Gene Regulation 10/19/05
|
|
|
- Iris George
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 10/19/05 Gene Regulation (formerly Gene Prediction - 2) Gene Prediction & Regulation Mon - Overview & Gene structure review: Eukaryotes vs prokaryotes Wed - Regulatory regions: Promoters & enhancers - Predicting genes Fri - Predicting genes - Predicting regulatory regions Next week: Predicting RNA structure (mirnas, too) 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 1 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 2 Reading Assignment (for Wed) Mount Bioinformatics Chp 9 Gene Prediction & Regulation pp Predicting Promoters Ck Errata: * Brown Genomes 2 (NCBI textbooks online) Sect 9 Overview: Assembly of Transcription Initiation Complex Reviews: Optional Reading 1) Zhang MQ (2002) Computational prediction of eukaryotic proteincoding genes. Nat Rev Genet 3: ) Wasserman WW & Sandelin (2004) Applied bioinformatics for the identification of regulatory elements. Nat Rev Genet 5: Sect DNA binding proteins, Transcription initiation * NOTE: Don t worry about the details!! 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 3 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 4 Review last lecture: Genes & Genomes Eukaryotes vs prokaryotes Cells Genome organization Gene structure Eukaryotes vs Prokaryotes Typical human & bacterial cells drawn to scale. Eukaryotic cells are characterized by membrane-bound compartments, which are absent in prokaryotes. 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 5 Brown Fig /19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 6 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X 1
2 Comparison of Gene Structures Genes in eukaryotes vs prokaryotes Have different structures and regulatory signals Eukaryotic genomes Are packaged in chromatin and sequestered in a nucleus Are larger and have multiple chromosomes Contain mostly non-protein coding DNA (98-99%) Brown Fig /19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 7 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 8 Eukaryotic genes Are larger and more complex * Contain introns that are spliced to generate mature mrna * Undergo alternative splicing, giving rise to multiple RNAs Are transcribed by 3 different RNA polymerases * In biology, statements such as this include an implicit usually or often Gene regulation in eukaryotes vs prokaryotes Primary level of control? Prokaryotes: Transcription Eukaryotes: Transcription is important, but Expression is regulated at multiple levels e.g., RNA processing, transport, stability, protein processing, post-translational modification, localization, stability Recent discoveries: small RNAs (mirna, sirna) may play very important regulatory roles, often at post-transcriptional levels 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 9 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 10 Gene prediction? Prokaryotes: relatively easy Eukaryotes: harder Genomic organization and gene structures differ in different organisms Best results obtained with customized software for a particular species In general: Methods are good at locating genes Have trouble with details DNA Interactive: "Genomes" A tutorial on genomic sequencing, gene structure, genes prediction Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 11 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 12 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X 2
3 Today: Gene Regulation (formerly Gene Prediction - 2) But first: a few more words about cdna & ESTs Promoters & enhancers Gene prediction programs (?) Thanks to Jonathan Pevsner for following Figs & Slides Slightly modified from: "Introduction to Bioinformatics" based on Chp 6 in Pevsner's text: Bioinformatics & Functional Genomics J. Pevsner pevsner@jhmi.edu 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 13 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 14 exon 1 intron exon 2 intron exon 3 Transcription RNA splicing (remove introns) 7Me G Capping & polyadenylation AAAAA Export to cytoplasm Pevsner p161 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 15 Pevsner p160 DNA RNA cdna protein [1] Transcription [2] RNA processing (splicing) [3] RNA export [4] RNA surveillance Phenotype 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 16 Relationship of mrna to genomic DNA (for RBP4) Analysis of gene expression in cdna libraries A fundamental approach to studying gene expression is through cdna libraries Isolate RNA (always from a specific organism, region, and time point) Convert RNA to complementary DNA (with reverse transcriptase) Subclone into a vector Sequence the cdna inserts These are ESTs or Expressed Sequence Tags insert vector Pevsner p162 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 17 Pevsner p /19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 18 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X 3
4 UniGene: unique genes via ESTs Cluster sizes in UniGene Find UniGene at NCBI: UniGene clusters contain many ESTs This is a gene with 1 EST associated; the cluster size is 1 UniGene data come from many cdna libraries. Thus, when you look up a gene in UniGene you get information on its abundance and its regional distribution Pevsner p164 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 19 Pevsner p164 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 20 Cluster sizes in UniGene This is a gene with 10 ESTs associated; the cluster size is 10 Cluster sizes in UniGene - (in 2002) Cluster size Number of clusters 1 34, , , , , , ,000 3 >16,000 1 Pevsner p164 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 21 Pevsner p164 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 22 Other Resources Current Protocols in Bioinformatics Finding Genes 4.1 An Overview of Gene Identification: Approaches, Strategies, and Considerations 4.2 Using MZEF To Find Internal Coding Exons 4.3 Using GENEID to Identify Genes 4.4 Using GlimmerM to Find Genes in Eukaryotic Genomes 4.5 Prokaryotic Gene Prediction Using GeneMark and GeneMark.hmm 4.6 Eukaryotic Gene Prediction Using GeneMark.hmm 4.7 Application of FirstEF to Find Promoters and First Exons in the Human Genome 4.8 Using TWINSCAN to Predict Gene Structures in Genomic DNA Sequences 4.9 GrailEXP and Genome Analysis Pipeline for Genome Annotation 4.10 Using RepeatMasker to Identify Repetitive Elements in Genomic Sequences Gene Regulation Promoters & enhancers What does an RNA polymerase "see"? Eukaryotes vs prokaryotes Regulatory regions Prokaryotic operons & promoters Eukaryotic promoters & enhancers Eukaryotic transcription factors 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 23 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 24 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X 4
