Binary Systems Formed by Lead Bromide with (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs and Tl)Br: a DTA and Diffractometric Study
|
|
|
- Antony Carr
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Binary Systems Formed by Lead Bromide with (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs and Tl)Br: a DTA and Diffractometric Study MARIO COLA *, VINCENZO MASSAROTTI, RICCARDO RICCARDI, and CESARE SINISTRI Centro di studio per la termodinamica ed elettrochimica dei sistemi salini fusi e solid del C.N.R. Institute of Physical Chemistry University of Pavia, Italy (Z. Naturforsdi. 26 a, [1971] ; received 20 April 1971) The phase diagrams of the systems PbBr2 + MeBr(Me=Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Tl) have been measured by visual and DTA methods. The structures and the thermal characteristics of the intermediate compounds have been pointed out by X-ray diffractometric technique and by DTA-calorimetric measurements, respectively. Moreover, the thermodynamic behaviour of these systems has been discussed. During the last few years, the study of systems containing lead bromide has caught the attention of many authors. In particular, for the systems formed by PbBr2 + MeBr (Me = alkali metal or thallium), Russian authors 1 have investigated various combinations of different salts including binary, ternary and reciprocal systems. The present work was undertaken to continue the study of the thermodynamic properties of systems formed by two salts with bi-monovalent cations and common anion 2. In order to eliminate gaps found in the work of previous authors, particularly in the study of the solid phases, we have analyzed the systems formed by PbBr2 with (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs and Tl)Br. Diffractograms taken on intermediate compounds enabled us to characterize the lattice parameters. Moreover, measurements of transition and fusion effects were carried out for compounds with congruent melting points, in order to discuss the solidliquid (SL) curves in the phase diagrams on the basis of structural models. Experimental Section DTA measurements: The SL curves were measured by DTA and direct visual techniques already described 2. For the determination of the heats of transition Fig. 1. Oven in stainless steel: 1) General view; 2) Open section; 3) Sample holder seen from the top and the side: a) steel plates, b) alumina support, c) steel bolts, d) mica sheets, e) quartz tubes with heating elements, f) gold container, g) steel support, h) lodgment for thermocouples. * Istituto di Chimica Generale, Universitä di Pavia, Italy. 1 S. D. GROMAKOV, Zhur. Fiz. Khim. 24, 641 [1950]. - I. I. ILYASOV, S. D. DIONISEV, and A. G. BERGMAN, RUSS. J. Inorg. Chem. 5, 320, 546 [I960]. A. G. BERGMAN and Yu. I. ANDRYUSHCHENKO, RUSS. J. Inorg. Chem. 8, 882 [1963]. - I. I. ILYASOV, S. D. DIONISEV, and A. G. BERGMAN, Zhur. neorg. Khim. 11, 1981 [1966]. - I. I. ILYASOV and S. D. DIONISEV, Zhur. neorg. Khim. 11, 1986 [1966]. 2 C. SINISTRI, R. RICCARDI, and A. MAGISTRIS, Ber. Bunsenges. Phys. Chem. 71, 376 [1967]. - R. RICCARDI, C. SI- NISTRI, A. MAGISTRIS, and G. CAMPARI VIGANO, Z. Naturforsch. 25a, 781 [1970]. 3 N. F. M. HENRY, H. LIPSON, and W. A. WOOSTER, The Interpretation of X-ray Diffraction Photographs, McMillan & Co. Ltd., London P. M. DE WOLFF, Acta Cryst. 10, 590 [1957]; 11, 664 [1958].
2 and fusion, a Du Pont 900 Thermal Analyzer fitted with a Differential Scanning Calorimeter was used. X-ray measurements have been made by means of a Philips apparatus fitted with a high temperature camera (Materials Research Corporation mod. X-86 N-II) employing Ni-filtered CuKa radiation (A = Ä ). For measurements at relatively high temperature, we found it necessary to replace the original heating element (which also acted as sample holder) with a small furnace built in our laboratory. Thus, better temperature homogeneity and regulation were obtained. Our furnace, which was made of stainles steel is schematically illustrated in Fig. 1: it can reach a maximum temperature of about 600 C, and the temperature is controlled by a CAT (Leeds & Northrup) within a precision of ± 1 C. For the analysis of the diffractograms, the HESSELIPSON 3 and D E WOLFF 4 methods have been used. In some cases, the analysis of the crystals with a microscope using polarized light has also been very useful. Materials: All the salts (BDH) were dried following the rules suggested in the literature. Generally, the compounds for X-ray analysis have been prepared by mixing PbBr 2 and MeBr in the solid state; the mixture was then melted and held at the proper temperature as indicated by the phase diagram for a sufficient length of time. When possible, the compounds were also prepared by crystallization from aqueous solutions: this enabled us to compare diffractograms of samples obtained by different methods. compound obtained by crystallization from aqueous solution according to W E L L S 6 ' 7. Crystallization from aqueous solution yields crystals that can be studied by single crystal methods: therefore the elementary cell constants have been determined with a Buerger camera. On the basis of our measurements, the compound 2 P b B r 2 K B r at room temperature has orthorhombic symmetry, with constants: a = 9.280; Extinction conditions: Fig. 2 shows the phase diagrams of the systems studied, along with the temperatures and the compositions of the characteristic, points. Sometimes it proved impossible to determine the composition of the incongruent intermediate compounds by the D T A technique because the formation reaction of the compound was not sufficiently fast. In these cases, a choice among the possible compositions was made possible by diffractometric measurements at different temperatures on samples having appropriate compositions. Compound 2 PbBr2 KBr. This compound has been studied by P O W E L L and T A S K E R 5 who reported a tetragonal structure (isomorphous with 2 PbBr 2 RbBr and 2 P b B r - N H 4 B r ). The compound we obtained by slowly cooling the melt showed a diffractogram identical to that of the 5 H. M. POWELL a n d H. S. TASKER, J. C h e m. S o c , C = Ä. for hol Z= 2n+1; most probable space groups: n. 2 6 ( P m c 2 1 ) ; n. 2 8 ( P 2 c m ) ; n. 5 1 ( P m c m ) ; Z = 4 ; c?0bs = ; c?caic = 5.60 g / c m 3. The D T A curves recorded f o r this compound (see Fig. 2) show a transition at 242 C, with a small thermal effect ( ^ 0.1 kcal/mole). The diffractograms at C differ f r o m those at room temperature only f o r a uniform shift toward smaller diffraction angles and for the intensities of some peaks. From these diffractograms a new cell cannot be suggested. Compound PbBr2-2 KBr. It is possible to assign indexes to the diffractogram of this compound on the basis of a orthorhombic cell with the following constants: a = 12.97; Results and Discussion 1. Phase Diagrams and Structure of the Intermediate Compounds b = 8.393; b = 20.72; C = 14.20Ä; Z = 1 6 ; c/ obs = ; dcslic = 4.24 g/cm 3. There is no extinction characteristic of a particular type of lattice, thus the cell seems to be primitive. Compound 2 PbBr2'RbBr. A tetragonal cell has been previously 5 assigned to this salt: a = ; C = Ä ; Z = 4 ; space g r o u p : n. 140 I ( 4 / m c m ). Our results well confirm this structure with constants: a = ; C = Ä ; Z = 4 ; </obs = ; ^caic = 5.82 g/cm 3. Compound PbBr2-RbBr. The D T A curves measured on this compound (see Fig. 2) show peaks at the constant temperature of C : the estimated thermal effect is kcal/mole. X-ray measurements have been carried out at room temperature, at 310 C and C. At room temperature it was not possible to obtain a compound of formula P b B r 2 - R b B r, not even with quenching: the sample at room temperature constantly showed peaks of the 2 PbBr 2 RbBr com6 7 H. L. WELLS, A m e r. J. Sei. 4 5, [ ]. H. L. WELLS, Z. A n o r g. C h e m. 4, [ ].
3 pound, along with other peaks that remained unidentified. It is thus probable that DTA peaks at 267 C are due to a disproportionation reaction (7 RbPbBr3 3 RbPb2Br5 + Rb4PbBr6) instead of a polymorphic transition. Diffractograms obtained at 310 C show that PbBr2RbBr has a pseudo-cubic structure type perowskite (probably with a monoclinic symmetry). It is possible to assigne indexes to the diffractograms, with sufficient precision, on the basis of a cell with dimensions: a = 11.53; b = 11.47; C = Ä, 7 = 91 7'. Diffractograms at 370 C are very similar to those observed at 310 C. Thus the PbBr2-RbBr compound does not assume the perfect perowskite structure. Compound PbBr2-4 RbBr. Diffractograms for this compound give a tetragonal cell with constants: (l = ; C = Ä; Z=16; dohs = 3.99; c?cai0 = 3.99 g/cm 3. There is no extinction charac- Fig. 2. Phase diagrams. The compound PbBr2-CsBr shows also a transition at 123 C.
