Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology
|
|
|
- Clinton Dean
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology
2 Ecosystem Ecology Examines Interactions Between the Living and Non-Living World Ecosystem- A particular location on Earth distinguished by its particular mix of interacting biotic and abiotic components.
3 Ecosystem Boundaries Some ecosystems, such as a caves and lakes have very distinctive boundaries. However, in most ecosystems it is difficult to determine where one ecosystems stops and the next begins.
4
5 Ecosystem Processes Even though it is helpful to distinguish between two different ecosystems, ecosystems interact with other ecosystems.
6 Energy Flows through Ecosystems
7 Photosynthesis and Respiration Producers (autotrophs) are able to use the suns energy to produce usable energy through the process called photosynthesis.
8
9 Photosynthesis and Respiration Cellular respiration is the process by which other organisms gain energy from eating the tissues of producers.
10 Trophic Levels, Food Chains, and Food Webs Consumers (heterotrophs)-obtain energy by consuming other organisms. Primary Consumers (herbivores)-consume producers. Secondary Consumers (carnivores)-obtain their energy by eating primary consumers. Tertiary Consumers (carnivores)-eat secondary consumers.
11
12 Food Chain-The sequence of consumption from producers through tertiary consumers. Food Web-A more realistic type of food chain that takes into account the complexity of nature.
13
14 Ecosystem Productivity Gross primary productivity (GPP)-The total amount of solar energy that the producers in an ecosystem capture via photosynthesis over a given amount of time. Net primary productivity (NPP)- The energy captured (GPP) minus the energy respired by producers.
15
16 Energy Transfer Efficiency and Trophic Pyramids Biomass-The energy in an ecosystem is measured in terms of biomass. Standing crop-the amount of biomass present in an ecosystem at a particular time. Ecological efficiency- The proportion of consumed energy that can be passed from one trophic level to another. Trophic pyramid- The representation of the distribution of biomass among trophic levels.
17 Matter cycles through the biosphere Biosphere-The combination of all ecosystems on Earth. Biogeochemical cycles- The movement of matter within and between ecosystems involving biological, geologic and chemical processes.
18 The Hydrologic Cycle The movement of water through the biosphere.
19
20 The Hydrologic Cycle Transpiration-The process where plants release water from their leaves into the atmosphere. Evapotranspiration-The combined amount of evaporation and transpiration. Runoff- When water moves across the land surface into streams and rivers, eventually reaching the ocean.
21 The Carbon Cycle
22 The Nitrogen Cycle
23 The Phosphorus Cycle
24 Ecosystems respond to disturbance Disturbance- An event caused by physical, chemical or biological agents that results in changes in population size or community composition.
25
26 Watershed Studies Watershed-All of the land in a given landscape that drains into a particular stream, river, lake or wetland.
27
28 Resistance versus Resilience Resistance-A measure of how much a disturbance can affect its flows of energy and matter. Resilience-The rate at which an ecosystem returns to its original state after a disturbance. Restoration ecology- A new scientific discipline that is interested in restoring damaged ecosystems.
29 The Intermediate Disturbance Hypothesis The intermediate disturbance hypothesisstates that ecosystems experiencing intermediate levels of disturbance are more diverse than those with high or low disturbance levels.
30
31 Ecosystems Provide Valuable Services
32 Cultural services- Ecosystems provide cultural or aesthetic benefits to many people. Instrumental Values of Ecosystems Provisions- Goods that humans can use directly. Regulating services- The service provided by natural systems that helps regulate environmental conditions. Support systems- The support services that natural ecosystems provide such as pollination, natural filters and pest control. Resilience- Resilience of an ecosystem ensures that it will continue to provide benefits to humans. This greatly depends on species diversity.
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology. Reading Questions
 APES Name 22 Module 7 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 17 Module 6 The Movement of Energy 18 Ecosystem Field Walk 19 Module 7 The 23 Module 8 Responses to Disturbances
APES Name 22 Module 7 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 17 Module 6 The Movement of Energy 18 Ecosystem Field Walk 19 Module 7 The 23 Module 8 Responses to Disturbances
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology. Tuesday, September 19, 17
 Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Reversing Deforestation in Haiti Answers the following: Why is deforestation in Haiti so common? What the negative impacts of deforestation? Name three actions intended counteract
Chapter 3 Ecosystem Ecology Reversing Deforestation in Haiti Answers the following: Why is deforestation in Haiti so common? What the negative impacts of deforestation? Name three actions intended counteract
Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs
 How Ecosystems Work Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs Autotrophs make their own food so they are called PRODUCERS Heterotrophs get their food from another source so they are called CONSUMERS Two Main forms of
How Ecosystems Work Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs Autotrophs make their own food so they are called PRODUCERS Heterotrophs get their food from another source so they are called CONSUMERS Two Main forms of
Unit 2: Ecology. Chapters 2: Principles of Ecology
 Unit 2: Ecology Chapters 2: Principles of Ecology Ecology Probe: Answer the questions and turn it in! This is a standard aquarium with a population of fish. There is no filter in this aquarium and no one
Unit 2: Ecology Chapters 2: Principles of Ecology Ecology Probe: Answer the questions and turn it in! This is a standard aquarium with a population of fish. There is no filter in this aquarium and no one
Energy Transfer p
 Energy Transfer 22-1 p. 415-419 Essential Questions 1. Identify and describe the main types of producers and consumers in an ecosystem. 2. Calculate the amount of energy stored in biomass transferred from
Energy Transfer 22-1 p. 415-419 Essential Questions 1. Identify and describe the main types of producers and consumers in an ecosystem. 2. Calculate the amount of energy stored in biomass transferred from
Multiple Choice. Name Class Date
 Chapter 3 The Biosphere Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. 1. Which of the following descriptions about the
Chapter 3 The Biosphere Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. 1. Which of the following descriptions about the
Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology
 E Stuart Chapin III Pamela A. Matson Harold A. Mooney Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology Illustrated by Melissa C. Chapin With 199 Illustrations Teehnische Un.fversitSt Darmstadt FACHBEREIGH 10
E Stuart Chapin III Pamela A. Matson Harold A. Mooney Principles of Terrestrial Ecosystem Ecology Illustrated by Melissa C. Chapin With 199 Illustrations Teehnische Un.fversitSt Darmstadt FACHBEREIGH 10
Dynamics of Ecosystems. Chapter 57
 Dynamics of Ecosystems Chapter 57 1 The Water Cycle Nutrient Cycles Trophic Levels Primary Productivity Outline The Energy in Food Chains Ecological Pyramids Interactions Among Trophic Levels Species Richness
Dynamics of Ecosystems Chapter 57 1 The Water Cycle Nutrient Cycles Trophic Levels Primary Productivity Outline The Energy in Food Chains Ecological Pyramids Interactions Among Trophic Levels Species Richness
Principles of Ecology
 Principles of Ecology 1 Keystone Anchors Describe ecological levels of organization in the biosphere. o Describe the levels of ecological organization (i.e., organism, population, community, ecosystem,
Principles of Ecology 1 Keystone Anchors Describe ecological levels of organization in the biosphere. o Describe the levels of ecological organization (i.e., organism, population, community, ecosystem,
Principles of Ecology
 Principles of Ecology Ecology Study of interactions that take place between organisms and their environments Living things are affected by nonliving and living parts of the environment Abiotic factors:
Principles of Ecology Ecology Study of interactions that take place between organisms and their environments Living things are affected by nonliving and living parts of the environment Abiotic factors:
What is Ecology? ECOLOGY is a branch of biology that studies ecosystems.
