Supporting Online Material for
|
|
|
- Amie Matthews
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supporting Online Material for Embryological Evidence Identifies Wing Digits in Birds as Digits 1, 2, and 3 Koji Tamura,* Naoki Nomura, Ryohei Seki, Sayuri Yonei-Tamura, Hitoshi Yokoyama *To whom correspondence should be addressed. tam@m.tohoku.ac.jp This PDF file includes: Materials and Methods Figs. S1 to S7 References Published 11 February 2011, Science 331, 753 (2011) DOI: /science
2 Materials and Methods Animal Procedures. Eggs of white Leghorn chicken (G. gallus) and quail (C. japonica) were purchased from several local farms, incubated at 38 C, and staged according to Hamburger and Hamilton (S1) and Ainsworth et al. (S2). Gecko embryos were obtained from individuals of P. pictus, which were hatched and kept in our laboratory, and the embryos were staged according to Noro et al. (S3). Mouse embryos were collected at various gestation times from pregnant mice (M. musculus) that were also obtained from local suppliers and staged following Theiler (S4). Transplantation experiments. A small piece of tissue was excised from the center ZPA (see Fig. S1 and the legend) and implanted into a slit under the AER made at the anterior margin of a host stage 20/21 limb bud using sharpened tungsten needles. In some cases, the ectoderm of graft tissue was removed by trypsin before implantation; the results obtained were the same as from the grafts with ectoderm. For the analysis of skeletal pattern, embryos seven days after the above manipulations were fixed in Tyrode s solution containing 10% formalin, stained in 0.1% alcian blue, dehydrated in graded alcohols, and cleared in methyl salicylate. Quail-chick chimera. Chick (host) and quail (donor) embryos were used for the analysis of chimeras to determine the distribution of graft tissue in host limb buds. Tissue fragments from the quail limb buds were implanted into chick limb buds, as described above. After 5-6 days, excised limbs were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde/phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) at 4 C for 12 hours, washed in PBS at 4 C for 3 hours, and immersed in 10% and 20% sucrose PBS for 6 hours and overnight, respectively. Samples were embedded in O.C.T. compound (Miles), frozen in liquid nitrogen, and sectioned at 10μm using a cryostat (Leica). The QCPN monoclonal antibody (the Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank), a quail-specific antibody, was used for examining the distribution of grafted quail tissues. Dye injection. Administration of DiI (1,1-dioctadecyl-3,3,3,3 -tetramethyl indocarbocyanine perchlorate; Molecular Probes) and DiO (3,3 -dioctadecyloxacarbocyanine perchlorate; Molecular Probes) was performed as described previously (S5). Dye administration by pressure of expiration was performed using a pulled micropipette with an open tip. In order to determine the position and area injected with dye, dye-labeling was performed under a fluorescence microscope, and the labeled limb buds were photographed immediately after dye administration. The anterior-posterior position of the dye spot were calculated with the aid of a micrometer. At 5 6 days after the above process, operated limb buds were re-photographed. Whole-mount in situ hybridization. Mouse, chick, and gecko embryos were processed for whole mount in situ hybridization, as described respectively (S3, S6, S7). Riboprobes for chicken shh, fgf8, aggrecan1 (proteoglycan-h), gecko shh and fgf8, mouse shh and fgf8 were generated as described previously (S3, S5, S6, S7).
3 Supplementary figures Figure S1. Scheme of experimental procedures. (A-C) Swapping transplantation of the ZPA at stages 21/22 and 25. A single graft tissue from the center of the ZPA (the middle region of shh expression, region outlined in D F outside the posterior edge (yellow arrowheads) of the AER) was excised from a donor limb bud at each stage. The same region as that used for transplantation was also used for homotopic chimera analysis in Figure S2 (orange and blue-outlined cube). The two pink dots in D and E are the points for fate mapping of the region inside and outside the ZPA at stage 22 in Figure 2.
4 Figure S2. Chimera analysis for fate-mapping of stage 22 ZPA. (A-D, I, J) Chick forelimb buds 6 days after the central region of the ZPA homotopically replaced with quail tissue. (C, D) show details from (A, B) at higher magnification. Few cells can be seen in the cartilage of the posteriomost digit (asterisks), and the quail ZPA are seen scattered in connective tissue surrounding the cartilage (n=7). Another example of forelimb ZPA
5 chimera shows the contribution of ZPA cells in a small cartilage in the wrist (asterisks in I, J). (E-H) Hindlimb buds six days after the central region of the ZPA had been replaced with quail tissue. (G, H) show details from (E, F) at higher magnification. Metatarsi and phalanges (asterisks) of the posteriormost digit are composed of ZPA-derived cells (n=5). In summary, forelimb ZPA transplanted at stage 22 did not contribute to digit cartilage; the descendants of the ZPA cells were instead scattered in connective and dermal tissues in the posterior peripheral region of the forelimb autopod and zeugopod. Descendants of ZPA cells did however contribute to the formation of a small, rounded cartilage in the base of the forelimb autopod, which may represent a rudimentary P5-derived cartilage (fifth condensation of digit primordium shown at bottom panel in Fig. 4). In the hindlimb, the homotopic ZPA descendants generated the digit D4.
6 Figure S3. Fate maps based on labeling experiments at stage 20. (A, B, D, E) Independent specimens of DiI/DiO labeling of stage 20 forelimb (A, B) and hindlimb (D, E) buds. Relative position of the injected point is indicated to the left in (A, D). (A) Two points at 15.7% and 4.7% were labeled in this sample. The labeled cells at 15.7% contributed to digit D3, and cells at 4.7% were involved not in a digit but in the extreme periphery in (B). (C) Diagram of the fate of the posterior forelimb bud at stage 20. Points that contributed to digits D2 and D3 and posterior periphery (PP) are indicated by pink, orange, and blue circles, respectively. Black circles indicate the average position of each color (32.6% for pink (n=11), 17.7% for orange (n=15), and 6.6% for blue (n=26)). Yellow circles indicate the anterior margin of the shh-expression domain, and the average position is at 21.4% (n=12). (D) Two points at 12.3% and 3.4% are labeled in this sample. The labeled cells at 12.3% were involved in digit D4, and the labeled cells at 3.4% were distributed to the posterior periphery in (E). (F) shows a diagram of the fate of the posterior hindlimb bud at stage 20. Black circles indicate the average position of each color (36.2% for pink (n=12), 18.9% for orange (n=22), and 6.6% for blue (n=16)). Yellow circles indicate the anterior margin of the shh-expression domain, and its average position at 23.1% (n=12). Figure S4. Separation of digit 3 progenitor from the ZPA in the forelimb bud. Labeling of anterior and middle ZPA. (A, B) Forelimb bud. In this sample, a point at 17.5% (inside shh-expressing domain, see Fig. 3 and Fig. S3) was labeled at stage 20. After 18 hours, the labeled cells were seen outside the shh-expressing domain. (C, D) Hindlimb bud. In this sample, an anterior point inside the ZPA (at 21.6%) was labeled at stage 20. After 18 hours, the labeled cells were seen inside the shh-expressing domain. (E, F) Labeled cells at 15.5% of stage 20 forelimb bud (E) were located outside the shh-expressing domain after 18 hours (F). Labeling of posterior ZPA is shown in Fig. 3, C and F.
