ε = Strain rate, s -1 ε = Strain σ = Stress, MPa δ = Deflection, mm Subscripts b Bending dyn Dynamic recrystallization
|
|
|
- Bryan Collins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sudipta Sikdar et al Sudipta Sikdar Shylu John Ashwin Pandit Raju Dasu Analysis of Roll Stack Deflection in a Hot Strip Mill Predictive models are required to provide the bending set point for bending for the flatness control devices at rolling stands of finishing mill of Hot Strip Mill (HSM). A simple model for roll stack deflection at the finishing mill has been illustrated where a modified Misaka s equation has been used to obtain mean flow-stress. Investigation has been performed to understand the effect of width of roll on roll stack deflection. The bending on the deflection has been found to have a positive effect to reduce the amount of the stack deflection. The results from the sensitivity analysis of the roll width on roll deflection are also described. Keywords: hot strip mill (HSM), finishing stands, mean flow stress (MFS), continuously variable crown (CVC), shear stress, bending. Introduction Predictive models are required to provide the bending set point for bending for the flatness control devices at rolling stands of finishing mill of Hot Strip Mill (HSM). A simple model for roll stack deflection at the finishing mill has been illustrated where a modified Misaka s equation has been used to obtain mean flowstress. Investigation has been performed to understand the effect of width of roll on roll stack deflection. The bending on the deflection has been found to have a positive effect to reduce the amount of the stack deflection. The results from the sensitivity analysis of the roll width on roll deflection are also described. Nomenclature A = Area of cross section of roll, m C = Carbon concentration in wt % D = Roll diameter at center, mm E = Young s Modulus, N/m F = Bending force, Newton I = Moment of Inertia, m 4 G = Shear modulus, N/m H = Entry thickness, mm h = Exit thickness, mm K = A constant (= 4/3) k = Constant in equation (9) L = Contact length between work roll and backup roll, m L = Moment arm for bending force, metre. M = Bending Moment, N-m. MFS = Mean flow stress, MPa Mn = Manganese concentration in wt % Nb = Niobium concentration in wt % P (x) = Force on work roll due to strip, Newton q(x) = Force on work roll due to backup roll, Newton Q = Geometrical factor R = Roll radius, mm r = Reduction at each pass, % S = Shearing force, Newton S r-bur = Shearing force due to back up roll, Newton S r-strip = Shearing force due to strip, Newton T = Temperature, o K Paper accepted March, 7. Technical Editor: Anselmo E. Diniz. Ti = Titanium concentration in wt % w = Width, mm X = Softening fraction x = Segmented length with reference to center, mm Y = Thickness of roll gap at neutral point, mm t = Tube thickness, m U = Overall heat transfer coefficient, W/(m K) Greek Symbols Φ = Neutral angle, radian ε = Strain rate, s - ε = Strain σ = Stress, MPa δ = Deflection, mm Subscripts b Bending dyn Dynamic recrystallization M Reference to Misaka s equation ss Steady state s Shear Scope and Policy Today s steel market is guided by the fulfillment of customer demand to meet the stringent requirement of strip quality. Out of various qualities required for the hot rolled product from steel producer, the most important one is the flatness on the strip produced from a Hot Strip Mill (HSM). In a typical HSM, shown in Fig., the strip from the roughing mill is passed through the finishing mill via intermediate coilbox. In general, the various contributing factors in the finishing mill of a hot strip mill such as, (i) The thermal crown (ii) The deflection of the work roll and back up roll (iii) The wear in the work roll, leads to the final shape of the strip produced. The final roll gap between the work roll is the cumulative effect of these three factors, which dictates the profile of the strip produced. The roll shifting and bending moment are applied in the rolls of the finishing mills to maintain the required crown and flatness in the strip produced. In a four-high hot strip mill, the finishing mill of the hot strip mill is equipped with two work-rolls and two back-up rolls and is shown in Fig.. During the passage of the strip between the two work rolls, a large amount of roll separating force is developed. This changes the initial set value of roll gap between the work rolls 84 / Vol. XXIX, No. 3, July-September 7 ABCM
2 Analysis of Roll Stack Deflection in a Hot Strip Mill (Wilms et al. (985)). Flatness is dependent on the roll gap or clearance between the working rolls during the process of rolling. Strip profile and flatness can be influenced by the mill features like work roll bending and CVC (Continuous Variable Crown) shifting. Roughing Mill Coil Box - Back-up Roll Run-out Table Finishing Mill Work Roll Figure. Layout of a typical Hot Strip Mill. Coil Down Coiler Hence, the knowledge of the contribution of the effect from work roll bending is essential to the people associated with the improvement of profile and flatness. In general, the roll separating force acting between the strip and the work rolls has a parabolic profile. In order to predict flatness and thickness of roll strips, it becomes indispensable to analyze the amount of roll. Bending Force strip Back-up roll Back-up roll q (x) p (x) Work roll Figure. Schematic diagram of forces acting during rolling conditions. A vast literature with different techniques fills the subject of the roll stack deflection. Out of various simple models, the roll deflection has been obtained from the beam theory in the model of Stone and Gray (965) where the rolls are presented as a simple beam. Later on this has been adopted by many workers. Another roll deflection model based on the beam theory for the evaluation of the roll deflection in plate rolling was used by Ohe et al. (994), where they assumed the pressure distribution between the rolled plate and the work roll as well as between the backup roll and the work roll to be a polynomial of fourth degree. Many other workers have also worked to determine the roll stack deflection for reducing the profile and flatness error. Steel producers can achieve improvement in the productivity and quality by improving the profile and flatness and for this reason; it is of utmost importance to analyze the effect of various parameters in improving the quality such as work roll deflection, backup roll deflection. This article describes a mathematical model based on simple deflection equations for each stand of six finishing mills in a hot strip mill and this describes the effect for a whole schedule of rolling. This simple model is an easy resort to estimate the roll deflection instead of several complex models described in the literature. The purpose of this work is to find out the effect of different parameters on roll deflection. For six stands, the overall roll deflection values are evaluated. The effects of the size of the strip width and roll bending values have also been studied. Strip Profile and Shape Profile and flatness in the rolling of strip are related to each other in rolling operation. Achieving the flatness requirements in rolling thinner gauge sheets has always been greater challenge as we encounter fewer flatness problems in rolling of thicker gauge sheets. Crown is the difference in thickness between the centre and at a point 4 mm from the edge of the strip (taken average of both sides). Flatness or Shape is defined by the degree to which a flat rolled product is planar, when not subjected to external constraining forces. The deflection of the work rolls results in a widthwise distribution of strip thickness in the form of a convex crown, in which the thickness is greater at the center of the width and smaller at the edges. This widthwise difference in thickness is known as the strip crown. To reduce the convex shape, in general, a bending force is applied in the opposite direction. The work roll bending forces are applied to the work roll chocks that are located at the roll ends. When roll bending forces are applied in the direction of opening the roll gap, this is known as positive or crown-in roll bending. Inversely, when the roll bending forces are applied in the direction of closing the roll gap, this type of bending is termed negative or crown-out roll bending. Positive roll bending causes the strip profile to be concave whereas negative roll bending causes the strip profile to be convex. Mill Configuration In the hot strip mill under study, the slabs from the slab caster are rolled into strips by reducing their thickness from mm to a value ranging from.6 mm to mm, with the width of the strip ranging from 86 to 54 mm. The slabs are heated and soaked in a Walking Beam type-reheating furnace up to a temperature of almost 5 o C. At four-high reversing roughing stand, the heated slabs are reduced to a thickness of 3 mm with seven passes. Finally, the required thickness is achieved in a four-high six-stand tandem finishing mill (F to F 6 ) at a finish rolling temperature of 87-9 o C, depending on the grades. Centrifugally cast high chrome rolls are used for the purpose of work rolls of six finishing mill having a barrel length of mm and a diameter ranging from 66 mm to 7 mm. With the objective to achieve required metallurgical properties at different coiling temperature, the strip from finishing stands are cooled in the Run Out Table (ROT), where it is water cooled and coiled finally in the down coiler. A large number of slabs are rolled in a schedule of rolling by the work rolls of finishing stands until work rolls are replaced at the end of the schedule. A whole schedule contains the mixture of the slabs of different grades of steels of different width and different target thickness in the hot strip mill. In general the number of strips produced from a schedule varies from 45-6 depending on the requirement and availability of slabs. A coffin schedule is followed in hot strip rolling to arrange the width of the slabs to be rolled. In this arrangement, slabs with lower width are placed at the beginning of the rolling and the width of slabs are gradually increased up to a maximum value and after that the width is reduced to close the starting values of slab width. In nutshell, the slabs arranged in this way looks like the shape of a coffin. Shapes of work roll As the length of the work roll and back up roll are equal, the effect of roll bending is not prominent to reduce the crown. To obviate this problem, the use of tapered crown work rolls in a Japanese steel plant, as mentioned in the paper by Kitahama et al. (987), was introduced, where shifting of the work roll was made to compensate for crown developed. Later on many plants use CVC J. of the Braz. Soc. of Mech. Sci. & Eng. Copyright 7 by ABCM July-September 7, Vol. XXIX, No. 3 / 85
