Stocks, Breeding Records, and Tank Tags
|
|
|
- Silvester Wilkinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Stocks, Breeding Records, and Tank Tags Good record keeping is essential. We can trace most of our stocks all the way back to founding lines at the University of Oregon (c. 1980). We aim to preserve this continuity and in so doing avoid errors that could cost the lab months or years of lost effort. Stock basics All stocks of fish have an assigned stock name. Sometimes this name is provisional; names can change as projects are published, as crosses are performed, etc. Please ask Dave if you are not sure what a particular stock should be called, or whether two or more stocks are equivalent. Never, ever combine stocks without checking with Dave. Some stocks look alike but are very different genetically. For example, the lab maintains several lines of wild-type zebrafish that are nearly indistinguishable from one another. Some of these are inbred stocks used for genetic mapping (e.g., AB, wik, Tubingen); others are out-bred stocks used for embryo and larva production (e.g., WT). Phenotypes of several different mutants also resemble one another, as do some of our other danio species. Precautions must be taken to avoid accidental mixing of these phenotypically similar but genetically distinct stocks, including: placing tanks far apart on the racks, avoiding simultaneous breeding or tank cleaning, keeping tanks covered at all times, etc. Fish jump. Be aware of this as the fish can themselves contribute to stock mixing through such ballistic activity. Tank covers are a deterrent but do not eliminate jumping: fish occasionally launch themselves through feeding holes, sometimes landing on other tanks and diving in. Really. If you find a live fish outside of a tank, do not try to guess where it came from; instead, put it in a beaker with fish water and ask Dave what to do with it. Likewise, if you see a tank with an obvious contaminant phenotype, check with Dave to see what steps should be taken. Despite one s best intentions, mistakes happen. Please consult with Dave If you know or suspect you have made a mistake that affects a stock (e.g., accidentally mixing two stocks or mislabeling something). Most such errors are easily corrected. It is much better to fix problems as they arise than to discover them only weeks, months, or years later. 1 Allele Designations New mutants or transgenic lines are given allele designations that must always remain associated with the stock. Careful naming and tracking of alleles is critical for all of our analyses. Use the following guidelines in naming alleles: all formal allele designations carry the wp lab identifier (i.e., UW-Parichy lab); some older alleles are ut 1 Ask Dave for some specific and frightening examples. Parichy Lab 1 of 6 9/6/05, mod. 11/22/08, DP
2 our lab allele designations keep track of species, locus, mutation source, and allele number; this differs from many labs that use only sequential numbers the correct format for naming is: o wp.(species)(locus number)(mutation source)(unique allele ID) o species: r=rerio; a=albolineatus; b=burma; c=choprae n=nigrofasciatus; s=shanensis o locus number: each mutant locus in the lab has a unique identifier; currently used numbers are: 1=tuba8l3a/puma; 2=erbb3/picasso; 3=trpm7/nutria; 4=fms/csf1r/panther; 5=ednrb1; 6=TS38; 8=pissarro; 10=cx41.8/leopard; 11=kir7.1/jaguar; 12=oberon; 13= sox10/colourless; 14=kita/sparse; 15=seurat; 16=bnc2l/bonaparte; 17=cezanne; 18=degas; 19=duchamp; 20=chagall; 21=dali o mutation source: e=enu-induced; g=gamma-ray induced; s=spontaneous or from natural populations o allele ID: typically a series starting at 1 for each locus, though sometimes referring to the stock number of origin o using these conventions, for example, the ENU-induced D. albolineatus kit mutant is: kit wp.a14e1 temporary allele designations can be used for on-going screens; typically these will have just the locus name and the stock number in which they were identified (with a, b, etc. for multiple alleles from the same stock) transgenic lines should be named as: wp.(species)(transgene type)(clone ID)-(unique line ID) Breeding records o transgene type: t=tol2, b=bac o clone ID: as appears in the Parichy lab clones database (typically the LR clone); for example, wild-type from the second founding line for hsp70:xldio3-drires-nlscfp would receive the allele designation: wp.t532-2 (and might have on their tank tag hsp:dio3-cfp ; see below) All stocks of fish have a stock number and a stock name. Both are assigned shortly after embryos are fertilized and this information travels with the fish throughout their lives. For filling out breeding records (kept in the stock book), please see the example below follow these guidelines: Breeding records (stock number, stock name, etc.) are completed the same day that embryos for the stock are produced. Usually this is done when the embryos are sorted (see Embryo Care SOP). It is imperative that breeding records be written the day of breeding so that mix-ups can be avoided. Parichy Lab 2 of 6 9/6/05, mod. 11/22/08, DP
3 For assigning a stock number, use the following system: o New stocks are always assigned the next stock number in sequence. Check the current stock book to see what the last stock number (S#) was. (Fish arriving from other facilities also are assigned the next number in sequence, though such fish may remain in quarantine.) o If fish are bred pairwise so that every family has known parents, and the families are to remain separate, assign a numerical suffix to the stock number to identify families (e.g., , ). This information can greatly assist subsequent stock propagation and interpretation of phenotypes. o If fish are allowed to spawn naturally and in groups (i.e., >2 fish per tank), then it will not be certain how many parents contributed to the next generation. This information also is very important for stock propagation decisions and interpreting phenotypes. If batches are to be kept separate, then label the progeny resulting from each tank or batch with an alphabetical suffix (e.g., 1234A, 1234B); if the batches are to be combined subsequently, add an N to the stock name to indicate natural group spawning (1234N). For assigning a stock name, you should provide as much detail as possible, given the constraints of the tank tags (see below). In general: o This information should include the strain and allele (possibly in abbreviated form); for example, homozygous fms ut.r4e174a fish are labeled simply fms-174 ; homozygous fish doubly mutant for fms j4e1 and kit b5 are labeled simply fms kit. o Include in the name information about genetic background; this is especially true for outcrosses. For instance, fish outcrossed to wik should be named stock name x wik whereas fish outcrossed to AB should be named stock name x AB (e.g., fms-174 x AB ). o If a homozygous stock is intercrossed (i.e., brother-sister matings), no special designation is required. o If a heterozygous stock is intercrossed and the embryos can be sorted before they are placed on the rack, it can be labeled with the homozygous designation; for example progeny of kit/+ fish can be named kit if they are sorted for the embryonic kit mutant phenotype and fish placed on the rack are all mutants. If the heterozygous stock cannot be sorted, or there Parichy Lab 3 of 6 9/6/05, mod. 11/22/08, DP