7 Figure S5. Overlapping zone of the ZPA and the AER. All images are magnified, and focused on the posterior distal region of developing limb buds. (A-C) Chick forelimb buds. (D F) Chick hindlimb bud. Stage 22 (A, D). Stage 24 (B, E). Stage 26 (C, F). (G I) Mouse forelimb buds. E10.5 (G). E11 (H). E11.5 (I). (J-L) Gecko forelimb buds. 6 days postoviposition (dpo) (J). 9 dpo (K). 12 dpo (L). These mouse and gecko limb buds morphologically correspond to chick stage 22, 24, and 26 limb buds. Note that the domain of overlap between the AER and the ZPA (distance between arrowhead and red dot) is correlated with digit numbers of chick forelimb (three digits), chick hindlimb (four digits), and mouse/gecko forelimbs (five digits). The early reduction of the overlap
8 in the chick forelimb might be involved in heterochronic shift of digit anlagen. Red dots show the anterior margin of the shh-expression domain. Arrowheads show the posterior edge of the fgf8-expression domain. Scale bar, 100 μm. Figure S6. Artificial posteriormost digit reallocated on the primary axis. (A) Image representation of posterior removal of a stage 22/23 hindlimb bud. Red broken arrows indicate approximate position of tissue removal (ZPA and the AER being visualized by shh and fgf8expression). (B) A sample resulting from the removal in (A). Only the anterior two digits (D1 and D2) form (n=8/10). (C) Mesenchymal condensation after posterior removal, visualized by expression of aggrecan 1. The second digit (digit D2) is located on the primary axis (yellow arrow). (D) Hindlimb of contralateral side of (C) as a control, showing the fourth digit (digit D4) located on the primary axis (yellow arrow). Ti, Tibia. Fi, Fibula. Similar results have also been obtained with Cyclopamine inhibition of Shh signaling (S8)
9 Figure S7. Contributions of fore- and hindlimb ZPAs to duplicated digit cartilage. Some typical examples are shown in Fig. 1. (A) Table showing donor-type digit in forelimb-hindlimb transplantation of the ZPA. (B) A specimen of forelimb ZPA to
10 hindlimb, which has a small forelimb digit-like digit (arrowheads). This sample is categorized in with a forelimb digit. (C) A specimen of forelimb ZPA to hindlimb, which has a small unidentified digit (arrowheads). This sample is categorized in with an unidentified digit. (D) A specimen of hindlimb ZPA to forelimb, which has an extra-segment at the distal tip of the anteriormost digit (arrowheads). This digit may represent the hindlimb digit, but it is vague. Therefore, this sample is categorized in only forelimb digits. Supplemental References S1. V. Hamburger, H. L. Hamilton, J. Morphol. 88, 49 (1951). S2. S. J. Ainsworth, R. L. Stanley, D. J. Evans, J. Anat. 216, 3 (2010). S3. M. Noro et al., Dev. Dyn. 238, 100 (2009). S4. K. Theiler, The house mouse. Atlas of embryonic development (Springer-Verlag, New York, 1989). S5. K. Sato et al., Development 134, 1397 (2007). S6. S. Yonei-Tamura et al., Dev. Biol. 211, 133 (1999). S7. S. Yonei-Tamura et al., Evol. & Dev. 10, 737 (2008). S8. A. O. Vargas, G. P.Wagner, Evol. & Dev. 11, 163 (2009).
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Preaxial dominance during salamander limb development. Panel (a, b) shows RNA in situ hybridisation on whole-mount limbs with Sox9 sense probe as a control. Note the absence of reactivity
Supplementary Figure 1 Preaxial dominance during salamander limb development. Panel (a, b) shows RNA in situ hybridisation on whole-mount limbs with Sox9 sense probe as a control. Note the absence of reactivity
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 a before amputation regeneration regenerated limb DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS developmental origin: lateral plate mesoderm presomitic mesoderm
a before amputation regeneration regenerated limb DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS DERMIS SKELETON MUSCLE SCHWANN CELLS EPIDERMIS developmental origin: lateral plate mesoderm presomitic mesoderm
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Ihh interacts preferentially with its upstream neighboring gene Nhej1. Genes are indicated by gray lines, and Ihh and Nhej1 are highlighted in blue. 4C seq performed in E14.5 limbs
Supplementary Figure 1 Ihh interacts preferentially with its upstream neighboring gene Nhej1. Genes are indicated by gray lines, and Ihh and Nhej1 are highlighted in blue. 4C seq performed in E14.5 limbs
7.22 Example Problems for Exam 1 The exam will be of this format. It will consist of 2-3 sets scenarios.
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Biology 7.22, Fall 2005 - Developmental Biology Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor Martha Constantine-Paton 1 of 10 7.22 Fall 2005 sample exam
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Biology 7.22, Fall 2005 - Developmental Biology Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor Martha Constantine-Paton 1 of 10 7.22 Fall 2005 sample exam
Stimulation of division in mouse 3T3 cells by coculture with embryonic chick limb tissue
 J. Embryol. exp. Morph. 86, 219-226 (1985) 219 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1985 Stimulation of division in mouse 3T3 cells by coculture with embryonic chick limb tissue K.
J. Embryol. exp. Morph. 86, 219-226 (1985) 219 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1985 Stimulation of division in mouse 3T3 cells by coculture with embryonic chick limb tissue K.
