Spatial Disparity of Groundwater Depletion in Dhaka City
|
|
|
- Bernice Webster
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 15 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 31 August to 2 September 2017 Spatial Disparity of Groundwater Depletion in Dhaka City Dr. Md. Serajul Islam Farzeen Farhana Islam Abstract [Groundwater is of course a valuable natural resource for the people of Dhaka City as surface water such as lake, river, reservoir etc. are not accessible to them sufficiently. People of Dhaka City depend on groundwater specially to meet their urgent daily needs. But the present conditions of groundwater in the city are not favorable for its population. In many parts of the city there is scarcity of pure water. This study shows that the groundwater in Dhaka city is declining at an alarming rate. The continuous over withdrawal of ground water and irregular and insufficient recharge causes depletion of groundwater. Rapid growing urbanization in the past 30 years also contributed to the present condition of Dhaka City. Recently, it is found out that the declining trend of groundwater in Dhaka City is 3 meters per year. Moreover, predictions show that the demand is increasing day by day and no chances of improving the situation is there. The volume of groundwater in storage is decreasing in many areas of the Dhaka City due to permanent over pumping. Thus, it has become obligatory to find out solutions for improvement. Therefore, scientific research on groundwater depletion in Dhaka City is very crucial to bring out fruitful solutions.] Keywords : Spatial disparity, Ground water, Depletion, Dhaka City, Introduction In the past few decades the groundwater of many parts of Bangladesh has declined to a large extent. Many areas of the capital Dhaka showed similar outcomes. Indeed, most densely populated areas of the country faces relatively more depletion of groundwater than others. But still people are unaware of this acute condition. One of the reasons of this unawareness is lack of availability of information to the public domain. Many research works have been done with the same issue, but very few books and articles are written on this particular issue of groundwater decline in Dhaka City. Moreover, every day the condition of groundwater is changing. Therefore, updated study is required on the topic since it s being one of the vital problems of the country which is likely to become a threat to the survival of the future Dhaka as well as of the future Bangladesh. Background of the study The heart of Bangladesh, Dhaka City has been noticed with threatening decline of groundwater last two decades. The main reasons lie under overconsumption and lack of recharge due to urbanization. Almost 82 % of the supply of water in Dhaka City is depended on groundwater. To fulfill this huge demand of water, groundwater level is declining by 2-3 meters each year (Anwar Zahid, 2011). Considering the existing depletion rate, the study predicts that the groundwater table will go down to about 110 to 115 meters by 2050 if any preventive measure would not be taken. The Ground water Hydrology (GWH) department of Bangladesh Water Development Board (BWDB) has placed 1250 piezometers throughout the country to monitor the depth of the groundwater level. All the piezometers placed in Dhaka City shows the declining trend of water table. In the past, the underground vacuum in Dhaka used to be recharged by the water flowing from the north aquifer of Gazipur district and its adjoining areas. But now these areas also suffer from severe depletion of groundwater level. For such reasons the present study has been taken as of a great importance to show the trend in groundwater decline in Dhaka City. Details of the study area Dhaka City is situated in the middle of Bangladesh. Being the capital of the country Dhaka is facing more problems due to groundwater depletion. The groundwater level of main commercial and residential areas of Dhaka City is studied. Seven important points as Mirpur, Motijheel, Mohammadpur, Gulshan, Sutrapur, Lalbagh and Dhanmondi have been taken into consideration are intensely studied. Findings of the study showed a drastic fall in groundwater level since Geographically Dhaka City is located within the Latitude and Longitude bounded by Gazipur at the North, Narayanganj at the east, Savar at the North-West, Keraniganj at the South-West. The river Buriganga flows through South-West end of the city, Turag flows from the North-West end and Shitalaxya (Tongi Khal) at the Southeastern part of the city. The city is situated on the southern part of the Pleistocene alluvial terrace, Madhupur Tract. Most part of the Dhaka city is dominated by Holocene deposits and have developed as low-lying flood plains. The elevation of the city ranges from 2 to 13 meters above sea level. The subsurface of Dhaka is composed of 10 meters thick compact upper clay which hinders rainwater to penetrate down into the soil surface (GSB, 2013). With a few exceptions, Dhaka has a tropical monsoon climate characterized by wide seasonal variations in rainfall, high temperatures, and high humidity. Figure 01 : Study area
2 Source : BCAS, 1999 Data Source and Identification It was very important to have clear understanding on the topic and present situation of the Dhaka aquifers to adhere to the expert community. Interviews regarding causes and consequences of groundwater declining in Dhaka were made and the declining trend was analyzed. Many experts were approached from the Department of Geography and Environment, and Geology, University of Dhaka, Institute of Water Modeling (IWM), DWASA, BWDB to present their important experiences. The interviews were nonstructured, only consists of open ended questions. In conducting the interview a Cold Calling process was applied. The prime source of information was secondary data collection. Secondary data on level of groundwater from 1970 to 2010 were collected from Ground Water Circle II (GWC II) under Groundwater Hydrology section of BWDB. Groundwater level data from more than10 piezometers around Dhaka city were collected at regular intervals. Data on depth of water in different parts of Dhaka city in various times were collected from Water & Hydrology Department of DWASA. Ground water assessment and demand management data were collected from IWM, Dhaka. Besides this, relevant data and information were collected from the Department of Geology, University of Dhaka. Findings and analysis Ground water level Declining of groundwater level has become one of the main problems of Dhaka City. Therefore, to understand the present condition of water level and to work for its stability it is very important to research on the issue. It is high time that practical steps should be taken to stop the depletion of groundwater and use it in a sustainable manner. The piezometric survey made by the Bangladesh Water Development Board (BWDB) represent the data of seven important points of Dhaka city obtained by a survey in 2010 given below. Table 1: Location and recorded groundwater level of selected piezometers in Dhaka City Well ID Location Thana Latitude Longitude Groundwater Level in meters (2010) GT Joar Shahara Cantonment GT Khilgaon Sabujbag GT Palashi Lalbagh GT Monipur Mirpur GT PC Culture Mohammadpur GT Sultanganj Dhanmondi GT Gandaria Sutrapur Source: Bangladesh Water Development Board (BWDB), 2014 Groundwater declining scenario The reduction of groundwater table in 30 years from 1980 to 2010 showing continuous declining scenario. It is clear that the trend of depletion or reduction of groundwater is alarming and urgently needed to take necessary action to reduce the depletion as well as to save the city people from severe natural disaster. Comparative study of ground water level between the years 1980 and 1990 shows that water table decline were almost similar in Mirpur, Mohammadpur, Dhanmondi, Gulshan. In 1990, Sabujbagh along with Lalbagh showed extreme decline. By 2010 Dhanmondi and Mirpur seemed to have highest depth of groundwater table (figure 16). But in the period of 2000 to 2010 the highest depletion rate found in Mirpur and Dhanmondi area. Declining trends of different thanas (administrative unit) mentioned in table 1 described below: Mirpur The declining trend is quite high at Mirpur area. From 1980s to 1990s the water table lowered from 8 meters to 15 meters. But from 1990s it declined in double rate in every decade. Within the span of 10 years from 1990 to 2000 groundwater level decreased from 15 to 35 meters. The worst situation found between 2000 and 2005 when water level dropped as much as 28 meters in only 5 years. Since then a relatively stable condition is observed in the height of the water table. No specific causes identified behind this depletion. But it is said by the local people that, this time (2000 to 2005) the number of resident population and number of building rapidly increased at Mirpur area. Mohammadpur The level of groundwater at Mohammadpur area found lowered maximum between 1990 to 1995 by 6 meters and 2000 to 2005 by 12 meters. The current depth (2014) of groundwater is 31 meters which is relatively lower than other parts of the city. It is assumed that due to the goodness of situation of some nearby lakes and stream, the groundwater in this area still can be found within 30 meters below whereas in many other parts of the city it has
