Energy: Fossil Fuels
|
|
|
- Dwight Hood
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Energy: Fossil Fuels
2 Power Units Power is the at which work is done/energy is consumed. Energy= to do work. The joule is a unit of both work and energy. Power = energy/time or work/time Power Units: Watt = I Joule/second Kilowatt (kw) = 10 3 W Megawatt(MW) = 10 6 W Gigawatt (GW) = 10 9 W Terawatt (TW) = W
3 Discuss with your table partner: Rewrite the power formula to solve for energy. Determine which of the following is a correct unit for energy and explain why. A. Watt/hour C. Watt B/ Watt-hour D. Hour/Watt
4 Energy Laws first law of thermodynamics: energy is neither created nor destroyed, but may be from one form to another. energy is ; implication that bookkeeping is possible, e.g., in ecological study, energy flow can be followed; also stated, "you can't get something for nothing", in terms of energy quantity. Einstein showed energy & matter can be interconverted; E = mc 2
5 Energy Laws Second Law of Thermodynamics: when energy is converted from one form to another, some of the useful energy is always degraded to energy. Also can be stated: entropy increases. entropy is a measure of disorder; increased entropy means increased randomness or dispersion; degraded energy generally in form of ;
6 Evaluating Energy Resources Most commercial energy: nonrenewable fossil fuels Less developed countries use more renewable sources than more developed countries. More Developed Nations Less Developed Nations
7 Fig. S10-1, p. S59
8 Energy Use in the U.S. The United States is the largest user (& waster) of commercial energy. U.S. has 4.6% of world population, but uses of the commercial energy; 84% of the U.S. commercial energy comes from nonrenewable fossil fuels (oil, coal, & natural gas); 8% of the U.S. commercial energy comes from power; only of the U.S. commercial energy comes from renewable sources (hydropower, geothermal, biomass). solar,
9 Nuclear power 6% Geothermal, solar, wind 2.5% Hydropower 4.5% Nuclear power 8% Geothermal, solar, wind 1% Hydropower 3% Natural gas 21% Natural gas 23% Coal 22% Oil 33% Biomass 11% Coal 23% Oil 39% Biomass 3% World United States
10 Energy consumption in the US: Past and Near Future Oil Coal Natural gas Nonhydro renewables Nuclear Hydropower Fig. S10-3, p. S60
11 Total Energy Consumption and Per Capita Energy Consumption in the United States Fig. S10-2, p. S60
12 What is Net Energy? Net energy: the total useful energy from a resource over its lifetime minus the amount of energy, automatically wasted, & unnecessarily wasted to find, process, & transport it. example: if 8 units of energy are wasted for every 10 units extracted, then there is a net energy of 2 units; Net energy ratio is the ratio of useful energy produced to the useful energy used to produce it; the the ratio the the net energy yield; example: for the above problem the net energy ratio is 10/8 = 1.25.
13 Net Energy Ratios Space Heating Passive solar 5.8 Natural gas 4.9 Oil 4.5 Active solar 1.9 Coal gasification 1.5 Electric heating (coal-fired plant) 0.4 Electric heating (natural-gas-fired plant) 0.4 Electric heating (nuclear plant) 0.3 High-Temperature Industrial Heat Surface-mined coal 28.2 Underground-mined coal 25.8 Natural gas 4.9 Oil 4.7 Coal gasification 1.5 Direct solar (concentrated) 0.9 Transportation Ethanol from sugarcane residue 8.0 Ethanol from switchgrass 5.4 Natural gas 4.9 Gasoline (refined crude oil) 4.1 Coal liquefaction 1.4 Oil shale 1.2 Ethanol from corn 1.1 (but can reach 1.5) Fig. 15-A, p. 374
14 How to Evaluate Energy Resources? Criteria: How much of an energy source is available? - near future = next 15 years - intermediate future = next 30 years - long term = next 50 years What is the source's net energy yield? How much does it cost to develop, phase in, & use? How does extraction, transport, & use affect the environment? What will using an energy source do to help sustain humans & other species living on Earth?
15 Oil Petroleum or crude oil is a fossil fuel, produced by the decomposition of deeply buried organic matter from plants & animals. is a complex liquid mixture of hydrocarbons, with small amounts of sulfur, oxygen, & nitrogen impurities; primary oil recovery involves drilling a well & pumping oil that flows by gravity into the bottom of the well; secondary oil recovery involves injecting in nearby wells to force remaining heavy oil to the surface; tertiary or enhanced oil recovery involves using or CO 2 gas to force still more oil into the well.
16 Crude oil and natural gas are generally found together in sedimentary rock layers, with the oil dispersed in pores and cracks of the rock formation. Oil storage Oil drilling platform Oil well Pipeline Gas well Pump Mined coal Coal seam
17 Low Boiling point High Boiling point Crude Oil Refining Refining of crude oil involves separating components based on their. gasoline & aviation fuel are among the most volatile components; heating oil is less volatile, but still burns readily; diesel oil is still less volatile, and is a common fuel for trucks, buses, & heavy machinery; grease, wax, & asphalt are the least volatile, most dense materials separated; petrochemicals derived from oil are used for synthesizing industrial organic chemicals, pesticides, plastics, synthetic fibers, paints, medicines, & many other products.
18 Lowest Boiling Point Gases Gasoline Aviation fuel Heating oil Diesel oil Naphtha Heated crude oil Furnace Grease and wax Asphalt Highest Boiling Point
19 World Oil Consumption Fig. S10-4, p. S61
20 World Oil Consumption consumption: 1000 barrels/day Change in consumption since 1990
21 Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) In 2006 OPEC produced of the world's oil (down from in 1973) OPEC members: Algeria, Ecuador, Gabon, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, UAE & Venezuela Important Non-OPEC oil producers include Mexico and Canada (oil sand) 1 barrel = 42 gal
22 Crude Oil Sources Thirteen countries that make up the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) have 67% of the world's reserves of oil. = OPEC Member in 1997 OPEC produced 40% of the world's oil (down from 65% in 1973); by 2010 OPEC is expected to supply almost half of the world's oil; OPEC members: Algeria, Ecuador, Gabon, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, & Venezuela; other important oil producers include Alaska, Siberia, & Mexico.
23 Oil Production in 2003 and Change in Production
24
25 Fig. S10-6, p. S62
26 ANWR (Arctic National Wildlife Reserves) potential oil 14 supply compared to US projected demand. Barrels of oil per year (billions) Projected U.S. oil consumption Arctic refuge oil output over 50 years Year
27 Conventional Oil: Advantages Ample supply for years cost Easily within & between countries Low land use Technology is well developed distribution system
28 Conventional Oil: Disadvantages Releases CO 2 when burned Can cause pollution Pollutes air when produced and burned. Will need to find substitute in the future Large government Environmental costs not included in market price Artificially low price encourages and discourages search
29 Oil Sands and Oil Shale Oil Sand Synthetic crude oil can be produced from oil shale or from tar sands. However of landscape Damage to Rivers/Lakes Large Quantities of CO 2 released Net Energy yield Oil Shale
30 Oil Sands and Oil Shale Reserves Oil Shale Deposits Oil Sands Deposits Oil Shale
31 Mining Terms : The layer of material that lies over the mineral resource. : The material (overburden) that has been removed from over a mineral resource. Overburden Mineral Resource Spoil
32 Oil Sands (Tar Sands) Oil sand, tar sand -contains bitumen Canada and Venezuela: -oil sands have more oil than in Saudi Arabia Extraction metric tons of overburden removed to produce metric ton of bitumen Each barrel of oil requires 4-5 barrels of Releases times as much CO 2 as conventional oil net energy yield: Is it cost effective?
