ppdb: a plant promoter database
|
|
|
- Crystal Elliott
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Published online 18 October 2007 Nucleic Acids Research, 2008, Vol. 36, Database issue D977 D981 doi: /nar/gkm785 ppdb: a plant promoter database Yoshiharu Y. Yamamoto and Junichi Obokata* Center for Gene Research, Nagoya University, Nagoya , Japan Received August 14, 2007; Revised September 13, 2007; Accepted September 17, 2007 ABSTRACT ppdb ( is a plant promoter database that provides promoter annotation of Arabidopsis and rice. The database contains information on promoter structures, transcription start sites (TSSs) that have been identified from full-length cdna clones and also a vast amount of TSS tag data. In ppdb, the promoter structures are determined by sets of promoter elements identified by a position-sensitive extraction method called local distribution of short sequences (LDSS). By using this database, the core promoter structure, the presence of regulatory elements and the distribution of TSS clusters can be identified. Although no differentiation of promoter architecture among plant species has been reported, there is some divergence of utilized sequences for promoter elements. Therefore, ppdb is based on species-specific sets of promoter elements, rather than on general motifs for multiple species. Each regulatory sequence is hyperlinked to literary information, a PLACE entry served by a plant cis-element database, and a list of promoters containing the regulatory sequence. BACKGROUND A promoter database can be generated from a combination of genome sequence, information of promoter positions and a list of cis-regulatory elements. Currently a major restriction on the quality of a promoter database is our limited knowledge of cis-elements. There are several established genome-wide plant promoter databases available today (RARGE: (1), AGRIS: (2), AthaMap: (3), and which are based on cis-regulatory sequences from PlantCARE [(4), PLACE [(5), PLACE/] or TRANSFAC [(6), com/pub/databases.html]. These three promoter databases focus on cis-regulatory elements rather than core promoter structure, aiming to reveal the regulatory machinery that give the expression profiles. Unfortunately, these databases provide information only for Arabidopsis, and there are no genomewide plant promoter databases available for other plant species. Local distribution of short sequences (LDSS) analysis is a method to extract promoter constituents by genomewide statistical analysis (7,8). We have applied this method to the Arabidopsis and rice genomes, and identified 1000 octamer sequences per genome as LDSS-positive promoter elements (8). According to their distribution profiles, the identified octamers have been classified into regulatory element group (REG), TATA box and Y Patch as three major promoter element groups. REG is a direction-insensitive element that is preferentially found around 100 bp relative to the major transcription start site (TSS), and contains many established cis-regulatory sequences. Y Patch is a direction-sensitive plant core promoter element that appears around TSS. We found that utilized sequences of all three groups, including TATA element, are moderately differentiated between Arabidopsis and rice, demonstrating the importance of individual preparation of promoter elements for each genome. The large collection of extracted promoter elements can be utilized as a tool to reveal precise promoter architecture. Therefore, here we present a novel searchable ppdb database, based on the LDSS-positive elements. Utilization of a genome-specific set of promoter elements and the detection of the core promoter structure are the two unique features of this database. Currently, ppdb is the only one plant promoter database with information about core promoter types on a genomic scale, and the first genome-wide database for rice promoters. PROMOTER SELECTION AND OUTPUT WINDOWS Major function of ppdb is to detect promoter elements in the genome sequence and to summarize promoter structures. Data source of ppdb is shown in Table 1. The database detects REG, TATA box and Y Patch. *To whom correspondence should be addressed. Tel/Fax: ; obokata@gene.nagoya-u.ac.jp ß 2007 The Author(s) This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( by-nc/2.0/uk/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
2 D978 Nucleic Acids Research, 2008, Vol. 36, Database issue Table 1. Source of ppdb Specification Source Size Arabidopsis Genome sequence TAIR 6 and gene annotation TSS information Cap signatured CT-MSS tags Yamamoto, Y. Y. et al., unpublished data Selected RAFL cdna Promoter elements LDSS-positive octamers (8) 659 PLACE entries corresponding 21 (only matched motifs) to LDSS elements Rice Genome sequence and gene annotation RGSP build TSS information Selected fl cdna Promoter elements LDSS-positive octamers (8) 600 PLACE entries corresponding to LDSS elements 4 (only matched motifs) Promoters of interest can be identified by a word search (e.g. photosystem ) or a gene number (e.g. At5g38410, Os01g or AK121523) on the front page ( Selection of a specific gene model gives the following information: (i) sequence data, (ii) TSS data, (iii) a summary of the core promoter structure and (iv) REG data (Figure 1). At the sequence window, octamer elements identified by the LDSS analysis (8) are highlighted. There are two modes for detection, Reliable and ALL. Reliable is a default setting where only elements at appropriate positions relative to the peak TSS are detected. Promoters without any TSS information do not show any elements. In this case, selecting ALL allows global detection without any positional restriction. The sensitive area in the Reliable mode for each element group is described on the front page. The TSS information table provides the expressional strength of each TSS. Tag per million (TPM) in the window shows the relative counts of TSS tags in a tag library, and this information comes from CT-MPSS analysis (Yamamoto,Y.Y. et al., unpublished data). The methods and quality assessment of the data will be described elsewhere. The table of Core promoter information shows the presence and absence of TATA box and Y Patch. Currently, a search for Inr (Initiator for the consensus around TSS) is not executed, thus all promoters will show Not Available for it. We have a plan to add Inr information in a near future as a minor update. The REG information table shows a REG list of a promoter and its corresponding PPDB and PLACE motifs. For example, the table in Figure 1 shows that AtREG379 belongs to the ACGT group of PPDB and corresponds to ACGT, ACGTG, GCCAC and ACGTGKC motifs of PLACE (5). PPDB motifs have been extracted from REG sequences with the aid of a two-dimensional (2D) REG-promoter clustering (8). REG sequences, as well as PPDB and PLACE motifs, are linked to other pages for biological information. REG information is shown under the category of Promoter Summary. Selection of ALL adds another category, Not Reliable Promoter Summary. This category can be used when searching for regulatory elements (REG) from wider regions or when there is no TSS information on the promoter of interest. ADDITIONAL PAGES Some biological information of REGs is also provided by ppdb. As shown in Figure 2, there is a page with a whole list of REGs, the ALL REG List. This list presents the relationship between REG sequences, PPDB motifs and PLACE motifs. Selection of a specific REG sequence leads to Summary of the REG, followed by Hit Gene List of the REG. The Summary of the REG section shows corresponding PPDB and PLACE motifs and a brief description of the motifs. Selection of each motif leads to PLACE ID and also to the original article(s) for the motif. The Hit Gene List section gives information about promoters sharing the REG. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This work was supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Priority Areas Comparative Genomics (Y.Y.Y. and J.O.), Scientific Research (B) (J.O.) and Scientific Research (C) (Y.Y.Y.) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan. Funding to pay the Open Access publication charges for this article was provided by Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan. Conflict of interest statement. None declared.
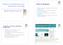
3 Nucleic Acids Research, 2008, Vol. 36, Database issue D979 Promoter Sequence 5 end of cdna clone TSS tag of CT-MPSS Peak TSS Figure 1. Selection of a specific gene model gives the following information: (i) sequence data, (ii) TSs data, (iii) a summary of the core promoter structure and (iv) REG data. Peak TSS is highlighted. TPM means tag per million and this is an indication of expression level at each TSS.
