T G T A. artificial chimera
|
|
|
- Blanche Burns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 False mutation detection caused by WA artifacts original genome A C A artifacts in amplified DNA C C A A false detection of local variants true ssnv mistaken as error artificial chimera false LOH early MDA error as ssnv Supplementary Figure False mutation detection due to whole-genome amplification artifacts. From left to right: false negative SNV detection due to allelic distortion; false positive translocation detection due to artificial chimera; false positive loss-of-heterozygosity due to chromosomal segments dropping out of amplification; false positive SNV detection due to early amplification errors. here are two major differences between allelic distortion and chromosome segments dropping out of amplification. First, allelic distortion is primarily caused by preferential amplification of one chromosome allele; from the auto-correlation analysis, such preferential amplification extends roughly to the amplicon size ( kb). But false LOH here refers to much longer chromosomal segments (> Mb) that drop out of amplification. Second, it is possible to perform deep targeted sequencing by PCR amplification from the MDA product to uncover both chromosome alleles even under allelic distortion. It is impossible to reveal the chromosome segment that has dropped out of amplification by targeted sequencing of the MDA product; a biological replicate is needed to validate if such dropout is an artifact or true deletion.
2 a Coverage correlations at different scales Bulk DNA sequencing Single-cell sequencing... read length bp x x x fragment length bp correlation at the fragment level correlation at the amplicon level MDA.x.x.x x x x x bulk. x 9x x b Amplicon-level correlation fitting in RPE libraries by MDA RPE #.x Miseq.x Hiseq from fitting. kb. kb correlation magnitude at kb.. RPE # RPE #.x.x.x.7x. kb. kb. kb. kb..7.. c Coverage predictions for single RPE MDA libraries.... RPE # RPE # RPE # prediction.x MDA.x MDA observation.x MDA.... prediction.x MDA.x MDA observation.7x MDA.... prediction.x MDA.x MDA observation.x MDA normalized depth normalized depth normalized depth Supplementary Figure Analysis of amplification bias and genome coverage in MDA-generated libraries of RPE- cells. (a) Correlation at the scale of sequencing read length and fragment length is present in both bulk and single-cell libraries (- bp), but correlation at the scale of amplicons ( kb) only appears in MDA-derived libraries. (b) Amplicon-level correlation independent of the sequencing depth is demonstrated in disomic Chr. in three MDA-generated libraries of twocell RPE samples. (c) Independent sequencing of three MDA-generated RPE libraries to.x and to.x confirms that the bin-level depth-of-coverage predicted from low-pass sequencing agrees with the observed single-base depth-of-coverage in higher-depth sequencing, reflecting the dominant non-uniformity generated at the amplicon level. All correlation functions are calculated for disomic Chr.
3 a Depth-of-coverage yield curve for bulk and MDA libraries Bulk RPE library Single RPE MDA library Normalized DoC yield.... x 9x x.....x x x.... depth (x) depth (x) depth / mean depth b Normalized depth-of-coverage yield curve at different bin sizes Bulk RPE library Single RPE MDA library bin-level coverage.... base-level coverage 9x x kb kb kb kb kb bp bp.... base-level coverage.x x depth / mean depth optimal bin size = fragment length (- bp) depth / mean depth optimal bin size = amplicon size (- kbp) c Lorenz distribution curves for bulk and MDA libraries evaluated at different bin sizes Bulk RPE library, 9x Single RPE MDA library,.x Single RPE MDA library,.x cumulative read count fraction..... mb kb kb kb bp bp bp bp.... cumulative read count fraction..... mb kb kb kb bp bp bp bp.... cumulative read count fraction..... mb kb kb kb bp bp bp bp.... cumulative cumulative cumulative
4 Supplementary Figure Coverage non-uniformity in bulk and MDA-derived libraries of RPE- cells evaluated at different bin sizes. (a) he depth-of-coverage (DoC) curves at different sequencing depths reflect the same underlying density distribution of the coverage at different loci in the sequencing library when the coverage depth is normalized by the mean sequencing depth. (b) he depth-of-coverage yield evaluated at the single-base level is almost identical to the depth-of-coverage evaluated at the level where the dominant variation is generated. For bulk DNA libraries, the dominant variation occurs at the level of sequencing fragments (presumably in the PCR step of library preparation). herefore, the DoC curve evaluated at bin size - bp is indistinguishable from the DoC curve evaluated at the single-base level, but at larger bin sizes, the coverage bias is further attenuated. For MDA-generated libraries, the DoC curve is almost invariant until the bin size reaches the level of single amplicons kb. herefore, the DoC curve at the single-base level can be reliably estimated from the bin-level ( kb) coverage in low-pass sequencing data (.x). (c) Lorenz curves evaluated at different bin sizes also confirm the dominant variation at bp scale for the bulk DNA library and at kb scale for the MDA library. In the bulk DNA library (left panel), the Lorenz curve for the bin-level coverage (black curves) is similar to the Lorenz curve at the single base level (red curve) but deviates towards more uniformity as the bin size exceeds bp. In the MDA library sequenced to.x (middle panel), the Lorenz curve is essentially unchanged until the bin size reaches kb and deviates towards more uniformity as the bin size exceeds kb, consistent with an amplicon size kb. In the same MDA library sequenced to.x (right panel), the majority of the chromosome is uncovered. In the uncovered region, amplification non-uniformity cannot be evaluated from the singlebase level coverage (red curve); however, the bin-level coverage ( kb bins) agrees well with the single-base level coverage observed in. x sequencing (dashed red curve), suggesting that this distribution is intrinsic to the MDA but not dependent on the sequencing depth. All Lorenz curves are evaluated for disomic Chr.
5 a Correlation analysis of single glioblastoma MDA libraries.x x x Chr (CN=) Chr (CN=) Chr (CN=). kb 7.9 kb. kb 7. kb b Coverage predictions for single glioblastoma MDA libraries. BM # BM # prediction from x MDA Chr. (CN=) Chr. (CN=) Chr. (CN=).... observation in x MDA Chr. (CN=) Chr. (CN=) Chr. (CN=)... normalized depth normalized depth Supplementary Figure Analysis of amplification bias and genome coverage in MDA-generated libraries of frozen glioblastoma nuclei (B) in Francis et al. (). (a) (Left) he same amplicon-level correlation (red dashed curve, l c = 7. kb) is revealed from independent sequencing of a single glioblastoma library (BM #) to.x, x, and x. (Right) Chromosomes with different copy number show the same amplicon size but different magnitude of amplification bias, reflecting differential priming efficiencies (from one copy of monosomic chromosome vs. two copies of disomic chromosomes) during the early stage of amplification. (b) he cumulative coverage curve at higher sequencing depths can be accurately predicted from the bin-level coverage at lower depths for chromosomes with different copy number.
6 a Auto-correlation analysis of single and bulk DNA libraries in Hou et al. () 7 (read level) (fragment level) YH_single.x (downsample) 7.x YH_bulk 9x YH_single.7x (downsample).x YH_bulk 9x (fragment level) (amplicon level) (read level) (amplicon level) b Prediction of allelic coverages of single-cell DNA libraries in Hou et al. () percentage of SNPs.7.. observation from -x combined ref allele alt allele prediction from.x locus-level MM SM percentage of SNPs.7.. c YH bulk DNA library showed considerable C bias at the fragment level bin size: kb RPE bulk YH bulk A %. YH bulk RPE bulk x x x x 9 Chr. pos (Mb) relative abundance A % Supplementary Figure Analysis of amplification bias and genome/allele coverage in bulk and MDA-derived libraries of diploid lymphoblastoid YH cells. (a) Comparison of coverage correlation in single-cell and bulk libraries confirms the dominant bias occurring at the amplicon level kb. here is considerable fragment-level correlation in both the bulk and one of the two single-cell libraries that is likely introduced during the PCR step of library preparation. (b) he coverage at heterozygous sites (reference, alternate, or both alleles combined) evaluated at high sequencing depths agrees well with predictions from low-pass sequencing. (c) he fragment-level bias in the bulk DNA library shows a strong correlation with the local sequence content (A%) that is absent in the bulk library of RPE- cells shown in Supplementary Figure.
