Effect of Electrodeposition Parameters on Morphology of Copper Thin Films
|
|
|
- Abigayle Harmon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN) e-issn: , p-issn: Vol. 3, Issue 8 (August. 2013), V3 PP Effect of Electrodeposition Parameters on Morphology of Copper Thin Films Jaishree Mathur, and Manish Gupta 1 (Department of Physics, Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya, Mandaphia, Chittorgarh, Rajasthan, India) 2 (Project director Department of Science and Technology, Jaipur, Rajasthan) Abstract: - In this work a simple approach of highly dispersed electro catalytically active copper nano-structured thin film has been electrodeposited on conducting Indium Tin Oxide coated (ITO) glass plate from non cyanide acidic electrolyte. The influence of deposition variables such as: ph, deposition time and current density on film composition, morphology and crystal orientation associated with the growth of the film was investigated. The copper dendrites are characterized by Optical microscopy, SEM, X-Ray Diffraction, Electrical resistivity as well as by cyclic voltammetry under different conditions. Optimal conditions for uniform growth of nanoparticles well-dispersed, golden shiny cubic copper on the ITO glass plate have been determined. Keywords: - Electrodeposition, morphology, Scanning electron microscopy, XRD, Electrical conductivity of thin film. I. INTRODUCTION The Copper is electrodeposited for numerous engineering and decorative applications requiring wide range of mechanical and physical properties. This range extends from properties superior to full hard, wrought copper to properties equivalent to an annealed, pure copper, resistivity, elastic modulus and coefficient of thermal expansion are important physical properties which can be controlled. The desired properties will be obtained only when the plating baths and operating conditions are properly selected [1-3]. Copper is the metal of choice for interconnects because it addresses issues such as performances of integrated circuits with the continuing trend toward miniaturization of devices, successful applications of copper electrodeposition in nano interconnects could strongly depend on its surface roughness scattering. The increase in electronic resistivity due to surface scattering is a fundamental quantum mechanics problem, while the elimination of surface roughness scattering and grain boundary scattering is a morphological issue which can be controlled by fabrication technique [4]. Copper thin films are also used in the multilayer sandwiches of GMR hard disk read heads. Among various methods of thin film deposition of copper onto substrates such as PVD, CVD and sputtering [5], The electrochemical methods have proven to be at least expensive, highly productive and readily adoptable [6-7]. The electrodeposition of materials allows formation of thin layers, like monolayers, with the added advantage of a better kinetic control [8]; this is expected because there is effective control over the coverage of the deposited material monolayer. Electrodeposition of copper from cyanide solutions is a long established industrial practice [9-11]. But this process is now used infrequently, not only because of its toxicity but also due to photo resistive attack during the plating process. Thus an extensive search has been made for satisfactory alternative electrolytes. In this context we have undertaken a complete study of copper electrodeposition on ITO coated glass substrate in CuSO4.5H2O solution by varying different deposition parameters. The work described here illustrates how the sulfate and OH- ions can modify the morphology of the copper electrodeposits, undertaking the dynamics of these processes is essential in the design of chemical systems for practical applications. II. EXPERIMENTAL DETAILS Electrolytic solution was prepared using CuSO4.5H2O (Sigma Aldrich) 99.99% pure and deionized water (milipore) with concentration of 0.5 M of solution, 0.20 M sodium acetate and NaOH. Solution was adjusted to ph 1-5 by adding diluted reagent grade sulfuric acid. Substrate were cleaned and rinsed with distilled water and acetone before deposition of the films. Here Copper plate was used as counter electrode, ITO as working electrode and Ag/AgCl as reference electrode. All experiments were carried out at room temperature. Electrodeposition cell was designed and constructed manually in the laboratory. Thin films of copper have been electrodeposited by varying deposition parameters as follows: (i) Keeping current density and ph of the electrolyte as constant but varying deposition time. (ii) Keeping current density and deposition time as constant but varying ph of the electrolytic solution. (iii) Keeping deposition time and ph as constant but varying current density. All above variations are done at room temperature. 55 P a g e
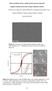
2 These thin films are characterized by X-ray diffraction, SEM, optical microscopy, cyclic voltammetry and surface resistivity measurements. III. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 3.1 Keeping ph and deposition time as constant but varying current density Here thin films of copper are electrodeposited at ph=5 and deposition time was kept for 10 minutes with concentration of electrolyte as 0.5 M. In Fig. 3.1 the optical micrographs shows that as the current density increases, coalescence is more [12]. At high constant current density of 1.2mAcm- 2 the morphology of copper particles is similar to that of the particles formed at 0.5mAcm -2. However the particle sizes are not uniform and most of them are as small as only 100 nm. At a very high current density of 1.6mAcm- 2, the edges and corners of the roundest nuclei grow faster than their other regions and finally grow into copper nanosheets The SEM results (as shown in Fig. 3.2) that the growth of copper nanostructure can be regarded as an instantaneous nucleation process. This shows that due to increase in current density of 1.6mAcm- 2, the size of cluster decreased gradually and the deposits obtained were clear, uniform and golden. Here sulfate anions act as brighteners. Figure 3.1 Optical micrographs of Films electrodeposited at deposition time 10 minutes and current density (a) 0.5mAcm -2, (b)0.8macm -2 (c) 1.2mAcm -2 and (d)1.6macm -2 Figure3.2 SEM of electrodeposited copper thin films deposited at current density 1.6 macm -2 at ph=5 and deposition time 10 minutes. 3.2 Keeping current density and deposition time as constant but varying ph of the electrolytic solution 56 P a g e
3 In order to study the role of ph in the electro deposition of Cu thin films ph is varied in the range from 3 to 13. Concentration of the electrolytic solution was 0.5 M current density was kept at 1.6mAcm -2 and deposition time for 10 minutes. It is cleared from Fig. 3.3 that at ph =3, copper was deposited in the form of equally sized and somewhat rounded grains. At ph=4, the grains were no longer equally sized. Some of the grains at ph=4 were of quite larger size than at ph =3. Thus ph increase was responsible for the grain shapes and the decrease of surface nuclei population density. The surface morphology is found to be ph dependent. It is observed that Cu film deposited at ph=5 exhibits cubic structure. As ph increases from 5 to 13 the grain size of the film is found to be decreased. It is due to the role of rate of deposition. The rate of deposition increased gradually up to ph=4 and then increased steeply for ph values exceeding 4. Such higher rate of deposition caused the change in orientation and reduction in grain size at ph =9. During such grain size reduction the shape of the grains gets damaged and hence it changes from cubic to fibrous structure at ph 13 as shown in Fig Further if the deposition was carried out at ph greater than 5, the grains with well defined shape could not be detected. Instead these films showed surfaces with a spongy looking texture as shown in Fig. 3.3(c). An increase in ph value results in increase in copper concentration in the film with improved uniformity. As the ph value increases cathode potential increases and hence more copper gets electrodeposited in the film. The films which are grown at a ph value 5.0 exhibit better physical properties. The SEM micrographs show decrease in grain size with an increase in ph value in Figure 3.3. A fine grained nanostructure is observed at a ph value of 5. Figure 3.3 SEM of electrodeposited copper thin films deposited at ph (a) 4.0 (b) 5.0 and (c) ph=9. Figure 3.4 SEM of electrodeposited copper film deposited