Later Development. Caenorhabditis elegans. Later Processes 10/06/12. Cytoplasmic Determinants Fate Mapping & Cell Fate Limb Development
 Later Development Cytoplasmic Determinants Fate Mapping & Cell Fate Limb Development Caenorhabditis elegans Nematoda 10,000 worms/petri dish in cultivation short life cycle (~ 3 days egg to egg) wild-type
Later Development Cytoplasmic Determinants Fate Mapping & Cell Fate Limb Development Caenorhabditis elegans Nematoda 10,000 worms/petri dish in cultivation short life cycle (~ 3 days egg to egg) wild-type
Modeling Periodic Aspect of Limb Pattern Formation
 Forum Forma, 27, S33 S37, 2012 Takashi Miura Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology, Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, Yoshida Konoe-cho, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto 606-8501, Japan E-mail address:
Forum Forma, 27, S33 S37, 2012 Takashi Miura Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology, Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, Yoshida Konoe-cho, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto 606-8501, Japan E-mail address:
ANAT2341 Embryology Introduction: Steve Palmer
 ANAT2341 Embryology Introduction: Steve Palmer Course overview Course lecturers specializations and roles Steve Palmer 9385 2957 Course overview Summary, aims and expected outcomes Course overview Graduate
ANAT2341 Embryology Introduction: Steve Palmer Course overview Course lecturers specializations and roles Steve Palmer 9385 2957 Course overview Summary, aims and expected outcomes Course overview Graduate
mrna IN SITU HYBRIDIZATION For Sectioned Zebrafish
 DAYS 1 2: Harvesting fish, tissue fixation, hybridization 1. Harvest and fix embryos in 4% paraformaldehyde overnight at 4C *Fix should be made fresh on the day it will be used. Do not store it for long
DAYS 1 2: Harvesting fish, tissue fixation, hybridization 1. Harvest and fix embryos in 4% paraformaldehyde overnight at 4C *Fix should be made fresh on the day it will be used. Do not store it for long
Supporting Online Material. Methods
 Supporting Online Material Methods Cell culture Cells were prepared from muscle tissue by enzymatic dissociation as previously described. Cells were plated on gelatin coated dishes in a 1:1mixture (v/v)
Supporting Online Material Methods Cell culture Cells were prepared from muscle tissue by enzymatic dissociation as previously described. Cells were plated on gelatin coated dishes in a 1:1mixture (v/v)
Distribution of polarizing activity and potential for limb formation in mouse and chick embryos and possible relationships to polydactyly
 Development 127, 4011-4021 (2000) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2000 DEV2573 4011 Distribution of polarizing activity and potential for limb formation in mouse and chick embryos
Development 127, 4011-4021 (2000) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 2000 DEV2573 4011 Distribution of polarizing activity and potential for limb formation in mouse and chick embryos
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full//59/ra7/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Dok-7 ctivates the Muscle Receptor Kinase MuSK and Shapes Synapse Formation kane Inoue, Kiyoko Setoguchi, Yosuke Matsubara,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full//59/ra7/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Dok-7 ctivates the Muscle Receptor Kinase MuSK and Shapes Synapse Formation kane Inoue, Kiyoko Setoguchi, Yosuke Matsubara,
LETTERS. Genetic evidence that FGFs have an instructive role in limb proximal distal patterning
 Vol 453 15 May 2008 doi:10.1038/nature06876 LETTERS Genetic evidence that FGFs have an instructive role in limb proximal distal patterning Francesca V. Mariani 1 *{, Christina P. Ahn 1 * & Gail R. Martin
Vol 453 15 May 2008 doi:10.1038/nature06876 LETTERS Genetic evidence that FGFs have an instructive role in limb proximal distal patterning Francesca V. Mariani 1 *{, Christina P. Ahn 1 * & Gail R. Martin
Pathogenesis of Limb Malformations in Mice Induced by Methoxyacetic Acid
 Hiroshima J. Med. Sci. Vol.40, No.3, 101-107, September, 1991 HIJM 40-18 101 Pathogenesis of Limb Malformations in Mice Induced by Methoxyacetic Acid Chairuddin RASJAD, Keisuke YAMASHITA, Abdul Razak DATU
Hiroshima J. Med. Sci. Vol.40, No.3, 101-107, September, 1991 HIJM 40-18 101 Pathogenesis of Limb Malformations in Mice Induced by Methoxyacetic Acid Chairuddin RASJAD, Keisuke YAMASHITA, Abdul Razak DATU
Introduction to histology and its methods of study
 Introduction to histology and its methods of study Li shulei lishulei@tom.com Department of Histology & Embryology 1 What is histology Definition Cell: smallest units functions in the human body Tissue
Introduction to histology and its methods of study Li shulei lishulei@tom.com Department of Histology & Embryology 1 What is histology Definition Cell: smallest units functions in the human body Tissue
Immunofluorescence Staining Protocol for 3 Well Chamber, removable
 Immunofluorescence Staining Protocol for 3 Well Chamber, removable This Application Note presents a simple protocol for the cultivation, fixation, and staining of cells using the 3 Well Chamber, removable.
Immunofluorescence Staining Protocol for 3 Well Chamber, removable This Application Note presents a simple protocol for the cultivation, fixation, and staining of cells using the 3 Well Chamber, removable.
Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization (FISH) Assay
 Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization (FISH) Assay 1 What is FISH 2 Probes 3 FISH Procedure 4 Application Definition, Principle and Sample Types The core of FISH technology A quick and simple FISH protocol
Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization (FISH) Assay 1 What is FISH 2 Probes 3 FISH Procedure 4 Application Definition, Principle and Sample Types The core of FISH technology A quick and simple FISH protocol
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/327/5969/1126/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Nodule-Specific Protein Secretory Pathway Required for Nitrogen- Fixing Symbiosis Dong Wang, Joel Griffitts, Colby
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/327/5969/1126/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Nodule-Specific Protein Secretory Pathway Required for Nitrogen- Fixing Symbiosis Dong Wang, Joel Griffitts, Colby
Materials and Methods Materials Required for Fixing, Embedding and Sectioning. OCT embedding matrix (Thermo Scientific, LAMB/OCT)
 Page 1 Introduction Tissue freezing and sectioning is a rapid method of generating tissue samples (cryosections) for histological analysis, and obviates the need for wax embedding. The method is popular
Page 1 Introduction Tissue freezing and sectioning is a rapid method of generating tissue samples (cryosections) for histological analysis, and obviates the need for wax embedding. The method is popular
Quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis of the expression levels of E-cadherin
 Supplementary Information 1 Quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis of the expression levels of E-cadherin and ribosomal protein L19 (RPL19) mrna in cleft and bud epithelial cells of embryonic salivary
Supplementary Information 1 Quantitative real-time RT-PCR analysis of the expression levels of E-cadherin and ribosomal protein L19 (RPL19) mrna in cleft and bud epithelial cells of embryonic salivary
A collection of 31 splenic specimens from patients (42.4±17.7 years old) with ITP
 Supplemental Materials & Methods Patients and patient samples. A collection of 31 splenic specimens from patients (42.4±17.7 years old) with ITP requiring splenectomy and 36 splenic specimens obtained
Supplemental Materials & Methods Patients and patient samples. A collection of 31 splenic specimens from patients (42.4±17.7 years old) with ITP requiring splenectomy and 36 splenic specimens obtained
ab BrdU Immunohistochemistry Kit
 ab125306 - BrdU Immunohistochemistry Kit Instructions for Use For the detection and localization of bromodeoxyuridine incorporated into newly synthesized DNA of actively proliferating cells. This product
ab125306 - BrdU Immunohistochemistry Kit Instructions for Use For the detection and localization of bromodeoxyuridine incorporated into newly synthesized DNA of actively proliferating cells. This product
Supplement Figure S1:
 Supplement Figure S1: A, Sequence of Xcadherin-11 Morpholino 1 (Xcad-11MO) and 2 (Xcad-11 MO2) and control morpholino in comparison to the Xcadherin-11 sequence. The Xcad-11MO binding sequence spans the
Supplement Figure S1: A, Sequence of Xcadherin-11 Morpholino 1 (Xcad-11MO) and 2 (Xcad-11 MO2) and control morpholino in comparison to the Xcadherin-11 sequence. The Xcad-11MO binding sequence spans the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Transcriptional output transiently spikes upon mitotic exit
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Transcriptional output transiently spikes upon mitotic exit Viola Vaňková Hausnerová 1, 2, Christian Lanctôt 1* 1 BIOCEV and Department of Cell Biology, Faculty of Science, Charles
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Transcriptional output transiently spikes upon mitotic exit Viola Vaňková Hausnerová 1, 2, Christian Lanctôt 1* 1 BIOCEV and Department of Cell Biology, Faculty of Science, Charles
Cycles of vascular plexus formation within the nephrogenic zone of the developing mouse kidney
 1 Supplementary text and data for: 2 3 4 5 Cycles of vascular plexus formation within the nephrogenic zone of the developing mouse kidney Authors: David A. D. Munro 1*, Peter Hohenstein 2, and Jamie A.
