cooperation such as setting up appropriate process and business organisation, operation and plant design, cooperation mechanisms, related
5 contractual and financial arrangements, better planning, good practices. Proposals need to include capacity building activities such as skills development and engagement of senior and executive management (e.g., CEO, CFO, energy managers) of companies from industrial parks and other related stakeholders. The development and testing of replicable business models and service concepts, at service provider level (i.e. ESCOs or other relevant 3rd party organisations), for joint energy services such as identification of horizontal energy services attractive for businesses, identification of the most relevant innovative technical solutions, setting up contractual and financial arrangements, best practices, cost-reduction models. Proposals need to include capacity building activities such as sharing skills, know-how and specific expertise of ESCOs or other 3rd party organisations that would boost the market uptake for such joint energy services contracting in industrial parks. LC-SC3-EE : ENABLING NEXT-GENERATION OF SMART ENERGY SERVICES VALORISING ENERGY EFFICIENCY AS ENERGY RESOURCE Scope: 2018: Actions should allow different market actors to get together and focus on developing integrated concepts and models which enhance and refine successful energy performance contracting models and/or; include pay-for-performance schemes and/or; engage new sectors and actors and/or; integrate energy efficiency services with distributed generation and demand response and including storage/hybrid energy systems; these should be endorsed by relevant stakeholders and validated (for example tested around existing projects or projects under development); factor in potential legal and contractual aspects (e.g. in relation to existing contracts or warranty, safety and data security issues linked to existing and newly deployed equipment). Proposed actions should cover at least two (but not necessarily all) of the relevant areas and aspects identified below: Energy service models (like EPC) and services that target new sectors and new actors; Business models which work equally for energy efficiency and other services, building on contractual arrangements across different actors (ESCOs, aggregators, DSOs, energy cooperatives, obliged parties under the Energy Efficiency Obligation Schemes
6 implementing art 7 EED and eventually the consumers) which traditionally cover different use cases business interests and different revenue; "Pay for performance"-schemes which focus on permanently reducing power consumption in particular at peak times, thus attracting new sources of financing; The use of 'big data' generated by smart meters, equipment, sensors and tools for standardised processes enabling a more accurate and dynamic measurement and verification of energy savings and flexible consumption, also in order to ex-ante identify and develop business opportunities; Additional non-energy features that support the up-take of innovative energy efficiency services and technologies; Improving the accessibility and quality of demand side service providers while enhancing their access to the market. 2019: Projects should focus on demonstrating and testing innovative services in a real environment, across several market segments and across different actors in the value chain. To be economically viable, these services need to be able to rely on sound measurement and verification methodologies. They should cover several but not necessarily all of the relevant areas and aspects identified above, blending in innovative manner different revenue streams coming from different market segments and they should in all cases include innovative verification and monitoring measures. Moreover, they should demonstrate how potential legal and contractual aspects (e.g. in relation to existing contracts or linked to the use of equipment) have been accounted for. Projects can include investment costs for the necessary infrastructure/equipment. They should demonstrate that the tested business models and services are self-sustainable after the end of the project. The upfront investments in energy efficiency measures (e.g. upgrading of building energy performance) and in smart building systems should be paid back at least in part by revenues coming from energy savings and remunerated flexibility. LC-SC3-EE : SUPPORTING PUBLIC AUTHORITIES TO IMPLEMENT THE ENERGY UNION Scope: a) Support to local and regional public authorities Proposers should aim to focus their proposed action on one of the following points:
7 Innovative approaches to facilitate the implementation of existing energy and climate plans (e.g. SEAPs/SECAPs or similar plans) at scale across municipalities, focussing on sectors with high energy savings potentials. Actions should lead to the development of tangible delivery plans such as investment concepts and demonstrate a clear replicability of the approach across Europe; Deliver higher quality and consistency of energy efficiency measures implemented through enhanced coordination of different administrative levels. Actions should lead to politically approved and jointly applied monitoring and verification schemes of energy efficiency measures across local and regional authorities, enhanced and better coordination of the energy efficiency measures implemented and more efficient use of public spending in energy efficiency; Support public authorities in the development of transition roadmaps that clearly outline the path to the European long-term 2050 targets and inform the ongoing implementation of SEAPs/SECAPs or similar plans and the development of future plans/targets for 2030 and beyond. Actions should link closely to the Covenant of Mayors and/or Smart Cities and Communities initiatives; Innovative ways to enable public engagement in the energy transition, developing interface capacities within public authorities to engage with civil society; Deliver large-scale and action-oriented peer-to-peer learning programmes targeting cities and/or regions, with a strong replication potential European-wide. Proposals should develop transparent, effective and compelling programmes, building on existing initiatives and real needs and ensure embedded conditionalities such as institutionalisation of the skill base and impact monitoring; Programmes should deliver public entrepreneurs able to drive the sustainable energy transition in their respective territories within the Covenant Mayors and beyond. b) Supporting the delivery of the Energy Efficiency Directive Support will be provided to actions that are assisting Member States to fulfil their obligations under the Energy Efficiency Directive and help with its efficient implementation taking into account existing effective practices and experiences from across Europe. Actions may address, for example, the harmonisation of energy savings calculations under Article 3, implementing Energy Efficiency Obligation Schemes or alternative measures and setting up effective and consistent monitoring and verification systems under Article 7 or the removal of barriers to higher efficiency of the generation, transmission, distribution systems including demand response under Article 15.
8 Proposals should link into existing, relevant initiatives such as ManagEnergy and target specific sector with high energy saving potential such as buildings, transport mobility, heating and cooling, or water infrastructure operation etc., as seen relevant by applicants. LC-SC3-RES : INCREASED PERFORMANCE OF TECHNOLOGIES FOR LOCAL HEATING AND COOLING SOLUTIONS Scope: The proposal is expected to address one or more of the following aspects: Optimisation of the different components of a renewable heating and cooling system; Development of tools and systems to optimize the design and monitoring of the different components of a heating and cooling system; Development of integrated control systems for the smart operation of a heating and cooling system. The proposed systems will harness renewable local energy sources to supply heating and cooling in residential and small and larger commercial buildings as they have different heat/cold needs. Residential building includes single houses and apartment blocks LC-SC3-RES : COMBINING RENEWABLE TECHNOLOGIES FOR A RENEWABLE DISTRICT HEATING SYSTEM Scope: Support will be given to cost-effective solutions for district heating systems which allow satisfying at least 50% of the energy demand of the system by the use in the district of one or more renewable energy technologies. The integration of available sources of otherwise wasted excess heat (e.g., waste heat from cooling processes) is in the scope. The solutions shall be demonstrated in real conditions within an operational district heating system. The consortium is expected to engage operators and final users (in particular if the users need different supply temperatures) so that they can contribute for an optimal and cost-effective design. The requirements of the final users (e.g., in terms of metering) for the day-to-day operation shall be taken into account and the relevant expertise in terms of social sciences and humanities should be included in the consortium.
9 LC-SC3-SCC : SMART CITIES AND COMMUNITIES Scope: Proposals should pay particular attention to: positive project contribution to the overall city goals and focus on mixed use urban quarters; the solutions' ability of being replicated/gradually scaled up (to city level); make energy communities an integral part of the solution strategy to ensure durability and sustainability of Positive Energy Blocks/Districts; active involvement of citizens - to best understand their real needs - as well as local government and city planning departments, increased energy awareness, pro-active energy management, crowdsourcing (intellectual or economic) etc.; create a "smart energy ownership" positive feedback loop; that solutions do not compromise air quality for decarbonisation. Projects are expected to cooperate with other projects in the area of Smart Cities and Communities funded under Horizon 2020 as well as the European Innovation Partnership on Smart Cities and Communities (EIP-SCC) 87 and carry out relevant research on issues including: business models and life cycle consideration; regulatory and legal aspects and data security/protection; citizen's acceptance including understandings of gender and socio-economics (Social Sciences and Humanities); big data, data management, digitalisation and integrated planning tools; electro-mobility: i) impact on energy system and ii) appropriate city planning measures Transition pathways guiding cities from planning to implementation to replication and scaling up of successful solutions.