33
34 Oil Shales Oil shales contain kerogen After distillation: shale oil 72% of the world s reserve is in arid areas of western Locked up in Lack of needed for extraction and processing Low yield
35 TRADE-OFFS Heavy Oils from Oil Shale and Oil Sand Advantages Moderate cost (oil sand) Disadvantages High cost (oil shale) Large potential supplies, especially oil sands in Canada Easily transported within and between countries Efficient distribution system in place Technology welldeveloped (oil sand) Low net energy yield Environmental costs not included in market price Large amounts of water needed for processing Severe land disruption Severe water pollution Air pollution and CO 2 emissions when produced and burned
36 Oil Reserves and How Long They Will Last
37 CAFE Standards: Corporate Average Fuel Economy After the 1973, the US Energy Policy & Conservation Act of 1975 set standards for the average fuel efficiency for each car manufacturer. From , the CAFE standards were mpg for passenger vehicles and mpg for light trucks/suv s Increases in standards through both the EISA (Energy Independence and Security Act in 2007 and Obama Administration regulations. Increases to mpg average for (new) passenger vehicles by 2025.
38 Since standards are lower for light trucks than for cars, manufacturers developed the for large-scale consumer use to get around the higher CAFE standard for passenger cars. Many manufacturers of SUV s chose to pay the fines since profits from SUV sales were large even with the fines The average mpg for all vehicles dropped from from This was due to the average weight of vehicles increasing from 3,220 to 4,066 lb when light truck (mainly SUV ownership) went from 28% to 53% CAFE Standards
39 Europe has a higher percentage of diesel cars, which have a better fuel efficiency.
40 The Price of Oil
41 The Price of Oil Oil field in Kuwait Oil prices can be highly volatile due to several factors: Instability in the Middle East Increase in global (i.e. China and India s growth) such as Hurricane Katrina Hurricane Katrina Damage
42 The Price of Oil Oil price increases affect not only gas prices, but the cost of most goods, since fuel is needed to manufacture and transport goods
43 The Price of Oil For the first time, Americans are driving less and are SUV s are losing popularity
44 Oil Spills Crude & refined petroleum are accidentally and deliberately released into the environment from various sources. most oil is released in operation of offshore wells, from washing tankers, & pipeline & storage tank leaks; tanker & offshore drilling rig accidents can release large amounts of oil in a short period of time
45 Oil Spills Some effects of oil on marine ecosystems: - volatile organics immediately kill of many aquatic organisms (especially plankton & larvae), as well as contaminate fish; - floating oil coats birds & marine mammals, destroying natural & buoyancy, & causing deaths; - heavy oil sinks to ocean bottom & washes into estuaries where it contaminates crabs, oysters, mussels, clams, etc. - oil slicks on beaches harm intertidal life & cause economic losses to tourism & fishing industries. - cleaning oil spills with high-powered jets of water can kill plants and animals in the rocks.
46 Exxon Valdez Oil Spill March 24, 1989, Exxon Valdez spilled oil in Prince William Sound Over 1,600 km ( ) of shoreline was coated Exxon spent $2.2 billion on cleanup Exxon ruled negligent in 1991federal lawsuit, and paid $1 billion to Alaska in fines Exxon ruled guilty in 1994 lawsuit, and fishing industry, landowners, and AK residents awarded $5 billion in damages. To date, Exxon has paid ~2.3 billion in damages
47 Exxon Valdez Oil Spill A may have prevented the catastrophe, but this requirement has been dropped by the government due to pressure from the oil industry All new tankers must have a double hull, and all single-hulled tankers are supposed to be phased out by 2015, but the oil industry is working to weaken these requirements. No more than of the oil from a spill can be recovered, even with a fast response of 1990 was supposed to regulate supertankers, but oil companies have found a way around the law by operating barges instead of tankers
48 Ocean Pollution: Oil Spills In late March, 2010, President Obama called for oil and natural gas exploration off the eastern coast of the US, from Delaware to Florida, approximately 167 million acres He also opened up exploration in parts of offshore Northern AK
49 Deep Horizon Oil Spill: Gulf of Mexico On April 20 th, 2010, methane in a BP s deep water oil well, Macondo, caused an explosion on the ship Deep Horizon. men were killed. For 3 months oil gushed into the deep ocean before being permanently capped on July 15 th, 2010 An estimated 4.9 million barrels ( million gallons) spilled.
50 Deep Horizon Oil Spill: Gulf of Mexico About more oil was spilled than in the Exxon Valdex spill Offshore drilling (drilling at >500 m depth) was suspended for 6 months until it could be determined that deepwater wells were safe This was challenged by oil companies and the rule was overturned in federal court
51 Deep Horizon Oil Spill: Gulf of Mexico Total miles of shoreline affected as of Nov., 2010: miles. Good news: spill did not reach the gulf stream as some feared, which would have polluted shorelines along east coast.
52 Deep Horizon Oil Spill: Gulf of Mexico While the oil has largely disappeared, as of Jan, 2011, tar balls continue to wash up on shorelines
53 Deep Horizon Oil Spill: Gulf of Mexico Initally, about were closed to fishing, but most areas were re-opened by mid-nov. In late November, 2011, due to tar balls appearing in shrimp nets, 4,200 mi 2 of the gulf was re-closed to shrimping.
54 Deep Horizon Oil Spill: Gulf of Mexico Clean-up efforts included: Burning Removal from beaches Use of However, up to 79% of the oil might still be in the gulf
55 Deep Horizon Oil Spill: Gulf of Mexico Corexit was the primary dispersant used and was highly controversial. Initally, BP was spraying gal/day Corexit is a with the potential to bioaccumulate. The OSHA Materials Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) states: No toxicity studies have been conducted on this product. On May 19 th, the EPA gave BP 24 hours to choose a less toxic dispersant. By May 26 th, BP had reduced its use to 23,250 gal/day (a 9% decrease). By July 30 th, about 1.8 million gallons of dispersant, mostly Corexit, had been deployed.
56 Deep Horizon Oil Spill: Gulf of Mexico On Aug 2, the EPA said that dispersants were no more harmful to the environment than the oil itself. Besides the potential toxic effects, some scientists believe that the small droplets of oil that dispersants create make it easier for oil to enter the food chain. The addition of dispersants creates very toxic substances called poly-aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) when mixed with crude oil. PAHs contain compounds that have been identified as carcinogenic, mutagenic, and teratogenic. The dispersants added to the water cause chemical compounds to become water soluble, which then makes it impossible to remove them.
57 Deep Horizon Oil Spill: Gulf of Mexico As of November 2, 6,814 dead animals had been collected, including 6,104 birds, 609 sea turtles, 100 dolphins and other mammals, and 1 other reptile. One estimate states that about 20% of juvenile blue fin tuna in the gulf were killed when a major spawning ground was damaged. Total damage to the ecosystem is unknown.
58 Deep Horizon Oil Spill: Gulf of Mexico As of Oct., 2010, a deep plume of oily water 35 km long was still detected in the Gulf at 1,100 m depth In places, up to 2 in. of oil-laden sediment sits on top of the ocean floor. Effects on deep-sea ecosystems might be severe, but it will be hard to determine exact levels of damage, since these systems have not been extensively studied. A ghost crab eats oil from the Gulf of Mexico spill, shown glowing yellow-orange under ultraviolet light, at Gulf Islands National Seashore near Pensacola, FL. Credit: National Geographic
59 Deep Horizon Oil Spill Methane: About 200,000 tons of CH 4 were released into the ocean during the spill As of Sept., 2010, most of the methane appeared to be gone Methane-eating microbes (methanotrophs) are probably responsible Downside: is consumed in the process, so waters became oxygen depleted. Some microbes also digest oil, but they mostly break up the oil into smaller droplets.
