Mobile Museum PowerPoint Presentation Discussion
|
|
|
- Madeleine Lyons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Mobile Museum PowerPoint Presentation Discussion Grades: K-2 Summary: The Mobile Museum (MoMu) is an RV converted into a mobile exhibit highlighting University of Iowa research. Funded by the University of Iowa, the MoMu travels to different schools and fairs, even stopping during RAGBRAI. This year the MoMu exhibits are: German Iowa, Wealth of Health: From Iowa to the World, and Hawkeye Power: Clean Energy for Iowans. This document provides teachers with a set of questions to be asked when using the PowerPoint presentation (see pages 5-7). Teachers can use these materials with students prior to, during and following their visit with the MoMu. Renewable Fuels Prior to Exhibit Engagement: The Renewable Fuels PowerPoint presentation engages students in thinking about how everyday items are powered by a variety of different materials. Through this engagement, students begin to develop an understanding of the concept of energy and where it comes from. During Exhibit Engagement: In the Mobile Museum exhibit, students identify and compare a variety of fuel sources including miscanthus, oat hulls, wood chips, and coal. Students identify differences in the carbon cycle of burning biomass versus coal. Post Exhibit Engagement: During class discussion, students recall their individual observations in the Mobile Museum exhibit to identify a variety of sources of fuel and how some of these sources are renewable and some are not.
2 2 Prior to Exhibit Engagement Questions Connection to Human Body How do you get energy for your body to function? What type of fuel does your body use to provide you energy? What are some things that you eat or drink that give you energy? o Some students may have the misconception that energy is fuel o Fuel is only one source of energy. It is not energy itself. Connection to Transportation Students identify how types of transportation, such as trains, get energy. Old Fashioned Train What is this? What type of fuel does this train use? Ask the students to look for something in the museum that could be burned instead of coal. Post Exhibit Engagement Questions Coal versus Renewable Fuels Did anyone see coal in the Mobile Museum? What is coal? Why are we looking for alternative fuels for coal? What plants did you see at the museum that could be used instead of coal? Do we want to use more coal or more plants for fuel? o Why? Wind Energy Prior to Exhibit Engagement The Wind Turbine PowerPoint presentation engages students in thinking about how wind turbines move and what they do by making a comparison to a pinwheel, something they may have seen before. During Exhibit Engagement Guide students to the interactive wind turbine activity in the Mobile Museum. o In the exhibit students will have the opportunity to push a button that will cause the blades on a miniature wind turbine to spin. As the blades of the turbine spin, LEDs will light up. The faster the blades move, the more LEDs will light up. Post Exhibit Engagement Through class discussion, students will make a connection between the wind they produce to move a pinwheel and the wind that is needed to move a wind turbine. o The connection between wind and wind turbines is reinforced when students observe that the faster the wheel is turned, the greater number of LEDs light up.
3 3 Prior to Exhibit Engagement Questions Connection to Pinwheels Have you seen this before? What is it? Where have you seen it? What does it do? How does it work? Connection to Wind Turbines Have you seen this before? What is it? Where have you seen it? What does it do? How does it work? Post Exhibit Engagement Questions Did you see a model of a wind turbine in the exhibit? What did it do? How did it work? Did any of you get the light to shine when you pushed the button on the wind turbine display? What does this mean? Where can we find wind turbines? Do you think Iowa is a good place for wind turbines? Why? Why are scientists at the University of Iowa designing wind turbines? Efficient Building Design Prior to Exhibit Engagement The Building Efficiency PowerPoint engages students in thinking about how clothes trap heat from their bodies. They will recognize that winter clothes will trap more heat than summer clothes. Students will begin thinking about the concept of insulation without using the word insulation. Here, they will make the connection between clothes and insulation. o Clothes keep bodies warm, as insulation keeps homes warm. During Exhibit Engagement Encourage students to look for the thermal imaging camera and advise them to aim it at the different building materials in the exhibit. o Have students point the gun at themselves as well, to see how much heat is emitted. Using the thermal imaging camera, students will be able to observe how much thermal radiation (heat) is coming off of their own bodies as well as how much is coming through the different materials.
4 4 This will show students that not all materials will keep themselves or their homes warm. Students will start thinking about the reason different materials are used to insulate their homes. Post Exhibit Engagement Through class discussion about their observations, Students will understand that different materials can be used to insulate (layer) houses and other buildings. Students will determine which of the materials presented in the Mobile Museum would be best to insulate (layer) a building with and why. o Different materials trap heat more effectively than others. o Similar to why we do not wear tank tops in the winter. Prior to Exhibit Engagement Questions Connection to Human Body When it is cold outside, what kinds of clothes do you wear (i.e. long sleeve shirts, gloves, earmuffs, hats, sweatshirts)? Do you wear more layers when it is cold than you would wear when it is warm? Why do you wear extra layers? Why do you feel warmer when you wear more layers? Connection to Houses What keeps your house warm in the winter? Would your house still feel warm if it was made out of leaves? o Why or why not? Post Exhibit Engagement Questions When you played with the infrared gun, what material let the most amount of heat through? Why? What material would you want your homes to be made of to keep you warm in the winter? Putting It All Together Prior to Exhibit Discussion Question What do all these topics have in common? Why is renewable energy important? Why is wind a better energy source than coal? Why other types of fuel can we use to power planes, trains, and cars? Why does it matter what our homes are made of?
5 5 PowerPoint Slides Renewable Fuels How do you get energy? How do you get energy? What are some foods and drinks that give you energy? What foods or drinks give you more energy than others? How do planes, cars, and boats get energy? How do planes, cars, and boats get energy? What is this? How does the train get energy to move? How does the train get energy from coal?