3 Sudipta Sikdar et al (Continuously Variable Crown) developed by SMS (Schloemann- Siemag ) where the shifting the work rolls in the opposite directions reduces the roll separating force. The finishing mill is equipped with Continuous Variable Crown (CVC) technology with a maximum biaxial shifting of ± 5 mm for stands F to F 6 and roll bending (F to F 6 ) for shape control. The work rolls in stand are cylindrical. In CVC system, two axially rolls have a shape of S and deviate from a cylindrical shape by a dimension of range of microns. The opposite shifting enables the operator to achieve symmetrical thickness profile. The movement of the both rolls in pair in the opposite direction acts like the conventional cylindrical rolls to produce a crown. A smaller or bigger size of crown can be achieved by the mode of the direction of the shifting. The work-roll shifting type aims to make the strip thickness uniform and improve the flatness over a wide range of strip widths by shifting CVC rolls. A linear relationship exists between the effective roll crown and the CVC shifting. The range of crown adjustment depends on the shifting distance and the difference between the maximum and minimum diameter of the S-shaped roll. Deflection by Bending, d δ E. I. dx b = M Deflection by shear stress, GA K dδ s. = S () dx where, E : Young s Modulus, I: Moment of inertia, S: Shearing force, A: Area of cross section of roll, M: bending Moment, G: Modulus of rigidity, K: 4/3. For the determination of bending moment, the roll force is required. In this model the roll force is calculated first. The flow diagram of roll stack deflection model is shown in Fig. 4. Entry & Exit Thickness Roll Diameter () Mathematical Model In this section, we describe the method of development of the deflection model, based on short beam deflection theory, to predict the deflection of the work roll at different positions along the length of the roll at the finishing stands of the Hot Strip Mill. This model takes into account the following assumptions: (i) The work roll is considered to be cylindrical instead of CVC roll. (ii) No work roll shifting is considered. Width of Coil Roll Force Model Roll force Stack Deflection Model Chemical composition S r_bur q(x)dx WR P (x)dx X S r_strip w/ L/ L / WR F/ Figure 3. Free body diagram of work roll. To develop a simple deflection model the deflection of the work-roll and back-up roll are considered. For the calculation of the roll deflection, the theory uses the roll as simply supported overhanging beam. The backup roll is considered as a simply supported beam. The elastic roll deformation is determined by superimposition of deflection due to bending ( δ b ) and deflection due to shear ( δ s ) on the roll. Figure 3 shows the free-body diagram depicting different forces acting on the work roll of a finishing stand. From the free-body diagram (Fig. 3) of the work-roll: X Deflection at each position along Barrel length Figure 4. Flow diagram for the development of stack deflection model for a number of coils in a schedule. The deflection of backup roll axis is calculated in a similar manner. To determine the work roll deflection along with the deflection of backup roll, the roll force between work roll and back up roll is necessary. The roll force is determined with roll force model, described in the following sections. This roll force is used in determining the bending and the shear force in Eq.() & Eq.(). The roll diameter and related thickness of the strip for the chosen schedule of rolling are given in the Table. The area of cross section of work roll can be determined from the data of the table. Table. Dimension of work roll and thickness of strip at finishing stands of the selected schedule for analysis. Finishing stand No. Roll diameter (mm) Strip thickness at the exit of individual stand (mm) / Vol. XXIX, No. 3, July-September 7 ABCM
4 Analysis of Roll Stack Deflection in a Hot Strip Mill Roll Force Model Specific force between the rolls (inter-roll specific force) has been calculated from the roll force model. This model uses the mean flow stress (MFS) of the material to calculate the rolling load. Several phenomena such as recrystallization, strain accumulation and phase transformation can be evaluated with the MFS behavior during rolling. The roll force for each stand was calculated using the Sims (954) approach. Essentially, this calculation requires the strip thickness, width and MFS of the material for each pass. The Sims equation used for the calculation is as follows: P =. MFS. w. ( R.( H h) ). Q (3) 3 where, MFS = Mean flow stress, w=width, R=Work roll radius, H=Entry thickness, h=exit thickness and, Q= Geometric constant. H h r= (4) H r r R π tan ln Y Q = ( r) (5) r r h h 4 R( cos ) h Y = Φ + (6) The flow stress is governed by the repeated recrystallization which can be either static or dynamic. It depends on the interpass time, strain, strain rate and temperature. Misaka s equation from Misaka and Yoshimoto (967) has been used to specify the MFS for C-Mn steels during hot strip rolling and the equation is given by:.. 3 (.75[ C].594[ C] + ) ε MFS M = 9.8exp.6 ε [ C] [ C] exp + + ε ε T where, MFS M is the modified Misaka s equation for MFS in MPa and [C] is the carbon concentration in weight %, T =Temperature, in o K Later on, Siciliano et al. (996) modified equation (7) to incorporate the effect of different alloying elements such as Mn, Nb, Ti etc. and the softening due to dynamic recrystallization, if any. The modified equation is restructured as follows: ( [ Nb] +.37[ Mn] + 4. [ Ti] ) * MFS = MFS M 7 (8) * MFS = MFS ( X ) + kσ X (9) dyn SS here a constant factor of k =.4 is introduced to convert the stress to mean flow stress. The MFS during rolling at each stand, as calculated by Eq. (9), was used in Eq. (3) for the calculation of roll force. The mean flow stress, determined from Eq.(7) is similar to the nature of the graphs of Pankaj et al. (4) for plain C-Mn grade and microalloyed grade steel: MFS = f ( / T ) () where T=Temperature In case of Nb microalloyed steels, the presence of Nb in solid solution causes the retardation of static recrystallisation (SRX). During finishing stages of strip rolling, strain accumulation occurs dyn (7) due to short interpass time, and dynamic recrystallisation (DRX) followed by metadynamic recrystallisation (MDRX) occurs. The evolution of MFS as a function of inverse absolute temperature is MFS, MPa For Nb grade steel ( Pankaj et al.) For C-Mn (base) grade steel ( Pankaj et al.) Siciliano's Model /T ( K - ) Figure 5. Comparison of MFS as a function of the inverse absolute temperature. depicted in Fig. 5 by comparison of the data from the work of Sicliano (4). Validation The comparison between the predicted and the measured (actual) roll force for a selected schedule at the finishing stand no. of the hot strip mill is shown in Fig. 6. The average of measured Roll Force, MN Roll Force in Stand No Coil No. Actual Predicted Figure 6. A comparison of predicted vs. actual roll force for stand no. in a complete schedule of rolling. force (in MN, MegaNewton) for each coil is taken from the hot strip mill (HSM). For the whole schedule, average values of actual force for each coil are captured by level-ii automation in HSM with the help of load cell located in the finishing mill housing. The predicted and the actual roll forces are found to be in good agreement. The deviations of the average of actual roll force for 8% of the coils are found to be with in 7-8%. In some cases, the prediction matches with the actual value of the average roll force. Similar results are found to be true for all the other stands. J. of the Braz. Soc. of Mech. Sci. & Eng. Copyright 7 by ABCM July-September 7, Vol. XXIX, No. 3 / 87
5 Sudipta Sikdar et al Results The results encompass the analysis of the model simulation with the data of strip rolled and the work rolls of the finishing stands of a complete schedule. The roll diameter, entry and exit thickness for each stand as well as chemical composition and width for each coil of the schedule have been used as input for the roll deflection model. Figure 7 displays the variation of deflection with the width for different finishing stands simulated by the model. For any stand of the finishing mill, the amount of deflection increases with the increase of the width of the work roll and after a particular value of width the deflection again starts drooping down. This result implies that the maximum deflection can be obtained for a particular width of the strip, which is about 55-6% of work roll length. A similar observation has been made in the reference literature by Ginzburg (995) also. It is noticed from the simulation study that the strip width has a significant effect on the roll deflection. The strip transmits the rolling load between the work rolls, which are generally greater in length than the strip width. The work roll deflection increases with an increase in strip width, whereas for wider widths deflection decreases with an increase in strip width, reaching its maximum value of 55-6% of the barrel length. This Deflection, microns Width, mm Stand No. Stand No. Stand No.3 Stand No.4 Stand No.5 Stand No.6 Figure 7. Effect of strip width on roll deflection at different stands (#). trend is basically due to the effect of strip width on the roll force i.e. with the increase in width, the roll force increases up to a value of width and then decreases. Deflection, microns Stand No Strip Width: 96mm Without Bending With Bending The effect of work roll bending at different stands of the finishing mill is illustrated in Fig. 8. The effect of bending and without bending creates two parallel curves. The relative profile at different stands with bending remains constant, as can be seen by the curves, which are parallel. Thus, the roll bending force is designed in such a way so as to maintain a uniform relative profile at different stands to avoid flatness error. Here, the roll force is decreasing with subsequent stands, thereby reducing the deflection. The difference of the deflection value with and without bending for the particular process