60 Deep Horizon Oil Spill: Gulf of Mexico Costs to BP (in billions): Plugging well, cleaning up spilled oil, paying claims: 10.7 Fund set up for individuals and businesses that were affected by spill: 20 (to date: 2.7 billion paid) Fines 5.4 to 21.1 (depend on whether BP is found grossly negligent with regard to cause of accident) Legal fees: up to 2 Lawsuits: up to 6 BP s stock value dropped to $27/share in June, By Jan, 2011, it had risen to $60.5
61 Pros: Pros & Cons of Oil oil is still relatively cheap; economy (infrastructure) is set up around use of oil; many useful products can be readily synthesized from oil; Cons: supply is limited pollution & environmental degradation result from extraction, processing, transport, & use, including global warming Many reserves are located in politically unstable countries Recent volatility of oil prices accidents can be environmentally devastating
62 TRADE-OFFS Advantages Conventional Oil Ample supply for years Low cost High net energy yield Easily transported within and between countries Low land use Technology is well developed Efficient distribution system Disadvantages Need to find substitutes within 50 years Large government subsidies Environmental costs not included in market price Artificially low price encourages waste and discourages search for alternatives Pollutes air when produced and burned Releases CO 2 when burned Can cause water pollution
Energy: Fossil Fuels
 Energy: Fossil Fuels Power Units Power is the at which work is done/energy is consumed. Energy= ability to do work. The joule is a unit of both work and energy. Power = energy/time or work/time Power Units:
Energy: Fossil Fuels Power Units Power is the at which work is done/energy is consumed. Energy= ability to do work. The joule is a unit of both work and energy. Power = energy/time or work/time Power Units:
Energy Classifications
 FOSSIL FUELS Energy Classifications Renewable Energy any source of energy that can be replaced as fast as it is used Examples: wind, hydroelectric, biofuels, solar, others Nonrenewable Energy any source
FOSSIL FUELS Energy Classifications Renewable Energy any source of energy that can be replaced as fast as it is used Examples: wind, hydroelectric, biofuels, solar, others Nonrenewable Energy any source
Overview of Chapter 11
 11 Fossil Fuels Overview of Chapter 11 Fossil Fuels Coal Coal Reserves Coal mining Environmental Effects of Burning Coal Oil and Natural Gas Exploration for Oil and Natural Gas Oil and Natural Gas reserves
11 Fossil Fuels Overview of Chapter 11 Fossil Fuels Coal Coal Reserves Coal mining Environmental Effects of Burning Coal Oil and Natural Gas Exploration for Oil and Natural Gas Oil and Natural Gas reserves
Non-Renewable Energy Resources: How do dead things power our lives?
 Non-Renewable Energy Resources: How do dead things power our lives? Life requires energy it is stored, transferred, and converted Ultimate source of energy for life the Sun For humans, our source of energy
Non-Renewable Energy Resources: How do dead things power our lives? Life requires energy it is stored, transferred, and converted Ultimate source of energy for life the Sun For humans, our source of energy
Chapter 11 Fossil Fuels
 Chapter 11 Fossil Fuels I. Energy Sources and Consumption A. Energy sources that were used were obtained locally and now they are worldwide Fossil fuels Nuclear energy Electricity B. Energy consumption
Chapter 11 Fossil Fuels I. Energy Sources and Consumption A. Energy sources that were used were obtained locally and now they are worldwide Fossil fuels Nuclear energy Electricity B. Energy consumption
Nonrenewable Energy. Chapter 15
 Nonrenewable Energy Chapter 15 Core Case Study: How Long Will Supplies of Conventional Oil Last? Oil: energy supplier How much is left? When will we run out? Three options Look for more Reduce oil use
Nonrenewable Energy Chapter 15 Core Case Study: How Long Will Supplies of Conventional Oil Last? Oil: energy supplier How much is left? When will we run out? Three options Look for more Reduce oil use
AP Environmental Science II. Unit 2-1: Energy Basics and Fossil Fuels
 NOTE/STUDY GUIDE: Unit 2-1, Energy Basics and Fossil Fuels AP Environmental Science II, Mr. Doc Miller, M.Ed. North Central High School Name: ID#: NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE AP Environmental
NOTE/STUDY GUIDE: Unit 2-1, Energy Basics and Fossil Fuels AP Environmental Science II, Mr. Doc Miller, M.Ed. North Central High School Name: ID#: NORTH CENTRAL HIGH SCHOOL NOTE & STUDY GUIDE AP Environmental
Chapter 17: Fossil Fuels and the Environment
 Chapter 17: Fossil Fuels and the Environment Fossil Fuels Fossil fuels are forms of stored solar energy Plants convert solar energy to chemical energy through photosynthesis Incomplete decomposed organic
Chapter 17: Fossil Fuels and the Environment Fossil Fuels Fossil fuels are forms of stored solar energy Plants convert solar energy to chemical energy through photosynthesis Incomplete decomposed organic
Fossil Fuels and the environment
 Lecture -11: Fossil Fuels and the environment ENV 107: Introduction to Environmental Science Dr. A.K.M. Saiful Islam 16.1 Fossil Fuels Fossil fuels are all forms of stored solar energy. We say because
Lecture -11: Fossil Fuels and the environment ENV 107: Introduction to Environmental Science Dr. A.K.M. Saiful Islam 16.1 Fossil Fuels Fossil fuels are all forms of stored solar energy. We say because
The Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill
 The Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill Learning from the disaster Jenan Kharbush Scripps Institution of Oceanography, San Diego, CA ASTA Conference November 2010 Photo Credit: Daniel Beltra Outline I. Deepwater
The Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill Learning from the disaster Jenan Kharbush Scripps Institution of Oceanography, San Diego, CA ASTA Conference November 2010 Photo Credit: Daniel Beltra Outline I. Deepwater
Energy. Test February 9 Study Guide Due February 9
 Energy Test February 9 Study Guide Due February 9 Bellwork 1/17 What we have left: Energy, Land/Water Use, and Ecology What units have we studied so far? Energy The ability to do work Most common - Joule
Energy Test February 9 Study Guide Due February 9 Bellwork 1/17 What we have left: Energy, Land/Water Use, and Ecology What units have we studied so far? Energy The ability to do work Most common - Joule
4. If the Earth is to continue to use oil its current rate, what must happen for us to sustain this rate?
 CHAPTER 15 Nonrenewable Energy Core Case Study: How Long Will Supplies of Conventional Oil Last? Oil supplies about of the world s energy. When do geologist predict that oil reserves will be 80% depleted?
CHAPTER 15 Nonrenewable Energy Core Case Study: How Long Will Supplies of Conventional Oil Last? Oil supplies about of the world s energy. When do geologist predict that oil reserves will be 80% depleted?
Oil Pollution (Spill)
 Coastal & Marine Oil Pollution (Spill) Mazen Abualtayef Assistant Prof., IUG, Palestine 1. What is an oil spill? An oil spill is a release of a liquid petroleum hydrocarbon into the environment due to
Coastal & Marine Oil Pollution (Spill) Mazen Abualtayef Assistant Prof., IUG, Palestine 1. What is an oil spill? An oil spill is a release of a liquid petroleum hydrocarbon into the environment due to
LESSON 3 OTHER LAND RESOURCES C H A P T E R 6, C O N S E R V I N G O U R R E S O U R C E S
 LESSON 3 OTHER LAND RESOURCES C H A P T E R 6, C O N S E R V I N G O U R R E S O U R C E S OBJECTIVES Compare renewable and nonrenewable resources. Describe how human activities affect the environment.
