Wet and Wild. Wet and Wild. Picture a jungle scene of dense vines and plants, buzzing insects, and brightly Rainforest area
|
|
|
- Elaine Thompson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Wet and Wild Wet and Wild Tropic of Cancer Equator Picture a jungle scene of dense vines and plants, buzzing insects, and brightly Rainforest area colored tropical birds. Now expand your view to add a lot more animals, acres of tall trees, and miles of rivers all in a hot, wet climate. Where are you? A tropical rain forest, of course! Although only 6% of the Earth s surface is covered in rain forest, more than half of the world s plant and animal species live in this important biome.
2 The Amazing Amazon The Amazing Amazon What s the one thing that defines every rain forest? Water, of course! It drips and puddles and pours and eventually drains into huge rivers. The largest river in the world the Amazon River flows through the Amazon rain forest. This amazing rain forest supports a greater variety of plant and animal life than any other place on the planet. There are more than 2,000 species of butterflies found in the Amazon rain forest. This malachite butterfly is one of them.
3 At the Top At the Top The tall, giant trees that poke above most others form the emergent layer of a rain forest. These trees get the greatest amount of sunlight. But they are also exposed to higher temperatures and wind. Emergent tree The rare Harpy eagle uses its post in the emergent layer to spot prey below.
4 Crowded Canopy Crowded Canopy Most of the animals in the rain forest live in the canopy layer which is directly below the emergent layer. Here the tree branches are densely covered with other plants and vines. Food is plentiful for all sorts of critters from birds and snakes to tree frogs and toucans. The colorful red-billed toucan flies among the canopy trees in search of its favorite fruit. The liana plant uses tall trees for support as it grows to reach the light it needs in the canopy.
5 The Light Grows Dim The Light Grows Dim The canopy of a rain forest is so thick it blocks much of the sunlight from getting to the understory layer beneath it. Although plants can still grow in the understory, they are more of the shade-loving variety. Shade-loving Elephant ear plants and ferns can grow beneath the canopy in the understory. Once you get to the forest floor, the light can be very dim. The leaves that fall to the rain forest floor decay, or break down, very quickly. This gaboon viper is almost invisible when it hides among the leaves of the rain forest floor.
6 Under Threat Under Threat In recent decades, rain forests have been greatly reduced. Why should we care? Lots of reasons! Many medicines have come from rain forest plants. Valuable products like fruits, nuts, coffee and chocolate also come from the rain forests. Just as importantly, the balance of nature may be at stake. When animal habitats are lost, whole species can be wiped out. Also, the plants in rain forests take in great amounts of carbon dioxide and release life-giving oxygen (during photosynthesis). Can people who live in the rain forests find ways to prosper while still protecting the rain forests? That is the hope for the future!
7 Tropic of Cancer Equator Rainforest area The Amazing Rain Forest Teacher Notes Wet and Wild Picture a jungle scene of dense vines and plants, buzzing insects, and brightly colored tropical birds. Now expand your view to add a lot more animals, acres of tall trees, and miles of rivers all in a hot, wet climate. Where are you? A tropical rain forest, of course! Although only 6% of the Earth s surface is covered in rain forest, more than half of the world s plant and animal species live in this important biome. Wet and Wild Wet and Wild There are a number of different types of rain forest. Tropical lowland rain forest is found near the equator and gets about 80 inches (200 cm) of rain a year. Nearer to the Tropics, conditions become more variable, especially in Asia, which has a monsoon climate. Here the rain forest is different because it is subject to seasonal changes, and has only 50 inches (125 cm) of rain a year. In coastal areas, the rain forest species are often replaced by mangroves. Tropical rain forest also changes with increasing altitude. It is richest and most diverse in lowland areas, progressing to montane forest at about 3,300 ft (1,000 m). High montane forest at over 6,600 ft (2,000 m) is often enveloped in cloud and mist hence, its alternative name of cloud forest. The Amazing Amazon The Amazing Amazon What s the one thing that defines every rain forest? Water, of course! It drips and puddles and pours and eventually drains into huge rivers. The largest river in the world the Amazon River flows through the Amazon rain forest. This amazing rain forest supports a greater variety of plant and animal life than any other place on the planet. There are more than 2,000 species of butterflies found in the Amazon rain forest. This malachite butterfly is one of them. The Amazing Amazon The rain forest is awash with water. It drips from the leaves, collects in puddles, runs down mountainsides, and eventually drains into huge, meandering rivers. The Amazon is the largest river of all. Together with its tributaries, which number 1,000 or more, it holds two-thirds of the world's freshwater. There is an incredible diversity of life supported by this vast water system. It contains around 5,000 species of freshwater fish, and there may be another 2,000 awaiting discovery. At the Top The tall, giant trees that poke above most others form the emergent layer of a rain forest. These trees get the greatest amount of sunlight. But they are also exposed to higher temperatures and wind. The rare Harpy eagle uses its post in the emergent layer to spot prey below. At the Top Emergent tree The Amazonian rain forest is still the largest in the world but, like all tropical forests, it is being overexploited. Twenty percent of it has been lost already, much of it transformed into pasture for cattle. Only small pockets of Atlantic coastal forest remain today. At the Top Tall emergent trees tower above the rest of the jungle canopy, a few reaching heights of ft (60 70 m). These scattered trees have straight trunks, often buttressed at the base and with a cauliflower-shaped crown. It is hotter and drier at the top of the canopy, with greater changes in temperature and humidity. The trees are also much more windblown, and the fruit or seeds of some species are dispersed by the moving air. Many emergent trees are leafless for short periods of time, but seldom all shed their leaves at once. The epiphytes that live on the boughs of these trees include droughtresistant species of bromeliads, lichens, and cacti. Crowded Canopy Crowded Canopy Most of the animals in the rain forest live in the canopy layer which is directly below the emergent layer. Here the tree branches are densely covered with other plants and vines. Food is plentiful for all sorts of critters from birds and snakes to tree frogs and toucans. The colorful red-billed toucan flies among the canopy trees in search of its favorite fruit. Lianas need a lot of light. To reach the canopy, their slender climbing stems use tall trees for support. Crowded Canopy In the canopy of a rain forest, reaching ft (25 45 m) above the ground, it is always green and leafy. The crown of each tree is taller than it is broad, making a sunspeckled layer around ft (6 7 m) thick. This leafy roof shields the ground and absorbs most of the sunlight. It also lessens the impact of heavy rainfall and high winds. The teeming life of a jungle canopy is only glimpsed from below. Some creatures are so well adapted to their treetop existence that they seldom, if ever, descend to the forest floor. It is difficult even to match up fallen fruits or flowers with the surrounding tree trunks. Many species were totally unknown or their numbers grossly underestimated before walkways strung up in the canopy allowed biologists to research and find out what life was really like in the treetops.