4 teristic of a particular type of lattice, thus the cell seems to be primitive. Compound 2 PbBr2 CsBr. Diffractograms for this compound give a tetragonal cell with constants: a = ; C = Ä ; Z = 4. This cell is isotopic with that of 2 PbBr 2 RbBr, but in this case the characteristic extinctions of the body-centered lattice are not observed. Compound PbBr2 CsBr. This compound was first prepared by W E L L S 6 who observed two different crystalline forms: the first one consists of orange prism, the second one of thin white needles. According to MOLLER 8 the orange form undergoes phase transitions at 1 2 0, and 135 C. At room temperature he observed a monoclinic structure ( d = b = ; C = A ; y = ' ), while at temperatures above 135 C the structure is cubic, type perowskite. By D T A measurements we found no evidence for the three different crystalline forms observed by Moller. Our DTA curves show only one transition at 123 C with a very small thermal effect ( < 0. 1 kcal/mole). Our diffractometric measurements at room temperature confirm Moller's elementary cell, for the orange compound, provided that the dimension are doubled. This is in agreement with Moller's observation that some diffraction peaks could be interpreted only assuming double parameters. Therefore the constant are: Cl = b = ; C = A ; 7 = ' ; Z = 8 ; d0bs = ; J c a l c = 4.82 g/cm 3. At temperatures above 135 C we observed a cubic structure in agreement with Moller's findings. Compound PbBr2-4 CsBr. This compound was studied by WELLS6 and by MÖLLER9. This latter found an hexagonal structure ( a = ; C = Ä. Space group: R3c [most probable], or R3c). Our measurements are an perfect agreement with Moller's ones. Compound 2 PbBr2 TlBr. The diffraction pattern of this compound is very similar to that of 2 PbBr 2 KBr and gives a orthorhombic cell with constants: 0 = 19.6^ b = ; C = Ä ; Z =16; e?obs = ; e?calc = 6.40 g/cm Compound PbBr2 3 TIBr. The diffraction pattern gives a orthorhombic cell with constants: a = 15.8!; b = ; C = Ä ; Z = 1 6 ; dobs = ; c?caic = 6.81 g/cm Thermal Effects and Thermodynamic For a discussion of the thermodynamic behaviour of these systems it is necessary to know the heats AHt and temperature Tf of fusion of all the congruent compounds, as well as those of the pure salts. The heats of fusion of alkali bromide and of thallium bromide are available in the literature 10 ' u. For PbBr 2 on the contrary, there are conflicting figures: G O O D W I N and KALMUS 12, who used a calorimetric method, found AHt = 3.60 kcal/mole and Ti = 761 K ; B L A N C and P E T I T 1 3 by cryoscopic method gave AHt = 5.00 kcal/mole and Tt = 643 K. The values determined in the present work are AHt = 4.41 ± 0.07 kcal/mole and 7, f = K. The heats of fusion of all the congruent compounds were also measured. The corresponding values (AHexp) are reported in Table 1 along with the additively calculated values (zl/7 c a l c ) and with A(AH) = (AHexp) - (zj# c a ic). T h e latest quantities, as it has been shown in previous work 2, enable us to predict the exothermic heats of mixing. It is possible to analyze the thermodynamic behaviour of these systems by assuming, for the melt, the total dissociation of the salt and the Temkin model. In particular, if there is no solubility in the solid phase, it is useful to consider the branches of the liquidus curves rich in alkali bromide. These, in fact, extend in large temperature and composition T a b l e 1. Heats of fusion (in k c a l / m o l e ) f o r P b B r 2 and the congruent c o m p o u n d s P b B r 2 - n M e B r. Compound PbBr2 2 PbBro-KBr 2 PbBr,-RbBr PbBr2-RbBr PbBr2-CsBr 2 PbBr,-TIBr P b B r, - 3 TIBr C. KN. MOLLER, K g l. Dan. Videnskab Selskab, Mat. Fis. Medd. 3 2, 1 [1959]. C. KN. MOLLER, K g l. Dan. Videnskab Selskab, Mat. Fis. Medd. 3 2, 1 [I960]. 11 A. S. DWORKIN a n d M. A. BREDIG, J. P h y s. C h e m. 6 4, [I960]. Behaviour D Ti ( K ) CUBICCIOTTI a n d AHex p AH calc H. EDING, J. C h e m. A (AH) Eng. Data 10, [1965]. H. M. GOODWIN and T. H. KALMUS, Phys. Rev. 28, 1 [1909]. M. BLANC a n d G. PETIT, C. R. A c a d. S e i. P a r i s 2 4 8, 1305 [1959].
5 ranges, whilst the liquidus curves rich in PbBr2 are always very short. Fig. 3 shows the quantity AT = as a function of the composition for the liquidus curves rich in alkali bromide. The T^ value has been calculated according to equations previously given 2 ' 14. As it can be observed, only the system LiBr + PbBr2 shows positive deviations with respect to ideality (AT>0), wherease all the other systems show negative deviations (AT <0) which increase as the radius of the alkali ion increases. As previously discussed, positive deviations from ideality can be interpreted on the basis of activity coefficients (/LiBr>l)? whereas negative deviations can be interpreted on the basis of either activity coefficients (/MeBr<l) or formation of complexes. Negative deviations from ideality are also in agreement with the prediction of a negative enthalpy of mixing for these systems. Figure 4 shows the ideal behaviour of the liquidus curves for the congruent compounds, along with the experimental values. Negative deviations are always observed: these deviations can sometimes be very noticeable (see for instance PbBr2 + CsBr). Fig. 4. Behaviour of the ideal curves regarding the congruent compounds (continuous lines) in comparison with the experimental data (small circles). Fig. 3. Deviations from ideal behaviour for the curves rich in alkali bromide {AT = Texp-Tid). 14 C. SINISTRI and P. FRANZOSINI, Ric. Sei. 33 (II A), 419 [1963J. This figure also shows for the complete system PbBr2 + TlBr, the comparison between the experimental data and the ideal behaviour. As it can be observed, deviations for this system are always negative and very small.
LECTURE 8. Dr. Teresa D. Golden University of North Texas Department of Chemistry
 LECTURE 8 Dr. Teresa D. Golden University of North Texas Department of Chemistry Practical applications for lattice parameter measurements: -determine composition (stoichiometry) of the sample -determine
LECTURE 8 Dr. Teresa D. Golden University of North Texas Department of Chemistry Practical applications for lattice parameter measurements: -determine composition (stoichiometry) of the sample -determine
MAKING SOLID SOLUTIONS WITH ALKALI HALIDES (AND BREAKING THEM)
 MAKING SOLID SOLUTIONS WITH ALKALI HALIDES (AND BREAKING THEM) John B. Brady Department of Geology Smith College Northampton, MA 01063 jbrady@science.smith.edu INTRODUCTION When two cations have the same
MAKING SOLID SOLUTIONS WITH ALKALI HALIDES (AND BREAKING THEM) John B. Brady Department of Geology Smith College Northampton, MA 01063 jbrady@science.smith.edu INTRODUCTION When two cations have the same
Equilibrium phase diagram of metallic alloy
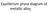 Equilibrium phase diagram of metallic alloy Motivation New structure, concentration (mixing level) (at what temperature? for how long? ) Phase Diagrams - Introduction. Many materials systems can exist
Equilibrium phase diagram of metallic alloy Motivation New structure, concentration (mixing level) (at what temperature? for how long? ) Phase Diagrams - Introduction. Many materials systems can exist
SECOND MIDTERM EXAM Chemistry April 2011 Professor Buhro
 SECOND MIDTERM EXAM Chemistry 465 1 April 011 Professor Buhro Signature Print Name Clearly ID Number: Information. This is a closed-book exam; no books, notes, other students, other student exams, or any
SECOND MIDTERM EXAM Chemistry 465 1 April 011 Professor Buhro Signature Print Name Clearly ID Number: Information. This is a closed-book exam; no books, notes, other students, other student exams, or any
Crystal Growth from Melts
 Crystal Growth from Melts Applications to Growth of Groups 1 and 2 Crystals Bimalendu Narayan Roy Sheffield City Polytechnic, UK JOHN WILEY & SONS Chichester New York Brisbane Toronto Singapore Contents
Crystal Growth from Melts Applications to Growth of Groups 1 and 2 Crystals Bimalendu Narayan Roy Sheffield City Polytechnic, UK JOHN WILEY & SONS Chichester New York Brisbane Toronto Singapore Contents
Now, let s examine how atoms are affected as liquids transform into solids.