 4.2 Energy Flow Through an Ecosystem Food Chains, Food Webs, and Ecological Pyramids What is Ecology? ECOLOGY is a branch of biology that studies ecosystems. Ecological Terminology Environment Ecology
4.2 Energy Flow Through an Ecosystem Food Chains, Food Webs, and Ecological Pyramids What is Ecology? ECOLOGY is a branch of biology that studies ecosystems. Ecological Terminology Environment Ecology
Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems
 Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems Preview Classroom Catalyst Objectives Life Depends on the Sun From Producers to Consumers An Exception: Deep-Ocean Ecosystems What Eats What Cellular Respiration: Burning
Section 1: Energy Flow in Ecosystems Preview Classroom Catalyst Objectives Life Depends on the Sun From Producers to Consumers An Exception: Deep-Ocean Ecosystems What Eats What Cellular Respiration: Burning
Niche and Habitat a species plays in a community. What it does all
 Ecosystem Dynamics What is ecology? Study of the interactions between parts of the environment Connections in nature Abiotic: soil comp. Biotic: and Abiotic and Biotic factors factors in the environment
Ecosystem Dynamics What is ecology? Study of the interactions between parts of the environment Connections in nature Abiotic: soil comp. Biotic: and Abiotic and Biotic factors factors in the environment
Guided Notes Unit 3B: Matter and Energy
 Name: Date: Block: Chapter 13: Principles of Ecology I. Concept 13.3: Energy in Ecosystems II. a. Review Vocabulary b. Autotrophs Guided Notes Unit 3B: Matter and Energy i. Producers: convert the light
Name: Date: Block: Chapter 13: Principles of Ecology I. Concept 13.3: Energy in Ecosystems II. a. Review Vocabulary b. Autotrophs Guided Notes Unit 3B: Matter and Energy i. Producers: convert the light
Biology Ecology Unit Chapter 2 Study Guide
 Name: Date: Block: Biology Ecology Unit Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. Directions: Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage. Ecology Biotic factors Nonliving Environments Atmosphere Humans
Name: Date: Block: Biology Ecology Unit Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. Directions: Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage. Ecology Biotic factors Nonliving Environments Atmosphere Humans
Ecosystem Ecology. Community (biotic factors) interacts with abiotic factors
 Ecosystem Ecology Community (biotic factors) interacts with abiotic factors Objectives Compare the processes of energy flow and chemical cycling as they relate to ecosystem dynamics. Define and list examples
Ecosystem Ecology Community (biotic factors) interacts with abiotic factors Objectives Compare the processes of energy flow and chemical cycling as they relate to ecosystem dynamics. Define and list examples
Ecology is the study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their physical environment
 Chapter 3 and 4 Study Guide Ecology is the study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their physical environment This includes both biotic and abiotic factors- biotic factors are living
Chapter 3 and 4 Study Guide Ecology is the study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their physical environment This includes both biotic and abiotic factors- biotic factors are living
Chapter Introduction. Matter. Ecosystems. Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Abiotic Factors Cycles of Matter Chapter Wrap-Up Energy in Ecosystems How do living things and the nonliving parts of the environment interact? What do you
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Abiotic Factors Cycles of Matter Chapter Wrap-Up Energy in Ecosystems How do living things and the nonliving parts of the environment interact? What do you
Name Class Date. In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: What Is an Ecosystem? In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase. 1. ecology 2. habitat 3. community 4. ecosystem
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: What Is an Ecosystem? In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase. 1. ecology 2. habitat 3. community 4. ecosystem
Forest Production Ecology
 Objectives Forest Production Ecology Overview of forest production ecology C cycling Primary productivity of trees and forest ecosystems ecologists and ecosystem managers are unlikely to achieve desired
Objectives Forest Production Ecology Overview of forest production ecology C cycling Primary productivity of trees and forest ecosystems ecologists and ecosystem managers are unlikely to achieve desired
The Law of Conservation of Matter. Matter cannot be created nor destroyed Matter only changes form There is no away
 Review Items Ecosystem Structure The Law of Conservation of Matter Matter cannot be created nor destroyed Matter only changes form There is no away Laws Governing Energy Changes First Law of Thermodynamics
Review Items Ecosystem Structure The Law of Conservation of Matter Matter cannot be created nor destroyed Matter only changes form There is no away Laws Governing Energy Changes First Law of Thermodynamics
What is an ecosystem?
