MODELLING SURFACE RUNOFF TO MITIGATE HARMFUL IMPACT OF SOIL EROSION
|
|
|
- Benedict Wade
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MODELLING SURFACE RUNOFF TO MITIGATE HARMFUL IMPACT OF SOIL EROSION Pavel KOVAR, Darina VASSOVA Faculty of Environmental Sciences Czech University of Life Sciences Prague HydroPredict Conference 2010 Prague, September 20 to 23, 2010
2 INTRODUCTION Problems Caused by Water Erosion Loss of soil is an important issue worldwide, due to: Increased frequency of hydrological extremes Inexistent or insufficient erosion control measures Improper land use Improper agricultural/forest management First steps for solving problems related to water erosion : Empirical models: USLE/MUSLE (Modified/Universal Soil Loss Equation, Delivery Ratio) Simulation models: CN-based models (EPIC, CREAMS, AGNPS,...) Surface Runoff and Erosion Processes (SMODERP, EROSION 2D,...) Advanced simulation models: EUROSEM (European Erosion Model, WEPP (Water Erosion Prediction Project,
3 INTRODUCTION CAN WATER EROSION BE PREDICTED USING A MODIFIED HYDROLOGIC MODEL? In this presentation we will try to determine the common principles of surface runoff and soil erosion analyses: Physically-based models Natural rainfall-runoff events data Simulated rainfall-runoff data (using rain simulator) Design rainfall data Observed and computed rain erosivity data assessment Soil loss analysis based on soil erodibility (rill and interrill erosion assessment)
4 EXPERIMENTAL RUNOFF PLOTS Area: TŘEBSÍN
5 EXPERIMENTAL SITES DESCRIPTION Soil characteristics: Brown soil Eutric Cambisol on weathered eluvials and deluvials Field capacity (average): 33.5% Porosity (average): 48.3% Plot parameters and crops Plot No. Length (m) Wide (m) Slope (%) Area (m 2 ) Crop 2007 Crop 2008 Crop 2009 Crop sunflower maize maize maize sunflower maize maize maize sunflower maize maize maize Average Soil hydraulic parameters Plot No. Satur. hydraulic conductivity K s (mm min -1 ) Sorptivity at FC So (mm min -0.5 ) SF Storage suction factor SF (mm) So 2 K s 2
6 RAIN SIMULATOR
7 RAIN SIMULATOR
8 SHEET FLOW
9 DISCHARGE/LOAD MEASUREMENT DEVICE
10 GRANULARITY CURVE FOR EXPERIMENTAL RUNOFF AREAS AT TŘEBSÍN percent (%) soil grain size Plot No. Grain <0.002 Grain <0.01 Grain Grain Grain
11 MODEL KINFIL PRINCIPLES EINFIL Part Infiltration computation: Green Ampt (and Morel- Seytoux) Storage suction factor: Ponding time: KINFIL Part Computation of flow on slopes using kinematic wave computation: (Lax-Wendroff numerical scheme) ) ( t i x y my t y K i i S t K So H S t i H K i e m s f p s f i s f p f i s s
12 THE KINFIL PARAMETERS ROOT depth of root zone (m) KS saturated hydraulic conductivity (m s -1 ) SO sorptivity at field capacity (m s -0.5 ) POR porosity ( ) FC field capacity ( ) SMC (or API) soil moisture content (mm) JJ number of planes in cascade ( ) SLO slope of plane ( ) LEN length of plane (m) WID width of plane (m) NM Manning roughness t x 1 my m1 DS mean soil particle diameter (mm) D(i) soil particle category diameters (mm) RO soil particle density (kg m -3 ) cascade of planes cascade of segments
13 IMPACT OF PHYSIOGRAPHIC CHARACTERISTICS ON SURFACE RUNOFF Length of slope Angle of slope Slope length vers. specific runoff (CN=88, slope α = 0,05, Manning n=0,100) Slope angle vers. time to peak (CN=88, length L=100m, Manning n=0,100) Specific discharge q (l s -1 m -1 ) Time to peak (hrs) Slope length L (m) Slope angle α (-) Hydraulic roughness Roughness vers. time to peak (CN = 88, length L=100m, slope α=0,05 ) Manning n Time to peak (hrs)
14 NATURAL RAINFALL-RUNOFF OBSERVATION DT = 30 min, area 250 m 2 ( m), 10 August 2007 Rainfall-runoff events Depths, velocity and shear velocity Soil loss: 5330 kg ha -1 Soil loss: 281 kg ha -1
15 SIMULATED RAINFALL-RUNOFF EVENTS TŘEBSÍN 9, DT = 1 min, area 30 m 2 ( m) 26 Aug (DRY, SMC o =23.4%, Maize) 26 Aug (WET, SMC o =39.3%, Maize) Depths and Velocities 26 Aug (DRY) 26 Aug (WET)
16 DESIGN RAINFALLS Rain gauge Benešov: P t,n =P 1d,N a t 1-c i t,n =P 1d,N a t -c Design rainfall depths P t,n (mm): Rain depths P t,n for duration t d (10 to 300 min), N-years reccurance Benešov P (mm) t (min) years
17 DESIGN RAIN INTENSITIES Design rain intensities i t,n (mm min -1 ): Rain intensity it,n for duration td (10 to 300 min), N-years reccurence Benešov i (mm min -1 ) t (min) years
18 SURFACE RUNOFF FROM DESIGN RAINFALL Locality: TŘEBSÍN 9, area 30 m 2, Maize
19 DESIGN RUNOFF: DEPTH, VELOCITIES AND SHEAR STRESS VALUES AT DIFFERENT TIME Locality: TŘEBSÍN 9, area 30m 2, N = 2 years, TD = 10 min 2.50 Time: 10 min Time: 20 min 0.06 Depth (m) SHEAR STRESS (Pa) VELOCITIES V (m.s -1 ) Depth (m) SHEAR STRESS (Pa) VELOCITIES V (m.s -1 ) Length (m) 0.00 Shear Stress Depth Velocity Shear Velocity Length (m) 0.00 Shear Stress Depth Velocity Shear Velocity 2.50 Time: 30 min Time: 40 min 0.06 Depth (m) SHEAR STRESS (Pa) VELOCITIES V (m.s -1 ) Depth (m) SHEAR STRESS (Pa) VELOCITIES V (m.s -1 ) Shear Stress Shear Stress Depth Length (m) 0.00 Depth Velocity Shear Velocity Length (m) 0.00 Velocity Shear Velocity
20 DESIGN RUNOFF: POTENTIAL SOIL LOSS Locality: TŘEBSÍN 9, N = 2 years, TD = 10 min Grain size categories and their critical shear stress: Category (mm) < t c (Pa) Effective medium grain size D s = mm, t c = 0.5 Pa Experimental runoff area: Potential soil loss (for D s ) at Pa
21 CONCLUSIONS ADVANTAGES OF THE KINFIL MODEL provides results from the physically-based scheme. provides possibilities to calibrate model parameters for natural rainfall-runoff event reconstructions. simulates surface runoff discharges, depths, velocities and shear stress accurately enough to be compared with measured discharges and soil losses measured by rain simulator equipment. simulates also the change of land use and farming management. MODELLERS AIM to extend research in soil losses caused by rill erosion (t 0 vers. t K for various granulometric spectra). to compare the KINFIL and WEPP models results.