8 The Amazing Rain Forest Teacher Notes The Light Grows Dim Shade-loving Elephant The Light Grows Dim ear plants and ferns can The canopy of a rain forest is so thick it blocks much grow beneath the canopy in the understory. of the sunlight from getting to the understory layer beneath it. Although plants can still grow in the understory, they are more of the shade-loving variety. Once you get to the forest floor, the light can be very dim. The leaves that fall to the rain forest floor decay, or break down, very quickly. This gaboon viper is almost invisible when it hides among the leaves of the rain forest floor. The Light Grows Dim In lowland rain forest close to the equator, the air near the forest floor is still and sultry. Only about two percent of light reaching the canopy penetrates the thick blanket of foliage. Small plants that do not need much light, such as ferns and mosses, grow here. Only when a tree falls can lianas, saplings, and other herbaceous plants get the light they need to grow and they do so rapidly. Monsoon rain-forest canopies are much more open and because there is more light, there is a vigorous growth of vegetation in the understory and on the forest floor. The gaboon viper is patterned just like the sun-flecked leaves on the forest floor. It remains motionless and invisible until a small mammal or bird strays too close. Its 2 in (5 cm) long fangs inject a venom that is almost instantly fatal. Under Threat In recent decades, rain forests have been greatly reduced. Why should we care? Lots of reasons! Many medicines have come from rain forest plants. Valuable products like fruits, nuts, coffee and chocolate also come from the rain forests. Just as importantly, the balance of nature may be at stake. When animal habitats are lost, whole species can be wiped out. Also, the plants in rain forests take in great amounts of carbon dioxide and release life-giving oxygen (during photosynthesis). Can people who live in the rain forests find ways to prosper while still protecting the rain forests? That is the hope for the future! Under Threat Under Threat In South and Central America, cleared tropical rain forest provides pasture for beef cattle. When ranchers move into the forest, they burn trees to clear the land for farming. After five years, each animal needs 12.5 acres (50,000 sq m) to graze. After 10 years the land is useless. Overgrazing, the impact of the animals' hooves, and the loss of the trees lead to soil erosion. Rain forests influence the carbon cycle and have a profound effect on rainfall. The uneven surface of treetops causes air turbulence that increases the amount of water evaporating from the forest. This forms clouds that fall as rain. If the forests disappear, less rain will fall, it will drain more quickly, and air and soil temperatures will rise. Green plants take up carbon dioxide, which they convert to sugars by means of photosynthesis, a process during which oxygen is released into the air.
Rainforest Photo Sort Information Gap. Investigating Three Different Texts to work out where the animals and plants belong and how they have adapted.
 Rainforest Photo Sort Information Gap Emergent layer (the tree tops) Canopy Investigating Three Different Texts to work out where the animals and plants belong and how they have adapted. Mid layer (under
Rainforest Photo Sort Information Gap Emergent layer (the tree tops) Canopy Investigating Three Different Texts to work out where the animals and plants belong and how they have adapted. Mid layer (under
Animals of the Rain Forest
 Animals of the Rain Forest Field Trip Packet 2 nd -3 rd Grade ---------------------------------------------------------- Rain forests are amazing places! Take a trip through a tropical rain forest. The
Animals of the Rain Forest Field Trip Packet 2 nd -3 rd Grade ---------------------------------------------------------- Rain forests are amazing places! Take a trip through a tropical rain forest. The
Rainforests and Tropical Diversity. Gaby Orihuela Visitor Experience Manager
 Rainforests and Tropical Diversity Gaby Orihuela Visitor Experience Manager Global Strategy for Plant Conservation Objective IV: Education and awareness about plant diversity, its role in sustainable livelihoods
Rainforests and Tropical Diversity Gaby Orihuela Visitor Experience Manager Global Strategy for Plant Conservation Objective IV: Education and awareness about plant diversity, its role in sustainable livelihoods
Tropical Rainforest. By: Mini Preston, Lily Guindon, Laila Mueller,and Joel Wifler
 Tropical Rainforest By: Mini Preston, Lily Guindon, Laila Mueller,and Joel Wifler Animals in the Tropical Rainforest By Joel Wifler Kinkajous Kinkajous live in Central and South America, where they spend
Tropical Rainforest By: Mini Preston, Lily Guindon, Laila Mueller,and Joel Wifler Animals in the Tropical Rainforest By Joel Wifler Kinkajous Kinkajous live in Central and South America, where they spend
Amazonia from A to Z. Picture book created using Amazonia: A World Resource at Risk map, GRMC, Ball State University Libraries
 Amazonia from A to Z Picture book created using Amazonia: A World Resource at Risk map, GRMC, Ball State University Libraries is for the Amazon Basin, or Amazonia. This basin houses an endangered gigantic
Amazonia from A to Z Picture book created using Amazonia: A World Resource at Risk map, GRMC, Ball State University Libraries is for the Amazon Basin, or Amazonia. This basin houses an endangered gigantic
Rainforest Scavenger Hunt My Research Account
 Rainforest Scavenger Hunt My Research Account World Book Student Did you know that tropical rainforests occupy only 6 to 7 percent of Earth's surface? Learn more about rainforests on the World Book Web.
Rainforest Scavenger Hunt My Research Account World Book Student Did you know that tropical rainforests occupy only 6 to 7 percent of Earth's surface? Learn more about rainforests on the World Book Web.
Live Foods from the Wild Part II Where to Find Wild Foods. A presentation for The Angelfish Society October 17, 2010 by Tamar Stephens
 Live Foods from the Wild Part II Where to Find Wild Foods A presentation for The Angelfish Society October 17, 2010 by Tamar Stephens About this presentation This is the second in a series of presentations
Live Foods from the Wild Part II Where to Find Wild Foods A presentation for The Angelfish Society October 17, 2010 by Tamar Stephens About this presentation This is the second in a series of presentations
What determines a terrestrial. biome?
 BIOMES What determines a terrestrial Climate Temperature Precipitation Similarly adapted plants & animals Can vary depending on external forces- human disturbance Fire important to many Controls tree
BIOMES What determines a terrestrial Climate Temperature Precipitation Similarly adapted plants & animals Can vary depending on external forces- human disturbance Fire important to many Controls tree
Rainforests. Middle school. Life Science TEKS. Life Science Vocabulary
 Rainforests Middle school Life Science TEKS Sixth Grade: 6.12E, 6.12F Seventh Grade: 7.11B, 7.12A, 7.13A, 7.13B Eighth Grade: 8.11A, 8.11B, 8.11C Life Science Vocabulary abiotic, adaptations, balance,
Rainforests Middle school Life Science TEKS Sixth Grade: 6.12E, 6.12F Seventh Grade: 7.11B, 7.12A, 7.13A, 7.13B Eighth Grade: 8.11A, 8.11B, 8.11C Life Science Vocabulary abiotic, adaptations, balance,
By Gerald Urquhart, Walter Chomentowski, David Skole, and Chris Barber
 By Gerald Urquhart, Walter Chomentowski, David Skole, and Chris Barber The clearing of tropical forests across the Earth has been occurring on a large scale basis for many centuries. This process, known
By Gerald Urquhart, Walter Chomentowski, David Skole, and Chris Barber The clearing of tropical forests across the Earth has been occurring on a large scale basis for many centuries. This process, known
Reading comprehension: The Tropical Rainforest
 Auteur Laatst gewijzigd Licentie Webadres Patricia Termeer 05 februari 2016 CC Naamsvermelding 3.0 Nederland licentie https://maken.wikiwijs.nl/71971 Dit lesmateriaal is gemaakt met Wikiwijs van Kennisnet.