7 a Auto-correlation analysis of single and bulk MDA libraries in Evrony et al. () (i) MDA of single neurons (ii) MDA of neurons (iii) MDA of, neurons read level correlation amplicon level correlation Sample read level correlation amplicon correlation -neuron- bp. kb -neuron- 9 bp. kb -neuron- bp. kb -neuron- bp. kb -neuron- bp. kb -neuron- bp. kb -bulkdna bp NA 9 9 single neuron (-cortex-mda-) 7 relative abundance relative abundance 7 9 neurons (-cortex--mda-) C % C % 9 # of bins with given C bulk (-cortex-bulkdna) 7 C %, neurons (-cortex-k-mda-) C % C % 7 Correlation between C content and library representation at the amplicon level (bin size: kb) relative abundance relative abundance b
8 Supplementary Figure Analysis of coverage correlation in MDA generated libraries of frozen neuron nuclei in Evrony et al. (). (a) MDA-generated libraries of single neurons, hundreds of neurons, or thousands of neurons show the same amplicon-level correlation reflecting amplicon size kb. he short-range correlation reflects the read length ( bp) at low sequencing depths. (b) Comparison of the relative abundance of sequence coverage with local C content at the amplicon level (evaluated at kb bins) suggests that there is a wide range of coverage variation in regions with similar C content. By contrast, there is little variation at kb scale in the bulk library. Error bars show standard deviation for each C stratum. he variation is especially evident for single-neuron libraries, where the range is proportional to the total number of bins with similar C content, reflecting random, instead of sequence-content generated bias.
9 a Auto-correlation analysis of single sperm DNA libraries in Wang et al. () 7-x Sample correlation length correlation magnitude sperm-. kb 9. sperm-. kb. sperm-. kb.9 sperm-. kb. sperm-. kb.9 sperm- 9. kb. sperm-7. kb 7. sperm-.9 kb. b Coverage predictions c Error rate estimates percentage of SNPs % sites with > ref. and alt. reads sperm- sperm- sperm- sperm- sperm- sperm- sperm-7 sperm- Supplementary Figure 7 Analysis of coverage variation in MDA generated libraries of single sperms in Wang et al. (). (a) Different single-sperm libraries exhibit dominant bias at - kb range consistent with the MDA amplicon size. (b) Cumulative coverage at higher sequencing depth (7-x) can be accurately predicted from the amplicon-level coverage evaluated from low-pass sequencing (<x). (c) About % sites showed heterozygosity (with > reads of both reference and alternate alleles) in the haploid sperm libraries, indicating an error frequency of % at allele frequency % or above. 9
10 a Coverage correlations in MALBAC, MDA, and bulk SW libraries (Zong et al. ) ~x ~x SW- (SRS77) SW- (SRS77) SW- (SRS77) SW- (SRS7) SW- (SRS7) MDA (SRS7) 9 kb bulk DNA (SRS7) b Snapshots of sequencing coverage in MDA and MALBAC libraries kb MDA MALBAC c Coverage predictions for single SW- libraries prediction. observation observation x SW-MDA. from x SW- (MALBAC) (bin size: bp) prediction from x SW-MDA (bin size:. kb)... x SW- MALBAC... Supplementary Figure Analysis of coverage variation in MDA and MALBAC generated libraries of SW tumor cells in Zong et al. (). (a) All five MALBAC-generated single SW libraries (blue symbols) show a much shorter amplicon compared to the MDAgenerated library (red squares). (b) Snapshots of local sequencing coverage confirm the shorter amplicons in MALBAC in comparison to MDA. (c) In both MDA and MALBAC-generated libraries, the dominant source of non-uniformity exists at the amplicon-level and can be accurately predicted from low-pass sequencing.
11 a Coverage correlations in DOP-PCR amplified single-cell libraries (Wang et al. ) read level correlation ~ bp amplicon level correlation ~ bp b Correlation magnitude and spread (amplicon size) in DOP-PCR libraries (Wang et al. ) correlation magnitude correlation length (bp) c Correlation magnitude and spread (amplicon size) in MDA and MALBAC libraries ploidy correlation magnitude sperms single BMs single SW RPEs (two-cell) YH Neuron N N N N N N N correlation length (kb) Supplementary Figure 9 Analysis of coverage variation in DOP-PCR libraries of tumor nuclei in Wang et al. () (a) Different libraries (9 total) exhibit similar fragment-level correlations (l c = bp) and amplicon-level bias (l c = bp). (b) Magnitude and spread of DOP-PCR bias. he amplicon size (estimated by the correlation length) agrees well with the size selection protocol in the original report (Navin et al., ). he magnitudes of correlation in DOP-PCR libraries are generally smaller than those observed in MDA-generated libraries as shown in (c), reflecting less overall bias in DOP-PCR. (c) Magnitude and spread of MDA bias in different studies. More DNA content in N samples results in better uniformity than N or N samples. his is consistent with improved uniformity of MDA from nuclei in Wang et al. ().
12 Mathematical models of allelic amplifications combined coverage from both alleles locus-level read counts and coverage sequencing coverage ( read): f ( ): f ( ): f ( ): f mixed template model (MM) symmetric binomial distribution at each locus segregated template model (SM) independent distribution at each locus allele read counts allele A allele B alellic coverage allele A ( read): λ allele B ( read): λ Supplementary Figure Schematic illustration of two models for allele bias. Details of the derivations are given in the Methods section.
13 a Allelic coverage predictions for single RPE MDA libraries observation from.x combined ref allele alt allele prediction from.x locus-level MM SM percentage of SNPs.... RPE # percentage of SNPs.... RPE # percentage of SNPs.... RPE # b Comparison of allelic coverage in disomic and monosomic chromosomes BM # BM # allelic coverage in Chr. predicted from x allelic coverage in Chr. predicted from x fraction of allele.... MM SM locus coverage observations chr. (.x, disomic) chr. (.x, monosomic) fraction of allele.... MM SM locus coverage observations chr. (.9x, disomic) chr. (.x, monosomic) normalized DoC normalized DoC BM # allelic coverage in Chr. predicted from x BM # allelic coverage in Chr. predicted from x. MM SM. MM SM fraction of allele... locus coverage observations chr. (.x, disomic) chr. (.9x, monosomic)... locus coverage observations chr. (9.7x, disomic) chr. (.x, monosomic) normalized DoC normalized DoC Supplementary Figure Allele-level amplification bias in fresh RPE- and frozen glioblastoma libraries generated by MDA. (a) Comparison of the allele coverage (A or B) predicted from the locus-level coverage (A+B) in two-cell RPE samples with the observation at heterozygous sites in Chr.. he observation suggests that amplification of homologous chromosomes more resembles the mixed template model (MM). (b) Comparison of the allele coverage prediction from disomic chromosome with the observed coverage in monosomic chromosome in frozen glioblastoma nuclei. he agreement between the segregated template model (SM) prediction and the observed coverage in the monosomic chromosome further supports that each chromosome in the single-cell genome is independently amplified.
14 a RPE #: Positive correlation between ref. and alt. allele counts B is alt. B is ref. allele SNPs covered at given depth. x... ref. allele coverage in Chr. alt. allele coverage in Chr. mean depth of allele B % of allele B of Chr. covered x.... allele allele MM prediction from x data allele A depth b BM #: Independence between ref. and alt. allele counts SNPs covered at given depth ref. allele coverage in Chr. alt. allele coverage in Chr. mean depth of allele B Chr. SNPs Chr. SNPs allele A depth % of allele B of Chr. covered x..... allele allele allele SM prediction from x data B is alt. B is ref. Supplementary Figure Distinct correlations between the amplification of homologous chromosomes. (a) he depth-of-coverage curves of reference (A) and alternate (B) alleles are identical (left panel) but exhibit a positive correlation (middle panel). he depth-of-coverage curve of allele B at sites where the A allele is covered at different depths (x, x, x) also shows a positive correlation with the allele A coverage but can be predicted by the method described above (right panel). he correlation between allele A and allele B coverage indicates that over-amplified regions are not dominated by amplification of one homologue but tend to represent both homologous chromosomes. (b) In a representative glioblastoma library, even though the depth-of-coverage curves of reference (A) and alternate (B) alleles are still identical but the correlation between allele A and allele B coverage is absent (middle panel). he depth-of-coverage curves of allele B at sites where the A allele is covered at different depths (x, x, x) are almost identical (right panels). hese results demonstrate independent amplifications of the two homologous chromosomes.