3 Groundwater Level(m) GW Level (m) gone under 60 meters. In the period 2000 to 2005 the depletion rate of the ground water of this area was rapid than other times from 1980 to Dhanmondi Ground water level at Dhanmondi area shows gradual declining trend from 1990 to present. Within the period of 10 years from 2000 to 2010, depth of groundwater table increased about 26 meters. Due to rapid increasing urbanization followed by population growth, the area observed scarcity of fresh water. The present depth of the water table is around 66 meters below the ground surface. The water table dropped from 15 to 60 meters with average declining trend of 3 meters per year within 15 years from 1990 to Lalbagh In the Lalbagh area, the declining trend is relatively low compared to the other areas of the Dhaka city. Within the time span of 5 years from 1981 to 1986 groundwater table declined about15 meters with an annual rate of 3 meters. Major gradual declining trend was noticed between1995 to 2001 and was sbout 17 meters. During this time, the yearly declining rate was 2.8 meters per year. In the period of 1986 to 1995 the declining rate of groundwater in Lalbag area was very slow. Only four to five meters fall of water level noticed within this period. Sutrapur Sutrapur area experiences one of the lowest trend areas of ground water depletion in the entire Dhaka city with an average declining rate less than 1 meter per year. This rate was more or less constant in last 30 years. From the year 1980 to 1990 the declining rate found quite slow. But in the period of 1990 to 2000 the trend of decline found comparatively high. In this period ground water level declined from 11 to 20 meters. It is the highest declining rate in this area for about 30 years long. After 2000 the declining trend is almost stable and more or less constant till now. Sabujbag Since 1980 the area Sabujbag experienced continuous declining trend in its water table as shown in the figure below. From the year 1990 to 1998 the declining rate was high. From 1999 to 2002 the same trend found gradual running down. In 2001, it was 3.5 meters per year and in 2002, it increased to 5.58 meters per annum. Thus the rate of groundwater depletion is becoming higher in short time intervals. After 2002, 2003 noticed no more decrease in water table height. Gulshan Gradual decline of groundwater has been observed at Gulshan area from 1998 to The annual rate of declining water table was 2.5meters. But still compared to the other areas of Dhaka city, at relatively low depth water can be found due to the presence of Gulshan Lake. In the period of 1990 to 1998, rapid declining trend of groundwater found in this area. After this period till 2003 the running down rate of groundwater level found slow and gradual. Spatial Disparity in Groundwater Depletion from 1980 to 2010 Throughout the Dhaka City, depletion of groundwater level is observed. There are variations in current groundwater level and in the rate of its decline in different areas of the city. Due to difference in topography, geology, environment, population and other factors this disparity is observed. The areas which are more populated show high depth of water table than that of the less populated areas. Rapid and alarming depletion of water table found in the Mirpur and Dhanmondi are where the depletion goes accordingly from 8.36 and from to meters in the this period (1980 to 2010). Second highest depletion found in the Sabujbag area from 3.13 to 54.4 meters. Sutrapur, Cantonment and Mohammadpur area found comparatively less depletion rate. The depletion rate of the selection eight points of the Dhaka city given below (table 2). Figure 02: Spatial Disparity in groundwater decline in 1980 & 1990 in Dhaka City Figure 03: Spatial Disparity in groundwater decline in 2000 & 2010 in Dhaka City Source: Bangladesh Water Development Board (BWDB), 2014 Thana Thana
4 Table 2 : Depth of Groundwater Table in different areas of Dhaka City in different year ( ) Year Mirpur Mohammadp Dhanmondi Gulshan Cantonment Lalbag Sabujbag Sutrapur ur Source: Bangladesh Water Development Board, 2014 meters. Only Sutrapur, Cantonment and Lalbagh showed Spatial Disparity of Groundwater Level from 1980 to 2010 The maximum depth of water table in 1980 was around 10 meter in Dhanmondi and the minimum was 1.67 meters in Lalbagh. The blue areas in the map express depth of groundwater is relatively low, the red areas indicate the depth less than 20 meters. The highest depth was in Sabujbagh. From the map it is noticed that by 1995, the central and southern part of Dhaka had high depth of groundwater table, while in 1990, the central part had relatively low depth of groundwater table. The map of 2000 shows that, in Motijheel, Hazaribagh, Sabujbagh, depth is relatively high (figure 02). In Mirpur, Dhanmondi the depth of water table was high. The closely Mohammadpur, Gulshan the depth was higher than Sabujbagh, Sutrapur and Lalbagh. But overall the condition of groundwater table was much better than spaced contours in these areas show high fluctuation of groundwater table within very small spatial distance. Thus the depth of groundwater level in these areas decreased present condition. Five years later in 1985, the depth rapidly. In Mirpur, groundwater can be found at lower increased in all the seven thanas. Mirpur, Mohammadpur, Dhanmondi and Sabujbagh showed similar depth. Gulshan and Sutrapur displayed lowest depth of groundwater table. In these 5 years lowest declining rate was of Gulshan area that is 0.08, whereas highest declining rate was in Lalbagh area is meters (table 2). From the map of 1990, it is depth. In Sutrapur, the depth of water level was still low. In Gulshan, Mohammadpur the rate of decline was lower than other areas. In 2005, the condition in Mirpur became vulnerable. The depth of groundwater became 63 meters. In 5 years it increased 29.8 meters with an annual rate of 5.56 meters per year.very high depth of groundwater table seen that in the southern part of the city the crisis of developed also in Motijheel, Sabujbagh, Ramna, groundwater started developing quickly; mainly in Lalbagh, Sabujbagh, Ramna, Motijheel areas. Population in these areas was rising quickly and to fulfill the demand good amount of groundwater was being extracted which resulted in gradual depletion of water in these areas. While in the northern part of the city, in Cantonment, Uttara the groundwater depth was relatively low as population in these areas were still very low. By 1995, depth of Dhanmondi, touching to almost 60 meters. Mohammadpur and Sutrapur were relatively in good conditions in the southern Dhaka. The northern Dhaka also had a low water table depth. The depth of groundwater table in 2010 was similar to that of Only in Gulshan, the water table fell by 5.36 meters and in Dhanmondi by 5.47 meters. In the other areas the depth of the water table increased 1 or 2 meters. groundwater in all areas increased more or less about 20 Figure 04 : Depth of Groundwater Table in Dhaka City in 1980 Figure 05 : Depth of Groundwater Table in Dhaka City in 1985 Figure 06: Depth of Groundwater Table in Dhaka City in 1990 Figure 07: Depth of Groundwater Table in Dhaka City in 1995 Figure 08: Depth of Groundwater Table in Dhaka City in 2000 Figure 09: Depth of Groundwater Table in Dhaka City in 2005
5 Figure 10 : Depth of Groundwater Table in Dhaka City in 2010 Source: Bangladesh Water Development Board, 2014 Causes of Spatial Disparity in Groundwater Level in Dhaka City Throughout the recent past 30 years Dhanmondi, Motijheel, Mirpur, Hazaribagh, Ramna area showed drastic decline in groundwater table. Therefore, most of the southern part is affected by groundwater depletion because of high rate of urbanization, commercialization and increase of population in these areas. Sutrapur and Sabujbagh are the places in southern Dhaka where the depth of the water table is lower compared to other places. This is because of presence of water body and river nearby. Withdrawn of groundwater in Sutrapur area is high as the number of population is more compared to the other areas. On the other hand, the northern part of the city is relatively less populated and industrialized, thus the pressure in groundwater resources is low. As a result, the depth of the water table is relatively low. Apart from urbanization and industrialization the characteristics of soil plays an important role in water table depth. The clay content in soil is one of the most important characteristic of soil. Summery Findings From 1980 to present, groundwater level in different parts of Dhaka City found declined extensively. Mirpur, Sabujbagh, Motijheel, Dhanmondi, Ramna, Tejgaon, Hazaribagh show high rate of groundwater depletion. The rate is relatively low in Sutrapur, Cantonment and Uttara areas. The main reasons behind groundwater decline are overexploitation of water, population increase, urbanization, rainfall fluctuation etc. Groundwater decline has great impact on Dhaka City. It lead to water scarcity, rise of expanses in constructing well, hamper in food production, ecological imbalance in the city, earthquake risk and many other problems. Government has taken a number of policies to control the depletion of groundwater and to meet the demand of the people. Experts have suggested to control increase population and to reduce dependency on groundwater. Recommendations Artificial recharging of groundwater needs to be executed so that groundwater could be recharged sufficiently. Treatment of the pollutants and wastes must be ensured by the industries. No industry without a treatment plant for waste water should be permitted to setup. Proper implementation of existing laws, formulation of a specific groundwater law, initiatives to stop misusing supplied water can reduce the burden on groundwater. Reducing number of population of the city. River dredging, the main rivers of the country: Padma, Meghna, Jamuna, Brahmaputra and others should be dredged regularly.