at ph=13 showing fibrous structure 3.3 Keeping current density, ph of the electrolyte as constant but varying deposition time In this case current density and ph of the solution was kept as constant and deposition time is varied. It is found that at low current density if deposition time is more, thickness of film increases, due to greater number of particles reaching the cathode and depositing on it. For longer deposition time, at higher current density, the film thickness achieves a maximum and then decreases due to larger amount of evolved hydrogen, which accumulates on the cathode and causes more pores in the deposited film. It can be concluded that optimal deposition time is 20 minute for an applied current density of 1.6mAcm -2. The optical micrograph of copper film obtained under the conditions is represented in Fig At the very beginning of the deposition process, the copper particles are attracted to the cathode surface. However a large percentage of film surfaces are covered by pores due to large number of pores existing in the film as a result of the hydrogen evolution reaction on the cathode. After a few seconds, the pores are filled with copper particles and consequently film porosity decreases and achieves a minimum value [13]. During further deposition, the film porosity increases but not significantly, due to the larger amount of evolved hydrogen [14]. This shows that this is the case of instantaneous nucleation. As instantaneous nucleation corresponds to a slow growth of nuclei on a small number of active sites, all activated at the same time [15]. 57 P a g e
4 Figure 3.5 Thin films of Copper deposited at 1.6 macm -2 current density at deposition time (a)5min.(b) 10 min. (c)15 min. and (d) 20 min. Fig. 3.6 shows XRD pattern of copper electrodeposited film for 20 minute at current density 0.5 macm -2, 0.8mAcm -2 and 1.6 macm -2 with approximate thickness 550nm, 600nm and 700nm respectively on ITO substrate confirmed the formation of crystalline Cu with peaks (111), (200) and (220). Here some peaks are observed between 25 to 40 and 60 to70 are may be due to background of ITO. Thickness of the films was determined by gravimetric method and ellipsometric measurements. Lattice constant a=0.3615nm for cubic copper [16]. XRD studies of the films deposited from the bath with ph values 5.0 have been carried out, The average crystal grain size was estimated from the full width at half maxima of the Cu peak using the Scherrer equation [17] for the film deposited at different current density; d 0.9 / cos (1) Where λ is the wavelength used (1.5Ǻ), the angular line width at half maximum intensity in radians and is the Bragg s angle. Figure 3.6 XRD pattern of electrodeposited Copper thin films deposited at different current density for 20 minutes Table 1: Crystal size of Cu thin films deposited at different current density Thickness of the film Average crystal Size Current density 550nm 16.77nm 0.5 macm nm 17.27nm 0.8 macm nm 19.54nm 1.6 macm P a g e
5 Table 1 shows that as the grain size increases with increase in current density. When the current density is increased, the reduction overpotential also increases, which exponentially enhanced the nucleation rate. At a low current density, the dendritic structure was dominant; however, the nanostructure became granular with increasing current density. Table2: Optimum bath composition and operating conditions for electrodeposition of thin films of copper. Bath Composition Quantity Operating Condition 1. CuSO 4.5H 2 O 0.5M Anode: Copper metal (99.99%) 2. CH 3 COONa (sodium acetate) 0.20M Cathode: ITO coated glass plate Temperature: K 3. NaOH 1.0M Current density: 1.6mAcm H 2 SO 4 Concentrate (adjusting to ph) ph: Cyclic Voltammetry Figure 3.7 Voltammetric curves for copper electrodeposition at (a) ph=4, (b) ph=5 and (c) ph=9 at scan rate 100mV/s. Fig. 3.7 shows the cyclic voltammograms of electrodeposition of thin film of copper at different ph. These curves show that the effect of ph is responsible for the deposition of the film. At ph =4 no clear deposition peak has been found but at ph = 5 sharp deposition peak at current 10 ma and cathodic potential of - 780mV has formed. If we increase the ph as shown in Fig. 3.7 (c) current decrease and shift oxidation peak up to more positive potential. In Fig. 3.7 (c) there is no reduction waves of oxygen in the potential range mv to -500 mv this wave shows catalytic reduction of oxygen. The crystals adsorbed oxygen molecules more easily and shows catalytic behavior [12]. 3.5 DC Electrical conductivity The non linear behavior of I-V curves is attributed to inter nanoparticle conduction in these films the electrical conductivity is found to be using two probe method is; Where I is current, L is thickness of the film, V is the applied voltage and A is the cross section area of the film. The decrease in conductivity in Cu thin films is due to contribution of grain boundaries Fig. 3.8 shows the I-V characteristic curves of the thin film of copper. Electrical conductivity for electrodeposited copper films is found to be approximately 960X10-10 Ω -1 m -1 for the calculated thickness of the film is 600nm at current density 1.6mAcm -2. This value of conductivity is in agreement with the value found from MS model by Juan et al [18] due to size effect at nano scale. Curves shows that resistance is less for the film deposited at ph 5 than film deposited at ph 4 and ph 3 because the crystallinity of the film becomes better at ph =5. The high leakage current of crystalline sample is expected to be due to grain boundaries that serve as high leakage path for the thin films. (2) 59 P a g e
6 Figure 3.8 I-V Characteristics of electrodeposited copper thin film deposited at different ph IV. CONCLUSION The electrodeposition of nanostructured thin film of copper was investigated here. This study was made to evaluate the influence of nano particle on morphologic and structure characteristics. SEM analysis and voltammetric studies corroborate the mechanism for the reduction process. It was found that deposition time, ph of the solution and deposition current density all had profound effects on the nucleation mechanism of copper on ITO surface. From XRD it is clear that at ph 5, for current density 1.6mAcm -2 if film is deposited for 20 minutes we get thin film of copper. Electrical conductivity is found to be decreased for electrodeposited copper thin films as compared to bulk material due to size effect. V. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The authors acknowledge the cooperation provided by Principal, Govt. MSJ College, Bharatpur for providing initial basic infrastructure support. The suggestions in Cyclic Voltametric predictions by Prof. P. S. Verma ( Retd. professor in Chemistry, University of Rajasthan, Jaipur) and valuable suggestions on other characterization techniques by Prof. Y. K. Vijay, University of Rajasthan, Jaipur is highly appreciated. REFERENCES [1] W.H. Safranek, The properties of electrodeposited metals and alloys A handbook (New York Elseveir co. 1974) 49. [2] Luisa Peraldo Bicelli, Benedetto Bozzini, Claudio Mele and Lucia D'Urzo, A Review of Nanostructural Aspects of Metal Electrodeposition, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 3, 2008, [3] A.Milchev, Electrocrystallization: Fundamentals of Nucleation and Growth, (Kluwer Academic Publishers,The Netherlands, 2002) [4] M Schlesinger and M Paunovic, Modern Electroplating (John Wiley and sons 5th edition, 2011)9. [5] A. Mallik and B. C. Ray, Evolution of principle and practice of electrodeposited thin film: A Review on effect of temperature and sonication, International Journal of Electrochemistry 16, [6] E. García, Mario Romero-Romo, María Teresa Ramírez-Silva, and Manuel Palomar-Pardavé, Overpotential Nucleation and Growth of Copper onto Polycrystalline and Single Crystal Gold Electrodes, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 7, 2012, [7] F A Lowenheim, Modern Electroplating, (J. Wiley and sons, New York, 1974). [8] Darko Grujicic and Batric Pesic, Electrodeposition of copper: the nucleation mechanisms, Electrochimica Acta 47, 2002, [9] C.L. Aravinda, S.M. Mayanna and V. S. Muralidharan, Electrochemical behaviour of alkaline copper complexes, Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Chem. Sci.), Vol. 112, No. 5,2000, [10] M.R.H. De Almeida, I.A. Carlos, L.L. Barbosa, R.M. Carlos, B.S. Lima-Neto and E.M.J.A. Pallone, Voltammetric and morphological characterization of copper electrodeposition from non-cyanide electrolyte, Journal of Applied Electrochemistry 32, 2002, [11] J.C. Ballesteros, E. Chainet, P. Ozil, Y. Meas and G. Trejo, Electrodeposition of copper from noncyanide alkaline solution containing tartrate, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 6, 2011, P a g e
