Old Exam II Questions. Give your full SID# on this page and the last page of this exam booklet.
|
|
|
- Camron Anderson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Old Exam II Questions SID#: Give your full SID# on this page and the last page of this exam booklet. Also fill in the grids of your full SID# in the Student Number Section of the computer scan sheet provided to you. Give your answer to each question in this exam booklet. Also give your answer (A, B, C, or D) to each Multiple Choice on the computer scan sheet (Each Multiple Choice question is worth 2 pts) Page numbers refer to Exam II Material pdf Chapter 7 Questions 16. Which of the following cell-cell interaction molecules forms a hydrated gel around cells that cushions them from crushing forces: pg. 2-4 and 14 A) cadherin B) collagen C) proteoglycans D) fibronectin 17. In which of the following tissues would you expect to find an abundance of gap junctions: pg 21 A) skeletal muscle B) smooth muscle lining the intestines C) epidermal cells of skin D) endothelial cells lining capillaries to the brain 18. Which of the following antibodies would be expected to interfere with the recruitment of neutrophils from the blood stream to a site of tissue injury: pg 18 A) anti-occludin B) anti-fibronectin antibody C) anti-selectin antibody D) anti-collagen antibody - 1 -
2 19. Low dose aspirin inhibits platelet aggregation by: pg 9 A) competing with fibrinogen for binding to integrin on the surface of platelets B) competing with fibronectin for binding to integrin on the surface of platelets C) preventing inside-out signaling that activates integrin on the surface of platelets D) acting as a COX-2 specific enzyme inhibitor 20. Which of the following molecules on the surface of a plant cell provides a function that is similar to collagen surrounding animal cells: pg 24 A) collagen B) cellulose C) hemicellulose D) pectin Chapter 9 Questions 21. The cross section of a muscle sarcomere shown below, in which both thick and thin filaments are observed, could have been taken through which portion of the sarcomere: pg 42 A) H zone in a relaxed muscle B) H zone in a contracted muscle C) Non-H zone of A band in a contracted or relaxed muscle D) I band in a relaxed muscle 22. In an in vitro motility assay, a newly discovered motor protein is found to transport an attached bead along a microtubule away from the end where fluorescently labeled tubulin dimers assembled. To which family of motor proteins does the protein belong? pg A) kinesin family B) dynein family C) myosin family D) More than one of the above could be correct - 2 -
3 23. A mutation in a motor protein of human neurons prevents neurotransmitter vesicles from being transported down the axonal projection away from the cell body where γ-tubulin staining is observed. This information tells you that the mutated motor protein belongs to which of the following families of motor proteins: pg A) kinesin family B) dynein family C) myosin family D) More than one of the above could be correct 24. Which of the following types of tubulin dimers assembles into the plus end of a microtubule:pg 26 A) α-gtp/β-gtp B) α-gdp/β-gdp C) α-gtp/β-gdp D) α-gdp/β-gtp 25. Which of the following features of the minus end of a microtubule causes it to be stable in comparison to the plus end: pg 26 Α) The α subunit of the α/β tubulin dimer is always in a GDP-bound state. B) The β subunit of the α/β tubulin dimer is always in a GDP-bound state. C) The α subunit of the α/β tubulin dimer is always in a GTP-bound state. D) The β subunit of the α/β tubulin dimer is always in a GTP-bound state. 26. Cytochalasin is to microfilaments as is to microtubules. pg 27 A) phalloidin B) cytochalasin C) nocodazole D) colchicine - 3 -
4 27. A protein induces anterior cell fates in a frog embryo must be transported to the anterior end of the developing egg during oogenesis. γ tubulin immunostaining is also concentrated at the anterior end of the developing egg. When developing eggs are treated with colchicine during oogenesis, the anterior fate protein does not become localized at the egg s anterior end. Which of the following conclusions can you draw about the process for transporting the anterior fate protein to the egg s anterior end: pg 30 and A) A microtubule/kinesin motor system is required to transport the anterior fate protein to the egg s anterior end. B) A microtubule/dynein motor system is required to transport the anterior fate protein to the egg s anterior end. C) A microfilament/kinesin motor system is required to transport the anterior fate protein to the egg s anterior end. D) A microfilament/dynein motor system is required to transport the anterior fate protein to the egg s anterior end. 28. The assembly of which of the following cytoskeletal fibers involves incorporation of its basic subunit throughout the length of the fiber rather than the specifically into one of the two ends: pg 51 (+26 and 40) A) microtubules B) microfilaments C) intermediate filaments D) actin polymers 29. Which of the following combinations of conditions will allow Myosin heads to bind actin filaments in the skeletal muscle sarcomere: pg and 45 A) binding of ATP to the myosin head and release of Ca 2+ from troponin. B) binding of ATP to the myosin head and binding of Ca 2+ to troponin C) hydrolysis of ATP by the myosin head and release of Ca 2+ from troponin. D) hydrolysis of ATP by the myosin head and binding of Ca 2+ to troponin. 30. Which of the following types of cytoskeletal fibers lacks polarity: pg 51 (+26 and 40) A) microtubules B) microfilaments C) actin polymers D) intermediate filaments - 4 -
5 Chapter 10 Questions 1. Which of the following scientists showed that chromosomes contain the genetic information: pg. 53 (+56, 60, and 68) A) James Watson B) Phil Sharp C) Mary Lou Pardue D) T. H. Morgan 2. Which of the following scientists is NOT a native Kentuckian: pg. 53 (+56, 60, and 68) A) James Watson B) Phil Sharp C) Mary Lou Pardue D) T. H. Morgan 3. Which of the following scientists was discussed in class as admitting to using data from a fellow scientist without permission: pg.56 (not in notes bonus to class attendees!) A) James Watson B) Phil Sharp C) Mary Lou Pardue D) T. H. Morgan Chapter 11 Questions 4. Which of the following RNA molecules has an inhibitory activity in translation of an mrna into protein: pg. 75 (+83 and 77) A) mirna B) rrna C) trna D) All of the above 5. Which of the following types of genes does NOT adhere to the Central Dogma of Molecular Biology pg. 84 A) mirna B) rrna C) trna D) All of the above - 5 -
6 6. Which of the following processes does NOT involve nucleotide base pairing: A) U2 snrna binding to intron sequence pg. 71 B) trna association with the mrna during translation pg C) Western blotting pg 86 D) Northern blotting pg Which of the following is responsible for forming the A bulge that carries out a cleavage at the 5 exon/intron junction during pre-mrna splicing: pg. 71 A) U2 B) U4 C) U6 D) snrnp Which of the following is NOT a correct statement about aminoactyl synthetases: pg. 78 A) Each aminoacyl synthetase is specific for a given amino acid. B) The aminoacyl sythetase activity for a given amino acid can recognize only one trna molecule that is specific for that amino acid. C) The aminoacyl sythetase activity for a given amino acid can recognize all of the trna molecules that are specific for that amino acid. D) Aminoacyl sythetases use the energy from two ATP equivalents to covalently link an amino acid to the corresponding trna. 9. Which of the following types of mutations is MOST LIKELY to be harmful: pg A) insertion of 3 nucleotides into an exon of a gene. B) insertion of 3 nucleotides into an intron of a gene. C) insertion of 1 nucleotide into an exon of a gene. D) insertion of 1 nucleotide into an intron of a gene. 10. Which of the above mutations is MOST LIKELY to produce a large enough change in the mutant protein to be visualized by Western blotting: pg A) insertion of 3 nucleotides into an exon of a gene. B) insertion of 3 nucleotides into an intron of a gene. C) insertion of 1 nucleotide into an exon of a gene. D) insertion of 1 nucleotide into an intron of a gene
