The Prevalence of Resistance to Methicillin in Staphylococcus aureus Strains Isolated from Patients by PCR Method for Detection of meca and nuc Genes
|
|
|
- Arron Parks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Iranian J Publ Health, Vol. 43, No. 1, Jan 2014, pp Original Article The Prevalence of Resistance to Methicillin in Staphylococcus aureus Strains Isolated from Patients by PCR Method for Detection of meca and nuc Genes Roxana SAHEBNASAGH 1, *Horieh SADERI 2, Parviz OWLIA 3 1. Dept. of Microbiology, Zanjan Branch, Islamic Azad University, Zanjan, Iran 2. Molecular Microbiology Research Center, Shahed University, Tehran, Iran 3. Dept. of Microbiology, School of Medicine, Shahed University, Tehran, Iran *Corresponding Author: Saderih@yahoo.com (Received 13 Aug 2013; accepted 16 Nov 2013) Abstract Background: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is the main cause of hospital infection emerged over the last decades. Rapid detection of MRSA is important for patient care and proper usage of infection control. Detection of meca genes (encoding resistance to methicillin and other similar antibiotics) and nuc genes (encoding staphylococcal thermostable nuclease) by PCR method is now considered for rapid identification of MRSA strain. The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence of MRSA isolated from patients in Tehran, Iran by PCR method for detection of meca and nuc genes. Methods: Phenotypic method such as microscopic and colony morphology and catalase and coagulase tests were used for identification of S. aureus isolates. DNA was extracted from all isolates and the presence of nuc and meca gene was detected by PCR method. For determination of MRSA by phenotypic methods, oxacillin disk diffusion test were used. Data were analyzed by SPSS software. Results: Out of 126 clinical sample identified by phenotypic method, 101 isolates had nuc gene. In disk diffusion tests by oxacillin disk, 78.2% of isolates were considered to be MRSA, but in PCR method for meca gene, 69% isolates were positive. Conclusions: The results showed a high prevalence of methicillin-resistance among S. aureus isolates. Identifying MRSA strains, isolating MRSA-positive patients and carrier s treatment in a hospital to prevent MRSA infection is important in limiting the spread of MRSA. The PCR method for detection of nuc and meca genes has potential for rapid and accurate diagnosis of MRSA strains. Keywords: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, MRSA, meca, nuc Introduction Staphylococcus aureus is one of the most important human pathogens, causing a wide range of nosocomial and community acquired infections, from mild skin and soft tissue infections to wound infections and bacteriemia (1). Currently several methods are used to distinguish S. aureus from other bacteria, which include culture methods, followed Gram s staining, grow in mannitol salt agar and fermentation of mannitol and catalase and coagulase tests; however these routine methods are time consuming and cumbersome and the accuracy of most of them has constantly been questioned the course of over time (2). PCR-based method is used as the single most reliable and 84 Available at:
2 Sahebnasagh et al.: The Prevalence of Resistance to Methicillin sensitive test for accurate and rapid identification of S. aureus (3). S. aureus produces an extracellular thermostable nuclease, encoded by nuc gene, which is one of the most distinguishing and successful characteristics that might be used for distinguishing S. aureus from other staphylococcus spp. This suggests that nuc gene is a specific marker gene and PCR is a useful method for identifying this gene in S. aureus (4). Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) is a variant of S. aureus bacteria that has evolved resistance to methicillin and other antibiotics including all other beta lactams, aminoglycosides and macrolides (5). Chromosome and plasmids mediated resistance to antimicrobial agents in S. aureus strains (6). Methicillin resistance in MRSA is mediated by the presence of 78-kDa penicillin binding protein PBP2 (or PBP2a) which has a very low affinity for beta-lactam antibiotics. PBP2a is encoded by the meca gene (7). meca gene is located on a mobile genetic element (from 21-to 67-kb), that is called staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec elements (SCCmec) (8). The first strain of MRSA was reported in the UK and Europe in 1961, just less than 1 year after the introduction of methicillin for clinical use. Since that time, MRSA has become a major public health problem worldwide and the prevalence of MRSA has been dramatically rising in recent years (9). Thus, rapid and exact methods for identification of MRSA in clinical specimens are essential for accurate diagnosis and antimicrobial therapy (10). Disk diffusion method and agar dilution method are the most commonly used methods in routine clinical diagnostic laboratories to determine methicillin resistance; but these methods have low specificity in detection of methicillin resistance and by the mere results of disk diffusion methods or agar dilution methods, the true prevalence of MRSA cannot be determined (11). Using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method for detection of meca gene is considered as the gold standard method for the detection and identification of prevalence of MRSA and has been described in recently published reports (12). The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence of resistance to methicillin in S. aureus isolated from patients in Tehran, Iran, by combination of phenotypic and genotypic (PCR method for detection of meca and nuc genes) methods. Materials and Methods Identification of S. aureus isolates A total of 126 Staphylococcus aureus isolates were collected from January 2008 to June 2008 from various clinical specimens of patients admitted to four university hospitals (Imam Khomeini, Mostafa Khomeini, Shariati, Motahari) in Tehran, Iran. These isolates were transferred to Microbiology Department of Medical School of Shahed University. Multiple isolates from the same patients, even if the site of infection was different, were excluded. After prepare the new cultures of isolates, Gram s staining were done on isolates smear to ensure the absence of contamination and study of bacteria morphology. All isolates were reconfirmed and identified as S. aureus based on colony and microscopic morphology (grape-like Gram-positive cocci) and positivity in catalase and coagulase tests. Altogether, 126 isolates were collected and stored at -70 C in freezing medium (nutrient broth containing 15% glycerol). Growth on mannitol salt agar medium and fermentation of mannitol were also checked for all isolates. Detection of methicillin resistance by phenotypic method Disk diffusion test was performed by oxacillin (1µg) disk (MAST Diagnostics, UK) on Mueller Hinton agar (Merck, Germany) plate inoculated by each isolate according to the Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines (13). Control strain was S. aureus ATCC Intermediateresistant strains were considered resistant. DNA extraction For rapid DNA extraction, five colonies from overnight growth on brain heart infusion (BHI) agar plates were picked up and suspended in 500 µl of sterile distilled water. The suspension was then heated at 100 C for 15 min. After Available at: 85
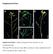
3 Iranian J Publ Health, Vol. 43, No.1, Jan 2014, pp centrifugation for 5 min at 14,000 rpm to sediment the debris, the clear supernatant was used as template DNA in PCR method (14). Primers for PCR All primers used in this study were synthesized and purchased from Cinnagen Company (Tehran, Iran), according to sequences obtained from Gen- Bank and compared with the sequence of nuc and meca genes published by Zhang et al. (4). The primer sequences were as follows: Nuc1 (5'-GCG ATT GAT GGT GAT ACG GTT-3') and Nuc2 (5 -AGC CAA GCC TTG ACG AAC TAA AGC- 3 ), for nuc gene, and MecA1 (5'-CCA ATT CCA CAT TGT TTC GGT CAT A- 3') and MecA2 (5'- GTA GAA ATG ACT GAA CGT CCG ATA A - 3') ), for meca gene. Molecular detection of nuc gene by PCR method PCR method were performed in a final volume of 20µl, containing 2 µl of template DNA, 2 µl of PCR buffer (10x), 1 µl of MgCl 2 (50mM), 4 µl of dntps (1mM), 1 µl of each Nuc1 and Nuc2 primers (10 Pmol), 0.25 µl of Taq DNA polymerase (5u/µl) and 8.75 µl of double distilled water. All materials were purchased from Cinnagen Company (Tehran, Iran). PCR amplifications were performed with Techne thermocycler (Touchgene Gradient, UK), using the following cycle conditions: an initial denaturation step at 94 C for 5 min; 30 cycles of 94 C for 1 min, 50 C for 1 min, and 72 C for 2 min, and a final extension step at 72 C for 10 min. The PCR products were electrophoresed in 2% agarose gels with 1X Tris-acetate- EDTA (TAE) buffer at 100V for 100 min and then gels were stained with ethidium bromide (Cinnagen Co., Tehran, Iran) to see the amplified DNA fragments (279 bp) under UV light box by comparison with a molecular size marker (100 bp ladders, eurobio, UK). Positive and negative controls were S. aureus ATCC29213 and molecular grade water, respectively (4). Detection of meca gene by PCR method The PCR reactions were carried out in a 20 µl reaction volume, containing 2 µl of template DNA, 2 µl of PCR buffer (10x), 1 µl of MgCl 2 (50mM), 4 µl of dntps (1mM), 4 µl of each MecA1 and MecA2 primers (10 Pmol), 0.25 µl of Taq DNA polymerase (5u/µl), and 2.75 µl of double distilled water. All materials were purchased from Cinnagen Company (Tehran, Iran). Thermocycling conditions in a Techne thermocycler (Touchgene Gradient,UK), were as follows: an initial denaturation step at 94 C for 5 min, followed by 30 cycles of 94 C for 30 sec, 52 C for 30 sec, and 72 C for 30 sec, with a final extension at 72 C for 5 min. PCR products were run on 2% agarose gel and analyzed as described above for amplified DNA (310 bp). Methicillin resistant S. aureus clinical isolate containing meca gene and molecular grade water were used as positive and negative controls, respectively (4). All the personal information of the patients was remained private during all steps of the research. Results A total of 126 isolates were identified as S. aureus by routine phenotypic methods including Gram s staining, colony morphology and catalase and coagulase test. The results of culture on mannitol salt agar have shown that, 95 (75.9%) of isolates showed positive results with grown on mannitol salt agar and fermentation of mannitol. Thus culture on mannitol salt agar to identify S. aureus, is not able to make a definite identification alone. Figure 1 show image of agarose gel electrophoresis after amplification of nuc gene (279 bp) for some isolates by PCR method. By applying PCR method, among the 126 clinical samples that were identified as S. aureus with phenotypic methods, 101 (80.2%) isolates were found to be nuc positive (Fig. 1). The presence of some discrepancies between the results of phenotypic and genotypic methods for detection of S. aureus strain, make it clear that, the method for identification of nuc genes is not sufficient alone. So, phenotypic and genotypic methods together were used for identification of S. aureus strain. Table 1 to 3 shows the frequency of S. aureus isolates, accor- 86 Available at:
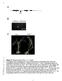
4 Sahebnasagh et al.: The Prevalence of Resistance to Methicillin ding to hospitals, admitted wards and type of clinical specimens. Table 1: Frequency of S. aureus isolates according to hospitals Hospital Number of S. aureus isolates Frequency distribution of strains (%) Imam Khomeini Mostafa Khomeini Motahari Shariati Total and clinical specimens were compared and significant differences were observed (Fig. 3 to 5). Table 2: Frequency of S. aureus isolates according to admitted wards/ Departments Wards/ Departments Number of S. aureus isolates Frequency distribution of strains (%) Operation 11 9 Intensive care unit Emergency 4 3 Respiratory Burn Internal Total Fig. 1: Image of agarose gel electrophoresis after amplification of nuc gene (270 bp) for some isolates by PCR method. Lane M is 100 bp DNA ladder, lanes 1 to 5 and 7 to 11 is nuc gene, NC: negative control, PC: positive control (S. aureus ATCC29213) Figure 2 show image of agarose gel electrophoresis after amplification of meca gene (310 bp) for some isolates by PCR method. From 126 S. aureus isolates, 87 (69%) isolates harbor the meca gene and identified as methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) and the remaining 39 (31%) isolates were methicillin-susceptible (MSSA). By disk diffusion test, among 126 isolates of S. aureus, 98 (78.2%) of isolates were determined MRSA and 21.8% MSSA. The results of comparison between the phenotypic and genotypic methods are displayed in Table 2. Frequency distribution (percentage) of MRSA and MSSA isolates according to different hospital, admitted wards Fig. 2: Image of agarose gel electrophoresis after amplification of meca gene (310 bp) for some isolates by PCR method. Lane M is molecular size marker (100 bp DNA ladder), lanes 3 to 6, 8 and 11 is meca gene, PC: Positive control (Methicillin resistant S. aureus clinical isolate containing meca gene), NC: Negative control Table 3: Frequency of S. aureus isolates according to type of clinical specimens Origin Number of S. aureus isolates Frequency distribution of strains (%) Respiratory Wound Blood Urine Others Total Available at: 87
5 Iranian J Publ Health, Vol. 43, No.1, Jan 2014, pp In this study, there was no significant difference between MRSA and MSSA isolates regarding the prevalence of presence of nuc gene; the nuc genes were observed in 69 (79.3%) of the MRSA isolates (out of 87 isolates) and in 32 (82.1%) of the MSSA isolates (out of 39 isolates). Table 4: Number of MRSA and MSSA strains detected by oxacillin disk diffusion test and PCR method for comparison of used tests for 126 strains Result in PCR method Disk diffusion test MRSA MSSA MRSA MSSA MRSA MSSA Imam Khomeini Mostafa Khomeini Motahari Shariati Fig 3: Frequency distribution of MRSA and MSSA isolates in hospitals. Most of MRSA strains were obtained from Imam Khomeini, Mostafa Khomeini and Motahari Hospitals, while most of MSSA strains were obtained from Shariati Hospital MRSA MSSA Operation ICU Respiratory Internal Fig. 4: Frequency distribution of MRSA and MSSA isolates in wards. The majority of the strains obtained from different hospital wards were identified as MRSA strains, except the respiratory ward that the prevalence of MRSA and MSSA were almost same 88 Available at:
6 Sahebnasagh et al.: The Prevalence of Resistance to Methicillin MRSA MSSA Wound Blood Respiratory Other Fig. 5: Frequency distribution of MRSA and MSSA isolates in clinical specimens. The prevalence of MRSA strains in all clinical specimens was significantly higher than MSSA, except for wounds specimen. Discussion MRSA is type of S. aureus that has developed resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics and is responsible for community-associated and nosocomial infections (8,15). Therefore, finding the rapid and accurate techniques for identification of these bacteria, can contribute to the rapid diagnosis and timely treatment of infections. Currently, various laboratory methods for detecting S. aureus and MRSA strains have been reported (16). The conventional phenotypic methods have a high ability to detect S. aureus and MRSA strains and they are still widely used in clinical laboratories as routine identifications tests. But phenotypic methods have some disadvantages. So many studies are being conducted to improve and increase the sensitivity and specificity of methods for determination of S. aureus. On the other hand, there is still no consensus on the best rapid and accurate detection method with high sensitivity; therefore, many articles are published about the comparison of different rapid methods for the detection of these bacteria and advantages of each technique (3). Our study showed that the mannitol salt agar test was negative for 5% of S. aureus isolates; as this shown in other studies (17, 18). S. aureus can be easily identified by PCR amplification of nuc gene; therefore, nuc gene has been used for the detection of S. aureus by some researchers (15, 19). The diagnostic values for detection of nuc gene by PCR based method were 93.3% sensitivity and 89.6% specificity (1). Brakstad et al. used the nuc gene as target DNA to identify S. aureus strains and recorded amplification product of nuc gene at 279 bp region for all 90 of 90 reference clinical isolates of S. aureus (20). Therefore, we used primers of their study in our project. A high percentage (80.2%) of S. aureus isolates were positive for the presence of nuc gene, that can confirm the ability of PCR method as fast and reliable method for detection of the nuc gene to identify S. aureus strains. However, some phenotypically S. aureus isolates were shown negative result probably due to non-optimal experimental conditions for PCR method, the differences in the nucleotide sequence among the nuc genes caused by some mutation or the absence of nuc gene in some S. aureus strains. So it just seems that, a negative PCR method result for nuc Available at: 89
7 Iranian J Publ Health, Vol. 43, No.1, Jan 2014, pp gene cannot prove the absence of S. aureus among clinical isolates. In this study, we used phenotypic (oxacillin disk diffusion test) and genotypic (PCR method for meca gene) methods for detection of MRSA. The results of our study showed that 78.2% and 69% of S. aureus isolates were recognized as MRSA by disc diffusion test and PCR method, respectively. Whenever 107 (84.9%) of isolates had shown similar results in phenotypic and genotypic assays, 10 (8.3%) of isolates were meca-positive in PCR but methicillin sensitive in disk diffusion test. This could be attributed to not consistently expression of meca gene. Besides, 19 (15.1%) of the phenotypically methicillin-resistant strains were negative for meca gene. This resistance can be due to the presence of other resistance mechanisms, such as large amounts of produced beta-lactamase or the lack of optimal PCR conditions or change in meca gene due to the mutations. Phenotypically methicillin resistant strains without meca gene and methicillin sensitive strains harboring meca gene are also shown in other studies (21, 22). Considering that detection of the meca gene by PCR method is gold standard method for identifying methicillin resistance in S. aureus isolates, the prevalence of MRSA in this study have determined 69%. This prevalence of MRSA is high and comparable to results of other studies in Tehran, Iran; 53% by Rahbar et al. (23) and 88% by Rahimi et al. (24). This prevalence is also similar to other international studies performed in other areas, such as United States, France, Canada, Australia, European countries (25-28). This study also demonstrates that the distribution of MRSA isolates vary in different hospital wards. This definitely shows that some patients are more likely to catch infection (26). In the present study, the maximum and minimum isolation of MRSA was from ICU and emergency ward respectively; as CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) reported that in the United States, more than 50% of S. aureus isolates in ICU and 40% of S. aureus infections in other hospital units are methicillin resistant (29). In this study, the prevalence of MRSA was significantly different among various clinical specimens and MRSA isolates showed higher prevalence in most clinical specimens (except wounded samples). The variation in prevalence of MRSA among S. aureus isolated from various specimens might be due to the variation in antibiotics usage, infection control practices in different hospitals and prolonged antibiotic treatment of severely sick patients, who generally stay longer in hospital (28). Finally, this study has demonstrated a high prevalence of MRSA, regarding this problem in community, the identification of MRSA in isolates by PCR method, offers a very specific, sensitive and relatively rapid alternative to conventional assays. Moreover, due to the absence of meca gene in some isolates of MRSA, the use of both phenotypic and genotypic tests combined may provide the best information for obtaining general result for detection of MRSA strains. Conclusion Considering a significant increase in the prevalence of methicillin-resistance in S. aureus strains caused by the indiscriminate and excessive use of antibiotics during the last decade, our study emphasize on identifying MRSA isolates, isolating MRSA-positive patients and carrier s treatment in a hospital to establish effective measures to prevent MRSA infection. This study shows that PCR method is a useful method for detection of nuc and meca genes which leads to rapid detection and identification of MRSA cultured from patient s specimens (in less than 6 h) and may provide substantial benefits for infection control by allowing prompt and cost-effective implementation of contact precautions. Here, it is suggested that in order to obtain more reliable results, further studies about the distribution of isolates according to different variables are required. Ethical considerations Ethical issues (Including plagiarism, Informed Consent, misconduct, data fabrication and/or falsification, double publication and/or submission, redundancy, etc.) have been completely observed by the authors. 90 Available at:
8 Sahebnasagh et al.: The Prevalence of Resistance to Methicillin Acknowledgement We thank the services of the Islamic Azad University of Zanjan. This study was done as a Master of Science thesis in Zanjan Branch of Islamic Azad University. The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest. References 1. Fang H, Hedin G (2003). Rapid screening and identification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from clinical samples by selectivebroth and real-time PCR assay. J Clin Microb, 41(7): Ihab M, Atef M (2009). Molecular characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus recovered from outpatient clinics in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med J, 30(5): Brown DF, Edwards DI, Hawkey PM, Morrison D, Ridgway GL, Towner KJ et al. (2005). Guidelines for the laboratory diagnosis and susceptibility testing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). J Antimicrob Chemother, 56: Zhang K, Sparling J, Chow BL, Elsayed S, Hussain Z, Church DL et al. (2004). New quadriplex PCR assay for detection of methicillin and mupirocin resistance and simultaneous discrimination of Staphylococcus aureus from coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Microb, 42(11): Choi S, Kim S, Kim S, Lee D, Choi J et al. (2003). Multiplex PCR for the detection of genes encoding aminoglycoside modifying enzymes and methicillin resistance among staphylococcus species. J Korean Med Sci, 18: Lowy FD (2003). Antimicrobial resistance: the example of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Invest, 111(9): Moreillon P (2008). New and emerging treatment of staphylococcus aureus infections in the hospital setting. Clin Microbiol Infect, 14 (3): Ammons DR, Puttagunta R, Granados J, Garza G, Eyambe G, Rampersad J (2010). An exploratory study of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus and SCCmec elements obtained from a community setting along the Texas border with Mexico. Curr Microbiol, 60: Louie L, Goodfellow J, Mathieu P, Glatt A, Louie M et al. (2002). Rapid detection of methicillinresistant staphylococci from blood culture bottles by using a multiplex PCR assay. J Clin Microb, 40(8): Huletsky A, Giroux R, Rossbach V, Gagnon M, Vaillancourt M (2004). New Real-Time PCR Assay for Rapid Detection of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Directly from Specimens Containing a Mixture of Staphylococci. J Clin Microb, 42(5): Cho, IL J, Jung H, Kim Y, Park S, Ha S, Kim S (2007). Detection of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus isolates using two-step triplex PCR and conventional methods. J Microbiol Biotechnol, 17(4): Woods S, Beiter E, Drake B, Engel A (2011). The prevalence of asymptomatic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in school-age children. Eastern J Med, 16: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (2006). Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; 16th informational supplement. M100-S16. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA. 14. Perez-Roth E, Claverie-Martin F, Villar J, Mendez-Alvarez S (2001). Multiplex PCR for simultaneous identification of Staphylococcus aureus and detection of methicillin and mupirocin resistance. J Clin Microb,39: Kilic A, Muldrew KL, Tangc YW, Basustaoglua AC (2010). Triplex real-time polymerase chain reaction assay for simultaneous detection of Staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci and determination of methicillin resistance directly from positive blood culture bottles. Diagn Microb Infect Dis, 66: Iraz M, Tekerekoglu M, Otlu B, Ay S (2012). Comparison of an automated system with four phenotypic methods for the detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Afr J Microb Res, 6(4): Ishii Y, Alba J, Maehara C, Murakami H, Matsumoto T, Tateda K et al. (2006). Identification of biochemically atypical Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates with three automated identification systems. J Med Microb, 55: Available at: 91
9 Iranian J Publ Health, Vol. 43, No.1, Jan 2014, pp Han Z, Lautenbach E, Fishman N, Nachamkin I (2007). Evaluation of mannitol salt agar, CHROM agar Staphylococcus aureus and CHROM agar MRSA for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from nasal swab specimens. J Med Microb, 56: Tang J, Zhou R, Shi X, Kang M, Wang H, Chen H (2008). Two thermostable nucleases coexisted in Staphylococcus aureus: evidence from mutagenesis and invitro expression. FEMS Microbiol Lett, 284: Brakstad OG, Aasbakk K, Maeland JA (1992). Detection of Staphylococcus aureus by polymerase chain reaction amplification of the nuc gene. J Clin Microb, 30(7): Jain A, Agarwal J, Bansal S (2004). Prevalence of methicillin-resistant, coagulase-negative staphylococci in neonatal intensive care units: findings from a tertiary care hospital in India. J Med Microbiol, 53: Rallapalli S, Verghese S, Verma RS (2006). Validation of multiplex PCR strategy for simultaneous detection and identification of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Indian J Med Micro, 26(4): Rahbar M, YaghoobiM, Fattahi A (2006). Comparison of different laboratory methods for detection of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Pak J Med Sci, 22(4): Rahimi F, Bouzari M, Vandyousefi J, Maleki Z, Saberi Kashani S et al. (2009). Analysis of antibiotic resistance and detection of meca gene in Staphylococcus aureus isolated from hospitals and medical laboratories in Tehran. Irn J Biol, 21(1): Fatholahzadeh B, Emaneini M, Gilbert G, Udo E, Aligholi M, Modarressi (2008). Staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) analysis and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolates in Tehran, Iran. Microbial Drug Resis, 14(3): Merlino J, Watson J, Rose B (2002). Detection and expression of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus in central Sydney,Australia. J Clin Microb. 49: Mamishi S, Pourakbari B, Ashtiani MH, Hashemi FB (2005). Frequency of isolation and antimicrobial susceptibility of bacteria isolated from bloodstream infections at Children's Medical Center, Tehran, Iran, Int J Antimicrob Agents, 26(5): Carvalho MJ, Pimenta FC, Hayashida M, Gir E, Silva AM, Barbosa CP, Canini S, Santiago S (2009). Prevalence of methicillin resistant and methicillin susceptible S. aureus in the Saliva of health professionals. CLINICS, 64(4): Croft AC, Antoni AV, Terzulli SL (2007). Update on the antibacterial resistance Crisis. Med Sci Monit, 13 (6): Available at:
Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)- Background and analysis
 Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus ()- Background and analysis Outline Staphylococcus aureus Classification Ecology Commensal vs pathogenic S. aureus Definition Resistance determinant and mechanism
Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus ()- Background and analysis Outline Staphylococcus aureus Classification Ecology Commensal vs pathogenic S. aureus Definition Resistance determinant and mechanism
Engineering D66N mutant using quick change site directed mutagenesis. Harkewal Singh 09/01/2010
 Engineering D66N mutant using quick change site directed mutagenesis Harkewal Singh 09/01/2010 1 1- What is quick change site directed mutagenesis? 2- An overview of the kit contents. 3- A brief information
Engineering D66N mutant using quick change site directed mutagenesis Harkewal Singh 09/01/2010 1 1- What is quick change site directed mutagenesis? 2- An overview of the kit contents. 3- A brief information
EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT PRIMERS FOR DETECTING
 SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT PRIMERS FOR DETECTING MECA GENE BY PCR IN COMPARISON WITH PHENOTYPIC METHODS FOR DISCRIMINATION OF METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS
SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT PRIMERS FOR DETECTING MECA GENE BY PCR IN COMPARISON WITH PHENOTYPIC METHODS FOR DISCRIMINATION OF METHICILLIN-RESISTANT STAPHYLOCOCCUS
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
 TM Primerdesign Ltd Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) meca (penicillin binding protein 2) & S. aureus FEMB gene (chromosomal gene) genesig Advanced Kit 150 tests For general laboratory
TM Primerdesign Ltd Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) meca (penicillin binding protein 2) & S. aureus FEMB gene (chromosomal gene) genesig Advanced Kit 150 tests For general laboratory
Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC
 Supplementary Appendixes Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC ACG TAG CTC CGG CTG GA-3 for vimentin, /5AmMC6/TCC CTC GCG CGT GGC TTC CGC
Supplementary Appendixes Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC ACG TAG CTC CGG CTG GA-3 for vimentin, /5AmMC6/TCC CTC GCG CGT GGC TTC CGC
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit
 HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
HiPer RT-PCR Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM024 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 4 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis: 45 minutes Storage Instructions: The
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
 Laboratory for Environmental Pathogens Research Department of Environmental Sciences University of Toledo Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Background information The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is an
Laboratory for Environmental Pathogens Research Department of Environmental Sciences University of Toledo Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Background information The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is an
FMF NIRCA PROTOCOL STEP 1.