7 [12] D. K. Yfantis, S. I. Kakos, S. Lamprakopoulos, S. Depountis and C. D. Yfantis, Copper electrodeposition on insulators (plastics) using highly conductive polypyrrole films, Proceedings of the 5th WSEAS International Conference on Environment, Ecosystems and Development, 2006, 190. [13] J. Mathur and M. Gupta, Nucleation growth of electrodeposited thin film of Cu, Proceedings of DAE SSPS, 2006, 571. [14] X. J. Zhou, A. J. Harmer, N. F. Heinig, and K. T. Leung, Parametric study on electrochemical deposition of Copper nanoparticles on an ultrathin polypyrrole film deposited on a gold film electrode, Langmuir 20, 2004, [15] Udit Surya Mohanty, S. Y. Chen and Kwang-Lung Lin, Nanoscale Electrodeposition of Copper on an AFM Tip and Its Morphological Investigations, Smart nanoparticles technology (174chapter 8, edited by Abbas Hashim, publisher In tech April, 2012). [16] JCPDS-ICDD 4-836, 1993 [17] A. Guinier, Xray diffraction, (San Francisco, 85, 1994). [18] Juan M. Camacho and A.I. Oliva, Morphology and electrical resistivity of metallic nanostructures, Microelectronics Journal 36, 2005, P a g e
METAL FINISHING. (As per revised VTU syllabus: )
 METAL FINISHING (As per revised VTU syllabus: 2015-16) Definition: It is a process in which a specimen metal (article) is coated with another metal or a polymer in order to modify the surface properties
METAL FINISHING (As per revised VTU syllabus: 2015-16) Definition: It is a process in which a specimen metal (article) is coated with another metal or a polymer in order to modify the surface properties
Cu(I)-Mediating Pt Reduction to Form Pt-Nanoparticle-Embedded Nafion Composites and Their Electrocatalytic O 2 Reduction
 Cu(I)-Mediating Pt Reduction to Form Pt-Nanoparticle-Embedded Nafion Composites and Their Electrocatalytic O 2 Reduction Jing-Fang Huang,* a and Wen-Rhone Chang a Supporting information Experimental Section
Cu(I)-Mediating Pt Reduction to Form Pt-Nanoparticle-Embedded Nafion Composites and Their Electrocatalytic O 2 Reduction Jing-Fang Huang,* a and Wen-Rhone Chang a Supporting information Experimental Section
Electrochemical Behaviors of PtRu/CNTs Catalysts Prepared by Pulse Potential Plating Methods
 Solid State Phenomena Vols. 124-126 (2007) pp 1039-1042 Online: 2007-06-15 (2007) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/ssp.124-126.1039 Electrochemical Behaviors of PtRu/CNTs
Solid State Phenomena Vols. 124-126 (2007) pp 1039-1042 Online: 2007-06-15 (2007) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/ssp.124-126.1039 Electrochemical Behaviors of PtRu/CNTs
DEVELOPMENT OF ELECTROLESS PROCESS FOR DEPOSITION OF ZN SILICATE COATINGS
 REPORT OF THE FINAL PROJECT ENTITLED: DEVELOPMENT OF ELECTROLESS PROCESS FOR DEPOSITION OF ZN SILICATE COATINGS by Veeraraghavan S Basker Department of Chemical Engineering University of South Carolina
REPORT OF THE FINAL PROJECT ENTITLED: DEVELOPMENT OF ELECTROLESS PROCESS FOR DEPOSITION OF ZN SILICATE COATINGS by Veeraraghavan S Basker Department of Chemical Engineering University of South Carolina
Investigation on the effect of Electro-co-deposition process parameter bath temperature on Nano Structured Ni-WC Composite coating properties
 International Journal of Materials Science ISSN 0973-4589 Volume 11, Number 1 (2016), pp. 9-15 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Investigation on the effect of Electro-co-deposition
International Journal of Materials Science ISSN 0973-4589 Volume 11, Number 1 (2016), pp. 9-15 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Investigation on the effect of Electro-co-deposition
A Parametric Study on the Electrodeposition of Copper Nanocrystals on a Gold Film Electrode. Andrea Harmer Co-op term #1 April 25, 2003
 A Parametric Study on the Electrodeposition of Copper Nanocrystals on a Gold Film Electrode Andrea Harmer Co-op term #1 April 25, 2003 Outline of Presentation: Introduction Purpose General method Parameters:
A Parametric Study on the Electrodeposition of Copper Nanocrystals on a Gold Film Electrode Andrea Harmer Co-op term #1 April 25, 2003 Outline of Presentation: Introduction Purpose General method Parameters:
Synthesis and characterization of pulsed electrodeposited Cu-Y 2 O 3 coating
 Synthesis and characterization of pulsed electrodeposited Cu-Y 2 O 3 coating H. S. Maharana, A. Basu* Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela 769008,
Synthesis and characterization of pulsed electrodeposited Cu-Y 2 O 3 coating H. S. Maharana, A. Basu* Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela 769008,
Growth Of TiO 2 Films By RF Magnetron Sputtering Studies On The Structural And Optical Properties
 Journal of Multidisciplinary Engineering Science and Technology (JMEST) Growth Of TiO 2 Films By RF Magnetron Sputtering Studies On The Structural And Optical Properties Ahmed K. Abbas 1, Mohammed K. Khalaf
Journal of Multidisciplinary Engineering Science and Technology (JMEST) Growth Of TiO 2 Films By RF Magnetron Sputtering Studies On The Structural And Optical Properties Ahmed K. Abbas 1, Mohammed K. Khalaf
Pulsed Electrodeposited Nickel Cerium for Hydrogen Production Studies 54
 Pulsed Electrodeposited Nickel Cerium for Hydrogen Production Studies 54 T. Sivaranjani 1, T.A. Revathy 1, K. Dhanapal 1, V. Narayanan 2, A. Stephen 1,a 1 Materials Science Centre, Department of Nuclear
Pulsed Electrodeposited Nickel Cerium for Hydrogen Production Studies 54 T. Sivaranjani 1, T.A. Revathy 1, K. Dhanapal 1, V. Narayanan 2, A. Stephen 1,a 1 Materials Science Centre, Department of Nuclear
A STUDY ON STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF ELECTROPLATED NANO CRYSTALLINE NICKEL BASED THIN FILMS
 ISSN: 0974-1496 e-issn: 0976-0083 CODEN: RJCABP http://www.rasayanjournal.com http://www.rasayanjournal.co.in A STUDY ON STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF ELECTROPLATED NANO CRYSTALLINE NICKEL BASED THIN FILMS R.
ISSN: 0974-1496 e-issn: 0976-0083 CODEN: RJCABP http://www.rasayanjournal.com http://www.rasayanjournal.co.in A STUDY ON STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF ELECTROPLATED NANO CRYSTALLINE NICKEL BASED THIN FILMS R.
ELECTRIDEPOSITION AND WEAR BEHAVIOR OF NANO-STRUCTURED Cr-WC COMPOSITE COATINGS FROM A TRIVALENT CHROMIUM BATH
 2nd International Conference on Ultrafine Grained & Nanostructured Materials (UFGNSM) International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series Vol. 5 (2012) 737 743 World Scientific Publishing Company
2nd International Conference on Ultrafine Grained & Nanostructured Materials (UFGNSM) International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series Vol. 5 (2012) 737 743 World Scientific Publishing Company
Metallization deposition and etching. Material mainly taken from Campbell, UCCS
 Metallization deposition and etching Material mainly taken from Campbell, UCCS Application Metallization is back-end processing Metals used are aluminum and copper Mainly involves deposition and etching,
Metallization deposition and etching Material mainly taken from Campbell, UCCS Application Metallization is back-end processing Metals used are aluminum and copper Mainly involves deposition and etching,
GROWTH AND CHARACTERIZATION OF NANOSTRUCTURED CdS THIN FILMS BY CHEMICAL BATH DEPOSITION TECHNIQUE
 Chalcogenide Letters Vol. 6, No. 8, September 29, p. 415 419 GROWTH AND CHARACTERIZATION OF NANOSTRUCTURED CdS THIN FILMS BY CHEMICAL BATH DEPOSITION TECHNIQUE V. B. SANAP *, B. H. PAWAR, * MSS s College
Chalcogenide Letters Vol. 6, No. 8, September 29, p. 415 419 GROWTH AND CHARACTERIZATION OF NANOSTRUCTURED CdS THIN FILMS BY CHEMICAL BATH DEPOSITION TECHNIQUE V. B. SANAP *, B. H. PAWAR, * MSS s College
Recrystallization in CdTe/CdS
 Thin Solid Films 361±362 (2000) 420±425 www.elsevier.com/locate/tsf Recrystallization in CdTe/CdS A. Romeo, D.L. BaÈtzner, H. Zogg, A.N. Tiwari* Thin Film Physics Group, Institute of Quantum Electronics,
Thin Solid Films 361±362 (2000) 420±425 www.elsevier.com/locate/tsf Recrystallization in CdTe/CdS A. Romeo, D.L. BaÈtzner, H. Zogg, A.N. Tiwari* Thin Film Physics Group, Institute of Quantum Electronics,
GROWTH ANALYSIS OF ELECTRODEPOSITED COPPER THIN FILM ON TUNGSTEN COATED SILICON SAMPLE
 Journal of Electron Devices, Vol. 16, 2012, pp. 1301-1305 JED [ISSN: 1682-3427 ] GROWTH ANALYSIS OF ELECTRODEPOSITED COPPER THIN FILM ON TUNGSTEN COATED SILICON SAMPLE Saurabh Kumar Pandey 1 and P. Ramshankar
