Golgi are located near the MTOC while the ER is spread throughout the cytoplasm, so which of the following is probably true?
|
|
|
- Elfrieda Bates
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Golgi are located near the MTOC while the ER is spread throughout the cytoplasm, so which of the following is probably true? A. COPII and COPI vesicles are transported with dynein. B. COPII and COPI vesicles are transported with kinesin1. C. COPII is transported with dynein and COPI is transported with kinesin 1. D. COPII is transported with kinesin 1 and COPI is transported with dynein.
2 Which statement about actin is false? A. They are shorter and skinnier than microtubules B. Monomeric actin binds ATP. C. The plus end is faster growing than the minus end D. ATP hydrolysis is not required for actin polymerization, but ATP is hydrolyzed as the filament lengthens. E. None of the above
3 If the Critical Concentration (CC) for the actin (+) end is.1 um and the CC for actin (-) end is.6 um, what would happen at.6 um free actin? a) The plus end of the filament will grow. b) Both ends will grow. c) The plus end will shorten and the minus end will grow. d) The minus end will shorten.
4 Which statement is the most accurate? A. A round mammalian cell is 2000X wider than a microtubule. B. A round mammalian cell is 100X wider than a microtubule. C. A round mammalian cell is 10X longer than a microtubule. D. Axons and dendrites are skinny because they have no microtubules.
5 How would you test if mitochondria traffic on microtubules? A. Make a movie of fluorescent mitochondria and add taxol during the movie. B. Make a movie of fluorescent mitochondria and add nocodazole during the middle. C. Make a movie of fluorescent mitochondria in a tubulin knockout mice. D. Two of the above.
6 In a round cell, the (+) end of a microtubule is A. Closer to the nucleus than the (-) end A. More positively charged C. Bound to the MTOC D. More dynamic than the (-) end
7 Which of the following is true? A. The MTOC is at the (-) end of the MT. B. In solution, Tubulin is a hetero-dimer. C. A microtubule is formed from 13 filaments. D. A microtubule gains strength from lateral bonds between filaments. E. Answers C and D. F. All of the above.
8 Which region of this MT would have the most GDP-tubulin in it? A. The newest section (+) end B. The minus end C. The plus end middle D. The middle MTOC (-) end
9 Which of the following would stabilize the plus end of microtubules A. A GAP that converts GTP-tubulin to GDP-tubulin B. A protein that stabilizes straight protofilaments. C. A GTPase activating protein. D. An increase in the number of gamma-tubulin ring complexes. E. A drug that binds tubulin and prevents its polymerization
10 Which of the following would stop transport by Kinesin-1? A. Taxol treatment. B. XMAP215 overexpression C. MCAK depletion. D. Katanin overexpression.
11 Which best describes microtubules? A.They are polymers of self assembling subunits, yet they have polarity. B. They have a positive and negatively charged end. C. A homo-dimer of alpha-tubulin forms the building block of MTs. D. In their polymerized state all of their tubulin is GDP-bound
12 Which of the following is a feature shared by all cytoskeletal fibers? A. They all have polarity. B. They are all self polymerizing. C. They are all used for trafficking by motors. D. They are all only found in the cytoplasm.
13 Microtubules are not equilibrium polymers because: A.Both ends can grow and shrink B.The (-) end is stabilized by the MTOC C.GTP hydrolysis weakens the tubule D. It is an equilibrium polymer
14 What kind of (+) tip binding protein would decrease the stability of the (+) end? A. a GEF (guanine exchange factor) note: cytoplasmic GTP >> GDP B. a GAP (GTPase activating protein) C. A protein that recruits free tubulin D. A protein that links MT filaments together
15 Katanin cuts microtubules in the middle How do you think it works? A. It binds in a circle around microtubules and weakens longitudinal and lateral bonds B. It recruits GDP-bound tubulin to the middle of the microtubule to cause fraying C. It stimulates GTP hydrolysis in the middle of the MT. D. It is a protease
16 Which of the following do NOT have analagous mechanism for regulating polymer formation? A. Katanin AND Cofilin B. Arp2/3 and gamma tubulin ring complex C. Thymosin B4 and nocodazole D. Profilin and MCAK
Microtubules. Forms a sheet of protofilaments that folds to a tube Both tubulins bind GTP
 Microtubules Polymerize from a-tubulin/ß-tubulin dimers Hollow tube of 13 protofilaments In vitro- filament number varies In vivo- always 13 protofilaments Forms a sheet of protofilaments that folds to
Microtubules Polymerize from a-tubulin/ß-tubulin dimers Hollow tube of 13 protofilaments In vitro- filament number varies In vivo- always 13 protofilaments Forms a sheet of protofilaments that folds to
Three major types of cytoskeleton
 The Cytoskeleton Organizes and stabilizes cells Pulls chromosomes apart Drives intracellular traffic Supports plasma membrane and nuclear envelope Enables cellular movement Guides growth of the plant cell
The Cytoskeleton Organizes and stabilizes cells Pulls chromosomes apart Drives intracellular traffic Supports plasma membrane and nuclear envelope Enables cellular movement Guides growth of the plant cell
1. The microtubule wall is composed of globular proteins arranged in longitudinal rows called.
 Name: Quiz name: Quiz 7 ate: 1. The microtubule wall is composed of globular proteins arranged in longitudinal rows called. microfilaments protofilaments prototubules microtubular subunits 2. Which of
Name: Quiz name: Quiz 7 ate: 1. The microtubule wall is composed of globular proteins arranged in longitudinal rows called. microfilaments protofilaments prototubules microtubular subunits 2. Which of
Chapter 15. Cytoskeletal Systems. Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 15 Cytoskeletal Systems Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Table 15-1 - Microtubules Table 15-1 - Microfilaments Table 15-1 Intermediate Filaments Table 15-3 Microtubules
Chapter 15 Cytoskeletal Systems Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Table 15-1 - Microtubules Table 15-1 - Microfilaments Table 15-1 Intermediate Filaments Table 15-3 Microtubules
Cell cycle oscillations
 Positive and negative feedback produce a cell cycle Fast Slow Cell cycle oscillations Active Cdk1-Cyclin Inactive Cdk1-Cyclin Active APC 1 Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis Glycine Isopeptide bond Lysine
Positive and negative feedback produce a cell cycle Fast Slow Cell cycle oscillations Active Cdk1-Cyclin Inactive Cdk1-Cyclin Active APC 1 Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis Glycine Isopeptide bond Lysine
BME Engineering Molecular Cell Biology. The Cytoskeleton (I): Actin The Cytoskeleton (II): Microtubule & Intermediate Filament
 BME 42-620 Engineering Molecular Cell Biology Lecture 09: The Cytoskeleton (I): Actin The Cytoskeleton (II): Microtubule & Intermediate Filament BME42-620 Lecture 09, September 27, 2011 1 Outline Overviewofcytoskeletal
BME 42-620 Engineering Molecular Cell Biology Lecture 09: The Cytoskeleton (I): Actin The Cytoskeleton (II): Microtubule & Intermediate Filament BME42-620 Lecture 09, September 27, 2011 1 Outline Overviewofcytoskeletal
Microtubule Cytoskeleton and Cell Patterning
 Microtubule Cytoskeleton and Cell Patterning 10:00 Anna Akhmanova Microtubule Dynamics 11:00 Lukas Kapitein Motors and Transport 12:00 12:30 Microscopy Facility Tour 13:00-14:30 Lunch and Self-study Jacobson
Microtubule Cytoskeleton and Cell Patterning 10:00 Anna Akhmanova Microtubule Dynamics 11:00 Lukas Kapitein Motors and Transport 12:00 12:30 Microscopy Facility Tour 13:00-14:30 Lunch and Self-study Jacobson
MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SIXTH EDITION. CHAPTER 18 Cell Organization and Movement II: Microtubules and Intermediate Filaments
 Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger Scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SIXTH EDITION CHAPTER 18 Cell Organization and Movement II: Microtubules and Intermediate Filaments 2008 W. H. Freeman
Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger Scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SIXTH EDITION CHAPTER 18 Cell Organization and Movement II: Microtubules and Intermediate Filaments 2008 W. H. Freeman
Section 10. Junaid Malek, M.D.
