ASSESSMENT OF THE EVOLUTION OF INFILTRATION IN COSTA DO ESTORIL DRAINAGE SUBSYSTEM
|
|
|
- Jemimah Elliott
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ASSESSMENT OF THE EVOLUTION OF INFILTRATION IN COSTA DO ESTORIL DRAINAGE SUBSYSTEM Abstract Alice Pereira Rosmaninho Civil Engineering Department May 2017 Infiltration problems tend to aggravate with infrastructure aging, with important consequences regarding its technical and economic performance. The present communication aims to assess the evolution of infiltration in Costa do Estoril drainage subsystem, based on monitoring data collected in the same flow measuring points in 2000 and The infiltration flow rates were estimated by conventional methods, and performance indicators were also determined. The results were compared to verify any decreases or rises infiltration flows during this period, relating them to rehabilitation interventions performed by the wastewater utility. Furthermore, in situations where an increase in stormwater contributions was observed, the results were used as a primary instrument for the proposed mitigating measures. Keywords - Infiltration, inflows, performance indicators, urban drainage, wastewater. Introduction In urban drainage systems, undue inflows are a concern for management entities. Certainly, those inflows contribute to increasing the cost of operating drainage systems and wastewater treatment plants (WWTP), reduce their effectiveness and compromise sustainability management of drainage systems in urban areas. The problem of infiltration tends to worsen with the age of the systems, having important consequences on their technical and economic performance. The costs associated with infiltration are high, justifying the investment in studies that allow to know the extent of the problem and quantify it. Correct quantification of infiltration in the drainage network is a key issue in problem-oriented rehabilitation management with a view to mitigating these issues (Kracht et al., 2008) and also in order to measure the effectiveness of actions implemented for this purpose. Although it is not feasible to eliminate all infiltration water from urban drainage systems, it is required to know and control the problem as much as possible. 1
2 One of the alternatives is the quantification of the magnitude of infiltration flows that can be made using a set of indicators that objectively evaluate the infiltration flows, considering the characteristics of the drainage systems (Cardoso et al., 2002). In short, the investment in the study and quantification of infiltration in urban drainage systems have high interest for fund managers, not only because it minimizes the various mentioned impacts, but also because it can function as an indicator of the structural state and environmental efficiency of the systems (Rodrigues, 2013). In the context of this document, it is intended to evaluate the evolution of the infiltration in the drainage subsystem of the Estoril Coast, based on monitoring data collected in 24 flow measurement points in 2000 (analysed by Cardoso et al., 2002) and The results were compared to verify eventual reductions or increases in infiltration flows in this period, relating them to interventions carried out by the management entity or using the results, in situations of increased contribution of infiltration flows, as a preliminary instrument for the proposal of measures to mitigate the problem. Infiltration in urban drainage systems The estimation of infiltration flow rates in a drainage system is not a simple matter and it is both in the design phase and in the exploration phase. In the design phase, the estimate is usually made, in accordance with Regulatory Decree No. 23/95, as being equal to the annual average flow, to estimate the design flow rates; In the exploration phase, the estimation can be made based on different methods and is carried out to evaluate the technical and economic performance of the system. The infiltration is defined as the infiltration of unwanted and unpolluted water into the drainage network, originating from groundwater (Metcalf and Eddy, 2003). It is common to consider undue flows (or simply infiltration), which flow to the systems through structural deficiencies in the sewers (joints, connections) or through the walls of the manholes, base infiltration (regardless of the state of conservation of the sewer). It is common to have additional infiltration to the base infiltration that occurs after a precipitation event ends and has a variable duration depending on the characteristics of the respective drainage basin, such as area, percentage of waterproofing, average slope, soil hydrogeological characteristics, conservation of networks, among others. In a drainage system, the infiltration flows present high spatial and temporal variability. The magnitude of this phenomenon depends on: the position of the network elements relative to the water table; the conservation status of drainage networks; the length of the nets, the diameter of the sewers, the number of the manholes and connecting junctions; Of the soil type; The occurrence of precipitation; among other factors (White et al., 1997; Gamboa et al., 2000). The determination of infiltration rates can be done using conventional or non-conventional analytical methods. Conventional methods are based on flow analysis or chemical analysis of water, the unconventional ones, allow to estimate infiltration rates based on the analysis of isotope ratios, being called by the isotope method. 2
3 The conventional methods of flow analysis are based on the hypothesis that the total flow rate circulating in the network in dry time is composed only of two components: one relative only to waste water (domestic or industrial) and another to infiltration. Some of the conventional and unconventional methods are described in De Bénédittis (2004) for evaluation of infiltration. The methodology expressed by equation (1) (Cohen, 1998) allows, from the analysis of the daily flow measurement logs in dry time, the minimum recorded flow, the quantification of the base infiltration that occurs in a drainage system. It is assumed that the nocturnal flow rate is, on average, about 8 to 12% of the average daily flow with no occurrence of precipitation in the urban basins. For this method, it is important to highlight the fact that the average flow rate is used to estimate the infiltration and therefore has the advantage of better reflecting the characteristics of the basin in question. However, the more urban the basin is, the larger the average flows, which can lead to negative infiltration flows at very low nightly flows. Another methodology is expressed by equation (2) and was proposed in Cardoso et al. (2002), which considers the infiltration flow corresponds to 88% of the minimum daily flow that is drained into the system. Q inf = Q mín 0,12Q méd (1) Q inf = 0,88 Q mín (2) where: Q inf infiltration flow; Q mín minimum daily flow; Q méd average daily flow. Even though there is no "perfect" method to calculate infiltration flow rate, a study of the dynamics of the basin is always necessary and the estimation of infiltration rates will be more approximate based on the flow measurement combined with a minimum flow analysis, when there is a greater expression of infiltration flows. To evaluate the performance of a drainage system, particularly about infiltration flows, it is advisable to determine performance indicators. According to Coelho and Alegre (1999), an indicator or measure of performance is a characteristic or state variable that allows, in function of the values that it assumes, to translate in quantitative terms the performance of the system. This measure can be obtained based on monitoring or modelling data of the network under analysis, varying spatially (from element to element of the network) and temporally (depending on the system requests). Cardoso et al. (2002) recommend the evaluation of performance indicators in Table 1, regarding the problems of infiltration in drainage systems. 3
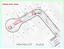
4 Table 1. Performance indicators to infiltration in urban drainage systems (adapted from Cardoso et. al., 2004). Performance PI1 PI2 PI3 PI4 PI5 indicators Q inf Q full Q inf Q mts Q inf nº M Q inf L sewer Q inf L sewer P Comments Infiltration full capacity utilization (%) this indicator allows us to the proportion of the sewer s full section flow capacity used by the infiltration flow. Its value may be assessed for a single sewer, for groups of sewers (subsystems) or for the entire system. Infiltration proportion of dry weather flow (%) The infiltration flow expressed as a percentage of the daily mean dry weather flow. This measure may indicate to the drainage management entities which sections are in good condition and which parts of sewer have to be rehabilitate. Infiltration per menhole (m 3 /day) Mean infiltration flow per manhole unit. Manholes are an important source of infiltration. This indicator gives an idea of the influence of the number of manholes on total infiltration Infiltration flow per unit sewer length (m 3 /day/km) mean infiltration flow per unit length of sewer. This indicator does not consider the influence of infiltration taking place in manholes or service connections. This indicator will give relevant results in systems where infiltration takes place predominantly along the sewers. Infiltration flow per unit sewer wall area (m 3 /day/(cm.km)) represents the influence that the area of the sewer wall has on the infiltration flows of the system. This indicator does not take into account the influence of infiltration taking place in manholes or service connections. This indicator will give relevant results in systems where infiltration takes place predominantly along the sewers too. Case study The Estoril Coast substation is managed by EPAL, Empresa Portuguesa de Águas Livres, SA and has an intervention area of about 246 km2, comprising several municipalities, namely the municipality of Amadora, Cascais, Oeiras and Sintra currently serving population. This system consists of several gravitational emitters, a main interceptor, for a length of 155 km, by elevating systems and by a WWTP. The emissaries receive the effluents from the municipal networks and develop in parallel with the main water lines, along elongated watersheds and with a north-south orientation, as can be observed in Image 1. In 1998, a large flow and precipitation monitoring system was installed in the Estoril Coast subsystem with many meters permanently installed in the sewers (Figure 1). This monitoring system allows a better knowledge of the operational operation of the network, provides data to allow the billing of volumes transacted between municipalities and provides information for studies of improvement or expansion of the intermunicipal system. 4