Journal of Electron Devices, Vol. 16, 2012, pp. 1301-1305 JED [ISSN: 1682-3427 ] GROWTH ANALYSIS OF ELECTRODEPOSITED COPPER THIN FILM ON TUNGSTEN COATED SILICON SAMPLE Saurabh Kumar Pandey 1 and P. Ramshankar
CHAPTER-VII SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS
 CHAPTER-VII SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS Chapter-VII Summary and Conclusions Sr. No. Title Page No. 7.1 Summary 167 7.2 Conclusions.. 171 CHAPTER SEVEN Summary and Conclusions 7.1: Summary The technologies
CHAPTER-VII SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS Chapter-VII Summary and Conclusions Sr. No. Title Page No. 7.1 Summary 167 7.2 Conclusions.. 171 CHAPTER SEVEN Summary and Conclusions 7.1: Summary The technologies
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Electrochemical reduction of CO 2 at Copper Nanofoams Sujat Sen a, Dan Liu a and G. Tayhas R. Palmore a, b, * a Department of Chemistry and b School of Engineering, Brown University,
Supporting Information Electrochemical reduction of CO 2 at Copper Nanofoams Sujat Sen a, Dan Liu a and G. Tayhas R. Palmore a, b, * a Department of Chemistry and b School of Engineering, Brown University,
Electro catalytic amorphous nickel alloy
 Indian Journal of Chemical Technology Vol. 14, March 2007, pp. 161-165 Electro catalytic amorphous nickel alloy V S Muralidharan Central Electrochemical Research Institute, Karaikudi 630 006, India Received
Indian Journal of Chemical Technology Vol. 14, March 2007, pp. 161-165 Electro catalytic amorphous nickel alloy V S Muralidharan Central Electrochemical Research Institute, Karaikudi 630 006, India Received
Formation of Cupric Oxide Films on Quartz Substrates by Annealing the Copper Films
 Journal of Applied Chemical Research, 9, 2, 73-79 (2015) Journal of Applied Chemical Research www.jacr.kiau.ac.ir Formation of Cupric Oxide Films on Quartz Substrates by Annealing the Copper Films Abstract
Journal of Applied Chemical Research, 9, 2, 73-79 (2015) Journal of Applied Chemical Research www.jacr.kiau.ac.ir Formation of Cupric Oxide Films on Quartz Substrates by Annealing the Copper Films Abstract
Synthesis, Characterization and Optical Properties of ZnS Thin Films
 Synthesis, Characterization and Optical Properties of ZnS Thin Films H. R. Kulkarni KJ College of Engineering and Management Research, Pune, India Abstract: ZnS thin films were prepared by pulsed electrodeposition
Synthesis, Characterization and Optical Properties of ZnS Thin Films H. R. Kulkarni KJ College of Engineering and Management Research, Pune, India Abstract: ZnS thin films were prepared by pulsed electrodeposition
ELECTROCHEMICAL SYNTHESIS OF POLYPYRROLE (PPy) and PPy METAL COMPOSITES ON COPPER and INVESTIGATION OF THEIR ANTICORROSIVE PROPERTIES
 ELECTROCHEMICAL SYNTHESIS OF POLYPYRROLE (PPy) and PPy METAL COMPOSITES ON COPPER and INVESTIGATION OF THEIR ANTICORROSIVE PROPERTIES Sibel Zor, Hatice Özkazanç Kocaeli University, Department of Chemistry,
ELECTROCHEMICAL SYNTHESIS OF POLYPYRROLE (PPy) and PPy METAL COMPOSITES ON COPPER and INVESTIGATION OF THEIR ANTICORROSIVE PROPERTIES Sibel Zor, Hatice Özkazanç Kocaeli University, Department of Chemistry,
Growth and Doping of SiC-Thin Films on Low-Stress, Amorphous Si 3 N 4 /Si Substrates for Robust Microelectromechanical Systems Applications
 Journal of ELECTRONIC MATERIALS, Vol. 31, No. 5, 2002 Special Issue Paper Growth and Doping of SiC-Thin Films on Low-Stress, Amorphous Si 3 N 4 /Si Substrates for Robust Microelectromechanical Systems
Journal of ELECTRONIC MATERIALS, Vol. 31, No. 5, 2002 Special Issue Paper Growth and Doping of SiC-Thin Films on Low-Stress, Amorphous Si 3 N 4 /Si Substrates for Robust Microelectromechanical Systems
Deposition and characterization of sputtered ZnO films
 Superlattices and Microstructures 42 (2007) 89 93 www.elsevier.com/locate/superlattices Deposition and characterization of sputtered ZnO films W.L. Dang, Y.Q. Fu, J.K. Luo, A.J. Flewitt, W.I. Milne Electrical
Superlattices and Microstructures 42 (2007) 89 93 www.elsevier.com/locate/superlattices Deposition and characterization of sputtered ZnO films W.L. Dang, Y.Q. Fu, J.K. Luo, A.J. Flewitt, W.I. Milne Electrical
CHAPTER 3 ELECTROPLATING OF FDM-ABS
 31 CHAPTER 3 ELECTROPLATING OF FDM-ABS 3.1 INTRODUCTION Electroplating can be referred to as, an electrodeposition process for producing a thick and consistent coating, using of metal or alloys, upon a
31 CHAPTER 3 ELECTROPLATING OF FDM-ABS 3.1 INTRODUCTION Electroplating can be referred to as, an electrodeposition process for producing a thick and consistent coating, using of metal or alloys, upon a
Effects of organic additive saccharin on the magnetic properties of CoMnP thin films
 Material Science Research India Vol. 7(1), 159-166 (2010) Effects of organic additive saccharin on the magnetic properties of CoMnP thin films M.RM. KRISHNAPPA¹*, N. RAJASEKARAN², S. GANESAN 3 and R.N.
Material Science Research India Vol. 7(1), 159-166 (2010) Effects of organic additive saccharin on the magnetic properties of CoMnP thin films M.RM. KRISHNAPPA¹*, N. RAJASEKARAN², S. GANESAN 3 and R.N.
The Effects of the Adding V2O5 on the Oxide Semiconductor Layer of a Dye-sensitized Solar Cell
 , pp.66-71 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016.140.14 The Effects of the Adding V2O5 on the Oxide Semiconductor Layer of a Dye-sensitized Solar Cell Don-Kyu Lee Electrical Engineering, Dong-Eui University,
, pp.66-71 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016.140.14 The Effects of the Adding V2O5 on the Oxide Semiconductor Layer of a Dye-sensitized Solar Cell Don-Kyu Lee Electrical Engineering, Dong-Eui University,
EFFECTS OF CURRENT DENSITY ON SIZE AND SURFACE MORPHOLOGY OF HIGH SPEED DIRECT NANO-CRYSTALLINE NICKEL PLATING ON TITANIUM SURFACE
 EFFECTS OF CURRENT DENSITY ON SIZE AND SURFACE MORPHOLOGY OF HIGH SPEED DIRECT NANO-CRYSTALLINE NICKEL PLATING ON TITANIUM SURFACE Noor Zaimah 1, Azieyanti Nurain 1 and Sakhawat Hussain 2 1 Department
EFFECTS OF CURRENT DENSITY ON SIZE AND SURFACE MORPHOLOGY OF HIGH SPEED DIRECT NANO-CRYSTALLINE NICKEL PLATING ON TITANIUM SURFACE Noor Zaimah 1, Azieyanti Nurain 1 and Sakhawat Hussain 2 1 Department
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of precursor coated on salt template. (a) SEM image of Mo precursor coated on NaCl. Scale bar, 50 μm. (b) EDS of Mo precursor coated on
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of precursor coated on salt template. (a) SEM image of Mo precursor coated on NaCl. Scale bar, 50 μm. (b) EDS of Mo precursor coated on
INFLUENCE OF PHOSPHOROUS AND UREA ON THE MAGNETIC AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF NANOSTRUCTURED FEPTP FILMS
 , pp. 276-281 INFLUENCE OF PHOSPHOROUS AND UREA ON THE MAGNETIC AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF NANOSTRUCTURED FEPTP FILMS T. M. Selvakumari a*, P. Muthukumar b, S. Ganesan c, and R. N. Emerson d a,b Department
, pp. 276-281 INFLUENCE OF PHOSPHOROUS AND UREA ON THE MAGNETIC AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF NANOSTRUCTURED FEPTP FILMS T. M. Selvakumari a*, P. Muthukumar b, S. Ganesan c, and R. N. Emerson d a,b Department
General Introduction to Microstructure Technology p. 1 What is Microstructure Technology? p. 1 From Microstructure Technology to Microsystems
 General Introduction to Microstructure Technology p. 1 What is Microstructure Technology? p. 1 From Microstructure Technology to Microsystems Technology p. 9 The Parallels to Microelectronics p. 15 The
General Introduction to Microstructure Technology p. 1 What is Microstructure Technology? p. 1 From Microstructure Technology to Microsystems Technology p. 9 The Parallels to Microelectronics p. 15 The
Preparation of porous manganese hydroxide film and its application in supercapacitors
 Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 46A, May 2007, pp. 736-741 Preparation of porous manganese hydroxide film and its application in supercapacitors Zhen Fan, Jinhua Chen*, Feng Sun, Lei Yang, Yan Xu & Yafei
Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 46A, May 2007, pp. 736-741 Preparation of porous manganese hydroxide film and its application in supercapacitors Zhen Fan, Jinhua Chen*, Feng Sun, Lei Yang, Yan Xu & Yafei
ITO. Crystal structure: Cubic, space group Ia3 No. 206, ci80, a = nm, Z = 16
 ITO Indium tin oxide (ITO) is a ternary composition of indium, tin and oxygen in varying proportions. Depending on the oxygen content, it can either be described as a ceramic or alloy. Indium tin oxide