6 6 Wind Turbines What is this? Where have you seen these before? How does it work? How does it work? What are these? Where have you seen these before? How do these work? How do these work? Energy Efficiency
7 7 When it is cold outside, how do you keep warm? Do you wear more clothes in the winter or in the summer? What keeps your home warm in the winter? Background Information and Resources Biomass All types of Biomass used at the University of Iowa are being co-fired with coal Miscanthus o A 12-foot tall grass, can be used on marginal crop land o Established on 2,500 acres will reduce 22,500 tons of coal used Wood Chips o Are taken from undesirable trees o 3,000 tons of wood chips are produced with 2,000 tons being actually used because the fuel boiler requires small chips 1 inch or less with no twigs or branches. o There is currently a 20% by volume blend of wood chips and coal for cofiring being used at a plant in Muscatine, Iowa. The University of Iowa is researching different types of fuel and their sustainability, including the types of plants seen at the Mobile Museum. o Industrial Organic Byproducts
8 8 o Byproducts, such as oat hulls from the production of cereals, are commonly unusable by most companies. o It can be produced locally, involving little to no transportation and involving no drilling or strip mining which is the process to extract coal from the earth. Student misconceptions about energy o II-Lessons/energy-misconceptions-PDF.pdf Wind Energy Wind is created by uneven heating of the Earth s surface by the sun Wind energy is a clean and renewable energy source Iowa has the second highest wind capacity in the United States at 6,212 MW, but is the nation leader in wind energy usage at 31%. o o Wind turbines can be built with 1, 2, or 3 blades, but wind turbines with 3 blades are the most efficient, and are what we most commonly see today By using more wind energy we can reduce carbon emissions and conserve water, which is used to cool power plants The Midwest has very strong wind speeds making it perfect for wind energy
9 9 Wind energy has been around for a long time o Windmills- which were used to mill grain or pump water o World s oldest windmill-persia AD o Building of a Wind Turbine o Building Design Heat moves from a spot of higher temperature to a spot of lower temperature, this is why in the summer, when the windows in houses are open the house is hot (the heat from outside travels to the cooler inside of the house); in the winter, if the windows were open the house would be cold (the heat from the inside of the house travels to the cooler outside of the house). The type and thickness of material are two key factors that traps heat in the home. o o While a thicker material generally traps heat better than a thinner material, thickness does not necessarily mean it is best for keeping something warm. The type of material matters as well. For example, Nylon rain coats are thinner than denim, but keep you warmer because the strands of fabric are closer together. This prevents heat from escaping without moving through the material.
10 10 External resources/links: Link to building design article featuring Dr. Craig Just from the University of Iowa: Online game students can play with parental permission (requires and internet access):
Mobile Museum. Hawkeye Power Curriculum Guide. Grades K-12
 Mobile Museum Hawkeye Power Curriculum Guide Grades K-12 As part of a collaboration between the University of Iowa Mobile Museum (MoMu) and the College of Education, pre-service education students developed
Mobile Museum Hawkeye Power Curriculum Guide Grades K-12 As part of a collaboration between the University of Iowa Mobile Museum (MoMu) and the College of Education, pre-service education students developed
Earth s Energy Resources: GeothermaL
 Earth s Energy Resources: GeothermaL Geothermal energy comes from heat deep under the ground. This energy is produced in the core of the Earth. The heat from the core can melt rock into magma. The magma
Earth s Energy Resources: GeothermaL Geothermal energy comes from heat deep under the ground. This energy is produced in the core of the Earth. The heat from the core can melt rock into magma. The magma
Science 7 Unit C: Heat and Temperature. Topic 7. Sources of Thermal Energy. pp WORKBOOK. Name:
 Science 7 Unit C: Heat and Temperature Topic 7 Sources of Thermal Energy pp. 238-247 WORKBOOK Name: Read p. 238 TASK: Complete the Find Out Activity on p. 238 Energy Inputs for Energy Outputs Please record
Science 7 Unit C: Heat and Temperature Topic 7 Sources of Thermal Energy pp. 238-247 WORKBOOK Name: Read p. 238 TASK: Complete the Find Out Activity on p. 238 Energy Inputs for Energy Outputs Please record
New Energy! PRE READING ACTIVITY (Energy Resources) SELECT THE CORRECT WORDS FROM THE BOX FOR THE PICTURES GIVEN. Natural Gas Gasoline Solar Coal
 Name: Class: Date: New Energy! Grade 11A Science Related Reading/Physics Physics Gr11A PRE READING ACTIVITY (Energy Resources) SELECT THE CORRECT WORDS FROM THE BOX FOR THE PICTURES GIVEN Natural Gas Gasoline
Name: Class: Date: New Energy! Grade 11A Science Related Reading/Physics Physics Gr11A PRE READING ACTIVITY (Energy Resources) SELECT THE CORRECT WORDS FROM THE BOX FOR THE PICTURES GIVEN Natural Gas Gasoline
Renewable vs. Non-Renewable Energy
 Renewable vs. Non-Renewable Energy In today s society, we are heavily reliant on electrical energy to complete a lot of the work that we do. It seems to be the most functional form of energy and the most
Renewable vs. Non-Renewable Energy In today s society, we are heavily reliant on electrical energy to complete a lot of the work that we do. It seems to be the most functional form of energy and the most
Save Energy! Grade Level K-1
 Save Energy! Grade Level K-1 Green and Healthy Home Topic 7: Energy While there are two types of energy, renewable and nonrenewable, most of the energy we use comes from burning nonrenewable fuels--coal,
Save Energy! Grade Level K-1 Green and Healthy Home Topic 7: Energy While there are two types of energy, renewable and nonrenewable, most of the energy we use comes from burning nonrenewable fuels--coal,
LESSON: Engineering Better Blades GRADE: 4 SUMMARY:
 LESSON: GRADE: 4 SUMMARY: Working in groups, students will design mini wind turbine blades from recycled materials, and measure the energy generated. After each trial, they will refine their design and