1 Supplementary text and data for: 2 3 4 5 Cycles of vascular plexus formation within the nephrogenic zone of the developing mouse kidney Authors: David A. D. Munro 1*, Peter Hohenstein 2, and Jamie A.
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Tissue Preparation and Microscopy. General Concepts. Chemical Fixation CHAPTER 1
 CHAPTER 1 Tissue Preparation and Microscopy General Concepts I. Biological tissues must undergo a series of treatments to be observed with light and electron microscopes. The process begins by stabilization
CHAPTER 1 Tissue Preparation and Microscopy General Concepts I. Biological tissues must undergo a series of treatments to be observed with light and electron microscopes. The process begins by stabilization
Figure legends for supplement
 Figure legends for supplement Supplemental Figure 1 Characterization of purified and recombinant proteins Relevant fractions related the final stage of the purification protocol(bingham et al., 1998; Toba
Figure legends for supplement Supplemental Figure 1 Characterization of purified and recombinant proteins Relevant fractions related the final stage of the purification protocol(bingham et al., 1998; Toba
Figure S1. Related to Figure 1, to show 3-D images of nerve/vessel patterning.
 Supplemental Information Inventory of Supplemental Information Figure S1. Related to Figure 1, to show 3-D images of nerve/vessel patterning. Figure S2. Related to Figure 4, to validate Npn-1 signaling
Supplemental Information Inventory of Supplemental Information Figure S1. Related to Figure 1, to show 3-D images of nerve/vessel patterning. Figure S2. Related to Figure 4, to validate Npn-1 signaling
Hydroxystilbamidine Protocol
 ab138870 Hydroxystilbamidine Protocol Instructions for Use Staining of DNA and RNA in cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. 1 Table of Contents 1. Biological
ab138870 Hydroxystilbamidine Protocol Instructions for Use Staining of DNA and RNA in cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. 1 Table of Contents 1. Biological
Supplementary Figure 1. Espn-1 knockout characterization. (a) The predicted recombinant Espn-1 -/- allele was detected by PCR of the left (5 )
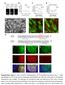 Supplementary Figure 1. Espn-1 knockout characterization. (a) The predicted recombinant Espn-1 -/- allele was detected by PCR of the left (5 ) homologous recombination arm (left) and of the right (3 )
Supplementary Figure 1. Espn-1 knockout characterization. (a) The predicted recombinant Espn-1 -/- allele was detected by PCR of the left (5 ) homologous recombination arm (left) and of the right (3 )
Retroviral Gene Transduction in Limb Bud Micromass Cultures
 Retroviral Gene Transduction 509 48 Retroviral Gene Transduction in Limb Bud Micromass Cultures N. Susan Stott and Cheng-Ming Chuong 1. Introduction Since Solursh and his coworkers set up the limb bud
Retroviral Gene Transduction 509 48 Retroviral Gene Transduction in Limb Bud Micromass Cultures N. Susan Stott and Cheng-Ming Chuong 1. Introduction Since Solursh and his coworkers set up the limb bud
Introduction to Histology
 Introduction to Histology The name "Histology" is derived from the Greek word for a tissue "Histos", and "-logos" = the study of It is tightly bounded to molecular biology, genetics, immunology and other
Introduction to Histology The name "Histology" is derived from the Greek word for a tissue "Histos", and "-logos" = the study of It is tightly bounded to molecular biology, genetics, immunology and other
Figure S1. Phenotypic characterization of AND-1_WASKO cell lines. AND- 1_WASKO_C1.1 (WASKO_C1.1) and AND-1_WASKO_C1.2 (WASKO_C1.
 LEGENDS TO SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Phenotypic characterization of AND-1_WASKO cell lines. AND- 1_WASKO_C1.1 (WASKO_C1.1) and AND-1_WASKO_C1.2 (WASKO_C1.2) were stained with the antibodies oct3/4
LEGENDS TO SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Phenotypic characterization of AND-1_WASKO cell lines. AND- 1_WASKO_C1.1 (WASKO_C1.1) and AND-1_WASKO_C1.2 (WASKO_C1.2) were stained with the antibodies oct3/4
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. In vitro determination of the detection limit of vanco-800cw (a) Specificity of vanco-800cw for different clinical bacterial isolates. The in vitro imaging
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. In vitro determination of the detection limit of vanco-800cw (a) Specificity of vanco-800cw for different clinical bacterial isolates. The in vitro imaging
We are walking and standing with parts of our bodies which could have been used for thinking had they developed in another part of the embryo.
 We are walking and standing with parts of our bodies which could have been used for thinking had they developed in another part of the embryo. Hans Spemann, 1943 Reading from Chapter 3 - types of cell
We are walking and standing with parts of our bodies which could have been used for thinking had they developed in another part of the embryo. Hans Spemann, 1943 Reading from Chapter 3 - types of cell
PREPARATION OF HISTOLOGICAL SPECIMENS
 PREPARATION OF HISTOLOGICAL SPECIMENS Histo-techniques Preparation of tissue for microscopic examination Series of processes Ultimate aim to make tissue visible as it is Pathology Vs Anatomy Steps vary
PREPARATION OF HISTOLOGICAL SPECIMENS Histo-techniques Preparation of tissue for microscopic examination Series of processes Ultimate aim to make tissue visible as it is Pathology Vs Anatomy Steps vary
Fluorescent in-situ Hybridization
 Fluorescent in-situ Hybridization Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 Definition In situ hybridization is the method of localizing/ detecting specific nucleotide sequences in morphologically preserved
Fluorescent in-situ Hybridization Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 Definition In situ hybridization is the method of localizing/ detecting specific nucleotide sequences in morphologically preserved
Frozen tissue section
 IHC Protocol - Frozen Tissue Author : Dan Souw Immunohistochemistry on Frozen tissues IHC Protocol - Frozen Tissue: An introduction This is the second post in a series on immunohistochemistry (IHC). The
IHC Protocol - Frozen Tissue Author : Dan Souw Immunohistochemistry on Frozen tissues IHC Protocol - Frozen Tissue: An introduction This is the second post in a series on immunohistochemistry (IHC). The
BrdU Immunohistochemistry Kit Instruction Manual
 BrdU Immunohistochemistry Kit Instruction Manual Features Easy to use system Reagents titered for success Proven protocol Ordering Information Catalog Number X1545K Size 50 Slides Format Immunohistochemistry
BrdU Immunohistochemistry Kit Instruction Manual Features Easy to use system Reagents titered for success Proven protocol Ordering Information Catalog Number X1545K Size 50 Slides Format Immunohistochemistry
Preparation of tissues for study
 Preparation of tissues for study HISTOLOGY : It is the branch of science which deals with the microscopic study of normal tissue HISTOPATHOLOGY : It is the branch of science which deals with the microscopic
Preparation of tissues for study HISTOLOGY : It is the branch of science which deals with the microscopic study of normal tissue HISTOPATHOLOGY : It is the branch of science which deals with the microscopic
BMP-2 and BMP-4 signalling in the developing spinal cord of human and rat embryos
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 74, No. 3, pp. 359 364 DOI: 10.5603/FM.2015.0054 Copyright 2015 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl BMP-2 and BMP-4 signalling in the developing
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 74, No. 3, pp. 359 364 DOI: 10.5603/FM.2015.0054 Copyright 2015 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl BMP-2 and BMP-4 signalling in the developing
BrdU IHC Kit. For the detection and localization of bromodeoxyuridine incorporated into newly synthesized DNA of actively proliferating cells
 K-ASSAY BrdU IHC Kit For the detection and localization of bromodeoxyuridine incorporated into newly synthesized DNA of actively proliferating cells Cat. No. KT-077 For Research Use Only. Not for Use in
K-ASSAY BrdU IHC Kit For the detection and localization of bromodeoxyuridine incorporated into newly synthesized DNA of actively proliferating cells Cat. No. KT-077 For Research Use Only. Not for Use in
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplemental Methods:
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Methods: Immunoprecipitation- As we described but with some modifications [22]. As part of another ongoing project, lysate from human umbilical vein endothelial cells
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Methods: Immunoprecipitation- As we described but with some modifications [22]. As part of another ongoing project, lysate from human umbilical vein endothelial cells
genotyped by PCR (Supplemental Figure 1 for primer locations and Supplemental
 Supplemental methods: Generation of Slc13a4 KOF/KOF mice and genotyping Heterozygous Slc13a4 +/KOF C57BL6/J mice were interbred to generate Slc13a4 KOF/KOF, Slc13a4 +/KOF and Slc13a4 +/+ embryos for analysis.