LESSON 3 OTHER LAND RESOURCES C H A P T E R 6, C O N S E R V I N G O U R R E S O U R C E S OBJECTIVES Compare renewable and nonrenewable resources. Describe how human activities affect the environment.
Chapter 16. Nonrenewable Energy TYPES OF ENERGY RESOURCES TYPES OF ENERGY RESOURCES TYPES OF ENERGY RESOURCES
 TYPES OF ENERGY RESOURCES Chapter 16 Nonrenewable Energy About 99% of the energy we use for heat comes from the sun and the other 1% comes mostly from burning fossil fuels. Solar energy indirectly supports
TYPES OF ENERGY RESOURCES Chapter 16 Nonrenewable Energy About 99% of the energy we use for heat comes from the sun and the other 1% comes mostly from burning fossil fuels. Solar energy indirectly supports
3. Forms when pre-existing rock is changed due to high temperatures, pressure, or chemicals.
 Unit 4 ENERGY Practice Quiz 1. The North American and Eurasian plates are moving apart from one another and creating the Mid-Atlantic ridge. This is an example of what type of plate boundary? (A) Convergent
Unit 4 ENERGY Practice Quiz 1. The North American and Eurasian plates are moving apart from one another and creating the Mid-Atlantic ridge. This is an example of what type of plate boundary? (A) Convergent
Oil on Troubled Waters: Recovery in the Gulf of Mexico
 Oil on Troubled Waters: Response and Outlook for Recovery in the Gulf of Mexico Nancy E. Kinner Coastal Response Research Center University of New Hampshire UNH Homecoming October 8, 2010 University of
Oil on Troubled Waters: Response and Outlook for Recovery in the Gulf of Mexico Nancy E. Kinner Coastal Response Research Center University of New Hampshire UNH Homecoming October 8, 2010 University of
Natural Resources. Mr. Dvorin Muir Middle School
 Natural Resources Mr. Dvorin Muir Middle School NONRENEWABLE AND RENEWABLE RESOURCES HMMMM... What do you think nonrenewable resources are? Break it down... Nonrenewable? Resource? NONRENEWABLE RESOURCES
Natural Resources Mr. Dvorin Muir Middle School NONRENEWABLE AND RENEWABLE RESOURCES HMMMM... What do you think nonrenewable resources are? Break it down... Nonrenewable? Resource? NONRENEWABLE RESOURCES
Environmental Impact: Nuclear Energy in Comparison with other Alternatives. Eric D. Graham
 Environmental Impact: Nuclear Energy in Comparison with other Alternatives Eric D. Graham Contents Introduction Greenhouse Gases Solid Waste Wildlife Effects Land Resource Use Other Effects Conclusion
Environmental Impact: Nuclear Energy in Comparison with other Alternatives Eric D. Graham Contents Introduction Greenhouse Gases Solid Waste Wildlife Effects Land Resource Use Other Effects Conclusion
Fossil Fuels: Natural Gas. Outline: Formation Global supply and Distribution NGCC Carbon management Biological Artificial
 Fossil Fuels: Natural Gas Outline: Formation Global supply and Distribution NGCC Carbon management Biological Artificial Formation of Natural Gas Migration Phases separate according to density, with the
Fossil Fuels: Natural Gas Outline: Formation Global supply and Distribution NGCC Carbon management Biological Artificial Formation of Natural Gas Migration Phases separate according to density, with the
Biomass. Coal. 10 Intermediate Energy Infobook Activities. Description of biomass: Renewable or nonrenewable: Description of photosynthesis:
 Biomass Description of biomass: Description of photosynthesis: Ways we turn biomass into energy we can use: Who uses biomass and for what purposes: Effect of using biomass on the environment: Important
Biomass Description of biomass: Description of photosynthesis: Ways we turn biomass into energy we can use: Who uses biomass and for what purposes: Effect of using biomass on the environment: Important
Should Fracking be legal in the United States? Structured Debate video: Structured Debate Part 1: Clarifying Questions:
 Should Fracking be legal in the United States? Structured Debate video: Introductory Clips: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uti2niw2bra http://www.mlive.com/environment/index.ssf/2014/05/fracking_a_divisive_practices.html
Should Fracking be legal in the United States? Structured Debate video: Introductory Clips: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uti2niw2bra http://www.mlive.com/environment/index.ssf/2014/05/fracking_a_divisive_practices.html
Protecting Our Water Keeping Our Water Healthy
 Protecting Our Water Keeping Our Water Healthy Draw a bubble map about "Why Water is Important in Our Daily Lives". Include at least 5 reasons. Compare answers with your neighbors, noting similarities
Protecting Our Water Keeping Our Water Healthy Draw a bubble map about "Why Water is Important in Our Daily Lives". Include at least 5 reasons. Compare answers with your neighbors, noting similarities
Do Now. Make sure you are signed up for THIS SATURDAY S study sesh. Grab a chromebook and go to my website, Unit 10, Energy!
 Do Now Make sure you are signed up for THIS SATURDAY S study sesh Tinyurl.com/APES-study-3-25 Grab a chromebook and go to my website, Unit 10, Energy! Part One Sources of Energy Sources of Energy We use
Do Now Make sure you are signed up for THIS SATURDAY S study sesh Tinyurl.com/APES-study-3-25 Grab a chromebook and go to my website, Unit 10, Energy! Part One Sources of Energy Sources of Energy We use
The price of oil. The disruption caused by the American shale oil industry. Martin Hvidt
 News Analysis January 2018 The price of oil. The disruption caused by the American shale oil industry Martin Hvidt News Following the OPEC meeting decision 30 November 2017 to continue the restriction
News Analysis January 2018 The price of oil. The disruption caused by the American shale oil industry Martin Hvidt News Following the OPEC meeting decision 30 November 2017 to continue the restriction
Renewable Energy Today
 Chapter 18 Renewable Energy Today Renewable Energy energy from a source that is constantly being reformed. Many governments are planning to increase their use of renewable energy resources. This will reduce
Chapter 18 Renewable Energy Today Renewable Energy energy from a source that is constantly being reformed. Many governments are planning to increase their use of renewable energy resources. This will reduce
What Are the Causes and Effects of Water Pollution?
 Water PolChapter 20 Ch20 Water Pollution SPARK Notes lution What Are the Causes and Effects of Water Pollution? Water pollution causes illness and death in humans and other species, and disrupts ecosystems.
Water PolChapter 20 Ch20 Water Pollution SPARK Notes lution What Are the Causes and Effects of Water Pollution? Water pollution causes illness and death in humans and other species, and disrupts ecosystems.