10 Proposals have to foresee inter-project cooperation and earmark appropriate resources (10% of the requested EU contribution) as contingency for common actions that become necessary to increase impact during the project. Projects need to have a performance monitoring during the full project duration and all relevant performance data must be incorporated into the Smart Cities Information System database (SCIS). Consortia shall be composed of 2 lighthouse cities and 5 follower cities (all situated in different EU Member states or associated countries) that will closely collaborate on shared challenges. LC-SC3-EE : DECARBONISATION OF THE EU BUILDING STOCK: INNOVATIVE APPROACHES AND AFFORDABLE SOLUTIONS CHANGING THE MARKET FOR BUILDINGS RENOVATION Scope: Proposals should demonstrate solutions of building fabric and/or systems that ensure faster and more cost-effective deep renovations that result in high energy performance. Proposals should include innovations in technology and in design and construction methods with low embodied energy and on-site works organisation, industrialization and lowering cost of energy retrofitting. They should also include innovations in business models and the holistic integration of disciplines across the value chain. Proposals should also consider energy efficient and low carbon solutions to retrofit building-level heating and cooling systems and the integration of on-site renewable energy generation. They could also consider further development and improvement of hybrid energy systems using fossil fuel based heating systems coupled with RES based heating systems. Solutions should include quick and simple installation of components and systems, minimizing disruption for building occupants and the time spent on site. Proposals should include monitoring and displaying of real time energy performance and other relevant data and consider the ways in which consumers and others could access and make use of such information. Solutions should ensure high levels of occupant comfort and indoor environmental quality (e.g. air quality, humidity) and should address the multiple benefits of energy efficiency. Proposals should demonstrate solutions that aim for large scale roll-out according to defined business models. LC-SC3-EE : UPGRADING SMARTNESS OF EXISTING BUILDINGS THROUGH INNOVATIONS FOR LEGACY EQUIPMENT Scope: Proposals should demonstrate cost-effective technological solutions to manage energy within existing buildings and interact with the grid providing energy efficiency, flexibility,
11 generation and storage, based on user preferences and requests. These solutions should be aimed to upgrade existing buildings, either residential or tertiary, using automation and IT to offer new services and control to the building users, thereby improving their comfort and increasing their satisfaction. Proposals should demonstrate how the smart systems, smart controls and smart appliances can be integrated seamlessly in existing buildings to interface and/or to control the major energy consuming domestic appliances that are already installed. These pilots should involve several types of domestic appliances with longer lifecycles (boilers, radiators, DHW preparation, motors for ventilation, windows opening and shading, lighting etc.) and with shorter lifecycles (dryers, washing machines, fridges, etc.), testing several types of control modes (ON/OFF, power modulation, etc.) possible for a given type of appliance. Recharging points for electric vehicles and other forms of energy storage should also be incorporated in the pilots. The proposed solutions should not adversely affect the original functionalities, product quality, lifetime, as well as warrantees of the appliances. Besides the pilot demonstrations, proposals should outline business models and strategies for the broad uptake of the proposed smart systems into specific building typologies in Europe and their integration with evolving electricity markets, e.g. dynamic pricing or other services and information offered by energy suppliers and/or aggregators. Integrations with other energy networks (e.g. DHC) can also be considered. The solutions should focus on cost-effectiveness and user-friendliness: easy installation and maintenance, maximising consumer comfort (e.g. self-learning) and information on own consumption (e.g. recommendations to the user in order to maximise savings) as well as on gains from its contribution to grid operation. A realistic estimate should be provided on the total energy savings/year and total power that will be available for demand response actions from the appliances integrated in the smart system through the innovations demonstrated in the proposal. The projects should involve technology providers (e.g. manufacturers of appliances, smart control/ home systems providers), energy services providers (aggregators and/or suppliers and/or ESCO's), electricity system operators and other actors as relevant. LC-SC3-EE : NEXT-GENERATION OF ENERGY PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT AND CERTIFICATION Scope: 2018:
12 Proposals should involve relevant stakeholders (including national and regional certification bodies) to stimulate and enable the roll-out of next-generation of energy performance assessment and certification, with a view to achieve enhanced reliability, cost-effectiveness and compliance with relevant EU standards 19 and the Energy Performance of Buildings Directive. Proposals should develop strategies to encourage convergence of EPC practices and tools across the EU so as to ensure a comparable level of high quality, independent control and verification. The applicability of assessment and the certification schemes should be assessed through a broad set of well-targeted and realistic cases, featuring various locations, building types, climatic conditions and field practices including existing national EPC schemes. The assessment will aim at demonstrating the potential of an EU-wide uptake of the proposed assessment and certification schemes, along well-defined criteria. Embedding the EPCs and their recommendations in broader concepts such as energy audits, widerbuildings related databases (e.g national EPC databases, national housing surveys, EU Building Stock Observatory) and oneshop-shops including administrative, financial and supply side information and linking EPCs to related concepts such as buildings renovation passports, individual buildings renovation roadmaps or building logbooks should also be considered. LC-SC3-EE : AGGREGATION - PROJECT DEVELOPMENT ASSISTANCE Scope: Project Development Assistance (PDA) will be provided to public and private project promoters such as public authorities or their groupings, public/private infrastructure operators and bodies, energy service companies, retail chains, large property owners and services/industry. The action will support building technical, economic and legal expertise needed for project development and leading to the launch of concrete investments, which are the final aim and deliverable of the project. Proposals should focus on one or more of the following sectors: existing public and private buildings including social housing, with the aim to significantly decrease energy consumption in heating/cooling and electricity; energy efficiency of industry and service; energy efficiency in all modes of urban transport (such as highly efficient transport fleets, efficient freight logistics in urban areas, e-mobility and modal change and shift); and energy efficiency in existing infrastructures such as street lighting, district heating/cooling and water/wastewater services.. LC-SC3-EE : INNOVATION PROCUREMENT FOR ENERGY EFFICIENCY
13 Scope: Actions should enable a group of procurers (buyers group) to undertake a PPI procurement for smart and integrated innovative solutions for, products, and/or services, and/or buildings which are not yet available on a large-scale commercial basis, and which have an overall energy performance level that is better than the best (aggregated) level for (a combination of) products and/or services and/or buildings that are readily available on the market. Proposals are encouraged to address wider socio-economic challenges, such as energy poverty reduction. The innovative solutions procured by all procurers in the buyers group must have the same core functionality and performance characteristics, but may have additional 'local' functionality due to differences in the local context of each individual procurer. Actions should lead to the first application/commercialization of the innovative solution, in order to assure its market uptake. Functional/performance based specifications should be ambitious but achievable without the procurement of research and development and without distorting competition. Other entities (e.g. public procurement expertise centres, endusers, certification bodies, private/ngo procurers that provide services of public interest and share the same procurement need) whose participation is well justified may participate in additional activities that clearly add value to the action. PPI action must engage in open market consultation with potential end-users and tenderers such as SME's that should be encouraged to provide innovative solutions. Proposals should include a clear action plan to communicate experiences and results towards potential replicators across the EU.. LC-SC3-EE : SOCIO-ECONOMIC RESEARCH CONCEPTUALISING AND MODELLING ENERGY EFFICIENCY AND ENERGY DEMAND Scope: 2018: The research projects should help to make the Energy Efficiency First principle more concrete and operational and to better understand its relevance for energy demand and supply and its broader impacts across sectors and markets. In particular, it needs to be analysed how energy efficiency programmes can compete in reality with supply side investments (e.g. new generation capacities or import capacities) including at the level of countries and having in mind limited public budgets. It would also be necessary to describe and assess how it interacts with and correlates to other policy objectives, at a policy level as well as at the level of implementation. Actions which conceptualise assess the impacts and model the energy efficiency first principle, in particular as regards:
14 its role and value in the energy system (e.g. for planning of generation assets and networks adequacy etc.) and the energy market (participation in capacity market, participation and impact on prices and costs on wholesale and balancing/reserve markets); its role and value in financing decisions; its economic and social impacts; its correlation and interaction with other policy objectives (e.g. renewable energy, demand response); existing best practices worldwide where energy efficiency projects are given priority over supply side measures. 2019: The aim of the action is to deepen the demand side-related parameters in existing models and to include new aspects and data sources (e.g. by tapping DSOs modelling for forecasting of distributed loads). In general, it is to be expected that the introduction of smart meters and smart equipment will lead to more accurate consumption data providing for a more holistic mapping of the demand side and thus for better projections inside energy policy development and a more effective regulatory framework. The action should complement the existing demand side energy models by developing multipleagent energy models and/or modelling segments and/or developing methodologies on how to improve and enhance the demand side aspects in modelling. These models and/or methodologies should: be compatible with the energy models most commonly used at European level; model more accurately those aspects not yet sufficiently considered in the existing models; make use of new data sources, including big data as for example generated by smart meters, smart buildings and smart equipment; identify and refine the structure and patterns of demand and how it will develop; contribute to an enhanced demand-side model to be consistently used at European level. LC-SC3-RES : DEVELOPING THE NEXT GENERATION OF RENEWABLE ENERGY TECHNOLOGIES
15 Scope: Proposals are expected to bring to TRL 3 or TRL 4 renewable energy technologies that will answer the challenge described. Beside the development of the technology, the proposal will have to clearly address the following related aspects: the potential lower environmental impact, the better resource efficiency, issues related to social acceptance or resistance to new energy technologies, related socioeconomic and livelihood issues. Support will be given to activities which focus on converting renewable energy sources into an energy vector, or the direct application of renewable energy sources. One of the following technology-specific challenges has to be addressed: Developing the new energy technologies that will form the backbone of the energy system by 2030 and 2050: Excluding specific technologies addressed in the other bullet points, the challenge is to develop energy technologies currently in the early phases of reserach. It is crucial that these new, more efficient, and cost-competitive energy generation and conversion technologies, demonstrate their potential value in the future European energy system. Developments in sectors other than energy may provide ideas, experiences, technology contributions, knowledge, new approaches, innovative materials and skills that are of relevance to the energy sector. Cross-fertilisation could offer mutually beneficial effects; Innovative materials for geothermal heat exchangers to maximize energy transfer and improve the overall conversion efficiency of a geothermal system; Innovative testing methods and design tools for acceleration of innovative wind technology development and increased life time extension; Sustainable fuels for energy and transport application through ground-breaking conversion technologies, addressing for example development of novel microorganisms, enzymes, catalysts, and separation techniques, improvement of biomass and microalgae yields, and development of novel technologies of combined indirect and direct artificial photosynthesis with chemical/ biochemical/biological systems; Innovative very high efficiency thin-film photovoltaics concepts considering advanced, sustainable and low-cost materials and processes. LC-SC3-RES : RENEWABLE ENERGY SYSTEM INTEGRATED AT THE BUILDING SCALE
16 Scope: Proposal will provide a combination of different renewable energy technologies to cover the highest possible share of electricity, heating and cooling needs of a multi-family residential or commercial or public or industrial building (in the case of the industrial building, the project is not expected to address the energy needs of the industrial process). Since the final application will be operated by users, their needs and requirements (e.g. in terms of space that they are willing to provide for the installation of the different components of the system) shall be taken into account and the relevant expertise in terms of social sciences and humanities has to be included in the consortium (this will be evaluated under the 'Impact' criterion). LC-SC3-RES : SOLAR ENERGY IN INDUSTRIAL PROCESSES Scope: Support will be given to solutions that cover by means of solar thermal energy the highest possible share of the heating and/or cooling demand of one or more industrial processes. In the case of heating, the process temperature shall be higher than 150 C. Individual industrial sites and/or industrial parks (also when coupled to a district heating and cooling network) are in the scope. LC-SC3-RES : DEVELOPING SOLUTIONS TO REDUCE THE COST AND INCREASE PERFORMANCE OF RENEWABLE TECHNOLOGIES Scope: Proposals will address one or more of the following issues: a) Floating Wind Technology development including reliable, sustainable and cost efficient anchoring and mooring system, dynamic cabling, installation techniques, and O&M concepts; b) Onshore Wind - Disruptive technologies for in the rotor and generator and support structures for the development of the advanced or next generation wind energy conversion systems; c) Ocean: New integrated design and testing of tidal rotors with behavioural modelling to achieve extended lifetime and high resistance in marine environment; d) Geothermal: Novel drilling technologies need to be developed to reach cost-effectively depths in the order of 5km and/or temperatures higher than 250 C;
17 e) CSP: Novel components and configurations for linear focusing and point focusing technologies need to be developed and tested; f) Hydropower: Novel components for hydropower hydraulic and electrical machinery which allow efficient utilization also in off-design operation conditions, especially during ramp up and ramp down phases and reduce related machinery wear and tear; g) Bioenergy: Improve small and medium-scale combined heat and power (CHP) from biomass to reduce overall costs of investments and operation through achieving at the same time high resource efficiency and high overall and electrical conversion performance. LC-SC3-RES : DEMONSTRATE SOLUTIONS THAT SIGNIFICANTLY REDUCE THE COST OF RENEWABLE POWER GENERATION Scope: Proposals will address one of the following issues: a. Offshore wind: Focus will be on the development and validation of new manufacturing, installation and/or operation techniques, introduction of new materials. The whole value chain, including dismantling and recycling procedures, will be involved to avoid overengineering. Issues for improved production will be identified. All aspects of health and environmental impact issues will be taken into account. b. Deep geothermal: Depending on the geological conditions, CO2 and other gases (e.g. H2S) emissions can be significant, current technologies for limitation of emission production and/or for gas condensation and re-injection have to be improved to reduce costs. In addition, turning emissions into commercial products would also contribute to cost reduction. c. CSP: Focus will be on the demonstration in operational environment of CSP solutions based on novel heat transfer fluids and/or of solutions which make an innovative use of a heat transfer fluid that is already used in other CSP applications. LC-SC3-RES : OPTIMISING MANUFACTURING AND SYSTEM OPERATION Scope: Proposals will address one of the following issues: Monitoring system for marine energy (ocean and offshore wind): New intelligent sensors and fault detection systems for accurate condition and structural health monitoring will enable predictive and preventive Operation and preventive Maintenance processes. Sufficient knowledge of potential failures and the right tools to detect and locate failures are crucial.
