HOW TO EFFICIENTLY SUPPORT RENEWABLE ELECTRICITY THE FUTURE TASK IN EUROPE
|
|
|
- Liliana Hunt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 HOW TO EFFICIENTLY SUPPORT RENEWABLE ELECTRICITY THE FUTURE TASK IN EUROPE Christian PANZER, Energy Economics Group Vienna University of Technology, Phone , Gustav Resch, Energy Economics Group Vienna University of Technology, Phone , Reinhard Haas, Energy Economics Group Vienna University of Technology, Phone , Thomas Faber, Elektrizitäts-Gesellschaft Laufenburg Austria GmbH (EGL), Phone , OVERVIEW Energy policy is the main driver for the enhanced deployment of electricity from renewable energy sources (RES-E) as observed in several countries worldwide. Now, to the first time in Europe, binding targets for renewable energy sources (RES), regardless the energy sector, have been set 20% RES up to 2020 indicates a huge future challenge for upcoming years. Despite, efforts have to be taken in all three energy sectors, the electricity sector will play a major role in achieving the overall target. Hereby, efficient and effective support measures have to be implemented in order to accompany a strong increase in the share of RES-E with low transfer costs for the society. Several policy options will be discussed with respect to their effectiveness the development of RES-E and their efficiency the associated costs to the development of RES-E1. Besides the Feed-In Tariffs and the quota systems based on Tradable Green Certificates (TGC), some flexibility mechanism are needed in order to support Member States with moderate RES potentials achieving their RES targets up to Since all these promotion schemes show different reaction in terms of RES deployment as well as the associated costs, the core objective of this paper is to depict the pros and cons of these policy design options with respect to their impact on future growth of RES and the corresponding costs, and finally draw recommendations for policy makers. METHODS The issue of effectiveness and efficiency of support schemes is discussed mainly based on the results of scenarios using the model Green-X funded by the European Commission (EC). It allows analyses for both, the EU as a whole as well as for every single member state. Within the model all relevant RES-E technologies e.g. biomass, wind, geothermal, PV, solar thermal...) technologies as well as demand-side conservation measures are described for every EU country by means of static (and further-on dynamic) cost-resource curves. A static cost curve provides for a point-of-time a relationship between (categories of) technical potentials (of e.g. wind energy, hydro, biogas..) and the corresponding (full) costs of utilisation of this potential at this point-of-time. To analyse various scenarios different policy schemes can be selected, (e.g. feed-in tariffs, tendering systems, investment subsidies, tax incentives, quotas, tradable certificates) and modelled in a dynamic framework. All the instruments can be applied to all RES technologies separately for the various energy sectors. In addition, general taxes can be adjusted and the effects simulated. These include energy taxes (to be applied to all primary energy carriers as well as to electricity and heat) and environmental taxes on CO 2 -emissions as well as policies supporting demand-side measures. The corresponding costs and benefits for companies and consumers are an output. RESULTS Investigations have been carried out, that strengthening the national RES-E support schemes would allow on the one hand to meet the target of 20% RES by 2020 and on the other hand keep the annual consumer expenditures on a moderate level (see Figure 1). Comparatively and relatively high transfer costs appear by introducing a common quota system based on a uniform tradable green certificate scheme although in this case only the most cost-efficient technologies would be installed, the hereby most expensive power plant determines the common 1 This assessment was conducted for the European Commission, DG TREN within the European research project OPTRES ( and futures-e (
3 support level, increasing the transfer costs for the society dramatically (see Figure 1). However, a quota system based on a technology specific support measure almost equals the strengthened national policy system with respect to both, the transfer costs for the society and the achieved overall RES target. Strengthening national policy schemes implies on the one hand to adjust the support level appropriate and on the other hand to overcome non-economic market barriers (as grid connection issue, planning bureaucracy, etc ). Average yearly consumer expenditures (due to RES support) for NEW RES plant (2006 to 2020) [Bill. ] % 15.0% 17.5% 20.0% RES deplyoment (in terms of (gross) final energy) [%] BAU BAU (removed barriers, DSM) National action 2011 Quota (uniform) 2011 Quota (banding) 2011 Feed-in premium 2011 BAU + Quota (uniform) 2015 BAU + Quota (banding) 2015 BAU + Feed-in premium 2015 National action Quota (uniform) 2015 National action Quota (banding) 2015 National action Feed-in premium 2015 Figure 1: Comparison of average yearly transfer cost / consumer expenditure for new RES plants in relation to the achieved RES deployment in terms of gross final energy within the European Union (EU27) CONCLUSIONS The key criterion for achieving an enhanced future deployment of RES-E in an effective and efficient manner, besides the continuity and long-term stability of any implemented policy, is the technology specification of the necessary support. Concentrating on only the currently most cost-competitive technologies would exclude the more innovative technologies needed in the long run. In other words technology neutrality may be cost-efficient in the short term, but is more expensive in the long term. The major part of possible efficiency gains can already be exploited by optimising RES-E support measures at the national level about two thirds of the overall cost reduction potential can be attributed to optimising national support schemes. Further efficiency improvements are possible through guaranteed but strictly limited duration of support as well as that support schemes are targeting solely new RES installations. Introducing a harmonized RES policy can only be favourable if it is designed technology-specific and, that a common European power market exists. REFERENCES Resch Gustav, C. Panzer, R. Haas, T. Faber, M. Ragwitz, A. Held, M. Rathmann, G. Reece, C. Huber: 20% RES by 2020 Scenarios on future European policies for RES-E. Project report of futures-e ( conducted for the European Commission EACI European Agency for Competitiveness and Innovations. TU Vienna, Energy Economics Group in cooperation with Fraunhofer ISI, Ecofys, EGL. Vienna, Austria, 2009.
4 HOW TO EFFICIENTLY SUPPORT RENEWABLE ELECTRICITY THE FUTURE TASK IN EUROPE Authors: Christian Panzer, Gustav Resch, Reinhard Haas, Thomas Faber* Energy Economics Group, Vienna University of Technology *EGL Austria Contact Web: based on calculations. made with the help of the. computer model Green-X. European IAEE conference Vienna - September 8 th, 2009 Slide 1
5 Content 1. Introduction European RES Directive 2020 targets 2. Background information Short characterisation of the Green-X model, scenario assumptions and future pathways 3. Results on the future deployment of RES in Europe Results on RES deployment, investment needs, costs & benefits 4. The policy context Assessment of future RES policy options Concluding remarks European IAEE conference Vienna - September 8 th, 2009 Slide 2
6 (1) Introduction National RES targets for 2020 the binding goal! RES in terms of final energy [% of demand] 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% RES potential share on current (2005) demand Proposed RES target for 2020 RES share 2005 AT BE BG CY CZ DK EE FI FR DE GR HU IE IT LA LT LU MT NL PL PT RO SK SI ES SE UK EU27 Note: Additional potentials do not include biofuel imports How the European Commission set the targets FLAT RATE & GDP-Variation European i.e.: RES-target IAEE conference 2020 = RES Vienna 2005% - September + 50% *RES 8 th, 2009 NEW % + Slide 50%* RES 3 NEW % GDP-weighting - first the future task mover in bonus Europe
7 Green-X model The Green (2) Background Simulation model for energy policy instruments in the European energy market RES-E, RES-H, RES-T and CHP, conventional power Based on the concept of dynamic cost-resource curves Allowing forecasts up to 2020/2030 on national / EU-27 level Base input information Country selection Technology selection Power generation (Access Database) Electricity demand reduction (Access Database) Economic market and policy assessment potential, costs, offer prices Simulation of market interactions RES-E, RES, CHP, DSM power market, EUAs Scenario Information Policy strategies selection Social behaviour Investor/consumer Externalities Framework Conditions (Access Database) Results Costs and Benefitson a yearly basis ( ( ) ) Reference clients: European Commission (DG RESEARCH, DG TREN, DG ENV), Sustainable Energy Ireland, German Ministry for Environment, European Environmental Agency, Consultation to Ministries in Serbia, Luxembourg, European Morocco, etc. IAEE conference Vienna - September 8 th, 2009 Slide 5
8 (2) Background Penetration (as share of longterm potential) [%] Technology diffusion in accordance with general diffusion theory, penetration of a market by any new commodity typically follows an S-curve pattern applied within the model to describe the impact of non-economic barriers on RES-E deployment 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% Historical record Market barrier - Model implementation e.g. development of wind power (onshore) in Germany Model implementation of P Mn P d F ( 1 F) dynamic non-economic market barriers Deployment Realisable potential due to non-economic Markt barriers European IAEE Year [t] conference Vienna - September 8 th, 2009 Slide 6 Yearly realisable potential (as share of long-term potential) [%] 14% 12% 10% 8% 6% 4% 2% 0% F d ΔP Mn P F General diffusion theory 1 e d ( t t0 ) 0% How 20% to efficiently 40% 60% support 80% RES-E 100% Penetration (as share of long-term potential) [%] Markt penetration Diffusion rate Yearly realisble potential (according to market barrier) Long-term realisable potential 1
9 (2) Background The Green-X approach: Dynamic cost-resource cost-resource curves curves Potentials Costs of electricity by RES-E technology (by band) by RES-E technology (by band) by country by country DYNAMIC COST-RESOURCE CURVES by RES-E technology by country by year Dynamic aspects Costs: Dynamic cost assessment Potentials: Dynamic restrictions costs potential European IAEE conference Vienna - September 8 th, 2009 Slide 7
10 Energy generation Historical deployment (2) Background: Potentials and cost for RES Definition of the (additional) realisable mid-term potential (up to 2020) Theoretical potential Technical potential Maximal time-path for penetration (Realisable Potential) Barriers (non-economic) Economic Potential (without additional support) Policy, Society 2020 European IAEE conference Vienna - September 8 th, 2009 Slide 11 R&D Mid-term potential Definition of potential terms Theoretical potential... based on the determination of the energy flow. Technical potential based on technical boundary conditions (i.e. efficiencies of conversion technologies, overall technical limitations as e.g. the available land area to install wind turbines) Long-term potential Realisable potential Additional realisable mid-term potential (up to 2020) Achieved potential (2005) The realisable potential represents the maximal achievable potential assuming that all existing barriers can be overcome and all driving forces are active. Thereby, general parameters as e.g. market growth rates, planning constraints are taken into account in a dynamic context i.e. the realisable potential has to refer to a How to efficiently support certain RES-E year.
11 (2) Background realisable RES potentials How far can we go with the renewable energy sources within the electricity sector as applicable in the years up to 2020? RES-E - Electricity generation potential [% of gross electricity demand] 120% 110% 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% RES share 2005 RES potential share on 2020 demand (baseline case) RES potential share on 2020 demand (energy efficiency case) RES potential share on current (2005) demand AT BE BG CY CZ DK EE FI FR DE GR HU IE IT LA LT LU MT NL PL PT RO SK SI ES SE UK EU27 Achieved potential 2005 und additional realisable potential (up to 2020) for RES-E (in terms of final electricity demand) in the EU-27 by country European IAEE conference Vienna - September 8 th, 2009 Slide 12
12 RES cost Cost reduction - share of initial investment costs (as in the year 2006) [%] 120% 115% 110% 105% 100% 95% 90% 85% 80% 75% 70% 65% 60% 55% 50% 45% 40% 35% (2) Background RES cost 2006 RES-Electricity technologies European IAEE conference Vienna - September 8 th, 2009 Slide Assumptions on expected future technological progress (technological learning) Moderate learning High energy prices changed the overall situation Prior learning expectations will not be met with a continuation of high energy prices (i.e. an increase of investment cost could be observed for almost all energy technologies in 2006 to 2008 caused by increasing energy and raw material prices) Hydropower Geothermal electricity Solid biomass - cofiring & large-scale plant Solid biomass - smallscale CHP Gaseous biomass Gaseous biomass CHP Wind energy Tidal & wave Solar thermal electricity Photovoltaics Resulting (investment) cost reduction due to technological progress (learning) How to efficiently (according support RES-E to the the future policytask scenario) in Europe
13 (2) Background Overview on RE scenarios (Green-X) Geographical scope: EU27 Member States Time horizon: 2006 to 2020 BAU case: RES policies are applied as currently implemented (without any adaptation) business as usual (BAU) forecast and a baseline energy (electricity) demand scenario. Strengthened national policies: Accelerated RES deployment, assuming that the national RES policy framework will be improved with respect to its efficiency & effectiveness. These changes will become effective by 2011 in order to meet the agreed national targets of 20% RES by Improvements refer to both the financial support conditions (if necessary) as well as to non-financial barriers (i. e. administrative deficiencies etc.) where a rapid removal is also preconditioned. Additional cases for the policy assessment are carried out: Harmonized technology-specific or uniform RES support European IAEE conference Vienna - September 8 th, 2009 Slide 18
14 (2) Objective / Policy Assessment Core Objective - Method of approach Support instruments have to be effective for increasing the penetration of RES-E and efficient with respect to minimising the resulting public costs over time. Public costs or transfer cost for consumer / society (due to the promotion of RES-E) are defined as direct premium financial transfer costs from the consumer to the producer due to the RES-E policy compared to the case that consumers would purchase conventional electricity from the power market. This means that these costs do not consider any indirect costs / benefits or externalities (environmental benefits, change of employment, etc.). The criteria used for the evaluation of various instruments are based on: Minimise generation costs Lower producer profits p MC Market clearing price = price for certificate p C price, costs [ /MWh] Producer surplus (PS) Transfer cost for consumer / society Transfer costs for consumer (additional costs for society) Generation Costs (GC) Quota Q = PS + GC p C * Q MC quantity [GWh/year] p C... market price for (conventional) European IAEE conference Vienna - September 8 th, 2009 electricity Slide 19 p MC... marginal price for MC... marginal How RES-E to (due efficiently to support generation RES-E costs quota obligation)
15 (3) Results RES deployment Sectoral contributions to achieve 20% RES by 2020? RES-deployment - in relative terms (i.e. as share of corresponding (gross) demand) [%] 40% 35% 30% 25% 20% 15% 10% 5% 35.3% 19.8% 19.6% 17.7% 8.1% RES-electricity RES-heat RES-transport RES primary (EUROSTAT) 0% RES final Deployment of RES-E, RES-H, RES-T and RES in total as shares of corresponding gross demands up to 2020 within the European Union (EU27) (according to the strengthened national policy scenario) European IAEE conference Vienna - September 8 th, 2009 Slide 20
16 (3) Results RES deployment RES contribution to achieve 20% RES by 2020 within the electricity sector RES-E - energy output [TWh/year] Historical development Future development Wind offshore Wind onshore Tide & wave Solar thermal electricity Photovoltaics Hydro large-scale Hydro small-scale Geothermal electricity Biowaste Solid biomass Biogas Historical and projected future deployment of RES in the electricity sector up to 2020 within the European Union (EU27) (according to the strengthened national policy scenario) European IAEE conference Vienna - September 8 th, 2009 Slide 21
17 (3) Results RES deployment RES-E E contribution and associated capital expenditures New RES-E installations Breakdown by RES-electricity category BAU (Business as usual) Strengthened national policies [Unit] Biogas BG MW 1,588 1,700 2,341 5,629 1,803 3,364 7,330 12,498 (Solid) Biomass BM MW 7,612 7,013 6,054 20,679 8,498 11,577 8,803 28,878 Biowaste BW MW 1,479 1,158 1,011 3,648 1,661 1, ,674 Geothermal electricity GE MW Hydro large-scale HY-LS MW 6,876 3,064 1,391 11,331 6,991 2,432 1,378 10,802 Hydro small-scale HY-SS MW 1,424 2, ,771 1,631 2, ,928 Photovoltaics SO-PV MW 2,834 1,096 2,580 6,510 2,963 8,366 17,372 28,700 Solar thermal electricity SO-ST MW ,348 2, ,498 4,850 Tide & Wave TW MW , ,755 Wind onshore WI-ON MW 33,951 33,038 39, ,324 34,717 56,436 27, ,152 Wind offshore WI-OFF MW 1,727 1, ,404 2,149 12,817 37,851 52,817 RES-E TOTAL RES-E MW 58,409 52,389 56, ,101 61, , , ,419 Capital expenditure [Mill. ] 250, , , ,000 50, Wind offshore Wind onshore Tide & Wave Solar thermal electricity Photovoltaics Hydro large-scale Hydro small-scale Geothermal electricity Biowaste (Solid) Biomass Biogas Tremendous increase in wind offshore and PV in terms of installed capacity and capital expenditures (according to the strengthened national policy scenario compared to BAU ) Capital expenditure [Mill. ] 250, , , ,000 50, European IAEE conference Vienna - September 8 th, 2009 Slide 22
18 RES-E deployment (as share on gross electricity demand) [%] 36% 34% 32% 30% 28% 26% 24% 22% 20% 18% 16% 2006 (4) Results / Policy Assessment Total electricity generation from RES (EU27) as share of gross electricity demand Required RES-E deployment European IAEE conference Vienna - September 8 th, 2009 Slide BAU BAU (removed barriers, DSM) National action 2011 Quota (uniform) 2011 Quota (banding) 2011 Feed-in premium 2011 Overview on assessed policy scenarios MAIN CASES BAU - continuation of current national RES policies BAU with removed barriers and active DSM Strengthened national RES support Harmonised uniform RES support by 2011 (quota) Harmonised technologyspecific RES support by 2011 (quota with banding) Harmonised technologyspecific to efficiently RES support RES-E by How 2011 (feed-in the future premium) task in Europe
19 (4) Results / Policy Assessment Transfer costs for consumer (due to the support of RES-E) Transfer costs for consumer / society (sometimes also called additional / premium costs for consumer / society) are defined as direct premium financial transfer costs from the consumer to the producer due to the RES-E policy compared to the case that consumers would purchase conventional electricity from the power market. Overview on assessed policy scenarios MAIN CASES Yearly consumer expenditures due to RES-E support (as premium per MWh gross demand) [ /MWh DEMAND ] accelerating RES-E deployment: higher RES deployment requires higher transfer cost in absolute terms (but with lower specific RES support) European IAEE conference Vienna - September 8 th, 2009 Slide BAU BAU (removed barriers, DSM) National action 2011 Quota (uniform) 2011 Quota (banding) 2011 Feed-in premium 2011
20 (4) Results / Policy Assessment Costs of (an enhanced) RES deployment Average yearly additional generation cost for NEW RES plant (2006 to 2020) [Bill. ] least cost policies lead to lower additional generation cost (~ 2 billion per year)! Average (2006 to 2020) yearly additional cost (generation & policy cost (consumer expenditures) referring to the required new RES deployment (2006 to 2020) (EU27) for the assessed policy scenarios BAU BAU (removed barriers, DSM) National action 2011 Quota (uniform) 2011 Quota (banding) 2011 Feed-in premium 2011 BAU + Quota (uniform) 2015 BAU + Quota (banding) 2015 BAU + Feed-in premium 2015 National action Quota (uniform) 2015 National action Quota (banding) % 15.0% 17.5% 20.0% RES deplyoment European IAEE (in conference terms of (gross) Vienna final - September energy) 8 [%] th, 2009 Slide 31 National action Feed-in premium 2015
21 (4) Results / Policy Assessment Costs of (an enhanced) RES deployment Average yearly consumer expenditures (due to RES support) for NEW RES plant (2006 to 2020) [Bill. ] least cost policies lead to higher policy cost (consumer expenditures) (~ billion per year)! removal of noneconomic barriers is crucial to reduce cost and speed-up RES diffusion 12.5% 15.0% 17.5% 20.0% RES deplyoment European IAEE(in conference terms of (gross) Vienna - September final energy) 8 th, 2009 [%] Slide 32 Average (2006 to 2020) yearly additional cost (generation & policy cost (consumer expenditures) referring to the required new RES deployment (2006 to 2020) (EU27) for the assessed policy scenarios BAU BAU (removed barriers, DSM) National action 2011 Quota (uniform) 2011 Quota (banding) 2011 Feed-in premium 2011 BAU + Quota (uniform) 2015 BAU + Quota (banding) 2015 BAU + Feed-in premium 2015 National action Quota (uniform) 2015 National action Quota (banding) 2015 National action Feed-in premium 2015
22 Concluding remarks RES policies should be supported by a strong energy efficiency policy. The RES policy framework needs an integrated perspective on the use of biomass. Biomass is a crucial element of RES policy, used in all three sectors Efforts are needed in all Member States All modelling exams clearly illustrate Each MS has to contribute! A wide range of technologies has to be supported Even in a pure least cost case a broad portfolio of RE technologies is needed to achieve the 20% target! Costs vary over time, but even more between RES technologies Any future policy framework has to address this sufficiently by providing technology specific support to the various RES options. European IAEE conference Vienna - September 8 th, 2009 Slide 34
23 The discussion on adequate flexibility for target achievement should not lead to quick and too simplistic policy answers that directs us into a wrong policy direction and hinder the move towards effective & efficient RES support Thanks for your attention! In case of questions / remarks panzer@eeg.tuwien.ac.at Phone: or European IAEE conference Vienna - September 8 th, 2009 Slide 35
Short characterisation of the Green-X model
 Short characterisation of the Authors: Gustav Resch, Andre Ortner, Sebastian Busch, Thomas Faber, Reinhard Haas all Energy Economics Group, Vienna University of Technology Contact Web: http://eeg.tuwien.ac.at
Short characterisation of the Authors: Gustav Resch, Andre Ortner, Sebastian Busch, Thomas Faber, Reinhard Haas all Energy Economics Group, Vienna University of Technology Contact Web: http://eeg.tuwien.ac.at
EUROPE TAKES THE CHALLENGE THE WAY FORWARD IN PROMOTING RENEWABLE ELECTRICITY
 EUROPE TAKES THE CHALLENGE THE WAY FORWARD IN PROMOTING RENEWABLE ELECTRICITY Christian PANZER, Energy Economics Group Vienna University of Technology, Phone +43-1-58801-37360, E-mail: panzer@eeg.tuwien.ac.at
EUROPE TAKES THE CHALLENGE THE WAY FORWARD IN PROMOTING RENEWABLE ELECTRICITY Christian PANZER, Energy Economics Group Vienna University of Technology, Phone +43-1-58801-37360, E-mail: panzer@eeg.tuwien.ac.at
Short characterisation of the model Green-X
 Short characterisation of the model Green-X Year of implementation: Client: Consortium: Publications / Web: 2002-2004 European Commission, DG Research; FP5 Programme (ENG2-CT- 2002-00607) Project co-ordinator:
Short characterisation of the model Green-X Year of implementation: Client: Consortium: Publications / Web: 2002-2004 European Commission, DG Research; FP5 Programme (ENG2-CT- 2002-00607) Project co-ordinator:
Core projects and scientific studies as background for the NREAPs. 9th Inter-Parliamentary Meeting on Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency
 Core projects and scientific studies as background for the NREAPs 9th Inter-Parliamentary Meeting on Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency Brussels, 18.11.2009 Mario Ragwitz Fraunhofer Institute Systems
Core projects and scientific studies as background for the NREAPs 9th Inter-Parliamentary Meeting on Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency Brussels, 18.11.2009 Mario Ragwitz Fraunhofer Institute Systems
SEVILLA, 21st March2007
 ON MODELING THE FUTURE OF RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES IN EUROPE FROM A TECHNO INSTITUTIONAL PERSPECTIVE Reinhard Haas, Gustav Resch, Thomas Faber Energy Economics Group, Vienna University of Technology SEVILLA,
ON MODELING THE FUTURE OF RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCES IN EUROPE FROM A TECHNO INSTITUTIONAL PERSPECTIVE Reinhard Haas, Gustav Resch, Thomas Faber Energy Economics Group, Vienna University of Technology SEVILLA,
RES in SEERMAP some key inputs to the analysis
 some key inputs to the analysis Authors: Gustav Resch, Lukas Liebmann, Albert Hiesl all Energy Economics Group, TU Wien Contact Web: http://eeg.tuwien.ac.at Email: resch@eeg.tuwien.ac.at developed initially
some key inputs to the analysis Authors: Gustav Resch, Lukas Liebmann, Albert Hiesl all Energy Economics Group, TU Wien Contact Web: http://eeg.tuwien.ac.at Email: resch@eeg.tuwien.ac.at developed initially
European Commission. Communication on Support Schemes for electricity from renewable energy sources
 European Commission Communication on Support Schemes for electricity from renewable energy sources External Costs of energy and their internalisation in Europe Beatriz Yordi DG Energy and Transport External
European Commission Communication on Support Schemes for electricity from renewable energy sources External Costs of energy and their internalisation in Europe Beatriz Yordi DG Energy and Transport External
Energy policy support instruments for renewable energy sources: key principles & lessons learnt
 Energy policy support instruments for renewable energy sources: key principles & lessons learnt Author: Gustav Resch Energy Economics Group (EEG) Technische Universität Wien (TU Wien) Contact: Web: http://eeg.tuwien.ac.at
Energy policy support instruments for renewable energy sources: key principles & lessons learnt Author: Gustav Resch Energy Economics Group (EEG) Technische Universität Wien (TU Wien) Contact: Web: http://eeg.tuwien.ac.at
Renewable energy sources in Slovakia a quantitative assessment and policy conclusion towards, and beyond, 2020
 Renewable energy sources in Slovakia a quantitative assessment and policy conclusion towards, and beyond, 2020 Author: Dr. Christian Panzer Company: Vienna University of Technology Energy Economics Group
Renewable energy sources in Slovakia a quantitative assessment and policy conclusion towards, and beyond, 2020 Author: Dr. Christian Panzer Company: Vienna University of Technology Energy Economics Group
Developments and achievements of Feed-In. evaluation conducted for the IFIC. Cooperation (IFIC) 18th/19th November 2010, Berlin
 Developments and achievements of Feed-In Systems - Key findings from an evaluation conducted for the IFIC Mario Ragwitz Fraunhofer Institute Systems and Innovation Research 8th Workshop of the International
Developments and achievements of Feed-In Systems - Key findings from an evaluation conducted for the IFIC Mario Ragwitz Fraunhofer Institute Systems and Innovation Research 8th Workshop of the International
Assessment of European RES policy pathways beyond 2020 results of the quantitative assessment of RES policy pathways beyond 2020
 Authors: Gustav Resch1, Pablo del Rio2, Mario Ragwitz3, Sebastian Busch1, Andre Ortner1 1Energy Economics Group, Vienna University of Technology, Austria 2Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas,
Authors: Gustav Resch1, Pablo del Rio2, Mario Ragwitz3, Sebastian Busch1, Andre Ortner1 1Energy Economics Group, Vienna University of Technology, Austria 2Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas,
20% RES by 2020 Biomass role in the Renewable Energy Directive 2020 energy futures
 20% RES by 2020: Biomass role in the Renewable Energy Directive 2020 energy futures 20% RES by 2020 Biomass role in the Renewable Energy Directive 2020 energy futures Authors: Christian Panzer, Gustav
20% RES by 2020: Biomass role in the Renewable Energy Directive 2020 energy futures 20% RES by 2020 Biomass role in the Renewable Energy Directive 2020 energy futures Authors: Christian Panzer, Gustav
20% RES by 2020 a balanced scenario to meet Europe s renewable energy target
 20% RES by 2020 a balanced scenario to meet Europe s renewable energy target Authors: Gustav Resch, Thomas Faber, Mario Ragwitz, Anne Held, Christian Panzer, Reinhard Haas Vienna University of Technology,
20% RES by 2020 a balanced scenario to meet Europe s renewable energy target Authors: Gustav Resch, Thomas Faber, Mario Ragwitz, Anne Held, Christian Panzer, Reinhard Haas Vienna University of Technology,
Best practice support schemes for RES-E in a dynamic European electricity market
 Report (D9) of the IEE project OPTRES: Assessment and optimisation of renewable energy support schemes in the European electricity market Best practice support schemes for RES-E in a dynamic European electricity
Report (D9) of the IEE project OPTRES: Assessment and optimisation of renewable energy support schemes in the European electricity market Best practice support schemes for RES-E in a dynamic European electricity
RES in SEERMAP some key inputs to the analysis
 some key inputs to the analysis Authors: Gustav Resch, Lukas Liebmann, Albert Hiesl all Energy Economics Group, TU Wien Contact Web: http://eeg.tuwien.ac.at Email: resch@eeg.tuwien.ac.at developed initially
some key inputs to the analysis Authors: Gustav Resch, Lukas Liebmann, Albert Hiesl all Energy Economics Group, TU Wien Contact Web: http://eeg.tuwien.ac.at Email: resch@eeg.tuwien.ac.at developed initially
Economic analysis of reaching a 20% share of renewable energy sources in 2020
 Executive Summary Economic analysis of reaching a 20% share of renewable energy sources in 2020 Mario Ragwitz, Felipe Toro Fraunhofer - ISI Gustav Resch, Thomas Faber, Reinhard Haas - EEG Monique Hoogwijk,
Executive Summary Economic analysis of reaching a 20% share of renewable energy sources in 2020 Mario Ragwitz, Felipe Toro Fraunhofer - ISI Gustav Resch, Thomas Faber, Reinhard Haas - EEG Monique Hoogwijk,
Wind Energy The Facts
 Wind Energy The Facts Bruce Douglas Chief Operating Officer European Wind Energy Association Riga 22 May 2009 WHAT IS THE EUROPEAN WIND ENERGY ASSOCIATION? EWEA is the voice of the wind industry, actively
Wind Energy The Facts Bruce Douglas Chief Operating Officer European Wind Energy Association Riga 22 May 2009 WHAT IS THE EUROPEAN WIND ENERGY ASSOCIATION? EWEA is the voice of the wind industry, actively
Approach and key assumptions in our modelling exercise on RES in SEE countries. a regional approach to support renewable energies
 SEERMAP: Modelling results & conclusions Focus on Renewable Energies Gustav Resch, Lukas Liebmann, Albert Hiesl TU Wien, Energy Economics Group László Szabó, András Mezősi, Zsuzsanna Pató, Ágnes Kelemen
SEERMAP: Modelling results & conclusions Focus on Renewable Energies Gustav Resch, Lukas Liebmann, Albert Hiesl TU Wien, Energy Economics Group László Szabó, András Mezősi, Zsuzsanna Pató, Ágnes Kelemen
ENERGIE. with the support of the EUROPEAN COMMISSION Directorate-General for Research LEGAL NOTICE
 This Energie publication is one of a series highlighting the potential for innovative non-nuclear energy technologies to become widely applied and contribute superior services to the citizen. European
This Energie publication is one of a series highlighting the potential for innovative non-nuclear energy technologies to become widely applied and contribute superior services to the citizen. European
Titelmasterformat durch Klicken bearbeiten
 RES-E POTENTIALS AND POLICIES IN THE LIGHT OF GROWING ENERGY DEMAND Reinhard HAAS, Gustav RESCH Energy Economics Group, Vienna University of Technology Salzburg, September, 16th 28 1 SURVEY: 1. Introduction:
RES-E POTENTIALS AND POLICIES IN THE LIGHT OF GROWING ENERGY DEMAND Reinhard HAAS, Gustav RESCH Energy Economics Group, Vienna University of Technology Salzburg, September, 16th 28 1 SURVEY: 1. Introduction:
Renewable Energies versus Nuclear Power: Comparison of Financial Support. Gustav Resch, Demet Suna (e-think)
 Renewable Energies versus Nuclear Power: Comparison of Financial Support Gustav Resch, Demet Suna (e-think) Vienna, 16 April 2015 NURIS 2015... a study done on behalf of the Vienna Ombuds Office for Environment,
Renewable Energies versus Nuclear Power: Comparison of Financial Support Gustav Resch, Demet Suna (e-think) Vienna, 16 April 2015 NURIS 2015... a study done on behalf of the Vienna Ombuds Office for Environment,
The Dynamic Computer-model
 Project Workshop The Dynamic Computer-model model Claus Huber, Thomas Faber, Energy Economics Group (EEG) Project Workshop Overview! Introduction! State of the art international simulation tools! Overview
Project Workshop The Dynamic Computer-model model Claus Huber, Thomas Faber, Energy Economics Group (EEG) Project Workshop Overview! Introduction! State of the art international simulation tools! Overview
The EU Renewable Energy Framework for Biogas. Giulio Volpi Renewable Energy and CCS Unit DG Energy, European Commission
 The EU Renewable Energy Framework for Biogas Giulio Volpi Renewable Energy and CCS Unit DG Energy, European Commission The 20-20-20 EU policy, by 2020-20% -20% 100% 20% Greenhouse gas levels Energy consumption
The EU Renewable Energy Framework for Biogas Giulio Volpi Renewable Energy and CCS Unit DG Energy, European Commission The 20-20-20 EU policy, by 2020-20% -20% 100% 20% Greenhouse gas levels Energy consumption
OPTRES. Proceedings from thematic workshops. Karlsruhe (Germany) December Supported by: CONTRACT N : EIE/04/073/S
 Proceedings from thematic workshops Supported by: Karlsruhe (Germany) December 26 CONTRACT N : EIE/4/73/S7.38567 Renewable energies in the EU up to 22 - Current markets, future scenarios and the role of
Proceedings from thematic workshops Supported by: Karlsruhe (Germany) December 26 CONTRACT N : EIE/4/73/S7.38567 Renewable energies in the EU up to 22 - Current markets, future scenarios and the role of
Renewable energy sources in Greece and the EU a quantitative assessment and policy conclusion towards, and beyond, 2020
 Renewable energy sources in Greece and the EU a quantitative assessment and policy conclusion towards, and beyond, 2020 Simone Steinhilber Fraunhofer Institute for Systems and Innovation Research ISI http://www.isi.fraunhofer.de
Renewable energy sources in Greece and the EU a quantitative assessment and policy conclusion towards, and beyond, 2020 Simone Steinhilber Fraunhofer Institute for Systems and Innovation Research ISI http://www.isi.fraunhofer.de
European Commission Renewable Energy Policy The Renewables Roadmap Tom Howes, DG TREN European Sustainable Energy Policy Seminar, March 20, 2007
 European Commission Renewable Energy Policy The Renewables Roadmap Tom Howes, DG TREN European Sustainable Energy Policy Seminar, March 20, 2007 Organised by INFORSE, EUFORES, EREF www.inforse.org/europe/seminar07_bxl.htm
European Commission Renewable Energy Policy The Renewables Roadmap Tom Howes, DG TREN European Sustainable Energy Policy Seminar, March 20, 2007 Organised by INFORSE, EUFORES, EREF www.inforse.org/europe/seminar07_bxl.htm
Wind Power in Romania: Potential, Benefits, Barriers
 Wind Power in Romania: Potential, Benefits, Barriers Jannik Termansen, Vestas Wind Systems A/S, 2 June 2009 vestas.com Agenda 1. Romania s wind potential 2. Wind benefits for Romania 3. Barriers and recommendations
Wind Power in Romania: Potential, Benefits, Barriers Jannik Termansen, Vestas Wind Systems A/S, 2 June 2009 vestas.com Agenda 1. Romania s wind potential 2. Wind benefits for Romania 3. Barriers and recommendations
Effective and efficient long-term oriented RE support policies
 Effective and efficient long-term oriented RE support policies Dr. Mario Ragwitz Fraunhofer Institute Systems and Innovation Research Saudi Solar Energy Forum Workshop on Renewable Energy Financing Mechanisms
Effective and efficient long-term oriented RE support policies Dr. Mario Ragwitz Fraunhofer Institute Systems and Innovation Research Saudi Solar Energy Forum Workshop on Renewable Energy Financing Mechanisms
The interactions of complementary policies with a GHG cap and trade program: the case of Europe
 The interactions of complementary policies with a GHG cap and trade program: the case of Europe David Harrison, Ph.D. Senior Vice-President Daniel Radov Associate Director EPRI-IETA IETA Joint Symposium
The interactions of complementary policies with a GHG cap and trade program: the case of Europe David Harrison, Ph.D. Senior Vice-President Daniel Radov Associate Director EPRI-IETA IETA Joint Symposium
Erneuerbare Energien: Energiepolitik und Marktentwicklungen in Europa
 Erneuerbare Energien: Energiepolitik und Marktentwicklungen in Europa Christine Lins Secretary General European Renewable Energy Council WEC Workshop: Die Zukunft der erneuerbaren Energien zwischen Politik
Erneuerbare Energien: Energiepolitik und Marktentwicklungen in Europa Christine Lins Secretary General European Renewable Energy Council WEC Workshop: Die Zukunft der erneuerbaren Energien zwischen Politik
Innovative grid-impacting technologies for pan-european system analyses: key GridTech results on Demand Response application
 Innovative grid-impacting technologies for pan-european system analyses: key GridTech results on Demand Response application Angelo L'Abbate RSE SpA EC JRC Smart Mediterraneo workshop Bari, 24 June 2016
Innovative grid-impacting technologies for pan-european system analyses: key GridTech results on Demand Response application Angelo L'Abbate RSE SpA EC JRC Smart Mediterraneo workshop Bari, 24 June 2016
The support of electricity from renewable energy sources
 COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, 23.1.2008 SEC(2008) 57 COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT The support of electricity from renewable energy sources Accompanying document to the Proposal
COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, 23.1.2008 SEC(2008) 57 COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT The support of electricity from renewable energy sources Accompanying document to the Proposal
Electricity sector transformation in Europe Taking local idiosyncrasies into account
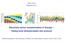 Electricity generation in TWh IAEE Vienna September 217 4.5 4. 3.5 3. 2.5 2. 1.5 1. 5 215 22 225 23 235 24 245 25 Electricity sector transformation in Europe Taking local idiosyncrasies into account Clemens
Electricity generation in TWh IAEE Vienna September 217 4.5 4. 3.5 3. 2.5 2. 1.5 1. 5 215 22 225 23 235 24 245 25 Electricity sector transformation in Europe Taking local idiosyncrasies into account Clemens
Efficient RES-E Support in Europe and its Impact on the Conventional Power Market
 Institute of Energy Economics at the University of Cologne Efficient RES-E Support in Europe and its Impact on the Conventional Power Market IAEE International Conference June 22nd, 2009 San Francisco
Institute of Energy Economics at the University of Cologne Efficient RES-E Support in Europe and its Impact on the Conventional Power Market IAEE International Conference June 22nd, 2009 San Francisco
The European Commission s renewable energy proposal
 The European Commission s renewable energy proposal 11/13/08 EUROPEAN COMMISSION Tom Howes, European Commission Renewable energy promotion since 1997 National targets for RE electricity since 2001 National
The European Commission s renewable energy proposal 11/13/08 EUROPEAN COMMISSION Tom Howes, European Commission Renewable energy promotion since 1997 National targets for RE electricity since 2001 National
Maritime Regions and energy
 Maritime Regions and energy Prof. Samuel Furfari CPMR Workshop Opatija, 8/11/07 Samuele Furfari, European Commission, DG TREN 1 EU is active, but need to speak with one voice The Internal Market Review
Maritime Regions and energy Prof. Samuel Furfari CPMR Workshop Opatija, 8/11/07 Samuele Furfari, European Commission, DG TREN 1 EU is active, but need to speak with one voice The Internal Market Review
Consortium. Imprint. Financial Support
 Consortium Imprint Vienna University of Technology Energy Economics Group (EEG) Gusshausstrasse 25-29/373-2 A 1040 Vienna Austria Printed in Austria May 2007 Graphic Design: Moosmoar Financial Support
Consortium Imprint Vienna University of Technology Energy Economics Group (EEG) Gusshausstrasse 25-29/373-2 A 1040 Vienna Austria Printed in Austria May 2007 Graphic Design: Moosmoar Financial Support
EIE/04/049/S GreenNet-EU27 GUIDING A LEAST COST GRID INTEGRATION OF RES-ELECTRICITY IN AN EXTENDED EUROPE.
 EIE/04/049/S07.38561 GreenNet-EU27 GUIDING A LEAST COST GRID INTEGRATION OF RES-ELECTRICITY IN AN EXTENDED EUROPE Intelligent Energy Europe (EIE) Type of action: Type 1: General Action (GA) Key action:
EIE/04/049/S07.38561 GreenNet-EU27 GUIDING A LEAST COST GRID INTEGRATION OF RES-ELECTRICITY IN AN EXTENDED EUROPE Intelligent Energy Europe (EIE) Type of action: Type 1: General Action (GA) Key action:
Financing Renewable Energy in the European Energy Market
 Financing Renewable Energy in the European Energy Market A SUSTAINABLE ENE RGY SUPPLY FOR EVERYONE Financing Renewable Energy in the European Energy Market -Final Report- By: Ecofys: David de Jager, Corinna
Financing Renewable Energy in the European Energy Market A SUSTAINABLE ENE RGY SUPPLY FOR EVERYONE Financing Renewable Energy in the European Energy Market -Final Report- By: Ecofys: David de Jager, Corinna
PROMOTING RENEWABLE ELECTRICITY INVESTMENTS EFFECTIVELY Reinhard HAAS
 PROMOTING RENEWABLE ELECTRICITY INVESTMENTS EFFECTIVELY Reinhard HAAS Institute of Power Systems and Energy Economics, Vienna University of Technology PARIS, 25 March 2003 SURVEY 1 Introduction, Historical
PROMOTING RENEWABLE ELECTRICITY INVESTMENTS EFFECTIVELY Reinhard HAAS Institute of Power Systems and Energy Economics, Vienna University of Technology PARIS, 25 March 2003 SURVEY 1 Introduction, Historical
National action plans Prospects and requirements for the new renewables action plans in Italy
 National action plans 2030 - Prospects and requirements for the new renewables action plans in Italy Autoren: Lukas Liebmann, Gustav Resch Energy Economics Group (EEG) Technische Universität Wien Kontakt:
National action plans 2030 - Prospects and requirements for the new renewables action plans in Italy Autoren: Lukas Liebmann, Gustav Resch Energy Economics Group (EEG) Technische Universität Wien Kontakt:
Renewable energy in Europe. E-turn 21 workshop Cologne, 10 May 2006
 Renewable energy in Europe E-turn 21 workshop Cologne, 10 May 2006 Content 1. Introduction to Essent 2. EU policy 3. Support for renewable energy 4. Success factors 5. Outlook and recommendations Content
Renewable energy in Europe E-turn 21 workshop Cologne, 10 May 2006 Content 1. Introduction to Essent 2. EU policy 3. Support for renewable energy 4. Success factors 5. Outlook and recommendations Content
PUBLIZIERBARER Endbericht Studien
 PUBLIZIERBARER Endbericht Studien A) Projektdaten Titel: ASSESSING FLEXIBILITY MECHANISMS FOR ACHIEVING THE AUSTRIAN 2020 RENEWABLE ENERGY TARGET (ReFlex) Programm: ACRP 1 Koordinator/ Projekteinreicher:
PUBLIZIERBARER Endbericht Studien A) Projektdaten Titel: ASSESSING FLEXIBILITY MECHANISMS FOR ACHIEVING THE AUSTRIAN 2020 RENEWABLE ENERGY TARGET (ReFlex) Programm: ACRP 1 Koordinator/ Projekteinreicher:
Pan European TIMES Model General Description
 Energy Systems Modelling Addressing Energy Security and Climate Change Least Cost Optimisation Modelling of the 22 Energy and Environmental targets in EU27 Dr George Giannakidis Centre for Renewable Energy
Energy Systems Modelling Addressing Energy Security and Climate Change Least Cost Optimisation Modelling of the 22 Energy and Environmental targets in EU27 Dr George Giannakidis Centre for Renewable Energy
EU Bioenergy policy. COMPETE: Bioenergy for sustainable development in Africa. Ewout Deurwaarder, European Commission EUROPEAN COMMISSION
 EU Bioenergy policy COMPETE: Bioenergy for sustainable development in Africa Ewout Deurwaarder, European Commission EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 2411/2009 Policy background.renewable Energy promotion
EU Bioenergy policy COMPETE: Bioenergy for sustainable development in Africa Ewout Deurwaarder, European Commission EUROPEAN COMMISSION Brussels, 2411/2009 Policy background.renewable Energy promotion
The employment and growth effects of sustainable energies in the European Union
 The employment and growth effects of sustainable energies in the European Union 122 The Commission Communication Renewable Energy: a major player in the European energy market clearly states the objectives
The employment and growth effects of sustainable energies in the European Union 122 The Commission Communication Renewable Energy: a major player in the European energy market clearly states the objectives
IEA data collection on RES
 IEA data collection on RES Samantha Ölz Renewable Energy Unit Workshop on Data Gathering on Renewable Energies for New Member States and Candidate Countries Scientific Technical Reference System on Renewable
IEA data collection on RES Samantha Ölz Renewable Energy Unit Workshop on Data Gathering on Renewable Energies for New Member States and Candidate Countries Scientific Technical Reference System on Renewable
Design options and critical issues of European GO Trade
 Design options and critical issues of European GO Trade Corinna Kleßmann Ecofys Germany International Feed-in Cooperation October 18, 2007 Background RE trade based on Guarantees of Origin (GOs) as proposed
Design options and critical issues of European GO Trade Corinna Kleßmann Ecofys Germany International Feed-in Cooperation October 18, 2007 Background RE trade based on Guarantees of Origin (GOs) as proposed
Methodology for calculating subsidies to renewables
 1 Introduction Each of the World Energy Outlook scenarios envisages growth in the use of renewable energy sources over the Outlook period. World Energy Outlook 2012 includes estimates of the subsidies
1 Introduction Each of the World Energy Outlook scenarios envisages growth in the use of renewable energy sources over the Outlook period. World Energy Outlook 2012 includes estimates of the subsidies
Climate Change and Energy Package
 Climate Change and Energy Package The 4th International Conference NEUF 2008 Warszawa, 6 June 2008 Piotr J. Tulej Head of Unit Energy and Environment Directorate-General Environment European Commission
Climate Change and Energy Package The 4th International Conference NEUF 2008 Warszawa, 6 June 2008 Piotr J. Tulej Head of Unit Energy and Environment Directorate-General Environment European Commission
EIE/04/049/S GreenNet-EU27 GUIDING A LEAST COST GRID INTEGRATION OF RES-ELECTRICITY IN AN EXTENDED EUROPE. Deliverable D7
 GreenNet-EU27 Supported by EIE/04/049/S07.38561 GreenNet-EU27 GUIDING A LEAST COST GRID INTEGRATION OF RES-ELECTRICITY IN AN EXTENDED EUROPE Intelligent Energy Europe (EIE) Type of action: Type 1: General
GreenNet-EU27 Supported by EIE/04/049/S07.38561 GreenNet-EU27 GUIDING A LEAST COST GRID INTEGRATION OF RES-ELECTRICITY IN AN EXTENDED EUROPE Intelligent Energy Europe (EIE) Type of action: Type 1: General
Climate Action and Renewable Energy Package
 Climate Action and Renewable Energy Package Objectives agreed for 2020 20% GHG reduction compared to 1990 ª Independent commitment 30% GHG reduction compared to 1990 ª In context of international agreement
Climate Action and Renewable Energy Package Objectives agreed for 2020 20% GHG reduction compared to 1990 ª Independent commitment 30% GHG reduction compared to 1990 ª In context of international agreement
energy in figures Energy
 EU energy in figures Statistical pocketbook 2015 Energy This publication does not involve the European Commission in liability of any kind. Europe Direct is a service to help you find answers to your questions
EU energy in figures Statistical pocketbook 2015 Energy This publication does not involve the European Commission in liability of any kind. Europe Direct is a service to help you find answers to your questions
Bio-energy and the European pulp and paper industry an impact assessment
 Document Date Bio-energy and the European pulp and paper industry an impact assessment Summary of a study conducted by McKinsey & Company and Pöyry Forest Industry Consulting Our key message The Forest
Document Date Bio-energy and the European pulp and paper industry an impact assessment Summary of a study conducted by McKinsey & Company and Pöyry Forest Industry Consulting Our key message The Forest
ISSN energy. in figures. Energy
 ISSN 1977-4559 EU energy in figures STATISTICAL POCKETBOOK 2014 Energy EU ENERGY IN FIGURES POCKETBOOK 2014 1 This publication does not involve the European Commission in liability of any kind. Europe
ISSN 1977-4559 EU energy in figures STATISTICAL POCKETBOOK 2014 Energy EU ENERGY IN FIGURES POCKETBOOK 2014 1 This publication does not involve the European Commission in liability of any kind. Europe
Renewable energy: regulatory and market issues
 Renewable energy: regulatory and market issues László Szabó Please feel free to add your logo here! www. erranet.org Outline Renewable electricity outlook Policy context Technology development Regional
Renewable energy: regulatory and market issues László Szabó Please feel free to add your logo here! www. erranet.org Outline Renewable electricity outlook Policy context Technology development Regional
KEY FIGURES June 2011
 KEY FIGURES June 2011 1 KEY FIGURES Content 1. ENERGY IN THE WORLD 2. EU ENERGY DEPENDENCY 3. EU ENERGY CONSUMPTION BY FUEL 4. EU FINAL ENERGY CONSUMPTION 5. EU ENERGY PRODUCTION 6. EU ELECTRICITY GENERATION
KEY FIGURES June 2011 1 KEY FIGURES Content 1. ENERGY IN THE WORLD 2. EU ENERGY DEPENDENCY 3. EU ENERGY CONSUMPTION BY FUEL 4. EU FINAL ENERGY CONSUMPTION 5. EU ENERGY PRODUCTION 6. EU ELECTRICITY GENERATION
Renewable energy technologies/sources path within EU 2020 strategy
 Renewable energy technologies/sources path within EU 2020 strategy Analysis according to national renewable energy action plans and 2013 progress reports Manjola Banja, Fabio Monforti-Ferrario, Katalin
Renewable energy technologies/sources path within EU 2020 strategy Analysis according to national renewable energy action plans and 2013 progress reports Manjola Banja, Fabio Monforti-Ferrario, Katalin
SNAPSHOT OF RENEWABLE ENERGY DEVELOPMENT IN THE EU-28 Volume 2
 SNAPSHOT OF RENEWABLE ENERGY DEVELOPMENT IN THE EU-28 Volume 2 Current status and expected progress in comparison with national renewable energy action plans Manjola Banja, Fabio Monforti-Ferrario, Nicolae
SNAPSHOT OF RENEWABLE ENERGY DEVELOPMENT IN THE EU-28 Volume 2 Current status and expected progress in comparison with national renewable energy action plans Manjola Banja, Fabio Monforti-Ferrario, Nicolae
The Renewable Energy Directive the role of National Renewable Energy Action Plans in reaching the 2020 targets
 The Renewable Energy Directive the role of National Renewable Energy Action Plans in reaching the 2020 targets EUROPEAN COMMISSION Wind Energy the Facts Integrating wind power in Hungary, EWEA workshop
The Renewable Energy Directive the role of National Renewable Energy Action Plans in reaching the 2020 targets EUROPEAN COMMISSION Wind Energy the Facts Integrating wind power in Hungary, EWEA workshop
RENEWABLE ELECTRICITY MARKET DEVELOPMENTS IN THE EUROPEAN UNION
 October 2003 ECN-C--03-082 RENEWABLE ELECTRICITY MARKET DEVELOPMENTS IN THE EUROPEAN UNION Final report of the ADMIRE REBUS project M.A. Uyterlinde B.W. Daniels M. de Noord H.J. de Vries C. de Zoeten -
October 2003 ECN-C--03-082 RENEWABLE ELECTRICITY MARKET DEVELOPMENTS IN THE EUROPEAN UNION Final report of the ADMIRE REBUS project M.A. Uyterlinde B.W. Daniels M. de Noord H.J. de Vries C. de Zoeten -
Future of Europe Climate change Special Eurobarometer 479
 Future of Europe Climate change Special Eurobarometer 479 October-November 2018 Methodology Survey conducted face-to-face at respondents home Fieldwork dates: October 24th to November 7th 2018 Population
Future of Europe Climate change Special Eurobarometer 479 October-November 2018 Methodology Survey conducted face-to-face at respondents home Fieldwork dates: October 24th to November 7th 2018 Population
Adding value to IRENA s REmap 2030 project using a European Electricity Model
 Adding value to IRENA s REmap 2030 project using a European Electricity Model Seán Collins, Deger Saygin, Paul Deane, Dolf Gielen, Brian Ó Gallachóir ESRI-UCC Workshop ESRI 7 th June 2016 Overview Adds
Adding value to IRENA s REmap 2030 project using a European Electricity Model Seán Collins, Deger Saygin, Paul Deane, Dolf Gielen, Brian Ó Gallachóir ESRI-UCC Workshop ESRI 7 th June 2016 Overview Adds
Promotion systems for electricity from renewable energy sources Lessons learned from EU countries. Reinhard Haas. Vienna University of Technology
 Promotion systems for electricity from renewable energy sources Lessons learned from EU countries Reinhard Haas Vienna University of Technology 1 SURVEY 1. Introduction 2. Historical developments 3. Success
Promotion systems for electricity from renewable energy sources Lessons learned from EU countries Reinhard Haas Vienna University of Technology 1 SURVEY 1. Introduction 2. Historical developments 3. Success
Target setting for RES-H/C in Upper Austria D6 of WP3 from the RES-H Policy project
 Target setting for RES-H/C in Upper Austria D6 of WP3 from the RES-H Policy project A report prepared as part of the IEE project "Policy development for improving RES-H/C penetration in European Member
Target setting for RES-H/C in Upper Austria D6 of WP3 from the RES-H Policy project A report prepared as part of the IEE project "Policy development for improving RES-H/C penetration in European Member
Modelling Biomass in TIMES models
 Modelling Biomass in TIMES models Hilke Rösler, Sander Lensink Amsterdam 22 th October 2007 www.ecn.nl Introduction NEEDS project: building 29 country models, representation of the complete energy system
Modelling Biomass in TIMES models Hilke Rösler, Sander Lensink Amsterdam 22 th October 2007 www.ecn.nl Introduction NEEDS project: building 29 country models, representation of the complete energy system
Introducing the JRC-IDEES database
 Introducing the JRC-IDEES database Seville, 01/03/2016 Joint Research Centre the European Commission's in-house science service JRC-IDEES Integrated Database of the European Energy Sector 2 OVERVIEW JRC-IDEES
Introducing the JRC-IDEES database Seville, 01/03/2016 Joint Research Centre the European Commission's in-house science service JRC-IDEES Integrated Database of the European Energy Sector 2 OVERVIEW JRC-IDEES
Cogeneration perspectives in the EU from the focus of CODE project
 Cogeneration perspectives in the EU from the focus of CODE project Stane Merše CODE leader Eastern Region Jozef Stefan Institute, Energy Efficiency Centre, Ljubljana, Slovenia. Cogeneration Directive requirements
Cogeneration perspectives in the EU from the focus of CODE project Stane Merše CODE leader Eastern Region Jozef Stefan Institute, Energy Efficiency Centre, Ljubljana, Slovenia. Cogeneration Directive requirements
Climate friendly, reliable, affordable: 100% renewable electricity supply by 2050
 Climate friendly, reliable, affordable: 100% renewable electricity supply by 2050 Prof. Dr. Olav Hohmeyer German Council of Environmental Advisors (SRU) CDREN workshop Perspectives on hydropower s role
Climate friendly, reliable, affordable: 100% renewable electricity supply by 2050 Prof. Dr. Olav Hohmeyer German Council of Environmental Advisors (SRU) CDREN workshop Perspectives on hydropower s role
Energy Demand in The EU
 Energy Demand in The EU A comparison of forecasts and ambitions - January 2011 - a contributing research paper to Energy Savings 2020: how to triple the impact of energy saving policies in Europe Energy
Energy Demand in The EU A comparison of forecasts and ambitions - January 2011 - a contributing research paper to Energy Savings 2020: how to triple the impact of energy saving policies in Europe Energy
When the Wind Blows Over Europe European Experiences with RES
 When the Wind Blows Over Europe European Experiences with RES Harvard electricity Policy Group Fifty-Second Plenary Session Chicago, 02-03 October 2008 Hannes Weigt Chair of Energy Economics and Public
When the Wind Blows Over Europe European Experiences with RES Harvard electricity Policy Group Fifty-Second Plenary Session Chicago, 02-03 October 2008 Hannes Weigt Chair of Energy Economics and Public
Renewable Energy: Wind Energy
 Environmental Policy Renewable Energy: Wind Energy Prof. C. San Juan Annika Karstadt, Martin Galonska Wind energy - Agenda 1 2 3 4 5 What is renewable energy Wind energy Wind farms EU policy (White Paper
Environmental Policy Renewable Energy: Wind Energy Prof. C. San Juan Annika Karstadt, Martin Galonska Wind energy - Agenda 1 2 3 4 5 What is renewable energy Wind energy Wind farms EU policy (White Paper
Present and future of Renewable Energies in Europe
 Present and future of Renewable Energies in Europe Arnulf Jäger-Waldau and Nicolae Scarlat Scientific Technical Reference System on RE & EEE Renewable Energies Unit 1 The Renewable Energies Unit MISSION:
Present and future of Renewable Energies in Europe Arnulf Jäger-Waldau and Nicolae Scarlat Scientific Technical Reference System on RE & EEE Renewable Energies Unit 1 The Renewable Energies Unit MISSION:
Renewable Energy Mapping & Monitoring Assessment of the availability of agricultural crop residues
 Renewable Energy Mapping & Monitoring Assessment of the availability of agricultural crop residues N. Scarlat European Commission Joint Research Centre (JRC) Institute for Energy and Transport Renewables
Renewable Energy Mapping & Monitoring Assessment of the availability of agricultural crop residues N. Scarlat European Commission Joint Research Centre (JRC) Institute for Energy and Transport Renewables
Eleanor Smith. Policy Officer of EREC
 Eleanor Smith Policy Officer of EREC Greenpeace Slovenia,7 th June 2011 Outline EREC & the REH 20% by 2020 Can we make it? RE-thinking 2050 A 100% Renewable Energy Vision for the European Union IPCC SRREN
Eleanor Smith Policy Officer of EREC Greenpeace Slovenia,7 th June 2011 Outline EREC & the REH 20% by 2020 Can we make it? RE-thinking 2050 A 100% Renewable Energy Vision for the European Union IPCC SRREN
State of play of CAP measure Agri-environment payments in the European Union
 State of play of CAP measure Agri-environment payments in the European Union Alexandros Papakonstantinou EN RD Contact Point CEDIA Seminar 1 st October 2010 THE ROLE OF RURAL DEVELOPMENT POLICY IN DELIVERING
State of play of CAP measure Agri-environment payments in the European Union Alexandros Papakonstantinou EN RD Contact Point CEDIA Seminar 1 st October 2010 THE ROLE OF RURAL DEVELOPMENT POLICY IN DELIVERING
Renewable Energy in Sweden an Overview
 Renewable Energy in Sweden an Overview Lars Guldbrand Director of R&D Strategy Swedish Energy Agency RENEWABLE ENERGY CONFERENCE: DEVELOPMENT AND SUSTAINABILITY Vilnius 10 June 2008 1 Characteristics Cold
Renewable Energy in Sweden an Overview Lars Guldbrand Director of R&D Strategy Swedish Energy Agency RENEWABLE ENERGY CONFERENCE: DEVELOPMENT AND SUSTAINABILITY Vilnius 10 June 2008 1 Characteristics Cold
SCENARIOS FOR DG/RES DEVELOPMENT ON CASE STUDY, COUNTRY AND EUROPEAN LEVEL
 SCENARIOS FOR DG/RES DEVELOPMENT ON CASE STUDY, COUNTRY AND EUROPEAN LEVEL Wolfgang PRÜGGLER, Carlo OBERSTEINER, Hans AUER Energy Economics Group (EEG), Technische Universität Wien Gusshausstraße 25-29/373-2;
SCENARIOS FOR DG/RES DEVELOPMENT ON CASE STUDY, COUNTRY AND EUROPEAN LEVEL Wolfgang PRÜGGLER, Carlo OBERSTEINER, Hans AUER Energy Economics Group (EEG), Technische Universität Wien Gusshausstraße 25-29/373-2;
SUPPORT SYSTEMS FOR RENEWABLE ENERGY: OVERVIEW OF EU MODELS AND EXPERIENCE
 SUPPORT SYSTEMS FOR RENEWABLE ENERGY: OVERVIEW OF EU MODELS AND EXPERIENCE INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR SCIENCE AND HIGH TECHNOLOGY The opinions expressed in this publication do not necessarily reflect the
SUPPORT SYSTEMS FOR RENEWABLE ENERGY: OVERVIEW OF EU MODELS AND EXPERIENCE INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR SCIENCE AND HIGH TECHNOLOGY The opinions expressed in this publication do not necessarily reflect the
Pro Europe EUROPEN EPR Seminar Packaging 2020 Cradle to Cradle Management Brussels, 6 October 2010
 ARA PRODUCER RESPONSIBILITY PUT INTO PRACTICE Pro Europe EUROPEN EPR Seminar Packaging 2020 Cradle to Cradle Management Brussels, 6 October 2010 AUSTRIA: FACTS AND FIGURES Capital Vienna Area 84,000 km²
ARA PRODUCER RESPONSIBILITY PUT INTO PRACTICE Pro Europe EUROPEN EPR Seminar Packaging 2020 Cradle to Cradle Management Brussels, 6 October 2010 AUSTRIA: FACTS AND FIGURES Capital Vienna Area 84,000 km²
PERSPECTIVES FOR BIOENERGY IN AUSTRIA AND OTHER CENTRAL EUROPEAN COUNTRIES (WITH A SPECIAL FOCUS ON THE 2020-RES-TARGETS)
 PERSPECTIVES FOR BIOENERGY IN AUSTRIA AND OTHER CENTRAL EUROPEAN COUNTRIES (WITH A SPECIAL FOCUS ON THE -RES-TARGETS) G. Kalt, L. Kranzl, R. Haas Energy Economics Group, Vienna University of Technology
PERSPECTIVES FOR BIOENERGY IN AUSTRIA AND OTHER CENTRAL EUROPEAN COUNTRIES (WITH A SPECIAL FOCUS ON THE -RES-TARGETS) G. Kalt, L. Kranzl, R. Haas Energy Economics Group, Vienna University of Technology
Report to the European Commission - DG ENV. Model based Analysis of the 2008 EU Policy Package on Climate Change and Renewables
 Report to the European Commission - DG ENV Model based Analysis of the 2008 EU Policy Package on Climate Change and Renewables By P. Capros, L. Mantzos, V. Papandreou, N. Tasios Primes Model E3MLab/NTUA
Report to the European Commission - DG ENV Model based Analysis of the 2008 EU Policy Package on Climate Change and Renewables By P. Capros, L. Mantzos, V. Papandreou, N. Tasios Primes Model E3MLab/NTUA
ACCELERATING GREEN ENERGY TOWARDS 2020 ACCELERATING GREEN ENERGY TOWARDS The Danish Energy Agreement of March 2012
 ACCELERATING GREEN ENERGY TOWARDS ACCELERATING GREEN ENERGY TOWARDS The Danish Energy Agreement of March Ministry of Climate, Energy and Building Design and layout: Solid Media Solutions Print: Prinfohhk.dk
ACCELERATING GREEN ENERGY TOWARDS ACCELERATING GREEN ENERGY TOWARDS The Danish Energy Agreement of March Ministry of Climate, Energy and Building Design and layout: Solid Media Solutions Print: Prinfohhk.dk
Evaluation of the National Renewable Energy Action Plans
 www.aebiom.org Evaluation of the National Renewable Energy Action Plans Jean-Marc Jossart Copenhagen, 6 October 2010 About AEBIOM European Biomass Association Represents and promotes interests of bioenergy
www.aebiom.org Evaluation of the National Renewable Energy Action Plans Jean-Marc Jossart Copenhagen, 6 October 2010 About AEBIOM European Biomass Association Represents and promotes interests of bioenergy
Supporting and integrating RE-Electricity in Italy The GSE experience IEA DSM Task XVII Seoul, Korea, September 2008
 Supporting and integrating RE-Electricity in Italy The GSE experience IEA DSM Task XVII Seoul, Korea, September 2008 Giancarlo Scorsoni 18/05/2006 1 Huge challenges To cope with: Global Climate Change
Supporting and integrating RE-Electricity in Italy The GSE experience IEA DSM Task XVII Seoul, Korea, September 2008 Giancarlo Scorsoni 18/05/2006 1 Huge challenges To cope with: Global Climate Change
Global Renewables Investment Renewables Networking Platform, Brussels
 Global Renewables Investment Renewables Networking Platform, Brussels Angus McCrone October 17, 2017 Contents Clean energy investment 2 Renewable energy costs 8 Sources of finance 11 EU policy dimension
Global Renewables Investment Renewables Networking Platform, Brussels Angus McCrone October 17, 2017 Contents Clean energy investment 2 Renewable energy costs 8 Sources of finance 11 EU policy dimension
Research and Development at the heart of a modern economy
 Item 15a: Research and Development ESTP course on National Accounts ESA 1 Luxembourg, 15-19 June 15 Research and Development at the heart of a modern economy R&D expenditure represents one of the major
Item 15a: Research and Development ESTP course on National Accounts ESA 1 Luxembourg, 15-19 June 15 Research and Development at the heart of a modern economy R&D expenditure represents one of the major
Group of Experts on Renewable Energy (GERE)
 Group of Experts on Renewable Energy (GERE) Status of Renewable Energy in the ECE Region Geneva, 18 November 2014 This project is part of the International Climate Initiative (IKI). The German Federal
Group of Experts on Renewable Energy (GERE) Status of Renewable Energy in the ECE Region Geneva, 18 November 2014 This project is part of the International Climate Initiative (IKI). The German Federal
The Contribution of Bioenergy to the 2020-RES-Targets
 The Contribution of Bioenergy to the -RES-Targets in Austria and Other Central European Countries Gerald Kalt, Lukas Kranzl, Reinhard Haas Energy Economics Group, Vienna University of Technology Objective
The Contribution of Bioenergy to the -RES-Targets in Austria and Other Central European Countries Gerald Kalt, Lukas Kranzl, Reinhard Haas Energy Economics Group, Vienna University of Technology Objective
EUMedRail Project - Kick-off Meeting Harmonised Regulation and Standards for Operations and Driver Training
 EUMedRail Project - Kick-off Meeting Harmonised Regulation and Standards for Operations and Driver Training 25/10/2017, Brussels Interoperability Unit I. Train Drivers DIRECTIVE 2007/59/EC OF THE EUROPEAN
EUMedRail Project - Kick-off Meeting Harmonised Regulation and Standards for Operations and Driver Training 25/10/2017, Brussels Interoperability Unit I. Train Drivers DIRECTIVE 2007/59/EC OF THE EUROPEAN
Effects of a White Certificate trading scheme on the energy system of the EU-27
 Ralf Kuder, Markus Blesl - 1 - Effects of a White Certificate trading scheme on the energy system of the EU-27 Dipl.-Kfm. Ralf Kuder, Dr.-Ing. Markus Blesl Institute of energy economics and the rational
Ralf Kuder, Markus Blesl - 1 - Effects of a White Certificate trading scheme on the energy system of the EU-27 Dipl.-Kfm. Ralf Kuder, Dr.-Ing. Markus Blesl Institute of energy economics and the rational
Wir schaffen Wissen heute für morgen
 Wir schaffen Wissen heute für morgen Paul Scherrer Institut Karin Treyer, Christian Bauer Laboratory for Energy Systems Analysis Basic LCI data for life cycle thinking in energy strategies: Electricity
Wir schaffen Wissen heute für morgen Paul Scherrer Institut Karin Treyer, Christian Bauer Laboratory for Energy Systems Analysis Basic LCI data for life cycle thinking in energy strategies: Electricity
Appendix D Comparison of Emissions Data with GAINS
 1 Appendix D Comparison of Emissions Data with 2 Comparison of Emissions Data with This section presents a comparison of emissions data from the Installation Database developed in this study and the data
1 Appendix D Comparison of Emissions Data with 2 Comparison of Emissions Data with This section presents a comparison of emissions data from the Installation Database developed in this study and the data
EU wide energy scenarios until 2050 generated with the TIMES model
 EU wide energy scenarios until 2050 generated with the TIMES model Rainer Friedrich, Markus Blesl Institut für Energiewirtschaft und Rationelle Energieanwendung, Universität Stuttgart EMEP CLRTAP TFIAM
EU wide energy scenarios until 2050 generated with the TIMES model Rainer Friedrich, Markus Blesl Institut für Energiewirtschaft und Rationelle Energieanwendung, Universität Stuttgart EMEP CLRTAP TFIAM
Renewable Energy Sources Act. Progress Report 2007
 Renewable Energy Sources Act Progress Report 2007 pursuant to Article 20 of the Act - Draft prepared by the Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety (BMU) Summary 5.7.2007
Renewable Energy Sources Act Progress Report 2007 pursuant to Article 20 of the Act - Draft prepared by the Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety (BMU) Summary 5.7.2007
CAP CONTEXT INDICATORS
 CAP CONTEXT INDICATORS 2014-2020 44. ENERGY USE IN AGRICULTURE, FORESTRY AND THE FOOD INDUSTRY 2017 update BE BG CZ DK DE EE IE EL ES FR HR IT CY LV LT LU HU MT NL AT PL PT RO SI SK FI SE UK CONTEXT INDICATOR
CAP CONTEXT INDICATORS 2014-2020 44. ENERGY USE IN AGRICULTURE, FORESTRY AND THE FOOD INDUSTRY 2017 update BE BG CZ DK DE EE IE EL ES FR HR IT CY LV LT LU HU MT NL AT PL PT RO SI SK FI SE UK CONTEXT INDICATOR
EECS Rules Fact Sheet 3 TYPES OF PUBLIC SUPPORT
 EECS Rules Fact Sheet 3 This document lists the Public Support schemes that are (or have been during the operation of EECS Schemes in that country) in place in the countries of members. Article E3.1 (Format
EECS Rules Fact Sheet 3 This document lists the Public Support schemes that are (or have been during the operation of EECS Schemes in that country) in place in the countries of members. Article E3.1 (Format
ENTSO-E scenarios- general overview. Daniel Huertas Hernando ENTSO-E System Planning Adviser
 ENTSO-E scenarios- general overview Daniel Huertas Hernando ENTSO-E System Planning Adviser SOAF TYNDP 18 June 2015 Page 2 Scenarios overall view Short term uncertainty increase Long term 1 year 5 years
ENTSO-E scenarios- general overview Daniel Huertas Hernando ENTSO-E System Planning Adviser SOAF TYNDP 18 June 2015 Page 2 Scenarios overall view Short term uncertainty increase Long term 1 year 5 years
Climate policy, Land and smart agriculture 2020, 2030
 Climate policy, Land and smart agriculture 2020, 2030 Simon Kay DG Climate Action, Unit A2 JRC workshop, Arona May 2014 Climate Action Treatment of emissions related to agriculture and LULUCF in the EU's
Climate policy, Land and smart agriculture 2020, 2030 Simon Kay DG Climate Action, Unit A2 JRC workshop, Arona May 2014 Climate Action Treatment of emissions related to agriculture and LULUCF in the EU's
Rural Development Policy
 Rural Development Policy Guido CASTELLANO Deputy Head of Unit H1 Consistency of Rural Development DG Agriculture and Rural Development European Commission Agriculture and Rural Development Importance of
Rural Development Policy Guido CASTELLANO Deputy Head of Unit H1 Consistency of Rural Development DG Agriculture and Rural Development European Commission Agriculture and Rural Development Importance of
