MS.LS1.A, MS.LS3.A, MS.LS3.B
|
|
|
- Jeffrey Dean
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HASPI Medical Biology Lab 02 Description NGSS HS-LS1-1 Teacher Information a. Genes, Proteins, and Disease Students will use normal and mutated DNA sequences to simulate/model transcription, translation, and resulting protein structure and function. Students tape together mrna nucleotides transcribed from a DNA strip, then match trna templates to codons and determine the amino acid sequence represented by different colored beads. The beads are ordered on pipe cleaners and then folded into a functional protein. Students test the functionality of the normal and mutated proteins. Next Generation Science/Common Core Standards Students who demonstrate understanding can: HS-LS1-1. Construct an explanation based on evidence for how the structure of DNA determines the structure of proteins which carry out the essential functions of life through systems of specialized cells. a. Medical Application: Comparison of normal and abnormal DNA of the CFTR gene that results in cystic fibrosis. Simulate/model DNA à mrna à amino acids à protein structure and function of the normal and abnormal proteins. HS-LS3-1. Ask questions to clarify relationships about the role of DNA and chromosomes in coding the instructions for characteristic traits passed from parents to offspring. a. Medical Application: Passing of the normal or abnormal CFTR DNA/gene from parent to offspring to produce normal or abnormal proteins, which may result in cystic fibrosis. Science and Engineering Practices Disciplinary Core Ideas Crosscutting Concepts Constructing Explanations and Designing Solutions Construct an explanation based on valid and reliable evidence obtained from a variety of sources (including students own investigations, models, theories, simulations, peer review) and the assumption that theories and laws that describe the natural world operate today as they did in the past and will continue to do so in the future. LS1.A: Structure and Function Systems of specialized cells within organisms help them perform the essential functions of life. All cells contain genetic information in the form of DNA molecules. Genes are regions in the DNA that contain the instructions that code for the formation of proteins, which carry out most of the work of cells (linked to HS-LS3-1.) Structure and Function Investigating or designing new systems or structures requires a detailed examination of the properties of different materials, the structures of different components, and connections of components to reveal its function and/or solve a problem. Asking Questions and Defining Problems Ask questions that arise from examining models or a theory to clarify relationships. LS3.A: Inheritance of Traits Each chromosome consists of a single very long DNA molecule, and each gene on the chromosome is a particular segment of that DNA. The instructions for forming species characteristics are carried in DNA. All cells in an organism have the same genetic content, but the genes are used (expressed) by the cell may be regulated in different ways. Not all DNA codes for a protein; some segments of DNA are involved in regulatory or structural functions, and some have no as-yet known function. Cause and Effect Empirical evidence is required to differentiate between cause and correlation and make claims about specific causes and effects. Connections to other DCIs in this grade-band: HS.LS3.A Articulation to DCIs across grade-levels: MS.LS1.A, MS.LS3.A, MS.LS3.B Common Core State Standards Connections: ELA/Literacy RST Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of science and technical texts, attending to Important distinctions the author makes and to any gaps or inconsistencies in the account. WHST Write informative/explanatory texts, including the narration of historical events, scientific procedures/experiments, or technical processes. WHST Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. HASPI Medical Biology Lab 02, Teacher Info; Revised July
2 Essential Question By the end of this activity students will be able to: explain how the structure of DNA determines the structure of proteins. model protein carrying out essential functions within cells. clarify the relationship between DNA and chromosomes coding for characteristic traits. model the difference between normal and mutated DNA in the proteins produced. Describe the impact of cystic fibrosis on individuals who inherit a mutated CFTR gene. Time This is an extensive activity summarizing the central dogma (DNA à RNA à protein.) If you are planning on having the students cut out the nucleotides and templates in class, plan on at least four minute class periods. You could have the students cut out the templates at home to save some time. The thorough coverage and opportunity for students to model this complex process will be worth the time spent. Estimated Time Actual Time (please make note below) Part A: Set-Up minutes Part B: Transcription minutes Part C: Translation minutes Part D & E: Protein Folding & Function minutes Note: Share the actual time on the forum ( or at HASPI curriculum conference Materials HASPI is a grant-funded project and on occasion we are able to provide supplies to participating sites. Provided supplies are for 10 lab groups or 40 students. If we are unable to provide supplies, the company, item number, and approximate cost have been included. Supply Provided (P) or Needed (N) Quantity Company/ Item # Estimated Cost Normal DNA template P 10 HASPI cost of copies Abnormal DNA template P 10 HASPI cost of copies mrna Nucleotides template P 10 HASPI cost of copies trna Template P 10 HASPI cost of copies The Amino Acids chart P 10 HASPI cost of copies RNA Polymerase template P 20 HASPI cost of copies Ribosome template P 20 HASPI cost of copies Cell Membrane template P 1 HASPI cost of copies Masking tape P 1 roll any office store $1.99 Large marble P 1 LandofMarbles/ chin103 $0.29 Glue dots ½ P 120 ConsumerCrafts/ TW3783 $3.77 Pipe cleaners P 22 ConsumerCrafts/ $ mm Starflake bead - clear P 22 ConsumerCrafts/ T1 $ HASPI Medical Biology Lab 02, Teacher Info; Revised July 2014
3 Pony beads pink opaque P 50 PonyBeadStore/SP64304 $0.99 Pony beads hot pink P 50 PonyBeadStore/SP64305 $0.99 Pony beads - red P 50 PonyBeadStore/SP64301 $0.99 Pony beads jade pearl P 50 PonyBeadStore/SP64434 $0.99 Pony beads kiwi marbled P 50 PonyBeadStore/SP64407 $0.99 Pony beads navy blue P 50 PonyBeadStore/SP64315 $0.99 Pony beads burgundy P 50 PonyBeadStore/SP64393 $0.99 Pony beads coral P 50 PonyBeadStore/SP64382 $0.99 Pony beads orange opaque P 50 PonyBeadStore/SP64308 $0.99 Pony beads yellow opaque P 50 PonyBeadStore/SP64310 $0.99 Pony beads sage P 50 PonyBeadStore/SP64400 $0.99 Pony beads light blue P 50 PonyBeadStore/SP64313 $0.99 Pony beads dark teal P 50 PonyBeadStore/SP64435 $0.99 Pony beads lilac P 50 PonyBeadStore/SP64414 $0.99 Pony beads plum P 50 PonyBeadStore/SP64370 $0.99 Pony beads white P 50 PonyBeadStore/SP64319 $0.99 Pony beads clear P 100 PonyBeadStore/SP64340 $0.99 Pony beads gray P 50 PonyBeadStore/SP64320 $0.99 Pony beads black P 50 PonyBeadStore/SP64318 $0.99 Scissors N Company Contact Information: HASPI Download free online Consumer Crafts Pony Bead Store Land of Marbles Common Student Misconceptions The following is a list of possible misconceptions that students experience. Please feel free to add any additional misconceptions students experienced during this activity to be better prepared for the future use of this lab/activity. The link between transcription, translation, and protein function is often difficult for students. Reinforcing the link between each of these processes throughout this activity is crucial to understanding. Students may be confused on DNA vs. RNA structure (why is thymine in DNA and uracil in RNA?). Proteins and protein function can cause confusion. Make sure every student has the opportunity to observe the function of the normal simulated protein compared to the mutated simulated protein. Additional Misconception Notes: HASPI Medical Biology Lab 02, Teacher Info; Revised July