5 What does an RNA polymerase (or a transcription factor) see? Promoters for prokaryotic RNA polymerases (e.g., bacterium, E. coli) /19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 25 Brown Fig /19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 26 Prokaryotic genes & operons Prokaryotic promoters Genes with related functions are often clustered in operons (e.g., lac operon) Operons are transcriptionally regulated as a single unit - one promoter controls several proteins mrnas produced are polycistronic - one mrna encodes several proteins; i.e., there are multiple ORFs, each with AUG (START) & STOP codons RNA polymerase complex recognizes promoter sequences located very close to & on side ( upstream ) of initiation site RNA polymerase complex binds directly to these. with no requirement for transcription factors Prokaryotic promoter sequences are highly conserved -10 region -35 region 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 27 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 28 Eukaryotic genes Genes with related functions are not clustered, but share common regulatory regions (promoters, enhancers, etc.) Chromatin structure must be in right configuration for transcription Eukaryotic genes have large & complex regulatory regions Cis-acting regulatory elements include: Promoters,enhancers, silencers Trans-acting regulatory factors include: Transcription factors, chromatin remodeling enzymes, small RNAs 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 29 Brown Fig /19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 30 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X 5
6 Eukaryotic genes are transcribed by 3 different RNA polymerases Eukaryotic promoters & enhancers Promoters located relatively close to initiation site (but can be located within gene, rather than upstream!) Enhancers also required for regulated transcription (these control expression in specific cell types, developmental stages, in response to environment) RNA polymerase complexes do not specifically recognize promoter sequences directly Transcription factors bind first and serve as landmarks for recognition by RNA polymerase complexes Brown Fig /19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 31 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 32 Assembly of an initiation complex for eukaryotic RNA polymerase II But, it s actually more complicated: Activator & Mediator protein actually represent a large complex of transcription factors (connected via DNA-protein & protein-protein interactions) that are usually associated with clusters of TF binding sites 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 33 Brown Fig /19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 34 Eukaryotic transcription factors Zinc finger-containing transcription factors Transcription factors (TFs) are DNA binding proteins that also interact with RNA polymerase complex to activate or repress transcription TFs contain characteristic DNA binding motifs TFs recognize specific short DNA sequence motifs transcription factor binding sites Several databases for these, e.g. TRANSFAC 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 35 Brown Fig 9.12 Common in eukaryotic proteins Estimated 1% of mammalian genes encode zinc-finger proteins In C. elegans, there are 500! Can be used as highly specific DNA binding modules Potentially valuable tools for directed genome modification (esp. in plants) & human gene therapy 10/19/05 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X: Gene Regulation 36 D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X 6
7 Building Designer Zinc Finger DNA-binding Proteins J Sander, Fengli Fu, J Townsend, R Winfrey D Wright, K Joung, D Dobbs, D Voytas (ISU) D Dobbs ISU - BCB 444/544X 7
Gene Prediction 10/21/05
 Gene Prediction 1/21/5 1/21/5 Gene Prediction Announcements Eam 2 - net Friday Posted online: Eam 2 Study Guide 544 Reading Assignment (2 papers) (formerly Gene Prediction - ) 1/21/5 D Dobbs ISU - BCB
Gene Prediction 1/21/5 1/21/5 Gene Prediction Announcements Eam 2 - net Friday Posted online: Eam 2 Study Guide 544 Reading Assignment (2 papers) (formerly Gene Prediction - ) 1/21/5 D Dobbs ISU - BCB
Promoter Prediction (really) 10/26/05
 10/26/05 Promoter Prediction (really!) Announcements BCB Link for Seminar Schedules (updated) http://www.bcb.iastate.edu/seminars/inde.html Seminar (Fri Oct 28) 12:10 PM BCB Faculty Seminar in E164 Lagomarcino
10/26/05 Promoter Prediction (really!) Announcements BCB Link for Seminar Schedules (updated) http://www.bcb.iastate.edu/seminars/inde.html Seminar (Fri Oct 28) 12:10 PM BCB Faculty Seminar in E164 Lagomarcino
#28 - Promoter Prediction 10/29/07
 BCB 444/544 Required Reading (before lecture) Lecture 28 Mon Oct 29 - Lecture 28 Promoter & Regulatory Element Prediction Chp 9 - pp 113-126 Gene Prediction - finish it Wed Oct 30 - Lecture 29 Phylogenetics
BCB 444/544 Required Reading (before lecture) Lecture 28 Mon Oct 29 - Lecture 28 Promoter & Regulatory Element Prediction Chp 9 - pp 113-126 Gene Prediction - finish it Wed Oct 30 - Lecture 29 Phylogenetics
Lecture 15. Promoters, TFs. #15_Sept26
 BCB 444/544 Lecture 15 More Review: RNA, Proteins, Promoters, TFs Next time: Profiles & Hidden Markov Models (HMMs) #15_Sept26 BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #15 - RNA, Proteins, Promoters, TFs 9/26/07 1 Required
BCB 444/544 Lecture 15 More Review: RNA, Proteins, Promoters, TFs Next time: Profiles & Hidden Markov Models (HMMs) #15_Sept26 BCB 444/544 F07 ISU Dobbs #15 - RNA, Proteins, Promoters, TFs 9/26/07 1 Required
Make the protein through the genetic dogma process.
 Make the protein through the genetic dogma process. Coding Strand 5 AGCAATCATGGATTGGGTACATTTGTAACTGT 3 Template Strand mrna Protein Complete the table. DNA strand DNA s strand G mrna A C U G T A T Amino
Make the protein through the genetic dogma process. Coding Strand 5 AGCAATCATGGATTGGGTACATTTGTAACTGT 3 Template Strand mrna Protein Complete the table. DNA strand DNA s strand G mrna A C U G T A T Amino
Chapter 17 Lecture. Concepts of Genetics. Tenth Edition. Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Chapter 17 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Chapter Contents 17.1 Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Can Occur at Any of the Steps Leading from DNA to Protein
Chapter 17 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Chapter Contents 17.1 Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Can Occur at Any of the Steps Leading from DNA to Protein
Regulation of bacterial gene expression
 Regulation of bacterial gene expression Gene Expression Gene Expression: RNA and protein synthesis DNA ----------> RNA ----------> Protein transcription translation! DNA replication only occurs in cells
Regulation of bacterial gene expression Gene Expression Gene Expression: RNA and protein synthesis DNA ----------> RNA ----------> Protein transcription translation! DNA replication only occurs in cells
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes
 Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 3, 2004 Eukaryotic Gene Structure eukaryotic genomes are considerably more complex than those of prokaryotes eukaryotic cells have organelles
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 3, 2004 Eukaryotic Gene Structure eukaryotic genomes are considerably more complex than those of prokaryotes eukaryotic cells have organelles
Biotechnology Unit 3: DNA to Proteins. From DNA to RNA
 From DNA to RNA Biotechnology Unit 3: DNA to Proteins I. After the discovery of the structure of DNA, the major question remaining was how does the stored in the 4 letter code of DNA direct the and of
From DNA to RNA Biotechnology Unit 3: DNA to Proteins I. After the discovery of the structure of DNA, the major question remaining was how does the stored in the 4 letter code of DNA direct the and of
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE SLIDES
 CHAPTER 13 LECTURE SLIDES Prepared by Brenda Leady University of Toledo To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off.
