Gordon Bonan and William Wieder National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado, USA
|
|
|
- Oscar Stephens
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Evaluating litter decomposition and soil organic matter dynamics in earth system models: contrasting analysis of long-term litter decomposition and steady-state soil carbon Gordon Bonan and William Wieder National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado, USA with contributions from: Melannie Hartman & William Parton (Colorado State University) Oleksandra Hararuk & Yiqi Luo (University of Oklahoma) 2012 AGU Fall Meeting San Francisco, California 3 December 2012 NCAR is sponsored by the National Science Foundation
2 CESM/CLM4cn 20th century carbon cycle 2 Net atmosphere flux Net land-atmosphere flux Fossil fuel Ocean Land GCP estimate GCP estimate The atmosphere accumulates too much carbon, because the land is mostly a source of carbon. Lindsay et al. (2012) J Climate, submitted
3 Soil carbon biases 3 Harmonized World Soil Database Model CLM4cn has far too little soil carbon Possible causes of soil carbon bias Litterfall and litter chemistry Turnover rates Model structure (pools) Abiotic controls (temperature, moisture, ph, texture, nitrogen)
4 Long-Term Intersite Decomposition Experiment (LIDET) 4 Observations 10-year study of litter dynamics for a variety of litter types placed in different environments 20 sites: 2 tundra, 2 boreal forest, 5 conifer forest, 3 deciduous forest, 3 tropical forest, 2 humid grassland, 3 arid grassland 9 litter types (6 species of leaves, 3 species of root) that vary in chemistry Litter bags sampled once a year for C and N Model simulations CLM4cn, DAYCENT Follow a cohort of litter (100 g C m -2 ) deposited on October 1 Specified climatic decomposition index (CDI) to account for temperature and moisture Soil mineral nitrogen DAYCENT SOM C:N ratios vary with mineral N. Use low and high C:N ratios CLM4cn Soil mineral N reduces decomposition rates, but only for flows with immobilization. Configure simulations so that N does not limit decomposition & immobilization (fpi=1) and so that N is rate limiting (fpi<1) Bonan et al (2012) Global Change Biol, doi: /gcb.12031
5 Leaf litter mass loss conifer forest 5 5 sites & 6 leaf litter types Shown are the site x litter mean and ± 1 SD CLM underestimates carbon mass remaining (overestimates mass loss), especially during first several years. This is common to all sites.
6 Leaf litter mass loss all sites 6
7 Nitrogen dynamics 7 Maple, 0.81 %N Observations are sampled once per year. Shown are data for maple leaf litter at all biomes except arid grassland. Model data are sampled similar to the observations. CLM4cn overestimates immobilization. Larger biases for leaf litter types with lower initial %N
8 CLM4cn nitrogen limitation 8 N limitation reduces decomposition rates in CLM4cn and improves carbon dynamics. Here we use fpi = 0.05 Similar results can be obtained for other biomes using fpi= Decomposition rates in DAYCENT do not need to be similarly reduced Different underlying philosophies for the two models, particularly with respect to the influence of soil mineral N on litter C-N dynamics N limitation
9 CLM4cn nitrogen limitation 9 Conifer forest, maple leaf litter (0.81 %N) N not limiting N limiting N limitation (fpi=0.05) reduces bias. Similar results are obtained for other biomes and litter types using fpi=
10 Is DAYCENT a solution to the soil carbon biases? 10 LIDET (10-year litter decomposition) CLM4cn has too rapid carbon turnover, unless N severely restricts decomposition rates (fpi = ) CESM/CLM4cn global simulations do not show such N limitation (fpi > 0.6 in many regions) DAYCENT has better litter decomposition. Would DAYCENT improve CLM soil carbon? Steady-state analysis (Xia et al. Geosci. Model Dev., 5, , 2012) but forced soil BGC models with litterfall litterfall (Matthews, JGR 102: , 1997) soil temperature and moisture from a control CLM4cn simulation soil texture and ph from HWSD (for DAYCENT)
11 Steady-state analysis 11 Observed litterfall increases soil C compared with CLM4cn litterfall Base DAYCENT (0-20 cm) Deep DAYCENT (0-100 cm) CLM4cn has more soil carbon than DAYCENT, but deep DAYCENT (0-100 cm) accumulates the most carbon
12 Conclusions 12 LIDET (10-year litter decomposition) Steady-state analysis DAYCENT better simulates litter C and N dynamics compared with CLM4cn (20 sites x 9 litter types) Both CLM4cn and DAYCENT significantly underestimate soil carbon, DAYCENT more than CLM4cn CLM4cn has too rapid C loss and to high N immobilization, unless N severely restricts decomposition rates DAYCENT simulation can be improved by adjusting the model to represent cm depth but WEDNESDAY, DECEMBER 05, :45 PM - 6:00 PM 2006 (Moscone West)??? William Wieder et al. B34B-08. Integrating Observations to Inform Soil Biogeochemistry in CLM4
Ecosystem feedbacks in a 21st century climate: carbon, nitrogen, and land cover change
 Ecosystem feedbacks in a 21st century climate: carbon, nitrogen, and land cover change Gordon Bonan National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado, USA 19 October 2012 Fall Environmental Sciences
Ecosystem feedbacks in a 21st century climate: carbon, nitrogen, and land cover change Gordon Bonan National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado, USA 19 October 2012 Fall Environmental Sciences
Development of a Microbial Module, CLM-Microbe in CESM: framework and preliminary results
 Development of a Microbial Module, CLM-Microbe in CESM: framework and preliminary results Xiaofeng Xu 1, Peter Thornton 1, Fengming Yuan 1, David Graham 2, Dwayne A. Elias 1,2, Santonu Goswami 1, Joshua
Development of a Microbial Module, CLM-Microbe in CESM: framework and preliminary results Xiaofeng Xu 1, Peter Thornton 1, Fengming Yuan 1, David Graham 2, Dwayne A. Elias 1,2, Santonu Goswami 1, Joshua
Land Ecosystems and Climate a modeling perspective
 Land Ecosystems and Climate a modeling perspective Samuel Levis Community Land Model Science Liaison Terrestrial Sciences Section, CGD, ESSL, NCAR 12 August 2009 Why the Land? the land surface is a critical
Land Ecosystems and Climate a modeling perspective Samuel Levis Community Land Model Science Liaison Terrestrial Sciences Section, CGD, ESSL, NCAR 12 August 2009 Why the Land? the land surface is a critical
The Land Use Forcing of Climate: Models, Observations, and Research Needs
 The Land Use Forcing of Climate: Models, Observations, and Research Needs Gordon Bonan National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado Ameriflux Science Team Meeting Boulder, Colorado October
The Land Use Forcing of Climate: Models, Observations, and Research Needs Gordon Bonan National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado Ameriflux Science Team Meeting Boulder, Colorado October
From climate models to earth system models: the stomatal paradigm and beyond
 From climate models to earth system models: the stomatal paradigm and beyond Gordon Bonan National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado, USA Academy Colloquium Stomatal conductance through
From climate models to earth system models: the stomatal paradigm and beyond Gordon Bonan National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado, USA Academy Colloquium Stomatal conductance through
Unsaved Test, Version: 1 1
 Name: Key Concepts Select the term that best completes the statement. A. abiotic B. light C. biotic D. organisms E. ecology F. soil G. ecosystem H. temperature I. factors J. water Date: 1. A(n) is made
Name: Key Concepts Select the term that best completes the statement. A. abiotic B. light C. biotic D. organisms E. ecology F. soil G. ecosystem H. temperature I. factors J. water Date: 1. A(n) is made
Nutrients elements required for the development, maintenance, and reproduction of organisms.
