Atmospheric Sciences 211. Who are we? About Me
|
|
|
- Jennifer Willa Pearson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Surface Temperature Atmospheric Sciences 211 Climate of the present. We will examine the nature of the global climate system and the factors controlling its present state. Topics covered will include the global energy balance, the greenhouse effect, atmospheric circulation, the role of oceans and ice in climate, and the natural carbon cycle. Climate of the past. In this part of the class we will discuss how climate changed in the past on timescales ranging from billions of years to thousands of years. And we will use this information to help understand what future climates might be like. Climate of the future. How will climate change over the next 100 years, and how do we know this? Should you be concerned? What are technologies for potentially addressing human-induced global climate change? Who are we? Prof. David Battisti 304 ATG ; battisti@uw.edu; Phone: More: Étienne Tétreault-Pinard 402 ATG; etienne@uw.edu About Me Prof. of Atmospheric Sciences BS. In Physics, MS. In Oceanography, Ph.D. in Atmospheric Sciences Scientific Interests: Year-to-Year Climate Variability (e.g., El Nino) Past Climates (e.g., Eocene, Ice Ages) Impacts of Climate Variability and Climate Change on Global Food Production Sea Surface Temperature Anomalies Aug 2012 My other hats Prof, University of Bergen Norway Affiliate Prof, Food Security and Environment Program, Stanford Chief Climate Scientist, Global Food Bank, Svalbard Norway
2 Course Goals 1. Develop an understanding of how the climate system works, how it has changed in the past, and how it is now being changed by human activity. What this course is/isn t about YES: Science: the what, how, and why of climate and climate change NO: philosophies, values, politics, etc 2. Learn skills to analyze and critically evaluate public discussions of climate issues. Course Overview The Climate System (Present) Tools: Radiative Transfer & Energy Balance Earth s Energy Balance & Climate Tools: Force Balance and Winds General Circulation of the Atmosphere Regional Climates Things we will understand Why is Southern California so dry and Seattle so wet? Climate Change (Past-Present) How we know pre-instrumental climate Orbital Forcing & the Ice Ages Solar and Volcanic Forcing The natural carbon cycle and past warm climates The Human Influence on the climate of the 20 th Century Global Warming (Future) Projected forcing and climate response
3 Things we will understand Why is Europe so warm in winter compared to New England? The Gulf Stream 350M Europeans release much more CO 2 than 20M N Englanders and Canadians The Rocky Mts +2C Annual Global Average Surface Temperature -15C Deg C How do we know the 20 th Century trend in is not due to natural variability? To changes in the Sun s output? Carbon Dioxide in the Atmosphere Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Today 394 ppm What does the geological record tell us about the climates of the past, when CO 2 was much lower than today? How do we know the 20 th Century trend in CO 2 is not natural?
4 CO 2 and Temperature at the S. Pole (Vostok St) Things we will understand: the Great Ice Ages The Ice Ages lasted 2.6 Myr BP to about 10,000 yrs ago Large Ice sheets covered Northwestern Europe and Northern North America At the S. Pole, temperature goes hand-in-hand with CO 2 : high CO 2 goes with high temperature. What does this imply about the globe? About causality? Things we will understand: the Great Ice Ages The Ice Ages lasted 2.6 Myr BP to about 10,000 yrs ago Things we will understand: the Great Ice Ages The Ice Ages lasted 2.6 Myr BP to about 10,000 yrs ago Times of High Land Ice Volume Ice volume changes are coordinated with CO 2 changes (shift of carbon between atmosphere and oceans) The Ice Ages are caused by orbitally induced changes in northern hemisphere summer insolation Changes in CO 2 act enhance the temperature and land ice changes due to the insolation changes (a positive feedback)
5 Carbon Dioxide in the Atmosphere Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide A2 (as usual) - 800! GEOCARB II model (black line; shaded area encloses model uncertainty) Estimate from plant stomata & C 13 /C 12 (vertical bars) What does the geological record tell us about the climates of the past when CO 2 was much higher than today? 2100 AD! A1B - 600! B1 (utopia) CO 2 has been much higher in the past than today. How do we know the 20 th Century trend in CO 2 is not due to natural causes? Scenario A2 Temperature Change (deg C) How are these projections made and what do they say about the climate at the end of this Century? Range of Model Answers In 100 years, the atmospheric CO 2 will reach ppm, which was last experienced during the EOCENE (55 to 36 million years ago) The Eocene climate was warm, even at high latitudes: -palm trees flourished in Wyoming and Antarctica was a pine forest -crocodiles lived in the Arctic -deep ocean temperature was 55 F (today it is ~35 F) -sea level was at least 300 feet higher than today! * Climate models with mid-range climate sensitivity simulate an Eocene that is much too cold compared to the fossil records
6 Very Tentative Syllabus Very Tentative Syllabus Sept Introduction; Origin of Earth s Atmosphere; Atmosphere Composition Today Oct 29- Nov 1 Midterm 1 st The Cryosphere Today; Ice Ages and How We Know They Happened; Milankovitch Theory; Precessional Forcing Oct 1-4 Heat and Temperature; Heat Forms and Transport; Radiation; Concepts in EM Radiation; Solar Radiation and the Earth; Albedo Nov 5-8 The Carbon Cycle and Warm Climates of the Past Oct 8-11 Energy Balance; Greenhouse gases and the Greenhouse Effect Nov (12 th Holiday) Natural and Human Induced Forcing and their Impact on Climate of the 20 th Century Oct Greenhouse Effect (cont.) Seasonal Temperature Cycles; Pressure Force, Hydrostatic Balance; Coriolis Effect and Geostrophic Wind; Jet Streams; Nov (22 nd Holiday) The 20 th Century Climate (cont) Oct General Circulation of the Atmosphere; The Role of Mountains in Climate; The Role of the Ocean in Climate Nov Dec 3-6 Projected Climate Change (today to 2100 and beyond) Geo-engineering; wrap-up Prerequisites & Required Materials Math is the language of the natural sciences You will see and learn to use a few equations This course and your grades are based on concepts (NOT mathematical ability) Textbook: Kump, Kasting, Crane, 3 rd edition (2010) The Earth System Logistics Assessment & Grading Policy Assessment Homework and Quizzes 35% Mid-Term Exam (Nov 1) 30% Final Exam 35% Tentative: Monday Dec , OTB 014 Grading Method Likely course mean (B- to B) Curve if necessary Lectures here MTWTh 10:30-11:20 Discussion/Quiz Sections Friday 10:30 JHN 111 or 11:30 JHN 175
7 Assessment & Grading Policy (cont) There will be no makeup exams except in case of serious illness, death in the family or something of that nature. You must be excused by Prof. Battisti in advance of the date of the exam. Plagiarism - Working Together see UW policy on plagiarism discussions are encouraged! on your own for exams, homework, etc Course Guidelines and Philosophy UW Credit Hours 2hrs/week outside per credit hour 15 hrs/week dedicated to this class (5 in class, 10 outside) Lectures/Discussion FOR YOUR BENEFIT! Stop me, ask questions! Mix of writing on board and powerpoint slides Comfortable Atmosphere Let me know immediately We want you to do well! 1. COME TO CLASS 2. TAKE GOOD NOTES 3. REVIEW YOUR NOTES Chapter 1 Chapter 10 Reading for this week Note: you can skip the blue-boxed text in both chapters 4. TALK TO YOUR CLASSMATES, YOUR TA AND ME 5. TEST YOURSELF 6. RELAX GET YOUR QUESTIONS ANSWERED!
