SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Plasmid construction
|
|
|
- Albert Parrish
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Plasmid construction pkm288 [dnax-yfp (phleo)] was generated by subcloning an EcoRI-PstI fragment (dnax-yfp) from pkl183 (Lemon and Grossman, 1998) into pdt2. pdt2 is a puc19 derivative containing a phleomycin resistance cassette between EcoRI and NdeI (T. Doan and D.Z.R., unpublished). pkm322 [amye::psweet-dnaa-gfp (spec)] was generated in a three-way ligation with a NheI- PstI PCR product containing dnaa (oligonucleotide primers odr694 and odr701 with PY79 genomic DNA as template) and a PstI-BamHI PCR product containing gfp (oligonucleotide primers odr702 and odr78 with pkl147 (Lemon and Grossman, 1998) as template DNA) and pdr160 cut with BamHI and EcoRI. pdr160 [amye::psweet-xylr (spec)] is an ectopic integration vector containing the xylose-inducible Psweet promoter (Bhavsar et al., 2001) (D.R.Z., unpublished). pjw002 [amye::phyperspank-opt.rbs-sira (spec)] was generated in a two-way ligation with a HindIII-NheI PCR product containing sira (oligonucleotide primers ojw001 and ojw002 with PY79 genomic DNA as template) and pdr111 [amye::phypespank (spec)] cut with HindIII and NheI (D.R.Z., unpublished). pjw005 [yhdg::phyperspank-opt.rbs-sira (phleo)] was generated in a two-way ligation with a PCR product containing sira by cloning ynee (oligonucleotide primers ojw001 and ojw002 with PY79 genomic DNA as template) and pjw004 cut with HindIII and NheI. pjw004 [yhdg::phyperspank (phleo)] was generated in a two way ligation by cloning the 1770 bp BamHI EcoRI fragment containing Phyperspank and laci from pdr111 into pbb280 cut with EcoRI and BamHI. pbb280 [yhdg::phleo] is an ectopic integration vector for double crossover insertions into the nonessential yhdg locus (B. Burton and D.Z.R., unpublished). pjw006 [amye::phyperspank-gfp-sira (spec)] was generated in a two-way ligation with a HindIII-NheI PCR product containing gfp-sira (oligonucleotide primers olm022 and ojw002 and plm021 as template DNA) and pdr111 cut with HindIII and NheI.
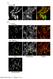
2 pjw020 [ycgo::pxyla-gfp-sira (erm)] was generated by subcloning the HindIII-BamHI fragment containing gfp-ynee from pjw006 into the prb036. prb036 [ycgo::pxyla-xylr (erm)] was generated by cloning the EcoRI-BamHI PxylA-xylR fragment from pdr150 into pkm084 cut with EcoRI and BamHI. pdr150 [amye::pxyla-xylr (spec)] is an ectopic integration containing the xylose-inducible promoter PxylA (D.Z.R., unpublished). pkm084 [ycgo::erm] is an ectopic integration vector for double crossover insertions into the nonessential ycgo locus (K.M. and D.Z.R., unpublished). pjw022 [BK-dnaA (kan)] was generated by cloning a NdeI-BamHI PCR product containing dnaa (oligonucleotide primers ojw021 and odr692 with PY79 genomic DNA as template) into the pgbkt7 (Clontech) cut with NdeI and BamHI. pjw023 [ADT7-sirA (amp)] was generated by cloning an EcoRI-BamHI PCR product containing sira (oligonucleotide primers ojw009 and ojw002 with PY79 genomic DNA as template) into pgadt7 (Clontech) cut with EcoRI BamHI. SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Figure S1. SirA expression is lethal to vegetatively growing cells. Cells (strain BJW38) harboring an IPTG-inducible promoter (P hyperspank ) fused to sira were analyzed before and after the addition of IPTG. Time (in min) after induction is indicated. Membranes were stained with the fluorescent dye FM4-64 (red) and DNA was stained with DAPI (false-colored green). Examples of anucleate cells (white carets) and guillotined nucleoids (yellow carets) are indicated. Figure S2. Replisome and origin foci are unaffected by the addition of IPTG. To control for the loss of DnaX-YFP foci (and reduction in number of TetR-GFP origin foci) upon the induction of SirA, cells (BKM1585 and BKM865) lacking P hyperspank -sira were treated with IPTG for 60 min. The replisome and origin foci were indistinguishable before and after addition of IPTG. Time (in min) before and after induction is indicated. DnaX-YFP and TetR-GFP foci were Wagner et al page 2
3 false-colored green. Membranes were stained with fluorescent dye FM4-64 (red) and DNA was stained with DAPI (blue). Figure S3. SirA inhibits DNA replication. (A) Cells were analyzed for ongoing replication using an SSB-GFP fusion. The Images show cells (strain BKM1797) before and after SirA induction. Time (in minutes) after induction is indicated. Prior to SirA induction all cells are actively replicating as evidenced by SSB-GFP (green) foci. Membranes were stained with fluorescent dye FM4-64 (red) and DNA was stained with DAPI (blue). Immunoblot analysis shows that SSB-GFP remains intact after SirA induction. SSB-GFP was analyzed using anti- GFP antibodies and the caret identifies the predicted size of free GFP. EzrA and σ A were used to control for loading. (B) Cells were analyzed for origin content using TetR-GFP bound to an array of tet operators adjacent to oric. Images show cells (strain BJW141) before and after SirA induction. Prior to SirA induction, most cells have 2 or 4 origin foci per DNA mass. After SirA induction, cells have a single origin focus per nucleoid. Figure S4. GFP-SirA is less potent inhibitor of growth than SirA. Cells harboring an IPTGinducible promoter (P hyperspank ) fused to sira (P hy -sira; strain BJW38), gfp-sira (P hy -gfp-sira; strain BJW101) or gfp (P hy -gfp; strain BDR1003) were streaked on LB agar plates with and without IPTG. Figure S5. The localization of GFP-SirA produced at low and high levels. At low levels, GFP- SirA does not efficiently inhibit replication and localizes in nucleoid-associated foci. At high levels, GFP-SirA inhibits replication and is present as a diffuse cytosolic haze. (A) Cells harboring an IPTG-inducible promoter (P hyperspank ) (strain BJW101) or a xylose-inducible promoter (P xyla ) (strain BJW196) fused to gfp-sira were visualized after 60 min of induction. Membranes were stained with the fluorescent dye FM4-64 (red) and DNA was stained with DAPI (blue). (B) Comparison of protein levels in the two strains shown in A. Upper panel: Immunoblot analysis of GFP-SirA over an induction time course. Time (in min) is indicated. GFP-SirA was analyzed using anti-gfp antibodies. Lower Panel: Quantitative comparison of GFP-SirA levels. Immunoblot analysis of serial dilutions of whole-cell extracts from strain BJW101 (P hyperspank -gfp-sira) and strain BJW196 (P xyla -gfp-sira). The lysates were from cells Wagner et al page 3
4 induced for 60 min. The lysate from strain BJW196 was serially diluted into a whole-cell extract from wild-type cells (lacking GFP) such that each lane contained the same amount of total protein. Expression from the P xyla promoter resulted in ~10-fold lower steady-state levels of the GFP-SirA than expression from P hyperspank. Figure S6. GFP-SirA co-localizes with oric. Cells (strain BJW252) harboring a teto array adjacent to oric and producing low levels of GFP-SirA and TetR-mCherry were visualized by fluorescence microscopy. Membranes were stained with TMA-DPH (blue). GFP-SirA (green), TetR-mCherry (red) bound near oric, and the merged image are shown. Carets highlight prominent foci present in all channels. Figure S7. KinA induction in nutrient replete conditions results in over-replication and production of twins. (A) Cells sporulated in rich medium by induction of the sensor kinase KinA were analyzed for origin content using TetR-GFP bound to a teto array adjacent to oric. The images show the SirA mutant (strain BJW279) after 2 hrs of KinA induction. Yellow carets highlight cells with more than two origin foci (green) in the forespore. White carets highlight cells with more than two origin foci in the mother cell. The pink caret highlights a representative twin, possessing two developing forespores with four origin markers and four nucleoids. Membranes were stained with FM4-64 (red) and DNA was stained with DAPI (blue). (B) An example of a mother cell and twin forespores after 4 hr of KinA induction. White carets indicate the location of phase-grey endospores. At this late stage, DAPI is unable to access the forespore chromosomes. SUPPLEMENTAL REFERENCES Berkmen, M.B., and Grossman, A.D. (2007) Subcellular positioning of the origin region of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome is independent of sequences within oric, the site of replication initiation, and the replication initiator DnaA. Mol Microbiol 63: Bhavsar, A.P., Zhao, X., and Brown, E.D. (2001) Development and characterization of a xylosedependent system for expression of cloned genes in Bacillus subtilis: conditional complementation of a teichoic acid mutant. Appl Environ Microbiol 67: Fujita, M., and Losick, R. (2005) Evidence that entry into sporulation in Bacillus subtilis is governed by a gradual increase in the level and activity of the master regulator Spo0A. Genes Dev 19: Wagner et al page 4