Supplemental methods: Generation of Slc13a4 KOF/KOF mice and genotyping Heterozygous Slc13a4 +/KOF C57BL6/J mice were interbred to generate Slc13a4 KOF/KOF, Slc13a4 +/KOF and Slc13a4 +/+ embryos for analysis.
We are walking and standing with parts of our bodies which could have been used for thinking had they developed in another part of the embryo.
 We are walking and standing with parts of our bodies which could have been used for thinking had they developed in another part of the embryo. Hans Spemann, 1943 Reading from Chapter 3 - types of cell
We are walking and standing with parts of our bodies which could have been used for thinking had they developed in another part of the embryo. Hans Spemann, 1943 Reading from Chapter 3 - types of cell
Nature Medicine doi: /nm.2548
 Supplementary Table 1: Genotypes of offspring and embryos from matings of Pmm2 WT/F118L mice with Pmm2 WT/R137H mice total events Pmm2 WT/WT Pmm2 WT/R137H Pmm2 WT/F118L Pmm2 R137H/F118L offspring 117 (100%)
Supplementary Table 1: Genotypes of offspring and embryos from matings of Pmm2 WT/F118L mice with Pmm2 WT/R137H mice total events Pmm2 WT/WT Pmm2 WT/R137H Pmm2 WT/F118L Pmm2 R137H/F118L offspring 117 (100%)
Germline chimeric chickens from dispersed donor blastodermal cells and compromised recipient embryos
 Development 117, 669-675 (1993) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1993 669 Germline chimeric chickens from dispersed donor blastodermal cells and compromised recipient embryos
Development 117, 669-675 (1993) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1993 669 Germline chimeric chickens from dispersed donor blastodermal cells and compromised recipient embryos
Functions of FGF signalling from the apical ectodermal ridge in limb development
 Functions of FGF signalling from the apical ectodermal ridge in limb development Xin Sun*, Francesca V. Mariani & Gail R. Martin Department of Anatomy and Program in Developmental Biology, School of Medicine,
Functions of FGF signalling from the apical ectodermal ridge in limb development Xin Sun*, Francesca V. Mariani & Gail R. Martin Department of Anatomy and Program in Developmental Biology, School of Medicine,
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Wossidlo et al. S1 Supplementary Figure S1 5hmC (clone 63.3) immunostaining on mouse zygotes. a, Representative images of indirect immunostainings using antibodies against 5hmC (clone
Supplementary Figures Wossidlo et al. S1 Supplementary Figure S1 5hmC (clone 63.3) immunostaining on mouse zygotes. a, Representative images of indirect immunostainings using antibodies against 5hmC (clone
Chapter 10: Classification of Microorganisms
 Chapter 10: Classification of Microorganisms 1. The Taxonomic Hierarchy 2. Methods of Identification 1. The Taxonomic Hierarchy Phylogenetic Tree of the 3 Domains Taxonomic Hierarchy 8 successive taxa
Chapter 10: Classification of Microorganisms 1. The Taxonomic Hierarchy 2. Methods of Identification 1. The Taxonomic Hierarchy Phylogenetic Tree of the 3 Domains Taxonomic Hierarchy 8 successive taxa
HistoMark Double Staining Procedures. Where Better Science Begins.
 HistoMark Double Staining Procedures Where Better Science Begins www.kpl.com HistoMark Double Staining Procedures Researchers often need the ability to visualize multiple proteins in one tissue sample.
HistoMark Double Staining Procedures Where Better Science Begins www.kpl.com HistoMark Double Staining Procedures Researchers often need the ability to visualize multiple proteins in one tissue sample.
Positional information in the forelimb of the axolotl: properties of the posterior skin
 /. Embryol. exp. Morph. 73, 233-247, 1983 233 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1983 Positional information in the forelimb of the axolotl: properties of the posterior skin By
/. Embryol. exp. Morph. 73, 233-247, 1983 233 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1983 Positional information in the forelimb of the axolotl: properties of the posterior skin By
Supplemental Information. Zika Virus Can Strongly Infect and Disrupt. Secondary Organizers in the Ventricular. Zone of the Embryonic Chicken Brain
 Cell Reports, Volume 23 Supplemental Information Zika Virus Can Strongly Infect and Disrupt Secondary Organizers in the Ventricular Zone of the Embryonic Chicken Brain Ankita Thawani, Devika Sirohi, Richard
Cell Reports, Volume 23 Supplemental Information Zika Virus Can Strongly Infect and Disrupt Secondary Organizers in the Ventricular Zone of the Embryonic Chicken Brain Ankita Thawani, Devika Sirohi, Richard
Research Methodology; UNSTAINED Formalin Fixed Paraffin Embedded tissue sections with
 COLLEGE OF AMERICAN Methodology and Controls: Research Methodology; UNSTAINED Formalin Fixed Paraffin Embedded tissue sections with Page 1 FISH method DNA Probe in Situ Hybridization [ FISH] of peripheral
COLLEGE OF AMERICAN Methodology and Controls: Research Methodology; UNSTAINED Formalin Fixed Paraffin Embedded tissue sections with Page 1 FISH method DNA Probe in Situ Hybridization [ FISH] of peripheral
Note that steps 1-16 are identical to steps 1-16 in the immunostaining protocol, except 0.5X PBtween is used in this protocol rather than 0.5X PBT.