 Now, let s examine how atoms are affected as liquids transform into solids. 1 Before we deal with PROPERTIES of materials, it s beneficial to remember where we have come from, and where we are going. Later,
Now, let s examine how atoms are affected as liquids transform into solids. 1 Before we deal with PROPERTIES of materials, it s beneficial to remember where we have come from, and where we are going. Later,
Characterization of Nano-Scale Fine Precipitates in Al-Mg-Si Alloys for Automotive Applications
 UDC 669. 715 721 782 : 629. 11. 011. 5 Characterization of Nano-Scale Fine Precipitates in Al-Mg-Si Alloys for Automotive Applications Makoto SAGA* 1 Naoki MARUYAMA* 1 Abstract Bake-hadenable Al-Mg-Si
UDC 669. 715 721 782 : 629. 11. 011. 5 Characterization of Nano-Scale Fine Precipitates in Al-Mg-Si Alloys for Automotive Applications Makoto SAGA* 1 Naoki MARUYAMA* 1 Abstract Bake-hadenable Al-Mg-Si
 Solid State-1 1) Ionic solids are characterised by 1) Good conductivity in solid state 2) High vapour pressure 3) Low melting point 4) Solubility in polar solvents 2) Three metals X, Y and Z are crystallised
Solid State-1 1) Ionic solids are characterised by 1) Good conductivity in solid state 2) High vapour pressure 3) Low melting point 4) Solubility in polar solvents 2) Three metals X, Y and Z are crystallised
The germanium-selenium phase diagram1
 The germanium-selenium phase diagram1 L. Ross AND M. BOURGON Department of Chemistry, University of Montreal, Montreal, Quebec Received January 31, 1969 The Ge-Se phase diagram was determined in the composition
The germanium-selenium phase diagram1 L. Ross AND M. BOURGON Department of Chemistry, University of Montreal, Montreal, Quebec Received January 31, 1969 The Ge-Se phase diagram was determined in the composition
Intermolecular Forces. Part 2 The Solid State: Crystals
 Intermolecular Forces Part 2 The Solid State: Crystals 1 Prof. Zvi C. Koren 20.07.2010 Calculation of Lattice Energy, U, from a Thermodynamic Cycle What are the energies, virtual and real, involved in
Intermolecular Forces Part 2 The Solid State: Crystals 1 Prof. Zvi C. Koren 20.07.2010 Calculation of Lattice Energy, U, from a Thermodynamic Cycle What are the energies, virtual and real, involved in
Solution Chemistry of Molten Amide-Nitrate Eutectics
 Solution Chemistry of Molten Amide-Nitrate Eutectics a E. I. EWEKA and b D. H. KERRIDGE a Department of Chemistry, University of Southampton, Highfield, Southampton, SO17 1BJ United Kingdom b Department
Solution Chemistry of Molten Amide-Nitrate Eutectics a E. I. EWEKA and b D. H. KERRIDGE a Department of Chemistry, University of Southampton, Highfield, Southampton, SO17 1BJ United Kingdom b Department
Physico-chemical interaction in the Tl 2 Se SnSe PbSe quasiternary system
 118-122 Ivan Franko National University of Lviv www.chemetal-journal.org Physico-chemical interaction in the Tl 2 Se SnSe PbSe quasiternary system M.J. FILEP 1 *, M.Yu. SABOV 1, I.E. BARCHIY 1 1 Department
118-122 Ivan Franko National University of Lviv www.chemetal-journal.org Physico-chemical interaction in the Tl 2 Se SnSe PbSe quasiternary system M.J. FILEP 1 *, M.Yu. SABOV 1, I.E. BARCHIY 1 1 Department
Phase Equilibria in Copper(I) Bromide-MBr Systems (M = Li, Na, K)
 Phase Equilibria in Copper(I) Bromide-MBr Systems (M = Li, Na, K) Alina Wojakowska a,edwardkrzyżak a, Andrzej Wojakowski b, and Marek Wołcyrz b a Wrocław Medical University, Department of Inorganic Chemistry,
Phase Equilibria in Copper(I) Bromide-MBr Systems (M = Li, Na, K) Alina Wojakowska a,edwardkrzyżak a, Andrzej Wojakowski b, and Marek Wołcyrz b a Wrocław Medical University, Department of Inorganic Chemistry,
PHEN 612 SPRING 2008 WEEK 13 LAURENT SIMON
 PHEN 612 SPRING 2008 WEEK 13 LAURENT SIMON Crystallization Crystallization is a common separation process in Commodity inorganic industry (e.g., salts) Food industry (e.g., sugars) Pharmaceutical manufacturing
PHEN 612 SPRING 2008 WEEK 13 LAURENT SIMON Crystallization Crystallization is a common separation process in Commodity inorganic industry (e.g., salts) Food industry (e.g., sugars) Pharmaceutical manufacturing
Structure of silica glasses (Chapter 12)
 Questions and Problems 97 Glass Ceramics (Structure) heat-treated so as to become crystalline in nature. The following concept map notes this relationship: Structure of noncrystalline solids (Chapter 3)
Questions and Problems 97 Glass Ceramics (Structure) heat-treated so as to become crystalline in nature. The following concept map notes this relationship: Structure of noncrystalline solids (Chapter 3)
TitlePhase Diagram Investigations of the. Author(s) Maruyama, Sho; Kado, Yuya; Uda, Tet.
 TitlePhase Diagram Investigations of the Author(s) Maruyama, Sho; Kado, Yuya; Uda, Tet Citation Journal of Phase Equilibria 296 and Dif Issue Date 2013-08 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/191004 This paper
TitlePhase Diagram Investigations of the Author(s) Maruyama, Sho; Kado, Yuya; Uda, Tet Citation Journal of Phase Equilibria 296 and Dif Issue Date 2013-08 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/191004 This paper
SECTION A. NATURAL SCIENCES TRIPOS Part IA. Friday 4 June to 4.30 MATERIALS AND MINERAL SCIENCES
 NATURAL SCIENCES TRIPOS Part IA Friday 4 June 1999 1.30 to 4.30 MATERIALS AND MINERAL SCIENCES Answer five questions; two from each of sections A and B and one from section C. Begin each answer at the
NATURAL SCIENCES TRIPOS Part IA Friday 4 June 1999 1.30 to 4.30 MATERIALS AND MINERAL SCIENCES Answer five questions; two from each of sections A and B and one from section C. Begin each answer at the
MAKING SOLID SOLUTIONS WITH ALKALI HALIDES (AND BREAKING THEM)
 MAKING SOLID SOLUTIONS WITH ALKALI HALIDES (AND BREAKING THEM) John B. Brady Department of Geology Smith College Northampton, MA 01063 jbrady@science.smith.edu INTRODUCTION When two cations have the same
MAKING SOLID SOLUTIONS WITH ALKALI HALIDES (AND BREAKING THEM) John B. Brady Department of Geology Smith College Northampton, MA 01063 jbrady@science.smith.edu INTRODUCTION When two cations have the same
Institute of Physics and Chemistry of Metals, University of Silesia, Bankowa 12, Katowice, Poland
 J. Phys. IV France 11 (2001) Pr8-345 EDP Sciences, Les Ulis Structure of melt spun 2 5Ti 5 ocu 2 5 ribbons studied by X-ray diffraction T. Goryczka, M. Karolus, P. Ochin 1 and H. Morawiec Institute of
J. Phys. IV France 11 (2001) Pr8-345 EDP Sciences, Les Ulis Structure of melt spun 2 5Ti 5 ocu 2 5 ribbons studied by X-ray diffraction T. Goryczka, M. Karolus, P. Ochin 1 and H. Morawiec Institute of
STRUCTURE AND MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF THE Zr 30
 Structure Rev.Adv.Mater.Sci. and magnetic 18(2008) properties 379-383 of the Zr 30 379 STRUCTURE AND MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF THE Zr 30 ALLOY FORMED BY MECHANICAL ALLOYING A. Grabias 1, D. Oleszak 2 and
Structure Rev.Adv.Mater.Sci. and magnetic 18(2008) properties 379-383 of the Zr 30 379 STRUCTURE AND MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF THE Zr 30 ALLOY FORMED BY MECHANICAL ALLOYING A. Grabias 1, D. Oleszak 2 and
Solids. The difference between crystalline and non-crystalline materials is in the extent of ordering
 Chapter 3 The Structure t of Crystalline Solids The difference between crystalline and non-crystalline materials is in the extent of ordering Both materials have the same composition but one is ordered
Chapter 3 The Structure t of Crystalline Solids The difference between crystalline and non-crystalline materials is in the extent of ordering Both materials have the same composition but one is ordered
What is a crystal? Historic definition before the advent of crystallography. - A material with a regularly repeating structural motif
 What is a crystal? Historic definition before the advent of crystallography - A solid with well-defined faces Crystallographic definition - A material with a regularly repeating structural motif The strict