4 Guiding Questions These questions are meant to support discussion of the concept/standard. Why is it important that DNA is copied or transcribed correctly? Why is mrna used for translation rather than just translating straight from DNA? How does the structure of DNA determine the structure of a protein? What are some of the essential functions of proteins within the body? How could a change in the structure of a protein impact its function? If an individual inherits a single mutated CFTR gene from a parent, what are the chances they will have cystic fibrosis? Explain your answer. The Task/Response System Through multiple discussions and suggestions HASPI has decided to use the task/response system for lab procedures and directions. The response column can be utilized to: provide space for answers to questions provided in the task column. provide space for data/observation records. provide images to help relay a step. support reinforcement of the standards/concepts immediately during the lab investigations. any other way you see fit to use it! Additional Information Information Page # Location Lab 02: Genes, Proteins, and Disease The background includes information to help students understand the activity and would be best used as a prelab assignment. Students should already have a decent Pages Background grasp of DNA structure and function before completing this activity. This is a simulation and not the actual sequence for the CFTR gene. In actuality there are more than 1500 possible Page 93 Background mutations that cause varying severities of CF. This activity is setup for groups of 4 with a pair of students following the lab with the normal gene and the other pair following the lab with the mutated gene. Both pairs will Page 94 Part A have the same experience creating the gene and will compare their end products at the conclusion. You will need to glue or tape the marble onto The Cell Membrane sheet, and tape that up on the wall or board somewhere in the classroom. Students will be testing their proteins to see if they are able to hold onto the marble and attach to the cell membrane. Page 100 Part E The connections and applications are meant to reinforce the concept(s) within the NGSS/CCSS practices and connections. Each question is extensive and requires either research, critical thinking, or graphing. Feel free to assign or allow students to choose any or all, but realize each is a lengthy assignment in itself. Page Connections & Applications 86 HASPI Medical Biology Lab 02, Teacher Info; Revised July 2014
5 Expected Results Normal mrna and Amino Acid Sequence of CFTR Gene: Methionine AUG TAC AUC TAG TCC GGC CCG GCG CGC Histidine CAC GTG AAU TTA AAG TTC Proline CCU CCT AUC TAG AGA TCT AAG TTC Proline CCU Leucine UUG AAU TTA GGU CCA Valine GUC CAG GGG CCC AUU TAA UCC Phenylalanine UUU AAA Glutamate GAA CTT Cysteine UGU ACA TCC GGC CCG Glutamine CAA GTT GGC CCG TTG ACA TGT Aspartate GAC CTG STOP UGA ACT Cystic Fibrosis mrna and Amino Acid Sequence of CFTR Gene: Methionine AUG TAC UCC CCT GCA CGT GCG CGC ACG TGC AUA TAT AAA TTT Proline CCU Aspartate GAC CTG UCU AGA Glutamate GAA CTT TTG Leucine CUG GAC Tryptophan UGG ACC AUA TAT GGU CCA UCU AGA GGG CCC Phenylalanine UUU AAA UCC Leucine UUG TTG Valine GUG CAC TCC GCA CGT AAG TTC GCU CGA ACA TGT Glutamine CAA GTT ACG TGC - GA CT HASPI Medical Biology Lab 02, Teacher Info; Revised July
6 Resources and References NIH How Genes Work. NIH, National Institute of Health, National Institute of General Medical Sciences Basic Discoveries for Better Health; Bartoshesky, L.E When There Are Problems With Genes. Images (in order of appearance) x1024.jpg HASPI Medical Biology Lab 02, Teacher Info; Revised July 2014
Just one nucleotide! Exploring the effects of random single nucleotide mutations
 Dr. Beatriz Gonzalez In-Class Worksheet Name: Learning Objectives: Just one nucleotide! Exploring the effects of random single nucleotide mutations Given a coding DNA sequence, determine the mrna Based
Dr. Beatriz Gonzalez In-Class Worksheet Name: Learning Objectives: Just one nucleotide! Exploring the effects of random single nucleotide mutations Given a coding DNA sequence, determine the mrna Based
Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation
 Review Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Protein synthesis requires two steps: transcription and translation. DNA contains codes Three bases in DNA code
Review Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation Central Dogma of Molecular Biology Protein synthesis requires two steps: transcription and translation. DNA contains codes Three bases in DNA code
UNIT I RNA AND TYPES R.KAVITHA,M.PHARM LECTURER DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACEUTICS SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY KATTANKULATUR
 UNIT I RNA AND TYPES R.KAVITHA,M.PHARM LECTURER DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACEUTICS SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY KATTANKULATUR RNA, as previously mentioned, is an acronym for ribonucleic acid. There are many forms
UNIT I RNA AND TYPES R.KAVITHA,M.PHARM LECTURER DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACEUTICS SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY KATTANKULATUR RNA, as previously mentioned, is an acronym for ribonucleic acid. There are many forms
Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA. Structure of DNA. Structure of DNA. Nucleotide. Nucleotides 5/13/2013
 Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA The Secret of Life DNA is the molecule responsible for controlling the activities of the cell It is the hereditary molecule DNA directs the production of protein In 1953, Watson
Deoxyribonucleic Acid DNA The Secret of Life DNA is the molecule responsible for controlling the activities of the cell It is the hereditary molecule DNA directs the production of protein In 1953, Watson
Materials Protein synthesis kit. This kit consists of 24 amino acids, 24 transfer RNAs, four messenger RNAs and one ribosome (see below).
 Protein Synthesis Instructions The purpose of today s lab is to: Understand how a cell manufactures proteins from amino acids, using information stored in the genetic code. Assemble models of four very
Protein Synthesis Instructions The purpose of today s lab is to: Understand how a cell manufactures proteins from amino acids, using information stored in the genetic code. Assemble models of four very
Protein Synthesis. Application Based Questions
 Protein Synthesis Application Based Questions MRNA Triplet Codons Note: Logic behind the single letter abbreviations can be found at: http://www.biology.arizona.edu/biochemistry/problem_sets/aa/dayhoff.html
Protein Synthesis Application Based Questions MRNA Triplet Codons Note: Logic behind the single letter abbreviations can be found at: http://www.biology.arizona.edu/biochemistry/problem_sets/aa/dayhoff.html
Molecular Level of Genetics
 Molecular Level of Genetics Most of the molecules found in humans and other living organisms fall into one of four categories: 1. carbohydrates (sugars and starches) 2. lipids (fats, oils, and waxes) 3.