5 Lemon, K.P., and Grossman, A.D. (1998) Localization of bacterial DNA polymerase: evidence for a factory model of replication. Science 282: Marquis, K.A., Burton, B.M., Nollmann, M., Ptacin, J.L., Bustamante, C., Ben-Yehuda, S., and Rudner, D.Z. (2008) SpoIIIE strips proteins off the DNA during chromosome translocation. Genes Dev 22: Murray, H., and Errington, J. (2008) Dynamic control of the DNA replication initiation protein DnaA by Soj/ParA. Cell 135: Simmons, L.A., Grossman, A.D., and Walker, G.C. (2007) Replication is required for the RecA localization response to DNA damage in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104: Youngman, P.J., Perkins, J.B., and Losick, R. (1983) Genetic transposition and insertional mutagenesis in Bacillus subtilis with Streptococcus faecalis transposon Tn917. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 80: Wagner et al page 5
6 Figure S1 Wagner et al. SirA induction T0 T60 T90 T120
7 Figure S2 Wagner et al. Replisome foci before and after addition of IPTG T0 T60 DnaX-YFP mb/dnax-yfp mb/yfp/dna Origin foci before and after addition of IPTG T0 T60 TetR-GFP -7 ::(teto) 25 mb/tetr-gfp mb/gfp/dna
8 Figure S3 Wagner et al. A SirA induction T0 T0 T60 SSB-GFP EzrA T60 σ A B SirA induction SSB-GFP SSB-GFP/mb SSB-GFP/mb/DNA T0 T60 T90-7 ::(teto) 25, TetR-GFP
9 Figure S4 Wagner et al. P hy -gfp P hy -gfp P hy -sira Phy -sira Phy -gfp-sira -IPTG +IPTG Phy -gfp-sira
10 Figure S5 Wagner et al. A GFP-SirA GFP-SirA GFP-SirA/mb mb/dna merge P hyspank -gfp-sira P xyla -gfp-sira T0 T20 T40 T60 T80 T0 T20 T40 T60 T80 GFP-SirA P hyspank -gfp-sira P xyla -gfp-sira 1 1/2 1/4 1/8 1/16 1/32 1/64 1 P xyla P hyperspank B GFP-SirA
11 GFP-SirA origin marker merge Figure S6 Wagner et al.
12 Figure S7 Wagner et al. A KinA induction (hour 2) -7 ::(teto) 25 TetR-GFP sira B KinA induction (hour 4) membranes phase contrast DNA
13 Table S1 Strains Used in this study Strain Genotype Reference Figure PY79 wild-type Youngman et al BDR1003 amye::phyperspank-gfp(spec) This work 2A, S3 LAS223 dnaaωpspac-dnaa (tet) Simmons et al B, 3C BJW38 amye::phyperspank-sira (spec) This work 2A, 2B, 3C, S1 BJW82 dnaaωpspac-dnaa (tet), dnaxω-yfp (phleo) This work BJW84 amye::phyperspank-sira (spec),dnaxω-yfp (phleo) This work 3A BJW91 dnaxω-yfp (phleo), sira::tet This work 7A BJW101 amye::phyperspank-gfp-sira (spec) This work S3, S4A, S4B, S4C BJW118 amye::pspac(c)-tetr-gfp (spec), yycr::(teto)25 (erm), sira::tet This work BJW136 amye::pspac(c)-tetr-gfp (spec), yycr::(teto)25 (erm), dnaaωpspac-dnaa (tet) This work BJW141 amye::pspac(c)-tetr-gfp (spec), yycr::(teto)25 (erm), yhdg::phyperspank-sira (phleo) This work 3B, S2B BJW145 amye::pspac(c)-tetr-gfp (spec), ywji::(teto)25 (erm) This work BJW156 amye::pspac(c)-tetr-gfp (spec), ywji::(teto)25 (erm), sira::tet This work BJW173* phea1, 359 ::orin repn (kan), oric-s, yhdg::phypespank-sira (phleo) This work 4 BJW174* trpc2, phea1, 359 ::oric dnaan (kan), (oric-l)::spec, yhdg::phyperspank-sira (phleo) This work 4 BJW192 yhdg::phyperspank-sira (phleo), amye::pspac(c)-tetr-gfp (spec), ywji::(teto)25 (erm) This work BJW196 ycgo::pxyla-gfp-sira (erm) This work 6A, S4A, S4B, S4C BJW197 dnaaωpspac-dnaa (tet), ycgo::pxyla-gfp-sira (erm) This work 5B, 5C, 6B BJW218 amye::psweet-dnaa-gfp (spec), yhdg::phyperspank-sira (phleo) This work 5A BJW230 kinaωphyperspank-kina (cat), dnaxω-yfp (phleo) This work 7C BJW232 kinaωphyperspank-kina (cat), dnaxω-yfp (phleo), sira::tet This work 7C BJW252 amye::pxyla-tetr-mcherry (spec), yycr::(teto)120 (cat), ycgo::pxyla-gfp-sira (erm) This work S5 BJW271 amye::pxyla-ssb-gfp (cat), spo0aωphyperspank-spo0a(sad67) (spec) This work 7B BJW275 amye::pxyla-ssb-gfp (cat), spo0aωphyperspank-spo0a(sad67) (spec), sira::tet This work 7B BJW279 amye::pspac(c)-tetr-gfp(spec), yycr::(teto)25 (erm), kinaaωphyperspank-kina (cat) This work 7D BJW280 amye::pspac(c)-tetr-gfp(spec), yycr::(teto)25 (erm), kinaaωphyperspank-kina (cat), sira::tet This work 7D, S6 BKM830 amye::pspac(c)-tetr-gfp (spec) Marquis et al BKM838 yycr::(teto)120 (cat) Marquis et al BKM865 amye::pspac(c)-tetr-gfp (spec), yycr::(teto)25 (cat) This work BKM918 yycr::(teto)25(erm) This work BKM1585 dnaxω-yfp (phleo) This work 7A BKM1797 yhdg::phyperspank-sira (phleo), amye::pxyla-ssb-gfp (cat) This work S2A BNS1733 dnab134 (ts-) zhb-83::tn917 (erm) This work 3C HM422 amye::pxyla-tetr-mcherry (spec), trpc2 Murray & Errington 2008 MF1913 kinaaωphyperspank-kina(cat) Fujita & Losick 2005 MF2146 spo0aωphyperspank-spo0a(sad67) (spec) Fujita & Losick 2005 MMB208* phea1, 359 ::orin repn (kan), oric-s Berkmen & Grossman 2007 MMB612* trpc2, phea1, 359 ::oric dnaan (kan), (oric-l)::spec Berkmen & Grossman 2007 RL2285 amye::pxyla-ssb-gfp (cat) a gift from M Yang & R Losick AH109 MATa, trp1-901, leu2-3, 112, ura3-52, his3-200, gal4d, gal80d, LYS2::GAL1UAS-GAL1TATA- HIS3, GAL2UAS-GAL2TATA-ADE2, URA3::MEL1UAS-MEL1TATA-lacZ, MEL1 Clontech * Derived from the wild-type strain JH642 (trpc2, phea1)
14 Table S2 Plasmids used in this study plasmid description reference pkm288 dnax-yfp (phleo) This work pkm322 amye::psweet-dnaa-gfp (spec) This work pjw002 amye::phyperspank-opt.rbs-sira (spec) This work pjw005 yhdg::phyperspank-opt.rbs-sira (phleo) This work pjw006 amye::phyperspank-gfp-sira (spec) This work pjw020 ycgo::pxyla-gfp-sira (erm) This work pjw022 BK-dnaA (kan) This work pjw023 ADT7-sirA (amp) This work Table S3 Oligonucleotides used in this study Primer Sequence (5 to 3 ) odr078 gccggatccttatttgtatagttcatccatgcc odr098 cggctgcagcaacgttcttgccattgctgc odr458 gccaagcttagtgatagagaagacgaaccgtcc odr459 cggctcgagcattacagtttacgaaccgaacagg odr692 cgcggatcctatttaagctgttctttaatttc odr701 cggctgcagtttaagctgttctttaatttcttttac odr702 cggctgcagggttccggaatgagtaaaggag ojw001 cgcaagcttacataaggaggaactactatggaacgtcactactatacg ojw002 gccgctagcggatccggttttagacaaaatttctttc ojw009 gccgaattcatggaacgtcactactatacg ojw014 cgcaagcttacataaggaggaactactatgaaagtaagcaccaaagacaaa ojw015 tttgctagcggatcccggtgctagttggtgagcgccac ojw021 cggcatatggaaaatatattagacctgtgg ojw022 aatacgactcactatagggc ojw023 agatggtgcacgatgcac olm022 gccgaattccttctcagttccgaacg
Plasmid construction SUPPLEMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
 SUPPLEMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Plasmid construction pjk005 [amye::phy-refz-gfp (spec)(amp)] was generated in a two-way ligation with a PCR product containing refz-gfp (oligonucleotide primers ojw020
SUPPLEMENTAL EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Plasmid construction pjk005 [amye::phy-refz-gfp (spec)(amp)] was generated in a two-way ligation with a PCR product containing refz-gfp (oligonucleotide primers ojw020
-7 ::(teto) ::(teto) 120. GFP membranes merge. overexposed. Supplemental Figure 1 (Marquis et al.)