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE SLIDES Prepared by Brenda Leady University of Toledo To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off.
Transcription is the first stage of gene expression
 Transcription is the first stage of gene expression RNA synthesis is catalyzed by RNA polymerase, which pries the DNA strands apart and hooks together the RNA nucleotides The RNA is complementary to the
Transcription is the first stage of gene expression RNA synthesis is catalyzed by RNA polymerase, which pries the DNA strands apart and hooks together the RNA nucleotides The RNA is complementary to the
Enzyme that uses RNA as a template to synthesize a complementary DNA
 Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics PRACTICE FINAL EXAM 2006 Part I: Definitions Homology: Comparison of two or more protein or DNA sequence to ascertain similarities in sequences. If two genes have
Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics PRACTICE FINAL EXAM 2006 Part I: Definitions Homology: Comparison of two or more protein or DNA sequence to ascertain similarities in sequences. If two genes have
Chapter 2. An Introduction to Genes and Genomes
 PowerPoint Lectures for Introduction to Biotechnology, Second Edition William J.Thieman and Michael A.Palladino Chapter 2 An Introduction to Genes and Genomes Lectures by Lara Dowland Chapter Contents
PowerPoint Lectures for Introduction to Biotechnology, Second Edition William J.Thieman and Michael A.Palladino Chapter 2 An Introduction to Genes and Genomes Lectures by Lara Dowland Chapter Contents
Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives)
 Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) 1. Compare and contrast chromatin and chromosome: composition, proteins involved and level of packing. Explain the structure and function of
Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives) 1. Compare and contrast chromatin and chromosome: composition, proteins involved and level of packing. Explain the structure and function of
Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley
Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley
Computational gene finding
 Computational gene finding Devika Subramanian Comp 470 Outline (3 lectures) Lec 1 Lec 2 Lec 3 The biological context Markov models and Hidden Markov models Ab-initio methods for gene finding Comparative
Computational gene finding Devika Subramanian Comp 470 Outline (3 lectures) Lec 1 Lec 2 Lec 3 The biological context Markov models and Hidden Markov models Ab-initio methods for gene finding Comparative
There are four major types of introns. Group I introns, found in some rrna genes, are self-splicing: they can catalyze their own removal.
 1 2 Continuous genes - Intron: Many eukaryotic genes contain coding regions called exons and noncoding regions called intervening sequences or introns. The average human gene contains from eight to nine
1 2 Continuous genes - Intron: Many eukaryotic genes contain coding regions called exons and noncoding regions called intervening sequences or introns. The average human gene contains from eight to nine
Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra
 Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra 1 Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Only one strand of DNA serves
Year III Pharm.D Dr. V. Chitra 1 Genome entire genetic material of an individual Transcriptome set of transcribed sequences Proteome set of proteins encoded by the genome 2 Only one strand of DNA serves
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 08: Transcription, Translation and the Genetic Code
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 08: Transcription, Translation and the Genetic Code Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about how genes function is correct? Question #1 (A)
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 08: Transcription, Translation and the Genetic Code Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about how genes function is correct? Question #1 (A)
REGULATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. II. Eukaryotes
 REGULATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS II. Eukaryotes Complexities of eukaryotic gene expression! Several steps needed for synthesis of mrna! Separation in space of transcription and translation! Compartmentation
REGULATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS II. Eukaryotes Complexities of eukaryotic gene expression! Several steps needed for synthesis of mrna! Separation in space of transcription and translation! Compartmentation
AP Biology Gene Expression/Biotechnology REVIEW
 AP Biology Gene Expression/Biotechnology REVIEW Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Gene expression can be a. regulated before transcription.
AP Biology Gene Expression/Biotechnology REVIEW Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Gene expression can be a. regulated before transcription.
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA
 TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA 1. The steps of gene expression. 2. General characterization of transcription: steps, components of transcription apparatus. 3. Transcription of eukaryotic structural
GENE REGULATION. Gene regulation occurs at the level of transcription or production of mrna
 GENE REGULATION Virtually every cell in your body contains a complete set of genes But they are not all turned on in every tissue Each cell in your body expresses only a small subset of genes at any time
GENE REGULATION Virtually every cell in your body contains a complete set of genes But they are not all turned on in every tissue Each cell in your body expresses only a small subset of genes at any time
#26 - Gene Prediction 10/22/07
 BCB 444/544 Required Reading (before lecture) Lecture 26 Mon Oct 22 - Lecture 26 Gene Prediction Chp 8 - pp 97-112 Gene Prediction Wed Oct 24 - Lecture 27 (will not be covered on Exam 2) Regulatory Element
BCB 444/544 Required Reading (before lecture) Lecture 26 Mon Oct 22 - Lecture 26 Gene Prediction Chp 8 - pp 97-112 Gene Prediction Wed Oct 24 - Lecture 27 (will not be covered on Exam 2) Regulatory Element
Wednesday, November 22, 17. Exons and Introns
 Exons and Introns Introns and Exons Exons: coded regions of DNA that get transcribed and translated into proteins make up 5% of the genome Introns and Exons Introns: non-coded regions of DNA Must be removed
Exons and Introns Introns and Exons Exons: coded regions of DNA that get transcribed and translated into proteins make up 5% of the genome Introns and Exons Introns: non-coded regions of DNA Must be removed
BIO 311C Spring Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr.
 BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr. Synthesis of a Polypeptide Chain 5 direction of ribosome movement along the mrna 3 ribosome mrna NH 2 polypeptide chain direction of mrna movement through
BIO 311C Spring 2010 1 Lecture 36 Wednesday 28 Apr. Synthesis of a Polypeptide Chain 5 direction of ribosome movement along the mrna 3 ribosome mrna NH 2 polypeptide chain direction of mrna movement through
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Gene Expression: Transcription, Translation, RNAs and the Genetic Code
 Lecture 28-29 Gene Expression: Transcription, Translation, RNAs and the Genetic Code Central dogma of molecular biology During transcription, the information in a DNA sequence (a gene) is copied into a
Lecture 28-29 Gene Expression: Transcription, Translation, RNAs and the Genetic Code Central dogma of molecular biology During transcription, the information in a DNA sequence (a gene) is copied into a
The Flow of Genetic Information
 Chapter 17 The Flow of Genetic Information The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific traits by dictating the synthesis of proteins and of RNA molecules involved in protein synthesis. Proteins
Chapter 17 The Flow of Genetic Information The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific traits by dictating the synthesis of proteins and of RNA molecules involved in protein synthesis. Proteins
Differential Gene Expression
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 19, 2008 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression June 19, 2008 Differential Gene Expression Overview Chromatin structure Gene anatomy RNA processing and protein production Initiating transcription:
Transcription in Eukaryotes
 Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
Transcription in Eukaryotes Biology I Hayder A Giha Transcription Transcription is a DNA-directed synthesis of RNA, which is the first step in gene expression. Gene expression, is transformation of the
DNA makes RNA makes Proteins. The Central Dogma
 DNA makes RNA makes Proteins The Central Dogma TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-mrna) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION
DNA makes RNA makes Proteins The Central Dogma TRANSCRIPTION DNA RNA transcript RNA polymerase RNA PROCESSING Exon RNA transcript (pre-mrna) Intron Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase NUCLEUS CYTOPLASM FORMATION
Transcription. The sugar molecule found in RNA is ribose, rather than the deoxyribose found in DNA.
 Transcription RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a key intermediary between a DNA sequence and a polypeptide. RNA is an informational polynucleotide similar to DNA, but it differs from DNA in three ways: RNA generally
Transcription RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a key intermediary between a DNA sequence and a polypeptide. RNA is an informational polynucleotide similar to DNA, but it differs from DNA in three ways: RNA generally
Transcriptomics. Marta Puig Institut de Biotecnologia i Biomedicina Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona
 Transcriptomics Marta Puig Institut de Biotecnologia i Biomedicina Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona Central dogma of molecular biology Central dogma of molecular biology Genome Complete DNA content of
Transcriptomics Marta Puig Institut de Biotecnologia i Biomedicina Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona Central dogma of molecular biology Central dogma of molecular biology Genome Complete DNA content of
Chapter 12 Packet DNA 1. What did Griffith conclude from his experiment? 2. Describe the process of transformation.
 Chapter 12 Packet DNA and RNA Name Period California State Standards covered by this chapter: Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions
Chapter 12 Packet DNA and RNA Name Period California State Standards covered by this chapter: Cell Biology 1. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions
CHAPTERS , 17: Eukaryotic Genetics
 CHAPTERS 14.1 14.6, 17: Eukaryotic Genetics 1. Review the levels of DNA packing within the eukaryote nucleus. Label each level. (A similar diagram is on pg 188 of your textbook.) 2. How do the coding regions
CHAPTERS 14.1 14.6, 17: Eukaryotic Genetics 1. Review the levels of DNA packing within the eukaryote nucleus. Label each level. (A similar diagram is on pg 188 of your textbook.) 2. How do the coding regions
Biology. Biology. Slide 1 of 39. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology Biology 1 of 39 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis 2 of 39 Essential Question What is transcription and translation and how do they take place? 3 of 39 12 3 RNA and Protein Synthesis Genes are coded
Biology Biology 1 of 39 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis 2 of 39 Essential Question What is transcription and translation and how do they take place? 3 of 39 12 3 RNA and Protein Synthesis Genes are coded
Biology. Biology. Slide 1 of 39. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology Biology 1 of 39 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis 2 of 39 12 3 RNA and Protein Synthesis Genes are coded DNA instructions that control the production of proteins. Genetic messages can be decoded by
Biology Biology 1 of 39 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis 2 of 39 12 3 RNA and Protein Synthesis Genes are coded DNA instructions that control the production of proteins. Genetic messages can be decoded by
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 09: Gene Expression in Prokaryotes
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 09: Gene Expression in Prokaryotes Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about gene expression in prokaryotes is correct? Question #1 (A) In prokaryotes,
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 09: Gene Expression in Prokaryotes Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about gene expression in prokaryotes is correct? Question #1 (A) In prokaryotes,
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 7 - GENE EXPRESSION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION BASICS Gene expression is the process through which cells selectively to express some genes and not others Every cell in an organism is a clone
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CONTROL OF GENE EXPRESSION BASICS Gene expression is the process through which cells selectively to express some genes and not others Every cell in an organism is a clone
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.10 TRANSCRIPTION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF TRANSCRIPTION Transcription is the process of using DNA as a template to RNA RNA polymerase is the enzyme that transcribes DNA - There are many different types
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF TRANSCRIPTION Transcription is the process of using DNA as a template to RNA RNA polymerase is the enzyme that transcribes DNA - There are many different types
Bioinformatics of Transcriptional Regulation
 Bioinformatics of Transcriptional Regulation Carl Herrmann IPMB & DKFZ c.herrmann@dkfz.de Wechselwirkung von Maßnahmen und Auswirkungen Einflussmöglichkeiten in einem Dialog From genes to active compounds
Bioinformatics of Transcriptional Regulation Carl Herrmann IPMB & DKFZ c.herrmann@dkfz.de Wechselwirkung von Maßnahmen und Auswirkungen Einflussmöglichkeiten in einem Dialog From genes to active compounds
Name AP Biology Mrs. Laux Take home test #11 on Chapters 14, 15, and 17 DUE: MONDAY, DECEMBER 21, 2009
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Inducible genes are usually actively transcribed when: A. the molecule degraded by the enzyme(s) is present in the cell. B. repressor molecules bind to the promoter. C. lactose
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Inducible genes are usually actively transcribed when: A. the molecule degraded by the enzyme(s) is present in the cell. B. repressor molecules bind to the promoter. C. lactose
Section C: The Control of Gene Expression
 Section C: The Control of Gene Expression 1. Each cell of a multicellular eukaryote expresses only a small fraction of its genes 2. The control of gene expression can occur at any step in the pathway from
Section C: The Control of Gene Expression 1. Each cell of a multicellular eukaryote expresses only a small fraction of its genes 2. The control of gene expression can occur at any step in the pathway from