Atmospheric Sciences 211. Who are we? About Me. Course Goals. What this course is/isn t about
 Surface Temperature 1960-1991 Atmospheric Sciences 211 Climate of the present. We will examine the nature of the global climate system and the factors controlling its present state. Topics covered will
Surface Temperature 1960-1991 Atmospheric Sciences 211 Climate of the present. We will examine the nature of the global climate system and the factors controlling its present state. Topics covered will
Announcements. Homework 8 - paper 2 topics, questions and sources due Tuesday, Nov. 13 Midterm Paper 2 - due Tuesday, Nov. 20
 Thursday, November 6th. Announcements. Homework 8 - paper 2 topics, questions and sources due Tuesday, Nov. 13 Midterm Paper 2 - due Tuesday, Nov. 20 Lecture #18-1 Lecture #18-2 http://dotearth.blogs.nytimes.com/2007/11/06/project-to-harness-plankton-puts-to-sea/index.html
Thursday, November 6th. Announcements. Homework 8 - paper 2 topics, questions and sources due Tuesday, Nov. 13 Midterm Paper 2 - due Tuesday, Nov. 20 Lecture #18-1 Lecture #18-2 http://dotearth.blogs.nytimes.com/2007/11/06/project-to-harness-plankton-puts-to-sea/index.html
How things work college course/cumulative global warming exam/testbank
 How things work college course/cumulative global warming exam/testbank From Wikiversity Contents 1 GlobalWarmingCumulative 1.1 GlobalWarmingCumulative v1s1 1.1.1 Key to GlobalWarmingCumulative v1s1 1.2
How things work college course/cumulative global warming exam/testbank From Wikiversity Contents 1 GlobalWarmingCumulative 1.1 GlobalWarmingCumulative v1s1 1.1.1 Key to GlobalWarmingCumulative v1s1 1.2
Announcements. Homework 7 - due today Homework 8 - paper 2 topics, questions and sources due Tuesday, Nov. 13 Midterm Paper 2 - due Tuesday, Nov.
 Tuesday, November 6th. Announcements. Homework 7 - due today Homework 8 - paper 2 topics, questions and sources due Tuesday, Nov. 13 Midterm Paper 2 - due Tuesday, Nov. 20 Lecture #17-1 For next week..homework
Tuesday, November 6th. Announcements. Homework 7 - due today Homework 8 - paper 2 topics, questions and sources due Tuesday, Nov. 13 Midterm Paper 2 - due Tuesday, Nov. 20 Lecture #17-1 For next week..homework
The IPCC Working Group I Assessment of Physical Climate Change
 The IPCC Working Group I Assessment of Physical Climate Change Martin Manning Director, IPCC Working Group I Support Unit 1. Observed climate change 2. Drivers of climate change 3. Attribution of cause
The IPCC Working Group I Assessment of Physical Climate Change Martin Manning Director, IPCC Working Group I Support Unit 1. Observed climate change 2. Drivers of climate change 3. Attribution of cause
PHY392S Physics of Climate. Lecture 1. Introduction
 PHY392S Physics of Climate Lecture 1 Introduction Slides based on material from Prof. K. Strong PHY392S - Physics of Climate Lecture 1, Page 1 Some Definitions Weather the fluctuating state of the atmosphere
PHY392S Physics of Climate Lecture 1 Introduction Slides based on material from Prof. K. Strong PHY392S - Physics of Climate Lecture 1, Page 1 Some Definitions Weather the fluctuating state of the atmosphere
High School Climate Science Curriculum Course learning goals. October 2011
 1 High School Climate Science Curriculum Course learning goals October 2011 Current Climate 1. Earth climate is determined by a balance between absorbed sunlight and emitted infrared radiation. Because
1 High School Climate Science Curriculum Course learning goals October 2011 Current Climate 1. Earth climate is determined by a balance between absorbed sunlight and emitted infrared radiation. Because
The Water Cycle, Atmosphere, and Cryosphere. OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 12 April 2018
 The Water Cycle, Atmosphere, and Cryosphere OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 12 April 2018 Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs) At the completion of today s section, students should be able to: 1. Summarize components
The Water Cycle, Atmosphere, and Cryosphere OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 12 April 2018 Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs) At the completion of today s section, students should be able to: 1. Summarize components
11/15. Agenda. Albedo Effect Simulator: Discussion Climate Change Notes
 Agenda 11/15 Albedo Effect Simulator: Discussion Climate Change Notes Announcements -Test (11/20) -Notebook check (tomorrow) -Lab due (11.59pm, tomorrow) -No quiz tomorrow Criteria Table of contents labeled
Agenda 11/15 Albedo Effect Simulator: Discussion Climate Change Notes Announcements -Test (11/20) -Notebook check (tomorrow) -Lab due (11.59pm, tomorrow) -No quiz tomorrow Criteria Table of contents labeled
Lecture 11: Global Warming
 Lecture 11: Global Warming CO 2 CH 4 How much of the global warming is caused by Natural climate change and by human activities? What is the sensitivity of Earth s climate to the increases of greehouse
Lecture 11: Global Warming CO 2 CH 4 How much of the global warming is caused by Natural climate change and by human activities? What is the sensitivity of Earth s climate to the increases of greehouse
LESSON 9: CONCEPTUALIZING MODULE II Factors Influencing Temperature
 LESSON 9: CONCEPTUALIZING MODULE II Factors Influencing Temperature PURPOSE/QUESTION To understand the need to compare data sets over different parameters thus increasing the strength for students climate
LESSON 9: CONCEPTUALIZING MODULE II Factors Influencing Temperature PURPOSE/QUESTION To understand the need to compare data sets over different parameters thus increasing the strength for students climate
Carbon Dioxide and Global Warming Case Study
 Carbon Dioxide and Global Warming Case Study Key Concepts: Greenhouse Gas Carbon dioxide El Niño Global warming Greenhouse effect Greenhouse gas La Niña Land use Methane Nitrous oxide Radiative forcing
Carbon Dioxide and Global Warming Case Study Key Concepts: Greenhouse Gas Carbon dioxide El Niño Global warming Greenhouse effect Greenhouse gas La Niña Land use Methane Nitrous oxide Radiative forcing