 P spoiie -gfp -7 ::(teto) 120-91 ::(teto) 120 GFP membranes merge overexposed Supplemental Figure 1 (Marquis et al.) Figure S1 TetR-GFP is stripped off the teto array in sporulating cells that contain
P spoiie -gfp -7 ::(teto) 120-91 ::(teto) 120 GFP membranes merge overexposed Supplemental Figure 1 (Marquis et al.) Figure S1 TetR-GFP is stripped off the teto array in sporulating cells that contain
The SMC Condensin Complex Is Required for Origin Segregation in Bacillus subtilis
 Current Biology, Volume 24 Supplemental Information The SMC Condensin Complex Is Required for Origin Segregation in Bacillus subtilis Xindan Wang, Olive W. Tang, Eammon P. Riley, and David Z. Rudner Inventory
Current Biology, Volume 24 Supplemental Information The SMC Condensin Complex Is Required for Origin Segregation in Bacillus subtilis Xindan Wang, Olive W. Tang, Eammon P. Riley, and David Z. Rudner Inventory
Δsig. ywa. yjbm. rela -re. rela
 A wt A. A, P rela -re la A/Δ yjbm A/Δ ywa C A, P hy-s igd, D (A, P IPTG hy-s igd, ) D D (+ IPTG ) D/Δ rela Figure S1 SigD B. Figure S1. SigD levels and swimming motility in (p)ppgpp synthetase mutants.
A wt A. A, P rela -re la A/Δ yjbm A/Δ ywa C A, P hy-s igd, D (A, P IPTG hy-s igd, ) D D (+ IPTG ) D/Δ rela Figure S1 SigD B. Figure S1. SigD levels and swimming motility in (p)ppgpp synthetase mutants.
Figure S1A Doan et al. T2.5
 Figure S1A T2 wild-type spoiiie T2.5 Figure S1B T2 wild-type spoiiie T2.5 Figure S2 wt membranes T 3.5 T3 T 2.5 T2 T 1.5 membranes T4 CFP T 4.5 phase ΔfisB CFP phase FM4-64 TMA-DPH TMA-DPH + CFP Figure
Figure S1A T2 wild-type spoiiie T2.5 Figure S1B T2 wild-type spoiiie T2.5 Figure S2 wt membranes T 3.5 T3 T 2.5 T2 T 1.5 membranes T4 CFP T 4.5 phase ΔfisB CFP phase FM4-64 TMA-DPH TMA-DPH + CFP Figure
Briana M. Burton, Kathleen A. Marquis, Nora L. Sullivan, Tom A. Rapoport, and David Z. Rudner
 Cell, Volume 131 Supplemental Data The ATPase SpoIIIE Transports DNA across Fused Septal Membranes during Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis Briana M. Burton, Kathleen A. Marquis, Nora L. Sullivan, Tom A.
Cell, Volume 131 Supplemental Data The ATPase SpoIIIE Transports DNA across Fused Septal Membranes during Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis Briana M. Burton, Kathleen A. Marquis, Nora L. Sullivan, Tom A.
FtsEX is required for CwlO peptidoglycan hydrolase activity during cell wall elongation in Bacillus subtilis
 FtsEX is required for CwlO peptidoglycan hydrolase activity during cell wall elongation in Bacillus subtilis Jeffrey Meisner, Paula Montero Llopis, Lok-To Sham, Ethan Garner, Thomas G. Bernhardt, David
FtsEX is required for CwlO peptidoglycan hydrolase activity during cell wall elongation in Bacillus subtilis Jeffrey Meisner, Paula Montero Llopis, Lok-To Sham, Ethan Garner, Thomas G. Bernhardt, David
Supporting information
 Supporting information Construction of strains and plasmids To create ptc67, a PCR product obtained with primers cc2570-162f (gcatgggcaagcttgaggacggcgtcatgt) and cc2570+512f (gaggccgtggtaccatagaggcgggcg),
Supporting information Construction of strains and plasmids To create ptc67, a PCR product obtained with primers cc2570-162f (gcatgggcaagcttgaggacggcgtcatgt) and cc2570+512f (gaggccgtggtaccatagaggcgggcg),
Figure S1. gfp tola and pal mcherry can complement deletion mutants of tola and pal respectively. (A)When strain LS4522 was grown in the presence of
 Figure S1. gfp tola and pal mcherry can complement deletion mutants of tola and pal respectively. (A)When strain LS4522 was grown in the presence of xylose, inducing expression of gfp-tola, localization
Figure S1. gfp tola and pal mcherry can complement deletion mutants of tola and pal respectively. (A)When strain LS4522 was grown in the presence of xylose, inducing expression of gfp-tola, localization
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1203285/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Coupled, Circumferential Motions of the Cell Wall Synthesis Machinery and MreB Filaments in B. subtilis Ethan C. Garner,*
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.1203285/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Coupled, Circumferential Motions of the Cell Wall Synthesis Machinery and MreB Filaments in B. subtilis Ethan C. Garner,*
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Study of mgtl translation in vitro. (A) Detection of 5 LR RNA using wild-type and anti-sd (91-95) substituted templates in a transcription-translation
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Study of mgtl translation in vitro. (A) Detection of 5 LR RNA using wild-type and anti-sd (91-95) substituted templates in a transcription-translation
A fail-safe mechanism in the septal ring assembly pathway generated by the sequential recruitment of cell separation amidases and their activators
 Supplemental Information for: A fail-safe mechanism in the septal ring assembly pathway generated by the sequential recruitment of cell separation amidases and their activators Nick T. Peters, Thuy Dinh,
Supplemental Information for: A fail-safe mechanism in the septal ring assembly pathway generated by the sequential recruitment of cell separation amidases and their activators Nick T. Peters, Thuy Dinh,
P52A/R67A. The plasmids expressing AD-fused Atg1 variants were constructed as follows: DNA
 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA The Autophagy-Related Protein Kinase Atg1 Interacts with the Ubiquitin-Like Protein Atg8 via the Atg8 Family Interacting Motif to Facilitate Autophagosome Formation Hitoshi Nakatogawa,
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA The Autophagy-Related Protein Kinase Atg1 Interacts with the Ubiquitin-Like Protein Atg8 via the Atg8 Family Interacting Motif to Facilitate Autophagosome Formation Hitoshi Nakatogawa,
A) (5 points) As the starting step isolate genomic DNA from
 GS Final Exam Spring 00 NAME. bub ts is a recessive temperature sensitive mutation in yeast. At º C bub ts cells grow normally, but at º C they die. Use the information below to clone the wild-type BUB
GS Final Exam Spring 00 NAME. bub ts is a recessive temperature sensitive mutation in yeast. At º C bub ts cells grow normally, but at º C they die. Use the information below to clone the wild-type BUB
Freire et al. - Supplemental Material for Trypanosoma brucei translation-initiation factor homolog EIF4E6 is linked to posttranscriptional regulation
 Freire et al. - Supplemental Material for Trypanosoma brucei translation-initiation factor homolog EIF4E6 is linked to posttranscriptional regulation Table S1 Oligonucleotides used in this study Table
Freire et al. - Supplemental Material for Trypanosoma brucei translation-initiation factor homolog EIF4E6 is linked to posttranscriptional regulation Table S1 Oligonucleotides used in this study Table