Molecular Level of Genetics Most of the molecules found in humans and other living organisms fall into one of four categories: 1. carbohydrates (sugars and starches) 2. lipids (fats, oils, and waxes) 3.
DNA sentences. How are proteins coded for by DNA? Materials. Teacher instructions. Student instructions. Reflection
 DNA sentences How are proteins coded for by DNA? Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the molecule of life. DNA is one of the most recognizable nucleic acids, a double-stranded helix. The process by which DNA
DNA sentences How are proteins coded for by DNA? Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the molecule of life. DNA is one of the most recognizable nucleic acids, a double-stranded helix. The process by which DNA
The Monster Mash A lesson about transcription and translation By Michelle Kelly, Donald Huesing, & Heather Miller
 The Monster Mash A lesson about transcription and translation By Michelle Kelly, Donald Huesing, & Heather Miller Focus on Inquiry The students will model the process of protein synthesis and then model
The Monster Mash A lesson about transcription and translation By Michelle Kelly, Donald Huesing, & Heather Miller Focus on Inquiry The students will model the process of protein synthesis and then model
Chapter 3: Information Storage and Transfer in Life
 Chapter 3: Information Storage and Transfer in Life The trapped scientist examples are great for conceptual purposes, but they do not accurately model how information in life changes because they do not
Chapter 3: Information Storage and Transfer in Life The trapped scientist examples are great for conceptual purposes, but they do not accurately model how information in life changes because they do not
PGRP negatively regulates NOD-mediated cytokine production in rainbow trout liver cells
 Supplementary Information for: PGRP negatively regulates NOD-mediated cytokine production in rainbow trout liver cells Ju Hye Jang 1, Hyun Kim 2, Mi Jung Jang 2, Ju Hyun Cho 1,2,* 1 Research Institute
Supplementary Information for: PGRP negatively regulates NOD-mediated cytokine production in rainbow trout liver cells Ju Hye Jang 1, Hyun Kim 2, Mi Jung Jang 2, Ju Hyun Cho 1,2,* 1 Research Institute
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Study Guide
 PART A. Read the following: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Study Guide Protein synthesis is the process used by the body to make proteins. The first step of protein synthesis is called Transcription. It occurs in the
PART A. Read the following: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Study Guide Protein synthesis is the process used by the body to make proteins. The first step of protein synthesis is called Transcription. It occurs in the
Lecture 19A. DNA computing
 Lecture 19A. DNA computing What exactly is DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)? DNA is the material that contains codes for the many physical characteristics of every living creature. Your cells use different
Lecture 19A. DNA computing What exactly is DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)? DNA is the material that contains codes for the many physical characteristics of every living creature. Your cells use different
Create a model to simulate the process by which a protein is produced, and how a mutation can impact a protein s function.
 HASPI Medical Biology Lab 0 Purpose Create a model to simulate the process by which a protein is produced, and how a mutation can impact a protein s function. Background http://mssdbio.weebly.com/uploads/1//7/6/17618/970_orig.jpg
HASPI Medical Biology Lab 0 Purpose Create a model to simulate the process by which a protein is produced, and how a mutation can impact a protein s function. Background http://mssdbio.weebly.com/uploads/1//7/6/17618/970_orig.jpg
Codon Bias with PRISM. 2IM24/25, Fall 2007
 Codon Bias with PRISM 2IM24/25, Fall 2007 from RNA to protein mrna vs. trna aminoacid trna anticodon mrna codon codon-anticodon matching Watson-Crick base pairing A U and C G binding first two nucleotide
Codon Bias with PRISM 2IM24/25, Fall 2007 from RNA to protein mrna vs. trna aminoacid trna anticodon mrna codon codon-anticodon matching Watson-Crick base pairing A U and C G binding first two nucleotide
INTRODUCTION TO THE MOLECULAR GENETICS OF THE COLOR MUTATIONS IN ROCK POCKET MICE
 The Making of the The Fittest: Making of the Fittest Natural Selection Natural and Adaptation Selection and Adaptation Educator Materials TEACHER MATERIALS INTRODUCTION TO THE MOLECULAR GENETICS OF THE
The Making of the The Fittest: Making of the Fittest Natural Selection Natural and Adaptation Selection and Adaptation Educator Materials TEACHER MATERIALS INTRODUCTION TO THE MOLECULAR GENETICS OF THE
1. DNA, RNA structure. 2. DNA replication. 3. Transcription, translation
 1. DNA, RNA structure 2. DNA replication 3. Transcription, translation DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides DNA is a nucleic acid, made of long chains of nucleotides Nucleotide Phosphate group Nitrogenous
1. DNA, RNA structure 2. DNA replication 3. Transcription, translation DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides DNA is a nucleic acid, made of long chains of nucleotides Nucleotide Phosphate group Nitrogenous
Level 2 Biology, 2017
 91159 911590 2SUPERVISOR S Level 2 Biology, 2017 91159 Demonstrate understanding of gene expression 2.00 p.m. Wednesday 22 November 2017 Credits: Four Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with
91159 911590 2SUPERVISOR S Level 2 Biology, 2017 91159 Demonstrate understanding of gene expression 2.00 p.m. Wednesday 22 November 2017 Credits: Four Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with
SAY IT WITH DNA: Protein Synthesis Activity by Larry Flammer
 TEACHER S GUIDE SAY IT WITH DNA: Protein Synthesis Activity by Larry Flammer SYNOPSIS This activity uses the metaphor of decoding a secret message for the Protein Synthesis process. Students teach themselves
TEACHER S GUIDE SAY IT WITH DNA: Protein Synthesis Activity by Larry Flammer SYNOPSIS This activity uses the metaphor of decoding a secret message for the Protein Synthesis process. Students teach themselves
The combination of a phosphate, sugar and a base forms a compound called a nucleotide.
 History Rosalin Franklin: Female scientist (x-ray crystallographer) who took the picture of DNA James Watson and Francis Crick: Solved the structure of DNA from information obtained by other scientist.
History Rosalin Franklin: Female scientist (x-ray crystallographer) who took the picture of DNA James Watson and Francis Crick: Solved the structure of DNA from information obtained by other scientist.
Biomolecules: lecture 6
 Biomolecules: lecture 6 - to learn the basics on how DNA serves to make RNA = transcription - to learn how the genetic code instructs protein synthesis - to learn the basics on how proteins are synthesized
Biomolecules: lecture 6 - to learn the basics on how DNA serves to make RNA = transcription - to learn how the genetic code instructs protein synthesis - to learn the basics on how proteins are synthesized
Chemistry 121 Winter 17
 Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
How life. constructs itself.
