Wind power density loss for wind turbines due to upstream hills
|
|
|
- Irma Todd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Wind power density loss for wind turbines due to upstream hills BODO RUCK & MANUEL GRUBER Laboratory of Building- and Environmental Aerodynamics Institute for Hydromechanics Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) Kaiserstr. 12, Karlsruhe GERMANY Abstract: The installation of wind turbines in hilly terrain is not straightforward. For the planning, an accurate and reliable estimation of the annual energy production has to be performed. The local wind potential is a crucial quantity within this assessment, however, it is unknown in most cases. In order to obtain more reliable data about wind potential in hilly terrain, an investigation in an atmospheric boundary layer tunnel is presented, delivering detailed information on the interaction of upstream hills and wind power potential for wind turbines. The investigations were performed for the case, when wind turbine height and hill height are at least in the same order of magnitude. Specific exposure coefficients are given depending on the distance of the upstream hill, the surface roughness of the terrain and the ratio of turbine height to hill height. Key-Words: wind turbine power, wind power density, upstream hill, orographically structured terrain 1 Introduction Wind turbines are installed increasingly in hilly terrain. To assess the efficiency of a wind turbine and to estimate the annual energy production, the wind climatology at the turbine location must be known. Unfortunately, the site-specific wind data are not known in most cases, so that wind data from remote weather stations are taken and 'extrapolated' by flow models to the wind turbine site ('micrositing'). For this purpose, flow models of different type are used. Linear flow models [1,2] compute the wind climatology by parameterizing relevant factors of influence (surface roughness, site-near obstacle dimensions, height contour lines of terrain). However, the incorporated orographic flow model [3] can be applied only to neutrally stable wind flows over gently sloping terrain and low hills. In rugged or complex terrain, linear flow models show wellknown limitations e.g. overestimating wind speedup [4,5,6]. In contrast to linear models, 3-D nonlinear flow models [7] compute the 3-D wind field with input data from a digital terrain model, a roughnesss map and from wind climatology data derived from at least one met station within the modeled area. The wind field computation is based on the solution of the time-averaged Navier-Stokes equations (RANS = Reynolds-averaged Navier- Stokes equations). To close the system of equations, the k-ε turbulence model is used in most of these non-linear flow models. However, it is known from various fields of fluid research that RANS models tend to overestimate turbulent kinetic energy and to underestimate mean flow recirculation zones and often lead to uncertainties when large-scale turbulent transport phenomena and sharp bends in the flow field are present [8,9]. More sophisticated or even time-resolved flow computations with Large Eddy Simulation (LES) or Direct Numerical Simulation (DNS) are either not practical for industrial use because of their costs or not feasible because of their physical limitation (transition not predictable, Reynolds numbers too high). As reported in literature, 3-D nonlinear flow models show better agreement with mast measurements than results obtained with linear models. However, independent studies on this subject [10] are rare and indicate that terrain complexity can generate substantial modeling uncertainties obviously with both model types. Thus, the question how accurate the wind energy resources can be estimated for a specific location cannot easily be answered by existing commercial wind resource assessment programs As a consequence of the shortcomings of software-based models, it seems that physical modeling in an atmospheric boundary layer wind tunnel can deliver more detailed and realistic data on wind power density loss in hilly terrain where wind field conditions are characterized by specific ISBN:
2 orographically generated turbulence and wind profile shapes. 2 Experimental details There is no doubt that orography exerts a great influence on instant, time-averaged or climatologic wind speed at a given site. Thus, in mountainous regions, the energy production of wind turbines is in most cases smaller than in the plane countryside. Additionally, surface roughness and atmospheric stability influence the wind power density [11,12]. In many cases, even a doubling of the hub height cannot compensate the loss induced by a fully rough or forested surface when compared to a smooth surface. Keeping in mind that a wind reduction of 20 % results in a wind energy loss of about 50%, it is worthwhile to investigate in detail the wind conditions at projected turbine sites in hilly terrain as sketched in Fig. 1. Fig. 1: Erection of wind turbines in hilly terrain In this context, it is most interesting how an upstream hill alters the wind power density for a wind turbine, see Fig. 2. Thus, in order to contribute to the fluid mechanical understanding of wind potential in orographically structured terrain, the influence of upstream hills on wind power density has been investigated in an atmospheric boundary layer wind tunnel. The use of such wind tunnels to investigate wind flows over complex and forested terrain is well established in building- and environmental aerodynamics [13-15]. 2.1 Boundary layer simulation The simulation of an atmospheric boundary layer in the wind tunnel was realized according to the criteria given in Tab. 1. For a detailed description of the simulation of atmospheric boundary layers see also [16,17]. The simulation and measurement of the flow field were carried out in the atmospheric boundary layer wind tunnel (length 29 m) of the Laboratory of Building- and Environmental Aerodynamics at KIT. This constant pressure wind tunnel has a closed recirculation and an octagonal cross-section with a width of 1.5 m. The test section is divided into a 4 m long fetch needed for the formation of the boundary layer and a 4 m long measuring section in which the boundary layer with a height of about 0:55 m is almost constant. The velocity field at the entrance of the measuring section corresponds to a roughness height of category suburbs/forests according to DIN EN : Using the logarithmic wall law, the roughness length for the model amounts to z 0 = 1,1 mm. The shear stress velocity is u * = m/sec with a wall shear stress of τ 0 = N/m. Fig. 2: Upstream hill changes the wind profile and the wind power density ISBN:
3 Tab. 1: Similarity criteria for the model investigation in an atmospheric boundary layer wind tunnel: Tab. 2: Properties of LDA-system Two double Bragg cells (TSI ColorBurst) were used for the frequency shift of the partial beams. The scattered light was detected in forward direction by a photomultiplier unit (TSI; Color Link). The data processing was performed with two TSI signal processors (Model IFA 550). 2.2 Measuring technique For the flow measurements, a two-dimensional LDA system was used, whose properties are listed in Table 2. It uses an argon-ion laser with a power of 4 watts (Manufacturer: Coherent, model Innova 90) as light source. The system operates in dualbeam mode. Fig. 3 shows a photo of the 2D-LDA system used during the measurement process. 2.3 Hill modeling The two-dimensional model hill (scale 1:300) was made of plywood and has a cosine shape according to: 2 π x z h (x) = H cos ( ) L < x < L (7) 2 L with H = 0.2 m and L = 0.5 m. The length L is defined as the distance between the foot and the top of the hill. After the wooden construction was completed, the surface of the hill was covered with a layer of styrofoam. 2.4 Calculation of wind power and power coefficient The wind power computed with the mean horizontal wind velocity u, which falls onto the rotor swept area is obtained via the solution of the intergral (8), see Fig. 4 for notation, characterizes the wind energy content. z= ( N+ r) 1 3 P( N, r) = ρ u ( z) s( z) dz 2 z= ( N+ r) z= ( N r) = ρ u ( z) r ( N z) dz z= ( N r) (8) Fig. 3: 2D-LDA system for flow measurements The maximum energy content available for wind turbines can be computed by multiplying equation ISBN:
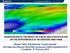
4 (8) with the Betz constant of If the velocity field is disturbed by an upstream hill, the wind energy content depends on the streamwise position x behind the hill, the hill height H, the hub height N and the rotor swept area diameter r. z = ( N+ r) P( N, r,x, H) = ρ u ( x, z) s( z) dz (9) 2 z 0 = ( N r) Referring the wind power for a given hub height and swept area diameter behind an upstream hill to the corresponding wind power in the undisturbed approach flow before the hill delivers an exposure coefficient, which quantifies the decrease or increase of wind power due to the hill. ε H after N r,x H P ( N, r,x, H ) = (10) Pbefore( N, r) Fig. 4: Notation for wind power computation (,, ) Fig. 5: Exposure coefficient for different turbine positions downstream of the hill; top: smooth hill; bottom: forested hill with tree density 600 tree/ha, tree height 16.5 m, permeability 0.7 m -1 ISBN:
5 3 Results Figure 5 shows the exposure coefficient for a wind turbine with rotor swept area diameter of 70 m. As can be inferred from Fig. 5, the distance from the wind turbine to the upstream hill plays an important role for the available wind power. Additionally, comparing Fig. 5 top with Fig. 5 bottom reveals that the fully rough forested hill surface induces a significant loss of wind power when compared to the smooth hill surface. For a wind turbine with hub height of 120 m and rotor swept area diameter of 70 m, the loss amounts to 24%. The interpretation of the curves in Figure 5 is easy, because each curve refers to a fixed and specified distance from the hill. The rotor swept area diameter is specified with 70 m in Fig. 5. Going upwardly along a curve means that at the same x-position the hub height is pushed upwards, which usually increases the exposure coefficient. As can be seen, the exposure coefficient can obtain values greater than 1 or less than 1 denoting turbine positions and/or hub heights, where an increase or decrease of wind power is introduced by the hill. Thus, for a fixed rotor swept area diameter, there are many possible positions behind a hill, in both, horizontal and vertical directions. On the basis of the wind tunnel measurements, one can calculate the exposure coefficient for all possible positions and display these values in an isoplot, see Fig. 6. Each point in the colored area denotes an exposure coefficient for the chosen swept area diameter. Fig. 6: Isoplots of exposure coefficients for different turbine positions downstream of the hill top: smooth hill; bottom: forested hill with tree density 600 tree/ha, tree height 16.5 m, permeability 0.7 m -1 References: [1] Mortensen, N.G., Landberg, L., Troen, I., Petersen, E.L., Wind Atlas Analysis and Application Program (WAsP). Vol. 2: User's Guide, Risø-I-666(v.2) (EN), Risø National Laboratory, Roskilde, Denmark, [2] Troen, I. and Petersen, E.L., European Wind Atlas, Published for the Commission of the European Communities, Brussels, Belgium, by Risø National Laboratory,Roskilde, Denmark, ISBN , [3] Jackson, P.S., Hunt, J.C.R., Turbulent wind over a low hill, Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc., 101, 1975, pp [4] Anthony J. Bowen, A.J., Mortensen, N.G., WAsP prediction errors due to site orography, Report Risø-R-995(EN), Risø National Laboratory Roskilde Denmark, 2004, ISSN , ISBN [5] Botta, G., Castagna, R., Borghetti, M. and Mantegna, D., Wind analysis on complex terrain The case of Acqua Spruzza, Jour. ISBN:
6 Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 39, 1992, pp [6] Ayotte, K.W., Computational Modelling for Wind Energy Assessment. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerod., 96, 2008, pp [7] Gravdahl AR, Harstveit K. WindSim Flow simulations in complex terrain, As sessment of wind resources along the Norwegian coast, Deutsche Windenergie Konferenz DEWEK, [8] Schmidt, T., Mockett, C., Thiele, F., Minimization and Quantification of Errors and Uncertainties in RANS Modeling, Management and Minimisation of Uncertainties and Errors in Numerical Aerodynamics, Notes on Numer-ical Fluid Mechanics and Multidisciplinary Design, Volume 122, 2013, pp [9] Sumner, J., Watters, C.S., Masson, C., CFD in Wind Energy: The Virtual, Multiscale Wind Tunnel, Energies, 3, 2010, pp [10] Walmsley, J.L., Troen, I., Lalas, D.P., and Mason, P.J., Surface-layer flow in complex terrain: Comparison of models and fullscale observations. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 52, 1990, pp [11] Gasch, R.; Twele, J., Windkraftanlagen: Grundlagen, Entwurf, Planung und Betrieb, 7. Aufl. Vieweg & Teubner Verlag: Stuttgart, 2011 [12] Focken U, Heinemann D, Influence of thermal stratification on wind profiles for heights up to 140 m. Proceedings of the European Wind Energy Conference, Madrid, [13] Meroney, R. N., Characteristics of Wind and Turbulence in and above Model Forests, J. Appl. Meteorol., 7, 1968, pp [14] Neff, D. E; Meroney, R. N., Wind-tunnel modeling of hill and vegetation influence on wind power availability, Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, (0), 1998, pp [15] Ruck, B., Frank, C., Tischmacher, M., On the influence of windward edge structure and stand density on the flow characteristics at forest edges, European Journal of Forest Research, 131, 2012, pp [16] Counihan, J., Wind tunnel determination of the roughness length as a function of the fetch and the roughness density of threedimensional roughness elements, Atmospheric Environment, 5 (8), 1971, pp [17] Plate, E.J., Wind tunnel modelling of wind effects in engineering, Engineering Meteorology, (edited by Plate E.J.), Elsevier, 1982, pp ISBN:
WIND ENERGY RESOURCE ASSESSMENT: A CASE STUDY
 WIND ENERGY RESOURCE ASSESSMENT: A CASE STUDY Norman Maphosa. National university of Science and Technology, Department of Technical Teacher Education, NUST, Box AC 939, Ascot, Bulawayo, Zimbabwe. Tel:
WIND ENERGY RESOURCE ASSESSMENT: A CASE STUDY Norman Maphosa. National university of Science and Technology, Department of Technical Teacher Education, NUST, Box AC 939, Ascot, Bulawayo, Zimbabwe. Tel:
Fluctuating Inlet Flow Conditions for Use in Urban Air Quality CFD Studies
 Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering Vol II, WCE, July -,, London, U.K. Fluctuating Inlet Flow Conditions for Use in Urban Air Quality CFD Studies S. M. Kwa, S. M. Salim Abstract Fluctuating
Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering Vol II, WCE, July -,, London, U.K. Fluctuating Inlet Flow Conditions for Use in Urban Air Quality CFD Studies S. M. Kwa, S. M. Salim Abstract Fluctuating
WINDSIM STUDY OF HYBRID WIND FARM IN COMPLEX TERRAIN. A thesis PAUL HINES
 WINDSIM STUDY OF HYBRID WIND FARM IN COMPLEX TERRAIN A thesis by PAUL HINES Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Gotland University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of
WINDSIM STUDY OF HYBRID WIND FARM IN COMPLEX TERRAIN A thesis by PAUL HINES Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Gotland University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of
On the Improvement of Wind Power Predictions Based on Terrain Characteristics and Measurements of the Annual Energy Production
 Journal of Flow Control, Measurement & Visualization, 2017, 5, 1-20 http://www.scirp.org/journal/jfcmv ISSN Online: 2329-3330 ISSN Print: 2329-3322 On the Improvement of Wind Power Predictions Based on
Journal of Flow Control, Measurement & Visualization, 2017, 5, 1-20 http://www.scirp.org/journal/jfcmv ISSN Online: 2329-3330 ISSN Print: 2329-3322 On the Improvement of Wind Power Predictions Based on
TREES IN URBAN STREET CANYONS AND THEIR IMPACT ON THE DISPERSION OF AUTOMOBILE EXHAUSTS. Christof Gromke*, Bodo Ruck
 TREES IN URBAN STREET CANYONS AND THEIR IMPACT ON THE DISPERSION OF AUTOMOBILE EXHAUSTS Christof Gromke*, Bodo Ruck Laboratory of Building- and Environmental Aerodynamics Institute for Hydromechanics,
TREES IN URBAN STREET CANYONS AND THEIR IMPACT ON THE DISPERSION OF AUTOMOBILE EXHAUSTS Christof Gromke*, Bodo Ruck Laboratory of Building- and Environmental Aerodynamics Institute for Hydromechanics,
INVESTIGATION OF THE IMPACT OF WAKES AND STRATIFICATION ON THE PERFORMANCE OF AN ONSHORE WIND FARM
 INVESTIGATION OF THE IMPACT OF WAKES AND STRATIFICATION ON THE PERFORMANCE OF AN ONSHORE WIND FARM Mandar Tabib, Adil Rasheed, Trond Kvamsdal 12th Deep Sea Offshore Wind R&D Conference, EERA DeepWind'2015,
INVESTIGATION OF THE IMPACT OF WAKES AND STRATIFICATION ON THE PERFORMANCE OF AN ONSHORE WIND FARM Mandar Tabib, Adil Rasheed, Trond Kvamsdal 12th Deep Sea Offshore Wind R&D Conference, EERA DeepWind'2015,
H POLLUTANT DISPERSION OVER TWO-DIMENSIONAL IDEALIZED STREET CANYONS: A LARGE-EDDY SIMULATION APPROACH. Colman C.C. Wong and Chun-Ho Liu*
 H14-117 POLLUTANT DISPERSION OVER TWO-DIMENSIONAL IDEALIZED STREET CANYONS: A LARGE-EDDY SIMULATION APPROACH Colman C.C. Wong and Chun-Ho Liu* Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Hong
H14-117 POLLUTANT DISPERSION OVER TWO-DIMENSIONAL IDEALIZED STREET CANYONS: A LARGE-EDDY SIMULATION APPROACH Colman C.C. Wong and Chun-Ho Liu* Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Hong
H AIR QUALITY MODELLING OF ROAD PROJECTS USING A 3D COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) MODEL. Malo Le Guellec, Lobnat Ait Hamou, Amita Tripathi
 H13-198 AIR QUALITY MODELLING OF ROAD PROJECTS USING A 3D COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) MODEL Malo Le Guellec, Lobnat Ait Hamou, Amita Tripathi FLUIDYN France, Saint-Denis, France Abstract: The air
H13-198 AIR QUALITY MODELLING OF ROAD PROJECTS USING A 3D COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS (CFD) MODEL Malo Le Guellec, Lobnat Ait Hamou, Amita Tripathi FLUIDYN France, Saint-Denis, France Abstract: The air
Numerical simulation of atmospheric boundary layer and wakes of horizontal-axis wind turbines
 Numerical simulation of atmospheric boundary layer and wakes of horizontal-axis wind turbines Ali M AbdelSalam Ramalingam Velraj Institute for Energy Studies, Anna University, Chennai, India Abstract Simulations
Numerical simulation of atmospheric boundary layer and wakes of horizontal-axis wind turbines Ali M AbdelSalam Ramalingam Velraj Institute for Energy Studies, Anna University, Chennai, India Abstract Simulations
SAWEP Workshop. Cape Town, 4 th March Wind farm calculations - Annual Energy Production
 SAWEP Workshop Wind Atlas for South Africa (WASA) Cape Town, 4 th March 2010 Wind farm calculations - Annual Energy Production What is AEP? AEP = Annual Energy Production Watt-hours produced over an average
SAWEP Workshop Wind Atlas for South Africa (WASA) Cape Town, 4 th March 2010 Wind farm calculations - Annual Energy Production What is AEP? AEP = Annual Energy Production Watt-hours produced over an average
THRUST COEFFICIENTS USED FOR ESTIMATION OF WAKE EFFECTS FOR FATIGUE LOAD CALCULATION
 European Wind Energy Conference 1, Warsaw, Poland THRUST COEFFICIENTS USED FOR ESTIMATION OF WAKE EFFECTS FOR FATIGUE LOAD CALCULATION Peter Frohboese, Christian Schmuck GL Garrad Hassan WINDTEST Kaiser-Wilhelm-Koog
European Wind Energy Conference 1, Warsaw, Poland THRUST COEFFICIENTS USED FOR ESTIMATION OF WAKE EFFECTS FOR FATIGUE LOAD CALCULATION Peter Frohboese, Christian Schmuck GL Garrad Hassan WINDTEST Kaiser-Wilhelm-Koog
CODASC: A DATABASE FOR THE VALIDATION OF STREET CANYON DISPERSION MODELS. Christof Gromke
 CODASC: A DATABASE FOR THE VALIDATION OF STREET CANYON DISPERSION MODELS Christof Gromke Building Physics and Services, Department of the Built Environment, Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven,
CODASC: A DATABASE FOR THE VALIDATION OF STREET CANYON DISPERSION MODELS Christof Gromke Building Physics and Services, Department of the Built Environment, Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven,
Three-Dimensional Numerical Simulation of a Model Wind Turbine
 Three-Dimensional Numerical Simulation of a Model Wind Turbine N. Tabatabaei 1, M.J. Cervantes 1,2, C. Trivedi 2, J-O Aidanpää 1 1 Luleå University of Technology, Sweden 2 Norwegian University of Science
Three-Dimensional Numerical Simulation of a Model Wind Turbine N. Tabatabaei 1, M.J. Cervantes 1,2, C. Trivedi 2, J-O Aidanpää 1 1 Luleå University of Technology, Sweden 2 Norwegian University of Science
INVESTIGATIONS ON PERFORMANCE OF A SAVONIUS HYDROKINETIC TURBINE
 INVESTIGATIONS ON PERFORMANCE OF A SAVONIUS HYDROKINETIC TURBINE Ph.D. THESIS by ANUJ KUMAR ALTERNATE HYDRO ENERGY CENTRE INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ROORKEE ROORKEE-247667 (INDIA) AUGUST, 2017 INVESTIGATIONS
INVESTIGATIONS ON PERFORMANCE OF A SAVONIUS HYDROKINETIC TURBINE Ph.D. THESIS by ANUJ KUMAR ALTERNATE HYDRO ENERGY CENTRE INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ROORKEE ROORKEE-247667 (INDIA) AUGUST, 2017 INVESTIGATIONS
Comparison of RANS, URANS and LES in the Prediction of Airflow and Pollutant Dispersion
 Comparison of RANS, URANS and LES in the Prediction of Airflow and Pollutant Dispersion S. M. Salim, K. C. Ong, S. C. Cheah Abstract The performance of three different numerical techniques, i.e. RANS,
Comparison of RANS, URANS and LES in the Prediction of Airflow and Pollutant Dispersion S. M. Salim, K. C. Ong, S. C. Cheah Abstract The performance of three different numerical techniques, i.e. RANS,
Modelling wind flow in forested area: a parametric study