 FMF NIRCA PROTOCOL STEP 1. After you have isolated patient s DNA and DNA from a healthy donor (wild type), you perform a nested PCR. The primers used to amplify exon 2 and exon 10 of the mefv gene are
FMF NIRCA PROTOCOL STEP 1. After you have isolated patient s DNA and DNA from a healthy donor (wild type), you perform a nested PCR. The primers used to amplify exon 2 and exon 10 of the mefv gene are
MRSA GENSPEED MRSA. One test, two genes High sensitivity and short turnaround time.
 MRSA GENSPEED MRSA One test, two genes High sensitivity and short turnaround time www.genspeed-biotech.com MRSA? ü One test ü 2 genes GENSPEED MRSA Test System Full Speed just a few steps to reliable test
MRSA GENSPEED MRSA One test, two genes High sensitivity and short turnaround time www.genspeed-biotech.com MRSA? ü One test ü 2 genes GENSPEED MRSA Test System Full Speed just a few steps to reliable test
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Dissecting binding of a β-barrel outer membrane
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Dissecting binding of a β-barrel outer membrane
Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH).
 Bisulfite Treatment of DNA Dilute DNA sample to 2µg DNA in 50µl ddh 2 O. Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH). Incubate in a 37ºC water bath for 30 minutes. To 55µl samples
Bisulfite Treatment of DNA Dilute DNA sample to 2µg DNA in 50µl ddh 2 O. Add 5µl of 3N NaOH to DNA sample (final concentration 0.3N NaOH). Incubate in a 37ºC water bath for 30 minutes. To 55µl samples
strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular
![strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular strain devoid of the aox1 gene [1]. Thus, the identification of AOX1 in the intracellular](/thumbs/72/66361212.jpg) Additional file 2 Identification of AOX1 in P. pastoris GS115 with a Mut s phenotype Results and Discussion The HBsAg producing strain was originally identified as a Mut s (methanol utilization slow) strain
Additional file 2 Identification of AOX1 in P. pastoris GS115 with a Mut s phenotype Results and Discussion The HBsAg producing strain was originally identified as a Mut s (methanol utilization slow) strain
Ezy MIC Strip FEATURES AND ADVANTAGES
 Imipenem with & without EDTA Ezy MIC Strips (IPM+EDTA/IPM) (Imipenem + EDTA: 1-64 mcg/ml) (Imipenem : 4-256 mcg/ml) Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing For In Vitro Diagnostic use EM078 Not for Medicinal
Imipenem with & without EDTA Ezy MIC Strips (IPM+EDTA/IPM) (Imipenem + EDTA: 1-64 mcg/ml) (Imipenem : 4-256 mcg/ml) Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing For In Vitro Diagnostic use EM078 Not for Medicinal
Designing and creating your gene knockout Background The rada gene was identified as a gene, that when mutated, caused cells to become hypersensitive
 Designing and creating your gene knockout Background The rada gene was identified as a gene, that when mutated, caused cells to become hypersensitive to ionizing radiation. However, why these mutants are
Designing and creating your gene knockout Background The rada gene was identified as a gene, that when mutated, caused cells to become hypersensitive to ionizing radiation. However, why these mutants are
HiPer Random Amplification of Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) Teaching Kit
 HiPer Random Amplification of Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM031 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 3.5 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis:
HiPer Random Amplification of Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) Teaching Kit Product Code: HTBM031 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5 Duration of Experiment: Protocol: 3.5 hours Agarose Gel Electrophoresis:
Biofilm Protocol Optimization For Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Introduction. Materials and Methods. Culture Media, Incubation Time, and Biofilm Measurement
 Biofilm Protocol Optimization For Pseudomonas aeruginosa Culture Media, Incubation Time, and Biofilm Measurement Introduction In addition to the conventional arsenal of antibiotic resistance mechanisms
Biofilm Protocol Optimization For Pseudomonas aeruginosa Culture Media, Incubation Time, and Biofilm Measurement Introduction In addition to the conventional arsenal of antibiotic resistance mechanisms
PCR Laboratory Exercise
 PCR Laboratory Exercise Advance Protocol (updated 1/2018) Introduction Detection of TPA-25 Alu by PCR A Human DNA Fingerprinting Lab Protocol 1994 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory DNA Learning Center In this
PCR Laboratory Exercise Advance Protocol (updated 1/2018) Introduction Detection of TPA-25 Alu by PCR A Human DNA Fingerprinting Lab Protocol 1994 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory DNA Learning Center In this
MightyAmp DNA Polymerase Ver.3
 Cat. # R076A For Research Use MightyAmp DNA Polymerase Ver.3 Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Storage... 3 IV. General PCR Reaction Mix... 3 V. Primer Design...
Cat. # R076A For Research Use MightyAmp DNA Polymerase Ver.3 Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Storage... 3 IV. General PCR Reaction Mix... 3 V. Primer Design...
The Prevalence of TEM-1 gene causing resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics in Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from clinical samples and plasmid curing
 Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 11:557-561 The Prevalence of TEM-1 gene causing resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics
Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 11:557-561 The Prevalence of TEM-1 gene causing resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics
TaKaRa PCR Amplification Kit
 Cat. # R011 For Research Use TaKaRa PCR Amplification Kit Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Storage... 4 IV. Materials Required but not Provided... 4 V. Principle...
Cat. # R011 For Research Use TaKaRa PCR Amplification Kit Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Storage... 4 IV. Materials Required but not Provided... 4 V. Principle...
Site-directed mutagenesis of proteins
 IFM/Kemi Linköpings Universitet August 2013/LGM Labmanual Site-directed mutagenesis of proteins Figur 1: Flow-chart of the site-directed mutagenesis lab exercise 2 Site-specific mutagenesis Introduction
IFM/Kemi Linköpings Universitet August 2013/LGM Labmanual Site-directed mutagenesis of proteins Figur 1: Flow-chart of the site-directed mutagenesis lab exercise 2 Site-specific mutagenesis Introduction
Quant One Step RT-PCR Kit
 1. Quant One Step RT-PCR Kit For fast and sensitive one-step RT-PCR www.tiangen.com/en RT121221 Quant One Step RT-PCR Kit Kit Contents Cat. no. KR113 Contents Hotmaster Taq Polymerase (2.5 U/μl) Quant
1. Quant One Step RT-PCR Kit For fast and sensitive one-step RT-PCR www.tiangen.com/en RT121221 Quant One Step RT-PCR Kit Kit Contents Cat. no. KR113 Contents Hotmaster Taq Polymerase (2.5 U/μl) Quant
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information A general solution for opening double-stranded DNA for isothermal amplification Gangyi Chen, Juan Dong, Yi Yuan, Na Li, Xin Huang, Xin Cui* and Zhuo Tang* Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Information A general solution for opening double-stranded DNA for isothermal amplification Gangyi Chen, Juan Dong, Yi Yuan, Na Li, Xin Huang, Xin Cui* and Zhuo Tang* Supplementary Materials
qpcr Kit, DNA-free Product components 100 rxn 250 rxn Product description
 qpcr Kit, DNA-free For the PCR detection and identification of bacterial and fungal DNA using custom primers Product code A8514 Product components 100 rxn 250 rxn A 2.5x mastermix (3 mm MgCl 2 final concentration)
qpcr Kit, DNA-free For the PCR detection and identification of bacterial and fungal DNA using custom primers Product code A8514 Product components 100 rxn 250 rxn A 2.5x mastermix (3 mm MgCl 2 final concentration)
Mycobacterium tuberculosis End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP42100
 3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Mycobacterium tuberculosis End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP42100
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Mycobacterium tuberculosis End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP42100
FOCUS ON MRSA/SA SSTI ASSAY FAILURE IN PROSTHETIC JOINT. Institute of Microbiology, Lille University Hospital, F Lille, France
 JCM Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 16 November 2016 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.01658-16 Copyright 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. FOCUS ON MRSA/SA SSTI ASSAY FAILURE
JCM Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 16 November 2016 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.01658-16 Copyright 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. FOCUS ON MRSA/SA SSTI ASSAY FAILURE
Bacterial 16S rdna PCR Kit Fast (800)
 Cat. # RR182A For Research Use Bacterial 16S rdna PCR Kit Fast (800) Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Materials Required but not Provided... 4 IV. Storage...
