New paradigms and developments for the future of train traffic management. Paris, France
|
|
|
- Anthony Powell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 New paradigms and developments for the future of train traffic management C. Lérin 1, X. Baumgard 2, G. Dessagne 1, F. Pinton 3, C. Weber 1 1 SNCF Innovation & Research Dept, 2 SNCF Engineering Dept, 3 SNCF Traffic Operation Dept, Paris, France Abstract The research program is carried out to design, prototype and experiment new decision support functions dedicated to the traffic management. In a final step, the objective is to connect these functions with the control and command layer, especially for route programming and transmission of speed or schedule instructions to trains. A new concept which is supported and modelled through the research program is the forecast train traffic plan. It updates the train traffic plan with the confirmed traffic management decisions and their foreseen consequences. This paper gives an overview of the target decision support system subject of the SNCF research program. Introduction When incidents or delays occur during train operating, decisions have to be made quickly to limit the consequences of this situation and to avoid snow-ball effects. This problem is complex because of the limited efficiency of local decisions and the quasi-necessity to build a global view of the potential consequences before choosing the best solution, or at least good ones. From the mathematical point of view, this problem is difficult and highly combinatorial. Despite of their great expertise, traffic managers and dispatchers come up against difficulties for estimating the impact of the occurring events, the consequences of their potential decisions, and to inform concerned people once decisions have been made. Additional difficulties arise from the fact that train traffic is increasing whereas traffic control centres become larger and larger in order to manage the whole traffic more globally. The research program is carried out to prototype and experiment helpful decision support functions for traffic management. The main objectives of such a program are to: - allow operators to better control disrupted situations and to improve their reactivity face to deviations and disruptions, - improve the quality of service of traffic management: reliability of the process; punctuality of trains; quality and precision of information given to train operating companies about the incidents and events, and about their consequences. Methodology The research program is carried out upon five main directions. Three axes concern the design and prototyping of decision support tools for the main traffic management functions which are: - traffic supervision, with projection of the foreseen consequences of the events and incidents; - primary incident management, with, among other themes, statistical estimation of the incident duration; - management of the incident consequences, with the help of what-if functions allowing the traffic manager to simulate solutions of his own, and re-scheduling functions proposing solutions to the operator. Beyond the simulation and optimisation approaches used for the prototyping of such tools, important themes are: the acquisition of knowledge about events and incidents, and the new representation modes for the user interfaces.
2 The research program follows also two transversal axes dealing with: co-operation methods and tools between the different actors of the traffic management process including external actors such as train operating companies, who interact a lot with the traffic management process; and human management, which mainly focuses on the ergonomics and acceptability of the new generation of decision support tools. These five axes are not sequential. There are linked all together and their interaction is a fundamental key of the traffic efficiency. A new concept: forecast train traffic plan Today, traffic management mainly relies on knowledge and representations of theoretical and current train traffic. The theoretical traffic plan stays the reference to comply with, whereas the situation and disruption of traffic make it temporarily unreachable in many real cases. Co-ordinating all involved actors is difficult, particularly when information about the state of the global system, the train location, etc. are imprecise and give too limited prediction for inferring the consequences of deviations from the plan. In order to overcome these difficulties, operational actors are quite free to interpret and act consequently the better as they can, according to their great professional experience, but without a real vision of the global objective. The new paradigm will give the priority to the global objective and plan, which the actions relative to local constraints should be subordinated to. The new concept which is supported and modelled through the research program is the forecast train traffic plan. It is the updated reference of the train traffic plan with the more recent decisions and their foreseen consequences. This is a great vector for information and decision broadcasting to concerned actors and systems. Theoretical train traffic plan t0 Forecast train traffic plan ti Traffic management Decisions taken between ti and tj Forecast train traffic plan tj Figure 1: forecast traffic plan The communication of this plan is done by: - display on man machine interfaces such as space-time diagrams, - transmission to the control-command layer mainly the system in charge of program and command of train routes, - transmission to other concerned systems and actors. The research program aims to allow planning and broadcasting of the forecast train traffic with the help of new decision support functions. Several steps are concerned, which are described in the following of the paper.
3 The target users of the new decision support system Three main responsibility levels are concerned by the traffic management process: - The control and command level, which is achieved by operators named agents circulation, that today are mainly in charge of security actions, and programming and command of train routes. The new system in deployment phase dedicated to these actors is MISTRAL. It provides accurate control views of the traffic in real-time and adapted mamachine interfaces for programming and commanding the routes for the trains. Automatism for local traffic management can be parameterised; for example, rules similar to the FIFO principle (for homogeneous traffic) or automatic programming of the theoretical traffic plan can be set. These automatisms can of course be bypassed by operator. In the target version of our system, the forecast traffic plan will be automatically programmed into the control and command system. The control and command level is not a target user of our decision support system, as it has a limited role in traffic management. This is the subject of other prospective studies relative to new human-machine interaction for example, that are outside the scope of this paper. - The regional traffic management level, organised around several juxtaposed centres covering the national infrastructure. This level is in charge of traffic management within its concerned geographical area: supervision of the train traffic, diagnostic and management of occurring incidents, management of the consequences of the incidents on the planned traffic and works (rescheduling). Traffic managers indeed mentally build the forecast traffic plans dealing only with their geographical areas. Existing tools support their missions, with graphical outputs such as space-time diagrams (GALITE tool) superimposing theoretical and current traffic. However, when incidents occur and disrupt the traffic, the current tools are not adapted for facing and solving the problems. Intensive oral communication must be engaged between actors in order to characterise the situation, find solutions and broadcast them. This level of management is the first privileged target of our system. - The national traffic management level, constituted by one national centre. Around the national traffic managers, operators from train operating companies are present to dialog and built new transport plans in case of major incidents or events. The national traffic management level is in charge of directly managing special traffic axis, such as high speed lines, and co-ordinating actions of the regional traffic centres in case of important incident or event often involving reduction of capacity. Today, the national traffic managers rely mainly upon the EXCALIBUR system [4]. This system centralises information about the network characteristics in order to quickly provide detailed information on and around the location of incidents. Incidents characteristics and management steps are described in realtime by operators into the system. That allows to broadcast information automatically, via Intranet geographical views or alert s. Moreover, this activity feeds a database that is used to estimate the duration of incidents in real-time, by comparison with similar incidents and statistical analysis of durations. Although the EXCALIBUR system is a first advanced step for decision support, two main complementary axes are to be developed. The first one aims to increase the effectiveness of the management system with the regional traffic management level and the train operating companies. The second one aims to improve and increase the decision support functions. This level of management is the second privileged target of our system. Traffic supervision and diagnostic The objectives of our supervision functions are classically to help operators for: 1. following the effective running of operations in order to correct it if necessary, 2. anticipating problems in order to have more time to solve them.
4 Knowledge of the current state of the traffic system Today, existing systems that follow the effective running of traffic are based on detectors installed on the infrastructure that are often too much spaced to give an accurate view of the traffic running and to detect problems in real-time. A system based on GPS technology enables to follow in real-time how the traffic is going on the network (current location, speed, delays, unexpected stops of trains, etc.). Combined with the ground detectors, this should be the basis of our system. Knowing the current state of the traffic system also means being aware in real time of the occurring (or foreseen) events and incidents that may have an impact on the traffic. This knowledge is today mainly acquired by oral and phone communication and is not always formalised into numerical systems. The EXCALIBUR system already stores and broadcasts real-time information about the main disruptions on the network (cf. figure 2). It constitutes the first milestone of our future information system about events and incidents tracking. We cannot get away from manual input for this kind of information, but we pay particular attention to the development, where possible, of automatic capture of data and alarm correlation and diagnosis. Figure 2: EXCALIBUR national view of incidents Estimation of the forecast state of the traffic system and anticipating problems Providing the forecast state of the traffic system to the operators will be helpful for anticipating problems, and then having more time to solve them. This function will be allowed by the continuous simulation and projection of the future states of the system, according to: - the last forecast traffic plan, - the current state of the traffic system (cf. previous paragraph), including the events and incidents occurring on the network and their estimated duration, - the knowledge, when possible, of future problems; for example, train operating companies shall inform as soon as possible the traffic manager of departures foreseen with delays, - the routes programmed by control operators who may have bypassed the last forecast traffic plan for some reason.