7 11. In which of the following protein compositions would you expect to find in a protein-coding gene that is in the elongation phase of transcription: pg. 66 A) carboxyterminal domain (CTD)-phosphorylated RNA polymerase II associated with TFIIH. B) unphosphorylated RNA polymerase II associated with TFIIH. C) unphosphorylated RNA polymerase II associated with TATA binding protein. D) RNA polymerase III and TFIIH. 12. Which of the following snrnp functions as a negative regulator of splicing: pg. 71 A) U1 B) U2 C) U4 D) U6 13. Which of the following components of the eukaryotic transcriptional machinery is responsible for the initial melting of the double stranded promoter region during the initiation of transcription: pg. 66 (+65) A) TBP B) RNA polymerase II C) sigma factor D) TFIIH 14. How many bands would you observe on a Northern blot of mature mrna produced from a gene containing 4 exons and 3 introns (assuming no tissuespecific alternative splicing): pg. 67 A) one B) two C) three D) four - 7 -
8 Chapter 8 Questions 15. A budding yeast mutant for which of the following proteins of the endomembrane system would cause lysosomal proteins, integral membrane proteins, and secretory proteins to accumulate in the ER: pg. 92 and 102 A) COP I B) COP II C) Clathrin D) Dynamin 16. GTP analogues that can bind to G-proteins but cannot be hydrolysed to GDP by them would NOT affect which of the following processes involving the endomembrane system: A) localization of a Growth Factor Receptor on the plasma membrane lysosome pg 96 B) moving resident ER enzymes back to the ER from the cis Golgi layer pg 102 C) secretion of Growth Factor from a cell pg. 95 D) None of the above 17. Which of the following would you expect to make a human less susceptible to atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease: pg. 105 A) high blood levels of LDL relative to HDL (high LDL/HDL ratio) B) a loss of function mutation in the Apo B-100 receptor C) a loss of function mutation in the CETP enyzme D) More than one of the above 18. Which of the following types of enzymes are specifically found in the Golgi layers of the endomembrane system: pg. 97 A) enzymes that transfer carbohydrates to asparagine residues of proteins (97) B) enzymes that transfer carbohydrates to serine residues of proteins (99) C) GT-monitoring enzymes (97) D) hydrolytic enzymes (103) 19. Which of the following is required to process a plasma membrane protein but not secreted protein through the endomembrane system: pg. 96 A) the N-terminal signal peptide B) binding of the SRP to the SRP receptor C) the presence of a stop-transfer sequence in the nascent protein D) binding of GTP to the SRP receptor - 8 -
9 20. A budding yeast mutant for the COPI protein would be expected to accumulate which of the following proteins in the transgolgi layer: pg. 102 A) integral membrane proteins B) lysosomal acid hydrolases C) N-linking glycosyltransferases D) secretory proteins 21. Which of the following is involved in ensuring that a secretory protein is properly folded before it is allowed to move from the RER to the cis Golgi layer: pg. 97 A) mannose 6-PO 4 modifications B) SRP receptor C) GT-monitoring enzymes D) COP I 22. Which of the following proteins mediates the fusion of a vesicle membrane with a target membrane in exocytosis: pg. 106 A) SNARE proteins B) mannose-6-po 4 receptor C) Sar-1 D) Rab 23. Which of the following proteins is mutated in I cell disease autophagy disorder: pg. 103 A) Clathrin B) lysosomal acid hydrolase C) mannose 6-phosphorylating enzyme D) mannose 6-PO 4 receptor 24. Which of the following is a function of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum:pg.94 A) synthesis of secretory proteins B) sequestration of Ca 2+ C) synthesis of integral plasma membrane proteins D) all of the above - 9 -
10 Essay Questions 31. List three molecules discussed in class that would inhibit the inflammatory response: (3 pt) pg List two molecules or treatments that have been experimentally shown to extend the life span of organisms ranging from budding yeast to humans. (2 pt) From Exam I Material- pg.55 (won t be on this exam) 34. It is possible to make analog of GTP that can bind to GTP-binding proteins but are not able to be hydrolyzed. These were used to determine the role of GTP in microtubule assembly. In one or two sentences, predict what effect this nonhydrolyzable GTP would have in an in vitro microtubule assembly assay and explain why. (2 pt) pg. 26 What effect would you predict a non-hydrolyzable ATP analog to have on actin microfilament assembly? (2 pt) pg
11 35. Briefly describe how a fibroblast cell is able to adhere to its extracellular matrix substrate lining the bottom of a culture dish and the internal processes that allow it to move across the surface of the substrate as was observed in the video shown in class. Be sure to include names and activities of proteins involved. (6 pt total) pg and Describe the process of skeletal muscle contraction/relaxation. Begin with stimulation of an action potential on the plasma membrane of the skeletal muscle cell and include details of changes that occur in the structure of basic contractile unit of skeletal muscle (sarcomere). Be sure to include the roles of ATP and Ca 2+ in regulating this process. (10 pt) pg and
12 Questions 37 through 47 are worth 2 pts. each. The molecular map of the normal allele of a disease-associated gene is shown below. The locations of the: 1) TATA box, 2) translation Start site, 3) translation STOP site, 4) 3 exons, 5) 2 introns, and 6) EcoRI restriction endonuclease sites are indicated. In the diagrams representing Southern, Northern, and Western blots, draw lines to represent the DNA, RNA, or protein bands that would be observed in of samples from a person that is homozygous for the normal allele (#31, 32, and 33). Write the name of the molecule (DNA, mrna, protein) that is being analyzed on each type of blot in the blanks labeled 34, 35, and 36. (Assume no alternative splicing and that your probes for Southern and Northern blots covers the entire mapped region.) pg and Lab 4-6 Discussion Molecular Map of wild type gene allele from healthy family members Scale = 1 kb (1000 bp) Assume that 1 kb DNA encodes 10 kda protein Start STOP TATA Exon 1 Intron 1 Exon 2 Intron 2 Exon 3 box EcoRI EcoRI EcoRI EcoRI Southern Blot- Northern Blot- Western Blot- Molecule Molecule Molecule Mkrs Sample Mkrs Sample Mkrs Sample (kb) (kb) (kda)
13 Based on the molecular map for a mutant allele of the same gene found in family members of a pedigree analysis having a particular disease, similarly draw lines representing the DNA, RNA, or protein bands you would expect to be observed in samples from a person who is homozygous for that mutant allele (#31, 32, 33) next to a lane loaded with a sample from a healthy person who is homozygous for the wild type allele. pg and Lab 4-6 Discussion Molecular Map of mutant gene allele from diseased family members Scale = 1 kb (1000 bp) Assume that 1 kb DNA encodes 10 kda protein Start STOP TATA Exon 1 Intron 1 Exon 2 Intron 2 Exon 3 box EcoRI EcoRI EcoRI EcoRI Nucleotide substitution in EcoRI site (GAATTC) to GAAATC (creating an early STOP codon in mrna) Mkrs wt mutant Mkrs wt mutant Mkrs wt mutant (kb) (kb) (kda)