parameter lies between 5-6 microns. The table in the inset shows the parameters of roll force and bending force considered for the analysis. The inset in the Fig. 7 also shows the roll force and bending force values considered for the analysis. Deflection, microns Barrel Length, mm kn 45 kn 5 kn 55 kn 6 kn Figure 9. Effect of roll bending on roll deflection of stand (Roll Force: 4.7 MN, Strip Width: 9 mm, Entry Thickness: 9.7 mm, Exit thickness:. mm). Figure 9 portrays the result of the variation in deflection along the barrel length of stand for increasing bending forces, keeping the roll force and strip width constant. Significant point to be observed is the decreasing trend of the amount of deflection with the increase in bending force up to a particular barrel ( roll) length. Thus roll bending is a controllable parameter to modify the roll gap and hence the crown and flatness of the strip rolled in the finishing mill of the hot strip mill. Conclusions Roll stack deflection is an important issue in the determination of profile and flatness of a strip rolled in hot strip mill. A simple roll deflection model has been developed to predict the deflection of the finishing stands of a hot strip mill. The roll deflection model indicates the effect of width for deflection as well as the effect of bending. The effect of work roll bending and the roll width has been studied by this model. It has been observed that the increase of width of work roll leads to the increase of roll deflection upto a certain value following which it again decreases with the increase of width of work roll. The amount of deflection of rolls at different stands can be changed by applying roll bending. The roll stack deflection calculated in the above method can be used as an input for determining the roll gap along the barrel length for flatness. Figure 8. Comparison of bending and no bending on roll deflection (Entry Thickness: 9.7 mm, Exit thickness:. mm ). 88 / Vol. XXIX, No. 3, July-September 7 ABCM
6 Analysis of Roll Stack Deflection in a Hot Strip Mill Acknowledgement The authors acknowledge the kind permission of the management of Tata Steel, India for the publication of this paper. References Bald, W., Beiseman, G.., Feldmann, H. and Schultes, T., 987, Continuous Variable Crown (CVC) Rolling, AISE Year Book, pp Ginzburg, V.B., 995, Profile and Flatness of Flat Rolled Products, Rolling Mill Technology Series, Part II, International Rolling Mill Consultants, Inc., Pittsburgh, PA, USA, pp.4-3. Kitahama, M., Yarita, I., Abe, H. and Awazuhara, H., 987, Profile Control of hot rolled strip by work roll shifting (K-WRS) mill, AISE Year Book, pp Misaka, Y. & Yoshimoto, T., 967, J. Jpn. Soc. Technol. Plast., Vol. 8, pp.44. Ohe, K., Morimoto, Y., Kajiura, S., Fujino, T., Simada, S., Anarku, K. and Mizuta, A., 994, Development of Shape Control in Plate Rolling, METEC Congress 94 Proceedings, Vol., 6 th International Rolling Conference, VDEh, Dusseldorf, Germany, pp Pankaj, Venugopalan, T., Mohapatra, S., Ravi, R. S. and Sadhu, M.C., 4, New Product Development using the Hot Strip Mill as an Experimental Tool, Tata Search, Vol., pp Pospiech, J., 5, Calculation method for deformation of stands and rolls to obtain products with small dimension of tolerances, Journal of Materials Processing Technology, Vol. 66, pp Siciliano Jr, F., Minami, K., Maccagno, T.M. and Jonas, J.J., 996, Mathematical Modeling of the Mean Flow Stress, Fractional Softening and Grain Size during the Hot Strip Rolling of C-Mn Steels, ISIJ International, Vol. 36, pp Siciliano, F., 4, Modeling the Mean Flow Stress and Grain Sizes During the Hot Rolling of Niobium Microalloyed Steels using Industrial Data, SimPro'4, International Conference on Thermo-mechanical Simulations and Processing of Steels, Ranchi, Jharkhand, India, pp Sims, R.B., 954, The calculation of roll force and torque in hot rolling mills, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng., Vol. 68, pp.9-. Stone, M.D. & Gray, R., 965, Theory and Practical Aspects in Crown Control, Iron and Steel Engineer Year Book, pp Wilms,W., Vogtmann, L., Klockner, J., Beisemann, G. and Rohde, W., 985, Profile and Flatness Control in Hot Strip Mills, Metallurgical Plant and Technology, Vol. 8, pp J. of the Braz. Soc. of Mech. Sci. & Eng. Copyright 7 by ABCM July-September 7, Vol. XXIX, No. 3 / 89
OPTIMIZATION OF HIGH QUALITY PRODUCTION IN HOT ROLLING MILLS USING ADVANCED PROCESS MODELS*
 OPTIMIZATION OF HIGH QUALITY PRODUCTION IN HOT ROLLING MILLS USING ADVANCED PROCESS MODELS* Detlef Ehlert 1 Olaf Jepsen 2 Gregor Schneider 3 Abstract Flexibility in terms of producing high sophisticated
OPTIMIZATION OF HIGH QUALITY PRODUCTION IN HOT ROLLING MILLS USING ADVANCED PROCESS MODELS* Detlef Ehlert 1 Olaf Jepsen 2 Gregor Schneider 3 Abstract Flexibility in terms of producing high sophisticated
Rolling processes. Fig. (5-1)
 Page1 Rolling processes 5-1 introduction: Rolling is the process of reducing the thickness or changing the cross section of a long workpiece by compressive forces applied through a set of rolls, as shown
Page1 Rolling processes 5-1 introduction: Rolling is the process of reducing the thickness or changing the cross section of a long workpiece by compressive forces applied through a set of rolls, as shown
A New Rolling Pressure Model for an Actual Reversing Cold Rolling Strip Mill
 Int J Advanced Design and Manufacturing Technology, Vol. 8/ No. 2/ June - 2015 73 A New Rolling Pressure Model for an Actual Reversing Cold Rolling Strip Mill M. Heydari Vini Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Int J Advanced Design and Manufacturing Technology, Vol. 8/ No. 2/ June - 2015 73 A New Rolling Pressure Model for an Actual Reversing Cold Rolling Strip Mill M. Heydari Vini Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Modelling the Microstructural Evolution During Hot Strip Rolling of Niobium Microalloyed Steels
 Modelling the Microstructural Evolution During Hot Rolling of Niobium Microalloyed Steels Antonio Gorni 1, Marcelo Rebellato 2, Vishwanathan Nagarajan 3 and Ronaldo Barbosa 4 1 Aranda Editora, Alameda
Modelling the Microstructural Evolution During Hot Rolling of Niobium Microalloyed Steels Antonio Gorni 1, Marcelo Rebellato 2, Vishwanathan Nagarajan 3 and Ronaldo Barbosa 4 1 Aranda Editora, Alameda
Question Paper Code : 11410
 Reg. No. : Question Paper Code : 11410 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, APRIL/MAY 2011 Fourth Semester Mechanical Engineering ME 2254 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS (Common to Automobile Engineering and Production
Reg. No. : Question Paper Code : 11410 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, APRIL/MAY 2011 Fourth Semester Mechanical Engineering ME 2254 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS (Common to Automobile Engineering and Production
KES Transactions on Sustainable Design and Manufacturing I Sustainable Design and Manufacturing 2014 : pp : Paper sdm14-109
 KES Transactions on Sustainable Design and Manufacturing I Sustainable Design and Manufacturing 2014 : pp.744-756 : Paper sdm14-109 Suitability of multi-layer perceptron neural network model for the prediction
KES Transactions on Sustainable Design and Manufacturing I Sustainable Design and Manufacturing 2014 : pp.744-756 : Paper sdm14-109 Suitability of multi-layer perceptron neural network model for the prediction
Simulation of Microstructural Evolution in Rod Rolling of a Medium C-Mn Steel. P. A. Manohar, Kyuhwan Lim, A. D. Rollett and Youngseog Lee *
 Simulation of Microstructural Evolution in Rod Rolling of a Medium C-Mn Steel P. A. Manohar, Kyuhwan Lim, A. D. Rollett and Youngseog Lee * Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Carnegie Mellon
Simulation of Microstructural Evolution in Rod Rolling of a Medium C-Mn Steel P. A. Manohar, Kyuhwan Lim, A. D. Rollett and Youngseog Lee * Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Carnegie Mellon
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN AERONAUTICAL AND MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 ISSN (ONLINE): 2321-3051 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN AERONAUTICAL AND MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Finite element analysis of deflection of rolls and its correction by providing camber on rolls Vijay
ISSN (ONLINE): 2321-3051 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN AERONAUTICAL AND MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Finite element analysis of deflection of rolls and its correction by providing camber on rolls Vijay
Application of between- stand cooling in the production hot rolled strips
 Focused on Fracture Mechanics in Central and East Europe Application of between- stand cooling in the production hot rolled strips U. Muhin, S. Belskij, E.Makarov Lipetsk State Technical University, Lipetsk,
Focused on Fracture Mechanics in Central and East Europe Application of between- stand cooling in the production hot rolled strips U. Muhin, S. Belskij, E.Makarov Lipetsk State Technical University, Lipetsk,
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK CE 6306 - STRENGTH OF MATERIALS UNIT I STRESS STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART- A (2 Marks) 1. What is Hooke s Law? 2.
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK CE 6306 - STRENGTH OF MATERIALS UNIT I STRESS STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART- A (2 Marks) 1. What is Hooke s Law? 2.
Multi-pass Hot Rolling of Steels
 Multi-pass Hot Rolling of Steels Multi-pass hot rolling is a general practice in the production of plates. An illustration of a plate mill, Fig. 1, is shown below to demonstrate how a series of processes
Multi-pass Hot Rolling of Steels Multi-pass hot rolling is a general practice in the production of plates. An illustration of a plate mill, Fig. 1, is shown below to demonstrate how a series of processes
Simulation Analysis and Application of Hot Rolled Large Size H-beams
 Simulation Analysis and Application of Hot Rolled Large Size H-beams Guoming Zhu, Xingye Guo, Chao Lu, Yonglin Kang, Sixun Zhang School of Material Science and Engineering, University of Science and Technology
Simulation Analysis and Application of Hot Rolled Large Size H-beams Guoming Zhu, Xingye Guo, Chao Lu, Yonglin Kang, Sixun Zhang School of Material Science and Engineering, University of Science and Technology
Hot Rolled. AK Steel produces Hot Rolled Steels to meet the strictest chemistry and dimensional requirements, in a wide variety of grades.