 Section 10 Junaid Malek, M.D. Cell Division Make sure you understand: How do cells know when to divide? (What drives the cell cycle? Why is it important to regulate this?) How is DNA replication regulated?
Section 10 Junaid Malek, M.D. Cell Division Make sure you understand: How do cells know when to divide? (What drives the cell cycle? Why is it important to regulate this?) How is DNA replication regulated?
ANAT Cell Biology Lecture 11 School of Medical Sciences The University of New South Wales. UNSW Copyright Notice
 ANAT3231 - Cell Biology Lecture 11 School of Medical Sciences The University of New South Wales The actin cytoskeleton Prof Peter Gunning Oncology Research Unit Room 502A Wallace Wurth Building Email:
ANAT3231 - Cell Biology Lecture 11 School of Medical Sciences The University of New South Wales The actin cytoskeleton Prof Peter Gunning Oncology Research Unit Room 502A Wallace Wurth Building Email:
Mathematical Modeling of Dynamic Instability in Microtubules
 Mathematical Modeling of Dynamic Instability in Microtubules Christine Lucille Kuryla 2013 NSF/REU Program Department of Physics, University of Notre Dame Advisors: Mark Alber, Dept. of Applied and Computational
Mathematical Modeling of Dynamic Instability in Microtubules Christine Lucille Kuryla 2013 NSF/REU Program Department of Physics, University of Notre Dame Advisors: Mark Alber, Dept. of Applied and Computational
Chapter 17. Molecular Motors. to accompany Biochemistry, 2/e by Reginald Garrett and Charles Grisham. Biochemistry 2/e - Garrett & Grisham
 Chapter 17 Molecular Motors to accompany Biochemistry, 2/e by Reginald Garrett and Charles Grisham All rights reserved. Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to:
Chapter 17 Molecular Motors to accompany Biochemistry, 2/e by Reginald Garrett and Charles Grisham All rights reserved. Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to:
Topic 11 Introduction to the Cytoskeleton and Actin
 BIOL 201 Cell Biology and Metabolism C. Aikins Notes II: Topic 11-15 (Cell Cycle) Winter 2011 Topic 11 Introduction to the Cytoskeleton and Actin Overview Cells come in many shapes Ex. muscle cells are
BIOL 201 Cell Biology and Metabolism C. Aikins Notes II: Topic 11-15 (Cell Cycle) Winter 2011 Topic 11 Introduction to the Cytoskeleton and Actin Overview Cells come in many shapes Ex. muscle cells are
Cell cycle oscillations. Active Cdk1-Cyclin Inactive Cdk1-Cyclin Active APC
 Cell cycle oscillations Active Cdk1-Cyclin Inactive Cdk1-Cyclin Active APC 20 Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis Glycine Isopeptide bond Lysine Many biological processes are regulated by controlling the stability
Cell cycle oscillations Active Cdk1-Cyclin Inactive Cdk1-Cyclin Active APC 20 Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis Glycine Isopeptide bond Lysine Many biological processes are regulated by controlling the stability
Introduction: The eukaryotic cytoskeleton and actin-microtubule coordination
 Chapter 1 Introduction: The eukaryotic cytoskeleton and actin-microtubule coordination In this introductory chapter we first outline the general properties of the three eukaryotic cytoskeletal systems:
Chapter 1 Introduction: The eukaryotic cytoskeleton and actin-microtubule coordination In this introductory chapter we first outline the general properties of the three eukaryotic cytoskeletal systems:
Old Exam II Questions. Give your full SID# on this page and the last page of this exam booklet.
 Old Exam II Questions SID#: Give your full SID# on this page and the last page of this exam booklet. Also fill in the grids of your full SID# in the Student Number Section of the computer scan sheet provided
Old Exam II Questions SID#: Give your full SID# on this page and the last page of this exam booklet. Also fill in the grids of your full SID# in the Student Number Section of the computer scan sheet provided
Old Exam II Questions. Give your full SID# on this page and the last page of this exam booklet.