B. Incorrect! Centromeric DNA is largely heterochromatin, which is inactive DNA.
 MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 06: Molecular Biology of Eukaryotes Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which type of DNA would have the highest level of expression? Question #01 (A) Heterochromatin. (B) Centromeric
MCAT Biology - Problem Drill 06: Molecular Biology of Eukaryotes Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which type of DNA would have the highest level of expression? Question #01 (A) Heterochromatin. (B) Centromeric
Chapter 11: Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter Review 1. It has long been known that there is probably a genetic link for alcoholism. Researchers studying rats have begun to elucidate this link. Briefly describe the genetic mechanism found
Chapter Review 1. It has long been known that there is probably a genetic link for alcoholism. Researchers studying rats have begun to elucidate this link. Briefly describe the genetic mechanism found
BIOLOGY. Chapter 16 GenesExpression
 BIOLOGY Chapter 16 GenesExpression CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 18 Gene Expression 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 16.1 Differential Gene Expression results
BIOLOGY Chapter 16 GenesExpression CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 18 Gene Expression 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 16.1 Differential Gene Expression results
Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4)
 Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4) Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture Notes: Transcriptome: Molecular Biology of Gene Expression I Flow of information: DNA to polypeptide DNA Start Exon1 Intron Exon2 Termination
Computational Biology I LSM5191 (2003/4) Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture Notes: Transcriptome: Molecular Biology of Gene Expression I Flow of information: DNA to polypeptide DNA Start Exon1 Intron Exon2 Termination
Chapter 6: Transcription and RNA Processing in Eukaryotes
 3. Basic Genetics Plant Molecular Biology Chapter 6: Transcription and RNA Processing in Eukaryotes - Genetic organization in eukaryote - Transcription in eukaryote - - RNA processing in eukaryote - Translation
3. Basic Genetics Plant Molecular Biology Chapter 6: Transcription and RNA Processing in Eukaryotes - Genetic organization in eukaryote - Transcription in eukaryote - - RNA processing in eukaryote - Translation
(c) 2014 Dr. Alice Heicklen & Dr. Deborah Mowshowitz, Columbia University, New York, NY. Last update 02/26/ :57 PM
 C2006/F2402 '14 OUTLINE OF LECTURE #11 (c) 2014 Dr. Alice Heicklen & Dr. Deborah Mowshowitz, Columbia University, New York, NY. Last update 02/26/2014 12:57 PM Handouts: 10C -- Typical Eukaryotic Gene,
C2006/F2402 '14 OUTLINE OF LECTURE #11 (c) 2014 Dr. Alice Heicklen & Dr. Deborah Mowshowitz, Columbia University, New York, NY. Last update 02/26/2014 12:57 PM Handouts: 10C -- Typical Eukaryotic Gene,
Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Part I: Definitions. Homology: Reverse transcriptase. Allostery: cdna library
 Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics PRACTICE FINAL EXAM 2006 Part I: Definitions Homology: Reverse transcriptase Allostery: cdna library Transformation Part II Short Answer 1. Describe the reasons for
Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics PRACTICE FINAL EXAM 2006 Part I: Definitions Homology: Reverse transcriptase Allostery: cdna library Transformation Part II Short Answer 1. Describe the reasons for
Themes: RNA and RNA Processing. Messenger RNA (mrna) What is a gene? RNA is very versatile! RNA-RNA interactions are very important!
 Themes: RNA is very versatile! RNA and RNA Processing Chapter 14 RNA-RNA interactions are very important! Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have many important differences. Messenger RNA (mrna) Carries genetic
Themes: RNA is very versatile! RNA and RNA Processing Chapter 14 RNA-RNA interactions are very important! Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have many important differences. Messenger RNA (mrna) Carries genetic
Lecture 11. Initiation of RNA Pol II transcription. Transcription Initiation Complex
 Lecture 11 *Eukaryotic Transcription Gene Organization RNA Processing 5 cap 3 polyadenylation splicing Translation Initiation of RNA Pol II transcription Consensus sequence of promoter TATA Transcription
Lecture 11 *Eukaryotic Transcription Gene Organization RNA Processing 5 cap 3 polyadenylation splicing Translation Initiation of RNA Pol II transcription Consensus sequence of promoter TATA Transcription
DNA Transcription. Dr Aliwaini
 DNA Transcription 1 DNA Transcription-Introduction The synthesis of an RNA molecule from DNA is called Transcription. All eukaryotic cells have five major classes of RNA: ribosomal RNA (rrna), messenger
DNA Transcription 1 DNA Transcription-Introduction The synthesis of an RNA molecule from DNA is called Transcription. All eukaryotic cells have five major classes of RNA: ribosomal RNA (rrna), messenger
Fermentation. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview 13.1 RNA
 13.1 RNA THINK ABOUT IT DNA is the genetic material of cells. The sequence of nucleotide bases in the strands of DNA carries some sort of code. In order for that code to work, the cell must be able to
13.1 RNA THINK ABOUT IT DNA is the genetic material of cells. The sequence of nucleotide bases in the strands of DNA carries some sort of code. In order for that code to work, the cell must be able to
Genome annotation & EST
 Genome annotation & EST What is genome annotation? The process of taking the raw DNA sequence produced by the genome sequence projects and adding the layers of analysis and interpretation necessary
Genome annotation & EST What is genome annotation? The process of taking the raw DNA sequence produced by the genome sequence projects and adding the layers of analysis and interpretation necessary
How to Use This Presentation
 How to Use This Presentation To View the presentation as a slideshow with effects select View on the menu bar and click on Slide Show. To advance through the presentation, click the right-arrow key or
How to Use This Presentation To View the presentation as a slideshow with effects select View on the menu bar and click on Slide Show. To advance through the presentation, click the right-arrow key or
Fig Ch 17: From Gene to Protein
 Fig. 17-1 Ch 17: From Gene to Protein Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation RNA is the intermediate between genes and the proteins for which they code Transcription is the synthesis of RNA