14 40.A) Give a definition for the term G protein. (2 pt) Pg.26-first one you learn about B) List one G protein that functions in translation (general category ok).(2 pt) pg C) List one G protein that functions in exocytosis (specific protein).(2 pt) pg. 102 D) List one G protein that functions in endocytosis (specific protein). (2 pt) pg Briefly describe the process of cholesterol endocytosis by cells (4 pts) (pg. 319 Text, pg Notes)
MOLECULAR GENETICS PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1
 AP BIOLOGY MOLECULAR GENETICS ACTIVITY #2 NAME DATE HOUR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1 GENETIC CODE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS OVERVIEW Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 2 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
AP BIOLOGY MOLECULAR GENETICS ACTIVITY #2 NAME DATE HOUR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1 GENETIC CODE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS OVERVIEW Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 2 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
Chapter 14: Gene Expression: From Gene to Protein
 Chapter 14: Gene Expression: From Gene to Protein This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect
Chapter 14: Gene Expression: From Gene to Protein This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect
Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein
 Name Period This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect to spend at least 6 hours to truly master
Name Period This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect to spend at least 6 hours to truly master
Chapter 14 Active Reading Guide From Gene to Protein
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 14 Active Reading Guide From Gene to Protein This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 14 Active Reading Guide From Gene to Protein This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single
From Gene to Protein transcription, messenger RNA (mrna) translation, RNA processing triplet code, template strand, codons,
 From Gene to Protein I. Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein. A. RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes
From Gene to Protein I. Transcription and translation are the two main processes linking gene to protein. A. RNA is chemically similar to DNA, except that it contains ribose as its sugar and substitutes
BIO 311C Spring Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr.
 BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr. Synthesis of a Polypeptide Chain 5 direction of ribosome movement along the mrna 3 ribosome mrna NH 2 polypeptide chain direction of mrna movement through
BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr. Synthesis of a Polypeptide Chain 5 direction of ribosome movement along the mrna 3 ribosome mrna NH 2 polypeptide chain direction of mrna movement through
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 01: Introduction to Molecular Cell Biology
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 01: Introduction to Molecular Cell Biology Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement describes how an organism is organized from most simple to most complex? Question
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 01: Introduction to Molecular Cell Biology Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement describes how an organism is organized from most simple to most complex? Question
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN. Section C: The Synthesis of Protein
 CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN Section C: The Synthesis of Protein 1. Translation is the RNA-directed synthesis of a polypeptide: a closer look 2. Signal peptides target some eukaryotic polypeptides to
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN Section C: The Synthesis of Protein 1. Translation is the RNA-directed synthesis of a polypeptide: a closer look 2. Signal peptides target some eukaryotic polypeptides to
Gene Expression: Transcription
 Gene Expression: Transcription The majority of genes are expressed as the proteins they encode. The process occurs in two steps: Transcription = DNA RNA Translation = RNA protein Taken together, they make
Gene Expression: Transcription The majority of genes are expressed as the proteins they encode. The process occurs in two steps: Transcription = DNA RNA Translation = RNA protein Taken together, they make
Fig Ch 17: From Gene to Protein
 Fig. 17-1 Ch 17: From Gene to Protein Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation RNA is the intermediate between genes and the proteins for which they code Transcription is the synthesis of RNA
Fig. 17-1 Ch 17: From Gene to Protein Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation RNA is the intermediate between genes and the proteins for which they code Transcription is the synthesis of RNA
Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of..
 Gene expression Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of.. In a protein, the sequence of amino acid determines its which determines the protein s A protein with an enzymatic
Gene expression Review of Protein (one or more polypeptide) A polypeptide is a long chain of.. In a protein, the sequence of amino acid determines its which determines the protein s A protein with an enzymatic
Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4)
 Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4) Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture Notes: Transcriptome: Molecular Biology of Gene Expression I Flow of information: DNA to polypeptide DNA Start Exon1 Intron Exon2 Termination
Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4) Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture Notes: Transcriptome: Molecular Biology of Gene Expression I Flow of information: DNA to polypeptide DNA Start Exon1 Intron Exon2 Termination
DNA makes RNA makes Proteins. The Central Dogma
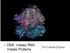 DNA makes RNA makes Proteins The Central Dogma TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-mrna) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION
DNA makes RNA makes Proteins The Central Dogma TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-mrna) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION
Protein Synthesis & Gene Expression
 DNA provides the instructions for how to build proteins Each gene dictates how to build a single protein in prokaryotes The sequence of nucleotides (AGCT) in DNA dictates the order of amino acids that
DNA provides the instructions for how to build proteins Each gene dictates how to build a single protein in prokaryotes The sequence of nucleotides (AGCT) in DNA dictates the order of amino acids that
8/21/2014. From Gene to Protein
 From Gene to Protein Chapter 17 Objectives Describe the contributions made by Garrod, Beadle, and Tatum to our understanding of the relationship between genes and enzymes Briefly explain how information
From Gene to Protein Chapter 17 Objectives Describe the contributions made by Garrod, Beadle, and Tatum to our understanding of the relationship between genes and enzymes Briefly explain how information
Chapter 8 Lecture Outline. Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics
 Chapter 8 Lecture Outline Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics Replication, Transcription, Translation n Repetitive processes Build polymers of nucleotides or amino acids n All have 3 major steps
Chapter 8 Lecture Outline Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics Replication, Transcription, Translation n Repetitive processes Build polymers of nucleotides or amino acids n All have 3 major steps
Section 10.3 Outline 10.3 How Is the Base Sequence of a Messenger RNA Molecule Translated into Protein?