 Old Exam II Questions SID#: Give your full SID# on this page and the last page of this exam booklet. Also fill in the grids of your full SID# in the Student Number Section of the computer scan sheet provided
Old Exam II Questions SID#: Give your full SID# on this page and the last page of this exam booklet. Also fill in the grids of your full SID# in the Student Number Section of the computer scan sheet provided
Movement at the Molecular Level
 Movement at the Molecular Level Diffusion: = 6 D t (D 6 π µ a) Typical numbers: 10 nm protein in water D= 10-10 m 2 /s.in cells D= 10-12 m 2 /s (D= 10-14 m 2 /s lipids) [] 1/2 =1 µm, t ~0.2
Movement at the Molecular Level Diffusion: = 6 D t (D 6 π µ a) Typical numbers: 10 nm protein in water D= 10-10 m 2 /s.in cells D= 10-12 m 2 /s (D= 10-14 m 2 /s lipids) [] 1/2 =1 µm, t ~0.2
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 01: Introduction to Molecular Cell Biology
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 01: Introduction to Molecular Cell Biology Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement describes how an organism is organized from most simple to most complex? Question
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 01: Introduction to Molecular Cell Biology Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement describes how an organism is organized from most simple to most complex? Question
MOLECULAR BASIS FOR THE DUAL FUNCTION OF EPS8 IN CONTROLLING ACTIN CYTOSKELETON DYNAMICS: BUNDLING AND CAPPING
 PhD degree in Molecular Medicine European School of Molecular Medicine (SEMM), University of Milan and University of Naples Federico II Faculty of Medicine Settore disciplinare: BIO/10 MOLECULAR BASIS
PhD degree in Molecular Medicine European School of Molecular Medicine (SEMM), University of Milan and University of Naples Federico II Faculty of Medicine Settore disciplinare: BIO/10 MOLECULAR BASIS
Acetylated Microtubules Are Preferentially Bundled Leading to Enhanced
 Biophysical Journal, Volume 113 Supplemental Information Acetylated Microtubules Are Preferentially Bundled Leading to Enhanced Kinesin-1 Motility Linda Balabanian, Christopher L. Berger, and Adam G. Hendricks
Biophysical Journal, Volume 113 Supplemental Information Acetylated Microtubules Are Preferentially Bundled Leading to Enhanced Kinesin-1 Motility Linda Balabanian, Christopher L. Berger, and Adam G. Hendricks
A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY. Alexei Olegovich Demchouk
 Microtubule Tip Tracking and Tip Structures at the Nanometer Scale Using Digital Fluorescence Microscopy A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Alexei
Microtubule Tip Tracking and Tip Structures at the Nanometer Scale Using Digital Fluorescence Microscopy A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Alexei
Self assembly and organization of nanofibers using biological molecular motors
 2006 International Conference on Nanotechnology, April 26-28, 2006 Atlanta, GA Self assembly and organization of nanofibers using biological molecular motors Presented by: Jeffrey M. Catchmark Assistant
2006 International Conference on Nanotechnology, April 26-28, 2006 Atlanta, GA Self assembly and organization of nanofibers using biological molecular motors Presented by: Jeffrey M. Catchmark Assistant
A Design of a Molecular Communication System for Nanomachines Using Molecular Motors
 A Design of a Molecular Communication System for Nanomachines Using Molecular Motors Michael Moore *, Akihiro Enomoto *, Tadashi Nakano *, Ryota Egashira *, Tatsuya Suda * Atsushi Kayasuga +, Hiroaki Kojima
A Design of a Molecular Communication System for Nanomachines Using Molecular Motors Michael Moore *, Akihiro Enomoto *, Tadashi Nakano *, Ryota Egashira *, Tatsuya Suda * Atsushi Kayasuga +, Hiroaki Kojima
Microtubule Assembly Dynamics at the Nanoscale
 Microtubule Assembly Dynamics at the Nanoscale Melissa K. Gardner, Henry T. Schek III*, Alan J. Hunt, and David J. Odde Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55455
Microtubule Assembly Dynamics at the Nanoscale Melissa K. Gardner, Henry T. Schek III*, Alan J. Hunt, and David J. Odde Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55455
THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY SCHREYER HONORS COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
 THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY SCHREYER HONORS COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY THE DEVELOPMENT OF MICROTUBULE POLARITY AND ORGANELLE LOCALIZATION IN THE DENDRITES OF DROSOPHILA
THE PENNSYLVANIA STATE UNIVERSITY SCHREYER HONORS COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY THE DEVELOPMENT OF MICROTUBULE POLARITY AND ORGANELLE LOCALIZATION IN THE DENDRITES OF DROSOPHILA
Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section B and ONE question from Section C.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2013-2014 CELL BIOLOGY BIO-2B06 Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2013-2014 CELL BIOLOGY BIO-2B06 Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in
Nano-Scale Engineering III Bio-Molecular Motors for Engineering
 Nano-Scale Engineering III Bio-Molecular Motors for Engineering Y. C. Lee Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Colorado Boulder, CO 80309-0427 leeyc@colorado.edu March 4, 2014 1 MLD of Hybrid
Nano-Scale Engineering III Bio-Molecular Motors for Engineering Y. C. Lee Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Colorado Boulder, CO 80309-0427 leeyc@colorado.edu March 4, 2014 1 MLD of Hybrid
Studies on microtubule nucleation. during axon growth
 Studies on microtubule nucleation during axon growth Dissertation zur Erlangung des Doktorgrades der Naturwissenschaften an der Fakultät für Biologie der Ludwig Maximilians Universität München Angefertigt
Studies on microtubule nucleation during axon growth Dissertation zur Erlangung des Doktorgrades der Naturwissenschaften an der Fakultät für Biologie der Ludwig Maximilians Universität München Angefertigt
Part I. Progress toward the Total Synthesis of Tubulysin Analogs
 Part I. Progress toward the Total Synthesis of Tubulysin Analogs Zhiyong Wang Research Topic Presentation September 16, 2006 Ac S Ph C Four Stage of a Cell Cycle G1-S-G2-M A General Look at the Cell Cycle
Part I. Progress toward the Total Synthesis of Tubulysin Analogs Zhiyong Wang Research Topic Presentation September 16, 2006 Ac S Ph C Four Stage of a Cell Cycle G1-S-G2-M A General Look at the Cell Cycle
Supplementary Figures
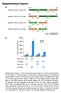 Supplementary Figures a HindIII XbaI pcdna3.1/v5-his A_Nfluc-VVD 1-398 37-186 Nfluc Linker 1 VVD HindIII XhoI pcdna3.1/v5-his A_VVD-Nfluc 37-186 1-398 VVD Linker 2 Nfluc HindIII XbaI pcdna3.1/v5-his A_Cfluc-VVD
Supplementary Figures a HindIII XbaI pcdna3.1/v5-his A_Nfluc-VVD 1-398 37-186 Nfluc Linker 1 VVD HindIII XhoI pcdna3.1/v5-his A_VVD-Nfluc 37-186 1-398 VVD Linker 2 Nfluc HindIII XbaI pcdna3.1/v5-his A_Cfluc-VVD
DNA STRUCTURE. Nucleotides: Nitrogenous Bases (Carry the Genetic Code) Expectation Sheet: DNA & Cell Cycle. I can statements: Basic Information:
 Expectation Sheet: DNA & Cell Cycle NAME: Test is 11/8/17 I can statements: I can discuss how DNA is found in all organisms and that the structure is common to all living things. I can diagram and label
Expectation Sheet: DNA & Cell Cycle NAME: Test is 11/8/17 I can statements: I can discuss how DNA is found in all organisms and that the structure is common to all living things. I can diagram and label
Biomolecular motors at the intersection of. nanotechnology and polymer science
 Biomolecular motors at the intersection of nanotechnology and polymer science Ashutosh Agarwal 1 and Henry Hess 2 * 1 Department of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Florida, Gainesville,
Biomolecular motors at the intersection of nanotechnology and polymer science Ashutosh Agarwal 1 and Henry Hess 2 * 1 Department of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Florida, Gainesville,
Stability properties of neuronal microtubules
 Review Article Cytoskeleton DOI 10.1002/cm.21286 Stability properties of neuronal microtubules Peter W. Baas, Anand N. Rao, Andrew J. Matamoros, and Lanfranco Leo Department of Neurobiology and Anatomy
Review Article Cytoskeleton DOI 10.1002/cm.21286 Stability properties of neuronal microtubules Peter W. Baas, Anand N. Rao, Andrew J. Matamoros, and Lanfranco Leo Department of Neurobiology and Anatomy
Microtubule Minus-End Stabilization by Polymerization-Driven CAMSAP Deposition
 Article Microtubule Minus-End Stabilization by Polymerization-Driven CAMSAP Deposition Kai Jiang, 1 Shasha Hua, 1 Renu Mohan, 1 Ilya Grigoriev, 1 Kah Wai Yau, 1 Qingyang Liu, 1,2 Eugene A. Katrukha, 1
Article Microtubule Minus-End Stabilization by Polymerization-Driven CAMSAP Deposition Kai Jiang, 1 Shasha Hua, 1 Renu Mohan, 1 Ilya Grigoriev, 1 Kah Wai Yau, 1 Qingyang Liu, 1,2 Eugene A. Katrukha, 1
H zone narrows; light band narrows; outer darker regions of A / dark band widen; 2 max
 M. (a) (i) A / dark band is mainly due to myosin filaments; H zone only myosin filaments; darker band has both types of filament; light band has only actin filaments; max H zone narrows; light band narrows;
M. (a) (i) A / dark band is mainly due to myosin filaments; H zone only myosin filaments; darker band has both types of filament; light band has only actin filaments; max H zone narrows; light band narrows;
MICB688L/MOCB639 Advanced Cell Biology Exam II
 MICB688L/MOCB639 Advanced Cell Biology Exam II May 10, 2001 Name: 1. Briefly describe the four major classes of cell surface receptors and their modes of action (immediate downstream only) (8) 2. Please
MICB688L/MOCB639 Advanced Cell Biology Exam II May 10, 2001 Name: 1. Briefly describe the four major classes of cell surface receptors and their modes of action (immediate downstream only) (8) 2. Please
Molecular Communication: Simulation of a Molecular Motor Communication System
 Molecular Communication: Simulation of a Molecular Motor Communication System Michael Moore, Akihiro Enomoto, Tadashi Nakano, Tatsuya Suda Department of Computer Science Donald Bren School of Information
Molecular Communication: Simulation of a Molecular Motor Communication System Michael Moore, Akihiro Enomoto, Tadashi Nakano, Tatsuya Suda Department of Computer Science Donald Bren School of Information
Active Transport by Biomolecular Motors: A New Tool for Nanotechnology
 Active Transport by Biomolecular Motors: A New Tool for Nanotechnology H. Hess, C. Brunner, J. Clemmens, K. H. Ernst, T. Nitta, S. Ramachandran, R.Tucker, D. Wu and V. Vogel Dep. of Bioengineering, University
Active Transport by Biomolecular Motors: A New Tool for Nanotechnology H. Hess, C. Brunner, J. Clemmens, K. H. Ernst, T. Nitta, S. Ramachandran, R.Tucker, D. Wu and V. Vogel Dep. of Bioengineering, University
Fluorescence Imaging with One Nanometer Accuracy Lab
 I. Introduction. Fluorescence Imaging with One Nanometer Accuracy Lab Traditional light microscope is limited by the diffraction limit of light, typically around 250 nm. However, many biological processes
I. Introduction. Fluorescence Imaging with One Nanometer Accuracy Lab Traditional light microscope is limited by the diffraction limit of light, typically around 250 nm. However, many biological processes
Tubulin Polymerization Assay Kit
 The Protein Experts Manual Cytoskeleton, Inc. V 3.0 Tubulin Polymerization Assay Kit Cat. # BK006P cytoskeleton.com Phone: (303) 322.2254 Fax: (303) 322.2257 Customer Service: cserve@cytoskeleton.com Technical
The Protein Experts Manual Cytoskeleton, Inc. V 3.0 Tubulin Polymerization Assay Kit Cat. # BK006P cytoskeleton.com Phone: (303) 322.2254 Fax: (303) 322.2257 Customer Service: cserve@cytoskeleton.com Technical
EFFECTS OF CYSTEINE MODIFICATION ON MICROTUBULE-MOTOR FUNCTION AND TUBULIN ASSEMBLY. by Kalmia Kniel Phelps
 EFFECTS OF CYSTEINE MODIFICATION ON MICROTUBULE-MOTOR FUNCTION AND TUBULIN ASSEMBLY by Kalmia Kniel Phelps Thesis submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in
EFFECTS OF CYSTEINE MODIFICATION ON MICROTUBULE-MOTOR FUNCTION AND TUBULIN ASSEMBLY by Kalmia Kniel Phelps Thesis submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in
Kinesin-5 is a microtubule polymerase
 Received 1 ec 214 Accepted 25 Jul 215 Published 6 Oct 215 OI: 1.138/ncomms916 Kinesin-5 is a microtubule polymerase Yalei Chen 1,2 & William O. Hancock 1,2 OPEN Kinesin-5 slides antiparallel microtubules
Received 1 ec 214 Accepted 25 Jul 215 Published 6 Oct 215 OI: 1.138/ncomms916 Kinesin-5 is a microtubule polymerase Yalei Chen 1,2 & William O. Hancock 1,2 OPEN Kinesin-5 slides antiparallel microtubules
Microtubule nucleation by γ tubulin complexes
 Microtubule nucleation by γ tubulin complexes Justin M. Kollman*, Andreas Merdes, Lionel Mourey and David A. Agard* Abstract Microtubule nucleation is regulated by the γ tubulin ring complex (γturc) and
Microtubule nucleation by γ tubulin complexes Justin M. Kollman*, Andreas Merdes, Lionel Mourey and David A. Agard* Abstract Microtubule nucleation is regulated by the γ tubulin ring complex (γturc) and
BIO 311C Spring Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr.
 BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr. Synthesis of a Polypeptide Chain 5 direction of ribosome movement along the mrna 3 ribosome mrna NH 2 polypeptide chain direction of mrna movement through
BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr. Synthesis of a Polypeptide Chain 5 direction of ribosome movement along the mrna 3 ribosome mrna NH 2 polypeptide chain direction of mrna movement through
Biosensors. DNA Microarrays (for chemical analysis) Protein Sensors (for identifying viruses)
 Biosensors DNA Microarrays (for chemical analysis) Protein Sensors (for identifying viruses) DNA Microarrays 40 000 detectors in parallel, each detecting a specific DNA sequence. Combinatorial Chemistry
Biosensors DNA Microarrays (for chemical analysis) Protein Sensors (for identifying viruses) DNA Microarrays 40 000 detectors in parallel, each detecting a specific DNA sequence. Combinatorial Chemistry
Supplemental Movie Legend.