Whole Genome Amplification (WGA): What to Do When You Don t Have Enough Genomic DNA
 Whole Genome Amplification (WGA): What to Do When You Don t Have Enough Genomic DNA Rob Brazas, Ph.D. Senior Product Manager, Lucigen January, 2017 www.lucigen.com Agenda Improving Whole Genome Amplified
Whole Genome Amplification (WGA): What to Do When You Don t Have Enough Genomic DNA Rob Brazas, Ph.D. Senior Product Manager, Lucigen January, 2017 www.lucigen.com Agenda Improving Whole Genome Amplified
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic representation of enrichment of amplification errors through allelic bias.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of enrichment of amplification errors through allelic bias. (a) When there is no allelic amplification bias, amplification errors occurring in the first
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of enrichment of amplification errors through allelic bias. (a) When there is no allelic amplification bias, amplification errors occurring in the first
Single Nucleotide Variant Analysis. H3ABioNet May 14, 2014
 Single Nucleotide Variant Analysis H3ABioNet May 14, 2014 Outline What are SNPs and SNVs? How do we identify them? How do we call them? SAMTools GATK VCF File Format Let s call variants! Single Nucleotide
Single Nucleotide Variant Analysis H3ABioNet May 14, 2014 Outline What are SNPs and SNVs? How do we identify them? How do we call them? SAMTools GATK VCF File Format Let s call variants! Single Nucleotide
Haplotype phasing in single-cell DNA-sequencing data
 Bioinformatics, 34, 2018, i211 i217 doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty286 ISMB 2018 Haplotype phasing in single-cell DNA-sequencing data Gryte Satas 1,2 and Benjamin J. Raphael 1, * 1 Department of Computer
Bioinformatics, 34, 2018, i211 i217 doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty286 ISMB 2018 Haplotype phasing in single-cell DNA-sequencing data Gryte Satas 1,2 and Benjamin J. Raphael 1, * 1 Department of Computer
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures A B Supplementary Figure 1. Examples of discrepancies in predicted and validated breakpoint coordinates. A) Most frequently, predicted breakpoints were shifted relative to those derived
Supplementary Figures A B Supplementary Figure 1. Examples of discrepancies in predicted and validated breakpoint coordinates. A) Most frequently, predicted breakpoints were shifted relative to those derived
Figure S1. Unrearranged locus. Rearranged locus. Concordant read pairs. Region1. Region2. Cluster of discordant read pairs, bundle
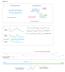 Figure S1 a Unrearranged locus Rearranged locus Concordant read pairs Region1 Concordant read pairs Cluster of discordant read pairs, bundle Region2 Concordant read pairs b Physical coverage 5 4 3 2 1
Figure S1 a Unrearranged locus Rearranged locus Concordant read pairs Region1 Concordant read pairs Cluster of discordant read pairs, bundle Region2 Concordant read pairs b Physical coverage 5 4 3 2 1
Single-cell sequencing
 Single-cell sequencing Jie He 2017-10-31 The Core of Biology Is All About One Cell Forward Approaching The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2004 Dr. Richard Axel Dr. Linda Buck Hypothesis 1. The odorant
Single-cell sequencing Jie He 2017-10-31 The Core of Biology Is All About One Cell Forward Approaching The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2004 Dr. Richard Axel Dr. Linda Buck Hypothesis 1. The odorant
Chang Xu Mohammad R Nezami Ranjbar Zhong Wu John DiCarlo Yexun Wang
 Supplementary Materials for: Detecting very low allele fraction variants using targeted DNA sequencing and a novel molecular barcode-aware variant caller Chang Xu Mohammad R Nezami Ranjbar Zhong Wu John
Supplementary Materials for: Detecting very low allele fraction variants using targeted DNA sequencing and a novel molecular barcode-aware variant caller Chang Xu Mohammad R Nezami Ranjbar Zhong Wu John
SNP calling. Jose Blanca COMAV institute bioinf.comav.upv.es
 SNP calling Jose Blanca COMAV institute bioinf.comav.upv.es SNP calling Genotype matrix Genotype matrix: Samples x SNPs SNPs and errors A change in a read may due to: Sample contamination Cloning or PCR
SNP calling Jose Blanca COMAV institute bioinf.comav.upv.es SNP calling Genotype matrix Genotype matrix: Samples x SNPs SNPs and errors A change in a read may due to: Sample contamination Cloning or PCR
Variant calling workflow for the Oncomine Comprehensive Assay using Ion Reporter Software v4.4
 WHITE PAPER Oncomine Comprehensive Assay Variant calling workflow for the Oncomine Comprehensive Assay using Ion Reporter Software v4.4 Contents Scope and purpose of document...2 Content...2 How Torrent
WHITE PAPER Oncomine Comprehensive Assay Variant calling workflow for the Oncomine Comprehensive Assay using Ion Reporter Software v4.4 Contents Scope and purpose of document...2 Content...2 How Torrent
HaloPlex HS. Get to Know Your DNA. Every Single Fragment. Kevin Poon, Ph.D.
 HaloPlex HS Get to Know Your DNA. Every Single Fragment. Kevin Poon, Ph.D. Sr. Global Product Manager Diagnostics & Genomics Group Agilent Technologies For Research Use Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic
HaloPlex HS Get to Know Your DNA. Every Single Fragment. Kevin Poon, Ph.D. Sr. Global Product Manager Diagnostics & Genomics Group Agilent Technologies For Research Use Only. Not for Use in Diagnostic
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Number and length distributions of the inferred fosmids.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Number and length distributions of the inferred fosmids. Fosmid were inferred by mapping each pool s sequence reads to hg19. We retained only those reads that mapped to within a
Supplementary Figure 1 Number and length distributions of the inferred fosmids. Fosmid were inferred by mapping each pool s sequence reads to hg19. We retained only those reads that mapped to within a
Digital RNA allelotyping reveals tissue-specific and allelespecific gene expression in human
 nature methods Digital RNA allelotyping reveals tissue-specific and allelespecific gene expression in human Kun Zhang, Jin Billy Li, Yuan Gao, Dieter Egli, Bin Xie, Jie Deng, Zhe Li, Je-Hyuk Lee, John
nature methods Digital RNA allelotyping reveals tissue-specific and allelespecific gene expression in human Kun Zhang, Jin Billy Li, Yuan Gao, Dieter Egli, Bin Xie, Jie Deng, Zhe Li, Je-Hyuk Lee, John
Simultaneous genome and transcriptome sequencing
 Simultaneous genome and transcriptome sequencing Technical Journal Club 31.01.2017 Christina Müller Introduction Rapid growth of single cell genomics www.biomarkerinsights.qiagen.com Introduction Single
Simultaneous genome and transcriptome sequencing Technical Journal Club 31.01.2017 Christina Müller Introduction Rapid growth of single cell genomics www.biomarkerinsights.qiagen.com Introduction Single
RIPTIDE HIGH THROUGHPUT RAPID LIBRARY PREP (HT-RLP)
 Application Note: RIPTIDE HIGH THROUGHPUT RAPID LIBRARY PREP (HT-RLP) Introduction: Innovations in DNA sequencing during the 21st century have revolutionized our ability to obtain nucleotide information
Application Note: RIPTIDE HIGH THROUGHPUT RAPID LIBRARY PREP (HT-RLP) Introduction: Innovations in DNA sequencing during the 21st century have revolutionized our ability to obtain nucleotide information