Fig. 17-1 Ch 17: From Gene to Protein Basic Principles of Transcription and Translation RNA is the intermediate between genes and the proteins for which they code Transcription is the synthesis of RNA
Biotechnology and DNA Technology
 11/27/2017 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College CHAPTER 9 Biotechnology and DNA Technology Introduction to Biotechnology Learning Objectives Compare
11/27/2017 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College CHAPTER 9 Biotechnology and DNA Technology Introduction to Biotechnology Learning Objectives Compare
I. Gene Expression Figure 1: Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
 I. Gene Expression Figure 1: Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Central Dogma: Gene Expression: RNA Structure RNA nucleotides contain the pentose sugar Ribose instead of deoxyribose. Contain the bases
I. Gene Expression Figure 1: Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Central Dogma: Gene Expression: RNA Structure RNA nucleotides contain the pentose sugar Ribose instead of deoxyribose. Contain the bases
Differential Gene Expression
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression September 28, 2006 Chromatin Structure ~140 bp ~60 bp Transcriptional Regulation: 1. Packing prevents access CH 3 2. Acetylation ( C O )
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Differential Gene Expression September 28, 2006 Chromatin Structure ~140 bp ~60 bp Transcriptional Regulation: 1. Packing prevents access CH 3 2. Acetylation ( C O )
Regulation of Gene Expression
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 15 Regulation of Gene Expression Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 15 Regulation of Gene Expression Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
Synthetic cells: do bacteria need all its genes? No.
 NO NEED TO REFER TO THE SLIDES. بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Do we need all the non coding regions of the DNA? Two weeks ago, they discovered that the genome of a plant is very small (recall that plant genome
NO NEED TO REFER TO THE SLIDES. بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Do we need all the non coding regions of the DNA? Two weeks ago, they discovered that the genome of a plant is very small (recall that plant genome
Chapter 8 Lecture Outline. Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics
 Chapter 8 Lecture Outline Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics Replication, Transcription, Translation n Repetitive processes Build polymers of nucleotides or amino acids n All have 3 major steps
Chapter 8 Lecture Outline Transcription, Translation, and Bioinformatics Replication, Transcription, Translation n Repetitive processes Build polymers of nucleotides or amino acids n All have 3 major steps
The Genetic Code and Transcription. Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot
 The Genetic Code and Transcription Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot TRANSCRIPTION Copy SAME language DNA to RNA Nucleic Acid to Nucleic Acid TRANSLATION Copy DIFFERENT language RNA to Amino
The Genetic Code and Transcription Chapter 12 Honors Genetics Ms. Susan Chabot TRANSCRIPTION Copy SAME language DNA to RNA Nucleic Acid to Nucleic Acid TRANSLATION Copy DIFFERENT language RNA to Amino
MBioS 503: Section 1 Chromosome, Gene, Translation, & Transcription. Gene Organization. Genome. Objectives: Gene Organization
 Overview & Recap of Molecular Biology before the last two sections MBioS 503: Section 1 Chromosome, Gene, Translation, & Transcription Gene Organization Joy Winuthayanon, PhD School of Molecular Biosciences
Overview & Recap of Molecular Biology before the last two sections MBioS 503: Section 1 Chromosome, Gene, Translation, & Transcription Gene Organization Joy Winuthayanon, PhD School of Molecular Biosciences
From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype
 12 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype 12.1 What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? The gene-enzyme relationship is one-gene, one-polypeptide relationship. Example: In hemoglobin, each
12 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype 12.1 What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? The gene-enzyme relationship is one-gene, one-polypeptide relationship. Example: In hemoglobin, each
Videos. Lesson Overview. Fermentation
 Lesson Overview Fermentation Videos Bozeman Transcription and Translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Drawing transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/6yqplgnjr4q Objectives 29a) I can contrast
Lesson Overview Fermentation Videos Bozeman Transcription and Translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Drawing transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/6yqplgnjr4q Objectives 29a) I can contrast
Bis2A 12.0 Transcription *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m56068 1 Bis2A 12.0 Transcription * Mitch Singer Based on Transcription by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
OpenStax-CNX module: m56068 1 Bis2A 12.0 Transcription * Mitch Singer Based on Transcription by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
Lesson Overview. Fermentation 13.1 RNA
 13.1 RNA The Role of RNA Genes contain coded DNA instructions that tell cells how to build proteins. The first step in decoding these genetic instructions is to copy part of the base sequence from DNA
13.1 RNA The Role of RNA Genes contain coded DNA instructions that tell cells how to build proteins. The first step in decoding these genetic instructions is to copy part of the base sequence from DNA
Big Idea 3C Basic Review
 Big Idea 3C Basic Review 1. A gene is a. A sequence of DNA that codes for a protein. b. A sequence of amino acids that codes for a protein. c. A sequence of codons that code for nucleic acids. d. The end
Big Idea 3C Basic Review 1. A gene is a. A sequence of DNA that codes for a protein. b. A sequence of amino acids that codes for a protein. c. A sequence of codons that code for nucleic acids. d. The end
From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype
 12 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype 12.1 What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? The gene-enzyme relationship is one-gene, one-polypeptide relationship. Example: In hemoglobin, each
12 From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype 12.1 What Is the Evidence that Genes Code for Proteins? The gene-enzyme relationship is one-gene, one-polypeptide relationship. Example: In hemoglobin, each
CH 17 :From Gene to Protein
 CH 17 :From Gene to Protein Defining a gene gene gene Defining a gene is problematic because one gene can code for several protein products, some genes code only for RNA, two genes can overlap, and there