4 is some other reason for keeping mixed phenotypes, the intercrossed stock name should include the designation i.c. (e.g., kit/+ i.c. ). o Naming of transgenic lines should include the allele designation (which refers to the clone identification number), as well as any pertinent information about promoter, fluorophore, and protein expressed. Additionally, fish should be labeled according to whether they are F0 (newly injected and mosaic) or F1 (ifrom a germ-line carrier and presumably non-mosaic). o As always, if you are not sure how to name a stock, ask Dave! Record your initials and the date the fish were bred (or when they arrived) in the breeding record. Note that fish room dates are always in the format numerical day / alphabetical month / numerical year ; e.g., 24 JUN 05. Record the stock numbers and complete stock names for the maternal and paternal stocks. Be careful that information read off of tank tags is transcribed accurately! Record whether the stock resulted from natural spawning or in vitro fertilization by circling natural or squeezed, respectively. This is important to record because fish generally need longer to recover from in vitro fertilization than natural spawning. In the Comments box indicate why the fish were bred (e.g., stock maintenance, complementation test, non-complementation screening, double mutant production) and how many were successfully bred (e.g., 2 pair; 4 male, 2 female; etc.). This is critical information that allows correct handling of the stock later on, and also can provide important information about the extent of inbreeding, etc. Tank tags All tanks, dishes, or other containers with embryos or fish are labeled with a tank tag. This tag travels with the fish throughout their lives and contains several important pieces of information. It is very important that all tags use a consistent format so that mistakes can be avoided. Please use the following guidelines: Tank tags must be written the day a stock is generated (or arrives). Every dish, tank, etc. must have its own tank tag. Labels must be written legibly in permanent ink (i.e., fine point sharpie). The bottom of the tag (illustrated below) includes the stock number, stock name, date of breeding (or arrival) in standard fish room format, initials of the researcher who generated or received the stock, and starting number of individuals in the container. The top of the tag is reserved for: survival data (how many remaining at hatching, etc.), whether fish have been sorted (must include initials and date of sorting), and breeding history (date, initials, and an indication of how successful the Parichy Lab 4 of 6 9/6/05, mod. 11/22/08, DP
5 breeding was). Collectively, these data are extremely important for stock maintenance and correct use. Tags are placed on the upper right corner of tanks so as not to obscure fish from view. Should a tag become too full of information or too faded, a new tag with just the bottom information is written and the old tag retained on the side of the tank. When fish are discarded, the tank tags are retained in a notebook kept in the fish room for this purpose. Parichy Lab 5 of 6 9/6/05, mod. 11/22/08, DP
6 I have read and understood the Stocks, Breeding Records, and Tank Tags SOP and I agree to abide by it. Name Signature Date Parichy Lab 6 of 6 9/6/05, mod. 11/22/08, DP
Genetics Lab Biology 322 Fall 2013
 Genetics Lab Biology 322 Fall 2013 CAENORHABDITIS ELEGANS AND MENDEL'S SECOND LAW REVISITED: Independent assortment versus linkage of gene pairs during gamete formation Allele and genotype symbolism: application
Genetics Lab Biology 322 Fall 2013 CAENORHABDITIS ELEGANS AND MENDEL'S SECOND LAW REVISITED: Independent assortment versus linkage of gene pairs during gamete formation Allele and genotype symbolism: application
7.22 ANSWERS to Problem set #1
 7.22 ANSWERS to Problem set #1 1. List whether the pairs marked by the arrows are orthologous or paralogous. α tubulin (mouse) α tubulin (fly) α tubulin (worm) α tubulin (yeast) paralogous Tubulin β tubulin
7.22 ANSWERS to Problem set #1 1. List whether the pairs marked by the arrows are orthologous or paralogous. α tubulin (mouse) α tubulin (fly) α tubulin (worm) α tubulin (yeast) paralogous Tubulin β tubulin
Tile Theory of Pre-Breeding
 189 Tile Theory of Pre-Breeding G. A. Smith USDA-Agricultural Research Service, Northern Crop Science Laboratory, Fargo, ND 58105 ABSTRACT Population changes and their dependent gene frequencies are affected
189 Tile Theory of Pre-Breeding G. A. Smith USDA-Agricultural Research Service, Northern Crop Science Laboratory, Fargo, ND 58105 ABSTRACT Population changes and their dependent gene frequencies are affected
Trasposable elements: Uses of P elements Problem set B at the end
 Trasposable elements: Uses of P elements Problem set B at the end P-elements have revolutionized the way Drosophila geneticists conduct their research. Here, we will discuss just a few of the approaches
Trasposable elements: Uses of P elements Problem set B at the end P-elements have revolutionized the way Drosophila geneticists conduct their research. Here, we will discuss just a few of the approaches
Fish room manual for visiting scientists. Ahituv Lab
 Fish room manual for visiting scientists Ahituv Lab Purpose This document is intended to give a brief overview of the Ahituv lab Zebrafish facility. Visitors working with zebrafish should known and understand
Fish room manual for visiting scientists Ahituv Lab Purpose This document is intended to give a brief overview of the Ahituv lab Zebrafish facility. Visitors working with zebrafish should known and understand
Biol 432L Midterm Oct 6, 2008 Name: 1. Midterm 1, Answer Key Oct. 26, 2009
 Biol 432L Midterm Oct 6, 2008 Name: 1 Midterm 1, Answer Key Oct. 26, 2009 Honor Pledge: I have neither given nor received any unauthorized help on this exam: Name Printed: Signature: 1a. (2 pts) Imagine
Biol 432L Midterm Oct 6, 2008 Name: 1 Midterm 1, Answer Key Oct. 26, 2009 Honor Pledge: I have neither given nor received any unauthorized help on this exam: Name Printed: Signature: 1a. (2 pts) Imagine
Answers to additional linkage problems.
 Spring 2013 Biology 321 Answers to Assignment Set 8 Chapter 4 http://fire.biol.wwu.edu/trent/trent/iga_10e_sm_chapter_04.pdf Answers to additional linkage problems. Problem -1 In this cell, there two copies
Spring 2013 Biology 321 Answers to Assignment Set 8 Chapter 4 http://fire.biol.wwu.edu/trent/trent/iga_10e_sm_chapter_04.pdf Answers to additional linkage problems. Problem -1 In this cell, there two copies
Additional Practice Problems for Reading Period
 BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Reading Period Additional Practice Problems for Reading Period Question 1. In patients with a particular type of leukemia, their leukemic B lymphocytes display a translocation
BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Reading Period Additional Practice Problems for Reading Period Question 1. In patients with a particular type of leukemia, their leukemic B lymphocytes display a translocation
Biology 163 Laboratory in Genetics Midterm 2, Nov. 14, Honor Pledge: I have neither given nor received any unauthorized help on this exam:
 1 Biology 163 Laboratory in Genetics Midterm 2, Nov. 14, 2005 Honor Pledge: I have neither given nor received any unauthorized help on this exam: Name Printed: ignature: 1. Normally you need to cross two
1 Biology 163 Laboratory in Genetics Midterm 2, Nov. 14, 2005 Honor Pledge: I have neither given nor received any unauthorized help on this exam: Name Printed: ignature: 1. Normally you need to cross two
Chapter 12 (Part III) Complementation Analysis
 Biology 234 J. G. Doheny Chapter 12 (Part III) Complementation Analysis You can use a Genetic Dissection analysis to find which genes and which proteins are involved in a biochemical process. (For example,
Biology 234 J. G. Doheny Chapter 12 (Part III) Complementation Analysis You can use a Genetic Dissection analysis to find which genes and which proteins are involved in a biochemical process. (For example,
A) (5 points) As the starting step isolate genomic DNA from
 GS Final Exam Spring 00 NAME. bub ts is a recessive temperature sensitive mutation in yeast. At º C bub ts cells grow normally, but at º C they die. Use the information below to clone the wild-type BUB
GS Final Exam Spring 00 NAME. bub ts is a recessive temperature sensitive mutation in yeast. At º C bub ts cells grow normally, but at º C they die. Use the information below to clone the wild-type BUB
Fertility Factors Fertility Research: Genetic Factors that Affect Fertility By Heather Smith-Thomas
 Fertility Factors Fertility Research: Genetic Factors that Affect Fertility By Heather Smith-Thomas With genomic sequencing technology, it is now possible to find genetic markers for various traits (good
Fertility Factors Fertility Research: Genetic Factors that Affect Fertility By Heather Smith-Thomas With genomic sequencing technology, it is now possible to find genetic markers for various traits (good
1a. What is the ratio of feathered to unfeathered shanks in the offspring of the above cross?
