Chapter 1: Introduction
|
|
|
- Hugh Barton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 1: Introduction 1.1 Background and Context Bihar is one of the largest maize growing state and the crop was grown primarily as a subsistence crop to meet food needs for a long time till recently. But now like in nontraditional areas (Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh), it is also grown for commercial purposes (i.e., mainly to meet the raw material requirements of the animal feed sector). It is third largest maize producing state contributing around 10 percent to national production. Around 0.65 million hectare is presently under maize cultivation, which is about 7 per cent of Gross Cropped Area (GCA) in the state and over 13 lakh farmers are engaged in maize cultivation. During , the state produced about 1.4 million MT, which is about 5 per cent of the total crop production. Maize can be utilized in many different forms by converting it into a variety of products, through grinding, alkali processing, boiling, cooking and fermenting, such as corn starch, corn flakes and cereals, ethanol etc. It also has many industrial applications, which can make it a profitable crop in the state. Maize processing and utilization pattern shows that in India, around 60 per cent of the total produce is for animal feed, 28 per cent for human consumption and 12 per cent is used by the industry (starch, brewery etc). In Bihar only 8-10% of maize (5% directly by the processors and another 3-5% is being used by road side snack joints etc.) is processed within the state despite the fact that the state has huge and rising marketable surplus. While the area under cultivation, maize production & yield have increased during 1977 to 2007, there are only 8-10 maize processing units in Bihar. They are mainly into milling of flour and production poultry feed. In absence of adequate processing facility, the huge marketable surplus of Bihar, especially in rabi season depends completely on other states for its consumption. Any obstruction in this trading chain in future may lead into spoilage of that surplus, affecting the entire value chain. 26
2 Also due to inadequate processing facilities in the state, result more than 80% of Bihar maize goes outside the state and gets processed there depriving it of value addition and higher income for the people in the state. The processed maize in the form of poultry feed and seeds then comes back to the state. There is potential for processing of both high & low value added products in maize sector in the state itself. There are factors contributing to increase in the demand of processed maize. Some of them are (1) growing demand for eggs and chicken leading to increased demand for poultry feed in the state; (2) the state has 8 lakh hectare land under water which is suitable for fish farming; (3) increased demand for ethanol as a fuel additive; (4) growing urbanization leading to increased demand for processed food like corn flakes etc; (5) dairy sector is on growth path and this sector can provide a good market for cattle feed products. Thus there is growing demand for processed maize in the state and there is also adequate supply of good quality maize in the state. Yet the processing industry in Bihar is almost non-existent as there are only 10 processing units in the state engaged mainly in manufacturing of traditional food products (flour, besan, suji etc) and poultry feed. It is therefore important to study the reasons and factors restricting the growth of processing industry in the state. It is in this context the study was commissioned by World Bank to study the maize sector in Bihar with the following objectives 1.2 Objectives The broad objective of the study is to assess the investment climate for processing of maize (corn) into value added products in Bihar. 1. To assess and analyse the status of maize cultivation with respect to inputs, harvesting and post harvesting practices and infrastructure (including storage, warehousing etc) 2. To map major mandis and analyse price movements 3. To study the trade channels (marketing network) and value chain in maize cultivation 27
3 4. Study the status of maize processing in the state 5. To find potential of maize processing industry in the state, 6. To out line the regulatory/policy guidelines of the government, 7. To identify the constraints with farmers, traders and processors. 8. Suggest measures for improving investment climate for maize processing in the state Approach, Database and Methodology The assignment involved collection and scanning of secondary data available about the maize sector with a focus on status of maize processing industry in the state. It was felt that benchmarking the sector in Bihar with other states would enable us identify the constraints and draw best practice cases. Therefore information has also been collected from Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka. Primary data collection Data was collected from both primary and secondary sources. The Primary data was collected through a diagnostic survey of the farmers/growers, traders and maize processors in the state in order to study existing cultivation and post harvesting practices, storage systems, maize arrivals and price movements, marketing channels, value chains etc and identifying the factors constraining the growth of the sector at different levels of production and marketing. A structured questionnaire was developed for data collection and collate the critical information. The quantitative data was mainly collected by interviewing over 60 growers, 20 traders and all 10 processors operating in the state. The data on physical infrastructure in mandis, monthly prices and corresponding arrivals, name and share of the markets (local as well as outside state), etc has been collected directly from mandis. All major mandis trading in maize i.e Gulabagh, Katihar, Mansi etc have been covered by the survey for studying the trade channels and value chain mapping in maize cultivation. 28
4 The diagnostic survey itself was carried out in two phases: qualitative and quantitative surveys. The survey was carried out in the identified 4 districts of Bihar, namely Begusarai, Khagaria, Purnea and Bhagalpur. Secondary data was used as the basis for short-listing the target group for obtaining trade feedback and critical inputs from various stakeholders including government agencies. The short listing was done on the basis of following parametres: Current area, production, productivity of all districts for maize production Marketable surplus of maize in these districts Linkages of production hubs to different consumption sources. The ultimate objective of the survey was to come out with credible inputs and database for the formulation of recommendations to improve the competitiveness of the sector. Secondary Data Collection The secondary database sources included published books, Reports of multi-lateral bodies like World Bank, articles published in national and international journals, magazines, newspapers, Reports of the various Government departments, consultancy firms, research projects etc. It was used to study the status of maize production in world with a focus on India and Bihar. This included data related to production, productivity and area of the crop in India and Bihar, existence, role and relevance of concerned institutions, policy framework etc. The data have been sourced from various sources including government agencies including Department of Agriculture (DoA), and Rajendra Agricultural University (RAU), Department of Industry, CGIAR (Maize Regional Research Centre and Seed Production), Begusarai and Confederation of Indian Industry (CII), Patna. In addition to the above structured interviews, 4 Focussed Group Discussions (FGDs) were held among farmers, commission agents, traders, processors, industry associations, and research institutions to get the first hand information on the sector with a primary focus on maize trading and processing. 29
5 The data and information have also been collected through interactions and in-depth interviews with various stakeholders including Government departments like Department of Agriculture (DoA), Industrial Development Commissioner (IDC), Department of Fisheries, Research Institutions, bankers, trade and industry associations etc. Study Tools As stated, separate structured questionnaires were developed for farmers/growers, traders and processors in accordance with the objectives of the study. They were pre-tested and later administered in the field. Similarly, guides for FGDs and indepth interviews were developed and finalized to get optimum results. Field Operations and Data Management In all, 4 field investigators and 2 supervisors were deployed for conducting the field study. All of them have had prior experience in conducting such surveys. These field officials administered the quantitative questionnaire among the target group. The gaps and inconsistencies found in the filled - in questionnaires were rectified in the field itself. The information collected through field survey was tabulated and analysed. The issues that emerged during FGDs and discussion with various stakeholders, including state government officials, have also been captured in the Report. 30
6 Chapter 2 : Maize Production Global and National Scenario Maize (Zea mays) is the third most important crop after rice and wheat and is an important staple food in many countries of the world. It is also known as the Miracle Crop or Queen of Cereals due to its high productivity potential as compared to other crops of Graminacea family. Besides, being extensively used as human food and animal feed it is a source of a large number of diversified industrial products. Maize can be processed to utilize any or all components to manufacture large number of end products including corn starch, corn oil, baby corns, popcorns, alcoholic beverages, food sweeteners and more recently, fuel have added to its demand thereby increasingly making it a high value product. Figure 2.1: Components of Maize 10% 4% 4% 3% 79% Source: ICAR Annual Report Starch Protein Oil Fibre Minerals Maize is high yielding, easy to process, readily digested, and costs less than other cereals. It is also a versatile crop, allowing it to grow across a range of agroecological zones. Every part of the maize plant has economic value: the grain, leaves, stalk, tassel, 31
7 and cob can all be used to produce a large variety of food and nonfood products etc. Generally following three types of corn is grown Grain or field corn, Sweet corn used mainly as food Popcorn. Maize in India is an important cereal. Its area and production have steadily increased during the past two decades. Maize has varied usages from food preparation to poultry feed. In India, it is mainly used in poultry feed manufacturing Trend in Global Production, Consumption and Trade in Maize Status of Maize Production in the World The area under cultivation and as well as the production of maize have been increasing continuously over last decades. Though the acreage has increased consistently, production pattern has been erratic owing to the variations in the yield. There are many factors that have contributed towards changes in yield like weather during crop growth, pest and disease attack, technological advances and development of new hybrids and varieties etc. Figure 2.2: World Area, Production and Yield (In Kgs/Ha) of Maize (2005) 32
8 Production (in 000 tonnes) Area Harvested (in 000 hectares) Year Production Area harvested Yield per hectar Source: Estimated from data downloaded from According to USDA report, acreage under corn increased to million hectares in from million hectares during Accordingly the production figure has also increased to million tones from million tonnes. This increase has been mainly due to increased acreage coupled with favorable weather conditions and use of high yielding hybrids. Major rise in production contributed from Brazil due to congenial climatic conditions like adequate rain fall and low heat stress during the growth period 1. Table 2.1: Area, Production and Yield of Major Maize Producing Countries in 2005 Country Production (Quantity in 000 tonnes) Area Harvested (in 000 Ha) Yield per Hectare (kg/ha) United States of America China Brazil Argentina Mexico India France Indonesia South Africa Italy Karvy Comtrade Limited (2008) Seasonal Report on Maize 33