 Section 10.3 Outline 10.3 How Is the Base Sequence of a Messenger RNA Molecule Translated into Protein? Messenger RNA Carries Information for Protein Synthesis from the DNA to Ribosomes Ribosomes Consist
Section 10.3 Outline 10.3 How Is the Base Sequence of a Messenger RNA Molecule Translated into Protein? Messenger RNA Carries Information for Protein Synthesis from the DNA to Ribosomes Ribosomes Consist
Protein Synthesis Notes
 Protein Synthesis Notes Protein Synthesis: Overview Transcription: synthesis of mrna under the direction of DNA. Translation: actual synthesis of a polypeptide under the direction of mrna. Transcription
Protein Synthesis Notes Protein Synthesis: Overview Transcription: synthesis of mrna under the direction of DNA. Translation: actual synthesis of a polypeptide under the direction of mrna. Transcription
MICB688L/MOCB639 Advanced Cell Biology Exam II
 MICB688L/MOCB639 Advanced Cell Biology Exam II May 10, 2001 Name: 1. Briefly describe the four major classes of cell surface receptors and their modes of action (immediate downstream only) (8) 2. Please
MICB688L/MOCB639 Advanced Cell Biology Exam II May 10, 2001 Name: 1. Briefly describe the four major classes of cell surface receptors and their modes of action (immediate downstream only) (8) 2. Please
1. The microtubule wall is composed of globular proteins arranged in longitudinal rows called.
 Name: Quiz name: Quiz 7 ate: 1. The microtubule wall is composed of globular proteins arranged in longitudinal rows called. microfilaments protofilaments prototubules microtubular subunits 2. Which of
Name: Quiz name: Quiz 7 ate: 1. The microtubule wall is composed of globular proteins arranged in longitudinal rows called. microfilaments protofilaments prototubules microtubular subunits 2. Which of
Transcription in Eukaryotes
 Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra
 Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra 1 Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Only one strand of DNA serves
Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra 1 Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Only one strand of DNA serves
Hello! Outline. Cell Biology: RNA and Protein synthesis. In all living cells, DNA molecules are the storehouses of information. 6.
 Cell Biology: RNA and Protein synthesis In all living cells, DNA molecules are the storehouses of information Hello! Outline u 1. Key concepts u 2. Central Dogma u 3. RNA Types u 4. RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
Cell Biology: RNA and Protein synthesis In all living cells, DNA molecules are the storehouses of information Hello! Outline u 1. Key concepts u 2. Central Dogma u 3. RNA Types u 4. RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
BIOLOGY. Chapter 15 Genes & Proteins
 BIOLOGY Chapter 15 Genes & Proteins CMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 17 Protein Synthesis 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Fig. 17-1 Figure 17.1a n albino racoon Condition
BIOLOGY Chapter 15 Genes & Proteins CMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 17 Protein Synthesis 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Fig. 17-1 Figure 17.1a n albino racoon Condition
The Genetic Code and Transcription. Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot
 The Genetic Code and Transcription Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot TRANSCRIPTION Copy SAME language DNA to RNA Nucleic Acid to Nucleic Acid TRANSLATION Copy DIFFERENT language RNA to Amino
The Genetic Code and Transcription Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot TRANSCRIPTION Copy SAME language DNA to RNA Nucleic Acid to Nucleic Acid TRANSLATION Copy DIFFERENT language RNA to Amino
From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype
 12 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype 12.1 What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? The gene-enzyme relationship is one-gene, one-polypeptide relationship. Example: In hemoglobin, each
12 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype 12.1 What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? The gene-enzyme relationship is one-gene, one-polypeptide relationship. Example: In hemoglobin, each
Microtubules. Forms a sheet of protofilaments that folds to a tube Both tubulins bind GTP
 Microtubules Polymerize from a-tubulin/ß-tubulin dimers Hollow tube of 13 protofilaments In vitro- filament number varies In vivo- always 13 protofilaments Forms a sheet of protofilaments that folds to
Microtubules Polymerize from a-tubulin/ß-tubulin dimers Hollow tube of 13 protofilaments In vitro- filament number varies In vivo- always 13 protofilaments Forms a sheet of protofilaments that folds to
RNA : functional role
 RNA : functional role Hamad Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw RNA mrna rrna trna 1 From DNA to Protein -Outline- From DNA to RNA From RNA to Protein From DNA to RNA Transcription: Copying
RNA : functional role Hamad Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw RNA mrna rrna trna 1 From DNA to Protein -Outline- From DNA to RNA From RNA to Protein From DNA to RNA Transcription: Copying
Chapter 13. From DNA to Protein
 Chapter 13 From DNA to Protein Proteins All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequenceof a gene The Path From Genes to
Chapter 13 From DNA to Protein Proteins All proteins consist of polypeptide chains A linear sequence of amino acids Each chain corresponds to the nucleotide base sequenceof a gene The Path From Genes to
BEADLE & TATUM EXPERIMENT
 FROM DNA TO PROTEINS: gene expression Chapter 14 LECTURE OBJECTIVES What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? How Does Information Flow from Genes to Proteins? How Is the Information Content in
FROM DNA TO PROTEINS: gene expression Chapter 14 LECTURE OBJECTIVES What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? How Does Information Flow from Genes to Proteins? How Is the Information Content in
GENE EXPRESSION AT THE MOLECULAR LEVEL. Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 GENE EXPRESSION AT THE MOLECULAR LEVEL Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Gene expression Gene function at the level of traits Gene function
GENE EXPRESSION AT THE MOLECULAR LEVEL Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Gene expression Gene function at the level of traits Gene function
Lecture for Wednesday. Dr. Prince BIOL 1408
 Lecture for Wednesday Dr. Prince BIOL 1408 THE FLOW OF GENETIC INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genes are expressed as proteins A gene is a segment of DNA that
Lecture for Wednesday Dr. Prince BIOL 1408 THE FLOW OF GENETIC INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genes are expressed as proteins A gene is a segment of DNA that
Exam 2 BIO200, Winter 2012
 Exam 2 BIO200, Winter 2012 Name: Multiple Choice Questions: Circle the one best answer for each question. (2 points each) 1. The 5 cap structure is often described as a backwards G. What makes this nucleotide