 Embryo In-situ Hybridization: This protocol is based closely on an immunostaining protocol for Hypsibius dujardini (Gabriel and Goldstein 2007) and available in-situ protocols for both insects (Tomoysu
Embryo In-situ Hybridization: This protocol is based closely on an immunostaining protocol for Hypsibius dujardini (Gabriel and Goldstein 2007) and available in-situ protocols for both insects (Tomoysu
Segments of the obstructed intestinal loops were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde
 Supplementary text Supplementary materials and methods Histopathological examination Segments of the obstructed intestinal loops were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) and embedded in paraffin wax with
Supplementary text Supplementary materials and methods Histopathological examination Segments of the obstructed intestinal loops were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) and embedded in paraffin wax with
Understanding embryonic head development. ANAT2341 Tennille Sibbritt Embryology Unit Children s Medical Research Institute
 Understanding embryonic head development ANAT2341 Tennille Sibbritt Embryology Unit Children s Medical Research Institute Head malformations among the most common category of congenital malformations in
Understanding embryonic head development ANAT2341 Tennille Sibbritt Embryology Unit Children s Medical Research Institute Head malformations among the most common category of congenital malformations in
Supplementary figures (Zhang)
 Supplementary figures (Zhang) Supplementary figure 1. Characterization of hesc-derived astroglia. (a) Treatment of astroglia with LIF and CNTF increases the proportion of GFAP+ cells, whereas the percentage
Supplementary figures (Zhang) Supplementary figure 1. Characterization of hesc-derived astroglia. (a) Treatment of astroglia with LIF and CNTF increases the proportion of GFAP+ cells, whereas the percentage
Supplementary Methods. Li J.-Y. et al. Lewy bodies in grafted neurons in Parkinson s patients suggest host to. graft disease propagation
 1 Supplementary Methods Li J.-Y. et al. Lewy bodies in grafted neurons in Parkinson s patients suggest host to graft disease propagation Neural transplantation and clinical assessment Detailed information
1 Supplementary Methods Li J.-Y. et al. Lewy bodies in grafted neurons in Parkinson s patients suggest host to graft disease propagation Neural transplantation and clinical assessment Detailed information
Cartilage Staining Kit (Chondrocyte and Cartilage Tissue Staining Kit)
 Cat. # MK310 For Research Use Cartilage Staining Kit (Chondrocyte and Cartilage Tissue Staining Kit) Product Manual v201009 Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Kit Components... 3 III. Materials
Cat. # MK310 For Research Use Cartilage Staining Kit (Chondrocyte and Cartilage Tissue Staining Kit) Product Manual v201009 Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Kit Components... 3 III. Materials
Figure S1 is related to Figure 1B, showing more details of outer segment of
 Supplemental Information Supplementary Figure legends and Figures Figure S1. Electron microscopic images in Sema4A +/+ and Sema4A / retinas Figure S1 is related to Figure 1B, showing more details of outer
Supplemental Information Supplementary Figure legends and Figures Figure S1. Electron microscopic images in Sema4A +/+ and Sema4A / retinas Figure S1 is related to Figure 1B, showing more details of outer
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 3. Supplememtary Note 3, Wehr et al., Monitoring Regulated Protein-Protein Interactions Using Split-TEV 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 3 Fluorescent Proteolysis-only TEV-Reporters We generated TEV reporter that allow visualizing TEV activity at the membrane and in the cytosol of living cells not relying on the addition
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTE 3 Fluorescent Proteolysis-only TEV-Reporters We generated TEV reporter that allow visualizing TEV activity at the membrane and in the cytosol of living cells not relying on the addition
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Rodríguez-Fraticelli et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201203075/dc1 Figure S1. Cell spreading and lumen formation in confined
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Rodríguez-Fraticelli et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201203075/dc1 Figure S1. Cell spreading and lumen formation in confined
Methods Western blot analysis of plg Quantification of plasminogen accumulation by ELISA Immunohistochemical analysis
 Methods Western blot analysis of plg Wild-type mice first received a standardized burn wound and then were intravenously administered 2 mg of human plg (Omnio AB, Umeå, Sweden). 24 hours after wounding
Methods Western blot analysis of plg Wild-type mice first received a standardized burn wound and then were intravenously administered 2 mg of human plg (Omnio AB, Umeå, Sweden). 24 hours after wounding
Supplementary Figure 1. Mouse genetic models used for identification of Axin2-
 Supplementary Figure 1. Mouse genetic models used for identification of Axin2- expressing cells and their derivatives. Schematic representations illustrate genetic cell labeling strategies to identify
Supplementary Figure 1. Mouse genetic models used for identification of Axin2- expressing cells and their derivatives. Schematic representations illustrate genetic cell labeling strategies to identify
Technical Note. Tissue Section Imaging. Published August The most recent version of this Technical Note is posted at licor.com/bio/support.
 Technical Note Tissue Section Imaging Published August 2017. The most recent version of this Technical Note is posted at licor.com/bio/support. Page 2 - Tissue Section Imaging Table of Contents Page I.
Technical Note Tissue Section Imaging Published August 2017. The most recent version of this Technical Note is posted at licor.com/bio/support. Page 2 - Tissue Section Imaging Table of Contents Page I.
Misexpression of Hoxa-13 induces cartilage homeotic transformation
 Misexpression of Hoxa-13 induces cartilage homeotic transformation and chan P es cell adhesiveness in chick imb buds Yuji ~okouchi,' Satoru ~akazato,' Masakazu ~amamoto,' Yoshihiro ~oto,' ~akashi ~ameda?
Misexpression of Hoxa-13 induces cartilage homeotic transformation and chan P es cell adhesiveness in chick imb buds Yuji ~okouchi,' Satoru ~akazato,' Masakazu ~amamoto,' Yoshihiro ~oto,' ~akashi ~ameda?