 1. Whether or not the shanks of chickens contains feathers is due to two independently assorting genes. Individuals have unfeathered shanks when they are homozygous for recessive genes at two loci; the
1. Whether or not the shanks of chickens contains feathers is due to two independently assorting genes. Individuals have unfeathered shanks when they are homozygous for recessive genes at two loci; the
Problem Set 2
 ame: 2006 7.012 Problem Set 2 Due before 5 PM on FRIDAY, September 29, 2006. Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YUR ASWERS THIS PRITUT. 1. You are doing a genetics experiment with
ame: 2006 7.012 Problem Set 2 Due before 5 PM on FRIDAY, September 29, 2006. Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YUR ASWERS THIS PRITUT. 1. You are doing a genetics experiment with
Genetics - Fall 2004 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Professor Chris Kaiser Professor Gerry Fink Professor Leona Samson
 7.03 - Genetics - Fall 2004 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Professor Chris Kaiser Professor Gerry Fink Professor Leona Samson 1 1. Consider an autosomal recessive trait that occurs at a frequency
7.03 - Genetics - Fall 2004 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Professor Chris Kaiser Professor Gerry Fink Professor Leona Samson 1 1. Consider an autosomal recessive trait that occurs at a frequency
Lecture 8: Transgenic Model Systems and RNAi
 Lecture 8: Transgenic Model Systems and RNAi I. Model systems 1. Caenorhabditis elegans Caenorhabditis elegans is a microscopic (~1 mm) nematode (roundworm) that normally lives in soil. It has become one
Lecture 8: Transgenic Model Systems and RNAi I. Model systems 1. Caenorhabditis elegans Caenorhabditis elegans is a microscopic (~1 mm) nematode (roundworm) that normally lives in soil. It has become one
Fall 2004 Animal Science 213 Animal Genetics EXAM Points Exam must be completed in INK!
 Fall 2004 Animal Science 213 Animal Genetics EXAM 3 125 Points Exam must be completed in INK! Name: KEY Multiple Choice (4 points each) 1. If an individual plant homozygous dominant for the single gene
Fall 2004 Animal Science 213 Animal Genetics EXAM 3 125 Points Exam must be completed in INK! Name: KEY Multiple Choice (4 points each) 1. If an individual plant homozygous dominant for the single gene
1a. What is the ratio of feathered to unfeathered shanks in the offspring of the above cross?
 Problem Set 5 answers 1. Whether or not the shanks of chickens contains feathers is due to two independently assorting genes. Individuals have unfeathered shanks when they are homozygous for recessive
Problem Set 5 answers 1. Whether or not the shanks of chickens contains feathers is due to two independently assorting genes. Individuals have unfeathered shanks when they are homozygous for recessive
B) You can conclude that A 1 is identical by descent. Notice that A2 had to come from the father (and therefore, A1 is maternal in both cases).
 Homework questions. Please provide your answers on a separate sheet. Examine the following pedigree. A 1,2 B 1,2 A 1,3 B 1,3 A 1,2 B 1,2 A 1,2 B 1,3 1. (1 point) The A 1 alleles in the two brothers are
Homework questions. Please provide your answers on a separate sheet. Examine the following pedigree. A 1,2 B 1,2 A 1,3 B 1,3 A 1,2 B 1,2 A 1,2 B 1,3 1. (1 point) The A 1 alleles in the two brothers are
Enzyme that uses RNA as a template to synthesize a complementary DNA
 Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics PRACTICE FINAL EXAM 2006 Part I: Definitions Homology: Comparison of two or more protein or DNA sequence to ascertain similarities in sequences. If two genes have
Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics PRACTICE FINAL EXAM 2006 Part I: Definitions Homology: Comparison of two or more protein or DNA sequence to ascertain similarities in sequences. If two genes have
Biological Sciences 50 Practice Final Exam. Allocate your time wisely.
 NAME: Fall 2005 TF: Biological Sciences 50 Practice Final Exam A. Be sure to write your name on the top of each of page of the examination. B. Write each answer only on the same page as the pertinent question.
NAME: Fall 2005 TF: Biological Sciences 50 Practice Final Exam A. Be sure to write your name on the top of each of page of the examination. B. Write each answer only on the same page as the pertinent question.
A systematic approach to breeding programs for game PART 1
 A systematic approach to breeding programs for game PART 1 Japie van der Westhuizen South African Stud Book and Animal Improvement Association japie@studbook.co.za As with many other things in life, the
A systematic approach to breeding programs for game PART 1 Japie van der Westhuizen South African Stud Book and Animal Improvement Association japie@studbook.co.za As with many other things in life, the
Chapter 9. Gene Interactions. As we learned in Chapter 3, Mendel reported that the pairs of loci he observed segregated independently
 Chapter 9 Gene Interactions Figure 9-1 The coat colour on this juvenile horse is called Bay Roan Tobiano. Bay is the brown base coat colour; Roan is the mixture of white hairs with the base coat, making
Chapter 9 Gene Interactions Figure 9-1 The coat colour on this juvenile horse is called Bay Roan Tobiano. Bay is the brown base coat colour; Roan is the mixture of white hairs with the base coat, making
7.03 Final Exam. TA: Alex Bagley Alice Chi Dave Harris Max Juchheim Doug Mills Rishi Puram Bethany Redding Nate Young
 7.03 Final Exam Name: TA: Alex Bagley Alice Chi Dave Harris Max Juchheim Doug Mills Rishi Puram Bethany Redding Nate Young Section time: There are 13 pages including this cover page Please write your name
7.03 Final Exam Name: TA: Alex Bagley Alice Chi Dave Harris Max Juchheim Doug Mills Rishi Puram Bethany Redding Nate Young Section time: There are 13 pages including this cover page Please write your name
Genetics & The Work of Mendel
 Genetics & The Work of Mendel 2011-2012 Gregor Mendel Modern genetics began in the mid-1800s in an abbey garden, where a monk named Gregor Mendel documented inheritance in peas used experimental method
Genetics & The Work of Mendel 2011-2012 Gregor Mendel Modern genetics began in the mid-1800s in an abbey garden, where a monk named Gregor Mendel documented inheritance in peas used experimental method
Name: Genetics - Fall 2004 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Professor Chris Kaiser Professor Gerry Fink Professor Leona Samson
 7.03 - Genetics - Fall 2004 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Professor Chris Kaiser Professor Gerry Fink Professor Leona Samson 1 1. You are studying three autosomal recessive mutations in the fruit
7.03 - Genetics - Fall 2004 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Professor Chris Kaiser Professor Gerry Fink Professor Leona Samson 1 1. You are studying three autosomal recessive mutations in the fruit
Biology 163 Laboratory in Genetics, Final Exam, Dec. 10, 2005