Genome-Wide Detection of Single-Nucleotide and Copy-Number Variations of a Single Human Cell
 Genome-Wide Detection of Single-Nucleotide and Copy-Number Variations of a Single Human Cell The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
Genome-Wide Detection of Single-Nucleotide and Copy-Number Variations of a Single Human Cell The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
Bio5488 Practice Midterm (2018) 1. Next-gen sequencing
 1. Next-gen sequencing 1. You have found a new strain of yeast that makes fantastic wine. You d like to sequence this strain to ascertain the differences from S. cerevisiae. To accurately call a base pair,
1. Next-gen sequencing 1. You have found a new strain of yeast that makes fantastic wine. You d like to sequence this strain to ascertain the differences from S. cerevisiae. To accurately call a base pair,
Cancer Genetics Solutions
 Cancer Genetics Solutions Cancer Genetics Solutions Pushing the Boundaries in Cancer Genetics Cancer is a formidable foe that presents significant challenges. The complexity of this disease can be daunting
Cancer Genetics Solutions Cancer Genetics Solutions Pushing the Boundaries in Cancer Genetics Cancer is a formidable foe that presents significant challenges. The complexity of this disease can be daunting
Package falcon. April 21, 2016
 Version 0.2 Date 2016-04-20 Package falcon April 21, 2016 Title Finding Allele-Specific Copy Number in Next-Generation Sequencing Data Author Hao Chen and Nancy R. Zhang Maintainer Hao Chen
Version 0.2 Date 2016-04-20 Package falcon April 21, 2016 Title Finding Allele-Specific Copy Number in Next-Generation Sequencing Data Author Hao Chen and Nancy R. Zhang Maintainer Hao Chen
Incorporating Molecular ID Technology. Accel-NGS 2S MID Indexing Kits
 Incorporating Molecular ID Technology Accel-NGS 2S MID Indexing Kits Molecular Identifiers (MIDs) MIDs are indices used to label unique library molecules MIDs can assess duplicate molecules in sequencing
Incorporating Molecular ID Technology Accel-NGS 2S MID Indexing Kits Molecular Identifiers (MIDs) MIDs are indices used to label unique library molecules MIDs can assess duplicate molecules in sequencing
Comparison of variations detection between whole-genome amplification methods used in single-cell resequencing
 Hou et al. GigaScience (2015) 4:37 DOI 10.1186/s13742-015-0068-3 RESEARCH Open Access Comparison of variations detection between whole-genome amplification methods used in single-cell resequencing Yong
Hou et al. GigaScience (2015) 4:37 DOI 10.1186/s13742-015-0068-3 RESEARCH Open Access Comparison of variations detection between whole-genome amplification methods used in single-cell resequencing Yong
Package falconx. February 24, 2017
 Version 0.2 Date 2017-02-16 Package falconx February 24, 2017 Title Finding Allele-Specific Copy Number in Whole-Exome Sequencing Data Author Hao Chen and Nancy R. Zhang Maintainer Hao Chen
Version 0.2 Date 2017-02-16 Package falconx February 24, 2017 Title Finding Allele-Specific Copy Number in Whole-Exome Sequencing Data Author Hao Chen and Nancy R. Zhang Maintainer Hao Chen
Detection of Rare Variants in Degraded FFPE Samples Using the HaloPlex Target Enrichment System
 Detection of Rare Variants in Degraded FFPE Samples Using the HaloPlex Target Enrichment System Application Note Author Linus Forsmark Henrik Johansson Agilent Technologies Inc. Santa Clara, CA USA Abstract
Detection of Rare Variants in Degraded FFPE Samples Using the HaloPlex Target Enrichment System Application Note Author Linus Forsmark Henrik Johansson Agilent Technologies Inc. Santa Clara, CA USA Abstract
POPULATION GENETICS studies the genetic. It includes the study of forces that induce evolution (the
 POPULATION GENETICS POPULATION GENETICS studies the genetic composition of populations and how it changes with time. It includes the study of forces that induce evolution (the change of the genetic constitution)
POPULATION GENETICS POPULATION GENETICS studies the genetic composition of populations and how it changes with time. It includes the study of forces that induce evolution (the change of the genetic constitution)
Figure 1. Distinguishable and Indistinguishable Genotypes
 Figure 1. Distinguishable and Indistinguishable Genotypes When the wild-type and mutant homozygous genotypes are symmetric with respect to nearest-neighbor thermodynamics, their normalized melting curves
Figure 1. Distinguishable and Indistinguishable Genotypes When the wild-type and mutant homozygous genotypes are symmetric with respect to nearest-neighbor thermodynamics, their normalized melting curves
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Science. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2013 June 21.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Science. 2012 December 21; 338(6114): 1622 1626. doi:10.1126/science.1229164. Genome-Wide Detection of Single Nucleotide and Copy
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Science. 2012 December 21; 338(6114): 1622 1626. doi:10.1126/science.1229164. Genome-Wide Detection of Single Nucleotide and Copy
Wu et al., Determination of genetic identity in therapeutic chimeric states. We used two approaches for identifying potentially suitable deletion loci
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS AND DATA General strategy for identifying deletion loci We used two approaches for identifying potentially suitable deletion loci for PDP-FISH analysis. In the first approach, we
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS AND DATA General strategy for identifying deletion loci We used two approaches for identifying potentially suitable deletion loci for PDP-FISH analysis. In the first approach, we
Outline. General principles of clonal sequencing Analysis principles Applications CNV analysis Genome architecture
 The use of new sequencing technologies for genome analysis Chris Mattocks National Genetics Reference Laboratory (Wessex) NGRL (Wessex) 2008 Outline General principles of clonal sequencing Analysis principles
The use of new sequencing technologies for genome analysis Chris Mattocks National Genetics Reference Laboratory (Wessex) NGRL (Wessex) 2008 Outline General principles of clonal sequencing Analysis principles
QIAGEN Whole Genome Amplification REPLI-g Eliminating Sample Limitations, Potential Use for Reference Material
 QIAGEN Whole Genome Amplification REPLI-g Eliminating Sample Limitations, Potential Use for Reference Material MDA Technology Protocols Locus Bias Applications Kits & Service Summary QIAGEN REPLI-g WGA
QIAGEN Whole Genome Amplification REPLI-g Eliminating Sample Limitations, Potential Use for Reference Material MDA Technology Protocols Locus Bias Applications Kits & Service Summary QIAGEN REPLI-g WGA
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Contents De novo assembly... 2 Assembly statistics for all 150 individuals... 2 HHV6b integration... 2 Comparison of assemblers... 4 Variant calling and genotyping... 4 Protein truncating variants (PTV)...
Contents De novo assembly... 2 Assembly statistics for all 150 individuals... 2 HHV6b integration... 2 Comparison of assemblers... 4 Variant calling and genotyping... 4 Protein truncating variants (PTV)...