 Nutrient Cycles Energy flows through ecosystems (one way trip). Unlike energy, however, nutrients (P, N, C, K, S ) cycle within ecosystems. Nutrients are important in controlling NPP in ecosystems. Bottom-up
Nutrient Cycles Energy flows through ecosystems (one way trip). Unlike energy, however, nutrients (P, N, C, K, S ) cycle within ecosystems. Nutrients are important in controlling NPP in ecosystems. Bottom-up
Soils and Climate Change
 Soils and Climate Change Susan Trumbore Max-Planck Institute for Biogeochemistry and Earth System Science, UC Irvine thanks to Marion Schrumpf, MPI-BGC and EAG Schuur, Northern Arizona University CO 2
Soils and Climate Change Susan Trumbore Max-Planck Institute for Biogeochemistry and Earth System Science, UC Irvine thanks to Marion Schrumpf, MPI-BGC and EAG Schuur, Northern Arizona University CO 2
Arctic ecosystems as key biomes in climate-carbon feedback. Hanna Lee Climate and Global Dynamics Division National Center for Atmospheric Research
 Arctic ecosystems as key biomes in climate-carbon feedback Hanna Lee Climate and Global Dynamics Division National Center for Atmospheric Research Outline Permafrost carbon Permafrost carbon-climate feedback
Arctic ecosystems as key biomes in climate-carbon feedback Hanna Lee Climate and Global Dynamics Division National Center for Atmospheric Research Outline Permafrost carbon Permafrost carbon-climate feedback
SNC1D BIOLOGY 5/10/2013. SUSTAINABLE ECOSYSTEMS L Biomes (P.16-17) Biomes. Biomes
 SNC1D BIOLOGY SUSTAINABLE ECOSYSTEMS L Biomes (P.16-17) Biomes Areas of the world that have a similar climate and similar organisms are known as biomes. Desert, coral reef, tundra, and tropical rainforest
SNC1D BIOLOGY SUSTAINABLE ECOSYSTEMS L Biomes (P.16-17) Biomes Areas of the world that have a similar climate and similar organisms are known as biomes. Desert, coral reef, tundra, and tropical rainforest
Ecosystems and the Biosphere Outline
 Ecosystems and the Biosphere Outline Ecosystems Processes in an ecosystem Production, respiration, decomposition How energy and nutrients move through an ecosystem Biosphere Biogeochemical Cycles Gaia
Ecosystems and the Biosphere Outline Ecosystems Processes in an ecosystem Production, respiration, decomposition How energy and nutrients move through an ecosystem Biosphere Biogeochemical Cycles Gaia
Unit III Nutrients & Biomes
 Unit III Nutrients & Biomes Nutrient Cycles Carbon Cycle Based on CO 2 cycling from animals to plants during respiration and photosynthesis. Heavy deposits are stored in wetland soils, oceans, sedimentary
Unit III Nutrients & Biomes Nutrient Cycles Carbon Cycle Based on CO 2 cycling from animals to plants during respiration and photosynthesis. Heavy deposits are stored in wetland soils, oceans, sedimentary
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 20 September 2016 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 2016 Frank Sansone 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 20 September 2016 Reading: Schlesinger & Bernhardt, Chapter 6 2016 Frank Sansone 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen
Influence of carbon-nitrogen cycle coupling on land model response to CO 2 fertilization and climate variability
 Click Here for Full Article GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 21,, doi:10.1029/2006gb002868, 2007 Influence of carbon-nitrogen cycle coupling on land model response to CO 2 fertilization and climate variability
Click Here for Full Article GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 21,, doi:10.1029/2006gb002868, 2007 Influence of carbon-nitrogen cycle coupling on land model response to CO 2 fertilization and climate variability
Human perturbations to the global Nitrogen cycle
 Human perturbations to the global Nitrogen cycle Lecture for Biogeochemistry and Global Change Edzo Veldkamp The pace of human caused global change has increased in modern history, but none so rapidly
Human perturbations to the global Nitrogen cycle Lecture for Biogeochemistry and Global Change Edzo Veldkamp The pace of human caused global change has increased in modern history, but none so rapidly
New findings from CMIP5 Long term climate change projection using the Earth Simulator
 New findings from CMIP5 Long term climate change projection using the Earth Simulator H. Kondo Japan Agency for Marine Earth Science and Technology (JAMSTEC, Japan) (MEXT) Climate change projection using
New findings from CMIP5 Long term climate change projection using the Earth Simulator H. Kondo Japan Agency for Marine Earth Science and Technology (JAMSTEC, Japan) (MEXT) Climate change projection using
Guide 34. Ecosystem Ecology: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles. p://www.mordantorange.com/blog/archives/comics_by_mike_bannon/mordant_singles/0511/
 Guide 34 Ecosystem Ecology: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles p://www.mordantorange.com/blog/archives/comics_by_mike_bannon/mordant_singles/0511/ Overview: Ecosystems, Energy, and Matter An ecosystem consists
Guide 34 Ecosystem Ecology: Energy Flow and Nutrient Cycles p://www.mordantorange.com/blog/archives/comics_by_mike_bannon/mordant_singles/0511/ Overview: Ecosystems, Energy, and Matter An ecosystem consists
Chapter 22: Energy in the Ecosystem
 Chapter 22: Energy in the Ecosystem What is ecology? Global human issues Physical limits Ecosystems Organisms Populations Species Interactions Communities Energy flows and nutrients cycle C, H 2 0, P,
Chapter 22: Energy in the Ecosystem What is ecology? Global human issues Physical limits Ecosystems Organisms Populations Species Interactions Communities Energy flows and nutrients cycle C, H 2 0, P,