 How life constructs itself Life constructs itself using few simple rules of information processing. On the one hand, there is a set of rules determining how such basic chemical reactions as transcription,
How life constructs itself Life constructs itself using few simple rules of information processing. On the one hand, there is a set of rules determining how such basic chemical reactions as transcription,
CONVERGENT EVOLUTION. Def n acquisition of some biological trait but different lineages
 CONVERGENT EVOLUTION Def n acquisition of some biological trait but different lineages Living Rock cactus Baseball plant THE QUESTION From common ancestor or independent acquisition? By Lineage By Convergence
CONVERGENT EVOLUTION Def n acquisition of some biological trait but different lineages Living Rock cactus Baseball plant THE QUESTION From common ancestor or independent acquisition? By Lineage By Convergence
A Zero-Knowledge Based Introduction to Biology
 A Zero-Knowledge Based Introduction to Biology Konstantinos (Gus) Katsiapis 25 Sep 2009 Thanks to Cory McLean and George Asimenos Cells: Building Blocks of Life cell, membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondrion
A Zero-Knowledge Based Introduction to Biology Konstantinos (Gus) Katsiapis 25 Sep 2009 Thanks to Cory McLean and George Asimenos Cells: Building Blocks of Life cell, membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondrion
Human Gene,cs 06: Gene Expression. Diversity of cell types. How do cells become different? 9/19/11. neuron
 Human Gene,cs 06: Gene Expression 20110920 Diversity of cell types neuron How do cells become different? A. Each type of cell has different DNA in its nucleus B. Each cell has different genes C. Each type
Human Gene,cs 06: Gene Expression 20110920 Diversity of cell types neuron How do cells become different? A. Each type of cell has different DNA in its nucleus B. Each cell has different genes C. Each type
Thr Gly Tyr. Gly Lys Asn
 Your unique body characteristics (traits), such as hair color or blood type, are determined by the proteins your body produces. Proteins are the building blocks of life - in fact, about 45% of the human
Your unique body characteristics (traits), such as hair color or blood type, are determined by the proteins your body produces. Proteins are the building blocks of life - in fact, about 45% of the human
Fishy Amino Acid Codon. UUU Phe UCU Ser UAU Tyr UGU Cys. UUC Phe UCC Ser UAC Tyr UGC Cys. UUA Leu UCA Ser UAA Stop UGA Stop
 Fishy Code Slips Fish 1 GGTTATAGAGGTACTACC Fish 2 GGCTTCAGAGGTACTACC Fish 3 CATAGCAGAGGTACTACC Fish 4 GGTTATTCTGTCTTATTG Fish 5 GGCTTCTCTGTCTTATTG Fish 6 CATAGCGCTGCAACTACC Fishy Amino Acid Codon UUU Phe
Fishy Code Slips Fish 1 GGTTATAGAGGTACTACC Fish 2 GGCTTCAGAGGTACTACC Fish 3 CATAGCAGAGGTACTACC Fish 4 GGTTATTCTGTCTTATTG Fish 5 GGCTTCTCTGTCTTATTG Fish 6 CATAGCGCTGCAACTACC Fishy Amino Acid Codon UUU Phe
Student Exploration: RNA and Protein Synthesis Due Wednesday 11/27/13
 http://www.explorelearning.com Name: Period : Student Exploration: RNA and Protein Synthesis Due Wednesday 11/27/13 Vocabulary: Define these terms in complete sentences on a separate piece of paper: amino
http://www.explorelearning.com Name: Period : Student Exploration: RNA and Protein Synthesis Due Wednesday 11/27/13 Vocabulary: Define these terms in complete sentences on a separate piece of paper: amino
ANCIENT BACTERIA? 250 million years later, scientists revive life forms
 ANCIENT BACTERIA? 250 million years later, scientists revive life forms Thursday, October 19, 2000 U.S. researchers say they have revived bacteria that have been dormant for more then 250 million years,
ANCIENT BACTERIA? 250 million years later, scientists revive life forms Thursday, October 19, 2000 U.S. researchers say they have revived bacteria that have been dormant for more then 250 million years,
Honors packet Instructions
 Honors packet Instructions The following are guidelines in order for you to receive FULL credit for this bio packet: 1. Read and take notes on the packet in full 2. Answer the multiple choice questions
Honors packet Instructions The following are guidelines in order for you to receive FULL credit for this bio packet: 1. Read and take notes on the packet in full 2. Answer the multiple choice questions
7.016 Problem Set 3. 1 st Pedigree
 7.016 Problem Set 3 Question 1 The following human pedigree shows the inheritance pattern of a specific disease within a family. Assume that the individuals marrying into the family for all generations
7.016 Problem Set 3 Question 1 The following human pedigree shows the inheritance pattern of a specific disease within a family. Assume that the individuals marrying into the family for all generations
Biomolecules: lecture 6
 Biomolecules: lecture 6 - to learn the basics on how DNA serves to make RNA = transcription - to learn how the genetic code instructs protein synthesis - to learn the basics on how proteins are synthesized
Biomolecules: lecture 6 - to learn the basics on how DNA serves to make RNA = transcription - to learn how the genetic code instructs protein synthesis - to learn the basics on how proteins are synthesized
iclicker Question #28B - after lecture Shown below is a diagram of a typical eukaryotic gene which encodes a protein: start codon stop codon 2 3
 Bio 111 Handout for Molecular Biology 4 This handout contains: Today s iclicker Questions Information on Exam 3 Solutions Fall 2008 Exam 3 iclicker Question #28A - before lecture Which of the following
Bio 111 Handout for Molecular Biology 4 This handout contains: Today s iclicker Questions Information on Exam 3 Solutions Fall 2008 Exam 3 iclicker Question #28A - before lecture Which of the following
HASPI Medical Biology Lab 02 Background/Introduction
 HASPI Medical Biology Lab 02 Background/Introduction Before humans even knew of the existence of DNA, they recognized that certain traits were inherited. Through observation they saw that plants and animals
HASPI Medical Biology Lab 02 Background/Introduction Before humans even knew of the existence of DNA, they recognized that certain traits were inherited. Through observation they saw that plants and animals
Chapter 10. The Structure and Function of DNA. Lectures by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 10 The Structure and Function of DNA PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey,
Chapter 10 The Structure and Function of DNA PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey,
(a) Which enzyme(s) make 5' - 3' phosphodiester bonds? (c) Which enzyme(s) make single-strand breaks in DNA backbones?
 EXAMPLE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 1. Topoisomerase does which one of the following? (a) Makes new DNA strands. (b) Unties knots in DNA molecules. (c) Joins the ends of double-stranded DNA molecules. (d) Is
EXAMPLE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 1. Topoisomerase does which one of the following? (a) Makes new DNA strands. (b) Unties knots in DNA molecules. (c) Joins the ends of double-stranded DNA molecules. (d) Is
Describe the features of a gene which enable it to code for a particular protein.