 Modelling wind flow in forested area: a parametric study Stéphane SANQUER (1), Julien Berthaut-Gerentes (1), Luis Cosculluela Soteras (2) (1) Meteodyn (2) Iberdrola Renovables Introduction Forested areas
Modelling wind flow in forested area: a parametric study Stéphane SANQUER (1), Julien Berthaut-Gerentes (1), Luis Cosculluela Soteras (2) (1) Meteodyn (2) Iberdrola Renovables Introduction Forested areas
Project Title: Development of a High-Resolution Virtual Wind Simulator for Optimal Design of Wind Energy Projects
 Twin Cities Campus Saint Anthony Falls Laboratory Engineering, Environmental, Biological and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics College of Science and Engineering Mississippi River at 3 rd Avenue S.E. Minneapolis,
Twin Cities Campus Saint Anthony Falls Laboratory Engineering, Environmental, Biological and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics College of Science and Engineering Mississippi River at 3 rd Avenue S.E. Minneapolis,
To whom it may concern
 Department of the Built Environment Building Physics and Services Den Dolech 2, 5612 AZ Eindhoven Postbus 513, 5600 MB Eindhoven Internal address: Vertigo 6.B14 www.urbanphysics.net To whom it may concern
Department of the Built Environment Building Physics and Services Den Dolech 2, 5612 AZ Eindhoven Postbus 513, 5600 MB Eindhoven Internal address: Vertigo 6.B14 www.urbanphysics.net To whom it may concern
Modelling urban pollution dispersion by using MISKAM
 Modelling urban pollution dispersion by using MISKAM Márton Balczó 1, Tamás Faragó 2, Tamás Lajos 3 PhD Student 1, Student 2, Professor 3 Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Department of
Modelling urban pollution dispersion by using MISKAM Márton Balczó 1, Tamás Faragó 2, Tamás Lajos 3 PhD Student 1, Student 2, Professor 3 Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Department of
College of Science and Engineering. Project Title: Development of a High-Resolution Virtual Wind Simulator for Optimal Design of Wind Energy Projects
 Twin Cities Campus Saint Anthony Falls Laboratory Engineering, Environmental, Biological and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics College of Science and Engineering Mississippi River at 3 rd Avenue S.E. Minneapolis,
Twin Cities Campus Saint Anthony Falls Laboratory Engineering, Environmental, Biological and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics College of Science and Engineering Mississippi River at 3 rd Avenue S.E. Minneapolis,
Numerical Simulation of the Aerodynamic Performance of a H-type Wind Turbine during Self-Starting
 Numerical Simulation of the Aerodynamic Performance of a H-type Wind Turbine during Self-Starting Wei Zuo a, Shun Kang b Key Laboratory of Condition Monitoring and Control for Power Plant Equipment, Ministry
Numerical Simulation of the Aerodynamic Performance of a H-type Wind Turbine during Self-Starting Wei Zuo a, Shun Kang b Key Laboratory of Condition Monitoring and Control for Power Plant Equipment, Ministry
arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 11 Oct 2013
![arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 11 Oct 2013 arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 11 Oct 2013](/thumbs/90/101817614.jpg) arxiv:1310.3294v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 11 Oct 2013 Wake Turbulence of Two NREL 5-MW Wind Turbines Immersed in a Neutral Atmospheric Boundary-Layer Flow Jessica L. Bashioum, Pankaj K. Jha, Dr. Sven Schmitz
arxiv:1310.3294v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 11 Oct 2013 Wake Turbulence of Two NREL 5-MW Wind Turbines Immersed in a Neutral Atmospheric Boundary-Layer Flow Jessica L. Bashioum, Pankaj K. Jha, Dr. Sven Schmitz
OpenFOAM in Wind Energy
 OpenFOAM in Wind Energy GOFUN 2018, Braunschweig Matthias Schramm Fraunhofer IWES and ForWind Oldenburg University started with wind physics Research on wind fields, aerodynamics and turbulence CFD is
OpenFOAM in Wind Energy GOFUN 2018, Braunschweig Matthias Schramm Fraunhofer IWES and ForWind Oldenburg University started with wind physics Research on wind fields, aerodynamics and turbulence CFD is
THE IMPACT OF ROADSIDE BARRIERS ON NEAR-ROAD CONCENTRATIONS OF TRAFFIC RELATED POLLUTANTS Nico Schulte 1 and Akula Venkatram 1
 THE IMPACT OF ROADSIDE BARRIERS ON NEAR-ROAD CONCENTRATIONS OF TRAFFIC RELATED POLLUTANTS Nico Schulte 1 and Akula Venkatram 1 1 Mechanical Engineering, University of California, Riverside, USA Abstract:
THE IMPACT OF ROADSIDE BARRIERS ON NEAR-ROAD CONCENTRATIONS OF TRAFFIC RELATED POLLUTANTS Nico Schulte 1 and Akula Venkatram 1 1 Mechanical Engineering, University of California, Riverside, USA Abstract:
NUMERICAL STUDY ON FILM COOLING AND CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS IN THE CUTBACK REGION OF TURBINE BLADE TRAILING EDGE
 S643 NUMERICAL STUDY ON FILM COOLING AND CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS IN THE CUTBACK REGION OF TURBINE BLADE TRAILING EDGE by Yong-Hui XIE *, Dong-Ting YE, and Zhong-Yang SHEN School of Energy
S643 NUMERICAL STUDY ON FILM COOLING AND CONVECTIVE HEAT TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS IN THE CUTBACK REGION OF TURBINE BLADE TRAILING EDGE by Yong-Hui XIE *, Dong-Ting YE, and Zhong-Yang SHEN School of Energy
Riccardo Buccolieri 1, Mats Sandberg 2
 STUDY OF TE EFFECTS OF BUILDING DENSITY AND OVERALL SAPE OF A CITY ON POLLUTANT DISPERSION BY COMBINATION OF WIND TUNNEL EXPERIMENTS AND CFD SIMULATIONS Riccardo Buccolieri 1, Mats Sandberg 2 1 Dipartimento
STUDY OF TE EFFECTS OF BUILDING DENSITY AND OVERALL SAPE OF A CITY ON POLLUTANT DISPERSION BY COMBINATION OF WIND TUNNEL EXPERIMENTS AND CFD SIMULATIONS Riccardo Buccolieri 1, Mats Sandberg 2 1 Dipartimento
CFD/FEM Based Analysis Framework for Wind Effects on Tall Buildings in Urban Areas
 2017 2nd International Conference on Industrial Aerodynamics (ICIA 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-481-3 CFD/FEM Based Analysis Framework for Wind Effects on Tall Buildings in Urban Areas Qiao Yan, Dalong Li,
2017 2nd International Conference on Industrial Aerodynamics (ICIA 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-481-3 CFD/FEM Based Analysis Framework for Wind Effects on Tall Buildings in Urban Areas Qiao Yan, Dalong Li,
Interference of Wind Turbines with Different Yaw Angles of the Upstream Wind Turbine
 42nd AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference and Exhibit 25-28 June 2012, New Orleans, Louisiana AIAA 2012-2719 Interference of Wind Turbines with Different Yaw Angles of the Upstream Wind Turbine Ahmet Ozbay 1,
42nd AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference and Exhibit 25-28 June 2012, New Orleans, Louisiana AIAA 2012-2719 Interference of Wind Turbines with Different Yaw Angles of the Upstream Wind Turbine Ahmet Ozbay 1,
Interaction between large wind farms and the atmospheric boundary layer
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia IUTAM 10 (2014 ) 307 318 23rd International Congress of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics Interaction between large wind farms and the atmospheric
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia IUTAM 10 (2014 ) 307 318 23rd International Congress of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics Interaction between large wind farms and the atmospheric