1. Where are nutrients accumulated or stored for short or long periods?
 Use with textbook pages 68 87. Nutrient cycles Answer the questions below. Comprehension 1. Where are nutrients accumulated or stored for short or long periods? 2. Name a biotic process and an abiotic
Use with textbook pages 68 87. Nutrient cycles Answer the questions below. Comprehension 1. Where are nutrients accumulated or stored for short or long periods? 2. Name a biotic process and an abiotic
Terrestrial Biogeochemistry in UKESM! Anna Harper, Andy Wiltshire, Rich Ellis, Spencer Liddicoat, Nic Gedney, Gerd Folberth, Eddy Robertson, T
 Terrestrial Biogeochemistry in UKESM! Anna Harper, Andy Wiltshire, Rich Ellis, Spencer Liddicoat, Nic Gedney, Gerd Folberth, Eddy Robertson, T Davies-Barnard, Doug Clark, Margriet Groenendijk, Chris Jones,
Terrestrial Biogeochemistry in UKESM! Anna Harper, Andy Wiltshire, Rich Ellis, Spencer Liddicoat, Nic Gedney, Gerd Folberth, Eddy Robertson, T Davies-Barnard, Doug Clark, Margriet Groenendijk, Chris Jones,
The Nutrient Cycle. Atmospheric pool. Organic material. 5 Soil solution storage
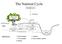 The Nutrient Cycle Atmospheric pool Precipitation Canopy, wood, and root Litter fall SOIL 2 Soil and rock minerals cations 1 2 3 Groundwater level Organic material 5 Soil solution storage 4 4 Channel BEDROCK
The Nutrient Cycle Atmospheric pool Precipitation Canopy, wood, and root Litter fall SOIL 2 Soil and rock minerals cations 1 2 3 Groundwater level Organic material 5 Soil solution storage 4 4 Channel BEDROCK
Forest carbon allocation as a determinant of net primary productivity. Ivan Janssens
 Forest carbon allocation as a determinant of net primary productivity Ivan Janssens 4. Take home messages: 1. Variation in forest GPP* is predominantly climate-controlled, In contrast: variation in NPP**/GPP
Forest carbon allocation as a determinant of net primary productivity Ivan Janssens 4. Take home messages: 1. Variation in forest GPP* is predominantly climate-controlled, In contrast: variation in NPP**/GPP
ECOSYSTEMS. Follow along in chapter 54. *Means less important
 ECOSYSTEMS Follow along in chapter 54 *Means less important How do ecosystems function? What is an ecosystem? All living things in an area and their abiotic environment Ecosystem function can be easily
ECOSYSTEMS Follow along in chapter 54 *Means less important How do ecosystems function? What is an ecosystem? All living things in an area and their abiotic environment Ecosystem function can be easily
BIOMES. Living World
 BIOMES Living World Biomes Biomes are large regions of the world with distinctive climate, wildlife and vegetation. They are divided by terrestrial (land) or aquatic biomes. Terrestrial Biomes Terrestrial
BIOMES Living World Biomes Biomes are large regions of the world with distinctive climate, wildlife and vegetation. They are divided by terrestrial (land) or aquatic biomes. Terrestrial Biomes Terrestrial
Terrestrial Net Primary Productivity - introduction
 TNPP Lancaster Dec 2013 Terrestrial Net Primary Productivity - introduction E Tipping Centre for Ecology & Hydrology Lancaster UK Background In current UK-based research projects within the NERC BESS and
TNPP Lancaster Dec 2013 Terrestrial Net Primary Productivity - introduction E Tipping Centre for Ecology & Hydrology Lancaster UK Background In current UK-based research projects within the NERC BESS and
Intro to Biogeochemical Modeling Ocean & Coupled
 Intro to Biogeochemical Modeling Ocean & Coupled Keith Lindsay, NCAR/CGD NCAR is sponsored by the National Science Foundation Lecture Outline 1) Large Scale Ocean Biogeochemical Features 2) Techniques
Intro to Biogeochemical Modeling Ocean & Coupled Keith Lindsay, NCAR/CGD NCAR is sponsored by the National Science Foundation Lecture Outline 1) Large Scale Ocean Biogeochemical Features 2) Techniques
Chapter Introduction. Matter. Ecosystems. Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Abiotic Factors Cycles of Matter Chapter Wrap-Up Energy in Ecosystems How do living things and the nonliving parts of the environment interact? What do you
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Abiotic Factors Cycles of Matter Chapter Wrap-Up Energy in Ecosystems How do living things and the nonliving parts of the environment interact? What do you
CONTINENTAL SCALE VARIABILITY IN ECOSYSTEM PROCESSES: MODELS, DATA, AND THE ROLE OF DISTURBANCE
 Ecological Monographs, 67(2), 1997, pp. 251 271 1997 by the Ecological Society of America CONTINENTAL SCALE VARIABILITY IN ECOSYSTEM PROCESSES: MODELS, DATA, AND THE ROLE OF DISTURBANCE DAVID S. SCHIMEL,
Ecological Monographs, 67(2), 1997, pp. 251 271 1997 by the Ecological Society of America CONTINENTAL SCALE VARIABILITY IN ECOSYSTEM PROCESSES: MODELS, DATA, AND THE ROLE OF DISTURBANCE DAVID S. SCHIMEL,
Environmental Science Exam 5 Biomes Conserve Paper Don t Write on This Test!