LESSON: GRADE: 4 SUMMARY: Working in groups, students will design mini wind turbine blades from recycled materials, and measure the energy generated. After each trial, they will refine their design and
Introduction to Energy
 Introduction to Energy Get Energized! What are two types of energy? Energy is the ability to cause change. Energy takes many different forms and causes many different effects. There are two general types
Introduction to Energy Get Energized! What are two types of energy? Energy is the ability to cause change. Energy takes many different forms and causes many different effects. There are two general types
Digging Deeper SOLAR ENERGY. Forms of Solar Energy
 a) Is the wind speed the same in the morning; the afternoon; the evening? b) Move your anemometer to another location. Is it windier in other places? c) Do trees or buildings block the wind? 7. Back in
a) Is the wind speed the same in the morning; the afternoon; the evening? b) Move your anemometer to another location. Is it windier in other places? c) Do trees or buildings block the wind? 7. Back in
Fuel Information Sheet
 Wood (Biomass) Maine has 17 million acres of forest. Wood is a renewable energy source; we can grow more trees and manage forested areas. Wood must be transported to where it is used. Wood requires storage
Wood (Biomass) Maine has 17 million acres of forest. Wood is a renewable energy source; we can grow more trees and manage forested areas. Wood must be transported to where it is used. Wood requires storage
Section 1: Renewable Energy Today
 Section 1: Renewable Energy Today Preview Bellringer Objectives Renewable Energy Solar Energy-Power from the Sun Passive Solar Heating Active Solar Heating Photovoltaic Cells Section 1: Renewable Energy
Section 1: Renewable Energy Today Preview Bellringer Objectives Renewable Energy Solar Energy-Power from the Sun Passive Solar Heating Active Solar Heating Photovoltaic Cells Section 1: Renewable Energy
Lesson Plan Time Requirements: Objectives: Materials: Methods: Lesson Information: Clean, Green Power (Target: Grades 1-4)
 Lesson Plan 050106 Clean, Green Power (Target: Grades 1-4) Time Requirements: 1. 30-minutes during science or reading time Objectives: 1. Create awareness for alternative energies 2. Create awareness for
Lesson Plan 050106 Clean, Green Power (Target: Grades 1-4) Time Requirements: 1. 30-minutes during science or reading time Objectives: 1. Create awareness for alternative energies 2. Create awareness for
The Clubhouse Kids Make a Big Difference: An Energy-Saving Adventure Teacher s Guide
 The Clubhouse Kids Make a Big Difference: An Energy-Saving Adventure Teacher s Guide INTRODUCTION The Clubhouse Kids Make a Big Difference: An Energy-Saving Adventure introduces students to the importance
The Clubhouse Kids Make a Big Difference: An Energy-Saving Adventure Teacher s Guide INTRODUCTION The Clubhouse Kids Make a Big Difference: An Energy-Saving Adventure introduces students to the importance
PRE- VISIT POWERPOINT SCRIPT FOR TEACHERS TEP BRIGHT STUDENTS: THE CONSERVATION GENERATION
 PRE- VISIT POWERPOINT SCRIPT FOR TEACHERS TEP BRIGHT STUDENTS: THE CONSERVATION GENERATION Slide 1 Intro Welcome to the Bright Students: The Conservation Generation pre- -visit PowerPoint presentation.
PRE- VISIT POWERPOINT SCRIPT FOR TEACHERS TEP BRIGHT STUDENTS: THE CONSERVATION GENERATION Slide 1 Intro Welcome to the Bright Students: The Conservation Generation pre- -visit PowerPoint presentation.
The Greenhouse Effect
 Name: #: Date: 5.8 The Greenhouse Effect The greenhouse effect traps heat in the atmosphere. This helps the Earth remain warm enough for humans. Without the greenhouse effect, human would not be able to
Name: #: Date: 5.8 The Greenhouse Effect The greenhouse effect traps heat in the atmosphere. This helps the Earth remain warm enough for humans. Without the greenhouse effect, human would not be able to
Chapter 18 Renewable Energy
 Chapter 18 Renewable Energy MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Habitat loss, soil erosion, and air pollution are disadvantages of which renewable energy source? a. solar c. biomass fuel b. wind d. moving water C DIF:
Chapter 18 Renewable Energy MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Habitat loss, soil erosion, and air pollution are disadvantages of which renewable energy source? a. solar c. biomass fuel b. wind d. moving water C DIF:
Voltage: electrical energy that is used to push electricity through a wire
 Energy Resources Wednesday, March 25 th, 2015 EQ#12 Block #3 EQ: What is a KWH? How big is it? Kilo-Watt Hour, 3,600,000 J AA: If the period of a pendulum is 3 s when the bob has a mass of 100 g, what
Energy Resources Wednesday, March 25 th, 2015 EQ#12 Block #3 EQ: What is a KWH? How big is it? Kilo-Watt Hour, 3,600,000 J AA: If the period of a pendulum is 3 s when the bob has a mass of 100 g, what
Name Class Date. What is an energy resource? How do we use nonrenewable energy resources? What are renewable energy resources?
 CHAPTER 5 4 Energy Resources SECTION Energy and Energy Resources BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is an energy resource? How do we use nonrenewable
CHAPTER 5 4 Energy Resources SECTION Energy and Energy Resources BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is an energy resource? How do we use nonrenewable
Fossil fuels (non-renewable energy)
 1a Fossil fuels (non-renewable energy) Electricity We need electricity to make lots of things work. How is electricity made? Most electricity is made in big buildings called power stations. The electricity
1a Fossil fuels (non-renewable energy) Electricity We need electricity to make lots of things work. How is electricity made? Most electricity is made in big buildings called power stations. The electricity
Weather has always been a hot topic of conversation. We talk about whether it is hot or cold, windy or calm, snowy or dry. We listen to the radio to
 Weather has always been a hot topic of conversation. We talk about whether it is hot or cold, windy or calm, snowy or dry. We listen to the radio to figure out if the weather will be different tomorrow.
Weather has always been a hot topic of conversation. We talk about whether it is hot or cold, windy or calm, snowy or dry. We listen to the radio to figure out if the weather will be different tomorrow.
Remember... Kinetic energy is the energy an object has because of its motion.