5 At the finest level, the kernel of this function calculates the forecast running of the trains, knowing their current characteristics and performances, the routes they have to follow (taking into account the current state of the infrastructure speed limitations, ), according to the last forecast traffic plan. The automatisms parameterised in the control and command system and the programming actions of operators are taken into account in the simulation, in order to allow the traffic managers to detect the eventual deviations from the last forecast traffic plan. Moreover, the events and incidents known by the system are included in the simulation, in order to allow the operators to anticipate their consequences on the traffic. This simulation will allow the operators to anticipate the deviations from the last forecast traffic plan, by: - visualisation of the projections on graphical interfaces (e.g. Space-time diagrams), - warnings about predicted conflicts between trains (and/or works), - indicators of deviations from the forecast traffic plan (delays, alerts on level of disruption, capacity reduction, ). Aggregated views of the forecast state of traffic have to be defined and produced, according to the levels of traffic management. Research works particularly concern here the real-time capacity and accurateness of simulation. A compromise has to be found between: - Microscopic simulation, that is up to give the more pertinent results, but needs many detailed data, particularly on infrastructure, and could require too much calculation time for real-time application; this kind of simulation is used in the SISYFE simulator [3], today used in traffic studies and robustness evaluation (cf. figure 3). - Macroscopic simulation, that provides less precise projections, but should be more compliant with real-time needs. This kind of projection is used in the LIPARI simulation environment of traffic management systems [6]. Figure 3: traffic simulation with SISYFE A train is delayed (bold dotted line) and SISYFE simulates the consequences on the other trains. Estimation of incident duration Concerning important incidents generally involving capacity reduction, the estimation of their impact on the traffic is strongly related to the value of the estimation of their duration. The
6 duration of an incident depends on many factors, such as the type (and subtype) of incident, its location, etc. EXCALIBUR provides today estimation about incident duration, statistically calculated from stored similar incidents (cf. figure 4). Research works are realised for refining this estimation (see [2] and next paragraph). 50% of this kind of incidents last less than 2h30 (median) 50% of this kind of incidents last between 1h30 and 4h03 If the incident lasts more than 4h00, its duration may reach 16h Figure 4: EXCALIBUR information box plot about estimated duration of incidents Incident management According to the nature, location and context of the incident, a lot of operations are to be done and supervised (emergency operations, infrastructure release interventions, etc.). Different scenarios can be built and evaluated for re-establishing the normal situation, in particular when a choice is possible between immediate, partially or totally postponed, repair of infrastructure. The impact of these scenarios on the traffic is evaluated in adapting and re-planning the forecast traffic plan see next paragraph. Once a scenario has been chosen, the effective running of operations has to be followed in order to be able to identify deviations from the scenario, re-evaluate the incident duration if necessary and re-plan the traffic forecast plan. It is considered to help the incident manager with tools to pilot the incident in a project management way, with the help of GANTT-like predefined diagrams (or on-demand built). Each of the needed operations for the incident management will be clearly formalised, with the necessary human resources team, the dependencies with other operations, the estimated duration time, etc. The global incident duration will be re-estimated automatically according to the endings of operations. These diagrams will be managed in real-time, and will allow the system to provide appropriate alerts about deviations of the forecast traffic plan. Adapting and re-scheduling forecast train traffic plan The supervision and diagnosis functions will allow the operators to estimate the level of disruption, to know which problem(s) they are facing, and then to enter a solving mode. A first level of decision support will offer what-if functions to the traffic manager in order to allow him to simulate solutions of his own, and to check their efficiency, before confirming one or several of those. The efficiency is measured by projecting and simulating the consequences of the decisions, and providing consequently performance indicators, for example the expected delays at strategic points (main stations, forks, etc.). A second level of decision support, that can be combined with the first one, will propose scenarios or new solutions to adapt the traffic plan or re-plan it, according to the level of
7 disruption (minor or extensive). This level will rely on predefined scenarios (when possible), case-based reasoning, and optimisation techniques. We can distinguish two main levels of disruption: - minor disruption level, which can be solved with actions such as re-ordering of trains or changing routes inside nodes. These disruptions are generally solved at the regional traffic management level, as they do not need strong co-ordination between centres. The adapted partial forecast traffic plan, once confirmed, is propagated to the next centres via the projection functions (cf. figure 5). - extensive disruption level, which is often related to reduction of capacity and which is mainly solved at the national level of traffic management. In that case, the traffic management has first to make the trains already on the network reach their destination, and then to determine the new traffic plan according to the available capacity. Decisions such as re-routing of trains or partitioning of line operations are made. This level of disruption needs interactive communication between the traffic manager and the train operating companies, for building the upper level forecast traffic plan. Once built and confirmed, the plan will be transmitted to the concerned regional traffic management centres to be eventually refined according to local constraints (track affectation in stations, residual conflict solving, etc.). After confirmation by the traffic managers, the forecast traffic plan will update the programming sequences at the control and command level for application. National traffic management centre (NTM) Regional traffic management centre (RTM) System NTM System RTM Regional traffic management centre (RTM) Remarkable points (RP) : Important RP visible at NTM System RTM Flow: Forecast times and speeds at boundary RP of enlarged NTM Forecast times at important RP Boundary point between two enlarged RTM Other point Figure 5: transmission of forecast traffic plans between regional traffic management centres Research works deal here in particular with the design and application of models and solving techniques for the traffic adapting and re-scheduling problem. Collaborative works with universities and public research centres are carried out in the framework of this research field (cf. [5] for some details about them). Schedule or speed instructions to trains A further step concerns the transmission of schedule or speed instructions to trains, in order to enhance free flow traffic in nodes or in line. Once the forecast traffic plan has been determined
8 and programmed, residual potential conflicts may locally remain (or appear). These small disturbances could be managed precisely by local free flow functions that aim to minimise the impact of the conflicts. The figure 6 gives an example of free-flow traffic simulation with the LIPARI tool. Train T1 Train T3 Train T2 Figure 6: free-flow traffic with LIPARI of three trains running on a track crossing Planned paths are in black. Train T1 has a delay of 5 minutes. Without speed instructions (red paths), the trains T2 and T3 lost time because of conflicts with respectively T1 and T2. With reduction speed instruction before the track crossing (blue paths), T2 and T3 encounter line clear signals, and delays are reduced. Research works and prospective studies have been realised on free-flow traffic (cf. [1] and [6] for the more recent ones). If it is recognised that the performance of the traffic system is increased with such techniques, some prerequisites must be achieved before operating them: train precise location and speed acquisition, means for transmission and presentation of instructions to drivers, coherence with signalling information, etc. The deployment of free-flow techniques will be facilitated in the framework of the present research program, in addition with other current prospective works about new information system for drivers. Ergonomic approach of new traffic management decision support functions The research works on decision support tools for traffic management have to take into consideration their use by the operators and the impact of these new artefacts on their competences. The operators activities could be deeply modified by the new concepts and functionalities that are studied. For that reason, research studies also include the determination of traffic management cognitive mechanisms and the modelling of the human-machine interaction. This topic includes also ergonomic improvement for the screen views, and new representation modes, in particular for supervision functions.
9 An early implication in the project of the concerned actors is also realised to ensure the success and acceptability of the project. Potential for implementation The main SNCF opportunity for the implementation of such a research program is the current RFF 1 project for the concentration of command and control centres. This project will lead to the generalisation of infrastructure installations remote control, and in the homogenisation of control centres technologies. These two important aspects of the project give the potentiality for the deployment of innovative decision support tools. This research program offers two major interests for railway business. The first and main one is of course turned towards Traffic Managers who this research program is dedicated to. The second concerns Train Operating Companies who will appreciate to increase the punctuality of their trains and to obtain better and more precise information about the current situation and the estimated delays of their trains; that will allow them to better master their production and anticipate the consequences of incidents on their resources planning, as to better inform their customers. Acknowledgements We gratefully acknowledge all the SNCF staff participating to the research program as well as our precious academic and industrial partners. We also want to address special thanks to our PhD students, trainee engineers, and service suppliers for their involvement and realizations in our projects. References [1] X. Baumgard, C. Lérin and A. Gouvernaire, Automatic speed management of the trains within a node, Proc. of WCRR Seoul, (2008) [2] M. Chandesris, Dynamic and real-time prediction of duration of incident, Proc. of WCRR Seoul, (2008). [3] M. Fontaine, D Gauyacq. SISYFE: a toolbox to simulate the railway network functioning for many purposes. Some cases of application, Proc. of WCRR Köln, (2001). [4] D. Gauyacq, P. Tariel, A. Lhote, D. De Almedia and M. Pellion. Outils d aide à la supervision et à la gestion en opérationnel des circulations, Revue Générale des Chemins de fer, n 143, p.17 (2005) [5] L. Gély, G. Dessagne and C. Lérin, Modelling Train Re-scheduling with Optimization and Operational research techniques, Proc. of WCRR Montreal, (2006) [6] C. Lérin, C. Joie, LIPARI: train management solutions for very dense traffic flows, Computers in Railways, (2004). 1 As owner and manager of the French rail network, RFF (Réseau Ferré de France) is responsible for its maintenance and operation. As required by the French government, these responsibilities are carried out by RFF and SNCF, to which management has been delegated.