Lecture 7 Global Warming/Climate Change (Observations and Attribution of Cause) METR/ENVS 113 Spring Semester 2011 May 3, 2011
 Lecture 7 Global Warming/Climate Change (Observations and Attribution of Cause) METR/ENVS 113 Spring Semester 2011 May 3, 2011 Reading Henson Rough Guide Chapter 1 Pages 75 127; 215; 227-244 Other pages
Lecture 7 Global Warming/Climate Change (Observations and Attribution of Cause) METR/ENVS 113 Spring Semester 2011 May 3, 2011 Reading Henson Rough Guide Chapter 1 Pages 75 127; 215; 227-244 Other pages
describe and discuss the process of, and controls on, the transfer of radiant and nonradiant energy in the Earth-Atmosphere system explain, describe a
 e GEOG 1180 Summer, 2011 GEOG 1180 (Section 2) Physical Geography (Meteorology, Climatology and Biogeography) Lecture Lab Instructor Instructor's Office Office Hours Monday 13:30-15:20 am, Wednesday 13:30-14:20
e GEOG 1180 Summer, 2011 GEOG 1180 (Section 2) Physical Geography (Meteorology, Climatology and Biogeography) Lecture Lab Instructor Instructor's Office Office Hours Monday 13:30-15:20 am, Wednesday 13:30-14:20
Climate Change Connected Curriculum
 Climate Change Connected Curriculum Climate change is happening, humans are causing it, and I think this is perhaps the most serious environmental issue facing us. - - - - -Bill Nye Climate Change across
Climate Change Connected Curriculum Climate change is happening, humans are causing it, and I think this is perhaps the most serious environmental issue facing us. - - - - -Bill Nye Climate Change across
The Science of Climate Change
 The Science of Climate Change http://data.giss.nasa.gov/gistemp/ Glaciers are retreating worldwide, including Colorado Arapahoe Glacier, 1917 Arapahoe Glacier, 2004 Sea Level is Rising End of summer ice
The Science of Climate Change http://data.giss.nasa.gov/gistemp/ Glaciers are retreating worldwide, including Colorado Arapahoe Glacier, 1917 Arapahoe Glacier, 2004 Sea Level is Rising End of summer ice
Causes of past climate change and projections of future changes in climate. Peter Stott Met Office Hadley Centre, UK
 Causes of past climate change and projections of future changes in climate Peter Stott Met Office Hadley Centre, UK Overview 1.The causes of observed climate change 2.Global and regional climate projections
Causes of past climate change and projections of future changes in climate Peter Stott Met Office Hadley Centre, UK Overview 1.The causes of observed climate change 2.Global and regional climate projections
Scientific Foundation of Climate Change. Human Responsibility for Climate Change
 Scientific Foundation of Climate Change EOH 468 CSU Northridge Spring 2010 Peter Bellin, CIH, Ph.D. 1 Human Responsibility for Climate Change The IPCC finds that it is very likely that emissions of heat-trapping
Scientific Foundation of Climate Change EOH 468 CSU Northridge Spring 2010 Peter Bellin, CIH, Ph.D. 1 Human Responsibility for Climate Change The IPCC finds that it is very likely that emissions of heat-trapping
Greenhouse Effect & Climate Change
 Greenhouse Effect & Climate Change Greenhouse Effect Light energy from the sun (solar radiation) is either reflected or absorbed by the Earth. Greenhouse Effect When it is absorbed by the Earth (or something
Greenhouse Effect & Climate Change Greenhouse Effect Light energy from the sun (solar radiation) is either reflected or absorbed by the Earth. Greenhouse Effect When it is absorbed by the Earth (or something
Physics 100 Lecture 17. The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming April 2, 2018
 1 Physics 100 Lecture 17 The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming April 2, 2018 2 Class Quiz Ch. 7: Suppose your car burned bituminous coal instead of gasoline. How much coal would provide the same energy
1 Physics 100 Lecture 17 The Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming April 2, 2018 2 Class Quiz Ch. 7: Suppose your car burned bituminous coal instead of gasoline. How much coal would provide the same energy
Global CO 2 and Climate Change
 Global CO 2 and Climate Change A deeper look at the carbon dioxide cycle, greenhouse gases, and oceanic processes over the last 200 years OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 17 April 2018 Reading: Libes, Chapter
Global CO 2 and Climate Change A deeper look at the carbon dioxide cycle, greenhouse gases, and oceanic processes over the last 200 years OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 17 April 2018 Reading: Libes, Chapter
Global warming. Models for global warming Sand analogy
 8.10 Global warming Assessment statements 8.6.1 Describe some possible models of global warming. 8.6. State what is meant by the enhanced greenhouse effect. 8.6.3 Identify the increased combustion of fossil
8.10 Global warming Assessment statements 8.6.1 Describe some possible models of global warming. 8.6. State what is meant by the enhanced greenhouse effect. 8.6.3 Identify the increased combustion of fossil
Evidence and implications of anthropogenic climate change
 Evidence and implications of anthropogenic climate change Earth s Climate has always been changing 1) Is climate changing now? Global Warming? Sea level rising IPCC 2007 Fig. 5.13 (p. 410) Recontructed
Evidence and implications of anthropogenic climate change Earth s Climate has always been changing 1) Is climate changing now? Global Warming? Sea level rising IPCC 2007 Fig. 5.13 (p. 410) Recontructed
LECTURE #24: Mega Disasters Climate Change
 GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #24: Mega Disasters Climate Change Date: 17 April 2018 I. Early Earth was more similar to present-day Venus o very high amounts of carbon dioxide
GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #24: Mega Disasters Climate Change Date: 17 April 2018 I. Early Earth was more similar to present-day Venus o very high amounts of carbon dioxide
How Might Global Warming Affect Your Community?