Design. Construction. Characterization
 Design Construction Characterization DNA mrna (messenger) A C C transcription translation C A C protein His A T G C T A C G Plasmids replicon copy number incompatibility selection marker origin of replication
Design Construction Characterization DNA mrna (messenger) A C C transcription translation C A C protein His A T G C T A C G Plasmids replicon copy number incompatibility selection marker origin of replication
Nucleoid occlusion prevents cell division during replication fork arrest in Bacillus subtilismmi_
 Molecular Microbiology (2010) 78(4), 866 882 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07369.x First published online 23 September 2010 Nucleoid occlusion prevents cell division during replication fork arrest in Bacillus
Molecular Microbiology (2010) 78(4), 866 882 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07369.x First published online 23 September 2010 Nucleoid occlusion prevents cell division during replication fork arrest in Bacillus
The fusion used in most of these studies (MinC4-GFP) contains GFP and
 Gregory, Becker and Pogliano, Supplemental Materials page 1 Supplemental Methods Description of the MinC and MinD GFP insertions The fusion used in most of these studies (MinC4-GFP) contains GFP and flanking
Gregory, Becker and Pogliano, Supplemental Materials page 1 Supplemental Methods Description of the MinC and MinD GFP insertions The fusion used in most of these studies (MinC4-GFP) contains GFP and flanking
Supplemental Material: Rev1 promotes replication through UV lesions in conjunction with DNA
 Supplemental Material: Rev1 promotes replication through UV lesions in conjunction with DNA polymerases,, and, but not with DNA polymerase Jung-Hoon Yoon, Jeseong Park, Juan Conde, Maki Wakamiya, Louise
Supplemental Material: Rev1 promotes replication through UV lesions in conjunction with DNA polymerases,, and, but not with DNA polymerase Jung-Hoon Yoon, Jeseong Park, Juan Conde, Maki Wakamiya, Louise
Product Information GetClone PCR Cloning Vector II. Storage -20 C for 24 months
 www.smobio.com Product Information GetClone PCR Cloning Vector II CV1100 20 RXN pget II Vector (25 ng/μl) pget-for Primer (10 μm) pget-rev Primer (10 μm) Storage -20 C for 24 months 23 μl 100 μl 100 μl
www.smobio.com Product Information GetClone PCR Cloning Vector II CV1100 20 RXN pget II Vector (25 ng/μl) pget-for Primer (10 μm) pget-rev Primer (10 μm) Storage -20 C for 24 months 23 μl 100 μl 100 μl
Supplemental Material. Supplemental Tables. Table S1. Strains used in this study.
 Supplemental Material Supplemental Tables Table S1. Strains used in this study. Strain Genotype Reference E. coli strains S17-1λpir Wild-type (1) BL21(DE3) Wild-type Life Technologies DH10B Wild-type Life
Supplemental Material Supplemental Tables Table S1. Strains used in this study. Strain Genotype Reference E. coli strains S17-1λpir Wild-type (1) BL21(DE3) Wild-type Life Technologies DH10B Wild-type Life
Supplemental Materials and Methods. Yeast strains. Strain genotypes are listed in Table S1. To generate MATainc::LEU2,
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Yeast strains. Strain genotypes are listed in Table S1. To generate MATainc::LEU2, the LEU2 marker was inserted by PCR-mediated recombination (BRACHMANN et al. 1998)
Supplemental Materials and Methods Yeast strains. Strain genotypes are listed in Table S1. To generate MATainc::LEU2, the LEU2 marker was inserted by PCR-mediated recombination (BRACHMANN et al. 1998)
Differential regulation of the hmscde operon in Yersinia pestis and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. by the Rcs phosphorelay system
 Differential regulation of the hmscde operon in Yersinia pestis and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis by the Rcs phosphorelay system Xiao-Peng Guo 1,2, Gai-Xian Ren 1,2, Hui Zhu 1, Xu-Jian Mao 1, Yi-Cheng Sun
Differential regulation of the hmscde operon in Yersinia pestis and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis by the Rcs phosphorelay system Xiao-Peng Guo 1,2, Gai-Xian Ren 1,2, Hui Zhu 1, Xu-Jian Mao 1, Yi-Cheng Sun
Reading Lecture 3: 24-25, 45, Lecture 4: 66-71, Lecture 3. Vectors. Definition Properties Types. Transformation
 Lecture 3 Reading Lecture 3: 24-25, 45, 55-66 Lecture 4: 66-71, 75-79 Vectors Definition Properties Types Transformation 56 VECTORS- Definition Vectors are carriers of a DNA fragment of interest Insert
Lecture 3 Reading Lecture 3: 24-25, 45, 55-66 Lecture 4: 66-71, 75-79 Vectors Definition Properties Types Transformation 56 VECTORS- Definition Vectors are carriers of a DNA fragment of interest Insert
pget1.1 Vector (50 ng/μl) 23 μl pget-for Primer (10 μm) 100 μl pget-rev Primer (10 μm) 100 μl
 www.smobio.com Product Information GetClone PCR Cloning Vector CV1000 20 RXN pget1.1 Vector (50 ng/μl) 23 μl pget-for Primer (10 μm) 100 μl pget-rev Primer (10 μm) 100 μl Storage -20 C for 24 months Features
www.smobio.com Product Information GetClone PCR Cloning Vector CV1000 20 RXN pget1.1 Vector (50 ng/μl) 23 μl pget-for Primer (10 μm) 100 μl pget-rev Primer (10 μm) 100 μl Storage -20 C for 24 months Features
Supplemental Data. Farmer et al. (2010) Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure 1. Amino acid sequence comparison of RAD23 proteins. Identical and similar residues are shown in the black and gray boxes, respectively. Dots denote gaps. The sequence of plant Ub is
Supplemental Figure 1. Amino acid sequence comparison of RAD23 proteins. Identical and similar residues are shown in the black and gray boxes, respectively. Dots denote gaps. The sequence of plant Ub is
Materials and methods. by University of Washington Yeast Resource Center) from several promoters, including
 Supporting online material for Elowitz et al. report Materials and methods Strains and plasmids. Plasmids expressing CFP or YFP (wild-type codons, developed by University of Washington Yeast Resource Center)
Supporting online material for Elowitz et al. report Materials and methods Strains and plasmids. Plasmids expressing CFP or YFP (wild-type codons, developed by University of Washington Yeast Resource Center)
Supplemental Fig. S1. Key to underlines: Key to amino acids:
 AspA-F1 AspA 1 MKQMETKGYGYFRKTKAYGLVCGIT--------------LAGALTLGTTSVSADDVTTLNPATNLTTLQTPPTADQTQLAHQAGQQSGELVSEVSNTEWD 86 SspB 1 MQKREV--FG-FRKSKVAKTLCGAV-LGAALIAIADQQVLADEVTETNSTANVAVTTTGNPATNLPEAQGEATEAASQSQAQAGSKDGALPVEVSADDLN
AspA-F1 AspA 1 MKQMETKGYGYFRKTKAYGLVCGIT--------------LAGALTLGTTSVSADDVTTLNPATNLTTLQTPPTADQTQLAHQAGQQSGELVSEVSNTEWD 86 SspB 1 MQKREV--FG-FRKSKVAKTLCGAV-LGAALIAIADQQVLADEVTETNSTANVAVTTTGNPATNLPEAQGEATEAASQSQAQAGSKDGALPVEVSADDLN
Gene expression. What is gene expression?