 Environmental Science Exam 5 Biomes Conserve Paper Don t Write on This Test! 1. What are the two most significant abiotic factors that influence what type of biome is found in a geographic area? a. Wind
Environmental Science Exam 5 Biomes Conserve Paper Don t Write on This Test! 1. What are the two most significant abiotic factors that influence what type of biome is found in a geographic area? a. Wind
The Global Carbon Cycle
 The Global Carbon Cycle In a nutshell We are mining fossil CO 2 and titrating into the oceans, (buffered by acid-base chemistry) Much of the fossil CO 2 will remain in the atmosphere for thousands of years
The Global Carbon Cycle In a nutshell We are mining fossil CO 2 and titrating into the oceans, (buffered by acid-base chemistry) Much of the fossil CO 2 will remain in the atmosphere for thousands of years
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions of N gases from soils
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P and S OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions of N gases from soils
Fire Modelling in JULES using SPITFIRE: Spread and Intensity of Fires and Emissions Model
 Fire Modelling in JULES using SPITFIRE: Spread and Intensity of Fires and Emissions Model Allan Spessa National Centre for Atmosphere Science Department of Meteorology Reading University JULES Summer 2009
Fire Modelling in JULES using SPITFIRE: Spread and Intensity of Fires and Emissions Model Allan Spessa National Centre for Atmosphere Science Department of Meteorology Reading University JULES Summer 2009
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K
 Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 18 September 2012 Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions
Cycling and Biogeochemical Transformations of N, P, S, and K OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 18 September 2012 Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 6 1. Nitrogen cycle Soil nitrogen cycle Nitrification Emissions
Distribution Limits. Kangaroo Distributions and Climate. Kangaroo Distributions and Climate
 Distribution Limits Physical environment limits geographic distribution of a species. Organisms can only compensate so much for environmental variation Kangaroo Distributions and Climate Caughley found
Distribution Limits Physical environment limits geographic distribution of a species. Organisms can only compensate so much for environmental variation Kangaroo Distributions and Climate Caughley found
Co-evolution of Climate and Life
 Co-evolution of Climate and Life Gordon Bonan National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado 20 October 2010 Center for Astrobiology University of Colorado Boulder, Colorado NCAR is sponsored
Co-evolution of Climate and Life Gordon Bonan National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado 20 October 2010 Center for Astrobiology University of Colorado Boulder, Colorado NCAR is sponsored
DYNAMIC VEGETATION MODELLING in JULES using the ED (ECOSYSTEM DEMOGRAPHY) MODEL. Allan Spessa
 DYNAMIC VEGETATION MODELLING in JULES using the ED (ECOSYSTEM DEMOGRAPHY) MODEL Allan Spessa National Centre for Atmospheric Science Department of Meteorology University of Reading JULES Summer 2009 meeting
DYNAMIC VEGETATION MODELLING in JULES using the ED (ECOSYSTEM DEMOGRAPHY) MODEL Allan Spessa National Centre for Atmospheric Science Department of Meteorology University of Reading JULES Summer 2009 meeting
Climate and Biodiversity
 LIVING IN THE ENVIRONMENT, 18e G. TYLER MILLER SCOTT E. SPOOLMAN 7 Climate and Biodiversity Core Case Study: A Temperate Deciduous Forest Why do forests grow in some areas and not others? Climate Tropical
LIVING IN THE ENVIRONMENT, 18e G. TYLER MILLER SCOTT E. SPOOLMAN 7 Climate and Biodiversity Core Case Study: A Temperate Deciduous Forest Why do forests grow in some areas and not others? Climate Tropical
GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 9, NO. 4, PAGES , DECEMBER 1995
 GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 9, NO. 4, PAGES 407-437, DECEMBER 1995 Vegetation/ecosystem modeling and analysis project- Comparing biogeography and biogeochemistry models in a continental-scale study
GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 9, NO. 4, PAGES 407-437, DECEMBER 1995 Vegetation/ecosystem modeling and analysis project- Comparing biogeography and biogeochemistry models in a continental-scale study
Ecosystem Mass Balances and Models of Terrestrial Nutrient Cycling
 Ecosystem Mass Balances and Models of Terrestrial Nutrient Cycling OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 22 September 2016 Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 6 2016 Frank Sansone Outline 1. Ecosystem mass balances
Ecosystem Mass Balances and Models of Terrestrial Nutrient Cycling OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 22 September 2016 Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 6 2016 Frank Sansone Outline 1. Ecosystem mass balances
Soil fertility Patma Vityakon Rambo, PhD
 100 713 Land Resources and Environment in Sustainable Agriculture Soil fertility Patma Vityakon Rambo, PhD Soil fertility studies Soil fertility is the study of soils as a source of plant nutrients. The
100 713 Land Resources and Environment in Sustainable Agriculture Soil fertility Patma Vityakon Rambo, PhD Soil fertility studies Soil fertility is the study of soils as a source of plant nutrients. The
Modelling the global carbon cycle
 Modelling the global carbon cycle Chris Jones, Eleanor Burke, Angela Gallego-Sala (U. Exeter)» UNFCCC, Bonn, 24 October 2013 Introduction Why model the global carbon cycle? Motivation from climate perspective
Modelling the global carbon cycle Chris Jones, Eleanor Burke, Angela Gallego-Sala (U. Exeter)» UNFCCC, Bonn, 24 October 2013 Introduction Why model the global carbon cycle? Motivation from climate perspective
Slide 1. Earth Science. Chapter 11 Living Systems
 Slide 1 Earth Science Chapter 11 Living Systems Slide 2 Biomes A biome is a region with a certain climate and certain forms of vegetation. It is mostly the climate temperature and precipitation in an area
Slide 1 Earth Science Chapter 11 Living Systems Slide 2 Biomes A biome is a region with a certain climate and certain forms of vegetation. It is mostly the climate temperature and precipitation in an area
Kathryn Piatek 1. Professor of Forest Management and Soils, West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV
 Nitrogen Dynamics Post-harvest: the Role of Woody Residues Kathryn Piatek 1 Abstract The role of woody residues in N dynamics in harvested forests has not been fully elucidated. Woody residues have been
Nitrogen Dynamics Post-harvest: the Role of Woody Residues Kathryn Piatek 1 Abstract The role of woody residues in N dynamics in harvested forests has not been fully elucidated. Woody residues have been
Carbon fluxes and sequestration opportunities in grassland ecosystems
 GCP, Beijing, 15-18 November 2004. Regional Carbon Budgets: from methodologies to quantification Carbon fluxes and sequestration opportunities in grassland ecosystems Jean-Francois Soussana INRA, Grassland
GCP, Beijing, 15-18 November 2004. Regional Carbon Budgets: from methodologies to quantification Carbon fluxes and sequestration opportunities in grassland ecosystems Jean-Francois Soussana INRA, Grassland
Factors Affecting Gas Species Released in BB. Factors Affecting Gas Species Released in BB. Factors Affecting Gas Species Released in BB
 Factors Affecting Gas Species Trace from Biomass Burning. The Main Variables* The Amount and Type of gas species released from fire are conditioned by: Chemical and Physical features of the Ecosystem *(Alicia
Factors Affecting Gas Species Trace from Biomass Burning. The Main Variables* The Amount and Type of gas species released from fire are conditioned by: Chemical and Physical features of the Ecosystem *(Alicia
Atul Jain University of Illinois, Urbana, IL 61801, USA
 Brian O Neill, NCAR 2010 LCLUC Spring Science Team Meeting Bethesda, MD April 20-22, 2010 Land-Use Change and Associated Changes in Biogeochemical and Biophysical Processes in Monsoon Asian Region (MAR)
Brian O Neill, NCAR 2010 LCLUC Spring Science Team Meeting Bethesda, MD April 20-22, 2010 Land-Use Change and Associated Changes in Biogeochemical and Biophysical Processes in Monsoon Asian Region (MAR)
Carbon, Part 3, Net Ecosystem Production
 Carbon, Part 3, Net Ecosystem Production Carbon Balance of Ecosystems NEP,NPP, GPP Seasonal Dynamics of Ecosystem Carbon Fluxes Carbon Flux Partitioning Chain-saw and Shovel Ecology Dennis Baldocchi ESPM
Carbon, Part 3, Net Ecosystem Production Carbon Balance of Ecosystems NEP,NPP, GPP Seasonal Dynamics of Ecosystem Carbon Fluxes Carbon Flux Partitioning Chain-saw and Shovel Ecology Dennis Baldocchi ESPM
The Nutrient Cycle. Atmospheric pool. Organic material. 5 Soil solution storage
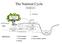 The Nutrient Cycle Atmospheric pool Precipitation Canopy, wood, and root Litter fall SOIL 2 Soil and rock minerals cations 1 2 3 Groundwater level Organic material 5 Soil solution storage 4 4 Channel BEDROCK
The Nutrient Cycle Atmospheric pool Precipitation Canopy, wood, and root Litter fall SOIL 2 Soil and rock minerals cations 1 2 3 Groundwater level Organic material 5 Soil solution storage 4 4 Channel BEDROCK
Peatland Carbon Stocks and Fluxes:
 Peatland Carbon Stocks and Fluxes: monitoring, measurements and modelling Dr Andreas Heinemeyer ah126@york.ac.uk University of York, Stockholm Environment Institute UNFCCC 24 th October 2013 South Africa:
Peatland Carbon Stocks and Fluxes: monitoring, measurements and modelling Dr Andreas Heinemeyer ah126@york.ac.uk University of York, Stockholm Environment Institute UNFCCC 24 th October 2013 South Africa:
Long-term changes in forest carbon under temperature and nitrogen amendments in a temperate northern hardwood forest
 Global Change Biology (2013) 19, 2389 2400, doi: 10.1111/gcb.12224 Long-term changes in forest carbon under temperature and nitrogen amendments in a temperate northern hardwood forest KATHLEEN E. SAVAGE*,
Global Change Biology (2013) 19, 2389 2400, doi: 10.1111/gcb.12224 Long-term changes in forest carbon under temperature and nitrogen amendments in a temperate northern hardwood forest KATHLEEN E. SAVAGE*,
Fifteen years after TransCom3: are global CO 2 inverse calculations robust?