Exam 2 BIO200, Winter 2012 Name: Multiple Choice Questions: Circle the one best answer for each question. (2 points each) 1. The 5 cap structure is often described as a backwards G. What makes this nucleotide
Pauling/Itano Experiment
 Chapter 12 Pauling/Itano Experiment Linus Pauling and Harvey Itano knew that hemoglobin, a molecule in red blood cells, contained an electrical charge. They wanted to see if the hemoglobin in normal RBC
Chapter 12 Pauling/Itano Experiment Linus Pauling and Harvey Itano knew that hemoglobin, a molecule in red blood cells, contained an electrical charge. They wanted to see if the hemoglobin in normal RBC
Chromosomes. Chromosomes. Genes. Strands of DNA that contain all of the genes an organism needs to survive and reproduce
 Chromosomes Chromosomes Strands of DNA that contain all of the genes an organism needs to survive and reproduce Genes Segments of DNA that specify how to build a protein genes may specify more than one
Chromosomes Chromosomes Strands of DNA that contain all of the genes an organism needs to survive and reproduce Genes Segments of DNA that specify how to build a protein genes may specify more than one
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells
 Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
Transcription Eukaryotic Cells Packet #20 1 Introduction Transcription is the process in which genetic information, stored in a strand of DNA (gene), is copied into a strand of RNA. Protein-encoding genes
Genetics Biology 331 Exam 3B Spring 2015
 Genetics Biology 331 Exam 3B Spring 2015 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) DNA methylation may be a significant mode of genetic regulation
Genetics Biology 331 Exam 3B Spring 2015 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) DNA methylation may be a significant mode of genetic regulation
2. From the first paragraph in this section, find three ways in which RNA differs from DNA.
 Name Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein Begin reading at page 328 Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect to spend at least 6 hours
Name Chapter 17: From Gene to Protein Begin reading at page 328 Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect to spend at least 6 hours
DNA Function: Information Transmission
 DNA Function: Information Transmission DNA is called the code of life. What does it code for? *the information ( code ) to make proteins! Why are proteins so important? Nearly every function of a living
DNA Function: Information Transmission DNA is called the code of life. What does it code for? *the information ( code ) to make proteins! Why are proteins so important? Nearly every function of a living
Bio11 Announcements. Ch 21: DNA Biology and Technology. DNA Functions. DNA and RNA Structure. How do DNA and RNA differ? What are genes?
 Bio11 Announcements TODAY Genetics (review) and quiz (CP #4) Structure and function of DNA Extra credit due today Next week in lab: Case study presentations Following week: Lab Quiz 2 Ch 21: DNA Biology
Bio11 Announcements TODAY Genetics (review) and quiz (CP #4) Structure and function of DNA Extra credit due today Next week in lab: Case study presentations Following week: Lab Quiz 2 Ch 21: DNA Biology
Section A: The Connection Between Genes and Proteins
 CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN Section A: The Connection Between Genes and Proteins 1. The study of metabolic defects provided evidence that genes specify proteins 2. Transcription and translation are
CHAPTER 17 FROM GENE TO PROTEIN Section A: The Connection Between Genes and Proteins 1. The study of metabolic defects provided evidence that genes specify proteins 2. Transcription and translation are
Protein Synthesis. Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy
 Protein Synthesis Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy STRUCTURE OF RNA RNA, adenine forms a base pair with
Protein Synthesis Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy STRUCTURE OF RNA RNA, adenine forms a base pair with
Chapter 8: DNA and RNA
 Chapter 8: DNA and RNA Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 8-1 DNA and the Importance of Proteins Proteins play
Chapter 8: DNA and RNA Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 8-1 DNA and the Importance of Proteins Proteins play
From Gene to Protein. Chapter 17. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Name Class Date. Practice Test
 Name Class Date 12 DNA Practice Test Multiple Choice Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. 1. What do bacteriophages infect? a. mice. c. viruses.
Name Class Date 12 DNA Practice Test Multiple Choice Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. 1. What do bacteriophages infect? a. mice. c. viruses.
7.06 Cell Biology QUIZ #3
 Recitation Section: 7.06 Cell Biology QUIZ #3 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books and notes, but not computers or any other types of electronic devices. Please write your answers
Recitation Section: 7.06 Cell Biology QUIZ #3 This is an open book exam, and you are allowed access to books and notes, but not computers or any other types of electronic devices. Please write your answers
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein
 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein This is also known as: The central dogma of molecular biology Protein Proteins are made
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Flow of Genetic Information The flow of genetic information can be symbolized as: DNA RNA Protein This is also known as: The central dogma of molecular biology Protein Proteins are made
Protein Synthesis
 HEBISD Student Expectations: Identify that RNA Is a nucleic acid with a single strand of nucleotides Contains the 5-carbon sugar ribose Contains the nitrogen bases A, G, C and U instead of T. The U is
HEBISD Student Expectations: Identify that RNA Is a nucleic acid with a single strand of nucleotides Contains the 5-carbon sugar ribose Contains the nitrogen bases A, G, C and U instead of T. The U is
SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat
 SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat TRANSCRIPTION: AN OVERVIEW Transcription: the synthesis of a single-stranded RNA from a doublestranded DNA template.
SIBC504: TRANSCRIPTION & RNA PROCESSING Assistant Professor Dr. Chatchawan Srisawat TRANSCRIPTION: AN OVERVIEW Transcription: the synthesis of a single-stranded RNA from a doublestranded DNA template.
Transcription & post transcriptional modification
 Transcription & post transcriptional modification Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be transferred from DNA to RNA Similarity
Transcription & post transcriptional modification Transcription The synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA strands as the templates so that the genetic information can be transferred from DNA to RNA Similarity
Answers to Module 1. An obligate aerobe is an organism that has an absolute requirement of oxygen for growth.