Auteur Laatst gewijzigd Licentie Webadres Patricia Termeer 05 februari 2016 CC Naamsvermelding 3.0 Nederland licentie https://maken.wikiwijs.nl/71971 Dit lesmateriaal is gemaakt met Wikiwijs van Kennisnet.
Biology Ecology Unit Chapter 2 Study Guide
 Name: Date: Block: Biology Ecology Unit Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. Directions: Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage. Ecology Biotic factors Nonliving Environments Atmosphere Humans
Name: Date: Block: Biology Ecology Unit Chapter 2 Study Guide 1. Directions: Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage. Ecology Biotic factors Nonliving Environments Atmosphere Humans
BIOMES. Living World
 BIOMES Living World Biomes Biomes are large regions of the world with distinctive climate, wildlife and vegetation. They are divided by terrestrial (land) or aquatic biomes. Terrestrial Biomes Terrestrial
BIOMES Living World Biomes Biomes are large regions of the world with distinctive climate, wildlife and vegetation. They are divided by terrestrial (land) or aquatic biomes. Terrestrial Biomes Terrestrial
The Connection Between Selective Logging and Deforestation. within the Amazonian Rainforest
 Hart 1 The Connection Between Selective Logging and Deforestation within the Amazonian Rainforest Jessyca Hart Stockton University Spring 2015 Hart 2 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Selective Logging...
Hart 1 The Connection Between Selective Logging and Deforestation within the Amazonian Rainforest Jessyca Hart Stockton University Spring 2015 Hart 2 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Selective Logging...
Rainforest Detective Notebook. This book belongs to:
 Rainforest Detective Notebook This book belongs to: 1 What Is a Rainforest? The rainforest is a special place where many animals and plants live. Cut out each animal and paste it in the area where it lives.
Rainforest Detective Notebook This book belongs to: 1 What Is a Rainforest? The rainforest is a special place where many animals and plants live. Cut out each animal and paste it in the area where it lives.
Unit A: Introduction to Forestry. Lesson 3: Recognizing the Importance of Forests
 Unit A: Introduction to Forestry Lesson 3: Recognizing the Importance of Forests 1 Terms Forest Forest canopy Piling Pulpwood Timberland Total forest land Urban forestry Veneer Reserved forest land 2 What
Unit A: Introduction to Forestry Lesson 3: Recognizing the Importance of Forests 1 Terms Forest Forest canopy Piling Pulpwood Timberland Total forest land Urban forestry Veneer Reserved forest land 2 What
Climate: describes the average condition, including temperature and precipitation, over long periods in a given area
 Ch. 6 - Biomes Section 6.1: Defining Biomes Biome: a group of ecosystems that share similar biotic and abiotic conditions, large region characterized by a specific type of climate, plants, and animals
Ch. 6 - Biomes Section 6.1: Defining Biomes Biome: a group of ecosystems that share similar biotic and abiotic conditions, large region characterized by a specific type of climate, plants, and animals
Amazon rainforest abiotic factors
 P ford residence southampton, ny Amazon rainforest abiotic factors Mar 5, 2012. Biotic and abiotic factors. 1. Biotic Factors; 2. Animal Adaptations The tropical rainforest is a wet, warm forest of trees
P ford residence southampton, ny Amazon rainforest abiotic factors Mar 5, 2012. Biotic and abiotic factors. 1. Biotic Factors; 2. Animal Adaptations The tropical rainforest is a wet, warm forest of trees
The Living world. Tropical rainforests (core content) Revisio n undert aken. Cover ed in class?
 The Living world Using an example from the UK, I can explain the interrelationship within the natural system. I can define and give UK examples of producers consumers, decomposer, food chain, food web
The Living world Using an example from the UK, I can explain the interrelationship within the natural system. I can define and give UK examples of producers consumers, decomposer, food chain, food web
Ecosystems and Biomes
 Content Vocabulary LESSON 1 Ecosystems and Biomes Directions: Use the clues and the terms listed below to complete the puzzle. NOTE: There is no empty square in the puzzle between the words of two-word
Content Vocabulary LESSON 1 Ecosystems and Biomes Directions: Use the clues and the terms listed below to complete the puzzle. NOTE: There is no empty square in the puzzle between the words of two-word
Trees are Terrific and forests are too!! Arbor Day Poster Contest Sponsored by Keep Allen Beautiful
 Trees are Terrific and forests are too!! Arbor Day Poster Contest Sponsored by Keep Allen Beautiful Who May Enter? Who may enter the contest? 4 th & 5 th graders enrolled in the AISD How does the contest
Trees are Terrific and forests are too!! Arbor Day Poster Contest Sponsored by Keep Allen Beautiful Who May Enter? Who may enter the contest? 4 th & 5 th graders enrolled in the AISD How does the contest
Foundation Course. Semester 3 THREATS TO THE ENVIRONMENT
 Foundation Course Semester 3 THREATS TO THE ENVIRONMENT INTRODUCTION Atmosphere, water and soil are the most important components of environment in which we live. Atmospheric factors like rainfall, humidity,
Foundation Course Semester 3 THREATS TO THE ENVIRONMENT INTRODUCTION Atmosphere, water and soil are the most important components of environment in which we live. Atmospheric factors like rainfall, humidity,
Rain Forests. Linda Aspen-Baxter
 Rain Forests Linda Aspen-Baxter Published by Weigl Publishers Inc. 350 5 th Avenue, Suite 3304, PMB 6G New York, NY 10118-0069 Web site: www.weigl.com Copyright 2007 Weigl Publishers Inc. All rights reserved.
Rain Forests Linda Aspen-Baxter Published by Weigl Publishers Inc. 350 5 th Avenue, Suite 3304, PMB 6G New York, NY 10118-0069 Web site: www.weigl.com Copyright 2007 Weigl Publishers Inc. All rights reserved.
OUR FORESTS, OUR LIFE
 OUR FORESTS, OUR LIFE Asia/Pacific Cultural Centre for UNESCO (ACCU) LET'S GO INTO A FOREST! A forest gives us a lot of benefits and happiness in our daily lives. I want to know more about the forest.
OUR FORESTS, OUR LIFE Asia/Pacific Cultural Centre for UNESCO (ACCU) LET'S GO INTO A FOREST! A forest gives us a lot of benefits and happiness in our daily lives. I want to know more about the forest.