 Fifteen years after TransCom3: are global CO 2 inverse calculations robust? Benjamin Gaubert 1, Britton B. Stephens 1, Andrew R. Jacobson 2, Sourish Basu 2, Frederic Chevallier 3, Christian Roedenbeck
Fifteen years after TransCom3: are global CO 2 inverse calculations robust? Benjamin Gaubert 1, Britton B. Stephens 1, Andrew R. Jacobson 2, Sourish Basu 2, Frederic Chevallier 3, Christian Roedenbeck
Modelling Forest Growth and Carbon Dynamics:
 Modelling Forest Growth and Carbon Dynamics: TRIPLEX Model Development and Applications Changhui Peng (www.crc.uqam.ca) Université du Quebec à Montreal (UQAM) Laboratoire de modélisation écologique et
Modelling Forest Growth and Carbon Dynamics: TRIPLEX Model Development and Applications Changhui Peng (www.crc.uqam.ca) Université du Quebec à Montreal (UQAM) Laboratoire de modélisation écologique et
Data Model Intercomparison of Ecosystem Carbon & Water Surface Fluxes Across Amazonia
 Data Model Intercomparison of Ecosystem Carbon & Water Surface Fluxes Across Amazonia Bradley Christoffersen University of Arizona Organizers: Scott R. Saleska, Inez Fung, Luis Gustavo G. de Gonçalves,
Data Model Intercomparison of Ecosystem Carbon & Water Surface Fluxes Across Amazonia Bradley Christoffersen University of Arizona Organizers: Scott R. Saleska, Inez Fung, Luis Gustavo G. de Gonçalves,
Fluxes: measurements and modeling. Flux
 Fluxes: measurements and modeling Schlesinger and Bernhardt Pg 135-150 Gustin flux paper Griffis, Timothy J. 2013 paper Denmead 2008 Discussion 2 - Work in groups of 2 Papers due to Mae Sept 24 Pick one
Fluxes: measurements and modeling Schlesinger and Bernhardt Pg 135-150 Gustin flux paper Griffis, Timothy J. 2013 paper Denmead 2008 Discussion 2 - Work in groups of 2 Papers due to Mae Sept 24 Pick one
The Law of Conservation of Matter. Matter cannot be created nor destroyed Matter only changes form There is no away
 Review Items Ecosystem Structure The Law of Conservation of Matter Matter cannot be created nor destroyed Matter only changes form There is no away Laws Governing Energy Changes First Law of Thermodynamics
Review Items Ecosystem Structure The Law of Conservation of Matter Matter cannot be created nor destroyed Matter only changes form There is no away Laws Governing Energy Changes First Law of Thermodynamics
1. Energy Flow in Ecosystems
 Ecosystems & Biomes 1. Energy Flow in Ecosystems What are energy roles in ecosystems? What are energy roles in ecosystems? Producers An organism that can make its own food = AUTOTROPHS! Source of all the
Ecosystems & Biomes 1. Energy Flow in Ecosystems What are energy roles in ecosystems? What are energy roles in ecosystems? Producers An organism that can make its own food = AUTOTROPHS! Source of all the
A dynamic global vegetation model for use with climate models: concepts and description of simulated vegetation dynamics
 Global Change Biology (2003) 9, 1543 1566, doi: 10.1046/j.1529-8817.2003.00681.x A dynamic global vegetation model for use with climate models: concepts and description of simulated vegetation dynamics
Global Change Biology (2003) 9, 1543 1566, doi: 10.1046/j.1529-8817.2003.00681.x A dynamic global vegetation model for use with climate models: concepts and description of simulated vegetation dynamics
Cross-biome transplants of plant litter show decomposition models extend to a broader climatic range but lose predictability at the decadal time scale
 Global Change Biology (2010) 16, 1744 1761, doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2009.02086.x Cross-biome transplants of plant litter show decomposition models extend to a broader climatic range but lose predictability
Global Change Biology (2010) 16, 1744 1761, doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2009.02086.x Cross-biome transplants of plant litter show decomposition models extend to a broader climatic range but lose predictability
Chapter 4. Ecosystems
 Chapter 4 Ecosystems Chapter 4 Section 1: What Is an Ecosystem Key Vocabulary Terms 7 Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Community A group of various species that live in the same habitat and interact with
Chapter 4 Ecosystems Chapter 4 Section 1: What Is an Ecosystem Key Vocabulary Terms 7 Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Community A group of various species that live in the same habitat and interact with