What is a crystal? Historic definition before the advent of crystallography - A solid with well-defined faces Crystallographic definition - A material with a regularly repeating structural motif The strict
Chapter 12 The Solid State The Structure of Metals and Alloys
 Chapter 12 The Solid State The Structure of Metals and Alloys The Solid State Crystalline solid a solid made of an ordered array of atoms, ion, or molecules Amorphous solids a solid that lacks long-range
Chapter 12 The Solid State The Structure of Metals and Alloys The Solid State Crystalline solid a solid made of an ordered array of atoms, ion, or molecules Amorphous solids a solid that lacks long-range
Comparison of Hydration Properties Between Monoclinic and Inverted Triclinic Alite
 Comparison of Hydration Properties Between Monoclinic and Inverted Triclinic Alite GORO YAMAGUCHI, KOHEI SHIRASUKA, and TAKE SHI OTA Faculty of Engineering, University of Tokyo.TRICALCIUM silicate forms
Comparison of Hydration Properties Between Monoclinic and Inverted Triclinic Alite GORO YAMAGUCHI, KOHEI SHIRASUKA, and TAKE SHI OTA Faculty of Engineering, University of Tokyo.TRICALCIUM silicate forms
These metal centres interact through metallic bonding
 The structures of simple solids The majority of inorganic compounds exist as solids and comprise ordered arrays of atoms, ions, or molecules. Some of the simplest solids are the metals, the structures
The structures of simple solids The majority of inorganic compounds exist as solids and comprise ordered arrays of atoms, ions, or molecules. Some of the simplest solids are the metals, the structures
Crystallization study of Te Bi Se glasses
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 26, No. 5, August 2003, pp. 547 551. Indian Academy of Sciences. Crystallization study of Te Bi Se glasses MANISH SAXENA* and P K BHATNAGAR Department of Sciences and Humanities,
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 26, No. 5, August 2003, pp. 547 551. Indian Academy of Sciences. Crystallization study of Te Bi Se glasses MANISH SAXENA* and P K BHATNAGAR Department of Sciences and Humanities,
Growth of K(D x H 1 x ) 2 PO 4 Single Crystals from Solutions in the K 2 O P 2 O 5 (D,H) 2 O System
 Crystallography Reports, Vol. 47, No., 00, pp. 30 34. Translated from Kristallografiya, Vol. 47, No., 00, pp. 44. Original Russian Text Copyright 00 by Soboleva, Voloshin, Kirikov, Biglova. CRYSTAL GROWTH
Crystallography Reports, Vol. 47, No., 00, pp. 30 34. Translated from Kristallografiya, Vol. 47, No., 00, pp. 44. Original Russian Text Copyright 00 by Soboleva, Voloshin, Kirikov, Biglova. CRYSTAL GROWTH
XRD, DTA AND DENSITY STUDIES OF LITHIUM BORATE GLASSES CONTAINING COPPER A. A. Soliman
 , pp. 188 197 XRD, DTA AND DENSITY STUDIES OF LITHIUM BORATE GLASSES CONTAINING COPPER A. A. Soliman Physics Department, Faculty of Girls, Ain Shams University, Heliopolis, Egypt Received 4 November, 2008
, pp. 188 197 XRD, DTA AND DENSITY STUDIES OF LITHIUM BORATE GLASSES CONTAINING COPPER A. A. Soliman Physics Department, Faculty of Girls, Ain Shams University, Heliopolis, Egypt Received 4 November, 2008
EXPERIMENT 1 SOLID LIQUID PHASE DIAGRAM
 EXPERIMENT 1 SOLID LIQUID PHASE DIAGRAM Important: bring a formatted 3.5 floppy diskette/usb flash drive for this laboratory you will need it to save your data files! Introduction The relation of cooling
EXPERIMENT 1 SOLID LIQUID PHASE DIAGRAM Important: bring a formatted 3.5 floppy diskette/usb flash drive for this laboratory you will need it to save your data files! Introduction The relation of cooling
PHASE DIAGRAMS. IE-114 Materials Science and General Chemistry Lecture-10
 PHASE DIAGRAMS IE-114 Materials Science and General Chemistry Lecture-10 Importance of Phase Diagrams There is a strong correlation between microstructure and mechanical properties. Phase diagrams provides
PHASE DIAGRAMS IE-114 Materials Science and General Chemistry Lecture-10 Importance of Phase Diagrams There is a strong correlation between microstructure and mechanical properties. Phase diagrams provides
Thermodynamics and Phase Diagram of the Ni-Sb-Sn System
 Thermodynamics and Phase Diagram of the Ni-Sb-Sn System Ratikanta Mishra & Herbert Ipser Department of Inorganic Chemistry / Materials Chemistry, University of Vienna, Austria Traditional Solder Materials
Thermodynamics and Phase Diagram of the Ni-Sb-Sn System Ratikanta Mishra & Herbert Ipser Department of Inorganic Chemistry / Materials Chemistry, University of Vienna, Austria Traditional Solder Materials
STUDY OF POLYMORPHIC TRANSFORMATION OF ORNIDAZOLE DRUG BY DIFFERENTIAL SCANNING CALORIMETRY AND OTHER COMPLEMENTARY TECHNIQUES
 Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 65 No. 4 pp. 409ñ413, 2008 ISSN 00016837 Polish Pharmaceutical Society STUDY OF POLYMORPHIC TRANSFORMATION OF ORNIDAZOLE DRUG BY DIFFERENTIAL SCANNING
Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica ñ Drug Research, Vol. 65 No. 4 pp. 409ñ413, 2008 ISSN 00016837 Polish Pharmaceutical Society STUDY OF POLYMORPHIC TRANSFORMATION OF ORNIDAZOLE DRUG BY DIFFERENTIAL SCANNING
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name METALLURGY AND MATERIAL SCIENCE Course Code AME005 Class III Semester
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name METALLURGY AND MATERIAL SCIENCE Course Code AME005 Class III Semester
12/3/ :12 PM. Chapter 9. Phase Diagrams. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 9 Phase Diagrams 1 2 Learning Objectives 1. Isomorphous and eutectic phase diagrams: a. label various phase regions b. Label liquidus, solidus, and solvus lines 2. Given a binary phase diagram
Chapter 9 Phase Diagrams 1 2 Learning Objectives 1. Isomorphous and eutectic phase diagrams: a. label various phase regions b. Label liquidus, solidus, and solvus lines 2. Given a binary phase diagram
USE OF IN-SITU XRD TO DEVELOP CONDUCTING CERAMICS WITH THE AURIVILLIUS CRYSTAL STRUCTURE
 Copyright (c)jcpds-international Centre for Diffraction Data 2002, Advances in X-ray Analysis, Volume 45. 117 USE OF IN-SITU XRD TO DEVELOP CONDUCTING CERAMICS WITH THE AURIVILLIUS CRYSTAL STRUCTURE Scott
Copyright (c)jcpds-international Centre for Diffraction Data 2002, Advances in X-ray Analysis, Volume 45. 117 USE OF IN-SITU XRD TO DEVELOP CONDUCTING CERAMICS WITH THE AURIVILLIUS CRYSTAL STRUCTURE Scott
Alloy by Synchrotron Radiation
 1 Analysis of Glass-forming Alloy by Synchrotron Radiation T. A. Başer /NIS Università degli Studi di Torino/ITALY European School-BMGs/ 13-1 Sept /Torino-ITALY Fe-based Bulk Metallic Glasses with Y Addition
1 Analysis of Glass-forming Alloy by Synchrotron Radiation T. A. Başer /NIS Università degli Studi di Torino/ITALY European School-BMGs/ 13-1 Sept /Torino-ITALY Fe-based Bulk Metallic Glasses with Y Addition
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE TERMS
 CRYSTAL STRUCTURE TERMS crystalline material - a material in which atoms, ions, or molecules are situated in a periodic 3-dimensional array over large atomic distances (all metals, many ceramic materials,
CRYSTAL STRUCTURE TERMS crystalline material - a material in which atoms, ions, or molecules are situated in a periodic 3-dimensional array over large atomic distances (all metals, many ceramic materials,
ENGINEERING COUNCIL CERTIFICATE LEVEL ENGINEERING MATERIALS C102 TUTORIAL 3 THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM (PHASE) DIAGRAMS
 ENGINEERING COUNCIL CERTIFICATE LEVEL ENGINEERING MATERIALS C102 TUTORIAL 3 THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM (PHASE) DIAGRAMS UNIT OUTCOMES On successful completion of the unit the candidate will be able to: 1. Recognise
ENGINEERING COUNCIL CERTIFICATE LEVEL ENGINEERING MATERIALS C102 TUTORIAL 3 THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM (PHASE) DIAGRAMS UNIT OUTCOMES On successful completion of the unit the candidate will be able to: 1. Recognise
Solids SECTION Critical Thinking
 SECTION 10.3 Solids A gas has neither a definite volume nor a definite shape. A liquid has a definite volume, but not a definite shape. A solid, the third state, has a definite volume and a definite shape.