18 Geothermal fluids: Better understanding of the chemical and physical properties of these fluids, including super-hot and hot fluids, as transport media are necessary to optimize site development and operation. Photovoltaics: Development of innovative crystalline silicon wafer growth techniques to produce high-efficiency solar cells and modules. LC-SC3-RES : DEVELOPMENT OF SOLUTIONS BASED ON RENEWABLE SOURCES THAT PROVIDE FLEXIBILITY TO THE ENERGY SYSTEM Scope: Proposals will address one of the following issues: Bioenergy carriers: Development of intermediate bioenergy carriers for energy and transport from biogenic residues and wastes at a conversion cost reduced by at least 25% from the state-of-the-art, excluding the feedstock cost, and with increased energy density, storage and trade characteristics, where relevant, and improved GHG performance. The state-of the art for conversion costs per technology will be clearly presented in the proposal with cost figures and versatility of use where appropriate. Hydropower: to develop low and ultra-low head equipment and sea water resistant equipment (such as for example bulb-pump turbines) guaranteeing at least 70% roundtrip efficiency and making low-head seawater storage and other low head applications of hydropower viable, for example at unexplored locations (e.g. like at coastal dams and islands) Virtual Power Plant: Increase the performance of an integrated portfolio of renewable energy sources (namely a combination of fluctuating and dispatchable renewable sources) to operate together as a Virtual Power Plant, capable of providing flexibility and ancillary services to the energy system. The solution has to be competitive compared with solutions combining fluctuating renewables with electrochemical storage. LC-SC3-RES : DEMONSTRATION OF SOLUTIONS BASED ON RENEWABLE SOURCES THAT PROVIDE FLEXIBILITY TO THE ENERGY SYSTEM Scope: Proposals will address one of the following issues: a. Intermediate bioenergy carriers: Focus will be on the demonstration of the most costefficient intermediate bioenergy carrier pathways for energy and transport, which improve the economic viability of the subsequent energy production by addressing solid, liquid and gaseous intermediate bioenergy carriers from biogenic residues and wastes with increased energy
19 density, storage and trade characteristics where relevant. Reduced conversion costs and improved energy efficiency and GHG performance of the intermediate bioenergy carrier pathway will be demonstrated. Production at a scale of up to 5000 tons and process feasibility through applications to fuel production including for the heavy duty and maritime sectors, as well as to combined heat and power generation, is to be included. b. Hydropower: Focus will be on the improvement of the average annual overall efficiency of hydroelectric machinery. Projects are expected to provide high availability of hydropower plants and to maximise performance of hydropower plants of all sizes. The aim is adapting to variable speed generation the hydropower plants (new, refurbished and uprated and especially existing ones); it is important that by optimising maintenance intervals for all hydro plants (especially those delivering balancing power because of the related dynamic operation, dynamic loads and increased wear and tear) the outage time will be minimised. c. Thermal energy storage in Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) plants: The focus will be on the demonstration of innovative storage systems for CSP plants. The thermal energy storage solutions proposed (e.g. by means of thermo-chemical reactions) have to achieve much higher storage densities than current mainstream solutions (i.e. at least two times higher) while guaranteeing similar performance in terms of cycles. LC-SC3-RES : MARKET UPTAKE SUPPORT Scope: The proposal will develop solutions which can be easily implemented for overcoming barriers to the broad deployment of renewable energy solutions. In particular, the proposal will address one or more of the following issues: Recommendation for harmonisation of regulations, life cycle assessment approaches, environmental impact of renewable energy power plants; Development of additional features for RES to be compliant with the electricity market requirements, making them "market fit", such as developing the possibility to provide additional services to the grid such as peak power, role in electricity balancing/reserve market; Support sharing of best practice between public funding bodies for the cross-border participation in RES electricity support schemes, increasing the use of the "RES cooperation mechanisms" foreseen in the legislation;
20 Development of insurance schemes available in Europe and worldwide to mitigate risks, such as in geothermal drilling and offshore installation; Development of financing mechanisms, schemes and best practices for cost-effective support for uptake of renewable sources, such as through the use of Public Procurement of Innovative Solutions instrument or smartly designed tenders; Development of support tools to facilitate export markets, especially for technologies where export market potential is much higher than internal market e.g. for hydropower. The focus will be on capacity building for market activities in developing and emerging countries, including identifying research needs, with the scope of developing countryspecific technologies and solutions, and/or adapting existing ones, taking into account local aspects of social, economic and environmental sustainability; Development of tools (methods and models) for environmental impact assessments of renewable energy projects; Use of global earth observation data to support development and deployment of renewable energy sources; Determining conditions and defining options for retrofitting existing energy and industrial installations (first generation biofuels, pulp and paper, fossil refineries, fossil firing power and Combined Heat and Power (CHP) plants) for the complete or partial integration of bioenergy, with concrete proposals for such retrofitting for the different cases of bioethanol, biodiesel, bio-kerosene, intermediate bioenergy carriers and other advanced biofuels and renewable fuels and biomass based heat and power generation, on the basis of the assessment of the capital expenditure (CAPEX) reduction and market benefit; Development of optimisation strategies regarding cost, energy-performance and LCA for bioenergy and sustainable renewable fuels in upgraded energy and industrial installations;
21 Development of cost-effective logistics, feedstock mobilisation strategies and tradecentres for intermediate bioenergy carriers. The complexity of these challenges and of the related market uptake barriers calls for multidisciplinary research designs, which should include contributions also from the social sciences and humanities. Regional specificities, socio-economic, spatial and environmental aspects from a life-cycle perspective will be considered. For all actions, the consortia have to involve and/or engage relevant stakeholders and market actors who are committed to adopting/implementing the results. Where relevant, proposals are expected to also critically evaluate the legal, institutional and political frameworks at local, national and European level and how, why and under what conditions these (could) act as a barrier or an enabling element. Participation of developing and emerging countries is encouraged, in particular if these countries have identified energy as a priority area for their development and whenever common interest and mutual benefits are clearly identified. LC-SC3-EC : THE ROLE OF CONSUMERS IN CHANGING THE MARKET WITH INFORMED DECISION OR COLLECTIVE ACTIONS Scope: The proposed action should cover one or more of the following, as relevant: Inform and facilitate consumer adoption of active demand side services (energy efficiency, generation, storage and/or flexibility); this includes support for consumers in identifying appropriate services; Support different forms of collective action for energy efficiency and active demand side services (energy efficiency, distributed generation, storage and flexibility); Setting up and supporting consumer cooperatives/collective purchase groups/other community actions to increase domestic uptake of energy efficient and low-carbon energy products and services, to provide energy audits and advice, facilitate switching and improved billing, provide collective solutions to storage and for split incentives, etc; Identify and implement solutions to address split incentives (e.g. allowing tenants to benefit from active demand side services); Identify and address regulatory barriers and contractual conditions with utilities, suppliers, etc., including linking activities with structural solutions involving public authorities; Inform and motivate consumers to change old and inefficient installed appliances leading to the highest energy saving potential (e.g. boilers, local space heaters, air heaters).