Equipment for Engineering Education
 Equipment for Engineering Education Operating Instructions HM70.24 Boundary Layer Plate G.U.N.T. Gerätebau GmbH P.O. Box 25 D-2288 Barsbüttel Germany Phone (040) 670854-0 Fax (040) 670854-4 Table of Contents
Equipment for Engineering Education Operating Instructions HM70.24 Boundary Layer Plate G.U.N.T. Gerätebau GmbH P.O. Box 25 D-2288 Barsbüttel Germany Phone (040) 670854-0 Fax (040) 670854-4 Table of Contents
Large-Eddy Simulation of Porous-Like Canopy Forest Flows Using Real. Field Measurement Data for Wind Energy Application
 Large-Eddy Simulation of Porous-Like Canopy Forest Flows Using Real Field Measurement Data for Wind Energy Application *Zeinab Ahmadi Zeleti¹, Antti Hellsten1,2, Ashvinkumar Chaudhari¹, Heikki Haario1
Large-Eddy Simulation of Porous-Like Canopy Forest Flows Using Real Field Measurement Data for Wind Energy Application *Zeinab Ahmadi Zeleti¹, Antti Hellsten1,2, Ashvinkumar Chaudhari¹, Heikki Haario1
Engineering, Environmental, Biological and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics. Department of Civil Engineering College of Science and Engineering
 Twin Cities Campus Saint Anthony Falls Laboratory Engineering, Environmental, Biological and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Department of Civil Engineering College of Science and Engineering Mississippi River
Twin Cities Campus Saint Anthony Falls Laboratory Engineering, Environmental, Biological and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Department of Civil Engineering College of Science and Engineering Mississippi River
MODELLING THE URBAN MICROCLIMATE AND ITS INFLUENCE ON BUILDING ENERGY DEMANDS OF AN URBAN NEIGHBOURHOOD
 MODELLING THE URBAN MICROCLIMATE AND ITS INFLUENCE ON BUILDING ENERGY DEMANDS OF AN URBAN NEIGHBOURHOOD J. Allegrini 1,2 ; J. Kämpf 3 ; V. Dorer 1 ; J. Carmeliet 1,2 1: Empa, Laboratory for Building Science
MODELLING THE URBAN MICROCLIMATE AND ITS INFLUENCE ON BUILDING ENERGY DEMANDS OF AN URBAN NEIGHBOURHOOD J. Allegrini 1,2 ; J. Kämpf 3 ; V. Dorer 1 ; J. Carmeliet 1,2 1: Empa, Laboratory for Building Science
Dr. J. Wolters. FZJ-ZAT-379 January Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH, FZJ
 Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH, FZJ ZAT-Report FZJ-ZAT-379 January 2003 Benchmark Activity on Natural Convection Heat Transfer Enhancement in Mercury with Gas Injection authors Dr. J. Wolters abstract A
Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH, FZJ ZAT-Report FZJ-ZAT-379 January 2003 Benchmark Activity on Natural Convection Heat Transfer Enhancement in Mercury with Gas Injection authors Dr. J. Wolters abstract A
Forest Model WindSim 7 interim report WKN AG renewable energies for today and tomorrow
 Forest Model WindSim 7 interim report WKN AG renewable energies for today and tomorrow Forest Modeling inside WindSim 7.0 interim report Karsten Busch (Uni OL, WKN AG) Catherine Meißner (WindSim AS) Eva-Maria
Forest Model WindSim 7 interim report WKN AG renewable energies for today and tomorrow Forest Modeling inside WindSim 7.0 interim report Karsten Busch (Uni OL, WKN AG) Catherine Meißner (WindSim AS) Eva-Maria
Framework for the Categorisation of Losses and Uncertainty for Wind Energy Assessments
 Framework for the Categorisation of Losses and Uncertainty for Wind Energy Assessments In collaboration with: Introduction A typical wind resource and energy yield assessment derives gross generation from
Framework for the Categorisation of Losses and Uncertainty for Wind Energy Assessments In collaboration with: Introduction A typical wind resource and energy yield assessment derives gross generation from
A Guide to Design Load Validation
 A Guide to Design Load Validation Holger Söker, Martina Damaschke, Deutsches Windenergie-Institut GmbH, Ebertstr. 96, D-26382 Wilhelmshaven, Germany, Tel. : +49-4421-4808 0, Fax: +49-4421-4808-43, h.soeker@dewi.de
A Guide to Design Load Validation Holger Söker, Martina Damaschke, Deutsches Windenergie-Institut GmbH, Ebertstr. 96, D-26382 Wilhelmshaven, Germany, Tel. : +49-4421-4808 0, Fax: +49-4421-4808-43, h.soeker@dewi.de
Modeling for Wind Farm Control
 Modeling for Wind Farm Control A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Jennifer Annoni IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER
Modeling for Wind Farm Control A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA BY Jennifer Annoni IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER
3D Simulation of a fire inside a river tunnel and optimisation of the ventilation using Computational Fluid Dynamics
 3D Simulation of a fire inside a river tunnel and optimisation of the ventilation using Computational Fluid Dynamics Authors: B. TRUCHOT, A. TRIPATHI Fluidyn-France Abstract CFD simulation is used to predict
3D Simulation of a fire inside a river tunnel and optimisation of the ventilation using Computational Fluid Dynamics Authors: B. TRUCHOT, A. TRIPATHI Fluidyn-France Abstract CFD simulation is used to predict
Optimal Location of Wind Turbines in a Wind Farm using Genetic Algorithm
 TELKOMNIKA Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering Vol. 1, No. 8, August 014, pp. 5869 ~ 5876 DOI: 10.11591/telkomnika.v1i8.6054 5869 Optimal Location of Wind Turbines in a Wind Farm using Genetic
TELKOMNIKA Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering Vol. 1, No. 8, August 014, pp. 5869 ~ 5876 DOI: 10.11591/telkomnika.v1i8.6054 5869 Optimal Location of Wind Turbines in a Wind Farm using Genetic
Lungs of the city of Eindhoven
 Lungs of the city of Eindhoven ir. Rob Vervoort (r.p.m.vervoort@tue.nl), Eindhoven University of Technology, PDEng-trainee Smart Buildings & Cities, Department of the Built Environment, Building Physics
Lungs of the city of Eindhoven ir. Rob Vervoort (r.p.m.vervoort@tue.nl), Eindhoven University of Technology, PDEng-trainee Smart Buildings & Cities, Department of the Built Environment, Building Physics
CERC activities under the TOPFARM project: Wind turbine wake modelling using ADMS
 CERC activities under the TOPFARM project: Wind turbine wake modelling using ADMS Final report Prepared for Risø DTU, National Laboratory for Sustainable Energy 13 th January 211 Report Information FM766
CERC activities under the TOPFARM project: Wind turbine wake modelling using ADMS Final report Prepared for Risø DTU, National Laboratory for Sustainable Energy 13 th January 211 Report Information FM766
WIND FLOW MODELING IN BUSINESS!!
 WIND FLOW MODELING IN BUSINESS!! Do more sophisticated models produce more accurate wind resource estimates???? Mytrah Energy (India) Limited WindSim User Meeting June 2014 As we ago along. MYTRAH : A
WIND FLOW MODELING IN BUSINESS!! Do more sophisticated models produce more accurate wind resource estimates???? Mytrah Energy (India) Limited WindSim User Meeting June 2014 As we ago along. MYTRAH : A
WIND ENERGY MODELING FOR RESIDENTIAL-SCALE WIND POWER AND SENSITIVITY OF ECONOMIC VALUATION TO ERRORS IN WIND SPEED ESTIMATES
 WIND ENERGY MODELING FOR RESIDENTIAL-SCALE WIND POWER AND SENSITIVITY OF ECONOMIC VALUATION TO ERRORS IN WIND SPEED ESTIMATES Teuku Indra Dominique Bain Thomas L. Acker, Ph.D Institute for Sustainable