22 Thank you for your attention
Climate Simulation Irrigation Winter Processes Surface Hydrology Water Balance & Percolation Subsurface Hydrology Soil Component Plant Growth Residue
 Climate Simulation Irrigation Winter Processes Surface Hydrology Water Balance & Percolation Subsurface Hydrology Soil Component Plant Growth Residue Decomposition and Management Overland Flow Hydraulics
Climate Simulation Irrigation Winter Processes Surface Hydrology Water Balance & Percolation Subsurface Hydrology Soil Component Plant Growth Residue Decomposition and Management Overland Flow Hydraulics
The Texas A&M University and U.S. Bureau of Reclamation Hydrologic Modeling Inventory (HMI) Questionnaire
 The Texas A&M University and U.S. Bureau of Reclamation Hydrologic Modeling Inventory (HMI) Questionnaire May 4, 2010 Name of Model, Date, Version Number Dynamic Watershed Simulation Model (DWSM) 2002
The Texas A&M University and U.S. Bureau of Reclamation Hydrologic Modeling Inventory (HMI) Questionnaire May 4, 2010 Name of Model, Date, Version Number Dynamic Watershed Simulation Model (DWSM) 2002
KINEMATIC WAVE MODELING IN WATER RESOURCES Environmental Hydrology
 KINEMATIC WAVE MODELING IN WATER RESOURCES Environmental Hydrology VIJAY P. SINGH Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Louisiana State University Baton Rouge, Louisiana A Wiley-lnterscience
KINEMATIC WAVE MODELING IN WATER RESOURCES Environmental Hydrology VIJAY P. SINGH Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Louisiana State University Baton Rouge, Louisiana A Wiley-lnterscience
History of Model Development at Temple, Texas. J. R. Williams and J. G. Arnold
 History of Model Development at Temple, Texas J. R. Williams and J. G. Arnold INTRODUCTION Then Model development at Temple A long history (1937-present) Many scientists participating in: Data collection
History of Model Development at Temple, Texas J. R. Williams and J. G. Arnold INTRODUCTION Then Model development at Temple A long history (1937-present) Many scientists participating in: Data collection
SOUTHEAST TEXAS CONTINUING EDUCATION
 EXAM No. 118 FLOOD - RUNOFF ANALYSIS 1. Information gained from flood - runoff analysis includes which one: A. Stage, discharge, volume. B. Measure depth, volume. C. Velocity, depth, storm occurrence.
EXAM No. 118 FLOOD - RUNOFF ANALYSIS 1. Information gained from flood - runoff analysis includes which one: A. Stage, discharge, volume. B. Measure depth, volume. C. Velocity, depth, storm occurrence.
Evaluating WEPP Predicted On-field Furrow Irrigation Erosion
 This paper was peer-reviewed for scientific content. Pages 693-698. In: D.E. Stott, R.H. Mohtar and G.C. Steinhardt (eds). 21. Sustaining the Global Farm. Selected papers from the 1th International Soil
This paper was peer-reviewed for scientific content. Pages 693-698. In: D.E. Stott, R.H. Mohtar and G.C. Steinhardt (eds). 21. Sustaining the Global Farm. Selected papers from the 1th International Soil
Learning objectives. Upon successful completion of this lecture, the participants will be able to describe:
 Solomon Seyoum Learning objectives Upon successful completion of this lecture, the participants will be able to describe: The different approaches for estimating peak runoff for urban drainage network
Solomon Seyoum Learning objectives Upon successful completion of this lecture, the participants will be able to describe: The different approaches for estimating peak runoff for urban drainage network
Examination of PRZM5.0 Storm Rainfall Depth and Distribution Algorithms Compared to Current U.S. Storm Trends
 Examination of PRZM5.0 Storm Rainfall Depth and Distribution Algorithms Compared to Current U.S. Storm Trends August 24, 2016 Tammara L. Estes (Stone Environmental Inc.) Kevin L. Armbrust, Ph.D. (Louisiana
Examination of PRZM5.0 Storm Rainfall Depth and Distribution Algorithms Compared to Current U.S. Storm Trends August 24, 2016 Tammara L. Estes (Stone Environmental Inc.) Kevin L. Armbrust, Ph.D. (Louisiana
Introduction to KINEROS2
 Introduction to KINEROS2 Running KINEROS2 Introduction: Goal: Assignment: In this exercise you will learn about the files and instructions to run KINEROS2 for a simple single overland flow runoff element
Introduction to KINEROS2 Running KINEROS2 Introduction: Goal: Assignment: In this exercise you will learn about the files and instructions to run KINEROS2 for a simple single overland flow runoff element
Choosing an Appropriate Hydrological Model for Rainfall-Runoff Extremes in Small Catchments
 Soil & Water Res.,, (): doi:.//-swr Choosing an Appropriate Hydrological Model for Rainfall-Runoff Extremes in Small Catchments Pavel KOVÁŘ, Michaela HRABALÍKOVÁ, Martin NERUDA, Roman NERUDA, Jan ŠREJBER,
Soil & Water Res.,, (): doi:.//-swr Choosing an Appropriate Hydrological Model for Rainfall-Runoff Extremes in Small Catchments Pavel KOVÁŘ, Michaela HRABALÍKOVÁ, Martin NERUDA, Roman NERUDA, Jan ŠREJBER,
Comparison of Green-Ampt and Curve Number Infiltration Methods in a single-gauged Brazilian watershed
 Comparison of Green-Ampt and Curve Number Infiltration Methods in a single-gauged Brazilian watershed Julio Issao Kuwajima Toulouse, 2013 Introduction The volume and rate of runoff of rain events are of
Comparison of Green-Ampt and Curve Number Infiltration Methods in a single-gauged Brazilian watershed Julio Issao Kuwajima Toulouse, 2013 Introduction The volume and rate of runoff of rain events are of
Drainage Analysis. Appendix E
 Drainage Analysis Appendix E The existing and proposed storm drainage systems have been modeled with Bentley CivilStorm V8 computer modeling software. The peak stormwater discharge was determined for
Drainage Analysis Appendix E The existing and proposed storm drainage systems have been modeled with Bentley CivilStorm V8 computer modeling software. The peak stormwater discharge was determined for
1. Stream Network. The most common approach to quantitatively describing stream networks was postulated by Strahler (1952).
 1. Stream Network The most common approach to quantitatively describing stream networks was postulated by Strahler (1952). First Order Streams streams with no tributaries. Second Order Streams begin at
1. Stream Network The most common approach to quantitatively describing stream networks was postulated by Strahler (1952). First Order Streams streams with no tributaries. Second Order Streams begin at
Water Resources Engineering. Prof. R. Srivastava. Department of Water Resources Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur.
 Water Resources Engineering Prof. R. Srivastava Department of Water Resources Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture # 13 Today we will continue to discuss some of the abstractions
Water Resources Engineering Prof. R. Srivastava Department of Water Resources Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture # 13 Today we will continue to discuss some of the abstractions
Water balance at the field and watershed scale.
 Water balance at the field and watershed scale. Marco Bittelli Department of Agro-Environmental Science and Technology, University of Bologna, Italy Water Balance Water Balance: computed processes Penman
Water balance at the field and watershed scale. Marco Bittelli Department of Agro-Environmental Science and Technology, University of Bologna, Italy Water Balance Water Balance: computed processes Penman
Chapter 3 THEORY OF INFILTRATION. 3.1 General
 Chapter 3 THEORY OF INFILTRATION 3.1 General Water entering the soil at the surface of ground is termed as infiltration. It replaces the soil moisture deficit and the excess water moves downward by the
Chapter 3 THEORY OF INFILTRATION 3.1 General Water entering the soil at the surface of ground is termed as infiltration. It replaces the soil moisture deficit and the excess water moves downward by the
Design Guide for Vegetative Filter Strips Using VFSMOD
 Paper No. 99-2147 An ASAE Meeting Presentation Design Guide for Vegetative Filter Strips Using VFSMOD By Librianto Suwandono John E. Parsons Rafael Muñoz-Carpena Graduate Student Associate Professor Researcher
Paper No. 99-2147 An ASAE Meeting Presentation Design Guide for Vegetative Filter Strips Using VFSMOD By Librianto Suwandono John E. Parsons Rafael Muñoz-Carpena Graduate Student Associate Professor Researcher
Infiltration. Infiltration is the term applied to the process of water entry into the soil. The rate of infiltration determines
 Infiltration Infiltration is the term applied to the process of water entry into the soil. The rate of infiltration determines The time at which superficial water appears on the soil surface The amount
Infiltration Infiltration is the term applied to the process of water entry into the soil. The rate of infiltration determines The time at which superficial water appears on the soil surface The amount
Development of Portable Artificial Rainfall Simulator for Evaluating Sustainable Farming in Kenya
 erd Development of Portable Artificial Rainfall Simulator for Evaluating Sustainable Farming in Kenya Research article JACOB MURIUNGI MAORE Graduate School of Agriculture, Tokyo University of Agriculture,
erd Development of Portable Artificial Rainfall Simulator for Evaluating Sustainable Farming in Kenya Research article JACOB MURIUNGI MAORE Graduate School of Agriculture, Tokyo University of Agriculture,
Autumn semester of Prof. Kim, Joong Hoon
 1 Autumn semester of 2010 Prof. Kim, Joong Hoon Water Resources Hydrosystems System Engineering Laboratory Laboratory 2 A. HEC (Hydrologic Engineering Center) 1 Established in the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers(USACE)
1 Autumn semester of 2010 Prof. Kim, Joong Hoon Water Resources Hydrosystems System Engineering Laboratory Laboratory 2 A. HEC (Hydrologic Engineering Center) 1 Established in the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers(USACE)
Runoff and soil loss. (Quantification and modeling of watershed discharge and sediment yield) Kassa Tadele (Dr.Ing) Arba Minch University
 Runoff and soil loss (Quantification and modeling of watershed discharge and sediment yield) Kassa Tadele (Dr.Ing) Arba Minch University Part I. Runoff Contents 1. Fundamental Concepts 2. Generation of
Runoff and soil loss (Quantification and modeling of watershed discharge and sediment yield) Kassa Tadele (Dr.Ing) Arba Minch University Part I. Runoff Contents 1. Fundamental Concepts 2. Generation of
Evaluating BMP selection and placement in intermittent channels in Fort Cobb watershed
 Evaluating BMP selection and placement in intermittent channels in Fort Cobb watershed Preliminary Research Solmaz Rasoulzadeh, Arthur Stoecker Ph.D Student, Environmental Science Professor, Agricultural
Evaluating BMP selection and placement in intermittent channels in Fort Cobb watershed Preliminary Research Solmaz Rasoulzadeh, Arthur Stoecker Ph.D Student, Environmental Science Professor, Agricultural
FAST WATER / SLOW WATER AN EVALUATION OF ESTIMATING TIME FOR STORMWATER RUNOFF
 FAST WATER / SLOW WATER AN EVALUATION OF ESTIMATING TIME FOR STORMWATER RUNOFF Factors Affecting Stormwater Runoff: Rainfall intensity % Impervious surfaces Watershed size Slope Soil type, soil compaction
FAST WATER / SLOW WATER AN EVALUATION OF ESTIMATING TIME FOR STORMWATER RUNOFF Factors Affecting Stormwater Runoff: Rainfall intensity % Impervious surfaces Watershed size Slope Soil type, soil compaction
LID PLANTER BOX MODELING
 LID PLANTER BOX MODELING Clear Creek Solutions, Inc., 2010 Low Impact Development (LID) planter boxes are small, urban stormwater mitigation facilities. They are rain gardens in a box. WWHM4 provides the
LID PLANTER BOX MODELING Clear Creek Solutions, Inc., 2010 Low Impact Development (LID) planter boxes are small, urban stormwater mitigation facilities. They are rain gardens in a box. WWHM4 provides the
Soil Water Relationship. Dr. M. R. Kabir
 CHAPTER 4 Soil Water Relationship Dr. M. R. Kabir Professor and Head, Department of Civil Engineering University of Asia Pacific (UAP), Dhaka LECTURE 10 Introduction Root zone (depth of soil penetrated
CHAPTER 4 Soil Water Relationship Dr. M. R. Kabir Professor and Head, Department of Civil Engineering University of Asia Pacific (UAP), Dhaka LECTURE 10 Introduction Root zone (depth of soil penetrated
Water balance in soil
 Technische Universität München Water balance Water balance in soil Arno Rein Infiltration = + precipitation P evapotranspiration ET surface runoff Summer course Modeling of Plant Uptake, DTU Wednesday,
Technische Universität München Water balance Water balance in soil Arno Rein Infiltration = + precipitation P evapotranspiration ET surface runoff Summer course Modeling of Plant Uptake, DTU Wednesday,
Unit 2: Geomorphologic and Hydrologic Characteristics of Watersheds. ENVS 435: Watershed Management INSTR.: Dr. R.M. Bajracharya
 Unit 2: Geomorphologic and Hydrologic Characteristics of Watersheds ENVS 435: Watershed Management INSTR.: Dr. R.M. Bajracharya Watersheds are hydro-geologic units Water flow and cycling are basic and
Unit 2: Geomorphologic and Hydrologic Characteristics of Watersheds ENVS 435: Watershed Management INSTR.: Dr. R.M. Bajracharya Watersheds are hydro-geologic units Water flow and cycling are basic and
Learning objectives. Upon successful completion of this lecture, the participants will be able to:
 Solomon Seyoum Learning objectives Upon successful completion of this lecture, the participants will be able to: Describe and perform the required step for designing sewer system networks Outline Design
Solomon Seyoum Learning objectives Upon successful completion of this lecture, the participants will be able to: Describe and perform the required step for designing sewer system networks Outline Design
Analysis and Simulation of Drainage Capacity of Urban Pipe Network
 Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 6(3): 387-392, 2013 ISSN: 2040-7459; e-issn: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2013 Submitted: July 17, 2012 Accepted: August 28,
Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 6(3): 387-392, 2013 ISSN: 2040-7459; e-issn: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2013 Submitted: July 17, 2012 Accepted: August 28,
Effects of Input Uncertainty on VFSMOD Modeling of Water, Sediment, and Pesticide Trapping by Vegetative Filter Strips
 Effects of Input Uncertainty on VFSMOD Modeling of Water, Sediment, and Pesticide Trapping by Vegetative Filter Strips Solomon M. Folle 1, Michael F. Winchell 1, Tammara L. Estes 1, Katie Budreski 1, John
Effects of Input Uncertainty on VFSMOD Modeling of Water, Sediment, and Pesticide Trapping by Vegetative Filter Strips Solomon M. Folle 1, Michael F. Winchell 1, Tammara L. Estes 1, Katie Budreski 1, John
Introduction, HYDROGRAPHS
 HYDROGRAPHS Sequence of lecture Introduction Types of Hydrograph Components of Hydrograph Effective Rainfall Basin Lag or Time Lag Parts of Hydrograph Hydrograph Analysis Factors Affecting Hydrograph Shape
HYDROGRAPHS Sequence of lecture Introduction Types of Hydrograph Components of Hydrograph Effective Rainfall Basin Lag or Time Lag Parts of Hydrograph Hydrograph Analysis Factors Affecting Hydrograph Shape
Chapter 6. The Empirical version of the Rational Method
 Chapter 6 The Empirical version of the Rational Method The Empirical version is named because the parameters it uses (apart from rainfall data) are arbitrary and are generally based on experience or observation
Chapter 6 The Empirical version of the Rational Method The Empirical version is named because the parameters it uses (apart from rainfall data) are arbitrary and are generally based on experience or observation
Utah State University Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering CEE 3430 Engineering Hydrology Test 2. Date: 3/31/2014
 Utah State University Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering CEE 3430 Engineering Hydrology Test 2. Date: 3/31/2014 D.G. Tarboton Time: 50 min 45 Points Open Book. Answer all questions. Please
Utah State University Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering CEE 3430 Engineering Hydrology Test 2. Date: 3/31/2014 D.G. Tarboton Time: 50 min 45 Points Open Book. Answer all questions. Please
2015 International SWAT Conference Sardinia, Italy Date: (24 th June 2015)
 2015 International SWAT Conference Sardinia, Italy Date: (24 th June 2015) By Pratiksha Jain Research Scholar Remote Sensing Applications Group Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology
2015 International SWAT Conference Sardinia, Italy Date: (24 th June 2015) By Pratiksha Jain Research Scholar Remote Sensing Applications Group Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology
River Processes River action (fluvial)
 River action (fluvial) is probably the single most important geomorphic agent and their influence in geomorphology can hardly be overestimated. 1 To understand the complexity associated with river flow
River action (fluvial) is probably the single most important geomorphic agent and their influence in geomorphology can hardly be overestimated. 1 To understand the complexity associated with river flow
CEE3430 Engineering Hydrology
 CEE3430 Engineering Hydrology Practice Exam (There are multiple practice questions here A 110 min test will likely not have more than four questions) 1. Water Balance Write the water balance as Δ Where
CEE3430 Engineering Hydrology Practice Exam (There are multiple practice questions here A 110 min test will likely not have more than four questions) 1. Water Balance Write the water balance as Δ Where
Level 6 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Hydraulics and hydrology
 910-103 Level 6 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Hydraulics and hydrology Sample Paper You should have the following for this examination one answer book ordinary graph paper pen, pencil, ruler Work sheet
910-103 Level 6 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Hydraulics and hydrology Sample Paper You should have the following for this examination one answer book ordinary graph paper pen, pencil, ruler Work sheet
Rainfall-Runoff Analysis of Flooding Caused by Typhoon RUSA in 2002 in the Gangneung Namdae River Basin, Korea
 Journal of Natural Disaster Science, Volume 26, Number 2, 2004, pp95-100 Rainfall-Runoff Analysis of Flooding Caused by Typhoon RUSA in 2002 in the Gangneung Namdae River Basin, Korea Hidetaka CHIKAMORI
Journal of Natural Disaster Science, Volume 26, Number 2, 2004, pp95-100 Rainfall-Runoff Analysis of Flooding Caused by Typhoon RUSA in 2002 in the Gangneung Namdae River Basin, Korea Hidetaka CHIKAMORI
Hydrologic Engineering Center Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS) Sunil KUMAR Director, National Water Academy
 Hydrologic Engineering Center Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS) Sunil KUMAR Director, National Water Academy 22 April 2015 NWA, Pune Exercise Objective: To determine hydrological Response of the given
Hydrologic Engineering Center Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS) Sunil KUMAR Director, National Water Academy 22 April 2015 NWA, Pune Exercise Objective: To determine hydrological Response of the given
Hydrology for Drainage Design. Design Considerations Use appropriate design tools for the job at hand:
 Hydrology for Drainage Design Robert Pitt Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering University of Alabama Tuscaloosa, AL Objectives for Urban Drainage Systems are Varied Ensure personal safety
Hydrology for Drainage Design Robert Pitt Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering University of Alabama Tuscaloosa, AL Objectives for Urban Drainage Systems are Varied Ensure personal safety
Precipitation Surface Cover Topography Soil Properties
 Precipitation Surface Cover Topography Soil Properties Intrinsic capacity of rainfall to cause erosion Influenced by Amount, intensity, terminal velocity, drop size and drop size distribution of rain.
Precipitation Surface Cover Topography Soil Properties Intrinsic capacity of rainfall to cause erosion Influenced by Amount, intensity, terminal velocity, drop size and drop size distribution of rain.
Introduction. Keywords: Oil Palm, hydrology, HEC-HMS, HEC-RAS. a * b*
 The Effect of Land Changes Towards in Sg. Pandan Perwira Bin Khusairi Rahman 1,a* and Kamarul Azlan bin Mohd Nasir 1,b 1 Faculty of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia a * wirakhusairirahman@gmail.com,
The Effect of Land Changes Towards in Sg. Pandan Perwira Bin Khusairi Rahman 1,a* and Kamarul Azlan bin Mohd Nasir 1,b 1 Faculty of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia a * wirakhusairirahman@gmail.com,
Lecture 6: Soil Water
 6-1 GEOG415 Lecture 6: Soil Water Infiltration Movement of water into soil. Importance? - flood prediction -erosion -agriculture - water resources Infiltration capacity Expressed in the same unit as rainfall
6-1 GEOG415 Lecture 6: Soil Water Infiltration Movement of water into soil. Importance? - flood prediction -erosion -agriculture - water resources Infiltration capacity Expressed in the same unit as rainfall
AnnAGNPS. Annualized AGricultural Non-Point Source Pollurant Loading Model. Annualized Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollutant Loading Model
 AnnAGNPS Annualized AGricultural Non-Point Source Pollurant Loading Model 1 Erosion Erosion can be expresed as: E=f(C, S, T, SS, M) E = erosion C = climate S = soil properties T = topography SS = soil
AnnAGNPS Annualized AGricultural Non-Point Source Pollurant Loading Model 1 Erosion Erosion can be expresed as: E=f(C, S, T, SS, M) E = erosion C = climate S = soil properties T = topography SS = soil
Index. Page numbers followed by f indicate figures.
 Index Aerodynamic method, 103, 110 111 Algae, 131, 173, 175 Alternate depth, 88 Alternating block method, 132, 140 141 Attenuation, 106, 107f, 118, 120 Page numbers followed by f indicate figures. Baseflow
Index Aerodynamic method, 103, 110 111 Algae, 131, 173, 175 Alternate depth, 88 Alternating block method, 132, 140 141 Attenuation, 106, 107f, 118, 120 Page numbers followed by f indicate figures. Baseflow
SECTION IV WATERSHED TECHNICAL ANALYSIS
 A. Watershed Modeling SECTION IV WATERSHED TECHNICAL ANALYSIS An initial step in the preparation of this stormwater management plan was the selection of a stormwater simulation model to be utilized. It
A. Watershed Modeling SECTION IV WATERSHED TECHNICAL ANALYSIS An initial step in the preparation of this stormwater management plan was the selection of a stormwater simulation model to be utilized. It
DETERMINATION OF DESIGN INFLOW RATE IN FURROW IRRIGATION USING SIMULATED ADVANCE AND RECESSION CURVES
 Nigerian Journal of Technology, Vol. 24, No. 1, March 2005 Okereke, Duru, Nwachukwu & Madubuike 1 DETERMINATION OF DESIGN INFLOW RATE IN FURROW IRRIGATION USING SIMULATED ADVANCE AND RECESSION CURVES N.A.A.Okereke,
Nigerian Journal of Technology, Vol. 24, No. 1, March 2005 Okereke, Duru, Nwachukwu & Madubuike 1 DETERMINATION OF DESIGN INFLOW RATE IN FURROW IRRIGATION USING SIMULATED ADVANCE AND RECESSION CURVES N.A.A.Okereke,
CVEN 339 Summer 2009 Final Exam. 120 minutes allowed. 36 Students. No curve applied to grades. Median 70.6 Mean 68.7 Std. Dev High 88 Low 24.
 CVEN 339 Final Exam 120 minutes allowed 36 Students No curve applied to grades Median 70.6 Mean 68.7 Std. Dev. 13.7 High 88 Low 24.5 Name: CVEN 339 Water Resources Engineering Summer Semester 2009 Dr.
CVEN 339 Final Exam 120 minutes allowed 36 Students No curve applied to grades Median 70.6 Mean 68.7 Std. Dev. 13.7 High 88 Low 24.5 Name: CVEN 339 Water Resources Engineering Summer Semester 2009 Dr.
Overview of NRCS (SCS) TR-20 By Dr. R.M. Ragan
 Overview of NRCS (SCS) TR-20 By Dr. R.M. Ragan TR-20 is a computer program for the simulation of runoff occurring from a single storm event. The program develops flood hydrographs from runoff and routes
Overview of NRCS (SCS) TR-20 By Dr. R.M. Ragan TR-20 is a computer program for the simulation of runoff occurring from a single storm event. The program develops flood hydrographs from runoff and routes
Measuring discharge. Climatological and hydrological field work
 Measuring discharge Climatological and hydrological field work 1. Background Discharge (or surface runoff Q s) refers to the horizontal water flow occurring at the surface in rivers and streams. It does
Measuring discharge Climatological and hydrological field work 1. Background Discharge (or surface runoff Q s) refers to the horizontal water flow occurring at the surface in rivers and streams. It does
APPENDIX F RATIONAL METHOD
 7-F-1 APPENDIX F RATIONAL METHOD 1.0 Introduction One of the most commonly used procedures for calculating peak flows from small drainages less than 200 acres is the Rational Method. This method is most
7-F-1 APPENDIX F RATIONAL METHOD 1.0 Introduction One of the most commonly used procedures for calculating peak flows from small drainages less than 200 acres is the Rational Method. This method is most
Continuous Simulation Example Problem
 Continuous Simulation Example Problem The following examples provided an introduction to the continuous simulation hydrograph in the PONDS 3.2 Refined Method software, with an emphasis on wetland hydroperiod
Continuous Simulation Example Problem The following examples provided an introduction to the continuous simulation hydrograph in the PONDS 3.2 Refined Method software, with an emphasis on wetland hydroperiod
Introduction. The Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE, Wischmeir and Smith, 1978), including the revised version of it (RUSLE, Renard et al.
 Comparison of the abilities of the Q R EI 3 index and the EI 3 index to estimate event erosion on bare fallow plots P.I.. Kinnell University of Canberra Introduction The Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE,
Comparison of the abilities of the Q R EI 3 index and the EI 3 index to estimate event erosion on bare fallow plots P.I.. Kinnell University of Canberra Introduction The Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE,
Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering. Department of Civil Engineering. Hydrology and Hydraulics. Final Exam, April 21, 2017
 F Name: Student #: University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Department of Civil Engineering C1V250 - Hydrology and Hydraulics Final Exam, April 21, 2017 Duration: 2 and V2 hrs The
F Name: Student #: University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Department of Civil Engineering C1V250 - Hydrology and Hydraulics Final Exam, April 21, 2017 Duration: 2 and V2 hrs The
DRAINAGE & DESIGN OF DRAINAGE SYSTEM
 Drainage on Highways DRAINAGE & DESIGN OF DRAINAGE SYSTEM P. R.D. Fernando Chartered Engineer B.Sc.(Hons), M.Eng. C.Eng., MIE(SL) Drainage Requirement of Highway Drainage System Introduction Drainage means
Drainage on Highways DRAINAGE & DESIGN OF DRAINAGE SYSTEM P. R.D. Fernando Chartered Engineer B.Sc.(Hons), M.Eng. C.Eng., MIE(SL) Drainage Requirement of Highway Drainage System Introduction Drainage means
GIS-based components for rainfall-runoff models
 HydroGIS 96: Application of Geographic Information Systems in Hydrology and Water Resources Management (Proceedings of the Vienna Conference, April 1996). IAHS Publ. no. 235, 1996. 477 GIS-based components
HydroGIS 96: Application of Geographic Information Systems in Hydrology and Water Resources Management (Proceedings of the Vienna Conference, April 1996). IAHS Publ. no. 235, 1996. 477 GIS-based components
ENGN.4010 ENGINEERING CAPSTONE DESIGN Watershed Analysis. CiA
 RATIONAL METHOD Q CiA Where: Q = Maximum Rate of Runoff (cfs) C = Runoff Coefficient i = Average Rainfall Intensity (in/hr) A = Drainage Area (in acres) RATIONAL METHOD Assumptions and Limitations: Watershed
RATIONAL METHOD Q CiA Where: Q = Maximum Rate of Runoff (cfs) C = Runoff Coefficient i = Average Rainfall Intensity (in/hr) A = Drainage Area (in acres) RATIONAL METHOD Assumptions and Limitations: Watershed
EART 204. Water. Dr. Slawek Tulaczyk. Earth Sciences, UCSC
 EART 204 Water Dr. Slawek Tulaczyk Earth Sciences, UCSC 1 Water is an amazing liquid, (high heat capacity - particularly in phase transitions, maximum density at ca. 4 deg. C) 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Basin Hydrologic
EART 204 Water Dr. Slawek Tulaczyk Earth Sciences, UCSC 1 Water is an amazing liquid, (high heat capacity - particularly in phase transitions, maximum density at ca. 4 deg. C) 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Basin Hydrologic
Soil Properties that influence detachment and runoff
 Soil Properties that influence detachment and runoff Texture Structure Aggregation Density/compaction Wettability Antecedent soil moisture Organic Matter Sandy soils Sands are easily detacted However,
Soil Properties that influence detachment and runoff Texture Structure Aggregation Density/compaction Wettability Antecedent soil moisture Organic Matter Sandy soils Sands are easily detacted However,
Soil and Water Conservation and Management as a Potential Strategy for Climate Change Adaptation
 Soil and Water Conservation and Management as a Potential Strategy for Climate Change Adaptation by Victor B. Ella, Ph.D. Professor Land and Water Resources Division, Institute of Agricultural Engineering
Soil and Water Conservation and Management as a Potential Strategy for Climate Change Adaptation by Victor B. Ella, Ph.D. Professor Land and Water Resources Division, Institute of Agricultural Engineering
Effect of Land Surface on Runoff Generation
 Effect of Land Surface on Runoff Generation Context: Hydrologic Cycle Runoff vs Infiltration Infiltration: Process by which water on the ground surface enters the soil Runoff: Water (from rain, snowmelt,
Effect of Land Surface on Runoff Generation Context: Hydrologic Cycle Runoff vs Infiltration Infiltration: Process by which water on the ground surface enters the soil Runoff: Water (from rain, snowmelt,
Use of IDF Curves Design of a roof drainage system
 Use of IDF Curves Design of a roof drainage system Your engineering firm is currently planning the construction of a residential apartment building in Davos, Switzerland. Your task is to design the roof
Use of IDF Curves Design of a roof drainage system Your engineering firm is currently planning the construction of a residential apartment building in Davos, Switzerland. Your task is to design the roof
MODULE 1 RUNOFF HYDROGRAPHS WORKSHEET 1. Precipitation
 Watershed MODULE 1 RUNOFF HYDROGRAPHS WORKSHEET 1 A watershed is an area of land thaaptures rainfall and other precipitation and funnels it to a lake or stream or wetland. The area within the watershed
Watershed MODULE 1 RUNOFF HYDROGRAPHS WORKSHEET 1 A watershed is an area of land thaaptures rainfall and other precipitation and funnels it to a lake or stream or wetland. The area within the watershed
WHAT IS SOIL? soil is a complex system of organic and inorganic (mineral) compounds Soil properties depend on formation process particle size climate
 Lecture 5, Soil water and infiltration WHAT IS SOIL? soil is a complex system of organic and inorganic (mineral) compounds Soil properties depend on formation process particle size climate THE IMPORTANCE
Lecture 5, Soil water and infiltration WHAT IS SOIL? soil is a complex system of organic and inorganic (mineral) compounds Soil properties depend on formation process particle size climate THE IMPORTANCE
Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS
 Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS Why Measure Streamflow? Water supply planning How much water can we take out (without harming ecosystems we want to protect) Flood protection How much
Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS Why Measure Streamflow? Water supply planning How much water can we take out (without harming ecosystems we want to protect) Flood protection How much
Sixth Semester B. E. (R)/ First Semester B. E. (PTDP) Civil Engineering Examination
 CAB/2KTF/EET 1221/1413 Sixth Semester B. E. (R)/ First Semester B. E. (PTDP) Civil Engineering Examination Course Code : CV 312 / CV 507 Course Name : Engineering Hydrology Time : 3 Hours ] [ Max. Marks
CAB/2KTF/EET 1221/1413 Sixth Semester B. E. (R)/ First Semester B. E. (PTDP) Civil Engineering Examination Course Code : CV 312 / CV 507 Course Name : Engineering Hydrology Time : 3 Hours ] [ Max. Marks
Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS
 Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS Why Measure Streamflow? Water supply planning How much water can we take out (without harming ecosystems we want to protect) Flood protection How much
Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS Why Measure Streamflow? Water supply planning How much water can we take out (without harming ecosystems we want to protect) Flood protection How much
RETENTION BASIN EXAMPLE
 -7 Given: Total Tributary Area = 7.5 ac o Tributary Area within Existing R/W = 5.8 ac o Tributary Area, Impervious, Outside of R/W = 0.0 ac o Tributary Area, Pervious, Outside of R/W = 1.7 ac o Tributary
-7 Given: Total Tributary Area = 7.5 ac o Tributary Area within Existing R/W = 5.8 ac o Tributary Area, Impervious, Outside of R/W = 0.0 ac o Tributary Area, Pervious, Outside of R/W = 1.7 ac o Tributary
Thanks to Bill Elliot, Research Leader U.S. Department of Agriculture Forest Service
 Thanks to Bill Elliot, Research Leader U.S. Department of Agriculture Forest Service To present an overview Forest Soil Erosion Processes 2 Precipitation or melting snow Evapotranspiration Infiltration
Thanks to Bill Elliot, Research Leader U.S. Department of Agriculture Forest Service To present an overview Forest Soil Erosion Processes 2 Precipitation or melting snow Evapotranspiration Infiltration
Ward s Stormwater - Floodplain Model Train the Trainer Workshop INAFSM Workshop, South Bend, IN September 7, 2017
 Ward s Stormwater - Floodplain Model Train the Trainer Workshop INAFSM Workshop, South Bend, IN September 7, 2017 Presenter Training for the Stormwater Floodplain Model: A Hands-on Workshop for Education
Ward s Stormwater - Floodplain Model Train the Trainer Workshop INAFSM Workshop, South Bend, IN September 7, 2017 Presenter Training for the Stormwater Floodplain Model: A Hands-on Workshop for Education
Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS
 Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS Why Measure Streamflow? Water supply planning How much water can we take out (without harming ecosystems we want to protect) Flood protection How much
Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS Why Measure Streamflow? Water supply planning How much water can we take out (without harming ecosystems we want to protect) Flood protection How much
How to irrigate. How much to irrigate. When to irrigate
 CROPWAT 8.0 How to irrigate How much to irrigate When to irrigate The designer s point of view The operator s point of view How to irrigate the designer s point of view How much to irrigate When to irrigate
CROPWAT 8.0 How to irrigate How much to irrigate When to irrigate The designer s point of view The operator s point of view How to irrigate the designer s point of view How much to irrigate When to irrigate
UPDATE OF ARC TP108 RUN-OFF CALCULATION GUIDELINE
 UPDATE OF ARC TP108 RUN-OFF CALCULATION GUIDELINE Bodo Hellberg, Stormwater Action Team, Auckland Regional Council Matthew Davis, Stormwater Action Team, Auckland Regional Council ABSTRACT This paper focuses
UPDATE OF ARC TP108 RUN-OFF CALCULATION GUIDELINE Bodo Hellberg, Stormwater Action Team, Auckland Regional Council Matthew Davis, Stormwater Action Team, Auckland Regional Council ABSTRACT This paper focuses
Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS
 Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS Why Measure Streamflow? Water supply planning How much water can we take out (without harming ecosystems we want to protect) Flood protection How much
Water Budget III: Stream Flow P = Q + ET + G + ΔS Why Measure Streamflow? Water supply planning How much water can we take out (without harming ecosystems we want to protect) Flood protection How much
HY-12 User Manual. Aquaveo. Contents
 Y-12 User Manual Aquaveo Contents Overview...2 Watershed Parameters...3 Channel Parameters...3 Storm Drain Parameters...3 Design of new systems...4 Analysis of existing systems...4 Steady flow...4 ydrographic
Y-12 User Manual Aquaveo Contents Overview...2 Watershed Parameters...3 Channel Parameters...3 Storm Drain Parameters...3 Design of new systems...4 Analysis of existing systems...4 Steady flow...4 ydrographic
Water Balance Methodology
 Water Balance Methodology Integrating the Site with the Watershed and the Stream March 2012 An initiative under the umbrella of the Water Sustainability Action Plan for British Columbia Water Balance Methodology
Water Balance Methodology Integrating the Site with the Watershed and the Stream March 2012 An initiative under the umbrella of the Water Sustainability Action Plan for British Columbia Water Balance Methodology
The soil is a very. The soil can. The manure. Soil Characteristics. effective manure treatment system if manures are applied at the proper rate.
 The soil is a very effective manure treatment system if manures are applied at the proper rate. The soil can filter pollutants and prevent them from reaching groundwater. The manure application rate should
The soil is a very effective manure treatment system if manures are applied at the proper rate. The soil can filter pollutants and prevent them from reaching groundwater. The manure application rate should
0.0. Pervious CN = 40. (Unconnected impervious) (Total impervious) Total impervious area (percent) Composite CN
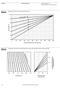 Figure 2-3 Composite CN with connected impervious area. 100 Composite CN 90 80 70 60 Pervious CN = 90 80 70 60 50 40 50 40 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Connected impervious area (percent) Figure 2-4
Figure 2-3 Composite CN with connected impervious area. 100 Composite CN 90 80 70 60 Pervious CN = 90 80 70 60 50 40 50 40 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Connected impervious area (percent) Figure 2-4
A NEW HYDROLOGIC RESPONSE FUNCTION PHYSICALLY DERIVED FROM DEM AND REMOTE SENSING IMAGE
 Proc. of the 2nd Asia Pacific Association of Hydrology and Water Resources (APHW) Conference, July 5-8, 2004, Suntec Singapore International Convention Exhibition Centre, Singapore, vol. 2, pp. 268-275,
Proc. of the 2nd Asia Pacific Association of Hydrology and Water Resources (APHW) Conference, July 5-8, 2004, Suntec Singapore International Convention Exhibition Centre, Singapore, vol. 2, pp. 268-275,
Simulation of Event Based Runoff Using HEC-HMS Model for an Experimental Watershed
 International Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 213, 2(2): 28-33 DOI: 1.5923/j.ijhe.21322.2 Simulation of Event Based Runoff Using HEC-HMS Model for an Experimental Watershed Reshma T *, Venkata Reddy K,
International Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 213, 2(2): 28-33 DOI: 1.5923/j.ijhe.21322.2 Simulation of Event Based Runoff Using HEC-HMS Model for an Experimental Watershed Reshma T *, Venkata Reddy K,
Lecture 5: Transpiration
 5-1 GEOG415 Lecture 5: Transpiration Transpiration loss of water from stomatal opening substomatal cavity chloroplasts cuticle epidermis mesophyll cells CO 2 H 2 O guard cell Evaporation + Transpiration
5-1 GEOG415 Lecture 5: Transpiration Transpiration loss of water from stomatal opening substomatal cavity chloroplasts cuticle epidermis mesophyll cells CO 2 H 2 O guard cell Evaporation + Transpiration
Testing, Analyses, and Performance Values for Slope Interruption and Perimeter Control BMPs
 Testing, Analyses, and Performance Values for Slope Interruption and Perimeter Control BMPs Kurt Kelsey Research Scientist American Excelsior Company 831 Pioneer Ave Rice Lake, WI 54868 Phone: 715-236-5643
Testing, Analyses, and Performance Values for Slope Interruption and Perimeter Control BMPs Kurt Kelsey Research Scientist American Excelsior Company 831 Pioneer Ave Rice Lake, WI 54868 Phone: 715-236-5643
The Hydrosphere. Introduction To Surface Water. What Do You Think?
 Introduction To Surface Water Unit Essential Questions: How does the Earth cycle its water through its major reservoirs? How does society s use of resources affect water quality? Presentation Objectives:
Introduction To Surface Water Unit Essential Questions: How does the Earth cycle its water through its major reservoirs? How does society s use of resources affect water quality? Presentation Objectives:
BUILDING A MODEL BASED ON THE EUROSEM SOIL EROSION MODEL
 University of Szeged Department of Physical Geography and Geoinformatics BUILDING A MODEL BASED ON THE EUROSEM SOIL EROSION MODEL Theses Károly Barta Szeged 2004 1. Introduction Water erosion on agricultural
University of Szeged Department of Physical Geography and Geoinformatics BUILDING A MODEL BASED ON THE EUROSEM SOIL EROSION MODEL Theses Károly Barta Szeged 2004 1. Introduction Water erosion on agricultural
Quantifying Runoff Mitigation in STEP 4 Calculations with VFSMOD EU-Scenarios in SWAN 3.0
 Quantifying Runoff Mitigation in STEP 4 Calculations with VFSMOD EU-Scenarios in SWAN 3.0 Bjoern Roepke 6 th European Modelling Workshop, Paris 10 th 12 th June 2012 Existing Vegetated Filter Strip (VFS)
Quantifying Runoff Mitigation in STEP 4 Calculations with VFSMOD EU-Scenarios in SWAN 3.0 Bjoern Roepke 6 th European Modelling Workshop, Paris 10 th 12 th June 2012 Existing Vegetated Filter Strip (VFS)
BMP Design Aids. w w w. t r a n s p o r t a t i o n. o h i o. g o v. Equations / Programs
 BMP Design Aids 1 Equations / Programs Outlet Discharge Equations Hydrograph and Pond Routing Programs USGS StreamStats 2 Ohio Department of Transportation 1 Training Intent Introduction and overview of
BMP Design Aids 1 Equations / Programs Outlet Discharge Equations Hydrograph and Pond Routing Programs USGS StreamStats 2 Ohio Department of Transportation 1 Training Intent Introduction and overview of
Re-plumbing Roadside Ditch Networks
 Re-plumbing Roadside Ditch Networks Ditches Improving management to reduce flooding, water pollution, and in-stream erosion and habitat degradation Rebecca Schneider Dept. Natural Resources Cornell University,
Re-plumbing Roadside Ditch Networks Ditches Improving management to reduce flooding, water pollution, and in-stream erosion and habitat degradation Rebecca Schneider Dept. Natural Resources Cornell University,
Stormwater Retention Pond Recovery Analysis
 Stormwater Retention Pond Recovery Analysis By Nicolas E Andreyev The first in a series of courses on Green Drainage Design www.suncam.com Page 1 of 33 Forward To design a stormwater retention pond, one
Stormwater Retention Pond Recovery Analysis By Nicolas E Andreyev The first in a series of courses on Green Drainage Design www.suncam.com Page 1 of 33 Forward To design a stormwater retention pond, one
San Luis Obispo Creek Watershed Hydrologic Model Inputs
 Jeff Werst San Luis Obispo County Department of Public Works 1050 Monterey Street San Luis Obispo CA 93408 December 14, 2007 Subject: San Luis Obispo Creek Watershed Hydrology and Hydraulic Model Dear
Jeff Werst San Luis Obispo County Department of Public Works 1050 Monterey Street San Luis Obispo CA 93408 December 14, 2007 Subject: San Luis Obispo Creek Watershed Hydrology and Hydraulic Model Dear
BUVARD: an online tool to design vegetative buffer zones in a french context
 BUVARD: an online tool to design vegetative buffer zones in a french context Claire Lauvernet, Clotaire Catalogne, Etienne Leblois, Nadia Carluer Irstea. Non point source pollutions team www.irstea.fr
BUVARD: an online tool to design vegetative buffer zones in a french context Claire Lauvernet, Clotaire Catalogne, Etienne Leblois, Nadia Carluer Irstea. Non point source pollutions team www.irstea.fr
Estimating Field-Scale Runoff and Sediment Delivery. Seth M. Dabney, USDA-ARS Dalmo A. N. Vieira, USDA-ARS Daniel C. Yoder, Univ.
 Estimating Field-Scale Runoff and Sediment Delivery Seth M. Dabney, USDA-ARS Dalmo A. N. Vieira, USDA-ARS Daniel C. Yoder, Univ. of Tennessee Organization Buffers for concentrated flow control Distributed
Estimating Field-Scale Runoff and Sediment Delivery Seth M. Dabney, USDA-ARS Dalmo A. N. Vieira, USDA-ARS Daniel C. Yoder, Univ. of Tennessee Organization Buffers for concentrated flow control Distributed
The hydrological effects of wildfire. David Scott The University of British Columbia, Kelowna, BC
 The hydrological effects of wildfire David Scott The University of British Columbia, Kelowna, BC Effects of fire on hydrology Scientific literature is full of contrasting reports Fires: little effect or
The hydrological effects of wildfire David Scott The University of British Columbia, Kelowna, BC Effects of fire on hydrology Scientific literature is full of contrasting reports Fires: little effect or
Evaluating the Reduction Effect of Nonpoint Source Pollution Loads from Upland Crop Areas by Rice Straw Covering Using SWAT
 SESSION J2 : Water Resources Applications - I New Delhi, India 2012 International SWAT Conference Evaluating the Reduction Effect of Nonpoint Source Pollution Loads from Upland Crop Areas by Rice Straw
SESSION J2 : Water Resources Applications - I New Delhi, India 2012 International SWAT Conference Evaluating the Reduction Effect of Nonpoint Source Pollution Loads from Upland Crop Areas by Rice Straw
Stormwater: Too Simple?
 Stormwater: Too Simple? Getting Closer to Advertised Level of Service Brandon Klenzendorf, Ph.D., P.E. 13 December 2017 - CWEA Fall Seminar Introduction Traditional approaches to solving stormwater problems
Stormwater: Too Simple? Getting Closer to Advertised Level of Service Brandon Klenzendorf, Ph.D., P.E. 13 December 2017 - CWEA Fall Seminar Introduction Traditional approaches to solving stormwater problems
Rational Method Hydrological Calculations with Excel COURSE CONTENT
 Rational Method Hydrological Calculations with Excel Harlan H. Bengtson, PhD, P.E. COURSE CONTENT 1. Introduction Calculation of peak storm water runoff rate from a drainage area is often done with the
Rational Method Hydrological Calculations with Excel Harlan H. Bengtson, PhD, P.E. COURSE CONTENT 1. Introduction Calculation of peak storm water runoff rate from a drainage area is often done with the
Water quality of road runoff in the Blue Mountains, NSW, Australia
 Geo-Environment and Landscape Evolution III 151 Water quality of road runoff in the Blue Mountains, NSW, Australia S. Riley 1, S. Shrestha 1, P. Hackney 2 & R. A. Mann 3 1 Sustainable Engineering and Technology
Geo-Environment and Landscape Evolution III 151 Water quality of road runoff in the Blue Mountains, NSW, Australia S. Riley 1, S. Shrestha 1, P. Hackney 2 & R. A. Mann 3 1 Sustainable Engineering and Technology
Water Budget IV: Soil Water Processes P = Q + ET + G + ΔS
 Water Budget IV: Soil Water Processes P = Q + ET + G + ΔS Infiltration Infiltration capacity: The maximum rate at which water can enter soil. Infiltration capacity curve: A graph showing the time-variation
Water Budget IV: Soil Water Processes P = Q + ET + G + ΔS Infiltration Infiltration capacity: The maximum rate at which water can enter soil. Infiltration capacity curve: A graph showing the time-variation
HIGHWAY DRAINAGE.
 Chapter VI HIGHWAY DRAINAGE Tewodros N. www.tnigatu.wordpress.com tedynihe@gmail.com I. INTRODUCTION Provision o of adequate drainage is an essential part of pavement design. Protection of pavement structure
Chapter VI HIGHWAY DRAINAGE Tewodros N. www.tnigatu.wordpress.com tedynihe@gmail.com I. INTRODUCTION Provision o of adequate drainage is an essential part of pavement design. Protection of pavement structure
Soil and farm practices data concerning the case study Svratka were collected according to questionnaire 1 by the expert on soil protection.
 Soil and farm practices data concerning the case study Svratka were collected according to questionnaire 1 by the expert on soil protection. Farmers in the case study region were interviewed according
Soil and farm practices data concerning the case study Svratka were collected according to questionnaire 1 by the expert on soil protection. Farmers in the case study region were interviewed according
FLOW REGULATING SYSTEM USING WEIR AND ORIFICE IN A MANHOLE
 FLOW REGULATING SYSTEM USING WEIR AND ORIFICE IN A MANHOLE Masahiro Maeda and Makoto Akiba * Metropolitan Tokyo Sewage Bureau, Chubu Construction Office Kuramae 2-1-8 Taito-ku KEYWORDS Flow Regulating
FLOW REGULATING SYSTEM USING WEIR AND ORIFICE IN A MANHOLE Masahiro Maeda and Makoto Akiba * Metropolitan Tokyo Sewage Bureau, Chubu Construction Office Kuramae 2-1-8 Taito-ku KEYWORDS Flow Regulating