Cat. # RR182A For Research Use Bacterial 16S rdna PCR Kit Fast (800) Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Materials Required but not Provided... 4 IV. Storage...
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes
 Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 1, 2004 Prokaryotic Gene Structure prokaryotes are simplest free-living organisms studying prokaryotes can give us a sense what is the minimum
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 1, 2004 Prokaryotic Gene Structure prokaryotes are simplest free-living organisms studying prokaryotes can give us a sense what is the minimum
A portable microfluidic platform for rapid molecular diagnostic. testing of patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms
 A portable microfluidic platform for rapid molecular diagnostic testing of patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms Hua Wang 1, Xinju zhang 1, Xiao Xu 1, Qunfeng Zhang 1, Hengliang Wang 2, Dong Li 3,
A portable microfluidic platform for rapid molecular diagnostic testing of patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms Hua Wang 1, Xinju zhang 1, Xiao Xu 1, Qunfeng Zhang 1, Hengliang Wang 2, Dong Li 3,
SuperScript IV Reverse Transcriptase as a better alternative to AMV-based enzymes
 WHITE PAPER SuperScript IV Reverse Transcriptase SuperScript IV Reverse Transcriptase as a better alternative to AMV-based enzymes Abstract Reverse transcriptases (RTs) from avian myeloblastosis virus
WHITE PAPER SuperScript IV Reverse Transcriptase SuperScript IV Reverse Transcriptase as a better alternative to AMV-based enzymes Abstract Reverse transcriptases (RTs) from avian myeloblastosis virus
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1.
 Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL ACADEMIC RESEARCH FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY Impact Factor 1.393, ISSN: , Volume 2, Issue 8, September 2014
 EVALUATION OF CHROMAGAR-CTX FOR THE DETECTION OF CTX-M-ESBL- PRODUCING GRAM NEGATIVE BACTERIAL ISOLATES RASHA H. ELSHERIF* LAMIAA A. MADKOUR** REHAM A. DWEDAR*** *Clinical Pathology Department, Faculty
EVALUATION OF CHROMAGAR-CTX FOR THE DETECTION OF CTX-M-ESBL- PRODUCING GRAM NEGATIVE BACTERIAL ISOLATES RASHA H. ELSHERIF* LAMIAA A. MADKOUR** REHAM A. DWEDAR*** *Clinical Pathology Department, Faculty
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 10 Ver. VII (Oct. 2017), PP 76-81 www.iosrjournals.org Molecular Characterization of TEM, SHV
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 10 Ver. VII (Oct. 2017), PP 76-81 www.iosrjournals.org Molecular Characterization of TEM, SHV
KOD -Plus- Mutagenesis Kit
 Instruction manual KOD -Plus- Mutagenesis Kit 0811 F0936K KOD -Plus- Mutagenesis Kit SMK-101 20 reactions Store at -20 C Contents [1] Introduction [2] Flow chart [3] Components [4] Notes [5] Protocol 1.
Instruction manual KOD -Plus- Mutagenesis Kit 0811 F0936K KOD -Plus- Mutagenesis Kit SMK-101 20 reactions Store at -20 C Contents [1] Introduction [2] Flow chart [3] Components [4] Notes [5] Protocol 1.
Providing clear solutions to microbiological challenges TM. cgmp/iso CLIA. Polyphasic Microbial Identification & DNA Fingerprinting
 Providing clear solutions to microbiological challenges TM Cert. No. 2254.01 Polyphasic Microbial Identification & DNA Fingerprinting Microbial Contamination Tracking & Trending cgmp/iso-17025-2005 CLIA
Providing clear solutions to microbiological challenges TM Cert. No. 2254.01 Polyphasic Microbial Identification & DNA Fingerprinting Microbial Contamination Tracking & Trending cgmp/iso-17025-2005 CLIA
Fungal rdna (D1/D2) PCR Kit Fast
 Cat. # RR184A For Research Use Fungal rdna (D1/D2) PCR Kit Fast Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Materials Required but not Provided... 4 IV. Storage... 4 V.
Cat. # RR184A For Research Use Fungal rdna (D1/D2) PCR Kit Fast Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Materials Required but not Provided... 4 IV. Storage... 4 V.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Its Applications
 Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Its Applications What is PCR? PCR is an exponentially progressing synthesis of the defined target DNA sequences in vitro. It was invented in 1983 by Dr. Kary Mullis,
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Its Applications What is PCR? PCR is an exponentially progressing synthesis of the defined target DNA sequences in vitro. It was invented in 1983 by Dr. Kary Mullis,
Department of Clinical Microbiology and Infection Control, The County Hospital of Halmstad, Sweden
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2005.01291.x Use of broth enrichment and real-time PCR to exclude the presence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in clinical samples: a sensitive screening
ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2005.01291.x Use of broth enrichment and real-time PCR to exclude the presence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in clinical samples: a sensitive screening
Mutating Asn-666 to Glu in the O-helix region of the taq DNA polymerase gene
 Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, April 2010; 5(1): 15-19 Received: Oct 2009 Accepted: Jan 2010 School of Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences 15 Isfahan University of Medical Sciences Original Article
Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences, April 2010; 5(1): 15-19 Received: Oct 2009 Accepted: Jan 2010 School of Pharmacy & Pharmaceutical Sciences 15 Isfahan University of Medical Sciences Original Article
2x PCR LongNova-RED PCR Master Mix
 2x PCR LongNova-RED Components RP85L 100 reactions (50 μl) RP85L-10 1000 reactions (50 μl) 2x PCR LongNova-RED 2 x 1.25 ml 20 x 1.25 ml PCR grade water 2 x 1.5 ml 20 x 1.5 ml Storage & Shiing Storage conditions
2x PCR LongNova-RED Components RP85L 100 reactions (50 μl) RP85L-10 1000 reactions (50 μl) 2x PCR LongNova-RED 2 x 1.25 ml 20 x 1.25 ml PCR grade water 2 x 1.5 ml 20 x 1.5 ml Storage & Shiing Storage conditions
Molekulargenetische Reagenzien. Raumtemperaturstabile PCR und qpcr Reagenzien
 Molekulargenetische Reagenzien Raumtemperaturstabile PCR und qpcr Reagenzien Polypeptide Stabilization Technology: Stability TAG Ice-free reaction set-up Our temperature stable enzymes allow you to change
Molekulargenetische Reagenzien Raumtemperaturstabile PCR und qpcr Reagenzien Polypeptide Stabilization Technology: Stability TAG Ice-free reaction set-up Our temperature stable enzymes allow you to change
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: (905) Fax: (905)
 3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com E.coli O157:H7 End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP41300 Product Insert
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com E.coli O157:H7 End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP41300 Product Insert
BIOLOGY Dr.Locke Lecture# 27 An Introduction to Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
 BIOLOGY 207 - Dr.Locke Lecture# 27 An Introduction to Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Required readings and problems: Reading: Open Genetics, Chapter 8.1 Problems: Chapter 8 Optional Griffiths (2008) 9
BIOLOGY 207 - Dr.Locke Lecture# 27 An Introduction to Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Required readings and problems: Reading: Open Genetics, Chapter 8.1 Problems: Chapter 8 Optional Griffiths (2008) 9
Sensitivity vs Specificity
 Viral Detection Animal Inoculation Culturing the Virus Definitive Length of time Serology Detecting antibodies to the infectious agent Detecting Viral Proteins Western Blot ELISA Detecting the Viral Genome
Viral Detection Animal Inoculation Culturing the Virus Definitive Length of time Serology Detecting antibodies to the infectious agent Detecting Viral Proteins Western Blot ELISA Detecting the Viral Genome
Inoculate: Media. Physical State of Media: Liquid. The Five I s: Basic Techniques to Culture Microbes Tools of the Microbiology Laboratory
 The Five I s: Basic Techniques to Culture Microbes Tools of the Microbiology Laboratory 1. Inoculate 2. Incubate 3. Isolate 4. Inspect 5. Identify The Five I s: Inoculate Inoculate: Media Classified according
The Five I s: Basic Techniques to Culture Microbes Tools of the Microbiology Laboratory 1. Inoculate 2. Incubate 3. Isolate 4. Inspect 5. Identify The Five I s: Inoculate Inoculate: Media Classified according
Rapid Bacterial Identification Using a Mass Spectrometry Based Molecular Diagnostics Approach: Evaluation of the Iridica Platform
 Rapid Bacterial Identification Using a Mass Spectrometry Based Molecular Diagnostics Approach: Evaluation of the Iridica Platform Alec Saitman, PhD, Jane Y. Yang PhD, Sharon Reed, David Pride, Michele
Rapid Bacterial Identification Using a Mass Spectrometry Based Molecular Diagnostics Approach: Evaluation of the Iridica Platform Alec Saitman, PhD, Jane Y. Yang PhD, Sharon Reed, David Pride, Michele
STUDY OF VNTR HUMAN POLYMORPHISMS BY PCR
 STUDY OF VNTR HUMAN POLYMORPHISMS BY PCR Ref. PCR1 1. OBJECTIVE OF THE EXPERIMENT The objective of this experiment is to introduce students to the principles and practice of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
STUDY OF VNTR HUMAN POLYMORPHISMS BY PCR Ref. PCR1 1. OBJECTIVE OF THE EXPERIMENT The objective of this experiment is to introduce students to the principles and practice of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
BD GeneOhm MRSA ACP Lysis Kit
 REF 441638 100 Tests DOPS09-09-V1E1 USA Date: 2010-01 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTENDED USE...3 SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION OF THE PROCEDURE...3 REAGENTS...3 PRECAUTIONS...3 MATERIALS PROVIDED...4 STORAGE, HANDLING
REF 441638 100 Tests DOPS09-09-V1E1 USA Date: 2010-01 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTENDED USE...3 SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION OF THE PROCEDURE...3 REAGENTS...3 PRECAUTIONS...3 MATERIALS PROVIDED...4 STORAGE, HANDLING
Staphylococcus aureus
 Techne qpcr test Staphylococcus aureus FEMB gene (chromosomal gene) 150 tests For general laboratory and research use only 1 Introduction to Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus is a spherical,
Techne qpcr test Staphylococcus aureus FEMB gene (chromosomal gene) 150 tests For general laboratory and research use only 1 Introduction to Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus is a spherical,
Staphylococcus aureus
 TM Primerdesign Ltd Staphylococcus aureus FEMB gene (chromosomal gene) genesig Standard Kit 150 tests For general laboratory and research use only 1 Introduction to Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus
TM Primerdesign Ltd Staphylococcus aureus FEMB gene (chromosomal gene) genesig Standard Kit 150 tests For general laboratory and research use only 1 Introduction to Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus
Use of Drosophila Melanogaster as a Model System in the Study of Human Sodium- Dependent Multivitamin Transporter. Michael Brinton BIOL 230W.