4 D980 Nucleic Acids Research, 2008, Vol. 36, Database issue Figure 2. Page showing the whole list of REGs, the All REG List, Summary of the REG followed by Hit Gene List of the REG. This also shows the relationship between REG Sequences, PPDB motifs and PLACE motifs. REFERENCES 1. Seki,M., Narusaka,M., Kamiya,A., Ishida,J., Satou,M., Sakurai,T., Nakajima,M., Enju,A., Akiyama,K. et al. (2002) Functional annotation of a full-length Arabidopsis cdna collection. Science, 296, Davuluri,R.V., Sun,H., Palaniswamy,S.K., Matthews,N., Molina,C., Kurtz,M. and Grotewold,E. (2003) AGRIS: Arabidopsis gene regulatory information server, an information resource of Arabidopsis cis-regulatory elements and transcription factors. BMC Bioinformatics, 4, Bu low,l., Steffens,N.O., Galuschka,C., Shindler,M. and Hehl,R. (2006) AthaMap: from in silico data to real transcription factor binding sites. In Silico Biol., 6, Lescot,M., Déhais,P., Thijs,G., Marchal,K., Moreau,Y., Van de Peer,Y., Rouze,P. and Rombauts,S. (2002) PlantCARE, a database
5 Nucleic Acids Research, 2008, Vol. 36, Database issue D981 of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res., 30, Higo,K., Ugawa,Y., Iwamoto,M. and Korenaga,T. (1999) Plant cis-acting regulatory DNA elements (PLACE) database: Nucleic Acids Res., 27, Matys,V., Kel-Margoulis,O.V., Fricke,E., Liebich,I., Land,S., Barre-Dirrie,A., Reuter,I., Chekmenev,D., Krull,M. et al. (2006) TRANSFAC and its module TRANSCompel: transcriptional gene regulation in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res., 34, D108 D FitzGerald,P.C., Shlyakhtenko,A., Mir,A.A. and Vinson,C. (2004) Clustering of DNA sequences in human promoters. Genome Res., 14, Yamamoto,Y.Y., Ichida,H., Matsui,M., Obokata,J., Sakurai,T., Satou,M., Seki,M., Shinozaki,K. and Abe,T. (2007) Identification of plant promoter constituents by analysis of local distribution of short sequences. BMC Genomics, 8, 67.
ppdb: a plant promoter database
 Nucleic Acids Research Advance Access published October 18, 2007 ppdb: a plant promoter database Yoshiharu Y. Yamamoto and Junichi Obokata* Center for Gene Research, Nagoya University, Nagoya 464-8602,
Nucleic Acids Research Advance Access published October 18, 2007 ppdb: a plant promoter database Yoshiharu Y. Yamamoto and Junichi Obokata* Center for Gene Research, Nagoya University, Nagoya 464-8602,
ORTHOMINE - A dataset of Drosophila core promoters and its analysis. Sumit Middha Advisor: Dr. Peter Cherbas
 ORTHOMINE - A dataset of Drosophila core promoters and its analysis Sumit Middha Advisor: Dr. Peter Cherbas Introduction Challenges and Motivation D melanogaster Promoter Dataset Expanding promoter sequences
ORTHOMINE - A dataset of Drosophila core promoters and its analysis Sumit Middha Advisor: Dr. Peter Cherbas Introduction Challenges and Motivation D melanogaster Promoter Dataset Expanding promoter sequences
Regulation of eukaryotic transcription:
 Promoter definition by mass genome annotation data: in silico primer extension EMBNET course Bioinformatics of transcriptional regulation Jan 28 2008 Christoph Schmid Regulation of eukaryotic transcription:
Promoter definition by mass genome annotation data: in silico primer extension EMBNET course Bioinformatics of transcriptional regulation Jan 28 2008 Christoph Schmid Regulation of eukaryotic transcription:
Differentiation of core promoter architecture between plants and mammals revealed by LDSS analysis
 Published online 12 September 27 Nucleic Acids Research, 27, Vol. 35, No. 18 6219 6226 doi:1.193/nar/gkm685 Differentiation of core promoter architecture between plants and mammals revealed by LDSS analysis
Published online 12 September 27 Nucleic Acids Research, 27, Vol. 35, No. 18 6219 6226 doi:1.193/nar/gkm685 Differentiation of core promoter architecture between plants and mammals revealed by LDSS analysis
High-throughput Transcriptome analysis
 High-throughput Transcriptome analysis CAGE and beyond Dr. Rimantas Kodzius, Singapore, A*STAR, IMCB rkodzius@imcb.a-star.edu.sg for KAUST 2008 Agenda 1. Current research - PhD work on discovery of new
High-throughput Transcriptome analysis CAGE and beyond Dr. Rimantas Kodzius, Singapore, A*STAR, IMCB rkodzius@imcb.a-star.edu.sg for KAUST 2008 Agenda 1. Current research - PhD work on discovery of new
Applied Bioinformatics - Lecture 16: Transcriptomics
 Applied Bioinformatics - Lecture 16: Transcriptomics David Hendrix Oregon State University Feb 15th 2016 Transcriptomics High-throughput Sequencing (deep sequencing) High-throughput sequencing (also
Applied Bioinformatics - Lecture 16: Transcriptomics David Hendrix Oregon State University Feb 15th 2016 Transcriptomics High-throughput Sequencing (deep sequencing) High-throughput sequencing (also
UniPROBE, Update 2011: Expanded Content and Search Tools in the Online Database of Protein-Binding Microarray Data on Protein DNA Interactions
 UniPROBE, Update 2011: Expanded Content and Search Tools in the Online Database of Protein-Binding Microarray Data on Protein DNA Interactions The Harvard community has made this article openly available.
UniPROBE, Update 2011: Expanded Content and Search Tools in the Online Database of Protein-Binding Microarray Data on Protein DNA Interactions The Harvard community has made this article openly available.