CH 17 :From Gene to Protein Defining a gene gene gene Defining a gene is problematic because one gene can code for several protein products, some genes code only for RNA, two genes can overlap, and there
Expressed genes profiling (Microarrays) Overview Of Gene Expression Control Profiling Of Expressed Genes
 Expressed genes profiling (Microarrays) Overview Of Gene Expression Control Profiling Of Expressed Genes Genes can be regulated at many levels Usually, gene regulation, are referring to transcriptional
Expressed genes profiling (Microarrays) Overview Of Gene Expression Control Profiling Of Expressed Genes Genes can be regulated at many levels Usually, gene regulation, are referring to transcriptional
Chapter 13 - Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 13 - Regulation of Gene Expression 1. Describe the typical components of an operon in an E. coli (prokaryotic) cell. (p. 238-239) a. regulator gene - b. promoter - c. operator - d. structural gene
Chapter 13 - Regulation of Gene Expression 1. Describe the typical components of an operon in an E. coli (prokaryotic) cell. (p. 238-239) a. regulator gene - b. promoter - c. operator - d. structural gene
Reading Lecture 8: Lecture 9: Lecture 8. DNA Libraries. Definition Types Construction
 Lecture 8 Reading Lecture 8: 96-110 Lecture 9: 111-120 DNA Libraries Definition Types Construction 142 DNA Libraries A DNA library is a collection of clones of genomic fragments or cdnas from a certain
Lecture 8 Reading Lecture 8: 96-110 Lecture 9: 111-120 DNA Libraries Definition Types Construction 142 DNA Libraries A DNA library is a collection of clones of genomic fragments or cdnas from a certain
Ch. 10 From DNA to Protein. AP Biology
 Ch. 10 From DNA to Protein Protein Synthesis Metabolism and Gene Expression n Inheritance of metabolic diseases suggests that genes coded for enzymes n Diseases (phenotypes) caused by non-functional gene
Ch. 10 From DNA to Protein Protein Synthesis Metabolism and Gene Expression n Inheritance of metabolic diseases suggests that genes coded for enzymes n Diseases (phenotypes) caused by non-functional gene
Unit IX Problem 3 Genetics: Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology
 Unit IX Problem 3 Genetics: Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated to synthesize
Unit IX Problem 3 Genetics: Basic Concepts in Molecular Biology - The central dogma (principle) of molecular biology: Information from DNA are transcribed to mrna which will be further translated to synthesize
Videos. Bozeman Transcription and Translation: Drawing transcription and translation:
 Videos Bozeman Transcription and Translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Drawing transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/6yqplgnjr4q Objectives 29a) I can contrast RNA and DNA. 29b) I can explain
Videos Bozeman Transcription and Translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Drawing transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/6yqplgnjr4q Objectives 29a) I can contrast RNA and DNA. 29b) I can explain
17.5 Eukaryotic Transcription Initiation Is Regulated by Transcription Factors That Bind to Cis-Acting Sites
 17.5 Eukaryotic Transcription Initiation Is Regulated by Transcription Factors That Bind to Cis-Acting Sites 1 Section 17.5 Transcription regulatory proteins, transcription factors, target cis-acting sites
17.5 Eukaryotic Transcription Initiation Is Regulated by Transcription Factors That Bind to Cis-Acting Sites 1 Section 17.5 Transcription regulatory proteins, transcription factors, target cis-acting sites
Computational gene finding. Devika Subramanian Comp 470
 Computational gene finding Devika Subramanian Comp 470 Outline (3 lectures) The biological context Lec 1 Lec 2 Lec 3 Markov models and Hidden Markov models Ab-initio methods for gene finding Comparative
Computational gene finding Devika Subramanian Comp 470 Outline (3 lectures) The biological context Lec 1 Lec 2 Lec 3 Markov models and Hidden Markov models Ab-initio methods for gene finding Comparative
GENE REGULATION IN PROKARYOTES
 GENE REGULATION IN PROKARYOTES Prepared by Brenda Leady, University of Toledo Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Gene regulation refers to
GENE REGULATION IN PROKARYOTES Prepared by Brenda Leady, University of Toledo Copyright (c) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Gene regulation refers to
Biology 3201 Genetics Unit #5
 Biology 3201 Genetics Unit #5 Protein Synthesis Protein Synthesis Protein synthesis: this is the process whereby instructions from DNA are used to create polypeptides that make up a protein. This process
Biology 3201 Genetics Unit #5 Protein Synthesis Protein Synthesis Protein synthesis: this is the process whereby instructions from DNA are used to create polypeptides that make up a protein. This process
3'A C G A C C A G T A A A 5'
 AP Biology Chapter 14 Reading Guide Gene Expression: From Gene to Protein Overview 1. What is gene expression? Concept 14.1 Genes specify proteins via transcription and translation Basic Principles of
AP Biology Chapter 14 Reading Guide Gene Expression: From Gene to Protein Overview 1. What is gene expression? Concept 14.1 Genes specify proteins via transcription and translation Basic Principles of
BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Week of Oct 24
 BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Week of Oct 24 Additional Practice Problems for Section Question 1: The following table contains a list of statements that apply to replication, transcription, both, or neither.
BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Week of Oct 24 Additional Practice Problems for Section Question 1: The following table contains a list of statements that apply to replication, transcription, both, or neither.
Lecture for Wednesday. Dr. Prince BIOL 1408
 Lecture for Wednesday Dr. Prince BIOL 1408 THE FLOW OF GENETIC INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genes are expressed as proteins A gene is a segment of DNA that
Lecture for Wednesday Dr. Prince BIOL 1408 THE FLOW OF GENETIC INFORMATION FROM DNA TO RNA TO PROTEIN Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Genes are expressed as proteins A gene is a segment of DNA that
Genes and How They Work. Chapter 15
 Genes and How They Work Chapter 15 The Nature of Genes They proposed the one gene one enzyme hypothesis. Today we know this as the one gene one polypeptide hypothesis. 2 The Nature of Genes The central
Genes and How They Work Chapter 15 The Nature of Genes They proposed the one gene one enzyme hypothesis. Today we know this as the one gene one polypeptide hypothesis. 2 The Nature of Genes The central
Lecture Summary: Regulation of transcription. General mechanisms-what are the major regulatory points?