THE ROLE OF HUMAN-COMPUTER INTERACTION IN DESIGN OF NEW TRAIN TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
 Bengt Sandblad 1 THE ROLE OF HUMAN-COMPUTER INTERACTION IN DESIGN OF NEW TRAIN TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS Bengt Sandblad1, Arne W. Andersson1, Ingemar Frej2 and Anders Gideon2 1CMD, Center for Human-Computer
Bengt Sandblad 1 THE ROLE OF HUMAN-COMPUTER INTERACTION IN DESIGN OF NEW TRAIN TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS Bengt Sandblad1, Arne W. Andersson1, Ingemar Frej2 and Anders Gideon2 1CMD, Center for Human-Computer
PRINCIPLES OF EMERGENCY PROCEDURES IN THE GAS TRANSMISSION: THE SNAM RETE GAS EXPERIENCE
 PRINCIPLES OF EMERGENCY PROCEDURES IN THE GAS TRANSMISSION: THE SNAM RETE GAS EXPERIENCE PRINCIPES DES PROCEDURES D ALERTE POUR LE TRANSPORT DU GAZ: L EXPERIENCE DE SNAM RETE GAS A. Cappanera, Snam Rete
PRINCIPLES OF EMERGENCY PROCEDURES IN THE GAS TRANSMISSION: THE SNAM RETE GAS EXPERIENCE PRINCIPES DES PROCEDURES D ALERTE POUR LE TRANSPORT DU GAZ: L EXPERIENCE DE SNAM RETE GAS A. Cappanera, Snam Rete
Transactions on the Built Environment vol 34, 1998 WIT Press, ISSN
 Improving the Dutch railway services by network-wide timetable simulation Jurjen S. Hooghiemstra", Dick M. Middelkoop", Maurice J.G. Teunisse^ " Railned, Dept. of Innovation, P.O.Box 2025, 3500 HA Utrecht,
Improving the Dutch railway services by network-wide timetable simulation Jurjen S. Hooghiemstra", Dick M. Middelkoop", Maurice J.G. Teunisse^ " Railned, Dept. of Innovation, P.O.Box 2025, 3500 HA Utrecht,
The project A cooperative ITS pilot in France
 43 RD ASECAP STUDY & INFORMATION DAYS 2015 43 RD ASECAP STUDY & INFORMATION DAYS 2015 The SCOOP@F project A cooperative ITS pilot in France 1 Guy Frémont - sanef 28/05/2015 PROJECT FIGURES Duration: 5
43 RD ASECAP STUDY & INFORMATION DAYS 2015 43 RD ASECAP STUDY & INFORMATION DAYS 2015 The SCOOP@F project A cooperative ITS pilot in France 1 Guy Frémont - sanef 28/05/2015 PROJECT FIGURES Duration: 5
MERLIN Project Project
 MERLIN Newsletter Issue 1, November 2014 MERLIN Project Project MERLIN Making Energy Management in the Rail System Smarter Background This project has received funding from the European Union s Seventh
MERLIN Newsletter Issue 1, November 2014 MERLIN Project Project MERLIN Making Energy Management in the Rail System Smarter Background This project has received funding from the European Union s Seventh
COMBINE: A decision support system for real time traffic control
 COMBINE: A decision support system for real time traffic control D. de Vries Holland Railconsult, The Netherlands Abstract This paper addresses the need for and benefits of advanced real-time traffic management
COMBINE: A decision support system for real time traffic control D. de Vries Holland Railconsult, The Netherlands Abstract This paper addresses the need for and benefits of advanced real-time traffic management
European Traffic Management Approaches for Increased Automation and Safety SUMMARY 1 INTRODUCTION 2 TRAFFIC OPTIMISATION APPROACHES
 European Traffic Management Approaches for Increased Automation and Safety Emmanuel Houriez, Alstom Ello Weits, Movares SUMMARY Many European countries are launching ambitious programs for Traffic Management
European Traffic Management Approaches for Increased Automation and Safety Emmanuel Houriez, Alstom Ello Weits, Movares SUMMARY Many European countries are launching ambitious programs for Traffic Management
SNCF eliminates disruptions and delays on its telecommunication services with remote wireless backup power monitoring
 SNCF eliminates disruptions and delays on its telecommunication services with remote wireless backup power monitoring Telecommunication systems are vital to the performance of France s national railway,
SNCF eliminates disruptions and delays on its telecommunication services with remote wireless backup power monitoring Telecommunication systems are vital to the performance of France s national railway,
INTRODUCTION 1 COMMERCIAL RESULTS TYPOLOGY. Performance of Yield Management. Challenge G: An even more competitive and cost efficient railway
 Performance of Yield Management TOPIC: Economic efficiency ABSTRACT NO: SESSION: A. REMY, E-mail: anais.remy2@sncf.fr, Phone: 33-1-53429278, Fax: 33-1-53429254 SNCF Innovation and Research Department,
Performance of Yield Management TOPIC: Economic efficiency ABSTRACT NO: SESSION: A. REMY, E-mail: anais.remy2@sncf.fr, Phone: 33-1-53429278, Fax: 33-1-53429254 SNCF Innovation and Research Department,
Tel (+49) , Fax (+49) ,
 Corresponding author: Jörg Schacht Mailing address: Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, Teilinstitut Greifswald, Wendelsteinstr. 1, D-17491 Greifswald, Tel (+49) 3834 882761, Fax (+49) 3834 882709, E-Mail:
Corresponding author: Jörg Schacht Mailing address: Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, Teilinstitut Greifswald, Wendelsteinstr. 1, D-17491 Greifswald, Tel (+49) 3834 882761, Fax (+49) 3834 882709, E-Mail:
Describing DSTs Analytics techniques
 Describing DSTs Analytics techniques This document presents more detailed notes on the DST process and Analytics techniques 23/03/2015 1 SEAMS Copyright The contents of this document are subject to copyright
Describing DSTs Analytics techniques This document presents more detailed notes on the DST process and Analytics techniques 23/03/2015 1 SEAMS Copyright The contents of this document are subject to copyright
Electrical Networks Principles and Performance
 Engineering Standard Electrical Networks Electrical Networks Principles and Performance Version: 1 Issued: January 2015 Owner: Chief Engineer Approved By: Paul O Halloran Chief Engineer PRINTOUT MAY NOT
Engineering Standard Electrical Networks Electrical Networks Principles and Performance Version: 1 Issued: January 2015 Owner: Chief Engineer Approved By: Paul O Halloran Chief Engineer PRINTOUT MAY NOT
Blueprint. What is U-space?