ITO Indium tin oxide (ITO) is a ternary composition of indium, tin and oxygen in varying proportions. Depending on the oxygen content, it can either be described as a ceramic or alloy. Indium tin oxide
Effects of Lead on Tin Whisker Elimination
 Effects of Lead on Tin Whisker Elimination Wan Zhang and Felix Schwager Rohm and Haas Electronic Materials Lucerne, Switzerland inemi Tin Whisker Workshop at ECTC 0 May 30, 2006, in San Diego, CA Efforts
Effects of Lead on Tin Whisker Elimination Wan Zhang and Felix Schwager Rohm and Haas Electronic Materials Lucerne, Switzerland inemi Tin Whisker Workshop at ECTC 0 May 30, 2006, in San Diego, CA Efforts
High Resolution X-ray Diffraction
 High Resolution X-ray Diffraction Nina Heinig with data from Dr. Zhihao Donovan Chen, Panalytical and slides from Colorado State University Outline Watlab s new tool: Panalytical MRD system Techniques:
High Resolution X-ray Diffraction Nina Heinig with data from Dr. Zhihao Donovan Chen, Panalytical and slides from Colorado State University Outline Watlab s new tool: Panalytical MRD system Techniques:
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Experimental Methods Pt ALD. The precursor used for ALD was trimethyl-methylcyclopentadienyl-platinum(iv) (MeCpPtMe 3 ) (Strem Chemicals, 99%), which has been widely reported for
Supporting Information Experimental Methods Pt ALD. The precursor used for ALD was trimethyl-methylcyclopentadienyl-platinum(iv) (MeCpPtMe 3 ) (Strem Chemicals, 99%), which has been widely reported for
6th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 2016)
 6th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 2016) Porous Co3O4 irregular Micro-cubes with lithium storage performances Ting Wanga, Hao Zhengb, Jinsong Chengc,
6th International Conference on Advanced Design and Manufacturing Engineering (ICADME 2016) Porous Co3O4 irregular Micro-cubes with lithium storage performances Ting Wanga, Hao Zhengb, Jinsong Chengc,
Fundamentals of X-ray diffraction and scattering
 Fundamentals of X-ray diffraction and scattering Don Savage dsavage@wisc.edu 1231 Engineering Research Building (608) 263-0831 X-ray diffraction and X-ray scattering Involves the elastic scattering of
Fundamentals of X-ray diffraction and scattering Don Savage dsavage@wisc.edu 1231 Engineering Research Building (608) 263-0831 X-ray diffraction and X-ray scattering Involves the elastic scattering of
Silver Diffusion Bonding and Layer Transfer of Lithium Niobate to Silicon
 Chapter 5 Silver Diffusion Bonding and Layer Transfer of Lithium Niobate to Silicon 5.1 Introduction In this chapter, we discuss a method of metallic bonding between two deposited silver layers. A diffusion
Chapter 5 Silver Diffusion Bonding and Layer Transfer of Lithium Niobate to Silicon 5.1 Introduction In this chapter, we discuss a method of metallic bonding between two deposited silver layers. A diffusion
Effects of Bath Temperature on Electrodeposited Permanent Magnetic Co-Pt-W(P) Films
 2214 Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2007, Vol. 28, No. 12 Hongliang Ge et al. Effects of Bath Temperature on Electrodeposited Permanent Magnetic Co-Pt-W(P) Films Hongliang Ge, * Qiong Wu, Guoying Wei, Xinyan
2214 Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2007, Vol. 28, No. 12 Hongliang Ge et al. Effects of Bath Temperature on Electrodeposited Permanent Magnetic Co-Pt-W(P) Films Hongliang Ge, * Qiong Wu, Guoying Wei, Xinyan
PbS NANO THIN FILM PHOTOCONDUCTIVE DETECTOR
 International Journal of Physics and Research (IJPR) ISSN 2250-0030 Vol. 3, Issue 3, Aug 2013, 21-26 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. PbS NANO THIN FILM PHOTOCONDUCTIVE DETECTOR SUDAD S. AHMED, EMAN K. HASSAN & FATN EMAD
International Journal of Physics and Research (IJPR) ISSN 2250-0030 Vol. 3, Issue 3, Aug 2013, 21-26 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. PbS NANO THIN FILM PHOTOCONDUCTIVE DETECTOR SUDAD S. AHMED, EMAN K. HASSAN & FATN EMAD
Cadmium Oxide Nano Particles by Sol-Gel and Vapour- Liquid-Solid Methods
 Nano Vision, Vol.1 (1), 47-53 (2011) Cadmium Oxide Nano Particles by Sol-Gel and Vapour- Liquid-Solid Methods S. SAKTHIVEL* and D. MANGALARAJ 1 *PG and Research Department of Physics, Rajah Serfoji Govt.
Nano Vision, Vol.1 (1), 47-53 (2011) Cadmium Oxide Nano Particles by Sol-Gel and Vapour- Liquid-Solid Methods S. SAKTHIVEL* and D. MANGALARAJ 1 *PG and Research Department of Physics, Rajah Serfoji Govt.
More Thin Film X-ray Scattering and X-ray Reflectivity
 Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory More Thin Film X-ray Scattering and X-ray Reflectivity Mike Toney, SSRL 1. Introduction (real space reciprocal space) 2. Polycrystalline film (no texture) RuPt
Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory More Thin Film X-ray Scattering and X-ray Reflectivity Mike Toney, SSRL 1. Introduction (real space reciprocal space) 2. Polycrystalline film (no texture) RuPt
Effect of bath types on sonoelectrodeposited Cu/Ni Multilayer at low temperature
 Archived in http://dspace.nitrkl.ac.in/dspace Silver Jubilee International Conference 10 th Conference of International Academy of Physical Sciences CONIAPS-X January 12-14 2008 Guru Ghasidas University,
Archived in http://dspace.nitrkl.ac.in/dspace Silver Jubilee International Conference 10 th Conference of International Academy of Physical Sciences CONIAPS-X January 12-14 2008 Guru Ghasidas University,
Properties and Barrier Material Interactions of Electroless Copper used for Seed Enhancement
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 766 2003 Materials Research Society E1.4.1 Properties and Barrier Material Interactions of Electroless Copper used for Seed Enhancement C. Witt a,b,k.pfeifer a,c a International
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 766 2003 Materials Research Society E1.4.1 Properties and Barrier Material Interactions of Electroless Copper used for Seed Enhancement C. Witt a,b,k.pfeifer a,c a International
Synthesis and Characterization of Cadmium Sulfide Nanoparticles
 Synthesis and Characterization of Cadmium Sulfide Nanoparticles R.Hepzi Pramila Devamani 1*, R.Kiruthika, P.Mahadevi and S.Sagithapriya 2 1 1. Assistant Professor, Department of Physics, V.V.Vanniaperumal
Synthesis and Characterization of Cadmium Sulfide Nanoparticles R.Hepzi Pramila Devamani 1*, R.Kiruthika, P.Mahadevi and S.Sagithapriya 2 1 1. Assistant Professor, Department of Physics, V.V.Vanniaperumal
Size dependent optical characteristics of chemically deposited nanostructured ZnS thin films
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 30, No. 2, April 2007, pp. 147 151. Indian Academy of Sciences. Size dependent optical characteristics of chemically deposited nanostructured ZnS thin films A U UBALE*, V S SANGAWAR
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 30, No. 2, April 2007, pp. 147 151. Indian Academy of Sciences. Size dependent optical characteristics of chemically deposited nanostructured ZnS thin films A U UBALE*, V S SANGAWAR
Tin Coated Viral-Nanoforests as Sodium-Ion. Battery Anodes
 Supporting information Tin Coated Viral-Nanoforests as Sodium-Ion Battery Anodes Yihang Liu, Yunhua Xu, Yujie Zhu, James N. Culver, Cynthia A. Lundgren, Kang Xu,*, and Chunsheng Wang*, Sn anodes fabrication:
Supporting information Tin Coated Viral-Nanoforests as Sodium-Ion Battery Anodes Yihang Liu, Yunhua Xu, Yujie Zhu, James N. Culver, Cynthia A. Lundgren, Kang Xu,*, and Chunsheng Wang*, Sn anodes fabrication:
Studying Effect of Mg Doping on the Structural Properties of Tin Oxide Thin Films Deposited by the Spray Pyrolysis Technique
 Studying Effect of Mg Doping on the Structural Properties of Tin Oxide Thin Films Deposited by the Spray Pyrolysis Technique Abdul Rahman Sakhta 1* Ahmad Khdro Ali Darwisho 3 1.MSc Student, Department
Studying Effect of Mg Doping on the Structural Properties of Tin Oxide Thin Films Deposited by the Spray Pyrolysis Technique Abdul Rahman Sakhta 1* Ahmad Khdro Ali Darwisho 3 1.MSc Student, Department
Supporting Information for
 Supporting Information for 3D Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Aerogel-Supported Fe 3 O 4 Nanoparticles as Efficient Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction Zhong-Shuai Wu, Shubin Yang, Yi Sun, Khaled
Supporting Information for 3D Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Aerogel-Supported Fe 3 O 4 Nanoparticles as Efficient Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction Zhong-Shuai Wu, Shubin Yang, Yi Sun, Khaled
Supplementary Figure 1 The lithium polysulfide distribution on the patterned electrode.