15.1 Life in the Earth System. KEY CONCEPT The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems.
 15.1 Life in the Earth System KEY CONCEPT The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems. 15.1 Life in the Earth System The biosphere is the portion of Earth that is inhabited by life. The
15.1 Life in the Earth System KEY CONCEPT The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems. 15.1 Life in the Earth System The biosphere is the portion of Earth that is inhabited by life. The
Prof Brendan Mackey, PhD
 Role of forests in global carbon cycle and mitigation Presentation for Land use and Forests in the Paris Agreement, real world implications of negative emissions and Bioenergy CCS (BECCS) May 12 th & 13
Role of forests in global carbon cycle and mitigation Presentation for Land use and Forests in the Paris Agreement, real world implications of negative emissions and Bioenergy CCS (BECCS) May 12 th & 13
Yasso07 soil carbon model and user-interface
 Yasso07 soil carbon model and user-interface Jari Liski 1, Mikko Tuomi 1,2 and Jussi Rasinmäki 3 1 Finnish Environment Institute 2 Department of Applied Mathematics and Statistics, University of Helsinki
Yasso07 soil carbon model and user-interface Jari Liski 1, Mikko Tuomi 1,2 and Jussi Rasinmäki 3 1 Finnish Environment Institute 2 Department of Applied Mathematics and Statistics, University of Helsinki
BAEN 673 / February 18, 2016 Hydrologic Processes
 BAEN 673 / February 18, 2016 Hydrologic Processes Assignment: HW#7 Next class lecture in AEPM 104 Today s topics SWAT exercise #2 The SWAT model review paper Hydrologic processes The Hydrologic Processes
BAEN 673 / February 18, 2016 Hydrologic Processes Assignment: HW#7 Next class lecture in AEPM 104 Today s topics SWAT exercise #2 The SWAT model review paper Hydrologic processes The Hydrologic Processes
Threats to Forest Ecosystem Health Activities together influence ecosystem structure & function
 Threats to Forest Ecosystem Health Activities together influence ecosystem structure & function introduced species poor management air pollution global warming habitat fragmentation American Chestnut From
Threats to Forest Ecosystem Health Activities together influence ecosystem structure & function introduced species poor management air pollution global warming habitat fragmentation American Chestnut From
What is ECOLOGY? The study of the biotic and abiotic factors in an environment and their interactions.
 Ecology What is ECOLOGY? The study of the biotic and abiotic factors in an environment and their interactions. Biotic Factors Living things in the environment. Animals Plants Fungi Protists Bacteria Abiotic
Ecology What is ECOLOGY? The study of the biotic and abiotic factors in an environment and their interactions. Biotic Factors Living things in the environment. Animals Plants Fungi Protists Bacteria Abiotic
Chapter 4, sec. 1 Prentice Hall Biology Book p (This material is similar to Ch.17, sec.3 in our book)
 Chapter 4, sec. 1 Prentice Hall Biology Book p.87-89 (This material is similar to Ch.17, sec.3 in our book) Term Definition Weather Day-to-day condition of earth s atmosphere at a particular time and place
Chapter 4, sec. 1 Prentice Hall Biology Book p.87-89 (This material is similar to Ch.17, sec.3 in our book) Term Definition Weather Day-to-day condition of earth s atmosphere at a particular time and place
Simulation of mesoscale patterns and diurnal variations of atmospheric CO 2 mixing ratios with the model system TerrSysMP-CO 2
 Simulation of mesoscale patterns and diurnal variations of atmospheric CO 2 mixing ratios with the model system TerrSysMP-CO 2 CarboCount-CH final meeting Markus Übel Meteorological Institute, University
Simulation of mesoscale patterns and diurnal variations of atmospheric CO 2 mixing ratios with the model system TerrSysMP-CO 2 CarboCount-CH final meeting Markus Übel Meteorological Institute, University
CURRICULUM VITAE OF: DANIEL ANTHONY LACK (26/11/1975)
 CURRICULUM VITAE OF: DANIEL ANTHONY LACK (26/11/1975) ADDRESS: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration 325 Broadway R/AL2 1A126 Boulder Colorado, USA, 80305 www.esrl.noaa.gov CONTACT: 2637 Tumwater
CURRICULUM VITAE OF: DANIEL ANTHONY LACK (26/11/1975) ADDRESS: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration 325 Broadway R/AL2 1A126 Boulder Colorado, USA, 80305 www.esrl.noaa.gov CONTACT: 2637 Tumwater
The Ecological Theory of Climate Models Gordon Bonan National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado
 The Ecological Theory of Climate Models Gordon Bonan National Center for 2 nd Integrated Land Ecosystem-Atmosphere Processes Study (ileaps) science conference Melbourne, Australia 24 August 2009 Forests
The Ecological Theory of Climate Models Gordon Bonan National Center for 2 nd Integrated Land Ecosystem-Atmosphere Processes Study (ileaps) science conference Melbourne, Australia 24 August 2009 Forests
Biophysical modulators of interannual variability in eddy-covariance data
 Biophysical modulators of interannual variability in eddy-covariance data Trevor F. Keenan Lawrence Berkeley National Lab. www.sites.google.com/trevorfkeenan @trevorkeenan Variability in the growth rate
Biophysical modulators of interannual variability in eddy-covariance data Trevor F. Keenan Lawrence Berkeley National Lab. www.sites.google.com/trevorfkeenan @trevorkeenan Variability in the growth rate
FACT SHEET. Understanding Soil Microbes and Nutrient Recycling. Agriculture and Natural Resources SAG-16-10
 FACT SHEET Agriculture and Natural Resources Understanding Soil Microbes and Nutrient Recycling James J. Hoorman Cover Crops and Water Quality Extension Educator Ohio State University Extension Rafiq Islam
FACT SHEET Agriculture and Natural Resources Understanding Soil Microbes and Nutrient Recycling James J. Hoorman Cover Crops and Water Quality Extension Educator Ohio State University Extension Rafiq Islam
GEO 827: Hyperspectral RS and Land Surface Model Benchmarking
 GEO 827: Hyperspectral RS and Land Surface Model Benchmarking November 10 & 12, 2015 Kyla Dahlin Assistant Professor, Geography Department Outline for the next 2 days Intro to Kyla Intro to Hyperspectral
GEO 827: Hyperspectral RS and Land Surface Model Benchmarking November 10 & 12, 2015 Kyla Dahlin Assistant Professor, Geography Department Outline for the next 2 days Intro to Kyla Intro to Hyperspectral
Carbon cycle and climate change, a tale of increasing emissions and uncertain sinks
 Carbon cycle and climate change, a tale of increasing emissions and uncertain sinks Philippe Peylin On behalf of Chapter-6 Philippe Ciais and Chris Sabine Govindasamy Bala (India), Laurent Bopp (France),
Carbon cycle and climate change, a tale of increasing emissions and uncertain sinks Philippe Peylin On behalf of Chapter-6 Philippe Ciais and Chris Sabine Govindasamy Bala (India), Laurent Bopp (France),
Tropical Forests and Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide: Current Knowledge and Potential Future Scenarios
 Tropical Forests and Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide: Current Knowledge and Potential Future Scenarios Simon L. Lewis 1 Oliver L. Phillips 1, Tim R. Baker 1, Yadvinder Malhi 2, Jon Lloyd 1 1 Earth & Biosphere
Tropical Forests and Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide: Current Knowledge and Potential Future Scenarios Simon L. Lewis 1 Oliver L. Phillips 1, Tim R. Baker 1, Yadvinder Malhi 2, Jon Lloyd 1 1 Earth & Biosphere
Soils and Global Warming. Temperature and Atmosphere. Soils and Water, Spring Lecture 9, Soils and Global Warming 1
 Soils and Global Warming Reading: Lecture Notes Objectives: Introduce climate change Describe measured and expected effects on soil systems Describe prediction of climate change effect on food production.