 1 What is an ecosystem? System = regularly interacting and interdependent components forming a unified whole Ecosystem = an ecological system; = a community and its physical environment treated together
1 What is an ecosystem? System = regularly interacting and interdependent components forming a unified whole Ecosystem = an ecological system; = a community and its physical environment treated together
What is ECOLOGY? The study of the biotic and abiotic factors in an environment and their interactions.
 Ecology What is ECOLOGY? The study of the biotic and abiotic factors in an environment and their interactions. Biotic Factors Living things in the environment. Animals Plants Fungi Protists Bacteria Abiotic
Ecology What is ECOLOGY? The study of the biotic and abiotic factors in an environment and their interactions. Biotic Factors Living things in the environment. Animals Plants Fungi Protists Bacteria Abiotic
Unit 3: Ecology II Section 1: Environmental Systems and Nutrient Cycling
 Unit 3: Ecology II Section 1: Environmental Systems and Nutrient Cycling Systems in the Environment are not Independent of one Another Central Case Study: The Vanishing Oysters of the Chesapeake Bay Chesapeake
Unit 3: Ecology II Section 1: Environmental Systems and Nutrient Cycling Systems in the Environment are not Independent of one Another Central Case Study: The Vanishing Oysters of the Chesapeake Bay Chesapeake
Energy Flow In Ecosystems
 Energy Flow In Ecosystems Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Ecological Niche Producers & Consumers Herbivores, Omnivores & Carnivores Scavenger Food Chain Trophic Levels Food Webs Ecological Pyramids
Energy Flow In Ecosystems Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration Ecological Niche Producers & Consumers Herbivores, Omnivores & Carnivores Scavenger Food Chain Trophic Levels Food Webs Ecological Pyramids
Ecology the scientific study of interactions between different organisms and between organisms and their environment or surroundings
 Ecology the scientific study of interactions between different organisms and between organisms and their environment or surroundings Biotic living factors that influence an ecosystem Abiotic non-living
Ecology the scientific study of interactions between different organisms and between organisms and their environment or surroundings Biotic living factors that influence an ecosystem Abiotic non-living
Feeding Relationships and trophic levels
 Feeding Relationships and trophic levels All life needs a source of energy. Therefore, the life in an ecosystem need energy too! The sun provides that energy. The sun s energy is not DIRECTLY usable by
Feeding Relationships and trophic levels All life needs a source of energy. Therefore, the life in an ecosystem need energy too! The sun provides that energy. The sun s energy is not DIRECTLY usable by
Crosswalk of Georgia Performance Standards & Georgia Standards of Excellence GSE Implementation in Environmental Science
 SEV1. Students will investigate the flow of energy and cycling of matter within an ecosystem and relate these phenomena to human society. a. Interpret biogeochemical cycles including hydrologic, nitrogen,
SEV1. Students will investigate the flow of energy and cycling of matter within an ecosystem and relate these phenomena to human society. a. Interpret biogeochemical cycles including hydrologic, nitrogen,
Cycles of Ma,er. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview. 3.4 Cycles of Matter
 Lesson Overview Cycles of Ma,er Lesson Overview 3.4 Cycles of Matter THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these
Lesson Overview Cycles of Ma,er Lesson Overview 3.4 Cycles of Matter THINK ABOUT IT A handful of elements combine to form the building blocks of all known organisms. Organisms cannot manufacture these
Cycles of Matter. Slide 1 of 33. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Cycles of Matter 1 of 33 The purpose of this lesson is to learn the water, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycles. This PowerPoint will provide most of the required information you need to accomplish
Cycles of Matter 1 of 33 The purpose of this lesson is to learn the water, carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycles. This PowerPoint will provide most of the required information you need to accomplish
Chapter 36: Population Growth
 Chapter 36: Population Growth Population: Population Concepts interbreeding group of same species Carrying Capacity: maximum population size an ecosystem can sustainably support Critical Number: minimum
Chapter 36: Population Growth Population: Population Concepts interbreeding group of same species Carrying Capacity: maximum population size an ecosystem can sustainably support Critical Number: minimum
The Nonliving Environment
 Chapter Review The Nonliving Environment Part A. Vocabulary Review Directions: Write the correct term in the spaces beside each definition. Unscramble the boxed letters to find a word that describes a
Chapter Review The Nonliving Environment Part A. Vocabulary Review Directions: Write the correct term in the spaces beside each definition. Unscramble the boxed letters to find a word that describes a
ANSWER KEY - Ecology Review Packet
 ANSWER KEY - Ecology Review Packet OBJECTIVE 1: Ecosystem Structure 1. What is the definition of an abiotic factor? Give one example. A nonliving part of an ecosystem. Example: water 2. What is the definition
ANSWER KEY - Ecology Review Packet OBJECTIVE 1: Ecosystem Structure 1. What is the definition of an abiotic factor? Give one example. A nonliving part of an ecosystem. Example: water 2. What is the definition
2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems Name: Date: (Reference: BC Science 10 pp. 68 to 91) Block: NUTRIENT CYCLING IN THE BIOSPHERE. nutrients: aka.
 2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems Name: Date: (Reference: BC Science 10 pp. 68 to 91) Block: NUTRIENT CYCLING IN THE BIOSPHERE nutrients: stores: aka Nutrients are accumulated for short or long periods
2.2 Nutrient Cycles in Ecosystems Name: Date: (Reference: BC Science 10 pp. 68 to 91) Block: NUTRIENT CYCLING IN THE BIOSPHERE nutrients: stores: aka Nutrients are accumulated for short or long periods
1. All the interconnected feeding relationships in an ecosystem make up a food. a. Interaction b. Chain c. Network d. Web
 Ecology Unit Test DO NOT WRITE ON TEST!!! Take a deep breath, take your time, and make sure you understand exactly what the question is asking you. For true/false, fill in the correct bubble ( A for true
Ecology Unit Test DO NOT WRITE ON TEST!!! Take a deep breath, take your time, and make sure you understand exactly what the question is asking you. For true/false, fill in the correct bubble ( A for true
Levels of Ecological Organization. 1. The chart below shows three ecological terms used to describe levels of organization on Earth.