 1. Answers should be written in continuous prose. Credit will be given for biological accuracy, the organisation and presentation of the information and the way in which the answer is expressed. Cancer
1. Answers should be written in continuous prose. Credit will be given for biological accuracy, the organisation and presentation of the information and the way in which the answer is expressed. Cancer
Forensic Science: DNA Evidence Unit
 Day 2 : Cooperative Lesson Topic: Protein Synthesis Duration: 55 minutes Grade Level: 10 th Grade Forensic Science: DNA Evidence Unit Purpose: The purpose of this lesson is to review and build upon prior
Day 2 : Cooperative Lesson Topic: Protein Synthesis Duration: 55 minutes Grade Level: 10 th Grade Forensic Science: DNA Evidence Unit Purpose: The purpose of this lesson is to review and build upon prior
Bioinformatics CSM17 Week 6: DNA, RNA and Proteins
 Bioinformatics CSM17 Week 6: DNA, RNA and Proteins Transcription (reading the DNA template) Translation (RNA -> protein) Protein Structure Transcription - reading the data enzyme - transcriptase gene opens
Bioinformatics CSM17 Week 6: DNA, RNA and Proteins Transcription (reading the DNA template) Translation (RNA -> protein) Protein Structure Transcription - reading the data enzyme - transcriptase gene opens
Homework. A bit about the nature of the atoms of interest. Project. The role of electronega<vity
 Homework Why cited articles are especially useful. citeulike science citation index When cutting and pasting less is more. Project Your protein: I will mail these out this weekend If you haven t gotten
Homework Why cited articles are especially useful. citeulike science citation index When cutting and pasting less is more. Project Your protein: I will mail these out this weekend If you haven t gotten
Lecture 10, 20/2/2002: The process of solution development - The CODEHOP strategy for automatic design of consensus-degenerate primers for PCR
 Lecture 10, 20/2/2002: The process of solution development - The CODEHOP strategy for automatic design of consensus-degenerate primers for PCR 1 The problem We wish to clone a yet unknown gene from a known
Lecture 10, 20/2/2002: The process of solution development - The CODEHOP strategy for automatic design of consensus-degenerate primers for PCR 1 The problem We wish to clone a yet unknown gene from a known
GENETICS and the DNA code NOTES
 GENETICS and the DNA code NOTES BACKGROUND DNA is the hereditary material of most organisms. It is an organic compound made of two strands, twisted around one another to form a double helix. Each strand
GENETICS and the DNA code NOTES BACKGROUND DNA is the hereditary material of most organisms. It is an organic compound made of two strands, twisted around one another to form a double helix. Each strand
ORFs and genes. Please sit in row K or forward
 ORFs and genes Please sit in row K or forward https://www.flickr.com/photos/teseum/3231682806/in/photostream/ Question: why do some strains of Vibrio cause cholera and others don t? Methods Mechanisms
ORFs and genes Please sit in row K or forward https://www.flickr.com/photos/teseum/3231682806/in/photostream/ Question: why do some strains of Vibrio cause cholera and others don t? Methods Mechanisms
UNIT (12) MOLECULES OF LIFE: NUCLEIC ACIDS
 UNIT (12) MOLECULES OF LIFE: NUCLEIC ACIDS Nucleic acids are extremely large molecules that were first isolated from the nuclei of cells. Two kinds of nucleic acids are found in cells: RNA (ribonucleic
UNIT (12) MOLECULES OF LIFE: NUCLEIC ACIDS Nucleic acids are extremely large molecules that were first isolated from the nuclei of cells. Two kinds of nucleic acids are found in cells: RNA (ribonucleic
Mechanisms of Genetics
 2.B.6.A of nucleic acids and the principles of Mendelian Genetics. The student is expected to (A) identify components of DNA, and describe how information for specifying the traits of an organism is carried
2.B.6.A of nucleic acids and the principles of Mendelian Genetics. The student is expected to (A) identify components of DNA, and describe how information for specifying the traits of an organism is carried
Evolution of protein coding sequences
 Evolution of protein coding sequences Kinds of nucleo-de subs-tu-ons Given 2 nucleo-de sequences, how their similari-es and differences arose from a common ancestor? We assume A the common ancestor: Single
Evolution of protein coding sequences Kinds of nucleo-de subs-tu-ons Given 2 nucleo-de sequences, how their similari-es and differences arose from a common ancestor? We assume A the common ancestor: Single
Degenerate Code. Translation. trna. The Code is Degenerate trna / Proofreading Ribosomes Translation Mechanism
 Translation The Code is Degenerate trna / Proofreading Ribosomes Translation Mechanism Degenerate Code There are 64 possible codon triplets There are 20 naturally-encoding amino acids Several codons specify
Translation The Code is Degenerate trna / Proofreading Ribosomes Translation Mechanism Degenerate Code There are 64 possible codon triplets There are 20 naturally-encoding amino acids Several codons specify
Disease and selection in the human genome 3
 Disease and selection in the human genome 3 Ka/Ks revisited Please sit in row K or forward RBFD: human populations, adaptation and immunity Neandertal Museum, Mettman Germany Sequence genome Measure expression
Disease and selection in the human genome 3 Ka/Ks revisited Please sit in row K or forward RBFD: human populations, adaptation and immunity Neandertal Museum, Mettman Germany Sequence genome Measure expression
PRINCIPLES OF BIOINFORMATICS
 PRINCIPLES OF BIOINFORMATICS BIO540/STA569/CSI660, Fall 2010 Lecture 3 (Sep-13-2010) Primer on Molecular Biology/Genomics Igor Kuznetsov Department of Epidemiology & Biostatistics Cancer Research Center
PRINCIPLES OF BIOINFORMATICS BIO540/STA569/CSI660, Fall 2010 Lecture 3 (Sep-13-2010) Primer on Molecular Biology/Genomics Igor Kuznetsov Department of Epidemiology & Biostatistics Cancer Research Center
6. Which nucleotide part(s) make up the rungs of the DNA ladder? Sugar Phosphate Base
 DNA Unit Review Worksheet KEY Directions: Correct your worksheet using a non blue or black pen so your corrections can be clearly seen. DNA Basics 1. Label EVERY sugar (S), phosphate (P), and nitrogen
DNA Unit Review Worksheet KEY Directions: Correct your worksheet using a non blue or black pen so your corrections can be clearly seen. DNA Basics 1. Label EVERY sugar (S), phosphate (P), and nitrogen
CHAPTER 12- RISE OF GENETICS I. DISCOVERY OF DNA A. GRIFFITH (1928) 11/15/2016
 CHAPTER 12- RISE OF GENETICS KENNEDY BIOL. 1AB I. DISCOVERY OF DNA DNA WAS FIRST DISCOVERED IN 1898 BY MIESHNER. HE USED PROTEASE TO DIGEST THE PROTEIN AWAY FROM WHITE BLOOD CELLS. HE DESCRIBED WHAT HE
CHAPTER 12- RISE OF GENETICS KENNEDY BIOL. 1AB I. DISCOVERY OF DNA DNA WAS FIRST DISCOVERED IN 1898 BY MIESHNER. HE USED PROTEASE TO DIGEST THE PROTEIN AWAY FROM WHITE BLOOD CELLS. HE DESCRIBED WHAT HE
Flow of Genetic Information
 Flow of Genetic Information Transcription and Translation Links to the Next Generation Standards Scientific and Engineering Practices: Asking Questions (for science) and Defining Problems (for engineering)
Flow of Genetic Information Transcription and Translation Links to the Next Generation Standards Scientific and Engineering Practices: Asking Questions (for science) and Defining Problems (for engineering)
Four different segments of a DNA molecule are represented below.