9 Romania Others (Average) World (Average) Source: Estimated from data downloaded from The US has the largest harvested area of corn and contributes one fifth of the world corn harvested area. China, Brazil, Mexico, India and Indonesia are the other countries, which contribute significantly to the world harvested area. These six countries have around 60% of the world corn harvested area. USA is the largest producer of maize in the world accounting for about 40% of the global production. Other major maize producers are China (20%), EU (14%), Brazil (5%) and India The global average productivity of maize is around 4000 Kgs / hectare. Italy recorded the highest yield of 9368 Kgs / ha followed by USA (9287 Kgs / ha), France (8371 Kgs / ha) and Argentina (7359 Kgs / ha). India at around 2000 Kgs /ha has the lowest yield among major maize growing countries in the world Global Consumption Scenario Globally, there has been continuous increase in the consumption demand of corn mainly owing to increase in the demand from meat and starch sector. There is growing requirement of maize from poultry sector, which use corn as feed. Consumption of corn for both the purpose feed purpose as well human consumption purpose is increasing. Major consuming of corn countries are USA and China with respective shares of 35% and 19%. Other important consuming countries are EU-27 (8%), and Brazil (5.5%). India s share in total global consumption is accounted to only around 2% International Trade in Maize The global export market for corn presently stands at about 95 million tones. United States with a share of 65% in total global exports is the largest exporter of corn in the world followed by Argentina and Brazil with individual respective shares of 15% and 2 ibid. 34
10 11%. Other exporting countries are Paraguay, South Africa (each contributing 2%) and India (1%) 3 though their shares remain low. As far as imports are concerned, Japan (17%), EU- 27 (11%) and Mexico (10%), Korea (9%) and Egypt (6%) are the major importing countries of corn in the world. respectively 4. Fig 2.3: Share in Global Exports ( ) Fig 2.4: Share in Global Imports ( ) Paraguay India 2% S. Africa Others Brazil 1% 2% 4% 11% Argentina 15% USA 65% Ot he rs 47% Egypt 6% J a pa n 17% Kore a 9% EU (27) 11% Me xic o 10% Source: Karvy Comtrade Limited (2008) Seasonal Report on Maize 2.2. Trend in Production, Consumption and Trade in Maize in India 2.1. Maize Seasonality in India It is a seasonal crop and can be harvested thrice in a year. In India, maize is grown in all the seasons i.e., kharif (Monsoon), rabi (winter) and summer but it is essentially a 3 ibid. 4 ibid. 35
11 warm weather (kharif) crop as nearly 90% of the production is from kharif season and is rain dependent. It is cultivated during winter (rabi) in Peninsular India and Bihar. About 7-8% of the production is during rabi season, and the rest is from spring season (summer maize) grown mainly in Northern India. It is usually grown as a pure crop but is also grown as inter-crop with different crop combinations like sugarcane, cotton, legumes, vegetables etc. Higher yields have been recorded in the rabi and spring crops. The higher yields are primarily due to long crop duration, better water management and lower incidence of disease and pests. In most parts of India, maize during kharif is sown with the break of monsoon, the actual dates varying from region to region. It is sown in early March in north-eastern hills, in April to early May in north-western hills, in May-June in Peninsular India, in the end of June to mid-july in the Indo-Gangetic Plains. The late sowing of maize may extend up to late August in certain irrigated tracts of Punjab. Spring maize is sown in late January to the end. Rabi maize is generally sown in Bihar, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and Karnataka in the end of October to mid-november. Both the spring and the rabi crops are raised, more or less, under irrigation. Fig 2.5: Seasonality Chart for Maize Arrivals in India Andhra Pradesh (K) Andhra Pradesh (R) Karnataka (K) Karnataka (R) Bihar (K) Bihar (R) Maharashtra (K) Madhya Pradesh (K) Uttar Pradesh (K) May June July Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Jan Feb March April Lean Peak Source: Discussions with traders 36
12 Area and Production Yield Maize can grow from sea level to 3000 metre altitudes under diverse conditions. Maize does however, require considerable moisture and warmth from germination to flowering. The ideal temperature for germination is 21 C and for growth 32 C cms of well-distributed rainfall is conducive to growth. It can be successfully grown where the night temperature does not go below 15.6 o C (60 o F). It cannot withstand frost at any stage of its growth. In India, its cultivation extends from the hot arid plains of Rajasthan and Gujarat to the wet hill of Assam and Bengal (receiving over 400 cm of rainfall) Maize in India Acreage, Production and Yield India is the fifth largest producer of maize in the world contributing 2% of the global production. Maize area, production and yield in India have seen a phenomenal growth over the last five decades. The total area under maize in India expanded from 3 mn ha in 1951 to 7.8 m ha in 2006, growing annually at an average rate of around 3%. In the early 1970s, expansion in area under maize cultivation slowed dramatically but after that for three decades the maize area remained virtually unchanged till The acreage started to increase after The yield has also increased over the years but continues to be very low as compared to other maize producing countries. Figure 2.6: Maize Area, Production and Yield in India Year Area (in 000 Hectares) Yield (Kg per Hectare) Production (in 000 Tonnes) Source: Estimated from data downloaded from
13 Rising yields, coupled with a steady expansion in area, led to growth in maize production of 5.9% and 5.2% per annum in the 1950s and 1960s, respectively. After slowing down in the 1970s as the area under cultivation stabilized, growth in maize production, fueled by continuing improvements in yield, averaged about 2.6% per annum in the 1980s and 3.2% per annum during 1990s. A significant shift occurred in the 1990s when irrigated winter (rabi) maize cultivation expanded rapidly, particularly in the states of Bihar, Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka. Total maize production exceeded 10 million tons in Production of corn in India has shown an increasing trend consistently except the year 2002 when production showed a little decline due to drought conditions in some of the states in India. Though kharif maize dominates the acreage and thus the production, productivity is highest for Rabi maize. The average yield of kharif maize is about 2 tonnes/hectare while that of rabi maize is more than 3 tonnes /hectare. The average yield for spring season is also around 3 tonnes per hectare. The higher yield during rabi and spring are primarily due to (a) relatively mild climatic conditions rabi and spring seasons during which the duration of the crop is longer resulting in sustained harvesting of solar energy leading to higher recovery of grain and biomass; (b) larger coverage of hybrid seeds having higher productivity. The states with favourable ecosystem specially Bihar (rabi) are witnessing expansion of winter maize area. Almost 90% of the total hybrid seed production of the country is confined to Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka in rabi season due to seasonal and productivity advantages 6. Fig 2.7: Season Wise Area Under Cultivation Fig 2.8: Season Wise Production R a b i S u m m e r (8%) (2%) R a b i (11%) S u m m e r (3%) ( Kh a r i f ) 90% Kha rif (86%) 6 ICAR (2007) Vision
14 Fig 2.9: Season Wise Productivity (Kgs per Hectare) Kharif Rabi Summer Source: ICAR (2007) Vision State Wise Production of Maize Maize, like any other cereal is grown across all the states in India and in many states it is one of the important staple foods. Indian maize production has traditionally been concentrated in the southern Corn Belt states of Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh, where it is grown during the kharif season. In recent years, introduction of cold-tolerant varieties has led to the emergence of an irrigated rabi maize crop in the northern states of Bihar and Uttar Pradesh. Table 2.2: State-Wise Maize Area, Production and Yield during State Area (in 000 Hectares) % of Total Area Production (in ooo tonnes) % of Total Production Yield (Kgs per Hectare) Andhra Pradesh Karnataka Bihar Madhya Pradesh Rajasthan Uttar Pradesh Maharashtra Gujarat Himachal Pradesh Jammu & Kashmir Punjab Jharkhand Tamil Nadu West Bengal Others All India Source: Estimated from data downloaded from 39
15 Among the major producing states, Andhra Pradesh tops the list with the contribution of over 20% to the total Indian maize production. Other producers are Karnataka (18.6%), Bihar (9.2%), Madhya Pradesh (8.5%), Rajasthan (7.5%), Uttar Pradesh (7%), and Maharashtra (6.8%). The maize growing states can be divided into two groups 1. High Productivity States: Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Bihar (Rabi) Maharashtra, Punjab and West Bengal account for about 30 percent of the national maize acreage and their productivity levels range from 2 4 tonnes per hectare. 2. Low Productivity States : Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar (Kharif) which together cover about 50 percent of the area have yields ranging 1 2 tonnes / hectare (i.e. < 2 tonnes/hectare) which is lower than the national average Utilisation / Consumption Pattern of Maize in India Diversified uses of maize have prompted higher production in India. Presently, maize is mainly used for preparation of poultry feed and extraction of starch in the country. In India both white and yellow both types of maize are grown. While white maize in grown mostly for human food purpose, yellow maize is consumed primarily in the manufacturing of poultry and animal feed. The maize consumption pattern in given in the following graph. Direct human consumption of maize has declined over time, while feed and industrial uses have increased. A recent study by NCAP has shown that the per capita human maize consumption which stands at around 3 kg per annum (average rural 3.89 kg per annum; and urban average 0.61 kg per annum) is declining at 2% per annum due to greater availability of maize and rice at subsidized rates through Public Distribution System (PDS). Rising household incomes have also shifted consumption from maize to other cereals like rice and wheat. This has also led to an increased consumption of meat, particularly of poultry, which has in turn increased the demand for maize as feed. Increased industrial demand for maize comes primarily from the 40
16 starch and milling industry which in turn caters to textiles, paper, glue, alcohol, confectionery, food processing, pharmaceutical industry etc 7. The utilization pattern indicated that about 28% of the maize produced in India is consumed directly as food, 59% goes for poultry, fishery, piggery and livestock feed, about 12% to milling and brewery industry (like starch, oil, and dry milling) and the balance 1% for the seed. The utilization pattern of maize varies from state to state an according to the size of the farm. Fig 2.10: Mize Consumption Pattern in India Starch 11% Brewery 1% Seed 1% Food 28% Poultry Feed 48% Animal Feed 11% Source: ICAR (2007) Vision 2025 Dry, shelled cobs are used as fuel. Green leaves and stems, from thinning the maize crop, are used as animal fodder. Maize grain is often fed to dairy cattle, whose milk yield is reported to increase by 20-25% if fed maize grain. Maize gives higher conversion of dry substance to milk, meat, and eggs as compared to other cereals. Maize grain is either fed directly to animals or is dried, milled, and mixed with other ingredients. Other Industries (mainly starch, dextrose, corn syrup, corn oil, ethanol, etc) also uses maize as their raw-material/input 8. 7 Multi Commodity Exchange of India Ltd (2007) Maize Futures: Feasibility Study and ICAR Vision 2025 Document
17 Import & Export (In Lakh MT India s International trade in Maize The production in 2007 was estimated at around 138 lakh tonnes. India was exporting maize to the world and the exports also increased during It declined in 2003 due to fall in production. Exports increased again in subsequent years of 2004 and 2005 but declined again in This time the decline was due to imposition of certain restrictions on maize exports from India. Imports of maize into India has significantly declined since 2000 and according to CMIE, India imported 1.6 million MT of maize valued at Rs 30.7 million in However, imports have been witnessing a rising trend in since 2003 onwards. Graph 2.11: India s Exports and Imports of Maize During Year Imports Export Source: CMIE database Maize is an important crop in India. Besides being used for human consumption, it is a key ingredient of poultry and livestock feeds. The poultry industry in India is rapidly increasing. The country s requirement for poultry feed is increasing at over 10 % per annum. Its demand for industrial uses is expected to increase. The maize sector has lot of potential for growth. 42