Activities for Exhibit Exploration
 This worksheet will help guide you as you investigate our exhibits. If you have a camera, some questions can be answered by taking a picture. Otherwise, you may write your answers into the space provided.
This worksheet will help guide you as you investigate our exhibits. If you have a camera, some questions can be answered by taking a picture. Otherwise, you may write your answers into the space provided.
2018 ECOLOGY SAMPLE-C (YEAR 2)
 STATION A: FD WEB 2018 ECOLOGY SAMPLE-C (YEAR 2) PART 1 GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF ECOLOGY 1. Almost all of the energy used by living organisms comes from where? 2. A stable environment should include: why?
STATION A: FD WEB 2018 ECOLOGY SAMPLE-C (YEAR 2) PART 1 GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF ECOLOGY 1. Almost all of the energy used by living organisms comes from where? 2. A stable environment should include: why?
Understanding tropical deforestation
 Understanding tropical deforestation By NASA on 03.13.17 Word Count 2,411 Two logging trucks on the Kalabakan-Sapulot-Road take heavy tropical timber logs to the log pond in Kalabakan, Indonesia. NASA
Understanding tropical deforestation By NASA on 03.13.17 Word Count 2,411 Two logging trucks on the Kalabakan-Sapulot-Road take heavy tropical timber logs to the log pond in Kalabakan, Indonesia. NASA
It s A Jungle Out There Written by Heather Nisbett-Loewenstein January 2014 stonelionpuppettheatre. Teacher s Guide
 Grade Level: PS-3 Subject Areas: Science It s A Jungle Out There Written by Heather Nisbett-Loewenstein January 2014 stonelionpuppettheatre Teacher s Guide Objectives and Goals Science objectives o Students
Grade Level: PS-3 Subject Areas: Science It s A Jungle Out There Written by Heather Nisbett-Loewenstein January 2014 stonelionpuppettheatre Teacher s Guide Objectives and Goals Science objectives o Students
Unit 6: Ecosystems Module 15: Ecological Principles
 Unit 6: Ecosystems Module 15: Ecological Principles NC Essential Standard: 2.1 Analyze the interdependence of living organisms within their environments Did you know The water you poop in today is the
Unit 6: Ecosystems Module 15: Ecological Principles NC Essential Standard: 2.1 Analyze the interdependence of living organisms within their environments Did you know The water you poop in today is the
HUMA N IMPA C T O N BIO MES A RO UN D THE W O RLD
 HUMA N IMPA C T O N BIO MES A RO UN D THE W O RLD HOMEWORK DIRECTIONS (due Wed/Thurs): For EACH of these biomes (yes, go through all), look for evidence of HIPPCO in the article (these are the main ways
HUMA N IMPA C T O N BIO MES A RO UN D THE W O RLD HOMEWORK DIRECTIONS (due Wed/Thurs): For EACH of these biomes (yes, go through all), look for evidence of HIPPCO in the article (these are the main ways
The Geography of Russia
 The Geography of Russia Russia is HUMONGOUS! It is the largest country in the world. It is more than twice the size of the United States. It contains a sixth of the earth s land. Russia has three major
The Geography of Russia Russia is HUMONGOUS! It is the largest country in the world. It is more than twice the size of the United States. It contains a sixth of the earth s land. Russia has three major
Unit A: Introduction to Forestry. Lesson 2:Understanding Forest Ecology
 Unit A: Introduction to Forestry Lesson 2:Understanding Forest Ecology 1 Terms Bole Ecology Ecosystem Forest ecology Hardening-off Hardiness Material cycle Mycorrhizae Overstory Photoperiod Stratification
Unit A: Introduction to Forestry Lesson 2:Understanding Forest Ecology 1 Terms Bole Ecology Ecosystem Forest ecology Hardening-off Hardiness Material cycle Mycorrhizae Overstory Photoperiod Stratification
Draw disruptive, stabilizing, and directional selection on the board. Explain disruptive selection using an example. What effects speciation most?
 Draw disruptive, stabilizing, and directional selection on the board. disruptive selection using an Disruptive selection is when the average physical characteristic of a population is not beneficial. Example:
Draw disruptive, stabilizing, and directional selection on the board. disruptive selection using an Disruptive selection is when the average physical characteristic of a population is not beneficial. Example:
Station 1: Who are the Rainforest People?
 Station 1: Who are the Rainforest People? Station 1: Rainforest People Q: Who are indigenous people? A: Rainforests are bursting with life. Not only do millions of species of plants and animals live in
Station 1: Who are the Rainforest People? Station 1: Rainforest People Q: Who are indigenous people? A: Rainforests are bursting with life. Not only do millions of species of plants and animals live in
Biodiversity and Conservation
 Chapter Test A CHAPTER 5 Biodiversity and Conservation Part A: Multiple Choice In the space at the left, write the letter of the phrase or sentence that best answers each question. Part B: Matching 1.
Chapter Test A CHAPTER 5 Biodiversity and Conservation Part A: Multiple Choice In the space at the left, write the letter of the phrase or sentence that best answers each question. Part B: Matching 1.
Chapter Biodiversity
 Chapter 6 6.3 Biodiversity Key Questions: 1) Why is biodiversity important? 2) What are the most significant threats to biodiversity? 3) How do we preserve biodiversity? Types of Biodiversity Biological
Chapter 6 6.3 Biodiversity Key Questions: 1) Why is biodiversity important? 2) What are the most significant threats to biodiversity? 3) How do we preserve biodiversity? Types of Biodiversity Biological
Nancy L. Young, Forester USAID/USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service
 Forest Management Nancy L. Young, Forester USAID/USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service Material translated by: Mohammadullah Karimi, Training & Liaison Officer Afghan Conservation Corps Managing
Forest Management Nancy L. Young, Forester USAID/USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service Material translated by: Mohammadullah Karimi, Training & Liaison Officer Afghan Conservation Corps Managing
Class IX Chapter 14 Natural Resources Science
 Question 1: How is our atmosphere different from the atmospheres on Venus and Mars? Earth s atmosphere is different from those of Venus and Mars. This difference lies essentially in their compositions.
Question 1: How is our atmosphere different from the atmospheres on Venus and Mars? Earth s atmosphere is different from those of Venus and Mars. This difference lies essentially in their compositions.
Forests. NEW INTERNATIONALIST EASIER ENGLISH Intermediate READY LESSON
 Forests NEW INTERNATIONALIST EASIER ENGLISH Intermediate READY LESSON Today s lesson: Quiz Reading Speaking Writing Discuss: How much do you know about forests? Now do the quiz on the next slide and check
Forests NEW INTERNATIONALIST EASIER ENGLISH Intermediate READY LESSON Today s lesson: Quiz Reading Speaking Writing Discuss: How much do you know about forests? Now do the quiz on the next slide and check
Sunlight. Air. The sun provides light, energy, and warmth. It also affects the weather on Earth.