WIND ENERGY MODELING FOR RESIDENTIAL-SCALE WIND POWER AND SENSITIVITY OF ECONOMIC VALUATION TO ERRORS IN WIND SPEED ESTIMATES Teuku Indra Dominique Bain Thomas L. Acker, Ph.D Institute for Sustainable
Visualization of the tip vortices in a wind turbine wake
 J Vis (2012) 15:39 44 DOI 10.1007/s12650-011-0112-z SHORT PAPER Zifeng Yang Partha Sarkar Hui Hu Visualization of the tip vortices in a wind turbine wake Received: 30 December 2010 / Revised: 19 September
J Vis (2012) 15:39 44 DOI 10.1007/s12650-011-0112-z SHORT PAPER Zifeng Yang Partha Sarkar Hui Hu Visualization of the tip vortices in a wind turbine wake Received: 30 December 2010 / Revised: 19 September
Comparative analysis of dust emissions: isolated stockpile vs two nearby stockpiles
 Air Pollution XX 285 Comparative analysis of dust emissions: isolated stockpile vs two nearby stockpiles B. Furieri 1,S.Russeil 1,J.-L.Harion 1,J.Santos 2 & M. Milliez 3 1 Department of Industrial Energetics,
Air Pollution XX 285 Comparative analysis of dust emissions: isolated stockpile vs two nearby stockpiles B. Furieri 1,S.Russeil 1,J.-L.Harion 1,J.Santos 2 & M. Milliez 3 1 Department of Industrial Energetics,
Wind Farm parametrization in the mesoscale model WRF
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 21, 2018 Wind Farm parametrization in the mesoscale model WRF Volker, Patrick; Badger, Jake; Hahmann, Andrea N.; Ott, Søren Published in: Proceedings Publication date:
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Sep 21, 2018 Wind Farm parametrization in the mesoscale model WRF Volker, Patrick; Badger, Jake; Hahmann, Andrea N.; Ott, Søren Published in: Proceedings Publication date:
Limits to the power density of very large wind farms
 Draft (18th September 213) Short Communication Limits to the power density of very large wind farms Takafumi Nishino Department of Engineering Science, University of Oxford, Oxford OX1 3PJ, UK ABSTRACT
Draft (18th September 213) Short Communication Limits to the power density of very large wind farms Takafumi Nishino Department of Engineering Science, University of Oxford, Oxford OX1 3PJ, UK ABSTRACT
CFD modelling of dispersion in neutral and stable atmospheric boundary layers:
 Health and Safety Executive CFD modelling of dispersion in neutral and stable atmospheric boundary layers: Results for Prairie Grass and Thorney Island 9 th May 2016 Rachel Batt, Simon Gant, Jean-Marc
Health and Safety Executive CFD modelling of dispersion in neutral and stable atmospheric boundary layers: Results for Prairie Grass and Thorney Island 9 th May 2016 Rachel Batt, Simon Gant, Jean-Marc
Wind loads at solar and photovoltaic modules for large plants
 Ruscheweyh Consult GmbH Aachen Veröffentlichung Wind loads at solar and photovoltaic modules for large plants Hans Ruscheweyh, Reiner Windhövel Ruscheweyh Consult GmbH, Teichstr. 8, Aachen, Germany, info@ruscheweyh.de
Ruscheweyh Consult GmbH Aachen Veröffentlichung Wind loads at solar and photovoltaic modules for large plants Hans Ruscheweyh, Reiner Windhövel Ruscheweyh Consult GmbH, Teichstr. 8, Aachen, Germany, info@ruscheweyh.de
Visualising Forest Edge Effects Ralph Torr Senior Engineer 25 June 2013
 Visualising Forest Edge Effects Ralph Torr Senior Engineer 25 June 2013 Carbon Trust Project Power From Onshore Wind Farms: Advanced Measurement and Modelling (POWFARM) Acknowledgement of Work Conducted
Visualising Forest Edge Effects Ralph Torr Senior Engineer 25 June 2013 Carbon Trust Project Power From Onshore Wind Farms: Advanced Measurement and Modelling (POWFARM) Acknowledgement of Work Conducted
Performance of a Vertical Axis Wind Turbine under Accelerating and Decelerating Flows
 Performance of a Vertical Axis Wind Turbine under Accelerating and Decelerating Flows Atif Shahzad, Taimoor Asim*, Rakesh Mishra, Achilleos Paris School of Computing & Engineering, University of Huddersfield,
Performance of a Vertical Axis Wind Turbine under Accelerating and Decelerating Flows Atif Shahzad, Taimoor Asim*, Rakesh Mishra, Achilleos Paris School of Computing & Engineering, University of Huddersfield,
The Influence of Atmospheric Turbulence on the Kinetic Energy Available During Small Wind Turbine Power Performance Testing
 The Influence of Atmospheric Turbulence on the Kinetic Energy Available During Small Wind Turbine Power Performance Testing By Brad C. Cochran Sr. Project Engineer Cermak Peterka Petersen, Inc Fort Collins,
The Influence of Atmospheric Turbulence on the Kinetic Energy Available During Small Wind Turbine Power Performance Testing By Brad C. Cochran Sr. Project Engineer Cermak Peterka Petersen, Inc Fort Collins,
On Plume Dispersion over Two-Dimensional Urban-like Idealized Roughness Elements with Height Variation
 On Plume Dispersion over Two-Dimensional Urban-like Idealized Roughness Elements with Height Variation Colman C.C. Wong and Chun-Ho Liu Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Hong Kong,
On Plume Dispersion over Two-Dimensional Urban-like Idealized Roughness Elements with Height Variation Colman C.C. Wong and Chun-Ho Liu Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Hong Kong,
Smoke Dispersion from Stacks on Pitched-Roof Buildings: Model Calculations Using MISKAM in Comparison with Wind Tunnel Results
 Smoke Dispersion from Stacks on Pitched-Roof Buildings: Model Calculations Using MISKAM in Comparison with Wind Tunnel Results Konstantinos E. Kakosimos 1 Marc J. Assael 1 Matthias Ketzel 2 Helge Rørdam
Smoke Dispersion from Stacks on Pitched-Roof Buildings: Model Calculations Using MISKAM in Comparison with Wind Tunnel Results Konstantinos E. Kakosimos 1 Marc J. Assael 1 Matthias Ketzel 2 Helge Rørdam
FLUID STRUCTURE INTERACTION MODELLING OF WIND TURBINE BLADES BASED ON COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS AND FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
 Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5769 FLUID STRUCTURE INTERACTION
Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5769 FLUID STRUCTURE INTERACTION
APEC-WW2012 Economy Report: Chinese Taipei
 APEC-WW2012 Economy Report: Chinese Taipei Chii-Ming Cheng a, Cheng-Hsin Chang a a Department of Civil Engineering, Tamkang University, Taipei, Taiwan ABSTRACT: This article describes the current status
APEC-WW2012 Economy Report: Chinese Taipei Chii-Ming Cheng a, Cheng-Hsin Chang a a Department of Civil Engineering, Tamkang University, Taipei, Taiwan ABSTRACT: This article describes the current status
PHYSICAL MODELING OF A FINITE FOREST AREA TRANSPORT OF BIOGENIC EMISSIONS
 International Conference Wind Effects on Trees September 6-8,, University of Karlsruhe, Germany PHYSICAL MODELING OF A FINITE FOREST AREA TRANSPORT OF BIOGENIC EMISSIONS Sandrine Aubrun, Bernd Leitl, Michael
International Conference Wind Effects on Trees September 6-8,, University of Karlsruhe, Germany PHYSICAL MODELING OF A FINITE FOREST AREA TRANSPORT OF BIOGENIC EMISSIONS Sandrine Aubrun, Bernd Leitl, Michael
Influence of trees on the dispersion of pollutants in an urban street canyon Experimental investigation of the flow and concentration field
 First published in: Atmospheric Environment 41 (2007) 3287 3302 www.elsevier.com/locate/atmosenv Influence of trees on the dispersion of pollutants in an urban street canyon Experimental investigation