22 LC-SC3-EC : Mitigating household energy poverty Scope: Actions should contribute to actively alleviating energy poverty and developing a better understanding of the types and needs of energy poor households and how to identify them, building on any existing initiatives such as the European Energy Poverty Observatory. The proposed action should cover one or more of the following: Facilitate behaviour change and implementation of low-cost energy efficiency measures tailored for energy poor households (e.g. provision of information and advice, energy efficiency services such as draught proofing or optimisation of existing building technology systems, as well as energy efficiency devices & kits such as low-energy lighting); Support the set-up of financial and non-financial support schemes for energy efficiency and/or small scale renewable energy investments for energy poor households. These actions should be embedded in, and add value to, structural frameworks and activities involving local, regional, and national authorities, and/or networks such as the Covenant of Mayors; Develop, test and disseminate innovative schemes for energy efficiency/res investments established by utilities or other obliged parties under Article 7. LC-SC3-EC : CONSUMER ENGAGEMENT AND DEMAND RESPONSE Scope: Proposals will develop and demonstrate solutions for demand response which may include different types of consumers (residential, industrial, commercial and tertiary, including prosumers who are self-consuming part of the energy they produce). Proposals can also target one or multiple types of loads (e.g. industrial loads, appliances, electric vehicles, power to heat / cool, etc.), include energy storage and one or several methods of aggregation (e.g. local energy communities) preferably relying on advanced automation, advanced ICT tools and approaches (e.g. IoT, Big Data), communication protocols and interoperability. Appropriate smart metering, links and communication with grid operators should be ensured so as to optimise and facilitate the use of the provided services. Solutions should aim at providing a fair share of the benefits of variable prices so as to remunerate the services provided by the consumers and to create sufficient incentives for them to engage. Services for grid operators, customer information, engagement strategies and contracts should
23 be designed, tested and conclusions should be drawn from the different types of consumers (e.g. social category, age, technology literacy, gender), on the considered geographical location and climatic conditions and on the type and magnitude of incentives, putting the citizen at the centre of the proposed approach. The participation of local energy communities, energy cooperatives, aggregators and local actors (e.g. local DSOs) is encouraged. The direct or indirect participation of Consumer associations is an added value. EU wide geographical diversity is a further asset. An open access approach towards real time information and forecast for the energy system demand and supply situation is encouraged. Proposals are expected to include clear business model development and a clear path to finance and deployment. Key partners should have the capability and interest in making the developed solution a core part of their business/service model to their clients. The study of the behaviour and practice of the different stakeholders based on Social sciences and humanities should be part of the tasks in the proposal. Proposals should include tasks or a specific work-package on the analysis of obstacles to innovation under the current context but also under the future market design context and foresee the coordination on policy relevant issues and obstacle to innovation (e.g. regulatory framework, business models, data management, consumer engagement) with similar EUfunded projects through the BRIDGE initiative58. An indicative budget share of at least 2% is recommended for the research work associated with these issues and an additional 2% for the coordination effort are recommended. Proposal should build upon the insights and results of projects that have already been selected in this field under H2020 (information can be found on the BRIGDE web site 59 ) and demonstrate their innovative character. Regarding data handling, data management and standardisation issues, proposers should comply with the requirements sated in the section 'Common requirements' of the introduction to the part on the Smart citizen-centred energy system. LC-SC3-ES : INTEGRATED LOCAL ENERGY SYSTEMS (ENERGY ISLANDS)
24 Scope: Proposals will develop and demonstrate solutions which analyse and combine, in a well delimited system, all the energy vectors that are present and interconnect them where appropriate. Proposals should present a preliminary analysis of the local case as part of the content of the proposal and propose to develop solutions and tools for the optimisation of the local energy network, but having a high replication potential across Europe. Local consumer should be heavily involved in the projects from the start. LC-SC3-NZE : ADVANCED CAPTURE TECHNOLOGIES Scope: The objective is the validation and pilot demonstration of advanced capture technologies that have shown a high potential for reduction of the energy penalty and a significant overall improvement of cost-efficiency of the whole capture process, but that are not yet commercial. Projects will test operating conditions and provide proof of the reliability and cost-effectiveness of these concepts, whilst at the same time evaluating the cost, technical requirements and operational and safety impacts on the associated transportation infrastructure, storage or utilisation, as part of their integration in a cluster. The proposal should state credible and clearly defined targets and key performance indicators (KPIs) for the energy penalty reduction, the capture rate and the relative incremental operating costs of the capture process. Environmentally benign technologies have to be pursued and their environmental impact addressed in the project also in view of future scaling up.
Thomas SCHLEKER, PhD. Global Leadership in Renewables
 Thomas SCHLEKER, PhD Global Leadership in Renewables LC-SC3-RES-11-2018 1/2 Achieving or maintaining global leadership in renewable energy technologies requires cost reductions TRL 3-4 to 4-5 RIA EUR 2
Thomas SCHLEKER, PhD Global Leadership in Renewables LC-SC3-RES-11-2018 1/2 Achieving or maintaining global leadership in renewable energy technologies requires cost reductions TRL 3-4 to 4-5 RIA EUR 2
WP Future opportunities for geothermal and energy system integrated
 WP 2018-2020 Future opportunities for geothermal and energy system integrated Horizon 2020 WP 2018-2020 14:00 15:00 16:00 Deep geothermal underground RES1, RES11, RES14, RES28 Shallow geothermal RES1 &
WP 2018-2020 Future opportunities for geothermal and energy system integrated Horizon 2020 WP 2018-2020 14:00 15:00 16:00 Deep geothermal underground RES1, RES11, RES14, RES28 Shallow geothermal RES1 &
Overview of H funding opportunities
 Overview of H2020 2019 funding opportunities Maria Smietanka maria.smietanka@kpk.gov.pl This project has received funding from the European Union s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under
Overview of H2020 2019 funding opportunities Maria Smietanka maria.smietanka@kpk.gov.pl This project has received funding from the European Union s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under
WP Future opportunities for geothermal and energy system integrated
 WP 2018-2020 Future opportunities for geothermal and energy system integrated Horizon 2020 WP 2018-2020 Horizon 2020 WP 2018-2020 Many opportunities for geothermal h&c projects Horizon 2020 WP 2018-2020
WP 2018-2020 Future opportunities for geothermal and energy system integrated Horizon 2020 WP 2018-2020 Horizon 2020 WP 2018-2020 Many opportunities for geothermal h&c projects Horizon 2020 WP 2018-2020
Overview of Calls in the H2020 Work Program Energy
 Overview of Calls in the H2020 Work Program Energy 2018 2020 Selected topics for discussion in Hermes Partnership The Work program is still tentative and not for publication, based on draft version May
Overview of Calls in the H2020 Work Program Energy 2018 2020 Selected topics for discussion in Hermes Partnership The Work program is still tentative and not for publication, based on draft version May
Efficacité énergétique et Energy Efficient Building
 Horizon-2020 appels 2019 Efficacité énergétique et Energy Efficient Building Les slides seront disponibles sur le site web du NCP-Wallonie Géraldine DUPIN Crosscutting activities - 2 - EeB-EE Summer 2018
Horizon-2020 appels 2019 Efficacité énergétique et Energy Efficient Building Les slides seront disponibles sur le site web du NCP-Wallonie Géraldine DUPIN Crosscutting activities - 2 - EeB-EE Summer 2018
Topics Renewable Energy - Near Zero Emission - Joint Actions - Cross-Cutting - Prizes
 Philippe Schild Renewable Energy Unit DG Research and Innovation Topics 2018 2019 - Renewable Energy - Near Zero Emission - Joint Actions - Cross-Cutting - Prizes Deadlines in 2018 28 topics 481M Contracts
Philippe Schild Renewable Energy Unit DG Research and Innovation Topics 2018 2019 - Renewable Energy - Near Zero Emission - Joint Actions - Cross-Cutting - Prizes Deadlines in 2018 28 topics 481M Contracts
SET PLAN and HORIZON Helder Gonçalves LNEG 29 September 2015
 SET PLAN and HORIZON 2020 Helder Gonçalves LNEG 29 September 2015 Energy Union Built with the ambition to achive in a cost efective way a fundamental transformation of Europe s Energy System. Smarter,
SET PLAN and HORIZON 2020 Helder Gonçalves LNEG 29 September 2015 Energy Union Built with the ambition to achive in a cost efective way a fundamental transformation of Europe s Energy System. Smarter,
Circular Economy SPIRE Opportunities for
 Circular Economy SPIRE Opportunities for 2018-2019 CITIES OF THE FUTURE 2017 Brussels 26-27 th Oct 2017 Cristina FERNANDEZ-RAMOS Unit D2. Advanced Manufacturing Systems and Biotechnologies Industrial Technologies
Circular Economy SPIRE Opportunities for 2018-2019 CITIES OF THE FUTURE 2017 Brussels 26-27 th Oct 2017 Cristina FERNANDEZ-RAMOS Unit D2. Advanced Manufacturing Systems and Biotechnologies Industrial Technologies
Horizont 2020 Secure, clean and efficient energy
 Horizont 2020 Secure, clean and efficient energy Mari Habicht Zagreb January 26, 2016 This project has received funding from the European Union s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant
Horizont 2020 Secure, clean and efficient energy Mari Habicht Zagreb January 26, 2016 This project has received funding from the European Union s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant
HORIZON Competitive Low Carbon Energy Call DG RTD K1. Esperanza Arrizabalaga Vena
 THE EU FRAMEWORK PROGRAMME FOR RESEARCH AND INNOVATION HORIZON 2020 Competitive Low Carbon Energy 2014-2015 Call Esperanza Arrizabalaga Vena DG RTD K1 Thematic scope of the Energy Challenge (according