6 Practicing rain water harvesting in every building of the Institute of Water Modelling (2013) Water Supply Master City should be developed as early as possible so that Plan for Dhaka City, demand of ground water could be minimized. Institute of Water Modelling, Resource Assessment and Finally, Government should look into the matter seriously Monitoring of Water Supply Sources of Dhaka City,IWM. to reduce the risk of natural hazard like earthquake or severe shortage of ground water in future. Conclusion Spatial disparity prevails in different areas of Dhaka City. Some areas show high declining trend and some low, but all the areas is subjected to lowering of water table. To have a sustainable groundwater utilization system the trend of groundwater decline must be stopped. By identifying reasons behind the spatial disparity, steps can be taken to reduce in different areas and stop groundwater declining. It is believed that this study can help to understand the real scenarios of ground water decline of the city Dhaka to the policy makers for their future plan. References Dhaka's groundwater drops 6m in 7 years. The Daily Star (25 th October, 2011) Retrieved May 3, 2014 from archive.thedailystar.net Groundwater level in Dhaka drops 3m a year (2013). Retrieved May 3, 2014 from risingbd.com Khan, A.K.M.,Md. TariqulAlam, Md. T. and. Islam, Md. J. (2010) Urbanization in Bangladesh: Present Status and Policy Implications, ASA University Review, Vol. 4 No. 2. Rahman,A.A, and Ravenscroft,P. (2003) Groundwater Resources and Development in Bangladesh, The University Press Limited: Dhaka. Rasheed, K.B.S. (2008) Bangladesh: Resource and Environmental Profile, A.H. Development Publishing House:Dhaka Shamsudduha, M.,Chandler,R.E., Taylor, R. G. and Ahmed, K. M. (2009) Recent trends in groundwater levels in a highly seasonal hydrological system: the Ganges- Brahmaputra-Meghna Delta.Retrived on April,2014, from html Tanim F. K. (2008, October 31) Groundwater decrease in Dhaka - research, the problems and counteractive steps to curb. Uddin, A.F.M andbaten, M. A. (2011) Water Supply of Dhaka City: Murky Future, the issue of access and inequality. Wadud,M.(2011)Dhaka turns to rainwater harvesting to ease water crisis, Thomson Reuters Foundation. Zahid,A., Hossain, A., Uddin, Md. E.,Deeba, F. (2004) Groundwater Level Declining Trend in Dhaka City Aquifer Zahid, A. and Ahmed, S. R.U., Groundwater Resources Development in Bangladesh: Contribution to Irrigation for Food Security and Constraints to Sustainability, Ground Water Hydrology Division, Bangladesh Water Development Board. Retrived on April, 2014, from /10/groundwater-decrease-indhaka-research.html
Groundwater Balance Study in the High Barind, Bangladesh. A.H.M.Selim Reza 1, Quamrul Hasan Mazumder 1 and Mushfique Ahmed 1
 Rajshahi University J. of Sci. 39, 11-26 (2011) ISSN 1681-0708 Groundwater Balance Study in the High Barind, Bangladesh A.H.M.Selim Reza 1, Quamrul Hasan Mazumder 1 and Mushfique Ahmed 1 1 Department of
Rajshahi University J. of Sci. 39, 11-26 (2011) ISSN 1681-0708 Groundwater Balance Study in the High Barind, Bangladesh A.H.M.Selim Reza 1, Quamrul Hasan Mazumder 1 and Mushfique Ahmed 1 1 Department of
Climate Change, Food and Water Security in Bangladesh
 12 29 March 2016 Climate Change, Food and Water Security in Bangladesh Haweya Ismail Research Analyst Global Food and Water Crises Research Programme Key Points Bangladesh s geographical location, poverty
12 29 March 2016 Climate Change, Food and Water Security in Bangladesh Haweya Ismail Research Analyst Global Food and Water Crises Research Programme Key Points Bangladesh s geographical location, poverty
100 YEAR FLOOD SIMULATION FOR DHAKA CITY USING MULTIPLE MODELS
 100 YEAR FLOOD SIMULATION FOR DHAKA CITY USING MULTIPLE MODELS lsmat Pervin 1,*, M. Feroz Islam 1, Imtiaz Taher 1, David Khan 1 1 Institute of Water Modelling, Bangladesh; * House # 496, Road # 32, New
100 YEAR FLOOD SIMULATION FOR DHAKA CITY USING MULTIPLE MODELS lsmat Pervin 1,*, M. Feroz Islam 1, Imtiaz Taher 1, David Khan 1 1 Institute of Water Modelling, Bangladesh; * House # 496, Road # 32, New
ASSESSMENT OF TRENDS AND MAJOR DRIVERS OF WATER POLICY TO INFORM SCENARIO DEVELOPMENT FOR INTEGRATED WATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT IN BANGLADESH
 ASSESSMENT OF TRENDS AND MAJOR DRIVERS OF WATER POLICY TO INFORM SCENARIO DEVELOPMENT FOR INTEGRATED WATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT IN BANGLADESH Catharien Terwisscha van Scheltinga Catharien.Terwisscha@wur.nl
ASSESSMENT OF TRENDS AND MAJOR DRIVERS OF WATER POLICY TO INFORM SCENARIO DEVELOPMENT FOR INTEGRATED WATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT IN BANGLADESH Catharien Terwisscha van Scheltinga Catharien.Terwisscha@wur.nl
Status, Quality and Management of Groundwater in India
 International Journal of Information and Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 3, Number 7 (2013), pp. 717-722 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com /ijict.htm Status,
International Journal of Information and Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 3, Number 7 (2013), pp. 717-722 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com /ijict.htm Status,
The role of dams in securing the surface water in the northern and eastern parts of the United Arab Emirates (UAE)
 Changes in Water Resources Systems: Methodologies to Maintain Water Security and Ensure Integrated Management (Proceedings of Symposium HS at IUGG, Perugia, July ). IAHS Publ.,. The role of dams in securing
Changes in Water Resources Systems: Methodologies to Maintain Water Security and Ensure Integrated Management (Proceedings of Symposium HS at IUGG, Perugia, July ). IAHS Publ.,. The role of dams in securing
CORFU PROJECT EXPERIENCE FROM THE RAPIDLY DEVELOPING CITY OF DHAKA, BANGLADESH
 CORFU PROJECT EXPERIENCE FROM THE RAPIDLY DEVELOPING CITY OF DHAKA, BANGLADESH S M Mahbubur Rahman 1,*, David M Khan 1, Abu Saleh Khan 1, M Monowar Hossain 1 1 Institute of Water Modelling, Bangladesh;
CORFU PROJECT EXPERIENCE FROM THE RAPIDLY DEVELOPING CITY OF DHAKA, BANGLADESH S M Mahbubur Rahman 1,*, David M Khan 1, Abu Saleh Khan 1, M Monowar Hossain 1 1 Institute of Water Modelling, Bangladesh;
Impact of Irrigation on Cropping Intensity and Potentiality of Groundwater in Murshidabad District of West Bengal, India
 International Journal of Ecosystem 2015, 5(3A): 55-64 DOI: 10.5923/c.ije.201501.08 Impact of Irrigation on Cropping Intensity and Potentiality of Groundwater in Murshidabad District of West Bengal, India
International Journal of Ecosystem 2015, 5(3A): 55-64 DOI: 10.5923/c.ije.201501.08 Impact of Irrigation on Cropping Intensity and Potentiality of Groundwater in Murshidabad District of West Bengal, India
The Dublin Statement on Water and Sustainable Development
 The Dublin Statement on Water and Sustainable Development Dublín, Ireland, January 31, 1992 Contents Introduction Guiding Principles Principle 1 Principle 2 Principle 3 Principle 4 The Action Agenda Alleviation
The Dublin Statement on Water and Sustainable Development Dublín, Ireland, January 31, 1992 Contents Introduction Guiding Principles Principle 1 Principle 2 Principle 3 Principle 4 The Action Agenda Alleviation
Issue paper: Aquifer Water Balance
 Issue paper: Aquifer Water Balance 1. Introduction And Background 1.1. Purpose and Scope The population in Kitsap County has grown rapidly in recent years and is expected to increase substantially in the
Issue paper: Aquifer Water Balance 1. Introduction And Background 1.1. Purpose and Scope The population in Kitsap County has grown rapidly in recent years and is expected to increase substantially in the
Groundwater resources in the Indo Gangetic Basin
 Groundwater resources in the Indo Gangetic Basin Resilience to climate change and abstraction Executive Summary Groundwater within the Indo Gangetic Basin (IGB) alluvial aquifer system forms one of the
Groundwater resources in the Indo Gangetic Basin Resilience to climate change and abstraction Executive Summary Groundwater within the Indo Gangetic Basin (IGB) alluvial aquifer system forms one of the
CHAPTER 13 OUTLINE The Hydrologic Cycle and Groundwater. Hydrologic cycle. Hydrologic cycle cont.