 Remember... Kinetic energy is the energy an object has because of its motion. A thermal photo Thermal energy is the total energy of the thermal (or kinetic) motion of all the particles that make up an
Remember... Kinetic energy is the energy an object has because of its motion. A thermal photo Thermal energy is the total energy of the thermal (or kinetic) motion of all the particles that make up an
TEP Bright Students: The Conservation Generation Pre- Visit PowerPoint Script for Teachers
 Slide 1 Intro Welcome to the Bright Students: The Conservation Generation pre- visit PowerPoint presentation. The information we ll learn in this activity will help us prepare for our guest presenters
Slide 1 Intro Welcome to the Bright Students: The Conservation Generation pre- visit PowerPoint presentation. The information we ll learn in this activity will help us prepare for our guest presenters
Period 26 Solutions: Using Energy Wisely
 Period 26 Solutions: Using Energy Wisely Activity 26.1: Comparison of Energy Sources for Generating Electricity 1) Comparison of energy sources a) Fill in the table below to describe the advantages and
Period 26 Solutions: Using Energy Wisely Activity 26.1: Comparison of Energy Sources for Generating Electricity 1) Comparison of energy sources a) Fill in the table below to describe the advantages and
Chapter: Energy and Energy Resources
 Table of Contents Chapter: Energy and Energy Resources Section 1: What is energy? Section 2: Energy Transformations Section 3: Sources of Energy 1 What is energy? The Nature of Energy When an object has
Table of Contents Chapter: Energy and Energy Resources Section 1: What is energy? Section 2: Energy Transformations Section 3: Sources of Energy 1 What is energy? The Nature of Energy When an object has
Now, click on the word Oil (Petroleum) 2.) How is oil formed? 3.) What does the word petroleum mean? 4.) Describe crude oil and where it is found.
 Energy Kids Page WebQuest You must follow the instructions step by step. Do not jump ahead. You will be using the website below to answer questions about energy resources. Log in to the computer. Open
Energy Kids Page WebQuest You must follow the instructions step by step. Do not jump ahead. You will be using the website below to answer questions about energy resources. Log in to the computer. Open
Natural Resources. Renewable Energy Resources. Renewable Energy Resources
 Natural Resources Renewable Energy Resources What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Natural Resources Renewable Energy Resources What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
UES Bright Students: The Conservation Generation Pre Visit PowerPoint Script for Teachers
 Slide 1 UES / Bright Students Title Slide Slide 2 Energy Introduction Energy. It s in you, your home, your environment it s in everyone and it s everywhere. Energy is what moves us, what makes life happen.
Slide 1 UES / Bright Students Title Slide Slide 2 Energy Introduction Energy. It s in you, your home, your environment it s in everyone and it s everywhere. Energy is what moves us, what makes life happen.
Sixth Grade Energy and Conservation Unit Parent Background Information
 Sixth Grade Energy and Conservation Unit Parent Background Information WHAT IS ENERGY? The nature of energy is very complex, but it is best described by these characteristics: energy is the ability to
Sixth Grade Energy and Conservation Unit Parent Background Information WHAT IS ENERGY? The nature of energy is very complex, but it is best described by these characteristics: energy is the ability to
Energy Conservation Grade Level 4-5
 Green and Healthy Home Topic 7: Energy Energy Conservation Grade Level 4-5 While there are two types of energy, renewable and nonrenewable, most of the energy we use comes from burning nonrenewable fuels--coal,
Green and Healthy Home Topic 7: Energy Energy Conservation Grade Level 4-5 While there are two types of energy, renewable and nonrenewable, most of the energy we use comes from burning nonrenewable fuels--coal,
Reliant on fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas)
 Reliant on fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) Those will not last forever, need to have a back up plan Using fossil fuels creates greenhouse gases, which impact climate change Renewable energy is better
Reliant on fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) Those will not last forever, need to have a back up plan Using fossil fuels creates greenhouse gases, which impact climate change Renewable energy is better
Power Technologies. Question. Answer. Energy is the ability to do work or change the system. Answer. Question. What are the various sources of energy?
 What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work or change the system. What are the various sources of energy? Fossil fuels Oil (Petroleum) Propane Natural gas Coal Alternative fuels Nuclear Wind Solar
What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work or change the system. What are the various sources of energy? Fossil fuels Oil (Petroleum) Propane Natural gas Coal Alternative fuels Nuclear Wind Solar
Section 5. Renewable Energy Sources Solar and Wind. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 7 Earth s Natural Resources Section 5 Renewable Energy Sources Solar and Wind What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Construct a solar water heater and determine its maximum
Chapter 7 Earth s Natural Resources Section 5 Renewable Energy Sources Solar and Wind What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Construct a solar water heater and determine its maximum
2010 Culver Media, LLC 1
 Alternating current Also known as AC power, alternating current is electricity that reverses direction within a circuit. The electricity we use in our homes does this 120 times per second. Appliances Devices
Alternating current Also known as AC power, alternating current is electricity that reverses direction within a circuit. The electricity we use in our homes does this 120 times per second. Appliances Devices
Climate Change Pupil Notes
 Climate Change Pupil Notes Name...... @concrete2cookers.org www.kelso.scotborders.sch.uk/climate_change Page 1 SCN 3-05b Climate Change This will be a brief introduction to some of the issues surrounding
Climate Change Pupil Notes Name...... @concrete2cookers.org www.kelso.scotborders.sch.uk/climate_change Page 1 SCN 3-05b Climate Change This will be a brief introduction to some of the issues surrounding
Explain how energy is conserved within a closed system. Explain the law of conservation of energy.