ChIP-Seq Data Analysis. J Fass UCD Genome Center Bioinformatics Core Wednesday 15 June 2015
 ChIP-Seq Data Analysis J Fass UCD Genome Center Bioinformatics Core Wednesday 15 June 2015 What s the Question? Where do Transcription Factors (TFs) bind genomic DNA 1? (Where do other things bind DNA
ChIP-Seq Data Analysis J Fass UCD Genome Center Bioinformatics Core Wednesday 15 June 2015 What s the Question? Where do Transcription Factors (TFs) bind genomic DNA 1? (Where do other things bind DNA
VOMBAT: prediction of transcription factor binding sites using variable order Bayesian trees
 VOMBAT: prediction of transcription factor binding sites using variable order Bayesian trees Jan Grau, Irad Ben-Gal 1, Stefan Posch and Ivo Grosse 2, * Nucleic Acids Research, 2006, Vol. 34, Web Server
VOMBAT: prediction of transcription factor binding sites using variable order Bayesian trees Jan Grau, Irad Ben-Gal 1, Stefan Posch and Ivo Grosse 2, * Nucleic Acids Research, 2006, Vol. 34, Web Server
ChIP-Seq Tools. J Fass UCD Genome Center Bioinformatics Core Wednesday September 16, 2015
 ChIP-Seq Tools J Fass UCD Genome Center Bioinformatics Core Wednesday September 16, 2015 What s the Question? Where do Transcription Factors (TFs) bind genomic DNA 1? (Where do other things bind DNA or
ChIP-Seq Tools J Fass UCD Genome Center Bioinformatics Core Wednesday September 16, 2015 What s the Question? Where do Transcription Factors (TFs) bind genomic DNA 1? (Where do other things bind DNA or
ChIP-Seq Data Analysis. J Fass UCD Genome Center Bioinformatics Core Wednesday December 17, 2014
 ChIP-Seq Data Analysis J Fass UCD Genome Center Bioinformatics Core Wednesday December 17, 2014 What s the Question? Where do Transcription Factors (TFs) bind genomic DNA 1? (Where do other things bind
ChIP-Seq Data Analysis J Fass UCD Genome Center Bioinformatics Core Wednesday December 17, 2014 What s the Question? Where do Transcription Factors (TFs) bind genomic DNA 1? (Where do other things bind
Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers
 Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers A typical gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II has a promoter that usually extends upstream from the site where transcription is initiated the (#1) of transcription
Chapter 24: Promoters and Enhancers A typical gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II has a promoter that usually extends upstream from the site where transcription is initiated the (#1) of transcription
nature methods A paired-end sequencing strategy to map the complex landscape of transcription initiation
 nature methods A paired-end sequencing strategy to map the complex landscape of transcription initiation Ting Ni, David L Corcoran, Elizabeth A Rach, Shen Song, Eric P Spana, Yuan Gao, Uwe Ohler & Jun
nature methods A paired-end sequencing strategy to map the complex landscape of transcription initiation Ting Ni, David L Corcoran, Elizabeth A Rach, Shen Song, Eric P Spana, Yuan Gao, Uwe Ohler & Jun
RiceGAAS: an automated annotation system and database for rice genome sequence
 98 102 Nucleic Acids Research, 2002, Vol. 30, No. 1 2002 Oxford University Press RiceGAAS: an automated annotation system and database for rice genome sequence Katsumi Sakata*, Yoshiaki Nagamura, Hisataka
98 102 Nucleic Acids Research, 2002, Vol. 30, No. 1 2002 Oxford University Press RiceGAAS: an automated annotation system and database for rice genome sequence Katsumi Sakata*, Yoshiaki Nagamura, Hisataka
MODULE TSS1: TRANSCRIPTION START SITES INTRODUCTION (BASIC)
 MODULE TSS1: TRANSCRIPTION START SITES INTRODUCTION (BASIC) Lesson Plan: Title JAMIE SIDERS, MEG LAAKSO & WILSON LEUNG Identifying transcription start sites for Peaked promoters using chromatin landscape,
MODULE TSS1: TRANSCRIPTION START SITES INTRODUCTION (BASIC) Lesson Plan: Title JAMIE SIDERS, MEG LAAKSO & WILSON LEUNG Identifying transcription start sites for Peaked promoters using chromatin landscape,
PromSearch: A Hybrid Approach to Human Core-Promoter Prediction
 PromSearch: A Hybrid Approach to Human Core-Promoter Prediction Byoung-Hee Kim, Seong-Bae Park, and Byoung-Tak Zhang Biointelligence Laboratory, School of Computer Science and Engineering Seoul National
PromSearch: A Hybrid Approach to Human Core-Promoter Prediction Byoung-Hee Kim, Seong-Bae Park, and Byoung-Tak Zhang Biointelligence Laboratory, School of Computer Science and Engineering Seoul National
Community-assisted genome annotation: The Pseudomonas example. Geoff Winsor, Simon Fraser University Burnaby (greater Vancouver), Canada
 Community-assisted genome annotation: The Pseudomonas example Geoff Winsor, Simon Fraser University Burnaby (greater Vancouver), Canada Overview Pseudomonas Community Annotation Project (PseudoCAP) Past
Community-assisted genome annotation: The Pseudomonas example Geoff Winsor, Simon Fraser University Burnaby (greater Vancouver), Canada Overview Pseudomonas Community Annotation Project (PseudoCAP) Past
AGRIS: the Arabidopsis Gene Regulatory Information Server, an update
 D1118 D1122 Published online 8 November 2010 doi:10.1093/nar/gkq1120 AGRIS: the Arabidopsis Gene Regulatory Information Server, an update Alper Yilmaz 1, *, Maria Katherine Mejia-Guerra 1, Kyle Kurz 2,
D1118 D1122 Published online 8 November 2010 doi:10.1093/nar/gkq1120 AGRIS: the Arabidopsis Gene Regulatory Information Server, an update Alper Yilmaz 1, *, Maria Katherine Mejia-Guerra 1, Kyle Kurz 2,
Lecture 7 Motif Databases and Gene Finding
 Introduction to Bioinformatics for Medical Research Gideon Greenspan gdg@cs.technion.ac.il Lecture 7 Motif Databases and Gene Finding Motif Databases & Gene Finding Motifs Recap Motif Databases TRANSFAC
Introduction to Bioinformatics for Medical Research Gideon Greenspan gdg@cs.technion.ac.il Lecture 7 Motif Databases and Gene Finding Motif Databases & Gene Finding Motifs Recap Motif Databases TRANSFAC
Gene Identification in silico
 Gene Identification in silico Nita Parekh, IIIT Hyderabad Presented at National Seminar on Bioinformatics and Functional Genomics, at Bioinformatics centre, Pondicherry University, Feb 15 17, 2006. Introduction
Gene Identification in silico Nita Parekh, IIIT Hyderabad Presented at National Seminar on Bioinformatics and Functional Genomics, at Bioinformatics centre, Pondicherry University, Feb 15 17, 2006. Introduction
The Ensembl Database. Dott.ssa Inga Prokopenko. Corso di Genomica
 The Ensembl Database Dott.ssa Inga Prokopenko Corso di Genomica 1 www.ensembl.org Lecture 7.1 2 What is Ensembl? Public annotation of mammalian and other genomes Open source software Relational database
The Ensembl Database Dott.ssa Inga Prokopenko Corso di Genomica 1 www.ensembl.org Lecture 7.1 2 What is Ensembl? Public annotation of mammalian and other genomes Open source software Relational database
MODULE TSS2: SEQUENCE ALIGNMENTS (ADVANCED)
 MODULE TSS2: SEQUENCE ALIGNMENTS (ADVANCED) Lesson Plan: Title MEG LAAKSO AND JAMIE SIDERS Identifying the TSS for a gene in D. eugracilis using sequence alignment with the D. melanogaster ortholog Objectives
MODULE TSS2: SEQUENCE ALIGNMENTS (ADVANCED) Lesson Plan: Title MEG LAAKSO AND JAMIE SIDERS Identifying the TSS for a gene in D. eugracilis using sequence alignment with the D. melanogaster ortholog Objectives
TRED: a Transcriptional Regulatory Element Database and a platform for in silico gene regulation studies
 TRED: a Transcriptional Regulatory Element Database and a platform for in silico gene regulation studies Fang Zhao, Zhenyu Xuan, Lihua Liu and Michael Q. Zhang* D103 D107 doi:10.1093/nar/gki004 Cold Spring
TRED: a Transcriptional Regulatory Element Database and a platform for in silico gene regulation studies Fang Zhao, Zhenyu Xuan, Lihua Liu and Michael Q. Zhang* D103 D107 doi:10.1093/nar/gki004 Cold Spring
Serial Analysis of Gene Expression
 Serial Analysis of Gene Expression Cloning of Tissue-Specific Genes Using SAGE and a Novel Computational Substraction Approach. Genomic (2001) Hung-Jui Shih Outline of Presentation SAGE EST Article TPE
Serial Analysis of Gene Expression Cloning of Tissue-Specific Genes Using SAGE and a Novel Computational Substraction Approach. Genomic (2001) Hung-Jui Shih Outline of Presentation SAGE EST Article TPE
In silico identification of transcriptional regulatory regions
 In silico identification of transcriptional regulatory regions Martti Tolvanen, IMT Bioinformatics, University of Tampere Eija Korpelainen, CSC Jarno Tuimala, CSC Introduction (Eija) Program Retrieval
In silico identification of transcriptional regulatory regions Martti Tolvanen, IMT Bioinformatics, University of Tampere Eija Korpelainen, CSC Jarno Tuimala, CSC Introduction (Eija) Program Retrieval
Biology 644: Bioinformatics
 Processes Activation Repression Initiation Elongation.... Processes Splicing Editing Degradation Translation.... Transcription Translation DNA Regulators DNA-Binding Transcription Factors Chromatin Remodelers....