 CHAPTER 13 OUTLINE The Hydrologic Cycle and Groundwater Does not contain complete lecture notes. To be used to help organize lecture notes and home/test studies. Hydrologic cycle The hydrologic cycle is
CHAPTER 13 OUTLINE The Hydrologic Cycle and Groundwater Does not contain complete lecture notes. To be used to help organize lecture notes and home/test studies. Hydrologic cycle The hydrologic cycle is
CLIMATE AND DISASTER RESILIENCE OF GREATER DHAKA AREA: A MICRO LEVEL ANALYSIS. Bangladesh Development Series Paper No. 32
 Public Disclosure Authorized Climate and Disaster Resilience of Greater Dhaka Area: A Micro Level Analysis 101066 CLIMATE AND DISASTER RESILIENCE OF GREATER DHAKA AREA: A MICRO LEVEL ANALYSIS Public Disclosure
Public Disclosure Authorized Climate and Disaster Resilience of Greater Dhaka Area: A Micro Level Analysis 101066 CLIMATE AND DISASTER RESILIENCE OF GREATER DHAKA AREA: A MICRO LEVEL ANALYSIS Public Disclosure
Climate change science, knowledge and impacts on water resources in South Asia
 Climate change science, knowledge and impacts on water resources in South Asia DIAGNOSTIC PAPER 1 GUILLAUME LACOMBE, PENNAN CHINNASAMY Regional Conference on Risks and Solutions: Adaptation Frameworks
Climate change science, knowledge and impacts on water resources in South Asia DIAGNOSTIC PAPER 1 GUILLAUME LACOMBE, PENNAN CHINNASAMY Regional Conference on Risks and Solutions: Adaptation Frameworks
Unit 5 Lesson 1 What Is the Water Cycle? Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Water on the Move warm up 1 Water on the Move About three-fourths of Earth s surface is covered by water. Water on the Move Video!!! Water on the Move Water moves between Earth s surface and the atmosphere
Water on the Move warm up 1 Water on the Move About three-fourths of Earth s surface is covered by water. Water on the Move Video!!! Water on the Move Water moves between Earth s surface and the atmosphere
Japanese ODA Loan. Ex-Ante Evaluation
 Japanese ODA Loan Ex-Ante Evaluation 1. Project Country: People's Republic of Bangladesh Name of the Project: Haor Flood Management and Livelihood Improvement Project Loan Agreement: June 16, 2014 Loan
Japanese ODA Loan Ex-Ante Evaluation 1. Project Country: People's Republic of Bangladesh Name of the Project: Haor Flood Management and Livelihood Improvement Project Loan Agreement: June 16, 2014 Loan
Potential of Rainwater Harvesting in Dhaka City: An Empirical Study
 ASA University Review, Vol. 7 No. 1, January June, 2013 Potential of Rainwater Harvesting in Dhaka City: An Empirical Study Abstract Sabina Yeasmin * Khan Ferdousour Rahman ** The inability of public water
ASA University Review, Vol. 7 No. 1, January June, 2013 Potential of Rainwater Harvesting in Dhaka City: An Empirical Study Abstract Sabina Yeasmin * Khan Ferdousour Rahman ** The inability of public water
Rainwater Harvesting Structures - A Case Study
 Rainwater Harvesting Structures - A Case Study C.L.Jejurkar 1, N.S.Naik 2 1 Asso.Professor, SRES College of Engineering, Kopargaon, Dist. Ahmed Nagar, India 2 Asst. Professor, SRES College of Engineering,
Rainwater Harvesting Structures - A Case Study C.L.Jejurkar 1, N.S.Naik 2 1 Asso.Professor, SRES College of Engineering, Kopargaon, Dist. Ahmed Nagar, India 2 Asst. Professor, SRES College of Engineering,
Groundwater Drought Assessment for Barind Irrigation Project in Northwestern Bangladesh
 th International Congress on Modelling and Simulation, Adelaide, Australia, 6 December www.mssanz.org.au/modsim Groundwater Drought Assessment for Barind Irrigation Project in Northwestern Bangladesh S.K.
th International Congress on Modelling and Simulation, Adelaide, Australia, 6 December www.mssanz.org.au/modsim Groundwater Drought Assessment for Barind Irrigation Project in Northwestern Bangladesh S.K.
Numerical Simulation and Prediction of Groundwater Flow in a Coastal Aquifer of Southern India
 Journal of Water Resource and Protection, 2015, 7, 1483-1494 Published Online December 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jwarp http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jwarp.2015.717122 Numerical Simulation
Journal of Water Resource and Protection, 2015, 7, 1483-1494 Published Online December 2015 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jwarp http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jwarp.2015.717122 Numerical Simulation
Genetic Algorithm based Simulation Optimization Approach to Seawater Intrusion
 International Symposium on Genetic Algorithm based Simulation Optimization Approach to Seawater Intrusion 1313 Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM 2014) February 19 21, 2014, CWRDM, Kozhikode,
International Symposium on Genetic Algorithm based Simulation Optimization Approach to Seawater Intrusion 1313 Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM 2014) February 19 21, 2014, CWRDM, Kozhikode,
Texas Water Resources Institute
 Texas Water Resources Institute April 1975 Volume 1 No. 5 Opportunities for Artificial Recharge By Jim Valliant, Research Engineer, Texas Agricultural Experiment Station Put "dirty" water back underground--i'd
Texas Water Resources Institute April 1975 Volume 1 No. 5 Opportunities for Artificial Recharge By Jim Valliant, Research Engineer, Texas Agricultural Experiment Station Put "dirty" water back underground--i'd
A REVIEW OF THE ESTIMATIONS ON SEA LEVEL RISE FOR THE BAY OF BENGAL DUE TO CLIMATE CHANGE
 A REVIEW OF THE ESTIMATIONS ON SEA LEVEL RISE FOR THE BAY OF BENGAL DUE TO CLIMATE CHANGE Fariba Halim Aurin 1* and A.K.M. Saiful Islam 2 1 Graduate student, Institute of Water and Flood Management, University
A REVIEW OF THE ESTIMATIONS ON SEA LEVEL RISE FOR THE BAY OF BENGAL DUE TO CLIMATE CHANGE Fariba Halim Aurin 1* and A.K.M. Saiful Islam 2 1 Graduate student, Institute of Water and Flood Management, University
Groundwater Resource Management an introduction to its scope and practice
 Sustainable Groundwater Management: Concepts and Tools Sustainable Groundwater Management Concepts & Tools Briefing Note Series Note 1 Groundwater Resource Management an introduction to its scope and practice
Sustainable Groundwater Management: Concepts and Tools Sustainable Groundwater Management Concepts & Tools Briefing Note Series Note 1 Groundwater Resource Management an introduction to its scope and practice
Climate Change Adaptation Case Example: Adaptation in Bangladesh
 Climate Change Adaptation Case Example: Adaptation in Bangladesh Dr. Atiq Rahman Executive Director: Bangladesh Centre for Advanced Studies (BCAS) Founding Chairman: Climate Action Network South Asia (CANSA)
Climate Change Adaptation Case Example: Adaptation in Bangladesh Dr. Atiq Rahman Executive Director: Bangladesh Centre for Advanced Studies (BCAS) Founding Chairman: Climate Action Network South Asia (CANSA)
Concept of Flood Shelter to Cope with Flood
 M. A. Ali, S. M. Seraj and S. Ahmad (eds): ISBN 984-823-002-5 Concept of Flood Shelter to Cope with Flood M. J. B. Alam and Md. Hossain Ali Department of Civil Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering
M. A. Ali, S. M. Seraj and S. Ahmad (eds): ISBN 984-823-002-5 Concept of Flood Shelter to Cope with Flood M. J. B. Alam and Md. Hossain Ali Department of Civil Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering
Potential effects evaluation of dewatering an underground mine on surface water and groundwater located in a rural area
 Potential effects evaluation of dewatering an underground mine on surface water and groundwater located in a rural area ITRODUCTIO Michel Mailloux* Eng. M.Sc, Vincent Boisvert, M.Sc, Denis Millette, Eng.,
Potential effects evaluation of dewatering an underground mine on surface water and groundwater located in a rural area ITRODUCTIO Michel Mailloux* Eng. M.Sc, Vincent Boisvert, M.Sc, Denis Millette, Eng.,
Country Profile - Republic of Korea INFORMATION
 INFORMATION Geography The Republic of Korea occupies the southern portion of the Korean Peninsula, which extends some 1,100 km from the Asian mainland. This mountainous peninsula is flanked by the Yellow
INFORMATION Geography The Republic of Korea occupies the southern portion of the Korean Peninsula, which extends some 1,100 km from the Asian mainland. This mountainous peninsula is flanked by the Yellow
ESTIMATION OF IRRIGATION WATER SUPPLY FROM NONLOCAL WATER SOURCES IN GLOBAL HYDROLOGICAL MODEL
 ESTIMATION OF IRRIGATION WATER SUPPLY FROM NONLOCAL WATER SOURCES IN GLOBAL HYDROLOGICAL MODEL S. Kitamura 1, S. Yoshikawa 2, and S. Kanae 3 11 Tokyo Institute of Technology, kitamura.s.ag@m.titech.ac.jp:
ESTIMATION OF IRRIGATION WATER SUPPLY FROM NONLOCAL WATER SOURCES IN GLOBAL HYDROLOGICAL MODEL S. Kitamura 1, S. Yoshikawa 2, and S. Kanae 3 11 Tokyo Institute of Technology, kitamura.s.ag@m.titech.ac.jp:
Susan P. Abano Engineer IV Policy and Program Division
 National Water Resources Board Integrated Water Resources Management Susan P. Abano Engineer IV Policy and Program Division National Water Resources Board Outline Philippines Water Resources Situationer
National Water Resources Board Integrated Water Resources Management Susan P. Abano Engineer IV Policy and Program Division National Water Resources Board Outline Philippines Water Resources Situationer
Implications of Climate Change on Water Management in Bangladesh
 Implications of Climate Change on Water Management in Bangladesh February 6, 28 Jahir Uddin Chowdhury Professor Institute of Water and Flood Management BUET, Dhaka-1, Bangladesh 1. Introduction Bangladesh
Implications of Climate Change on Water Management in Bangladesh February 6, 28 Jahir Uddin Chowdhury Professor Institute of Water and Flood Management BUET, Dhaka-1, Bangladesh 1. Introduction Bangladesh
Priyanka Dissanayake Regional Coordinator GWP South Asia (GWP SAS) September 4, 2013 Kathmandu, Nepal
 Priyanka Dissanayake Regional Coordinator GWP South Asia (GWP SAS) September 4, 2013 Kathmandu, Nepal South Asia spreads over about 4% of the World s land area Possesses about 4.5% of the water resources
Priyanka Dissanayake Regional Coordinator GWP South Asia (GWP SAS) September 4, 2013 Kathmandu, Nepal South Asia spreads over about 4% of the World s land area Possesses about 4.5% of the water resources
Intended Nationally Determined Contributions
 Intended Nationally Determined Contributions Objective: The State of Kuwait - November 2015 In accordance with Decision 1/CP.19 and based on the information mentioned in decision 1/CP.20 which invites
Intended Nationally Determined Contributions Objective: The State of Kuwait - November 2015 In accordance with Decision 1/CP.19 and based on the information mentioned in decision 1/CP.20 which invites
27 29 January Washington DC - USA
 27 29 January Washington DC - USA Paper of Mr. Jean - François DONZIER General Manager International Office for Water Permanent Technical Secretary International Network of Basin Organizations If the greenhouse-effect
27 29 January Washington DC - USA Paper of Mr. Jean - François DONZIER General Manager International Office for Water Permanent Technical Secretary International Network of Basin Organizations If the greenhouse-effect
RAINWATER HARVESTING FOR DOMESTIC CONSUMPTION IN BANGLADESH
 RAINWATER HARVESTING FOR DOMESTIC CONSUMPTION IN BANGLADESH Ifte Choudhury & Farzana Sultana March 25-26, 2013 1 Introduction Problem Statement The purpose of this study is to assess a sustainable rainwater
RAINWATER HARVESTING FOR DOMESTIC CONSUMPTION IN BANGLADESH Ifte Choudhury & Farzana Sultana March 25-26, 2013 1 Introduction Problem Statement The purpose of this study is to assess a sustainable rainwater
Utilization and Conservation of Water Resources in Bangladesh
 Utilization and Conservation of Water Resources in Bangladesh Abu Musa Md. Motaher AHMED 1, Ph.D and Kingshuk ROY, Ph.D 2 1 Senior Scientific Officer, River Research Institute, Faridpur 7800, Bangladesh
Utilization and Conservation of Water Resources in Bangladesh Abu Musa Md. Motaher AHMED 1, Ph.D and Kingshuk ROY, Ph.D 2 1 Senior Scientific Officer, River Research Institute, Faridpur 7800, Bangladesh
Refining the water footprint concept to account for non- renewable
 Sarah Dickin McMaster University, Canada Refining the water footprint concept to account for non- renewable water resources Discussion Paper 1303 January 2013 This article outlines the rationale for further
Sarah Dickin McMaster University, Canada Refining the water footprint concept to account for non- renewable water resources Discussion Paper 1303 January 2013 This article outlines the rationale for further
Long Island: Water Resources. Water Sayings. Water Issues. Water Quality Issues specific to LI Coastal Areas. Agriculture and Water Regulation
 Water Sayings Long Island: Water Resources Copyright 2011 AFG 1 All living things need water to survive after air. Water, water everywhere but not a drop to drink. The quality of water is just as important
Water Sayings Long Island: Water Resources Copyright 2011 AFG 1 All living things need water to survive after air. Water, water everywhere but not a drop to drink. The quality of water is just as important
Effects of sluice gate on fisheries and crops production at Jugini CPP Area, Tangail, Bangladesh
 International Journal of Biosciences IJB ISSN: 2220-6655 (Print) 2222-5234 (Online) http://www.innspub.net Vol. 4, No. 8, p. 8-13, 2014 RESEARCH PAPER OPEN ACCESS Effects of sluice gate on fisheries and
International Journal of Biosciences IJB ISSN: 2220-6655 (Print) 2222-5234 (Online) http://www.innspub.net Vol. 4, No. 8, p. 8-13, 2014 RESEARCH PAPER OPEN ACCESS Effects of sluice gate on fisheries and
BAEN 673 / February 18, 2016 Hydrologic Processes
 BAEN 673 / February 18, 2016 Hydrologic Processes Assignment: HW#7 Next class lecture in AEPM 104 Today s topics SWAT exercise #2 The SWAT model review paper Hydrologic processes The Hydrologic Processes
BAEN 673 / February 18, 2016 Hydrologic Processes Assignment: HW#7 Next class lecture in AEPM 104 Today s topics SWAT exercise #2 The SWAT model review paper Hydrologic processes The Hydrologic Processes
Hydrology and Water Management. Dr. Mujahid Khan, UET Peshawar
 Hydrology and Water Management Dr. Mujahid Khan, UET Peshawar Course Outline Hydrologic Cycle and its Processes Water Balance Approach Estimation and Analysis of Precipitation Data Infiltration and Runoff
Hydrology and Water Management Dr. Mujahid Khan, UET Peshawar Course Outline Hydrologic Cycle and its Processes Water Balance Approach Estimation and Analysis of Precipitation Data Infiltration and Runoff
The KUND System: A sustainable way to ensure drinking water supply in the rural Mekong Delta under flood conditions
 A Project Proposal under the theme of Infrastructure development under increased flooding/storm intensity The KUND System: A sustainable way to ensure drinking water supply in the rural Mekong Delta under
A Project Proposal under the theme of Infrastructure development under increased flooding/storm intensity The KUND System: A sustainable way to ensure drinking water supply in the rural Mekong Delta under
UNESCO EOLSS. The various methods available for the treating and disposing of treated sewerage in natural receiving water bodies are outlined.
 POTABLE WATER S. Pagliara and D. Dazzini Department of Civil Engineering, University of Pisa, Italy Keywords: Water supply, water uses, effluent disposal, wastewater impact, sewer network, aqueduct, receiving
POTABLE WATER S. Pagliara and D. Dazzini Department of Civil Engineering, University of Pisa, Italy Keywords: Water supply, water uses, effluent disposal, wastewater impact, sewer network, aqueduct, receiving
Foundation Course. Semester 3 THREATS TO THE ENVIRONMENT
 Foundation Course Semester 3 THREATS TO THE ENVIRONMENT INTRODUCTION Atmosphere, water and soil are the most important components of environment in which we live. Atmospheric factors like rainfall, humidity,
Foundation Course Semester 3 THREATS TO THE ENVIRONMENT INTRODUCTION Atmosphere, water and soil are the most important components of environment in which we live. Atmospheric factors like rainfall, humidity,
FACTSHEET INTRODUCTION. help rebalance the water cycle, mitigate the effects of climate change and improve human health and livelihoods.
 1 FACTSHEET INTRODUCTION World Water Day, on 22 March every year, is about focusing attention on the importance of water. This year s theme, Nature for Water, explores nature-based solutions (NBS) to the
1 FACTSHEET INTRODUCTION World Water Day, on 22 March every year, is about focusing attention on the importance of water. This year s theme, Nature for Water, explores nature-based solutions (NBS) to the
Flood Risk Assessment. Reach Community Solar Farm
 Flood Risk Assessment Reach Community Solar Farm Andy Rankin 4 th February 2014 Introduction 1.1 Reach is a village of approximately 100 households on the edge of the Fens. We intend to construct a small
Flood Risk Assessment Reach Community Solar Farm Andy Rankin 4 th February 2014 Introduction 1.1 Reach is a village of approximately 100 households on the edge of the Fens. We intend to construct a small
Ground Water Management in Bangladesh: Policy and Institutional Arrangement in Bangladesh
 National Workshop On Groundwater Management in IWRM Dhaka, Bangladesh Course Contents Ground Water Management in Bangladesh: Policy and Institutional Arrangement in Bangladesh Dr. Kazi Matin Ahmed, Professor
National Workshop On Groundwater Management in IWRM Dhaka, Bangladesh Course Contents Ground Water Management in Bangladesh: Policy and Institutional Arrangement in Bangladesh Dr. Kazi Matin Ahmed, Professor
Climate Change and the Eastern Mediterranean Precipitation Regime
 Climate Change and the Eastern Mediterranean Precipitation Regime Manfred A. Lange Energy, Environment and Water Research Center, The Cyprus Institute EWACC2010 Energy, Water & Climate Change in the Mediterranean
Climate Change and the Eastern Mediterranean Precipitation Regime Manfred A. Lange Energy, Environment and Water Research Center, The Cyprus Institute EWACC2010 Energy, Water & Climate Change in the Mediterranean
ROLES AND EFFORTS OF THE IRRIGATION SECTOR IN MYANMAR AGRICULTURE PRACTICE
 ROLES AND EFFORTS OF THE IRRIGATION SECTOR IN MYANMAR AGRICULTURE PRACTICE Mu Mu Than 1 ABSTRACT Agriculture has always been the dominant sector in Myanmar economy. Agriculture sector contributes 22.1%
ROLES AND EFFORTS OF THE IRRIGATION SECTOR IN MYANMAR AGRICULTURE PRACTICE Mu Mu Than 1 ABSTRACT Agriculture has always been the dominant sector in Myanmar economy. Agriculture sector contributes 22.1%
Battle for the Biosphere
 Battle for the Biosphere Biome: A large community of plants and animals that occupies a distinct region e.g. the Tropical rainforest. Biosphere: The parts of the land, sea and atmosphere where organisms
Battle for the Biosphere Biome: A large community of plants and animals that occupies a distinct region e.g. the Tropical rainforest. Biosphere: The parts of the land, sea and atmosphere where organisms
Drought conditions and management strategies in Iran
 Drought conditions and management strategies in Iran Parviz Garshasbi Deputy head of watershed management forest, range and watershed management organization, Jihad-agriculture ministry p.garsh@yahoo.com
Drought conditions and management strategies in Iran Parviz Garshasbi Deputy head of watershed management forest, range and watershed management organization, Jihad-agriculture ministry p.garsh@yahoo.com
WATER SUPPLY NOW AND FOR THE FUTURE Steps toward sustainable water supplies
 WATER SUPPLY NOW AND FOR THE FUTURE Steps toward sustainable water supplies 2017 REPORT OF THE METROPOLITAN AREA WATER SUPPLY ADVISORY COMMITTEE TO THE MINNESOTA LEGISLATURE WE LIVE IN THE LAND OF 10,000
WATER SUPPLY NOW AND FOR THE FUTURE Steps toward sustainable water supplies 2017 REPORT OF THE METROPOLITAN AREA WATER SUPPLY ADVISORY COMMITTEE TO THE MINNESOTA LEGISLATURE WE LIVE IN THE LAND OF 10,000
Illinois State Water Survey Division
 Illinois State Water Survey Division GROUND-WATER SECTION SWS Contract Report 456 SUMMARY REPORT: REGIONAL ASSESSMENT OF THE GROUND-WATER RESOURCES IN EASTERN KANKAKEE AND NORTHERN IROQUOIS COUNTIES by
Illinois State Water Survey Division GROUND-WATER SECTION SWS Contract Report 456 SUMMARY REPORT: REGIONAL ASSESSMENT OF THE GROUND-WATER RESOURCES IN EASTERN KANKAKEE AND NORTHERN IROQUOIS COUNTIES by
Issues include coverage gaps, delays, measurement continuity and consistency, data format and QC, political restrictions
 Satellite-based Estimates of Groundwater Depletion, Ph.D. Chief, Hydrological Sciences Laboratory NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Greenbelt, MD Groundwater Monitoring Inadequacy of Surface Observations
Satellite-based Estimates of Groundwater Depletion, Ph.D. Chief, Hydrological Sciences Laboratory NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Greenbelt, MD Groundwater Monitoring Inadequacy of Surface Observations
Drought Conditions and Management Strategies in Botswana
 Drought Conditions and Management Strategies in Botswana Dr. M. Manthe-Tsuaneng Acting Deputy Permanent Secretary- Natural Resources Ministry of Environment, Wildlife and Tourism Private Bag BO 199 Gaborone,
Drought Conditions and Management Strategies in Botswana Dr. M. Manthe-Tsuaneng Acting Deputy Permanent Secretary- Natural Resources Ministry of Environment, Wildlife and Tourism Private Bag BO 199 Gaborone,
Flood Damage Prediction for Provincial Governments in Korea Based on Climate Change Scenarios
 Flood Damage Prediction for Provincial Governments in Korea Based on Climate Change Scenarios B. Park, K. Oh, and D. Lee Abstract Climate change is a major problem for Earth and its inhabitants. Thus,
Flood Damage Prediction for Provincial Governments in Korea Based on Climate Change Scenarios B. Park, K. Oh, and D. Lee Abstract Climate change is a major problem for Earth and its inhabitants. Thus,
City Growth in Poor Countries: Urban Dwellers Face Climate-Related Risks
 in Poor Countries: Urban Dwellers Face Climate-Related Risks Mark R. Stony Brook University and Population Council April 9, 2010 Three Trends Will Shape the 21st Century: Urbanization in Poor Countries
in Poor Countries: Urban Dwellers Face Climate-Related Risks Mark R. Stony Brook University and Population Council April 9, 2010 Three Trends Will Shape the 21st Century: Urbanization in Poor Countries
Water Status in the Gaza Strip and Future Plans
 ` Water Status in the Gaza Strip and Future Plans April 2010 1.0 Background and Introduction Gaza Strip is one of the semi-arid area where rainfall is falling in the winter season from September to April,
` Water Status in the Gaza Strip and Future Plans April 2010 1.0 Background and Introduction Gaza Strip is one of the semi-arid area where rainfall is falling in the winter season from September to April,
DRAINAGE AND NATURAL AQUIFER GROUNDWATER RECHARGE ELEMENT
 Goal 7.0. To optimize integrated stormwater management in order to reduce damage and impacts from sea level rise and flooding, promotes recharge to the Surficial Aquifer System (SAS), improve and protect
Goal 7.0. To optimize integrated stormwater management in order to reduce damage and impacts from sea level rise and flooding, promotes recharge to the Surficial Aquifer System (SAS), improve and protect
GROUNDWATER General Facts and Concepts
 GROUNDWATER General Facts and Concepts General schematic of hydrologic cycle. As the term implies, water moves within the cycle and groundwater (aquifer) is just one zone of the cycle. Aquifers and Wells
GROUNDWATER General Facts and Concepts General schematic of hydrologic cycle. As the term implies, water moves within the cycle and groundwater (aquifer) is just one zone of the cycle. Aquifers and Wells
Temperature extremes, moisture deficiency and their impacts on dryland agriculture in Gujarat, India
 Drought: Research and Science-Policy Interfacing Andreu et al. (Eds) 2015 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-02779-4 Temperature extremes, moisture deficiency and their impacts on dryland agriculture
Drought: Research and Science-Policy Interfacing Andreu et al. (Eds) 2015 Taylor & Francis Group, London, ISBN 978-1-138-02779-4 Temperature extremes, moisture deficiency and their impacts on dryland agriculture
Dr. M. Monowar Hossain, Executive Director Institute of Water Modelling (IWM) & Coordinator, Delta Alliance Bangladesh Wing (DABW)
 Dr. M. Monowar Hossain, Executive Director Institute of Water Modelling (IWM) & Coordinator, Delta Alliance Bangladesh Wing (DABW) Paper presented at Delta Coalition Ministerial Conference and Working
Dr. M. Monowar Hossain, Executive Director Institute of Water Modelling (IWM) & Coordinator, Delta Alliance Bangladesh Wing (DABW) Paper presented at Delta Coalition Ministerial Conference and Working
Lecturer in GED, Environmental Studies, Manarat International University, Dhaka, Bangladesh. **
 Manarat International University Studies, 2 (1): 119-125, December 2011 ISSN 1815-6754 @ Manarat International University, 2011 Impact of Flyovers in Dhaka City of Bangladesh: A Study on the Affected People
Manarat International University Studies, 2 (1): 119-125, December 2011 ISSN 1815-6754 @ Manarat International University, 2011 Impact of Flyovers in Dhaka City of Bangladesh: A Study on the Affected People