 Gene expression What is gene expression? Methods for measuring a single gene. Northern Blots Reporter genes Quantitative RT-PCR Operons, regulons, and stimulons. DNA microarrays. Expression profiling Identifying
Gene expression What is gene expression? Methods for measuring a single gene. Northern Blots Reporter genes Quantitative RT-PCR Operons, regulons, and stimulons. DNA microarrays. Expression profiling Identifying
Microbiology 微生物学 Spring-Summer
 Microbiology 微生物学 2017 Spring-Summer Relevant Information and Resources Course slides can be found at http://mypage.zju.edu.cn/haichun 教学工作 Course-related questions will be answered through emails. Textbook:
Microbiology 微生物学 2017 Spring-Summer Relevant Information and Resources Course slides can be found at http://mypage.zju.edu.cn/haichun 教学工作 Course-related questions will be answered through emails. Textbook:
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Chen et al. 1.173/pnas.153331112 Fig. S1. The sae2δ-suppressing mre11 alleles: protein level and location. (A) Protein level of Mre11 and Mre11 P11L expressed from the endogenous
Supporting Information Chen et al. 1.173/pnas.153331112 Fig. S1. The sae2δ-suppressing mre11 alleles: protein level and location. (A) Protein level of Mre11 and Mre11 P11L expressed from the endogenous
Supplementary figures
 Supplementary figures A ΔrelAΔlon ΔrelA ΔrelAΔlon Δlon ppgpp 0 Δlon B ΔrelAΔlon ΔrelA ΔrelAΔlon Δlon ppgpp 0 Δlon Fig. S1. Growth defect of strains in LB medium. Strains whose relevant genotypes are indicated
Supplementary figures A ΔrelAΔlon ΔrelA ΔrelAΔlon Δlon ppgpp 0 Δlon B ΔrelAΔlon ΔrelA ΔrelAΔlon Δlon ppgpp 0 Δlon Fig. S1. Growth defect of strains in LB medium. Strains whose relevant genotypes are indicated
Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of PALB2 -/- and BRCA2 -/- /PALB2 -/- DT40 cells. (A) Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs carrying
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of PALB2 -/- and BRCA2 -/- /PALB2 -/- DT40 cells. (A) Schematic representation of the endogenous PALB2 locus and gene-disruption constructs carrying
Table S1. List of DNA constructs and primers, part 1 Construct
 SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES: Table S1. List of DNA constructs and primers, part 1 Construct Comment (Expressed protein) Vector, PCR primers and template or source of Restriction Sites name Resistance construct
SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES: Table S1. List of DNA constructs and primers, part 1 Construct Comment (Expressed protein) Vector, PCR primers and template or source of Restriction Sites name Resistance construct
Regulation of ARE transcript 3 end processing by the. yeast Cth2 mrna decay factor
 Regulation of ARE transcript 3 end processing by the yeast Cth2 mrna decay factor Manoël Prouteau, Marie-Claire Daugeron and Bertrand Séraphin Supplementary Information Material and Methods Plasmid construction
Regulation of ARE transcript 3 end processing by the yeast Cth2 mrna decay factor Manoël Prouteau, Marie-Claire Daugeron and Bertrand Séraphin Supplementary Information Material and Methods Plasmid construction
Genetics Lecture Notes Lectures 13 16
 Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 13 16 Lecture 13 Transposable elements Transposons are usually from 10 3 to 10 4 base pairs in length, depending on the transposon type. The key property of transposons
Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 13 16 Lecture 13 Transposable elements Transposons are usually from 10 3 to 10 4 base pairs in length, depending on the transposon type. The key property of transposons
BIO 202 Midterm Exam Winter 2007
 BIO 202 Midterm Exam Winter 2007 Mario Chevrette Lectures 10-14 : Question 1 (1 point) Which of the following statements is incorrect. a) In contrast to prokaryotic DNA, eukaryotic DNA contains many repetitive
BIO 202 Midterm Exam Winter 2007 Mario Chevrette Lectures 10-14 : Question 1 (1 point) Which of the following statements is incorrect. a) In contrast to prokaryotic DNA, eukaryotic DNA contains many repetitive
Recombinant DNA Libraries and Forensics
 MIT Department of Biology 7.014 Introductory Biology, Spring 2005 A. Library construction Recombinant DNA Libraries and Forensics Recitation Section 18 Answer Key April 13-14, 2005 Recall that earlier
MIT Department of Biology 7.014 Introductory Biology, Spring 2005 A. Library construction Recombinant DNA Libraries and Forensics Recitation Section 18 Answer Key April 13-14, 2005 Recall that earlier
Fig. S1. CrgA intracellular levels in M. tuberculosis. Ten and twenty micrograms of
 Supplementary data Fig. S1. CrgA intracellular levels in M. tuberculosis. Ten and twenty micrograms of cell free protein lysates from WT M. tuberculosis (Rv) together with various known concentrations
Supplementary data Fig. S1. CrgA intracellular levels in M. tuberculosis. Ten and twenty micrograms of cell free protein lysates from WT M. tuberculosis (Rv) together with various known concentrations
Step 1: Digest vector with Reason for Step 1. Step 2: Digest T4 genomic DNA with Reason for Step 2: Step 3: Reason for Step 3:
 Biol/Chem 475 Spring 2007 Study Problems for Quiz 2 Quiz 2 (~50 pts) is scheduled for Monday May 14 It will cover all handouts and lab exercises to date except the handout/worksheet (yet to be distributed)
Biol/Chem 475 Spring 2007 Study Problems for Quiz 2 Quiz 2 (~50 pts) is scheduled for Monday May 14 It will cover all handouts and lab exercises to date except the handout/worksheet (yet to be distributed)
Materials and Methods: All strains were derivatives of SK1 and are listed in Supplemental Table 1.
 Supplemental Online Material: Materials and Methods: All strains were derivatives of SK1 and are listed in Supplemental Table 1. Constructs: pclb2-3ha-cdc5 and pclb2-3ha-cdc2 strains were constructed by
Supplemental Online Material: Materials and Methods: All strains were derivatives of SK1 and are listed in Supplemental Table 1. Constructs: pclb2-3ha-cdc5 and pclb2-3ha-cdc2 strains were constructed by
Figure S1 early log mid log late log stat.
 Figure S1 early log mid log late log stat. C D E F Fig. S1. The chromosome-expressed EI localizes to the cell poles independent of the growth phase and growth media. MG1655 (ptsi-mcherry) cells, which
Figure S1 early log mid log late log stat. C D E F Fig. S1. The chromosome-expressed EI localizes to the cell poles independent of the growth phase and growth media. MG1655 (ptsi-mcherry) cells, which
Figure 1. Map of cloning vector pgem T-Easy (bacterial plasmid DNA)
 Texas A&M University-Corpus Christi CHEM4402 Biochemistry II Laboratory Laboratory 6: Ligation & Bacterial Transformation (Bring your text and laptop to class if you wish to work on your assignment during
Texas A&M University-Corpus Christi CHEM4402 Biochemistry II Laboratory Laboratory 6: Ligation & Bacterial Transformation (Bring your text and laptop to class if you wish to work on your assignment during
Chapter 20 DNA Technology & Genomics. If we can, should we?
 Chapter 20 DNA Technology & Genomics If we can, should we? Biotechnology Genetic manipulation of organisms or their components to make useful products Humans have been doing this for 1,000s of years plant
Chapter 20 DNA Technology & Genomics If we can, should we? Biotechnology Genetic manipulation of organisms or their components to make useful products Humans have been doing this for 1,000s of years plant
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Risser and Callahan 10.1073/pnas.0909152106 SI Text Plasmid Construction. Plasmid pdr211 is a mobilizable shuttle vector containing P pete -pats. A fragment containing P pete was
Supporting Information Risser and Callahan 10.1073/pnas.0909152106 SI Text Plasmid Construction. Plasmid pdr211 is a mobilizable shuttle vector containing P pete -pats. A fragment containing P pete was
Chapter 4. Recombinant DNA Technology
 Chapter 4 Recombinant DNA Technology 5. Plasmid Cloning Vectors Plasmid Plasmids Self replicating Double-stranded Mostly circular DNA ( 500 kb) Linear : Streptomyces, Borrelia burgdorferi Replicon
Chapter 4 Recombinant DNA Technology 5. Plasmid Cloning Vectors Plasmid Plasmids Self replicating Double-stranded Mostly circular DNA ( 500 kb) Linear : Streptomyces, Borrelia burgdorferi Replicon
Supplementary Methods
 Supplementary Methods Reverse transcribed Quantitative PCR. Total RNA was isolated from bone marrow derived macrophages using RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen), DNase-treated (Promega RQ1), and reverse transcribed
Supplementary Methods Reverse transcribed Quantitative PCR. Total RNA was isolated from bone marrow derived macrophages using RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen), DNase-treated (Promega RQ1), and reverse transcribed
1a. What is the ratio of feathered to unfeathered shanks in the offspring of the above cross?