Processes Activation Repression Initiation Elongation.... Processes Splicing Editing Degradation Translation.... Transcription Translation DNA Regulators DNA-Binding Transcription Factors Chromatin Remodelers....
Non-coding Function & Variation, MPRAs. Mike White Bio5488 3/5/18
 Non-coding Function & Variation, MPRAs Mike White Bio5488 3/5/18 Outline MONDAY Non-coding function and variation The barcode Basic versions of MRPA technology WEDNESDAY More varieties of MRPAs Some key
Non-coding Function & Variation, MPRAs Mike White Bio5488 3/5/18 Outline MONDAY Non-coding function and variation The barcode Basic versions of MRPA technology WEDNESDAY More varieties of MRPAs Some key
Nagahama Institute of Bio-Science and Technology. National Institute of Genetics and SOKENDAI Nagahama Institute of Bio-Science and Technology
 A Large-scale Batch-learning Self-organizing Map for Function Prediction of Poorly-characterized Proteins Progressively Accumulating in Sequence Databases Project Representative Toshimichi Ikemura Authors
A Large-scale Batch-learning Self-organizing Map for Function Prediction of Poorly-characterized Proteins Progressively Accumulating in Sequence Databases Project Representative Toshimichi Ikemura Authors
Figure S4 A-H : Initiation site properties and evolutionary changes
 A 0.3 Figure S4 A-H : Initiation site properties and evolutionary changes G-correction not used 0.25 Fraction of total counts 0.2 0.5 0. tag 2 tags 3 tags 4 tags 5 tags 6 tags 7tags 8tags 9 tags >9 tags
A 0.3 Figure S4 A-H : Initiation site properties and evolutionary changes G-correction not used 0.25 Fraction of total counts 0.2 0.5 0. tag 2 tags 3 tags 4 tags 5 tags 6 tags 7tags 8tags 9 tags >9 tags
Chapter 1. from genomics to proteomics Ⅱ
 Proteomics Chapter 1. from genomics to proteomics Ⅱ 1 Functional genomics Functional genomics: study of relations of genomics to biological functions at systems level However, it cannot explain any more
Proteomics Chapter 1. from genomics to proteomics Ⅱ 1 Functional genomics Functional genomics: study of relations of genomics to biological functions at systems level However, it cannot explain any more
Deep learning sequence-based ab initio prediction of variant effects on expression and disease risk
 Summer Review 7 Deep learning sequence-based ab initio prediction of variant effects on expression and disease risk Jian Zhou 1,2,3, Chandra L. Theesfeld 1, Kevin Yao 3, Kathleen M. Chen 3, Aaron K. Wong
Summer Review 7 Deep learning sequence-based ab initio prediction of variant effects on expression and disease risk Jian Zhou 1,2,3, Chandra L. Theesfeld 1, Kevin Yao 3, Kathleen M. Chen 3, Aaron K. Wong
A: 1.2 STIF Algorithm
 APPENDIX 1 A new algorithm for identification of Stress responsive TranscrIption Factor binding sites (STIF) and a database of abiotic stress responsive transcription factors in Arabidopsis thaliana (STIFDB)
APPENDIX 1 A new algorithm for identification of Stress responsive TranscrIption Factor binding sites (STIF) and a database of abiotic stress responsive transcription factors in Arabidopsis thaliana (STIFDB)
Using mutants to clone genes
 Using mutants to clone genes Objectives 1. What is positional cloning? 2. What is insertional tagging? 3. How can one confirm that the gene cloned is the same one that is mutated to give the phenotype
Using mutants to clone genes Objectives 1. What is positional cloning? 2. What is insertional tagging? 3. How can one confirm that the gene cloned is the same one that is mutated to give the phenotype
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK VII SEMESTER BM6005 BIO INFORMATICS Regulation 2013 Academic Year 2018-19 Prepared
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur 603 203 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK VII SEMESTER BM6005 BIO INFORMATICS Regulation 2013 Academic Year 2018-19 Prepared
Supplementary Figure 1 Strategy for parallel detection of DHSs and adjacent nucleosomes
 Supplementary Figure 1 Strategy for parallel detection of DHSs and adjacent nucleosomes DNase I cleavage DNase I DNase I digestion Sucrose gradient enrichment Small Large F1 F2...... F9 F1 F1 F2 F3 F4
Supplementary Figure 1 Strategy for parallel detection of DHSs and adjacent nucleosomes DNase I cleavage DNase I DNase I digestion Sucrose gradient enrichment Small Large F1 F2...... F9 F1 F1 F2 F3 F4
Identifying Regulatory Regions using Multiple Sequence Alignments
 Identifying Regulatory Regions using Multiple Sequence Alignments Prerequisites: BLAST Exercise: Detecting and Interpreting Genetic Homology. Resources: ClustalW is available at http://www.ebi.ac.uk/tools/clustalw2/index.html
Identifying Regulatory Regions using Multiple Sequence Alignments Prerequisites: BLAST Exercise: Detecting and Interpreting Genetic Homology. Resources: ClustalW is available at http://www.ebi.ac.uk/tools/clustalw2/index.html
Genome annotation & EST
 Genome annotation & EST What is genome annotation? The process of taking the raw DNA sequence produced by the genome sequence projects and adding the layers of analysis and interpretation necessary
Genome annotation & EST What is genome annotation? The process of taking the raw DNA sequence produced by the genome sequence projects and adding the layers of analysis and interpretation necessary
Introduction to NGS analyses
 Introduction to NGS analyses Giorgio L Papadopoulos Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology Bioinformatics Support Group 04/12/2015 Papadopoulos GL (IMBB, FORTH) IMBB NGS Seminar 04/12/2015 1
Introduction to NGS analyses Giorgio L Papadopoulos Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology Bioinformatics Support Group 04/12/2015 Papadopoulos GL (IMBB, FORTH) IMBB NGS Seminar 04/12/2015 1
The Gene Resource Locator: gene locus maps for transcriptome analysis
 2002 Oxford University Press Nucleic Acids Research, 2002, Vol. 30, No. 1 221 225 The Gene Resource Locator: gene locus maps for transcriptome analysis Toshihiko Honkura 1, Jun Ogasawara 2, Tomoyuki Yamada
2002 Oxford University Press Nucleic Acids Research, 2002, Vol. 30, No. 1 221 225 The Gene Resource Locator: gene locus maps for transcriptome analysis Toshihiko Honkura 1, Jun Ogasawara 2, Tomoyuki Yamada
Gene Regulation 10/19/05
 10/19/05 Gene Regulation (formerly Gene Prediction - 2) Gene Prediction & Regulation Mon - Overview & Gene structure review: Eukaryotes vs prokaryotes Wed - Regulatory regions: Promoters & enhancers -
10/19/05 Gene Regulation (formerly Gene Prediction - 2) Gene Prediction & Regulation Mon - Overview & Gene structure review: Eukaryotes vs prokaryotes Wed - Regulatory regions: Promoters & enhancers -
Genome Biology and Biotechnology
 Genome Biology and Biotechnology Functional Genomics Prof. M. Zabeau Department of Plant Systems Biology Flanders Interuniversity Institute for Biotechnology (VIB) University of Gent International course
Genome Biology and Biotechnology Functional Genomics Prof. M. Zabeau Department of Plant Systems Biology Flanders Interuniversity Institute for Biotechnology (VIB) University of Gent International course
In silico analysis of complete bacterial genomes: PCR, AFLP-PCR, and endonuclease
 Bioinformatics Advance Access published January 29, 2004 In silico analysis of complete bacterial genomes: PCR, AFLP-PCR, and endonuclease restriction Joseba Bikandi*, Rosario San Millán, Aitor Rementeria,
Bioinformatics Advance Access published January 29, 2004 In silico analysis of complete bacterial genomes: PCR, AFLP-PCR, and endonuclease restriction Joseba Bikandi*, Rosario San Millán, Aitor Rementeria,
Sequence Databases and database scanning
 Sequence Databases and database scanning Marjolein Thunnissen Lund, 2012 Types of databases: Primary sequence databases (proteins and nucleic acids). Composite protein sequence databases. Secondary databases.