 Supplementary Figure 1.The lithium polysulfide distribution on the patterned electrode. SEM image of the ITO-carbon electrode after dipping into Li 2 S 8 solution and drying, which shows the random distribution
Supplementary Figure 1.The lithium polysulfide distribution on the patterned electrode. SEM image of the ITO-carbon electrode after dipping into Li 2 S 8 solution and drying, which shows the random distribution
Optimization of DPC Process Applied by Electroless Copper Plating
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Optimization of DPC Process Applied by Electroless Copper Plating Xinnang Lang Huazhong University of Science and Technology Abstract: With the continuous improvement of chip power, the
RESEARCH ARTICLE Optimization of DPC Process Applied by Electroless Copper Plating Xinnang Lang Huazhong University of Science and Technology Abstract: With the continuous improvement of chip power, the
Nano structure black cobalt coating for solar absorber
 Nano structure black cobalt coating for solar absorber G.Toghdori 1, S.M.Rozati 1*, N. Memarian 1, M.Arvand 2, M.H.Bina 3 1 Department of Physics, University of Guilan, Rasht42335, Iran 2 Department of
Nano structure black cobalt coating for solar absorber G.Toghdori 1, S.M.Rozati 1*, N. Memarian 1, M.Arvand 2, M.H.Bina 3 1 Department of Physics, University of Guilan, Rasht42335, Iran 2 Department of
Roman Chistyakov and Bassam Abraham Zond Inc/Zpulser LLC, Mansfield, MA
 HIPIMS Arc-Free Reactive Sputtering of Non-conductive Films Using the ENDURA 200 mm Cluster Tool: Direct Comparison Between Pulsed DC Pinnacle Plus and HIPIMS Cyprium Roman Chistyakov and Bassam Abraham
HIPIMS Arc-Free Reactive Sputtering of Non-conductive Films Using the ENDURA 200 mm Cluster Tool: Direct Comparison Between Pulsed DC Pinnacle Plus and HIPIMS Cyprium Roman Chistyakov and Bassam Abraham
Applied Surface Science
 Applied Surface Science 255 (2009) 4192 4196 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Applied Surface Science journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/apsusc Electrodeposited ruthenium oxide thin films
Applied Surface Science 255 (2009) 4192 4196 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Applied Surface Science journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/apsusc Electrodeposited ruthenium oxide thin films
Evolution of nanostructures, mechanical and magnetic properties in electrochemically deposited Cu/Ni multilayers under ultrasound
 Evolution of nanostructures, mechanical and magnetic properties in electrochemically deposited Cu/Ni multilayers under ultrasound A. Mallik and B. C. Ray Dept. of Metallurgical and Materials Engg., National
Evolution of nanostructures, mechanical and magnetic properties in electrochemically deposited Cu/Ni multilayers under ultrasound A. Mallik and B. C. Ray Dept. of Metallurgical and Materials Engg., National
Bipolar performance of the electroplated iron nickel deposits for water electrolysis
 Materials Chemistry and Physics 8 (00) 588 596 Bipolar performance of the electroplated iron nickel deposits for water electrolysis Chi-Chang Hu, Yau-Ruen Wu Department of Chemical Engineering, National
Materials Chemistry and Physics 8 (00) 588 596 Bipolar performance of the electroplated iron nickel deposits for water electrolysis Chi-Chang Hu, Yau-Ruen Wu Department of Chemical Engineering, National
Chapter 7 Conclusions
 Conclusions Nowadays, much awareness has been devoted in developing sensors for monitoring the pollutants and hazardous gases in various environments. Considerable development work is being carried out
Conclusions Nowadays, much awareness has been devoted in developing sensors for monitoring the pollutants and hazardous gases in various environments. Considerable development work is being carried out
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Fabrication of (001)-oriented monoclinic WO 3 films on FTO substrates Jin You Zheng, Guang Song, Chang Woo Kim and Young Soo Kang* Korea Center for Artificial Photosynthesis (KCAP),
Supplementary Information Fabrication of (001)-oriented monoclinic WO 3 films on FTO substrates Jin You Zheng, Guang Song, Chang Woo Kim and Young Soo Kang* Korea Center for Artificial Photosynthesis (KCAP),
Effect of Doping Concentration on the Structural Properties of Zn: SnO 2
 IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861.Volume 7, Issue 3 Ver. II (May. - Jun. 2015), PP 45-49 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of Doping Concentration on the Structural Properties of Zn:
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861.Volume 7, Issue 3 Ver. II (May. - Jun. 2015), PP 45-49 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of Doping Concentration on the Structural Properties of Zn:
Simple fabrication of highly ordered AAO nanotubes
 Journal of Optoelectronic and Biomedical Materials Volume 1, Issue 1, March 2009, p. 79-84 Simple fabrication of highly ordered AAO nanotubes N. Taşaltin a, S. Öztürk a, H. Yüzer b, Z. Z. Öztürk a,b* a
Journal of Optoelectronic and Biomedical Materials Volume 1, Issue 1, March 2009, p. 79-84 Simple fabrication of highly ordered AAO nanotubes N. Taşaltin a, S. Öztürk a, H. Yüzer b, Z. Z. Öztürk a,b* a
Supporting Information. High Performance Platinized Titanium Nitride Catalyst for Methanol Oxidation
 Supporting Information High Performance Platinized Titanium Nitride Catalyst for Methanol Oxidation O.T. Muhammed Musthafa and S.Sampath* Department of Inorganic and Physical Chemistry Indian Institute
Supporting Information High Performance Platinized Titanium Nitride Catalyst for Methanol Oxidation O.T. Muhammed Musthafa and S.Sampath* Department of Inorganic and Physical Chemistry Indian Institute
Microtexture measurement of copper damascene line with EBSD
 Material Science Forum Vols. 408-412(2002) pp. 529-534 2002 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Microtexture measurement of copper damascene line with EBSD Dong-Ik Kim 1*, Jong-Min Paik 1, Young-Chang
Material Science Forum Vols. 408-412(2002) pp. 529-534 2002 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Microtexture measurement of copper damascene line with EBSD Dong-Ik Kim 1*, Jong-Min Paik 1, Young-Chang
Formation mechanism of new corrosion resistance magnesium thin films by PVD method
 Surface and Coatings Technology 169 170 (2003) 670 674 Formation mechanism of new corrosion resistance magnesium thin films by PVD method a, a a a b M.H. Lee *, I.Y. Bae, K.J. Kim, K.M. Moon, T. Oki a
Surface and Coatings Technology 169 170 (2003) 670 674 Formation mechanism of new corrosion resistance magnesium thin films by PVD method a, a a a b M.H. Lee *, I.Y. Bae, K.J. Kim, K.M. Moon, T. Oki a
Annealing Effects on the Properties of Copper Selenide Thin Films for Thermoelectric Applications
 IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861. Volume 4, Issue 5 (Sep. - Oct. 2013), PP 65-71 Annealing Effects on the Properties of Copper Selenide Thin Films for Thermoelectric Applications
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861. Volume 4, Issue 5 (Sep. - Oct. 2013), PP 65-71 Annealing Effects on the Properties of Copper Selenide Thin Films for Thermoelectric Applications
Synthesis and Polymerization of Pyrole Characterization of Polypyrole
 Leonardo Electronic Journal of Practices and Technologies ISSN 1583-1078 Issue 11, July-December 2007 p. 1-6 Synthesis and Polymerization of Pyrole Characterization of Polypyrole Moulay Abderrahim EL MHAMMEDI,
Leonardo Electronic Journal of Practices and Technologies ISSN 1583-1078 Issue 11, July-December 2007 p. 1-6 Synthesis and Polymerization of Pyrole Characterization of Polypyrole Moulay Abderrahim EL MHAMMEDI,
NASF SURFACE TECHNOLOGY WHITE PAPERS 81 (5), (May 2017) 4 th Quarterly Report October-December 2016 AESF Research Project #R-118
 4 th Quarterly Report October-December 2016 AESF Research Project #R-118 Crack Formation during Electrodeposition and Post-deposition Aging of Thin Film Coatings by Prof. Stanko R. Brankovic * University
4 th Quarterly Report October-December 2016 AESF Research Project #R-118 Crack Formation during Electrodeposition and Post-deposition Aging of Thin Film Coatings by Prof. Stanko R. Brankovic * University
De-ionized water. Nickel target. Supplementary Figure S1. A schematic illustration of the experimental setup.