THE EU FRAMEWORK PROGRAMME FOR RESEARCH AND INNOVATION HORIZON 2020 Competitive Low Carbon Energy 2014-2015 Call Esperanza Arrizabalaga Vena DG RTD K1 Thematic scope of the Energy Challenge (according
HORIZON Energy Calls Croatian Energy Info Days Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computing Zagreb 21/12/2015
 THE EU FRAMEWORK PROGRAMME FOR RESEARCH AND INNOVATION HORIZON 2020 Energy Calls 2016-2017 Croatian Energy Info Days Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computing Zagreb 21/12/2015 Rémy Dénos DG Energy
THE EU FRAMEWORK PROGRAMME FOR RESEARCH AND INNOVATION HORIZON 2020 Energy Calls 2016-2017 Croatian Energy Info Days Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computing Zagreb 21/12/2015 Rémy Dénos DG Energy
HORIZON 2020 Low Carbon Energy
 THE EU FRAMEWORK PROGRAMME FOR RESEARCH AND INNOVATION HORIZON 2020 Low Carbon Energy The next waves of calls Philippe Schild DG Research & Innovation Low Carbon Energy - Orientations Context Policy &
THE EU FRAMEWORK PROGRAMME FOR RESEARCH AND INNOVATION HORIZON 2020 Low Carbon Energy The next waves of calls Philippe Schild DG Research & Innovation Low Carbon Energy - Orientations Context Policy &
Horizon Introduction to Horizon 2020 & the Societal challenge Energy including heat/cold. 20 maart Kathrin Braun
 Horizon 2020 Introduction to Horizon 2020 & the Societal challenge Energy including heat/cold 20 maart 2014 Kathrin Braun A new programme 2007-2013 2014-2020 2 Horizon 2020 three pillars 1. Excellent science
Horizon 2020 Introduction to Horizon 2020 & the Societal challenge Energy including heat/cold 20 maart 2014 Kathrin Braun A new programme 2007-2013 2014-2020 2 Horizon 2020 three pillars 1. Excellent science
Horizon 2020 Work Programme :
 Horizon 2020 Work Programme 2016-2017: 10. Secure, clean and efficient energy Call: Energy Efficiency Waste heat recovery from urban facilities and re-use to increase energy efficiency of district EE-01-2017
Horizon 2020 Work Programme 2016-2017: 10. Secure, clean and efficient energy Call: Energy Efficiency Waste heat recovery from urban facilities and re-use to increase energy efficiency of district EE-01-2017
The issues faced by the transport and energy sectors go however beyond the need for emission reduction. There are several challenges to be tackled, in
 4. CLUSTER 'CLIMATE, ENERGY AND MOBILITY' 4.1. Rationale The intersection of research and innovation on climate, energy and mobility will address in a highly integrated and effective way, one of the most
4. CLUSTER 'CLIMATE, ENERGY AND MOBILITY' 4.1. Rationale The intersection of research and innovation on climate, energy and mobility will address in a highly integrated and effective way, one of the most
EUROCITIES position on clean energy for all Europeans package. May 2017
 EUROCITIES position on clean energy for all Europeans package May 2017 Executive summary As European cities, we play a crucial role triggering energy transition at the local level, often surpassing the
EUROCITIES position on clean energy for all Europeans package May 2017 Executive summary As European cities, we play a crucial role triggering energy transition at the local level, often surpassing the
Energy efficiency Buildings Calls 2018/2019
 A joint presentation by Project Advisers of the EASME ENERGY Unit chaired by Agata Kotkowska Head of Buildings, Heating and Cooling Sector Energy efficiency Buildings Calls 2018/2019 A joint presentation
A joint presentation by Project Advisers of the EASME ENERGY Unit chaired by Agata Kotkowska Head of Buildings, Heating and Cooling Sector Energy efficiency Buildings Calls 2018/2019 A joint presentation
Energy Efficiency Info Day 25 th of October 2017, Brussels. Energy Consumers and Energy Services
 Energy Efficiency Info Day 25 th of October 2017, Brussels Energy Consumers and Energy Services 11.00-11.05 Welcome and Introduction Anette Jahn, EASME 11.05 11.35 Legal framework: Energy consumers and
Energy Efficiency Info Day 25 th of October 2017, Brussels Energy Consumers and Energy Services 11.00-11.05 Welcome and Introduction Anette Jahn, EASME 11.05 11.35 Legal framework: Energy consumers and
Leonardo Piccinetti E4Business
 CIP Competitiveness and Innovation Programme, 2007-20132013 Leonardo Piccinetti E4Business Expected funding areas 2009 Renewable energy & local and special initiatives The policy framework Action Plan
CIP Competitiveness and Innovation Programme, 2007-20132013 Leonardo Piccinetti E4Business Expected funding areas 2009 Renewable energy & local and special initiatives The policy framework Action Plan
Les opportunités dans les énergies vertes et les Smart Cities
 Horizon-2020 appels 2018 Les opportunités dans les énergies vertes et les Smart Cities Les slides seront disponibles sur le site web du NCP-Wallonie Les informations communiquées n ont pas encore été adoptées
Horizon-2020 appels 2018 Les opportunités dans les énergies vertes et les Smart Cities Les slides seront disponibles sur le site web du NCP-Wallonie Les informations communiquées n ont pas encore été adoptées
Heating & cooling (and geothermal) in the Intelligent Energy Europe & Energy Efficiency part of the Horizon 2020 programme of the EC
 Heating & cooling (and geothermal) in the Intelligent Energy Europe & Energy Efficiency part of the Horizon 2020 programme of the EC Antonio Aguilo Project Advisor 5 October 2015, Brussels Intelligent
Heating & cooling (and geothermal) in the Intelligent Energy Europe & Energy Efficiency part of the Horizon 2020 programme of the EC Antonio Aguilo Project Advisor 5 October 2015, Brussels Intelligent
3.2: Smart Cities and Communities (Create technologies and services for smart homes that provide smart solutions to energy consumers)
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION RTD - Energy ENER - Renewables, R&I, Energy Efficiency JRC Institute for Energy and Transport SET Plan Secretariat Issues Paper No.3 - DRAFT Version 17/12/2015 3.2: Smart Cities and
EUROPEAN COMMISSION RTD - Energy ENER - Renewables, R&I, Energy Efficiency JRC Institute for Energy and Transport SET Plan Secretariat Issues Paper No.3 - DRAFT Version 17/12/2015 3.2: Smart Cities and
Renewable energy technologies
 Renewable energy technologies The next deadlines and topics Horizon 2020 Energy Virtual Info Day Philippe Schild Senior Expert for Renewable Energy Sources Unit G3, DG RTD Low Carbon Energy 2016/2017 Calls
Renewable energy technologies The next deadlines and topics Horizon 2020 Energy Virtual Info Day Philippe Schild Senior Expert for Renewable Energy Sources Unit G3, DG RTD Low Carbon Energy 2016/2017 Calls
The Intelligent Energy Europe Programme: Call for Proposals 2012
 The Intelligent Energy Europe Programme: Call for Proposals 2012 Emilio FONT DE MORA Project Officer Executive Agency for Competitiveness and Innovation Renewable Energy Unit Sofia, 28 February 2012 The
The Intelligent Energy Europe Programme: Call for Proposals 2012 Emilio FONT DE MORA Project Officer Executive Agency for Competitiveness and Innovation Renewable Energy Unit Sofia, 28 February 2012 The
CALL COMPETITIVE LOW-CARBON ENERGY
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS CALL COMPETITIVE LOW-CARBON ENERGY GENERAL QUESTIONS NEW Q: An applicant needs to buy some very specialized equipment to conduct the research in a Research and Innovation Action.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS CALL COMPETITIVE LOW-CARBON ENERGY GENERAL QUESTIONS NEW Q: An applicant needs to buy some very specialized equipment to conduct the research in a Research and Innovation Action.
Energy Performance of Buildings Status and Strategy for using Dynamical Calculation Methods
 Energy Performance of Buildings Status and Strategy for using Dynamical Calculation Methods H. BLOEM DG JRC Institute for Energy and Transport Prepared for 2 nd General Consortium Meeting 26-27 May 2015
Energy Performance of Buildings Status and Strategy for using Dynamical Calculation Methods H. BLOEM DG JRC Institute for Energy and Transport Prepared for 2 nd General Consortium Meeting 26-27 May 2015
A VISION FOR HEATING AND COOLING PRIORITIES FOR TODAY AND TOMORROW
 A VISION FOR HEATING AND COOLING PRIORITIES FOR TODAY AND TOMORROW EXECUTIVE SUMMARY EPEE, representing the heating, cooling and refrigeration industry in Europe, strongly supports the energy efficiency
A VISION FOR HEATING AND COOLING PRIORITIES FOR TODAY AND TOMORROW EXECUTIVE SUMMARY EPEE, representing the heating, cooling and refrigeration industry in Europe, strongly supports the energy efficiency
EPEE CONTRIBUTION TO THE EU CONSULTATION ON THE EED REVIEW JANUARY 2016
 EPEE CONTRIBUTION TO THE EU CONSULTATION ON THE EED REVIEW JANUARY 2016 The key messages of the EPEE contribution to the EU consultation the EED review include: The necessity to couple renewable energies
EPEE CONTRIBUTION TO THE EU CONSULTATION ON THE EED REVIEW JANUARY 2016 The key messages of the EPEE contribution to the EU consultation the EED review include: The necessity to couple renewable energies
Conclusions on clean and energy-efficient vehicles for a competitive automotive industry and decarbonised road transport
 COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION Conclusions on clean and energy-efficient vehicles for a competitive automotive industry and decarbonised road transport The Council adopted the following conclusions: 3016th
COUNCIL OF THE EUROPEAN UNION Conclusions on clean and energy-efficient vehicles for a competitive automotive industry and decarbonised road transport The Council adopted the following conclusions: 3016th
The new Heating and Cooling Strategy
 COGEN Europe Annual Conference Crowne Plaza Hotel Brussels, 23 March 2016 The new Heating and Cooling Strategy Claudia CANEVARI Deputy Head, Energy Efficiency Unit DG ENER, European Commission 1 Energy
COGEN Europe Annual Conference Crowne Plaza Hotel Brussels, 23 March 2016 The new Heating and Cooling Strategy Claudia CANEVARI Deputy Head, Energy Efficiency Unit DG ENER, European Commission 1 Energy
Philip Cheasty Enterprise Ireland National Contact Point For Energy in Horizon
 Philip Cheasty Enterprise Ireland National Contact Point For Energy in Horizon2020 http://www.horizon2020.ie/ Horizon 2020 (H2020) is the EU s Programme to support Research and Innovation. It has a budget
Philip Cheasty Enterprise Ireland National Contact Point For Energy in Horizon2020 http://www.horizon2020.ie/ Horizon 2020 (H2020) is the EU s Programme to support Research and Innovation. It has a budget
CHIARA POCATERRA APRE - EU Horizon 2020 National Contact Point Secure, clean and efficient energy
 L APRE per i finanziamenti europei delle tecnologie energetiche Perugia, 11 Novembre 2016 CHIARA POCATERRA APRE - EU Horizon 2020 National Contact Point Secure, clean and efficient energy Excellent Science
L APRE per i finanziamenti europei delle tecnologie energetiche Perugia, 11 Novembre 2016 CHIARA POCATERRA APRE - EU Horizon 2020 National Contact Point Secure, clean and efficient energy Excellent Science