Supplementary Information for:
 Supplementary Information for: A streamlined and high-throughput targeting approach for human germline and cancer genomes using Oligonucleotide-Selective Sequencing Samuel Myllykangas 1, Jason D. Buenrostro
Supplementary Information for: A streamlined and high-throughput targeting approach for human germline and cancer genomes using Oligonucleotide-Selective Sequencing Samuel Myllykangas 1, Jason D. Buenrostro
SureSelect Target Enrichment for the Ion Proton TM Next Generation Sequencing System
 SureSelect Target Enrichment for the Ion Proton TM Next Generation Sequencing System Demonstrated performance you can count on Christina Chiu Product Manager, SureSelect Kyeong Jeong Ph.D. R&D Scientist
SureSelect Target Enrichment for the Ion Proton TM Next Generation Sequencing System Demonstrated performance you can count on Christina Chiu Product Manager, SureSelect Kyeong Jeong Ph.D. R&D Scientist
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Concept of barcoding to suppress error in sequencing. Each template DNA molecule is barcoded with a random and unique sequence (marked as red, turquoise and green). All PCR generated
Supplementary Figure 1 Concept of barcoding to suppress error in sequencing. Each template DNA molecule is barcoded with a random and unique sequence (marked as red, turquoise and green). All PCR generated
Sample to Insight. Dr. Bhagyashree S. Birla NGS Field Application Scientist
 Dr. Bhagyashree S. Birla NGS Field Application Scientist bhagyashree.birla@qiagen.com NGS spans a broad range of applications DNA Applications Human ID Liquid biopsy Biomarker discovery Inherited and somatic
Dr. Bhagyashree S. Birla NGS Field Application Scientist bhagyashree.birla@qiagen.com NGS spans a broad range of applications DNA Applications Human ID Liquid biopsy Biomarker discovery Inherited and somatic
Add 2016 GBS Poster As Slide One
 Add 2016 GBS Poster As Slide One GBS Adapters and Enzymes Barcode Adapter P1 Sticky Ends Common Adapter P2 Illumina Sequencing Primer 2 Barcode (4 8 bp) Restriction Enzymes Illumina Sequencing Primer 1
Add 2016 GBS Poster As Slide One GBS Adapters and Enzymes Barcode Adapter P1 Sticky Ends Common Adapter P2 Illumina Sequencing Primer 2 Barcode (4 8 bp) Restriction Enzymes Illumina Sequencing Primer 1
C3BI. VARIANTS CALLING November Pierre Lechat Stéphane Descorps-Declère
 C3BI VARIANTS CALLING November 2016 Pierre Lechat Stéphane Descorps-Declère General Workflow (GATK) software websites software bwa picard samtools GATK IGV tablet vcftools website http://bio-bwa.sourceforge.net/
C3BI VARIANTS CALLING November 2016 Pierre Lechat Stéphane Descorps-Declère General Workflow (GATK) software websites software bwa picard samtools GATK IGV tablet vcftools website http://bio-bwa.sourceforge.net/
Mutations during meiosis and germ line division lead to genetic variation between individuals
 Mutations during meiosis and germ line division lead to genetic variation between individuals Types of mutations: point mutations indels (insertion/deletion) copy number variation structural rearrangements
Mutations during meiosis and germ line division lead to genetic variation between individuals Types of mutations: point mutations indels (insertion/deletion) copy number variation structural rearrangements
PaSD-qc: quality control for single cell whole-genome sequencing data using power spectral density estimation
 Published online 25 November 2017 Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, Vol. 46, No. 4 e20 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1195 PaSD-qc: quality control for single cell whole-genome sequencing data using power spectral density
Published online 25 November 2017 Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, Vol. 46, No. 4 e20 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1195 PaSD-qc: quality control for single cell whole-genome sequencing data using power spectral density
Structural variation analysis using NGS sequencing
 Structural variation analysis using NGS sequencing Victor Guryev NBIC NGS taskforce meeting April 15th, 2011 Scale of genomic variants Scale 1 bp 10 bp 100 bp 1 kb 10 kb 100 kb 1 Mb Variants SNPs Short
Structural variation analysis using NGS sequencing Victor Guryev NBIC NGS taskforce meeting April 15th, 2011 Scale of genomic variants Scale 1 bp 10 bp 100 bp 1 kb 10 kb 100 kb 1 Mb Variants SNPs Short
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Quantifying RNA allelic ratios by microfluidic multiplex PCR and sequencing Rui Zhang¹, Xin Li², Gokul Ramaswami¹, Kevin S Smith², Gustavo Turecki 3, Stephen B Montgomery¹, ²,
Supplementary Information Quantifying RNA allelic ratios by microfluidic multiplex PCR and sequencing Rui Zhang¹, Xin Li², Gokul Ramaswami¹, Kevin S Smith², Gustavo Turecki 3, Stephen B Montgomery¹, ²,
GDMS Templates Documentation GDMS Templates Release 1.0
 GDMS Templates Documentation GDMS Templates Release 1.0 1 Table of Contents 1. SSR Genotyping Template 03 2. DArT Genotyping Template... 05 3. SNP Genotyping Template.. 08 4. QTL Template.. 09 5. Map Template..
GDMS Templates Documentation GDMS Templates Release 1.0 1 Table of Contents 1. SSR Genotyping Template 03 2. DArT Genotyping Template... 05 3. SNP Genotyping Template.. 08 4. QTL Template.. 09 5. Map Template..
Microsatellite markers
 Microsatellite markers Review of repetitive sequences 25% 45% 8% 21% 13% 3% Mobile genetic elements: = dispersed repeat included: transposition: moving in the form of DNA by element coding for transposases.
Microsatellite markers Review of repetitive sequences 25% 45% 8% 21% 13% 3% Mobile genetic elements: = dispersed repeat included: transposition: moving in the form of DNA by element coding for transposases.
SureSelect XT HS. Target Enrichment
 SureSelect XT HS Target Enrichment What Is It? SureSelect XT HS joins the SureSelect library preparation reagent family as Agilent s highest sensitivity hybrid capture-based library prep and target enrichment
SureSelect XT HS Target Enrichment What Is It? SureSelect XT HS joins the SureSelect library preparation reagent family as Agilent s highest sensitivity hybrid capture-based library prep and target enrichment
Targeted Sequencing Using Droplet-Based Microfluidics. Keith Brown Director, Sales
 Targeted Sequencing Using Droplet-Based Microfluidics Keith Brown Director, Sales brownk@raindancetech.com Who we are: is a Provider of Microdroplet-based Solutions The Company s RainStorm TM Technology
Targeted Sequencing Using Droplet-Based Microfluidics Keith Brown Director, Sales brownk@raindancetech.com Who we are: is a Provider of Microdroplet-based Solutions The Company s RainStorm TM Technology
CS273B: Deep Learning in Genomics and Biomedicine. Recitation 1 30/9/2016
 CS273B: Deep Learning in Genomics and Biomedicine. Recitation 1 30/9/2016 Topics Genetic variation Population structure Linkage disequilibrium Natural disease variants Genome Wide Association Studies Gene
CS273B: Deep Learning in Genomics and Biomedicine. Recitation 1 30/9/2016 Topics Genetic variation Population structure Linkage disequilibrium Natural disease variants Genome Wide Association Studies Gene
Deep learning sequence-based ab initio prediction of variant effects on expression and disease risk
 Summer Review 7 Deep learning sequence-based ab initio prediction of variant effects on expression and disease risk Jian Zhou 1,2,3, Chandra L. Theesfeld 1, Kevin Yao 3, Kathleen M. Chen 3, Aaron K. Wong
Summer Review 7 Deep learning sequence-based ab initio prediction of variant effects on expression and disease risk Jian Zhou 1,2,3, Chandra L. Theesfeld 1, Kevin Yao 3, Kathleen M. Chen 3, Aaron K. Wong
Shaare Zedek Medical Center (SZMC) Gaucher Clinic. Peripheral blood samples were collected from each
 SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Sample collection and DNA extraction Pregnant Ashkenazi Jewish (AJ) couples, carrying mutation/s in the GBA gene, were recruited at the Shaare Zedek Medical Center (SZMC) Gaucher Clinic.
SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Sample collection and DNA extraction Pregnant Ashkenazi Jewish (AJ) couples, carrying mutation/s in the GBA gene, were recruited at the Shaare Zedek Medical Center (SZMC) Gaucher Clinic.