HD1 - Introduction to Human Development
 Human Development Ed Laufer, PhD Course Director elaufer@columbia.edu Ping Feng Course Administrator pf2013@columbia.edu Michael Shen, PhD Patricia Ducy, PhD Michael Gershon, MD Cathy Mendelsohn, PhD Richard
Human Development Ed Laufer, PhD Course Director elaufer@columbia.edu Ping Feng Course Administrator pf2013@columbia.edu Michael Shen, PhD Patricia Ducy, PhD Michael Gershon, MD Cathy Mendelsohn, PhD Richard
Characterization of Xenopus Digits and Regenerated Limbs of the Froglet
 DEVELOPMENTAL DYNAMICS 235:3316 3326, 2006 RESEARCH ARTICLE Characterization of Xenopus Digits and Regenerated Limbs of the Froglet Akira Satoh, Tetsuya Endo, Masahiro Abe, Nayuta Yakushiji, Shiro Ohgo,
DEVELOPMENTAL DYNAMICS 235:3316 3326, 2006 RESEARCH ARTICLE Characterization of Xenopus Digits and Regenerated Limbs of the Froglet Akira Satoh, Tetsuya Endo, Masahiro Abe, Nayuta Yakushiji, Shiro Ohgo,
BIO 315 Lab Exam I. Section #: Name:
 Section #: Name: Also provide this information on the computer grid sheet given to you. (Section # in special code box) BIO 315 Lab Exam I 1. In labeling the parts of a standard compound light microscope
Section #: Name: Also provide this information on the computer grid sheet given to you. (Section # in special code box) BIO 315 Lab Exam I 1. In labeling the parts of a standard compound light microscope
Supplementary Methods
 Caussinus and Gonzalez Supplementary Methods Mitotic clones Clones of NBs homozygous for numb 03235, mira ZZ176, pros 17 or apkc k06403 were generated by FLP/FRT mediated mitotic recombination (1). As
Caussinus and Gonzalez Supplementary Methods Mitotic clones Clones of NBs homozygous for numb 03235, mira ZZ176, pros 17 or apkc k06403 were generated by FLP/FRT mediated mitotic recombination (1). As
Supplementary Information. Isl2b regulates anterior second heart field development in zebrafish
 Supplementary Information Isl2b regulates anterior second heart field development in zebrafish Hagen R. Witzel 1, Sirisha Cheedipudi 1, Rui Gao 1, Didier Y.R. Stainier 2 and Gergana D. Dobreva 1,3* 1 Origin
Supplementary Information Isl2b regulates anterior second heart field development in zebrafish Hagen R. Witzel 1, Sirisha Cheedipudi 1, Rui Gao 1, Didier Y.R. Stainier 2 and Gergana D. Dobreva 1,3* 1 Origin
ab BrdU Immunohistochemistry Kit
 ab125306 - BrdU Immunohistochemistry Kit Instructions for Use For the detection and localization of bromodeoxyuridine incorporated into newly synthesized DNA of actively proliferating cells. This product
ab125306 - BrdU Immunohistochemistry Kit Instructions for Use For the detection and localization of bromodeoxyuridine incorporated into newly synthesized DNA of actively proliferating cells. This product
Assembly of Trunk and Limb Blood Vessels Involves Extensive Migration and Vasculogenesis of Somite-Derived Angioblasts
 Developmental Biology 234, 352 364 (2001) doi:10.1006/dbio.2001.0267, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Assembly of Trunk and Limb Blood Vessels Involves Extensive Migration and Vasculogenesis
Developmental Biology 234, 352 364 (2001) doi:10.1006/dbio.2001.0267, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Assembly of Trunk and Limb Blood Vessels Involves Extensive Migration and Vasculogenesis
7.22 Final Exam points
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Biology 7.22, Fall 2005 - Developmental Biology Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor Martha Constantine-Paton 1 of 11 7.22 2004 FINAL FOR STUDY
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Biology 7.22, Fall 2005 - Developmental Biology Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor Martha Constantine-Paton 1 of 11 7.22 2004 FINAL FOR STUDY
Results and discussion In one of eight transgenic lines carrying a random insertion of a Hoxb1/human placental alkaline phosphatase (HPAP)
 Brief Communication 97 Identification of Sonic hedgehog as a candidate gene responsible for the polydactylous mouse mutant Sasquatch James Sharpe*, Laura Lettice, Jacob Hecksher-Sørensen, Margaret Fox,
Brief Communication 97 Identification of Sonic hedgehog as a candidate gene responsible for the polydactylous mouse mutant Sasquatch James Sharpe*, Laura Lettice, Jacob Hecksher-Sørensen, Margaret Fox,
At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Barrier function assays At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in acidic X-gal mix (100 mm phosphate buffer at ph4.3, 3 mm
Supplementary Materials and Methods Barrier function assays At E17.5, the embryos were rinsed in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and immersed in acidic X-gal mix (100 mm phosphate buffer at ph4.3, 3 mm
Methodology for Immunohistochemistry. Learning Objectives:
 Proteomics Methodology for Immunohistochemistry Methodology for Immunohistochemistry A staining process for identifying the proteins location in cells, tissues by using antigen-antibody property. Immuno
Proteomics Methodology for Immunohistochemistry Methodology for Immunohistochemistry A staining process for identifying the proteins location in cells, tissues by using antigen-antibody property. Immuno
Figure legend. The expression of BAFF and its receptors in macrophages was detected at lesion areas of atherosclerosis and arthritis.
 Data supplement #1 Figure legend. The expression of BAFF and its receptors in macrophages was detected at lesion areas of atherosclerosis and arthritis. A. Consecutive sections of an atherosclerotic plaque
Data supplement #1 Figure legend. The expression of BAFF and its receptors in macrophages was detected at lesion areas of atherosclerosis and arthritis. A. Consecutive sections of an atherosclerotic plaque
Supplementary Figure 1. Botrocetin induces binding of human VWF to human
 Supplementary Figure 1: Supplementary Figure 1. Botrocetin induces binding of human VWF to human platelets in the absence of elevated shear and induces platelet agglutination as detected by flow cytometry.
Supplementary Figure 1: Supplementary Figure 1. Botrocetin induces binding of human VWF to human platelets in the absence of elevated shear and induces platelet agglutination as detected by flow cytometry.
Tbx genes and limb identity in chick embryo development
 Development 125, 1867-1875 (1998) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1998 DEV2258 1867 Tbx genes and limb identity in chick embryo development Alison Isaac 1, *, Concepción Rodriguez-Esteban
Development 125, 1867-1875 (1998) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1998 DEV2258 1867 Tbx genes and limb identity in chick embryo development Alison Isaac 1, *, Concepción Rodriguez-Esteban
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Wang et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201405026/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Generation and characterization of unc-40 alleles. (A and
Supplemental material Wang et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201405026/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Generation and characterization of unc-40 alleles. (A and
Histological preparation of embryonic and adult zebrafish eyes
 Histological preparation of embryonic and adult zebrafish eyes Richard J. Nuckels 1 and Jeffrey M. Gross 1,2,3 1 Section of Molecular Cell and Developmental Biology 2 Institute of Cell and Molecular Biology
Histological preparation of embryonic and adult zebrafish eyes Richard J. Nuckels 1 and Jeffrey M. Gross 1,2,3 1 Section of Molecular Cell and Developmental Biology 2 Institute of Cell and Molecular Biology
-RT RT RT -RT XBMPRII
 Base pairs 2000 1650 1000 850 600 500 400 Marker Primer set 1 Primer set 2 -RT RT RT -RT XBMPRII kda 100 75 50 37 25 20 XAC p-xac A 300 B Supplemental figure 1. PCR analysis of BMPRII expression and western
Base pairs 2000 1650 1000 850 600 500 400 Marker Primer set 1 Primer set 2 -RT RT RT -RT XBMPRII kda 100 75 50 37 25 20 XAC p-xac A 300 B Supplemental figure 1. PCR analysis of BMPRII expression and western
Technical Advancement
 INVITED ARTICLE Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 35 (5): 361 365, 2002 Technical Advancement Using Antisense Morpholino Oligos to Knockdown Gene Expression in the Chicken Embryo Richard P. Tucker 1 1 Department
INVITED ARTICLE Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 35 (5): 361 365, 2002 Technical Advancement Using Antisense Morpholino Oligos to Knockdown Gene Expression in the Chicken Embryo Richard P. Tucker 1 1 Department
Supplementary Information. Real-time imaging of oxidative and nitrosative stress in the liver of live animals for drug-toxicity testing
 Supplementary Information Real-time imaging of oxidative and nitrosative stress in the liver of live animals for drug-toxicity testing Adam J. Shuhendler 1*, Kanyi Pu 1*, Lina Cui 1, Jack P. Uetrecht &
Supplementary Information Real-time imaging of oxidative and nitrosative stress in the liver of live animals for drug-toxicity testing Adam J. Shuhendler 1*, Kanyi Pu 1*, Lina Cui 1, Jack P. Uetrecht &
Cell Lineage in the Development of the Leech Nervous System
 Cell Lineage in the Development of the Leech Nervous System DAVID A. WEISBLAT Department of Molecular Biology, University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720 (U.S.A) INTRODUCTION Knowledge of the lines of
Cell Lineage in the Development of the Leech Nervous System DAVID A. WEISBLAT Department of Molecular Biology, University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720 (U.S.A) INTRODUCTION Knowledge of the lines of
Immunohistochemistry guide
 Immunohistochemistry guide overview immunohistochemistry Overview Immunohistochemistry is a laboratory technique utilized for the visual detection of antigens in tissue. When working with cells this technique
Immunohistochemistry guide overview immunohistochemistry Overview Immunohistochemistry is a laboratory technique utilized for the visual detection of antigens in tissue. When working with cells this technique
+ + Development and Evolution Dorsoventral axis. Developmental Readout. Foundations. Stem cells. Organ formation.