NONRENEWABLE RESOURCES
 ENERGY RESOURCES NONRENEWABLE RESOURCES Energy is the ability to cause change. Fossil fuels com from the remains of ancient animals. They include: petroleum, coal, and natural gas and are nonrenewable,
ENERGY RESOURCES NONRENEWABLE RESOURCES Energy is the ability to cause change. Fossil fuels com from the remains of ancient animals. They include: petroleum, coal, and natural gas and are nonrenewable,
Critique of Natural Energy Resources
 In this activity, you will differentiate renewable and non-renewable and develop an argument/claim for one resource. Please answer the following questions in complete sentences. Part 1: Natural Review
In this activity, you will differentiate renewable and non-renewable and develop an argument/claim for one resource. Please answer the following questions in complete sentences. Part 1: Natural Review
ENERGY RESOURCES RESEARCH NOTES
 Fusion: The Unlikely Union of Physics and English Comp NAME: ENERGY RESOURCES RESEARCH NOTES Use this handout as a guideline for the research you need to do for the final project. The first page is an
Fusion: The Unlikely Union of Physics and English Comp NAME: ENERGY RESOURCES RESEARCH NOTES Use this handout as a guideline for the research you need to do for the final project. The first page is an
Unit 2: Understanding Common Energy Conversion Systems. Lesson Objectives: Introduction. Lesson
 Unit 2: Understanding Common Energy Conversion Systems Lesson 7 - The Formation & Extraction of Fossil Fuels Approximate Lesson Length: 3hours Save your assignment as: SCI24U2L7 Lesson Objectives: Upon
Unit 2: Understanding Common Energy Conversion Systems Lesson 7 - The Formation & Extraction of Fossil Fuels Approximate Lesson Length: 3hours Save your assignment as: SCI24U2L7 Lesson Objectives: Upon
STAAR Science Tutorial 55 TEK 8.11D: Human Dependence on Ocean Systems
 Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 55 TEK 8.11D: Human Dependence on Ocean Systems TEK 8.11D: Recognize human dependence on ocean systems and explain how human activities such as runoff, artificial
Name: Teacher: Pd. Date: STAAR Science Tutorial 55 TEK 8.11D: Human Dependence on Ocean Systems TEK 8.11D: Recognize human dependence on ocean systems and explain how human activities such as runoff, artificial
Botkin & Keller: Environmental Science: Earth as a Living Planet 8th Edition Guided Reading Assignment: Energy Unit- Chapters
 Botkin & Keller: Environmental Science: Earth as a Living Planet 8th Edition Guided Reading Assignment: Energy Unit- Chapters 14-15 Name: Chapter #14- Energy: Some Basics 1: How does the energy crisis
Botkin & Keller: Environmental Science: Earth as a Living Planet 8th Edition Guided Reading Assignment: Energy Unit- Chapters 14-15 Name: Chapter #14- Energy: Some Basics 1: How does the energy crisis
World Energy Sources & Fossil Fuel Power Production. Josh Barnes, Cyrus Hughlett...and Karl. SL/AP Physics Hour 2
 World Energy Sources & Fossil Fuel Power Production Josh Barnes, Cyrus Hughlett...and Karl. SL/AP Physics Hour 2 Different World Energy Sources There are many different forms of energy used throughout
World Energy Sources & Fossil Fuel Power Production Josh Barnes, Cyrus Hughlett...and Karl. SL/AP Physics Hour 2 Different World Energy Sources There are many different forms of energy used throughout
Global Energy Reserves
 CH2356 Energy Engineering Unit I Global Energy Reserves Dr. M. Subramanian Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College of Engineering Kalavakkam 603 110, Kanchipuram
CH2356 Energy Engineering Unit I Global Energy Reserves Dr. M. Subramanian Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College of Engineering Kalavakkam 603 110, Kanchipuram
The Oceans Global Garbage
 The Oceans Global Garbage Lesson Overview: The world s oceans are intentionally used as a disposal ground. Students will learn how the oceans are polluted through a review of examples of pollution and
The Oceans Global Garbage Lesson Overview: The world s oceans are intentionally used as a disposal ground. Students will learn how the oceans are polluted through a review of examples of pollution and
11/16/2014. Abiotic Oil?
 ES 10 Nonrenewable Energy Resources Oil and Natural Gas continued http://www.poodwaddle.com/worldclock.swf Past to Present (1 st 31 slides) What are fossil fuels Why use Oil / Natural Gas Drawbacks Where
ES 10 Nonrenewable Energy Resources Oil and Natural Gas continued http://www.poodwaddle.com/worldclock.swf Past to Present (1 st 31 slides) What are fossil fuels Why use Oil / Natural Gas Drawbacks Where
The Energy Challenge
 The Energy Challenge Joan F. Brennecke Dept. of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Director, Notre Dame Energy Center Siemens Westinghouse Science and Technology Competition November 12, 2005 ENERGY
The Energy Challenge Joan F. Brennecke Dept. of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Director, Notre Dame Energy Center Siemens Westinghouse Science and Technology Competition November 12, 2005 ENERGY
Lipow Oil Associates, LLC. January 3, Energy Independence: Can We Really Do It?
 January 3, 2008 Energy Independence: Can We Really Do It? On December 19, 2007, President Bush signed into law the Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007. The act legislated changes in three major
January 3, 2008 Energy Independence: Can We Really Do It? On December 19, 2007, President Bush signed into law the Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007. The act legislated changes in three major
Lesson th Grade * Teacher Prep. Photocopy ESP Worksheet Assignment 3
 Lesson 130 9 th Grade * Teacher Prep Photocopy ESP Worksheet Assignment 3 Lesson 130 9 th Grade * Teacher Prep Standard & Objective: S5 O2 USOE Text Pages: 229-231 Materials: Portfolio 6 Lesson 130 * 9
Lesson 130 9 th Grade * Teacher Prep Photocopy ESP Worksheet Assignment 3 Lesson 130 9 th Grade * Teacher Prep Standard & Objective: S5 O2 USOE Text Pages: 229-231 Materials: Portfolio 6 Lesson 130 * 9
Ch Nonrenewable Energy Resources
 Ch. 15 - Nonrenewable Energy Resources Evaluating Energy Resources What Types of Energy Do We Use? 99% of energy we use to heat the earth and all our buildings comes directly form the sun. 1% of energy
Ch. 15 - Nonrenewable Energy Resources Evaluating Energy Resources What Types of Energy Do We Use? 99% of energy we use to heat the earth and all our buildings comes directly form the sun. 1% of energy
RENEWABLE ENERGY AND ALTERNATIVE FUELS
 RENEWABLE ENERGY AND ALTERNATIVE FUELS There is absolutely no doubt the entire world is dependent upon the generation and transmission of electricity. Those countries without electrical power are considered
RENEWABLE ENERGY AND ALTERNATIVE FUELS There is absolutely no doubt the entire world is dependent upon the generation and transmission of electricity. Those countries without electrical power are considered
Art caption: Natural resources such as rocks are mined in rock quarries (KWOR-eez) like this one. DRAFT
 1 OBSERVING EARTH S RESOURCES INVESTIGATION Humans use a lot of materials found naturally on Earth. There are many materials, including metals such as copper and woods such as pine. Materials that are
1 OBSERVING EARTH S RESOURCES INVESTIGATION Humans use a lot of materials found naturally on Earth. There are many materials, including metals such as copper and woods such as pine. Materials that are
Energy, Environment, Hydrogen: A Case For Fuel Cells
 Energy, Environment, Hydrogen: A Case For Fuel Cells Why Do We Need Energy? Heating/Cooking Transportation Manufacturing What Energy Sources Have We Used Over Time? Why Do We Care About Finding New Sources
Energy, Environment, Hydrogen: A Case For Fuel Cells Why Do We Need Energy? Heating/Cooking Transportation Manufacturing What Energy Sources Have We Used Over Time? Why Do We Care About Finding New Sources
THE WORLD FACES two energy challenges.