Sequence Databases and database scanning Marjolein Thunnissen Lund, 2012 Types of databases: Primary sequence databases (proteins and nucleic acids). Composite protein sequence databases. Secondary databases.
I nternet Resources for Bioinformatics Data and Tools
 ~i;;;;;;;'s :.. ~,;;%.: ;!,;s163 ~. s :s163:: ~s ;'.:'. 3;3 ~,: S;I:;~.3;3'/////, IS~I'//. i: ~s '/, Z I;~;I; :;;; :;I~Z;I~,;'//.;;;;;I'/,;:, :;:;/,;'L;;;~;'~;~,::,:, Z'LZ:..;;',;';4...;,;',~/,~:...;/,;:'.::.
~i;;;;;;;'s :.. ~,;;%.: ;!,;s163 ~. s :s163:: ~s ;'.:'. 3;3 ~,: S;I:;~.3;3'/////, IS~I'//. i: ~s '/, Z I;~;I; :;;; :;I~Z;I~,;'//.;;;;;I'/,;:, :;:;/,;'L;;;~;'~;~,::,:, Z'LZ:..;;',;';4...;,;',~/,~:...;/,;:'.::.
ECS 234: Genomic Data Integration ECS 234
 : Genomic Data Integration Heterogeneous Data Integration DNA Sequence Microarray Proteomics >gi 12004594 gb AF217406.1 Saccharomyces cerevisiae uridine nucleosidase (URH1) gene, complete cds ATGGAATCTGCTGATTTTTTTACCTCACGAAACTTATTAAAACAGATAATTTCCCTCATCTGCAAGGTTG
: Genomic Data Integration Heterogeneous Data Integration DNA Sequence Microarray Proteomics >gi 12004594 gb AF217406.1 Saccharomyces cerevisiae uridine nucleosidase (URH1) gene, complete cds ATGGAATCTGCTGATTTTTTTACCTCACGAAACTTATTAAAACAGATAATTTCCCTCATCTGCAAGGTTG
A Brief History. Bootstrapping. Bagging. Boosting (Schapire 1989) Adaboost (Schapire 1995)
 A Brief History Bootstrapping Bagging Boosting (Schapire 1989) Adaboost (Schapire 1995) What s So Good About Adaboost Improves classification accuracy Can be used with many different classifiers Commonly
A Brief History Bootstrapping Bagging Boosting (Schapire 1989) Adaboost (Schapire 1995) What s So Good About Adaboost Improves classification accuracy Can be used with many different classifiers Commonly
A tutorial introduction into the MIPS PlantsDB barley&wheat database instances
 transplant 2 nd user training workshop Poznan, Poland, June, 27 th, 2013 A tutorial introduction into the MIPS PlantsDB barley&wheat database instances TUTORIAL ANSWERS Please direct any questions related
transplant 2 nd user training workshop Poznan, Poland, June, 27 th, 2013 A tutorial introduction into the MIPS PlantsDB barley&wheat database instances TUTORIAL ANSWERS Please direct any questions related
Bis2A 12.2 Eukaryotic Transcription
 OpenStax-CNX module: m56061 1 Bis2A 12.2 Eukaryotic Transcription Mitch Singer Based on Eukaryotic Transcription by OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative
OpenStax-CNX module: m56061 1 Bis2A 12.2 Eukaryotic Transcription Mitch Singer Based on Eukaryotic Transcription by OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative
DNAFSMiner: A Web-Based Software Toolbox to Recognize Two Types of Functional Sites in DNA Sequences
 DNAFSMiner: A Web-Based Software Toolbox to Recognize Two Types of Functional Sites in DNA Sequences Huiqing Liu Hao Han Jinyan Li Limsoon Wong Institute for Infocomm Research, 21 Heng Mui Keng Terrace,
DNAFSMiner: A Web-Based Software Toolbox to Recognize Two Types of Functional Sites in DNA Sequences Huiqing Liu Hao Han Jinyan Li Limsoon Wong Institute for Infocomm Research, 21 Heng Mui Keng Terrace,
Supplemental Figure 1. Floral commitment in Arabidopsis WT and mutants.