18 Chapter 3: Policy and Institutional Framework for Maize Sector in Bihar This chapter will map the institutional framework and the policies/programmes relating to maize sector in Bihar. The presence and role of major institutions and associations that are associated directly or indirectly with maize have been discussed Institutions in Maize Sector in Bihar Following institutions are working in Bihar on maize sector. 1. Bihar Veterinary College, Patna - This College helps the farmers & the industries, related to poultry & dairy sector. It also does technology transfer (Lab to Land program) through its respective Krishi Vigyan Kendra s (KVKs). Poultry in Bihar is not a great success story due to socio-economic constrains, but dairy is a success. 2. College of Agricultural Engineering, Samastipur, Rajendra Agricultural University, Pusa, Samastipur - This institute is primarily responsible for the irrigation aspects of maize in Bihar. Good work is being done on spring maize. The exponential increment in the quality & quantity of spring maize yields in the last half a decade is the proof of it. 3. College of Fisheries, Dholi & College of Fisheries, Tirhut, College of Agriculture (TCA) campus, Muzaffarpur Pusa Road, Doli, Muzaffarpur Though traditionally a fish eating state, these two colleges has not been exploited by the fishermen & government to make fisheries an industry. This is evident from the fact quoted by Deputy Director Fisheries, Department of Fisheries, GoB, who had an interview with World Bank & IL&FS-CDI that presently 25% of the water bodies are being utilized with a capture fishing process not the culture fishing process. The state imports 20% of its requirement from West Bengal & Andhra Pradesh. At present, the total fish requirement in Bihar is 2 lakh tons per year with an average yield of 3-5 t per ha per year. There are no fish feed unit in Bihar. According to a recent research 43
19 carried out in the Institute, fish feed should contain about 45% of maize for better fish production per year. Presently the fishermen are using cow-dung & organic manures to grow phytons for the fish while they use mustard cake with rice bran cake, mixed in molasses to directly feed the fish. This feed is works out to be cheaper than maize as in the fish producing districts of Bihar, maize is not adequately produced/available. These flood prone fish producing districts mostly grow paddy in kharif followed by mustard in Rabi. GoB is planning to double its fish volume by 2013, by bringing in additional ha under fish culture to make it a total of ha of area under fish culture. The output will also be increased from 3 tons to 5 tons fish per ha per year. To make this happen by 2013, about 2.58 lakh tons of fish feed is required which would have over one lakh tons of maize in it. These two colleges are now consulting Central Institute of Fresh Water Aquaculture (CIFWA), Bhubneshwar to make fish feed units in Bihar. A proposal is with GoB submitted by the department that 25% subsidy with a cap of Rs.12 lakh will be given to fisheries graduate for setting up a new fish feed unit. To make these feed units viable Rs.20000/- per acre of pond will be given to energize it. This one acre can hold 1 lakh fingerlings which can be paise per fingerlings. Feeding the fish from these feed units can produce 1kg of Katla (local freshwater fish Rs.50 per kg, in a year from the fingerlings. The proposal looks to be viable but requires initiatives from fishermen & fisheries graduate. 4. Rajendra Agricultural University, Faculty Of Agriculture, P O Pusa, Samastipur - Established on 3 rd December 1974, it has a mandate for overall development of the maize sector. This institute has done good work in the initial stages till 1979 for white corn. Presently it has a full-fledged maize research team with the Maize Coordinator as head. It produces small quantity of seed for Bihar Beej Nigam, but the volumes are decreasing as the seed sector is dominated by the private players. The university is helping GoB in drafting the Bihar Road Map for Agriculture with the following highlights on maize: 44
20 DoA will soon bring out a MAIZE MISSION for Bihar. The highlights of it will be as follows 1) Growing maize in flood prone areas. 2) Setting up 12 godowns in all the maize growing districts 3) Setting up of rural godowns in 216 blocks of each 250 MT. 4) Target production by 2012 to be 3 million MT per annum from 1 million hectare with yield of 3t/ha Seed production will be private companies' domain Immediate investment in farm mechanization and rural warehousing. Warehousing will cost Rs.2.5 million for 1000 MT. With the joint effort of this university and Directorate of Maize Research (DMR), Begusarai some good Quality Protein Maize (QPM) has been released. GoB is promoting QPM as mid-day meal in all government schools. To make this happen, the university is helping the processors like Katyani Makka Udayog, to set up a unit in Khagaria. The World Bank & IL&FS-CDI, has visited this processing unit at Chautham in Khagaria district. This unit is temporarily closed due to financial issues. One of the best cases of technology transfer by the university can be observed as given below: 45
21 Source: 5. Sanjay Gandhi Institute of Dairy Science and Tech., Pusa, Samastipur & Sanjay Gandhi Institute of Dairy Technology, Patna, Rajendra Agricultural University, P O Dhelwan, Lohiyanagar, Patna These two institutes have done a commendable job creating an oldest (25 years old) single most success story of Bihar, i.e., Bihar State. Cooperative Milk Producers Federations Limited (COMPFED). As per interview conducted by World Bank and IL&FS-CDI with the General Manager, Operations, COMPFED, will be doubling its capacity to 200t/day of cattle feed in the next four years with 16% growth per annum. COMPFED procures 60-70% of its maize requirement from Bihar. COMPFED prepares the following animal feeds with different maize compositions: 46
22 Type of Animal feed Maize content Adult cattle feed 08-12% Milking cow feed 15% Poultry feed 50-60% Pig feed 25-30% Source: COMPFED, Patna The irony here is that cattle & cow feed is picking up but not poultry & piggery. COMPFED has more than 99% business in cattle & cow feed. It does some poultry & pig feed production for the government like military farms, Central dairy farms etc. The two institutes have done some good research work on maize as cattle feed. In collaboration with National Dairy Research Institute (NDRI), Karnal. 6. Directorate of Maize Research (DMR) Regional Research and Seed Production Centre, Kushmahout, Bishnupuri, Begusarai - Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR) ( Begusarai, was established on 4 th May, 1997 exclusively for maize as a Regional Research & Seed Production Centre, has no mandate for industrial research. This institute is one of the best resources for all the private seed companies. Exchange of parent seed & endorsement of hybrids, do happen unofficially, boosting the private seed companies to produce the best performing hybrids for Bihar Rabi. 7. Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVK) All the 16 KVKs in Bihar are governed by different organizations like Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), State Agriculture University (SAU), Non-Government Organizations (NGO) and state Govt., Central/State Public undertaking, Educational Institutions including Central Universities. KVK at Begusarai is the only one which has the main mandate for maize. Remaining KVKs indirectly help the maize farmers & processors like distribution of mid-day meals in primary schools, health awareness among the fishermen cooperatives, increasing the milk production & for a particular down trodden community, to increase the piggery sector. 47
23 Table 3.1: Details of KVKs Operating in Bihar S.N. Name & Address of KVK Host Organization Est. Year & governed by 1. Training Organizer, Krishi Vigyan Kendra, P.O. Sankarpur, Munger (Bihar) Vice- Chancellor, Rajendra Agriculture University, Samastipur (Bihar) 1979 S 2. Training Organizer, Krishi Vigyan Kendra, Darbhanga (Bihar) 3. Training Organizer, Krishi Vigyan Kendra, Hajipur Farm, Vaisali (Bihar) 4. Training Organizer, Krishi Vigyan Kendra, P.O. Meghaul, Khodawanpur, Begusarai (Bihar) 5. Training Organizer, Krishi Vigyan Kendra, Agwanpur, Saharsa (Bihar) 6. Training Organizer, Krishi Vigyan Kendra, P.O. Harnaut, Nalanda (Bihar) 7. Training Organizer, Krishi Vigyan Kendra, P.O. Vijay nagar, Banka (Bihar) 8. Chief Training Organizer, Krishi Vigyan Kendra, Barh, Patna (Bihar) 9. Training Organizer, Krishi Vigyan Kendra, Sekhupura (Bihar) 10. Training Organizer, Krishi Vigyan Kendra, Saraiah Farm, Muzaffarpur (Bihar) -do S -do S -do S -do S -do S -do S -do S -do S -do S 11. Training Organizer, Krishi Vigyan Kendra, SCADA P.O. Arra, Bhojpur (Bihar) Chairman, Sone Command Area Deve.Agency, Sone Bhavan, Patna (Bihar) 1993 O 12. Training Organizer, Krishi Vigyan Kendra, Jahanabad (Bihar) -do O 48
24 13. Training Organizer, Krishi Vigyan Kendra, P.O. Sokhodeora, Nawada (Bihar) 14. Training Organizer, Krishi Vigyan Kendra, Vanavasi Seva Kendra, P.O. Adhaura, Bhabua Training Organizer, Krishi Vigyan Kendra, Sharma Bharti Khadigram, Khadigram, P.O.Jamui General Secretary, Gram Nirman Mandal Ashram, Sokhodera, Nawada (Bihar) President, Banavasi Seva Kendra, Adhaura, Bhabhua (Bihar) Chairman, Khadi Gramydog Sangh, Khadigram, Jamui N 1992 N 1994 N 16. Training Organizer, Krishi Vigyan Kendra, VPO Basaith,Chandpura, Madhubani (Bihar) Chairman, S.K.Choudhary Edn. Trust, New Delhi 1994 N Notes: I ICAR; S SAUs; N NGOs; O -Others, includes state Govt., Central/State Public undertaking, Educational Institutions including Central Universities Source: Policy Incentives for Maize Sector in Bihar On the policy front, DoA is providing lot of policy support for the development of maize sector in the state. The Institutional Reforms ( ) are Establishment of Soil Testing Laboratories in every district (16 new laboratories added during ). All the maize producing districts have now a laboratory. Establishment of State Pesticide Testing Laboratory at Patna for Sanitary and Phyto Sanitary certification Mechanization: 25% additional subsidy from State plan for DoA has allowed Leading commodity bourse NCDEX to launch the country's first spot exchange in Bihar in September-end 2007 with trading in maize contracts. The NCDEX-promoted spot exchange, initially trading in maize -- a major crop in Bihar. Since agriculture is a state subject, an electronic spot exchange cannot be launched at the national level. For any spot exchange to get a presence in all states, it has to ask permission from 49
25 each state separately. The sellers would be from Bihar but buyers could be from anywhere in the country. Traders functioning in futures market can also buy from the spot market. (Source: Fifth Column in KOILAKH NEWS on August 27, :39:00 PM & DoA) On seed, DoA is still following the National Seeds Policy, The present government under the initiative for development of agriculture in state of Bihar has formulated a Bihar Seed Plan, mainly comprising of 1. Revival of Bihar State Seed Corporation 2. Revival of State Seed Farms 3. Establishment of Seed Testing Laboratory at district, subdivision, and block levels subsequently. 4. To promote the use of hybrid maize seeds during kharif up to 50 percent. 5. Development of very short duration seed banks in flood prone areas. Bihar Government has started working on Bihar Seed Plan, but substantial progress is yet to be made in this direction. In addition to above, DoA is also planning for Implementation of Vaidyanathan Committee Report on Cooperative Credit. Krishak Salahkar (Agri-consultants) as para extension service providers to farmers in all Panchayats Department of Industries has not yet taken any concrete steps exclusively for development of maize processing sector in Bihar. The policy remains the same which is in general for all the industries. 9 Source: www. indian seed act 2002_files 50
26 Chapter 4: Status of Maize Production in Bihar Bihar is the 8 th populous state in India and depends primarily on agriculture. It produces a variety of crops like maize, sugarcane, potato, jute and many other vegetables and fruits due to its soil fertility and climatic conditions. The geographical location and climatic condition of eastern part of Bihar namely Purnea, Katihar, Samsatipur, Saharasa districts are favourable for cultivation of maize. Maize is thus an important crop in Bihar which is third largest producer of maize in the country after Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka and accounts for about 10% of national maize output. Cultivation of maize provides livelihood to about 1.3 million farmers in Bihar, majority of whom are marginal and small farmers. According to the figures of , Bihar produced 1.7 million tonnes of maize valued at Rs billion (at MSP of Rs. 620/qntl). Table 4.1: Number of Farmers Involved in Maize Cultivation in in Bihar Season Bihar maize area (lakh ha) Number of farmers attached Kharif Rabi Summer Production, Acreage and Yield of Maize in Bihar Bihar is a traditional maize growing state and the crop was grown primarily as a subsistence crop to meet food needs for a long time till recently. But now like in nontraditional areas (Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh), it is also grown for commercial purposes (i.e., mainly to meet the feed requirements of the animal feed sector). It is third largest maize producing state contributing around 10 percent to national production. Around 0.65 million hectare is presently under maize cultivation, which is about 7 per cent of Gross Cropped Area (GCA) in the state and over 13 lakh farmers engaged in maize cultivation. 51