What is genetic variation?
 enetic Variation Applied Computational enomics, Lecture 05 https://github.com/quinlan-lab/applied-computational-genomics Aaron Quinlan Departments of Human enetics and Biomedical Informatics USTAR Center
enetic Variation Applied Computational enomics, Lecture 05 https://github.com/quinlan-lab/applied-computational-genomics Aaron Quinlan Departments of Human enetics and Biomedical Informatics USTAR Center
High-Resolution Oligonucleotide- Based acgh Analysis of Single Cells in Under 24 Hours
 High-Resolution Oligonucleotide- Based acgh Analysis of Single Cells in Under 24 Hours Application Note Authors Paula Costa and Anniek De Witte Agilent Technologies, Inc. Santa Clara, CA USA Abstract As
High-Resolution Oligonucleotide- Based acgh Analysis of Single Cells in Under 24 Hours Application Note Authors Paula Costa and Anniek De Witte Agilent Technologies, Inc. Santa Clara, CA USA Abstract As
Understanding Accuracy in SMRT Sequencing
 Understanding Accuracy in SMRT Sequencing Jonas Korlach, Chief Scientific Officer, Pacific Biosciences Introduction Single Molecule, Real-Time (SMRT ) DNA sequencing achieves highly accurate sequencing
Understanding Accuracy in SMRT Sequencing Jonas Korlach, Chief Scientific Officer, Pacific Biosciences Introduction Single Molecule, Real-Time (SMRT ) DNA sequencing achieves highly accurate sequencing
SNP calling and VCF format
 SNP calling and VCF format Laurent Falquet, Oct 12 SNP? What is this? A type of genetic variation, among others: Family of Single Nucleotide Aberrations Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) Single Nucleotide
SNP calling and VCF format Laurent Falquet, Oct 12 SNP? What is this? A type of genetic variation, among others: Family of Single Nucleotide Aberrations Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) Single Nucleotide
NUCLEOTIDE RESOLUTION STRUCTURAL VARIATION DETECTION USING NEXT- GENERATION WHOLE GENOME RESEQUENCING
 NUCLEOTIDE RESOLUTION STRUCTURAL VARIATION DETECTION USING NEXT- GENERATION WHOLE GENOME RESEQUENCING Ken Chen, Ph.D. kchen@genome.wustl.edu The Genome Center, Washington University in St. Louis The path
NUCLEOTIDE RESOLUTION STRUCTURAL VARIATION DETECTION USING NEXT- GENERATION WHOLE GENOME RESEQUENCING Ken Chen, Ph.D. kchen@genome.wustl.edu The Genome Center, Washington University in St. Louis The path
Parts of a standard FastQC report
 FastQC FastQC, written by Simon Andrews of Babraham Bioinformatics, is a very popular tool used to provide an overview of basic quality control metrics for raw next generation sequencing data. There are
FastQC FastQC, written by Simon Andrews of Babraham Bioinformatics, is a very popular tool used to provide an overview of basic quality control metrics for raw next generation sequencing data. There are
Genomic Technologies. Michael Schatz. Feb 1, 2018 Lecture 2: Applied Comparative Genomics
 Genomic Technologies Michael Schatz Feb 1, 2018 Lecture 2: Applied Comparative Genomics Welcome! The primary goal of the course is for students to be grounded in theory and leave the course empowered to
Genomic Technologies Michael Schatz Feb 1, 2018 Lecture 2: Applied Comparative Genomics Welcome! The primary goal of the course is for students to be grounded in theory and leave the course empowered to
DNA is contained in the nucleus of every cell in your body. Cell Nucleus
 DNA is contained in the nucleus of every cell in your body Cell Nucleus 1 DNA has a spiral staircase-like structure. The steps are formed by the nitrogen bases of the nucleotides where adenine pairs with
DNA is contained in the nucleus of every cell in your body Cell Nucleus 1 DNA has a spiral staircase-like structure. The steps are formed by the nitrogen bases of the nucleotides where adenine pairs with
Get to Know Your DNA. Every Single Fragment.
 HaloPlex HS NGS Target Enrichment System Get to Know Your DNA. Every Single Fragment. High sensitivity detection of rare variants using molecular barcodes How Does Molecular Barcoding Work? HaloPlex HS
HaloPlex HS NGS Target Enrichment System Get to Know Your DNA. Every Single Fragment. High sensitivity detection of rare variants using molecular barcodes How Does Molecular Barcoding Work? HaloPlex HS
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt.4166
 Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of correct targeting at targeted locus. (a) by immunofluorescence staining of 2C-HR-CRISPR microinjected embryos cultured to the blastocyst stage. Embryos were stained
Supplementary Figure 1 Validation of correct targeting at targeted locus. (a) by immunofluorescence staining of 2C-HR-CRISPR microinjected embryos cultured to the blastocyst stage. Embryos were stained
SUPPLEMENT MATERIALS FOR CURTIN,
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 SUPPLEMENT MATERIALS FOR CURTIN, et al. Validating genome-wide association candidates: Selecting, testing, and characterizing
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 SUPPLEMENT MATERIALS FOR CURTIN, et al. Validating genome-wide association candidates: Selecting, testing, and characterizing
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Pilot CrY2H-seq experiments to confirm strain and plasmid functionality.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Pilot CrY2H-seq experiments to confirm strain and plasmid functionality. (a) RT-PCR on HIS3 positive diploid cell lysate containing known interaction partners AT3G62420 (bzip53)
Supplementary Figure 1 Pilot CrY2H-seq experiments to confirm strain and plasmid functionality. (a) RT-PCR on HIS3 positive diploid cell lysate containing known interaction partners AT3G62420 (bzip53)
GENE MAPPING. Genetica per Scienze Naturali a.a prof S. Presciuttini
 GENE MAPPING Questo documento è pubblicato sotto licenza Creative Commons Attribuzione Non commerciale Condividi allo stesso modo http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/deed.it Genetic mapping
GENE MAPPING Questo documento è pubblicato sotto licenza Creative Commons Attribuzione Non commerciale Condividi allo stesso modo http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/deed.it Genetic mapping
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth.4396
 Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of technical replicate consistency between and across the standard ATAC-seq method, DNase-seq, and Omni-ATAC. (a) Heatmap-based representation of ATAC-seq quality control
Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of technical replicate consistency between and across the standard ATAC-seq method, DNase-seq, and Omni-ATAC. (a) Heatmap-based representation of ATAC-seq quality control
Mate-pair library data improves genome assembly
 De Novo Sequencing on the Ion Torrent PGM APPLICATION NOTE Mate-pair library data improves genome assembly Highly accurate PGM data allows for de Novo Sequencing and Assembly For a draft assembly, generate
De Novo Sequencing on the Ion Torrent PGM APPLICATION NOTE Mate-pair library data improves genome assembly Highly accurate PGM data allows for de Novo Sequencing and Assembly For a draft assembly, generate
Performance of the Newly Developed Non-Invasive Prenatal Multi- Gene Sequencing Screen
 1 // Performance of the Newly Developed Non-Invasive Prenatal Multi- Gene Sequencing Screen ABSTRACT Here we describe the analytical performance of the newly developed non-invasive prenatal multi-gene
1 // Performance of the Newly Developed Non-Invasive Prenatal Multi- Gene Sequencing Screen ABSTRACT Here we describe the analytical performance of the newly developed non-invasive prenatal multi-gene
Introduction to some aspects of molecular genetics
 Introduction to some aspects of molecular genetics Julius van der Werf (partly based on notes from Margaret Katz) University of New England, Armidale, Australia Genetic and Physical maps of the genome...
Introduction to some aspects of molecular genetics Julius van der Werf (partly based on notes from Margaret Katz) University of New England, Armidale, Australia Genetic and Physical maps of the genome...