 Use of Drosophila Melanogaster as a Model System in the Study of Human Sodium- Dependent Multivitamin Transporter Michael Brinton BIOL 230W.001 28 October 2013 TA: Sashi Gollapudi Introduction Many human
Use of Drosophila Melanogaster as a Model System in the Study of Human Sodium- Dependent Multivitamin Transporter Michael Brinton BIOL 230W.001 28 October 2013 TA: Sashi Gollapudi Introduction Many human
Clostridium difficile PCR Detection Kit Product # 37100
 3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Clostridium difficile PCR Detection Kit Product # 37100 Product
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Clostridium difficile PCR Detection Kit Product # 37100 Product
Colony-PCR Is a Rapid and Sensitive Method for DNA Amplification
 Iranian J Publ Health, Vol. 36, No.1, 2007, Iranian pp.40-44 J Publ Health, Vol. 36, No.1, 2007, pp.40-44 Original Article Colony-PCR Is a Rapid and Sensitive Method for DNA Amplification in Yeasts *H
Iranian J Publ Health, Vol. 36, No.1, 2007, Iranian pp.40-44 J Publ Health, Vol. 36, No.1, 2007, pp.40-44 Original Article Colony-PCR Is a Rapid and Sensitive Method for DNA Amplification in Yeasts *H
P HENIX. PHENIX PCR Enzyme Guide Tools For Life Science Discovery RESEARCH PRODUCTS
 PHENIX PCR Enzyme Guide PHENIX offers a broad line of premium quality PCR Enzymes. This PCR Enzyme Guide will help simplify your polymerase selection process. Each DNA Polymerase has different characteristics
PHENIX PCR Enzyme Guide PHENIX offers a broad line of premium quality PCR Enzymes. This PCR Enzyme Guide will help simplify your polymerase selection process. Each DNA Polymerase has different characteristics
Total Test Questions: 66 Levels: Grades Units of Credit: 1.0 STANDARD 2. Demonstrate appropriate use of personal protective devices.
 DESCRIPTION Biotechnology is designed to create an awareness of career possibilities in the field of biotechnology. Students are introduced to diagnostic and therapeutic laboratory procedures that support
DESCRIPTION Biotechnology is designed to create an awareness of career possibilities in the field of biotechnology. Students are introduced to diagnostic and therapeutic laboratory procedures that support
DGGE FOR Symbiodinium
 DGGE FOR Symbiodinium By Camila Granados Cifuentes, IMaGeS Lab (Modified from Dr. Todd LaJeunesse and Dr. Juan Armando Sanchez BIOMMAR ) This protocol explains the step by step process for running a DGGE
DGGE FOR Symbiodinium By Camila Granados Cifuentes, IMaGeS Lab (Modified from Dr. Todd LaJeunesse and Dr. Juan Armando Sanchez BIOMMAR ) This protocol explains the step by step process for running a DGGE
Development of diagnostic kits for selected markers of resistance, virulence and zoonotic transmission among methicillinresistant
 Development of diagnostic kits for selected markers of resistance, virulence and zoonotic transmission among methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus strains Dr. Boris Oberheitmann, Constanze Seidel
Development of diagnostic kits for selected markers of resistance, virulence and zoonotic transmission among methicillinresistant Staphylococcus aureus strains Dr. Boris Oberheitmann, Constanze Seidel
Int.J.Curr.Microbiol.App.Sci (2014) 3(10)
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 10 (2014) pp. 810-815 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Comparison of Tissue Culture plate method, Tube Method and Congo Red Agar Method for the detection
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 10 (2014) pp. 810-815 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Comparison of Tissue Culture plate method, Tube Method and Congo Red Agar Method for the detection
that cannot be assigned to any known spa type
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 2 December 2009 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00933-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 2 December 2009 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00933-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
Product# EP Product Description
 3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Chlamydia End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP31400 Product Insert Intended
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Chlamydia End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP31400 Product Insert Intended
Molecular Techniques Third-year Biology
 PLANNING Genetics Lab practices Molecular Techniques. Genetics Lab practices protocol. 2015-16 PCR-DIRECTED MUTAGENESIS, MOLECULAR CLONING AND RESTRICTION ANALYSIS Sessions 1 & 2 (2x3 hours): PCR-directed
PLANNING Genetics Lab practices Molecular Techniques. Genetics Lab practices protocol. 2015-16 PCR-DIRECTED MUTAGENESIS, MOLECULAR CLONING AND RESTRICTION ANALYSIS Sessions 1 & 2 (2x3 hours): PCR-directed
DETECTION OF ESCHERICHIA COLI O157:H7 AND STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS IN BROILER MEAT AVAILABLE IN LOCAL MARKETS OF WAYANAD, KERALA
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 2, 2016, 599 604 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) DETECTION OF ESCHERICHIA COLI O157:H7 AND STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS IN BROILER MEAT
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 2, 2016, 599 604 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) DETECTION OF ESCHERICHIA COLI O157:H7 AND STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS IN BROILER MEAT
Forecast diagnostics for antimicrobial resistance (AMR)
 Forecast diagnostics for antimicrobial resistance (AMR) Authors: Ann Van den Bruel, Philip Turner NIHR Diagnostic Evidence Cooperative Oxford, University of Oxford Context When asked to make forecasts
Forecast diagnostics for antimicrobial resistance (AMR) Authors: Ann Van den Bruel, Philip Turner NIHR Diagnostic Evidence Cooperative Oxford, University of Oxford Context When asked to make forecasts
This Product Description is only valid for Lot No. 42R.
 HLA Wipe Test Negative Control Product Insert Page 1 of 12 Olerup SSP HLA Wipe Test Negative Control Product number: 102.101-01 including Taq polymerase Product number: 102.101-01u without Taq polymerase
HLA Wipe Test Negative Control Product Insert Page 1 of 12 Olerup SSP HLA Wipe Test Negative Control Product number: 102.101-01 including Taq polymerase Product number: 102.101-01u without Taq polymerase
Molecular methods for detection of Antibiotic Resistance in environmental matrices: limits, prospects and challenges.