27 Figure 4.1: Maize in Bihar Acreage, Production and Yield Area (in 000 Hectares) Yield (Kg per Hectare) Production (in 000 MT) Source: Department of Agriculture, Government of Bihar During , the state produced about 1.4 million MT, which is about 5 per cent of the total crop production. Though yield in Bihar is higher than the national average, it has come down between and indicating a decline in the productivity levels in maize cultivation in Bihar. The total production of maize for the last seven years in Bihar is presented in Appendix table. Table 4.2: Cropwise Cultivation of Maize in Bihar Year Crop (Estimates) Area Prodn. Yield Area Prodn. Yield Area Prodn. Yield Autumn Maize Rabi Maize Summer (Spring) Maize Total Area in Million Hectares; Production in Million Tonnes ; Yield in Kgs/Hectare Source: Department of Agriculture, Government of Bihar 52
28 Fig 4.2: Agricultural Map of Bihar 4.2. Status of Maize Cultivation in Bihar Size of Farm Land Holdings Maize is mainly grown by small and marginal farmers in Bihar. The fragmentation of land holdings is much more pronounced in Bihar than other states as the average per capita operational holding in the state was 0.75 hectares in much below the national average and nearly one quarter of the size of Punjab. About one-third of the operational holdings are marginal (less than one hectare) in which the average size is merely 0.34 hectare. This explains the largely unorganised nature of maize cultivation in the state where about 91% of the cropped area is dissected into 53
29 plots less than 2 hectares each. It also leads to the inference that due to the small land size the farmers find it unviable to invest in better harvesting technologies, seeds etc., thereby leading to a comparatively lower yield per hectare. The low yield limits their incomes and this again in turn leads to poor investment capacities. This vicious cycle of limited capacity to invest and thus the ensuing low returns has largely hampered the growth of the sector in the state. The category wise farmers and their operated area are indicated in the following table. Table 4.3: Size Class-wise Number and Area of Operational Holdings in Bihar ( ) Total Holdings Size Class (In Hectare) Number ('000) Percentage Area ('000 Hectares) Percentage Average Area per Holding (Hectares) Below Marginal Small Semi- Medium Medium and Above Large All Sizes Source: Directorate of Statistics and Evaluation, Govt. of Bihar. Although the state has a very low amount of land per capita, in some parts of the state there are still significant numbers of landholders having large amount of land leased in their possession, in violation of the ceiling law. Most of such landholders are absentees and consequently the state reports one of the largest land area under tenancy in the country, although a significant amount of land leased out is also by small and petty landholders engaged in a variety of occupations outside the village. According to the NSS survey in the proportion of cultivated land under tenancy was about 10 54
30 percent. Thus farmers have limited interest and capacity to invest in farm land fertility etc. Maize is grown throughout the year in Bihar all three seasonal crops of maize are cultivated; however, main crop is Rabi maize. Winter (Rabi) maize is the USP of the state that dominates total maize production in the state with a 40 percent share. Monsoon (Kharif) maize and Summer maize each contributes about 23 percent to the total maize area. Maize is grown in almost all the districts of Bihar. The leading district is Khagaria, which accounts for about 12 per cent of maize production in the state. Other important maize producing districts include Begusarai, Madhepura, Saharsa, Purnea, Katihar, Muzaffarpur, Vaishali, and Samstipur. As maize is grown in most of the districts of the state, there is not much movement of the grains within the state. Entire stretch form Begusarai to Khagaria on the north side of national highway, having highly fertile land of Gangetic plains provides very favourable soil for maize cultivation. The acreage, production and yield of major maize (Rabi, Kharif and Summer) growing districts in Bihar during is indicated in the following table Table 4.4: Area and Production of Summer Maize (Gamma) in Major Districts in Bihar During S. No Name of Districts Area (ha.) % Share Prod. (M.T.) % Share 1 Purnea Katihar Madhepura Saharsa Sapaul Araria Bhagalpur Khagaria Vaishali Muzaffarpur Samastipur Others Total Source: Directorate of Statistics and Evaluation, Government of Bihar Around one-fourth of land under maize cultivation in Bihar is for summer maize which contributes about 28% of total maize produced in the state. The yield is also very high. 55
31 It is mainly grown in the districts pf Purnea, Katihar, Madhepura, Saharsa, and Supaul. These together account for 45% of acreage and 50% of production of summer maize in the state. Table 4.5: Area and Production of Kharif in Major Districts in Bihar During Sl. No. Name of Districts Area (ha.) % Share Prod. (M.T.) % Share 1 Begusarai Purnea Bhagalpur Saran Vaishali Araria Katihar Samastipur Khagaria Siwan Patna Others Total Source: Directorate of Statistics and Evaluation, Government of Bihar Kharif is mailnly grown in the districts of Begusarai, Purnea. Bhagalpur, Saran and Vaishali. These five districts together account for about 45% of acreage and production of kharif maize in the state. Table 4.6: Area and Production of Rabi Maize in Major Districts in Bihar During Sl. No. Name of Districts Area (ha.) % Share Prod. (M.T.) % Share 1 Khagaria Samastipur Begusarai Katihar Madhepura Saharsa Bhagalpur Purnia Muzaffarpur Darbhanga Vaishali Others Total Source: Directorate of Statistics and Evaluation, Government of Bihar 56
32 As far as Rabi maize is concerned Khagaria alone accounts for about one-fourth of total production in the state. Samastipur, Begusarai and Katihar are other important districts for maize production. These 4 districts together contribute 44% to acreage and 56% of total rabi maize produced in the state Cropping Pattern There are two distinct maize cropping patterns in Bihar. In the flood prone areas of Khagaria, Saharsa (Kosi) and parts of Samastipur maize is being cultivated during rabi. In these districts sowing starts in October (after flood water recedes) and continues up to early January. The majority of the sowing is done during December. Maize harvest starts towards the end of February and continues till the end of June. Majority of the crop is harvested during the months of May and June. In these parts of Bihar maize is the major and in some cases the only crop. In Begusarai and Samastipur, maize is cultivated during both seasons Rabi and Khariff. The sowing, during the khariff season, starts during the month of June and continues up to July. The harvesting starts around the month of September and last up to October. The sowing and harvesting during rabi follow the similar pattern as observed in other places. The seasonality chart is given below: Khariff Rabi Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Since most of the maize cultivation is concentrated in the districts of Khagaria, Saharsa, Katihar and Purnea where it is grown only in Rabi, it can be concluded that the proportion of Rabi maize (including both winter and spring) in the total maize production of Bihar can be up to 80%. This was also corroborated during discussions with farmer groups. 57
33 Figure 4.2 : Major Maize Growing Districts in Bihar Note: In kharif maize is scattered through-out Bihar as it is a rainfed crop. Map for kharif is not being captured by the satellite as the cropping density is below 100ha, hence no data is available. Source: CGIAR Practices in Maize cultivation in Bihar Following maize cultivation practices were observed in Bihar. Land Preparation The first step in maize cultivation is ploughing. Farmers use tractors to deep plough the land. Normally ploughing is done thrice to break down the soil. During ploughing, 50 Kg of DAP, 50 Kg of Urea and 25 Kg of Potash is used alongwith some organic manure. At field level, there is very limited use of bio-techniques to protect the fertility of land for future crops. Chemical fertilizer is used to enhance the productivity, but in long-run, it affects the fertility of land. Sowing Farmers on an average use around 11 Kg of seeds per acre, which is about 20% higher than the average seed requirement. The seed requirement is 58
Potato Short Note. 31 Jan Introduction. Seasonality
 31 Jan 2008 Potato Short Note Introduction Potato is the world's fourth important food crop after wheat, rice and maize because of its higher yield potential along with high nutritive value. With an annual
31 Jan 2008 Potato Short Note Introduction Potato is the world's fourth important food crop after wheat, rice and maize because of its higher yield potential along with high nutritive value. With an annual
Castor. Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Jan Feb Mar
 Castor Castor (Ricinus communis L.) is a non edible oilseed, belonging to the Euphorbiaceae family. India is the world leader in castor production and dominates the international castor oil trade. The
Castor Castor (Ricinus communis L.) is a non edible oilseed, belonging to the Euphorbiaceae family. India is the world leader in castor production and dominates the international castor oil trade. The
At a Glance. Area under wheat cultivation is on higher side compared to last year.
 At a Glance Area under wheat cultivation is on higher side compared to last year. During October 1 st to December 15 th, area covered under wheat cultivation was 232.59 lakh hectares, up by 10.4% from
At a Glance Area under wheat cultivation is on higher side compared to last year. During October 1 st to December 15 th, area covered under wheat cultivation was 232.59 lakh hectares, up by 10.4% from
Maize Average Monthly Price Trend
 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: All maize cash markets traded firm during the month of September on the expectation of lower kharif crop production amid higher demand from south Indian feed makers as compared to last
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: All maize cash markets traded firm during the month of September on the expectation of lower kharif crop production amid higher demand from south Indian feed makers as compared to last
India. India Grain Voluntary Update - October 2017
 THIS REPORT CONTAINS ASSESSMENTS OF COMMODITY AND TRADE ISSUES MADE BY USDA STAFF AND NOT NECESSARILY STATEMENTS OF OFFICIAL U.S. GOVERNMENT POLICY Voluntary - Public Date: 10/3/2017 GAIN Report Number:
THIS REPORT CONTAINS ASSESSMENTS OF COMMODITY AND TRADE ISSUES MADE BY USDA STAFF AND NOT NECESSARILY STATEMENTS OF OFFICIAL U.S. GOVERNMENT POLICY Voluntary - Public Date: 10/3/2017 GAIN Report Number:
10 March Barley: A Parabolic Move
 Barley: A Parabolic Move 1 Barley is an annual cereal crop consumed as a major food and feed. Basically a grass crop, it belongs to the family of Poaceae, and is considered to be the fourth most-important
Barley: A Parabolic Move 1 Barley is an annual cereal crop consumed as a major food and feed. Basically a grass crop, it belongs to the family of Poaceae, and is considered to be the fourth most-important
Progress and Potential of Horticulture in India
 Ind. Jn. of Agri.Econ. Vol.63, No.3, July-Sept. 2008 SUBJECT I TRIGGERING AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT THROUGH HORTICULTURE CROPS Progress and Potential of Horticulture in India Ramesh Chand, S.S. Raju and
Ind. Jn. of Agri.Econ. Vol.63, No.3, July-Sept. 2008 SUBJECT I TRIGGERING AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT THROUGH HORTICULTURE CROPS Progress and Potential of Horticulture in India Ramesh Chand, S.S. Raju and
CHAPTER I 1.1 Introduction
 CHAPTER I 1.1 Introduction Pulses in India have long been considered as the poor man s source of protein. Pulses are grown in 22-23 million hectares of area with an annual production of 13-15 million tones
CHAPTER I 1.1 Introduction Pulses in India have long been considered as the poor man s source of protein. Pulses are grown in 22-23 million hectares of area with an annual production of 13-15 million tones
Achieving self sufficiency in pulse production in India
 Achieving self sufficiency in pulse production in India Towards self sufficiency in pulse production On average, over the last three years Indian s consumed approximately 22 million tonnes of pulses per
Achieving self sufficiency in pulse production in India Towards self sufficiency in pulse production On average, over the last three years Indian s consumed approximately 22 million tonnes of pulses per
Enhanced utilization of Sorghum Exploring Domestic and International markets
 Enhanced utilization of Sorghum Exploring Domestic and International markets Sorghum Sorghum is one of the most important cereal crops of India, cultivated in about 8 million hectares annually. Sorghum
Enhanced utilization of Sorghum Exploring Domestic and International markets Sorghum Sorghum is one of the most important cereal crops of India, cultivated in about 8 million hectares annually. Sorghum
Content. Monsoon Report and Sowing Update. Highlights. Southwest Monsoon: A flashback of Southwest Monsoon A slow beginning
 Content Highlights Southwest Monsoon: A flashback of 2011 Southwest Monsoon 2012- A slow beginning Hike in MSP of Kharif crops Sowing Progress of Kharif crops - Cereals - Pulses - Oilseeds - Cotton - Sugarcane
Content Highlights Southwest Monsoon: A flashback of 2011 Southwest Monsoon 2012- A slow beginning Hike in MSP of Kharif crops Sowing Progress of Kharif crops - Cereals - Pulses - Oilseeds - Cotton - Sugarcane
MUSTARD SEED REPORT NCDEX STRATEGY RANGE TARGET STOP LOSS. June 2011 Buy / July 2011 Buy /
 27 May 2011 MUSTARD SEED REPORT Recommendations: NCDEX STRATEGY RANGE TARGET STOP LOSS June 2011 Buy 2770-2820 3100/3250 2580 July 2011 Buy 2870-2900 3150/3200 2750 Aug 2011 Buy 2900-2930 3200/3250 2700
27 May 2011 MUSTARD SEED REPORT Recommendations: NCDEX STRATEGY RANGE TARGET STOP LOSS June 2011 Buy 2770-2820 3100/3250 2580 July 2011 Buy 2870-2900 3150/3200 2750 Aug 2011 Buy 2900-2930 3200/3250 2700
Growth and Inclusion: Theoretical and Applied Perspectives
 THE WORLD BANK WORKSHOP Growth and Inclusion: Theoretical and Applied Perspectives Session I Food Inflation: Drivers and Policy Implications Subir Gokarn Reserve Bank of India January 12, 212 The Claridges
THE WORLD BANK WORKSHOP Growth and Inclusion: Theoretical and Applied Perspectives Session I Food Inflation: Drivers and Policy Implications Subir Gokarn Reserve Bank of India January 12, 212 The Claridges
Vietnam. Grain and Feed Update. October 2012
 THIS REPORT CONTAINS ASSESSMENTS OF COMMODITY AND TRADE ISSUES MADE BY USDA STAFF AND NOT NECESSARILY STATEMENTS OF OFFICIAL U.S. GOVERNMENT POLICY Required Report - public distribution Vietnam Grain and
THIS REPORT CONTAINS ASSESSMENTS OF COMMODITY AND TRADE ISSUES MADE BY USDA STAFF AND NOT NECESSARILY STATEMENTS OF OFFICIAL U.S. GOVERNMENT POLICY Required Report - public distribution Vietnam Grain and
PULSES SPECIAL BULLETIN 10 th June, 2013 STOCK POSITION OF CHANA AT NCDEX ACCREDITED WAREHOUSES AS ON 10 JUNE 2013
 PULSES SPECIAL BULLETIN 10 th June, 2013 Pulses Market Summary Pulses traded mix in the spot, however with the monsoon rains covering major geographical area of the country supplies have been limited and
PULSES SPECIAL BULLETIN 10 th June, 2013 Pulses Market Summary Pulses traded mix in the spot, however with the monsoon rains covering major geographical area of the country supplies have been limited and
GROUNDNUT PRICES LIKELY TO BE AROUND Rs. 4800/q AT HARVEST
 GROUNDNUT PRICES LIKELY TO BE AROUND Rs. 4800/q AT HARVEST India is the second largest producer of groundnut in the world. On the global front, China leads in production, making up some 42 per cent of
GROUNDNUT PRICES LIKELY TO BE AROUND Rs. 4800/q AT HARVEST India is the second largest producer of groundnut in the world. On the global front, China leads in production, making up some 42 per cent of
AGRICULTURE SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS]
![AGRICULTURE SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS] AGRICULTURE SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS]](/thumbs/79/79737240.jpg) AGRICULTURE SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS] 1. Distinguish between primitive subsistence farming and intensive subsistence farming. The following are the differences between primitive subsistence
AGRICULTURE SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS] 1. Distinguish between primitive subsistence farming and intensive subsistence farming. The following are the differences between primitive subsistence
2012 Farm Outlook. Highlights
 2012 Farm Outlook Office of the Chief Economist USDA Highlights A promising spring planting was followed by historic drought. Record high commodity prices followed. Farm incomes are expected to be near
2012 Farm Outlook Office of the Chief Economist USDA Highlights A promising spring planting was followed by historic drought. Record high commodity prices followed. Farm incomes are expected to be near
IMPORTANCE OF AGRICULTURE FOR GROWTH OF INDIAN ECONOMY
 IMPORTANCE OF AGRICULTURE FOR GROWTH OF INDIAN ECONOMY Dr. Fulwinder Pal Singh Associate Professor of Economics, Cum Principal SBJS Khalsa College,Satlani Sahib,Amritsar ABSTRACT Agriculture is the backbone
IMPORTANCE OF AGRICULTURE FOR GROWTH OF INDIAN ECONOMY Dr. Fulwinder Pal Singh Associate Professor of Economics, Cum Principal SBJS Khalsa College,Satlani Sahib,Amritsar ABSTRACT Agriculture is the backbone
Maize Monthly Research Report
 Maize Monthly Research Report Contents Outlook and Review Recommendations International Corn Market Summary AW Maize Index India Maize Balance Sheet State Wise Market Dynamics Domestic Price Outlook On
Maize Monthly Research Report Contents Outlook and Review Recommendations International Corn Market Summary AW Maize Index India Maize Balance Sheet State Wise Market Dynamics Domestic Price Outlook On
Importance, area, production and productivity of major cereals, pulses, oilseeds, sugar crops, medicinal and aromatics and forage crops
 LECTURE 1 Importance, area, production and productivity of major cereals, pulses, oilseeds, sugar crops, medicinal and aromatics and forage crops Importance of cereals Grains are generally classified as
LECTURE 1 Importance, area, production and productivity of major cereals, pulses, oilseeds, sugar crops, medicinal and aromatics and forage crops Importance of cereals Grains are generally classified as
SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE DEVELOPMENT IN INDIA: A CASE STUDY OF UTTAR PRADESH ABSTRACT
 SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE DEVELOPMENT IN INDIA: A CASE STUDY OF UTTAR PRADESH ABSTRACT Agriculture is a critical sector of the Indian economy. It forms the backbone of development in the country. An average
SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE DEVELOPMENT IN INDIA: A CASE STUDY OF UTTAR PRADESH ABSTRACT Agriculture is a critical sector of the Indian economy. It forms the backbone of development in the country. An average
1 What are three cropping seasons of India? Explain any one in brief. 2 Discuss three main impacts of globalization on Indian agriculture.
 1 What are three cropping seasons of India? Explain any one in brief. 2 Discuss three main impacts of globalization on Indian agriculture. 3.Distinguish between rabi and kharif season? 4. What is Horticulture?
1 What are three cropping seasons of India? Explain any one in brief. 2 Discuss three main impacts of globalization on Indian agriculture. 3.Distinguish between rabi and kharif season? 4. What is Horticulture?
Basmati rice, guargum drive India s April-June agri exports. Buffalo meat shipments stay flat
 01.08.2017 Basmati rice, guargum drive India s April-June agri exports Buffalo meat shipments stay flat India s agri exports for the April-June quarter rose by almost a tenth in dollar terms and 7 per
01.08.2017 Basmati rice, guargum drive India s April-June agri exports Buffalo meat shipments stay flat India s agri exports for the April-June quarter rose by almost a tenth in dollar terms and 7 per
SITE PRIORITIZATION FOR IBFI
 SITE PRIORITIZATION FOR IBFI Rajesh K Pandey, Giriraj Amarnath, Niranga Alahacoon, Karthikeyan Matheswaran IWMI, Colombo Inception Workshop on Index Based Flood Insurance (IBFI) for Agriculture Risk Management
SITE PRIORITIZATION FOR IBFI Rajesh K Pandey, Giriraj Amarnath, Niranga Alahacoon, Karthikeyan Matheswaran IWMI, Colombo Inception Workshop on Index Based Flood Insurance (IBFI) for Agriculture Risk Management
SELL GROUNDNUT ON HARVEST
 SELL GROUNDNUT ON HARVEST Grown under rainfed conditions, groundnut is a major oilseed crop and it plays a vital role in bringing vegetable oil deficit in the country. India is the second largest producer
SELL GROUNDNUT ON HARVEST Grown under rainfed conditions, groundnut is a major oilseed crop and it plays a vital role in bringing vegetable oil deficit in the country. India is the second largest producer
Chapter 4 Agriculture
 Chapter 4 Agriculture Types of Farming Primitive Subsistence Farming Practiced on small patches of land. Involves family/community labour. Uses primitive tools such as hoe, digging sticks etc. Predominance
Chapter 4 Agriculture Types of Farming Primitive Subsistence Farming Practiced on small patches of land. Involves family/community labour. Uses primitive tools such as hoe, digging sticks etc. Predominance
Government of India Ministry of Agriculture & Famers Welfare (Deptt. of Agri., Coopn. & Farmers Welfare) Directorate of Pulses Development Bhopal
 Government of India Ministry of Agriculture & Famers Welfare (Deptt. of Agri., Coopn. & Farmers Welfare) Directorate of Pulses Development Bhopal ***** SUB: ALL INDIA PULSES: CURRENT KHARIF PRODUCTION
Government of India Ministry of Agriculture & Famers Welfare (Deptt. of Agri., Coopn. & Farmers Welfare) Directorate of Pulses Development Bhopal ***** SUB: ALL INDIA PULSES: CURRENT KHARIF PRODUCTION
Rice Production and Nutrient Management in India
 I n d i a Rice Production and Nutrient Management in India By K.N. Tiwari The demand for rice in India is projected at 28 million tonnes (M t) for the year 202 and will require a production level of 3,000
I n d i a Rice Production and Nutrient Management in India By K.N. Tiwari The demand for rice in India is projected at 28 million tonnes (M t) for the year 202 and will require a production level of 3,000
DISTRIBUTION OF CROPS AND THEIR REQUIREMENT
 DISTRIBUTION OF CROPS AND THEIR REQUIREMENT Cropping Seasons in India Agriculture in India also follows three distinct cropping seasons i.e. rabi, kharif and zaid. Rabi crops are sown from October to December
DISTRIBUTION OF CROPS AND THEIR REQUIREMENT Cropping Seasons in India Agriculture in India also follows three distinct cropping seasons i.e. rabi, kharif and zaid. Rabi crops are sown from October to December
14 Indian Res. J. Ext. Edu. 11 ( 3 ), September, Issues Related to Low Productivity of Maize in Haryana
 14 Indian Res. J. Ext. Edu. 11 ( 3 ), September, 2011 Issues Related to Low Productivity of Maize in Haryana V.K. Yadav 1, P. Supriya², Shailesh Kumar 3 and C.Y. Manikanhaiya 4 1. Sr. Scientist (Agril.
14 Indian Res. J. Ext. Edu. 11 ( 3 ), September, 2011 Issues Related to Low Productivity of Maize in Haryana V.K. Yadav 1, P. Supriya², Shailesh Kumar 3 and C.Y. Manikanhaiya 4 1. Sr. Scientist (Agril.
Castor Weekly Research Report
 Castor Weekly Research Report Contents Outlook and Review Castor Seed price Chart Export NCDEX Spot Price Outlook Future Chart Progressive Sowing Weekly Spot Price change International Market Update Castor
Castor Weekly Research Report Contents Outlook and Review Castor Seed price Chart Export NCDEX Spot Price Outlook Future Chart Progressive Sowing Weekly Spot Price change International Market Update Castor
RISING FOOD PRICE AND ITS CONSEQUENCES
 RISING FOOD PRICE AND ITS CONSEQUENCES Hem Raj Regmi (Msc) 19 ABSTRACT Agricultural prices have risen worldwide sharply in the last two years, which has been a dilemma especially to policy makers. Higher
RISING FOOD PRICE AND ITS CONSEQUENCES Hem Raj Regmi (Msc) 19 ABSTRACT Agricultural prices have risen worldwide sharply in the last two years, which has been a dilemma especially to policy makers. Higher
Government of India s Perspective and Initiatives on Integration of Future Smart Food in Rice-Fallows
 Government of India s Perspective and Initiatives on Integration of Future Smart Food in Rice-Fallows Dr. B. Rajender, Joint Secretary (Crops & Oilseeds) Department of Agriculture, Cooperation & Farmers
Government of India s Perspective and Initiatives on Integration of Future Smart Food in Rice-Fallows Dr. B. Rajender, Joint Secretary (Crops & Oilseeds) Department of Agriculture, Cooperation & Farmers
Seed Market.
 Indian Seed The seed industry has witnessed a substantial change in the past century, with farmers relying on purchasing seeds from market with better traits rather than relying on seeds from previous
Indian Seed The seed industry has witnessed a substantial change in the past century, with farmers relying on purchasing seeds from market with better traits rather than relying on seeds from previous
COTTON unfazed by synthetics
 By: Dr P. CHENNAKRISHNAN COTTON unfazed by synthetics Cotton exports from India are on a steady rise year after year. In fact, recently, the Indian government had to ban cotton exports to ensure steady
By: Dr P. CHENNAKRISHNAN COTTON unfazed by synthetics Cotton exports from India are on a steady rise year after year. In fact, recently, the Indian government had to ban cotton exports to ensure steady
Trends and regional disparity of maize production in India
 Vol. 8(9), pp. 193-199, September, 2016 DOI: 10.5897/JDAE2015-0702 Article Number: 5F08EB260362 ISSN 2006-9774 Copyright 2016 Author(s) retain the copyright of this article http://www.academicjournals.org/jdae
Vol. 8(9), pp. 193-199, September, 2016 DOI: 10.5897/JDAE2015-0702 Article Number: 5F08EB260362 ISSN 2006-9774 Copyright 2016 Author(s) retain the copyright of this article http://www.academicjournals.org/jdae
Indian Pulses Market.
 Indian Pulses Market Indian Pulses Market India is the largest producer, importer and consumer of pulses, accounting for 25% of global production from 35% of global area under pulses. However, the productivity
Indian Pulses Market Indian Pulses Market India is the largest producer, importer and consumer of pulses, accounting for 25% of global production from 35% of global area under pulses. However, the productivity
Progress and Performance of Kisan Credit Card Scheme with a Case Study of Bihar
 Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 25(No.1) January-June 2012 pp 125-135 Progress and Performance of Kisan Credit Card Scheme with a Case Study of Bihar Diwas Raj Bista*, Pramod Kumar and V.C.
Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 25(No.1) January-June 2012 pp 125-135 Progress and Performance of Kisan Credit Card Scheme with a Case Study of Bihar Diwas Raj Bista*, Pramod Kumar and V.C.
S E A S O N A L COMMODITY INSIGHT
 S E A S O N A L COMMODITY INSIGHT 17 th December 2014 Chana (Chickpea) India produces a quarter of the world s pulses, accounting for one third of the total acreage under pulses. Indians consume 30 per
S E A S O N A L COMMODITY INSIGHT 17 th December 2014 Chana (Chickpea) India produces a quarter of the world s pulses, accounting for one third of the total acreage under pulses. Indians consume 30 per
UPL Group of Companies
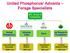 UPL Group of Companies United Phosphorus Advanta India Tatva Jai Research Foundation Crop Protection Chemicals Seeds & Biotech Environment Services Contract Research (CRO) ` 12000 crore ` 1000 crore `
UPL Group of Companies United Phosphorus Advanta India Tatva Jai Research Foundation Crop Protection Chemicals Seeds & Biotech Environment Services Contract Research (CRO) ` 12000 crore ` 1000 crore `
WHEAT SEASONAL REPORT
 1 st March 2011 WHEAT SEASONAL REPORT Investment strategies: Positions (NCDEX) Contracts TP SL Risk Reward Roll over Sell at 1270-1290 March 1180/1150 1368-8800 10000 15 th March Sell at1220-1240 April
1 st March 2011 WHEAT SEASONAL REPORT Investment strategies: Positions (NCDEX) Contracts TP SL Risk Reward Roll over Sell at 1270-1290 March 1180/1150 1368-8800 10000 15 th March Sell at1220-1240 April
CONSTRAINT ANALYSIS IN MARKETING OF POTATOES IN TELANGANA STATE OF INDIA
 International Journal of Agricultural Science and Research (IJASR) ISSN(P): 2250-0057; ISSN(E): 2321-0087 Vol. 7, Issue 5 Oct 2017, 77-82 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. CONSTRAINT ANALYSIS IN MARKETING OF POTATOES IN
International Journal of Agricultural Science and Research (IJASR) ISSN(P): 2250-0057; ISSN(E): 2321-0087 Vol. 7, Issue 5 Oct 2017, 77-82 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. CONSTRAINT ANALYSIS IN MARKETING OF POTATOES IN
Turmeric Seasonal Report
 Turmeric Seasonal Report 23 March 2009 Market review The year 2009 has proved to be a year for turmeric as prices rallied from the very first day of the year and has never looked back since. Turmeric futures
Turmeric Seasonal Report 23 March 2009 Market review The year 2009 has proved to be a year for turmeric as prices rallied from the very first day of the year and has never looked back since. Turmeric futures
6. LAND RESOURCES : AGRICULTURE
 6. LAND RESOURCES : AGRICULTURE 38 MT EDUCARE LTD. Q.1 (A) Choose the correct alternative from the brackets and rewrite the statements : 1. India ranks... in the world regarding area under cultivation.
6. LAND RESOURCES : AGRICULTURE 38 MT EDUCARE LTD. Q.1 (A) Choose the correct alternative from the brackets and rewrite the statements : 1. India ranks... in the world regarding area under cultivation.
Climate variability and Rubber production in Kerala
 231 Chapter 9 Climate variability and Rubber production in Kerala 9.1 TREND IN AREA, PRODUCTION AND PRODUCTIVITY Area under rubber was just 62.6 thousand ha in 1952-53. It has increased by 727 per cent
231 Chapter 9 Climate variability and Rubber production in Kerala 9.1 TREND IN AREA, PRODUCTION AND PRODUCTIVITY Area under rubber was just 62.6 thousand ha in 1952-53. It has increased by 727 per cent
INDIAN RICE LANDSCAPE: Trade, Production & Government Intervention in Marketing Shweta Saini and Ashok Gulati
 INDIAN RICE LANDSCAPE: Trade, Production & Government Intervention in Marketing Shweta Saini and Ashok Gulati paper presented at Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan Focus of the Presentation Evolution of
INDIAN RICE LANDSCAPE: Trade, Production & Government Intervention in Marketing Shweta Saini and Ashok Gulati paper presented at Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan Focus of the Presentation Evolution of
Guidelines for Implementation of fisheries Scheme under the National Mission for Protein Supplements (NMPS) in States during
 Annexure-III Guidelines for Implementation of fisheries Scheme under the National Mission for Protein Supplements (NMPS) in States during 2012-13 The Department of Animal Husbandry, Dairying & Fisheries,
Annexure-III Guidelines for Implementation of fisheries Scheme under the National Mission for Protein Supplements (NMPS) in States during 2012-13 The Department of Animal Husbandry, Dairying & Fisheries,
S E A S O N A L COMMODITY INSIGHT
 S E A S O N A L COMMODITY INSIGHT 12 th January 2015 Wheat Domestic Scenario India is the second largest producer of wheat in the world after China, contributing to about 13.66 per cent of the world s
S E A S O N A L COMMODITY INSIGHT 12 th January 2015 Wheat Domestic Scenario India is the second largest producer of wheat in the world after China, contributing to about 13.66 per cent of the world s
DEMAND FOR FRUITS AND VEGETABLES IN INDIA
 Agric. Econ. Res. Rev., Vol. 8(2), pp. 7-17 (1995) DEMAND FOR FRUITS AND VEGETABLES IN INDIA Praduman Kumar and Mruthyunjaya Division of Agricultural Economics, IARI, New Delhi India is a vast country,
Agric. Econ. Res. Rev., Vol. 8(2), pp. 7-17 (1995) DEMAND FOR FRUITS AND VEGETABLES IN INDIA Praduman Kumar and Mruthyunjaya Division of Agricultural Economics, IARI, New Delhi India is a vast country,
Maize Production Viability-A Study of Economics, Constants and Policy Implications for Eastern Uttar Pradesh, India
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 06 (2018) s` Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.706.326
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 06 (2018) s` Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.706.326
INTERNATIONAL FOOD POLICY RESEARCH INSTITUTE. Page 1
 Page 1 Food and Energy Security for Development in India Ashok Gulati & Kavery Ganguly Presentation at Third IBSA Summit Academic Forum IBSA Partnership for Shared Prosperity and Inclusive Globalization
Page 1 Food and Energy Security for Development in India Ashok Gulati & Kavery Ganguly Presentation at Third IBSA Summit Academic Forum IBSA Partnership for Shared Prosperity and Inclusive Globalization
USDA WASDE Report. Friday April 9 th 2010 World AG Supply & Demand Estimates. Office Friday April 09, 2010
 Friday April 9 th 2010 World AG Supply & Demand Estimates The trade was expecting the new carry out to incorporate additional stocks resulting from the March 31 grain stocks report which was not reflected
Friday April 9 th 2010 World AG Supply & Demand Estimates The trade was expecting the new carry out to incorporate additional stocks resulting from the March 31 grain stocks report which was not reflected
PROGRAMMES AND SCHEMES Monsoon and Crop Sowing Situation during Kharif-2012
 PROGRAMMES AND SCHEMES Monsoon and Crop Sowing Situation during Kharif-2012 As per India Meteorological Department (IMD) data SW Monsoon rainfall for the country as a whole during June- September, 2012
PROGRAMMES AND SCHEMES Monsoon and Crop Sowing Situation during Kharif-2012 As per India Meteorological Department (IMD) data SW Monsoon rainfall for the country as a whole during June- September, 2012
For the year Period Outlook Target (Delhi spot) Medium Term (July-Aug) Bullish Current spot market (Delhi) price: 2300
 17 April 2009 Chana Seasonal Report update For the year 2009 Period Outlook Target (Delhi spot) Medium Term (July-Aug) Bullish 2600-2650 Current spot market (Delhi) price: 2300 Prepared by: Research Desk
17 April 2009 Chana Seasonal Report update For the year 2009 Period Outlook Target (Delhi spot) Medium Term (July-Aug) Bullish 2600-2650 Current spot market (Delhi) price: 2300 Prepared by: Research Desk
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX TOPIC/CHAPTER: 1: The Story Of Palampur THE GREEN REVOLUTION IN PUNJAB
 INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX TOPIC/CHAPTER: : The Story Of Palampur WORKSHEET: No SUMMARY OF THE LESSON:- Farming is the main production activity in the villages
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX TOPIC/CHAPTER: : The Story Of Palampur WORKSHEET: No SUMMARY OF THE LESSON:- Farming is the main production activity in the villages
Zero Tillage Technique with High Yielding Variety for Wheat Cultivation as Compared to Traditional Method of Farmers: Evidences of FLD
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 08 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.708.255
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 7 Number 08 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2018.708.255
The Sugarcane: An Agriculture Aspect
 Chapter 2 The Sugarcane: An Agriculture Aspect 2.1 Introduction Sugarcane growing countries of the world are lying between the latitude 36.70 0 north and 31.00 0 south of the equator extending from tropical
Chapter 2 The Sugarcane: An Agriculture Aspect 2.1 Introduction Sugarcane growing countries of the world are lying between the latitude 36.70 0 north and 31.00 0 south of the equator extending from tropical
Welcome! Rallis India Limited
 Welcome! Rallis India Limited Q3-12 Performance V Shankar 23 rd January 2012 Rallis Consolidated 3 rd Quarter Crs Q3 2010-11 Q3-12 Net Sales 268.1 317.9 PBT 48.0 12.4 Add Depreciation 4.4 7.2 Add Interest
Welcome! Rallis India Limited Q3-12 Performance V Shankar 23 rd January 2012 Rallis Consolidated 3 rd Quarter Crs Q3 2010-11 Q3-12 Net Sales 268.1 317.9 PBT 48.0 12.4 Add Depreciation 4.4 7.2 Add Interest
Policy Matters: Prospects from National Consortium on SRI. Round Table at Council for Social Development Jan 13 th 2011
 Policy Matters: Prospects from National Consortium on SRI Round Table at Council for Social Development Jan 13 th 2011 Policy Pivots for SRI Food Security Irrigation Reforms Sustainabil ity in Rice Eco
Policy Matters: Prospects from National Consortium on SRI Round Table at Council for Social Development Jan 13 th 2011 Policy Pivots for SRI Food Security Irrigation Reforms Sustainabil ity in Rice Eco
PROMOTION OF DRY LAND MANGO CULTIVATION FOR INCOME SECURITY
 PROMOTION OF DRY LAND MANGO CULTIVATION FOR INCOME SECURITY A CASE STUDY K.H.PATIL KRISHI VIGYAN KENDAR HULKOTI-582205 GADAG DISTRICT KARNATAKA STATE Impact/Case study series: No.8 Promotion of dry land
PROMOTION OF DRY LAND MANGO CULTIVATION FOR INCOME SECURITY A CASE STUDY K.H.PATIL KRISHI VIGYAN KENDAR HULKOTI-582205 GADAG DISTRICT KARNATAKA STATE Impact/Case study series: No.8 Promotion of dry land
INDIAN STATE-LEVEL SORGHUM PRODUCTIVITY MEASURES
 INDIAN STATE-LEVEL SORGHUM PRODUCTIVITY MEASURES BY DAYAKAR BENHUR AND SALEEM SHAIK CORRESPONDING AUTHOR: SALEEM SHAIK 310 Lloyd-Ricks, West Wing Dept of Agricultural Economics MSU, Mississippi State,
INDIAN STATE-LEVEL SORGHUM PRODUCTIVITY MEASURES BY DAYAKAR BENHUR AND SALEEM SHAIK CORRESPONDING AUTHOR: SALEEM SHAIK 310 Lloyd-Ricks, West Wing Dept of Agricultural Economics MSU, Mississippi State,
Dynamics and Performance of Livestock and Poultry Sector in India: A Temporal Analysis
 Volume 3, Issue 1 June 2014 1 RESEARCH ARTICLE ISSN: 2278-5213 Dynamics and Performance of Livestock and Poultry Sector in India: A Temporal Analysis M. Borah* and R.A. Halim Dept. of Agricultural Economics
Volume 3, Issue 1 June 2014 1 RESEARCH ARTICLE ISSN: 2278-5213 Dynamics and Performance of Livestock and Poultry Sector in India: A Temporal Analysis M. Borah* and R.A. Halim Dept. of Agricultural Economics
KNOWLEDGE OF IMPROVED RICE PRODUCTION TECHNOLOGY BY THE FARMERS IN DUNGARPUR DISTRICT OF RAJASTHAN
 Raj. J. Extn. Edu. 20 : 97-101, 2012 KNOWLEDGE OF IMPROVED RICE PRODUCTION TECHNOLOGY BY THE FARMERS IN DUNGARPUR DISTRICT OF RAJASTHAN Ram Lal Khatik*, B. Bhimawat** and B. Upadhyay*** ABSTRACT India
Raj. J. Extn. Edu. 20 : 97-101, 2012 KNOWLEDGE OF IMPROVED RICE PRODUCTION TECHNOLOGY BY THE FARMERS IN DUNGARPUR DISTRICT OF RAJASTHAN Ram Lal Khatik*, B. Bhimawat** and B. Upadhyay*** ABSTRACT India
22: List of Studies Conducted by Agro-Economic Research Centres
 22: List of Studies Conducted by Agro-Economic Research Centres 2006-07 1 India s Global Tea Trade Reducing Share, Declining Competitiveness. 2 Developing India s Strategic Responses to the Global Debate
22: List of Studies Conducted by Agro-Economic Research Centres 2006-07 1 India s Global Tea Trade Reducing Share, Declining Competitiveness. 2 Developing India s Strategic Responses to the Global Debate
Macro Level Priorities for Livestock Research and Development for Bihar
 Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 28 (No.2) July-December 2015 pp 271-283 DOI: 10.5958/0974-0279.2016.00006.9 Macro Level Priorities for Livestock Research and Development for Bihar Awadhesh
Agricultural Economics Research Review Vol. 28 (No.2) July-December 2015 pp 271-283 DOI: 10.5958/0974-0279.2016.00006.9 Macro Level Priorities for Livestock Research and Development for Bihar Awadhesh
Understanding the 2011 Planting Outlook, Ethanol, and Food Pricing. March 31, 2011
 Understanding the 2011 Planting Outlook, Ethanol, and Food Pricing March 31, 2011 Planted acres by crop USDA Prospective Plantings report based on farmer surveys conducted during first two weeks of March
Understanding the 2011 Planting Outlook, Ethanol, and Food Pricing March 31, 2011 Planted acres by crop USDA Prospective Plantings report based on farmer surveys conducted during first two weeks of March
Food Prices January February 2012 update Little movement in cereals spot & futures prices Maize stocks a concern
 Feb 29th 12 Food Prices January February 12 update Little movement in cereals spot & futures prices Maize stocks a concern KEY POINTS International spot prices of maize, rice, and wheat are little changed
Feb 29th 12 Food Prices January February 12 update Little movement in cereals spot & futures prices Maize stocks a concern KEY POINTS International spot prices of maize, rice, and wheat are little changed
Evaluation of BioAg Biotechnical Nutrients in the Production of Bananas in North India
 Evaluation of BioAg Biotechnical Nutrients in the Production of Bananas in North India Dr S.K. Barthan Roy, Centre for Strategic Studies, Kolkata, India 1. Introduction In 2011, BioAg Pty Ltd commissioned
Evaluation of BioAg Biotechnical Nutrients in the Production of Bananas in North India Dr S.K. Barthan Roy, Centre for Strategic Studies, Kolkata, India 1. Introduction In 2011, BioAg Pty Ltd commissioned
Inter-Linkages Among Agricultural Research Investment, Agricultural Productivity and Rural Poverty in India
 Inter-Linkages Among Agricultural Research Investment, Agricultural Productivity and Rural Poverty in India Kiresur V.R and Melinamani V.P. Paper prepared for presentation at the 12 th EAAE Congress People,
Inter-Linkages Among Agricultural Research Investment, Agricultural Productivity and Rural Poverty in India Kiresur V.R and Melinamani V.P. Paper prepared for presentation at the 12 th EAAE Congress People,
BENEFITS OF MICRO IRRIGATION SYSTEM SUGAR RECOVERY & PRODUCTIVITY AMIT BHARDWAJ DY. HEAD - INDIAN SUGAR MILLS ASSOCIATION 8 TH OCT, 2013
 BENEFITS OF MICRO IRRIGATION SYSTEM SUGAR RECOVERY & PRODUCTIVITY AMIT BHARDWAJ DY. HEAD - INDIAN SUGAR MILLS ASSOCIATION 8 TH OCT, 2013 Flow of Presentation PART I o o Water requirement for sugarcane
BENEFITS OF MICRO IRRIGATION SYSTEM SUGAR RECOVERY & PRODUCTIVITY AMIT BHARDWAJ DY. HEAD - INDIAN SUGAR MILLS ASSOCIATION 8 TH OCT, 2013 Flow of Presentation PART I o o Water requirement for sugarcane
Presented by : Chowda Reddy Commodities Research Desk
 Fundamentals of Cotton Presented by : Chowda Reddy Commodities Research Desk 1 Introduction Cotton - King of Fibres (belongs to the order Malvales, family Malvaceae) Sowing : June - July, Harvest: September
Fundamentals of Cotton Presented by : Chowda Reddy Commodities Research Desk 1 Introduction Cotton - King of Fibres (belongs to the order Malvales, family Malvaceae) Sowing : June - July, Harvest: September
SOYBEANS: LOW PRICES TO PERSIST
 SOYBEANS: LOW PRICES TO PERSIST JANUARY 2002 Darrel Good 2002 - NO. 2 Summary Soybean prices received some support from the USDA s January 11 final U.S. production estimate for the 2001 crop. At 2.891
SOYBEANS: LOW PRICES TO PERSIST JANUARY 2002 Darrel Good 2002 - NO. 2 Summary Soybean prices received some support from the USDA s January 11 final U.S. production estimate for the 2001 crop. At 2.891
INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 1
 INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Globally, maize (Zea mays L., 2n= 10) is the number one cereal crop in the world (FAOSTAT, 2011). Being a C 4 crop, it is most versatilee in terms of wide adaptability
INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION Globally, maize (Zea mays L., 2n= 10) is the number one cereal crop in the world (FAOSTAT, 2011). Being a C 4 crop, it is most versatilee in terms of wide adaptability
SINGLE SUPER PHOSPHATE
 PROJECT REPORT FOR MANUFACTURE OF SINGLE SUPER PHOSPHATE 350 TPD PSSP WITH 300 TPD GSSP ON THE BASIS OF 300 WORKING DAYS AT VILLAGE: DHORIA TEHSIL : NIMBAHEDA DIST. CHITTOR GARH BY `ANAPOORANA FERTILIZER
PROJECT REPORT FOR MANUFACTURE OF SINGLE SUPER PHOSPHATE 350 TPD PSSP WITH 300 TPD GSSP ON THE BASIS OF 300 WORKING DAYS AT VILLAGE: DHORIA TEHSIL : NIMBAHEDA DIST. CHITTOR GARH BY `ANAPOORANA FERTILIZER
Volume 1, Issue 1, June Issues of Food Self Sufficiency in Jammu and Kashmir. Sakeena Rather( PhD Scholar)
 Issues of Food Self Sufficiency in Jammu and Kashmir Sakeena Rather( PhD Scholar) UNESCO Madanjeet Singh s Institute of Kashmir studies University of Kashmir Srinagar, India. Email Id:- Sakeena.rather@gmail.com
Issues of Food Self Sufficiency in Jammu and Kashmir Sakeena Rather( PhD Scholar) UNESCO Madanjeet Singh s Institute of Kashmir studies University of Kashmir Srinagar, India. Email Id:- Sakeena.rather@gmail.com
MONTHLY FOOD SECURITY BULLETIN OF SOUTH AFRICA: DECEMBER 2012
 MONTHLY FOOD SECURITY BULLETIN OF SOUTH AFRICA: DECEMBER 2012 Issued: 17 January 2013 Directorate: Statistics and Economic Analysis Highlights: During December 2012 significant rainfall events were recorded
MONTHLY FOOD SECURITY BULLETIN OF SOUTH AFRICA: DECEMBER 2012 Issued: 17 January 2013 Directorate: Statistics and Economic Analysis Highlights: During December 2012 significant rainfall events were recorded
A Comparative Study on Socio Economic Impact of Bt cotton and Non-Bt cotton Farm Households in Warangal District of Telangana State, India
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-770 Volume 7 Number 05 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.2054/ijcmas.2018.705.185
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-770 Volume 7 Number 05 (2018) Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.2054/ijcmas.2018.705.185
PRODUCTIVITY STATUS OF RICE DURING NINTH PLAN
 1 PRODUCTIVITY STATUS OF RICE DURING NINTH PLAN Prepared and Edited by Dr. M.C. Diwakar, Director DIRECTORATE OF RICE DEVELOPMENT GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF AGRICULTURE (DEPTT. OF AGRI. & CO-OPERATION)