 Section 3 Conservation of Energy Objectives Explain how energy is conserved within a closed system. Explain the law of conservation of energy. Give examples of how thermal energy is always a result of
Section 3 Conservation of Energy Objectives Explain how energy is conserved within a closed system. Explain the law of conservation of energy. Give examples of how thermal energy is always a result of
NATURAL, BUT NOT FOREVER
 ENERGY IS THE KEY We use a lot of energy to live. Whether we re playing, studying or eating, energy makes these activities possible. We also use energy for production to run machines, for instance. Much
ENERGY IS THE KEY We use a lot of energy to live. Whether we re playing, studying or eating, energy makes these activities possible. We also use energy for production to run machines, for instance. Much
Chapter 16: Energy: Some Basics
 Chapter 16: Energy: Some Basics Energy Crisis in Ancient Greece and Rome Greeks and Romans used wood to heat there homes. As local supplies ran out had to bring it in from farther away. Eventually both
Chapter 16: Energy: Some Basics Energy Crisis in Ancient Greece and Rome Greeks and Romans used wood to heat there homes. As local supplies ran out had to bring it in from farther away. Eventually both
Post Assessment - Energy
 Post Assessment - Energy Concept(s) Addressed Time The sun is a major source of energy on Earth. Solar energy from the sun reaches the Earth mostly as visible light through radiation. Convection currents
Post Assessment - Energy Concept(s) Addressed Time The sun is a major source of energy on Earth. Solar energy from the sun reaches the Earth mostly as visible light through radiation. Convection currents
WORK Potential Kinetic
 Energy What is energy? - Ability to do WORK - The transfer of energy is work, power is the rate at which energy is transferred. - There are many forms of energy (chemical, mechanical, nuclear, thermal,
Energy What is energy? - Ability to do WORK - The transfer of energy is work, power is the rate at which energy is transferred. - There are many forms of energy (chemical, mechanical, nuclear, thermal,
Human Dependence on Natural Resources
 You use Earth s resources every day. When you eat cereal with milk for breakfast, you use resources from plants and animals. When you ride the bus to school, you use energy (fuel) resources. When you take
You use Earth s resources every day. When you eat cereal with milk for breakfast, you use resources from plants and animals. When you ride the bus to school, you use energy (fuel) resources. When you take
Attached Solar Greenhouse Plans for a solar heated greenhouse attached to your home
 Attached Solar Greenhouse Plans for a solar heated greenhouse attached to your home Designed and built by New Mexico landscape architect John Mosely for his own Santa Fe home. The solar greenhouse shown
Attached Solar Greenhouse Plans for a solar heated greenhouse attached to your home Designed and built by New Mexico landscape architect John Mosely for his own Santa Fe home. The solar greenhouse shown
CHAPTER - 14 SOURCES OF ENERGY
 CHAPTER - 14 SOURCES OF ENERGY PREPARED BY NIKHIL V JONES 1) Characteristics of a good source of fuel :- i) It should have a high energy output per unit mass or volume. ii) It should be easily available.
CHAPTER - 14 SOURCES OF ENERGY PREPARED BY NIKHIL V JONES 1) Characteristics of a good source of fuel :- i) It should have a high energy output per unit mass or volume. ii) It should be easily available.
Renewable Energy Grade Level 2-3
 Green and Healthy Home Topic 7: Energy Renewable Energy Grade Level 2-3 While there are two types of energy, renewable and nonrenewable, most of the energy we use comes from burning nonrenewable fuels--coal,
Green and Healthy Home Topic 7: Energy Renewable Energy Grade Level 2-3 While there are two types of energy, renewable and nonrenewable, most of the energy we use comes from burning nonrenewable fuels--coal,
CREATIVE SPACES INFORMATION PACK THREE SUSTAINABLE DESIGN
 SUSTAINABLE DESIGN The information contained in this presentation is for general information purposes only and it is intended that there will be strictly no commercial gain from its production. The content
SUSTAINABLE DESIGN The information contained in this presentation is for general information purposes only and it is intended that there will be strictly no commercial gain from its production. The content
CREATIVE SPACES 2013 INFORMATION PACK THREE SUSTAINABLE DESIGN
 SUSTAINABLE DESIGN The information contained in this presentation is for general information purposes only and it is intended that there will be strictly no commercial gain from its production. The content
SUSTAINABLE DESIGN The information contained in this presentation is for general information purposes only and it is intended that there will be strictly no commercial gain from its production. The content
Section 2: Sources of Energy
 Section 2: Sources of Energy Types of Energy¹ All the things we use every day to meet our needs and wants are provided through the use of natural resources.natural resources are either renewable or nonrenewable.
Section 2: Sources of Energy Types of Energy¹ All the things we use every day to meet our needs and wants are provided through the use of natural resources.natural resources are either renewable or nonrenewable.
The greenhouse effect
 Sources of CO 2 It is an undisputable fact that the carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere is increasing, see next page for the evidence. There are of course many sources of the CO 2 in the atmosphere,
Sources of CO 2 It is an undisputable fact that the carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere is increasing, see next page for the evidence. There are of course many sources of the CO 2 in the atmosphere,
Calorie Unit to measure amount of energy in foods and fuels.
 Measuring Energy: Calorie Unit to measure amount of energy in foods and fuels. One calorie = amount of heat energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 degree Celsius. Watt Unit used
Measuring Energy: Calorie Unit to measure amount of energy in foods and fuels. One calorie = amount of heat energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 degree Celsius. Watt Unit used
Renewable Energy Today
 Chapter 18 Renewable Energy Today Renewable Energy energy from a source that is constantly being reformed. Many governments are planning to increase their use of renewable energy resources. This will reduce
Chapter 18 Renewable Energy Today Renewable Energy energy from a source that is constantly being reformed. Many governments are planning to increase their use of renewable energy resources. This will reduce
Energy in Agricultural Systems
 Energy in Agricultural Systems MODULE 5: WIND ENERGY IN AGRICULTURE Funding provided by The Minnesota Environment and Natural Resources Trust Fund as recommended by the Legislative-Citizen Commission on
Energy in Agricultural Systems MODULE 5: WIND ENERGY IN AGRICULTURE Funding provided by The Minnesota Environment and Natural Resources Trust Fund as recommended by the Legislative-Citizen Commission on
Now, click on the word Oil (Petroleum) 2.) How is oil formed? 3.) Describe crude oil and where it is found.
 Energy Kids Page WebQuest You must follow the instructions step by step. Do not jump ahead. You will be using the website below to answer questions about energy resources. Log in to the computer. Open
Energy Kids Page WebQuest You must follow the instructions step by step. Do not jump ahead. You will be using the website below to answer questions about energy resources. Log in to the computer. Open
Geothermal Heating and Cooling Overview. Why should I consider it?