 Percentage of induction Supplemental Data. Torti et al. (2012). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.111.092791 A +0 +0 LD LDs +1 LDs +3 +3 LDs +5 +5 LDs LD 50 μm AP1 B C 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0-20 -40 wt Col soc1-2
Percentage of induction Supplemental Data. Torti et al. (2012). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.111.092791 A +0 +0 LD LDs +1 LDs +3 +3 LDs +5 +5 LDs LD 50 μm AP1 B C 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0-20 -40 wt Col soc1-2
and Promoter Sequence Data
 : Combining Gene Expression and Promoter Sequence Data Outline 1. Motivation Functionally related genes cluster together genes sharing cis-elements cluster together transcriptional regulation is modular
: Combining Gene Expression and Promoter Sequence Data Outline 1. Motivation Functionally related genes cluster together genes sharing cis-elements cluster together transcriptional regulation is modular
Genome-Wide Survey of MicroRNA - Transcription Factor Feed-Forward Regulatory Circuits in Human. Supporting Information
 Genome-Wide Survey of MicroRNA - Transcription Factor Feed-Forward Regulatory Circuits in Human Angela Re #, Davide Corá #, Daniela Taverna and Michele Caselle # equal contribution * corresponding author,
Genome-Wide Survey of MicroRNA - Transcription Factor Feed-Forward Regulatory Circuits in Human Angela Re #, Davide Corá #, Daniela Taverna and Michele Caselle # equal contribution * corresponding author,
Applying Machine Learning Strategy in Transcription Factor DNA Bindings Site Prediction
 Applying Machine Learning Strategy in Transcription Factor DNA Bindings Site Prediction Ziliang Qian Key Laboratory of Systems Biology Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences,
Applying Machine Learning Strategy in Transcription Factor DNA Bindings Site Prediction Ziliang Qian Key Laboratory of Systems Biology Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences,
Neural Networks and Applications in Bioinformatics. Yuzhen Ye School of Informatics and Computing, Indiana University
 Neural Networks and Applications in Bioinformatics Yuzhen Ye School of Informatics and Computing, Indiana University Contents Biological problem: promoter modeling Basics of neural networks Perceptrons
Neural Networks and Applications in Bioinformatics Yuzhen Ye School of Informatics and Computing, Indiana University Contents Biological problem: promoter modeling Basics of neural networks Perceptrons
Sequence Annotation & Designing Gene-specific qpcr Primers (computational)
 James Madison University From the SelectedWorks of Ray Enke Ph.D. Fall October 31, 2016 Sequence Annotation & Designing Gene-specific qpcr Primers (computational) Raymond A Enke This work is licensed under
James Madison University From the SelectedWorks of Ray Enke Ph.D. Fall October 31, 2016 Sequence Annotation & Designing Gene-specific qpcr Primers (computational) Raymond A Enke This work is licensed under
Neural Networks and Applications in Bioinformatics
 Contents Neural Networks and Applications in Bioinformatics Yuzhen Ye School of Informatics and Computing, Indiana University Biological problem: promoter modeling Basics of neural networks Perceptrons
Contents Neural Networks and Applications in Bioinformatics Yuzhen Ye School of Informatics and Computing, Indiana University Biological problem: promoter modeling Basics of neural networks Perceptrons
9/19/13. cdna libraries, EST clusters, gene prediction and functional annotation. Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 3
 cdna libraries, EST clusters, gene prediction and functional annotation Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 3 1 2 3 4 5 6 Figure 2.14 Relationship between gene structure, cdna, and EST sequences
cdna libraries, EST clusters, gene prediction and functional annotation Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 3 1 2 3 4 5 6 Figure 2.14 Relationship between gene structure, cdna, and EST sequences
The University of California, Santa Cruz (UCSC) Genome Browser
 The University of California, Santa Cruz (UCSC) Genome Browser There are hundreds of available userselected tracks in categories such as mapping and sequencing, phenotype and disease associations, genes,
The University of California, Santa Cruz (UCSC) Genome Browser There are hundreds of available userselected tracks in categories such as mapping and sequencing, phenotype and disease associations, genes,
Transcription Gene regulation
 Transcription Gene regulation The machine that transcribes a gene is composed of perhaps 50 proteins, including RNA polymerase, the enzyme that converts DNA code into RNA code. A crew of transcription
Transcription Gene regulation The machine that transcribes a gene is composed of perhaps 50 proteins, including RNA polymerase, the enzyme that converts DNA code into RNA code. A crew of transcription
The TIGR Plant Transcript Assemblies database
 Nucleic Acids Research Advance Access published November 6, 2006 D1 D6 doi:10.1093/nar/gkl785 The TIGR Plant Transcript Assemblies database Kevin L. Childs, John P. Hamilton, Wei Zhu, Eugene Ly, Foo Cheung,
Nucleic Acids Research Advance Access published November 6, 2006 D1 D6 doi:10.1093/nar/gkl785 The TIGR Plant Transcript Assemblies database Kevin L. Childs, John P. Hamilton, Wei Zhu, Eugene Ly, Foo Cheung,
ABS: a database of Annotated regulatory Binding Sites from orthologous promoters
 Nucleic Acids Research, 2006, Vol. 34, Database issue D63 D67 doi:10.1093/nar/gkj116 ABS: a database of Annotated regulatory Binding Sites from orthologous promoters Enrique Blanco 1,2, *, Domènec Farré
Nucleic Acids Research, 2006, Vol. 34, Database issue D63 D67 doi:10.1093/nar/gkj116 ABS: a database of Annotated regulatory Binding Sites from orthologous promoters Enrique Blanco 1,2, *, Domènec Farré
Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers)
 1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
1 Multiple choice questions (numbers in brackets indicate the number of correct answers) February 1, 2013 1. Ribose is found in Nucleic acids Proteins Lipids RNA DNA (2) 2. Most RNA in cells is transfer
Gene Expression Technology
 Gene Expression Technology Bing Zhang Department of Biomedical Informatics Vanderbilt University bing.zhang@vanderbilt.edu Gene expression Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene
Gene Expression Technology Bing Zhang Department of Biomedical Informatics Vanderbilt University bing.zhang@vanderbilt.edu Gene expression Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene
Chapter 17 Lecture. Concepts of Genetics. Tenth Edition. Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Chapter 17 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Chapter Contents 17.1 Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Can Occur at Any of the Steps Leading from DNA to Protein
Chapter 17 Lecture Concepts of Genetics Tenth Edition Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Chapter Contents 17.1 Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Can Occur at Any of the Steps Leading from DNA to Protein
Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription
 Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription Cis-acting sequences Distance-independent cis-acting elements Dissecting regulatory elements Transcription factors Overview transcriptional regulation Transcription
Chapter 14 Regulation of Transcription Cis-acting sequences Distance-independent cis-acting elements Dissecting regulatory elements Transcription factors Overview transcriptional regulation Transcription
Analysis of data from high-throughput molecular biology experiments Lecture 6 (F6, RNA-seq ),
 Analysis of data from high-throughput molecular biology experiments Lecture 6 (F6, RNA-seq ), 2012-01-26 What is a gene What is a transcriptome History of gene expression assessment RNA-seq RNA-seq analysis
Analysis of data from high-throughput molecular biology experiments Lecture 6 (F6, RNA-seq ), 2012-01-26 What is a gene What is a transcriptome History of gene expression assessment RNA-seq RNA-seq analysis
Illumina Sequencing Error Profiles and Quality Control
 Illumina Sequencing Error Profiles and Quality Control RNA-seq Workflow Biological samples/library preparation Sequence reads FASTQC Adapter Trimming (Optional) Splice-aware mapping to genome Counting
Illumina Sequencing Error Profiles and Quality Control RNA-seq Workflow Biological samples/library preparation Sequence reads FASTQC Adapter Trimming (Optional) Splice-aware mapping to genome Counting
Finding Eukaryotic Genes Computationally
 Gene Identification Finding Eukaryotic Genes Computationally ü Content-based Methods GC content, hexamer repeats, composition statistics, codon frequencies ü Site-based Methods donor sites, acceptor sites,
Gene Identification Finding Eukaryotic Genes Computationally ü Content-based Methods GC content, hexamer repeats, composition statistics, codon frequencies ü Site-based Methods donor sites, acceptor sites,
Soil invertebrates as a genomic model to study pollutants in the field