 1 Biology 163 Laboratory in Genetics, Final Exam, Dec. 10, 2005 Honor Pledge: I have neither given nor received any unauthorized help on this exam: Name Printed: Signature: 1. (2 pts) If you see the following
1 Biology 163 Laboratory in Genetics, Final Exam, Dec. 10, 2005 Honor Pledge: I have neither given nor received any unauthorized help on this exam: Name Printed: Signature: 1. (2 pts) If you see the following
7.03 Exam 3 Review GENE REGULATION
 GENE REGULATION Example Problem You are studying the regulation of a yeast enzyme Cal1, whose activity you can measure directly. Expression of the gene encoding Cal1 is inhibited by the presence of calcium
GENE REGULATION Example Problem You are studying the regulation of a yeast enzyme Cal1, whose activity you can measure directly. Expression of the gene encoding Cal1 is inhibited by the presence of calcium
RFLP Method - Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism
 RFLP Method - Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism RFLP (often pronounced "rif lip", as if it were a word) is a method used by molecular biologists to follow a particular sequence of DNA as it is passed
RFLP Method - Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism RFLP (often pronounced "rif lip", as if it were a word) is a method used by molecular biologists to follow a particular sequence of DNA as it is passed
Biotech Applications Nucleic acid therapeutics, Antibiotics, Transgenics. BIT 220 End of Chapter 22 (Snustad/Simmons)
 Biotech Applications Nucleic acid therapeutics, Antibiotics, Transgenics BIT 220 End of Chapter 22 (Snustad/Simmons) Nucleic Acids as Therapeutic Agents Many diseases (cancer, inflammatory diseases) from
Biotech Applications Nucleic acid therapeutics, Antibiotics, Transgenics BIT 220 End of Chapter 22 (Snustad/Simmons) Nucleic Acids as Therapeutic Agents Many diseases (cancer, inflammatory diseases) from
7.03 Final Exam Review 12/19/2006
 7.03 Final Exam Review 12/19/2006 1. You have been studying eye color mutations in Drosophila, which normally have red eyes. White eyes is a recessive mutant trait that is caused by w, a mutant allele
7.03 Final Exam Review 12/19/2006 1. You have been studying eye color mutations in Drosophila, which normally have red eyes. White eyes is a recessive mutant trait that is caused by w, a mutant allele
Linkage & Genetic Mapping in Eukaryotes. Ch. 6
 Linkage & Genetic Mapping in Eukaryotes Ch. 6 1 LINKAGE AND CROSSING OVER! In eukaryotic species, each linear chromosome contains a long piece of DNA A typical chromosome contains many hundred or even
Linkage & Genetic Mapping in Eukaryotes Ch. 6 1 LINKAGE AND CROSSING OVER! In eukaryotic species, each linear chromosome contains a long piece of DNA A typical chromosome contains many hundred or even
of heritable factor ). 1. The alternative versions of genes are called alleles. Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance
 Chapter 9 Biology and Society: Our Longest-Running Genetic Experiment: Dogs Patterns of Inheritance People have selected and mated dogs with preferred traits for more than 15,000 years. Over thousands
Chapter 9 Biology and Society: Our Longest-Running Genetic Experiment: Dogs Patterns of Inheritance People have selected and mated dogs with preferred traits for more than 15,000 years. Over thousands
Genetics & The Work of Mendel
 Genetics & The Work of Mendel He studied at the University of Vienna from 1851 to 1853 where he was influenced by a physicist who encouraged experimentation and the application of mathematics to science
Genetics & The Work of Mendel He studied at the University of Vienna from 1851 to 1853 where he was influenced by a physicist who encouraged experimentation and the application of mathematics to science
a) Stock 4: 126 flies total: 120 are P[w+]: 64 are CyO; 56 are TM3; all are females. 132 are w-: 68 are CyO; 64 are TM3; all are males.
![a) Stock 4: 126 flies total: 120 are P[w+]: 64 are CyO; 56 are TM3; all are females. 132 are w-: 68 are CyO; 64 are TM3; all are males. a) Stock 4: 126 flies total: 120 are P[w+]: 64 are CyO; 56 are TM3; all are females. 132 are w-: 68 are CyO; 64 are TM3; all are males.](/thumbs/88/116538069.jpg) Drosophila Problem Set 2012 1) You have created P element transformants of a construct that contains the mini-white gene, which confers an orange eye color in a homozygous white mutant background. For
Drosophila Problem Set 2012 1) You have created P element transformants of a construct that contains the mini-white gene, which confers an orange eye color in a homozygous white mutant background. For
No, because expression of the P elements and hence transposase in suppressed in the F1.
 Problem set B 1. A wild-type ry+ (rosy) gene was introduced into a ry mutant using P element-mediated gene transformation, and a strain containing a stable ry+ gene was established. If a transformed male
Problem set B 1. A wild-type ry+ (rosy) gene was introduced into a ry mutant using P element-mediated gene transformation, and a strain containing a stable ry+ gene was established. If a transformed male
Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Part I: Definitions. Homology: Reverse transcriptase. Allostery: cdna library
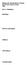 Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics PRACTICE FINAL EXAM 2006 Part I: Definitions Homology: Reverse transcriptase Allostery: cdna library Transformation Part II Short Answer 1. Describe the reasons for
Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics PRACTICE FINAL EXAM 2006 Part I: Definitions Homology: Reverse transcriptase Allostery: cdna library Transformation Part II Short Answer 1. Describe the reasons for
GENOME 371, Problem Set 6
 GENOME 371, Problem Set 6 1. S. pombe is a distant relative of baker s yeast (which you used in quiz section). Wild type S. pombe can grow on plates lacking tryptophan (-trp plates). A mutant has been
GENOME 371, Problem Set 6 1. S. pombe is a distant relative of baker s yeast (which you used in quiz section). Wild type S. pombe can grow on plates lacking tryptophan (-trp plates). A mutant has been
(i) A trp1 mutant cell took up a plasmid containing the wild type TRP1 gene, which allowed that cell to multiply and form a colony
 1. S. pombe is a distant relative of baker s yeast (which you used in quiz section). Wild type S. pombe can grow on plates lacking tryptophan (-trp plates). A mutant has been isolated that cannot grow
1. S. pombe is a distant relative of baker s yeast (which you used in quiz section). Wild type S. pombe can grow on plates lacking tryptophan (-trp plates). A mutant has been isolated that cannot grow
Lesson: Measuring Microevolution
 Lesson: Measuring Microevolution Recall that a GENE is a unit of inheritance. Different forms of the same gene are called LLELES (uh-leelz ) lleles arise from an original gene via the process of MUTTION.
Lesson: Measuring Microevolution Recall that a GENE is a unit of inheritance. Different forms of the same gene are called LLELES (uh-leelz ) lleles arise from an original gene via the process of MUTTION.