Soils and Global Warming Reading: Lecture Notes Objectives: Introduce climate change Describe measured and expected effects on soil systems Describe prediction of climate change effect on food production.
Nutrient Cycling 1: The nitrogen cycle
 Nutrient Cycling 1: The nitrogen cycle I. Introduction A. Changes to the global N cycle (Ch. 15) 1. Global pools and fluxes 2. Changes 3. Consequences B. Overview of the ecosystem N cycle (Ch. 9) 1. Major
Nutrient Cycling 1: The nitrogen cycle I. Introduction A. Changes to the global N cycle (Ch. 15) 1. Global pools and fluxes 2. Changes 3. Consequences B. Overview of the ecosystem N cycle (Ch. 9) 1. Major
Evaluation and improvement of the Community Land Model (CLM4) in Oregon forests
 Biogeosciences, 10, 453 470, 2013 doi:10.5194/bg-10-453-2013 Author(s) 2013. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Biogeosciences Evaluation and improvement of the Community Land Model (CLM4) in Oregon forests T.
Biogeosciences, 10, 453 470, 2013 doi:10.5194/bg-10-453-2013 Author(s) 2013. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Biogeosciences Evaluation and improvement of the Community Land Model (CLM4) in Oregon forests T.
Snowpack controls on soil nitrogen dynamics in the Colorado alpine
 Biogeochemistry of Seasonally Snow-Covered Catchments (Proceedings of a Boulder Symposium, July 1995). IAHS Publ. no. 228, 1995. 283 Snowpack controls on soil nitrogen dynamics in the Colorado alpine PAUL
Biogeochemistry of Seasonally Snow-Covered Catchments (Proceedings of a Boulder Symposium, July 1995). IAHS Publ. no. 228, 1995. 283 Snowpack controls on soil nitrogen dynamics in the Colorado alpine PAUL
Human Biology 100A Biome Images
 Human Biology 100A Biome Images Coastal Zone Kelp Forest (temperate latitudes) Instructor: Mark Eberle Oregon Coast Aquarium, Newport, Oregon (photographs by Megan Rohweder) Coral Reef (tropical latitudes)
Human Biology 100A Biome Images Coastal Zone Kelp Forest (temperate latitudes) Instructor: Mark Eberle Oregon Coast Aquarium, Newport, Oregon (photographs by Megan Rohweder) Coral Reef (tropical latitudes)
Fluxes: measurements and modeling. Flux
 Fluxes: measurements and modeling Schlesinger and Bernhardt Pg 135-150 Denmead, 2008 Flux C time Amount of material transferred from one reservoir to the other Source Sink Budget-balance of sources and
Fluxes: measurements and modeling Schlesinger and Bernhardt Pg 135-150 Denmead, 2008 Flux C time Amount of material transferred from one reservoir to the other Source Sink Budget-balance of sources and
SCIENCE Grade 7 Standard: Earth & Space
 Standard: Earth & Space Earth Systems C. Describe interactions of matter and energy throughout the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere (e.g., water cycle, weather, and pollution). 1.a Explain the
Standard: Earth & Space Earth Systems C. Describe interactions of matter and energy throughout the lithosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere (e.g., water cycle, weather, and pollution). 1.a Explain the
Slide 1 / All of Earth's water, land, and atmosphere within which life exists is known as a. Population Community Biome Biosphere
 Slide 1 / 40 1 ll of Earth's water, land, and atmosphere within which life exists is known as a Population ommunity iome iosphere Slide 2 / 40 2 ll the plants, animals, fungi living in a pond make up a
Slide 1 / 40 1 ll of Earth's water, land, and atmosphere within which life exists is known as a Population ommunity iome iosphere Slide 2 / 40 2 ll the plants, animals, fungi living in a pond make up a
Climate: describes the average condition, including temperature and precipitation, over long periods in a given area
 Ch. 6 - Biomes Section 6.1: Defining Biomes Biome: a group of ecosystems that share similar biotic and abiotic conditions, large region characterized by a specific type of climate, plants, and animals
Ch. 6 - Biomes Section 6.1: Defining Biomes Biome: a group of ecosystems that share similar biotic and abiotic conditions, large region characterized by a specific type of climate, plants, and animals
Greenhouse Gas Measurements from Space. Chris O Dell Colorado State University
 Greenhouse Gas Measurements from Space Chris O Dell Colorado State University 1 Climate Forcings & Feedbacks Forcings Greenhouse Gases Aerosols Volcanic Eruptions Solar Forcing Temperature Change Feedbacks
Greenhouse Gas Measurements from Space Chris O Dell Colorado State University 1 Climate Forcings & Feedbacks Forcings Greenhouse Gases Aerosols Volcanic Eruptions Solar Forcing Temperature Change Feedbacks
Answer Test Questions Finish Climate Discussion
 NREM 301 Forest Ecology & Soils Day 30 December 4, 2008 Answer Test Questions Finish Climate Discussion Take-Home Test Due Dec 11 5 pm No Final Exam Lab Today Finish & e-mail all materials to Dick Class
NREM 301 Forest Ecology & Soils Day 30 December 4, 2008 Answer Test Questions Finish Climate Discussion Take-Home Test Due Dec 11 5 pm No Final Exam Lab Today Finish & e-mail all materials to Dick Class
15.1. The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems. The Biosphere CHAPTER 15 LIFE IN THE EARTH SYSTEM KEY CONCEPT
 SECTION 15.1 LIFE IN THE EARTH SYSTEM Study Guide KEY CONCEPT The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems. VOCABULARY biosphere hydrosphere geosphere biota atmosphere The biosphere is the
SECTION 15.1 LIFE IN THE EARTH SYSTEM Study Guide KEY CONCEPT The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems. VOCABULARY biosphere hydrosphere geosphere biota atmosphere The biosphere is the
1: Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology 2: National Institute for Environmental Studies. Hajima et al. 2014, J.