 Four different segments of a DNA molecule are represented below. There is an error in the DNA in which molecule? A. segment 1 only B. segment 3 only C. segment 2 and 3 D. segment 2 and 4 Explain the basic
Four different segments of a DNA molecule are represented below. There is an error in the DNA in which molecule? A. segment 1 only B. segment 3 only C. segment 2 and 3 D. segment 2 and 4 Explain the basic
Today in Astronomy 106: polymers to life
 Today in Astronomy 106: polymers to life Translation: the current fashion in protein manufacture. The chicken-egg problem Protein-based primitive life? RNA World Emergence of the genetic code. How long
Today in Astronomy 106: polymers to life Translation: the current fashion in protein manufacture. The chicken-egg problem Protein-based primitive life? RNA World Emergence of the genetic code. How long
Important points from last time
 Important points from last time Subst. rates differ site by site Fit a Γ dist. to variation in rates Γ generally has two parameters but in biology we fix one to ensure a mean equal to 1 and the other parameter
Important points from last time Subst. rates differ site by site Fit a Γ dist. to variation in rates Γ generally has two parameters but in biology we fix one to ensure a mean equal to 1 and the other parameter
Lezione 10. Bioinformatica. Mauro Ceccanti e Alberto Paoluzzi
 Lezione 10 Bioinformatica Mauro Ceccanti e Alberto Paoluzzi Dip. Informatica e Automazione Università Roma Tre Dip. Medicina Clinica Università La Sapienza Lezione 10: Sintesi proteica Synthesis of proteins
Lezione 10 Bioinformatica Mauro Ceccanti e Alberto Paoluzzi Dip. Informatica e Automazione Università Roma Tre Dip. Medicina Clinica Università La Sapienza Lezione 10: Sintesi proteica Synthesis of proteins
Supporting information for Biochemistry, 1995, 34(34), , DOI: /bi00034a013
 Supporting information for Biochemistry, 1995, 34(34), 10807 10815, DOI: 10.1021/bi00034a013 LESNIK 10807-1081 Terms & Conditions Electronic Supporting Information files are available without a subscription
Supporting information for Biochemistry, 1995, 34(34), 10807 10815, DOI: 10.1021/bi00034a013 LESNIK 10807-1081 Terms & Conditions Electronic Supporting Information files are available without a subscription
UNIT 7. DNA Structure, Replication, and Protein Synthesis
 UNIT 7 DNA Structure, Replication, and Protein Synthesis Section 3 Objectives Describe the difference between DNA and RNA. Define transcription. Define translation. Apply to rules of base pairing to replicate,
UNIT 7 DNA Structure, Replication, and Protein Synthesis Section 3 Objectives Describe the difference between DNA and RNA. Define transcription. Define translation. Apply to rules of base pairing to replicate,
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1.
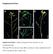 Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
Supplemental Data Supplemental Figure 1. Silique arrangement in the wild-type, jhs, and complemented lines. Wild-type (WT) (A), the jhs1 mutant (B,C), and the jhs1 mutant complemented with JHS1 (Com) (D)
CISC 1115 (Science Section) Brooklyn College Professor Langsam. Assignment #6. The Genetic Code 1
 CISC 1115 (Science Section) Brooklyn College Professor Langsam Assignment #6 The Genetic Code 1 Deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA, is a molecule that contains the instructions used in the development and functioning
CISC 1115 (Science Section) Brooklyn College Professor Langsam Assignment #6 The Genetic Code 1 Deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA, is a molecule that contains the instructions used in the development and functioning
It has not escaped our notice that the specific paring we have postulated immediately suggest a possible copying mechanism for the genetic material
 5-carbon sugar hosphate functional group Nitrogenous base 2 types urines = 2 rings 5 & 6 member N containing ring yrimidines = 1 ring 6 member N containing ring Geometry and space requires complimentary
5-carbon sugar hosphate functional group Nitrogenous base 2 types urines = 2 rings 5 & 6 member N containing ring yrimidines = 1 ring 6 member N containing ring Geometry and space requires complimentary
Phosphate and R2D2 Restrict the Substrate Specificity of Dicer-2, an ATP- Driven Ribonuclease
 Supplemental Information Molecular Cell, Volume 42 hosphate and R2D2 Restrict the Substrate Specificity of Dicer-2, an AT- Driven Ribonuclease Elif Sarinay Cenik, Ryuya Fukunaga, Gang Lu, Robert Dutcher,
Supplemental Information Molecular Cell, Volume 42 hosphate and R2D2 Restrict the Substrate Specificity of Dicer-2, an AT- Driven Ribonuclease Elif Sarinay Cenik, Ryuya Fukunaga, Gang Lu, Robert Dutcher,
NAME:... MODEL ANSWER... STUDENT NUMBER:... Maximum marks: 50. Internal Examiner: Hugh Murrell, Computer Science, UKZN
 COMP710, Bioinformatics with Julia, Test One, Thursday the 20 th of April, 2017, 09h30-11h30 1 NAME:...... MODEL ANSWER... STUDENT NUMBER:...... Maximum marks: 50 Internal Examiner: Hugh Murrell, Computer
COMP710, Bioinformatics with Julia, Test One, Thursday the 20 th of April, 2017, 09h30-11h30 1 NAME:...... MODEL ANSWER... STUDENT NUMBER:...... Maximum marks: 50 Internal Examiner: Hugh Murrell, Computer
Folding simulation: self-organization of 4-helix bundle protein. yellow = helical turns
 Folding simulation: self-organization of 4-helix bundle protein yellow = helical turns Protein structure Protein: heteropolymer chain made of amino acid residues R + H 3 N - C - COO - H φ ψ Chain of amino
Folding simulation: self-organization of 4-helix bundle protein yellow = helical turns Protein structure Protein: heteropolymer chain made of amino acid residues R + H 3 N - C - COO - H φ ψ Chain of amino
The Pieces Inside of You that Make You Who You Are. Genes and DNA
 The Pieces Inside of You that Make You Who You Are Genes and DNA Who are you? This question can be answered many ways Personality traits Kindness Vegetarian or Carnivore Athlete ***Traits you can control
The Pieces Inside of You that Make You Who You Are Genes and DNA Who are you? This question can be answered many ways Personality traits Kindness Vegetarian or Carnivore Athlete ***Traits you can control
Today in Astronomy 106: the important polymers and from polymers to life
 Today in Astronomy 106: the important polymers and from polymers to life Replication or mass production of nucleic acids and proteins Interdependence: which came first, protein mass production or nucleic-acid
Today in Astronomy 106: the important polymers and from polymers to life Replication or mass production of nucleic acids and proteins Interdependence: which came first, protein mass production or nucleic-acid
p-adic GENETIC CODE AND ULTRAMETRIC BIOINFORMATION
 p-adic GENETIC CODE AND ULTRAMETRIC BIOINFORMATION Branko Dragovich http://www.phy.bg.ac.yu/ dragovich dragovich@ipb.ac.rs Institute of Physics, Mathematical Institute SASA, Belgrade 6th International