 Blueprint The demand for drone services is steadily increasing, with the potential to generate significant economic growth and societal benefits 1, as recognised in the 2015 EU Aviation Strategy 2, and
Blueprint The demand for drone services is steadily increasing, with the potential to generate significant economic growth and societal benefits 1, as recognised in the 2015 EU Aviation Strategy 2, and
Directive 96/48/EC - Interoperability of the trans- European high speed rail system
 EN Directive 96/48/EC - Interoperability of the trans- European high speed rail system Technical Specification for Interoperability "Operations and traffic management" Sub-System - 1 / 155 - 1. INTRODUCTION
EN Directive 96/48/EC - Interoperability of the trans- European high speed rail system Technical Specification for Interoperability "Operations and traffic management" Sub-System - 1 / 155 - 1. INTRODUCTION
THEFUTURERAILWAY THE INDUSTRY S RAIL TECHNICAL STRATEGY 2012 CONTROL, COMMAND AND COMMUNICATION
 THEFUTURERAILWAY THE INDUSTRY S RAIL TECHNICAL STRATEGY 2012 17 CONTROL, COMMAND AND COMMUNICATION Control centre optimises the positions of trains in real time Drivers receive information to optimise
THEFUTURERAILWAY THE INDUSTRY S RAIL TECHNICAL STRATEGY 2012 17 CONTROL, COMMAND AND COMMUNICATION Control centre optimises the positions of trains in real time Drivers receive information to optimise
Global position system technology to monitoring auto transport in Latvia
 Peer-reviewed & Open access journal www.academicpublishingplatforms.com The primary version of the journal is the on-line version ATI - Applied Technologies & Innovations Volume 8 Issue 3 November 2012
Peer-reviewed & Open access journal www.academicpublishingplatforms.com The primary version of the journal is the on-line version ATI - Applied Technologies & Innovations Volume 8 Issue 3 November 2012
Publishable Executive summary
 Publishable Executive summary Project no.: 516233 Project acronym: REACT Project title: Realizing Enhanced Safety and Efficiency in European Road Transport Instrument: Specific Targeted Research Project
Publishable Executive summary Project no.: 516233 Project acronym: REACT Project title: Realizing Enhanced Safety and Efficiency in European Road Transport Instrument: Specific Targeted Research Project
Integrated Product Developmenta Key to Affordability
 Integrated Product Developmenta Key to Affordability Gunnar Holmberg Future Products and Technology Saab AB (publ.) Abstract Integrated Product Development (IPD) has been a major approach to improve performance
Integrated Product Developmenta Key to Affordability Gunnar Holmberg Future Products and Technology Saab AB (publ.) Abstract Integrated Product Development (IPD) has been a major approach to improve performance
IRSE ETCS Seminar, Presentation Dr Laube, 15 November 2011
 IRSE ETCS Seminar, Presentation Dr Laube, 15 November 2011 ETCS IN DENMARK Gesamtlösungen sind unser Plus. l Emch+Berger AG Bern Schlösslistrasse 23 l Pf 6025 l CH 3001 Bern l Tel. +41 31 385 61 11 l bern@emchberger.ch
IRSE ETCS Seminar, Presentation Dr Laube, 15 November 2011 ETCS IN DENMARK Gesamtlösungen sind unser Plus. l Emch+Berger AG Bern Schlösslistrasse 23 l Pf 6025 l CH 3001 Bern l Tel. +41 31 385 61 11 l bern@emchberger.ch
Fall-Back Mode Operation on Remotely Controlled Railway Lines
 TRANSPORT Fall-Back Mode Operation on Remotely... Fall-Back Mode Operation on Remotely Controlled Railway Lines Attila Cseh, Balázs Sághi, Géza Tarnai Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Hungary
TRANSPORT Fall-Back Mode Operation on Remotely... Fall-Back Mode Operation on Remotely Controlled Railway Lines Attila Cseh, Balázs Sághi, Géza Tarnai Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Hungary
ViziRail Description
 ViziRail Description Table of Contents ViziRail Train Scheduling Software... 3 Timetabling and Trains... 4 Train Graphing... 9 Possessions... 14 Speed Restrictions... 16 Train Notices... 17 Train Control
ViziRail Description Table of Contents ViziRail Train Scheduling Software... 3 Timetabling and Trains... 4 Train Graphing... 9 Possessions... 14 Speed Restrictions... 16 Train Notices... 17 Train Control
Application for the UIC digital award: Productivity
 Application for the UIC digital award: Productivity Contact: Pierre JOLY Phone: +33(0) 6 67 31 20 94 E-mail: pierre.joly@ermeo.com Table of contents 1. Executive summary... 3 2. Project origin... 4 3.
Application for the UIC digital award: Productivity Contact: Pierre JOLY Phone: +33(0) 6 67 31 20 94 E-mail: pierre.joly@ermeo.com Table of contents 1. Executive summary... 3 2. Project origin... 4 3.
Asset Management Policy
 Asset Management Policy January 2018 Introduction Our Asset Management Policy was last published in 2014. It is being updated to reflect our commitment to regularly review and improve all of our Asset
Asset Management Policy January 2018 Introduction Our Asset Management Policy was last published in 2014. It is being updated to reflect our commitment to regularly review and improve all of our Asset
Evaluation of energy saving strategies in heavily used rail networks by implementing an integrated real-time rescheduling system
 Energy Management in the Train Operation 75 Evaluation of energy saving strategies in heavily used rail networks by implementing an integrated real-time rescheduling system M. Luethi Swiss Federal Institute
Energy Management in the Train Operation 75 Evaluation of energy saving strategies in heavily used rail networks by implementing an integrated real-time rescheduling system M. Luethi Swiss Federal Institute
Recovery from Railway Incidents
 Recovery from Railway Incidents Contact: Lynne Collis Tel: 07872158531 E-Mail: lmc883@bham.ac.uk Supervisors:Assoc. Professor Felix Schmid Dr Andrew Tobias Research Problem When railway incidents occur,
Recovery from Railway Incidents Contact: Lynne Collis Tel: 07872158531 E-Mail: lmc883@bham.ac.uk Supervisors:Assoc. Professor Felix Schmid Dr Andrew Tobias Research Problem When railway incidents occur,
Joint design standard for running times, dwell times and headway times
 Computers in Railways X 611 Joint design standard for running times, dwell times and headway times V. A. Weeda & P. B. L. Wiggenraad Department of Transport & Planning, Delft University of Technology,
Computers in Railways X 611 Joint design standard for running times, dwell times and headway times V. A. Weeda & P. B. L. Wiggenraad Department of Transport & Planning, Delft University of Technology,
TRANSCONTROL Project presentation. Marc POLLINA
 TRANSCONTROL Project presentation Marc POLLINA pollina@m3systems.net SCUTUM THINK TANK - LYON 7 th June 2011 1 SUMMARY CONCEPT & BACKGROUND PROJECT OVERVIEW TECHNICAL PROTOTYPE OPERATIONNAL TRIAL BENEFITS
TRANSCONTROL Project presentation Marc POLLINA pollina@m3systems.net SCUTUM THINK TANK - LYON 7 th June 2011 1 SUMMARY CONCEPT & BACKGROUND PROJECT OVERVIEW TECHNICAL PROTOTYPE OPERATIONNAL TRIAL BENEFITS
TAMING COMPLEXITY ON MAJOR RAIL PROJECTS WITH A COLLABORATIVE SYSTEMS ENGINEERING APPROACH
 TAMING COMPLEXITY ON MAJOR RAIL PROJECTS WITH A COLLABORATIVE SYSTEMS ENGINEERING APPROACH Chris Rolison CEO, Comply Serve Limited The Collaborative Systems Engineering Approach Collaboration A system
TAMING COMPLEXITY ON MAJOR RAIL PROJECTS WITH A COLLABORATIVE SYSTEMS ENGINEERING APPROACH Chris Rolison CEO, Comply Serve Limited The Collaborative Systems Engineering Approach Collaboration A system
FLOTATION CONTROL & OPTIMISATION
 FLOTATION CONTROL & OPTIMISATION A global leader in mineral and metallurgical innovation FLOATSTAR OVERVIEW Flotation is a complex process that is affected by a multitude of factors. These factors may
FLOTATION CONTROL & OPTIMISATION A global leader in mineral and metallurgical innovation FLOATSTAR OVERVIEW Flotation is a complex process that is affected by a multitude of factors. These factors may