Outlook on the 2019 H2020 Work Programme and results of the SPIRE-2018 calls
 Outlook on the 2019 H2020 Work Programme and results of the SPIRE-2018 calls SPIRE Brokerage event Achema Frankfurt 14 June 2018 Carmine Marzano DG Research and Innovation European Commission 2018 SPIRE
Outlook on the 2019 H2020 Work Programme and results of the SPIRE-2018 calls SPIRE Brokerage event Achema Frankfurt 14 June 2018 Carmine Marzano DG Research and Innovation European Commission 2018 SPIRE
COGEN Europe Position Paper
 COGEN Europe Position Paper Micro-CHP A cost-effective solution to save energy, reduce GHG emissions and partner with intermittent renewables Micro-CHP 1 is the state-of-the-art energy supply solution
COGEN Europe Position Paper Micro-CHP A cost-effective solution to save energy, reduce GHG emissions and partner with intermittent renewables Micro-CHP 1 is the state-of-the-art energy supply solution
Possibilities for wind energy projects in the Horizon 2020 programme
 HORIZON HORIZON 2020 2020 Possibilities for wind energy projects in the Horizon 2020 programme Matthijs SOEDE Research Programme Officer Unit K3 New and Renewable Energy Sources DG Research and Innovation
HORIZON HORIZON 2020 2020 Possibilities for wind energy projects in the Horizon 2020 programme Matthijs SOEDE Research Programme Officer Unit K3 New and Renewable Energy Sources DG Research and Innovation
New energy New opportunities. Our pathway to net zero and smart, sustainable workplaces
 New energy New opportunities Our pathway to net zero and smart, sustainable workplaces 1 The time is now Renewable energy New energy technology is rapidly evolving. Energy markets are transforming to unlock
New energy New opportunities Our pathway to net zero and smart, sustainable workplaces 1 The time is now Renewable energy New energy technology is rapidly evolving. Energy markets are transforming to unlock
CLEAN ENERGY FOR ALL EUROPEANS. Clean Energy latest EU policy developments Margot Pinault European Commission DG ENERGY Energy Efficiency unit
 Clean Energy latest EU policy developments Margot Pinault European Commission DG ENERGY Energy Efficiency unit POLICY BACKGROUND 1. Clean Energy Policy Package including: - The revision of Energy Performance
Clean Energy latest EU policy developments Margot Pinault European Commission DG ENERGY Energy Efficiency unit POLICY BACKGROUND 1. Clean Energy Policy Package including: - The revision of Energy Performance
Opportunities for African Participation in H2020. Information and Communication Technologies
 Opportunities for African Participation in H2020 Information and Communication Technologies 2016-2017 caast-net-plus.org CAAST-Net Plus is funded by the European Union s Seventh Framework Programme for
Opportunities for African Participation in H2020 Information and Communication Technologies 2016-2017 caast-net-plus.org CAAST-Net Plus is funded by the European Union s Seventh Framework Programme for
Secure, clean and efficient energy system Smart Citizen Centered Energy System Smart Cities
 Rémy Dénos Mark van Stiphout Jean-Marie Bemtgen DG ENER New Energy Technologies and Clean Coal Energy Info Days 2017 Secure, clean and efficient energy system Smart Citizen Centered Energy System Smart
Rémy Dénos Mark van Stiphout Jean-Marie Bemtgen DG ENER New Energy Technologies and Clean Coal Energy Info Days 2017 Secure, clean and efficient energy system Smart Citizen Centered Energy System Smart
Bioenergy research and innovation H2020 calls. Dr Maria GEORGIADOU Renewable Energy Sources DG Research & Innovation EUROPEAN COMMISSION
 Bioenergy research and innovation H2020 calls Dr Maria GEORGIADOU Renewable Energy Sources DG Research & Innovation EUROPEAN COMMISSION ETIP Bioenergy Workshop Emerging Technologies, Brussels,,4 June 2018
Bioenergy research and innovation H2020 calls Dr Maria GEORGIADOU Renewable Energy Sources DG Research & Innovation EUROPEAN COMMISSION ETIP Bioenergy Workshop Emerging Technologies, Brussels,,4 June 2018
Horizont 2020 Secure, clean and efficient energy
 Horizont 2020 Secure, clean and efficient energy Mari Habicht Minsk September 21, 2015 Smart cities and communities Energy efficiency Low carbon energy Smart grid Renewable energy sources Alternative fuels
Horizont 2020 Secure, clean and efficient energy Mari Habicht Minsk September 21, 2015 Smart cities and communities Energy efficiency Low carbon energy Smart grid Renewable energy sources Alternative fuels
EUROPEAN COMMISSION RTD - Energy ENER - Renewables, R&I, Energy Efficiency JRC Institute for Energy and Transport SET Plan Secretariat
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION RTD - Energy ENER - Renewables, R&I, Energy Efficiency JRC Institute for Energy and Transport SET Plan Secretariat SET-Plan Declaration of intent on strategic targets in the context
EUROPEAN COMMISSION RTD - Energy ENER - Renewables, R&I, Energy Efficiency JRC Institute for Energy and Transport SET Plan Secretariat SET-Plan Declaration of intent on strategic targets in the context
Tom Jennings Director, Policy & Markets. The role of innovation and collaboration in transforming the energy system
 Tom Jennings Director, Policy & Markets The role of innovation and collaboration in transforming the energy system Carbon Trust has accelerated sustainable, low carbon development for more than 10 years
Tom Jennings Director, Policy & Markets The role of innovation and collaboration in transforming the energy system Carbon Trust has accelerated sustainable, low carbon development for more than 10 years
European Investment Bank Climate Action. List of eligible sectors and eligibility criteria
 Climate Action List of eligible sectors and eligibility criteria REVISION HISTORY Revision No. Issue Date Amendment Description Version 1.0. 25 September 2015 First version included as Annex I of the EIB
Climate Action List of eligible sectors and eligibility criteria REVISION HISTORY Revision No. Issue Date Amendment Description Version 1.0. 25 September 2015 First version included as Annex I of the EIB
Putting energy efficiency first: consuming better, getting cleaner
 European Commission - Fact Sheet Putting energy efficiency first: consuming better, getting cleaner Brussels, 30 November 2016 A 30% energy efficiency target, efficient buildings, clarified ecodesign framework
European Commission - Fact Sheet Putting energy efficiency first: consuming better, getting cleaner Brussels, 30 November 2016 A 30% energy efficiency target, efficient buildings, clarified ecodesign framework
The intelligent cooperation between consumption and generation at the heart of the Smart Grid.
 Smart Energy Demand Coalition Position Paper The intelligent cooperation between consumption and generation at the heart of the Smart Grid. The SEDC Vision: To promote the active participation by the demand
Smart Energy Demand Coalition Position Paper The intelligent cooperation between consumption and generation at the heart of the Smart Grid. The SEDC Vision: To promote the active participation by the demand
The Smart Specialisation Platform on Energy
 The Smart Specialisation Platform on Energy Thematic Workshop on Energy Efficiency in Buildings Interreg Europe Policy Learning Platform Florence, 28 June 2018 What is Smart Specialisation? REGULATION
The Smart Specialisation Platform on Energy Thematic Workshop on Energy Efficiency in Buildings Interreg Europe Policy Learning Platform Florence, 28 June 2018 What is Smart Specialisation? REGULATION
Research and Innovation for the electricity networks in Europe
 Research and Innovation for the electricity networks in Europe Eric PEIRANO, TECHNOFI Grid+Storage Project Manager En.grids 016, Crystal Palace, Ljubljana, 11 May 2016 1 Outline The EU climate and energy
Research and Innovation for the electricity networks in Europe Eric PEIRANO, TECHNOFI Grid+Storage Project Manager En.grids 016, Crystal Palace, Ljubljana, 11 May 2016 1 Outline The EU climate and energy
Contractual Public-Private Partnerships in Horizon 2020
 Contractual Public-Private Partnerships in Horizon 2020 Evento PPPs 21 Gennaio 2014 Andrea GENTILI DG Research and Horizon 2020: Key elements A single programme with three pillars: societal challenges,
Contractual Public-Private Partnerships in Horizon 2020 Evento PPPs 21 Gennaio 2014 Andrea GENTILI DG Research and Horizon 2020: Key elements A single programme with three pillars: societal challenges,
We appreciate your feedback
 Publishing date: 22/09/2014 Document title: We appreciate your feedback Please click on the icon to take a 5 online survey and provide your feedback about this document ACER Trg Republike 3 1000 Ljubljana
Publishing date: 22/09/2014 Document title: We appreciate your feedback Please click on the icon to take a 5 online survey and provide your feedback about this document ACER Trg Republike 3 1000 Ljubljana
RES - Status Quo, Potential and Prospects Vasileios Tsolakidis, CRES
 RES - Status Quo, Potential and Prospects Vasileios Tsolakidis, CRES 20 June 2017, Thessaloniki Greek energy sector 2 Source: Eurostat (2017) RES targets Directive 2009/28/EC Gross final energy consumption
RES - Status Quo, Potential and Prospects Vasileios Tsolakidis, CRES 20 June 2017, Thessaloniki Greek energy sector 2 Source: Eurostat (2017) RES targets Directive 2009/28/EC Gross final energy consumption
Taking up the challenge of smart city refurbishment and energy efficiency in buildings. Astrid Severin Managing Director
 Taking up the challenge of smart city refurbishment and energy efficiency in buildings Astrid Severin Managing Director Greenovate! Europe is an independent, not-for-profit membership organisation. Profile
Taking up the challenge of smart city refurbishment and energy efficiency in buildings Astrid Severin Managing Director Greenovate! Europe is an independent, not-for-profit membership organisation. Profile
Energy Consumers and Energy Services
 Energy Consumers and Energy Services Talía Brun Marcén Project Advisor, Unit B.1 Energy Executive Agency for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (EASME) International Brokerage Event " Cities of the Future
Energy Consumers and Energy Services Talía Brun Marcén Project Advisor, Unit B.1 Energy Executive Agency for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (EASME) International Brokerage Event " Cities of the Future
Cefic Response to EC Consultation on the Review of Directive 2012/27/EU on Energy Efficiency
 Cefic Response to EC Consultation on the Review of Directive 2012/27/EU on Energy Efficiency 1.1 What is the key contribution of the EED to the achievement of the 2020 energy efficiency target? Unfortunately
Cefic Response to EC Consultation on the Review of Directive 2012/27/EU on Energy Efficiency 1.1 What is the key contribution of the EED to the achievement of the 2020 energy efficiency target? Unfortunately
THE EU FRAMEWORK PROGRAMME FOR RESEARCH AND INNOVATION HORIZON H Energy Calls European Commission