 BCH 401G Lecture 37 Andres Lecture Summary: Regulation of transcription. General mechanisms-what are the major regulatory points? RNA processing: Capping, polyadenylation, splicing. Why process mammalian
BCH 401G Lecture 37 Andres Lecture Summary: Regulation of transcription. General mechanisms-what are the major regulatory points? RNA processing: Capping, polyadenylation, splicing. Why process mammalian
Chapter 7: Genetics Lesson 7.1: From DNA to Proteins
 Chapter 7: Genetics Lesson 7.1: From DNA to Proteins The spiral structure in the picture is a large organic molecule. Can you guess what it is? Here s a hint: molecules like this one determine who you
Chapter 7: Genetics Lesson 7.1: From DNA to Proteins The spiral structure in the picture is a large organic molecule. Can you guess what it is? Here s a hint: molecules like this one determine who you
Gene expression DNA RNA. Protein DNA. Replication. Initiation Elongation Processing Export. DNA RNA Protein. Transcription. Degradation.
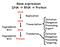 Gene expression DNA RNA Protein DNA DNA Degradation RNA Degradation Protein Replication Transcription Translation Initiation Elongation Processing Export Initiation Elongation Processing Targeting Chapter
Gene expression DNA RNA Protein DNA DNA Degradation RNA Degradation Protein Replication Transcription Translation Initiation Elongation Processing Export Initiation Elongation Processing Targeting Chapter
Bioinformatics: Sequence Analysis. COMP 571 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University
 Bioinformatics: Sequence Analysis COMP 571 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University Course Information Instructor: Luay Nakhleh (nakhleh@rice.edu); office hours by appointment (office: DH 3119) TA: Leo Elworth (DH
Bioinformatics: Sequence Analysis COMP 571 Luay Nakhleh, Rice University Course Information Instructor: Luay Nakhleh (nakhleh@rice.edu); office hours by appointment (office: DH 3119) TA: Leo Elworth (DH
BIO303, Genetics Study Guide II for Spring 2007 Semester
 BIO303, Genetics Study Guide II for Spring 2007 Semester 1 Questions from F05 1. Tryptophan (Trp) is encoded by the codon UGG. Suppose that a cell was treated with high levels of 5- Bromouracil such that
BIO303, Genetics Study Guide II for Spring 2007 Semester 1 Questions from F05 1. Tryptophan (Trp) is encoded by the codon UGG. Suppose that a cell was treated with high levels of 5- Bromouracil such that
Chapter 3. DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis
 Chapter 3. DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis 4. Transcription Gene Expression Regulatory region (promoter) 5 flanking region Upstream region Coding region 3 flanking region Downstream region Transcription
Chapter 3. DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis 4. Transcription Gene Expression Regulatory region (promoter) 5 flanking region Upstream region Coding region 3 flanking region Downstream region Transcription
Computational gene finding
 Computational gene finding Devika Subramanian Comp 470 Outline (3 lectures) Lec 1 Lec 2 Lec 3 The biological context Markov models and Hidden Markov models Ab-initio methods for gene finding Comparative
Computational gene finding Devika Subramanian Comp 470 Outline (3 lectures) Lec 1 Lec 2 Lec 3 The biological context Markov models and Hidden Markov models Ab-initio methods for gene finding Comparative
Transcription and Post Transcript Modification
 Transcription and Post Transcript Modification You Should Be Able To 1. Describe transcription. 2. Compare and contrast eukaryotic + prokaryotic transcription. 3. Explain mrna processing in eukaryotes.
Transcription and Post Transcript Modification You Should Be Able To 1. Describe transcription. 2. Compare and contrast eukaryotic + prokaryotic transcription. 3. Explain mrna processing in eukaryotes.
30 Gene expression: Transcription
 30 Gene expression: Transcription Gene structure. o Exons coding region of DNA. o Introns non-coding region of DNA. o Introns are interspersed between exons of a single gene. o Promoter region helps enzymes
30 Gene expression: Transcription Gene structure. o Exons coding region of DNA. o Introns non-coding region of DNA. o Introns are interspersed between exons of a single gene. o Promoter region helps enzymes
Control of Gene Expression
 Control of Gene Expression 1 How Gene Regulation Works 2 Control of Gene Expression Controlling gene expression is often accomplished by controlling transcription initiation Regulatory proteins bind to
Control of Gene Expression 1 How Gene Regulation Works 2 Control of Gene Expression Controlling gene expression is often accomplished by controlling transcription initiation Regulatory proteins bind to
SCBC203 Gene Expression. Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science PR318
 SCBC203 Gene Expression Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science PR318 Rutaiwan.toh@mahidol.ac.th 1 Gene Expression Gene expression is a process where by the genetic
SCBC203 Gene Expression Assoc. Prof. Rutaiwan Tohtong Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science PR318 Rutaiwan.toh@mahidol.ac.th 1 Gene Expression Gene expression is a process where by the genetic
Motivation From Protein to Gene
 MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 2003-4 Topic B Recombinant DNA -principles and tools Construct a library - what for, how Major techniques +principles Bioinformatics - in brief Chapter 7 (MCB) 1 Motivation From Protein
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 2003-4 Topic B Recombinant DNA -principles and tools Construct a library - what for, how Major techniques +principles Bioinformatics - in brief Chapter 7 (MCB) 1 Motivation From Protein
Nucleic Acids and the Encoding of Biological Information. Chapter 3
 Nucleic Acids and the Encoding of Biological Information Chapter 3 GRIFFITH S EXPERIMENT ON THE NATURE OF THE GENETIC MATERIAL In 1928, Frederick Griffith demonstrated that molecules can transfer genetic
Nucleic Acids and the Encoding of Biological Information Chapter 3 GRIFFITH S EXPERIMENT ON THE NATURE OF THE GENETIC MATERIAL In 1928, Frederick Griffith demonstrated that molecules can transfer genetic