TUNNEL OPERATION : THE E40-E25 LINK (LIEGE, BELGIUM) SPECIFIC SAFETY MEASURES AND EXPERIENCE FEEDBACK
 - 143 - TUNNEL OPERATION : THE E40-E25 LINK (LIEGE, BELGIUM) SPECIFIC SAFETY MEASURES AND EXPERIENCE FEEDBACK ABSTRACT Tillet D.; Blaszczak B. ISIS company, Walloon Ministry of Transport At the end of
- 143 - TUNNEL OPERATION : THE E40-E25 LINK (LIEGE, BELGIUM) SPECIFIC SAFETY MEASURES AND EXPERIENCE FEEDBACK ABSTRACT Tillet D.; Blaszczak B. ISIS company, Walloon Ministry of Transport At the end of
Available online at ScienceDirect. Transportation Research Procedia 14 (2016 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Transportation Research Procedia 14 (2016 ) 4582 4591 6th Transport Research Arena April 18-21, 2016 SCOOP@IdF: implementation of cooperative systems
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Transportation Research Procedia 14 (2016 ) 4582 4591 6th Transport Research Arena April 18-21, 2016 SCOOP@IdF: implementation of cooperative systems
How to reduce qualification time for new safety automated systems on rail infrastructure
 How to reduce qualification time for new safety automated systems on rail infrastructure Claire Guegan 1, Franck Corbier 2 1: RATP, 40 bis, rue Roger Salengro - 94724 Fontenay-sous-Bois Cedex 2: GEENSOFT,
How to reduce qualification time for new safety automated systems on rail infrastructure Claire Guegan 1, Franck Corbier 2 1: RATP, 40 bis, rue Roger Salengro - 94724 Fontenay-sous-Bois Cedex 2: GEENSOFT,
UIC CODE 406. Capacity. 1st edition, June 2004 Original. La Capacité Kapazität
 UIC CODE 1st edition, June 2004 Original Capacity La Capacité Kapazität Leaflet to be classified in Volume: IV - Operating Application: With effect from 1 June 2004 All members of the International Union
UIC CODE 1st edition, June 2004 Original Capacity La Capacité Kapazität Leaflet to be classified in Volume: IV - Operating Application: With effect from 1 June 2004 All members of the International Union
SP3 Framework development for capability trade-offs C4R Workshop M18 report 11 June 2015
 Capacity for Rail SP3 Framework development for capability trade-offs C4R Workshop M18 report 11 June 2015 Magnus Wahlborg Trafikverket, Swedish transport administration Working status Conclusion research
Capacity for Rail SP3 Framework development for capability trade-offs C4R Workshop M18 report 11 June 2015 Magnus Wahlborg Trafikverket, Swedish transport administration Working status Conclusion research
Automatic Development Tools. Abstract
 Automatic Development Tools in Software Engineering Courses Janusz Zalewski School of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science University of Central Florida Orlando, FL 32816-2450, USA jza@ece.engr.ucf.edu
Automatic Development Tools in Software Engineering Courses Janusz Zalewski School of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science University of Central Florida Orlando, FL 32816-2450, USA jza@ece.engr.ucf.edu
Auditing of Batch Processes
 Auditing of Batch Processes G. Janssens-Maenhout 1, L. Dechamp, J. B. Thevenon 2, P. Dransart 2 Institute for the Protection and the Security of the Citizen, Nuclear Safeguards Unit Joint Research Centre
Auditing of Batch Processes G. Janssens-Maenhout 1, L. Dechamp, J. B. Thevenon 2, P. Dransart 2 Institute for the Protection and the Security of the Citizen, Nuclear Safeguards Unit Joint Research Centre
ELECTRONIC TRAIN ORDERS
 ELECTRONIC TRAIN ORDERS and TRAIN CONTROL Inspired Systems Pty Ltd 70 Mordaunt Circuit, Canning Vale, Western Australia Ph +618 94565666 Fax +61 8 94565778 ELECTRONIC TRAIN ORDERS When you just don t have
ELECTRONIC TRAIN ORDERS and TRAIN CONTROL Inspired Systems Pty Ltd 70 Mordaunt Circuit, Canning Vale, Western Australia Ph +618 94565666 Fax +61 8 94565778 ELECTRONIC TRAIN ORDERS When you just don t have
Energy and Climate Change Committee Enquiry Progress on Smart Meter Roll Out
 Energy and Climate Change Committee Enquiry Progress on Smart Meter Roll Out 1. The roll out of smart meters is vitally important to our energy future; therefore we welcome the opportunity to submit evidence
Energy and Climate Change Committee Enquiry Progress on Smart Meter Roll Out 1. The roll out of smart meters is vitally important to our energy future; therefore we welcome the opportunity to submit evidence
INPUTS PROCESS OUTPUTS
 IM EXECUTIVE DIPLOM IN MNGEMENT OPERTIONS MNGEMENT The aim of the workshop is to introduce delegates to the concepts and tools and techniques used in Managing Operations and to consider the impact of legislation
IM EXECUTIVE DIPLOM IN MNGEMENT OPERTIONS MNGEMENT The aim of the workshop is to introduce delegates to the concepts and tools and techniques used in Managing Operations and to consider the impact of legislation
Innovation Programme 3:
 Innovation Programme 3: COST EFFICIENT - HIGH CAPACITY INFRASTRUCTURE Entreprise commune européenne Shift2Rail Information sur les appels à projets 2017 2 décembre 2016 2 Objectives High level objectives
Innovation Programme 3: COST EFFICIENT - HIGH CAPACITY INFRASTRUCTURE Entreprise commune européenne Shift2Rail Information sur les appels à projets 2017 2 décembre 2016 2 Objectives High level objectives
THE BALTIC SEA MOTORWAY - RECENT DEVELOPMENT AND OUTLOOK FOR THE FUTURE
 Journal of Maritime Research, Vol. IV. No. 2, pp. 21-30, 2007 Copyright 2007. SEECMAR Printed in Santander (Spain). All rights reserved ISSN: 1697-4840 THE BALTIC SEA MOTORWAY - RECENT DEVELOPMENT AND
Journal of Maritime Research, Vol. IV. No. 2, pp. 21-30, 2007 Copyright 2007. SEECMAR Printed in Santander (Spain). All rights reserved ISSN: 1697-4840 THE BALTIC SEA MOTORWAY - RECENT DEVELOPMENT AND
TECNOSITAF GET SMART GET INNOVATIVE
 TECNOSITAF GET SMART GET INNOVATIVE TECNOSITAF Tecnositaf designs, develops, manufactures, integrates, installs and manages systems, subsystems and equipment for controlling mobility and safety in the
TECNOSITAF GET SMART GET INNOVATIVE TECNOSITAF Tecnositaf designs, develops, manufactures, integrates, installs and manages systems, subsystems and equipment for controlling mobility and safety in the
Smarter Cities: Citizen Inclusion Citizen Collaboration & Social Media Analytics & Maturity Model Findings for Ljubljana
 Smarter Cities: Citizen Inclusion Citizen Collaboration & Social Media Analytics & Maturity Model Findings for Ljubljana Michele Leonardi, COO IBM Slovenia Big Data is the Next Great Natural Resource IBM
Smarter Cities: Citizen Inclusion Citizen Collaboration & Social Media Analytics & Maturity Model Findings for Ljubljana Michele Leonardi, COO IBM Slovenia Big Data is the Next Great Natural Resource IBM
Building and writing a competitive Marie Skłodowska-Curie Innovative Training Network (ITN) project proposal
 Building and writing a competitive Marie Skłodowska-Curie Innovative Training Network (ITN) project proposal Module 5 Writing a project Proposal (2) We will cover the most important sections of the proposal
Building and writing a competitive Marie Skłodowska-Curie Innovative Training Network (ITN) project proposal Module 5 Writing a project Proposal (2) We will cover the most important sections of the proposal
EDF EVALUATES SMART METERING IN MARTINIQUE: EXPECTATIONS & LOCAL REVIEW
 EDF EVALUATES SMART METERING IN MARTINIQUE: EXPECTATIONS & LOCAL REVIEW Joseph MAIRE Laure CHOSSEGROS Gilles RONDY EDF SEI France EDF SEI - France EDF Martinique - France Joseph.maire@edf.fr Laure.chossegros@edf.fr
EDF EVALUATES SMART METERING IN MARTINIQUE: EXPECTATIONS & LOCAL REVIEW Joseph MAIRE Laure CHOSSEGROS Gilles RONDY EDF SEI France EDF SEI - France EDF Martinique - France Joseph.maire@edf.fr Laure.chossegros@edf.fr
Asset management of computerized signaling systems: how to keep the balance between safety, security and investments?