SECTION 10.3 Solids A gas has neither a definite volume nor a definite shape. A liquid has a definite volume, but not a definite shape. A solid, the third state, has a definite volume and a definite shape.
VITRIFIED BOTTOM ASH SLAG FROM MUNICIPAL SOLID WASTE INCINERATORS - PHASE RELATIONS OF CaO-SiO 2 -Na 2 O OXIDE SYSTEM
 VITRIFIED BOTTOM ASH SLAG FROM MUNICIPAL SOLID WASTE INCINERATORS - PHASE RELATIONS OF CaO-SiO 2 -Na 2 O OXIDE SYSTEM Zhan Zhang, Yanping Xiao, Yongxiang Yang, Rob Boom & Jack Voncken Delft University
VITRIFIED BOTTOM ASH SLAG FROM MUNICIPAL SOLID WASTE INCINERATORS - PHASE RELATIONS OF CaO-SiO 2 -Na 2 O OXIDE SYSTEM Zhan Zhang, Yanping Xiao, Yongxiang Yang, Rob Boom & Jack Voncken Delft University
LN Introduction to Solid State Chemistry. Lecture Notes No. 10 PHASE EQUILIBRIA AND PHASE DIAGRAMS
 3.091 Introduction to Solid State Chemistry Lecture Notes No. 10 PHASE EQUILIBRIA AND PHASE DIAGRAMS * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Sources
3.091 Introduction to Solid State Chemistry Lecture Notes No. 10 PHASE EQUILIBRIA AND PHASE DIAGRAMS * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Sources
FIRST MIDTERM EXAM Chemistry March 2011 Professor Buhro
 FIRST MIDTERM EXAM Chemistry 465 1 March 2011 Professor Buhro Signature Print Name Clearly ID Number: Information. This is a closed-book exam; no books, notes, other students, other student exams, or any
FIRST MIDTERM EXAM Chemistry 465 1 March 2011 Professor Buhro Signature Print Name Clearly ID Number: Information. This is a closed-book exam; no books, notes, other students, other student exams, or any
Thermochemical Studies of Relevance for Black Liquor Combustion and Gasification - The System Na 2 CO 3 -Na 2 S
 Thermochemical Studies of Relevance for Black Liquor Combustion and Gasification - The System CO 3 - S Mathias Råberg Anders Larsson, Gustav Lindberg, Anders Nordin, Dan Boström, Björn Warnqvist, Erik
Thermochemical Studies of Relevance for Black Liquor Combustion and Gasification - The System CO 3 - S Mathias Råberg Anders Larsson, Gustav Lindberg, Anders Nordin, Dan Boström, Björn Warnqvist, Erik
Study of discrimination between natural graphite and artificial graphite
 65 * * * Study of discrimination between natural graphite and artificial graphite Kenji KIMURA*, Masanori KODA*, Naoki KURASHIMA* *Central Customs Laboratory, Ministry of Finance 6-3-5, Kashiwanoha, Kashiwa,
65 * * * Study of discrimination between natural graphite and artificial graphite Kenji KIMURA*, Masanori KODA*, Naoki KURASHIMA* *Central Customs Laboratory, Ministry of Finance 6-3-5, Kashiwanoha, Kashiwa,
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF PHASE EQUILIBRIA OF SUBSYSTEMS IN THE MnO-SiO 2 -Al 2 O 3 -MnS SYSTEM
 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF PHASE EQUILIBRIA OF SUBSYSTEMS IN THE MnO-SiO 2 -Al 2 O 3 -MnS SYSTEM Dae-Hee Woo, Henri Gaye & Hae-Geon Lee Pohang University of Science and Technology, Korea Youn-Bae Kang
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF PHASE EQUILIBRIA OF SUBSYSTEMS IN THE MnO-SiO 2 -Al 2 O 3 -MnS SYSTEM Dae-Hee Woo, Henri Gaye & Hae-Geon Lee Pohang University of Science and Technology, Korea Youn-Bae Kang
Nonisothermal Phase Transformation of the Glassy Composition TeSe 20
 Egypt. J. Sol., Vol. (23), No. (2), (2000) 259 Nonisothermal Phase Transformation of the Glassy Composition TeSe 20 M.B. El-Den Physics Department, Faculty of Science, Ain Shams University Cairo, Egypt
Egypt. J. Sol., Vol. (23), No. (2), (2000) 259 Nonisothermal Phase Transformation of the Glassy Composition TeSe 20 M.B. El-Den Physics Department, Faculty of Science, Ain Shams University Cairo, Egypt
Physics 6180: Graduate Physics Laboratory. Experiment CM5: X-ray diffraction and crystal structures
 Physics 6180: Graduate Physics Laboratory Experiment CM5: X-ray diffraction and crystal structures References: Preston and Dietz, Expt. 10 pp. 180-197 Eisberg and Resnick, Quantum Physics, Sec. 9 Kittel,
Physics 6180: Graduate Physics Laboratory Experiment CM5: X-ray diffraction and crystal structures References: Preston and Dietz, Expt. 10 pp. 180-197 Eisberg and Resnick, Quantum Physics, Sec. 9 Kittel,
Thermochemical Studies of Relevance for Black Liquor Combustion and Gasification - The System Na 2 CO 3 -Na 2 S
 Thermochemical Studies of Relevance for Black Liquor Combustion and Gasification - The System Na 2 CO 3 -Na 2 S Mathias Råberg Anders Larsson, Gustav Lindberg, Anders Nordin, Dan Boström, Björn Warnqvist,
Thermochemical Studies of Relevance for Black Liquor Combustion and Gasification - The System Na 2 CO 3 -Na 2 S Mathias Råberg Anders Larsson, Gustav Lindberg, Anders Nordin, Dan Boström, Björn Warnqvist,
PHASE EQUILIBRIUM P + F = C + 2
 PHASE EQUILIBRIUM Component: is either pure metal and/or compound of which an alloy is composed. They refer to the independent chemical species that comprise the system. Solid Solution: It consists of
PHASE EQUILIBRIUM Component: is either pure metal and/or compound of which an alloy is composed. They refer to the independent chemical species that comprise the system. Solid Solution: It consists of
Preparation and ionic conductivity of new Bi 12.5 Lu 1.5 ReO 24.5 phase
 Preparation and ionic conductivity of new Bi 12.5 Lu 1.5 ReO 24.5 phase A.N. Bryzgalova 1, N.I. Matskevich 1*, Th. Wolf 2, C. Greaves 3 1 Nikolaev Institute of Inorganic Chemistry, Siberian Branch of the
Preparation and ionic conductivity of new Bi 12.5 Lu 1.5 ReO 24.5 phase A.N. Bryzgalova 1, N.I. Matskevich 1*, Th. Wolf 2, C. Greaves 3 1 Nikolaev Institute of Inorganic Chemistry, Siberian Branch of the
CHEM J-2 June 2014
 CHEM1102 2014-J-2 June 2014 The diagram below shows the structure of an alloy of copper and gold with a gold atom at each of the corners and a copper atom in the centre of each of the faces. 2 What is
CHEM1102 2014-J-2 June 2014 The diagram below shows the structure of an alloy of copper and gold with a gold atom at each of the corners and a copper atom in the centre of each of the faces. 2 What is
A - Transformation of anatase into rutile
 Exercise-Course-XRD.doc 1/12 04/06/2012 A - Transformation of anatase into rutile Anatase and rutile are two distinct phases of titanium dioxide TiO 2. The stable phase is rutile. 1. Structural study Anatase:
Exercise-Course-XRD.doc 1/12 04/06/2012 A - Transformation of anatase into rutile Anatase and rutile are two distinct phases of titanium dioxide TiO 2. The stable phase is rutile. 1. Structural study Anatase:
Thermal Analysis phase diagrams