 Graphite Electrode Graphite Electrode De-ionized water Nickel target Supplementary Figure S1. A schematic illustration of the experimental setup. Intensity ( a.u.) Ni(OH) 2 deposited on the graphite blank
Graphite Electrode Graphite Electrode De-ionized water Nickel target Supplementary Figure S1. A schematic illustration of the experimental setup. Intensity ( a.u.) Ni(OH) 2 deposited on the graphite blank
CHAPTER 3. Experimental Results of Magnesium oxide (MgO) Thin Films
 CHAPTER 3 Experimental Results of Magnesium oxide (MgO) Thin Films Chapter: III ---------------------------------------------------------------- Experimental Results of Magnesium oxide (MgO) Thin Films
CHAPTER 3 Experimental Results of Magnesium oxide (MgO) Thin Films Chapter: III ---------------------------------------------------------------- Experimental Results of Magnesium oxide (MgO) Thin Films
NASF SURFACE TECHNOLOGY WHITE PAPERS 80 (7), 1-8 (April 2016) 10th Quarterly Report April - June 2015 AESF Research Project #R-117
 10th Quarterly Report April - June 2015 AESF Research Project #R-117 Electrodeposition of Ni-Fe-Mo-W Alloys by Prof. E.J. Podlaha-Murphy, * and A. Kola Northeastern University Boston, Massachusetts, USA
10th Quarterly Report April - June 2015 AESF Research Project #R-117 Electrodeposition of Ni-Fe-Mo-W Alloys by Prof. E.J. Podlaha-Murphy, * and A. Kola Northeastern University Boston, Massachusetts, USA
The electrodeposition of Zn-Mo and Zn-Sn-Mo alloys from citrate electrolytes
 Honorata Kazimierczak The electrodeposition of Zn-Mo and Zn-Sn-Mo alloys from citrate electrolytes Supervisor: Assoc. Prof. Piotr Ozga The electrodeposition of Zn-Mo and Zn-Sn-Mo alloys from citrate electrolytes
Honorata Kazimierczak The electrodeposition of Zn-Mo and Zn-Sn-Mo alloys from citrate electrolytes Supervisor: Assoc. Prof. Piotr Ozga The electrodeposition of Zn-Mo and Zn-Sn-Mo alloys from citrate electrolytes
Supplementary Information. Reversible superconductor-insulator transition in LiTi 2 O 4 induced by
 Supplementary Information Reversible superconductor-insulator transition in LiTi 2 O 4 induced by Li-ion electrochemical reaction K. Yoshimatsu 1,*, M. Niwa 1, H. Mashiko 1, T. Oshima 1 & A. Ohtomo 1,2
Supplementary Information Reversible superconductor-insulator transition in LiTi 2 O 4 induced by Li-ion electrochemical reaction K. Yoshimatsu 1,*, M. Niwa 1, H. Mashiko 1, T. Oshima 1 & A. Ohtomo 1,2
School of Materials Science and Engineering, South China University of Technology,
 Supporting information Zn/MnO 2 Battery Chemistry With H + and Zn 2+ Co-Insertion Wei Sun, Fei Wang, Singyuk Hou, Chongyin Yang, Xiulin Fan, Zhaohui Ma, Tao Gao, Fudong Han, Renzong Hu, Min Zhu *, Chunsheng
Supporting information Zn/MnO 2 Battery Chemistry With H + and Zn 2+ Co-Insertion Wei Sun, Fei Wang, Singyuk Hou, Chongyin Yang, Xiulin Fan, Zhaohui Ma, Tao Gao, Fudong Han, Renzong Hu, Min Zhu *, Chunsheng
EFFECT OF DIFFERENT FERROUS CONCENTRATION ON STRUCTURAL AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF ELECTRODEPOSITED FeNiCo THIN FILMS
 EFFECT OF DIFFERENT FERROUS CONCENTRATION ON STRUCTURAL AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF ELECTRODEPOSITED FeNiCo THIN FILMS K. Mohan Rangam Kadiresan 1,V. Senthil Kumar 2 1 Research Scholar, 2 Associate Professor,
EFFECT OF DIFFERENT FERROUS CONCENTRATION ON STRUCTURAL AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF ELECTRODEPOSITED FeNiCo THIN FILMS K. Mohan Rangam Kadiresan 1,V. Senthil Kumar 2 1 Research Scholar, 2 Associate Professor,
Polycrystalline and microcrystalline silicon
 6 Polycrystalline and microcrystalline silicon In this chapter, the material properties of hot-wire deposited microcrystalline silicon are presented. Compared to polycrystalline silicon, microcrystalline
6 Polycrystalline and microcrystalline silicon In this chapter, the material properties of hot-wire deposited microcrystalline silicon are presented. Compared to polycrystalline silicon, microcrystalline
DISSOLUTION OF ALUMINUM ELECTRODES IN CHLORIDE SOLUTIONS AT POLARIZATION BY THREE-PHASE CURRENT
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 11(4), 2013, 1793-1798 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DISSOLUTION OF ALUMINUM ELECTRODES IN CHLORIDE SOLUTIONS AT POLARIZATION BY THREE-PHASE CURRENT M. T. SARBAYEVA *,
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 11(4), 2013, 1793-1798 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DISSOLUTION OF ALUMINUM ELECTRODES IN CHLORIDE SOLUTIONS AT POLARIZATION BY THREE-PHASE CURRENT M. T. SARBAYEVA *,
HBLED packaging is becoming one of the new, high
 Ag plating in HBLED packaging improves reflectivity and lowers costs JONATHAN HARRIS, President, CMC Laboratories, Inc., Tempe, AZ Various types of Ag plating technology along with the advantages and limitations
Ag plating in HBLED packaging improves reflectivity and lowers costs JONATHAN HARRIS, President, CMC Laboratories, Inc., Tempe, AZ Various types of Ag plating technology along with the advantages and limitations
Supporting information
 Supporting information Cu 2 O-Cu Hybrid Foams as High-Performance Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Evolution Reaction in Alkaline Media Han Xu, Jin-Xian Feng, Ye-Xiang Tong, and Gao-Ren Li* MOE Laboratory of
Supporting information Cu 2 O-Cu Hybrid Foams as High-Performance Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Evolution Reaction in Alkaline Media Han Xu, Jin-Xian Feng, Ye-Xiang Tong, and Gao-Ren Li* MOE Laboratory of
High Efficiency Heterojunction Cadmium Sulphide (CdS) Thin Film Solar Cells by Thermal Evaporation Technique
 NANO VISION An International Open Free Access, Peer Reviewed Research Journal www.nano-journal.org ISSN 2231-2579 (Print) ISSN 2319-7633 (Online) Abbr: Nano Vision. 2013, Vol.3(3): Pg.179-183 High Efficiency
NANO VISION An International Open Free Access, Peer Reviewed Research Journal www.nano-journal.org ISSN 2231-2579 (Print) ISSN 2319-7633 (Online) Abbr: Nano Vision. 2013, Vol.3(3): Pg.179-183 High Efficiency
ScienceDirect. Formation of Cu and Ni Nanowires by Electrodeposition
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Materials Science 8 (2015 ) 617 622 International Congress of Science and Technology of Metallurgy and Materials, SAM - CONAMET 2013 Formation
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Materials Science 8 (2015 ) 617 622 International Congress of Science and Technology of Metallurgy and Materials, SAM - CONAMET 2013 Formation
Available online at ScienceDirect. Materials Today: Proceedings 2 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Materials Today: Proceedings 2 (2015 ) 5582 5586 International Conference on Solid State Physics 2013 (ICSSP 13) Thickness dependent optimization
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Materials Today: Proceedings 2 (2015 ) 5582 5586 International Conference on Solid State Physics 2013 (ICSSP 13) Thickness dependent optimization
Development of New Generation Of Coatings with Strength-Ductility Relationship, Wear, Corrosion and Hydrogen Embrittlement Resistance Beyond the
 Development of New Generation Of Coatings with Strength-Ductility Relationship, Wear, Corrosion and Hydrogen Embrittlement Resistance Beyond the Current Materials Accomplishments till date As the structural
Development of New Generation Of Coatings with Strength-Ductility Relationship, Wear, Corrosion and Hydrogen Embrittlement Resistance Beyond the Current Materials Accomplishments till date As the structural
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY DISCUSSION AND FIGURES 1. Chemical and Structural Characterization (a) Grazing-incidence small-angle X-ray scattering (GISAXS) The structural evolution of the mesoporous
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY DISCUSSION AND FIGURES 1. Chemical and Structural Characterization (a) Grazing-incidence small-angle X-ray scattering (GISAXS) The structural evolution of the mesoporous
Membraneless Hydrogen Peroxide Micro Semi-Fuel Cell for Portable Applications
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information for Membraneless Hydrogen Peroxide Micro Semi-Fuel Cell
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information for Membraneless Hydrogen Peroxide Micro Semi-Fuel Cell
Effect of lactic acid on nucleation morphology and surface roughness of electroless Ni P deposition in nanoscale
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 35, No. 4, August 2012, pp. 561 566. c Indian Academy of Sciences. Effect of lactic acid on nucleation morphology and surface roughness of electroless Ni P deposition in nanoscale
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 35, No. 4, August 2012, pp. 561 566. c Indian Academy of Sciences. Effect of lactic acid on nucleation morphology and surface roughness of electroless Ni P deposition in nanoscale
Synthesis and Characterization of Zinc Iron Sulphide (ZnFeS) Of Varying Zinc Ion Concentration
 International Journal of Science and Technology Volume 5 No. 5, May, 2016 Synthesis and Characterization of Zinc Iron Sulphide (ZnFeS) Of Varying Zinc Ion Concentration I. B. Obasi 1 and J. C. Osuwa 2
International Journal of Science and Technology Volume 5 No. 5, May, 2016 Synthesis and Characterization of Zinc Iron Sulphide (ZnFeS) Of Varying Zinc Ion Concentration I. B. Obasi 1 and J. C. Osuwa 2
Grain Sizes and Surface Roughness in Platinum and Gold Thin Films. L.L. Melo, A. R. Vaz, M.C. Salvadori, M. Cattani
 Journal of Metastable and Nanocrystalline Materials Vols. 20-21 (2004) pp. 623-628 online at http://www.scientific.net 2004 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Grain Sizes and Surface Roughness in Platinum
Journal of Metastable and Nanocrystalline Materials Vols. 20-21 (2004) pp. 623-628 online at http://www.scientific.net 2004 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Grain Sizes and Surface Roughness in Platinum
Effects of preparation temperature on the conductivity of polypyrrole conducting polymer
 Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Chem. Sci.), Vol. 114, No. 2, April 2002, pp 155 162 Indian Academy of Sciences Effects of preparation temperature on the conductivity of polypyrrole conducting polymer 1. Introduction
Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Chem. Sci.), Vol. 114, No. 2, April 2002, pp 155 162 Indian Academy of Sciences Effects of preparation temperature on the conductivity of polypyrrole conducting polymer 1. Introduction
Chapter 7. Evaluation of Electrode Performance by. Electrochemical Impedance
 Chapter 7 Evaluation of Electrode Performance by Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) 7.1 Introduction A significant fraction of internal resistance of a cell comes from the interfacial polarization
Chapter 7 Evaluation of Electrode Performance by Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) 7.1 Introduction A significant fraction of internal resistance of a cell comes from the interfacial polarization
Influence of oxygen to argon ratio on the optical and structural properties of rf magnetron sputtered Ba 0.7 Sr 0.3 TiO 3 thin films.