 Name Levels of Ecological Organization Date 1. The chart below shows three ecological terms used to describe levels of organization on Earth. Which diagram best represents the relationship of these ecological
Name Levels of Ecological Organization Date 1. The chart below shows three ecological terms used to describe levels of organization on Earth. Which diagram best represents the relationship of these ecological
1. The diagram below represents many species of plants and animals and their surroundings.
 1. The diagram below represents many species of plants and animals and their surroundings. 4. Which statement most accurately predicts what would happen in the aquarium shown below if it were tightly covered
1. The diagram below represents many species of plants and animals and their surroundings. 4. Which statement most accurately predicts what would happen in the aquarium shown below if it were tightly covered
3.4 Cycles of Matter. Recycling in the Biosphere. Lesson Objectives. Lesson Summary
 3.4 Cycles of Matter Lesson Objectives Describe how matter cycles among the living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem. Describe how water cycles through the biosphere. Explain why nutrients are important
3.4 Cycles of Matter Lesson Objectives Describe how matter cycles among the living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem. Describe how water cycles through the biosphere. Explain why nutrients are important
Environmental Science Ecology
 Sub-Categy Ce Aug. - Sept. Introduction to Environmental Science E2.1A Explain why earth is a closed system in terms of matter. 1) Students will be able to describe how earth's unique conditions suppt
Sub-Categy Ce Aug. - Sept. Introduction to Environmental Science E2.1A Explain why earth is a closed system in terms of matter. 1) Students will be able to describe how earth's unique conditions suppt
Ecology: The Flow of Matter and Energy In An Ecosystem. - the scientific of between and their, focusing on transfer
 Ecology: The Flow of Matter and Energy In An Ecosystem PS 12: Matter cycles and energy flows through living and nonliving components in ecosystems. The transfer of matter and energy is important for maintaining
Ecology: The Flow of Matter and Energy In An Ecosystem PS 12: Matter cycles and energy flows through living and nonliving components in ecosystems. The transfer of matter and energy is important for maintaining
Food Chains, Food Webs, and Bioaccumulation Background
 Food Chains, Food Webs, and Bioaccumulation Background Introduction Every living organism needs energy to sustain life. Organisms within a community depend on one another for food to create energy. This
Food Chains, Food Webs, and Bioaccumulation Background Introduction Every living organism needs energy to sustain life. Organisms within a community depend on one another for food to create energy. This
The Carbon Cycle. Goal Use this page to review the carbon cycle. CHAPTER 2 BLM 1-19 DATE: NAME: CLASS:
 CHAPTER 2 BLM 1-19 The Carbon Cycle Goal Use this page to review the carbon cycle. CHAPTER 2 BLM 1-20 The Carbon Cycle Concept Map Goal Use this page to make a concept map about the carbon cycle. What
CHAPTER 2 BLM 1-19 The Carbon Cycle Goal Use this page to review the carbon cycle. CHAPTER 2 BLM 1-20 The Carbon Cycle Concept Map Goal Use this page to make a concept map about the carbon cycle. What
Cycles in the Biosphere MiniLab: Test for Nitrates Assessment. Essential Questions. Review Vocabulary. Reading Preview
 Cycles in the Biosphere MiniLab: Test for Nitrates Assessment 11 Reading Preview Essential Questions How do nutrients move through biotic and abiotic parts of an ecosystem? Why are nutrients important
Cycles in the Biosphere MiniLab: Test for Nitrates Assessment 11 Reading Preview Essential Questions How do nutrients move through biotic and abiotic parts of an ecosystem? Why are nutrients important
2018 ECOLOGY YEAR 2 (2018) PART ONE GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF ECOLOGY
 2018 ECOLOGY YEAR 2 (2018) PART ONE GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF ECOLOGY KAREN L. LANCOUR National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science DISCLAIMER - This presentation was prepared using draft rules. There may
2018 ECOLOGY YEAR 2 (2018) PART ONE GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF ECOLOGY KAREN L. LANCOUR National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science DISCLAIMER - This presentation was prepared using draft rules. There may
Vocabulary An organism is a living thing. E.g. a fish
 Organisms in their Environment Vocabulary An organism is a living thing. E.g. a fish Vocabulary A habitat is where an organism lives E.g. a pond Vocabulary A group of the same kind of organisms living
Organisms in their Environment Vocabulary An organism is a living thing. E.g. a fish Vocabulary A habitat is where an organism lives E.g. a pond Vocabulary A group of the same kind of organisms living
Ecology Part 2: How Ecosystems Work
 Ecology Part 2: How Ecosystems Work Name: Unit 2 1 In this second part of Unit 2, our big idea questions are: SECTION 1 How is energy transferred from the Sun to producers and then to consumers? Why do
Ecology Part 2: How Ecosystems Work Name: Unit 2 1 In this second part of Unit 2, our big idea questions are: SECTION 1 How is energy transferred from the Sun to producers and then to consumers? Why do
Earth as a System. Chapter 2. Table of Contents. Section 1 Earth: A Unique Planet. Section 2 Energy in the Earth System.
 Earth as a System Table of Contents Section 1 Earth: A Unique Planet Section 2 Energy in the Earth System Section 3 Ecology Section 1 Earth: A Unique Planet Objectives Describe the size and shape of Earth.
Earth as a System Table of Contents Section 1 Earth: A Unique Planet Section 2 Energy in the Earth System Section 3 Ecology Section 1 Earth: A Unique Planet Objectives Describe the size and shape of Earth.