 Asset management of computerized signaling systems: how to keep the balance between safety, security and investments? 23th November 2016 Dr. Marc Antoni FIRSE AFFI VDEI Rail System Director antoni@uic.org
Asset management of computerized signaling systems: how to keep the balance between safety, security and investments? 23th November 2016 Dr. Marc Antoni FIRSE AFFI VDEI Rail System Director antoni@uic.org
MERLIN Project Project
 MERLIN Newsletter Issue 2, December 2015 MERLIN Project Project MERLIN Making Energy Management in Rail System Smarter A summary of the latest achievements Background Energy management is currently and
MERLIN Newsletter Issue 2, December 2015 MERLIN Project Project MERLIN Making Energy Management in Rail System Smarter A summary of the latest achievements Background Energy management is currently and
Requirement Analysis Document
 Requirement Analysis Document For A police vehicle command and control system Group Members: Barbara Anne Fernandiz (Group Leader) Girubalani a/p Garnarajan Patricia a/p Arokiasamy Subhashini a/p Ramalinggam
Requirement Analysis Document For A police vehicle command and control system Group Members: Barbara Anne Fernandiz (Group Leader) Girubalani a/p Garnarajan Patricia a/p Arokiasamy Subhashini a/p Ramalinggam
Ways and Ideas to train Aviation Professionals for Today and Tomorrow
 Ways and Ideas to train Aviation Professionals for Today and Tomorrow Farid ZIZI Montreal, 1-4 March 2010 How to assume That Initial training and Education prepare for a complete and perhaps long career
Ways and Ideas to train Aviation Professionals for Today and Tomorrow Farid ZIZI Montreal, 1-4 March 2010 How to assume That Initial training and Education prepare for a complete and perhaps long career
Building a Safety Case for Automated Mobility: Smart Cities and Autonomous Mobility Getting There Safely
 Building a Safety Case for Automated Mobility: Smart Cities and Autonomous Mobility Getting There Safely Building a Safety Case for Automated Mobility: Smart Cities and Autonomous Mobility Getting There
Building a Safety Case for Automated Mobility: Smart Cities and Autonomous Mobility Getting There Safely Building a Safety Case for Automated Mobility: Smart Cities and Autonomous Mobility Getting There
Usine Logicielle. Position paper
 Philippe Mils: Contact : Thales Resear & Technology Usine Logicielle Project Coordinator philippe.mils@thalesgroup.com Abstract Usine Logicielle Position paper Usine Logicielle is a project operated in
Philippe Mils: Contact : Thales Resear & Technology Usine Logicielle Project Coordinator philippe.mils@thalesgroup.com Abstract Usine Logicielle Position paper Usine Logicielle is a project operated in
An Architecture for the Agricultural Machinery Intelligent Scheduling in Cross-Regional Work Based on Cloud Computing and Internet of Things
 An Architecture for the Agricultural Machinery Intelligent Scheduling in Cross-Regional Work Based on Cloud Computing and Internet of Things Sun Zhiguo 1,2, Xia Hui 3, and Wang Wensheng 1,2 1 Agricultural
An Architecture for the Agricultural Machinery Intelligent Scheduling in Cross-Regional Work Based on Cloud Computing and Internet of Things Sun Zhiguo 1,2, Xia Hui 3, and Wang Wensheng 1,2 1 Agricultural
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter the background to the study is provided and the existing research gap is defined. The justification and aims of the study is provided and a scientific hypothesis
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION In this chapter the background to the study is provided and the existing research gap is defined. The justification and aims of the study is provided and a scientific hypothesis
IMPLEMENTATION, EVALUATION & MAINTENANCE OF MIS:
 IMPLEMENTATION, EVALUATION & MAINTENANCE OF MIS: The design of a management information system may seem to management to be an expensive project, the cost of getting the MIS on line satisfactorily may
IMPLEMENTATION, EVALUATION & MAINTENANCE OF MIS: The design of a management information system may seem to management to be an expensive project, the cost of getting the MIS on line satisfactorily may
DISCUSSION PAPER ON ACCESS TO SERVICE FACILITIES AND RAIL RELATED SERVICES
 DISCUSSION PAPER ON ACCESS TO SERVICE FACILITIES AND RAIL RELATED SERVICES Disclaimer: This discussion paper does not prejudge the existing or future positions of the European Commission and its services
DISCUSSION PAPER ON ACCESS TO SERVICE FACILITIES AND RAIL RELATED SERVICES Disclaimer: This discussion paper does not prejudge the existing or future positions of the European Commission and its services
Improvement on the Acceptance of a Conflict Resolution System by Air Traffic Controllers. R. Flicker, Technical University Berlin
 Improvement on the Acceptance of a Conflict Resolution System by Air Traffic Controllers R. Flicker, Technical University Berlin Outline 1. Background 1. Multi-Sector-Planning 2. Development of Conflict
Improvement on the Acceptance of a Conflict Resolution System by Air Traffic Controllers R. Flicker, Technical University Berlin Outline 1. Background 1. Multi-Sector-Planning 2. Development of Conflict
Architectures of Automatic Train Operation for the mainline railway
 Architectures of Automatic Operation for the mainline railway RailTech Intelligent Rail Summit, 28 November 2017 x.rao@systransis.ch systransis Ltd 2017 Speed(v) Time (t) Speed (v) Non-optimised v-s Time
Architectures of Automatic Operation for the mainline railway RailTech Intelligent Rail Summit, 28 November 2017 x.rao@systransis.ch systransis Ltd 2017 Speed(v) Time (t) Speed (v) Non-optimised v-s Time
How to map excellence in research and technological development in Europe
 COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, 12.3.2001 SEC(2001) 434 COMMISSION STAFF WORKING PAPER How to map excellence in research and technological development in Europe TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION...
COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, 12.3.2001 SEC(2001) 434 COMMISSION STAFF WORKING PAPER How to map excellence in research and technological development in Europe TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION...
International ejournals
 ISSN 2249 5460 Available online at www.internationalejournals.com International ejournals International Journal of Mathematical Sciences, Technology and Humanities 21 (2011) 205 212 ENERGY CONTROL CENTER
ISSN 2249 5460 Available online at www.internationalejournals.com International ejournals International Journal of Mathematical Sciences, Technology and Humanities 21 (2011) 205 212 ENERGY CONTROL CENTER
Keyword Constraint programming, Train traffic rescheduling system, Train operation, Car operation, Driver operation
 Constraints Based Effective railway Rescheduling System Hiroyuki SHIMIZU, Hirohisa FUJIMOTO JR East Japan Information Systems Company JR East Japan Head Office Bldg 9F 2-2-2 Yoyogi, Shibuya-ku, Tokyo,
Constraints Based Effective railway Rescheduling System Hiroyuki SHIMIZU, Hirohisa FUJIMOTO JR East Japan Information Systems Company JR East Japan Head Office Bldg 9F 2-2-2 Yoyogi, Shibuya-ku, Tokyo,
7 9 May 2012, Dubrovnik, Croatia 2 nd International Conference on Road and Rail Infrastructure
 7 9 May 2012, Dubrovnik, Croatia 2 nd International Conference on Road and Rail Infrastructure Using simulation to assess infrastructure performance in multicriteria evaluation of railway projects Giovanni
7 9 May 2012, Dubrovnik, Croatia 2 nd International Conference on Road and Rail Infrastructure Using simulation to assess infrastructure performance in multicriteria evaluation of railway projects Giovanni
PTA THIRD PARTY RAIL ACCESS TRAIN MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES Rev1.00
 PTA THIRD PARTY RAIL ACCESS TRAIN MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES PTA Third Party Rail Access - Train Management Guidelines Contents 1. INTRODUCTION 3 1.1 Background 3 1.2 Relevance of the Train Management Guidelines
PTA THIRD PARTY RAIL ACCESS TRAIN MANAGEMENT GUIDELINES PTA Third Party Rail Access - Train Management Guidelines Contents 1. INTRODUCTION 3 1.1 Background 3 1.2 Relevance of the Train Management Guidelines
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) Program C3 - Customer Prepays for Services
 AMI Use Case: C3 - Customer prepays for electric services June 6, 006 Author: Deborah Tillman Author: Deborah Tillman Page 1 of Document History Revision History Date of this revision: 01-6-06 Revision
AMI Use Case: C3 - Customer prepays for electric services June 6, 006 Author: Deborah Tillman Author: Deborah Tillman Page 1 of Document History Revision History Date of this revision: 01-6-06 Revision
Ground. Vehicle. Management System
 Ground Vehicle Management System 1 Introduction GVMS (Ground Vehicle Management System) is able to: Manage fleet of vehicles moving in airport, using a D- GPS and a UHF communication channel; show on the