 Climate Change Activity 6 How Might Global Warming Affect Your Community? Goals In this activity you will: Brainstorm the ways that global warming might influence the Earth. List ways that global warming
Climate Change Activity 6 How Might Global Warming Affect Your Community? Goals In this activity you will: Brainstorm the ways that global warming might influence the Earth. List ways that global warming
Lecture 11: Global Warming. Human Acticities. Natural Climate Changes. Global Warming: Natural or Man-Made CO 2 CH 4
 Lecture 11: Global Warming Human Acticities CO 2 CH 4 The initial appearance of human species: last 100,000 to 200,000 years Development of the first civilization: the last 10,000 years What is the sensitivity
Lecture 11: Global Warming Human Acticities CO 2 CH 4 The initial appearance of human species: last 100,000 to 200,000 years Development of the first civilization: the last 10,000 years What is the sensitivity
Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition
 Chapter Chapter 1 16 Clickers Lecture Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition The Oceans and Climate Change Alan P. Trujillo Harold V. Thurman Chapter Overview Humans are adding greenhouse gases to
Chapter Chapter 1 16 Clickers Lecture Essentials of Oceanography Eleventh Edition The Oceans and Climate Change Alan P. Trujillo Harold V. Thurman Chapter Overview Humans are adding greenhouse gases to
ATM S 111: Global Warming Global Warming Primer. Jennifer Fletcher Day 2: June
 ATM S 111: Global Warming Global Warming Primer Jennifer Fletcher Day 2: June 22 2010 Class Website! http://www.atmos.washington.edu/academics/classes/ 2010Q3/111/ (hopefully linked from your myuw page)
ATM S 111: Global Warming Global Warming Primer Jennifer Fletcher Day 2: June 22 2010 Class Website! http://www.atmos.washington.edu/academics/classes/ 2010Q3/111/ (hopefully linked from your myuw page)
1. Explain the role plants and animals have in the carbon cycle. How does this delicate
 1. Explain the role plants and animals have in the carbon cycle. How does this delicate balance remain in place? 2. How did the introduction of fossil fuels corrupt the existing carbon cycle? 3. What are
1. Explain the role plants and animals have in the carbon cycle. How does this delicate balance remain in place? 2. How did the introduction of fossil fuels corrupt the existing carbon cycle? 3. What are
1) Draw a diagram of the Greenhouse Effect with as much detail as you can.
 As you re coming in: 1) Draw a diagram of the Greenhouse Effect with as much detail as you can. (Then hang them up on the back wall) 2) Write down any words or ideas you need or would like me to define
As you re coming in: 1) Draw a diagram of the Greenhouse Effect with as much detail as you can. (Then hang them up on the back wall) 2) Write down any words or ideas you need or would like me to define
Lecture #42. Low Clouds Over the Ocean. Positive Feedback and Clouds. The First Estimate of Surface Warming Due to a Doubling of CO 2 - in 1896!
 The First Estimate of Surface Warming Due to a Doubling of CO 2 - in 1896! Original prediction: a doubling of CO 2 would increase temperature between and 6 C. Was attempting to explain ice age If the quantity
The First Estimate of Surface Warming Due to a Doubling of CO 2 - in 1896! Original prediction: a doubling of CO 2 would increase temperature between and 6 C. Was attempting to explain ice age If the quantity
How Can Thermal Effects Be Explained?
 How Can Thermal Effects Be Explained? Lesson 6, Part 3: Climate Science The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect The Earth will maintain equilibrium (constant stable temperature level) if the energy coming in is.
How Can Thermal Effects Be Explained? Lesson 6, Part 3: Climate Science The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect The Earth will maintain equilibrium (constant stable temperature level) if the energy coming in is.
TAs: Nicholas Cavanaugh Kaushik Srinivasan
 SIO 20 THE ATMOSPHERE Sam Iacobellis Scripps Institution of Oceanography Nierenberg Hall 204 phone: 534-3126 email: sam@ucsd.edu TAs: Nicholas Cavanaugh (ncavanaugh@ucsd.edu) Kaushik Srinivasan (ksriniva@ucsd.edu)
SIO 20 THE ATMOSPHERE Sam Iacobellis Scripps Institution of Oceanography Nierenberg Hall 204 phone: 534-3126 email: sam@ucsd.edu TAs: Nicholas Cavanaugh (ncavanaugh@ucsd.edu) Kaushik Srinivasan (ksriniva@ucsd.edu)
Lectures by ElenaYulaeva
 Lectures by ElenaYulaeva eyulaeva@ucsd.edu;858-534-6278 1. 07-13: Overview of Climate Change 2. 07-15:Climate change modeling (topic for research project) 3. 07-18:Forecasting climate (topic for research
Lectures by ElenaYulaeva eyulaeva@ucsd.edu;858-534-6278 1. 07-13: Overview of Climate Change 2. 07-15:Climate change modeling (topic for research project) 3. 07-18:Forecasting climate (topic for research
Global Climate Change: What the Future Holds, and What We Can Do About It
 Global Climate Change: What the Future Holds, and What We Can Do About It Dr. David Karowe Professor, Department of Biological Sciences Schedule of Topics September 29: Recent climate change (Dave Karowe)
Global Climate Change: What the Future Holds, and What We Can Do About It Dr. David Karowe Professor, Department of Biological Sciences Schedule of Topics September 29: Recent climate change (Dave Karowe)
ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007
 ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007 Name This examination consists of a total of 100 points. In each of the first two sections, you have a choice of which questions to answer. Please note that you
ATM S 211 Final Examination June 4, 2007 Name This examination consists of a total of 100 points. In each of the first two sections, you have a choice of which questions to answer. Please note that you
Atmosphere, the Water Cycle and Climate Change
 Atmosphere, the Water Cycle and Climate Change OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 16 April 2013 (Based on previous lectures by Barry Huebert) 2013 F.J. Sansone 1. The water cycle Outline 2. Climate and climate-change
Atmosphere, the Water Cycle and Climate Change OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 16 April 2013 (Based on previous lectures by Barry Huebert) 2013 F.J. Sansone 1. The water cycle Outline 2. Climate and climate-change
Climate Change Simple, serious, solveable