 Thermal Analysis phase diagrams R W McCallum Ames Laboratory And Materials Science and Engineering Why Phase Diagrams Thermal analysis gives us information about phase transitions which are the lines on
Thermal Analysis phase diagrams R W McCallum Ames Laboratory And Materials Science and Engineering Why Phase Diagrams Thermal analysis gives us information about phase transitions which are the lines on
Effect of titanium additions to low carbon, low manganese steels on sulphide precipitation
 University of Wollongong Thesis Collections University of Wollongong Thesis Collection University of Wollongong Year 2008 Effect of titanium additions to low carbon, low manganese steels on sulphide precipitation
University of Wollongong Thesis Collections University of Wollongong Thesis Collection University of Wollongong Year 2008 Effect of titanium additions to low carbon, low manganese steels on sulphide precipitation
Metals are used by industry for either one or combination of the following properties
 Basic Metallurgy Metals are the backbone of the engineering industry being the most important Engineering Materials. In comparison to other engineering materials such as wood, ceramics, fabric and plastics,
Basic Metallurgy Metals are the backbone of the engineering industry being the most important Engineering Materials. In comparison to other engineering materials such as wood, ceramics, fabric and plastics,
THERMAL RESISTANCE AND PHASE TRANSITIONS STUDIES FOR SOME COMPOSITE MATERIALS BASED ON Al 20 3
 Vol. 96 (1999) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 2 Proceedings of the III Int. School and Symposium on Physics in Materials Science, Jaszowiec '98 THERMAL RESISTANCE AND PHASE TRANSITIONS STUDIES FOR SOME COMPOSITE
Vol. 96 (1999) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 2 Proceedings of the III Int. School and Symposium on Physics in Materials Science, Jaszowiec '98 THERMAL RESISTANCE AND PHASE TRANSITIONS STUDIES FOR SOME COMPOSITE
Bulk Metallic Glasses
 2018 Spring Advanced Physical Metallurgy Bulk Metallic Glasses 03.28.2018 Eun Soo Park Office: 33 313 Telephone: 880 7221 Email: espark@snu.ac.kr Office hours: by appointment 1 * Development strategy of
2018 Spring Advanced Physical Metallurgy Bulk Metallic Glasses 03.28.2018 Eun Soo Park Office: 33 313 Telephone: 880 7221 Email: espark@snu.ac.kr Office hours: by appointment 1 * Development strategy of
On solid solutions in the system LiF Na 3
 On solid solutions in the system LiF * I KOŠTENSKÁ, bj ČORBA, and a M MALINOVSKÝ ^-Department of Inorganic Technology, Slovak Technical University, 880 37 Bratislava ^Institute of Inorganic Chemistry,
On solid solutions in the system LiF * I KOŠTENSKÁ, bj ČORBA, and a M MALINOVSKÝ ^-Department of Inorganic Technology, Slovak Technical University, 880 37 Bratislava ^Institute of Inorganic Chemistry,
G16 - THERMAL ANALYSIS
 001-1012PDG.pdf 1 1 G16 - THERMAL ANALYSIS 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Thermal analysis is a group of techniques in which the variation of a physical property of a substance is measured as a function of temperature.
001-1012PDG.pdf 1 1 G16 - THERMAL ANALYSIS 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Thermal analysis is a group of techniques in which the variation of a physical property of a substance is measured as a function of temperature.
AMORPHISATION PROCESS DURING MECHANICAL ALLOYING OF Al-Fe-Ti POWDERS AND CRYSTALLISATION OF THE MILLING PRODUCTS
 Amorphisation Rev.Adv.Mater.Sci. process 18(2008) during 393-397 mechanical alloying of Al-Fe-Ti powders and crystallisation of... 393 AMORPHISATION PROCESS DURING MECHANICAL ALLOYING OF Al-Fe-Ti POWDERS
Amorphisation Rev.Adv.Mater.Sci. process 18(2008) during 393-397 mechanical alloying of Al-Fe-Ti powders and crystallisation of... 393 AMORPHISATION PROCESS DURING MECHANICAL ALLOYING OF Al-Fe-Ti POWDERS
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Tetragonal faceted-nanorods of anatase TiO 2 with large percentage of active {100} facets and their hierarchical structure Jianming Li, Ke Cao, Qi Li and Dongsheng
Electronic Supplementary Information Tetragonal faceted-nanorods of anatase TiO 2 with large percentage of active {100} facets and their hierarchical structure Jianming Li, Ke Cao, Qi Li and Dongsheng
Phase Diagrams, Solid Solutions, Phase Strengthening, Phase Transformations
 Phase Diagrams, Solid Solutions, Phase Strengthening, Phase Transformations Components and Phases Components: The elements or compounds that are mixed initially (Al and Cu). Phases: A phase is a homogenous,
Phase Diagrams, Solid Solutions, Phase Strengthening, Phase Transformations Components and Phases Components: The elements or compounds that are mixed initially (Al and Cu). Phases: A phase is a homogenous,
Phase Diagrams of Pure Substances Predicts the stable phase as a function of P total and T. Example: water can exist in solid, liquid and vapor
 PHASE DIAGRAMS Phase a chemically and structurally homogenous region of a material. Region of uniform physical and chemical characteristics. Phase boundaries separate two distinct phases. A single phase
PHASE DIAGRAMS Phase a chemically and structurally homogenous region of a material. Region of uniform physical and chemical characteristics. Phase boundaries separate two distinct phases. A single phase
CHAPTER 9: PHASE DIAGRAMS
 CHAPTER 9: PHASE DIAGRAMS ISSUES TO ADDRESS... When we combine two elements... what equilibrium state do we get? In particular, if we specify... --a composition (e.g., wt%cu - wt%ni), and --a temperature
CHAPTER 9: PHASE DIAGRAMS ISSUES TO ADDRESS... When we combine two elements... what equilibrium state do we get? In particular, if we specify... --a composition (e.g., wt%cu - wt%ni), and --a temperature
CHAPTER THE SOLID STATE
 133 CHAPTER THE SOLID STATE 1. The ability of a substances to assume two or more crystalline structures is called [1990] Isomerism Polymorphism Isomorphism Amorphism 2. Most crystals show good cleavage
133 CHAPTER THE SOLID STATE 1. The ability of a substances to assume two or more crystalline structures is called [1990] Isomerism Polymorphism Isomorphism Amorphism 2. Most crystals show good cleavage
Synthesis of potassium manganese oxides under hydrothermal conditions
 MINERALOGICAL MAGAZINE, MARCH I974, VOL. 39, vv. 559-63. Synthesis of potassium manganese oxides under hydrothermal conditions T. ENDO AND S. KUME College of General Education, Osaka University AND M.
MINERALOGICAL MAGAZINE, MARCH I974, VOL. 39, vv. 559-63. Synthesis of potassium manganese oxides under hydrothermal conditions T. ENDO AND S. KUME College of General Education, Osaka University AND M.