 1. Whether or not the shanks of chickens contains feathers is due to two independently assorting genes. Individuals have unfeathered shanks when they are homozygous for recessive genes at two loci; the
1. Whether or not the shanks of chickens contains feathers is due to two independently assorting genes. Individuals have unfeathered shanks when they are homozygous for recessive genes at two loci; the
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1 Condensin is required for condensation of rdna array during starvation (A) Loss of condensin blocks rdna condensation during
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Figure 1 Condensin is required for condensation of rdna array during starvation (A) Loss of condensin blocks rdna condensation during
Supplemental Data Genetic and Epigenetic Regulation of the FLO Gene Family Generates Cell-Surface Variation in Yeast
 Supplemental Data Genetic and Epigenetic Regulation of the FLO Gene Family Generates Cell-Surface Variation in Yeast S1 Adrian Halme, Stacie Bumgarner, Cora Styles and Gerald R. Fink Yeast Strain Construction
Supplemental Data Genetic and Epigenetic Regulation of the FLO Gene Family Generates Cell-Surface Variation in Yeast S1 Adrian Halme, Stacie Bumgarner, Cora Styles and Gerald R. Fink Yeast Strain Construction
Figure S1. Immunoblotting showing proper expression of tagged R and AVR proteins in N. benthamiana.
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Immunoblotting showing proper expression of tagged R and AVR proteins in N. benthamiana. YFP:, :CFP, HA: and (A) and HA, CFP and YFPtagged and AVR1-CO39 (B) were expressed
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Immunoblotting showing proper expression of tagged R and AVR proteins in N. benthamiana. YFP:, :CFP, HA: and (A) and HA, CFP and YFPtagged and AVR1-CO39 (B) were expressed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature10331 Supplemental Figures and Legends Supplementary Figure 1. Pch2-dependent suppression of DSBs at the rdna borders. a, Example of a CHEF gel/southern blot
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature10331 Supplemental Figures and Legends Supplementary Figure 1. Pch2-dependent suppression of DSBs at the rdna borders. a, Example of a CHEF gel/southern blot
1a. What is the ratio of feathered to unfeathered shanks in the offspring of the above cross?
 Problem Set 5 answers 1. Whether or not the shanks of chickens contains feathers is due to two independently assorting genes. Individuals have unfeathered shanks when they are homozygous for recessive
Problem Set 5 answers 1. Whether or not the shanks of chickens contains feathers is due to two independently assorting genes. Individuals have unfeathered shanks when they are homozygous for recessive
Figure S1, related to Figure 1. Characterization of biosensor behavior in vivo.
 Developmental Cell, Volume 23 Supplemental Information Separase Biosensor Reveals that Cohesin Cleavage Timing Depends on Phosphatase PP2A Cdc55 Regulation Gilad Yaakov, Kurt Thorn, and David O. Morgan
Developmental Cell, Volume 23 Supplemental Information Separase Biosensor Reveals that Cohesin Cleavage Timing Depends on Phosphatase PP2A Cdc55 Regulation Gilad Yaakov, Kurt Thorn, and David O. Morgan
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Beauregard et al. 10.1073/pnas.1218984110 Fig. S1. Model depicting the regulatory pathway leading to expression of matrix genes. The master regulator Spo0A can be directly or indirectly
Supporting Information Beauregard et al. 10.1073/pnas.1218984110 Fig. S1. Model depicting the regulatory pathway leading to expression of matrix genes. The master regulator Spo0A can be directly or indirectly
A RRM1 H2AX DAPI. RRM1 H2AX DAPI Merge. Cont. sirna RRM1
 A H2AX DAPI H2AX DAPI Merge Cont sirna Figure S1: Accumulation of RRM1 at DNA damage sites (A) HeLa cells were subjected to in situ detergent extraction without IR irradiation, and immunostained with the
A H2AX DAPI H2AX DAPI Merge Cont sirna Figure S1: Accumulation of RRM1 at DNA damage sites (A) HeLa cells were subjected to in situ detergent extraction without IR irradiation, and immunostained with the
SAS6-like protein in Plasmodium indicates that conoid-associated apical complex proteins persist in invasive stages within the mosquito vector
 SAS6-like protein in Plasmodium indicates that conoid-associated apical complex proteins persist in invasive stages within the mosquito vector Richard J. Wall 1,#, Magali Roques 1,+, Nicholas J. Katris
SAS6-like protein in Plasmodium indicates that conoid-associated apical complex proteins persist in invasive stages within the mosquito vector Richard J. Wall 1,#, Magali Roques 1,+, Nicholas J. Katris
Bioprinting living biofilms through optogenetic manipulation
 Supporting Information Bioprinting living biofilms through optogenetic manipulation Yajia Huang,, Aiguo Xia,, Guang Yang, *, and Fan Jin *, Department of Biomedical Engineering, College of Life Science
Supporting Information Bioprinting living biofilms through optogenetic manipulation Yajia Huang,, Aiguo Xia,, Guang Yang, *, and Fan Jin *, Department of Biomedical Engineering, College of Life Science
Certificate of Analysis
 Certificate of Analysis Table of Contents Product Information... 1 Description... 2 Location of Features... 3 Additional Information... 3 Quality Control Data... 4 Catalog No. Amount Lot Number 631972
Certificate of Analysis Table of Contents Product Information... 1 Description... 2 Location of Features... 3 Additional Information... 3 Quality Control Data... 4 Catalog No. Amount Lot Number 631972
DNA Technology. Asilomar Singer, Zinder, Brenner, Berg
 DNA Technology Asilomar 1973. Singer, Zinder, Brenner, Berg DNA Technology The following are some of the most important molecular methods we will be using in this course. They will be used, among other
DNA Technology Asilomar 1973. Singer, Zinder, Brenner, Berg DNA Technology The following are some of the most important molecular methods we will be using in this course. They will be used, among other
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 Supplemental material Laloux and Jacobs-Wagner, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201303036/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Supporting data on the PopZ variants. Related
Supplemental material Laloux and Jacobs-Wagner, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201303036/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. Supporting data on the PopZ variants. Related
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION 1 Supplementary Figure S1. Proportion of HEK293T transfectants showing fluorescent foci after heat sho Blinded slides were counted for the appearance of fluorescent foci of tagrfp-t
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION 1 Supplementary Figure S1. Proportion of HEK293T transfectants showing fluorescent foci after heat sho Blinded slides were counted for the appearance of fluorescent foci of tagrfp-t
Confirming the Phenotypes of E. coli Strains
 Confirming the Phenotypes of E. coli Strains INTRODUCTION Before undertaking any experiments, we need to confirm that the phenotypes of the E. coli strains we intend to use in the planned experiments correspond
Confirming the Phenotypes of E. coli Strains INTRODUCTION Before undertaking any experiments, we need to confirm that the phenotypes of the E. coli strains we intend to use in the planned experiments correspond
7.03, 2005, Lecture 20 EUKARYOTIC GENES AND GENOMES I
 7.03, 2005, Lecture 20 EUKARYOTIC GENES AND GENOMES I For the last several lectures we have been looking at how one can manipulate prokaryotic genomes and how prokaryotic genes are regulated. In the next
7.03, 2005, Lecture 20 EUKARYOTIC GENES AND GENOMES I For the last several lectures we have been looking at how one can manipulate prokaryotic genomes and how prokaryotic genes are regulated. In the next
The Central Dogma. 1) A simplified model. 2) Played out across life. 3) Many points for control.
 Molecular Biology The Central Dogma 1) A simplified model. 2) Played out across life. 3) Many dis@nct points for control. Molecular Biology DNA: four nucleo@de bases (GC,AT) (2 bits) gene@c code in 3 base
Molecular Biology The Central Dogma 1) A simplified model. 2) Played out across life. 3) Many dis@nct points for control. Molecular Biology DNA: four nucleo@de bases (GC,AT) (2 bits) gene@c code in 3 base
Optimization of gene expression cassette for M. gryphiswaldense
 Optimization of gene expression cassette for M. gryphiswaldense A) 325 bp P mamdc 270 bp 170 bp 102 bp 45 bp egfp Gradual truncation P mamdc45 egfp minimal transcriptionally active promoter B) P mamdc45
Optimization of gene expression cassette for M. gryphiswaldense A) 325 bp P mamdc 270 bp 170 bp 102 bp 45 bp egfp Gradual truncation P mamdc45 egfp minimal transcriptionally active promoter B) P mamdc45
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1.
 Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
Hetero-Stagger PCR Cloning Kit
 Product Name: Code No: Size: DynaExpress Hetero-Stagger PCR Cloning Kit DS150 20 reactions Kit Components: Box 1 (-20 ) phst-1 Vector, linearized Annealing Buffer Ligase Mixture phst Forward Sequence Primer
Product Name: Code No: Size: DynaExpress Hetero-Stagger PCR Cloning Kit DS150 20 reactions Kit Components: Box 1 (-20 ) phst-1 Vector, linearized Annealing Buffer Ligase Mixture phst Forward Sequence Primer
7.1 Techniques for Producing and Analyzing DNA. SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau
 7.1 Techniques for Producing and Analyzing DNA SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau What is Biotechnology? From Merriam-Webster: the manipulation of living organisms or their components to produce useful usually commercial
7.1 Techniques for Producing and Analyzing DNA SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau What is Biotechnology? From Merriam-Webster: the manipulation of living organisms or their components to produce useful usually commercial
7.013 Practice Quiz
 MIT Department of Biology 7.013: Introductory Biology - Spring 2005 Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor Tyler Jacks, Dr. Claudette Gardel 7.013 Practice Quiz 2 2004 1 Question 1 A. The primer
MIT Department of Biology 7.013: Introductory Biology - Spring 2005 Instructors: Professor Hazel Sive, Professor Tyler Jacks, Dr. Claudette Gardel 7.013 Practice Quiz 2 2004 1 Question 1 A. The primer
Chapter 20 Recombinant DNA Technology. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 20 Recombinant DNA Technology Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 20.1 Recombinant DNA Technology Began with Two Key Tools: Restriction Enzymes and DNA Cloning Vectors Recombinant DNA refers
Chapter 20 Recombinant DNA Technology Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 20.1 Recombinant DNA Technology Began with Two Key Tools: Restriction Enzymes and DNA Cloning Vectors Recombinant DNA refers
Modules for cloning-free chromatin tagging in Saccharomyces cerevisae
 Yeast Yeast 2008; 25: 235 239. Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).1580 Yeast Functional Analysis Report Modules for cloning-free chromatin tagging in Saccharomyces cerevisae
Yeast Yeast 2008; 25: 235 239. Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).1580 Yeast Functional Analysis Report Modules for cloning-free chromatin tagging in Saccharomyces cerevisae
Supplemental Figure 1 HDA18 has an HDAC domain and therefore has concentration dependent and TSA inhibited histone deacetylase activity.
 Supplemental Figure 1 HDA18 has an HDAC domain and therefore has concentration dependent and TSA inhibited histone deacetylase activity. (A) Amino acid alignment of HDA5, HDA15 and HDA18. The blue line
Supplemental Figure 1 HDA18 has an HDAC domain and therefore has concentration dependent and TSA inhibited histone deacetylase activity. (A) Amino acid alignment of HDA5, HDA15 and HDA18. The blue line
3 Designing Primers for Site-Directed Mutagenesis
 3 Designing Primers for Site-Directed Mutagenesis 3.1 Learning Objectives During the next two labs you will learn the basics of site-directed mutagenesis: you will design primers for the mutants you designed
3 Designing Primers for Site-Directed Mutagenesis 3.1 Learning Objectives During the next two labs you will learn the basics of site-directed mutagenesis: you will design primers for the mutants you designed
Adenoviral Expression Systems. Lentivirus is not the only choice for gene delivery. Adeno-X
 Adenoviral Expression Systems Lentivirus is not the only choice for gene delivery 3 Adeno-X Why choose adenoviral gene delivery? Table I: Adenoviral vs. Lentiviral Gene Delivery Lentivirus Adenovirus Infects
Adenoviral Expression Systems Lentivirus is not the only choice for gene delivery 3 Adeno-X Why choose adenoviral gene delivery? Table I: Adenoviral vs. Lentiviral Gene Delivery Lentivirus Adenovirus Infects
BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Week of Nov 29
 BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Week of Nov 29 Additional Practice Problems for Section Problem 1. A linear piece of DNA is digested with restriction enzymes EcoRI and HinDIII, and the products are separated
BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Week of Nov 29 Additional Practice Problems for Section Problem 1. A linear piece of DNA is digested with restriction enzymes EcoRI and HinDIII, and the products are separated
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FIGURE LEGENDS Fig. S1. Radiation-induced phosphorylation of Rad50 at a specific site. A. Rad50 is an in vitro substrate for ATM. A series of Rad50-GSTs covering the entire molecule
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FIGURE LEGENDS Fig. S1. Radiation-induced phosphorylation of Rad50 at a specific site. A. Rad50 is an in vitro substrate for ATM. A series of Rad50-GSTs covering the entire molecule
7.02 Recombinant DNA Methods Spring 2005 Exam Study Questions Answer Key
 MIT Department of Biology 7.02 Experimental Biology & Communication, Spring 2005 7.02/10.702 Spring 2005 RDM Exam Study Questions 7.02 Recombinant DNA Methods Spring 2005 Exam Study Questions Answer Key
MIT Department of Biology 7.02 Experimental Biology & Communication, Spring 2005 7.02/10.702 Spring 2005 RDM Exam Study Questions 7.02 Recombinant DNA Methods Spring 2005 Exam Study Questions Answer Key
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Detection of MCM-subunit SUMOylation under normal growth conditions. a. Sumoylated forms of MCM subunits show differential shifts when SUMO is attached to differently sized tags.
Supplementary Figure 1 Detection of MCM-subunit SUMOylation under normal growth conditions. a. Sumoylated forms of MCM subunits show differential shifts when SUMO is attached to differently sized tags.
Recombinant DNA. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview Recombinant DNA
 Lesson Overview 15.2 Finding Genes In 1987, Douglas Prasher, a biologist at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institute in Massachusetts, wanted to find a specific gene in a jellyfish that codes for a molecule
Lesson Overview 15.2 Finding Genes In 1987, Douglas Prasher, a biologist at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institute in Massachusetts, wanted to find a specific gene in a jellyfish that codes for a molecule
Mutating Asn-666 to Glu in the O-helix region of the taq DNA polymerase gene
 Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, April 2010; 5(1): 15-19 Received: Oct 2009 Accepted: Jan 2010 School of Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences 15 Isfahan University of Medical Sciences Original Article
Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, April 2010; 5(1): 15-19 Received: Oct 2009 Accepted: Jan 2010 School of Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences 15 Isfahan University of Medical Sciences Original Article
SUPPLEMETARY INFORMATION. Cdk7 mediates RPB1-driven mrna synthesis in Toxoplasma gondii. Abhijit S. Deshmukh 1 *, Pallabi Mitra 2 and Mulaka Maruthi 3
 SUPPLEMETARY INFORMATION Cdk7 mediates RPB1-driven mrna synthesis in Toxoplasma gondii Abhijit S. Deshmukh 1 *, Pallabi Mitra 2 and Mulaka Maruthi 3 1 National Institute of Animal Biotechnology, Hyderabad,
SUPPLEMETARY INFORMATION Cdk7 mediates RPB1-driven mrna synthesis in Toxoplasma gondii Abhijit S. Deshmukh 1 *, Pallabi Mitra 2 and Mulaka Maruthi 3 1 National Institute of Animal Biotechnology, Hyderabad,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Gómez-Marín et al. 10.1073/pnas.1505463112 SI Materials and Methods Generation of BAC DK74B2-six2a::GFP-six3a::mCherry-iTol2. BAC clone (number 74B2) from DanioKey zebrafish BAC
Supporting Information Gómez-Marín et al. 10.1073/pnas.1505463112 SI Materials and Methods Generation of BAC DK74B2-six2a::GFP-six3a::mCherry-iTol2. BAC clone (number 74B2) from DanioKey zebrafish BAC
i-stop codon positions in the mcherry gene
 Supplementary Figure 1 i-stop codon positions in the mcherry gene The grnas (green) that can potentially generate stop codons from Trp (63 th and 98 th aa, upper panel) and Gln (47 th and 114 th aa, bottom
Supplementary Figure 1 i-stop codon positions in the mcherry gene The grnas (green) that can potentially generate stop codons from Trp (63 th and 98 th aa, upper panel) and Gln (47 th and 114 th aa, bottom
Cassette denotes the ORFs expressed by the expression cassette targeted by the PCR primers used to
 Stanyon, C.A., Limjindaporn, T., and Finley, Jr., R.L. Simultaneous transfer of open reading frames into several different expression vectors. Biotechniques, 35, 520-536, 2003. http://www.biotechniques.com
Stanyon, C.A., Limjindaporn, T., and Finley, Jr., R.L. Simultaneous transfer of open reading frames into several different expression vectors. Biotechniques, 35, 520-536, 2003. http://www.biotechniques.com
TABLE S1. Sequences of the primers used for RT-PCR and PCR
 TABLE S1. Sequences of the primers used for RT-PCR and PCR Primer Sequence (5 to 3 ) Purpose Cloning: posuprtid-1 & posuprtid-2 deletion plasmids DM01 AGCTCCAGCGGGTCGCCGGGGTTGGCC DM02 CCAGCGGGTCGCCGGGGTTGGCC
TABLE S1. Sequences of the primers used for RT-PCR and PCR Primer Sequence (5 to 3 ) Purpose Cloning: posuprtid-1 & posuprtid-2 deletion plasmids DM01 AGCTCCAGCGGGTCGCCGGGGTTGGCC DM02 CCAGCGGGTCGCCGGGGTTGGCC
Molecular Genetics Techniques. BIT 220 Chapter 20
 Molecular Genetics Techniques BIT 220 Chapter 20 What is Cloning? Recombinant DNA technologies 1. Producing Recombinant DNA molecule Incorporate gene of interest into plasmid (cloning vector) 2. Recombinant
Molecular Genetics Techniques BIT 220 Chapter 20 What is Cloning? Recombinant DNA technologies 1. Producing Recombinant DNA molecule Incorporate gene of interest into plasmid (cloning vector) 2. Recombinant
Supplementary Fig. 1 Proteomic analysis of ATR-interacting proteins. ATR, ARID1A and
 Supplementary Figure Legend: Supplementary Fig. 1 Proteomic analysis of ATR-interacting proteins. ATR, ARID1A and ATRIP protein peptides identified from our mass spectrum analysis were shown. Supplementary
Supplementary Figure Legend: Supplementary Fig. 1 Proteomic analysis of ATR-interacting proteins. ATR, ARID1A and ATRIP protein peptides identified from our mass spectrum analysis were shown. Supplementary
Mcbio 316: Exam 3. (10) 2. Compare and contrast operon vs gene fusions.