 Climate Change Simple, serious, solveable Mike Pritchard Professor of Earth System Sciences UC Irvine Acknowledging course content from Prof. Scott Denning, Colorado State University. About me I m a new(ish)
Climate Change Simple, serious, solveable Mike Pritchard Professor of Earth System Sciences UC Irvine Acknowledging course content from Prof. Scott Denning, Colorado State University. About me I m a new(ish)
Chapter 19 Global Change
 Chapter 19 Global Change Global Change change - any chemical, biological or physical property change of the planet. Examples include cold temperatures causing ice ages. Global change - changes in the climate
Chapter 19 Global Change Global Change change - any chemical, biological or physical property change of the planet. Examples include cold temperatures causing ice ages. Global change - changes in the climate
Chapter 19 Global Change
 Chapter 19 Global Change Global Change Global change- any chemical, biological or physical property change of the planet. Examples include cold temperatures causing ice ages. Global climate change-changes
Chapter 19 Global Change Global Change Global change- any chemical, biological or physical property change of the planet. Examples include cold temperatures causing ice ages. Global climate change-changes
Climate: Earth s Dynamic Equilibrium
 Climate: Earth s Dynamic Equilibrium review session CCIU April 30, 2016 High-school standard HS-ESS2-4 focuses on the role energy flows play in Earth s climate HS-ESS2-4 Use a model to describe how variations
Climate: Earth s Dynamic Equilibrium review session CCIU April 30, 2016 High-school standard HS-ESS2-4 focuses on the role energy flows play in Earth s climate HS-ESS2-4 Use a model to describe how variations
Earth s Climate from Space. Richard Allan Department of Meteorology University of Reading
 Earth s Climate from Space Richard Allan Department of Meteorology University of Reading Earth s energy balance in space S πr 2 4πr 2 Outgoing Thermal Radiative Energy Absorbed Solar Radiative Energy
Earth s Climate from Space Richard Allan Department of Meteorology University of Reading Earth s energy balance in space S πr 2 4πr 2 Outgoing Thermal Radiative Energy Absorbed Solar Radiative Energy
ENRP 6101: Environmental Sciences I: Physical Sciences Fall 2016
 ENRP 6101: Environmental Sciences I: Physical Sciences Fall 2016 Time and Location Wednesdays, 6:10 8:40 pm; PHIL 108 Instructor Office Hours Course Materials Dr. Velmurugan Vel Subramanian, PE, BCEE Phone:
ENRP 6101: Environmental Sciences I: Physical Sciences Fall 2016 Time and Location Wednesdays, 6:10 8:40 pm; PHIL 108 Instructor Office Hours Course Materials Dr. Velmurugan Vel Subramanian, PE, BCEE Phone:
Global warming: Evidence, risks and mitigation options (or: Why global warming is an energy issue) Filippo Giorgi Abdus Salam ICTP, Trieste
 Global warming: Evidence, risks and mitigation options (or: Why global warming is an energy issue) Filippo Giorgi Abdus Salam ICTP, Trieste Four frequent questions Is global warming happening? (If yes)
Global warming: Evidence, risks and mitigation options (or: Why global warming is an energy issue) Filippo Giorgi Abdus Salam ICTP, Trieste Four frequent questions Is global warming happening? (If yes)
Activity 1.4: GEEBITT (Global Equilibrium Energy Balance Interactive Tinker Toy)
 Activity 1.4: GEEBITT (Global Equilibrium Energy Balance Interactive Tinker Toy) Grades 5 6 Description: Students use the NASA Micro-GEEBITT modeling tool to explore how changing variables in Earth systems
Activity 1.4: GEEBITT (Global Equilibrium Energy Balance Interactive Tinker Toy) Grades 5 6 Description: Students use the NASA Micro-GEEBITT modeling tool to explore how changing variables in Earth systems
Comments on Human and Natural Forcings. Climate changes (1900 to 2000) due to human activity. Climate Variability and Climate Change
 Comments on Human and Natural Forcings Human input of GH gases (carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, CFCs ) has warmed the planet: net RF = +2.9 W/m 2 The largest single warming factor is increased
Comments on Human and Natural Forcings Human input of GH gases (carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, CFCs ) has warmed the planet: net RF = +2.9 W/m 2 The largest single warming factor is increased
ATOC 4800: Policy Implications of Climate ATOC 5000/ENVS5830: Critical Issues in Climate and the Environment Class Web Page:
 ATOC 4800: Policy Implications of Climate ATOC 5000/ENVS5830: Critical Issues in Climate and the Environment Class Web Page: http://atoc.colorado.edu/~whan/atoc4800_5000 Announcements 1. No Exams and Extra-credits;
ATOC 4800: Policy Implications of Climate ATOC 5000/ENVS5830: Critical Issues in Climate and the Environment Class Web Page: http://atoc.colorado.edu/~whan/atoc4800_5000 Announcements 1. No Exams and Extra-credits;
Major Volcanic Eruptions in the past. Major Volcanic Eruptions in the past. Volcanic Eruptions and Global Temperature
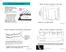 Mechanism of Volcanic Perturbation Amount of sunlight scattered depends greatly on size and amount of aerosol particles The global monitoring of aerosols began in ~1980 Hence, the history of the amplitude
Mechanism of Volcanic Perturbation Amount of sunlight scattered depends greatly on size and amount of aerosol particles The global monitoring of aerosols began in ~1980 Hence, the history of the amplitude
Introduction. This activity is in the style of a Unit 3 exam question.
 Introduction This activity is in the style of a Unit 3 exam question. Note that this activity, while being in the style of an exam question, has not been subject to the careful evaluation and revision
Introduction This activity is in the style of a Unit 3 exam question. Note that this activity, while being in the style of an exam question, has not been subject to the careful evaluation and revision
CHAPTER 16 Oceans & Climate Change Chapter Overview Earth s Climate System Earth s Climate System Earth s Climate System Earth s Climate System
 1 CHAPTER 16 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Oceans & Climate Change Chapter Overview Humans are adding greenhouse gases to Earth s atmosphere. Climate change will cause many severe problems in the ocean environment.
1 CHAPTER 16 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Oceans & Climate Change Chapter Overview Humans are adding greenhouse gases to Earth s atmosphere. Climate change will cause many severe problems in the ocean environment.