High Pressure Synthesis of Novel Compounds in Mg-TM Systems (TM = Ti Zn)* 1
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 45, No. 4 (2004) pp. 1350 to 1354 #2004 The Japan Institute of Metals High Pressure Synthesis of Novel Compounds in Mg-TM Systems (TM = Ti Zn)* 1 Hiroaki Watanabe* 2, Yasuyuki
Materials Transactions, Vol. 45, No. 4 (2004) pp. 1350 to 1354 #2004 The Japan Institute of Metals High Pressure Synthesis of Novel Compounds in Mg-TM Systems (TM = Ti Zn)* 1 Hiroaki Watanabe* 2, Yasuyuki
KEY FIRST MIDTERM EXAM Chemistry February 2009 Professor Buhro
 KEY FIRST MIDTERM EXAM Chemistry 465 19 February 2009 Professor Buhro Signature KEY Print Name Clearly ID Number: Information. This is a closed-book exam; no books, notes, other students, other student
KEY FIRST MIDTERM EXAM Chemistry 465 19 February 2009 Professor Buhro Signature KEY Print Name Clearly ID Number: Information. This is a closed-book exam; no books, notes, other students, other student
Phase diagram of carbon. Lecture 10. Simple eutectic systems. Greek, Eutektos easily melting Eu good, well + tekein to melt
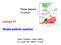 Phase diagram of carbon Lecture 10 Simple eutectic systems Greek, Eutektos easily melting Eu good, well + tekein to melt Motivation: A two component system is the simplest of multicomponent systems. A
Phase diagram of carbon Lecture 10 Simple eutectic systems Greek, Eutektos easily melting Eu good, well + tekein to melt Motivation: A two component system is the simplest of multicomponent systems. A
Electronic origin of melting T P curves of alkali metals with negative slope and minimum
 Electronic origin of melting T P curves of alkali metals with negative slope and minimum Degtyareva V.F. Institute of Solid State Physics, Russian Academy of Sciences, Chernogolovka, Russia degtyar@issp.ac.ru
Electronic origin of melting T P curves of alkali metals with negative slope and minimum Degtyareva V.F. Institute of Solid State Physics, Russian Academy of Sciences, Chernogolovka, Russia degtyar@issp.ac.ru
SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF LEAD ZIRCONATE BY HOMOGENEOUS PRECIPITATION AND CALCINATIONS
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 2, No 1, 2013, 38-47 SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF LEAD ZIRCONATE BY HOMOGENEOUS PRECIPITATION AND CALCINATIONS Suman Pawar* Department
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 2, No 1, 2013, 38-47 SYNTHESIS AND CHARACTERIZATION OF LEAD ZIRCONATE BY HOMOGENEOUS PRECIPITATION AND CALCINATIONS Suman Pawar* Department
Diffraction: Powder Method
 Diffraction: Powder Method Diffraction Methods Diffraction can occur whenever Bragg s law λ = d sin θ is satisfied. With monochromatic x-rays and arbitrary setting of a single crystal in a beam generally
Diffraction: Powder Method Diffraction Methods Diffraction can occur whenever Bragg s law λ = d sin θ is satisfied. With monochromatic x-rays and arbitrary setting of a single crystal in a beam generally
Chapter 9 Phase Diagrams. Dr. Feras Fraige
 Chapter 9 Phase Diagrams Dr. Feras Fraige Chapter Outline Definitions and basic concepts Phases and microstructure Binary isomorphous systems (complete solid solubility) Binary eutectic systems (limited
Chapter 9 Phase Diagrams Dr. Feras Fraige Chapter Outline Definitions and basic concepts Phases and microstructure Binary isomorphous systems (complete solid solubility) Binary eutectic systems (limited
Synthesis calcium-titanate (CaTiO 3 )
 Synthesis calcium-titanate (CaTiO 3 ) Vera Petrovic The Advanced School of Electrical Engineering,Belgrade, Vojvode Stepe 283, SCG Abstract Ceramic materials have been in use in many different areas of
Synthesis calcium-titanate (CaTiO 3 ) Vera Petrovic The Advanced School of Electrical Engineering,Belgrade, Vojvode Stepe 283, SCG Abstract Ceramic materials have been in use in many different areas of
1. Use the Ellingham Diagram (reproduced here as Figure 0.1) to answer the following.
 315 Problems 1. Use the Ellingham Diagram (reproduced here as Figure 0.1) to answer the following. (a) Find the temperature and partial pressure of O 2 where Ni(s), Ni(l), and NiO(s) are in equilibrium.
315 Problems 1. Use the Ellingham Diagram (reproduced here as Figure 0.1) to answer the following. (a) Find the temperature and partial pressure of O 2 where Ni(s), Ni(l), and NiO(s) are in equilibrium.
Review key concepts from last lecture (lattice + basis = unit cell) Bravais lattices Important crystal structures Intro to miller indices
 Outline: Review key concepts from last lecture (lattice + basis = unit cell) Bravais lattices Important crystal structures Intro to miller indices Review (example with square lattice) Lattice: square,
Outline: Review key concepts from last lecture (lattice + basis = unit cell) Bravais lattices Important crystal structures Intro to miller indices Review (example with square lattice) Lattice: square,
MAKING SOLID SOLUTIONS WITH ALKALI HALIDES (AND BREAKING THEM) John B. Brady
 MAKING SOLID SOLUTIONS WITH ALKALI HALIDES (AND BREAKING THEM) John B. Brady Department of Geology Smith College Northampton, MA jbrady@science.smith.edu INTRODUCTION When two cations have the same charge
MAKING SOLID SOLUTIONS WITH ALKALI HALIDES (AND BREAKING THEM) John B. Brady Department of Geology Smith College Northampton, MA jbrady@science.smith.edu INTRODUCTION When two cations have the same charge
PREPARATION OF TERNARY CHLORIDES OF A 2 MCL 4 (A = K, Cs, Li) (M = Sr, Ba) Using Solution Method
 IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC) e-issn: 2278-5736.Volume 9, Issue 8 Ver. II (Aug. 216), PP 52-59 www.iosrjournals.org PREPARATION OF TERNARY CHLORIDES OF A 2 MCL 4 (A = K, Cs, Li) (M = Sr,
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC) e-issn: 2278-5736.Volume 9, Issue 8 Ver. II (Aug. 216), PP 52-59 www.iosrjournals.org PREPARATION OF TERNARY CHLORIDES OF A 2 MCL 4 (A = K, Cs, Li) (M = Sr,
mole fraction at a temperature of 820 "C.
 Phase Relationships in the Calcium Chloride Calcium Carbide System J. F. MAILLOT Department of Engineering, Universiry of Moncton, Moncton, New Brunswick AND D. R. MORRIS Department of Cliemical Engineering,
Phase Relationships in the Calcium Chloride Calcium Carbide System J. F. MAILLOT Department of Engineering, Universiry of Moncton, Moncton, New Brunswick AND D. R. MORRIS Department of Cliemical Engineering,
Decomposition of Li 2 CO 3 in existence of SiO 2 in mould flux of steel casting
 KIM, J-W., LEE, Y-D., KANG, Y-D and LEE, H-G. Decomposition of Li 2 CO 3 in existence of SiO 2 in mould flux of steel casting. VII International Conference on Molten Slags Fluxes and Salts, The South African
KIM, J-W., LEE, Y-D., KANG, Y-D and LEE, H-G. Decomposition of Li 2 CO 3 in existence of SiO 2 in mould flux of steel casting. VII International Conference on Molten Slags Fluxes and Salts, The South African
SOLID STATE
 SOLID STATE Short Answer Questions: 1. Derive Bragg s equation? Ans. Bragg s equation: W.H. Bragg has proposed an equation to explain the relation between inter planar distance (d) and wave length ( λ
SOLID STATE Short Answer Questions: 1. Derive Bragg s equation? Ans. Bragg s equation: W.H. Bragg has proposed an equation to explain the relation between inter planar distance (d) and wave length ( λ
MgO modification of slag from stainless steelmaking
 ERIKSSON, J and BJÖRKMAN, B. MgO modification of slag from stainless steelmaking. VII International Conference on Molten Slags Fluxes and Salts, The South African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 2004.
ERIKSSON, J and BJÖRKMAN, B. MgO modification of slag from stainless steelmaking. VII International Conference on Molten Slags Fluxes and Salts, The South African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 2004.