 Mcbio 316: Exam 3 Name (15) 1. Transposons provide useful tools for genetic analysis. List 5 different uses of transposon insertions. ANSWER: Many answers are possible, however, if multiple items on the
Mcbio 316: Exam 3 Name (15) 1. Transposons provide useful tools for genetic analysis. List 5 different uses of transposon insertions. ANSWER: Many answers are possible, however, if multiple items on the
Molecular cloning: 6 RBS+ arac/ laci
 Molecular cloning: 6 RBS+ arac/ laci Resource: 6 RBS: from the parts: B0030, B0032, B0034, J61100, J61107, J61127; renamed as RBS1 RBS2 RBS6; arac: C0080 laci: C0012 July 6 th Plasmid mini prep: 6 RBS;
Molecular cloning: 6 RBS+ arac/ laci Resource: 6 RBS: from the parts: B0030, B0032, B0034, J61100, J61107, J61127; renamed as RBS1 RBS2 RBS6; arac: C0080 laci: C0012 July 6 th Plasmid mini prep: 6 RBS;
Supplemental material
 Supplemental material Diversity of O-antigen repeat-unit structures can account for the substantial sequence variation of Wzx translocases Yaoqin Hong and Peter R. Reeves School of Molecular Bioscience,
Supplemental material Diversity of O-antigen repeat-unit structures can account for the substantial sequence variation of Wzx translocases Yaoqin Hong and Peter R. Reeves School of Molecular Bioscience,
Molecular Biology Techniques Supporting IBBE
 Molecular Biology Techniques Supporting IBBE Jared Cartwright Protein Production Lab Head Contact Details: email jared.cartwright@york.ac.uk Phone 01904 328797 Presentation Aims Gene synthesis Cloning
Molecular Biology Techniques Supporting IBBE Jared Cartwright Protein Production Lab Head Contact Details: email jared.cartwright@york.ac.uk Phone 01904 328797 Presentation Aims Gene synthesis Cloning
transcription and the promoter occupancy of Smad proteins. (A) HepG2 cells were co-transfected with the wwp-luc reporter, and FLAG-tagged FHL1,
 Supplementary Data Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1 FHL-mediated TGFβ-responsive reporter transcription and the promoter occupancy of Smad proteins. (A) HepG2 cells were co-transfected
Supplementary Data Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1 FHL-mediated TGFβ-responsive reporter transcription and the promoter occupancy of Smad proteins. (A) HepG2 cells were co-transfected
Solutions to 7.02 Quiz III
 Solutions to 7.02 Quiz III Class Average = 79 Standard Deviation = 12 Range Grade % 85-100 A 40 72-84 B 37 55-71 C 20 > 54 D/F 3 Question 1 On day 1 of the genetics lab, the entire 7.02 class did a transposon
Solutions to 7.02 Quiz III Class Average = 79 Standard Deviation = 12 Range Grade % 85-100 A 40 72-84 B 37 55-71 C 20 > 54 D/F 3 Question 1 On day 1 of the genetics lab, the entire 7.02 class did a transposon
An estimate of the physical distance between two linked markers in Haemophilus influenzae
 J. Biosci., Vol. 13, No. 3, September 1988, pp. 223 228. Printed in India. An estimate of the physical distance between two linked markers in Haemophilus influenzae Ε. Β. SAMIWALA, VASUDHA P. JOSHI and
J. Biosci., Vol. 13, No. 3, September 1988, pp. 223 228. Printed in India. An estimate of the physical distance between two linked markers in Haemophilus influenzae Ε. Β. SAMIWALA, VASUDHA P. JOSHI and
The Size and Packaging of Genomes
 DNA Replication The Size and Packaging of Genomes Vary greatly in size Ø Smallest viruses- 4 or 5 genes Ø Escherichia coli- 4,288 genes Ø Human cell- 20,000 to 25,000 genes E. coli 4 million base pairs
DNA Replication The Size and Packaging of Genomes Vary greatly in size Ø Smallest viruses- 4 or 5 genes Ø Escherichia coli- 4,288 genes Ø Human cell- 20,000 to 25,000 genes E. coli 4 million base pairs
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 A gta2-1 gta2-2 1kb AT4G08350 B Col-0 gta2-1 LP+RP+LBb1.3 C Col-0 gta2-2 LP+RP+LB1 D Col-0 gta2-2 gta2-1 GTA2 TUBLIN E Col0 gta2-1 gta2-2 Supplemental Figure 1. Phenotypic analysis
Supplemental Figure 1 A gta2-1 gta2-2 1kb AT4G08350 B Col-0 gta2-1 LP+RP+LBb1.3 C Col-0 gta2-2 LP+RP+LB1 D Col-0 gta2-2 gta2-1 GTA2 TUBLIN E Col0 gta2-1 gta2-2 Supplemental Figure 1. Phenotypic analysis
Lecture 22: Molecular techniques DNA cloning and DNA libraries
 Lecture 22: Molecular techniques DNA cloning and DNA libraries DNA cloning: general strategy -> to prepare large quantities of identical DNA Vector + DNA fragment Recombinant DNA (any piece of DNA derived
Lecture 22: Molecular techniques DNA cloning and DNA libraries DNA cloning: general strategy -> to prepare large quantities of identical DNA Vector + DNA fragment Recombinant DNA (any piece of DNA derived
Antisense RNA Targeting the First Periplasmic Domain of YidC in Escherichia coli Appears to Induce Filamentation but Does Not Affect Cell Viability
 Antisense RNA Targeting the First Periplasmic Domain of YidC in Escherichia coli Appears to Induce Filamentation but Does Not Affect Cell Viability Riaaz Lalani, Nathaniel Susilo, Elisa Xiao, Andrea Xu
Antisense RNA Targeting the First Periplasmic Domain of YidC in Escherichia coli Appears to Induce Filamentation but Does Not Affect Cell Viability Riaaz Lalani, Nathaniel Susilo, Elisa Xiao, Andrea Xu
Packaging of P22 DNA requires a pac site while packaging of lambda DNA requires a cos site. Briefly describe:
 1). (12 Points) Packaging of P22 DNA requires a pac site while packaging of lambda DNA requires a cos site. Briefly describe: 1. The mechanisms used by P22 and lambda to package DNA. P22 uses a headfull
1). (12 Points) Packaging of P22 DNA requires a pac site while packaging of lambda DNA requires a cos site. Briefly describe: 1. The mechanisms used by P22 and lambda to package DNA. P22 uses a headfull