 Geothermal Heating and Cooling Overview Why should I consider it? GEOTHERMAL - A major source of energy is right under your feet The idea behind geothermal energy is simple. The earth stores a vast reservoir
Geothermal Heating and Cooling Overview Why should I consider it? GEOTHERMAL - A major source of energy is right under your feet The idea behind geothermal energy is simple. The earth stores a vast reservoir
Sample. Contents. Teachers' Notes 4 Curriculum Links 4-6
 Contents Teachers' Notes 4 Curriculum Links 4-6 Section 1: Sustainable Energy Electricity 8 Sustainable Energy 9 Human Energy 10 Geothermal Energy 11 Hydropower 12 Tidal Power 1 13 Tidal Power 2 14 Section
Contents Teachers' Notes 4 Curriculum Links 4-6 Section 1: Sustainable Energy Electricity 8 Sustainable Energy 9 Human Energy 10 Geothermal Energy 11 Hydropower 12 Tidal Power 1 13 Tidal Power 2 14 Section
Energy Resources. Nonrenewable Energy Resources. Fossil Fuels
 Energy Resources Renewable resources are resources that can be replaced within a human life span or as they are used. Nonrenewable resources are resources that exist in limited amounts and cannot be replaced
Energy Resources Renewable resources are resources that can be replaced within a human life span or as they are used. Nonrenewable resources are resources that exist in limited amounts and cannot be replaced
I ve Got the Power! Types of Energy and how it affects our lives.
 I ve Got the Power! Types of Energy and how it affects our lives. Categories Energy is broken down into 2 categories RENEWABLE And NON-RENEWABLE RENEWABLE Energy that comes from a source that can be replenished
I ve Got the Power! Types of Energy and how it affects our lives. Categories Energy is broken down into 2 categories RENEWABLE And NON-RENEWABLE RENEWABLE Energy that comes from a source that can be replenished
Energy Efficiency World Teacher s Guide
 Energy Efficiency World Teacher s Guide INTRODUCTION The Energy Efficiency World booklet teaches the basic principles of energy and how to use it efficiently. Topics include renewable and nonrenewable
Energy Efficiency World Teacher s Guide INTRODUCTION The Energy Efficiency World booklet teaches the basic principles of energy and how to use it efficiently. Topics include renewable and nonrenewable
Energy Efficiency World Teacher s Guide
 Energy Efficiency World Teacher s Guide INTRODUCTION The Energy Efficiency World booklet teaches the basic principles of energy and how to use it efficiently. Topics include renewable and nonrenewable
Energy Efficiency World Teacher s Guide INTRODUCTION The Energy Efficiency World booklet teaches the basic principles of energy and how to use it efficiently. Topics include renewable and nonrenewable
Energy Efficiency World Teacher s Guide
 Energy Efficiency World Teacher s Guide INTRODUCTION The Energy Efficiency World booklet teaches the basic principles of energy and how to use it efficiently. Topics include renewable and nonrenewable
Energy Efficiency World Teacher s Guide INTRODUCTION The Energy Efficiency World booklet teaches the basic principles of energy and how to use it efficiently. Topics include renewable and nonrenewable
Cooking Curanto. Hola. Tienes hambre? Biomass
 Cooking Curanto Hola. Tienes hambre? That s Spanish and it means, Are you hungry? How would you like to travel to Chile in South America and eat curanto? Curanto is like a stew with lots of yummy food.
Cooking Curanto Hola. Tienes hambre? That s Spanish and it means, Are you hungry? How would you like to travel to Chile in South America and eat curanto? Curanto is like a stew with lots of yummy food.
- Free resources for K-12 1/6
 Lesson: What is Energy? Summary copyright With an introduction to the ideas of energy, students discuss specific types of energy and the practical sources of energy. Hands-on activities help them identify
Lesson: What is Energy? Summary copyright With an introduction to the ideas of energy, students discuss specific types of energy and the practical sources of energy. Hands-on activities help them identify
Energy. Section A) Energy Sources 1. Review from the Mackenzie Valley Wetlands activity. Use the words below to help you fill out the answers below:
 Energy Section A) Energy Sources 1. Review from the Mackenzie Valley Wetlands activity. Use the words below to help you fill out the answers below: biodiesel hydro solar energy wind energy garbage nonrenewable
Energy Section A) Energy Sources 1. Review from the Mackenzie Valley Wetlands activity. Use the words below to help you fill out the answers below: biodiesel hydro solar energy wind energy garbage nonrenewable
A is any natural material that is used by humans.
 Chapter 5 Notes Energy Resources Section 1 Natural Resources Describe how humans use natural resources. Compare renewable resources with nonrenewable resources. Explain three ways that humans can conserve
Chapter 5 Notes Energy Resources Section 1 Natural Resources Describe how humans use natural resources. Compare renewable resources with nonrenewable resources. Explain three ways that humans can conserve
Energy Unit Framework
 Energy Unit Framework Driving Question: How do we plan for future energy use? Enduring Understandings: Distinguish among forms of energy (e.g. nuclear, electrical, gravitational), sources of energy (e.g.,
Energy Unit Framework Driving Question: How do we plan for future energy use? Enduring Understandings: Distinguish among forms of energy (e.g. nuclear, electrical, gravitational), sources of energy (e.g.,
RENEWABLE ENERGY IN THE PACIFIC NORTHWEST
 RENEWABLE ENERGY IN THE PACIFIC NORTHWEST Renewable energy comes from natural sources that are continually and sustainably replenished such as the sun, the flow of water, or other natural processes. By
RENEWABLE ENERGY IN THE PACIFIC NORTHWEST Renewable energy comes from natural sources that are continually and sustainably replenished such as the sun, the flow of water, or other natural processes. By
Energy in nature and technology
 Energy in nature and technology Objectives Provide examples of kinetic and potential energy and their transformations. Communicate and apply scientific information extracted from various sources. Research
Energy in nature and technology Objectives Provide examples of kinetic and potential energy and their transformations. Communicate and apply scientific information extracted from various sources. Research
Explore the forms of energy at:
 Explore the forms of energy at: www.eia.doe.gov/kids/energyfacts/science/formsofenergy.html While we are using energy in our home, scientists are studying energy in labs so that they understand the science
Explore the forms of energy at: www.eia.doe.gov/kids/energyfacts/science/formsofenergy.html While we are using energy in our home, scientists are studying energy in labs so that they understand the science
Different Forms of Water
 Different Forms of Water Different Forms of Water When you re thirsty, few things feel better than drinking a tall glass of water poured over ice. But as you re drinking, do you realize you are experiencing
Different Forms of Water Different Forms of Water When you re thirsty, few things feel better than drinking a tall glass of water poured over ice. But as you re drinking, do you realize you are experiencing
STATE DA VINCI DECATHLON 2017
 STATE DA VINCI DECATHLON 2017 CELEBRATING THE ACADEMIC GIFTS OF STUDENTS IN YEARS 7 & 8 SCIENCE TEAM NUMBER 1 The Coal Paradox: We can't live without it. But can we survive with it? On a scorching August
STATE DA VINCI DECATHLON 2017 CELEBRATING THE ACADEMIC GIFTS OF STUDENTS IN YEARS 7 & 8 SCIENCE TEAM NUMBER 1 The Coal Paradox: We can't live without it. But can we survive with it? On a scorching August
You Think the North is Cold! A Blanket Around Our World
 We know that climate change is being caused by the warming of our planet. But what causes this warming? Who or what is in control of the thermostat? This backgrounder provides the answers to these questions.