SCIENCE 1206 UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION TO ECOLOGY
 SCIENCE 1206 UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION TO ECOLOGY ECOLOGY The study of the interrelationships between organisms, and between those organisms and their environment. What are some natural resources, both RENEWABLE
SCIENCE 1206 UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION TO ECOLOGY ECOLOGY The study of the interrelationships between organisms, and between those organisms and their environment. What are some natural resources, both RENEWABLE
1.2 The Earth System s Four Spheres
 EXIT CHAPTER. A New View of Earth.2 The Earth System s Four Spheres.3 Cycles and the Earth CHAPTER OUTLINE Earth system science model system closed system. A New View of Earth Technological advances and
EXIT CHAPTER. A New View of Earth.2 The Earth System s Four Spheres.3 Cycles and the Earth CHAPTER OUTLINE Earth system science model system closed system. A New View of Earth Technological advances and
SCIENCE 1206 UNIT 1 Sustainability of Ecosystems. NAME: Corner Brook Regional High
 SCIENCE 1206 UNIT 1 Sustainability of Ecosystems NAME: Corner Brook Regional High SCIENCE 1206 Unit 1 Handout 1 SUSTAINABILITY and PARADIGM SHIFTS ECOLOGY: What are some natural resources, both RENEWABLE
SCIENCE 1206 UNIT 1 Sustainability of Ecosystems NAME: Corner Brook Regional High SCIENCE 1206 Unit 1 Handout 1 SUSTAINABILITY and PARADIGM SHIFTS ECOLOGY: What are some natural resources, both RENEWABLE
Water cycles through ecosystems.
 Water cycles through ecosystems. Water is stored on Earth s surface in lakes, rivers, and oceans. Water is found underground, filling the spaces between soil particles and cracks in rocks. Large amounts
Water cycles through ecosystems. Water is stored on Earth s surface in lakes, rivers, and oceans. Water is found underground, filling the spaces between soil particles and cracks in rocks. Large amounts
Energy Flow Through Living Systems
 1 The diagram below shows the overall flow of energy through living things. At each step, the transfer of energy involves a loss of energy in the form of heat and body activities. For example, when you
1 The diagram below shows the overall flow of energy through living things. At each step, the transfer of energy involves a loss of energy in the form of heat and body activities. For example, when you
Keystone Biology Remediation B4: Ecology
 Keystone Biology Remediation B4: Ecology Assessment Anchors: to describe the levels of ecological organization (i.e. organism, population, community, ecosystem, biome, biosphere) (B.4.1.1) to describe
Keystone Biology Remediation B4: Ecology Assessment Anchors: to describe the levels of ecological organization (i.e. organism, population, community, ecosystem, biome, biosphere) (B.4.1.1) to describe
Slide 1 / All of Earth's water, land, and atmosphere within which life exists is known as a. Population Community Biome Biosphere
 Slide 1 / 40 1 ll of Earth's water, land, and atmosphere within which life exists is known as a Population ommunity iome iosphere Slide 2 / 40 2 ll the plants, animals, fungi living in a pond make up a
Slide 1 / 40 1 ll of Earth's water, land, and atmosphere within which life exists is known as a Population ommunity iome iosphere Slide 2 / 40 2 ll the plants, animals, fungi living in a pond make up a
Unit 6: Ecosystems Module 15: Ecological Principles
 Unit 6: Ecosystems Module 15: Ecological Principles NC Essential Standard: 2.1 Analyze the interdependence of living organisms within their environments Did you know The water you poop in today is the
Unit 6: Ecosystems Module 15: Ecological Principles NC Essential Standard: 2.1 Analyze the interdependence of living organisms within their environments Did you know The water you poop in today is the
Science Grade 7 Assessment Anchors and Eligible Content
 Science Grade 7 Assessment Anchors and Eligible Content Pennsylvania Department of Education www.education.state.pa.us 2010 S.7.A The Nature of Science S.7.A.1 Reasoning and Analysis S.7.A.1.1 Explain,
Science Grade 7 Assessment Anchors and Eligible Content Pennsylvania Department of Education www.education.state.pa.us 2010 S.7.A The Nature of Science S.7.A.1 Reasoning and Analysis S.7.A.1.1 Explain,
12. How could forest fire change populations in the ecosystem? Populations could be destroyed or have to relocate,
 Name: Ecology Review Sheet 15-16 Directions: This review should be completed by using your Interactive Notebook (IAN). This review is worth +5 points on your Ecology test, if it is completed and turned
Name: Ecology Review Sheet 15-16 Directions: This review should be completed by using your Interactive Notebook (IAN). This review is worth +5 points on your Ecology test, if it is completed and turned
Energy Pyramid. mouse plant. snake. eagle. Which population contains the most available energy?
 Skill Development/Guided Practice 1. mouse plant eagle snake Which population contains the most available energy? If a population of snakes consumes a population of mice that contain 3,000 kcal of available
Skill Development/Guided Practice 1. mouse plant eagle snake Which population contains the most available energy? If a population of snakes consumes a population of mice that contain 3,000 kcal of available
Sample file. Author: Tina Griep. Understanding Science Series Ecosystems and Biomes Part 1
 Author: Tina Griep Understanding Science Series Ecosystems and Biomes Part 1 Copyright 2009 New Learning Publishing All rights reserved. Except as permitted under the United States Copyright Act, no portion
Author: Tina Griep Understanding Science Series Ecosystems and Biomes Part 1 Copyright 2009 New Learning Publishing All rights reserved. Except as permitted under the United States Copyright Act, no portion
Lab: Modeling Ecosystems Virtual Lab B I O L O G Y : I n t e r a c t i o n s i n E c o s y s t e m s
 Name Date Period Lab: Modeling Ecosystems Virtual Lab B I O L O G Y : I n t e r a c t i o n s i n E c o s y s t e m s Directions 1. Open the Virtual Lab titled Model Ecosystems. http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/genbio/virtual_labs/bl_02/bl_02.html
Name Date Period Lab: Modeling Ecosystems Virtual Lab B I O L O G Y : I n t e r a c t i o n s i n E c o s y s t e m s Directions 1. Open the Virtual Lab titled Model Ecosystems. http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/genbio/virtual_labs/bl_02/bl_02.html
Chapter Two: Cycles of Matter (pages 32-65)
 Biology 20 Chapter 2.1_keyed Chapter Two: Cycles of Matter (pages 32-65) 2.1 The Role of Water in the Cycles of Matter (pages 34 40) Due to its ability to form hydrogen bonds, water has several unique
Biology 20 Chapter 2.1_keyed Chapter Two: Cycles of Matter (pages 32-65) 2.1 The Role of Water in the Cycles of Matter (pages 34 40) Due to its ability to form hydrogen bonds, water has several unique
Where have we been. Where are we going today? Lecture Outline. Geoengineering. What is a system?