 Answers to Module 1 Short Answers 1) What is an obligate aerobe? An obligate aerobe is an organism that has an absolute requirement of oxygen for growth. What about facultative anaerobe? 2) Distinguish
Answers to Module 1 Short Answers 1) What is an obligate aerobe? An obligate aerobe is an organism that has an absolute requirement of oxygen for growth. What about facultative anaerobe? 2) Distinguish
Eukaryotic Transcription
 Eukaryotic Transcription I. Differences between eukaryotic versus prokaryotic transcription. II. (core vs holoenzyme): RNA polymerase II - Promotor elements. - General Pol II transcription factors (GTF).
Eukaryotic Transcription I. Differences between eukaryotic versus prokaryotic transcription. II. (core vs holoenzyme): RNA polymerase II - Promotor elements. - General Pol II transcription factors (GTF).
7.2 Protein Synthesis. From DNA to Protein Animation
 7.2 Protein Synthesis From DNA to Protein Animation Proteins Why are proteins so important? They break down your food They build up muscles They send signals through your brain that control your body They
7.2 Protein Synthesis From DNA to Protein Animation Proteins Why are proteins so important? They break down your food They build up muscles They send signals through your brain that control your body They
Higher Human Biology Unit 1: Human Cells Pupils Learning Outcomes
 Higher Human Biology Unit 1: Human Cells Pupils Learning Outcomes 1.1 Division and Differentiation in Human Cells I can state that cellular differentiation is the process by which a cell develops more
Higher Human Biology Unit 1: Human Cells Pupils Learning Outcomes 1.1 Division and Differentiation in Human Cells I can state that cellular differentiation is the process by which a cell develops more
Chem 465 Biochemistry II
 Chem 465 Biochemistry II Name: 2 points Multiple choice (4 points apiece): 1. Which of the following is not true of trna molecules? A) The 3'-terminal sequence is -CCA. B) Their anticodons are complementary
Chem 465 Biochemistry II Name: 2 points Multiple choice (4 points apiece): 1. Which of the following is not true of trna molecules? A) The 3'-terminal sequence is -CCA. B) Their anticodons are complementary
Transcription. DNA to RNA
 Transcription from DNA to RNA The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology replication DNA RNA Protein transcription translation Why call it transcription and translation? transcription is such a direct copy
Transcription from DNA to RNA The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology replication DNA RNA Protein transcription translation Why call it transcription and translation? transcription is such a direct copy
Chapter 12. DNA TRANSCRIPTION and TRANSLATION
 Chapter 12 DNA TRANSCRIPTION and TRANSLATION 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis WARM UP What are proteins? Where do they come from? From DNA to RNA to Protein DNA in our cells carry the instructions for making
Chapter 12 DNA TRANSCRIPTION and TRANSLATION 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis WARM UP What are proteins? Where do they come from? From DNA to RNA to Protein DNA in our cells carry the instructions for making
2012 GENERAL [5 points]
![2012 GENERAL [5 points] 2012 GENERAL [5 points]](/thumbs/75/72452386.jpg) GENERAL [5 points] 2012 Mark all processes that are part of the 'standard dogma of molecular' [ ] DNA replication [ ] transcription [ ] translation [ ] reverse transposition [ ] DNA restriction [ ] DNA
GENERAL [5 points] 2012 Mark all processes that are part of the 'standard dogma of molecular' [ ] DNA replication [ ] transcription [ ] translation [ ] reverse transposition [ ] DNA restriction [ ] DNA
Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene
 Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene For Next Week Lab -Hand in questions from 4 and 5 by TUES in my mailbox (Biology Office) -Do questions for Lab 6 for next week -Lab practical next week Lecture Read
Ch 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene For Next Week Lab -Hand in questions from 4 and 5 by TUES in my mailbox (Biology Office) -Do questions for Lab 6 for next week -Lab practical next week Lecture Read
Three major types of cytoskeleton
 The Cytoskeleton Organizes and stabilizes cells Pulls chromosomes apart Drives intracellular traffic Supports plasma membrane and nuclear envelope Enables cellular movement Guides growth of the plant cell
The Cytoskeleton Organizes and stabilizes cells Pulls chromosomes apart Drives intracellular traffic Supports plasma membrane and nuclear envelope Enables cellular movement Guides growth of the plant cell
Protein Synthesis. DNA to RNA to Protein
 Protein Synthesis DNA to RNA to Protein From Genes to Proteins Processing the information contained in DNA into proteins involves a sequence of events known as gene expression and results in protein synthesis.
Protein Synthesis DNA to RNA to Protein From Genes to Proteins Processing the information contained in DNA into proteins involves a sequence of events known as gene expression and results in protein synthesis.
DNA Transcription. Dr Aliwaini
 DNA Transcription 1 DNA Transcription-Introduction The synthesis of an RNA molecule from DNA is called Transcription. All eukaryotic cells have five major classes of RNA: ribosomal RNA (rrna), messenger
DNA Transcription 1 DNA Transcription-Introduction The synthesis of an RNA molecule from DNA is called Transcription. All eukaryotic cells have five major classes of RNA: ribosomal RNA (rrna), messenger
Answers to the multiple choice questions are at the bottom of the last page of this document.
 Review for Unit Test #2: Cell Parts, Functions and Protein Synthesis, Answers Answers to the multiple choice questions are at the bottom of the last page of this document. 1. Know all of the material on
Review for Unit Test #2: Cell Parts, Functions and Protein Synthesis, Answers Answers to the multiple choice questions are at the bottom of the last page of this document. 1. Know all of the material on
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch 17 Practice Questions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Garrod hypothesized that "inborn errors of metabolism" such as alkaptonuria
Ch 17 Practice Questions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Garrod hypothesized that "inborn errors of metabolism" such as alkaptonuria
MIT Department of Biology 7.013: Introductory Biology - Spring 2005 Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor Tyler Jacks, Dr.
 MIT Department of Biology 7.01: Introductory Biology - Spring 2005 Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor Tyler Jacks, Dr. Claudette Gardel iv) Would Xba I be useful for cloning? Why or why not?
MIT Department of Biology 7.01: Introductory Biology - Spring 2005 Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor Tyler Jacks, Dr. Claudette Gardel iv) Would Xba I be useful for cloning? Why or why not?
Self-test Quiz for Chapter 12 (From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype)
 Self-test Quiz for Chapter 12 (From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype) Question#1: One-Gene, One-Polypeptide The figure below shows the results of feeding trials with one auxotroph strain of Neurospora
Self-test Quiz for Chapter 12 (From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype) Question#1: One-Gene, One-Polypeptide The figure below shows the results of feeding trials with one auxotroph strain of Neurospora
Themes: RNA and RNA Processing. Messenger RNA (mrna) What is a gene? RNA is very versatile! RNA-RNA interactions are very important!