We know that climate change is being caused by the warming of our planet. But what causes this warming? Who or what is in control of the thermostat? This backgrounder provides the answers to these questions.
Student book answers Chapter 2
 P2 2.1 Food and fuels In-text A joules B Three from: wood, oil, coal, gas How far? 50 g of chocolate contains: 0.5 1500 = 750 kj You would need to run for: 750 60 = 12.5 minutes This means you will need
P2 2.1 Food and fuels In-text A joules B Three from: wood, oil, coal, gas How far? 50 g of chocolate contains: 0.5 1500 = 750 kj You would need to run for: 750 60 = 12.5 minutes This means you will need
Introduction to Energy. Energy
 Introduction to Energy Dossin Energy- What is It? Alternative Vs. Renewable Energy Energy- Two Main Forms Conservation of Energy Energy Efficiency Measuring Energy Using Energy RESOURCES Information copied
Introduction to Energy Dossin Energy- What is It? Alternative Vs. Renewable Energy Energy- Two Main Forms Conservation of Energy Energy Efficiency Measuring Energy Using Energy RESOURCES Information copied
Energy Vocabulary. Word Definition Memory Aid the ability to cause an object to 1. energy move, change, or work
 the ability to cause an object to 1. move, change, or work 2. trade-off something that you do not want, but have to accept in order to have something that you want (disadvantage) 3. variable a changing
the ability to cause an object to 1. move, change, or work 2. trade-off something that you do not want, but have to accept in order to have something that you want (disadvantage) 3. variable a changing
Climate Change Word Loop
 Teacher s Notes Summary Climate Change Word Loop This is a whole-class game to help reinforce the concepts and ideas covered and to help familiarise pupils with the terminology of Global Warming and Climate
Teacher s Notes Summary Climate Change Word Loop This is a whole-class game to help reinforce the concepts and ideas covered and to help familiarise pupils with the terminology of Global Warming and Climate
Pinwheel to Windmill. Grade Level: 4-5
 Pinwheel to Windmill Grade Level: 4-5 Lesson Overview Objectives: Students will be able to Explain where energy comes from and how we use it Define renewable and nonrenewable, and provide examples Preparation/Materials:
Pinwheel to Windmill Grade Level: 4-5 Lesson Overview Objectives: Students will be able to Explain where energy comes from and how we use it Define renewable and nonrenewable, and provide examples Preparation/Materials:
Renewable Energy. Visible light. Cool air. Warm air. Condensation. Precipitation. Evaporation
 Renewable Energy All renewable energy sources derive from the Sun. The Sun provides the energy that drives our weather systems and water cycle. It is the prime source of all energy on Earth and it is essential
Renewable Energy All renewable energy sources derive from the Sun. The Sun provides the energy that drives our weather systems and water cycle. It is the prime source of all energy on Earth and it is essential
SAMPLE PAGE. Sustainable Energy Sources By: Sue Peterson
 Page 38 Objective sight words (consumption, terrain, integral, orbit, originated, contemporary, remote); concepts (sustainable, renewable, photovoltaics, gasification) Vocabulary consumption originated
Page 38 Objective sight words (consumption, terrain, integral, orbit, originated, contemporary, remote); concepts (sustainable, renewable, photovoltaics, gasification) Vocabulary consumption originated
Ch 13 Achieving Energy Sustainability
 Ch 13 Achieving Energy Sustainability Module 38 Biomass and Water Module 39 Solar, Wind, Geothermal, and Hydrogen 4/16/18 Variation in Solar Radiation Potential Active Solar Energy captured from sunlight
Ch 13 Achieving Energy Sustainability Module 38 Biomass and Water Module 39 Solar, Wind, Geothermal, and Hydrogen 4/16/18 Variation in Solar Radiation Potential Active Solar Energy captured from sunlight
Lesson 5 Energy. OAA Science Lesson 5 52
 Lesson 5 Energy OAA Science Lesson 5 52 Name Date Period Student Lesson 5: Energy Reference Sheet: Energy - is the ability to do work or cause change - can be changed from one form to another - cannot
Lesson 5 Energy OAA Science Lesson 5 52 Name Date Period Student Lesson 5: Energy Reference Sheet: Energy - is the ability to do work or cause change - can be changed from one form to another - cannot
Hands-On Energy Efficiency Teacher s Guide
 Hands-On Energy Efficiency Teacher s Guide Introduction The Hands-On Energy Efficiency activity booklet can be used to teach students the principles of wise energy use at home and at school. The content
Hands-On Energy Efficiency Teacher s Guide Introduction The Hands-On Energy Efficiency activity booklet can be used to teach students the principles of wise energy use at home and at school. The content
ANet Quiz RI.4.2 English Language Arts, Grade 4
 ANet Quiz RI.4.2 English Language Arts, Grade 4 Student: Teacher: School: Read the text about solar power. Then, answer the questions. from Energy from the Sun by Anne Rooney 1 For thousands of years,
ANet Quiz RI.4.2 English Language Arts, Grade 4 Student: Teacher: School: Read the text about solar power. Then, answer the questions. from Energy from the Sun by Anne Rooney 1 For thousands of years,
Solar panels The Fizzics Organisation
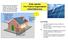 Most solar panels installed on houses in the last few years convert the energy of sunlight directly into electrical energy. These are photovoltaic cells. Solar panels 3 This electricity can be used around
Most solar panels installed on houses in the last few years convert the energy of sunlight directly into electrical energy. These are photovoltaic cells. Solar panels 3 This electricity can be used around
fossil fuel: You have to drill to get fossil fuels like coal, oil and natural gas.