 Hot Rolled STEELs P r o d u c t D ata B u l l e t i n AK Steel produces Hot Rolled Steels to meet the strictest chemistry and dimensional requirements, in a wide variety of grades. Consistency from coil
Hot Rolled STEELs P r o d u c t D ata B u l l e t i n AK Steel produces Hot Rolled Steels to meet the strictest chemistry and dimensional requirements, in a wide variety of grades. Consistency from coil
Revision (Class 18) Rolling. In this class Different MW Processes are revised
 Revision (Class 18) In this class Different MW Processes are revised Rolling The workpiece is subjected to compressive forces and is deformed plastically. The cross section decreases and length gets elongated
Revision (Class 18) In this class Different MW Processes are revised Rolling The workpiece is subjected to compressive forces and is deformed plastically. The cross section decreases and length gets elongated
FINITE ELEMENTS METHOD (FEM) SIMULATION OF BAR ROLLING IN OVAL - CIRCLE PASS SCHEDULE
 FINITE ELEMENTS METHOD (FEM) SIMULATION OF BAR ROLLING IN OVAL - CIRCLE PASS SCHEDULE Milan KOTAS a, Richard FABÍK b, Tomáš GAJDZICA a, Jiří KLIBER b a TŘINECKÉ ŽELEZÁRNY, a. s., Průmyslová 1000, 73970
FINITE ELEMENTS METHOD (FEM) SIMULATION OF BAR ROLLING IN OVAL - CIRCLE PASS SCHEDULE Milan KOTAS a, Richard FABÍK b, Tomáš GAJDZICA a, Jiří KLIBER b a TŘINECKÉ ŽELEZÁRNY, a. s., Průmyslová 1000, 73970
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R059210303 Set No. 1 II B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2006 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics, Metallurgy & Material Technology, Production
Code No: R059210303 Set No. 1 II B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2006 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Mechatronics, Metallurgy & Material Technology, Production
Effect of TMCP Parameters on the Microstructure and Properties of an Nb Ti Microalloyed Steel
 , pp. 851 857 Effect of TMCP Parameters on the Microstructure and Properties of an Nb Ti Microalloyed Steel Yanchun LIU, Fuxian ZHU, Yanmei LI and Guodong WANG The State Key Laboratory of Rolling & Automation,
, pp. 851 857 Effect of TMCP Parameters on the Microstructure and Properties of an Nb Ti Microalloyed Steel Yanchun LIU, Fuxian ZHU, Yanmei LI and Guodong WANG The State Key Laboratory of Rolling & Automation,
Bulk Deformation Forming - Rolling
 1 Bulk Deformation Forming - Rolling Overview - Shaping and Forming Powders Pressing SLS Special Injection Molding Firing/ Sintering 2 Raw Material Molten Material Continuous Casting/Rolling Ingot casting
1 Bulk Deformation Forming - Rolling Overview - Shaping and Forming Powders Pressing SLS Special Injection Molding Firing/ Sintering 2 Raw Material Molten Material Continuous Casting/Rolling Ingot casting
Part IA Paper 2: Structures and Materials MATERIALS Examples Paper 3 Stiffness-limited Design; Plastic Deformation and Properties
 Engineering Part IA Paper 2: Structures and Materials MATERIALS FIRST YEAR Examples Paper 3 Stiffness-limited Design; Plastic Deformation and Properties Straightforward questions are marked with a Tripos
Engineering Part IA Paper 2: Structures and Materials MATERIALS FIRST YEAR Examples Paper 3 Stiffness-limited Design; Plastic Deformation and Properties Straightforward questions are marked with a Tripos
Here: Dr.-Ing. Karl Heinrich Schröder ESW, Eisenwerk Sulzau-Werfen A-5451 Tenneck, Austria Phone:
 Here: Dr.-Ing. Karl Heinrich Schröder ESW, Eisenwerk Sulzau-Werfen A-5451 Tenneck, Austria Phone: +43 6468 5285 100 E-mail: ks@esw.co.at Key Words: work rolls, plate mills, roughing stands of HSM, rolling
Here: Dr.-Ing. Karl Heinrich Schröder ESW, Eisenwerk Sulzau-Werfen A-5451 Tenneck, Austria Phone: +43 6468 5285 100 E-mail: ks@esw.co.at Key Words: work rolls, plate mills, roughing stands of HSM, rolling
Investigation of shape recovery stress for ferrous shape memory alloy
 Computational Methods and Experimental Measurements XIV 485 Investigation of shape recovery stress for ferrous shape memory alloy H. Naoi 1, M. Wada 2, T. Koike 2, H. Yamamoto 2 & T. Maruyama 3 1 Faculty
Computational Methods and Experimental Measurements XIV 485 Investigation of shape recovery stress for ferrous shape memory alloy H. Naoi 1, M. Wada 2, T. Koike 2, H. Yamamoto 2 & T. Maruyama 3 1 Faculty
ANALYTICAL STUDY OF PUNCHING SHEAR ON WAFFLE SLAB WITH DIFFERENT RIB SIZES
 Jr. of Industrial Pollution Control 33(S2)(27) pp 323-327 www.icontrolpollution.com Research Article ANALYTICAL STUDY OF PUNCHING SHEAR ON WAFFLE SLAB WITH DIFFERENT RIB SIZES K. SAKETH*, C. ARUNKUMAR
Jr. of Industrial Pollution Control 33(S2)(27) pp 323-327 www.icontrolpollution.com Research Article ANALYTICAL STUDY OF PUNCHING SHEAR ON WAFFLE SLAB WITH DIFFERENT RIB SIZES K. SAKETH*, C. ARUNKUMAR
Mechanical behavior of crystalline materials- Comprehensive Behaviour
 Mechanical behavior of crystalline materials- Comprehensive Behaviour In the previous lecture we have considered the behavior of engineering materials under uniaxial tensile loading. In this lecture we
Mechanical behavior of crystalline materials- Comprehensive Behaviour In the previous lecture we have considered the behavior of engineering materials under uniaxial tensile loading. In this lecture we
ME 4563 ME 4563 ME Introduction to Manufacturing Processes. College of Engineering Arkansas State University.
 Introduction to Manufacturing Processes College of Engineering Arkansas State University 1 Bulk Deformation 2 1 Rolling 3 What is Rolling? A process of reducing the thickness (or changing the cross-section
Introduction to Manufacturing Processes College of Engineering Arkansas State University 1 Bulk Deformation 2 1 Rolling 3 What is Rolling? A process of reducing the thickness (or changing the cross-section
Subject with Code: Strength of Materials(16CE104) Course& Branch: B. Tech - CE Year &Sem : II-B. Tech &I-Sem Regulation: R16
 SIDDHARTH INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING &TECHNOLOGY:: PUTTUR (Approved by AICTE, New Delhi & Affiliated to JNTUA, Anantapuramu) (Accredited by NBA & Accredited by NAAC with A Grade) (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified
SIDDHARTH INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING &TECHNOLOGY:: PUTTUR (Approved by AICTE, New Delhi & Affiliated to JNTUA, Anantapuramu) (Accredited by NBA & Accredited by NAAC with A Grade) (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified
Level 6 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Structural analysis
 9210-111 Level 6 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Structural analysis Sample Paper You should have the following for this examination one answer book non-programmable calculator pen, pencil, ruler, drawing
9210-111 Level 6 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Structural analysis Sample Paper You should have the following for this examination one answer book non-programmable calculator pen, pencil, ruler, drawing
RECENT DEVELOPMENTS ON CONTROLLED ROLLING TECHNOLOGY AT COMPANHIA SIDERÚRGICA PAULISTA - COSIPA 1
 RECENT DEVELOPMENTS ON CONTROLLED ROLLING TECHNOLOGY AT COMPANHIA SIDERÚRGICA PAULISTA - COSIPA 1 Antonio Augusto Gorni 2 Jackson Soares de Souza Reis 3 José Herbert Dolabela da Silveira 4 - INTRODUCTION
RECENT DEVELOPMENTS ON CONTROLLED ROLLING TECHNOLOGY AT COMPANHIA SIDERÚRGICA PAULISTA - COSIPA 1 Antonio Augusto Gorni 2 Jackson Soares de Souza Reis 3 José Herbert Dolabela da Silveira 4 - INTRODUCTION
SET PROJECT STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF A TROUGH MODULE STRUCTURE, IN OPERATION AND EMERGENCY Luca Massidda
 SET PROJECT STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF A TROUGH MODULE STRUCTURE, IN OPERATION AND EMERGENCY Luca Massidda Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Finite element analysis... 3 Model description... 3 Mirrors...
SET PROJECT STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF A TROUGH MODULE STRUCTURE, IN OPERATION AND EMERGENCY Luca Massidda Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Finite element analysis... 3 Model description... 3 Mirrors...