 Sunlight The sun provides light, energy, and warmth. It also affects the weather on Earth. Sunlight is important on a farm, because the growing plants require the sun or a source of light energy to make
Sunlight The sun provides light, energy, and warmth. It also affects the weather on Earth. Sunlight is important on a farm, because the growing plants require the sun or a source of light energy to make
Activities for Exhibit Exploration
 This worksheet will help guide you as you investigate our exhibits. If you have a camera, some questions can be answered by taking a picture. Otherwise, you may write your answers into the space provided.
This worksheet will help guide you as you investigate our exhibits. If you have a camera, some questions can be answered by taking a picture. Otherwise, you may write your answers into the space provided.
Halifax County Schools 2 nd Grade Science Pacing Guide 1st Six Weeks Goal Activities Essential Questions Vocabulary
 Halifax County Schools 2 nd Grade Science Pacing Guide 1st Six Weeks Goal 2 Weather 2.01Investigate and describe how moving air interacts with objects. 2.02 Observe the force of air pressure pushing on
Halifax County Schools 2 nd Grade Science Pacing Guide 1st Six Weeks Goal 2 Weather 2.01Investigate and describe how moving air interacts with objects. 2.02 Observe the force of air pressure pushing on
There are 900 million (900,000,000) vehicles on the planet. 2) 80% of the Earth's mineral wealth is consumed by what percentage of the population?
 1) How many vehicles are there on the planet today? HOME Worksheet Part II There are 900 million (900,000,000) vehicles on the planet. 2) 80% of the Earth's mineral wealth is consumed by what percentage
1) How many vehicles are there on the planet today? HOME Worksheet Part II There are 900 million (900,000,000) vehicles on the planet. 2) 80% of the Earth's mineral wealth is consumed by what percentage
As Peat Bogs Burn, a Climate Threat Rises. By HENRY FOUNTAINAUG. 8, 2016
 As Peat Bogs Burn, a Climate Threat Rises By HENRY FOUNTAINAUG. 8, 2016 A lightning storm in Utikuma Lake, Alberta, in June. The area was burned from the 2011 wildfire. After each fire, peat moss grows
As Peat Bogs Burn, a Climate Threat Rises By HENRY FOUNTAINAUG. 8, 2016 A lightning storm in Utikuma Lake, Alberta, in June. The area was burned from the 2011 wildfire. After each fire, peat moss grows
Section 12. Crowns: Measurements and Sampling
 Section 12. Crowns: Measurements and Sampling 3.0 Phase 3 Field Guide - Crowns: Measurements and Sampling 12.1 OVERVIEW...2 12.2 CROWN DEFINITIONS...2 12.3 CROWN DENSITY-FOLIAGE TRANSPARENCY CARD...5 12.4
Section 12. Crowns: Measurements and Sampling 3.0 Phase 3 Field Guide - Crowns: Measurements and Sampling 12.1 OVERVIEW...2 12.2 CROWN DEFINITIONS...2 12.3 CROWN DENSITY-FOLIAGE TRANSPARENCY CARD...5 12.4
SILVICULTURE & WILDLIFE HABITAT MANAGEMENT
 SILVICULTURE & WILDLIFE HABITAT MANAGEMENT Ralph D. Nyland Department of Forest and Natural Resources Management SUNY College of Environmental Science and Forestry Syracuse, NY 13210 Nyland - 2010 All
SILVICULTURE & WILDLIFE HABITAT MANAGEMENT Ralph D. Nyland Department of Forest and Natural Resources Management SUNY College of Environmental Science and Forestry Syracuse, NY 13210 Nyland - 2010 All
Title of Lesson Plan Life Cycle of Trees Prepared By. Glenna MaKosky City and State
 Title of Lesson Plan Life Cycle of Trees Prepared By Glenna MaKosky City and State Rochester, MN Grade Level(s) 2 Keywords (subjects Life cycle (seed, seedling, sapling, adult tree, senescent tree, log);
Title of Lesson Plan Life Cycle of Trees Prepared By Glenna MaKosky City and State Rochester, MN Grade Level(s) 2 Keywords (subjects Life cycle (seed, seedling, sapling, adult tree, senescent tree, log);
Aquatic Communities Aquatic communities can be classified as freshwater
 Aquatic Communities Aquatic communities can be classified as freshwater or saltwater. The two sets of communities interact and are joined by the water cycle. Gravity eventually returns all fresh water
Aquatic Communities Aquatic communities can be classified as freshwater or saltwater. The two sets of communities interact and are joined by the water cycle. Gravity eventually returns all fresh water
2.4 MANAGING FOR HIGH-VALUE TREES
 2.4 MANAGING FOR HIGH-VALUE TREES BACKGROUND Quality timber trees are important to the region s wood products industry. Quality is determined by tree size and the amount of clear, knot-free lumber the
2.4 MANAGING FOR HIGH-VALUE TREES BACKGROUND Quality timber trees are important to the region s wood products industry. Quality is determined by tree size and the amount of clear, knot-free lumber the
General Themes (I) Lecture 12
 General Themes (I) Lecture 12 1 Sustainability Source: Adams, W.M. (2006). "The Future of Sustainability: Re-thinking Environment and Development in the Twenty-first Century." Report of the IUCN Renowned
General Themes (I) Lecture 12 1 Sustainability Source: Adams, W.M. (2006). "The Future of Sustainability: Re-thinking Environment and Development in the Twenty-first Century." Report of the IUCN Renowned
WILDLIFE ECOLOGY AND CONSERVATION STUDY NOTES
 WILDLIFE ECOLOGY AND CONSERVATION STUDY NOTES 1.0 Introduction: General principles of ecosystems management 2.0 Objectives 3.0 Main content 3.1. Principles of sustainable management of the ecosystems 3.2
WILDLIFE ECOLOGY AND CONSERVATION STUDY NOTES 1.0 Introduction: General principles of ecosystems management 2.0 Objectives 3.0 Main content 3.1. Principles of sustainable management of the ecosystems 3.2
Climates and Ecosystems
 Chapter 2, Section World Geography Chapter 2 Climates and Ecosystems Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter 2, Section
Chapter 2, Section World Geography Chapter 2 Climates and Ecosystems Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter 2, Section
ECOSYSTEMS, WATERSHEDS AND POLLUTION CONTROL REVIEW
 ECOSYSTEMS, WATERSHEDS AND POLLUTION CONTROL REVIEW ECOSYSTEMS: (6 th grade content) How biotic and abiotic factors make an ecosystem: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdlwptkg-vi 1. A/An ecosystem is a
ECOSYSTEMS, WATERSHEDS AND POLLUTION CONTROL REVIEW ECOSYSTEMS: (6 th grade content) How biotic and abiotic factors make an ecosystem: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdlwptkg-vi 1. A/An ecosystem is a
The GLAS is Half Full:
 The GLAS is Half Full: Photo courtesy of Image courtesy of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Satellites and Changing Tropical Forests 29 Meet the Scientists Dr. Eileen Helmer, Ecologist:
The GLAS is Half Full: Photo courtesy of Image courtesy of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Satellites and Changing Tropical Forests 29 Meet the Scientists Dr. Eileen Helmer, Ecologist:
INVASIVE SPECIES MADE BY: RIYA, LAVANYA, ADAI, PRACHI, RUDRA
 INVASIVE SPECIES MADE BY: RIYA, LAVANYA, ADAI, PRACHI, RUDRA WHAT ARE INVASIVE SPECIES? Any Kind Of Organism that is not native to an eco system and causes harm to that particular eco system It does not
INVASIVE SPECIES MADE BY: RIYA, LAVANYA, ADAI, PRACHI, RUDRA WHAT ARE INVASIVE SPECIES? Any Kind Of Organism that is not native to an eco system and causes harm to that particular eco system It does not
Roles of Organisms in Ecosystems. P Organisms that feed off dead organisms or the waste of other organisms are called scavengers.