Crossbreeding for the Commercial Beef Producer Alison Van Eenennaam, University of California, Davis
 2017-2 Crossbreeding for the Commercial Beef Producer Alison Van Eenennaam, University of California, Davis alvaneenennaam@ucdavis.edu Dr. Darrh Bullock Dr. Jared Decker Dr. Megan Rolf Dr. Matthew Spangler
2017-2 Crossbreeding for the Commercial Beef Producer Alison Van Eenennaam, University of California, Davis alvaneenennaam@ucdavis.edu Dr. Darrh Bullock Dr. Jared Decker Dr. Megan Rolf Dr. Matthew Spangler
Genetics Lecture Notes Lectures 6 9
 Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 6 9 Lecture 6 Until now our analysis of genes has focused on gene function as determined by phenotype differences brought about by different alleles or by a direct
Genetics Lecture Notes 7.03 2005 Lectures 6 9 Lecture 6 Until now our analysis of genes has focused on gene function as determined by phenotype differences brought about by different alleles or by a direct
Multiple Choice (3.35 each) Total = 100pts. Choice the choice that best answers the question! Good luck!
 NAME DATE Multiple Choice (3.35 each) Total = 100pts. Choice the choice that best answers the question! Good luck! 1. Could the characteristic followed in the pedigree be caused by an autosomal dominant
NAME DATE Multiple Choice (3.35 each) Total = 100pts. Choice the choice that best answers the question! Good luck! 1. Could the characteristic followed in the pedigree be caused by an autosomal dominant
Severity assessment of genetically altered fish (bony fish, teleost fish)
 Severity assessment of genetically altered fish (bony fish, teleost fish) Recommendation no. 001/2015 by the National Committee (TierSchG), 6 August 2015 On 11 and 21 June 2015, a workshop took place at
Severity assessment of genetically altered fish (bony fish, teleost fish) Recommendation no. 001/2015 by the National Committee (TierSchG), 6 August 2015 On 11 and 21 June 2015, a workshop took place at
B. Incorrect! 64% is all non-mm types, including both MN and NN. C. Incorrect! 84% is all non-nn types, including MN and MM types.
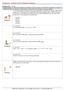 Genetics Problem Drill 23: Population Genetics No. 1 of 10 1. For Polynesians of Easter Island, the population has MN blood group; Type M and type N are homozygotes and type MN is the heterozygous allele.
Genetics Problem Drill 23: Population Genetics No. 1 of 10 1. For Polynesians of Easter Island, the population has MN blood group; Type M and type N are homozygotes and type MN is the heterozygous allele.
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.aaa5945/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The mutagenic chain reaction: A method for converting heterozygous to homozygous mutations Valentino M. Gantz* and Ethan
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.aaa5945/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The mutagenic chain reaction: A method for converting heterozygous to homozygous mutations Valentino M. Gantz* and Ethan
WA Zebrafish Facility
 WA Zebrafish Facility ARC LIEF grant Applicants University of Western Australia David Hunt Shaun Collin Wayne Davies Ryan Lister Nathan Pavlos Edith Cowan University Ralph Martins Simon Laws Giuseppe Verdile
WA Zebrafish Facility ARC LIEF grant Applicants University of Western Australia David Hunt Shaun Collin Wayne Davies Ryan Lister Nathan Pavlos Edith Cowan University Ralph Martins Simon Laws Giuseppe Verdile
A Brief Introduc/on to Zebrafish Gene/cs. 2 February 2012 hbp://monklab.wustl.edu
 A Brief Introduc/on to Zebrafish Gene/cs 2 February 2012 monkk@wustl.edu hbp://monklab.wustl.edu Outline I. History of zebrafish as a model organism II. Gene/c screening in zebrafish a) the first screens
A Brief Introduc/on to Zebrafish Gene/cs 2 February 2012 monkk@wustl.edu hbp://monklab.wustl.edu Outline I. History of zebrafish as a model organism II. Gene/c screening in zebrafish a) the first screens
RECOMBINATION IN DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER MALE1
 RECOMBINATION IN DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER MALE1 YUICHIRO HIRAIZUMI, BARTON SLATKO, CHARLES LANGLEY2 AND ANNEGKETH NILL Department of Zoology, the University of Texas at Austin, Austin, Texas 78712 Manuscript
RECOMBINATION IN DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER MALE1 YUICHIRO HIRAIZUMI, BARTON SLATKO, CHARLES LANGLEY2 AND ANNEGKETH NILL Department of Zoology, the University of Texas at Austin, Austin, Texas 78712 Manuscript
c) Assuming he does not run another endurance race, will the steady-state populations be affected one year later? If so, explain how.
 LS1a Fall 06 Problem Set #8 (100 points total) all questions including the (*extra*) one should be turned in 1. (18 points) Erythrocytes, mature red blood cells, are essential for transporting oxygen to
LS1a Fall 06 Problem Set #8 (100 points total) all questions including the (*extra*) one should be turned in 1. (18 points) Erythrocytes, mature red blood cells, are essential for transporting oxygen to
FINDING THE PAIN GENE How do geneticists connect a specific gene with a specific phenotype?
 FINDING THE PAIN GENE How do geneticists connect a specific gene with a specific phenotype? 1 Linkage & Recombination HUH? What? Why? Who cares? How? Multiple choice question. Each colored line represents
FINDING THE PAIN GENE How do geneticists connect a specific gene with a specific phenotype? 1 Linkage & Recombination HUH? What? Why? Who cares? How? Multiple choice question. Each colored line represents
2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Mapping Gene Linkage
 Mapping Gene Linkage Dihybrid Cross - a cross showing two traits e.g pea shape and pea color The farther apart the genes are to one another the more likely a break between them happens and there will
Mapping Gene Linkage Dihybrid Cross - a cross showing two traits e.g pea shape and pea color The farther apart the genes are to one another the more likely a break between them happens and there will
GENE 603 Exam 3 December 1, 2017 Name
 GENE 603 Exam 3 December 1, 2017 Name 1. When the arc gene of phage P22 is defective, the phage cannot enter lysogeny, so these strains are always lytic and cause clear plaques on lawns of S. typhimurium
GENE 603 Exam 3 December 1, 2017 Name 1. When the arc gene of phage P22 is defective, the phage cannot enter lysogeny, so these strains are always lytic and cause clear plaques on lawns of S. typhimurium
Genetic drift is change in allele frequencies due to chance fluctuations; its strength depends on population size.
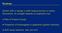 Roadmap Genetic drift is change in allele frequencies due to chance fluctuations; its strength depends on population size. Rate of fixation (recap) Proportion of homozygotes in population (genetic diversity)
Roadmap Genetic drift is change in allele frequencies due to chance fluctuations; its strength depends on population size. Rate of fixation (recap) Proportion of homozygotes in population (genetic diversity)
Advances in Genetics #101
 Questions: Five study Questions EQ1: What are 3 ways of producing organisms with desired traits? EQ2: What are 2 applications of DNA technology in human genetics? Like your fingerprints, your DNA is different
Questions: Five study Questions EQ1: What are 3 ways of producing organisms with desired traits? EQ2: What are 2 applications of DNA technology in human genetics? Like your fingerprints, your DNA is different
Analysis of gene function
 Genome 371, 22 February 2010, Lecture 12 Analysis of gene function Gene knockouts PHASE TWO: INTERPRETATION I THINK I FOUND A CORNER PIECE. 3 BILLION PIECES Analysis of a disease gene Gene knockout or
Genome 371, 22 February 2010, Lecture 12 Analysis of gene function Gene knockouts PHASE TWO: INTERPRETATION I THINK I FOUND A CORNER PIECE. 3 BILLION PIECES Analysis of a disease gene Gene knockout or
FINDING THE PAIN GENE How do geneticists connect a specific gene with a specific phenotype?