DANIELI CENTRO ALUMINIUM HOT ROLLING MILL TECHNOLOGY AMAG PROJECT
 ANDREA SCORDI SALES MANAGER DANIELI CENTRO ALUMINIUM 4 TH IIAC IRAN INTERNATIONAL ALUMINIUM CONFERENCE OLYMPIC HOTEL TEHRAN, IRAN 11-12 MAY 2016 DANIELI CENTRO ALUMINIUM HOT ROLLING MILL TECHNOLOGY AMAG
ANDREA SCORDI SALES MANAGER DANIELI CENTRO ALUMINIUM 4 TH IIAC IRAN INTERNATIONAL ALUMINIUM CONFERENCE OLYMPIC HOTEL TEHRAN, IRAN 11-12 MAY 2016 DANIELI CENTRO ALUMINIUM HOT ROLLING MILL TECHNOLOGY AMAG
GRAIN REFINEMENT AND TEXTURE CHANGE IN INTERSTITIAL FREE STEELS AFTER SEVERE ROLLING AND ULTRA-SHORT ANNEALING
 Materials Science Forum Online: 2004-10-15 ISSN: 1662-9752, Vols. 467-470, pp 287-292 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/msf.467-470.287 2004 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Citation & Copyright (to be
Materials Science Forum Online: 2004-10-15 ISSN: 1662-9752, Vols. 467-470, pp 287-292 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/msf.467-470.287 2004 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Citation & Copyright (to be
DYNAMIC CONTROL OF PLATE WITH EMBEDDED SHAPE MEMORY ALLOY WIRES
 27 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES DYNAMIC CONTROL OF PLATE WITH EMBEDDED SHAPE MEMORY ALLOY WIRES F. Hedayati Dezfuli, S. Khalilian, A. Abedian Keywords: shape memory alloys, natural
27 TH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS OF THE AERONAUTICAL SCIENCES DYNAMIC CONTROL OF PLATE WITH EMBEDDED SHAPE MEMORY ALLOY WIRES F. Hedayati Dezfuli, S. Khalilian, A. Abedian Keywords: shape memory alloys, natural
Fundamental Course in Mechanical Processing of Materials. Exercises
 Fundamental Course in Mechanical Processing of Materials Exercises 2017 3.2 Consider a material point subject to a plane stress state represented by the following stress tensor, Determine the principal
Fundamental Course in Mechanical Processing of Materials Exercises 2017 3.2 Consider a material point subject to a plane stress state represented by the following stress tensor, Determine the principal
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF STRAIGHTENING MECHANISM FOR COMMERCIAL STEEL BARS
 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF STRAIGHTENING MECHANISM FOR COMMERCIAL STEEL BARS Dr. Biju B 1, Dijin JS 2, Anujith C 3, Arun Augustine 4, Mohammad Anas P 5 1Professor, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, MACE, Kerala,
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF STRAIGHTENING MECHANISM FOR COMMERCIAL STEEL BARS Dr. Biju B 1, Dijin JS 2, Anujith C 3, Arun Augustine 4, Mohammad Anas P 5 1Professor, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, MACE, Kerala,
Predicting the Occurrence of Dynamic Transformation and Rolling Mill Loads Drops by Hot Torsion and Compression Testing
 International Journal of Metallurgical Engineering 2013, 2(1): 1-9 DOI: 10.5923/j.ijmee.20130201.01 Predicting the Occurrence of Dynamic Transformation and Rolling Mill Loads Drops by Hot Torsion and Compression
International Journal of Metallurgical Engineering 2013, 2(1): 1-9 DOI: 10.5923/j.ijmee.20130201.01 Predicting the Occurrence of Dynamic Transformation and Rolling Mill Loads Drops by Hot Torsion and Compression
Simulation of microstructures for Alloy 718 blade forging using 3D FEM simulator
 Journal of Materials Processing Technology 141 (2003) 337 342 Simulation of microstructures for Alloy 718 blade forging using 3D FEM simulator Young-Sang Na a,, Jong-Taek Yeom a, Nho-Kwang Park a, Jai-Young
Journal of Materials Processing Technology 141 (2003) 337 342 Simulation of microstructures for Alloy 718 blade forging using 3D FEM simulator Young-Sang Na a,, Jong-Taek Yeom a, Nho-Kwang Park a, Jai-Young
UNIT I SIMPLE STRESSES AND STRAINS, STRAIN ENERGY
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Year & Sem: II-B.Tech & I-Sem Course & Branch: B.Tech - ME Regulation:
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Year & Sem: II-B.Tech & I-Sem Course & Branch: B.Tech - ME Regulation:
PARAMETRIC ANALYSIS OF INDUSTRIAL COLD DRAWING PROCESS
 PARAMETRIC ANALYSIS OF INDUSTRIAL COLD DRAWING PROCESS Praveen Kumar Loharkar SVKM s NMIMS MPSTME Shirpur Campus Dhule 425405 India,ploharkar@gmail.com Abstract Seamless tube cold drawing is one of the
PARAMETRIC ANALYSIS OF INDUSTRIAL COLD DRAWING PROCESS Praveen Kumar Loharkar SVKM s NMIMS MPSTME Shirpur Campus Dhule 425405 India,ploharkar@gmail.com Abstract Seamless tube cold drawing is one of the
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R05310305 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2007 DESIGN OF MACHINE MEMBERS-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Production Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks:
Code No: R05310305 Set No. 1 III B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November 2007 DESIGN OF MACHINE MEMBERS-I ( Common to Mechanical Engineering and Production Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks:
Belleville Spring. The relation between the load F and the axial deflection y of each disc. Maximum stress induced at the inner edge
 Belleville Spring Disc spring, also called Belleville spring are used where high capacity compression springs must fit into small spaces. Each spring consists of several annular discs that are dished to
Belleville Spring Disc spring, also called Belleville spring are used where high capacity compression springs must fit into small spaces. Each spring consists of several annular discs that are dished to
Fig. 1: Schematic of roughing rolling unit of Mobarakeh Steel Company
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 13, Issue 5 Ver. I (Sep. - Oct. 2016), PP 88-98 www.iosrjournals.org. Investigation of Effects of
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) e-issn: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, Volume 13, Issue 5 Ver. I (Sep. - Oct. 2016), PP 88-98 www.iosrjournals.org. Investigation of Effects of
Thinnest High-Quality Hot-Rolled Coils at Lowest Production Costs with Arvedi ESP Technology
 26 Thinnest High-Quality Hot-Rolled Coils at Lowest Production Costs with Arvedi ESP Technology ANDREAS JUNGBAUER *1 BERND LINZER *2 THOMAS PFATSCHBACHER *3 Arvedi ESP, developed by Acciaieria Arvedi and
26 Thinnest High-Quality Hot-Rolled Coils at Lowest Production Costs with Arvedi ESP Technology ANDREAS JUNGBAUER *1 BERND LINZER *2 THOMAS PFATSCHBACHER *3 Arvedi ESP, developed by Acciaieria Arvedi and
Properties in Shear. Figure 7c. Figure 7b. Figure 7a
 Properties in Shear Shear stress plays important role in failure of ductile materials as they resist to normal stress by undergoing large plastic deformations, but actually fail by rupturing under shear
Properties in Shear Shear stress plays important role in failure of ductile materials as they resist to normal stress by undergoing large plastic deformations, but actually fail by rupturing under shear
Manufacturing Process - I
 Manufacturing Process - I UNIT II Metal Forming Processes Prepared By Prof. Shinde Vishal Vasant Assistant Professor Dept. of Mechanical Engg. NDMVP S Karmaveer Baburao Thakare College of Engg. Nashik
Manufacturing Process - I UNIT II Metal Forming Processes Prepared By Prof. Shinde Vishal Vasant Assistant Professor Dept. of Mechanical Engg. NDMVP S Karmaveer Baburao Thakare College of Engg. Nashik
Determination of Condition of Recrystallised Grains After Annealing of Cold Rolled IF Grade Steel Sheets Based on Ultrasonic Measurements
 Indian Society for Non-Destructive Testing Hyderabad Chapter Proc. National Seminar on Non-Destructive Evaluation Dec. 7-9, 2006, Hyderabad Determination of Condition of Recrystallised Grains After Annealing
Indian Society for Non-Destructive Testing Hyderabad Chapter Proc. National Seminar on Non-Destructive Evaluation Dec. 7-9, 2006, Hyderabad Determination of Condition of Recrystallised Grains After Annealing
Dynamic behavior of cellular materials under combined shear-compression
 Applied Mechanics and Materials Submitted: 5--5 ISSN: -7, Vol. 35, pp 9-53 Revised: 5--7 doi:./www.scientific.net/amm.35.9 Accepted: -- Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Online: -5- Dynamic behavior
Applied Mechanics and Materials Submitted: 5--5 ISSN: -7, Vol. 35, pp 9-53 Revised: 5--7 doi:./www.scientific.net/amm.35.9 Accepted: -- Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Online: -5- Dynamic behavior
MICROSTRUCTURE EVOLUTION AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF HOT ROLLED DUAL- PHASE STEEL. Yuriy A. BEZOBRAZOV, Anton A. NAUMOV
 MICROSTRUCTURE EVOLUTION AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF HOT ROLLED DUAL- PHASE STEEL Yuriy A. BEZOBRAZOV, Anton A. NAUMOV St. Petersburg State Polytechnic University, St. Petersburg, Russian Federation nw86master@mail.ru,