 THE EU FRAMEWORK PROGRAMME FOR RESEARCH AND INNOVATION HORIZON 2020 H2020 - Energy Calls 2016-2017 European Commission Content overview Context Relevant Calls 2016-2017 Energy Efficiency (EE) Competitive
THE EU FRAMEWORK PROGRAMME FOR RESEARCH AND INNOVATION HORIZON 2020 H2020 - Energy Calls 2016-2017 European Commission Content overview Context Relevant Calls 2016-2017 Energy Efficiency (EE) Competitive
Integrated SET Plan Actions No.1&2. ISSUES PAPER on OCEAN ENERGY
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION RTD - Energy ENER - Renewables, R&I, Energy Efficiency JRC Institute for Energy and Transport SET Plan Secretariat Integrated SET Plan Actions No.1&2 ISSUES PAPER on OCEAN ENERGY Purpose
EUROPEAN COMMISSION RTD - Energy ENER - Renewables, R&I, Energy Efficiency JRC Institute for Energy and Transport SET Plan Secretariat Integrated SET Plan Actions No.1&2 ISSUES PAPER on OCEAN ENERGY Purpose
REALISING VALUE FROM ELECTRICITY MARKETS WITH LOCAL SMART ELECTRIC THERMAL STORAGE TECHNOLOGY
 HORIZON 2020 CALL FOR COMPETITIVE LOW CARBON ENERGY REALISING VALUE FROM ELECTRICITY MARKETS WITH LOCAL SMART ELECTRIC THERMAL STORAGE TECHNOLOGY Rowena McCappin, Project Director Glen Dimplex April 2015
HORIZON 2020 CALL FOR COMPETITIVE LOW CARBON ENERGY REALISING VALUE FROM ELECTRICITY MARKETS WITH LOCAL SMART ELECTRIC THERMAL STORAGE TECHNOLOGY Rowena McCappin, Project Director Glen Dimplex April 2015
HORIZON Societal Challenges
 HORIZON 2020 Societal Challenges Addressing societal challenges: A political choice With the intensification and identification of the European and global challenges, the Europe 2020 Strategy called for
HORIZON 2020 Societal Challenges Addressing societal challenges: A political choice With the intensification and identification of the European and global challenges, the Europe 2020 Strategy called for
ERN Position Paper on Energy Performance of Buildings Directive
 ERN Position Paper on Energy Performance of Buildings Directive Introduction This paper sets out the key messages from the Europe Regional Network (ERN) of the World Green Building Council (WGBC) on the
ERN Position Paper on Energy Performance of Buildings Directive Introduction This paper sets out the key messages from the Europe Regional Network (ERN) of the World Green Building Council (WGBC) on the
Smart and Flexible 100 % Renewable District Heating and Cooling Systems for European Cities
 Smart and Flexible 100 % Renewable District Heating and Cooling Systems for European Cities Regional strategy Ireland (EN) Deliverable WP 2 Task 2.1 Del. 2.1 Improving the regional framework Survey of
Smart and Flexible 100 % Renewable District Heating and Cooling Systems for European Cities Regional strategy Ireland (EN) Deliverable WP 2 Task 2.1 Del. 2.1 Improving the regional framework Survey of
The catalyst for sustainable bio-based industries in Europe
 The catalyst for sustainable bio-based industries in Europe Bio-based Industries Joint Undertaking BBI JU The catalyst for sustainable bio-based industries in Europe 1 foreword When in October 2015 I
The catalyst for sustainable bio-based industries in Europe Bio-based Industries Joint Undertaking BBI JU The catalyst for sustainable bio-based industries in Europe 1 foreword When in October 2015 I
CLEAN TECHNOLOGY FUND INVESTMENT CRITERIA FOR PUBLIC SECTOR OPERATIONS 1
 CTF/TFC.2/3 January 16, 2009 Meeting of the CTF Trust Fund Committee Washington, D.C. January 29-30, 2009 CLEAN TECHNOLOGY FUND INVESTMENT CRITERIA FOR PUBLIC SECTOR OPERATIONS 1 1 These criteria are applicable
CTF/TFC.2/3 January 16, 2009 Meeting of the CTF Trust Fund Committee Washington, D.C. January 29-30, 2009 CLEAN TECHNOLOGY FUND INVESTMENT CRITERIA FOR PUBLIC SECTOR OPERATIONS 1 1 These criteria are applicable
LAW ON ENERGY EFFICIENCY
 Pursuant to article 82 paragraph 1 clause 2 and article 91 paragraph 1 of the Constitution of Montenegro, the Parliament of Montenegro during its 24th electoral term, on the fifth sitting in the first
Pursuant to article 82 paragraph 1 clause 2 and article 91 paragraph 1 of the Constitution of Montenegro, the Parliament of Montenegro during its 24th electoral term, on the fifth sitting in the first
Local and Regional State of Play and Policy Recommendations Concerning Sustainable Heating and Cooling: Focusing on EU Level Policy
 Local and Regional State of Play and Policy Recommendations Concerning Sustainable Heating and Cooling: Focusing on EU Level Policy This report was written by Christine Lucha and Andreas Prahl (Ecologic
Local and Regional State of Play and Policy Recommendations Concerning Sustainable Heating and Cooling: Focusing on EU Level Policy This report was written by Christine Lucha and Andreas Prahl (Ecologic
INCREASING THE NUMBER OF NEARLY ZERO ENERGY BUILDINGS
 INCREASING THE NUMBER OF NEARLY ZERO ENERGY BUILDINGS UK NATIONAL PLAN Contents Page Introduction 1 UK application of the nearly zero energy building definition 1 UK Government Strategy 3 Reducing demand
INCREASING THE NUMBER OF NEARLY ZERO ENERGY BUILDINGS UK NATIONAL PLAN Contents Page Introduction 1 UK application of the nearly zero energy building definition 1 UK Government Strategy 3 Reducing demand
Overview of renewable energy
 Overview of renewable energy Outline What is renewable energy? Renewable energy sources Renewable energy technologies: - Characteristics - Uses What is renewable energy? Energy that doesn t run out! Energy
Overview of renewable energy Outline What is renewable energy? Renewable energy sources Renewable energy technologies: - Characteristics - Uses What is renewable energy? Energy that doesn t run out! Energy
To the European Commission EU consultation on State aid for environmental protection
 EU consultation on State aid for environmental protection EDF thanks the Commission for the invitation for all interested parties to submit their comments on the review of the environmental protection
EU consultation on State aid for environmental protection EDF thanks the Commission for the invitation for all interested parties to submit their comments on the review of the environmental protection
WP LCE 1-5. Towards an integrated EU energy system. Rémy Dénos Henrik Dam DG Energy Unit C2 New Energy Technologies and Clean Coal
 1 WP 2016-2017 LCE 1-5 Towards an integrated EU energy system Rémy Dénos Henrik Dam DG Energy Unit C2 New Energy Technologies and Clean Coal Societal Challenge 3: Secure, Clean and Efficient Energy Main
1 WP 2016-2017 LCE 1-5 Towards an integrated EU energy system Rémy Dénos Henrik Dam DG Energy Unit C2 New Energy Technologies and Clean Coal Societal Challenge 3: Secure, Clean and Efficient Energy Main
D2.5 Country Report on Recommendations for Action for Development of EPC Markets
 D2.5 Country Report on Recommendations for Action for Development of EPC Markets NORWAY Transparense project This document has been conducted within the framework of project Transparense Increasing Transparency
D2.5 Country Report on Recommendations for Action for Development of EPC Markets NORWAY Transparense project This document has been conducted within the framework of project Transparense Increasing Transparency
HORIZON Why the challenge based approach?
 HORIZON 2020 Why the challenge based approach? Addressing societal challenges: A political choice With the intensification and identification of the European and global challenges, the Europe 2020 Strategy
HORIZON 2020 Why the challenge based approach? Addressing societal challenges: A political choice With the intensification and identification of the European and global challenges, the Europe 2020 Strategy
Sustainable development and climate
 Sustainable development and climate Gwendolyn Schaeken, Vinnova National Contact Point Legal & Financial issues and SC4; Transport Increased investment in sustainable development and climate related R&I:
Sustainable development and climate Gwendolyn Schaeken, Vinnova National Contact Point Legal & Financial issues and SC4; Transport Increased investment in sustainable development and climate related R&I:
EUROCITIES response to the circular economy package. February 2016
 EUROCITIES response to the circular economy package February 2016 Contents Executive summary:... 3 Introduction... 3 Production... 4 Product design... 4 New business models... 5 Consumption... 5 A resource
EUROCITIES response to the circular economy package February 2016 Contents Executive summary:... 3 Introduction... 3 Production... 4 Product design... 4 New business models... 5 Consumption... 5 A resource
THE COVENANT OF MAYORS FOR CLIMATE AND ENERGY
 THE COVENANT OF MAYORS FOR CLIMATE AND ENERGY We, the Mayors signing this Covenant, share a vision for a sustainable future - whatever the size of our municipality or its location on the world map. This
THE COVENANT OF MAYORS FOR CLIMATE AND ENERGY We, the Mayors signing this Covenant, share a vision for a sustainable future - whatever the size of our municipality or its location on the world map. This
European Energy Policy and Standardization Buildings and Building Components
 European Energy Policy and Standardization Buildings and Building Components J.J. BLOEM DG JRC http://ec.europa.eu/dgs/jrc Serving society Stimulating innovation Supporting legislation TOWARDS 2030 framework
European Energy Policy and Standardization Buildings and Building Components J.J. BLOEM DG JRC http://ec.europa.eu/dgs/jrc Serving society Stimulating innovation Supporting legislation TOWARDS 2030 framework
GLOBAL ENERGY TRANSFORMATION
 GLOBAL ENERGY TRANSFORMATION EXECUTIVE SUMMARY IRENA 2018 Unless otherwise stated, material in this publication may be freely used, shared, copied, reproduced, printed and/or stored, provided that appropriate
GLOBAL ENERGY TRANSFORMATION EXECUTIVE SUMMARY IRENA 2018 Unless otherwise stated, material in this publication may be freely used, shared, copied, reproduced, printed and/or stored, provided that appropriate
The CEEP should recognize the following initiatives that have been adopted by the City of Campbell River:
 CITY OF CAMPBELL RIVER REQUEST FOR PROPOSAL NO. 608 (SUSTAINABLE) OFFICIAL COMMUNITY PLAN (SOCP) UPDATE PARTNERS IN COMMUNITY APPENDIX B COMMUNITY ENERGY AND EMISSIONS PLAN Page 1 of 5 Proposal Background
CITY OF CAMPBELL RIVER REQUEST FOR PROPOSAL NO. 608 (SUSTAINABLE) OFFICIAL COMMUNITY PLAN (SOCP) UPDATE PARTNERS IN COMMUNITY APPENDIX B COMMUNITY ENERGY AND EMISSIONS PLAN Page 1 of 5 Proposal Background
DIRECTIVE (EU) 2018/2002 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 11 December 2018 amending Directive 2012/27/EU on energy efficiency
 L 328/210 DIRECTIVE (EU) 2018/2002 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 11 December 2018 amending Directive 2012/27/EU on energy efficiency (Text with EEA relevance) THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMT AND
L 328/210 DIRECTIVE (EU) 2018/2002 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 11 December 2018 amending Directive 2012/27/EU on energy efficiency (Text with EEA relevance) THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMT AND