 Supplemental Movie Legend. Transfected T cells were dropped onto SEE superantigen-pulsed Raji B cells (approximate location indicated by circle). Maximum-intensity projections from Z-stacks (17 slices,
Supplemental Movie Legend. Transfected T cells were dropped onto SEE superantigen-pulsed Raji B cells (approximate location indicated by circle). Maximum-intensity projections from Z-stacks (17 slices,
Microtubule stabilization/destabilization assay
 Microtubule stabilization/destabilization assay (BK012) 1/2 ページ Microtubule stabilization/destabilization assay Cat. # BK012 Product Uses Include To measure compound IC50s and specificity for microtubule
Microtubule stabilization/destabilization assay (BK012) 1/2 ページ Microtubule stabilization/destabilization assay Cat. # BK012 Product Uses Include To measure compound IC50s and specificity for microtubule
Polyamine Sharing between Tubulin Dimers Favours Microtubule Nucleation and Elongation via Facilitated Diffusion
 Polyamine Sharing between Tubulin Dimers Favours Microtubule Nucleation and Elongation via Facilitated Diffusion Alain Mechulam 1,2, Konstantin G. Chernov 1,2,3, Elodie Mucher 1,2, Loic Hamon 1,2, Patrick
Polyamine Sharing between Tubulin Dimers Favours Microtubule Nucleation and Elongation via Facilitated Diffusion Alain Mechulam 1,2, Konstantin G. Chernov 1,2,3, Elodie Mucher 1,2, Loic Hamon 1,2, Patrick
The Arp2/3 Activator WASH Controls the Fission of Endosomes through a Large Multiprotein Complex
 Article The Arp2/3 Activator WASH Controls the Fission of Endosomes through a Large Multiprotein Complex Emmanuel Derivery, 1,2,3 Carla Sousa, 3 Jérémie J. Gautier, 3 Bérangère Lombard, 1 Damarys Loew,
Article The Arp2/3 Activator WASH Controls the Fission of Endosomes through a Large Multiprotein Complex Emmanuel Derivery, 1,2,3 Carla Sousa, 3 Jérémie J. Gautier, 3 Bérangère Lombard, 1 Damarys Loew,
c) Given the pleiotropic phenotypes of this disease, state a hypothesis about what defect you think could underlie this condition? (1.
 QUESTION 1 You are starting your post-doc fellowship and developing your own project. You have become intrigued with a human disease that has pleiotropic phenotypes including: obesity; loss of sight; lack
QUESTION 1 You are starting your post-doc fellowship and developing your own project. You have become intrigued with a human disease that has pleiotropic phenotypes including: obesity; loss of sight; lack
Visualization of Microtubule Growth in Cultured Neurons via the Use of EB3-GFP (End-Binding Protein 3-Green Fluorescent Protein)
 The Journal of Neuroscience, April 1, 2003 23(7):2655 2664 2655 Visualization of Microtubule Growth in Cultured Neurons via the Use of EB3-GFP (End-Binding Protein 3-Green Fluorescent Protein) Tatiana
The Journal of Neuroscience, April 1, 2003 23(7):2655 2664 2655 Visualization of Microtubule Growth in Cultured Neurons via the Use of EB3-GFP (End-Binding Protein 3-Green Fluorescent Protein) Tatiana
1.5 Nucleic Acids and Their Functions Page 1 S. Preston 1
 AS Unit 1: Basic Biochemistry and Cell Organisation Name: Date: Topic 1.5 Nucleic Acids and their functions Page 1 From the syllabus: 1.5 Nucleic Acids and Their Functions Page 1 S. Preston 1 l. Nucleic
AS Unit 1: Basic Biochemistry and Cell Organisation Name: Date: Topic 1.5 Nucleic Acids and their functions Page 1 From the syllabus: 1.5 Nucleic Acids and Their Functions Page 1 S. Preston 1 l. Nucleic
Patronin Regulates the Microtubule Network by Protecting Microtubule Minus Ends
 Patronin Regulates the Microtubule Network by Protecting Microtubule Minus Ends Sarah S. Goodwin 1 and Ronald D. Vale 1, * 1 The Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Department of Cellular and Molecular
Patronin Regulates the Microtubule Network by Protecting Microtubule Minus Ends Sarah S. Goodwin 1 and Ronald D. Vale 1, * 1 The Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Department of Cellular and Molecular
Intermediate Filaments in Motion: Observations of Intermediate Filaments in Cells Using Green Fluorescent Protein-Vimentin V
 Molecular Biology of the Cell Vol. 10, 1289 1295, May 1999 Intermediate Filaments in Motion: Observations of Intermediate Filaments in Cells Using Green Fluorescent Protein-Vimentin V Jayme L. Martys,
Molecular Biology of the Cell Vol. 10, 1289 1295, May 1999 Intermediate Filaments in Motion: Observations of Intermediate Filaments in Cells Using Green Fluorescent Protein-Vimentin V Jayme L. Martys,
Dissociation of the Tubulin-sequestering and Microtubule Catastrophe-promoting Activities of Oncoprotein 18/Stathmin
 Molecular Biology of the Cell Vol. 10, 105 118, January 1999 Dissociation of the Tubulin-sequestering and Microtubule Catastrophe-promoting Activities of Oncoprotein 18/Stathmin Bonnie Howell,* Niklas
Molecular Biology of the Cell Vol. 10, 105 118, January 1999 Dissociation of the Tubulin-sequestering and Microtubule Catastrophe-promoting Activities of Oncoprotein 18/Stathmin Bonnie Howell,* Niklas
Chromosomes. Chromosomes. Genes. Strands of DNA that contain all of the genes an organism needs to survive and reproduce
 Chromosomes Chromosomes Strands of DNA that contain all of the genes an organism needs to survive and reproduce Genes Segments of DNA that specify how to build a protein genes may specify more than one
Chromosomes Chromosomes Strands of DNA that contain all of the genes an organism needs to survive and reproduce Genes Segments of DNA that specify how to build a protein genes may specify more than one
NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses)
 NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses) Consist of chemically linked sequences of nucleotides Nitrogenous base Pentose-
NUCLEIC ACIDS Genetic material of all known organisms DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid RNA: ribonucleic acid (e.g., some viruses) Consist of chemically linked sequences of nucleotides Nitrogenous base Pentose-
SONOMA STATE UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY BIOLOGY 344: CELL BIOLOGY Fall 2013
 SONOMA STATE UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY BIOLOGY 344: CELL BIOLOGY Fall 2013 Instructor Murali C. Pillai, PhD Office 214 Darwin Hall Telephone (707) 664-2981 E-mail pillai@sonoma.edu Website www.sonoma.edu/users/p/pillai
SONOMA STATE UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY BIOLOGY 344: CELL BIOLOGY Fall 2013 Instructor Murali C. Pillai, PhD Office 214 Darwin Hall Telephone (707) 664-2981 E-mail pillai@sonoma.edu Website www.sonoma.edu/users/p/pillai