2014 Water Resources Status Summary Report /Gaza Strip Water Resources Directorate (2015) Introduction:
 2014 Water Resources Status Summary Report /Gaza Strip Water Resources Directorate (2015) Introduction: The aim of this water resources summary report is throwing lights on the water resources situation
2014 Water Resources Status Summary Report /Gaza Strip Water Resources Directorate (2015) Introduction: The aim of this water resources summary report is throwing lights on the water resources situation
Implementing Stormwater Management through Split-Flow Drainage Design
 Implementing Stormwater Management through Split-Flow Drainage Design Stuart Patton Echols PhD, ASLA, RLA Assistant Professor - Department of Landscape Architecture 210 Engineering Unit D Center for Watershed
Implementing Stormwater Management through Split-Flow Drainage Design Stuart Patton Echols PhD, ASLA, RLA Assistant Professor - Department of Landscape Architecture 210 Engineering Unit D Center for Watershed
WATER FROM THE CLOUDS
 WATER FROM THE CLOUDS 814 mm per year on land or 110 000 km 3 56% is evapotranspirated by forests and natural landscapes 5% is evapotranspirated by rainfed agriculture 39% available for human uses (irrigation,
WATER FROM THE CLOUDS 814 mm per year on land or 110 000 km 3 56% is evapotranspirated by forests and natural landscapes 5% is evapotranspirated by rainfed agriculture 39% available for human uses (irrigation,
East Maui Watershed Partnership Adapted from Utah State University and University of Wisconsin Ground Water Project Ages 7 th -Adult
 INTRODUCTION What is groundwater? Water contained in saturated soil and rock materials below the surface of the earth. It is not NEW water, but is recycled water through the hydraulic cycle. The source
INTRODUCTION What is groundwater? Water contained in saturated soil and rock materials below the surface of the earth. It is not NEW water, but is recycled water through the hydraulic cycle. The source
WATER QUALITY MODELING FOR BOD and COD CONTROL STRATEGIES FOR THE BURIGANGA RIVER OF BANGLADESH
 Proceedings of the 13 th International Conference of Environmental Science and Technology Athens, Greece, 5-7 September 13 WATER QUALITY MODELING FOR BOD and COD CONTROL STRATEGIES FOR THE BURIGANGA RIVER
Proceedings of the 13 th International Conference of Environmental Science and Technology Athens, Greece, 5-7 September 13 WATER QUALITY MODELING FOR BOD and COD CONTROL STRATEGIES FOR THE BURIGANGA RIVER
DROUGHT DEFINITIONS: BACKGROUND INFORMATION:
 DROUGHT DEFINITIONS: Drought an extended period of abnormally low precipitation; a condition of climate dryness that is severe enough to reduce soil moisture as well as water and snow levels below the
DROUGHT DEFINITIONS: Drought an extended period of abnormally low precipitation; a condition of climate dryness that is severe enough to reduce soil moisture as well as water and snow levels below the
Climate Change Impact on Lake Ziway Watershed Water Availability, Ethiopia
 LARS 2007 Catchment and Lake Research Climate Change Impact on Lake Ziway Watershed Water Availability, Ethiopia Lijalem Zeray Abraham 1, Jackson Roehrig 2, and Dilnesaw Alamirew Chekol 3 1. Cologne University
LARS 2007 Catchment and Lake Research Climate Change Impact on Lake Ziway Watershed Water Availability, Ethiopia Lijalem Zeray Abraham 1, Jackson Roehrig 2, and Dilnesaw Alamirew Chekol 3 1. Cologne University
Groundwater Earth 9th Edition Chapter 17 Mass wasting: summary in haiku form Importance of groundwater Importance of groundwater
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Groundwater Earth 9 th Edition Chapter 17 Geology 100 Mass wasting: summary in haiku form The grass is greener over the septic system said Erma Bombeck. Importance of groundwater
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Groundwater Earth 9 th Edition Chapter 17 Geology 100 Mass wasting: summary in haiku form The grass is greener over the septic system said Erma Bombeck. Importance of groundwater
GEO-DRI Drought Monitoring Workshop, May 10-11, 2010, Winnipeg, Manitoba Drought in Southeast Asia
 GEO-DRI Drought Monitoring Workshop, May 10-11, 2010, Winnipeg, Manitoba Drought in Southeast Asia Orn-uma Polpanich Stockholm Environment Institute Asia Bangkok, Thailand Southeast Asia Is located on
GEO-DRI Drought Monitoring Workshop, May 10-11, 2010, Winnipeg, Manitoba Drought in Southeast Asia Orn-uma Polpanich Stockholm Environment Institute Asia Bangkok, Thailand Southeast Asia Is located on
Climate Change Adaptation in Europe and Spain. Cities.
 Climate Change Adaptation in Europe and Spain. Cities. Overview Introduction City Adaptation in Europe City Adaptation in Spain Barcelona Madrid Final reflections Overview Introduction City Adaptation
Climate Change Adaptation in Europe and Spain. Cities. Overview Introduction City Adaptation in Europe City Adaptation in Spain Barcelona Madrid Final reflections Overview Introduction City Adaptation
Windward and Leeward
 Terrestrial Biomes Biome Biomes are climatically and geographically defined as similar climatic conditions on the Earth, such as communities of plants, animals, and soil organisms, and are often referred
Terrestrial Biomes Biome Biomes are climatically and geographically defined as similar climatic conditions on the Earth, such as communities of plants, animals, and soil organisms, and are often referred
Recursos alimentares e impactes ambientais da agricultura no ambiente. Natural Capital. Page 276. Food crops. Food crops. Fiber crops.
 Recursos alimentares e impactes ambientais da agricultura no ambiente Ecological Services Ecological Services Natural Capital Figure Croplands 14-3 Page 276 Croplands Economic Services Economic Services
Recursos alimentares e impactes ambientais da agricultura no ambiente Ecological Services Ecological Services Natural Capital Figure Croplands 14-3 Page 276 Croplands Economic Services Economic Services
A CASE STUDY ON MANAGEMENT OF RAINWATER RESERVOIR IN HILLY AREAS OF BANGLADESH
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 7, Issue 6, November-December 2016, pp. 193 201, Article ID: IJCIET_07_06_021 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=7&itype=6
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 7, Issue 6, November-December 2016, pp. 193 201, Article ID: IJCIET_07_06_021 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=7&itype=6
Chapter 6 Water Resources
 Chapter 6 Water Resources Elemental Geosystems 5e Robert W. Christopherson Charles E. Thomsen 1 Water Resources The Hydrologic Cycle Groundwater Resources Our Water Supply The Hydrologic Cycle A Hydrologic
Chapter 6 Water Resources Elemental Geosystems 5e Robert W. Christopherson Charles E. Thomsen 1 Water Resources The Hydrologic Cycle Groundwater Resources Our Water Supply The Hydrologic Cycle A Hydrologic
SWIBANGLA. Managing Salt Water Impacts in Bangladesh. Marta Faneca Sanchez Gualbert Oude Essink Gijs Janssen Roelof Stuurman Yangxiao Zhou, UNESCO-IHE
 SWIBANGLA Managing Salt Water Impacts in Bangladesh Marta Faneca Sanchez Gualbert Oude Essink Gijs Janssen Roelof Stuurman Yangxiao Zhou, UNESCO-IHE Project duration spring 2013 to winter 2014 http://flood.firetree.net
SWIBANGLA Managing Salt Water Impacts in Bangladesh Marta Faneca Sanchez Gualbert Oude Essink Gijs Janssen Roelof Stuurman Yangxiao Zhou, UNESCO-IHE Project duration spring 2013 to winter 2014 http://flood.firetree.net
IV. ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ANALYSIS G. HYDROLOGY/WATER QUALITY
 IV. ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ANALYSIS G. HYDROLOGY/WATER QUALITY ENVIRONMENTAL SETTING The project site is located in the Wilshire community of the City of Los Angeles and is bound by S. Wetherly Drive to
IV. ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ANALYSIS G. HYDROLOGY/WATER QUALITY ENVIRONMENTAL SETTING The project site is located in the Wilshire community of the City of Los Angeles and is bound by S. Wetherly Drive to
Characteristics of Land Resources
 Chapter Chapter 1 Characteristics of Land Resources The geology, soils and topography of Woodford County T he geology, soils and topography of an area are important to the community planning process for
Chapter Chapter 1 Characteristics of Land Resources The geology, soils and topography of Woodford County T he geology, soils and topography of an area are important to the community planning process for
Flooding Vulnerability Assessment A Case Study of Hou-Jing Stream in Taiwan
 Flooding Vulnerability Assessment A Case Study of Hou-Jing Stream in Taiwan Doi:10.5901/mjss.2013.v4n10p513 Abstract Meng-Ru Tsay Department of Urban Planning, National Cheng Kung University, Tainan City
Flooding Vulnerability Assessment A Case Study of Hou-Jing Stream in Taiwan Doi:10.5901/mjss.2013.v4n10p513 Abstract Meng-Ru Tsay Department of Urban Planning, National Cheng Kung University, Tainan City