 Dr. Angela Cicatelli acicatelli@unisa.it Molecular methods for detection of Antibiotic Resistance in environmental matrices: limits, prospects and challenges. 1st Workshop on "Risk prognosis of environmental
Dr. Angela Cicatelli acicatelli@unisa.it Molecular methods for detection of Antibiotic Resistance in environmental matrices: limits, prospects and challenges. 1st Workshop on "Risk prognosis of environmental
Identification of the subtypes of Verocytotoxin encoding genes (vtx) of Escherichia coli by conventional PCR
 Identification of the subtypes of Verocytotoxin encoding genes (vtx) of Escherichia coli by conventional PCR 1. Aim and field of application Verocytotoxins (VT), synonymous Shiga toxins, are a toxin family
Identification of the subtypes of Verocytotoxin encoding genes (vtx) of Escherichia coli by conventional PCR 1. Aim and field of application Verocytotoxins (VT), synonymous Shiga toxins, are a toxin family
 PRODUCT INFORMATION Long PCR Enzyme Mix #K0182 500 u Lot Exp. 00.0000 Store at -20 C. CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS Long PCR Enzyme Mix is functionally tested in PCR amplification of 47.4 kb fragment from lambda
PRODUCT INFORMATION Long PCR Enzyme Mix #K0182 500 u Lot Exp. 00.0000 Store at -20 C. CERTIFICATE OF ANALYSIS Long PCR Enzyme Mix is functionally tested in PCR amplification of 47.4 kb fragment from lambda
Rift Valley Fever Virus RT-PCR Kit
 Revision No.: ZJ0002 Issue Date: Jan 2 nd, 2008 Rift Valley Fever Virus RT-PCR Kit Cat. No.: AR-0116-03 For use with Conventional PCR Instrument or Real time PCR Instrument User Manual For in vitro Diagnostic
Revision No.: ZJ0002 Issue Date: Jan 2 nd, 2008 Rift Valley Fever Virus RT-PCR Kit Cat. No.: AR-0116-03 For use with Conventional PCR Instrument or Real time PCR Instrument User Manual For in vitro Diagnostic
Diagnosis Sanger. Interpreting and Troubleshooting Chromatograms. Volume 1: Help! No Data! GENEWIZ Technical Support
 Diagnosis Sanger Interpreting and Troubleshooting Chromatograms GENEWIZ Technical Support DNAseq@genewiz.com Troubleshooting This troubleshooting guide is based on common issues seen from samples within
Diagnosis Sanger Interpreting and Troubleshooting Chromatograms GENEWIZ Technical Support DNAseq@genewiz.com Troubleshooting This troubleshooting guide is based on common issues seen from samples within
GENUS STAPHYLOCOCCUS: Isolation and Identification
 GENUS STAPHYLOCOCCUS: Isolation and Identification Staphylococcus is a genus of Gram +, nonspore-forming cocci belonging to the family Micrococcaceae that are often found as normal human microbiota of
GENUS STAPHYLOCOCCUS: Isolation and Identification Staphylococcus is a genus of Gram +, nonspore-forming cocci belonging to the family Micrococcaceae that are often found as normal human microbiota of
Cat # Box1 Box2. DH5a Competent E. coli cells CCK-20 (20 rxns) 40 µl 40 µl 50 µl x 20 tubes. Choo-Choo Cloning TM Enzyme Mix
 Molecular Cloning Laboratories User Manual Version 3.3 Product name: Choo-Choo Cloning Kits Cat #: CCK-10, CCK-20, CCK-096, CCK-384 Description: Choo-Choo Cloning is a highly efficient directional PCR
Molecular Cloning Laboratories User Manual Version 3.3 Product name: Choo-Choo Cloning Kits Cat #: CCK-10, CCK-20, CCK-096, CCK-384 Description: Choo-Choo Cloning is a highly efficient directional PCR
Description...1 Components...1 Storage... 1 Technical Information...1 Protocol...2 Examples using the kit...4 Troubleshooting...
 QuickClean II Gel Extraction Kit Cat. No. L00418 Technical Manual No. TM0594 Version: 03042011 I II III IV V VI VII VIII Description......1 Components.....1 Storage.... 1 Technical Information....1 Protocol.....2
QuickClean II Gel Extraction Kit Cat. No. L00418 Technical Manual No. TM0594 Version: 03042011 I II III IV V VI VII VIII Description......1 Components.....1 Storage.... 1 Technical Information....1 Protocol.....2
Chapter 9 Genetic Engineering
 Chapter 9 Genetic Engineering Biotechnology: use of microbes to make a protein product Recombinant DNA Technology: Insertion or modification of genes to produce desired proteins Genetic engineering: manipulation
Chapter 9 Genetic Engineering Biotechnology: use of microbes to make a protein product Recombinant DNA Technology: Insertion or modification of genes to produce desired proteins Genetic engineering: manipulation
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the sources of DNA used for molecular cloning is correct? Question #1 (A) cdna
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 11: Recombinant DNA Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the sources of DNA used for molecular cloning is correct? Question #1 (A) cdna
Absolute Human Telomere Length Quantification qpcr Assay Kit (AHTLQ) Catalog # reactions
 Absolute Human Telomere Length Quantification qpcr Assay Kit (AHTLQ) Catalog #8918 100 reactions Product Description Telomeres are repetitive nucleotide elements at the ends of chromosomes that protect
Absolute Human Telomere Length Quantification qpcr Assay Kit (AHTLQ) Catalog #8918 100 reactions Product Description Telomeres are repetitive nucleotide elements at the ends of chromosomes that protect
ABC. Methods for Determining Bactericidal Activity of Antimicrobial Agents; Approved Guideline. Volume 19 Number 18
 M26-A ISBN 1-56238-384-1 September 1999 ISSN 0273-3099 Methods for Determining Bactericidal Activity of Antimicrobial Agents; Approved Guideline Volume 19 Number 18 Arthur L. Barry, Ph.D. William A. Craig,
M26-A ISBN 1-56238-384-1 September 1999 ISSN 0273-3099 Methods for Determining Bactericidal Activity of Antimicrobial Agents; Approved Guideline Volume 19 Number 18 Arthur L. Barry, Ph.D. William A. Craig,
Laboratory Exercise 4. Multiplex PCR of Short Tandem Repeats and Vertical Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis.
 Laboratory Exercise 4 4 Multiplex PCR of Short Tandem Repeats and Vertical Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis B A C K G R O U N D The human genome contains over 3000 million base pairs, which are distributed
Laboratory Exercise 4 4 Multiplex PCR of Short Tandem Repeats and Vertical Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis B A C K G R O U N D The human genome contains over 3000 million base pairs, which are distributed
Taura Syndrome Virus (TSV) RT-PCR Kit
 Revision No.: ZJ0001 Issue Date: Aug 28th, 2007 Taura Syndrome Virus (TSV) RT-PCR Kit Cat. No.: AR-0200-03 For use with Conventional PCR Instrument or Real time PCR Instrument User Manual For in vitro
Revision No.: ZJ0001 Issue Date: Aug 28th, 2007 Taura Syndrome Virus (TSV) RT-PCR Kit Cat. No.: AR-0200-03 For use with Conventional PCR Instrument or Real time PCR Instrument User Manual For in vitro
Hosted by Paul Webber page 1
 A Webber Training Teleclass April 8, 24 Bacterial Typing Methods and Their Value in Infection Control Giles Edwards Consultant Microbiologist Stobhill Hospital, Glasgow, UK Scottish MRSA Reference Laboratory
A Webber Training Teleclass April 8, 24 Bacterial Typing Methods and Their Value in Infection Control Giles Edwards Consultant Microbiologist Stobhill Hospital, Glasgow, UK Scottish MRSA Reference Laboratory
toxa gene as a chromosomal marker for rapid identification of Otitis media Pseudomonas aeruginosa
 toxa gene as a chromosomal marker for rapid identification of Otitis media Pseudomonas aeruginosa Ibtesam Ghadban AUDA, Israa M.S. AL-KADMY*, Alaa Naseer MOHAMMED ALI, Sahira Nsayef MUSLIM & Istabreq Muhammed
toxa gene as a chromosomal marker for rapid identification of Otitis media Pseudomonas aeruginosa Ibtesam Ghadban AUDA, Israa M.S. AL-KADMY*, Alaa Naseer MOHAMMED ALI, Sahira Nsayef MUSLIM & Istabreq Muhammed
Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids
 Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids I. Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been created artificially. DNA from two or more sources is incorporated into a single
Lecture Four. Molecular Approaches I: Nucleic Acids I. Recombinant DNA and Gene Cloning Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been created artificially. DNA from two or more sources is incorporated into a single
Diagnosis and Quantification of Strawberry Vein Banding Virus Using Molecular Approaches
 Diagnosis and Quantification of Strawberry Vein Banding Virus Using Molecular Approaches Ali Mahmoudpour Department of Plant Pathology, University of California, Davis, CA, 95616, USA Current Address:
Diagnosis and Quantification of Strawberry Vein Banding Virus Using Molecular Approaches Ali Mahmoudpour Department of Plant Pathology, University of California, Davis, CA, 95616, USA Current Address:
1. COMPONENTS. PyroStart Fast PCR Master Mix (2X) (#K0211 for 250 reactions of 20µl) 2. STORAGE 3. DESCRIPTION
 1 2 1 PyroStart Fast PCR Master Mix (2X) (#K0211 for 250 reactions of 20µl) TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. COMPONENTS... 2 2. STORAGE... 2 3. DESCRIPTION... 2 4. PROTOCOL FOR FAST PCR... 3 4.1. General Considerations...