Greenhouse Effect. The Greenhouse Effect
 Greenhouse Effect The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse gases let short-wavelength radiation come into the Earth s atmosphere from the sun. However, they absorb and re-radiate Earth s long-wavelength radiation
Greenhouse Effect The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse gases let short-wavelength radiation come into the Earth s atmosphere from the sun. However, they absorb and re-radiate Earth s long-wavelength radiation
Concentrations of several of these greenhouse gases (CO 2, CH 4, N 2 O and CFCs) have increased dramatically in the last hundred years due to human
 Global Warming 1.1 The facts: With no atmosphere surrounding the earth the surface temperature would be 17 o C. However, due to the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that absorb infrared radiation emitted
Global Warming 1.1 The facts: With no atmosphere surrounding the earth the surface temperature would be 17 o C. However, due to the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that absorb infrared radiation emitted
Lecture 29: Detection of Climate Change and Attribution of Causes
 Lecture 29: Detection of Climate Change and Attribution of Causes 1. The Meaning of Detection and Attribution The response to anthropogenic changes in climate forcing occurs against a backdrop of natural
Lecture 29: Detection of Climate Change and Attribution of Causes 1. The Meaning of Detection and Attribution The response to anthropogenic changes in climate forcing occurs against a backdrop of natural
Climates and Ecosystems
 Chapter 2, Section World Geography Chapter 2 Climates and Ecosystems Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter 2, Section
Chapter 2, Section World Geography Chapter 2 Climates and Ecosystems Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter 2, Section
Feedback loops modify atmospheric processes
 Chapter Overview CHAPTER 16 Oceans & Climate Change Humans are adding greenhouse gases to Earth s atmosphere. Climate change will cause many severe problems in the ocean environment. It is necessary to
Chapter Overview CHAPTER 16 Oceans & Climate Change Humans are adding greenhouse gases to Earth s atmosphere. Climate change will cause many severe problems in the ocean environment. It is necessary to
ENVST-UA 9226 Climate Change
 ENVST-UA 9226 Climate Change Semester FALL 2015 Class code Instructor Details ENVST-UA 9226 Lisa Weber Lisa.weber@nyu.edu Class Details Climate Change Thursday 2-5pm Location to be confirmed. Prerequisites
ENVST-UA 9226 Climate Change Semester FALL 2015 Class code Instructor Details ENVST-UA 9226 Lisa Weber Lisa.weber@nyu.edu Class Details Climate Change Thursday 2-5pm Location to be confirmed. Prerequisites
FOLLOW: Green House on Twitter
 Jan 31, 2012 Recommend 773 208 By Wendy Koch, USA TODAY Updated 1d 13h ago CAPTION By William Fernando Martinez, AP A new NASA study tries to lay to rest the skepticism about climate change, especially
Jan 31, 2012 Recommend 773 208 By Wendy Koch, USA TODAY Updated 1d 13h ago CAPTION By William Fernando Martinez, AP A new NASA study tries to lay to rest the skepticism about climate change, especially
What is the truth about climate change? John E Midwinter FRS FREng
 What is the truth about climate change? John E Midwinter FRS FREng john.midwinter@btopenworld.com The course as planned! 1 Today Is the climate actually changing and are we the cause? 2. Wednesday 30th
What is the truth about climate change? John E Midwinter FRS FREng john.midwinter@btopenworld.com The course as planned! 1 Today Is the climate actually changing and are we the cause? 2. Wednesday 30th
Energy, Greenhouse Gases and the Carbon Cycle
 Energy, Greenhouse Gases and the Carbon Cycle David Allen Gertz Regents Professor in Chemical Engineering, and Director, Center for Energy and Environmental Resources Concepts for today Greenhouse Effect
Energy, Greenhouse Gases and the Carbon Cycle David Allen Gertz Regents Professor in Chemical Engineering, and Director, Center for Energy and Environmental Resources Concepts for today Greenhouse Effect
Climate Change. Some solar radiation is reflected by Earth and the atmosphere. Earth s Surface
 Q& A n The Basics of Greenhouse gases affect Earth s energy balance and climate The Sun serves as the primary energy source for Earth s climate. Some of the incoming sunlight is reflected directly back
Q& A n The Basics of Greenhouse gases affect Earth s energy balance and climate The Sun serves as the primary energy source for Earth s climate. Some of the incoming sunlight is reflected directly back
CLIMATE MODELS: LARGE SCALE AND PREDICTABLE
 CCS 5-1 CLIMATE MODELS: LARGE SCALE AND PREDICTABLE 1. Print this file (and associated linked images if any). Also answer the "Concept of the Week" questions in the Weekly Climate News File. (Check for
CCS 5-1 CLIMATE MODELS: LARGE SCALE AND PREDICTABLE 1. Print this file (and associated linked images if any). Also answer the "Concept of the Week" questions in the Weekly Climate News File. (Check for
IDS 102 The Greenhouse Effect Part II- The Data Trace Gases in the Atmosphere & Global Climate Change
 IDS 102 The Greenhouse Effect Part II- The Data Trace Gases in the Atmosphere & Global Climate Change Background & History of Earth s Atmosphere: The primary gases in Earth s atmosphere are 78% nitrogen,
IDS 102 The Greenhouse Effect Part II- The Data Trace Gases in the Atmosphere & Global Climate Change Background & History of Earth s Atmosphere: The primary gases in Earth s atmosphere are 78% nitrogen,
Earth s Dynamic Climate
 UNIT 3 Earth s Dynamic Climate Topic 3.1: What is climate, and how has it changed during Earth s history? Topic 3.2 : Where are the effects of climate change felt, and what is their impact? Topic 3.5:
UNIT 3 Earth s Dynamic Climate Topic 3.1: What is climate, and how has it changed during Earth s history? Topic 3.2 : Where are the effects of climate change felt, and what is their impact? Topic 3.5:
Understanding Global Warming
 Math 483 Spring Semester, 2013 California State University, Northridge Understanding Global Warming Global Warming is Real December 2012 is 334th consecutive Month with global temperatures above the 20th
Math 483 Spring Semester, 2013 California State University, Northridge Understanding Global Warming Global Warming is Real December 2012 is 334th consecutive Month with global temperatures above the 20th
Global ClimateChange. Pedro M.M. Soares. Instituto Dom Luiz University of Lisbon
 Global ClimateChange Pedro M.M. Soares Instituto Dom Luiz University of Lisbon pmsoares@fc.ul.pt IPCC 5th AssessmentReportfor ClimateChange2013: The Physical Basis Observed Changes in the Climate System
Global ClimateChange Pedro M.M. Soares Instituto Dom Luiz University of Lisbon pmsoares@fc.ul.pt IPCC 5th AssessmentReportfor ClimateChange2013: The Physical Basis Observed Changes in the Climate System
Global warming is already happening
 Climate change Global warming is already happening and it is not just temperature Is the change significant? why, yes We are no longer involved in just a scientific debate over how observations fit theories
Climate change Global warming is already happening and it is not just temperature Is the change significant? why, yes We are no longer involved in just a scientific debate over how observations fit theories
Grade 10 Academic Science Climate Change Unit Test
 Grade 10 Academic Science Climate Change Unit Test Part A - Multiple Choice: Circle the most correct answer. 1. What is the difference between weather and climate? a. Weather deals with wind and precipitation;
Grade 10 Academic Science Climate Change Unit Test Part A - Multiple Choice: Circle the most correct answer. 1. What is the difference between weather and climate? a. Weather deals with wind and precipitation;
Global Climate Change
 Global Climate Change Devizes & District U3A, 24 th November 2015 Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Why does Earth s climate change? Earth s Climate has always been changing
Global Climate Change Devizes & District U3A, 24 th November 2015 Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Why does Earth s climate change? Earth s Climate has always been changing
MPA in Environmental Science and Policy. ENV U6115: Water and Climate Schedule
 MPA in Environmental Science and Policy ENV U6115: Water and Climate Schedule Summer Semester 2005 Instructors: Dr. Patrick Louchouarn Associate professor Dept. of Earth & Environmental Science Earth Institute