 Themes: RNA is very versatile! RNA and RNA Processing Chapter 14 RNA-RNA interactions are very important! Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have many important differences. Messenger RNA (mrna) Carries genetic
Themes: RNA is very versatile! RNA and RNA Processing Chapter 14 RNA-RNA interactions are very important! Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have many important differences. Messenger RNA (mrna) Carries genetic
Differential Gene Expression
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 19, 2008 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 19, 2008 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
Today s lecture: Types of mutations and their impact on protein function
 Today s lecture: Types of mutations and their impact on protein function Mutations can be classified by their effect on the DNA sequence OR the encoded protein 1 From my Lecture 4 (10/1): Classification
Today s lecture: Types of mutations and their impact on protein function Mutations can be classified by their effect on the DNA sequence OR the encoded protein 1 From my Lecture 4 (10/1): Classification
Make the protein through the genetic dogma process.
 Make the protein through the genetic dogma process. Coding Strand 5 AGCAATCATGGATTGGGTACATTTGTAACTGT 3 Template Strand mrna Protein Complete the table. DNA strand DNA s strand G mrna A C U G T A T Amino
Make the protein through the genetic dogma process. Coding Strand 5 AGCAATCATGGATTGGGTACATTTGTAACTGT 3 Template Strand mrna Protein Complete the table. DNA strand DNA s strand G mrna A C U G T A T Amino
Bundle 5 Test Review
 Bundle 5 Test Review DNA vs. RNA DNA Replication Gene Mutations- Protein Synthesis 1. Label the different components and complete the complimentary base pairing. What is this molecule called? _Nucleic
Bundle 5 Test Review DNA vs. RNA DNA Replication Gene Mutations- Protein Synthesis 1. Label the different components and complete the complimentary base pairing. What is this molecule called? _Nucleic
Rapid Learning Center Presents. Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours
 Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presents Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours 1/35 *AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which does not
Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presents Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours 1/35 *AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which does not
Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression. 1. Gene Regulation in Bacteria 2. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes 3. Gene Regulation & Cancer
 Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression 1. Gene Regulation in Bacteria 2. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes 3. Gene Regulation & Cancer Gene Regulation Gene regulation refers to all aspects of controlling
Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression 1. Gene Regulation in Bacteria 2. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes 3. Gene Regulation & Cancer Gene Regulation Gene regulation refers to all aspects of controlling
DNA RNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS -NOTES-
 DNA RNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS -NOTES- THE COMPONENTS AND STRUCTURE OF DNA DNA is made up of units called nucleotides. Nucleotides are made up of three basic components:, called deoxyribose in DNA In DNA, there
DNA RNA PROTEIN SYNTHESIS -NOTES- THE COMPONENTS AND STRUCTURE OF DNA DNA is made up of units called nucleotides. Nucleotides are made up of three basic components:, called deoxyribose in DNA In DNA, there
Protein Synthesis. OpenStax College
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46032 1 Protein Synthesis OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
OpenStax-CNX module: m46032 1 Protein Synthesis OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
AP BIOLOGY RNA, DNA, & Proteins Chapters 16 & 17 Review
 AP BIOLOGY RNA, DNA, & Proteins Chapters 16 & 17 Review Enzyme that adds nucleotide subunits to an RNA primer during replication DNA polymerase III Another name for protein synthesis translation Sugar
AP BIOLOGY RNA, DNA, & Proteins Chapters 16 & 17 Review Enzyme that adds nucleotide subunits to an RNA primer during replication DNA polymerase III Another name for protein synthesis translation Sugar
Chapter 12 Packet DNA 1. What did Griffith conclude from his experiment? 2. Describe the process of transformation.
 Chapter 12 Packet DNA and RNA Name Period California State Standards covered by this chapter: Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions
Chapter 12 Packet DNA and RNA Name Period California State Standards covered by this chapter: Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions
Bio 101 Sample questions: Chapter 10
 Bio 101 Sample questions: Chapter 10 1. Which of the following is NOT needed for DNA replication? A. nucleotides B. ribosomes C. Enzymes (like polymerases) D. DNA E. all of the above are needed 2 The information
Bio 101 Sample questions: Chapter 10 1. Which of the following is NOT needed for DNA replication? A. nucleotides B. ribosomes C. Enzymes (like polymerases) D. DNA E. all of the above are needed 2 The information
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. copyright cmassengale
 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 1 DNA and Genes 2 Roles of RNA and DNA DNA is the MASTER PLAN RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan 3 RNA Differs from DNA RNA has a sugar ribose DNA has a sugar deoxyribose 4 Other
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS 1 DNA and Genes 2 Roles of RNA and DNA DNA is the MASTER PLAN RNA is the BLUEPRINT of the Master Plan 3 RNA Differs from DNA RNA has a sugar ribose DNA has a sugar deoxyribose 4 Other
Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 2 2/20/15
 Name: TRASK Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 2 2/20/15 Answer each of the following short and longer answer questions in the space provided; circle the BEST answer or answers for each multiple choice question
Name: TRASK Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 2 2/20/15 Answer each of the following short and longer answer questions in the space provided; circle the BEST answer or answers for each multiple choice question
Name 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene Test Date Study Guide You must know: The structure of DNA. The major steps to replication.