Reading Lecture 8: Lecture 9: Lecture 8. DNA Libraries. Definition Types Construction
 Lecture 8 Reading Lecture 8: 96-110 Lecture 9: 111-120 DNA Libraries Definition Types Construction 142 DNA Libraries A DNA library is a collection of clones of genomic fragments or cdnas from a certain
Lecture 8 Reading Lecture 8: 96-110 Lecture 9: 111-120 DNA Libraries Definition Types Construction 142 DNA Libraries A DNA library is a collection of clones of genomic fragments or cdnas from a certain
Mapping long-range promoter contacts in human cells with high-resolution capture Hi-C
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Genet. 47, 598 606 (2015) Mapping long-range promoter contacts in human cells with high-resolution capture Hi-C Borbala Mifsud, Filipe Tavares-Cadete, Alice N Young, Robert Sugar,
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Genet. 47, 598 606 (2015) Mapping long-range promoter contacts in human cells with high-resolution capture Hi-C Borbala Mifsud, Filipe Tavares-Cadete, Alice N Young, Robert Sugar,
High-yield, Scalable Library Preparation with the NEBNext Ultra II FS DNA Library Prep Kit
 be INSPIRED drive DISCOVERY stay GENUINE TECHNICAL NOTE High-yield, Scalable Library Preparation with the NEBNext Ultra II FS DNA Library Prep Kit Improving performance, ease of use and reliability of
be INSPIRED drive DISCOVERY stay GENUINE TECHNICAL NOTE High-yield, Scalable Library Preparation with the NEBNext Ultra II FS DNA Library Prep Kit Improving performance, ease of use and reliability of
Genomic resources. for non-model systems
 Genomic resources for non-model systems 1 Genomic resources Whole genome sequencing reference genome sequence comparisons across species identify signatures of natural selection population-level resequencing
Genomic resources for non-model systems 1 Genomic resources Whole genome sequencing reference genome sequence comparisons across species identify signatures of natural selection population-level resequencing
Normal-Tumor Comparison using Next-Generation Sequencing Data
 Normal-Tumor Comparison using Next-Generation Sequencing Data Chun Li Vanderbilt University Taichung, March 16, 2011 Next-Generation Sequencing First-generation (Sanger sequencing): 115 kb per day per
Normal-Tumor Comparison using Next-Generation Sequencing Data Chun Li Vanderbilt University Taichung, March 16, 2011 Next-Generation Sequencing First-generation (Sanger sequencing): 115 kb per day per
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09937 a Name Position Primersets 1a 1b 2 3 4 b2 Phenotype Genotype b Primerset 1a D T C R I E 10000 8000 6000 5000 4000 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 800 Donor (D)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09937 a Name Position Primersets 1a 1b 2 3 4 b2 Phenotype Genotype b Primerset 1a D T C R I E 10000 8000 6000 5000 4000 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000 800 Donor (D)
Nature Methods Optimal enzymes for amplifying sequencing libraries
 Nature Methods Optimal enzymes for amplifying sequencing libraries Michael A Quail, Thomas D Otto, Yong Gu, Simon R Harris, Thomas F Skelly, Jacqueline A McQuillan, Harold P Swerdlow & Samuel O Oyola Supplementary
Nature Methods Optimal enzymes for amplifying sequencing libraries Michael A Quail, Thomas D Otto, Yong Gu, Simon R Harris, Thomas F Skelly, Jacqueline A McQuillan, Harold P Swerdlow & Samuel O Oyola Supplementary
Processing Ion AmpliSeq Data using NextGENe Software v2.3.0
 Processing Ion AmpliSeq Data using NextGENe Software v2.3.0 July 2012 John McGuigan, Megan Manion, Kevin LeVan, CS Jonathan Liu Introduction The Ion AmpliSeq Panels use highly multiplexed PCR in order
Processing Ion AmpliSeq Data using NextGENe Software v2.3.0 July 2012 John McGuigan, Megan Manion, Kevin LeVan, CS Jonathan Liu Introduction The Ion AmpliSeq Panels use highly multiplexed PCR in order
Midterm 1 Results. Midterm 1 Akey/ Fields Median Number of Students. Exam Score
 Midterm 1 Results 10 Midterm 1 Akey/ Fields Median - 69 8 Number of Students 6 4 2 0 21 26 31 36 41 46 51 56 61 66 71 76 81 86 91 96 101 Exam Score Quick review of where we left off Parental type: the
Midterm 1 Results 10 Midterm 1 Akey/ Fields Median - 69 8 Number of Students 6 4 2 0 21 26 31 36 41 46 51 56 61 66 71 76 81 86 91 96 101 Exam Score Quick review of where we left off Parental type: the
Ad5 genome. Before filtering. After filtering. Suppl. File 4 PAGE mated reads. Ad5 DNA insertion site 5' 3' 293 unmated reads
 Before filtering 0 20 40 60 80 293 Ad5 DNA insertion site 5' 3' 0 20 60 100 48 000 000 48 100 000 48 200 000 48 300 000 48 400 000 48 500 000 After filtering 48 000 000 48 100 000 48 200 000 48 300 000
Before filtering 0 20 40 60 80 293 Ad5 DNA insertion site 5' 3' 0 20 60 100 48 000 000 48 100 000 48 200 000 48 300 000 48 400 000 48 500 000 After filtering 48 000 000 48 100 000 48 200 000 48 300 000
Full-length single-cell RNA-seq applied to a viral human. cancer: Applications to HPV expression and splicing analysis. Supplementary Information
 Full-length single-cell RNA-seq applied to a viral human cancer: Applications to HPV expression and splicing analysis in HeLa S3 cells Liang Wu 1, Xiaolong Zhang 1,2, Zhikun Zhao 1,3,4, Ling Wang 5, Bo
Full-length single-cell RNA-seq applied to a viral human cancer: Applications to HPV expression and splicing analysis in HeLa S3 cells Liang Wu 1, Xiaolong Zhang 1,2, Zhikun Zhao 1,3,4, Ling Wang 5, Bo
Human SNP haplotypes. Statistics 246, Spring 2002 Week 15, Lecture 1
 Human SNP haplotypes Statistics 246, Spring 2002 Week 15, Lecture 1 Human single nucleotide polymorphisms The majority of human sequence variation is due to substitutions that have occurred once in the
Human SNP haplotypes Statistics 246, Spring 2002 Week 15, Lecture 1 Human single nucleotide polymorphisms The majority of human sequence variation is due to substitutions that have occurred once in the
% Viability. isw2 ino isw2 ino isw2 ino isw2 ino mM HU 4-NQO CPT
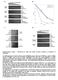 a Drug concentration b 1.3% MMS nhp1 nhp1 8 nhp1 mag1.5% MMS.3% MMS nhp1 nhp1 ino8 9 ino8 9 % Viability 4.5% MMS ino8 9 ino8 9 2.5.1.15 % MMS c d nhp1 nhp1 nhp1 nhp1 nhp1 nhp1 Control (YPD) γ IR (1 gy)
a Drug concentration b 1.3% MMS nhp1 nhp1 8 nhp1 mag1.5% MMS.3% MMS nhp1 nhp1 ino8 9 ino8 9 % Viability 4.5% MMS ino8 9 ino8 9 2.5.1.15 % MMS c d nhp1 nhp1 nhp1 nhp1 nhp1 nhp1 Control (YPD) γ IR (1 gy)
STR DNA Data Analysis. Genetic Analysis
 STR DNA Data Analysis Genetic Analysis Once a DNA profile is generated, how does one interpret the data? DNA data analysis is based on alleles detected DNA data analysis rarely can tell you time of deposit
STR DNA Data Analysis Genetic Analysis Once a DNA profile is generated, how does one interpret the data? DNA data analysis is based on alleles detected DNA data analysis rarely can tell you time of deposit
Single-cell genome sequencing at ultra-high-throughput with microfluidic droplet barcoding
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Biotechnol. doi:10.1038/nbt.3880 Single-cell genome sequencing at ultra-high-throughput with microfluidic droplet barcoding Freeman Lan, Benjamin Demaree, Noorsher Ahmed & Adam R
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Biotechnol. doi:10.1038/nbt.3880 Single-cell genome sequencing at ultra-high-throughput with microfluidic droplet barcoding Freeman Lan, Benjamin Demaree, Noorsher Ahmed & Adam R
Supplementary Figures Montero et al._supplementary Figure 1
 Montero et al_suppl. Info 1 Supplementary Figures Montero et al._supplementary Figure 1 Montero et al_suppl. Info 2 Supplementary Figure 1. Transcripts arising from the structurally conserved subtelomeres
Montero et al_suppl. Info 1 Supplementary Figures Montero et al._supplementary Figure 1 Montero et al_suppl. Info 2 Supplementary Figure 1. Transcripts arising from the structurally conserved subtelomeres
ACCEL-NGS 2S DNA LIBRARY KITS
 ACCEL-NGS 2S DNA LIBRARY KITS Accel-NGS 2S DNA Library Kits produce high quality libraries with an all-inclusive, easy-to-use format. The kits contain all reagents necessary to build high complexity libraries