 Decomposition of CO2 fertilization effect into contributions by land ecosystem processes: comparison among CMIP5 Earth system models Kaoru Tachiiri 1 Tomohiro Hajima 1 Akihiko Ito 1,2 Michio Kawamiya 1
Decomposition of CO2 fertilization effect into contributions by land ecosystem processes: comparison among CMIP5 Earth system models Kaoru Tachiiri 1 Tomohiro Hajima 1 Akihiko Ito 1,2 Michio Kawamiya 1
Use of Models to Simulate Agricultural Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Bill Parton Steve Del Grosso
 Use of Models to Simulate Agricultural Greenhouse Gas Emissions Bill Parton Steve Del Grosso My Biases 1. Computer Models are the main tool for estimating Greenhouse Gas (N 2 O, CH 4, CO 2 ) emissions
Use of Models to Simulate Agricultural Greenhouse Gas Emissions Bill Parton Steve Del Grosso My Biases 1. Computer Models are the main tool for estimating Greenhouse Gas (N 2 O, CH 4, CO 2 ) emissions
AP Biology Preliminary Information and Summer Assignment
 AP Biology Preliminary Information and Summer Assignment Requirements: AP Biology is a college level course that covers the same information as an introductory Biology course for Biology majors. It is
AP Biology Preliminary Information and Summer Assignment Requirements: AP Biology is a college level course that covers the same information as an introductory Biology course for Biology majors. It is
Major Feedbacks originating from Northern Eurasia that are of global change concern
 Major Feedbacks originating from Northern Eurasia that are of global change concern Guy P. Brasseur National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, CO Regions of Strong Influences on the Global Earth
Major Feedbacks originating from Northern Eurasia that are of global change concern Guy P. Brasseur National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, CO Regions of Strong Influences on the Global Earth
The evaluation of coupled WRF + Noah-MP and 1-d offline Noah-MP at the FLUXNET sites over Canada
 The evaluation of coupled WRF + Noah-MP and 1-d offline Noah-MP at the FLUXNET sites over Canada Yanping Li, Liang Chen Univ of Saskatchewan Fei Chen, NCAR Alan Barr, Environment Canada I. The calibration
The evaluation of coupled WRF + Noah-MP and 1-d offline Noah-MP at the FLUXNET sites over Canada Yanping Li, Liang Chen Univ of Saskatchewan Fei Chen, NCAR Alan Barr, Environment Canada I. The calibration
Carbon Sequestration and Cycling
 Carbon Sequestration and Cycling Darrel Jenerette University of California Riverside Acknowledgements Isaac Park, Amit Chatterjee, Jen Hooper, Edith Allen, Travis Bean US Forest Service, Kearney Foundation,
Carbon Sequestration and Cycling Darrel Jenerette University of California Riverside Acknowledgements Isaac Park, Amit Chatterjee, Jen Hooper, Edith Allen, Travis Bean US Forest Service, Kearney Foundation,
Intro to Biogeochemical Modeling Ocean & Coupled
 Intro to Biogeochemical Modeling Ocean & Coupled Keith Lindsay, NCAR/CGD NCAR is sponsored by the NaConal Science FoundaCon Lecture Outline 1) Large Scale Ocean Biogeochemical Features 2) Techniques for
Intro to Biogeochemical Modeling Ocean & Coupled Keith Lindsay, NCAR/CGD NCAR is sponsored by the NaConal Science FoundaCon Lecture Outline 1) Large Scale Ocean Biogeochemical Features 2) Techniques for
Microbial biomass, ammonium, and nitrate levels in the soil across a northeastern hardwood/mixed conifer chronosequence Abstract Intro
 Molly Radosevich EEB 381 General Ecology Dr. Shannon Pelini Microbial biomass, ammonium, and nitrate levels in the soil across a northeastern hardwood/mixed conifer chronosequence Abstract Wildfire is
Molly Radosevich EEB 381 General Ecology Dr. Shannon Pelini Microbial biomass, ammonium, and nitrate levels in the soil across a northeastern hardwood/mixed conifer chronosequence Abstract Wildfire is
The Biosphere. GETTING READY TO LEARN Preview Key Concepts 15.1 Life in the Earth System The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems.
 CHAPTER 15 The Biosphere GETTING READY TO LEARN Preview Key Concepts 15.1 Life in the Earth System The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems. 15.2 Climate Climate is a key abiotic factor
CHAPTER 15 The Biosphere GETTING READY TO LEARN Preview Key Concepts 15.1 Life in the Earth System The biosphere is one of Earth s four interconnected systems. 15.2 Climate Climate is a key abiotic factor
In Greek mythology, the Moirai often known in English as the Fates were the white-robed incarnations of destiny. Their number became fixed at three:
 FATES In Greek mythology, the Moirai often known in English as the Fates were the white-robed incarnations of destiny. Their number became fixed at three: Clotho (spinner), Lechesis (allotter) and Atropos
FATES In Greek mythology, the Moirai often known in English as the Fates were the white-robed incarnations of destiny. Their number became fixed at three: Clotho (spinner), Lechesis (allotter) and Atropos
9/23/2015 Question 1 Review Chapter 15 What biome do you live in? Biomes Answer 1 Question 2 Temperate Deciduous Forest Name the 6 Major biomes.
 Review Chapter 15 Biomes Question 1 What biome do you live in? Answer 1 Question 2 Temperate Deciduous Forest Name the 6 Major biomes. 1 Answer 2 Question 3 Fill in Tropical Rainforest Desert Temperate
Review Chapter 15 Biomes Question 1 What biome do you live in? Answer 1 Question 2 Temperate Deciduous Forest Name the 6 Major biomes. 1 Answer 2 Question 3 Fill in Tropical Rainforest Desert Temperate
Chapter 19. Nutrient Cycling and Retention. Chapter Focus. The hydrological cycle. Global biogeochemical cycles. Nutrient cycling
 Chapter Focus Chapter 19 Nutrient Cycling and Retention Nutrient cycling Phosphorus Nitrogen Carbon Water, Sulfur Decomposition Biotic effect on nutrient distribution and cycling Disturbance Global biogeochemical
Chapter Focus Chapter 19 Nutrient Cycling and Retention Nutrient cycling Phosphorus Nitrogen Carbon Water, Sulfur Decomposition Biotic effect on nutrient distribution and cycling Disturbance Global biogeochemical
General Themes (I) Lecture 12
 General Themes (I) Lecture 12 What is a Forest? A forest is a vegetative community dominated by trees and other woody perennials. Images courtesy of Bart van der Kamp What Is a Tree? A perennial woody
General Themes (I) Lecture 12 What is a Forest? A forest is a vegetative community dominated by trees and other woody perennials. Images courtesy of Bart van der Kamp What Is a Tree? A perennial woody
What is Ecology? Abiotic (non-living) Biotic (living)
 ECOLOGY What is Ecology? The scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment, or surroundings Factors involved in ecology Abiotic (non-living) Biotic (living)
ECOLOGY What is Ecology? The scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment, or surroundings Factors involved in ecology Abiotic (non-living) Biotic (living)