 Hybrid baseload nuclear power for variable electricity and fuels BY CHARLES FORSBERG THE WORLD FACES two energy challenges. The first is the release of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere from the burning
Hybrid baseload nuclear power for variable electricity and fuels BY CHARLES FORSBERG THE WORLD FACES two energy challenges. The first is the release of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere from the burning
Energy generation and use MR. BANKS 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE
 Energy generation and use MR. BANKS 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE Worldwide energy use As the world becomes more populated and technologically advanced, the demand for energy has increased. Before electricity was
Energy generation and use MR. BANKS 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE Worldwide energy use As the world becomes more populated and technologically advanced, the demand for energy has increased. Before electricity was
U.S. EIA s Liquid Fuels Outlook
 U.S. EIA s Liquid Fuels Outlook NCSL 2011 Energy Policy Summit: Fueling Tomorrow s Transportation John Staub, Team Lead August 8, 2011 San Antonio, Texas U.S. Energy Information Administration Independent
U.S. EIA s Liquid Fuels Outlook NCSL 2011 Energy Policy Summit: Fueling Tomorrow s Transportation John Staub, Team Lead August 8, 2011 San Antonio, Texas U.S. Energy Information Administration Independent
Response and Outlook for. Nancy E. Kinner Coastal Response Research Center University of New Hampshire
 Oil on Troubled Waters: Response and Outlook for Recovery in the Gulf of Mexico Nancy E. Kinner Coastal Response Research Center University of New Hampshire 1 Marine Oil Spills Tankers: Trend is Decreasing
Oil on Troubled Waters: Response and Outlook for Recovery in the Gulf of Mexico Nancy E. Kinner Coastal Response Research Center University of New Hampshire 1 Marine Oil Spills Tankers: Trend is Decreasing
Ch 19. Fossil Fuels, Their Impacts, and Energy Conservation. Part 2: Environmental Issues and the Search for Solutions
 Ch 19 Fossil Fuels, Their Impacts, and Energy Conservation Part 2: Environmental Issues and the Search for Solutions PowerPoint Slides prepared by Jay Withgott and Heidi Marcum Copyright 2006 Pearson Education,
Ch 19 Fossil Fuels, Their Impacts, and Energy Conservation Part 2: Environmental Issues and the Search for Solutions PowerPoint Slides prepared by Jay Withgott and Heidi Marcum Copyright 2006 Pearson Education,
first oil from deep offshore and remote regions, then to tar-sands, shale, and synthetic liquids from coal.
 U.S. HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES COMMITTEE ON FOREIGN AFFAIRS National security consequences of U.S. oil dependence John Deutch March 22, 2007 Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge MA, 02139 Mr.
U.S. HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES COMMITTEE ON FOREIGN AFFAIRS National security consequences of U.S. oil dependence John Deutch March 22, 2007 Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge MA, 02139 Mr.
TEKS Lesson 7.8C: Effects of Human Activity on Surface Water and Groundwater
 Class ----- Date -------- TEKS Lesson 7.SC TEKS 7.8e Model the effects of human activity on groundwater surface water in a watershed. and TEKS Lesson 7.8C: Effects of Human Activity on Surface Water and
Class ----- Date -------- TEKS Lesson 7.SC TEKS 7.8e Model the effects of human activity on groundwater surface water in a watershed. and TEKS Lesson 7.8C: Effects of Human Activity on Surface Water and
Remote Sensing and Non-renewable Energy Resources
 Remote Sensing and Non-renewable Energy Resources A presentation by Gregory Herman, TCNJ 2015 adapted from prior presentations by Karl Muessig, the University of West Florida, and Exxon-Mobil Corp Common
Remote Sensing and Non-renewable Energy Resources A presentation by Gregory Herman, TCNJ 2015 adapted from prior presentations by Karl Muessig, the University of West Florida, and Exxon-Mobil Corp Common
Section 1. Electricity and Your Community. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 7 Earth s Natural Resources Section 1 Electricity and Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Compare energy resources used to generate electricity in the United
Chapter 7 Earth s Natural Resources Section 1 Electricity and Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Compare energy resources used to generate electricity in the United
Nonrenewable Energy Resources. Energy: Conservation and Transfer
 Nonrenewable Energy Resources Energy: Conservation and Transfer Warm up 1. Which form of energy does a battery store? a. Nuclear energy b. Thermal energy c. Chemical energy d. Electrical energy 2. When
Nonrenewable Energy Resources Energy: Conservation and Transfer Warm up 1. Which form of energy does a battery store? a. Nuclear energy b. Thermal energy c. Chemical energy d. Electrical energy 2. When
Name Date Class. How do fuels provide energy? What are the three major fossil fuels? Why are fossil fuels considered nonrenewable resources?
 Chapter 12 Energy and Material Resources Section 1 Summary Fossil Fuels How do fuels provide energy? What are the three major fossil fuels? Why are fossil fuels considered nonrenewable resources? A fuel
Chapter 12 Energy and Material Resources Section 1 Summary Fossil Fuels How do fuels provide energy? What are the three major fossil fuels? Why are fossil fuels considered nonrenewable resources? A fuel
Sixth Grade Energy and Conservation Unit Parent Background Information
 Sixth Grade Energy and Conservation Unit Parent Background Information WHAT IS ENERGY? The nature of energy is very complex, but it is best described by these characteristics: energy is the ability to
Sixth Grade Energy and Conservation Unit Parent Background Information WHAT IS ENERGY? The nature of energy is very complex, but it is best described by these characteristics: energy is the ability to
Title: Wildlife Rescue. By Elizabeth Trowbridge. Theme: Oil spills can have a wide variety of effects on wildlife.
 Title: Wildlife Rescue By Elizabeth Trowbridge Theme: Oil spills can have a wide variety of effects on wildlife. Objectives: - Students will identify major habitats of southcoastal Alaska and their inhabitants.
Title: Wildlife Rescue By Elizabeth Trowbridge Theme: Oil spills can have a wide variety of effects on wildlife. Objectives: - Students will identify major habitats of southcoastal Alaska and their inhabitants.