 FINDING THE PAIN GENE How do geneticists connect a specific gene with a specific phenotype? 1 Linkage & Recombination HUH? What? Why? Who cares? How? Multiple choice question. Each colored line represents
FINDING THE PAIN GENE How do geneticists connect a specific gene with a specific phenotype? 1 Linkage & Recombination HUH? What? Why? Who cares? How? Multiple choice question. Each colored line represents
Modern Genetic Evaluation Procedures Why BLUP?
 Modern Genetic Evaluation Procedures Why BLUP? Hans-Ulrich Graser 1 Introduction The developments of modem genetic evaluation procedures have been mainly driven by scientists working with the dairy populations
Modern Genetic Evaluation Procedures Why BLUP? Hans-Ulrich Graser 1 Introduction The developments of modem genetic evaluation procedures have been mainly driven by scientists working with the dairy populations
Exam 1 Answers Biology 210 Sept. 20, 2006
 Exam Answers Biology 20 Sept. 20, 2006 Name: Section:. (5 points) Circle the answer that gives the maximum number of different alleles that might exist for any one locus in a normal mammalian cell. A.
Exam Answers Biology 20 Sept. 20, 2006 Name: Section:. (5 points) Circle the answer that gives the maximum number of different alleles that might exist for any one locus in a normal mammalian cell. A.
Examining the Parameters of the Hardy-Weinberg Equation using an Excel Spreadsheet Part 1
 Examining the Parameters of the Hardy-Weinberg Equation using an Excel Spreadsheet Part 1 Part A - Essential Knowledge Background Information 1 Key Vocabulary Hardy-Weinberg Equation Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
Examining the Parameters of the Hardy-Weinberg Equation using an Excel Spreadsheet Part 1 Part A - Essential Knowledge Background Information 1 Key Vocabulary Hardy-Weinberg Equation Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
Amplifying the ALU intron for Hardy- Weinberg Analysis Part 1
 Bio 212 Lab Name: Amplifying the ALU intron for Hardy- Weinberg Analysis Part 1 OBJECTIVES: Review the following terms and concepts presented in Biology 211: enzymes, DNA structure and replication, role
Bio 212 Lab Name: Amplifying the ALU intron for Hardy- Weinberg Analysis Part 1 OBJECTIVES: Review the following terms and concepts presented in Biology 211: enzymes, DNA structure and replication, role
Sydney Brenner: Present
 Sydney Brenner: 1927 - Present Born in the small town of Germiston, South Africa Won a scholarship to the University of Witwatersrand at the age of 15 Received his PhD from Exeter College, Oxford Made
Sydney Brenner: 1927 - Present Born in the small town of Germiston, South Africa Won a scholarship to the University of Witwatersrand at the age of 15 Received his PhD from Exeter College, Oxford Made
Bio 6 Natural Selection Lab
 Bio 6 Natural Selection Lab Overview In this laboratory you will demonstrate the process of evolution by natural selection by carrying out a predator/prey simulation. Through this exercise you will observe
Bio 6 Natural Selection Lab Overview In this laboratory you will demonstrate the process of evolution by natural selection by carrying out a predator/prey simulation. Through this exercise you will observe
THE STUDY OF GENETICS is extremely
 Exploring Animal Genetics and Probability THE STUDY OF GENETICS is extremely valuable to several areas of science. From medical to agricultural applications, the development of new techniques in studying
Exploring Animal Genetics and Probability THE STUDY OF GENETICS is extremely valuable to several areas of science. From medical to agricultural applications, the development of new techniques in studying
BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Spring 2011 Section A. Steve Thompson:
 BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Spring 2011 Section A Steve Thompson: stthompson@valdosta.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net 1 Human genetics Naturally the genetics of our own species,
BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Spring 2011 Section A Steve Thompson: stthompson@valdosta.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net 1 Human genetics Naturally the genetics of our own species,
7.03 Problem Set 2 Due before 5 PM on Friday, September 29 Hand in answers in recitation section or in the box outside of
 7.03 Problem Set 2 Due before 5 PM on Friday, September 29 Hand in answers in recitation section or in the box outside of 68-120 1. Hemophilia A is a X-linked recessive disorder characterized by dysfunctional
7.03 Problem Set 2 Due before 5 PM on Friday, September 29 Hand in answers in recitation section or in the box outside of 68-120 1. Hemophilia A is a X-linked recessive disorder characterized by dysfunctional
3. A form of a gene that is only expressed in the absence of a dominant alternative is:
 Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Robeson Assessment: 9_12 Agriculture AU71 - Biotech and Agrisci Rsch I Test 3 Description: Obj 12 - Simple Mendelian Genetics Form: 501 1. The genotype of an organism
Student Name: Teacher: Date: District: Robeson Assessment: 9_12 Agriculture AU71 - Biotech and Agrisci Rsch I Test 3 Description: Obj 12 - Simple Mendelian Genetics Form: 501 1. The genotype of an organism
LINKAGE AND CHROMOSOME MAPPING IN EUKARYOTES
 LINKAGE AND CHROMOSOME MAPPING IN EUKARYOTES Objectives: Upon completion of this lab, the students should be able to: Understand the different stages of meiosis. Describe the events during each phase of
LINKAGE AND CHROMOSOME MAPPING IN EUKARYOTES Objectives: Upon completion of this lab, the students should be able to: Understand the different stages of meiosis. Describe the events during each phase of
LAB. POPULATION GENETICS. 1. Explain what is meant by a population being in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
 Period Date LAB. POPULATION GENETICS PRE-LAB 1. Explain what is meant by a population being in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. 2. List and briefly explain the 5 conditions that need to be met to maintain a
Period Date LAB. POPULATION GENETICS PRE-LAB 1. Explain what is meant by a population being in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. 2. List and briefly explain the 5 conditions that need to be met to maintain a
AP BIOLOGY Population Genetics and Evolution Lab
 AP BIOLOGY Population Genetics and Evolution Lab In 1908 G.H. Hardy and W. Weinberg independently suggested a scheme whereby evolution could be viewed as changes in the frequency of alleles in a population
AP BIOLOGY Population Genetics and Evolution Lab In 1908 G.H. Hardy and W. Weinberg independently suggested a scheme whereby evolution could be viewed as changes in the frequency of alleles in a population
Quiz will begin at 10:00 am. Please Sign In
 Quiz will begin at 10:00 am Please Sign In You have 15 minutes to complete the quiz Put all your belongings away, including phones Put your name and date on the top of the page Circle your answer clearly
Quiz will begin at 10:00 am Please Sign In You have 15 minutes to complete the quiz Put all your belongings away, including phones Put your name and date on the top of the page Circle your answer clearly
Lecture 5: Genetic Variation and Inbreeding. September 7, 2012
 Lecture 5: Genetic Variation and Inbreeding September 7, 01 Announcements I will be out of town Thursday Sept 0 through Sunday, Sept 4 No office hours Friday, Sept 1: Prof. Hawkins will give a guest lecture
Lecture 5: Genetic Variation and Inbreeding September 7, 01 Announcements I will be out of town Thursday Sept 0 through Sunday, Sept 4 No office hours Friday, Sept 1: Prof. Hawkins will give a guest lecture
DESIGNER GENES * SOUTHERN POLY REGIONAL 2006
 DESIGNER GENES * SOUTHERN POLY REGIONAL 2006 1. A true-breeding plant with yellow seed is crossed to a true-breeding plant with green seeds. All of the F1s are yellow. The F1s are allowed to self. What
DESIGNER GENES * SOUTHERN POLY REGIONAL 2006 1. A true-breeding plant with yellow seed is crossed to a true-breeding plant with green seeds. All of the F1s are yellow. The F1s are allowed to self. What
Introduction. Thomas Hunt Morgan. Chromosomes and Inheritance. Drosophila melanogaster
 Chromosomes and Inheritance 1 4 Fig. 12-10, p. 244 Introduction It was not until 1900 that biology finally caught up with Gregor Mendel. Independently, Karl Correns, Erich von Tschermak, and Hugo de Vries
Chromosomes and Inheritance 1 4 Fig. 12-10, p. 244 Introduction It was not until 1900 that biology finally caught up with Gregor Mendel. Independently, Karl Correns, Erich von Tschermak, and Hugo de Vries
Exam Plant Genetics CSS/Hort 430/530
 Exam 1 2010 Plant Genetics CSS/Hort 430/530 Barley can produce seed which is hulled or hull-less. This trait is determined by one gene, hulled being the dominant phenotype and hull-less being the recessive.