ACCEL-NGS 2S DNA LIBRARY KITS Accel-NGS 2S DNA Library Kits produce high quality libraries with an all-inclusive, easy-to-use format. The kits contain all reagents necessary to build high complexity libraries
Agilent NGS Solutions : Addressing Today s Challenges
 Agilent NGS Solutions : Addressing Today s Challenges Charmian Cher, Ph.D Director, Global Marketing Programs 1 10 years of Next-Gen Sequencing 2003 Completion of the Human Genome Project 2004 Pyrosequencing
Agilent NGS Solutions : Addressing Today s Challenges Charmian Cher, Ph.D Director, Global Marketing Programs 1 10 years of Next-Gen Sequencing 2003 Completion of the Human Genome Project 2004 Pyrosequencing
Algorithms for Genetics: Introduction, and sources of variation
 Algorithms for Genetics: Introduction, and sources of variation Scribe: David Dean Instructor: Vineet Bafna 1 Terms Genotype: the genetic makeup of an individual. For example, we may refer to an individual
Algorithms for Genetics: Introduction, and sources of variation Scribe: David Dean Instructor: Vineet Bafna 1 Terms Genotype: the genetic makeup of an individual. For example, we may refer to an individual
Next GEM Next Generation Mutagenesis. Guri Johal. Department of Botany and Plant Pathology. Purdue University
 Next GEM Next Generation Mutagenesis Guri Johal Department of Botany and Plant Pathology Purdue University June 24, 2015 The focus of this approach is how to enhance genetic variation, which drives almost
Next GEM Next Generation Mutagenesis Guri Johal Department of Botany and Plant Pathology Purdue University June 24, 2015 The focus of this approach is how to enhance genetic variation, which drives almost
Implementation of Ion AmpliSeq in molecular diagnostics
 Implementation of Ion AmpliSeq in molecular diagnostics The Rotterdam Experience Ronald van Marion Deelnemersbijeenkomst SKML sectie Pathologie Amersfoort, 26 mei 2016 Molecular Diagnostics in Rotterdam
Implementation of Ion AmpliSeq in molecular diagnostics The Rotterdam Experience Ronald van Marion Deelnemersbijeenkomst SKML sectie Pathologie Amersfoort, 26 mei 2016 Molecular Diagnostics in Rotterdam
Next Generation Genetics: Using deep sequencing to connect phenotype to genotype
 Next Generation Genetics: Using deep sequencing to connect phenotype to genotype http://1001genomes.org Korbinian Schneeberger Connecting Genotype and Phenotype Genotyping SNPs small Resequencing SVs*
Next Generation Genetics: Using deep sequencing to connect phenotype to genotype http://1001genomes.org Korbinian Schneeberger Connecting Genotype and Phenotype Genotyping SNPs small Resequencing SVs*
A Genomics (R)evolution: Harnessing the Power of Single Cells
 A Genomics (R)evolution: Harnessing the Power of Single Cells Fundamental Question #1 If Transcriptional Heterogeneity ( Noise ) is so great in single cells What s the Point? Single Cells = True Biology
A Genomics (R)evolution: Harnessing the Power of Single Cells Fundamental Question #1 If Transcriptional Heterogeneity ( Noise ) is so great in single cells What s the Point? Single Cells = True Biology
Amplicon size (bp) E ± SD
 Development of a probe-based qpcr assay for the detection of constitutional and somatic deletions in the NF1 gene. Application to genetic testing and tumor analysis. Terribas E, Garcia-Linares C, Lázaro
Development of a probe-based qpcr assay for the detection of constitutional and somatic deletions in the NF1 gene. Application to genetic testing and tumor analysis. Terribas E, Garcia-Linares C, Lázaro
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information High-order chromatin architecture determines the landscape of chromosomal alterations in cancer Geoff Fudenberg 1, Gad Getz 2, Matthew Meyerson 2,3,4,5, Leonid Mirny 2,6,7,* Author
Supplementary Information High-order chromatin architecture determines the landscape of chromosomal alterations in cancer Geoff Fudenberg 1, Gad Getz 2, Matthew Meyerson 2,3,4,5, Leonid Mirny 2,6,7,* Author
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Ideograms showing scaffold boundaries and segmental duplication locations.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Ideograms showing scaffold boundaries and segmental duplication locations. Blue lines mark the boundaries of scaffolds. Black marks show the locations of segmental duplications.
Supplementary Figure 1 Ideograms showing scaffold boundaries and segmental duplication locations. Blue lines mark the boundaries of scaffolds. Black marks show the locations of segmental duplications.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS
 SUPPLEMENL MERILS Eh-seq: RISPR epitope tagging hip-seq of DN-binding proteins Daniel Savic, E. hristopher Partridge, Kimberly M. Newberry, Sophia. Smith, Sarah K. Meadows, rian S. Roberts, Mark Mackiewicz,
SUPPLEMENL MERILS Eh-seq: RISPR epitope tagging hip-seq of DN-binding proteins Daniel Savic, E. hristopher Partridge, Kimberly M. Newberry, Sophia. Smith, Sarah K. Meadows, rian S. Roberts, Mark Mackiewicz,
SURESELECTXT LOW INPUT TARGET ENRICHMENT
 SURESELECTXT LOW INPUT TARGET ENRICHMENT Low Input FFPE Optimized Streamlined Workflow SureSelect XT Low Input What is it? SureSelect XT Low Input is a low-input, FFPE-optimized library preparation kit.
SURESELECTXT LOW INPUT TARGET ENRICHMENT Low Input FFPE Optimized Streamlined Workflow SureSelect XT Low Input What is it? SureSelect XT Low Input is a low-input, FFPE-optimized library preparation kit.
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: The proportion of somatic SNVs in each tumor is shown in a trinucleotide context. The data represent 31 exome-sequenced osteosarcomas. Note that the mutation
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1: The proportion of somatic SNVs in each tumor is shown in a trinucleotide context. The data represent 31 exome-sequenced osteosarcomas. Note that the mutation
Certificate of Analysis of the Holotype HLA 24/7 Configuration A1 & CE
 Certificate of Analysis of the Holotype HLA 24/7 Configuration A1 & CE Product name Holotype HLA 24/7 Configuration A1 & CE Reference number H52 LOT number 00027 (N4/002-P5/006-E1/004-R2/006) Expiration
Certificate of Analysis of the Holotype HLA 24/7 Configuration A1 & CE Product name Holotype HLA 24/7 Configuration A1 & CE Reference number H52 LOT number 00027 (N4/002-P5/006-E1/004-R2/006) Expiration
Bi 8 Lecture 4. Ellen Rothenberg 14 January Reading: from Alberts Ch. 8
 Bi 8 Lecture 4 DNA approaches: How we know what we know Ellen Rothenberg 14 January 2016 Reading: from Alberts Ch. 8 Central concept: DNA or RNA polymer length as an identifying feature RNA has intrinsically
Bi 8 Lecture 4 DNA approaches: How we know what we know Ellen Rothenberg 14 January 2016 Reading: from Alberts Ch. 8 Central concept: DNA or RNA polymer length as an identifying feature RNA has intrinsically
Supplementary Figure 1 An overview of pirna biogenesis during fetal mouse reprogramming. (a) (b)
 Supplementary Figure 1 An overview of pirna biogenesis during fetal mouse reprogramming. (a) A schematic overview of the production and amplification of a single pirna from a transposon transcript. The
Supplementary Figure 1 An overview of pirna biogenesis during fetal mouse reprogramming. (a) A schematic overview of the production and amplification of a single pirna from a transposon transcript. The
Authors: Vivek Sharma and Ram Kunwar
 Molecular markers types and applications A genetic marker is a gene or known DNA sequence on a chromosome that can be used to identify individuals or species. Why we need Molecular Markers There will be
Molecular markers types and applications A genetic marker is a gene or known DNA sequence on a chromosome that can be used to identify individuals or species. Why we need Molecular Markers There will be
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.15 GENOMES AND GENOMICS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF GENOMICS Genomics is the study of genomes in their entirety Bioinformatics is the analysis of the information content of genomes - Genes, regulatory sequences,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF GENOMICS Genomics is the study of genomes in their entirety Bioinformatics is the analysis of the information content of genomes - Genes, regulatory sequences,