 Soil invertebrates as a genomic model to study pollutants in the field Dick Roelofs, Martijn Timmermans, Muriel de Boer, Ben Nota, Tjalf de Boer, Janine Mariën, Nico van Straalen ecogenomics Folsomia candida
Soil invertebrates as a genomic model to study pollutants in the field Dick Roelofs, Martijn Timmermans, Muriel de Boer, Ben Nota, Tjalf de Boer, Janine Mariën, Nico van Straalen ecogenomics Folsomia candida
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 AS-NMD modulates FLM-dependent thermosensory flowering response in Arabidopsis NATURE PLANTS www.nature.com/natureplants 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Genomic sequence of FLM along with the splice sites. Sequencing
AS-NMD modulates FLM-dependent thermosensory flowering response in Arabidopsis NATURE PLANTS www.nature.com/natureplants 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Genomic sequence of FLM along with the splice sites. Sequencing
Announcement Structure Analysis
 Announcement Structure Analysis BSC 4439/BSC 5436: Biomedical Informatics: Structure Analysis Spring 2019, CB117 Monday and Wednesday 12:00 1:15pm Office hour: Monday and Wednesday 1:15 2pm Topics include
Announcement Structure Analysis BSC 4439/BSC 5436: Biomedical Informatics: Structure Analysis Spring 2019, CB117 Monday and Wednesday 12:00 1:15pm Office hour: Monday and Wednesday 1:15 2pm Topics include
Predicting tissue specific cis-regulatory modules in the human genome using pairs of co-occurring motifs
 BMC Bioinformatics This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully formatted PDF and full text (HTML) versions will be made available soon. Predicting tissue specific
BMC Bioinformatics This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully formatted PDF and full text (HTML) versions will be made available soon. Predicting tissue specific
RNA-Seq data analysis course September 7-9, 2015
 RNA-Seq data analysis course September 7-9, 2015 Peter-Bram t Hoen (LUMC) Jan Oosting (LUMC) Celia van Gelder, Jacintha Valk (BioSB) Anita Remmelzwaal (LUMC) Expression profiling DNA mrna protein Comprehensive
RNA-Seq data analysis course September 7-9, 2015 Peter-Bram t Hoen (LUMC) Jan Oosting (LUMC) Celia van Gelder, Jacintha Valk (BioSB) Anita Remmelzwaal (LUMC) Expression profiling DNA mrna protein Comprehensive
Functional Enrichment Analysis & Candidate Gene Ranking
 Functional Enrichment Analysis & Candidate Gene Ranking Anil Jegga Biomedical Informatics Contact Information: Anil Jegga Biomedical Informatics Room # 232, S Building 10th Floor CCHMC Homepage: http://anil.cchmc.org
Functional Enrichment Analysis & Candidate Gene Ranking Anil Jegga Biomedical Informatics Contact Information: Anil Jegga Biomedical Informatics Room # 232, S Building 10th Floor CCHMC Homepage: http://anil.cchmc.org
Bioinformatics & Protein Structural Analysis. Bioinformatics & Protein Structural Analysis. Learning Objective. Proteomics
 The molecular structures of proteins are complex and can be defined at various levels. These structures can also be predicted from their amino-acid sequences. Protein structure prediction is one of the
The molecular structures of proteins are complex and can be defined at various levels. These structures can also be predicted from their amino-acid sequences. Protein structure prediction is one of the
Improvement of TRANSFAC Matrices Using Multiple Local Alignment of Transcription Factor Binding Site Sequences
 68 Genome Informatics 16(1): 68 72 (2005) Improvement of TRANSFAC Matrices Using Multiple Local Alignment of Transcription Factor Binding Site Sequences Yutao Fu 1 Zhiping Weng 1,2 bibin@bu.edu zhiping@bu.edu
68 Genome Informatics 16(1): 68 72 (2005) Improvement of TRANSFAC Matrices Using Multiple Local Alignment of Transcription Factor Binding Site Sequences Yutao Fu 1 Zhiping Weng 1,2 bibin@bu.edu zhiping@bu.edu
A Parzen window-based approach for the detection of locally enriched transcription factor binding sites
 Vandenbon et al. BMC Bioinformatics 2013, 14:26 METHODOLOGY ARTICLE Open Access A Parzen window-based approach for the detection of locally enriched transcription factor binding sites Alexis Vandenbon
Vandenbon et al. BMC Bioinformatics 2013, 14:26 METHODOLOGY ARTICLE Open Access A Parzen window-based approach for the detection of locally enriched transcription factor binding sites Alexis Vandenbon
SignalP Plugin USER MANUAL
 SignalP Plugin USER MANUAL User manual for SignalP 2.3 Windows, Mac OS X and Linux November 7, 2017 This software is for research purposes only. QIAGEN Aarhus Silkeborgvej 2 Prismet DK-8000 Aarhus C Denmark
SignalP Plugin USER MANUAL User manual for SignalP 2.3 Windows, Mac OS X and Linux November 7, 2017 This software is for research purposes only. QIAGEN Aarhus Silkeborgvej 2 Prismet DK-8000 Aarhus C Denmark
Exercises: Analysing ChIP-Seq data
 Exercises: Analysing ChIP-Seq data Version 2018-03-2 Exercises: Analysing ChIP-Seq data 2 Licence This manual is 2018, Simon Andrews. This manual is distributed under the creative commons Attribution-Non-Commercial-Share
Exercises: Analysing ChIP-Seq data Version 2018-03-2 Exercises: Analysing ChIP-Seq data 2 Licence This manual is 2018, Simon Andrews. This manual is distributed under the creative commons Attribution-Non-Commercial-Share
Assemblytics: a web analytics tool for the detection of assembly-based variants Maria Nattestad and Michael C. Schatz
 Assemblytics: a web analytics tool for the detection of assembly-based variants Maria Nattestad and Michael C. Schatz Table of Contents Supplementary Note 1: Unique Anchor Filtering Supplementary Figure
Assemblytics: a web analytics tool for the detection of assembly-based variants Maria Nattestad and Michael C. Schatz Table of Contents Supplementary Note 1: Unique Anchor Filtering Supplementary Figure
Using mutants to clone genes
 Using mutants to clone genes Objectives: 1. What is positional cloning? 2. What is insertional tagging? 3. How can one confirm that the gene cloned is the same one that is mutated to give the phenotype
Using mutants to clone genes Objectives: 1. What is positional cloning? 2. What is insertional tagging? 3. How can one confirm that the gene cloned is the same one that is mutated to give the phenotype
Ensembl workshop. Thomas Randall, PhD bioinformatics.unc.edu. handouts, papers, datasets
 Ensembl workshop Thomas Randall, PhD tarandal@email.unc.edu bioinformatics.unc.edu www.unc.edu/~tarandal/ensembl handouts, papers, datasets Ensembl is a joint project between EMBL - EBI and the Sanger
Ensembl workshop Thomas Randall, PhD tarandal@email.unc.edu bioinformatics.unc.edu www.unc.edu/~tarandal/ensembl handouts, papers, datasets Ensembl is a joint project between EMBL - EBI and the Sanger
File S1. Program overview and features
 File S1 Program overview and features Query list filtering. Further filtering may be applied through user selected query lists (Figure. 2B, Table S3) that restrict the results and/or report specifically
File S1 Program overview and features Query list filtering. Further filtering may be applied through user selected query lists (Figure. 2B, Table S3) that restrict the results and/or report specifically
A Hidden Markov Model for Identification of Helix-Turn-Helix Motifs
 A Hidden Markov Model for Identification of Helix-Turn-Helix Motifs CHANGHUI YAN and JING HU Department of Computer Science Utah State University Logan, UT 84341 USA cyan@cc.usu.edu http://www.cs.usu.edu/~cyan
A Hidden Markov Model for Identification of Helix-Turn-Helix Motifs CHANGHUI YAN and JING HU Department of Computer Science Utah State University Logan, UT 84341 USA cyan@cc.usu.edu http://www.cs.usu.edu/~cyan
Functional Enrichment Analysis & Candidate Gene Ranking
 Functional Enrichment Analysis & Candidate Gene Ranking Contact Information: Anil Jegga Biomedical Informatics Room # 232, S Building 10th Floor CCHMC Homepage: http://anil.cchmc.org Tel: 513 636 0261
Functional Enrichment Analysis & Candidate Gene Ranking Contact Information: Anil Jegga Biomedical Informatics Room # 232, S Building 10th Floor CCHMC Homepage: http://anil.cchmc.org Tel: 513 636 0261
KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
 1999 Oxford University Press Nucleic Acids Research, 1999, Vol. 27, No. 1 29 34 KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes Hiroyuki Ogata, Susumu Goto, Kazushige Sato, Wataru Fujibuchi, Hidemasa Bono
1999 Oxford University Press Nucleic Acids Research, 1999, Vol. 27, No. 1 29 34 KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes Hiroyuki Ogata, Susumu Goto, Kazushige Sato, Wataru Fujibuchi, Hidemasa Bono
Promoter Prediction (really) 10/26/05
 10/26/05 Promoter Prediction (really!) Announcements BCB Link for Seminar Schedules (updated) http://www.bcb.iastate.edu/seminars/inde.html Seminar (Fri Oct 28) 12:10 PM BCB Faculty Seminar in E164 Lagomarcino
10/26/05 Promoter Prediction (really!) Announcements BCB Link for Seminar Schedules (updated) http://www.bcb.iastate.edu/seminars/inde.html Seminar (Fri Oct 28) 12:10 PM BCB Faculty Seminar in E164 Lagomarcino
SSA Signal Search Analysis II
 SSA Signal Search Analysis II SSA other applications - translation In contrast to translation initiation in bacteria, translation initiation in eukaryotes is not guided by a Shine-Dalgarno like motif.