1 PRODUCTIVITY STATUS OF RICE DURING NINTH PLAN Prepared and Edited by Dr. M.C. Diwakar, Director DIRECTORATE OF RICE DEVELOPMENT GOVERNMENT OF INDIA MINISTRY OF AGRICULTURE (DEPTT. OF AGRI. & CO-OPERATION)
S E A S O N A L COMMODITY INSIGHT
 S E A S O N A L COMMODITY INSIGHT 09 th February 2015 Rice (Non - Basmati) Domestic Scenario India is the second largest producer of rice in the world after China, contributing to about 21.45 per cent
S E A S O N A L COMMODITY INSIGHT 09 th February 2015 Rice (Non - Basmati) Domestic Scenario India is the second largest producer of rice in the world after China, contributing to about 21.45 per cent
Onion & Garlic Crop Report. Feb WSC, Cochin. Vinayak Narain Olam Spices & Vegetable Ingredients. Creating value is our business
 Onion & Garlic Crop Report WSC, Cochin Feb 2014 Vinayak Narain Olam Spices & Vegetable Ingredients Overview (For both Onion & Garlic) Global supply and demand Fresh production, trends and International
Onion & Garlic Crop Report WSC, Cochin Feb 2014 Vinayak Narain Olam Spices & Vegetable Ingredients Overview (For both Onion & Garlic) Global supply and demand Fresh production, trends and International
Effect of Training Need for Papaya Growers in Begusarai District of Bihar
 Available online at www.ijpab.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5881 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (6): 1070-1074 (2017) Research Article Effect of Training Need for Papaya Growers
Available online at www.ijpab.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18782/2320-7051.5881 ISSN: 2320 7051 Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 5 (6): 1070-1074 (2017) Research Article Effect of Training Need for Papaya Growers
LAGGING EXPORTS SLIGHTLY NEGATIVE TO CORN PRICES
 November 5, 2001 Ames, Iowa Econ. Info. 1825 LAGGING EXPORTS SLIGHTLY NEGATIVE TO CORN PRICES While current utilization projections show record corn use for the year ahead, the slow start for corn export
November 5, 2001 Ames, Iowa Econ. Info. 1825 LAGGING EXPORTS SLIGHTLY NEGATIVE TO CORN PRICES While current utilization projections show record corn use for the year ahead, the slow start for corn export
Wednesday July 11, 2012 World Ag Supply & Demand Report
 World Ag Supply & Demand Report U.S. 2011/12 Old Crop Corn is neutral Global Old Crop Corn is neutral USDA estimates the 2011/12 U.S. corn carryout at 903 million bushels, up from 851 million bushels from
World Ag Supply & Demand Report U.S. 2011/12 Old Crop Corn is neutral Global Old Crop Corn is neutral USDA estimates the 2011/12 U.S. corn carryout at 903 million bushels, up from 851 million bushels from
TAC Meeting of APCAEM Hanoi, Vietnam, December 13-14, 2004
 TAC Meeting of APCAEM Hanoi, Vietnam, December 13-14, 2004 Country Report Dr. S. K. Tandon Assistant Director General (Engg.) INDIAN COUNCIL OF AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH, NEW DELHI(INDIA) INDIAN AGRICULTURE
TAC Meeting of APCAEM Hanoi, Vietnam, December 13-14, 2004 Country Report Dr. S. K. Tandon Assistant Director General (Engg.) INDIAN COUNCIL OF AGRICULTURAL RESEARCH, NEW DELHI(INDIA) INDIAN AGRICULTURE
MCQ s With Explanation Indian Agriculture
 MCQ s With Explanation Indian Agriculture 1. The main components of evergreen revolution are: 1. Up gradation soil health 2. Promote lab to land demonstrations 3. Promoting rain water harvesting 4. Increasing
MCQ s With Explanation Indian Agriculture 1. The main components of evergreen revolution are: 1. Up gradation soil health 2. Promote lab to land demonstrations 3. Promoting rain water harvesting 4. Increasing
Overview of Agriculture in Karnataka and Scope for PPP. Presentation by Commissioner for Agriculture Karnataka State Department of Agriculture
 Overview of Agriculture in Karnataka and Scope for PPP Presentation by Commissioner for Agriculture Karnataka State Department of Agriculture 30 Districts, 176 Taluks, 769 Hoblies (740 RSKs), 6019 Gram
Overview of Agriculture in Karnataka and Scope for PPP Presentation by Commissioner for Agriculture Karnataka State Department of Agriculture 30 Districts, 176 Taluks, 769 Hoblies (740 RSKs), 6019 Gram
Lesson 3 Sesame Sesamum indicum
 Lesson 3 Sesame Sesamum indicum Importance o It is regarded as queen of oilseeds Because of its quality (fatty acid composition) Its resistance to oxidation and rancidity o India is considered as basic
Lesson 3 Sesame Sesamum indicum Importance o It is regarded as queen of oilseeds Because of its quality (fatty acid composition) Its resistance to oxidation and rancidity o India is considered as basic
Grains & Oilseeds Outlook. USDA's Interagency Commodity Estimates Grains and Oilseeds Committees
 Agricultural Outlook Forum Presented: February 23-24, 2012 U.S. Department of Agriculture Grains & Oilseeds Outlook USDA's Interagency Commodity Estimates Grains and Oilseeds Committees United States Department
Agricultural Outlook Forum Presented: February 23-24, 2012 U.S. Department of Agriculture Grains & Oilseeds Outlook USDA's Interagency Commodity Estimates Grains and Oilseeds Committees United States Department
Growth Performance and Resource Use Efficiency of Maize in Bihar: An Economic Perspectives
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Growth Performance and Resource Use Efficiency of Maize in Bihar: An Economic Perspectives Nasim Ahmad and D.K. Sinha and K.M. Singh and R.R. Mishra Dr. Rajendra Prasad
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Growth Performance and Resource Use Efficiency of Maize in Bihar: An Economic Perspectives Nasim Ahmad and D.K. Sinha and K.M. Singh and R.R. Mishra Dr. Rajendra Prasad
From community seed banks to community seed enterprises. G. V. Ramanjaneyulu, G. Rajshekar and K. Radha Rani
 19 India From community seed banks to community seed enterprises G. V. Ramanjaneyulu, G. Rajshekar and K. Radha Rani Origin and process To restore farmers habit of saving and using seeds from their own
19 India From community seed banks to community seed enterprises G. V. Ramanjaneyulu, G. Rajshekar and K. Radha Rani Origin and process To restore farmers habit of saving and using seeds from their own
World Agricultural Supply and Demand Estimates
 World Agricultural Supply and Demand Estimates Report of Interagency Commodity Estimates Committee Forecasts World Agricultural Outlook Board, Chairing Agency Economic Research Service Foreign Agricultural
World Agricultural Supply and Demand Estimates Report of Interagency Commodity Estimates Committee Forecasts World Agricultural Outlook Board, Chairing Agency Economic Research Service Foreign Agricultural
Five-fold increase in food grains production since Moved away from food dependency to a net food exporter Largest producer of milk, annual
 May 2, 2017 Outline Agriculture in India- An overview Significance of Agricultural Statistics Release of national level estimates Validation of Data Collection of primary data by States Othersources of
May 2, 2017 Outline Agriculture in India- An overview Significance of Agricultural Statistics Release of national level estimates Validation of Data Collection of primary data by States Othersources of
Chapter VII: Economics of sweet sorghum feedstock production for bioethanol
 Chapter VII: Economics of sweet sorghum feedstock production for bioethanol A Ashok Kumar and Belum VS Reddy I. Introduction Sweet sorghum is similar to grain sorghum but possesses sugar-rich stalks, with
Chapter VII: Economics of sweet sorghum feedstock production for bioethanol A Ashok Kumar and Belum VS Reddy I. Introduction Sweet sorghum is similar to grain sorghum but possesses sugar-rich stalks, with
Zimbabwe. Grain and Feed Annual
 THIS REPORT CONTAINS ASSESSMENTS OF COMMODITY AND TRADE ISSUES MADE BY USDA STAFF AND NOT NECESSARILY STATEMENTS OF OFFICIAL U.S. GOVERNMENT POLICY Voluntary - Public Date: 7/13/2012 GAIN Report Number:
THIS REPORT CONTAINS ASSESSMENTS OF COMMODITY AND TRADE ISSUES MADE BY USDA STAFF AND NOT NECESSARILY STATEMENTS OF OFFICIAL U.S. GOVERNMENT POLICY Voluntary - Public Date: 7/13/2012 GAIN Report Number:
Impact Assessment of Agricultural Extension Reforms in Bihar. K.M. Singh 1, M.S. Meena 2 and A.K. Jha 3 ABSTRACT
 110 Indian Res. J Ext. Edu. 9 (2 ), May 2009 Impact Assessment of Agricultural Extension Reforms in Bihar K.M. Singh 1, M.S. Meena 2 and A.K. Jha 3 1. Head, 2. Sr.Scientist (Agril. Ext.), Division of Socio
110 Indian Res. J Ext. Edu. 9 (2 ), May 2009 Impact Assessment of Agricultural Extension Reforms in Bihar K.M. Singh 1, M.S. Meena 2 and A.K. Jha 3 1. Head, 2. Sr.Scientist (Agril. Ext.), Division of Socio
U.P. Council of Sugarcane Research, Shahjahanpur (U.P.), India. 2. A.P.S. University, Rewa (M.P.), India. 3
 Plant Archives Vol. 18, Special Issue (ICAAAS-2018), 2018 pp. 148-152 ISSN 0972-5210 PROSPECTS OF SUGARCANE FARMING WITH ITS FUTURE STRATEGIES TO ENHANCE PRODUCTIVITY AND INCOME OF FARMERS : AN ECOFRIENDLY
Plant Archives Vol. 18, Special Issue (ICAAAS-2018), 2018 pp. 148-152 ISSN 0972-5210 PROSPECTS OF SUGARCANE FARMING WITH ITS FUTURE STRATEGIES TO ENHANCE PRODUCTIVITY AND INCOME OF FARMERS : AN ECOFRIENDLY
ARE DISPARITIES IN INDIAN AGRICULTURE GROWING?
 ARE DISPARITIES IN INDIAN AGRICULTURE GROWING? Indian agriculture has witnessed tremendous changes during the last 3 decades following the adoption of green revolution technology during late 1960's The
ARE DISPARITIES IN INDIAN AGRICULTURE GROWING? Indian agriculture has witnessed tremendous changes during the last 3 decades following the adoption of green revolution technology during late 1960's The
8 th September, Medium term(dec Jan) Supply Demand Price
 8 th September, 2008 Seasonal Outlook On Chilli Medium term(dec Jan) Supply Demand Price Introduction Chilli is considered as one of the commercial spice crops. It is the most widely used universal spice,
8 th September, 2008 Seasonal Outlook On Chilli Medium term(dec Jan) Supply Demand Price Introduction Chilli is considered as one of the commercial spice crops. It is the most widely used universal spice,
Agrarian Stagnation in Eastern Gangetic Plains. Avinash Kishore IFPRI, New Delhi
 Agrarian Stagnation in Eastern Gangetic Plains Avinash Kishore IFPRI, New Delhi Agriculture is stagnant across India 17500 AgGDP of India (2011-12 billion rupees) 17000 16500 CAGR = 2.32% 16000 15500 15000
Agrarian Stagnation in Eastern Gangetic Plains Avinash Kishore IFPRI, New Delhi Agriculture is stagnant across India 17500 AgGDP of India (2011-12 billion rupees) 17000 16500 CAGR = 2.32% 16000 15500 15000