Growth of bulk single crystals β-fesi 2 by chemical vapour deposition
 Vol. 46 No. 1 SCIENCE IN CHINA (Series G) February 2003 Growth of bulk single crystals β-fesi 2 by chemical vapour deposition LI Yanchun ( ) 1,2, SUN Liling ( ) 1,3,CAOLimin( ) 1, ZHAO Jianhua ( ) 2,WANGHaiyan(
Vol. 46 No. 1 SCIENCE IN CHINA (Series G) February 2003 Growth of bulk single crystals β-fesi 2 by chemical vapour deposition LI Yanchun ( ) 1,2, SUN Liling ( ) 1,3,CAOLimin( ) 1, ZHAO Jianhua ( ) 2,WANGHaiyan(
The effect of nickel on the martensitic-type transformations of Pt 3 AI and TiPt
 J. Phys. IVFrance 11 (2001) Pr8-493 EDP Sciences, Les Ulis The effect of nickel on the martensitic-type transformations of Pt 3 AI and TiPt T. Biggs, L.A. Cornish 1, M.J. Witcomb 2 and M.B. Cortie Physical
J. Phys. IVFrance 11 (2001) Pr8-493 EDP Sciences, Les Ulis The effect of nickel on the martensitic-type transformations of Pt 3 AI and TiPt T. Biggs, L.A. Cornish 1, M.J. Witcomb 2 and M.B. Cortie Physical
MANUFACTURING AND EVALUATING CU-BASED SHAPE MEMORY ALLOY BY HOT EXTRUSION OF PM SAMPLES MADE BY MECHANICAL ALLOYING
 MANUFACTURING AND EVALUATING CU-BASED SHAPE MEMORY ALLOY BY HOT EXTRUSION OF PM SAMPLES MADE BY MECHANICAL ALLOYING Sajjad Pourkhorshidi, Mohammad Naeimi, Nader Parvin, Seyed Mohammad Mahdi Zamani, Hamid
MANUFACTURING AND EVALUATING CU-BASED SHAPE MEMORY ALLOY BY HOT EXTRUSION OF PM SAMPLES MADE BY MECHANICAL ALLOYING Sajjad Pourkhorshidi, Mohammad Naeimi, Nader Parvin, Seyed Mohammad Mahdi Zamani, Hamid
Introduction to the phase diagram Uses and limitations of phase diagrams Classification of phase diagrams Construction of phase diagrams
 Prof. A.K.M.B. Rashid Department of MME BUET, Dhaka Concept of alloying Classification of alloys Introduction to the phase diagram Uses and limitations of phase diagrams Classification of phase diagrams
Prof. A.K.M.B. Rashid Department of MME BUET, Dhaka Concept of alloying Classification of alloys Introduction to the phase diagram Uses and limitations of phase diagrams Classification of phase diagrams
9/28/2013 9:26 PM. Chapter 3. The structure of crystalline solids. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 3 The structure of crystalline solids 1 2 Why study the structure of crystalline solids? Properties of some materials are directly related to their crystal structure. Significant property differences
Chapter 3 The structure of crystalline solids 1 2 Why study the structure of crystalline solids? Properties of some materials are directly related to their crystal structure. Significant property differences
Are gamma amino acids promising tools of crystal engineering? Multicomponent crystals of baclofen
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Are gamma amino acids promising tools of crystal engineering?
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Are gamma amino acids promising tools of crystal engineering?
Lecture 42 Phase Diagram of Ceramic
 Phase Diagrams in Material Science Engineering Prof. Krishanu Biswas Department of Materials Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 42 Phase Diagram of Ceramic So, students
Phase Diagrams in Material Science Engineering Prof. Krishanu Biswas Department of Materials Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 42 Phase Diagram of Ceramic So, students
GROWTH AND CHARACTERIZATION OF NANOSTRUCTURED CdS THIN FILMS BY CHEMICAL BATH DEPOSITION TECHNIQUE
 Chalcogenide Letters Vol. 6, No. 8, September 29, p. 415 419 GROWTH AND CHARACTERIZATION OF NANOSTRUCTURED CdS THIN FILMS BY CHEMICAL BATH DEPOSITION TECHNIQUE V. B. SANAP *, B. H. PAWAR, * MSS s College
Chalcogenide Letters Vol. 6, No. 8, September 29, p. 415 419 GROWTH AND CHARACTERIZATION OF NANOSTRUCTURED CdS THIN FILMS BY CHEMICAL BATH DEPOSITION TECHNIQUE V. B. SANAP *, B. H. PAWAR, * MSS s College
Hahn-Meitner-Institut Berlin, Glienicker Str. 100, D-14109, Berlin, Germany
 Journal of Metastable and Nanocrystalline Materials Vols. 20-21 (2004) pp. 35-40 online at http://www.scientific.net (2004) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Crystallization of Pd 40 Cu 30 Ni 10 P 20
Journal of Metastable and Nanocrystalline Materials Vols. 20-21 (2004) pp. 35-40 online at http://www.scientific.net (2004) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Crystallization of Pd 40 Cu 30 Ni 10 P 20
Synthesis and characterization of Aln 2 O 4 indates, A ˆ Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba
 JOURNAL OF MATERIALS SCIENCE LETTERS 17 (1998) 619±623 Synthesis and characterization of Aln 2 O 4 indates, A ˆ Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba S. ESTHER DALI, V. V. S. S. SAI SUNDAR, M. JAYACHANDRAN, M. J. CHOCKALINGAM
JOURNAL OF MATERIALS SCIENCE LETTERS 17 (1998) 619±623 Synthesis and characterization of Aln 2 O 4 indates, A ˆ Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba S. ESTHER DALI, V. V. S. S. SAI SUNDAR, M. JAYACHANDRAN, M. J. CHOCKALINGAM
D. Ehrt*, H. T. Vu, A. Herrmann and G. Völksch
 Advanced Materials Research Online: 28-4-8 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vols. 39-4, pp 231-236 doi:1.428/www.scientific.net/amr.39-4.231 28 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Luminescent ZnO-Al 2 O 3 -SiO 2 glasses
Advanced Materials Research Online: 28-4-8 ISSN: 1662-8985, Vols. 39-4, pp 231-236 doi:1.428/www.scientific.net/amr.39-4.231 28 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Luminescent ZnO-Al 2 O 3 -SiO 2 glasses
MODELLING OF THE THERMO-PHYSICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES FOR SOLIDIFICATION OF AL-ALLOYS
 Light Metals 23 Edited by P. Crepeau (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 23), 999. MODELLING OF THE THERMO-PHYSICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES FOR SOLIDIFICATION OF AL-ALLOYS N.Saunders 1, X.Li 2, A.P.Miodownik 1 and J.-P.Schillé
Light Metals 23 Edited by P. Crepeau (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 23), 999. MODELLING OF THE THERMO-PHYSICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES FOR SOLIDIFICATION OF AL-ALLOYS N.Saunders 1, X.Li 2, A.P.Miodownik 1 and J.-P.Schillé
Studies on X doped (X = Al, Zn and Cu) and undoped Lead Iodide single crystals relating to XRD
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2011, 2 (6): 498-504 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC Studies on X doped (X = Al, Zn and Cu) and undoped Lead
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com Advances in Applied Science Research, 2011, 2 (6): 498-504 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC Studies on X doped (X = Al, Zn and Cu) and undoped Lead
[CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK]
![[CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK] [CLICK]](/thumbs/79/79522651.jpg) A major principle of materials science is that PROPERTIES are related to STRUCTURE. A material s structure is only partly described by reporting the composition. You must also report the phases, composition
A major principle of materials science is that PROPERTIES are related to STRUCTURE. A material s structure is only partly described by reporting the composition. You must also report the phases, composition
IF YOUR ONLY SINGLE CRYSTAL IS NOT REALLY SINGLE
 THE RIGAKU JOURNAL VOL. 12 / NO.1 / 1995 IF YOUR ONLY SINGLE CRYSTAL IS NOT REALLY SINGLE L. W. FINGER Geophysical Laboratory and Center for High-Pressure Research, 5251 Broad Branch Road, N.W. Washington,
THE RIGAKU JOURNAL VOL. 12 / NO.1 / 1995 IF YOUR ONLY SINGLE CRYSTAL IS NOT REALLY SINGLE L. W. FINGER Geophysical Laboratory and Center for High-Pressure Research, 5251 Broad Branch Road, N.W. Washington,
MODELLING OF THE THERMO-PHYSICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES FOR SOLIDIFICATION OF AL-ALLOYS
 Light Metals 23 Edited by P. Crepeau TMS (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society), 23 MODELLING OF THE THERMO-PHYSICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES FOR SOLIDIFICATION OF AL-ALLOYS N.Saunders 1, X.Li 2, A.P.Miodownik
Light Metals 23 Edited by P. Crepeau TMS (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society), 23 MODELLING OF THE THERMO-PHYSICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES FOR SOLIDIFICATION OF AL-ALLOYS N.Saunders 1, X.Li 2, A.P.Miodownik
Crystal Quality A Practical Guide
 Crystal Quality A Practical Guide Louis J Farrugia Suitability for Charge Density Analysis The suitability factor S,, which defines how likely you are to obtain a satisfactory charge density analysis from
Crystal Quality A Practical Guide Louis J Farrugia Suitability for Charge Density Analysis The suitability factor S,, which defines how likely you are to obtain a satisfactory charge density analysis from
Bulk Metallic Glasses
 2016 Spring Advanced Physical Metallurgy Bulk Metallic Glasses 03.16.2016 Eun Soo Park Office: 33 313 Telephone: 880 7221 Email: espark@snu.ac.kr Office hours: by appointment 1 * Development strategy of
2016 Spring Advanced Physical Metallurgy Bulk Metallic Glasses 03.16.2016 Eun Soo Park Office: 33 313 Telephone: 880 7221 Email: espark@snu.ac.kr Office hours: by appointment 1 * Development strategy of