First published in: Atmospheric Environment 41 (2007) 3287 3302 www.elsevier.com/locate/atmosenv Influence of trees on the dispersion of pollutants in an urban street canyon Experimental investigation
CFD Modeling of Reactive Pollutants in an Urban Street Canyon using Different Chemical Mechanisms
 CFD Modeling of Reactive Pollutants in an Urban Street Canyon using Different Chemical Mechanisms B Sanchez a,b, JL Santiago a, A Martilli a, M Palacios a, F Kirchner c a Center for Energy, Environment
CFD Modeling of Reactive Pollutants in an Urban Street Canyon using Different Chemical Mechanisms B Sanchez a,b, JL Santiago a, A Martilli a, M Palacios a, F Kirchner c a Center for Energy, Environment
6.5 THE INFLUENCE OF OBSTACLES ON THE FLOW AND POLLUTANT DISPERSION IN AN URBAN ENVIRONMENT
 6.5 THE NFLUENCE OF OBSTACLES ON THE FLOW AND POLLUTANT DSPERSON N AN URBAN ENVRONMENT Mohamed F. Yassin a, *, Masaaki Ohba b, Hideyuki Tanaka b a Faculty of Engineering, Assiut University, Assiut, Egypt
6.5 THE NFLUENCE OF OBSTACLES ON THE FLOW AND POLLUTANT DSPERSON N AN URBAN ENVRONMENT Mohamed F. Yassin a, *, Masaaki Ohba b, Hideyuki Tanaka b a Faculty of Engineering, Assiut University, Assiut, Egypt
768 SIMULATING WIND POWER DENSITY AROUND BUILDINGS FOR SITING BUILDING INTEGRATED WIND TURBINES
 768 SIMULATING WIND POWER DENSITY AROUND BUILDINGS FOR SITING BUILDING INTEGRATED WIND TURBINES Sue Ellen Haupt 1,2, Susan W. Stewart 2, Julia A. Cole 2, Frank J. Zajaczkowski, and Kerrie J. Schmehl 2
768 SIMULATING WIND POWER DENSITY AROUND BUILDINGS FOR SITING BUILDING INTEGRATED WIND TURBINES Sue Ellen Haupt 1,2, Susan W. Stewart 2, Julia A. Cole 2, Frank J. Zajaczkowski, and Kerrie J. Schmehl 2
CFD SIMULATION AND EXPERIMENTAL VALIDATION OF FLUID FLOW IN LIQUID DISTRIBUTORS
 CFD SIMULATION AND EXPERIMENTAL VALIDATION OF FLUID FLOW IN LIQUID DISTRIBUTORS Marc Heggemann 1, Sebastian Hirschberg 1, Lothar Spiegel 2, Christian Bachmann 2 1 Sulzer Innotec, Sulzer Markets & Technology
CFD SIMULATION AND EXPERIMENTAL VALIDATION OF FLUID FLOW IN LIQUID DISTRIBUTORS Marc Heggemann 1, Sebastian Hirschberg 1, Lothar Spiegel 2, Christian Bachmann 2 1 Sulzer Innotec, Sulzer Markets & Technology
Modelling Wind Turbine Inflow:
 Modelling Wind Turbine Inflow: The Induction zone Alexander R Meyer Forsting Main Supervisor: Niels Troldborg Co-supervisors: Andreas Bechmann & Pierre-Elouan Réthoré Why wind turbine inflow? Inflow KE
Modelling Wind Turbine Inflow: The Induction zone Alexander R Meyer Forsting Main Supervisor: Niels Troldborg Co-supervisors: Andreas Bechmann & Pierre-Elouan Réthoré Why wind turbine inflow? Inflow KE
Project Title: Development of a High-Resolution Virtual Wind Simulator for Optimal Design of Wind Energy Projects
 Twin Cities Campus Saint Anthony Falls Laboratory Engineering, Environmental, Biological and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics College of Science and Engineering Mississippi River at 3 rd Avenue S.E. Minneapolis,
Twin Cities Campus Saint Anthony Falls Laboratory Engineering, Environmental, Biological and Geophysical Fluid Dynamics College of Science and Engineering Mississippi River at 3 rd Avenue S.E. Minneapolis,
Numerical CFD Comparison of Lillgrund Employing RANS
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 2, 27 Numerical CFD Comparison of Lillgrund Employing RANS Simisiroglou, N.; Breton, S.-P.; Crasto, G.; Hansen, Kurt Schaldemose; Ivanell, S. Published in: Energy Procedia
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Dec 2, 27 Numerical CFD Comparison of Lillgrund Employing RANS Simisiroglou, N.; Breton, S.-P.; Crasto, G.; Hansen, Kurt Schaldemose; Ivanell, S. Published in: Energy Procedia
3D numerical modeling of the flow over a gravel river bed due to hydropower peaking
 Technische Universität Dresden Fakultät Bauingenieurwesen Institut für Wasserbau und Technische Hydromechanik 37. Dresdner Wasserbaukolloquium 2014 Simulationsverfahren und Modelle für Wasserbau und Wasserwirtschaft
Technische Universität Dresden Fakultät Bauingenieurwesen Institut für Wasserbau und Technische Hydromechanik 37. Dresdner Wasserbaukolloquium 2014 Simulationsverfahren und Modelle für Wasserbau und Wasserwirtschaft
Towards Simulating the Atmospheric Boundary Layer and Wind Farm Flows
 Towards Simulating the Atmospheric Boundary Layer and Wind Farm Flows 6 th OpenFOAM Workshop Matthew J. Churchfield Patrick J. Moriarty June 15, 2011 NREL is a national laboratory of the U.S. Department
Towards Simulating the Atmospheric Boundary Layer and Wind Farm Flows 6 th OpenFOAM Workshop Matthew J. Churchfield Patrick J. Moriarty June 15, 2011 NREL is a national laboratory of the U.S. Department
LIST OF ACRONYMS / ABBREVIATIONS USED IN THIS DOCUMENT Acronym / abbreviation Definition
 LIST OF ACRONYMS / ABBREVIATIONS USED IN THIS DOCUMENT Acronym / abbreviation Definition ACC CCGT CFD CSP DNI DoW EC GE IP IPR LCA LDA LSV MACC MENA MS/RA PIV PM PTC RANS SME WP WPS WT Air Cooled Condenser
LIST OF ACRONYMS / ABBREVIATIONS USED IN THIS DOCUMENT Acronym / abbreviation Definition ACC CCGT CFD CSP DNI DoW EC GE IP IPR LCA LDA LSV MACC MENA MS/RA PIV PM PTC RANS SME WP WPS WT Air Cooled Condenser
Assessment of Toxic Gas Dispersion using Phast and Panache
 Assessment of Toxic Gas Dispersion using Phast and Panache Tejeswi Ramprasad 1, Madhavi Gaonkar 2, Diptendu Das 3 1 ME Research Student, Department of Chemical Engineering, Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering
Assessment of Toxic Gas Dispersion using Phast and Panache Tejeswi Ramprasad 1, Madhavi Gaonkar 2, Diptendu Das 3 1 ME Research Student, Department of Chemical Engineering, Jawaharlal Nehru Engineering
Urban Wind Turbines: A Feasibility Study
 Urban Wind Turbines: A Feasibility Study Ben Dymock And Stephen Dance Urbines Urbines: The Issues Urban Wind Turbines Urbines Rooftop installation for energy generation Uncertainty of wind flow and knock
Urban Wind Turbines: A Feasibility Study Ben Dymock And Stephen Dance Urbines Urbines: The Issues Urban Wind Turbines Urbines Rooftop installation for energy generation Uncertainty of wind flow and knock
Comparison of Resource and Energy Yield Assessment Procedures What have we learned and what needs to be done?
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Nov 01, 2018 Comparison of Resource and Energy Yield Assessment Procedures 2011-2015 What have we learned and what needs to be done? Mortensen, Niels Gylling; Nielsen,
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Nov 01, 2018 Comparison of Resource and Energy Yield Assessment Procedures 2011-2015 What have we learned and what needs to be done? Mortensen, Niels Gylling; Nielsen,
WINDBREAK SHELTERING EFFECTS ON OUTDOOR OPEN SPACE. The School of the Built Environment, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh, UK 2
 Eighth International IBPSA Conference Eindhoven, Netherlands August -4, 3 WINDBREAK SHELTERING EFFECTS ON OUTDOOR OPEN SPACE Wei Li, Fan Wang, Simon Bell The School of the Built Environment, Heriot-Watt
Eighth International IBPSA Conference Eindhoven, Netherlands August -4, 3 WINDBREAK SHELTERING EFFECTS ON OUTDOOR OPEN SPACE Wei Li, Fan Wang, Simon Bell The School of the Built Environment, Heriot-Watt
Comparison of Resource and Energy Yield Assessment Procedures What have we learned and what needs to be done?