 Roles of Organisms in Ecosystems P Organisms that feed off dead organisms or the waste of other organisms are called scavengers. Roles of Organisms in Ecosystems P Organisms that break down dead organisms
Roles of Organisms in Ecosystems P Organisms that feed off dead organisms or the waste of other organisms are called scavengers. Roles of Organisms in Ecosystems P Organisms that break down dead organisms
Developing forestry practices. Managing for Timber and Wildlife Diversity NATIONAL WILD TURKEY FEDERATION PRE-HARVEST PLANNING:
 Managing for Timber and Wildlife Diversity by Joe McGlincy NWTF WILDLIFE BULLETIN NO.15 RON BRENNEMAN NATIONAL WILD TURKEY FEDERATION Developing forestry practices that could potentially benefit all wildlife
Managing for Timber and Wildlife Diversity by Joe McGlincy NWTF WILDLIFE BULLETIN NO.15 RON BRENNEMAN NATIONAL WILD TURKEY FEDERATION Developing forestry practices that could potentially benefit all wildlife
WHY DO WE NEED NITROGEN?? Nitrogen is needed to make up DNA and protein!
 Nitrogen Cycle 2.2 WHY DO WE NEED NITROGEN?? Nitrogen is needed to make up DNA and protein! In animals, proteins are vital for muscle function. In plants, nitrogen is important for growth. NITROGEN Nitrogen
Nitrogen Cycle 2.2 WHY DO WE NEED NITROGEN?? Nitrogen is needed to make up DNA and protein! In animals, proteins are vital for muscle function. In plants, nitrogen is important for growth. NITROGEN Nitrogen
Tropical Agro-Ecosystems
 ropical Agro-Ecosystems to Dry ropical Vegetation Acid soils Alkaline soils From ain Forests to Deserts 3000+ - 1000 mm 12-10 months 2000-500 mm 9-4 months 500-0 mm 4-0 months to Dry ropical Vegetation
ropical Agro-Ecosystems to Dry ropical Vegetation Acid soils Alkaline soils From ain Forests to Deserts 3000+ - 1000 mm 12-10 months 2000-500 mm 9-4 months 500-0 mm 4-0 months to Dry ropical Vegetation
4. (Mark all that apply) Which one(s) of these are predators of the desert? a. Grizzly Bears b. Coyotes c. Road runners d. Badgers
 School: Team Number: Competitor s Names: Score: /59 Ecology Test 1. (Mark all that apply) Which are limiting factors in a logistic growth model that results in a decreased biotic potential? a. Light, temperature,
School: Team Number: Competitor s Names: Score: /59 Ecology Test 1. (Mark all that apply) Which are limiting factors in a logistic growth model that results in a decreased biotic potential? a. Light, temperature,
Lesson 2-2: Riparian Zones
 2-14 Lesson 2-2: Riparian Zones Time of Lesson: 1 hour Rationale: The purpose of this lesson is to define what a riparian zone is and link its importance for fish and other animals, and humans, and the
2-14 Lesson 2-2: Riparian Zones Time of Lesson: 1 hour Rationale: The purpose of this lesson is to define what a riparian zone is and link its importance for fish and other animals, and humans, and the
A brief introduction to general terms and concepts related to the forestry learning objectives
 A brief introduction to general terms and concepts related to the forestry learning objectives The profession embracing the science, art, and practice of creating, managing, using, and conserving forests
A brief introduction to general terms and concepts related to the forestry learning objectives The profession embracing the science, art, and practice of creating, managing, using, and conserving forests
THE INTRODUCTION THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT
 THE INTRODUCTION The earth is surrounded by atmosphere composed of many gases. The sun s rays penetrate through the atmosphere to the earth s surface. Gases in the atmosphere trap heat that would otherwise
THE INTRODUCTION The earth is surrounded by atmosphere composed of many gases. The sun s rays penetrate through the atmosphere to the earth s surface. Gases in the atmosphere trap heat that would otherwise
Overview of Climate Science
 1 Overview of Climate Science This overview of climate science is written to support the development of a K- 14 climate education plan for the Pacific Islands Climate Education Partnership (PCEP). It aims
1 Overview of Climate Science This overview of climate science is written to support the development of a K- 14 climate education plan for the Pacific Islands Climate Education Partnership (PCEP). It aims
Chapter 16 Human Impact on Ecosystems DAY ONE
 Chapter 16 Human Impact on Ecosystems DAY ONE Earth s resources As the human population grows, the demand for resources increases. Our population continues to grow. Earth s carrying capacity is actually
Chapter 16 Human Impact on Ecosystems DAY ONE Earth s resources As the human population grows, the demand for resources increases. Our population continues to grow. Earth s carrying capacity is actually
Protecting Biodiversity in the Amazon Rain Forest Why is biodiversity important? Why is it critical to protect biodiversity in the Amazon rain forest?