5 Image 1 Schematic representation of Costa do Estoril subsystem (adapted from Cardoso et al., 2002) The drainage system sewer is located near the bed of the streams, with frequent crossings, often deployed below the water table, enhancing the inflow of infiltration flows into the system. In the present study, the infiltration flows determination was analysed for the winter period (November 2014 to April 2015) and for the summer period (May 2015 to October 2015). Flow data from 24 flow meters were analysed as well as the precipitation data obtained from the 5 spatially distributed meters in the basin. Methods To evaluate the evolution of the infiltration in the Estoril Coast subsystem between 2000 and 2016, the following methodology was applied: 1) Analysis and treatment of flow and precipitation data Dry weather hydrograms were plotted for each flow meter, for the winter period and for the summer period. For the determination of each hydrograph, only the data corresponding to the dry days were selected, that is, the daily logs with precipitation record were recorded in the udrometers, as well as the daily records whose hydrographs were influenced by the precipitation occurred in previous days (Delayed infiltration), since it was only intended to estimate the direct infiltration. Also, excluded from the analysis were data that could somehow show the occurrence of an error in the flow measurement. 5
6 2) Infiltration flows With the dry weather hydrograms traced and using equation (2), the daily infiltration flow rates and the daily volumes of dry weather were determined for the winter and summer periods. 3) Comparison of results obtained with previous studies Since the values presented in Cardoso et al. (2002) relate to records from the summer 2000 period, a comparison was made between these values and the infiltration volumes obtained for the summer period of 2015 (May to October), to evaluate the evolution of these flows to the Over 15 years. 4) Aplication of performance indicators Performance indicators associated with infiltration flows were determined, based on the proposed by Cardoso et al. (2002). However, since infiltration flows in the Estoril Coast subsystem are related to infiltration flows from the "downstream" network, and no cadastral information associated with the "downstream" drainage system (namely section flows Number of manholes) required for the calculation of indicators ID3, ID4 and ID5, only indicators ID1 and ID2 were evaluated. Results and discussion In Table 2 we present the comparison between the values obtained for the infiltration volume corresponding to the summer of 2015 with the values obtained in Cardoso et al. (2002), corresponding to the summer of Through the quotient between both, it is possible to find out in which sewers was a decrease or an increase in the volume of infiltration. Thus, the values in which the quotient is equal to or less than 1 (green) correspond to places where there was no increase in infiltration flows. The values between 1.1 and 1.3 (blue) represent the sewers with a small increase in infiltration flows over this period. Values greater than 1,3 and 3 (yellow) correspond to increases that may go up to a double increase in infiltration flow rate and values greater than 3 (red) corresponding to places where was a significant increase of flow rates infiltration. 6
7 Table 2. Comparison of results obtained to the summer of 2015 and to the summer of 2000 obtained in Cardoso et al. (2002) Basin Carenque Jamor Barcarena Laje Therefore, and considering that there may be some variation in the results resulting from the different statistical analysis at different times, it is possible to verify that in 70% (green) of the points was no increase of infiltration flows. This is also due to some rehabilitation that has taken place along the network. The major increase in daily infiltration flow was recorded in the Carenque sewer, with an estimated increase of four times the estimated flow rate in Compared to the daily volumes measured, points Q43 (Cadaveira) and Q35 (Caparide) show a relationship between the daily infiltration flow rate and the mean dry flow rate over 50%, which expresses significant volumes of infiltration, supported by the performance indicators presented in Table 3. The color scale shows that values can be considered as revealing a low (0-25%), medium (25-50%) or high (> 50%) infiltration rate ratio (green, yellow and red). To better analyse and evaluate the implication of these two indicators, the drainage system for ID1 and ID2, using the previous color scale, was schematized in the following figures. The sections presented in black in Image 2 and Image 3 were not analysed. V inf (2015) V daily (2015) V inf / V daily (2015) V inf (2000) V inf (2015)/ V inf (2000) (m 3 /day) (m 3 /dia) (%) (m 3 /dia) (%) Q % 86 4,1 Q % 432 2,3 Q 01B % ,5 Q % ,0 Legend: Q % ,2 > 3 Q % ,4 1,3 a 3 Q % ,8 < 1,3 Q % ,2 Q % 432 0,4 Sassoeiros Q % ,7 Marianas Q % ,9 Caparide Q % ,5 Q % ,8 Bicesse Q % ,1 Cadaveira Q % 691 0,8 Amoreira Q % 259 1,6 Castelhana Q % 86 1,3 Intercetor geral Flow meter Summer Q % ,8 Q % ,1 Q % ,1 Q % ,0 Q % ,8 Q % ,0 7
8 Basin Flow meter Table 3. Performance indicators values Winter (2015) Summer (2015) Summer (2000) PI1 PI2 PI1 PI2 PI1 PI2 (%) (%) (%) (%) (%) (%) Carenque Q20 1% 37% 1% 33% - 17% Q21 3% 32% 3% 33% - 24% Jamor Q01B 2% 42% 1% 32% 2% 32% Q02 5% 46% 3% 39% 1% 29% Q24 5% 40% 4% 34% 5% 40% Barcarena Q25 4% 37% 3% 30% 1% 24% Q27 7% 43% 5% 36% 5% 48% Laje Q07 22% 48% 13% 36% 7% 34% Q31-38% - 29% - 50% Sassoeiros Q37 5% 33% 3% 24% - 34% Marianas Q40 4% 56% 2% 33% - 34% Caparide Q35 14% 78% 6% 55% 5% 41% Q41 3% 60% 1% 47% 5% 48% Bicesse Q42 1% 48% 1% 37% - 34% Cadaveira Q43 1% 65% 1% 60% - 70% Amoreira Q44 1% 48% 0% 34% - 17% Castelhana Q45 1% 21% 0% 14% - 8% Q05 6% 42% 4% 34% - 35% Q06 6% 41% 4% 35% 3% 30% Intercetor Q08 8% 42% 5% 33% 4% 30% geral Q09 9% 45% 6% 36% - 29% Q10 23% 46% 16% 41% 4% 31% Q11-50% - 41% 7% 42% Image 2. Schematic representation of PI2 to the summer of 2000 Image 3. Schematic representation of PI2 to the summer of 2014/2015 8
9 Examining the ID1 indicator, it is possible to conclude that infiltration flows affluent to the drainage system do not compromise the transport capacity of the total inflow to the system, nor did they compromise in By comparing Image 2 with Image 3, it was concluded that there was a worsening of infiltration flows at the subsystem's global level, particularly in the initial sections of the Carenque, Caparide and Amoreira sewers. However, there was a reduction in the inflow of infiltration flows into the Sassoeiros sewer, because of some rehabilitation interventions carried out. Conclusions Comparing the infiltration volume data for the summers of 2000 and 2015, collected in the same measurement points, it is possible to observe the evolution of this parameter over time. It was concluded that, in 70% of the drainage system, the volume of infiltration did not increase significantly (Vinf (2015)/Vinf (2000) <1.3), and even declined in some places, due to the rehabilitation works that took place in the drainage system. The most serious situation occurred in the Carenque sewer, where are increase of 10%, approximately, was observed. This increase can be due to the structural deterioration of the sewers that worsens with time, so it is suggested a detailed inspection of the interceptor (with CCTV) to better access the causes of the problem. To evaluate the most problematic sections, two performance indicators were analysed. It was verified that most of the system presents infiltration contributions lower than 50% of the average flow, the guiding value mentioned by Regulatory Decree nº 23/95. In two sections of the interceptor (Cadaveira and Caparide), for ID2, percentages higher than 50% were obtained, which is considered a high value, indicative of the likely degradation of the sewers. These sections are presented as priorities for detailed inspection and eventual implementation of rehabilitation interventions. It was also verified that, for some sections where rehabilitation works were recently carried out, the infiltration percentages correspond to values lower than 25% (this is the case of the Sassoeiros sewer, with rehabilitation works carried out in 2013). 9
10 References Cardoso, A., Almeida, M.C. e Coelho, S.T. (2002). Avaliação do impacto da infiltração no desempenho de sistemas de drenagem urbana. 10º Encontro Nacional de Saneamento Básico. Braga. Cardoso, M. A., Coelho, S. T., Almeida, M. (2004). Sewer systems performance assessment methodology, formulation, computational application and case studies. Deliverable 9.2: Infiltration and exfiltration performance indicators, LNEC, Lisboa, Portugal. Coelho, S., Alegre, A. (1999). Indicadores de Desempenho de Sistemas de Saneamento Básico. LNEC, Lisboa. Cohen, B., Rozelman, S., Ryan,T. (1998). Removing extraneous flow in New York city A Systematic approach yielding results. ADS Corporation, New York. De Bénédittis J. (2004). Mesurage de l infiltration et de l exfiltration dans les réseaux d assainissement. Thése de Doctorat. Institut National des Sciences Appliquées de Lyon. 16 Avril. Ellis. (2001). Sewer infiltration/exfiltration and interactions with sewer flows and groundwater quality. INTERURBA II. Lisboa, Portugal. Gamboa, M., Almeida, M. C., Matos, M. R., Matos, J. S. (2000). - Controlo da descarga de excedentes no sistema de saneamento da Costa do Estoril. LNEC 324/00-NES, Lisboa. Kracht, O., Gresch, M., & Gujer, W. (2008). Innovative tracer methods for sewer infiltration monitoring. Urban Water Journal, 5 (3)(Research article), Metcalf e Eddy (2003). Wastewater Engineering: Treatment and Reuse (4ª ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. Rodrigues, V. (2013). Avaliação de Infiltração em Drenagem Urbana Recorrendo a Métodos Convencionais e não Convencionais - Aplicação ao Caneiro de Alcântara, em Lisboa. Dissertação para obtenção do Grau de Mestre em Engenharia Civil, Instituto Superior Técnico, Lisboa. White, M., Johnson, H., Anderson, G., Misstear, B. (1997) Control of infiltration to sewers. Report 175, CIRIA, UK. 10
RESILIENCE OF WATER SUPPLY SYSTEMS CASE STUDY OF QUINTA DO LAGO
 41 st IAHS WORLD CONGRESS Sustainability and Innovation for the Future 13-16 th September 2016 Albufeira, Algarve, Portugal RESILIENCE OF WATER SUPPLY SYSTEMS CASE STUDY OF QUINTA DO LAGO João Caetano
41 st IAHS WORLD CONGRESS Sustainability and Innovation for the Future 13-16 th September 2016 Albufeira, Algarve, Portugal RESILIENCE OF WATER SUPPLY SYSTEMS CASE STUDY OF QUINTA DO LAGO João Caetano
A case study of rainfall-derived infiltration and inflow on a separate sanitary sewer system
 A case study of rainfall-derived infiltration and inflow on a separate sanitary sewer system 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Nelson J. G. Carriço 1, Rita Brito 2, Manuel Baptista 1 1 Barreiro School of Technology,
A case study of rainfall-derived infiltration and inflow on a separate sanitary sewer system 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Nelson J. G. Carriço 1, Rita Brito 2, Manuel Baptista 1 1 Barreiro School of Technology,
*IST UL (University of Lisbon), Lisbon, Portugal. Corresponding author:
 Monitoring and simulation of saline water inflows to drainage systems in coastal areas. The Case of the Alcântara s Wastewaters System, in Lisbon, Portugal Catarina Pina Teixeira de Melo Amaro* *IST UL
Monitoring and simulation of saline water inflows to drainage systems in coastal areas. The Case of the Alcântara s Wastewaters System, in Lisbon, Portugal Catarina Pina Teixeira de Melo Amaro* *IST UL
Urban water infrastructure asset management: a structured approach in four Portuguese water utilities
 Urban water infrastructure asset management: a structured approach in four Portuguese water utilities M. A. Cardoso *, M. Santos Silva *, S. T. Coelho *, M. C. Almeida *, D.I.C Covas ** Laboratório Nacional
Urban water infrastructure asset management: a structured approach in four Portuguese water utilities M. A. Cardoso *, M. Santos Silva *, S. T. Coelho *, M. C. Almeida *, D.I.C Covas ** Laboratório Nacional
Town of New Castle, New Hampshire Sewer Infrastructure Evaluation
 Town of New Castle, New Hampshire Sewer Infrastructure Evaluation March 2016 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The Town of New Castle (Town) is working collaboratively with the City of Portsmouth (City) to consider options
Town of New Castle, New Hampshire Sewer Infrastructure Evaluation March 2016 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The Town of New Castle (Town) is working collaboratively with the City of Portsmouth (City) to consider options
OPERATIONAL DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM
 OPERATIONAL DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM APPLIED TO THE LISBON COMBINED SEWER SYSTEM: THE CASE OF AN EXTREME RAINFALL EVENT Nuno Pimentel 1, Pedro Póvoa 1 and José Saldanha Matos 2 1 R&D Department, Águas de
OPERATIONAL DECISION SUPPORT SYSTEM APPLIED TO THE LISBON COMBINED SEWER SYSTEM: THE CASE OF AN EXTREME RAINFALL EVENT Nuno Pimentel 1, Pedro Póvoa 1 and José Saldanha Matos 2 1 R&D Department, Águas de
Estimating groundwater infiltration into sewerages by using the moving minimum method a survey in Austria
 Estimating groundwater infiltration into sewerages by using the moving minimum method a survey in Austria Th. Ertl 1 *, G. Spatzierer², St. Wildt³ 1 University of Natural Resources and Applied Life Sciences
Estimating groundwater infiltration into sewerages by using the moving minimum method a survey in Austria Th. Ertl 1 *, G. Spatzierer², St. Wildt³ 1 University of Natural Resources and Applied Life Sciences
Fractionation of Infiltration and Inflow (I/I) components in urban sewer systems with regression analysis
 Fractionation of Infiltration and Inflow (I/I) components in urban sewer systems with regression analysis Détermination de l'origine de l'infiltration et des apports dans un système d'assainissement urbain
Fractionation of Infiltration and Inflow (I/I) components in urban sewer systems with regression analysis Détermination de l'origine de l'infiltration et des apports dans un système d'assainissement urbain
Potential reduction in potable water consumption by reusing rainwater in urban centers
 Potential reduction in potable water consumption by reusing rainwater in urban centers Catarina Viana de Araújo Lúcio Instituto Superior Técnico, University of Lisbon, Portugal October 2015 Abstract Rainwater
Potential reduction in potable water consumption by reusing rainwater in urban centers Catarina Viana de Araújo Lúcio Instituto Superior Técnico, University of Lisbon, Portugal October 2015 Abstract Rainwater
CHAPTER 4 SYSTEM DESIGN CRITERIA
 INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 4 SYSTEM DESIGN CRITERIA Adequate design of the District s wastewater conveyance facilities requires the determination of the quantity of wastewater from contributing sources. The
INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 4 SYSTEM DESIGN CRITERIA Adequate design of the District s wastewater conveyance facilities requires the determination of the quantity of wastewater from contributing sources. The
Modelling sludge drying bed dewatering processes
 Modelling sludge drying bed dewatering processes Eleonora de Carvalho Lampreia eleonoracl@hotmail.com Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal July 2017 Abstract: In recent years, the
Modelling sludge drying bed dewatering processes Eleonora de Carvalho Lampreia eleonoracl@hotmail.com Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal July 2017 Abstract: In recent years, the
LESSON 10 WASTEWATER DRAINAGE SYSTEMS
 SANITARY ENGINEERING LESSON 10 / SUMMARY LESSON 10 WASTEWATER DRAINAGE SYSTEMS Wastewater drainage systems evolution; Current situation in Portugal; Components of the systems; Examples of existing wastewater
SANITARY ENGINEERING LESSON 10 / SUMMARY LESSON 10 WASTEWATER DRAINAGE SYSTEMS Wastewater drainage systems evolution; Current situation in Portugal; Components of the systems; Examples of existing wastewater
Introduction. Keywords: Oil Palm, hydrology, HEC-HMS, HEC-RAS. a * b*
 The Effect of Land Changes Towards in Sg. Pandan Perwira Bin Khusairi Rahman 1,a* and Kamarul Azlan bin Mohd Nasir 1,b 1 Faculty of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia a * wirakhusairirahman@gmail.com,
The Effect of Land Changes Towards in Sg. Pandan Perwira Bin Khusairi Rahman 1,a* and Kamarul Azlan bin Mohd Nasir 1,b 1 Faculty of Civil Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia a * wirakhusairirahman@gmail.com,
ASPHALT ROAD PAVEMENTS LIFE CYCLE COST ANALYSIS
 ASPHALT ROAD PAVEMENTS LIFE CYCLE COST ANALYSIS Extended Abstract Hugo Bernardo Campos Branquinho Matos da Costa Dissertation to obtain the Degree of Master in Civil Engineering November 2008 ASPHALT ROAD
ASPHALT ROAD PAVEMENTS LIFE CYCLE COST ANALYSIS Extended Abstract Hugo Bernardo Campos Branquinho Matos da Costa Dissertation to obtain the Degree of Master in Civil Engineering November 2008 ASPHALT ROAD
Extended Abstract. PUC-Rio - Certificação Digital Nº /CA
 Extended Abstract Fonseca, Fabiana Lanzillotta da; Romanel, Celso (Advisor); Costa, Ernani de Souza (Co-advisor). Stormwater Management with watercourse valorization: computational simulation of the Tintas
Extended Abstract Fonseca, Fabiana Lanzillotta da; Romanel, Celso (Advisor); Costa, Ernani de Souza (Co-advisor). Stormwater Management with watercourse valorization: computational simulation of the Tintas
Chapter 8 Addressing I/I Issues and High Flows
 Chapter Outline Chapter 8 Addressing I/I Issues and High Flows This chapter is organized into the following sections: Introduction Background Estimation of Infiltration Volume Conveyance Costs Effect of
Chapter Outline Chapter 8 Addressing I/I Issues and High Flows This chapter is organized into the following sections: Introduction Background Estimation of Infiltration Volume Conveyance Costs Effect of
Springfield, MO SSO Control Program: Using Big Data to Chart Progress
 Springfield, MO SSO Control Program: Using Big Data to Chart Progress 30 August 2017 Richard Hayslett & Josh Tedder Springfield s Overflow Control Plan 10 year, $200 Million Phase 1 Foundation Projects
Springfield, MO SSO Control Program: Using Big Data to Chart Progress 30 August 2017 Richard Hayslett & Josh Tedder Springfield s Overflow Control Plan 10 year, $200 Million Phase 1 Foundation Projects
Infiltration in sewer systems: comparison of measurement methods
 Infiltration in sewer systems: comparison of measurement methods J. De Bénédittis *, J.-L. Bertrand-Krajewski * *URGC Hydrologie Urbaine, INSA de Lyon, 34 avenue des Arts, 69621 Villeurbanne cedex, France
Infiltration in sewer systems: comparison of measurement methods J. De Bénédittis *, J.-L. Bertrand-Krajewski * *URGC Hydrologie Urbaine, INSA de Lyon, 34 avenue des Arts, 69621 Villeurbanne cedex, France
Infiltration and Inflow. Michael Sassaman Phone
 Infiltration and Inflow Michael Sassaman msassaman@entecheng.com Phone 610-373-3345 Inflow and Infiltration PA DEP Learning Objectives Do you have Excessive I/I? Sources of Inflow and Infiltration I/I
Infiltration and Inflow Michael Sassaman msassaman@entecheng.com Phone 610-373-3345 Inflow and Infiltration PA DEP Learning Objectives Do you have Excessive I/I? Sources of Inflow and Infiltration I/I
CE 370. Wastewater Characteristics. Quantity. The design of a wastewater treatment plant requires knowledge of: Quantity or flowrate of wastewater.
 CE 370 Wastewater Characteristics Quantity 1 Introduction The design of a wastewater treatment plant requires knowledge of: Quantity or flowrate of wastewater. Required to determine the size of the various
CE 370 Wastewater Characteristics Quantity 1 Introduction The design of a wastewater treatment plant requires knowledge of: Quantity or flowrate of wastewater. Required to determine the size of the various
WEF Collection Systems Conference 2017
 Davenport, Iowa 14th District Diversion Study Karol Giokas, P.E., RJN Group Tom Leabhart, P.E., Davenport, IA ABSTRACT The 14 th District sanitary sewer basin in Davenport, Iowa has high levels of inflow
Davenport, Iowa 14th District Diversion Study Karol Giokas, P.E., RJN Group Tom Leabhart, P.E., Davenport, IA ABSTRACT The 14 th District sanitary sewer basin in Davenport, Iowa has high levels of inflow
Hydrology and Water Management. Dr. Mujahid Khan, UET Peshawar
 Hydrology and Water Management Dr. Mujahid Khan, UET Peshawar Course Outline Hydrologic Cycle and its Processes Water Balance Approach Estimation and Analysis of Precipitation Data Infiltration and Runoff
Hydrology and Water Management Dr. Mujahid Khan, UET Peshawar Course Outline Hydrologic Cycle and its Processes Water Balance Approach Estimation and Analysis of Precipitation Data Infiltration and Runoff
Wastewater System Environmental Setting Wastewater Conveyance Facilities
 February 20, 2017 To: Mr. Ryan Sawyer AICP Analytical Environmental Services 1801 7 th Street Sacramento, CA 95811 Subject: Comments on the Crystal Geyser Draft EIR (DEIR) Dear Mr. Sawyer: This letter
February 20, 2017 To: Mr. Ryan Sawyer AICP Analytical Environmental Services 1801 7 th Street Sacramento, CA 95811 Subject: Comments on the Crystal Geyser Draft EIR (DEIR) Dear Mr. Sawyer: This letter
Learning objectives. Upon successful completion of this lecture, the participants will be able to:
 Solomon Seyoum Learning objectives Upon successful completion of this lecture, the participants will be able to: Describe and perform the required step for designing sewer system networks Outline Design
Solomon Seyoum Learning objectives Upon successful completion of this lecture, the participants will be able to: Describe and perform the required step for designing sewer system networks Outline Design
RCCTE was published in February 1990, and have been in force since January It applies to buildings of both residential and tertiary sectors.
 Title of the measure: POR3 - Regulation on the Characteristics of the Thermal Performance of Buildings (RCCTE) - Decree-Law 40/90, of February 6th General description RCCTE was published in February 1990,
Title of the measure: POR3 - Regulation on the Characteristics of the Thermal Performance of Buildings (RCCTE) - Decree-Law 40/90, of February 6th General description RCCTE was published in February 1990,
UrbanSAT- Urban System Analysis Tool : For delivering urban water balancing and reporting
 19th International Congress on Modelling and Simulation, Perth, Australia, 12 16 December 2011 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim2011 UrbanSAT- Urban System Analysis Tool : For delivering urban water balancing
19th International Congress on Modelling and Simulation, Perth, Australia, 12 16 December 2011 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim2011 UrbanSAT- Urban System Analysis Tool : For delivering urban water balancing
Implementing tactical plans to improve water-energy loss management
 Implementing tactical plans to improve water-energy loss management D. Loureiro*, H. Alegre*, M.S. Silva*, R. Ribeiro*, A. Mamade*, A. Poças* * LNEC: National Civil Engineering Laboratory, Portugal. Avenida
Implementing tactical plans to improve water-energy loss management D. Loureiro*, H. Alegre*, M.S. Silva*, R. Ribeiro*, A. Mamade*, A. Poças* * LNEC: National Civil Engineering Laboratory, Portugal. Avenida
Modelling a Combined Sewage and Stormwater Flood Detention Basin
 Modelling a Combined Sewage and Stormwater Flood Detention Basin A. Pugh B.E. (Hons), Member A.W.A. Sales and Support Manager, Wallingford Software Pty Ltd, Australia S. Ratcliffe B.Sc(Hons), Grad Dip
Modelling a Combined Sewage and Stormwater Flood Detention Basin A. Pugh B.E. (Hons), Member A.W.A. Sales and Support Manager, Wallingford Software Pty Ltd, Australia S. Ratcliffe B.Sc(Hons), Grad Dip
CHAPTER ONE : INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER ONE : INTRODUCTION WHAT IS THE HYDROLOGY? The Hydrology means the science of water. It is the science that deals with the occurrence, circulation and distribution of water of the earth and earth
CHAPTER ONE : INTRODUCTION WHAT IS THE HYDROLOGY? The Hydrology means the science of water. It is the science that deals with the occurrence, circulation and distribution of water of the earth and earth
Performance analysis of flood control facilities in São Paulo Metropolitan Region during extreme rainfall events, based on hydrological simulation
 Performance analysis of flood control facilities in São Paulo Metropolitan Region during extreme rainfall events, based on hydrological simulation Graciosa, M.C.P. 1* ; Coelho, G.A. 2 ; Vieira, J.R.S 3.
Performance analysis of flood control facilities in São Paulo Metropolitan Region during extreme rainfall events, based on hydrological simulation Graciosa, M.C.P. 1* ; Coelho, G.A. 2 ; Vieira, J.R.S 3.
A Case Study on Integrated Urban Water Modelling using Aquacycle NTUA, 2007
 A Case Study on Integrated Urban Water Modelling using Aquacycle NTUA, 2007 Contents Motivation Input Data Requirements Case Study - Greater Athens Area Model calibration and validation Formulation and
A Case Study on Integrated Urban Water Modelling using Aquacycle NTUA, 2007 Contents Motivation Input Data Requirements Case Study - Greater Athens Area Model calibration and validation Formulation and
EFFECTS OF WATERSHED TOPOGRAPHY, SOILS, LAND USE, AND CLIMATE ON BASEFLOW HYDROLOGY IN HUMID REGIONS: A REVIEW
 PROGRESS IN PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY EFFECTS OF WATERSHED TOPOGRAPHY, SOILS, LAND USE, AND CLIMATE ON BASEFLOW HYDROLOGY IN HUMID REGIONS: A REVIEW KATIE PRICE 2011 Presented by: Jordan Martin Article Overview
PROGRESS IN PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY EFFECTS OF WATERSHED TOPOGRAPHY, SOILS, LAND USE, AND CLIMATE ON BASEFLOW HYDROLOGY IN HUMID REGIONS: A REVIEW KATIE PRICE 2011 Presented by: Jordan Martin Article Overview
The New Age for Sewer Planning at the City of Los Angeles
 The New Age for Sewer Planning at the City of Los Angeles Mario Dimzon 1 * P.E., Fernando Gonzalez 1 P.E., Ali Poosti 1 PE, Adel Hagekhalil 1 PE, Erick Heath 2 P.E., Rajan Ray 2 P.E., Erin Breen 2 P.E.
The New Age for Sewer Planning at the City of Los Angeles Mario Dimzon 1 * P.E., Fernando Gonzalez 1 P.E., Ali Poosti 1 PE, Adel Hagekhalil 1 PE, Erick Heath 2 P.E., Rajan Ray 2 P.E., Erin Breen 2 P.E.
WASTEWATER & STORM WATER COLLECTION AND REMOVAL
 CVE 471 WATER RESOURCES ENGINEERING WASTEWATER & STORM WATER COLLECTION AND REMOVAL Assist. Prof. Dr. Bertuğ Akıntuğ Civil Engineering Program Middle East Technical University Northern Cyprus Campus CVE
CVE 471 WATER RESOURCES ENGINEERING WASTEWATER & STORM WATER COLLECTION AND REMOVAL Assist. Prof. Dr. Bertuğ Akıntuğ Civil Engineering Program Middle East Technical University Northern Cyprus Campus CVE
Water efficiency in buildings: assessment of its impact on energy efficiency and reducing GHG emissions
 Recent Researches in & Environment efficiency in buildings: assessment of its impact on energy efficiency and reducing GHG emissions A. SILVA-AFONSO, F. RODRIGUES, C. PIMENTEL-RODRIGUES Civil Engineering
Recent Researches in & Environment efficiency in buildings: assessment of its impact on energy efficiency and reducing GHG emissions A. SILVA-AFONSO, F. RODRIGUES, C. PIMENTEL-RODRIGUES Civil Engineering
1. Introduction. Keywords Groundwater, Vulbnerability, Aquifer, Aquitard, Vadose zone. Alsharifa Hind Mohammad
 World Environment 2014, 4(1): 22-32 DOI: 10.5923/j.env.20140401.03 New Groundwater Vulnerability Index for the Main Aquifers in Central Catchment Area in Jordan and Validation of the Results Using NO 3
World Environment 2014, 4(1): 22-32 DOI: 10.5923/j.env.20140401.03 New Groundwater Vulnerability Index for the Main Aquifers in Central Catchment Area in Jordan and Validation of the Results Using NO 3
Public Information Centre No. 2 June 15, :00 8:00 pm. Valley Park Community Centre (GYM B) 970 Paramount Drive Stoney Creek
 Public Information Centre No. 2 June 15, 2017 6:00 8:00 pm Valley Park Community Centre (GYM B) 970 Paramount Drive Stoney Creek Please complete the sign-in sheet and review display materials. The project
Public Information Centre No. 2 June 15, 2017 6:00 8:00 pm Valley Park Community Centre (GYM B) 970 Paramount Drive Stoney Creek Please complete the sign-in sheet and review display materials. The project
HYDROLOGIC-HYDRAULIC STUDY ISABELLA OCEAN RESIDENCES ISLA VERDE, CAROLINA, PR
 HYDROLOGIC-HYDRAULIC STUDY ISABELLA OCEAN RESIDENCES ISLA VERDE, CAROLINA, PR 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Project Description and Location Isabella Ocean Residences is a residential development to be constructed
HYDROLOGIC-HYDRAULIC STUDY ISABELLA OCEAN RESIDENCES ISLA VERDE, CAROLINA, PR 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Project Description and Location Isabella Ocean Residences is a residential development to be constructed
Urban Flood Evaluation in Maceió, Brazil: Definition of the Critical Flood Event Supported by a Mathematical Cell Model
 Urban Flood Evaluation in Maceió, Brazil: Definition of the Critical Flood Event Supported by a Mathematical Cell Model Vidal, D.H.F 1*, Barbosa, F.R 1, and Miguez, M.G 1 1 Federal University of Rio de
Urban Flood Evaluation in Maceió, Brazil: Definition of the Critical Flood Event Supported by a Mathematical Cell Model Vidal, D.H.F 1*, Barbosa, F.R 1, and Miguez, M.G 1 1 Federal University of Rio de
Storm Water and Sanitary Sewer
 Public Works Department Summary Report on Planned Capital Improvements Storm Water and Sanitary Sewer Introduction Public Works has assembled this summary report to highlight major capital improvements
Public Works Department Summary Report on Planned Capital Improvements Storm Water and Sanitary Sewer Introduction Public Works has assembled this summary report to highlight major capital improvements
Improved Inflow & Infiltration (I&I) Monitoring Program
 City of Abbotsford Improved Inflow & Infiltration (I&I) Monitoring Program Submission For 2009 UBCM Community Excellence Awards Best Practices City of Abbotsford Improved Inflow & Infiltration (I&I) Monitoring
City of Abbotsford Improved Inflow & Infiltration (I&I) Monitoring Program Submission For 2009 UBCM Community Excellence Awards Best Practices City of Abbotsford Improved Inflow & Infiltration (I&I) Monitoring
Planning Committee February 10, 2015
 Leland Reservoir Replacement Planning Committee February 10, 2015 Open-Cut Reservoir Projects Permanently out of service Completed Next five years (FY2016-20) Construction beyond FY2020 LELAND RESERVOIR
Leland Reservoir Replacement Planning Committee February 10, 2015 Open-Cut Reservoir Projects Permanently out of service Completed Next five years (FY2016-20) Construction beyond FY2020 LELAND RESERVOIR
Water Management in the Upper Laje River Basin Rebecca Leonardson Rosey Jencks February 13, 2009
 Water Management in the Upper Laje River Basin Rebecca Leonardson Rosey Jencks February 13, 2009 Abstract Urban water management in Portugal will grow increasingly challenging over the 21 st century, due
Water Management in the Upper Laje River Basin Rebecca Leonardson Rosey Jencks February 13, 2009 Abstract Urban water management in Portugal will grow increasingly challenging over the 21 st century, due
Measurement of infiltration rates in urban sewer systems: use of oxygen isotopes
 Measurement of infiltration rates in urban sewer systems: use of oxygen isotopes J. De Bénédittis (1), J.-L. Bertrand-Krajewski (1) (1) URGC Hydrologie Urbaine, INSA de Lyon, Bâtiment Coulomb, 34 avenue
Measurement of infiltration rates in urban sewer systems: use of oxygen isotopes J. De Bénédittis (1), J.-L. Bertrand-Krajewski (1) (1) URGC Hydrologie Urbaine, INSA de Lyon, Bâtiment Coulomb, 34 avenue
Chapter 8: Water Supply & Sanitary Systems
 Chapter 8: Water Supply & Sanitary Systems Manage, Treat & Reserve Comprehensive Plan 2040 2 8. WATER SUPPLY & SANITARY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION This chapter of the City of Lauderdale s 2040 Comprehensive Plan
Chapter 8: Water Supply & Sanitary Systems Manage, Treat & Reserve Comprehensive Plan 2040 2 8. WATER SUPPLY & SANITARY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION This chapter of the City of Lauderdale s 2040 Comprehensive Plan
Degradation of Concrete Bridges by Internal Expansive Reactions Portuguese Case Studies
 Degradation of Concrete Bridges by Internal Expansive Reactions Portuguese Case Studies António Santos Silva, Arlindo Gonçalves, Manuela Salta Materials Department, Laboratório Nacional de Engenharia Civil,
Degradation of Concrete Bridges by Internal Expansive Reactions Portuguese Case Studies António Santos Silva, Arlindo Gonçalves, Manuela Salta Materials Department, Laboratório Nacional de Engenharia Civil,
LEHIGH COUNTY REGIONAL SEWER SYSTEM
 LEHIGH COUNTY AUTHORITY Lowhill Township New Tripoli, PA 18066 LEHIGH COUNTY REGIONAL SEWER SYSTEM Kline s Island WWTP EPA Administrative Order Public Meeting Lehigh County Government Center November 13,
LEHIGH COUNTY AUTHORITY Lowhill Township New Tripoli, PA 18066 LEHIGH COUNTY REGIONAL SEWER SYSTEM Kline s Island WWTP EPA Administrative Order Public Meeting Lehigh County Government Center November 13,
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Engineering 89 (2014 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 89 (2014 ) 557 564 16th Conference on Water Distribution System Analysis, WDSA 2014 Energy Auditing As a Tool for Improving
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 89 (2014 ) 557 564 16th Conference on Water Distribution System Analysis, WDSA 2014 Energy Auditing As a Tool for Improving
EIA POST-EVALUATION"
 Mestrado em Engenharia Civil " Master on Civil Engineering " Impactes Ambientais / Environmental Impacts 5/10" 12 EIA POST-EVALUATION" EIA links to other licensing regimes Prof. Doutora Maria do Rosário
Mestrado em Engenharia Civil " Master on Civil Engineering " Impactes Ambientais / Environmental Impacts 5/10" 12 EIA POST-EVALUATION" EIA links to other licensing regimes Prof. Doutora Maria do Rosário
Distribution Restriction Statement Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited.
 CECW-EH-Y Regulation No. 1110-2-1464 Department of the Army U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Washington, DC 20314-1000 Engineering and Design HYDROLOGIC ANALYSIS OF WATERSHED RUNOFF Distribution Restriction
CECW-EH-Y Regulation No. 1110-2-1464 Department of the Army U.S. Army Corps of Engineers Washington, DC 20314-1000 Engineering and Design HYDROLOGIC ANALYSIS OF WATERSHED RUNOFF Distribution Restriction
Diffuse Pollution in the Drainage System at Two Urban Catchments
 Diffuse Pollution in the Drainage System at Two Urban Catchments A.P. Z. Brites 1 and M. C. C. Gastaldini 2 1 Universidade Federal de Santa Maria Centro de Tecnologia Departamento de Hidráulica e Saneamento
Diffuse Pollution in the Drainage System at Two Urban Catchments A.P. Z. Brites 1 and M. C. C. Gastaldini 2 1 Universidade Federal de Santa Maria Centro de Tecnologia Departamento de Hidráulica e Saneamento
SEWERSHED PRIORITIZATION WORK PLAN. Department of Public Works Wastewater Infrastructure Redevelopment Program
 SEWERSHED PRIORITIZATION WORK PLAN Department of Public Works Wastewater Infrastructure Redevelopment Program SEPTEMBER 30, 2013 Sewershed Prioritization Work Plan Contents 1.0 Introduction... 1-1 1.1
SEWERSHED PRIORITIZATION WORK PLAN Department of Public Works Wastewater Infrastructure Redevelopment Program SEPTEMBER 30, 2013 Sewershed Prioritization Work Plan Contents 1.0 Introduction... 1-1 1.1
MODULE 1 RUNOFF HYDROGRAPHS WORKSHEET 1. Precipitation
 Watershed MODULE 1 RUNOFF HYDROGRAPHS WORKSHEET 1 A watershed is an area of land thaaptures rainfall and other precipitation and funnels it to a lake or stream or wetland. The area within the watershed
Watershed MODULE 1 RUNOFF HYDROGRAPHS WORKSHEET 1 A watershed is an area of land thaaptures rainfall and other precipitation and funnels it to a lake or stream or wetland. The area within the watershed
CHAPTER 6 COLLECTION SYSTEM HYDRAULIC MODEL
 CHAPTER 6 COLLECTION SYSTEM HYDRAULIC MODEL INTRODUCTION The District developed a hydraulic model of the sanitary sewer system as part the 2000 Wastewater Comprehensive Plan. The output from this model
CHAPTER 6 COLLECTION SYSTEM HYDRAULIC MODEL INTRODUCTION The District developed a hydraulic model of the sanitary sewer system as part the 2000 Wastewater Comprehensive Plan. The output from this model
Establishment of cost functions for construction of various types of public water services assets in Portugal
 Establishment of cost functions for construction of various types of public water services assets in Portugal Abstract This paper describes research on the establishment, validation and testing of construction
Establishment of cost functions for construction of various types of public water services assets in Portugal Abstract This paper describes research on the establishment, validation and testing of construction
SEWAGE TREATMENT AND DISPOSAL
 SEWAGE TREATMENT AND DISPOSAL QUANTITY OF SANITARY SEWAGE AND STORM WATER Zerihun Alemayehu Unpolluted cooling water Intercept or sewer Sources of Sewage Residential and commercial sewage Industrial wastewater
SEWAGE TREATMENT AND DISPOSAL QUANTITY OF SANITARY SEWAGE AND STORM WATER Zerihun Alemayehu Unpolluted cooling water Intercept or sewer Sources of Sewage Residential and commercial sewage Industrial wastewater
Water Optimization for Network Efficiency Reducing the Environmental & Water Footprint of a Major Water Utility
 Water Optimization for Network Efficiency Reducing the Environmental & Water Footprint of a Major Water Utility Andrew Donnelly PREFACE Water losses within distribution systems are a global problem, but
Water Optimization for Network Efficiency Reducing the Environmental & Water Footprint of a Major Water Utility Andrew Donnelly PREFACE Water losses within distribution systems are a global problem, but
A Happy Marriage? A CASE FOR INTEGRATING THE MANAGEMENT OF WASTEWATER & STORMWATER PROGRAMS
 A Happy Marriage? A CASE FOR INTEGRATING THE MANAGEMENT OF WASTEWATER & STORMWATER PROGRAMS 2018 Maine Sustainability & Water Conference ZACH HENDERSON WOODARD & CURRAN FRED DILLON CITY OF SOUTH PORTLAND
A Happy Marriage? A CASE FOR INTEGRATING THE MANAGEMENT OF WASTEWATER & STORMWATER PROGRAMS 2018 Maine Sustainability & Water Conference ZACH HENDERSON WOODARD & CURRAN FRED DILLON CITY OF SOUTH PORTLAND
SWOT ANALYSIS FOR THE PILOT RIVER BASIN: Irminio River Basin
 Project cofinanced by European Regional Development Fund Project cofinancé par le Fonds européen de développement régional 1G-MED08-515 Sustainable Water Management through Common Responsibility enhancement
Project cofinanced by European Regional Development Fund Project cofinancé par le Fonds européen de développement régional 1G-MED08-515 Sustainable Water Management through Common Responsibility enhancement
Scoring Groundwater Infiltration & Sewage Exfiltration Risk in a Sanitary Sewage Collection System. Meredith S. Moore Advisor: Dr.
 Scoring Groundwater Infiltration & Sewage Exfiltration Risk in a Sanitary Sewage Collection System Meredith S. Moore Advisor: Dr. Barry Evans July 20, 2015 Contents List of Figures... 2 List of Tables...
Scoring Groundwater Infiltration & Sewage Exfiltration Risk in a Sanitary Sewage Collection System Meredith S. Moore Advisor: Dr. Barry Evans July 20, 2015 Contents List of Figures... 2 List of Tables...
Appendix B Stormwater Site Plan Submittal Requirements Checklist
 Stormwater Site Plan Submittal Requirements Checklist The Submittal Requirements Checklist is intended to aid the design engineer in preparing a Stormwater Site Plan. All items included in the following
Stormwater Site Plan Submittal Requirements Checklist The Submittal Requirements Checklist is intended to aid the design engineer in preparing a Stormwater Site Plan. All items included in the following
Final Wastewater Collection Facilities Management Plan Report
 Final Wastewater Collection Facilities Management Plan Report This project was partially funded by Community Development Block Grants No.06-STBG-2590 and 06-EDBG-2608 Prepared for 416 N. Franklin Street
Final Wastewater Collection Facilities Management Plan Report This project was partially funded by Community Development Block Grants No.06-STBG-2590 and 06-EDBG-2608 Prepared for 416 N. Franklin Street
The effect of the raingauge distribution on stormwater models
 18 th World IMACS / MODSIM Congress, Cairns, Australia 13-17 July 2009 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim09 The effect of the raingauge distribution on stormwater models Cooper, M.R. 1 and D.A. K. Fernando 2
18 th World IMACS / MODSIM Congress, Cairns, Australia 13-17 July 2009 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim09 The effect of the raingauge distribution on stormwater models Cooper, M.R. 1 and D.A. K. Fernando 2
Pre-Event Activities. Blue River. Pre Field Trip Suggestions
 Blue River Have you heard we all live in a watershed? Well, it is true! This total body activity will allow students to demonstrate how water flows in a watershed while exploring how seasonal variations
Blue River Have you heard we all live in a watershed? Well, it is true! This total body activity will allow students to demonstrate how water flows in a watershed while exploring how seasonal variations
Study: Dynamic of wastewater effluent contributions to surface waters and potential challenges for drinking water abstraction in Germany
 German Environment Agency 1. August 2018 Study: Dynamic of wastewater effluent contributions to surface waters and potential challenges for drinking water abstraction in Germany Summary of the findings
German Environment Agency 1. August 2018 Study: Dynamic of wastewater effluent contributions to surface waters and potential challenges for drinking water abstraction in Germany Summary of the findings
CITY OF BOYNTON BEACH COMPREHENSIVE PLAN UTILITIES ELEMENT
 EXHIBIT B CITY OF BOYNTON BEACH COMPREHENSIVE PLAN UTILITIES ELEMENT PROPOSED AMENDMENTS Table of Contents Objective Page Sanitary Sewer Sub-Element 3A.1 Secure reserve capacity at the South Central Regional
EXHIBIT B CITY OF BOYNTON BEACH COMPREHENSIVE PLAN UTILITIES ELEMENT PROPOSED AMENDMENTS Table of Contents Objective Page Sanitary Sewer Sub-Element 3A.1 Secure reserve capacity at the South Central Regional
Implementation of an early warning system in urban drainage infrastructures for direct discharges and flood risk management
 Urban Water II 329 Implementation of an early warning system in urban drainage infrastructures for direct discharges and flood risk management R. Matos 1, F. Ferreira 1, J. Saldanha Matos 1, A. Oliveira
Urban Water II 329 Implementation of an early warning system in urban drainage infrastructures for direct discharges and flood risk management R. Matos 1, F. Ferreira 1, J. Saldanha Matos 1, A. Oliveira
City of Elmhurst Comprehensive Flooding Plan Task Force Meeting
 April 26, 2011 City of Elmhurst Comprehensive Flooding Plan Task Force Meeting Prepared by CBBEL RJN Group Meeting Overview Progress Report on Comprehensive Plan Sanitary Sewer System Storm Sewer System
April 26, 2011 City of Elmhurst Comprehensive Flooding Plan Task Force Meeting Prepared by CBBEL RJN Group Meeting Overview Progress Report on Comprehensive Plan Sanitary Sewer System Storm Sewer System
Exhibit A. Scope of Services for Flow Monitoring Program 2015 Flow Monitoring City of Lawrence, Kansas
 Exhibit A Scope of Services for Flow Monitoring Program 2015 Flow Monitoring City of Lawrence, Kansas Intent and Purpose The City of Lawrence has begun a Rapid Inflow and Infiltration (I/I) Reduction Program.
Exhibit A Scope of Services for Flow Monitoring Program 2015 Flow Monitoring City of Lawrence, Kansas Intent and Purpose The City of Lawrence has begun a Rapid Inflow and Infiltration (I/I) Reduction Program.
Using SWMM 5 in the continuous modelling of stormwater hydraulics and quality
 Using SWMM 5 in the continuous modelling of stormwater hydraulics and quality M.J. Cambez 1, J. Pinho 1, L.M. David 2 * 1 Trainee at Laboratório Nacional de Engenharia Civil (LNEC) 2 Research Officer at
Using SWMM 5 in the continuous modelling of stormwater hydraulics and quality M.J. Cambez 1, J. Pinho 1, L.M. David 2 * 1 Trainee at Laboratório Nacional de Engenharia Civil (LNEC) 2 Research Officer at
Chapter 8: Water Supply & Sanitary Systems
 Chapter 8: Water Supply & Sanitary Systems Manage, Treat & Reserve Comprehensive Plan 2040 2 8. WATER SUPPLY & SANITARY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION This chapter of the City of Lauderdale s 2040 Comprehensive Plan
Chapter 8: Water Supply & Sanitary Systems Manage, Treat & Reserve Comprehensive Plan 2040 2 8. WATER SUPPLY & SANITARY SYSTEM INTRODUCTION This chapter of the City of Lauderdale s 2040 Comprehensive Plan
4/28/17. Size of Floods - Hydrograph Depicts flood data from gaging station; Hydrographs usually show Q vs. time
 GEOL 118 Final Exam Format similar to exams 1 and 2 Covers Lectures #27 40 (Global Climate Change I - Meteorite Impacts III) #35 Floods - II (Size, Prediction, Urbanization, Mitigation) 8:00, Thursday,
GEOL 118 Final Exam Format similar to exams 1 and 2 Covers Lectures #27 40 (Global Climate Change I - Meteorite Impacts III) #35 Floods - II (Size, Prediction, Urbanization, Mitigation) 8:00, Thursday,
SECTION 1 SUMMARY, CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
 SECTION 1 SUMMARY, CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS This Combined Sewer Overflow (CSO) Master Plan was prepared to meet the conditions set forth in Special Condition A, Paragraph 4 of the February 6, 2009
SECTION 1 SUMMARY, CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS This Combined Sewer Overflow (CSO) Master Plan was prepared to meet the conditions set forth in Special Condition A, Paragraph 4 of the February 6, 2009
The Islamic University of Gaza- Civil Engineering Department Sanitary Engineering- ECIV 4325 L5. Storm water Management
 The Islamic University of Gaza- Civil Engineering Department Sanitary Engineering- ECIV 4325 L5. Storm water Management Husam Al-Najar Storm water management : Collection System Design principles The Objectives
The Islamic University of Gaza- Civil Engineering Department Sanitary Engineering- ECIV 4325 L5. Storm water Management Husam Al-Najar Storm water management : Collection System Design principles The Objectives
Issue paper: Aquifer Water Balance
 Issue paper: Aquifer Water Balance 1. Introduction And Background 1.1. Purpose and Scope The population in Kitsap County has grown rapidly in recent years and is expected to increase substantially in the
Issue paper: Aquifer Water Balance 1. Introduction And Background 1.1. Purpose and Scope The population in Kitsap County has grown rapidly in recent years and is expected to increase substantially in the
Wet Weather Planning for Wastewater Treatment Plants
 Wet Weather Planning for Wastewater Treatment Plants June 23, 217 Peak Flow Management: Collection vs. Treatment Collection System Peak Flow Management Single 24 hour design storm I/I reduction SSO elimination
Wet Weather Planning for Wastewater Treatment Plants June 23, 217 Peak Flow Management: Collection vs. Treatment Collection System Peak Flow Management Single 24 hour design storm I/I reduction SSO elimination
Environment and Natural Resources Trust Fund 2016 Request for Proposals (RFP)
 Environment and Natural Resources Trust Fund 2016 Request for Proposals (RFP) Project Title: Integrated Water Management for Hugo, Lino Lakes, Rosemount Category: B. Water Resources ENRTF ID: 087-B Total
Environment and Natural Resources Trust Fund 2016 Request for Proposals (RFP) Project Title: Integrated Water Management for Hugo, Lino Lakes, Rosemount Category: B. Water Resources ENRTF ID: 087-B Total
Drainage Servicing Report - Terms of Reference
 Urban Form and Corporate Strategic Development City Planning 7th Floor, Edmonton Tower 10111 104 Avenue NW Edmonton, AB T5J 0J4 edmonton.ca July 2018 1 Introduction: Drainage Servicing Reports Drainage
Urban Form and Corporate Strategic Development City Planning 7th Floor, Edmonton Tower 10111 104 Avenue NW Edmonton, AB T5J 0J4 edmonton.ca July 2018 1 Introduction: Drainage Servicing Reports Drainage
Tapping into Available Capacity in Existing Infrastructure to Create Water Supply and Water Quality Solutions. Los Angeles Area Chamber of Commerce
 Tapping into Available Capacity in Existing Infrastructure to Create Water Supply and Water Quality Solutions Los Angeles Area Chamber of Commerce May 29, 2018 David Pedersen, P.E. General Manager The
Tapping into Available Capacity in Existing Infrastructure to Create Water Supply and Water Quality Solutions Los Angeles Area Chamber of Commerce May 29, 2018 David Pedersen, P.E. General Manager The
REAL TIME INFLOW AND INFILTRATION ANALYSIS A NEW TOOL TO FOCUS YOUR RENEWAL SPEND
 REAL TIME INFLOW AND INFILTRATION ANALYSIS A NEW TOOL TO FOCUS YOUR RENEWAL SPEND Tom Joseph (AWT Water), Peter Stephens (AWT Water) ABSTRACT Rainfall derived inflow and infiltration (RDII) in sewers has
REAL TIME INFLOW AND INFILTRATION ANALYSIS A NEW TOOL TO FOCUS YOUR RENEWAL SPEND Tom Joseph (AWT Water), Peter Stephens (AWT Water) ABSTRACT Rainfall derived inflow and infiltration (RDII) in sewers has
APPENDIX 14. Inflow and Infiltration in the CRD
 APPENDIX 14 Inflow and Infiltration in the CRD As documented in the CRD-published discussion paper Cost versus Benefit of Reducing Inflow and Infiltration inflow and infiltration refers to rainwater and
APPENDIX 14 Inflow and Infiltration in the CRD As documented in the CRD-published discussion paper Cost versus Benefit of Reducing Inflow and Infiltration inflow and infiltration refers to rainwater and
THE INFLUENCE OF SAMPLING FREQUENCY AT THE QUANTIFICATION OF POLLUTANT LOADS IN THE DESCOBERTO RIVER DISTRITO FEDERAL, BRAZIL
 THE INFLUENCE OF SAMPLING FREQUENCY AT THE QUANTIFICATION OF POLLUTANT LOADS IN THE DESCOBERTO RIVER DISTRITO FEDERAL, BRAZIL Janaína Bezerra Mesquita 1, Sérgio Koide 1 & Nabil Joseph Eid 1 INTRODUCTION
THE INFLUENCE OF SAMPLING FREQUENCY AT THE QUANTIFICATION OF POLLUTANT LOADS IN THE DESCOBERTO RIVER DISTRITO FEDERAL, BRAZIL Janaína Bezerra Mesquita 1, Sérgio Koide 1 & Nabil Joseph Eid 1 INTRODUCTION
EPAL s Experience. in preparing for Emergency Situations
 Empresa Portuguesa das Águas Livres, PORTUGAL EPAL s Experience in preparing for Emergency Situations José Figueira Environmental and Physical Security Manager PROGRAM 1. EPAL OVERVIEW 2.1 WATER SAFETY
Empresa Portuguesa das Águas Livres, PORTUGAL EPAL s Experience in preparing for Emergency Situations José Figueira Environmental and Physical Security Manager PROGRAM 1. EPAL OVERVIEW 2.1 WATER SAFETY
RULES OF THE TENNESSEE DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENT AND CONSERVATION WATER RESOURCES DIVISION CHAPTER PRIORITY RANKING SYSTEM
 RULES OF THE TENNESSEE DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENT AND CONSERVATION WATER RESOURCES DIVISION CHAPTER 0400-46-01 PRIORITY RANKING SYSTEM TABLE OF CONTENTS 0400-46-01-.01 Priority Ranking System: General 0400-46-01-.03
RULES OF THE TENNESSEE DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENT AND CONSERVATION WATER RESOURCES DIVISION CHAPTER 0400-46-01 PRIORITY RANKING SYSTEM TABLE OF CONTENTS 0400-46-01-.01 Priority Ranking System: General 0400-46-01-.03
Sanitary Sewer Design. Sanitary Sewers, Page 1
 Sanitary Sewer Design Sanitary Sewers, Page 1 Sanitary Sewers, Page 2 Sanitary Sewer Design sanitary sewers collect and transport domestic and industrial wastes via gravity flow the ultimate destination
Sanitary Sewer Design Sanitary Sewers, Page 1 Sanitary Sewers, Page 2 Sanitary Sewer Design sanitary sewers collect and transport domestic and industrial wastes via gravity flow the ultimate destination
Sanitary Sewer. Infiltration & Inflow (I/I) Study. Presented by:
 Sanitary Sewer Infiltration & Inflow (I/I) Study City of Beatrice, Nebraska IAWEA Collection System Specialty Conference Presented by: Brian Mulinix, P.E. March 10, 2011 Discussion Topics Definition of
Sanitary Sewer Infiltration & Inflow (I/I) Study City of Beatrice, Nebraska IAWEA Collection System Specialty Conference Presented by: Brian Mulinix, P.E. March 10, 2011 Discussion Topics Definition of
2nd IWA Leading-Edge Conference & Exhibition on Strategic Asset Management
 2nd IWA Leading-Edge Conference & Exhibition on Strategic Asset Management Strategies for integrating alternative groundwater sources into the water supply system of the Algarve, Portugal T.Y. Stigter,
2nd IWA Leading-Edge Conference & Exhibition on Strategic Asset Management Strategies for integrating alternative groundwater sources into the water supply system of the Algarve, Portugal T.Y. Stigter,
1.0 Introduction / Study Area Authorization Purpose of Study Background 1
 Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction / Study Area... 1 1.1 Authorization 1 1.2 Purpose of Study 1 1.3 Background 1 2.0 Existing Wastewater Treatment Lagoon... 2 2.1 Existing Lagoon System 2 3.0 Future Wastewater
Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction / Study Area... 1 1.1 Authorization 1 1.2 Purpose of Study 1 1.3 Background 1 2.0 Existing Wastewater Treatment Lagoon... 2 2.1 Existing Lagoon System 2 3.0 Future Wastewater
Efficiency assessment of the household water use
 1 Efficiency assessment of the household water use Catarina Nunes Jorge Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa Lisbon, Portugal catarina.jorge@tecnico.ulisboa.pt Abstract Currently, the quality
1 Efficiency assessment of the household water use Catarina Nunes Jorge Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa Lisbon, Portugal catarina.jorge@tecnico.ulisboa.pt Abstract Currently, the quality
CITY OF MONTCLAIR Montclair Civic Center 5111 Benito Street Montclair, CA 91763
 CITY OF MONTCLAIR Montclair Civic Center 5111 Benito Street Montclair, CA 91763 I. Introduction Water Quality A National, State, and Local Concern Throughout the United States, many rivers, creeks, streams,
CITY OF MONTCLAIR Montclair Civic Center 5111 Benito Street Montclair, CA 91763 I. Introduction Water Quality A National, State, and Local Concern Throughout the United States, many rivers, creeks, streams,
Introduction to Hydrology, Part 2. Notes, Handouts
 Introduction to Hydrology, Part 2 Notes, Handouts Precipitation Much of hydrology deals with precipitation How much? How frequently/infrequently? What form? How quickly? Seasonal variation? Drought frequency?
Introduction to Hydrology, Part 2 Notes, Handouts Precipitation Much of hydrology deals with precipitation How much? How frequently/infrequently? What form? How quickly? Seasonal variation? Drought frequency?
Damaged Lines in Morro Bay s Wastewater Collection System
 Damaged Lines in Morro Bay s Wastewater Collection System Causes and Effects Richard E. T. Sadowski and Marla Jo Bruton B. S. Mechanical Engineering; CWEA Grade IV Wastewater Collection System Operator
Damaged Lines in Morro Bay s Wastewater Collection System Causes and Effects Richard E. T. Sadowski and Marla Jo Bruton B. S. Mechanical Engineering; CWEA Grade IV Wastewater Collection System Operator
Identification and characterization of industrial / rainwater effluents at the company Iberol
 Identification and characterization of industrial / rainwater effluents at the company Iberol Ana Cristina Narciso Figueira Mira The drainage network for industrial and rainwater effluents at Iberol was
Identification and characterization of industrial / rainwater effluents at the company Iberol Ana Cristina Narciso Figueira Mira The drainage network for industrial and rainwater effluents at Iberol was
New approach for optimization of construction and demolition waste management
 New approach for optimization of construction and demolition waste management Application to the Lisbon Metropolitan Area António Rebello de Andrade Mestrado em Engenharia Civil ABSTRACT: The growing concern
New approach for optimization of construction and demolition waste management Application to the Lisbon Metropolitan Area António Rebello de Andrade Mestrado em Engenharia Civil ABSTRACT: The growing concern
Somerset Raritan Valley Sewerage Authority SSO Abatement and Storm Control Treatment Facility
 Somerset Raritan Valley Sewerage Authority SSO Abatement and Storm Control Treatment Facility Michael Sanders, P.E., Kleinfelder Collection Systems Specialty Conference NEWEA September 12, 2016 Presentation
Somerset Raritan Valley Sewerage Authority SSO Abatement and Storm Control Treatment Facility Michael Sanders, P.E., Kleinfelder Collection Systems Specialty Conference NEWEA September 12, 2016 Presentation
Featherston Groundwater Infiltration Investigation
 South Wairarapa District ouncil TABLE OF ONTENTS 1 BAKGROUND... 1 2 METHODOLOGY... 1 2.1 Defining GWI... 1 2.2 Night Flow Isolation... 1 3 RESULTS... 4 4 REHABILITATION OST ESTIMATES... 7 4.1 Rehabilitation
South Wairarapa District ouncil TABLE OF ONTENTS 1 BAKGROUND... 1 2 METHODOLOGY... 1 2.1 Defining GWI... 1 2.2 Night Flow Isolation... 1 3 RESULTS... 4 4 REHABILITATION OST ESTIMATES... 7 4.1 Rehabilitation
INFLOW & INFILTRATION CORRECTION VIA LATERAL LINE DITCH LEAK REPAIRS
 1 of 5 8/1/2013 2:10 PM INFLOW & INFILTRATION CORRECTION VIA LATERAL LINE DITCH LEAK REPAIRS Project Location and Description Glen Mayberry, Project Manager Roy F. Weston, Houston, TX The project is in
1 of 5 8/1/2013 2:10 PM INFLOW & INFILTRATION CORRECTION VIA LATERAL LINE DITCH LEAK REPAIRS Project Location and Description Glen Mayberry, Project Manager Roy F. Weston, Houston, TX The project is in
Assessing SWMM 5 Hydrologic Parameter Benefits for Model Calibration
 Assessing SWMM 5 Hydrologic Parameter Benefits for Model Calibration Justin Siegrist, 1 Daniel Anderson, 2 Joseph Koran, 2 Mark Pribak, 3 Uzair M. (Sam) Shamsi 4 and Dave White 1 1 Wade Trim, Inc., Cincinnati,
Assessing SWMM 5 Hydrologic Parameter Benefits for Model Calibration Justin Siegrist, 1 Daniel Anderson, 2 Joseph Koran, 2 Mark Pribak, 3 Uzair M. (Sam) Shamsi 4 and Dave White 1 1 Wade Trim, Inc., Cincinnati,
ANALYSIS AND DESIGN FOR SEISMIC ACTION APPLICATION TO A CASE STUDY. Abstract. 1. Introduction
 Author: Florentino Miguel Luz Coelho Institution: Instituto Superior Técnico ANALYSIS AND DESIGN FOR SEISMIC ACTION APPLICATION TO A CASE STUDY Abstract This article describes the design and particularities
Author: Florentino Miguel Luz Coelho Institution: Instituto Superior Técnico ANALYSIS AND DESIGN FOR SEISMIC ACTION APPLICATION TO A CASE STUDY Abstract This article describes the design and particularities
5 CONSULTANT SELECTION FOR INFLOW AND INFILTRATION AUDIT AND FLOW MONITORING PROGRAM
 5 CONSULTANT SELECTION FOR INFLOW AND INFILTRATION AUDIT AND FLOW MONITORING PROGRAM The Environmental Services Committee recommends the adoption of the recommendation contained in the following report
5 CONSULTANT SELECTION FOR INFLOW AND INFILTRATION AUDIT AND FLOW MONITORING PROGRAM The Environmental Services Committee recommends the adoption of the recommendation contained in the following report