MICROSTRUCTURE EVOLUTION AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF HOT ROLLED DUAL- PHASE STEEL Yuriy A. BEZOBRAZOV, Anton A. NAUMOV St. Petersburg State Polytechnic University, St. Petersburg, Russian Federation nw86master@mail.ru,
STRENGTH OF MATERIALS laboratory manual
 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS laboratory manual By Prof. Shaikh Ibrahim Ismail M.H. Saboo Siddik College of Engineering, MUMBAI TABLE OF CONTENT Sr. No. Title of Experiment page no. 1. Study of Universal Testing
STRENGTH OF MATERIALS laboratory manual By Prof. Shaikh Ibrahim Ismail M.H. Saboo Siddik College of Engineering, MUMBAI TABLE OF CONTENT Sr. No. Title of Experiment page no. 1. Study of Universal Testing
Austral Deck Design for Construction Loading. Permanent formwork and Span capability
 Austral Deck Design for Construction Loading Permanent formwork and Span capability Introduction The purpose of this document is to demonstrate the process of designing Austral Deck as formwork complying
Austral Deck Design for Construction Loading Permanent formwork and Span capability Introduction The purpose of this document is to demonstrate the process of designing Austral Deck as formwork complying
Effect of fiber fatigue rupture on bridging stress degradation in fiber reinforced cementitious composites
 Effect of fiber fatigue rupture on bridging stress degradation in fiber reinforced cementitious composites T. Matsumoto, P. Chun, & P. Suthiwarapirak The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan. ABSTRACT: This
Effect of fiber fatigue rupture on bridging stress degradation in fiber reinforced cementitious composites T. Matsumoto, P. Chun, & P. Suthiwarapirak The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan. ABSTRACT: This
Effect of Austenitising Temperature and Cooling Condition on Mechanical Properties of Low Carbon Boron Containing Steel
 International Journal of Metallurgical Engineering 2012, 1(1): 1-6 DOI: 10.5923/j.ijmee.20120101.01 Effect of Austenitising Temperature and Cooling Condition on Mechanical Properties of Low Carbon Boron
International Journal of Metallurgical Engineering 2012, 1(1): 1-6 DOI: 10.5923/j.ijmee.20120101.01 Effect of Austenitising Temperature and Cooling Condition on Mechanical Properties of Low Carbon Boron
Product and hot rolling process development of NV40 steel plates 1
 Product and hot rolling process development of NV40 steel plates 1 A.A. Gorni 2, C.N. Paula Silva 3, F. Viana de Freitas 4, J. H. Dolabela da Silveira 5, M. M. Pereira 6, R. Pardo Alves 7. 1. INTRODUCTION
Product and hot rolling process development of NV40 steel plates 1 A.A. Gorni 2, C.N. Paula Silva 3, F. Viana de Freitas 4, J. H. Dolabela da Silveira 5, M. M. Pereira 6, R. Pardo Alves 7. 1. INTRODUCTION
DESIGN OF INNER HOOD OF BELL ANNEALING FURNACE FOR BETTER HEATING EFFICIENCY
 DESIGN OF INNER HOOD OF BELL ANNEALING FURNACE FOR BETTER HEATING EFFICIENCY Baskar.R 1, Jayanthi.K 2, Viswanathan P 3 and R.Subramanian 4 1234 Sri Krishna College of Technology, Kovaipudur, Coimbatore,
DESIGN OF INNER HOOD OF BELL ANNEALING FURNACE FOR BETTER HEATING EFFICIENCY Baskar.R 1, Jayanthi.K 2, Viswanathan P 3 and R.Subramanian 4 1234 Sri Krishna College of Technology, Kovaipudur, Coimbatore,
Prediction of Mean Flow Stress during Hot Strip Rolling Using Genetic Algorithms
 , pp. 171 178 Prediction of Mean Flow Stress during Hot Strip Rolling Using Genetic Algorithms Antonella DIMATTEO,* Marco VANNUCCI and Valentina COLLA TeCIP-PERCRO, Scuola Superiore Sant Anna via Alamanni
, pp. 171 178 Prediction of Mean Flow Stress during Hot Strip Rolling Using Genetic Algorithms Antonella DIMATTEO,* Marco VANNUCCI and Valentina COLLA TeCIP-PERCRO, Scuola Superiore Sant Anna via Alamanni
BASIC METALLURGY/PROCESSING DESIGN CONCEPTS FOR OPTIMIZED HOT STRIP STRUCTURAL STEEL IN YIELD STRENGTHS FROM MPA*
 BASIC METALLURGY/PROCESSING DESIGN CONCEPTS FOR OPTIMIZED HOT STRIP STRUCTURAL STEEL IN YIELD STRENGTHS FROM 300 700 MPA* Douglas Glenn Stalheim 1 Ronaldo Antonio Neves Marques Barbosa 2 Felipe Monteiro
BASIC METALLURGY/PROCESSING DESIGN CONCEPTS FOR OPTIMIZED HOT STRIP STRUCTURAL STEEL IN YIELD STRENGTHS FROM 300 700 MPA* Douglas Glenn Stalheim 1 Ronaldo Antonio Neves Marques Barbosa 2 Felipe Monteiro
The Use of Vanadium in Flat Rolled Products
 International Seminar 2005 on Application Technologies of Vanadium in Flat Rolled Steels - 1 - The Use of Vanadium in Flat Rolled Products P.S. Mitchell Chairman, Vanitec, Winterton House, High Street,
International Seminar 2005 on Application Technologies of Vanadium in Flat Rolled Steels - 1 - The Use of Vanadium in Flat Rolled Products P.S. Mitchell Chairman, Vanitec, Winterton House, High Street,
EVALUATION ON SHEAR CAPACITY OF RC BEAMS USING U-SHAPED UFC PERMANENT FORMWORK
 - Technical Paper - EVALUATION ON SHEAR CAPACITY OF RC BEAMS USING U-SHAPED PERMANENT FORMWORK Puvanai WIROJJANAPIROM *1, Koji MATSUMOTO *2, Katsuya KONO *3 and Junichiro NIWA *4 ABSTRACT Shear resistance
- Technical Paper - EVALUATION ON SHEAR CAPACITY OF RC BEAMS USING U-SHAPED PERMANENT FORMWORK Puvanai WIROJJANAPIROM *1, Koji MATSUMOTO *2, Katsuya KONO *3 and Junichiro NIWA *4 ABSTRACT Shear resistance
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES AND TESTS. Materials Science
 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES AND TESTS Materials Science Stress Stress is a measure of the intensity of the internal forces acting within a deformable body. Mathematically, it is a measure of the average force
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES AND TESTS Materials Science Stress Stress is a measure of the intensity of the internal forces acting within a deformable body. Mathematically, it is a measure of the average force
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE)
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code :Strength of Materials-II (16CE111) Course & Branch: B.Tech - CE Year
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code :Strength of Materials-II (16CE111) Course & Branch: B.Tech - CE Year
Analysis of Buried Arch Structures; Performance Versus Prediction
 Analysis of Buried Arch Structures; Performance Versus Prediction D.A. Jenkins: Reinforced Earth Pty Ltd, Somersby, NSW, Australia Synopsis: The Reinforced Earth Group introduced the TechSpan arch system
Analysis of Buried Arch Structures; Performance Versus Prediction D.A. Jenkins: Reinforced Earth Pty Ltd, Somersby, NSW, Australia Synopsis: The Reinforced Earth Group introduced the TechSpan arch system
Chapter 4 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF MATERIAL. By: Ardiyansyah Syahrom
 Chapter 4 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF MATERIAL By: Ardiyansyah Syahrom Chapter 2 STRAIN Department of Applied Mechanics and Design Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia 1 Expanding
Chapter 4 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF MATERIAL By: Ardiyansyah Syahrom Chapter 2 STRAIN Department of Applied Mechanics and Design Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia 1 Expanding
Reinforced Concrete Design. A Fundamental Approach - Fifth Edition
 CHAPTER REINFORCED CONCRETE Reinforced Concrete Design A Fundamental Approach - Fifth Edition Fifth Edition REINFORCED CONCRETE A. J. Clark School of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
CHAPTER REINFORCED CONCRETE Reinforced Concrete Design A Fundamental Approach - Fifth Edition Fifth Edition REINFORCED CONCRETE A. J. Clark School of Engineering Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
Mathematical Modelling of an Annealing Furnace for Process Control Applications
 Mathematical Modelling of an Annealing Furnace for Process Control Applications N.Depree 1, J.Sneyd 2, S.Taylor 2, M.P.Taylor 1, M.O Connor 3, J.J.J.Chen 4 1 Light Metals Research Centre, University of
Mathematical Modelling of an Annealing Furnace for Process Control Applications N.Depree 1, J.Sneyd 2, S.Taylor 2, M.P.Taylor 1, M.O Connor 3, J.J.J.Chen 4 1 Light Metals Research Centre, University of
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY
 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY UNIT II Hot & Cold Working Forging & Rolling Mechanical Working of Metals In this method no machining process is carried out, but it is used to achieve optimum mechanical properties
MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY UNIT II Hot & Cold Working Forging & Rolling Mechanical Working of Metals In this method no machining process is carried out, but it is used to achieve optimum mechanical properties
This is a repository copy of Softening Kinetics of Plain Carbon Steels Containing Dilute Nb Additions.