 Where have we been 1. Course Introduction 2. What is the environment 3. Examined in some detail weather disasters for 2010 and 2011 4. Touched on Scale 5. Touched on borders. Examples a) Air pollution
Where have we been 1. Course Introduction 2. What is the environment 3. Examined in some detail weather disasters for 2010 and 2011 4. Touched on Scale 5. Touched on borders. Examples a) Air pollution
buried in the sediment; the carbon they contain sometimes change into fossil fuels; this process takes millions of years
 STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER 8 - ANSWERS 1) THE CARBON CYCLE - Describe the transformations related to the circulation of carbon. DEFINITION: the carbon cycle is a set of processes by which the essential element
STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER 8 - ANSWERS 1) THE CARBON CYCLE - Describe the transformations related to the circulation of carbon. DEFINITION: the carbon cycle is a set of processes by which the essential element
7.014 Lecture 20: Biogeochemical Cycles April 1, 2007
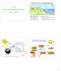 Global Nutrient Cycling - Biogeochemical Cycles 7.14 Lecture 2: Biogeochemical Cycles April 1, 27 Uptake Bioelements in Solution Weathering Precipitation Terrestrial Biomass Decomposition Volatile Elements
Global Nutrient Cycling - Biogeochemical Cycles 7.14 Lecture 2: Biogeochemical Cycles April 1, 27 Uptake Bioelements in Solution Weathering Precipitation Terrestrial Biomass Decomposition Volatile Elements
IB Environmental Systems & Societies
 IB Environmental Systems & Societies YEAR 1 Syllabus Content: Topics and Assessment Statements Mr. Rees Topic 7: Environmental Value Systems 7.1.1 State what it is meant by an environmental value system.
IB Environmental Systems & Societies YEAR 1 Syllabus Content: Topics and Assessment Statements Mr. Rees Topic 7: Environmental Value Systems 7.1.1 State what it is meant by an environmental value system.
GE Industry and the Environment Chapter I Introduction to Environment, Ecosystems, Environmental Components, Natural Cycles, and Development
 GE 302 - Industry and the Environment Chapter I Introduction to Environment, Ecosystems, Environmental Components, Natural Cycles, and Development GE 302 Second Semester 1433/1434 (2012/2013) - Chapter
GE 302 - Industry and the Environment Chapter I Introduction to Environment, Ecosystems, Environmental Components, Natural Cycles, and Development GE 302 Second Semester 1433/1434 (2012/2013) - Chapter
Chapter 22: Energy in the Ecosystem
 Chapter 22: Energy in the Ecosystem What is ecology? Global human issues Physical limits Ecosystems Organisms Populations Species Interactions Communities Energy flows and nutrients cycle C, H 2 0, P,
Chapter 22: Energy in the Ecosystem What is ecology? Global human issues Physical limits Ecosystems Organisms Populations Species Interactions Communities Energy flows and nutrients cycle C, H 2 0, P,
Interactions Within Ecosystems. Date: P. in ILL
 Interactions Within Ecosystems Date: P. in ILL Ecology the scientific study of interactions between different organisms their environment An ecologist would study organisms that live in an ecosystem. Ecosystems
Interactions Within Ecosystems Date: P. in ILL Ecology the scientific study of interactions between different organisms their environment An ecologist would study organisms that live in an ecosystem. Ecosystems
Chapter Two: Cycles of Matter (pages 32-65)
 Chapter Two: Cycles of Matter (pages 32-65) 2.2 Biogeochemical Cycles (pages 42 52) In order to survive and grow, organisms must obtain nutrients that serve as sources of energy or chemical building blocks,
Chapter Two: Cycles of Matter (pages 32-65) 2.2 Biogeochemical Cycles (pages 42 52) In order to survive and grow, organisms must obtain nutrients that serve as sources of energy or chemical building blocks,
Biogeochemical Cycles Webquest
 Name: Date: Biogeochemical Cycles Webquest In this webquest you will search for information that will answer questions about the water, carbon/oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorous cycles using the listed websites.
Name: Date: Biogeochemical Cycles Webquest In this webquest you will search for information that will answer questions about the water, carbon/oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorous cycles using the listed websites.
Ecosystem goods and services Ecosystem goods and services
 Course goals 1) Have you develop a firm understanding of the concepts and mechanisms of ecosystem ecology; 2) Have you enhance your understanding of how human society is altering ecosystems, some of the
Course goals 1) Have you develop a firm understanding of the concepts and mechanisms of ecosystem ecology; 2) Have you enhance your understanding of how human society is altering ecosystems, some of the
Biosphere & Biogeochemical Cycles
 Biosphere & Biogeochemical Cycles Biosphere Sphere of living organisms All the regions of the earth and its atmosphere in which living organisms are found or can live. Interacts with all the other spheres
Biosphere & Biogeochemical Cycles Biosphere Sphere of living organisms All the regions of the earth and its atmosphere in which living organisms are found or can live. Interacts with all the other spheres
Energy Flow UNIT 2: ENVIRONMENTAL BIOLOGY AND GENETICS
 Energy Flow UNIT 2: ENVIRONMENTAL BIOLOGY AND GENETICS Learning Objectives Components of an Ecosystem Give the meanings of the words; habitat, population, community and ecosystem What is Ecology / Environmental
Energy Flow UNIT 2: ENVIRONMENTAL BIOLOGY AND GENETICS Learning Objectives Components of an Ecosystem Give the meanings of the words; habitat, population, community and ecosystem What is Ecology / Environmental
Packet questions # Packet questions # Packet questions # Packet questions # Microscope worksheet 3.