p-adic GENETIC CODE AND ULTRAMETRIC BIOINFORMATION Branko Dragovich http://www.phy.bg.ac.yu/ dragovich dragovich@ipb.ac.rs Institute of Physics, Mathematical Institute SASA, Belgrade 6th International
DNA REPLICATION REVIEW
 Biology Ms. Ye DNA REPLICATION REVIEW 1. Number the steps of DNA replication the correct order (1, 2, 3): Name Date Block Daughter strands are formed using complementary base pairing DNA unwinds The DNA
Biology Ms. Ye DNA REPLICATION REVIEW 1. Number the steps of DNA replication the correct order (1, 2, 3): Name Date Block Daughter strands are formed using complementary base pairing DNA unwinds The DNA
From DNA to Proteins
 Name: Date: 2/29-3/1/12 Pd: Summary Notes for Chapter 8 Keep this Copy of notes in your binder!! From DNA to Proteins 8.1 Identifying DNA as the Genetic Material Scientist Key Points: What was their most
Name: Date: 2/29-3/1/12 Pd: Summary Notes for Chapter 8 Keep this Copy of notes in your binder!! From DNA to Proteins 8.1 Identifying DNA as the Genetic Material Scientist Key Points: What was their most
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch 17 Practice Questions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Garrod hypothesized that "inborn errors of metabolism" such as alkaptonuria
Ch 17 Practice Questions MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Garrod hypothesized that "inborn errors of metabolism" such as alkaptonuria
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Dissecting binding of a β-barrel outer membrane
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Dissecting binding of a β-barrel outer membrane
Connect the dots DNA to DISEASE
 Teachers Material Connect the dots DNA to DISEASE Developed by: M. Oltmann & A. James. California State Standards Cell Biology 1.d. Students know the central dogma of molecular biology outlines the flow
Teachers Material Connect the dots DNA to DISEASE Developed by: M. Oltmann & A. James. California State Standards Cell Biology 1.d. Students know the central dogma of molecular biology outlines the flow
From Gene to Protein Transcription and Translation i
 How do genes influence our characteristics? From Gene to Protein Transcription and Translation i A gene is a segment of DNA that provides the instructions for making a protein. Proteins have many different
How do genes influence our characteristics? From Gene to Protein Transcription and Translation i A gene is a segment of DNA that provides the instructions for making a protein. Proteins have many different
Det matematisk-naturvitenskapelige fakultet
 UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Det matematisk-naturvitenskapelige fakultet Exam in: MBV4010 Arbeidsmetoder i molekylærbiologi og biokjemi I MBV4010 Methods in molecular biology and biochemistry I Day of exam: Friday
UNIVERSITETET I OSLO Det matematisk-naturvitenskapelige fakultet Exam in: MBV4010 Arbeidsmetoder i molekylærbiologi og biokjemi I MBV4010 Methods in molecular biology and biochemistry I Day of exam: Friday
Gene Expression REVIEW Packet
 Name Pd. # Gene Expression REVIEW Packet 1. Fill-in-the-blank General Summary Transcription & the Big picture Like, ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a acid a molecule made of nucleotides linked together. RNA
Name Pd. # Gene Expression REVIEW Packet 1. Fill-in-the-blank General Summary Transcription & the Big picture Like, ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a acid a molecule made of nucleotides linked together. RNA
Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis
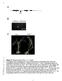 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis Information Research). Exons
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Figure S1. Characterization of the irx9l-1 mutant. (A) Diagram of the Arabidopsis IRX9L gene drawn based on information from TAIR (the Arabidopsis Information Research). Exons
3. Use the codon chart to translate the mrna sequence into an amino acid sequence.
 Honors Biology 317 The Beads of Translation: Using Beads to translate DNA into a Polypeptide Bracelet Objectives: 1. Using plastic beads, construct a representation of "standard" sequence of amino acids
Honors Biology 317 The Beads of Translation: Using Beads to translate DNA into a Polypeptide Bracelet Objectives: 1. Using plastic beads, construct a representation of "standard" sequence of amino acids
BioInformatics and Computational Molecular Biology. Course Website
 BioInformatics and Computational Molecular Biology Course Website http://bioinformatics.uchc.edu What is Bioinformatics Bioinformatics upgrades the information content of biological measurements. Discovery
BioInformatics and Computational Molecular Biology Course Website http://bioinformatics.uchc.edu What is Bioinformatics Bioinformatics upgrades the information content of biological measurements. Discovery
From Gene to Protein Transcription and Translation
 Name: Hour: From Gene to Protein Transcription and Translation Introduction: In this activity you will learn how the genes in our DNA influence our characteristics. For example, how can a gene cause albinism
Name: Hour: From Gene to Protein Transcription and Translation Introduction: In this activity you will learn how the genes in our DNA influence our characteristics. For example, how can a gene cause albinism
BIOSTAT516 Statistical Methods in Genetic Epidemiology Autumn 2005 Handout1, prepared by Kathleen Kerr and Stephanie Monks
 Rationale of Genetic Studies Some goals of genetic studies include: to identify the genetic causes of phenotypic variation develop genetic tests o benefits to individuals and to society are still uncertain
Rationale of Genetic Studies Some goals of genetic studies include: to identify the genetic causes of phenotypic variation develop genetic tests o benefits to individuals and to society are still uncertain
Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC
 Supplementary Appendixes Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC ACG TAG CTC CGG CTG GA-3 for vimentin, /5AmMC6/TCC CTC GCG CGT GGC TTC CGC
Supplementary Appendixes Supplement 1: Sequences of Capture Probes. Capture probes were /5AmMC6/CTG TAG GTG CGG GTG GAC GTA GTC ACG TAG CTC CGG CTG GA-3 for vimentin, /5AmMC6/TCC CTC GCG CGT GGC TTC CGC
From Gene to Protein via Transcription and Translation i
 How do genes influence our characteristics? From Gene to Protein via Transcription and Translation i A gene is a segment of DNA that provides the instructions for making a protein. Proteins have many different
How do genes influence our characteristics? From Gene to Protein via Transcription and Translation i A gene is a segment of DNA that provides the instructions for making a protein. Proteins have many different
Genetic diversity and polymorphism.