 This is a repository copy of Softening Kinetics of Plain Carbon Steels Containing Dilute Nb Additions. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/119751/ Version: Accepted
This is a repository copy of Softening Kinetics of Plain Carbon Steels Containing Dilute Nb Additions. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/119751/ Version: Accepted
STRENGTH CONSEQUENCE MINIMIZATION OF DIGGING OFF BURIED GAS PIPELINE AT ISOLATION COAT RENOVATION REALIZED DURING OPERATION
 STRENGTH CONSEQUENCE MINIMIZATION OF DIGGING OFF BURIED GAS PIPELINE AT ISOLATION COAT RENOVATION REALIZED DURING OPERATION Assoc. Prof. MSc. Roland JANČO, PhD. Institute of Applied Mechanics and Mechatronics,
STRENGTH CONSEQUENCE MINIMIZATION OF DIGGING OFF BURIED GAS PIPELINE AT ISOLATION COAT RENOVATION REALIZED DURING OPERATION Assoc. Prof. MSc. Roland JANČO, PhD. Institute of Applied Mechanics and Mechatronics,
Effect of Steel Core Bending on the Seismic Performance of Buckling-Restrained Braces Using Steel-and-Mortar Planks for Buckling-Restraining System
 6 th International Conference on Advances in Experimental Structural Engineering 11 th International Workshop on Advanced Smart Materials and Smart Structures Technology August 1-2, 215, University of
6 th International Conference on Advances in Experimental Structural Engineering 11 th International Workshop on Advanced Smart Materials and Smart Structures Technology August 1-2, 215, University of
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Materials Science 6 (2014 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Materials Science 6 (2014 ) 674 681 3rd International Conference on Materials Processing and Characterisation (ICMPC 2014) Deformation Behavior
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Materials Science 6 (2014 ) 674 681 3rd International Conference on Materials Processing and Characterisation (ICMPC 2014) Deformation Behavior
THE ANALYSIS OF STRESS DISTRIBUTION BASED ON MEASUREMENTS USING TWO METHODS OF X-RAY APPLICATION
 182 THE ANALYSIS OF STRESS DISTRIBUTION BASED ON MEASUREMENTS USING TWO METHODS OF X-RAY APPLICATION ABSTRACT Barbara Kucharska Institute of Materials Engineering, Czestochowa University of Technology,
182 THE ANALYSIS OF STRESS DISTRIBUTION BASED ON MEASUREMENTS USING TWO METHODS OF X-RAY APPLICATION ABSTRACT Barbara Kucharska Institute of Materials Engineering, Czestochowa University of Technology,
Abstract. 1 Introduction
 Ultimate deformation capacity of reinforced concrete slabs under blast load J.C.A.M. van Doormaal, J. Weeheijm TNO PrinsMaurits Laboratory, P.O. Box 45, 2280 AA Rijswijk, The Netherlands Abstract In this
Ultimate deformation capacity of reinforced concrete slabs under blast load J.C.A.M. van Doormaal, J. Weeheijm TNO PrinsMaurits Laboratory, P.O. Box 45, 2280 AA Rijswijk, The Netherlands Abstract In this
Induction Heating in the Processing of Ti & Zr
 Journal of Electromagnetic Analysis and Applications, 2014, 6, 404-412 Published Online November 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jemaa http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jemaa.2014.613042 Induction
Journal of Electromagnetic Analysis and Applications, 2014, 6, 404-412 Published Online November 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jemaa http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jemaa.2014.613042 Induction
New approach to improving distortional strength of intermediate length thin-walled open section columns
 New approach to improving distortional strength of intermediate length thin-walled open section columns R. S. Talikoti 1, K. M. Bajoria 2 1 Research Scholar (Email: rstalikoti@iitb.ac.in) 2 Associate Professor
New approach to improving distortional strength of intermediate length thin-walled open section columns R. S. Talikoti 1, K. M. Bajoria 2 1 Research Scholar (Email: rstalikoti@iitb.ac.in) 2 Associate Professor
Batch Annealing Model for Cold Rolled Coils and Its Application
 China Steel Technical Report, No. 28, pp.13-20, (2015) Chun-Jen Fang and Li-Wen Wu 13 Batch Annealing Model for Cold Rolled Coils and Its Application CHUN-JEN FANG and LI-WEN WU New Materials Research
China Steel Technical Report, No. 28, pp.13-20, (2015) Chun-Jen Fang and Li-Wen Wu 13 Batch Annealing Model for Cold Rolled Coils and Its Application CHUN-JEN FANG and LI-WEN WU New Materials Research
CITY AND GUILDS 9210 Unit 130 MECHANICS OF MACHINES AND STRENGTH OF MATERIALS OUTCOME 1 TUTORIAL 1 - BASIC STRESS AND STRAIN
 CITY AND GUILDS 910 Unit 130 MECHANICS O MACHINES AND STRENGTH O MATERIALS OUTCOME 1 TUTORIAL 1 - BASIC STRESS AND STRAIN Outcome 1 Explain static equilibrium, Newton's laws, and calculation of reaction
CITY AND GUILDS 910 Unit 130 MECHANICS O MACHINES AND STRENGTH O MATERIALS OUTCOME 1 TUTORIAL 1 - BASIC STRESS AND STRAIN Outcome 1 Explain static equilibrium, Newton's laws, and calculation of reaction
Yield Strength Estimation For Stainless Steel Using Plane Strain Compression Test
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 4(12): 6312-6318, 21 ISSN 1991-8178 Yield Strength Estimation For Stainless Steel Using Plane Strain Compression Test Aiyedun P.O., Nwaneto F.N, Adeleke
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 4(12): 6312-6318, 21 ISSN 1991-8178 Yield Strength Estimation For Stainless Steel Using Plane Strain Compression Test Aiyedun P.O., Nwaneto F.N, Adeleke
Effects of asymmetric creep-ageing behaviour on springback of AA2050-T34 after creep age forming
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 207 (2017) 287 292 International Conference on the Technology of Plasticity, ICTP 2017, 17-22 September 2017, Cambridge, United
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 207 (2017) 287 292 International Conference on the Technology of Plasticity, ICTP 2017, 17-22 September 2017, Cambridge, United
AMERICAN LUMBER STANDARD COMMITTEE, INCORPORATED POLICY FOR EVALUATION OF RECOMMENDED SPANS FOR SPAN RATED DECKING PRODUCTS
 AMERICAN LUMBER STANDARD COMMITTEE, INCORPORATED POLICY FOR EVALUATION OF RECOMMENDED SPANS FOR SPAN RATED DECKING PRODUCTS The Board of Review is authorized to use the information within this policy to
AMERICAN LUMBER STANDARD COMMITTEE, INCORPORATED POLICY FOR EVALUATION OF RECOMMENDED SPANS FOR SPAN RATED DECKING PRODUCTS The Board of Review is authorized to use the information within this policy to
SANDVIK CHROMFLEX STRIP STEEL
 SANDVIK CHROMFLEX STRIP STEEL DATASHEET Sandvik Chromflex is a family of hardened and tempered martensitic chromium steels characterized by: High strength combined with good shape High standard of surface
SANDVIK CHROMFLEX STRIP STEEL DATASHEET Sandvik Chromflex is a family of hardened and tempered martensitic chromium steels characterized by: High strength combined with good shape High standard of surface
ME 333 Manufacturing Processes II
 ME 333 Manufacturing Processes II Chapter 5 Metal Working Processes Mechanical Engineering University of Gaziantep Dr. A. Tolga Bozdana www.gantep.edu.tr/~bozdana Introduction Metal forming involves large
ME 333 Manufacturing Processes II Chapter 5 Metal Working Processes Mechanical Engineering University of Gaziantep Dr. A. Tolga Bozdana www.gantep.edu.tr/~bozdana Introduction Metal forming involves large
Monday, May 05, Chapter 6. Fatigue Failure Resulting from Variable Loading. Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE
 Monday, May 05, 2014 Chapter 6 Fatigue Failure Resulting from Variable Loading 1 Chapter Outline Introduction to Fatigue in Metals Approach to Fatigue Failure in Analysis and Design Fatigue-Life Methods
Monday, May 05, 2014 Chapter 6 Fatigue Failure Resulting from Variable Loading 1 Chapter Outline Introduction to Fatigue in Metals Approach to Fatigue Failure in Analysis and Design Fatigue-Life Methods
Compression characteristics of spheroidal graphite cast iron pipe members
 High Performance and Optimum Design of Structures and Materials 455 Compression characteristics of spheroidal graphite cast iron pipe members T. Yamaguchi 1 & Y. Kimura 2 1 HINODE Ltd, Japan 2 New Industry
High Performance and Optimum Design of Structures and Materials 455 Compression characteristics of spheroidal graphite cast iron pipe members T. Yamaguchi 1 & Y. Kimura 2 1 HINODE Ltd, Japan 2 New Industry
(a) Pin-Pin P cr = (b) Fixed-Fixed P cr = (d) Fixed-Pin P cr =
 1. The most critical consideration in the design of rolled steel columns carrying axial loads is the (a) Percent elongation at yield and the net cross-sectional area (b) Critical bending strength and axial
1. The most critical consideration in the design of rolled steel columns carrying axial loads is the (a) Percent elongation at yield and the net cross-sectional area (b) Critical bending strength and axial
Estimate the endurance strength in MPa if the rod is used in rotating bending.