 NAME PER ECOLOGY HW PACKET POINTS SCORES Packet questions #1-32 6 Packet questions #33-38 3 Packet questions #39-51 4 Packet questions #52-58 3 Microscope worksheet 3 Ecology Interactions Activity 6 Test
NAME PER ECOLOGY HW PACKET POINTS SCORES Packet questions #1-32 6 Packet questions #33-38 3 Packet questions #39-51 4 Packet questions #52-58 3 Microscope worksheet 3 Ecology Interactions Activity 6 Test
ECOLOGY 2/18/2017. Ecology. Levels of Organization. Factors Affecting Organisms. Ecology of Organisms
 ECOLOGY Ecology The study of the interactions between organisms and the living (biotic) and non living (abiotic) components of their environment field named in 1866 Levels of Organization 1. Biosphere:
ECOLOGY Ecology The study of the interactions between organisms and the living (biotic) and non living (abiotic) components of their environment field named in 1866 Levels of Organization 1. Biosphere:
3 3 Cycles of Matter. EOC Review
 EOC Review A freshwater plant is placed in a salt marsh. Predict the direction in which water will move across the plant s cell wall, and the effect of that movement on the plant. a. Water would move out
EOC Review A freshwater plant is placed in a salt marsh. Predict the direction in which water will move across the plant s cell wall, and the effect of that movement on the plant. a. Water would move out
Science & Engineering Practices Disciplinary Core Ideas Crosscutting Concepts
 HS-EVS1-1 RESOURCES AND RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Analyze and interpret data to identify the factors that affect sustainable development and natural resource management in Louisiana. Evidence of Louisiana s
HS-EVS1-1 RESOURCES AND RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Analyze and interpret data to identify the factors that affect sustainable development and natural resource management in Louisiana. Evidence of Louisiana s
Closed Systems A closed system is a system in which energy, but not matter is exchanged with the surroundings.
 2.2 Notes Objectives Compare an open system with a closed system. List the characteristics of Earth s four major spheres. Identify the two main sources of energy in the Earth system. Identify four processes
2.2 Notes Objectives Compare an open system with a closed system. List the characteristics of Earth s four major spheres. Identify the two main sources of energy in the Earth system. Identify four processes
Unit 11.1: The Science of Ecology
 Unit 11.1: The Science of Ecology These brilliant red feathers are actually animals called tube worms. They live in an extreme environment on the deep ocean floor, thousands of meters below the water s
Unit 11.1: The Science of Ecology These brilliant red feathers are actually animals called tube worms. They live in an extreme environment on the deep ocean floor, thousands of meters below the water s
Unsaved Test, Version: 1 1
 Name: Key Concepts Select the term that best completes the statement. A. abiotic B. light C. biotic D. organisms E. ecology F. soil G. ecosystem H. temperature I. factors J. water Date: 1. A(n) is made
Name: Key Concepts Select the term that best completes the statement. A. abiotic B. light C. biotic D. organisms E. ecology F. soil G. ecosystem H. temperature I. factors J. water Date: 1. A(n) is made
2) Biomass. Ecosystem. 6) Nutrients
 Part I Vocabulary #s 1-16 is a par5al review study all vocabulary words that are listed on PAGE 5!! 1) Carrying Capacity the largest number of individuals that an environment can support and maintain over
Part I Vocabulary #s 1-16 is a par5al review study all vocabulary words that are listed on PAGE 5!! 1) Carrying Capacity the largest number of individuals that an environment can support and maintain over
The Biosphere and Biogeochemical Cycles
 The Biosphere and Biogeochemical Cycles The Earth consists of 4 overlapping layers: Lithosphere Hydrosphere (and cryosphere) Atmosphere Biosphere The Biosphere The biosphere is the layer of life around
The Biosphere and Biogeochemical Cycles The Earth consists of 4 overlapping layers: Lithosphere Hydrosphere (and cryosphere) Atmosphere Biosphere The Biosphere The biosphere is the layer of life around
Modeling Food Webs in Darién, Panama
 Introduction This hands-on activity supports the WildCam Darién citizen science website. You will identify producers and consumers in the tropical forest ecosystem of Darién National Park in Panama. Using
Introduction This hands-on activity supports the WildCam Darién citizen science website. You will identify producers and consumers in the tropical forest ecosystem of Darién National Park in Panama. Using
Ecosystems: Nutrient Cycles
 Ecosystems: Nutrient Cycles Greeks, Native Peoples, Buddhism, Hinduism use(d) Earth, Air, Fire, and Water as the main elements of their faith/culture Cycling in Ecosystems the Hydrologic Cycle What are
Ecosystems: Nutrient Cycles Greeks, Native Peoples, Buddhism, Hinduism use(d) Earth, Air, Fire, and Water as the main elements of their faith/culture Cycling in Ecosystems the Hydrologic Cycle What are
BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES: The RECYCLING of MATERIALS through living organisms and the physical environment.
 BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES: The RECYCLING of MATERIALS through living organisms and the physical environment. BIOCHEMIST: Scientists who study how LIFE WORKS at a CHEMICAL level. The work of biochemists has
BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES: The RECYCLING of MATERIALS through living organisms and the physical environment. BIOCHEMIST: Scientists who study how LIFE WORKS at a CHEMICAL level. The work of biochemists has
The Earth s Ecosystems: Biomes, Energy Flow, and Change. I. Biomes and Ecosystems are divisions of the biosphere.