 Activityapply Protecting Biodiversity in the Amazon Rain Forest Why is biodiversity important? Why is it critical to protect biodiversity in the Amazon rain forest? Overview Students explore biodiversity
Activityapply Protecting Biodiversity in the Amazon Rain Forest Why is biodiversity important? Why is it critical to protect biodiversity in the Amazon rain forest? Overview Students explore biodiversity
Grade 6 Book 10. Biomes
 Grade 6 Book 10 Biomes 1 Biomes Those who dwell among the beauties and mysteries of the earth are never alone or weary of life. Rachel Carson Book 10 - Biomes Grade 6 Term 4 (SS and NS) THEMES Biomes Forest
Grade 6 Book 10 Biomes 1 Biomes Those who dwell among the beauties and mysteries of the earth are never alone or weary of life. Rachel Carson Book 10 - Biomes Grade 6 Term 4 (SS and NS) THEMES Biomes Forest
Improving Rainfall Effectiveness On Rangeland
 L-5029 Improving Rainfall Effectiveness On Rangeland Allan McGinty, Thomas L. Thurow and Charles A. Taylor, Jr.* Rainfall is a major limiting factor for livestock production from Texas rangelands. Everything
L-5029 Improving Rainfall Effectiveness On Rangeland Allan McGinty, Thomas L. Thurow and Charles A. Taylor, Jr.* Rainfall is a major limiting factor for livestock production from Texas rangelands. Everything
UNDERSTANDING THE ALTERNATE ELIGIBLE CONTENT IN SCIENCE
 1 UNDERSTANDING THE ALTERNATE ELIGIBLE CONTENT IN SCIENCE 2015 University of Pittsburgh PASA Science Project Team pasasci@pitt.edu 1 Table of Contents Introduction...3 Guide to Reading Alternate Eligible
1 UNDERSTANDING THE ALTERNATE ELIGIBLE CONTENT IN SCIENCE 2015 University of Pittsburgh PASA Science Project Team pasasci@pitt.edu 1 Table of Contents Introduction...3 Guide to Reading Alternate Eligible
ABOUT PEATLANDS? THE TRUTH BEHIND THE BOG
 ABOUT PEATLANDS? THE TRUTH BEHIND THE BOG Peatlands are wetland landscapes that are characterised by waterlogged organic soils made of dead and decaying plants. They may not sound or look much on first
ABOUT PEATLANDS? THE TRUTH BEHIND THE BOG Peatlands are wetland landscapes that are characterised by waterlogged organic soils made of dead and decaying plants. They may not sound or look much on first
RESTORING OLD-GROWTH FEATURES TO MANAGED FORESTS IN SOUTHERN ONTARIO
 AGDEX 324 RESTORING OLD-GROWTH FEATURES TO MANAGED FORESTS IN SOUTHERN ONTARIO Most of the old-growth forests of southern Ontario were removed by logging, forest fires and European settlement between the
AGDEX 324 RESTORING OLD-GROWTH FEATURES TO MANAGED FORESTS IN SOUTHERN ONTARIO Most of the old-growth forests of southern Ontario were removed by logging, forest fires and European settlement between the
Integrating Wildlife Conservation into the Management of Cameroon s Cacao Agricultural Landscapes
 Integrating Wildlife Conservation into the Management of Cameroon s Cacao Agricultural Landscapes by Thomas Dietsch, Ph.D., Postdoctoral Scholar, Center for Tropical Research, Institute of the Environment,
Integrating Wildlife Conservation into the Management of Cameroon s Cacao Agricultural Landscapes by Thomas Dietsch, Ph.D., Postdoctoral Scholar, Center for Tropical Research, Institute of the Environment,
Winter Tree ID! Use this interactive dichotomous key to help you identify and learn more about the tree species found around Upham Woods!
 Winter Tree ID! Use this interactive dichotomous key to help you identify and learn more about the tree species found around Upham Woods! Produced under a 2012-2013 grant from the Wisconsin Environmental
Winter Tree ID! Use this interactive dichotomous key to help you identify and learn more about the tree species found around Upham Woods! Produced under a 2012-2013 grant from the Wisconsin Environmental
What Animals Live In The Coniferous Forest Biome
 What Animals Live In The Coniferous Forest Biome Free Download WHAT ANIMALS LIVE IN THE CONIFEROUS FOREST BIOME LIST OF CONIFEROUS FOREST ANIMALS Sat, 30 Dec 2017 01:39:00 GMT list of coniferous_forest
What Animals Live In The Coniferous Forest Biome Free Download WHAT ANIMALS LIVE IN THE CONIFEROUS FOREST BIOME LIST OF CONIFEROUS FOREST ANIMALS Sat, 30 Dec 2017 01:39:00 GMT list of coniferous_forest
Land Biomes. Reading Preview. Effects of Latitude and Climate. Essential Questions
 Land Biomes Ecosystems on land are grouped into biomes primarily based on the plant communities within them. Real-World Reading Link If you live in the eastern part of the United States, you might live
Land Biomes Ecosystems on land are grouped into biomes primarily based on the plant communities within them. Real-World Reading Link If you live in the eastern part of the United States, you might live
Low-intensity fire burning on the forest floor. High-intensity crown fire
 Forest Fires: Answers to 12 Common Questions 1. Is wildfire bad for forests? No. Some forests need fire to be healthy, but it has to be the type of fire that the forest evolved with. Low-intensity fire
Forest Fires: Answers to 12 Common Questions 1. Is wildfire bad for forests? No. Some forests need fire to be healthy, but it has to be the type of fire that the forest evolved with. Low-intensity fire
Broadrick Secondary School Secondary 1 Normal (Academic) Geography EOY Revision Practise Paper (Suggested Answers)
 Question 1 a) Name two countries where tropical rainforests can be found. Malaysia / Indonesia / Singapore accept other plausible answers b) Describe the temperature and rainfall characteristics of the
Question 1 a) Name two countries where tropical rainforests can be found. Malaysia / Indonesia / Singapore accept other plausible answers b) Describe the temperature and rainfall characteristics of the
UNDERSTANDING THE ALTERNATE ELIGIBLE CONTENT IN SCIENCE
 1 UNDERSTANDING THE ALTERNATE ELIGIBLE CONTENT IN SCIENCE 2015 University of Pittsburgh PASA Science Project Team pasasci@pitt.edu 1 Understanding the Alternate Eligible Content in Science Table of Contents
1 UNDERSTANDING THE ALTERNATE ELIGIBLE CONTENT IN SCIENCE 2015 University of Pittsburgh PASA Science Project Team pasasci@pitt.edu 1 Understanding the Alternate Eligible Content in Science Table of Contents
Recognizing the Importance of Forests
 Lesson B1 3 Recognizing the Importance of Forests Unit B. Plant Wildlife Management Problem Area 1. Introduction to Forestry Lesson 3. Recognizing the Importance of Forests New Mexico Content Standard:
Lesson B1 3 Recognizing the Importance of Forests Unit B. Plant Wildlife Management Problem Area 1. Introduction to Forestry Lesson 3. Recognizing the Importance of Forests New Mexico Content Standard:
Fire Scars. Appropriate Grade Level: 6th- 12th. Time Required: 3 Hours (Each section can be presented as a 1-hour lesson.)