TSUNAMI DISASTER AND GROUNDWATER RESOURCES: THE SOUTHEASTERN COAST OF INDIA. Bhanu Neupane Regional Hydrologist, UNESCO
 TSUNAMI DISASTER AND GROUNDWATER RESOURCES: THE SOUTHEASTERN COAST OF INDIA Bhanu Neupane Regional Hydrologist, UNESCO Background On December 26, 2004, Tsunami waves struck the coast of the Indian subcontinent
TSUNAMI DISASTER AND GROUNDWATER RESOURCES: THE SOUTHEASTERN COAST OF INDIA Bhanu Neupane Regional Hydrologist, UNESCO Background On December 26, 2004, Tsunami waves struck the coast of the Indian subcontinent
WATER AND THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE
 WATER AND THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE Summary Water is essential for the support of life and can be considered as a fundamental environmental good. Water is needed to support human habitation, grow crops and
WATER AND THE HYDROLOGIC CYCLE Summary Water is essential for the support of life and can be considered as a fundamental environmental good. Water is needed to support human habitation, grow crops and
Vision 2030: The resilience of water supply and sanitation in the face of climate change Chee-Keong CHEW 28 October 2009
 Vision 2030: The resilience of water supply and sanitation in the face of climate change Chee-Keong CHEW 28 October 2009 1 Scope Why climate resilience is important? Overview of Vision 2030 Summary of
Vision 2030: The resilience of water supply and sanitation in the face of climate change Chee-Keong CHEW 28 October 2009 1 Scope Why climate resilience is important? Overview of Vision 2030 Summary of
Behavior Adaptations to Climatic Variability in the Use of Water for Drinking and Sanitation in the Dry Region of Sri Lanka
 Behavior Adaptations to Climatic Variability in the Use of Water for Drinking and Sanitation in the Dry Region of Sri Lanka Professor. G.M. Bandaranayake Water Resources Studies Department of Geography
Behavior Adaptations to Climatic Variability in the Use of Water for Drinking and Sanitation in the Dry Region of Sri Lanka Professor. G.M. Bandaranayake Water Resources Studies Department of Geography
The Water-Climate Nexus and Food Security in the Americas. Michael Clegg University of California, Irvine
 The Water-Climate Nexus and Food Security in the Americas Michael Clegg University of California, Irvine The Global Challenge Global population is projected to increase by about 30% between now and 2050
The Water-Climate Nexus and Food Security in the Americas Michael Clegg University of California, Irvine The Global Challenge Global population is projected to increase by about 30% between now and 2050
Performance Analysis of Sand Columns in Recharge Reservoir
 International Journal of Engineering and Technology Volume 4 No. 10, October, 2014 Performance Analysis of Sand Columns in Recharge Reservoir Akhmad Azis Civil Engineering, Polytechnic State of Ujung Pandang
International Journal of Engineering and Technology Volume 4 No. 10, October, 2014 Performance Analysis of Sand Columns in Recharge Reservoir Akhmad Azis Civil Engineering, Polytechnic State of Ujung Pandang
Sustainable Conservation Practices for Natural Resources
 Sustainable Conservation Practices for Natural Resources Rajdeep Mundiyara 1, Prem Kumar 2 and Mamta Bajya 3 1 Seed Officer, Rajasthan State Seeds Corporation,Mandore, Jodhpure 2 Department of Plant Philology,
Sustainable Conservation Practices for Natural Resources Rajdeep Mundiyara 1, Prem Kumar 2 and Mamta Bajya 3 1 Seed Officer, Rajasthan State Seeds Corporation,Mandore, Jodhpure 2 Department of Plant Philology,
Water Status in the Syrian Water Basins
 Open Journal of Modern Hydrology, 2012, 2, 15-20 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojmh.2012.21003 Published Online January 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojmh) 1 Khaldoon A. Mourad 1, Ronny Berndtsson 2 1
Open Journal of Modern Hydrology, 2012, 2, 15-20 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojmh.2012.21003 Published Online January 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojmh) 1 Khaldoon A. Mourad 1, Ronny Berndtsson 2 1
Phil Mashoko(Pr Eng) Director: W & S City of Cape Town South Africa
 Phil Mashoko(Pr Eng) Director: W & S City of Cape Town South Africa SECURITY OF WATER SUPPLY It is the ability to continuously produce and supply safe drinking water to the enduser ASSURANCE RISK LEVEL
Phil Mashoko(Pr Eng) Director: W & S City of Cape Town South Africa SECURITY OF WATER SUPPLY It is the ability to continuously produce and supply safe drinking water to the enduser ASSURANCE RISK LEVEL
Uncontrolled Urban Expansion of Amman City and the Disintegration of the Rainfed Lands
 Architecture Research 2017, 7(1): 24-28 DOI: 10.5923/j.arch.20170701.03 Uncontrolled Urban Expansion of Amman City and the Disintegration of the Rainfed Lands Numan Abu Hammad Department of Civil Engineering,
Architecture Research 2017, 7(1): 24-28 DOI: 10.5923/j.arch.20170701.03 Uncontrolled Urban Expansion of Amman City and the Disintegration of the Rainfed Lands Numan Abu Hammad Department of Civil Engineering,
Flood damage assessment for Dhaka City, Bangladesh
 Flood damage assessment for Dhaka City, Bangladesh D.M. Khan, S.M.M. Rahman & A.K.E. Haque Institute of Water Modelling, Dhaka, Bangladesh A.S. Chen, M.J. Hammond, S. Djordjević & D. Butler Centre for
Flood damage assessment for Dhaka City, Bangladesh D.M. Khan, S.M.M. Rahman & A.K.E. Haque Institute of Water Modelling, Dhaka, Bangladesh A.S. Chen, M.J. Hammond, S. Djordjević & D. Butler Centre for
Welcome to the Anthropocene. by Dr. John L. Hough Principal Technical Advisor - Biodiversity UNDP
 Welcome to the Anthropocene by Dr. John L. Hough Principal Technical Advisor - Biodiversity UNDP The 5 th great extinction crisis Emergence of Homo sapiens The 6 th great extinction crisis 6 billion people
Welcome to the Anthropocene by Dr. John L. Hough Principal Technical Advisor - Biodiversity UNDP The 5 th great extinction crisis Emergence of Homo sapiens The 6 th great extinction crisis 6 billion people
U.S. Water Budget. Figure Source:Data from The Nation s Water Resources , Vol. 1, U.S. Water Resources Council.
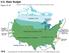 U.S. Water Budget Figure 10.18 10-9 Source:Data from The Nation s Water Resources 1975-2000, Vol. 1, U.S. Water Resources Council. Average U.S. Precipitation Figure 10.19 10-10 Source: U.S. Water Resources
U.S. Water Budget Figure 10.18 10-9 Source:Data from The Nation s Water Resources 1975-2000, Vol. 1, U.S. Water Resources Council. Average U.S. Precipitation Figure 10.19 10-10 Source: U.S. Water Resources
Lucknow City India: Groundwater Resource Use & Strategic Planning Needs
 GW MATE Briefing Note Series world bank Sustainable Groundwater Management: Concepts and Tools Sustainable Groundwater Management Lessons from Practice Case Profile Collection Number 23 Lucknow City India:
GW MATE Briefing Note Series world bank Sustainable Groundwater Management: Concepts and Tools Sustainable Groundwater Management Lessons from Practice Case Profile Collection Number 23 Lucknow City India:
Importance of irrigation return flow on the groundwater budget of a rural basin in India
 62 Hydrology of the Mediterranean and Semiarid Regions (Proceedings of an international symposium held at Montpellier. April 2003). IAHS Publ. no. 278. 2003. Importance of irrigation return flow on the
62 Hydrology of the Mediterranean and Semiarid Regions (Proceedings of an international symposium held at Montpellier. April 2003). IAHS Publ. no. 278. 2003. Importance of irrigation return flow on the
Climate change and groundwater resources in Lao PDR
 Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering Vol.5 Vol.4 No.1 No.2 Mar. Jun. 2016 2017 Climate change and groundwater resources in Lao PDR Khongsab Somphone 1*, OunakoneKone Xayviliya 1 1 Division of
Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering Vol.5 Vol.4 No.1 No.2 Mar. Jun. 2016 2017 Climate change and groundwater resources in Lao PDR Khongsab Somphone 1*, OunakoneKone Xayviliya 1 1 Division of
ENVIRONMENTAL HYDROGEOLOGY
 ENVIRONMENTAL HYDROGEOLOGY m LEWIS Mostafa M. Soliman Professor, Faculty of Engineering Ain Shams University Cairo, Egypt Philip E. LaMoreaux Senior Hydrogeologist Bashir A. Memon Executive Vice President
ENVIRONMENTAL HYDROGEOLOGY m LEWIS Mostafa M. Soliman Professor, Faculty of Engineering Ain Shams University Cairo, Egypt Philip E. LaMoreaux Senior Hydrogeologist Bashir A. Memon Executive Vice President
Keywords: groundwater, urbanization, water resources, water supply, sewage, underground structures, groundwater quality, water management
 URBAN HYDROGEOLOGY Xavier Sánchez-Vila Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain Keywords: groundwater, urbanization, water resources, water supply, sewage, underground structures, groundwater
URBAN HYDROGEOLOGY Xavier Sánchez-Vila Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain Keywords: groundwater, urbanization, water resources, water supply, sewage, underground structures, groundwater