 Chapter 4 Influence of oxygen to argon ratio on the optical and structural properties of rf magnetron sputtered Ba 0.7 Sr 0.3 TiO 3 thin films. The optical properties of barium strontium titanate thin
Chapter 4 Influence of oxygen to argon ratio on the optical and structural properties of rf magnetron sputtered Ba 0.7 Sr 0.3 TiO 3 thin films. The optical properties of barium strontium titanate thin
THIN NICKEL OXIDE LAYERS PREPARED BY ION BEAM SPUTTERING: FABRICATION AND THE STUDY OF ELECTROPHYSICAL PARAMETERS
 THIN NICKEL OXIDE LAYERS PREPARED BY ION BEAM SPUTTERING: FABRICATION AND THE STUDY OF ELECTROPHYSICAL PARAMETERS Pavel HORÁK a,b, Václav BEJŠOVEC b, Vasyl LAVRENTIEV b, Jiří VACÍK b, Martin VRŇATA a,
THIN NICKEL OXIDE LAYERS PREPARED BY ION BEAM SPUTTERING: FABRICATION AND THE STUDY OF ELECTROPHYSICAL PARAMETERS Pavel HORÁK a,b, Václav BEJŠOVEC b, Vasyl LAVRENTIEV b, Jiří VACÍK b, Martin VRŇATA a,
Electrochimica Acta 179 (2015) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Electrochimica Acta
 Electrochimica Acta 179 (2015) 482 494 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Electrochimica Acta journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/electacta On the electrochemistry of tin oxide coated tin
Electrochimica Acta 179 (2015) 482 494 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Electrochimica Acta journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/electacta On the electrochemistry of tin oxide coated tin
Ibn Al-Haitham Jour. for Pure & Appl. Sci Vol. 32 (1) 2019
 Novel Co-Precipitation Method for Synthesis of Nanostructured Nickel Oxide in Accordance to PH: Structural and Optical Properties as an Active Optical Filter Zehraa N. Abdul-Ameer Lecturer Remote Sensing
Novel Co-Precipitation Method for Synthesis of Nanostructured Nickel Oxide in Accordance to PH: Structural and Optical Properties as an Active Optical Filter Zehraa N. Abdul-Ameer Lecturer Remote Sensing
Applications of Successive Ionic Layer Adsorption and Reaction (SILAR) Technique for CZTS Thin Film Solar Cells
 NANO VISION An International Open Free Access, Peer Reviewed Research Journal www.nano-journal.org ISSN 2231-2579 (Print) ISSN 2319-7633 (Online) Abbr: Nano Vision. 2013, Vol.3(3): Pg.235-239 Applications
NANO VISION An International Open Free Access, Peer Reviewed Research Journal www.nano-journal.org ISSN 2231-2579 (Print) ISSN 2319-7633 (Online) Abbr: Nano Vision. 2013, Vol.3(3): Pg.235-239 Applications
Mechanical and magnetic properties of nanostructured CoNiP films
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 67, No. 2 journal of August 2006 physics pp. 341 349 Mechanical and magnetic properties of nanostructured CoNiP films R N EMERSON 1, C JOSEPH KENNADY 2, and S
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 67, No. 2 journal of August 2006 physics pp. 341 349 Mechanical and magnetic properties of nanostructured CoNiP films R N EMERSON 1, C JOSEPH KENNADY 2, and S
HIGH THROUGHPUT STUDIES OF HYDROGEN EVOLUTION ELECTROCATALYST FOR WATER ELECTROLYSIS
 HIGH THROUGHPUT STUDIES OF HYDROGEN EVOLUTION ELECTROCATALYST FOR WATER ELECTROLYSIS Radwinda Kurnia Putri 1, Brian Hayden², Agus Prasetya 3, Sihana 4 1 Magister of Engineering System, Universitas Gadjah
HIGH THROUGHPUT STUDIES OF HYDROGEN EVOLUTION ELECTROCATALYST FOR WATER ELECTROLYSIS Radwinda Kurnia Putri 1, Brian Hayden², Agus Prasetya 3, Sihana 4 1 Magister of Engineering System, Universitas Gadjah
Electrosynthesis of iron, cobalt and zinc microcrystals and. magnetic enhancement of the oxygen reduction reaction
 M / [A m 2 kg -1 ] Electrosynthesis of iron, cobalt and zinc microcrystals and magnetic enhancement of the oxygen reduction reaction Lorena M. A. Monzon*, Karsten Rode, M. Venkatesan and J.M.D. Coey School
M / [A m 2 kg -1 ] Electrosynthesis of iron, cobalt and zinc microcrystals and magnetic enhancement of the oxygen reduction reaction Lorena M. A. Monzon*, Karsten Rode, M. Venkatesan and J.M.D. Coey School
Electrodeposition of nickel plates on copper substrates using PC y PRC
 ISSN 1517-7076 Revista Matéria, v. 12, n. 4, pp. 583 588, 2007 http://www.materia.coppe.ufrj.br/sarra/artigos/artigo10705 Electrodeposition of nickel plates on copper substrates using PC y PRC ABSTRACT
ISSN 1517-7076 Revista Matéria, v. 12, n. 4, pp. 583 588, 2007 http://www.materia.coppe.ufrj.br/sarra/artigos/artigo10705 Electrodeposition of nickel plates on copper substrates using PC y PRC ABSTRACT
Supporting Information. Christina W. Li and Matthew W. Kanan* *To whom correspondence should be addressed.
 Supporting Information CO 2 Reduction at Low Overpotential on Cu Electrodes Resulting from the Reduction of Thick Cu 2 O Films Christina W. Li and Matthew W. Kanan* *To whom correspondence should be addressed.
Supporting Information CO 2 Reduction at Low Overpotential on Cu Electrodes Resulting from the Reduction of Thick Cu 2 O Films Christina W. Li and Matthew W. Kanan* *To whom correspondence should be addressed.
CHAPTER 4: The wetting behaviour and reaction of the diamond-si system
 CHAPTER 4: The wetting behaviour and reaction of the diamond-si system In this chapter, the wetting behaviour of diamond by silicon will be presented, followed by the study of the interaction between diamond
CHAPTER 4: The wetting behaviour and reaction of the diamond-si system In this chapter, the wetting behaviour of diamond by silicon will be presented, followed by the study of the interaction between diamond
Thin Film Characterizations Using XRD The Cases of VO2 and NbTiN
 Thin Film Characterizations Using XRD The Cases of VO2 and NbTiN A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the degree of Bachelor of Arts / Science in Physics from The College of
Thin Film Characterizations Using XRD The Cases of VO2 and NbTiN A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the degree of Bachelor of Arts / Science in Physics from The College of