Overview of global crude oil reserve estimates and supply patterns. Professor Wumi Iledare LSU Center for Energy studies Baton Rouge, LA 70803
 Overview of global crude oil reserve estimates and supply patterns Professor Wumi Iledare LSU Center for Energy studies Baton Rouge, LA 70803 Presentation at Audubon Kiwanis Weekly Meeting Baton Rouge,
Overview of global crude oil reserve estimates and supply patterns Professor Wumi Iledare LSU Center for Energy studies Baton Rouge, LA 70803 Presentation at Audubon Kiwanis Weekly Meeting Baton Rouge,
Biology 112 Introduction to Ecology. QUIZZAM Energy. Chapter Number 10
 Chapter Number 10 1. Which of the following is a true statement regarding sustainable building design? 1. Construction costs are usually less than traditional building practices. 2. There are currently
Chapter Number 10 1. Which of the following is a true statement regarding sustainable building design? 1. Construction costs are usually less than traditional building practices. 2. There are currently
Fossil Fuels, Chemistry of Fuels. Supplemental Textbook Materials Chapter 11 Pages
 Fossil Fuels, Chemistry of Fuels Supplemental Textbook Materials Chapter 11 Pages 225-238 Energy and Chemical Reactions Heat released or consumed in chemical reactions Measured in calories Food calorie
Fossil Fuels, Chemistry of Fuels Supplemental Textbook Materials Chapter 11 Pages 225-238 Energy and Chemical Reactions Heat released or consumed in chemical reactions Measured in calories Food calorie
Large gas reserves are found in: The Arctic Islands Beaufort Sea-Mackenzie Delta Eastern Canada offshore basin Western Canada
 1 12. Natural Gas It is formed from the remains of plankton that fell to the bottom of the sea, which were changed into gases over millions of years Since natural gas is lighter than both oil and water
1 12. Natural Gas It is formed from the remains of plankton that fell to the bottom of the sea, which were changed into gases over millions of years Since natural gas is lighter than both oil and water
US Oil and Gas Import Dependence: Department of Energy Projections in 2011
 1800 K Street, NW Suite 400 Washington, DC 20006 Phone: 1.202.775.3270 Fax: 1.202.775.3199 Email: acordesman@gmail.com Web: www.csis.org/burke/reports US Oil and Gas Import Dependence: Department of Energy
1800 K Street, NW Suite 400 Washington, DC 20006 Phone: 1.202.775.3270 Fax: 1.202.775.3199 Email: acordesman@gmail.com Web: www.csis.org/burke/reports US Oil and Gas Import Dependence: Department of Energy
Module 12: Oceanography Topic 6 Content: Ocean Pollution Notes. Ocean Pollution
 Ocean Pollution 1 Ocean pollution is an important modern-day environmental issue. Pollution occurs when chemical, physical, and/or biological agents are introduced into an environment and cause undesirable
Ocean Pollution 1 Ocean pollution is an important modern-day environmental issue. Pollution occurs when chemical, physical, and/or biological agents are introduced into an environment and cause undesirable
Conventional Energies (Oil & Gas)
 13 Conventional Energies (Oil & Gas) 162 Conventional Energies (Oil & Gas) Conventional Energies (Oil & Gas) I. History and Background The first documented systematic oil exploration and drilling in Iran
13 Conventional Energies (Oil & Gas) 162 Conventional Energies (Oil & Gas) Conventional Energies (Oil & Gas) I. History and Background The first documented systematic oil exploration and drilling in Iran
Earth's Systems: Natural resources
 Earth's Systems: Natural resources By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 04.13.17 Word Count 764 Level MAX Water, a renewable resource, gushes from a spring in Brazil. Photo by: Jonathan
Earth's Systems: Natural resources By Encyclopaedia Britannica, adapted by Newsela staff on 04.13.17 Word Count 764 Level MAX Water, a renewable resource, gushes from a spring in Brazil. Photo by: Jonathan
Overview. Key Energy Issues to Economic Growth
 Key Energy Issues to 225 The Energy Information Administration (EIA), in preparing model forecasts for its Annual Energy Outlook 25 (AEO25), evaluated a wide range of current trends and issues that could
Key Energy Issues to 225 The Energy Information Administration (EIA), in preparing model forecasts for its Annual Energy Outlook 25 (AEO25), evaluated a wide range of current trends and issues that could
Period 25: Energy from Wind and Biomass
 Period 25: Energy from Wind and Biomass Activity 25.1: Causes of Winds 1) The Earth s winds a) What causes wind circulation from the equator to the high latitudes? The uneven heating of the Earth s surface
Period 25: Energy from Wind and Biomass Activity 25.1: Causes of Winds 1) The Earth s winds a) What causes wind circulation from the equator to the high latitudes? The uneven heating of the Earth s surface
Unit 4. The secondary sector 1. The secondary sector - Industry is the activity that transforms raw materials into manufactured products.
 Unit 4. The secondary sector 1. The secondary sector - Industry is the activity that transforms raw materials into manufactured products. Industry requires raw materials, energy sources (provide the force)
Unit 4. The secondary sector 1. The secondary sector - Industry is the activity that transforms raw materials into manufactured products. Industry requires raw materials, energy sources (provide the force)
Chapter 1. Preliminaries
 Environmental Transport and Fate Chapter 1 Preliminaries Benoit Cushman-Roisin Thayer School of Engineering Dartmouth College Context possible effluent treatment How much? How clean? resources Industrial
Environmental Transport and Fate Chapter 1 Preliminaries Benoit Cushman-Roisin Thayer School of Engineering Dartmouth College Context possible effluent treatment How much? How clean? resources Industrial
Oil and natural gas: market outlook and drivers
 Oil and natural gas: market outlook and drivers for American Foundry Society May 18, 216 Washington, DC by Howard Gruenspecht, Deputy Administrator U.S. Energy Information Administration Independent Statistics
Oil and natural gas: market outlook and drivers for American Foundry Society May 18, 216 Washington, DC by Howard Gruenspecht, Deputy Administrator U.S. Energy Information Administration Independent Statistics
Energy. Solar Energy. Energy Resource A natural resource that. humans use to generate energy. Can be renewable are nonrenewable.
 Energy Solar Energy Energy Resource A natural resource that humans use to generate energy. Can be renewable are nonrenewable. energy sources are replaced by natural processes at least as quickly as they
Energy Solar Energy Energy Resource A natural resource that humans use to generate energy. Can be renewable are nonrenewable. energy sources are replaced by natural processes at least as quickly as they
LNG Facts A Primer. Presentation before US Department of Energy, Office of Fossil Energy, LNG Forums. March 10, Kristi A. R.
 LNG Facts A Primer Presentation before US Department of Energy, Office of Fossil Energy, LNG Forums March 10, 2006 Kristi A. R. Darby Center for Louisiana State University Overview What is Natural Gas?
LNG Facts A Primer Presentation before US Department of Energy, Office of Fossil Energy, LNG Forums March 10, 2006 Kristi A. R. Darby Center for Louisiana State University Overview What is Natural Gas?
Name Date Class. Living in North Africa, Southwest Asia, and Central Asia
 For use with textbook pages 463 468. Living in North Africa, Southwest Asia, and Central Asia Terms to Know arable Suitable for farming (page 464) commodity An economic product (page 465) petrochemical
For use with textbook pages 463 468. Living in North Africa, Southwest Asia, and Central Asia Terms to Know arable Suitable for farming (page 464) commodity An economic product (page 465) petrochemical
Chapter 20 Air Pollution
 Chapter 20 Air Pollution Overview of Chapter 20 Atmosphere as a Resource Types and Sources of Air Pollution Effects of Air Pollution Controlling Air Pollution in the US Ozone Depletion in the Stratosphere
Chapter 20 Air Pollution Overview of Chapter 20 Atmosphere as a Resource Types and Sources of Air Pollution Effects of Air Pollution Controlling Air Pollution in the US Ozone Depletion in the Stratosphere
Nonrenewable Energy Resources 5.1
 Nonrenewable Energy Resources 5.1 I. Energy Some energy resources on Earth are being used faster than nature can replace them these are called nonrenewable energy resources Most of the energy resources
Nonrenewable Energy Resources 5.1 I. Energy Some energy resources on Earth are being used faster than nature can replace them these are called nonrenewable energy resources Most of the energy resources
World Energy Outlook 2035: A focus on LNG supply and demand dynamics
 World Energy Outlook 2035: A focus on LNG supply and demand dynamics M.H. Siddiqui, Prescience, USA 1 Agenda The Energy Outlook in 2035 involving major landscape changes in supply, demand, fossil fuels,
World Energy Outlook 2035: A focus on LNG supply and demand dynamics M.H. Siddiqui, Prescience, USA 1 Agenda The Energy Outlook in 2035 involving major landscape changes in supply, demand, fossil fuels,
Urban Environmental Excursions
 Wayne State University Environmental Science Program Urban Environmental Excursions Fall 2007: Energy and Air Quality Where does our GASOLINE come from? How is our ELECTRICITY made? What ultimately happens
Wayne State University Environmental Science Program Urban Environmental Excursions Fall 2007: Energy and Air Quality Where does our GASOLINE come from? How is our ELECTRICITY made? What ultimately happens
Annual Energy Outlook 2010 Reference Case
 Annual Energy Outlook 21 Reference Case The Paul H. Nitze School of Advanced International Studies December 14, 29 Washington, DC Richard Newell, Administrator Richard Newell, SAIS, December 14, 29 1 How
Annual Energy Outlook 21 Reference Case The Paul H. Nitze School of Advanced International Studies December 14, 29 Washington, DC Richard Newell, Administrator Richard Newell, SAIS, December 14, 29 1 How
I ve Got the Power! Types of Energy and how it affects our lives.