 Glossary Using a Really Big Power Plant fossil fuel: You have to drill to get fossil fuels like coal, oil and natural gas. fossil fuel: energy resources that form beneath the ground from decayed animal
Glossary Using a Really Big Power Plant fossil fuel: You have to drill to get fossil fuels like coal, oil and natural gas. fossil fuel: energy resources that form beneath the ground from decayed animal
Teacher s Guide For. Life After Oil: The New Energy Alternatives
 Teacher s Guide For Life After Oil: The New Energy Alternatives For grade 7 - College Program produced by Centre Communications, Inc. for Ambrose Video Publishing, Inc. Executive Producer William V. Ambrose
Teacher s Guide For Life After Oil: The New Energy Alternatives For grade 7 - College Program produced by Centre Communications, Inc. for Ambrose Video Publishing, Inc. Executive Producer William V. Ambrose
Windmill Challenge STEM Module VCS April 24, 2012
 Windmill Challenge Teacher Notes Volusia County STEM-Extension Lesson Using the 5E Model Windmill Challenge Objective: Students will use background knowledge of energy to create a windmill and compete
Windmill Challenge Teacher Notes Volusia County STEM-Extension Lesson Using the 5E Model Windmill Challenge Objective: Students will use background knowledge of energy to create a windmill and compete
KS3 Renewable Energy. EcoStyle.co.uk. Introductory Presentation
 Introductory Presentation Energy Energy is a vital to our way of life. Here are a some examples of where energy is used: Homes: central heating, powering electrical appliances, and heating water Public
Introductory Presentation Energy Energy is a vital to our way of life. Here are a some examples of where energy is used: Homes: central heating, powering electrical appliances, and heating water Public
Vocabulary. Heat production and transfer
 Kick off 1 Heat is the transfer of energy between objects that are usually at different temperatures. Match the types of energy with the pictures. 1 chemical 3 mechanical 2 nuclear 4 electrical 2 Heat
Kick off 1 Heat is the transfer of energy between objects that are usually at different temperatures. Match the types of energy with the pictures. 1 chemical 3 mechanical 2 nuclear 4 electrical 2 Heat
Hands-On Energy Efficiency Teacher s Guide
 Hands-On Energy Efficiency Teacher s Guide Introduction The Hands-On Energy Efficiency activity booklet can be used to teach students the principles of wise energy use at home and at school. This presentation
Hands-On Energy Efficiency Teacher s Guide Introduction The Hands-On Energy Efficiency activity booklet can be used to teach students the principles of wise energy use at home and at school. This presentation
Energy and Energy Resources
 Energy and Energy Resources Energy Defined as the ability to do work or the ability to cause change. Two types of energy: Kinetic energy- energy of motion; anything that moves has kinetic energy, cars,
Energy and Energy Resources Energy Defined as the ability to do work or the ability to cause change. Two types of energy: Kinetic energy- energy of motion; anything that moves has kinetic energy, cars,
Chapter Two: Page 35
 Chapter Two: Page 35 Chapter Two: Page 36 Resources are things that we get from the living and nonliving environment to meet the needs and wants of a population. Some resources are basic materials, such
Chapter Two: Page 35 Chapter Two: Page 36 Resources are things that we get from the living and nonliving environment to meet the needs and wants of a population. Some resources are basic materials, such
Types of Energy Heat energy Heat energy is the transfer of thermal energy (associated with the motion) ll matter is made up of particles too small to
 1 Types of Energy Heat energy Heat energy is the transfer of thermal energy (associated with the motion) ll matter is made up of particles too small to be seen. As heat energy is added to a substance,
1 Types of Energy Heat energy Heat energy is the transfer of thermal energy (associated with the motion) ll matter is made up of particles too small to be seen. As heat energy is added to a substance,
Greenhouse Effect & Climate Change
 Greenhouse Effect & Climate Change Greenhouse Effect Light energy from the sun (solar radiation) is either reflected or absorbed by the Earth. Greenhouse Effect When it is absorbed by the Earth (or something
Greenhouse Effect & Climate Change Greenhouse Effect Light energy from the sun (solar radiation) is either reflected or absorbed by the Earth. Greenhouse Effect When it is absorbed by the Earth (or something
GN Department of Environment Environment Week 2018 Lesson Plan 3. Date: Wednesday, June 06 th, 2018 Grades: 4-6. Title: Let s talk Energy!
 GN Department of Environment Environment Week 2018 Lesson Plan 3 Date: Wednesday, June 06 th, 2018 Grades: 4-6 Title: Time: Let s talk Energy! 45min-1hr (Adapted from Energy Teacher Kit, Energy Secretariat,
GN Department of Environment Environment Week 2018 Lesson Plan 3 Date: Wednesday, June 06 th, 2018 Grades: 4-6 Title: Time: Let s talk Energy! 45min-1hr (Adapted from Energy Teacher Kit, Energy Secretariat,
Measuring School Electronics Energy at Work 1
 1 GRADE LEVEL 6-12 TIME NEEDED FOR COMPLETION 2 class periods or 1.5-2 hours STANDARDS LA GLEs and NGSS alignments are found in the Appendix starting on page A-1 MATERIALS 6 energy monitoring devices.
1 GRADE LEVEL 6-12 TIME NEEDED FOR COMPLETION 2 class periods or 1.5-2 hours STANDARDS LA GLEs and NGSS alignments are found in the Appendix starting on page A-1 MATERIALS 6 energy monitoring devices.
St. Olaf Sustainability
 St. Olaf Sustainability St. Olaf College is like a small city People live and work there They need what people need in a city: Water Electricity Heat Roads and sidewalks Food Garbage service Sewer and
St. Olaf Sustainability St. Olaf College is like a small city People live and work there They need what people need in a city: Water Electricity Heat Roads and sidewalks Food Garbage service Sewer and