 Development and Evolution 7.72 9.11.06 Dorsoventral axis Human issues Organ formation Stem cells Developmental Readout Axes Growth control Axon guidance 3D structure Analysis Model + + organisms Foundations
Development and Evolution 7.72 9.11.06 Dorsoventral axis Human issues Organ formation Stem cells Developmental Readout Axes Growth control Axon guidance 3D structure Analysis Model + + organisms Foundations
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Chakrabarty et al. 10.1073/pnas.1018001108 SI Materials and Methods Cell Lines. All cell lines were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection. Media and FBS were purchased
Supporting Information Chakrabarty et al. 10.1073/pnas.1018001108 SI Materials and Methods Cell Lines. All cell lines were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection. Media and FBS were purchased
Supplementary Data. Supplementary Methods Three-step protocol for spontaneous differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem (embryonic stem) cells
 Supplementary Data Supplementary Methods Three-step protocol for spontaneous differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem (embryonic stem) cells Mouse induced pluripotent stem cells (ipscs) were cultured
Supplementary Data Supplementary Methods Three-step protocol for spontaneous differentiation of mouse induced pluripotent stem (embryonic stem) cells Mouse induced pluripotent stem cells (ipscs) were cultured
Multiple abnormalities due to a nonsense mutation in the Alx4 gene
 Multiple abnormalities due to a nonsense mutation in the Alx4 gene B. Chen 1 *, Lu Chen 2 *, Y. Zhou 3 *, T. Mi 1, D.Y. Chen 1, Li Chen 1, J. Yin 1 and Z.F. Xue 1 1 Comparative Medicine Center, Yangzhou
Multiple abnormalities due to a nonsense mutation in the Alx4 gene B. Chen 1 *, Lu Chen 2 *, Y. Zhou 3 *, T. Mi 1, D.Y. Chen 1, Li Chen 1, J. Yin 1 and Z.F. Xue 1 1 Comparative Medicine Center, Yangzhou
Xenopus gastrulation. Dorsal-Ventral Patterning - The Spemann Organizer. Two mesoderm inducing signals
 Dorsal- atterning - The Spemann Organizer Two mesoderm inducing signals late-blastula early-gastrula nimal Blood Mesothelium Not Vegetal NC Endoderm Hans Spemann (1869-1941) Hilde Mangold (1898-1924) Dr
Dorsal- atterning - The Spemann Organizer Two mesoderm inducing signals late-blastula early-gastrula nimal Blood Mesothelium Not Vegetal NC Endoderm Hans Spemann (1869-1941) Hilde Mangold (1898-1924) Dr
Histology FISH Accessory Kit Step-by-Step Procedure
 PROCEDURE Histology FISH Accessory Kit Step-by-Step Procedure Code K5799 For probes diluted in Formamide based hybridization buffer Reagent Preparation Equilibration Deparaffinization/Rehydration Prepare
PROCEDURE Histology FISH Accessory Kit Step-by-Step Procedure Code K5799 For probes diluted in Formamide based hybridization buffer Reagent Preparation Equilibration Deparaffinization/Rehydration Prepare
Mice TRAMP mice were maintained in a C57BL/6J background. Syngeneic UBI-GFP/BL6 mice were used for bone marrow engraftment. 2
 Antibodies Chicken IgY polyclonal α-gfp antibodies were purchased from Abcam (Cambridge, MA) and were detected using α-chicken IgY-FITC or α-chicken-hrp (also purchased from Abcam). The CD31-PE, CD11b-PE,
Antibodies Chicken IgY polyclonal α-gfp antibodies were purchased from Abcam (Cambridge, MA) and were detected using α-chicken IgY-FITC or α-chicken-hrp (also purchased from Abcam). The CD31-PE, CD11b-PE,
Kazuki N. Sugahara, Tambet Teesalu, Priya Prakash Karmali, Venkata Ramana Kotamraju, Lilach
 Cancer Cell, Volume 16 Supplemental Data Tissue-Penetrating Delivery of Compounds and Nanoparticles into Tumors Kazuki N. Sugahara, Tambet Teesalu, Priya Prakash Karmali, Venkata Ramana Kotamraju, Lilach
Cancer Cell, Volume 16 Supplemental Data Tissue-Penetrating Delivery of Compounds and Nanoparticles into Tumors Kazuki N. Sugahara, Tambet Teesalu, Priya Prakash Karmali, Venkata Ramana Kotamraju, Lilach
Supplementary Figure 1. CryoTEM images of the barcoded nanoparticles (a) and
 a b Supplementary Figure 1. CryoTEM images of the barcoded nanoparticles (a) and size measurements of the particles (b). Liposomes were loaded with DNA barcodes and were imaged using cryo-tem and measured
a b Supplementary Figure 1. CryoTEM images of the barcoded nanoparticles (a) and size measurements of the particles (b). Liposomes were loaded with DNA barcodes and were imaged using cryo-tem and measured
DNA RESTRICTION ANALYSIS
 DNA RESTRICTION ANALYSIS In this experiment, DNA from the bacteriophage Lambda (48,502 base pairs in length) is cut with a variety of restriction enzymes and the resulting fragments are separated using
DNA RESTRICTION ANALYSIS In this experiment, DNA from the bacteriophage Lambda (48,502 base pairs in length) is cut with a variety of restriction enzymes and the resulting fragments are separated using
Developmental Biology. Cell Fate, Potency, and Determination
 Developmental Biology Cell Fate, Potency, and Determination Definitions Fate The sum of all structures that the cell or its descendants will form at a later stage of normal development. Cell Fate & Fate
Developmental Biology Cell Fate, Potency, and Determination Definitions Fate The sum of all structures that the cell or its descendants will form at a later stage of normal development. Cell Fate & Fate
Supplementary Figure 1. Serial deletion mutants of BLITz.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Serial deletion mutants of BLITz. (a) Design of TEVseq insertion into J -helix. C-terminal end of J -helix was serially deleted and replaced by TEVseq. TEV cleavage site is labeled
Supplementary Figure 1 Serial deletion mutants of BLITz. (a) Design of TEVseq insertion into J -helix. C-terminal end of J -helix was serially deleted and replaced by TEVseq. TEV cleavage site is labeled