Industrial Technology in Horizon KETs and PPPs - SPIRE. Søren Bøwadt DG Research and Innovation Directorate Industrial Technologies
 Industrial Technology in Horizon 2020 - KETs and PPPs - SPIRE Søren Bøwadt DG Research and Innovation Directorate Industrial Technologies Horizon 2020: Key elements A single programme with three pillars:
Industrial Technology in Horizon 2020 - KETs and PPPs - SPIRE Søren Bøwadt DG Research and Innovation Directorate Industrial Technologies Horizon 2020: Key elements A single programme with three pillars:
RWE Thames Water. GREEN PAPER ON PUBLIC-PRIVATE PARTNERSHIPS AND COMMUNITY LAW ON PUBLIC CONTRACTS AND CONCESSIONS COM(2004) 327 final
 GREEN PAPER ON PUBLIC-PRIVATE PARTNERSHIPS AND COMMUNITY LAW ON PUBLIC CONTRACTS AND CONCESSIONS COM(2004) 327 final Position RWE Thames Water Introduction: RWE Thames Water welcomes the Commission s Green
GREEN PAPER ON PUBLIC-PRIVATE PARTNERSHIPS AND COMMUNITY LAW ON PUBLIC CONTRACTS AND CONCESSIONS COM(2004) 327 final Position RWE Thames Water Introduction: RWE Thames Water welcomes the Commission s Green
Annex I : Description of the Project Development Services and the planned Investment Programme
 : Description of the Project Development Services and the planned Investment Programme Location of the Project Development Services Province of Bergamo, Italy. 1. Location Main purposes of the Project
: Description of the Project Development Services and the planned Investment Programme Location of the Project Development Services Province of Bergamo, Italy. 1. Location Main purposes of the Project
European Distribution System Operators for Smart Grids. Retail energy market: Supplementary response to the European Commission s public consultation
 European Distribution System Operators for Smart Grids Retail energy market: Supplementary response to the European Commission s public consultation April 2014 EDSO supplementary response to the European
European Distribution System Operators for Smart Grids Retail energy market: Supplementary response to the European Commission s public consultation April 2014 EDSO supplementary response to the European
Filippo Gagliardi. Global Leadership in Renewables
 Filippo Gagliardi Global Leadership in Renewables Next renewable energy solutions LC-SC3-RES-1-2019 Bringing these new energy conversion solutions, new renewable energy concepts and innovative renewable
Filippo Gagliardi Global Leadership in Renewables Next renewable energy solutions LC-SC3-RES-1-2019 Bringing these new energy conversion solutions, new renewable energy concepts and innovative renewable
Placing competitiveness at the heart of the Energy Package. 7 March, 2017
 Position Paper Placing competitiveness at the heart of the Energy Package 7 March, 2017 CEPI represents the European pulp and paper industry and gathers, through its 18 member countries, some 550 pulp,
Position Paper Placing competitiveness at the heart of the Energy Package 7 March, 2017 CEPI represents the European pulp and paper industry and gathers, through its 18 member countries, some 550 pulp,
(Text with EEA relevance) Having regard to the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union, and in particular Article 194(2) thereof,
 19.6.2018 Official Journal of the European Union L 156/75 DIRECTIVE (EU) 2018/844 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 30 May 2018 amending Directive 2010/31/EU on the energy performance of
19.6.2018 Official Journal of the European Union L 156/75 DIRECTIVE (EU) 2018/844 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 30 May 2018 amending Directive 2010/31/EU on the energy performance of
THE EU FRAMEWORK PROGRAMME FOR RESEARCH AND INNOVATION HORIZON H Energy Calls European Commission
 THE EU FRAMEWORK PROGRAMME FOR RESEARCH AND INNOVATION HORIZON 2020 H2020 - Energy Calls 2016-2017 European Commission Horizon 2020 Overall Objectives Responding to the economic crisis by investing in
THE EU FRAMEWORK PROGRAMME FOR RESEARCH AND INNOVATION HORIZON 2020 H2020 - Energy Calls 2016-2017 European Commission Horizon 2020 Overall Objectives Responding to the economic crisis by investing in
MACROECONOMIC IMPACTS OF THE LOW CARBON TRANSITION IN BELGIUM ANNEX 1 MAIN RESULTS
 MACROECONOMIC IMPACTS OF THE LOW CARBON TRANSITION IN BELGIUM ANNEX 1 MAIN RESULTS Analyzing the macroeconomic impacts of the transition to a low carbon society in Belgium Annex 1 Main results October
MACROECONOMIC IMPACTS OF THE LOW CARBON TRANSITION IN BELGIUM ANNEX 1 MAIN RESULTS Analyzing the macroeconomic impacts of the transition to a low carbon society in Belgium Annex 1 Main results October
The Smart Urban Energy Landscape
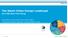 The Smart Urban Energy Landscape Micro MBA Smart Urban Energy Frits Verheij, Director Smart Green Cities, DNV GL Energy Delta Institute, Nyenrode - NL, September 22, 2016 1 27 September 2016 SAFER, SMARTER,
The Smart Urban Energy Landscape Micro MBA Smart Urban Energy Frits Verheij, Director Smart Green Cities, DNV GL Energy Delta Institute, Nyenrode - NL, September 22, 2016 1 27 September 2016 SAFER, SMARTER,
Eurogas Response to the CEER Public Consultation on Incentives Schemes for regulating DSOs, including for Innovation.
 Eurogas Response to the CEER Public Consultation on Incentives Schemes for regulating DSOs, including for Innovation. (A) Current principles and regulatory approaches 1. Is there any regulatory aim that
Eurogas Response to the CEER Public Consultation on Incentives Schemes for regulating DSOs, including for Innovation. (A) Current principles and regulatory approaches 1. Is there any regulatory aim that
A Clean Planet for all. A European strategic long term vision for a prosperous, modern, competitive and climate neutral economy
 A Clean Planet for all A European strategic long term vision for a prosperous, modern, competitive and climate neutral economy Political context Parties of the Paris Agreement to present long-term low
A Clean Planet for all A European strategic long term vision for a prosperous, modern, competitive and climate neutral economy Political context Parties of the Paris Agreement to present long-term low
Sant Cugat Smart City Strategy, achievements and perspectives
 Sant Cugat Smart City Strategy, achievements and perspectives Tuesday, May 31, 2016 Sant Cugat del Vallès, Barcelona, Spain This project is co-funded by the European Union Contents General information
Sant Cugat Smart City Strategy, achievements and perspectives Tuesday, May 31, 2016 Sant Cugat del Vallès, Barcelona, Spain This project is co-funded by the European Union Contents General information
ROADMAP. A. Context, Subsidiarity Check and Objectives
 TITLE OF THE INITIATIVE LEAD DG RESPONSIBLE UNIT AP NUMBER LIKELY TYPE OF INITIATIVE INDICATIVE PLANNING ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ROADMAP Communication on an EU strategy for Heating and Cooling the contribution
TITLE OF THE INITIATIVE LEAD DG RESPONSIBLE UNIT AP NUMBER LIKELY TYPE OF INITIATIVE INDICATIVE PLANNING ADDITIONAL INFORMATION ROADMAP Communication on an EU strategy for Heating and Cooling the contribution
EUROPEAN UNION HRIZON 2020 SMART CITY APPROACH AND ITS APPLICATION IN THE BULGARIAN CONTEXT
 23. Environmental Legislation, Multilateral Relations and Funding Opportunities EUROPEAN UNION HRIZON 2020 SMART CITY APPROACH AND ITS APPLICATION IN THE BULGARIAN CONTEXT Mrs. Ivanka Pandelieva-Dimova
23. Environmental Legislation, Multilateral Relations and Funding Opportunities EUROPEAN UNION HRIZON 2020 SMART CITY APPROACH AND ITS APPLICATION IN THE BULGARIAN CONTEXT Mrs. Ivanka Pandelieva-Dimova
Concept Note (Sept 2017)
 Concept Note (Sept 2017) Partnership of European Regions on Sustainable Buildings Opportunities for economic, social, environmental and territorial development linked to energy efficiency in buildings
Concept Note (Sept 2017) Partnership of European Regions on Sustainable Buildings Opportunities for economic, social, environmental and territorial development linked to energy efficiency in buildings
Building Energy and Location JRC Energy & Cities project; from building to urban area
 Building Energy and Location JRC Energy & Cities project; from building to urban area J.J. BLOEM DG JRC http://ec.europa.eu/dgs/jrc Serving society Stimulating innovation Supporting legislation BACKGROUND
Building Energy and Location JRC Energy & Cities project; from building to urban area J.J. BLOEM DG JRC http://ec.europa.eu/dgs/jrc Serving society Stimulating innovation Supporting legislation BACKGROUND
Sustainability: Building the future today
 Sustainability: Building the future today By: J.A.M. Baken, General Manager Ecofys BV 1 C.A.M. Stap, Managing Director Energy in the Built Environment, Ecofys BV 1. Introduction There is little need to
Sustainability: Building the future today By: J.A.M. Baken, General Manager Ecofys BV 1 C.A.M. Stap, Managing Director Energy in the Built Environment, Ecofys BV 1. Introduction There is little need to
Opportunities to Accelerate Smart Grid Deployment through Innovative Market Design
 2018-05-28 Opportunities to Accelerate Smart Grid Deployment through Innovative Market Design A discussion document prepared for the workshop and high-level panel discussion, Intelligent market design
2018-05-28 Opportunities to Accelerate Smart Grid Deployment through Innovative Market Design A discussion document prepared for the workshop and high-level panel discussion, Intelligent market design
CEOs OF LEADING EUROPEAN ENERGY COMPANIES CONTRIBUTION TO THE EUROPEAN COUNCIL, MARCH 2014
 CEOs OF LEADING EUROPEAN ENERGY COMPANIES CONTRIBUTION TO THE EUROPEAN COUNCIL, 20-21 MARCH 2014 The European energy and climate policy is at a crossroads. The three key pillars of competitiveness, security
CEOs OF LEADING EUROPEAN ENERGY COMPANIES CONTRIBUTION TO THE EUROPEAN COUNCIL, 20-21 MARCH 2014 The European energy and climate policy is at a crossroads. The three key pillars of competitiveness, security
Energy Performance of Buildings Directive and nearly-zero Energy Buildings
 Energy Performance of Buildings Directive and nearly-zero Energy Buildings J.J. BLOEM DG JRC http://ec.europa.eu/dgs/jrc Serving society Stimulating innovation Supporting legislation TOWARDS 2030 Framework
Energy Performance of Buildings Directive and nearly-zero Energy Buildings J.J. BLOEM DG JRC http://ec.europa.eu/dgs/jrc Serving society Stimulating innovation Supporting legislation TOWARDS 2030 Framework
Understanding the Energy Performance Contracting (EPC) model and process
 Understanding the Energy Performance Contracting (EPC) model and process Professor Theocharis Tsoutsos Director, Renewable and Sustainable Energy Systems Lab School of Environmental Engineering Technical
Understanding the Energy Performance Contracting (EPC) model and process Professor Theocharis Tsoutsos Director, Renewable and Sustainable Energy Systems Lab School of Environmental Engineering Technical