 I ve Got the Power! Types of Energy and how it affects our lives. Categories Energy is broken down into 2 categories RENEWABLE And NON-RENEWABLE RENEWABLE Energy that comes from a source that can be replenished
I ve Got the Power! Types of Energy and how it affects our lives. Categories Energy is broken down into 2 categories RENEWABLE And NON-RENEWABLE RENEWABLE Energy that comes from a source that can be replenished
Environmental Science 101. Chapter 11 Water Pollution
 Environmental Science 101 Chapter 11 Water Pollution Water Pollution Any change in water quality that causes harm to humans and other living organisms. Review Renewable vs nonrenewable Hydrological cycle
Environmental Science 101 Chapter 11 Water Pollution Water Pollution Any change in water quality that causes harm to humans and other living organisms. Review Renewable vs nonrenewable Hydrological cycle
COAL AND PETROLEUM. 1. What are Inexhaustible and Exhaustible Natural Resources? Answer: Inexhaustible Natural Resources:
 COAL AND PETROLEUM Main Concepts and Results: Coal, petroleum and natural gas are fossil fuels. Fossil fuels were formed from the dead remains of living organisms millions of years ago. Fossil fuels are
COAL AND PETROLEUM Main Concepts and Results: Coal, petroleum and natural gas are fossil fuels. Fossil fuels were formed from the dead remains of living organisms millions of years ago. Fossil fuels are
Plate Tectonics and the Geology of Montana. Energy Resources
 Plate Tectonics and the Geology of Montana Energy Resources http://www.scotese.com/earth.htm http://www.scotese.com/earth.htm http://www.scotese.com/earth.htm http://www.scotese.com/earth.htm http://www.scotese.com/earth.htm
Plate Tectonics and the Geology of Montana Energy Resources http://www.scotese.com/earth.htm http://www.scotese.com/earth.htm http://www.scotese.com/earth.htm http://www.scotese.com/earth.htm http://www.scotese.com/earth.htm
Work, Energy and Power.
 Work, Energy and Power. Work - Definition Of Work Work is the transfer of energy. If you put energy into an object, then you do work on that object. If an object is standing still, and you get it moving,
Work, Energy and Power. Work - Definition Of Work Work is the transfer of energy. If you put energy into an object, then you do work on that object. If an object is standing still, and you get it moving,
Bellringer. What Lies Beneath? Natural Resources
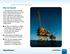 What Lies Beneath? Do deposits of oil or natural gas lie deep beneath this section of the ocean? The owners of these exploration rigs hope so. These rigs are used to drill small test wells in the ocean
What Lies Beneath? Do deposits of oil or natural gas lie deep beneath this section of the ocean? The owners of these exploration rigs hope so. These rigs are used to drill small test wells in the ocean
Fossil, Biomass, and Synthetic Fuels
 Fossil, Biomass, and Synthetic Fuels Why do we care about heat engines? Waste heat U. S. electricity generation = 1.3 x 10 19 J/y Assuming 40% efficiency = 8 x 10 18 J/y waste heat Volume Lake Superior
Fossil, Biomass, and Synthetic Fuels Why do we care about heat engines? Waste heat U. S. electricity generation = 1.3 x 10 19 J/y Assuming 40% efficiency = 8 x 10 18 J/y waste heat Volume Lake Superior
Mixtures in Industry
 3.7 Mixtures in Industry Key Question: How are mixtures separated in industry? Many industries separate mixtures to make pure products. In this section, you will learn about three industries that separate
3.7 Mixtures in Industry Key Question: How are mixtures separated in industry? Many industries separate mixtures to make pure products. In this section, you will learn about three industries that separate
Water Pollution. Objective: Name, describe, and cite examples of the eight major types of water pollution.
 Water Pollution Objective: Name, describe, and cite examples of the eight major types of water pollution. Types of Water Pollution Water pollutants are divided into eight categories: 1. Sediment pollution
Water Pollution Objective: Name, describe, and cite examples of the eight major types of water pollution. Types of Water Pollution Water pollutants are divided into eight categories: 1. Sediment pollution
World Energy Outlook 2010
 World Energy Outlook 2010 Nobuo Tanaka Executive Director International Energy Agency Cancun, 7 December 2010, IEA day The context: A time of unprecedented uncertainty The worst of the global economic
World Energy Outlook 2010 Nobuo Tanaka Executive Director International Energy Agency Cancun, 7 December 2010, IEA day The context: A time of unprecedented uncertainty The worst of the global economic
8. Confusion About Renewable Energy. Gail Tverberg Energy Economics and Analysis Modeling
 8. Confusion About Renewable Energy Gail Tverberg Energy Economics and Analysis Modeling We get free energy from the sun! Physicists describe the situation as a thermodynamically open system! Humans, animals,
8. Confusion About Renewable Energy Gail Tverberg Energy Economics and Analysis Modeling We get free energy from the sun! Physicists describe the situation as a thermodynamically open system! Humans, animals,
Energy and Resources-- Cuba
 Energy and Resources-- Cuba EarthTrends Country Profiles Energy Production and Consumption Cuba Central America & Caribbean World (in thousand metric tons of oil equivalent) {a} Total energy production,
Energy and Resources-- Cuba EarthTrends Country Profiles Energy Production and Consumption Cuba Central America & Caribbean World (in thousand metric tons of oil equivalent) {a} Total energy production,
Issues with petroleum
 Issues with petroleum Limited reserves (near peak in Hubbert curve) Trade deficit (most oil imported) Externalities (military costs, environmental impacts) Environmental pollution (persistent combustion
Issues with petroleum Limited reserves (near peak in Hubbert curve) Trade deficit (most oil imported) Externalities (military costs, environmental impacts) Environmental pollution (persistent combustion
THE GULF OF MEXICO OIL SPILL: MAPPING THE ENVIRONMENTAL AND
 THE GULF OF MEXICO OIL SPILL: MAPPING THE ENVIRONMENTAL AND SOCIAL COSTS OF THE GLOBAL OIL BUSINESS In April 2010, the Deepwater Horizon oil rig exploded in the Gulf of Mexico, leading to the deaths of
THE GULF OF MEXICO OIL SPILL: MAPPING THE ENVIRONMENTAL AND SOCIAL COSTS OF THE GLOBAL OIL BUSINESS In April 2010, the Deepwater Horizon oil rig exploded in the Gulf of Mexico, leading to the deaths of
Coal is obtained from mines. It's a black solid material that must be transported by ships, trains or big trucks to the power plants where it's burnt
 Energy Sources Fossil Fuels Coal, Oil and Gas are called "fossil fuels" because they have been formed from the fossilized remains of prehistoric plants and animals. They provide most of the world's total
Energy Sources Fossil Fuels Coal, Oil and Gas are called "fossil fuels" because they have been formed from the fossilized remains of prehistoric plants and animals. They provide most of the world's total
The Global Reaction to Water and Air Pollution
 The Global Reaction to Water and Air Pollution By History.com, adapted by Newsela staff on 05.30.17 Word Count 900 Level 1160L White plume smoke containing many pollutants is emitted from a quenching tower
The Global Reaction to Water and Air Pollution By History.com, adapted by Newsela staff on 05.30.17 Word Count 900 Level 1160L White plume smoke containing many pollutants is emitted from a quenching tower