 Genetic diversity and polymorphism http://genomed.dlearn.kmu.edu.tw Why is genetic diversity important? http://www.nps.gov/plants/restore/pubs/restgene/toc.htm Genotypes partly determine organisms physical
Genetic diversity and polymorphism http://genomed.dlearn.kmu.edu.tw Why is genetic diversity important? http://www.nps.gov/plants/restore/pubs/restgene/toc.htm Genotypes partly determine organisms physical
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes
 Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 1, 2004 Prokaryotic Gene Structure prokaryotes are simplest free-living organisms studying prokaryotes can give us a sense what is the minimum
Genomics and Gene Recognition Genes and Blue Genes November 1, 2004 Prokaryotic Gene Structure prokaryotes are simplest free-living organisms studying prokaryotes can give us a sense what is the minimum
From Gene to Protein Transcription and Translation i
 From Gene to Protein Transcription and Translation i How do the genes in our DNA influence our characteristics? A gene is a segment of DNA that provides the instructions for making a protein. Proteins
From Gene to Protein Transcription and Translation i How do the genes in our DNA influence our characteristics? A gene is a segment of DNA that provides the instructions for making a protein. Proteins
Genes and Proteins. Objectives
 Genes and Proteins Lecture 15 Objectives At the end of this series of lectures, you should be able to: Define terms. Explain the central dogma of molecular biology. Describe the locations, reactants, and
Genes and Proteins Lecture 15 Objectives At the end of this series of lectures, you should be able to: Define terms. Explain the central dogma of molecular biology. Describe the locations, reactants, and
Assessment Schedule 2013 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of gene expression (91159)
 NCEA Level 2 Biology (91159) 2013 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2013 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of gene expression (91159) Assessment Criteria with Merit with Excellence Demonstrate understanding
NCEA Level 2 Biology (91159) 2013 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2013 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of gene expression (91159) Assessment Criteria with Merit with Excellence Demonstrate understanding
DNA Begins the Process
 Biology I D N A DNA contains genes, sequences of nucleotide bases These Genes code for polypeptides (proteins) Proteins are used to build cells and do much of the work inside cells DNA Begins the Process
Biology I D N A DNA contains genes, sequences of nucleotide bases These Genes code for polypeptides (proteins) Proteins are used to build cells and do much of the work inside cells DNA Begins the Process
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Chapter 17 Genes to Proteins Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. The following questions refer to Figure 17.1, a simple metabolic
Exam Chapter 17 Genes to Proteins Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. The following questions refer to Figure 17.1, a simple metabolic
Transcription & Translation Practice Examination
 Name: Date: Students must provide an explanation for all problems. Students must have parent signature prior to submission. 1. A DNA molecule with the base sequence A-G-C-T-C-A was used as a template for
Name: Date: Students must provide an explanation for all problems. Students must have parent signature prior to submission. 1. A DNA molecule with the base sequence A-G-C-T-C-A was used as a template for
Supplementary. Table 1: Oligonucleotides and Plasmids. complementary to positions from 77 of the SRα '- GCT CTA GAG AAC TTG AAG TAC AGA CTG C
 Supplementary Table 1: Oligonucleotides and Plasmids 913954 5'- GCT CTA GAG AAC TTG AAG TAC AGA CTG C 913955 5'- CCC AAG CTT ACA GTG TGG CCA TTC TGC TG 223396 5'- CGA CGC GTA CAG TGT GGC CAT TCT GCT G
Supplementary Table 1: Oligonucleotides and Plasmids 913954 5'- GCT CTA GAG AAC TTG AAG TAC AGA CTG C 913955 5'- CCC AAG CTT ACA GTG TGG CCA TTC TGC TG 223396 5'- CGA CGC GTA CAG TGT GGC CAT TCT GCT G
Protein Synthesis Review Bi 12 /25
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Protein Synthesis Review Bi 12 /25 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A certain gene codes for a polypeptide that is
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Protein Synthesis Review Bi 12 /25 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A certain gene codes for a polypeptide that is
The Making of the Fittest: Natural Selection and Adaptation
 INTRODUCTION MOLECULAR GENETICS OF COLOR MUTATIONS IN ROCK POCKET MICE THE ROCK POCKET MOUSE The rock pocket mouse, Chaetodipus intermedius, is a small, nocturnal animal found in the deserts of the southwestern
INTRODUCTION MOLECULAR GENETICS OF COLOR MUTATIONS IN ROCK POCKET MICE THE ROCK POCKET MOUSE The rock pocket mouse, Chaetodipus intermedius, is a small, nocturnal animal found in the deserts of the southwestern
A 2D graphical representation of the sequences of DNA based on triplets and its application
 Zou et al. EURASIP Journal on Bioinformatics and Systems Biology 2014, 2014:1 RESEARCH Open Access A 2D graphical representation of the sequences of DNA based on triplets and its application Sai Zou, Lei
Zou et al. EURASIP Journal on Bioinformatics and Systems Biology 2014, 2014:1 RESEARCH Open Access A 2D graphical representation of the sequences of DNA based on triplets and its application Sai Zou, Lei
Supplementary Figure 1. Ratiometric fluorescence visualization of DNA cleavage by
 Supplementary Figure 1. Ratiometric fluorescence visualization of DNA cleavage by Cas9:gRNA. (a) A labeled by Cy3 and Cy5 with an inter-probe distance of > 30 bp was tethered to a PEG-coated surface via
Supplementary Figure 1. Ratiometric fluorescence visualization of DNA cleavage by Cas9:gRNA. (a) A labeled by Cy3 and Cy5 with an inter-probe distance of > 30 bp was tethered to a PEG-coated surface via
Lecture 11: Gene Prediction
 Lecture 11: Gene Prediction Study Chapter 6.11-6.14 1 Gene: A sequence of nucleotides coding for protein Gene Prediction Problem: Determine the beginning and end positions of genes in a genome Where are
Lecture 11: Gene Prediction Study Chapter 6.11-6.14 1 Gene: A sequence of nucleotides coding for protein Gene Prediction Problem: Determine the beginning and end positions of genes in a genome Where are