RESPONSE. A Thesis. Submitted to the College of. Graduate Studies and Research. In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
 MICROTUBULE INVOLVEMENT IN THE PLANT LOW TEMPERATURE RESPONSE A Thesis Submitted to the College of Graduate Studies and Research In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of Science
MICROTUBULE INVOLVEMENT IN THE PLANT LOW TEMPERATURE RESPONSE A Thesis Submitted to the College of Graduate Studies and Research In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of Science
Dynamics of Mitotic Microtubules in Fission Yeast
 University of Colorado, Boulder CU Scholar Undergraduate Honors Theses Honors Program Spring 2017 Dynamics of Mitotic Microtubules in Fission Yeast Patrick Flynn pafl9640@colorado.edu Follow this and additional
University of Colorado, Boulder CU Scholar Undergraduate Honors Theses Honors Program Spring 2017 Dynamics of Mitotic Microtubules in Fission Yeast Patrick Flynn pafl9640@colorado.edu Follow this and additional
9/3/2009. DNA RNA Proteins. DNA Genetic program RNAs Ensure synthesis of proteins Proteins Ensure all cellular functions Carbohydrates (sugars) Energy
 Structure Properties Functions of the cell Chemical organization of the cell Based on molecular substrate : DNA contains information RNA ensures protein synthesis Proteins ensure vitality Relations between
Structure Properties Functions of the cell Chemical organization of the cell Based on molecular substrate : DNA contains information RNA ensures protein synthesis Proteins ensure vitality Relations between
Corning Epic System. Applications. Therapeutic Application
 Corning Epic System Applications The Corning Epic System can be applied to probe many of the biomolecular interactions involved in cellular and molecular biology. Beyond its application to direct binding,
Corning Epic System Applications The Corning Epic System can be applied to probe many of the biomolecular interactions involved in cellular and molecular biology. Beyond its application to direct binding,
Differential interactions of the formins INF2, mdia1, and mdia2 with microtubules
 MBoC ARTICLE Differential interactions of the formins INF2, mdia1, and mdia2 with microtubules Jeremie Gaillard a, Vinay Ramabhadran b, Emmanuelle Neumanne c, Pinar Gurel b, Laurent Blanchoin a, Marylin
MBoC ARTICLE Differential interactions of the formins INF2, mdia1, and mdia2 with microtubules Jeremie Gaillard a, Vinay Ramabhadran b, Emmanuelle Neumanne c, Pinar Gurel b, Laurent Blanchoin a, Marylin
Chapter 8 Lecture Outline. Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics
 Chapter 8 Lecture Outline Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics Replication, Transcription, Translation n Repetitive processes Build polymers of nucleotides or amino acids n All have 3 major steps
Chapter 8 Lecture Outline Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics Replication, Transcription, Translation n Repetitive processes Build polymers of nucleotides or amino acids n All have 3 major steps
SDS-PAGE and Western Blot. Molecular Basis of Evolution
 1 SDS-PAGE and Western Blot Molecular Basis of Evolution Homology high level of DNA and protein sequence similarity due to common ancestry. Evidence Genomes of related organisms are very similar. Even
1 SDS-PAGE and Western Blot Molecular Basis of Evolution Homology high level of DNA and protein sequence similarity due to common ancestry. Evidence Genomes of related organisms are very similar. Even
The replication forks Summarising what we know:
 When does replication occur? MBLG1001 lecture 10 Replication the once in a lifetime event! Full blown replication only occurs once, just before cell division BUT the DNA template is constantly being repaired.
When does replication occur? MBLG1001 lecture 10 Replication the once in a lifetime event! Full blown replication only occurs once, just before cell division BUT the DNA template is constantly being repaired.
Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene
 Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene For Next Week Lab -Hand in questions from 4 and 5 by TUES in my mailbox (Biology Office) -Do questions for Lab 6 for next week -Lab practical next week Lecture Read
Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene For Next Week Lab -Hand in questions from 4 and 5 by TUES in my mailbox (Biology Office) -Do questions for Lab 6 for next week -Lab practical next week Lecture Read
Vorlesung Biophysik I - Molekulare Biophysik Kalbitzer/Kremer/Ziegler
 Vorlesung Biophysik I - Molekulare Biophysik Kalbitzer/Kremer/Ziegler 23.10. Zelle 30.10. Biologische Makromoleküle I 06.11. Biologische Makromoleküle II 13.11. Nukleinsäuren-Origami (DNA, RNA) 20.11.
Vorlesung Biophysik I - Molekulare Biophysik Kalbitzer/Kremer/Ziegler 23.10. Zelle 30.10. Biologische Makromoleküle I 06.11. Biologische Makromoleküle II 13.11. Nukleinsäuren-Origami (DNA, RNA) 20.11.
Figure 1. Schematic of Ats1p expression plasmid.
 Abstract: Anita Corbett page 2 The goal of my rotation project was to express, purify, and examine the exchange activity of a putative guanine nucleotide exchange factor, Ats1p. The S. cerevisiae ATS1
Abstract: Anita Corbett page 2 The goal of my rotation project was to express, purify, and examine the exchange activity of a putative guanine nucleotide exchange factor, Ats1p. The S. cerevisiae ATS1
Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 3 3/6/15
 Name: Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 3 3/6/15 Answer each of the following questions in the space provided; circle the correct answer or answers for each multiple choice question and circle either
Name: Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 3 3/6/15 Answer each of the following questions in the space provided; circle the correct answer or answers for each multiple choice question and circle either
MCB110 FINAL. Dec 13, Your name and student ID
 MCB110 FINAL Dec 13, 2007 Your name and student ID. QUESTION POINTS 1 (15 points) 2 (15 points) 3 (15 points) 4 (20 points) 5 (25 points) 6 (20 points) 7 (20 points) 8 (20 points) 9 (25 points) 10 (25
MCB110 FINAL Dec 13, 2007 Your name and student ID. QUESTION POINTS 1 (15 points) 2 (15 points) 3 (15 points) 4 (20 points) 5 (25 points) 6 (20 points) 7 (20 points) 8 (20 points) 9 (25 points) 10 (25
1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle.