Ground Vehicle Management System 1 Introduction GVMS (Ground Vehicle Management System) is able to: Manage fleet of vehicles moving in airport, using a D- GPS and a UHF communication channel; show on the
CONCEPTUAL DESIGN OF AN AUTOMATED REAL-TIME DATA COLLECTION SYSTEM FOR LABOR-INTENSIVE CONSTRUCTION ACTIVITIES
 CONCEPTUAL DESIGN OF AN AUTOMATED REAL-TIME DATA COLLECTION SYSTEM FOR LABOR-INTENSIVE CONSTRUCTION ACTIVITIES H. Randolph Thomas The Pennsylvania State University Research Building B University Park,
CONCEPTUAL DESIGN OF AN AUTOMATED REAL-TIME DATA COLLECTION SYSTEM FOR LABOR-INTENSIVE CONSTRUCTION ACTIVITIES H. Randolph Thomas The Pennsylvania State University Research Building B University Park,
ISO Smart Grid Use Case
 Smart Grid Roadmap DRAFT IC-2 ISO publishes indicators of grid conditions with expectations IC-2 ISO publishes indicators of grid conditions with expectations consumers will adjust usage ISO Smart Grid
Smart Grid Roadmap DRAFT IC-2 ISO publishes indicators of grid conditions with expectations IC-2 ISO publishes indicators of grid conditions with expectations consumers will adjust usage ISO Smart Grid
NETWORK OPERATOR RESPONSIBILITIES
 NETWORK OPERATOR RESPONSIBILITIES A: Introduction This paper considers what makes up the role of the operators (as Highway Authorities) of the Major Road Network (MRN), be they a county or unitary authority,
NETWORK OPERATOR RESPONSIBILITIES A: Introduction This paper considers what makes up the role of the operators (as Highway Authorities) of the Major Road Network (MRN), be they a county or unitary authority,
ON-TRIP TRAVELLER INFORMATION USING VMS - INCIDENT DETECTION AND VMS AT KÖLN - ZOO BRIDGE EUROSCOPE
 CAPE - GOOD PRACTICE EXAMPLES IN TRANSPORT TELEMATICS 1 DEMONSTRATION SITE: COLOGNE/GERMANY NAME OF THE DEMONSTRATION PROJECT (CASE STUDY): DURATION OF THE PROJECT: 1996-1999 NAME OF THE TAP PROJECT: URBAN
CAPE - GOOD PRACTICE EXAMPLES IN TRANSPORT TELEMATICS 1 DEMONSTRATION SITE: COLOGNE/GERMANY NAME OF THE DEMONSTRATION PROJECT (CASE STUDY): DURATION OF THE PROJECT: 1996-1999 NAME OF THE TAP PROJECT: URBAN
STRATEGIC INFRASTRUCTURES AND TRANSPORT PLAN PEIT. FIGURE 25. The rail network. Actions under the PEIT
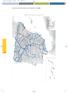 PEIT 2005-Cap-06 8/3/06 13:29 Página 94 FIGURE 25. The rail network. Actions under the PEIT 94 PEIT 2005-Cap-06 8/3/06 13:29 Página 95 FIGURE 26. The rail network. The 2020 horizon 95 PEIT 2005-Cap-06
PEIT 2005-Cap-06 8/3/06 13:29 Página 94 FIGURE 25. The rail network. Actions under the PEIT 94 PEIT 2005-Cap-06 8/3/06 13:29 Página 95 FIGURE 26. The rail network. The 2020 horizon 95 PEIT 2005-Cap-06
OJT INSTRUCTOR. Learning outcomes. Why study this course? Aim. ICAO Code 212
 OJT INSTRUCTOR ICAO Code 212 ATC Operational Training 10 days Air Traffic Controllers The younger generation expects to know how they are achieving and they want to engage and take responsibility for their
OJT INSTRUCTOR ICAO Code 212 ATC Operational Training 10 days Air Traffic Controllers The younger generation expects to know how they are achieving and they want to engage and take responsibility for their
On Board Use and Application of Computer based systems
 (Dec 2006 (Corr.1 Oct 2007) (Rev.1 Sept 2010) (Rev.2 June 2016 Complete Revision) On Board Use and Application of Computer based systems 1. Introduction 1.1 Scope These requirements apply to design, construction,
(Dec 2006 (Corr.1 Oct 2007) (Rev.1 Sept 2010) (Rev.2 June 2016 Complete Revision) On Board Use and Application of Computer based systems 1. Introduction 1.1 Scope These requirements apply to design, construction,
Improved operations control and real-time passenger information features allow for higher service quality
 istock Société de transport de Montréal (STM) Improved operations control and real-time passenger information features allow for higher service quality Public transport that attracts passengers is all
istock Société de transport de Montréal (STM) Improved operations control and real-time passenger information features allow for higher service quality Public transport that attracts passengers is all
Modeling Traffic Flow under Emergency Evacuation Situations: Current Practice and Future Direction
 Modeling Traffic Flow under Emergency Evacuation Situations: Current Practice and Future Direction Kevin D. Moriarty Research Assistant Transportation Engineering November 16, 2006 Overview Introduction
Modeling Traffic Flow under Emergency Evacuation Situations: Current Practice and Future Direction Kevin D. Moriarty Research Assistant Transportation Engineering November 16, 2006 Overview Introduction
Operational Excellence in Upstream Oil and Gas
 Operational Excellence in Upstream Oil and Gas What is Operational Excellence? Is a consulting process that benchmarks the automation in your company against Industry Best Practices, for the following
Operational Excellence in Upstream Oil and Gas What is Operational Excellence? Is a consulting process that benchmarks the automation in your company against Industry Best Practices, for the following
Diagnostic Study of the Implementation and Demand for New Technologies in Road and Rail
 Diagnostic Study of the Implementation and Demand for New Technologies in Road and Rail Ángel Cabo Astudillo Head of Projects Directorate General of Land Transport Ministry of Development 8th June 2012
Diagnostic Study of the Implementation and Demand for New Technologies in Road and Rail Ángel Cabo Astudillo Head of Projects Directorate General of Land Transport Ministry of Development 8th June 2012
Investigations and field results for high speed moving crossings
 Investigations and field results for high speed moving crossings Ph.Pouligny 1, S.Nierengarten 1, J. Plu 1, J.Y. Grunchec 1, JM.Pauchet 1 ; M.Sebes 2, D.Boulanger 3 ; Ph. Mugg 4, L.Winiar 5, W.Schöch 6
Investigations and field results for high speed moving crossings Ph.Pouligny 1, S.Nierengarten 1, J. Plu 1, J.Y. Grunchec 1, JM.Pauchet 1 ; M.Sebes 2, D.Boulanger 3 ; Ph. Mugg 4, L.Winiar 5, W.Schöch 6
Traffic management in moving block railway systems: the results of the EU project COMBINE
 Traffic management in moving block railway systems: the results of the EU project COMBINE M. Giannettoni & S. Savio Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettrica - Universita di Genova (Italy) Abstract In this
Traffic management in moving block railway systems: the results of the EU project COMBINE M. Giannettoni & S. Savio Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettrica - Universita di Genova (Italy) Abstract In this
GRP System FX. The «all in one» railway surveying solution
 GRP System FX The «all in one» railway surveying solution Rail traffic without limits New challenges for railway construction and operation Borders open, centres of economic activity spread, people and
GRP System FX The «all in one» railway surveying solution Rail traffic without limits New challenges for railway construction and operation Borders open, centres of economic activity spread, people and
Smart grids summit, Nice February 2015, 19th
 Smart grids summit, Nice February 2015, 19th Maryse Anbar, R&D project manager 1 12/09/2013 Flexibility 1. Key challenges for European energy market 2. Greenlys : the agregator model and lessons learned
Smart grids summit, Nice February 2015, 19th Maryse Anbar, R&D project manager 1 12/09/2013 Flexibility 1. Key challenges for European energy market 2. Greenlys : the agregator model and lessons learned
Variable Speed Warnings on DMS
 Variable Speed Warnings on DMS Evolving Tools for Better Safety and Service Jeanne Olubogun, P.E. District Traffic Engineer - St. Louis Region Jeanne.Olubogun@modot.mo.gov 314-275-1536 2014 Traffic and
Variable Speed Warnings on DMS Evolving Tools for Better Safety and Service Jeanne Olubogun, P.E. District Traffic Engineer - St. Louis Region Jeanne.Olubogun@modot.mo.gov 314-275-1536 2014 Traffic and
RAIL TRAFFIC MANAGEMENT. High-level full-scale solutions for centralised traffic management
 RAIL TRAFFIC MANAGEMENT High-level full-scale solutions for centralised traffic management PROVEN RAILWAY SAFETY EXPERTISE Mipro is a Finnish railway system specialist with nearly 30 years of experience
RAIL TRAFFIC MANAGEMENT High-level full-scale solutions for centralised traffic management PROVEN RAILWAY SAFETY EXPERTISE Mipro is a Finnish railway system specialist with nearly 30 years of experience
MIST Version 5. Transportation Management for the Smart City. Make the most of your energy SM
 MIST Version 5 Transportation Management for the Smart City Make the most of your energy SM 04 Magelis ipc MIST Version 5 Part of Schneider Electric s SmartMobility TM suite of tools, Management Information
MIST Version 5 Transportation Management for the Smart City Make the most of your energy SM 04 Magelis ipc MIST Version 5 Part of Schneider Electric s SmartMobility TM suite of tools, Management Information
SAP Integrated Business Planning (IBP) Towards Digital Now