1 2 1 PyroStart Fast PCR Master Mix (2X) (#K0211 for 250 reactions of 20µl) TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. COMPONENTS... 2 2. STORAGE... 2 3. DESCRIPTION... 2 4. PROTOCOL FOR FAST PCR... 3 4.1. General Considerations...
Pinpoint Slide DNA Isolation System Catalog No. D3001
 INSTRUCTIONS Pinpoint Slide DNA Isolation System Catalog No. D3001 Highlights Easily isolates genomic DNA in any targeted microscopic tissue area on a slide. The simple procedure combines Pinpoint tissue
INSTRUCTIONS Pinpoint Slide DNA Isolation System Catalog No. D3001 Highlights Easily isolates genomic DNA in any targeted microscopic tissue area on a slide. The simple procedure combines Pinpoint tissue
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Simultaneous Elimination of Carryover Contamination and Detection of DNA
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Simultaneous Elimination of Carryover Contamination and Detection of DNA
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY EXPERIMENT PCR & SEEDING
 BME MOLECULAR BIOLOGY EXPERIMENT PCR & SEEDING SKKU BME 3 RD GRADE, 2 ND SEMESTER FOR FUN PCR & SEEDING PCR: polymerase chain reaction Electrophoresis Seeding These are for amplifying DNA and cell PCR
BME MOLECULAR BIOLOGY EXPERIMENT PCR & SEEDING SKKU BME 3 RD GRADE, 2 ND SEMESTER FOR FUN PCR & SEEDING PCR: polymerase chain reaction Electrophoresis Seeding These are for amplifying DNA and cell PCR
Supplemental Data. mir156-regulated SPL Transcription. Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering. Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana
 Cell, Volume 138 Supplemental Data mir156-regulated SPL Transcription Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana Jia-Wei Wang, Benjamin Czech, and Detlef Weigel Table S1. Interaction
Cell, Volume 138 Supplemental Data mir156-regulated SPL Transcription Factors Define an Endogenous Flowering Pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana Jia-Wei Wang, Benjamin Czech, and Detlef Weigel Table S1. Interaction
Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis Information Research). Exons
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis Information Research). Exons
Genetics Lecture 21 Recombinant DNA
 Genetics Lecture 21 Recombinant DNA Recombinant DNA In 1971, a paper published by Kathleen Danna and Daniel Nathans marked the beginning of the recombinant DNA era. The paper described the isolation of
Genetics Lecture 21 Recombinant DNA Recombinant DNA In 1971, a paper published by Kathleen Danna and Daniel Nathans marked the beginning of the recombinant DNA era. The paper described the isolation of
AccuPower PCR PreMix 73. AccuPower Taq PCR PreMix 77. AccuPower PCR PreMix (with UDG) 79. AccuPower HotStart PCR PreMix 81
 PCR PreMix 73 AccuPower Taq PCR PreMix 77 AccuPower PCR PreMix (with UDG) 79 AccuPower HotStart PCR PreMix 81 AccuPower PyroHotStart Taq PCR PreMix 84 AccuPower HotStart PCR PreMix (with UDG) 87 AccuPower
PCR PreMix 73 AccuPower Taq PCR PreMix 77 AccuPower PCR PreMix (with UDG) 79 AccuPower HotStart PCR PreMix 81 AccuPower PyroHotStart Taq PCR PreMix 84 AccuPower HotStart PCR PreMix (with UDG) 87 AccuPower
Bacterial genetic exchange : Bacterial Transformation
 Experiment 11 Laboratory to Biology III: Diversity of Microorganisms 1 Experiment 11 Bacterial genetic exchange : Bacterial Transformation Advisor Munti Yuhana myuhana@botinst.unizh.ch Textbook Chapters
Experiment 11 Laboratory to Biology III: Diversity of Microorganisms 1 Experiment 11 Bacterial genetic exchange : Bacterial Transformation Advisor Munti Yuhana myuhana@botinst.unizh.ch Textbook Chapters
The Expression of Recombinant Sheep Prion Protein (RecShPrPC) and its Detection Using Western Blot and Immuno-PCR
 The Expression of Recombinant Sheep Prion Protein (RecShPrPC) and its Detection Using Western Blot and Immuno-PCR S. Thomas, C. S. Fernando, J. Roach, U. DeSilva and C. A. Mireles DeWitt The objective
The Expression of Recombinant Sheep Prion Protein (RecShPrPC) and its Detection Using Western Blot and Immuno-PCR S. Thomas, C. S. Fernando, J. Roach, U. DeSilva and C. A. Mireles DeWitt The objective
Guide-it Indel Identification Kit User Manual
 Clontech Laboratories, Inc. Guide-it Indel Identification Kit User Manual Cat. No. 631444 (120114) Clontech Laboratories, Inc. A Takara Bio Company 1290 Terra Bella Avenue, Mountain View, CA 94043, USA
Clontech Laboratories, Inc. Guide-it Indel Identification Kit User Manual Cat. No. 631444 (120114) Clontech Laboratories, Inc. A Takara Bio Company 1290 Terra Bella Avenue, Mountain View, CA 94043, USA
Sexing Bovine Preimplantation Embryos by PCR
 Sexing Bovine Preimplantation Embryos by PCR Katherine E.M. Hendricks 1, Leydson F. Martins 2, Justin M. Fear 1 and Peter J. Hansen 1 1 Dept. of Animal Sciences, University of Florida and Department of
Sexing Bovine Preimplantation Embryos by PCR Katherine E.M. Hendricks 1, Leydson F. Martins 2, Justin M. Fear 1 and Peter J. Hansen 1 1 Dept. of Animal Sciences, University of Florida and Department of
High Pure PCR Template Preparation Kit for preparation of 100 nucleic acid samples Cat. No
 for preparation of 100 nucleic acid samples Cat. No. 1 796 88 Principle Cells are lysed during a short incubation with Proteinase K in the presence of a chaotropic salt (guanidine HCl), which immediately
for preparation of 100 nucleic acid samples Cat. No. 1 796 88 Principle Cells are lysed during a short incubation with Proteinase K in the presence of a chaotropic salt (guanidine HCl), which immediately
Lack of Association between FKBP1A Gene and Susceptibility to Malignant Hyperthermia
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Central European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2017, 5 (2):17-23 ISSN: 2278-7364 Lack of Association between FKBP1A Gene and Susceptibility to Malignant
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Central European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2017, 5 (2):17-23 ISSN: 2278-7364 Lack of Association between FKBP1A Gene and Susceptibility to Malignant
Note: for laboratory research use only. RNA High-purity Total RNA Rapid Extraction Kit (Spin-column) Signalway Biotechnology
 Note: for laboratory research use only RNA High-purity Total RNA Rapid Extraction Kit (Spin-column) Cat. #: RP1202 (50preps) Signalway Biotechnology I. Kit Content, Storage Condition and Stability Content
Note: for laboratory research use only RNA High-purity Total RNA Rapid Extraction Kit (Spin-column) Cat. #: RP1202 (50preps) Signalway Biotechnology I. Kit Content, Storage Condition and Stability Content
Antibiotic resistance genes & susceptibility patterns in staphylococci
 Indian J Med Res 135, March 2012, pp 389-396 Antibiotic resistance genes & susceptibility patterns in staphylococci Nizami Duran, Burcin Ozer, Gulay Gulbol Duran *, Yusuf Onlen ** & Cemil Demir Mustafa
Indian J Med Res 135, March 2012, pp 389-396 Antibiotic resistance genes & susceptibility patterns in staphylococci Nizami Duran, Burcin Ozer, Gulay Gulbol Duran *, Yusuf Onlen ** & Cemil Demir Mustafa
Project 7: Wound Cultures and Identification
 Project 7: Wound Cultures and Identification Readings: https://labtestsonline.org/understanding/analytes/wound-culture/tab/test Identification of Gram-Positive & Gram-Negative Bacteria Guide to laboratory
Project 7: Wound Cultures and Identification Readings: https://labtestsonline.org/understanding/analytes/wound-culture/tab/test Identification of Gram-Positive & Gram-Negative Bacteria Guide to laboratory
TaKaRa Taq HS PCR Kit, UNG plus
 Cat. # R013S/A For Research Use TaKaRa Taq HS PCR Kit, UNG plus Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Storage... 4 IV. Materials Required but not Provided... 4 V.
Cat. # R013S/A For Research Use TaKaRa Taq HS PCR Kit, UNG plus Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description... 3 II. Components... 3 III. Storage... 4 IV. Materials Required but not Provided... 4 V.