MPA in Environmental Science and Policy ENV U6115: Water and Climate Schedule Summer Semester 2005 Instructors: Dr. Patrick Louchouarn Associate professor Dept. of Earth & Environmental Science Earth Institute
What Causes Climate? Reid Pierce Fulbright Jr. High Bentonville, AR
 What Causes Climate? Reid Pierce Fulbright Jr. High Bentonville, AR Weather: the outdoor conditions at a particular time and place Climate: an average of weather conditions in a given area over a period
What Causes Climate? Reid Pierce Fulbright Jr. High Bentonville, AR Weather: the outdoor conditions at a particular time and place Climate: an average of weather conditions in a given area over a period
Global Climate Change
 Global Climate Change 1 Climate Change Past Climate Trends Is the Earth Warming? Predictions of Climate Change Ocean Circulation and Sea Ice Vegetation Temperature Energy Policy and Greenhouse Gases 2
Global Climate Change 1 Climate Change Past Climate Trends Is the Earth Warming? Predictions of Climate Change Ocean Circulation and Sea Ice Vegetation Temperature Energy Policy and Greenhouse Gases 2
Global Climate Change
 Global Climate Change 1 Climate Change Past Climate Trends Is the Earth Warming? Predictions of Climate Change Ocean Circulation and Sea Ice Vegetation Temperature Energy Policy and Greenhouse Gases 2
Global Climate Change 1 Climate Change Past Climate Trends Is the Earth Warming? Predictions of Climate Change Ocean Circulation and Sea Ice Vegetation Temperature Energy Policy and Greenhouse Gases 2
LAB National Science Teachers Association. Lab Handout. Introduction
 LAB 22 Lab Handout Lab 22. Minimizing Carbon Emissions: What Type of Greenhouse Gas Emission Reduction Policy Will Different Regions of the World Need to Adopt to Prevent the Average Global Surface Temperature
LAB 22 Lab Handout Lab 22. Minimizing Carbon Emissions: What Type of Greenhouse Gas Emission Reduction Policy Will Different Regions of the World Need to Adopt to Prevent the Average Global Surface Temperature
The carbon and climate problem
 The carbon and climate problem What is the evidence? What are the caveats? What are the long-term implications? Prof. Ric Williams www.liv.ac.uk/climate 1 1. What is the evidence? data/simple theory CO
The carbon and climate problem What is the evidence? What are the caveats? What are the long-term implications? Prof. Ric Williams www.liv.ac.uk/climate 1 1. What is the evidence? data/simple theory CO
Name: Class: Date: 6. Most air pollution is produced by a. thermal inversions. c. ozone layer depletion. b. fuel burning. d. volcanic eruptions.
 Name: Class: Date: Air Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is often used to remove poisonous gases from industrial
Name: Class: Date: Air Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is often used to remove poisonous gases from industrial
TO THE PRESENTER. 1. Introduction 2. Climate change science 3. Climate change action 4. Quiz and discussion questions.
 TO THE PRESENTER This presentation which starts on Slide 4 includes the most important points about climate science and how climate change relates to the Chicago region, from the tool Climate Change in
TO THE PRESENTER This presentation which starts on Slide 4 includes the most important points about climate science and how climate change relates to the Chicago region, from the tool Climate Change in
Determining causes of warming: Climate models & the smoking gun
 Determining causes of warming: Climate models & the smoking gun Announcements TONIGHT: HW #6 (paper outlines) due in lecture! bring up at Break HW #7 (presentation outlines) due in section next week Email
Determining causes of warming: Climate models & the smoking gun Announcements TONIGHT: HW #6 (paper outlines) due in lecture! bring up at Break HW #7 (presentation outlines) due in section next week Email
Chapter 19 Global Change. Wednesday, April 18, 18
 Chapter 19 Global Change Module 62 Global Climate Change and the Greenhouse Effect After reading this module you should be able to distinguish among global change, global climate change, and global warming.
Chapter 19 Global Change Module 62 Global Climate Change and the Greenhouse Effect After reading this module you should be able to distinguish among global change, global climate change, and global warming.
Global Warming and Climate Change
 Global Warming and Climate Change 1800s: Scientists knew that: If the earth were a bare, airless rock, the surface would be much colder than it actually is. Why? Tens of thousands of years ago, thick layers
Global Warming and Climate Change 1800s: Scientists knew that: If the earth were a bare, airless rock, the surface would be much colder than it actually is. Why? Tens of thousands of years ago, thick layers
ENSC425/625 Climate Change and Global Warming
 ENSC425/625 Climate Change and Global Warming 1 Emission scenarios of greenhouse gases Projections of climate change Regional climate change (North America) Observed Changes and their Uncertainty 2 Figure
ENSC425/625 Climate Change and Global Warming 1 Emission scenarios of greenhouse gases Projections of climate change Regional climate change (North America) Observed Changes and their Uncertainty 2 Figure
CONTENTS. Introduction x
 CONTENTS Introduction x Chapter 1: Climate 1 Solar Radiation and Temperature 2 The Distribution of Radiant Energy from the Sun 2 The Effects of the Atmosphere 3 Average Radiation Budgets 6 Surface-Energy
CONTENTS Introduction x Chapter 1: Climate 1 Solar Radiation and Temperature 2 The Distribution of Radiant Energy from the Sun 2 The Effects of the Atmosphere 3 Average Radiation Budgets 6 Surface-Energy
2 Atmospheric Heating
 CHAPTER 15 2 Atmospheric Heating SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How does energy travel from the sun to Earth? What are
CHAPTER 15 2 Atmospheric Heating SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How does energy travel from the sun to Earth? What are
Past climates Past climates were different than today. Global climate change. Climate change
 Past climates Past climates were different than today Warmer: Europe 900 1300 AD (Medieval Times) Cooler: Northern Hemisphere - Little Ice Age 1500-1850 AD Wetter: North Africa 1 million+ y.o.: savanna
Past climates Past climates were different than today Warmer: Europe 900 1300 AD (Medieval Times) Cooler: Northern Hemisphere - Little Ice Age 1500-1850 AD Wetter: North Africa 1 million+ y.o.: savanna
Climate Change and the Future Impacts across the Southwest Region. Darren McCollum and Robert Bohlin. National Weather Service Flagstaff, Arizona
 Climate Change and the Future Impacts across the Southwest Region Darren McCollum and Robert Bohlin National Weather Service Flagstaff, Arizona What is Climate Change? DEFINITION Climate change: is a significant
Climate Change and the Future Impacts across the Southwest Region Darren McCollum and Robert Bohlin National Weather Service Flagstaff, Arizona What is Climate Change? DEFINITION Climate change: is a significant
- geographic patterns of energy balance
 (1 of 10) Further Reading: Chapter 04 of the text book Outline - geographic patterns of energy balance - net radiation - meridional transport (2 of 10) Introduction Previously, we discussed the energy
(1 of 10) Further Reading: Chapter 04 of the text book Outline - geographic patterns of energy balance - net radiation - meridional transport (2 of 10) Introduction Previously, we discussed the energy
What Are Global Temperatures Doing, and Why Are They Doing It? R.C. Shoup
 What Are Global Temperatures Doing, and Why Are They Doing It? R.C. Shoup 1) What are temperatures actually doing? The answer to this question should be reasonably straightforward, but it is not. An examination
What Are Global Temperatures Doing, and Why Are They Doing It? R.C. Shoup 1) What are temperatures actually doing? The answer to this question should be reasonably straightforward, but it is not. An examination
2. Climate Change: Projections of Climate Change: 2100 and beyond
 Global Warming: Science, Projections and Uncertainties Global Warming: Science, Projections and Uncertainties An overview of the basic science An overview of the basic science 1. A Brief History of Global
Global Warming: Science, Projections and Uncertainties Global Warming: Science, Projections and Uncertainties An overview of the basic science An overview of the basic science 1. A Brief History of Global
Teacher Guide Case Study: Carbon Dioxide and Global Warming: What is the Evidence?