 Unit 5 Study Guide Cell Cycle pg. 1 1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle. Interphase = period in between division G1 = growth phase S = DNA replication G2 = Preparation for division (extra copies
Unit 5 Study Guide Cell Cycle pg. 1 1. I can describe the stages of the cell cycle. Interphase = period in between division G1 = growth phase S = DNA replication G2 = Preparation for division (extra copies
Answers to the multiple choice questions are at the bottom of the last page of this document.
 Review for Unit Test #2: Cell Parts, Functions and Protein Synthesis, Answers Answers to the multiple choice questions are at the bottom of the last page of this document. 1. Know all of the material on
Review for Unit Test #2: Cell Parts, Functions and Protein Synthesis, Answers Answers to the multiple choice questions are at the bottom of the last page of this document. 1. Know all of the material on
IDENTIFICATION OF ALTERED RAS SIGNALING AND INTERMEDIATE FILAMENT HYPERPHOSPHORYLATION IN GIANT AXONAL NEUROPATHY. Kyle Benjamin Martin
 IDENTIFICATION OF ALTERED RAS SIGNALING AND INTERMEDIATE FILAMENT HYPERPHOSPHORYLATION IN GIANT AXONAL NEUROPATHY Kyle Benjamin Martin Submitted to the faculty of the University Graduate School in partial
IDENTIFICATION OF ALTERED RAS SIGNALING AND INTERMEDIATE FILAMENT HYPERPHOSPHORYLATION IN GIANT AXONAL NEUROPATHY Kyle Benjamin Martin Submitted to the faculty of the University Graduate School in partial
Solution Key Problem Set
 Solution Key- 7.013 Problem Set 5-2013 Question 1 During a summer hike you suddenly spot a huge grizzly bear. This emergency situation triggers a fight or flight response through a signaling pathway as
Solution Key- 7.013 Problem Set 5-2013 Question 1 During a summer hike you suddenly spot a huge grizzly bear. This emergency situation triggers a fight or flight response through a signaling pathway as
Chapter 8: DNA and RNA
 Chapter 8: DNA and RNA Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 8-1 DNA and the Importance of Proteins Proteins play
Chapter 8: DNA and RNA Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 8-1 DNA and the Importance of Proteins Proteins play
Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Key Concepts 3.1 Nucleic Acids Are Informational Macromolecules 3.2 Proteins Are Polymers with Important Structural
3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Key Concepts 3.1 Nucleic Acids Are Informational Macromolecules 3.2 Proteins Are Polymers with Important Structural
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN. Section C: The Synthesis of Protein
 CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN Section C: The Synthesis of Protein 1. Translation is the RNA-directed synthesis of a polypeptide: a closer look 2. Signal peptides target some eukaryotic polypeptides to
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN Section C: The Synthesis of Protein 1. Translation is the RNA-directed synthesis of a polypeptide: a closer look 2. Signal peptides target some eukaryotic polypeptides to
Fig. S1. Endocytosis of extracellular cargo does not depend on dia. (A) To visualize endocytosis, fluorescently labelled wheat germ agglutinin
 Fig. S1. Endocytosis of extracellular cargo does not depend on dia. (A) To visualize endocytosis, fluorescently labelled wheat germ agglutinin (WGA-Alexa555) was injected into the extracellular perivitteline
Fig. S1. Endocytosis of extracellular cargo does not depend on dia. (A) To visualize endocytosis, fluorescently labelled wheat germ agglutinin (WGA-Alexa555) was injected into the extracellular perivitteline
The processes involved in bacterial cell division are strikingly
 Rapid assembly dynamics of the Escherichia coli FtsZ-ring demonstrated by fluorescence recovery after photobleaching Jesse Stricker*, Paul Maddox, E. D. Salmon, and Harold P. Erickson* *Department of Cell
Rapid assembly dynamics of the Escherichia coli FtsZ-ring demonstrated by fluorescence recovery after photobleaching Jesse Stricker*, Paul Maddox, E. D. Salmon, and Harold P. Erickson* *Department of Cell
Chapter 10 - Molecular Biology of the Gene
 Bio 100 - Molecular Genetics 1 A. Bacterial Transformation Chapter 10 - Molecular Biology of the Gene Researchers found that they could transfer an inherited characteristic (e.g. the ability to cause pneumonia),
Bio 100 - Molecular Genetics 1 A. Bacterial Transformation Chapter 10 - Molecular Biology of the Gene Researchers found that they could transfer an inherited characteristic (e.g. the ability to cause pneumonia),
XMAP215 Is a Processive Microtubule Polymerase
 XMAP215 Is a Processive Microtubule Polymerase Gary J. Brouhard, 1,5 Jeffrey H. Stear, 1,4,5 Tim L. Noetzel, 1 Jawdat Al-Bassam, 2 Kazuhisa Kinoshita, 3 Stephen C. Harrison, 2 Jonathon Howard, 1, * and
XMAP215 Is a Processive Microtubule Polymerase Gary J. Brouhard, 1,5 Jeffrey H. Stear, 1,4,5 Tim L. Noetzel, 1 Jawdat Al-Bassam, 2 Kazuhisa Kinoshita, 3 Stephen C. Harrison, 2 Jonathon Howard, 1, * and
Dissection of the mitotic and nuclear functions of Chromator, a nuclear-derived spindle matrix component in Drosophila
 Retrospective Theses and Dissertations 2008 Dissection of the mitotic and nuclear functions of Chromator, a nuclear-derived spindle matrix component in Drosophila Yun Ding Iowa State University Follow
Retrospective Theses and Dissertations 2008 Dissection of the mitotic and nuclear functions of Chromator, a nuclear-derived spindle matrix component in Drosophila Yun Ding Iowa State University Follow
An N-terminal truncation of the ncd motor protein supports diffusional movement of microtubules in motility assays
 Journal of Cell Science 104, 899-906 (1993) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1993 899 An N-terminal truncation of the ncd motor protein supports diffusional movement of microtubules
Journal of Cell Science 104, 899-906 (1993) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1993 899 An N-terminal truncation of the ncd motor protein supports diffusional movement of microtubules
Mapping the Neuronal Cytoskeleton with Expansion Microscopy
 Mapping the Neuronal Cytoskeleton with Expansion Microscopy Development and Optimization for different Imaging Modalities V. van Batenburg Cover image: Microtubules of a glia cell in a culture of hippocampal