 SAP Integrated Business Planning (IBP) Towards Digital Now Digital transformation is changing the way we sell, buy, distribute, store, plan, communicate, organize, collaborate and generally speak the essence
SAP Integrated Business Planning (IBP) Towards Digital Now Digital transformation is changing the way we sell, buy, distribute, store, plan, communicate, organize, collaborate and generally speak the essence
Enterprise Asset Management. Enterprise Asset Management 1
 Enterprise Asset Management 1 Introduction Managing assets effectively is critical to the success of organisations that depend on complex physical assets to deliver services. Increasingly, operators and
Enterprise Asset Management 1 Introduction Managing assets effectively is critical to the success of organisations that depend on complex physical assets to deliver services. Increasingly, operators and
Ministère de l'ecologie, du Développement durable et de l'energie CONVENTION DE SUBVENTION N 10-MT-PREDITGO4-4-CVS
 Ministère de l'ecologie, du Développement durable et de l'energie CONVENTION DE SUBVENTION N 10-MT-PREDITGO4-4-CVS-124-20 Groupe Opérationnel 4 du PREDIT EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF PHYSICAL INTERNET SIMULATION
Ministère de l'ecologie, du Développement durable et de l'energie CONVENTION DE SUBVENTION N 10-MT-PREDITGO4-4-CVS-124-20 Groupe Opérationnel 4 du PREDIT EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF PHYSICAL INTERNET SIMULATION
MAKE LIFE EASIER FOR EVERYONE
 MAKE LIFE EASIER FOR EVERYONE Point-of-sale and information solutions for more efficient cities Increase revenues Improve traffic flows Reduce pollution www.parkeon.com THE CHALLENGES AHEAD Today, over
MAKE LIFE EASIER FOR EVERYONE Point-of-sale and information solutions for more efficient cities Increase revenues Improve traffic flows Reduce pollution www.parkeon.com THE CHALLENGES AHEAD Today, over
Safety Functions in Railways - a Structural Analysis of Safety Rules
 Preprint version of Harms-Ringdahl L. and Kecklund, L. Safety Functions in Railways - a Structural Analysis of Safety Rules. In Spitzer, U., Schmocker, U., and Dang, V.N. (eds.) Probabilistic Safety Assessment
Preprint version of Harms-Ringdahl L. and Kecklund, L. Safety Functions in Railways - a Structural Analysis of Safety Rules. In Spitzer, U., Schmocker, U., and Dang, V.N. (eds.) Probabilistic Safety Assessment
UIRNet as service infrastructure: The importance to be the National Logistics Platform. Andrea Campagna, Lazio Region Rodolfo De Dominicis, Uirnet
 UIRNet as service infrastructure: The importance to be the National Logistics Platform Andrea Campagna, Lazio Region Rodolfo De Dominicis, Uirnet Valencia - March 27, 2014 0 The context: Italian Logistics
UIRNet as service infrastructure: The importance to be the National Logistics Platform Andrea Campagna, Lazio Region Rodolfo De Dominicis, Uirnet Valencia - March 27, 2014 0 The context: Italian Logistics
1 Workshop on Power System Testing
 1 Workshop on Power System Testing DERlab/ SIRFN, 19 March 2015, 9:00 12:00 Moderators: Peter Vaessen (DNV GL), Wolfram Heckmann (Fraunhofer IWES) 1.1 Motivation Our society has become highly dependent
1 Workshop on Power System Testing DERlab/ SIRFN, 19 March 2015, 9:00 12:00 Moderators: Peter Vaessen (DNV GL), Wolfram Heckmann (Fraunhofer IWES) 1.1 Motivation Our society has become highly dependent
SUTRA : Sustainable Urban Transportation for the City of Tomorrow
 Preliminary Report SUTRA : Sustainable Urban Transportation for the City of Tomorrow WP 03: Multi-modal Transportation Modelling D03.3 User Manual and Example Test Data Sets First Draft Karlsruhe, January
Preliminary Report SUTRA : Sustainable Urban Transportation for the City of Tomorrow WP 03: Multi-modal Transportation Modelling D03.3 User Manual and Example Test Data Sets First Draft Karlsruhe, January
Evaluation of the emergency.lu project
 Evaluation of the emergency.lu project In 2016, the Directorate of Development Cooperation and humanitarian action of the Ministry of Foreign and European Affairs commissioned an independent evaluation
Evaluation of the emergency.lu project In 2016, the Directorate of Development Cooperation and humanitarian action of the Ministry of Foreign and European Affairs commissioned an independent evaluation
Rail stations: Typology, level of service and design process October 2013 Session 4-B; Connecting stations with the city
 Rail stations: Typology, level of service and design process de TILIERE; Guillaume Head of the Transport Group, Associate Professor Paris Est BG Consulting Engineers Session 4-B; Connecting stations with
Rail stations: Typology, level of service and design process de TILIERE; Guillaume Head of the Transport Group, Associate Professor Paris Est BG Consulting Engineers Session 4-B; Connecting stations with
1 Traffic information for applicants and traffic operators
 Traffic Information 1 Traffic information for applicants and traffic operators The information is supplied to applicants or traffic operators via a number of different channels, including e-mail, the internet,
Traffic Information 1 Traffic information for applicants and traffic operators The information is supplied to applicants or traffic operators via a number of different channels, including e-mail, the internet,
To define the size and nature of the opportunity realisable by effecting: a) quantum change within the organisation;
 The purpose of the Operational Due Diligence We firmly believe that packaged solutions, or predetermined outcomes, are an inadequate and inappropriate basis for a successful change process. In our experience,
The purpose of the Operational Due Diligence We firmly believe that packaged solutions, or predetermined outcomes, are an inadequate and inappropriate basis for a successful change process. In our experience,
Guidelines for the Application of Asset Management in Railway Infrastructure Organisations
 Guidelines for the Application of Asset Management in Railway Infrastructure Organisations INTERNATIONAL UNION OF RAILWAYS (UIC) 16 rue Jean Rey - F-75015 PARIS Tel: +33 (0)1 44 49 20 20 Fax: +33 (0)1
Guidelines for the Application of Asset Management in Railway Infrastructure Organisations INTERNATIONAL UNION OF RAILWAYS (UIC) 16 rue Jean Rey - F-75015 PARIS Tel: +33 (0)1 44 49 20 20 Fax: +33 (0)1
REPORT FROM THE COMMISSION TO THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT, THE COUNCIL, THE EUROPEAN ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COMMITTEE AND THE COMMITTEE OF THE REGIONS
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 19.9.2012 COM(2012) 515 final REPORT FROM THE COMMISSION TO THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT, THE COUNCIL, THE EUROPEAN ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COMMITTEE AND THE COMMITTEE OF THE REGIONS
EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 19.9.2012 COM(2012) 515 final REPORT FROM THE COMMISSION TO THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT, THE COUNCIL, THE EUROPEAN ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COMMITTEE AND THE COMMITTEE OF THE REGIONS
TRENOExport. The Simulationbooster
 TRENOExport The Simulationbooster TRENOEXPORT Microscopic simulation is the most accurate method for reproducing railway operations. It supports engineers in a series of tasks, from long-range to short-term
TRENOExport The Simulationbooster TRENOEXPORT Microscopic simulation is the most accurate method for reproducing railway operations. It supports engineers in a series of tasks, from long-range to short-term
Technological Training Programs
 Technological Training Programs On behalf of Noaman Engineering, I would like to introduce you to our training courses. All of our courses cover Theoretical, Practical, and software implementation and
Technological Training Programs On behalf of Noaman Engineering, I would like to introduce you to our training courses. All of our courses cover Theoretical, Practical, and software implementation and
Boosting International Rail Freight. Sector Statement on Rail Freight Corridors
 Boosting International Rail Freight Sector Statement on Rail Freight Corridors Brussels, 20 May 2016 1 Sector Statement on Rail Freight Corridors: Boosting International Rail Freight 20 May 2016 - final
Boosting International Rail Freight Sector Statement on Rail Freight Corridors Brussels, 20 May 2016 1 Sector Statement on Rail Freight Corridors: Boosting International Rail Freight 20 May 2016 - final
Graphical Systems Modeling with UML / SysML Activity diagrams
 Graphical Systems Modeling with UML / SysML Activity diagrams Piotr Ciskowski Perspectives - views: architecture class diagram object diagram composite structure diagram package diagram Logical view Use
Graphical Systems Modeling with UML / SysML Activity diagrams Piotr Ciskowski Perspectives - views: architecture class diagram object diagram composite structure diagram package diagram Logical view Use