 The Earth s Ecosystems: Biomes, Energy Flow, and Change I. Biomes and Ecosystems are divisions of the biosphere. A. Biomes: Biomes are the largest divisions of the biosphere. in other words biomes have
The Earth s Ecosystems: Biomes, Energy Flow, and Change I. Biomes and Ecosystems are divisions of the biosphere. A. Biomes: Biomes are the largest divisions of the biosphere. in other words biomes have
Overview Interactions of Living Things
 Directed Reading for Content Mastery Overview Interactions of Living Things Directions: Complete the concept map using the terms in the list below. air biotic soil communities water organisms populations
Directed Reading for Content Mastery Overview Interactions of Living Things Directions: Complete the concept map using the terms in the list below. air biotic soil communities water organisms populations
Ontario Envirothon LEARNING OBJECTIVES. Ontario Envirothon Learning Objectives
 Ontario Envirothon LEARNING OBJECTIVES Updated Fall 2015 5 Contents Contents... 6 Overall Objectives... 7 Aquatic Ecology... 8 Specific Objectives... 8 Overall Objectives... 8 Application/Analysis... 9
Ontario Envirothon LEARNING OBJECTIVES Updated Fall 2015 5 Contents Contents... 6 Overall Objectives... 7 Aquatic Ecology... 8 Specific Objectives... 8 Overall Objectives... 8 Application/Analysis... 9
Roles of Organisms in Ecosystems. P Organisms that feed off dead organisms or the waste of other organisms are called scavengers.
 Roles of Organisms in Ecosystems P Organisms that feed off dead organisms or the waste of other organisms are called scavengers. Roles of Organisms in Ecosystems P Organisms that break down dead organisms
Roles of Organisms in Ecosystems P Organisms that feed off dead organisms or the waste of other organisms are called scavengers. Roles of Organisms in Ecosystems P Organisms that break down dead organisms
Creating Chains and Webs to Model Ecological Relationships
 Creating Chains and Webs to Model Ecological Relationships Overview This hands-on activity supports the HHMI short film The Guide and the 2014 Holiday Lectures on Science: Biodiversity in the Age of Humans.
Creating Chains and Webs to Model Ecological Relationships Overview This hands-on activity supports the HHMI short film The Guide and the 2014 Holiday Lectures on Science: Biodiversity in the Age of Humans.
Primary Consumer Energy Flow
 Unit 9 - Ecology CLASSROOM COPY Advanced Biology AP Environmental Science Laboratory Primary Consumer Energy Flow Objectives Observe the life cycle of the painted lady butterfly (Vanessa cardui). Construct
Unit 9 - Ecology CLASSROOM COPY Advanced Biology AP Environmental Science Laboratory Primary Consumer Energy Flow Objectives Observe the life cycle of the painted lady butterfly (Vanessa cardui). Construct
ECOSYSTEM. MODULE - 2 Ecological Concepts and Issues OBJECTIVES 5.1 ECOSYSTEM. Environmental Science Senior Secondary Course.
 5 ECOSYSTEM You know that earth is perhaps the only planet in the solar system that supports life. The portion of the earth which sustains life is called biosphere. Biosphere is very huge and can not be
5 ECOSYSTEM You know that earth is perhaps the only planet in the solar system that supports life. The portion of the earth which sustains life is called biosphere. Biosphere is very huge and can not be
Principles of Ecology Ecosystem: Ecosystem Processes-I (Part-1)
 Paper No. : 12 Module : 29 Ecosystem: Ecosystem Processes-I (Part-I) Development Team Principal Investigator: Co-Principal Investigator: Paper Coordinator: Content Writer: Content Reviewer: Prof. Neeta
Paper No. : 12 Module : 29 Ecosystem: Ecosystem Processes-I (Part-I) Development Team Principal Investigator: Co-Principal Investigator: Paper Coordinator: Content Writer: Content Reviewer: Prof. Neeta
NOTEBOOK. Table of Contents: 9. Properties of Water 9/20/ Water & Carbon Cycles 9/20/16
 NOTEBOOK Table of Contents: 9. Properties of Water 9/20/16 10. Water & Carbon Cycles 9/20/16 NOTEBOOK Assignment Page(s): Agenda: Tuesday, September 20, 2016 Properties of Water Water & Carbon Cycles 1.
NOTEBOOK Table of Contents: 9. Properties of Water 9/20/16 10. Water & Carbon Cycles 9/20/16 NOTEBOOK Assignment Page(s): Agenda: Tuesday, September 20, 2016 Properties of Water Water & Carbon Cycles 1.
SCIENCE 2200 UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION TO ECOLOGY
 SCIENCE 2200 UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION TO ECOLOGY ECOLOGY The study of the interrelationships between organisms, and between those organisms and their environment. What are some natural resources, both RENEWABLE
SCIENCE 2200 UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION TO ECOLOGY ECOLOGY The study of the interrelationships between organisms, and between those organisms and their environment. What are some natural resources, both RENEWABLE
Downloaded from
 Class X: Biology Chapter 15: Our environment Chapter Notes Key learning: 1) Our environment is composed of various biotic and abiotic factors which interact with each other. 2) Human activities have a
Class X: Biology Chapter 15: Our environment Chapter Notes Key learning: 1) Our environment is composed of various biotic and abiotic factors which interact with each other. 2) Human activities have a
Nutrients elements required for the development, maintenance, and reproduction of organisms.
 Nutrient Cycles Energy flows through ecosystems (one way trip). Unlike energy, however, nutrients (P, N, C, K, S ) cycle within ecosystems. Nutrients are important in controlling NPP in ecosystems. Bottom-up
Nutrient Cycles Energy flows through ecosystems (one way trip). Unlike energy, however, nutrients (P, N, C, K, S ) cycle within ecosystems. Nutrients are important in controlling NPP in ecosystems. Bottom-up
Integrative/systems Biology
 56 & 57 Topics Ecology as a Systems Biology Connection to Medicine Ecology definitions Population Ecology Community Ecology Ecosystem and Biosphere Ecology Ecology vs. Economic Sense Integrative/systems
56 & 57 Topics Ecology as a Systems Biology Connection to Medicine Ecology definitions Population Ecology Community Ecology Ecosystem and Biosphere Ecology Ecology vs. Economic Sense Integrative/systems
Chapter 3 The Biosphere
 Chapter 3 The Biosphere A tawny owl prepares to seize a mouse. The mouse is carrying a berry in its mouth as it runs along a fallen, moss-covered tree trunk. The owl, the mouse, the tree trunk, and the
Chapter 3 The Biosphere A tawny owl prepares to seize a mouse. The mouse is carrying a berry in its mouth as it runs along a fallen, moss-covered tree trunk. The owl, the mouse, the tree trunk, and the