Exam 1 2010 Plant Genetics CSS/Hort 430/530 Barley can produce seed which is hulled or hull-less. This trait is determined by one gene, hulled being the dominant phenotype and hull-less being the recessive.
Unit 6: Genetics & Molecular Genetics Assessment
 Unit 6: Genetics & Molecular Genetics Assessment 1. NA replication takes place in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells during interphase. An enzyme called NA helicase relaxes the helix in certain places and
Unit 6: Genetics & Molecular Genetics Assessment 1. NA replication takes place in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells during interphase. An enzyme called NA helicase relaxes the helix in certain places and
Gen e e n t e i t c c V a V ri r abi b li l ty Biolo l gy g Lec e tur u e e 9 : 9 Gen e et e ic I n I her e itan a ce
 Genetic Variability Biology 102 Lecture 9: Genetic Inheritance Asexual reproduction = daughter cells genetically identical to parent (clones) Sexual reproduction = offspring are genetic hybrids Tendency
Genetic Variability Biology 102 Lecture 9: Genetic Inheritance Asexual reproduction = daughter cells genetically identical to parent (clones) Sexual reproduction = offspring are genetic hybrids Tendency
a) Stock 4: 252 flies total: 120 are P[w+]: 64 are CyO; 56 are TM3; all are females. 132 are w-: 68 are CyO; 64 are TM3; all are males.
![a) Stock 4: 252 flies total: 120 are P[w+]: 64 are CyO; 56 are TM3; all are females. 132 are w-: 68 are CyO; 64 are TM3; all are males. a) Stock 4: 252 flies total: 120 are P[w+]: 64 are CyO; 56 are TM3; all are females. 132 are w-: 68 are CyO; 64 are TM3; all are males.](/thumbs/91/106088469.jpg) Drosophila Problem Set 2018 1) You have created P element transformants of a construct that contains the mini-white gene, which confers an orange eye color in a homozygous white mutant background. For
Drosophila Problem Set 2018 1) You have created P element transformants of a construct that contains the mini-white gene, which confers an orange eye color in a homozygous white mutant background. For
Genome 371, 12 February 2010, Lecture 10. Analyzing mutants. Drosophila transposon mutagenesis. Genetics of cancer. Cloning genes
 Genome 371, 12 February 2010, Lecture 10 Analyzing mutants Drosophila transposon mutagenesis Genetics of cancer Cloning genes Suppose you are setting up a transposon mutagenesis screen in fruit flies starting
Genome 371, 12 February 2010, Lecture 10 Analyzing mutants Drosophila transposon mutagenesis Genetics of cancer Cloning genes Suppose you are setting up a transposon mutagenesis screen in fruit flies starting
We can use a Punnett Square to determine how the gametes will recombine in the next, or F2 generation.
 AP Lab 7: The Mendelian Genetics of Corn Objectives: In this laboratory investigation, you will: Use corn to study genetic crosses, recognize contrasting phenotypes, collect data from F 2 ears of corn,
AP Lab 7: The Mendelian Genetics of Corn Objectives: In this laboratory investigation, you will: Use corn to study genetic crosses, recognize contrasting phenotypes, collect data from F 2 ears of corn,
BA, BSc, and MSc Degree Examinations
 Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: BA, BSc, and MSc Degree Examinations 2017-8 Department : BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Genetics Time Allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Marking Scheme: Total marks available
Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: BA, BSc, and MSc Degree Examinations 2017-8 Department : BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Genetics Time Allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Marking Scheme: Total marks available
Mos1 insertion. MosTIC protocol-11/2006. repair template - Mos1 transposase expression - Mos1 excision - DSB formation. homolog arm.
 MosTIC (Mos1 excision induced Transgene Instructed gene Conversion) Valérie Robert (vrobert@biologie.ens.fr) and Jean-Louis Bessereau (jlbesse@biologie.ens.fr) (November 2006) Introduction: MosTIC (Robert
MosTIC (Mos1 excision induced Transgene Instructed gene Conversion) Valérie Robert (vrobert@biologie.ens.fr) and Jean-Louis Bessereau (jlbesse@biologie.ens.fr) (November 2006) Introduction: MosTIC (Robert
KEY Reproductive cloning Therapeutic cloning
 1. (20 pts) Define Reproductive and Therapeutic cloning. Make sure your descriptions clearly distinguish the critical differences between them. Describe an example of each. Reproductive cloning refers
1. (20 pts) Define Reproductive and Therapeutic cloning. Make sure your descriptions clearly distinguish the critical differences between them. Describe an example of each. Reproductive cloning refers
LECTURE 5: LINKAGE AND GENETIC MAPPING
 LECTURE 5: LINKAGE AND GENETIC MAPPING Reading: Ch. 5, p. 113-131 Problems: Ch. 5, solved problems I, II; 5-2, 5-4, 5-5, 5.7 5.9, 5-12, 5-16a; 5-17 5-19, 5-21; 5-22a-e; 5-23 The dihybrid crosses that we
LECTURE 5: LINKAGE AND GENETIC MAPPING Reading: Ch. 5, p. 113-131 Problems: Ch. 5, solved problems I, II; 5-2, 5-4, 5-5, 5.7 5.9, 5-12, 5-16a; 5-17 5-19, 5-21; 5-22a-e; 5-23 The dihybrid crosses that we
Revision Based on Chapter 15 Grade 10
 Revision Based on Chapter 15 Grade 10 Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following has the disadvantage of possibly bringing
Revision Based on Chapter 15 Grade 10 Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following has the disadvantage of possibly bringing
Before starting, write your name on the top of each page Make sure you have all pages
 Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics Name Student ID Before starting, write your name on the top of each page Make sure you have all pages You can use the back-side of the pages for scratch, but we will
Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics Name Student ID Before starting, write your name on the top of each page Make sure you have all pages You can use the back-side of the pages for scratch, but we will
Lab 2: Mathematical Modeling: Hardy-Weinberg 1. Overview. In this lab you will:
 AP Biology Name Lab 2: Mathematical Modeling: Hardy-Weinberg 1 Overview In this lab you will: 1. learn about the Hardy-Weinberg law of genetic equilibrium, and 2. study the relationship between evolution
AP Biology Name Lab 2: Mathematical Modeling: Hardy-Weinberg 1 Overview In this lab you will: 1. learn about the Hardy-Weinberg law of genetic equilibrium, and 2. study the relationship between evolution
Chapter 7. Linkage and Chromosome Mapping
 Chapter 7. Linkage and Chromosome Mapping Outline of Linkage, Recombination, and the Mapping of Genes on Chromosomes Linkage and Meiotic Recombination Genes linked together on the same chromosome usually
Chapter 7. Linkage and Chromosome Mapping Outline of Linkage, Recombination, and the Mapping of Genes on Chromosomes Linkage and Meiotic Recombination Genes linked together on the same chromosome usually
Genetic Variation Reading Assignment Answer the following questions in your JOURNAL while reading the accompanying packet. Genetic Variation 1.