SSA Signal Search Analysis II SSA other applications - translation In contrast to translation initiation in bacteria, translation initiation in eukaryotes is not guided by a Shine-Dalgarno like motif.
Wheat Genome Structural Annotation Using a Modular and Evidence-combined Annotation Pipeline
 Wheat Genome Structural Annotation Using a Modular and Evidence-combined Annotation Pipeline Xi Wang Bioinformatics Scientist Computational Life Science Page 1 Bayer 4:3 Template 2010 March 2016 17/01/2017
Wheat Genome Structural Annotation Using a Modular and Evidence-combined Annotation Pipeline Xi Wang Bioinformatics Scientist Computational Life Science Page 1 Bayer 4:3 Template 2010 March 2016 17/01/2017
PromAn: an integrated knowledge-based web server dedicated to promoter analysis
 W578 W583 Nucleic Acids Research, 2006, Vol. 34, Web Server issue doi:10.1093/nar/gkl193 PromAn: an integrated knowledge-based web server dedicated to promoter analysis Aurélie Lardenois, Frédéric Chalmel
W578 W583 Nucleic Acids Research, 2006, Vol. 34, Web Server issue doi:10.1093/nar/gkl193 PromAn: an integrated knowledge-based web server dedicated to promoter analysis Aurélie Lardenois, Frédéric Chalmel
TRED: a Transcriptional Regulatory Element Database, new entries and other development
 TRED: a Transcriptional Regulatory Element Database, new entries and other development Authors: C. Jiang 1,2, Z. Xuan 1, F. Zhao 1 and M.Q. Zhang 1 * Affiliations: 1 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, 1 Bungtown
TRED: a Transcriptional Regulatory Element Database, new entries and other development Authors: C. Jiang 1,2, Z. Xuan 1, F. Zhao 1 and M.Q. Zhang 1 * Affiliations: 1 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, 1 Bungtown
NCBI & Other Genome Databases. BME 110/BIOL 181 CompBio Tools
 NCBI & Other Genome Databases BME 110/BIOL 181 CompBio Tools Todd Lowe March 31, 2011 Admin Reading Dummies Ch 3 Assigned Review: "The impact of next-generation sequencing technology on genetics" by E.
NCBI & Other Genome Databases BME 110/BIOL 181 CompBio Tools Todd Lowe March 31, 2011 Admin Reading Dummies Ch 3 Assigned Review: "The impact of next-generation sequencing technology on genetics" by E.
Computational Analysis of Ultra-high-throughput sequencing data: ChIP-Seq
 Computational Analysis of Ultra-high-throughput sequencing data: ChIP-Seq Philipp Bucher Wednesday January 21, 2009 SIB graduate school course EPFL, Lausanne Data flow in ChIP-Seq data analysis Level 1:
Computational Analysis of Ultra-high-throughput sequencing data: ChIP-Seq Philipp Bucher Wednesday January 21, 2009 SIB graduate school course EPFL, Lausanne Data flow in ChIP-Seq data analysis Level 1:
Supplement to: The Genomic Sequence of the Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO)-K1 cell line
 Supplement to: The Genomic Sequence of the Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO)-K1 cell line Table of Contents SUPPLEMENTARY TEXT:... 2 FILTERING OF RAW READS PRIOR TO ASSEMBLY:... 2 COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS... 2 IMMUNOGENIC
Supplement to: The Genomic Sequence of the Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO)-K1 cell line Table of Contents SUPPLEMENTARY TEXT:... 2 FILTERING OF RAW READS PRIOR TO ASSEMBLY:... 2 COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS... 2 IMMUNOGENIC
Next Generation Sequencing
 Next Generation Sequencing Complete Report Catalogue # and Service: IR16001 rrna depletion (human, mouse, or rat) IR11081 Total RNA Sequencing (80 million reads, 2x75 bp PE) Xxxxxxx - xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Next Generation Sequencing Complete Report Catalogue # and Service: IR16001 rrna depletion (human, mouse, or rat) IR11081 Total RNA Sequencing (80 million reads, 2x75 bp PE) Xxxxxxx - xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
EECS 730 Introduction to Bioinformatics Sequence Alignment. Luke Huan Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 EECS 730 Introduction to Bioinformatics Sequence Alignment Luke Huan Electrical Engineering and Computer Science http://people.eecs.ku.edu/~jhuan/ Database What is database An organized set of data Can
EECS 730 Introduction to Bioinformatics Sequence Alignment Luke Huan Electrical Engineering and Computer Science http://people.eecs.ku.edu/~jhuan/ Database What is database An organized set of data Can
Il trascrittoma dei mammiferi
 29 Novembre 2005 Il trascrittoma dei mammiferi dott. Manuela Gariboldi Gruppo di ricerca IFOM: Genetica molecolare dei tumori (responsabile dott. Paolo Radice) Copyright 2005 IFOM Fondazione Istituto FIRC
29 Novembre 2005 Il trascrittoma dei mammiferi dott. Manuela Gariboldi Gruppo di ricerca IFOM: Genetica molecolare dei tumori (responsabile dott. Paolo Radice) Copyright 2005 IFOM Fondazione Istituto FIRC
Protein Bioinformatics Part I: Access to information
 Protein Bioinformatics Part I: Access to information 260.655 April 6, 2006 Jonathan Pevsner, Ph.D. pevsner@kennedykrieger.org Outline [1] Proteins at NCBI RefSeq accession numbers Cn3D to visualize structures
Protein Bioinformatics Part I: Access to information 260.655 April 6, 2006 Jonathan Pevsner, Ph.D. pevsner@kennedykrieger.org Outline [1] Proteins at NCBI RefSeq accession numbers Cn3D to visualize structures
Transcription Start Sites Project Report
 Transcription Start Sites Project Report Student name: Student email: Faculty advisor: College/university: Project details Project name: Project species: Date of submission: Number of genes in project:
Transcription Start Sites Project Report Student name: Student email: Faculty advisor: College/university: Project details Project name: Project species: Date of submission: Number of genes in project:
