The Fifth Assessment: A Discussion of the IPCC Working Group 1 AR5 Report
|
|
|
- Betty Pierce
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Fifth Assessment: A Discussion of the IPCC Working Group 1 AR5 Report Prof. Chris E. Forest The Pennsylvania State University (ceforest@psu.edu) Lead Author - Chapter 9 - Evaluation of Climate Models! 19th Annual Energy and Climate Change Research Seminar May 13, 2014 Washington Marriott at Metro Center
2 IPCC WG1 Summary! The human influence on Earth s climate is clear It s still warming... but with more observables. More warming to come. New lines of evidence New concepts
3
4 The Timeline 2010 MAY - IPCC WG1 Authors and Reviewers Selected 2010 NOVEMBER - First Lead Author Meeting - Kunming, China 2011 MARCH 18 - Zeroth Order Draft 2011 JULY - Second Lead Author Meeting - Brest, France 2011 NOVEMBER 18 - First Order Draft 2012 APRIL - Third Lead Author Meeting - Marrakech, Morocco 2012 AUGUST 10 - Second Order Draft 2013 JANUARY - Fourth Lead Author Meeting - Hobart, Australia 2013 MAY 13 - Final Draft 2013 SEPTEMBER 27 - IPCC Plenary Approval of SPM - Stockholm, Sweden
5
6
7 (b) Observed change in surface temperature Observed Surface Temperature Changes Figure SPM.1a (a) Observed globally averaged combined land and ocean surface temperature anomaly Annual average 0.4 Temperature anomaly ( C) relative to Decadal average (b) Observed change in surface temperature ( C) Year
8 Increased focus on observed precipitation changes Observed change in annual precipitation over land (mm yr -1 per decade) (IPCC WG1 AR5 Figure SPM.2)
9 Many additional observations are now used to assess historical climate change Year (a) 45 Northern Hemisphere spring snow cover (c) 20 Change in global average upper ocean heat content (million km 2 ) (10 22 J) (b) Year 14 Arctic summer sea ice extent (d) Year 200 Global average sea level change (million km 2 ) (mm) (c) Year Year (IPCC WG1 AR5 Figure SPM.3)
10 Including key Carbon Cycle observations (a) CO2 (ppm) Atmospheric CO Year (b) pco2 (μatm) Surface ocean CO 2 and ph Year in situ ph unit (IPCC WG1 AR5 Figure SPM.4)
11 Anthropogenic warming has mainly occurred in the ocean.! Evidence in the Global Energy Budget Accumulated Energy Increase since 1970 >90% of energy increase in ocean heat content ZJ = Joules IPCC WG1 AR5 Box 3.1, Figure 1
12 The Drivers of Climate Change Radiative Forcing: Figure SPM.5 Emitted compound Resulting atmospheric drivers Radiative forcing by emissions and drivers Level of confidence Well-mixed greenhouse gases CO 2 CH 4 Halocarbons N 2 O CO 2 CO 2 H 2 O str O 3 CH 4 O 3 N 2 O CFCs HCFCs 1.68 [1.33 to 2.03] 0.97 [0.74 to 1.20] 0.18 [0.01 to 0.35] 0.17 [0.13 to 0.21] VH H H VH Anthropogenic Short lived gases and aerosols CO NMVOC NO x Aerosols and precursors (Mineral dust, SO 2, NH 3, Organic carbon and Black carbon) CO 2 CH 4 O 3 CO 2 CH 4 O 3 Nitrate CH 4 O 3 Mineral dust Organic carbon Sulphate Black carbon Cloud adjustments due to aerosols Nitrate 0.23 [0.16 to 0.30] 0.10 [0.05 to 0.15] [-0.34 to 0.03] [-0.77 to 0.23] [-1.33 to -0.06] M M M H L Albedo change due to land use [-0.25 to -0.05] M Natural Changes in solar irradiance 0.05 [0.00 to 0.10] M Total anthropogenic RF relative to [1.13 to 3.33] 1.25 [0.64 to 1.86] 0.57 [0.29 to 0.85] Radiative forcing relative to 1750 (W m 2 ) H H 2.6 M Wm -2
13 IPCC WG1 AR5, Figure SPM.6
14 Can Climate Models capture the observed changes? Land surface Global averages Land and ocean surface Ocean heat content Observations Models using only natural forcings Models using both natural and anthropogenic forcings IPCC WG1 AR5 Figure SPM.6
15 Can Climate Models capture the observed changes? IPCC WG1 AR5 Figure SPM.6
16 Can Climate Models capture the observed changes? Sea Ice IPCC WG1 AR5 Figure SPM.6
17 Can Climate Models capture the observed changes? Sea Ice Ocean Heat Content IPCC WG1 AR5 Figure SPM.6
18 What are the causes of warming? Based on attributable warming using local detection of temperature trends Observed = HadCRUT4 IPCC WG1 AR5 Figure 10.5
19
20 RCP Scenarios have replaced SRES Scenarios (which replaced IS92 Scenarios RCP := Representative Concentration Pathways 2.6, 4.5, 6.0, & 8.5 := Radiative Forcing at 2100
21
22
23 RCP Scenarios have replaced SRES Scenarios (which replaced IS92 Scenarios RCP := Representative Concentration Pathways 2.6, 4.5, 6.0, & 8.5 := Radiative Forcing at 2100
24 Climate Projections using RCP Scenarios Temperature, NH Sea Ice, Ocean ph IPCC WG1 AR5 Figure SPM.7
25 Climate Projections using RCP Scenarios Temperature, NH Sea Ice, Ocean ph (a) ( o C) Global average surface temperature change historical RCP2.6 RCP Mean over RCP2.6 RCP4.5 RCP6.0 RCP8.5 (c) (ph unit) Global ocean surface ph Year RCP2.6 RCP4.5 RCP6.0 RCP8.5 (b) 10.0 Northern Hemisphere September sea ice extent (5) (10 6 km 2 ) (3) (5) RCP2.6 RCP4.5 RCP6.0 RCP8.5 (c) Global ocean surface ph IPCC WG1 AR5 Figure SPM.7
26 Chapter 9 Summary Figure
27 Climate Projections using RCP Scenarios Low (RCP2.6) High (RCP8.5) (a) RCP 2.6 RCP 8.5 Change in average surface temperature ( to ) ( C) 2 (b) Change in average precipitation ( to ) (c) (%) IPCC WG1 AR5 Figure SPM.8 Northern Hemisphere September sea ice extent (average )
28
29 2ºC Target 4ºC Target
30 Conclusions: The human influence on Earth s climate is clear
31 Conclusions: The human influence on Earth s climate is clear Past: It s still warming... but with more observables.
32 Conclusions: The human influence on Earth s climate is clear Past: It s still warming... but with more observables. Future: More warming. More sea level rise.
33 Conclusions: The human influence on Earth s climate is clear Past: It s still warming... but with more observables. Future: More warming. More sea level rise. New lines of evidence Deep Ocean, Carbon-cycle, sea-ice, ocean ph
34 Conclusions: The human influence on Earth s climate is clear Past: It s still warming... but with more observables. Future: More warming. More sea level rise. New lines of evidence Deep Ocean, Carbon-cycle, sea-ice, ocean ph New concepts Aerosol-Cloud effective forcing Earth System Models (emissions to response) Cumulative Carbon Emissions Temperature Target
IPCC 5 th Assessment Report
 The WGI Contribution to the IPCC 5 th Assessment Report Thomas Stocker & Qin Dahe 259 Authors from 39 Countries WGI Technical Support Unit Team Yann Arthus-Bertrand / Altitude Key SPM Messages 19 Headlines
The WGI Contribution to the IPCC 5 th Assessment Report Thomas Stocker & Qin Dahe 259 Authors from 39 Countries WGI Technical Support Unit Team Yann Arthus-Bertrand / Altitude Key SPM Messages 19 Headlines
Global Climate Change
 Global Climate Change Greenhouse Gases and Earth s Energy Balance 400 380 CO 2 in air 360 340 320 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 Year Global Climate Change 1 / 30 Outline of Topics 1 The Natural Earth System
Global Climate Change Greenhouse Gases and Earth s Energy Balance 400 380 CO 2 in air 360 340 320 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 Year Global Climate Change 1 / 30 Outline of Topics 1 The Natural Earth System
Transformational Climate Science. The future of climate change research following the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report
 Transformational Climate Science The future of climate change research following the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report www.exeter.ac.uk/climate2014 Working Group I The challenge of climate change #climate2014
Transformational Climate Science The future of climate change research following the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report www.exeter.ac.uk/climate2014 Working Group I The challenge of climate change #climate2014
Conclusions of the IPCC Working Group I Fifth Assessment Report, AR4, SREX and SRREN
 Conclusions of the IPCC Working Group I Fifth Assessment Report, AR4, SREX and SRREN R. K. Pachauri 11 November 2013 Warsaw, Poland Chairman, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change 1 Problems cannot
Conclusions of the IPCC Working Group I Fifth Assessment Report, AR4, SREX and SRREN R. K. Pachauri 11 November 2013 Warsaw, Poland Chairman, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change 1 Problems cannot
Evidence and implications of anthropogenic climate change
 Evidence and implications of anthropogenic climate change Earth s Climate has always been changing 1) Is climate changing now? Global Warming? Sea level rising IPCC 2007 Fig. 5.13 (p. 410) Recontructed
Evidence and implications of anthropogenic climate change Earth s Climate has always been changing 1) Is climate changing now? Global Warming? Sea level rising IPCC 2007 Fig. 5.13 (p. 410) Recontructed
IPCC WG1 AR5 Report & its relevance to Southeast Asia region
 IPCC WG1 AR5 Report & its relevance to Southeast Asia region Yann Arthus-Bertrand / Altitude Fredolin Tangang IPCC WG1 Vice-Chair IPCC WG1 AR5 Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis The IPCC has
IPCC WG1 AR5 Report & its relevance to Southeast Asia region Yann Arthus-Bertrand / Altitude Fredolin Tangang IPCC WG1 Vice-Chair IPCC WG1 AR5 Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis The IPCC has
Global Climate Change
 Global Climate Change Devizes & District U3A, 24 th November 2015 Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Why does Earth s climate change? Earth s Climate has always been changing
Global Climate Change Devizes & District U3A, 24 th November 2015 Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Why does Earth s climate change? Earth s Climate has always been changing
Climate Science from a Climate Scientist
 Climate Science from a Climate Scientist Professor Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology, University of Reading John Hall Venice Course, National Gallery, 25 th January 2017 Earth s Climate has always
Climate Science from a Climate Scientist Professor Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology, University of Reading John Hall Venice Course, National Gallery, 25 th January 2017 Earth s Climate has always
Implications of the IPCC AR5 Report for the UNFCCC Negotiations and Mitigation Options in AFOLU (Agriculture Forest and Other Land Use)
 Implications of the IPCC AR5 Report for the UNFCCC Negotiations and Mitigation Options in AFOLU (Agriculture Forest and Other Land Use) Shreekant Gupta Delhi School of Economics & LKY School of Public
Implications of the IPCC AR5 Report for the UNFCCC Negotiations and Mitigation Options in AFOLU (Agriculture Forest and Other Land Use) Shreekant Gupta Delhi School of Economics & LKY School of Public
Local and Global Impacts of Climate Change: Predictions of the 5th IPCC Report
 Local and Global Impacts of Climate Change: Predictions of the 5th IPCC Report Peter Schlosser Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences and Department of Earth and Environmental Engineering The Earth
Local and Global Impacts of Climate Change: Predictions of the 5th IPCC Report Peter Schlosser Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences and Department of Earth and Environmental Engineering The Earth
Chapter outline. introduction. Reference. Chapter 6: Climate Change Projections EST 5103 Climate Change Science
 Chapter 6: Climate Change Projections EST 5103 Climate Change Science Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of Science & Technology Chapter outline Future Forcing and Scenarios,
Chapter 6: Climate Change Projections EST 5103 Climate Change Science Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of Science & Technology Chapter outline Future Forcing and Scenarios,
Climate Change state of the science
 Climate Change state of the science Henley in Transition December 14 th 2015 Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Earth s Climate has always been changing The planet is
Climate Change state of the science Henley in Transition December 14 th 2015 Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Earth s Climate has always been changing The planet is
Overview of the IPCC AR5 (5 th Assessment Report) process
 Overview of the IPCC AR5 (5 th Assessment Report) process Jean-Pascal van Ypersele IPCC Vice-chair Université catholique de Louvain, Belgium @JPvanYpersele on Twitter European Commission, Brussels, 6 May
Overview of the IPCC AR5 (5 th Assessment Report) process Jean-Pascal van Ypersele IPCC Vice-chair Université catholique de Louvain, Belgium @JPvanYpersele on Twitter European Commission, Brussels, 6 May
Radiative Forcing Components
 Radiative Forcing Components Content Definition of Radiative Forcing Radiation Balance Climate sensitivity Solar forcing Forcing due to atmospheric gas Definition of Radiative Forcing In climate science,
Radiative Forcing Components Content Definition of Radiative Forcing Radiation Balance Climate sensitivity Solar forcing Forcing due to atmospheric gas Definition of Radiative Forcing In climate science,
Scientific Foundation of Climate Change. Human Responsibility for Climate Change
 Scientific Foundation of Climate Change EOH 468 CSU Northridge Spring 2010 Peter Bellin, CIH, Ph.D. 1 Human Responsibility for Climate Change The IPCC finds that it is very likely that emissions of heat-trapping
Scientific Foundation of Climate Change EOH 468 CSU Northridge Spring 2010 Peter Bellin, CIH, Ph.D. 1 Human Responsibility for Climate Change The IPCC finds that it is very likely that emissions of heat-trapping
GEF4400 The Earth System
 GEF4400 The Earth System Autumn 2015 25.11.2015 GEF4400 The Earth System Prof. Dr. Jon Egill Kristjansson, Prof. Dr. Kirstin Krüger (UiO) Email: kkruegergeo.uio.no Repetition for final exams 1 The Earth
GEF4400 The Earth System Autumn 2015 25.11.2015 GEF4400 The Earth System Prof. Dr. Jon Egill Kristjansson, Prof. Dr. Kirstin Krüger (UiO) Email: kkruegergeo.uio.no Repetition for final exams 1 The Earth
Observed Changes and their Causes. Vicente Barros, Co-Chair WGII Gian-Kasper Plattner, Head WGI TSU for the SYR Core Writing Team
 Observed Changes and their Causes Vicente Barros, Co-Chair WGII Gian-Kasper Plattner, Head WGI TSU for the SYR Core Writing Team Human influence on the climate system is clear. Recent climate changes have
Observed Changes and their Causes Vicente Barros, Co-Chair WGII Gian-Kasper Plattner, Head WGI TSU for the SYR Core Writing Team Human influence on the climate system is clear. Recent climate changes have
Changes to the Underlying Scientific-Technical Assessment to ensure consistency with the approved Summary for Policymakers
 THIRTY-SIXTH SESSION OF THE IPCC Stockholm, 26 September 2013 IPCC-XXXVI/Doc. 4 (27.IX.2013) Agenda Item: 3 ENGLISH ONLY ACCEPTANCE OF THE ACTIONS TAKEN AT THE TWELFTH SESSION OF WORKING GROUP I Working
THIRTY-SIXTH SESSION OF THE IPCC Stockholm, 26 September 2013 IPCC-XXXVI/Doc. 4 (27.IX.2013) Agenda Item: 3 ENGLISH ONLY ACCEPTANCE OF THE ACTIONS TAKEN AT THE TWELFTH SESSION OF WORKING GROUP I Working
Introduction to climate science : global climate variability and change, findings of IPCC AR5. Imad Khatib
 Environmental Quality Authority Introduction to climate science : global climate variability and change, findings of IPCC AR5 Imad Khatib Palestine National Training Seminar on Climate Change 26 28 January,
Environmental Quality Authority Introduction to climate science : global climate variability and change, findings of IPCC AR5 Imad Khatib Palestine National Training Seminar on Climate Change 26 28 January,
Key statements from the Summary for Policymakers, WG1 contribution to the AR5 of IPCC
 Key statements from the Summary for Policymakers, WG1 contribution to the AR5 of IPCC Jochem Marotzke Max-Planck-Institut für Meteorologie KlimaCampus, Hamburg Attribution of observed climate change to
Key statements from the Summary for Policymakers, WG1 contribution to the AR5 of IPCC Jochem Marotzke Max-Planck-Institut für Meteorologie KlimaCampus, Hamburg Attribution of observed climate change to
Climate Change and Energy
 1/31 Climate Change and Energy David S. Gutzler Earth & Planetary Sciences Dept gutzler@unm.edu * Global warming over the past century * Attribution of observed climate change à why we blame fossil fuels
1/31 Climate Change and Energy David S. Gutzler Earth & Planetary Sciences Dept gutzler@unm.edu * Global warming over the past century * Attribution of observed climate change à why we blame fossil fuels
Understanding and attributing recent climate change
 Understanding and attributing recent climate change Peter Stott, Nathan Bindoff, John Church, Peter Clark, Greg Flato, Piers Forster, Nathan Gillett, Gabi Hegerl, Reto Knutti, Jochem Marotzke, Rowan Sutton,
Understanding and attributing recent climate change Peter Stott, Nathan Bindoff, John Church, Peter Clark, Greg Flato, Piers Forster, Nathan Gillett, Gabi Hegerl, Reto Knutti, Jochem Marotzke, Rowan Sutton,
Climate Change Science Tutorial #1: Overview of Our Understanding of the Climate System and Observed Climate Impacts
 Climate Change Science Tutorial #1: Overview of Our Understanding of the Climate System and Observed Climate Impacts September 2013 ACS Climate Science Project, OMSI Others work, collected by Prof. Julie
Climate Change Science Tutorial #1: Overview of Our Understanding of the Climate System and Observed Climate Impacts September 2013 ACS Climate Science Project, OMSI Others work, collected by Prof. Julie
Section GCM: Climate models and projections
 Section GCM: Climate models and projections Outline GCM.1 Global climate models GCM.2 Using GCMs, Part 1: Attribution GCM.3 Using GCMs, Part 2: Future projections GCM.3.1 how to produce projections GCM.3.2
Section GCM: Climate models and projections Outline GCM.1 Global climate models GCM.2 Using GCMs, Part 1: Attribution GCM.3 Using GCMs, Part 2: Future projections GCM.3.1 how to produce projections GCM.3.2
Climate Change: What do we know and what do we guess?
 What do we know and what do we guess? Manfred Grasserbauer * Vienna University of Technology * Director Institute for Environment and Sustainability, Joint Research Centre, European Commission (Ispra)
What do we know and what do we guess? Manfred Grasserbauer * Vienna University of Technology * Director Institute for Environment and Sustainability, Joint Research Centre, European Commission (Ispra)
Climate system dynamics and modelling
 Climate system dynamics and modelling Hugues Goosse Chapter 6 Future climate changes Outline Methods used to estimate future climate changes. Description of the main results at different timescales. Interpretation
Climate system dynamics and modelling Hugues Goosse Chapter 6 Future climate changes Outline Methods used to estimate future climate changes. Description of the main results at different timescales. Interpretation
Radiative forcing of climate change
 Radiative forcing of climate change Joanna D. Haigh Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, London Radiative forcing concept, definition and applications On a global and annual average, and
Radiative forcing of climate change Joanna D. Haigh Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, London Radiative forcing concept, definition and applications On a global and annual average, and
Causes of past climate change and projections of future changes in climate. Peter Stott Met Office Hadley Centre, UK
 Causes of past climate change and projections of future changes in climate Peter Stott Met Office Hadley Centre, UK Overview 1.The causes of observed climate change 2.Global and regional climate projections
Causes of past climate change and projections of future changes in climate Peter Stott Met Office Hadley Centre, UK Overview 1.The causes of observed climate change 2.Global and regional climate projections
Radiative forcing of gases, aerosols and, clouds.
 Lecture 23. Radiative forcing of gases, aerosols and, clouds. 1. Concepts of radiative forcing, climate sensitivity, and radiation feedbacks. 2. Radiative forcing of anthropogenic greenhouse gases. 3.
Lecture 23. Radiative forcing of gases, aerosols and, clouds. 1. Concepts of radiative forcing, climate sensitivity, and radiation feedbacks. 2. Radiative forcing of anthropogenic greenhouse gases. 3.
Understanding Global Warming
 Math 483 Spring Semester, 2013 California State University, Northridge Understanding Global Warming Global Warming is Real December 2012 is 334th consecutive Month with global temperatures above the 20th
Math 483 Spring Semester, 2013 California State University, Northridge Understanding Global Warming Global Warming is Real December 2012 is 334th consecutive Month with global temperatures above the 20th
The use of non-co2 multipliers for the climate impact of aviation: The scientific basis
 Workshop on Aviation and Carbon Markets ICAO Headquarters Montreal, Quebec 18-19 June 2008 The use of non-co2 multipliers for the climate impact of aviation: The scientific basis by Dr. David W. Fahey
Workshop on Aviation and Carbon Markets ICAO Headquarters Montreal, Quebec 18-19 June 2008 The use of non-co2 multipliers for the climate impact of aviation: The scientific basis by Dr. David W. Fahey
The International Climate Change Regime: UNFCCC. International Climate Change and Energy Law Spring semester 2014 Dr.
 The International Climate Change Regime: UNFCCC International Climate Change and Energy Law Spring semester 2014 Dr. Christina Voigt 1. The Legal Status of the Atmosphere 2. 1992 UNFCCC 3. 1997 Kyoto Protocol
The International Climate Change Regime: UNFCCC International Climate Change and Energy Law Spring semester 2014 Dr. Christina Voigt 1. The Legal Status of the Atmosphere 2. 1992 UNFCCC 3. 1997 Kyoto Protocol
Scientific Facts on. Climate Change Assessment
 page 1/8 Scientific Facts on Climate Change 2001 Assessment Source document: IPCC (2001) Summary & Details: GreenFacts Context - The Earth's climate has changed over the last century and by 2001 there
page 1/8 Scientific Facts on Climate Change 2001 Assessment Source document: IPCC (2001) Summary & Details: GreenFacts Context - The Earth's climate has changed over the last century and by 2001 there
Comments on Human and Natural Forcings. Climate changes (1900 to 2000) due to human activity. Climate Variability and Climate Change
 Comments on Human and Natural Forcings Human input of GH gases (carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, CFCs ) has warmed the planet: net RF = +2.9 W/m 2 The largest single warming factor is increased
Comments on Human and Natural Forcings Human input of GH gases (carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, CFCs ) has warmed the planet: net RF = +2.9 W/m 2 The largest single warming factor is increased
Draft Environmental Impact Statement
 The Safer Affordable Fuel-Efficient (SAFE) Vehicles Rule for Model Year 2021 2026 Passenger Cars and Light Trucks Draft Environmental Impact Statement July 2018 Docket No. NHTSA-2017-0069 Greenhouse Gas
The Safer Affordable Fuel-Efficient (SAFE) Vehicles Rule for Model Year 2021 2026 Passenger Cars and Light Trucks Draft Environmental Impact Statement July 2018 Docket No. NHTSA-2017-0069 Greenhouse Gas
Lecture 7 Global Warming/Climate Change (Observations and Attribution of Cause) METR/ENVS 113 Spring Semester 2011 May 3, 2011
 Lecture 7 Global Warming/Climate Change (Observations and Attribution of Cause) METR/ENVS 113 Spring Semester 2011 May 3, 2011 Reading Henson Rough Guide Chapter 1 Pages 75 127; 215; 227-244 Other pages
Lecture 7 Global Warming/Climate Change (Observations and Attribution of Cause) METR/ENVS 113 Spring Semester 2011 May 3, 2011 Reading Henson Rough Guide Chapter 1 Pages 75 127; 215; 227-244 Other pages
What does IPCC AR5 say? IPCC as a radical inside the closet
 What does IPCC AR5 say? IPCC as a radical inside the closet What does IPCC AR5 say? Plan: * What is IPCC? * The Fifth Assessment Report (AR5) - WR1: The physical basis - WR2: Impacts, adaptation and vulnerability
What does IPCC AR5 say? IPCC as a radical inside the closet What does IPCC AR5 say? Plan: * What is IPCC? * The Fifth Assessment Report (AR5) - WR1: The physical basis - WR2: Impacts, adaptation and vulnerability
Chapter 6 of WGI AR6: Intention at the scoping meeting and the outline
 Chapter 6 of WGI AR6: Intention at the scoping meeting and the outline William Collins 1 and Hong Liao 2 Chapter 6 CLAs 1 Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory and University of California, Berkeley 2 Nanjing University
Chapter 6 of WGI AR6: Intention at the scoping meeting and the outline William Collins 1 and Hong Liao 2 Chapter 6 CLAs 1 Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory and University of California, Berkeley 2 Nanjing University
Global ClimateChange. Pedro M.M. Soares. Instituto Dom Luiz University of Lisbon
 Global ClimateChange Pedro M.M. Soares Instituto Dom Luiz University of Lisbon pmsoares@fc.ul.pt IPCC 5th AssessmentReportfor ClimateChange2013: The Physical Basis Observed Changes in the Climate System
Global ClimateChange Pedro M.M. Soares Instituto Dom Luiz University of Lisbon pmsoares@fc.ul.pt IPCC 5th AssessmentReportfor ClimateChange2013: The Physical Basis Observed Changes in the Climate System
Major Volcanic Eruptions in the past. Major Volcanic Eruptions in the past. Volcanic Eruptions and Global Temperature
 Mechanism of Volcanic Perturbation Amount of sunlight scattered depends greatly on size and amount of aerosol particles The global monitoring of aerosols began in ~1980 Hence, the history of the amplitude
Mechanism of Volcanic Perturbation Amount of sunlight scattered depends greatly on size and amount of aerosol particles The global monitoring of aerosols began in ~1980 Hence, the history of the amplitude
Committee on Energy Resources and the Environment
 Committee on Energy Resources and the Environment CLIMATE SCIENCE S P E C I A L R E P O R T U.S. National Climate Assessment Volume 1: Summary of Findings Don Wuebbles Department of Atmospheric Sciences
Committee on Energy Resources and the Environment CLIMATE SCIENCE S P E C I A L R E P O R T U.S. National Climate Assessment Volume 1: Summary of Findings Don Wuebbles Department of Atmospheric Sciences
Climate: Earth s Dynamic Equilibrium
 Climate: Earth s Dynamic Equilibrium review session CCIU April 30, 2016 High-school standard HS-ESS2-4 focuses on the role energy flows play in Earth s climate HS-ESS2-4 Use a model to describe how variations
Climate: Earth s Dynamic Equilibrium review session CCIU April 30, 2016 High-school standard HS-ESS2-4 focuses on the role energy flows play in Earth s climate HS-ESS2-4 Use a model to describe how variations
Aerosols. Liquid or solid particles suspended in the air. Some occur naturally, originating from volcanoes, dust storms, forest and grassland fires,
 Aerosols. Liquid or solid particles suspended in the air. Some occur naturally, originating from volcanoes, dust storms, forest and grassland fires, living vegetation, and sea spray.. Some are anthropogenic:
Aerosols. Liquid or solid particles suspended in the air. Some occur naturally, originating from volcanoes, dust storms, forest and grassland fires, living vegetation, and sea spray.. Some are anthropogenic:
IPCC WGI AR6 Needs for climate system observation data. Panmao Zhai. Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences, China
 IPCC WGI AR6 Needs for climate system observation data Panmao Zhai Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences, China 25 September 2017 AR5 WGI Outline 1: Introduction 2: Observations: Atmosphere and Surface
IPCC WGI AR6 Needs for climate system observation data Panmao Zhai Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences, China 25 September 2017 AR5 WGI Outline 1: Introduction 2: Observations: Atmosphere and Surface
PHY392S Physics of Climate. Lecture 1. Introduction
 PHY392S Physics of Climate Lecture 1 Introduction Slides based on material from Prof. K. Strong PHY392S - Physics of Climate Lecture 1, Page 1 Some Definitions Weather the fluctuating state of the atmosphere
PHY392S Physics of Climate Lecture 1 Introduction Slides based on material from Prof. K. Strong PHY392S - Physics of Climate Lecture 1, Page 1 Some Definitions Weather the fluctuating state of the atmosphere
Winter 2009: ATMS/OCN/ESS 588 The Global Carbon Cycle and Greenhouse Gases. Course Goals
 PCC 588 - January 6 and 8 2009 Winter 2009: ATMS/OCN/ESS 588 The Global Carbon Cycle and Greenhouse Gases T,Th 12:00-1:20 pm OSB 25 Course Goals The course focuses on factors controlling the global cycle
PCC 588 - January 6 and 8 2009 Winter 2009: ATMS/OCN/ESS 588 The Global Carbon Cycle and Greenhouse Gases T,Th 12:00-1:20 pm OSB 25 Course Goals The course focuses on factors controlling the global cycle
ENSC425/625 Climate Change and Global Warming
 ENSC425/625 Climate Change and Global Warming 1 Emission scenarios of greenhouse gases Projections of climate change Regional climate change (North America) Observed Changes and their Uncertainty 2 Figure
ENSC425/625 Climate Change and Global Warming 1 Emission scenarios of greenhouse gases Projections of climate change Regional climate change (North America) Observed Changes and their Uncertainty 2 Figure
Earth s Climate from Space. Richard Allan Department of Meteorology University of Reading
 Earth s Climate from Space Richard Allan Department of Meteorology University of Reading Earth s energy balance in space S πr 2 4πr 2 Outgoing Thermal Radiative Energy Absorbed Solar Radiative Energy
Earth s Climate from Space Richard Allan Department of Meteorology University of Reading Earth s energy balance in space S πr 2 4πr 2 Outgoing Thermal Radiative Energy Absorbed Solar Radiative Energy
Sec on 3-4: Radia on, Energy, Climate
 Sec on 3-4: Radia on, Energy, Climate Part 2 Learning outcomes list and describe the major natural and anthropogenic forcings of recent CC understand the effect of feedbacks on amplifying or dampening
Sec on 3-4: Radia on, Energy, Climate Part 2 Learning outcomes list and describe the major natural and anthropogenic forcings of recent CC understand the effect of feedbacks on amplifying or dampening
Concentrations of several of these greenhouse gases (CO 2, CH 4, N 2 O and CFCs) have increased dramatically in the last hundred years due to human
 Global Warming 1.1 The facts: With no atmosphere surrounding the earth the surface temperature would be 17 o C. However, due to the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that absorb infrared radiation emitted
Global Warming 1.1 The facts: With no atmosphere surrounding the earth the surface temperature would be 17 o C. However, due to the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that absorb infrared radiation emitted
Air Transportation: Emissions and Effects
 Air Transportation: Emissions and Effects Joyce E. Penner University of Michigan Report Co-ordinator: IPCC Special Report on Aviation and the Global Atmosphere Presentation to the First Regional Symposium
Air Transportation: Emissions and Effects Joyce E. Penner University of Michigan Report Co-ordinator: IPCC Special Report on Aviation and the Global Atmosphere Presentation to the First Regional Symposium
The Chemistry of Climate Change. Reading: Chapter 8 Environmental Chemistry, G. W. vanloon. S. J. Duffy
 The Chemistry of Climate Change Reading: Chapter 8 Environmental Chemistry, G. W. vanloon. S. J. Duffy The Science of Global Climate There's a lot of differing data, but as far as I can gather, over the
The Chemistry of Climate Change Reading: Chapter 8 Environmental Chemistry, G. W. vanloon. S. J. Duffy The Science of Global Climate There's a lot of differing data, but as far as I can gather, over the
Climate Change U C Irvine OLLI Class, Winter, 2013: SC 206 by Gary Oberts and Dennis Silverman Using Talks by NOAA for OLLI
 Climate Change U C Irvine OLLI Class, Winter, 2013: SC 206 by Gary Oberts and Dennis Silverman Using Talks by NOAA for OLLI Radiative Forcing Dennis Silverman Department of Physics and Astronomy, U C Irvine
Climate Change U C Irvine OLLI Class, Winter, 2013: SC 206 by Gary Oberts and Dennis Silverman Using Talks by NOAA for OLLI Radiative Forcing Dennis Silverman Department of Physics and Astronomy, U C Irvine
Bye-bye, two degree target? Recent development in observed CO 2 and CH 4 : Do we see any signs of reductions?
 Bye-bye, two degree target? Recent development in observed CO 2 and CH 4 : Do we see any signs of reductions? Cathrine Lund Myhre NILU - Norsk institutt for luftforskning Norwegian Institute for Air Research
Bye-bye, two degree target? Recent development in observed CO 2 and CH 4 : Do we see any signs of reductions? Cathrine Lund Myhre NILU - Norsk institutt for luftforskning Norwegian Institute for Air Research
Scenarios, Emissions Uncertainty, Climate Change, and Air Quality
 Scenarios, Emissions Uncertainty, Climate Change, and Air Quality Steven J. Smith Joint Global Change Research Institute College Park, MD Mid-Atlantic Regional Air Management Association SIP Coordination
Scenarios, Emissions Uncertainty, Climate Change, and Air Quality Steven J. Smith Joint Global Change Research Institute College Park, MD Mid-Atlantic Regional Air Management Association SIP Coordination
THE ANTHROPOGENIC INFLUENCE ON THE CLIMATE CHANGE IS CLEAR
 FROM IPCC AR5 WKG I: THE ANTHROPOGENIC INFLUENCE ON THE CLIMATE CHANGE IS CLEAR Excerpts from IPCC AR5 by Toni Federico Scientific Committee of Sustainable Development Foundation SUMMARY Note from editor
FROM IPCC AR5 WKG I: THE ANTHROPOGENIC INFLUENCE ON THE CLIMATE CHANGE IS CLEAR Excerpts from IPCC AR5 by Toni Federico Scientific Committee of Sustainable Development Foundation SUMMARY Note from editor
Lecture 22: Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate
 Lecture 22: Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate Required Reading: FP Chapter 14 (only sections that I cover) Suggested Introductory Reading: Jacob Chapter 7 Atmospheric Chemistry CHEM-5151 / ATOC-5151 Spring
Lecture 22: Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate Required Reading: FP Chapter 14 (only sections that I cover) Suggested Introductory Reading: Jacob Chapter 7 Atmospheric Chemistry CHEM-5151 / ATOC-5151 Spring
Past, current and projected changes of global GHG emissions and concentrations
 Past, current and projected changes of global GHG emissions and concentrations Corinne Le Quéré, University of East Anglia lead author, WGI Chapter 6 Yann Arthus-Bertrand / Altitude Change in greenhouse
Past, current and projected changes of global GHG emissions and concentrations Corinne Le Quéré, University of East Anglia lead author, WGI Chapter 6 Yann Arthus-Bertrand / Altitude Change in greenhouse
Drivers of Climate Change
 .3.3.1 Drivers of Climate Change Introduction Human activities have changed and continue to change the Earth s surface and atmospheric composition. Some of these changes have a direct or indirect impact
.3.3.1 Drivers of Climate Change Introduction Human activities have changed and continue to change the Earth s surface and atmospheric composition. Some of these changes have a direct or indirect impact
Risks from Geoengineering
 Risks from Geoengineering (Solar Radiation Management) Alan Robock Rutgers University, New Brunswick, New Jersey robock@envsci.rutgers.edu http://envsci.rutgers.edu/~robock Geoengineering is defined as
Risks from Geoengineering (Solar Radiation Management) Alan Robock Rutgers University, New Brunswick, New Jersey robock@envsci.rutgers.edu http://envsci.rutgers.edu/~robock Geoengineering is defined as
Klimaänderung. Robert Sausen Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Oberpfaffenhofen
 Klimaänderung Robert Sausen Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Oberpfaffenhofen Vorlesung WS 2017/18 LMU München 8. Anthropogener und natürlicher Strahlungsantrieb
Klimaänderung Robert Sausen Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Oberpfaffenhofen Vorlesung WS 2017/18 LMU München 8. Anthropogener und natürlicher Strahlungsantrieb
Earth s energy balance and the greenhouse effect
 Earth s energy balance and the greenhouse effect Average incident solar radiation 342 W/m 2 Reflection to space by atmosphere, clouds, and earth surface 102 W/m 2 Infrared radiation emitted to space 240
Earth s energy balance and the greenhouse effect Average incident solar radiation 342 W/m 2 Reflection to space by atmosphere, clouds, and earth surface 102 W/m 2 Infrared radiation emitted to space 240
The IPCC Working Group I Assessment of Physical Climate Change
 The IPCC Working Group I Assessment of Physical Climate Change Martin Manning Director, IPCC Working Group I Support Unit 1. Observed climate change 2. Drivers of climate change 3. Attribution of cause
The IPCC Working Group I Assessment of Physical Climate Change Martin Manning Director, IPCC Working Group I Support Unit 1. Observed climate change 2. Drivers of climate change 3. Attribution of cause
IPCC AR5: policy relevance and overview of new elements
 IPCC AR5: policy relevance and overview of new elements Jean-Pascal van Ypersele Vice-chair of the IPCC UNFCCC Event: IPCC technical briefing on AR 5 Panama, October 2011 Thanks to the Belgian Science
IPCC AR5: policy relevance and overview of new elements Jean-Pascal van Ypersele Vice-chair of the IPCC UNFCCC Event: IPCC technical briefing on AR 5 Panama, October 2011 Thanks to the Belgian Science
FORTY-SIXTH SESSION OF THE IPCC Montreal, Canada, 6 10 September 2017 SHORT-LIVED CLIMATE FORCERS
 FORTY-SIXTH SESSION OF THE IPCC Montreal, Canada, 6 10 September 2017 IPCC-XLVI/Doc. 7 (4.VIII.2017) Agenda Item: 11 ENGLISH ONLY SHORT-LIVED CLIMATE FORCERS (Prepared by the Co-Chairs of the Bureau of
FORTY-SIXTH SESSION OF THE IPCC Montreal, Canada, 6 10 September 2017 IPCC-XLVI/Doc. 7 (4.VIII.2017) Agenda Item: 11 ENGLISH ONLY SHORT-LIVED CLIMATE FORCERS (Prepared by the Co-Chairs of the Bureau of
TOPIC # 15 GLOBAL WARMING & ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING (cont.)
 TOPIC # 15 GLOBAL WARMING & ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING (cont.) Part B RADIATIVE FORCING Class Notes pp 89 THE KEY TO IT ALL: p 89 RADIATIVE FORCING (linked to the Energy Balance!) expressed in Watts per square
TOPIC # 15 GLOBAL WARMING & ANTHROPOGENIC FORCING (cont.) Part B RADIATIVE FORCING Class Notes pp 89 THE KEY TO IT ALL: p 89 RADIATIVE FORCING (linked to the Energy Balance!) expressed in Watts per square
Tuesday Dec 2nd TOPIC # 13 Global Warming Wrap Up TOPIC #14 IMPACTS & ISSUES
 Tuesday Dec 2nd TOPIC # 13 Global Warming Wrap Up TOPIC #14 IMPACTS & ISSUES SIT WITH YOUR GROUP TODAY ANNOUNCEMENTS: LINKING-TO-LIFE PROJECT PART A Your Ecological Footprint DUE in class TODAY! PART B
Tuesday Dec 2nd TOPIC # 13 Global Warming Wrap Up TOPIC #14 IMPACTS & ISSUES SIT WITH YOUR GROUP TODAY ANNOUNCEMENTS: LINKING-TO-LIFE PROJECT PART A Your Ecological Footprint DUE in class TODAY! PART B
Climate Change Scenarios. Dave Spittlehouse, Research Branch, BC Min. Forest & Range, Victoria, BC
 Climate Change Scenarios Dave Spittlehouse, Research Branch, BC Min. Forest & Range, Victoria, BC FFEI Seminar Series, 25 September 2008 1 Outline What we know - recent changes in the Earth s climate,
Climate Change Scenarios Dave Spittlehouse, Research Branch, BC Min. Forest & Range, Victoria, BC FFEI Seminar Series, 25 September 2008 1 Outline What we know - recent changes in the Earth s climate,
Critical thinking question for you:
 Critical thinking question for you: http://www.cnn.com/2017/07/12/us/weather-cities-inundated-climatechange/index.html ATOC 4800 Policy Implications of Climate ATOC 5000/ENVS 5830 Critical Issues in Climate
Critical thinking question for you: http://www.cnn.com/2017/07/12/us/weather-cities-inundated-climatechange/index.html ATOC 4800 Policy Implications of Climate ATOC 5000/ENVS 5830 Critical Issues in Climate
2. Climate Change: Projections of Climate Change: 2100 and beyond
 Global Warming: Science, Projections and Uncertainties Global Warming: Science, Projections and Uncertainties An overview of the basic science An overview of the basic science 1. A Brief History of Global
Global Warming: Science, Projections and Uncertainties Global Warming: Science, Projections and Uncertainties An overview of the basic science An overview of the basic science 1. A Brief History of Global
Greenhouse Effect & Climate Change
 Greenhouse Effect & Climate Change Greenhouse Effect Light energy from the sun (solar radiation) is either reflected or absorbed by the Earth. Greenhouse Effect When it is absorbed by the Earth (or something
Greenhouse Effect & Climate Change Greenhouse Effect Light energy from the sun (solar radiation) is either reflected or absorbed by the Earth. Greenhouse Effect When it is absorbed by the Earth (or something
Lecture 11: Global Warming
 Lecture 11: Global Warming CO 2 CH 4 How much of the global warming is caused by Natural climate change and by human activities? What is the sensitivity of Earth s climate to the increases of greehouse
Lecture 11: Global Warming CO 2 CH 4 How much of the global warming is caused by Natural climate change and by human activities? What is the sensitivity of Earth s climate to the increases of greehouse
Assessing Scientific Knowledge About Climate Change
 Assessing Scientific Knowledge About Climate Change David Wratt Chief Scientist Climate, NIWA, Wellington Presented by James Renwick, NIWA W O R L D M E T E O R O L O G I C A L O R G A N I Z A T I O N
Assessing Scientific Knowledge About Climate Change David Wratt Chief Scientist Climate, NIWA, Wellington Presented by James Renwick, NIWA W O R L D M E T E O R O L O G I C A L O R G A N I Z A T I O N
Lecture 11: Global Warming. Human Acticities. Natural Climate Changes. Global Warming: Natural or Man-Made CO 2 CH 4
 Lecture 11: Global Warming Human Acticities CO 2 CH 4 The initial appearance of human species: last 100,000 to 200,000 years Development of the first civilization: the last 10,000 years What is the sensitivity
Lecture 11: Global Warming Human Acticities CO 2 CH 4 The initial appearance of human species: last 100,000 to 200,000 years Development of the first civilization: the last 10,000 years What is the sensitivity
LESSON 9: CONCEPTUALIZING MODULE II Factors Influencing Temperature
 LESSON 9: CONCEPTUALIZING MODULE II Factors Influencing Temperature PURPOSE/QUESTION To understand the need to compare data sets over different parameters thus increasing the strength for students climate
LESSON 9: CONCEPTUALIZING MODULE II Factors Influencing Temperature PURPOSE/QUESTION To understand the need to compare data sets over different parameters thus increasing the strength for students climate
Future Climate Change in Southeast Asia and extreme events
 Future Climate Change in Southeast Asia and extreme events Prof. Dr. Edvin Aldrian (LA, Chapter 14) Director of Center for Research and Development BMKG Indonesia Yann Arthus-Bertrand / Altitude Presented
Future Climate Change in Southeast Asia and extreme events Prof. Dr. Edvin Aldrian (LA, Chapter 14) Director of Center for Research and Development BMKG Indonesia Yann Arthus-Bertrand / Altitude Presented
Current understanding of global climate change and of its possible impacts on agriculture. Maurizio Sciortino.
 Current understanding of global climate change and of its possible impacts on agriculture Maurizio Sciortino maurizio.sciortino@enea.it Outline 1. Scientific understanding of climate change The greenhouse
Current understanding of global climate change and of its possible impacts on agriculture Maurizio Sciortino maurizio.sciortino@enea.it Outline 1. Scientific understanding of climate change The greenhouse
Climate change in the Arctic region
 Photo credit: NASA Climate change in the Arctic region Stefan Fronzek Finnish Environment Institute (SYKE) Outline Introduction Climate change in the Arctic Impacts on nature Responses: mitigation + mitigation
Photo credit: NASA Climate change in the Arctic region Stefan Fronzek Finnish Environment Institute (SYKE) Outline Introduction Climate change in the Arctic Impacts on nature Responses: mitigation + mitigation
Analysis. Document of WARMING 5TH IPCC REPORT. THE CERTAINTY OF AN INHERITANCE, GLOBAL WARMING. Document of Analysis 51/2013 1
 Document of Analysis 51/2013 30 September 2013 Enter the WEB Sign up for our NEWSLETTER 5TH IPCC REPORT. THE CERTAINTY OF AN INHERITANCE, GLOBAL WARMING This document has been translated by a Translation
Document of Analysis 51/2013 30 September 2013 Enter the WEB Sign up for our NEWSLETTER 5TH IPCC REPORT. THE CERTAINTY OF AN INHERITANCE, GLOBAL WARMING This document has been translated by a Translation
Global warming: Evidence, risks and mitigation options (or: Why global warming is an energy issue) Filippo Giorgi Abdus Salam ICTP, Trieste
 Global warming: Evidence, risks and mitigation options (or: Why global warming is an energy issue) Filippo Giorgi Abdus Salam ICTP, Trieste Four frequent questions Is global warming happening? (If yes)
Global warming: Evidence, risks and mitigation options (or: Why global warming is an energy issue) Filippo Giorgi Abdus Salam ICTP, Trieste Four frequent questions Is global warming happening? (If yes)
The Science of Climate Change
 The Science of Climate Change http://data.giss.nasa.gov/gistemp/ Glaciers are retreating worldwide, including Colorado Arapahoe Glacier, 1917 Arapahoe Glacier, 2004 Sea Level is Rising End of summer ice
The Science of Climate Change http://data.giss.nasa.gov/gistemp/ Glaciers are retreating worldwide, including Colorado Arapahoe Glacier, 1917 Arapahoe Glacier, 2004 Sea Level is Rising End of summer ice
Modelling the global carbon cycle
 Modelling the global carbon cycle Chris Jones, Eleanor Burke, Angela Gallego-Sala (U. Exeter)» UNFCCC, Bonn, 24 October 2013 Introduction Why model the global carbon cycle? Motivation from climate perspective
Modelling the global carbon cycle Chris Jones, Eleanor Burke, Angela Gallego-Sala (U. Exeter)» UNFCCC, Bonn, 24 October 2013 Introduction Why model the global carbon cycle? Motivation from climate perspective
Normal equatorial flow. Climate Variability. El Niño-Southern Oscillation Human-caused climate change Alternative Energy sources
 Normal equatorial flow Climate Variability El Niño-Southern Oscillation Human-caused climate change Alternative Energy sources Vertical normal flow ENSO disruption of flow Vertical ENSO flow Normal vs.
Normal equatorial flow Climate Variability El Niño-Southern Oscillation Human-caused climate change Alternative Energy sources Vertical normal flow ENSO disruption of flow Vertical ENSO flow Normal vs.
AR5: main findings & knowledge gaps on Short-Lived Climate Forcers and their Radiative Forcing
 AR5: main findings & knowledge gaps on Short-Lived Climate Forcers and their Radiative Forcing Olivier Boucher Institut Pierre-Simon Laplace, Paris, France SLCF Some gas Some particulate Short-lived (CH
AR5: main findings & knowledge gaps on Short-Lived Climate Forcers and their Radiative Forcing Olivier Boucher Institut Pierre-Simon Laplace, Paris, France SLCF Some gas Some particulate Short-lived (CH
How Can Thermal Effects Be Explained?
 How Can Thermal Effects Be Explained? Lesson 6, Part 3: Climate Science The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect The Earth will maintain equilibrium (constant stable temperature level) if the energy coming in is.
How Can Thermal Effects Be Explained? Lesson 6, Part 3: Climate Science The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect The Earth will maintain equilibrium (constant stable temperature level) if the energy coming in is.
Global Climatic Change. GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 22 Ahrens: Chapter 16
 Global Climatic Change GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 22 Ahrens: Chapter 16 Global Climatic Change! Review: Radiation balance! Enhanced greenhouse effect! human-induced change! Climate feedbacks Climatic change!
Global Climatic Change GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 22 Ahrens: Chapter 16 Global Climatic Change! Review: Radiation balance! Enhanced greenhouse effect! human-induced change! Climate feedbacks Climatic change!
Climate Change : Facts and Future Scenarios
 Climate Change : Facts and Future Scenarios Dr Jim Salinger National Institute of Water & Atmospheric Research, Auckland, NZ FOA/MAF 6 th Annual Forest Biosecurity Workshop 8-9 th March 2007 Outline Facts
Climate Change : Facts and Future Scenarios Dr Jim Salinger National Institute of Water & Atmospheric Research, Auckland, NZ FOA/MAF 6 th Annual Forest Biosecurity Workshop 8-9 th March 2007 Outline Facts
Introduction to Climate Change. Rodel D. Lasco Professor University of the Philippines
 RD Lasco 1 Introduction to Climate Change Rodel D. Lasco Professor University of the Philippines Outline The climate system What is climate change? Evidence for climate change Predicted change in climate
RD Lasco 1 Introduction to Climate Change Rodel D. Lasco Professor University of the Philippines Outline The climate system What is climate change? Evidence for climate change Predicted change in climate
Climate Change and Air Quality
 Climate Change and Air Quality SW PA Air Quality Action June 6, 2007 Peter J. Adams Associate Professor Civil and Environmental Engineering Engineering and Public Policy Outline Climate Change Primer What
Climate Change and Air Quality SW PA Air Quality Action June 6, 2007 Peter J. Adams Associate Professor Civil and Environmental Engineering Engineering and Public Policy Outline Climate Change Primer What
Public Bodies Duties Reporting Adapting to Climate Change. Anna Beswick Programme Manager SSN reporting training day 22 June 2017
 Public Bodies Duties Reporting Adapting to Climate Change Anna Beswick Programme Manager SSN reporting training day 22 June 2017 Enabling organisations, businesses and communities to adapt to the impacts
Public Bodies Duties Reporting Adapting to Climate Change Anna Beswick Programme Manager SSN reporting training day 22 June 2017 Enabling organisations, businesses and communities to adapt to the impacts
Projection Outcomes from
 Japan-China-Korea Green Technology Forum (Tokyo, 14 March 2012) Projection Outcomes from KAKUSHIN towards IPCC/AR5 Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology Hiroki Kondo KAKUSHIN Program and
Japan-China-Korea Green Technology Forum (Tokyo, 14 March 2012) Projection Outcomes from KAKUSHIN towards IPCC/AR5 Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology Hiroki Kondo KAKUSHIN Program and
Lecture 28: Radiative Forcing of Climate Change
 Lecture 28: Radiative Forcing of Climate Change 1. Radiative Forcing In an unperturbed state, the net incoming solar radiation at the top of the atmosphere (Sn) must be balanced by the outgoing longwave
Lecture 28: Radiative Forcing of Climate Change 1. Radiative Forcing In an unperturbed state, the net incoming solar radiation at the top of the atmosphere (Sn) must be balanced by the outgoing longwave
The context: 6.7 billion people 1 planet. Is there a future?
 Global Warming: The Scientific Basis for Anthropogenic Climate Change The context: 6.7 billion people 1 planet. Is there a future? The global average net effect of human activities since 1750 has been
Global Warming: The Scientific Basis for Anthropogenic Climate Change The context: 6.7 billion people 1 planet. Is there a future? The global average net effect of human activities since 1750 has been
Global Climate Change: What the Future Holds, and What We Can Do About It
 Global Climate Change: What the Future Holds, and What We Can Do About It Dr. David Karowe Professor, Department of Biological Sciences Schedule of Topics September 29: Recent climate change (Dave Karowe)
Global Climate Change: What the Future Holds, and What We Can Do About It Dr. David Karowe Professor, Department of Biological Sciences Schedule of Topics September 29: Recent climate change (Dave Karowe)
Global Warming Potentials in AR4. V. Ramaswamy. NOAA/ Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory, Princeton University
 Global Warming Potentials in AR4 V. Ramaswamy NOAA/ Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory, Princeton University GWP Definition Defined as the ratio of the time-integrated radiative forcing from the instantaneous
Global Warming Potentials in AR4 V. Ramaswamy NOAA/ Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory, Princeton University GWP Definition Defined as the ratio of the time-integrated radiative forcing from the instantaneous
Some resources (more websites later)
 Some resources (more websites later) Intergovernmental Panel Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis at http://www.ipcc.ch/pub/reports.htm John Houghton Global Warming - the complete briefing Cambridge
Some resources (more websites later) Intergovernmental Panel Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis at http://www.ipcc.ch/pub/reports.htm John Houghton Global Warming - the complete briefing Cambridge
An independent, objective assessment of the Anthropogenic Global Warming (AGW) issue
 TRCS An independent, objective assessment of the Anthropogenic Global Warming (AGW) issue Harold H. Doiron, Chairman The Right Climate Stuff Research Team www.therightclimatestuff.com Presentation to Cruces
TRCS An independent, objective assessment of the Anthropogenic Global Warming (AGW) issue Harold H. Doiron, Chairman The Right Climate Stuff Research Team www.therightclimatestuff.com Presentation to Cruces
Aerosols (sources and processes)
 Aerosols (sources and processes) Soot is composed of aggregates of small particles (asbestos) rainout (wet deposition) Number Aerosol number is dominated by fine and ultrafine particles; aerosol mass
Aerosols (sources and processes) Soot is composed of aggregates of small particles (asbestos) rainout (wet deposition) Number Aerosol number is dominated by fine and ultrafine particles; aerosol mass
Lecture 29: Detection of Climate Change and Attribution of Causes
 Lecture 29: Detection of Climate Change and Attribution of Causes 1. The Meaning of Detection and Attribution The response to anthropogenic changes in climate forcing occurs against a backdrop of natural
Lecture 29: Detection of Climate Change and Attribution of Causes 1. The Meaning of Detection and Attribution The response to anthropogenic changes in climate forcing occurs against a backdrop of natural
Second Order Draft Chapter 7 IPCC WG1 Fourth Assessment Report
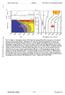 Second Order Draft Chapter IPCC WG Fourth Assessment Report 0 Box., Figure. Atmospheric release of CO from the burning of fossil fuels may give rise to a marked increase in ocean acidity. Panel a: Atmospheric
Second Order Draft Chapter IPCC WG Fourth Assessment Report 0 Box., Figure. Atmospheric release of CO from the burning of fossil fuels may give rise to a marked increase in ocean acidity. Panel a: Atmospheric