 Name 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene Test Date Study Guide You must know: The structure of DNA. The major steps to replication. The difference between replication, transcription, and translation. How
Name 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene Test Date Study Guide You must know: The structure of DNA. The major steps to replication. The difference between replication, transcription, and translation. How
Study Guide for Chapter 12 Exam DNA, RNA, & Protein Synthesis
 Name: Date: Period: Study Guide for Chapter 12 Exam DNA, RNA, & Protein Synthesis ***Completing this study guide in its entirety will result in extra credit on the exam. You must show me the DAY OF the
Name: Date: Period: Study Guide for Chapter 12 Exam DNA, RNA, & Protein Synthesis ***Completing this study guide in its entirety will result in extra credit on the exam. You must show me the DAY OF the
Prokaryotic Transcription
 Prokaryotic Transcription Transcription Basics DNA is the genetic material Nucleic acid Capable of self-replication and synthesis of RNA RNA is the middle man Nucleic acid Structure and base sequence are
Prokaryotic Transcription Transcription Basics DNA is the genetic material Nucleic acid Capable of self-replication and synthesis of RNA RNA is the middle man Nucleic acid Structure and base sequence are
RNA synthesis/transcription I Biochemistry 302. February 6, 2004 Bob Kelm
 RNA synthesis/transcription I Biochemistry 302 February 6, 2004 Bob Kelm Overview of RNA classes Messenger RNA (mrna) Encodes protein Relatively short half-life ( 3 min in E. coli, 30 min in eukaryotic
RNA synthesis/transcription I Biochemistry 302 February 6, 2004 Bob Kelm Overview of RNA classes Messenger RNA (mrna) Encodes protein Relatively short half-life ( 3 min in E. coli, 30 min in eukaryotic
Chapter 17. Molecular Motors. to accompany Biochemistry, 2/e by Reginald Garrett and Charles Grisham. Biochemistry 2/e - Garrett & Grisham
 Chapter 17 Molecular Motors to accompany Biochemistry, 2/e by Reginald Garrett and Charles Grisham All rights reserved. Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to:
Chapter 17 Molecular Motors to accompany Biochemistry, 2/e by Reginald Garrett and Charles Grisham All rights reserved. Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to:
Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers)
 1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy
 Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 7 Cellular differentiation and the regulation of gene expression. In this lecture we looked at two main questions: How is gene expression regulated? (revision
Developmental Biology BY1101 P. Murphy Lecture 7 Cellular differentiation and the regulation of gene expression. In this lecture we looked at two main questions: How is gene expression regulated? (revision
Matakuliah Genetika (BIO612206) Jurusan Biologi FMIPA Universitas Lampung. Priyambodo, M.Sc. staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo
 Matakuliah Genetika (BIO612206) Jurusan Biologi FMIPA Universitas Lampung Priyambodo, M.Sc. staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo Prokariotik Eukariotik staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo Regulasi ekspresi gen pada
Matakuliah Genetika (BIO612206) Jurusan Biologi FMIPA Universitas Lampung Priyambodo, M.Sc. staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo Prokariotik Eukariotik staff.unila.ac.id/priyambodo Regulasi ekspresi gen pada
What is RNA? Another type of nucleic acid A working copy of DNA Does not matter if it is damaged or destroyed
 RNA Section 3.1 What is RNA? Another type of nucleic acid A working copy of DNA Does not matter if it is damaged or destroyed Used to direct the production of proteins that determines an organisms characteristics
RNA Section 3.1 What is RNA? Another type of nucleic acid A working copy of DNA Does not matter if it is damaged or destroyed Used to direct the production of proteins that determines an organisms characteristics
Chapter 15. Cytoskeletal Systems. Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 15 Cytoskeletal Systems Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Table 15-1 - Microtubules Table 15-1 - Microfilaments Table 15-1 Intermediate Filaments Table 15-3 Microtubules
Chapter 15 Cytoskeletal Systems Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Table 15-1 - Microtubules Table 15-1 - Microfilaments Table 15-1 Intermediate Filaments Table 15-3 Microtubules
7.013 Practice Quiz
 MIT Department of Biology 7.013: Introductory Biology - Spring 2005 Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor Tyler Jacks, Dr. Claudette Gardel 7.013 Practice Quiz 2 2004 1 Question 1 A. The primer
MIT Department of Biology 7.013: Introductory Biology - Spring 2005 Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor Tyler Jacks, Dr. Claudette Gardel 7.013 Practice Quiz 2 2004 1 Question 1 A. The primer
Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in Section B and ONE question from Section C.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2013-2014 CELL BIOLOGY BIO-2B06 Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2013-2014 CELL BIOLOGY BIO-2B06 Time allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A, ALL PARTS of the question in
DNA Transcription. Visualizing Transcription. The Transcription Process
 DNA Transcription By: Suzanne Clancy, Ph.D. 2008 Nature Education Citation: Clancy, S. (2008) DNA transcription. Nature Education 1(1) If DNA is a book, then how is it read? Learn more about the DNA transcription
DNA Transcription By: Suzanne Clancy, Ph.D. 2008 Nature Education Citation: Clancy, S. (2008) DNA transcription. Nature Education 1(1) If DNA is a book, then how is it read? Learn more about the DNA transcription
Lab Module 7: Cell Adhesion
 Lab Module 7: Cell Adhesion Tissues are made of cells and materials secreted by cells that occupy the spaces between the individual cells. This material outside of cells is called the Extracellular Matrix
Lab Module 7: Cell Adhesion Tissues are made of cells and materials secreted by cells that occupy the spaces between the individual cells. This material outside of cells is called the Extracellular Matrix
DNA Model Stations. For the following activity, you will use the following DNA sequence.
 Name: DNA Model Stations DNA Replication In this lesson, you will learn how a copy of DNA is replicated for each cell. You will model a 2D representation of DNA replication using the foam nucleotide pieces.
Name: DNA Model Stations DNA Replication In this lesson, you will learn how a copy of DNA is replicated for each cell. You will model a 2D representation of DNA replication using the foam nucleotide pieces.
Differential Gene Expression
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression September 28, 2006 Chromatin Structure ~140 bp ~60 bp Transcriptional Regulation: 1. Packing prevents access CH 3 2. Acetylation ( C O )
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression September 28, 2006 Chromatin Structure ~140 bp ~60 bp Transcriptional Regulation: 1. Packing prevents access CH 3 2. Acetylation ( C O )
BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST DNA to PROTEIN & BIOTECHNOLOGY
 Biology Multiple Choice 016074 BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST DNA to PROTEIN & BIOTECHNOLOGY Test Code: 016074 Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested
Biology Multiple Choice 016074 BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST DNA to PROTEIN & BIOTECHNOLOGY Test Code: 016074 Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested
What happens after DNA Replication??? Transcription, translation, gene expression/protein synthesis!!!!
 What happens after DNA Replication??? Transcription, translation, gene expression/protein synthesis!!!! Protein Synthesis/Gene Expression Why do we need to make proteins? To build parts for our body as
What happens after DNA Replication??? Transcription, translation, gene expression/protein synthesis!!!! Protein Synthesis/Gene Expression Why do we need to make proteins? To build parts for our body as
Independent Study Guide The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to Protein (Chapter 7)
 Independent Study Guide The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to Protein (Chapter 7) I. General Principles (Chapter 7 introduction) a. Morse code distinct series of dots and dashes encode the 26 letters of the
Independent Study Guide The Blueprint of Life, from DNA to Protein (Chapter 7) I. General Principles (Chapter 7 introduction) a. Morse code distinct series of dots and dashes encode the 26 letters of the