 Objectives 1. Students will describe the historic role of fire in the forests of the Klamath-Siskiyou Mountains. 2. Students will identify fire scars and growth rings on a tree cookie. 3. Students will
Objectives 1. Students will describe the historic role of fire in the forests of the Klamath-Siskiyou Mountains. 2. Students will identify fire scars and growth rings on a tree cookie. 3. Students will
Lakes and Ponds. Questions to consider. Ponds breathe. Sinkhole pond. Oxbow lake. Farm pond. Reservoir
 8 Lakes and Ponds dane johnson / visuals unlimited Oxbow lake Farm pond Sinkhole pond Reservoir albert copley / visuals unlimited Questions to consider 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 How do oxygen levels in ponds change
8 Lakes and Ponds dane johnson / visuals unlimited Oxbow lake Farm pond Sinkhole pond Reservoir albert copley / visuals unlimited Questions to consider 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 How do oxygen levels in ponds change
Tropical Rainforests. receive an average rainfall of /yr. temperature almost always in the 70 s or 80 s F. average humidity is ~83%
 Tropical Rainforests lush, equatorial evergreen forests àa belt of green extending 10º N & S of equator receive an average rainfall of 50-260 /yr plants are so densely packed that rain falling on the canopy
Tropical Rainforests lush, equatorial evergreen forests àa belt of green extending 10º N & S of equator receive an average rainfall of 50-260 /yr plants are so densely packed that rain falling on the canopy
Unit 2L.3: Habitats. Animals and plants in. habitats. Visiting Habitats
 Unit 2L.3: Animals and plants in habitats. Visiting Science skills: Making and using models Observing Inferring Collecting and interpreting data(record) Concluding By the end of unit you should Identify
Unit 2L.3: Animals and plants in habitats. Visiting Science skills: Making and using models Observing Inferring Collecting and interpreting data(record) Concluding By the end of unit you should Identify
1 Everything Is Connected
 CHAPTER 18 1 Everything Is Connected SECTION Interactions of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What do organisms in an ecosystem depend
CHAPTER 18 1 Everything Is Connected SECTION Interactions of Living Things BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What do organisms in an ecosystem depend
1. The diagram below represents many species of plants and animals and their surroundings.
 1. The diagram below represents many species of plants and animals and their surroundings. 4. Which statement most accurately predicts what would happen in the aquarium shown below if it were tightly covered
1. The diagram below represents many species of plants and animals and their surroundings. 4. Which statement most accurately predicts what would happen in the aquarium shown below if it were tightly covered
Syllabus OB59 Study a local habitat, using appropriate instruments and simple keys to show the variety and distribution of named organisms
 Biology: 15. Ecology Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Syllabus OB59 Study a local habitat, using appropriate instruments and
Biology: 15. Ecology Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Syllabus OB59 Study a local habitat, using appropriate instruments and
tip ACTIVITY BOOK FOR CHILDREN ON OUR NATURAL ENVIRONMENT SERIES I: TREES & PLANTS
 tip ACTIVITY BOOK FOR CHILDREN ON OUR NATURAL ENVIRONMENT SERIES I: TREES & PLANTS 1 ACTIVITY BOOK FOR CHILDREN ON OUR NATURAL ENVIRONMENT SERIES I: TREES & PLANTS January 2013 Material developed by: Salmon
tip ACTIVITY BOOK FOR CHILDREN ON OUR NATURAL ENVIRONMENT SERIES I: TREES & PLANTS 1 ACTIVITY BOOK FOR CHILDREN ON OUR NATURAL ENVIRONMENT SERIES I: TREES & PLANTS January 2013 Material developed by: Salmon
4.9AB Producers, Consumers, and Food Webs
 4.9AB Producers, Consumers, and Food Webs Key Concept 1: Producers need sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to make (produce) their own food. Consumers depend on plants or other organisms for food. Questions:
4.9AB Producers, Consumers, and Food Webs Key Concept 1: Producers need sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to make (produce) their own food. Consumers depend on plants or other organisms for food. Questions:
Environmental Science Exam 5 Biomes Conserve Paper Don t Write on This Test!
 Environmental Science Exam 5 Biomes Conserve Paper Don t Write on This Test! 1. What are the two most significant abiotic factors that influence what type of biome is found in a geographic area? a. Wind
Environmental Science Exam 5 Biomes Conserve Paper Don t Write on This Test! 1. What are the two most significant abiotic factors that influence what type of biome is found in a geographic area? a. Wind
What is the carbon cycle?
 What is the carbon cycle? By NASA Earth Observatory, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.29.17 Word Count 1,160 Carbon is both the foundation of all life on Earth and the source of the majority of energy consumed
What is the carbon cycle? By NASA Earth Observatory, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.29.17 Word Count 1,160 Carbon is both the foundation of all life on Earth and the source of the majority of energy consumed
Life Science Grade 5 Standard 1
 Life Science Grade 5 Standard 1 Standard: 1: Classify plants and animals according to the physical characteristics that they share Essential Guiding Question: How do we group organisms? Focus Questions:
Life Science Grade 5 Standard 1 Standard: 1: Classify plants and animals according to the physical characteristics that they share Essential Guiding Question: How do we group organisms? Focus Questions:
Orienteering Secondary School Level Curragh Chase Forest Park
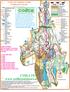 Orienteering Secondary School Level Curragh Chase Forest Park Name Today s Date There are 9 controls for you to find on this Adventure Challenge Control Point 1 Cairn Did you know that Ireland has been
Orienteering Secondary School Level Curragh Chase Forest Park Name Today s Date There are 9 controls for you to find on this Adventure Challenge Control Point 1 Cairn Did you know that Ireland has been
Directed Reading. Section: Global Change. than in the rest of the United States. b. In the United States and Canada, many lakes are dying as their ph
 Section: Global Change In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1. Scientists have discovered that acid rain is caused
Section: Global Change In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1. Scientists have discovered that acid rain is caused
OUR OCEANS FACTSHEET. Ocean life
 The ocean makes our planet a wonderful place to live. It gives us more than half of the oxygen we breathe. It regulates the climate, absorbs a quarter of the carbon that we put into the atmosphere every
The ocean makes our planet a wonderful place to live. It gives us more than half of the oxygen we breathe. It regulates the climate, absorbs a quarter of the carbon that we put into the atmosphere every
What is ECOLOGY? The study of the biotic and abiotic factors in an environment and their interactions.
 Ecology What is ECOLOGY? The study of the biotic and abiotic factors in an environment and their interactions. Biotic Factors Living things in the environment. Animals Plants Fungi Protists Bacteria Abiotic
Ecology What is ECOLOGY? The study of the biotic and abiotic factors in an environment and their interactions. Biotic Factors Living things in the environment. Animals Plants Fungi Protists Bacteria Abiotic
7 Energy Flow Through an Ecosystem NOW THAT YOU are familiar with producers and consumers,
 7 Energy Flow Through an Ecosystem NOW THAT YOU are familiar with producers and consumers, you are going to learn about how these organisms interact within an ecosystem. Picture a seal swimming in the
7 Energy Flow Through an Ecosystem NOW THAT YOU are familiar with producers and consumers, you are going to learn about how these organisms interact within an ecosystem. Picture a seal swimming in the
William S. Schmidt Outdoor Education Center WOODLAND ECOLOGY- ORME
 William S. Schmidt Outdoor Education Center WOODLAND ECOLOGY- ORME Introduction The Woodland Ecology lesson introduces the topic of forestry to students. It also shows the interconnectedness of the watershed,
William S. Schmidt Outdoor Education Center WOODLAND ECOLOGY- ORME Introduction The Woodland Ecology lesson introduces the topic of forestry to students. It also shows the interconnectedness of the watershed,