Mapping the Neuronal Cytoskeleton with Expansion Microscopy Development and Optimization for different Imaging Modalities V. van Batenburg Cover image: Microtubules of a glia cell in a culture of hippocampal
Resolution of Microscopes Visible light is nm Dry lens(0.5na), green(530nm light)=0.65µm=650nm for oil lens (1.4NA) UV light (300nm) = 0.13µm f
 Microscopes and Microscopy MCB 380 Good information sources: Alberts-Molecular Biology of the Cell http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/ http://www.microscopyu.com/ Approaches to Problems in Cell Biology
Microscopes and Microscopy MCB 380 Good information sources: Alberts-Molecular Biology of the Cell http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/ http://www.microscopyu.com/ Approaches to Problems in Cell Biology
CELL BIOLOGY BIOL3030, 3 credits Fall 2012, Aug 20, Dec 14, 2012 Tuesday/Thursday 8:00 am-9:15 am Bowman-Oddy Laboratories 1049
 INSTRUCTOR: Dr. Song-Tao Liu WO3254B Tel: 419-530-7853 Email: Song-Tao.Liu@utoledo.edu OFFICE HOURS CELL BIOLOGY BIOL3030, 3 credits Fall 2012, Aug 20, 2012 - Dec 14, 2012 Tuesday/Thursday 8:00 am-9:15
INSTRUCTOR: Dr. Song-Tao Liu WO3254B Tel: 419-530-7853 Email: Song-Tao.Liu@utoledo.edu OFFICE HOURS CELL BIOLOGY BIOL3030, 3 credits Fall 2012, Aug 20, 2012 - Dec 14, 2012 Tuesday/Thursday 8:00 am-9:15
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein
 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein This is also known as: The central dogma of molecular biology Protein Proteins are made
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein This is also known as: The central dogma of molecular biology Protein Proteins are made
Supplementary materials: Spatiotemporal analysis of RhoA/B/C activation in primary human endothelial cells
 Supplementary materials: Spatiotemporal analysis of RhoA/B/C activation in primary human endothelial cells Nathalie R. Reinhard 1,2, Suzanne F. van Helden 2, Eloise C. Anthony 2, Taofei Yin 3., Yi Wu 3,
Supplementary materials: Spatiotemporal analysis of RhoA/B/C activation in primary human endothelial cells Nathalie R. Reinhard 1,2, Suzanne F. van Helden 2, Eloise C. Anthony 2, Taofei Yin 3., Yi Wu 3,
Protein Synthesis Notes
 Protein Synthesis Notes Protein Synthesis: Overview Transcription: synthesis of mrna under the direction of DNA. Translation: actual synthesis of a polypeptide under the direction of mrna. Transcription
Protein Synthesis Notes Protein Synthesis: Overview Transcription: synthesis of mrna under the direction of DNA. Translation: actual synthesis of a polypeptide under the direction of mrna. Transcription
Sunday Driver/JIP3 binds kinesin heavy chain directly and enhances its motility
 The EMBO Journal (211), 416429 & 211 European Molecular Biology Organization All Rights Reserved 261-4189/11 www.embojournal.org Sunday Driver/JIP binds kinesin heavy chain directly and enhances its motility
The EMBO Journal (211), 416429 & 211 European Molecular Biology Organization All Rights Reserved 261-4189/11 www.embojournal.org Sunday Driver/JIP binds kinesin heavy chain directly and enhances its motility
Photoreceptors and Phototransduction
 Photoreceptors and Phototransduction Andrew Stockman NEUR 3045 Visual Neuroscience Background Light 400-700 nm is important for vision The retina is carpeted with lightsensitive rods and cones An inverted
Photoreceptors and Phototransduction Andrew Stockman NEUR 3045 Visual Neuroscience Background Light 400-700 nm is important for vision The retina is carpeted with lightsensitive rods and cones An inverted
nucleolus nucleus number proteins ribosomes type
 Name Use with textbook pages 123 129 Inside the nucleus Cloze Activity Section 41 Vocabulary 23 46 chromosomes DNA genes genetic molecule nucleolus nucleus number proteins ribosomes type Use the terms
Name Use with textbook pages 123 129 Inside the nucleus Cloze Activity Section 41 Vocabulary 23 46 chromosomes DNA genes genetic molecule nucleolus nucleus number proteins ribosomes type Use the terms
ELUCIDATING THE FUNCTIONS AND IMPACT OF INHIBITION OF MITOTIC KINESINS IN CANDIDA ALBICANS
 ELUCIDATING THE FUNCTIONS AND IMPACT OF INHIBITION OF MITOTIC KINESINS IN CANDIDA ALBICANS by Irsa Shoukat A thesis submitted to the Department of Biomedical and Molecular Sciences In conformity with the
ELUCIDATING THE FUNCTIONS AND IMPACT OF INHIBITION OF MITOTIC KINESINS IN CANDIDA ALBICANS by Irsa Shoukat A thesis submitted to the Department of Biomedical and Molecular Sciences In conformity with the
Cells and Tissues. Overview CELLS
 Cells and Tissues WIll The basic unit of structure and function in the human body is the cell. Each of a cell's parts, or organelles, as well as the entire cell, is organized to perform a specific function.
Cells and Tissues WIll The basic unit of structure and function in the human body is the cell. Each of a cell's parts, or organelles, as well as the entire cell, is organized to perform a specific function.
The Two-Hybrid System
 Encyclopedic Reference of Genomics and Proteomics in Molecular Medicine The Two-Hybrid System Carolina Vollert & Peter Uetz Institut für Genetik Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe PO Box 3640 D-76021 Karlsruhe
Encyclopedic Reference of Genomics and Proteomics in Molecular Medicine The Two-Hybrid System Carolina Vollert & Peter Uetz Institut für Genetik Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe PO Box 3640 D-76021 Karlsruhe
Stabilization of Microtubules by Tubulin-GDP-Pi Subunits?
 8136 Biochemistry 1989, 28, 8 136-8 141 Stabilization of Microtubules by Tubulin-GDP-Pi Subunits? M. Caplow,* R. Ruhlen, J. Shanks, R.. Walker, and E. D. Salmon Departments of Biochemistry and Biology,
8136 Biochemistry 1989, 28, 8 136-8 141 Stabilization of Microtubules by Tubulin-GDP-Pi Subunits? M. Caplow,* R. Ruhlen, J. Shanks, R.. Walker, and E. D. Salmon Departments of Biochemistry and Biology,
Hmwk # 8 : DNA-Binding Proteins : Part II
 The purpose of this exercise is : Hmwk # 8 : DNA-Binding Proteins : Part II 1). to examine the case of a tandem head-to-tail homodimer binding to DNA 2). to view a Zn finger motif 3). to consider the case
The purpose of this exercise is : Hmwk # 8 : DNA-Binding Proteins : Part II 1). to examine the case of a tandem head-to-tail homodimer binding to DNA 2). to view a Zn finger motif 3). to consider the case