 Teacher Guide Case Study: Carbon Dioxide and Global Warming: What is the Evidence? Developed by: Dan Shepardson Activity Focus: In this case study, students read and interpret data about the link between
Teacher Guide Case Study: Carbon Dioxide and Global Warming: What is the Evidence? Developed by: Dan Shepardson Activity Focus: In this case study, students read and interpret data about the link between
WRAP- UP of TOPIC #14 on ANTHROPOGENIC GLOBAL WARMING
 WRAP- UP of TOPIC #14 on ANTHROPOGENIC GLOBAL WARMING p 77 Energy Buildings Transport Industry Forestry Agriculture Waste TOPIC # 14, PART B: Evidence from Natural Archives Class Notes pp 78 KEY GRAPH!
WRAP- UP of TOPIC #14 on ANTHROPOGENIC GLOBAL WARMING p 77 Energy Buildings Transport Industry Forestry Agriculture Waste TOPIC # 14, PART B: Evidence from Natural Archives Class Notes pp 78 KEY GRAPH!
Generating Electricity
 Worksheet 3 Generating Electricity In most power stations, electricity is generated by burning fuels. Coal, oil and natural gas are the common fuels for generating electricity. Major parts of a power station
Worksheet 3 Generating Electricity In most power stations, electricity is generated by burning fuels. Coal, oil and natural gas are the common fuels for generating electricity. Major parts of a power station
Human Activity and Climate Change
 Human Activity and Climate Change Textbook pages 482 501 Section 11.1 11.2 Summary Before You Read How might climate change affect the region where you live? Record your thoughts in the lines below. What
Human Activity and Climate Change Textbook pages 482 501 Section 11.1 11.2 Summary Before You Read How might climate change affect the region where you live? Record your thoughts in the lines below. What
Weather has always been a hot topic of conversation. We talk about whether it is hot or cold, windy or calm, snowy or dry. We listen to the radio to
 Weather has always been a hot topic of conversation. We talk about whether it is hot or cold, windy or calm, snowy or dry. We listen to the radio to figure out if the weather will be different tomorrow.
Weather has always been a hot topic of conversation. We talk about whether it is hot or cold, windy or calm, snowy or dry. We listen to the radio to figure out if the weather will be different tomorrow.
What is climate change? - BBC News
 What is climate change? - BBC News Media caption Why we should care about climate change? In December, of cials from across the world will gather in Paris, France, to try to hammer out a deal to tackle
What is climate change? - BBC News Media caption Why we should care about climate change? In December, of cials from across the world will gather in Paris, France, to try to hammer out a deal to tackle
Today. Events. Terrestrial Planet Climate. Homework DUE. Review next time. Exam next week
 Today Terrestrial Planet Climate Events Homework DUE Review next time Exam next week Wonders of the Industrial Age From 1912 Weather and Climate Weather is the ever-varying combination of wind, clouds,
Today Terrestrial Planet Climate Events Homework DUE Review next time Exam next week Wonders of the Industrial Age From 1912 Weather and Climate Weather is the ever-varying combination of wind, clouds,
Monday, October 29, Coming up: Short-term organic carbon cycle (p ) Marine organic carbon cycle and nutrient limitation (p )
 Monday, October 29, 2017 Assessment available until Friday Topic - The Carbon Cycle (Chapter 8) Overview of the carbon cycle (p 149-151) Reservoirs (p 151-152) Steady State (p 152-153) Residence Time (p
Monday, October 29, 2017 Assessment available until Friday Topic - The Carbon Cycle (Chapter 8) Overview of the carbon cycle (p 149-151) Reservoirs (p 151-152) Steady State (p 152-153) Residence Time (p
CHAPTER 19. Global Change
 CHAPTER 19 Global Change WALKING ON THIN ICE Polar bears play important role in North Pole ecosystem Food seals Important as food and fur for clothing source for indigenous people Problem temperatures
CHAPTER 19 Global Change WALKING ON THIN ICE Polar bears play important role in North Pole ecosystem Food seals Important as food and fur for clothing source for indigenous people Problem temperatures
ANNOUNCEMENTS: I-4 LESSON 4 on Intro to Climate Modeling is due TONIGHT by 11:59 pm
 Thursday Nov 20th Topic #13 GLOBAL WARMING & ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING (cont.) SIT ANYWHERE TODAY! But pick up an INDEX CARD when you come it! ANNOUNCEMENTS: I-4 LESSON 4 on Intro to Climate Modeling is due
Thursday Nov 20th Topic #13 GLOBAL WARMING & ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING (cont.) SIT ANYWHERE TODAY! But pick up an INDEX CARD when you come it! ANNOUNCEMENTS: I-4 LESSON 4 on Intro to Climate Modeling is due
Climate system dynamics and modelling
 Climate system dynamics and modelling Hugues Goosse Chapter 6 Future climate changes Outline Methods used to estimate future climate changes. Description of the main results at different timescales. Interpretation
Climate system dynamics and modelling Hugues Goosse Chapter 6 Future climate changes Outline Methods used to estimate future climate changes. Description of the main results at different timescales. Interpretation
2. How did the introduction of fossil fuels corrupt the existing carbon cycle?
 1. Explain the role plants and animals have in the carbon cycle. How does this delicate balance remain in place? 2. How did the introduction of fossil fuels corrupt the existing carbon cycle?! I i 3. What
1. Explain the role plants and animals have in the carbon cycle. How does this delicate balance remain in place? 2. How did the introduction of fossil fuels corrupt the existing carbon cycle?! I i 3. What
Climatic Change: Scientific Issues
 Climate Change: Scientific Issues Anno Accademico, 2011/12 Valter Maggi Lab. di Glaciologia, Dip. Scienze dell Ambiente e del Territorio. http://geoserver.disat.unimib.it/valter What is climate change?
Climate Change: Scientific Issues Anno Accademico, 2011/12 Valter Maggi Lab. di Glaciologia, Dip. Scienze dell Ambiente e del Territorio. http://geoserver.disat.unimib.it/valter What is climate change?