 Genetic Variation Reading Assignment Answer the following questions in your JOURNAL while reading the accompanying packet. Genetic Variation 1. In the diagram about genetic shuffling, what two phenomena
Genetic Variation Reading Assignment Answer the following questions in your JOURNAL while reading the accompanying packet. Genetic Variation 1. In the diagram about genetic shuffling, what two phenomena
Ch. 14 Mendel and the Gene Idea
 Ch. 14 Mendel and the Gene Idea 2006-2007 Gregor Mendel Modern genetics began in the mid-1800s in an abbey garden, where a monk named Gregor Mendel documented inheritance in peas used experimental method
Ch. 14 Mendel and the Gene Idea 2006-2007 Gregor Mendel Modern genetics began in the mid-1800s in an abbey garden, where a monk named Gregor Mendel documented inheritance in peas used experimental method
17.1 Variation, 17.2 Chromosomes and DNA, 17.3 Monohybrid Inheritance, 17.4 Selection, 17.5 Genetic Engineering SYLLABUS CHECKLIST
 Topic 17 INHERITANCE 17.1 Variation, 17.2 Chromosomes and DNA, 17.3 Monohybrid Inheritance, 17.4 Selection, 17.5 Genetic Engineering SUFEATIN SURHAN BIOLOGY MSPSBS 2010 SYLLABUS CHECKLIST Candidates should
Topic 17 INHERITANCE 17.1 Variation, 17.2 Chromosomes and DNA, 17.3 Monohybrid Inheritance, 17.4 Selection, 17.5 Genetic Engineering SUFEATIN SURHAN BIOLOGY MSPSBS 2010 SYLLABUS CHECKLIST Candidates should
Identifying Genes Underlying QTLs
 Identifying Genes Underlying QTLs Reading: Frary, A. et al. 2000. fw2.2: A quantitative trait locus key to the evolution of tomato fruit size. Science 289:85-87. Paran, I. and D. Zamir. 2003. Quantitative
Identifying Genes Underlying QTLs Reading: Frary, A. et al. 2000. fw2.2: A quantitative trait locus key to the evolution of tomato fruit size. Science 289:85-87. Paran, I. and D. Zamir. 2003. Quantitative
Introduction Chapter 23 - EVOLUTION of
 Introduction Chapter 23 - EVOLUTION of POPULATIONS The blue-footed booby has adaptations that make it suited to its environment. These include webbed feet, streamlined shape that minimizes friction when
Introduction Chapter 23 - EVOLUTION of POPULATIONS The blue-footed booby has adaptations that make it suited to its environment. These include webbed feet, streamlined shape that minimizes friction when
SAMPLE MIDTERM QUESTIONS (Prof. Schoen s lectures) Use the information below to answer the next two questions:
 SAMPLE MIDTERM QUESTIONS (Prof. Schoen s lectures) Use the information below to answer the next two questions: Assume that high blood pressure is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait. You genotype
SAMPLE MIDTERM QUESTIONS (Prof. Schoen s lectures) Use the information below to answer the next two questions: Assume that high blood pressure is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait. You genotype
This is DUE: Tuesday, March 1, 2011 Come prepared to share your findings with your group.
 Biology 160 NAME: Reading Guide 12: Population Dynamics, Humans, Part II This is DUE: Tuesday, March 1, 2011 Come prepared to share your findings with your group. *As before, please turn in only the Critical
Biology 160 NAME: Reading Guide 12: Population Dynamics, Humans, Part II This is DUE: Tuesday, March 1, 2011 Come prepared to share your findings with your group. *As before, please turn in only the Critical
Chapter 9 WHAT IS DNA?
 Notes DNA Chapter 9 WHAT IS DNA? DNA= Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA s job is to hold the entire genetic code for the organism. Human, tree, bacteria, mushroom, paramecium, etc! ALL HAVE DNA! DNA is held on
Notes DNA Chapter 9 WHAT IS DNA? DNA= Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA s job is to hold the entire genetic code for the organism. Human, tree, bacteria, mushroom, paramecium, etc! ALL HAVE DNA! DNA is held on
[Presented by: Andrew Howlett, Cruise Slater, Mahmud Hasan, Greg Dale]
![[Presented by: Andrew Howlett, Cruise Slater, Mahmud Hasan, Greg Dale] [Presented by: Andrew Howlett, Cruise Slater, Mahmud Hasan, Greg Dale]](/thumbs/96/128035026.jpg) Mutational Dissection [Presented by: Andrew Howlett, Cruise Slater, Mahmud Hasan, Greg Dale] Introduction What is the point of Mutational Dissection? It allows understanding of normal biological functions
Mutational Dissection [Presented by: Andrew Howlett, Cruise Slater, Mahmud Hasan, Greg Dale] Introduction What is the point of Mutational Dissection? It allows understanding of normal biological functions
PopGen1: Introduction to population genetics
 PopGen1: Introduction to population genetics Introduction MICROEVOLUTION is the term used to describe the dynamics of evolutionary change in populations and species over time. The discipline devoted to
PopGen1: Introduction to population genetics Introduction MICROEVOLUTION is the term used to describe the dynamics of evolutionary change in populations and species over time. The discipline devoted to
I.1 The Principle: Identification and Application of Molecular Markers
 I.1 The Principle: Identification and Application of Molecular Markers P. Langridge and K. Chalmers 1 1 Introduction Plant breeding is based around the identification and utilisation of genetic variation.
I.1 The Principle: Identification and Application of Molecular Markers P. Langridge and K. Chalmers 1 1 Introduction Plant breeding is based around the identification and utilisation of genetic variation.