 348 Mechanical Engineering Design PROBLEMS Problems marked with an asterisk (*) are linked to problems in other chapters, as summarized in Table 1 1 of Sec. 1 16, p. 24. Problems 6 1 to 6 63 are to be
348 Mechanical Engineering Design PROBLEMS Problems marked with an asterisk (*) are linked to problems in other chapters, as summarized in Table 1 1 of Sec. 1 16, p. 24. Problems 6 1 to 6 63 are to be
Development of Hot Rolled Thin Steel and High Strength PosMAC Steel for Steel Structures
 Development of Hot Rolled Thin Steel and High Strength PosMAC Steel for Steel Structures Part 1. PO Martensite Steel Part 2. PosMAC Martensite Steel 2017. 11. 27 Kyong Su Park, Jaeyong Chae, Chul Min Bae
Development of Hot Rolled Thin Steel and High Strength PosMAC Steel for Steel Structures Part 1. PO Martensite Steel Part 2. PosMAC Martensite Steel 2017. 11. 27 Kyong Su Park, Jaeyong Chae, Chul Min Bae
Research on rolling force model in hot-rolling process of aluminum alloys
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 16 (2011 ) 745 754 International Workshop on Automobile, Power and Energy Engineering Research on rolling force model in hot-rolling process
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Engineering 16 (2011 ) 745 754 International Workshop on Automobile, Power and Energy Engineering Research on rolling force model in hot-rolling process
Nonlinear Analysis and Design of a Guyed Mast: Comparison of Two Design Proposals
 Advanced Materials Research Online: 2010-12-06 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vols. 163-167, pp 20-24 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.163-167.20 2011 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Nonlinear Analysis and Design
Advanced Materials Research Online: 2010-12-06 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vols. 163-167, pp 20-24 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.163-167.20 2011 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Nonlinear Analysis and Design
ME-313 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS October 11, 2000 TEST I OPEN TEXT BOOK
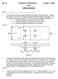 ME-313 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS October 11, 000 TEST I OEN TEXT BOOK Name: 1. Three plates of are bolted together as shown in the figure below. Design the bolted connection by choosing both plate thickness
ME-313 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS October 11, 000 TEST I OEN TEXT BOOK Name: 1. Three plates of are bolted together as shown in the figure below. Design the bolted connection by choosing both plate thickness
On the Recrystallisation Characteristics and Kinetics of a 9SMn28 Free Cutting Steel
 Materials Science Forum Vols. 558-559 (2007) pp. 333-338 online at http://www.scientific.net (2007) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland On the Recrystallisation Characteristics and Kinetics of a 9SMn28
Materials Science Forum Vols. 558-559 (2007) pp. 333-338 online at http://www.scientific.net (2007) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland On the Recrystallisation Characteristics and Kinetics of a 9SMn28
Influence of key test parameters on SPT results
 Indian Journal of Engineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 16, December 2009, pp. 385-389 Influence of key test parameters on SPT results K K Pathak a *, K K Dwivedi b, Manali Shukla a & E Ramadasan c a Advanced
Indian Journal of Engineering & Materials Sciences Vol. 16, December 2009, pp. 385-389 Influence of key test parameters on SPT results K K Pathak a *, K K Dwivedi b, Manali Shukla a & E Ramadasan c a Advanced
A Numerical Investigation of the Temperature Uniformity of a Billet due to Thermal Radiation in a Reheating Furnace
 Article A Numerical Investigation of the Temperature Uniformity of a Billet due to Thermal Radiation in a Reheating Furnace Tanawat Khoukit and Chittin Tangthieng* Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Article A Numerical Investigation of the Temperature Uniformity of a Billet due to Thermal Radiation in a Reheating Furnace Tanawat Khoukit and Chittin Tangthieng* Department of Mechanical Engineering,
PRODUCTION AND APPLICATION OF HIGH STRENGTH STEEL. Feng Yong Technology Center,Jinan Iron and Steel Co. Ltd., Jinan Shandong China
 PRODUCTION AND APPLICATION OF HIGH STRENGTH STEEL Feng Yong Technology Center,Jinan Iron and Steel Co. Ltd., Jinan Shandong China 250101 ABSTRACTS The rapidly development of modern metallurgy and manufacturing
PRODUCTION AND APPLICATION OF HIGH STRENGTH STEEL Feng Yong Technology Center,Jinan Iron and Steel Co. Ltd., Jinan Shandong China 250101 ABSTRACTS The rapidly development of modern metallurgy and manufacturing
COLUMNS 1- Definition: The Egyptian code defines columns as : 2- Types of concrete columns
 COLUMNS 1- Definition: Columns are vertical compression members which carry primarily axial compression load; the axial load may be associated with bending moments in one or two directions, as shown in
COLUMNS 1- Definition: Columns are vertical compression members which carry primarily axial compression load; the axial load may be associated with bending moments in one or two directions, as shown in
download from
 Chapter -1 From Tables A-0, A-1, A-, and A-4c, (a) UNS G1000 HR: S ut = 80 (55) MPa (kpsi), S yt = 10 (0) Mpa (kpsi) Ans. (b) SAE 1050 CD: S ut = 90 (100) MPa (kpsi), S yt = 580 (84) Mpa (kpsi) Ans. (c)
Chapter -1 From Tables A-0, A-1, A-, and A-4c, (a) UNS G1000 HR: S ut = 80 (55) MPa (kpsi), S yt = 10 (0) Mpa (kpsi) Ans. (b) SAE 1050 CD: S ut = 90 (100) MPa (kpsi), S yt = 580 (84) Mpa (kpsi) Ans. (c)
Computer Simulation of Hot Rolling of Flat Products
 Software Engineering 2016; 4(6): 75-81 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/se doi: 10.11648/j.se.20160406.11 ISSN: 2376-8029 (Print); ISSN: 2376-8037 (Online) Computer Simulation of Hot Rolling of
Software Engineering 2016; 4(6): 75-81 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/se doi: 10.11648/j.se.20160406.11 ISSN: 2376-8029 (Print); ISSN: 2376-8037 (Online) Computer Simulation of Hot Rolling of
In this issue Feature Story. No. 313 February The Genesis of Product Making Building Targeted Shapes into Steel Sheets
 No. 313 February 2004 Published monthly by Public Relations Center General Administration Div. Nippon Steel Corporation More about Nippon Steel http://www.nsc.co.jp WWW Notice If you have received the
No. 313 February 2004 Published monthly by Public Relations Center General Administration Div. Nippon Steel Corporation More about Nippon Steel http://www.nsc.co.jp WWW Notice If you have received the
MACHINES DESIGN SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION MECHANICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL MACHINES DESIGN
 1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION MECHANICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL C O N T E N T 2 1. MACHINE DESIGN 03-21 2. FLEXIBLE MECHANICAL ELEMENTS. 22-34 3. JOURNAL BEARINGS... 35-65 4. CLUTCH AND BRAKES.
1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION MECHANICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL C O N T E N T 2 1. MACHINE DESIGN 03-21 2. FLEXIBLE MECHANICAL ELEMENTS. 22-34 3. JOURNAL BEARINGS... 35-65 4. CLUTCH AND BRAKES.
Seismic performance of New Steel Concrete Composite Beam-Columns
 Seismic performance of New Steel Concrete Composite Beam-Columns Toshiaki FUJIMOTO, Hiroshi KOMATSU, Tomoyuki SAKURADA & Noritaka MOROHASHI College of Industrial Technology, Nihon University, Japan SUMMARY:
Seismic performance of New Steel Concrete Composite Beam-Columns Toshiaki FUJIMOTO, Hiroshi KOMATSU, Tomoyuki SAKURADA & Noritaka MOROHASHI College of Industrial Technology, Nihon University, Japan SUMMARY:
To have a clear idea about what really happened and to prevent the
 Failure Analysis on Skunk-Arm of Electrical Tower Failure Analysis on Skunk-Arm of Electrical Tower ABSTRACT Ahmad Rivai 1, Md Radzai Said 2 1, 2 Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti Teknikal
Failure Analysis on Skunk-Arm of Electrical Tower Failure Analysis on Skunk-Arm of Electrical Tower ABSTRACT Ahmad Rivai 1, Md Radzai Said 2 1, 2 Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Universiti Teknikal
ME 254 MATERIALS ENGINEERING 1 st Semester 1431/ rd Mid-Term Exam (1 hr)
 1 st Semester 1431/1432 3 rd Mid-Term Exam (1 hr) Question 1 a) Answer the following: 1. Do all metals have the same slip system? Why or why not? 2. For each of edge, screw and mixed dislocations, cite
1 st Semester 1431/1432 3 rd Mid-Term Exam (1 hr) Question 1 a) Answer the following: 1. Do all metals have the same slip system? Why or why not? 2. For each of edge, screw and mixed dislocations, cite
Field and Laboratory Performance of FRP Bridge Panels
 Field and Laboratory Performance of FRP Bridge s D. Stone, A. Nanni, & J. Myers University of Missouri Rolla, Rolla, Missouri, USA ABSTRACT: The objective of this research project is to examine the use
Field and Laboratory Performance of FRP Bridge s D. Stone, A. Nanni, & J. Myers University of Missouri Rolla, Rolla, Missouri, USA ABSTRACT: The objective of this research project is to examine the use
Hot deformation behavior of Nb-V microalloyed steel
 Journal of Mechanical Engineering Research Vol 2(5, pp 92-96, October 21 Available online at http://wwwacademicjournalsorg/jmer ISSN 2141-2383 21 Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper Hot deformation
Journal of Mechanical Engineering Research Vol 2(5, pp 92-96, October 21 Available online at http://wwwacademicjournalsorg/jmer ISSN 2141-2383 21 Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper Hot deformation