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Nov 08, 2017 Comparison of Resource and Energy Yield Assessment Procedures 2011-2015 What have we learned and what needs to be done? Mortensen, Niels Gylling; Nielsen,
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Nov 08, 2017 Comparison of Resource and Energy Yield Assessment Procedures 2011-2015 What have we learned and what needs to be done? Mortensen, Niels Gylling; Nielsen,
On the Effects of Directional Bin Size when Simulating Large Offshore Wind Farms with CFD
 On the Effects of Directional Bin Size when Simulating Large Offshore Wind Farms with CFD Peter Argyle, Simon Watson CREST, Loughborough University, ENGLAND p.argyle@lboro.ac.uk ABSTRACT Computational
On the Effects of Directional Bin Size when Simulating Large Offshore Wind Farms with CFD Peter Argyle, Simon Watson CREST, Loughborough University, ENGLAND p.argyle@lboro.ac.uk ABSTRACT Computational
TECHNICAL EVALUATION OF THE WIND RESOURCE IN VENEZUELA
 TECHNICAL EVALUATION OF THE WIND RESOURCE IN VENEZUELA Marisabel Contreras- Vielma and Victor Vasil evich Elistratov Peter the Great Saint-Petersburg Polytechnic University, Polytechnicheskaya Str., St.Petersburg,
TECHNICAL EVALUATION OF THE WIND RESOURCE IN VENEZUELA Marisabel Contreras- Vielma and Victor Vasil evich Elistratov Peter the Great Saint-Petersburg Polytechnic University, Polytechnicheskaya Str., St.Petersburg,
Spacing dependence on wind turbine array boundary layers
 Spacing dependence on wind turbine array boundary layers Raúl Bayoán Cal 1,*, Angelisse Ramos 2, Nicholas Hamilton 1, and Dan Houck 3 1 Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, Portland State
Spacing dependence on wind turbine array boundary layers Raúl Bayoán Cal 1,*, Angelisse Ramos 2, Nicholas Hamilton 1, and Dan Houck 3 1 Department of Mechanical and Materials Engineering, Portland State
CHAPTER 1. Introduction
 CHAPTER 1. Introduction.................................................. 1-1 CHAPTER 1. Introduction Topographic effects on air flow are important in many situations. Speed-up and enhanced fluctuations
CHAPTER 1. Introduction.................................................. 1-1 CHAPTER 1. Introduction Topographic effects on air flow are important in many situations. Speed-up and enhanced fluctuations
Critical Review of the Building Downwash Algorithms in AERMOD
 Critical Review of the Building Downwash Algorithms in AERMOD Paper #34 Presented at the conference: Guideline on Air Quality Models: The New Path April 12-14, 2016 Chapel Hill, NC Ron L. Petersen, 1 Sergio
Critical Review of the Building Downwash Algorithms in AERMOD Paper #34 Presented at the conference: Guideline on Air Quality Models: The New Path April 12-14, 2016 Chapel Hill, NC Ron L. Petersen, 1 Sergio
Prediction of odor dispersion according to ventilation type of pig house and facilities of reducing distance of odor dispersion using CFD technology
 Ref: 1064 Prediction of odor dispersion according to ventilation type of pig and facilities of reducing distance of odor dispersion using CFD technology Rack-woo Kim and In-bok Lee, Department of Rural
Ref: 1064 Prediction of odor dispersion according to ventilation type of pig and facilities of reducing distance of odor dispersion using CFD technology Rack-woo Kim and In-bok Lee, Department of Rural
Wedging Angle Effect on the Aerodynamic Structure of a Rutland 913 Horizontal Axis Wind Turbine
 International Journal of Fluid Mechanics & Thermal Sciences 2016; 2(1): 1-9 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijfmts doi: 10.11648/j.ijfmts.20160201.11 ISSN: 2469-8105 (Print); ISSN: 2469-8113 (Online)
International Journal of Fluid Mechanics & Thermal Sciences 2016; 2(1): 1-9 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijfmts doi: 10.11648/j.ijfmts.20160201.11 ISSN: 2469-8105 (Print); ISSN: 2469-8113 (Online)
WIND FARM LAYOUT OPTIMIZATION IN COMPLEX TERRAINS USING COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS
 Proceedings of the ASME 2015 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences & Computers and Information in Engineering Conference DETC 2015 August 2-5, 2015, Boston, USA DETC2015-47651 WIND FARM
Proceedings of the ASME 2015 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences & Computers and Information in Engineering Conference DETC 2015 August 2-5, 2015, Boston, USA DETC2015-47651 WIND FARM
Optimizational Analysis of a Windmill Hub
 Optimizational Analysis of a Windmill Hub P.Rama Chandra Rao M.Tech Student, Machine Design, Sarada Institute of Science Technology and Management (Approved By AICTE, Approved By JNTUKakinada) Srikakulam.
Optimizational Analysis of a Windmill Hub P.Rama Chandra Rao M.Tech Student, Machine Design, Sarada Institute of Science Technology and Management (Approved By AICTE, Approved By JNTUKakinada) Srikakulam.
Potentials of the new design concepts of district heating and cooling toward integration with renewable energy sources
 Potentials of the new design concepts of district heating and cooling toward integration with renewable energy sources Julio Efrain Vaillant Rebollar 1, Arnold Janssens 1, Eline Himpe 1, 1 Ghent University,
Potentials of the new design concepts of district heating and cooling toward integration with renewable energy sources Julio Efrain Vaillant Rebollar 1, Arnold Janssens 1, Eline Himpe 1, 1 Ghent University,
Volume 7 - Number 12 - November 2011 (29-34) Numerical Modeling of Wind Effect on Plume Dispersion from a Point Source around Buildings
 ISESCO JOURNAL of Science and Technology Volume 7 - Number 12 - November 2011 (29-34) Abstract Dispersion from the polluted point source within the atmosphere is the major concern in the urban areas. The
ISESCO JOURNAL of Science and Technology Volume 7 - Number 12 - November 2011 (29-34) Abstract Dispersion from the polluted point source within the atmosphere is the major concern in the urban areas. The
WIND LOADS ON BUILDINGS MWFRS (ENVELOPE PROCEDURE)
 Chapter C28 WIND LOADS ON BUILDINGS MWFRS (ENVELOPE PROCEDURE) The Envelope Procedure is the former low-rise buildings provision in Method 2 of ASCE 7-05 for MWFRS. The simplified method in this chapter
Chapter C28 WIND LOADS ON BUILDINGS MWFRS (ENVELOPE PROCEDURE) The Envelope Procedure is the former low-rise buildings provision in Method 2 of ASCE 7-05 for MWFRS. The simplified method in this chapter
Modeling of pollutant dispersion in street canyon by means of CFD
 Modeling of pollutant dispersion in street canyon by means of CFD Davide Meschini a, Valentina Busini * a, Sjoerd W. van Ratingen b, Renato Rota a a Department of Chemistry, Materials and Chemical Engineering
Modeling of pollutant dispersion in street canyon by means of CFD Davide Meschini a, Valentina Busini * a, Sjoerd W. van Ratingen b, Renato Rota a a Department of Chemistry, Materials and Chemical Engineering
Extensions of TerrSysMP-CO 2 to resolve dynamic processes induced by tall vegetation
 Extensions of TerrSysMP-CO 2 to resolve dynamic processes induced by tall vegetation Markus Übel and Andreas Bott Meteorological Institute, University of Bonn TerrSysMP-CO 2 model domain General Meeting,
Extensions of TerrSysMP-CO 2 to resolve dynamic processes induced by tall vegetation Markus Übel and Andreas Bott Meteorological Institute, University of Bonn TerrSysMP-CO 2 model domain General Meeting,
Reducing Uncertainty in Wind Project Energy Estimates
 www.vaisala.com Reducing Uncertainty in Wind Project Energy Estimates A Cost-Benefit Analysis of Additional Measurement Campaign Methods Wind project energy production estimates are a key element in determining
www.vaisala.com Reducing Uncertainty in Wind Project Energy Estimates A Cost-Benefit Analysis of Additional Measurement Campaign Methods Wind project energy production estimates are a key element in determining
Lateral Outflow from Supercritical Channels
 Lateral Outflow from Supercritical Channels J. Coonrod 1, J. Ho 2 and N. Bernardo 3 1 Associate Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM 87131; PH (505) 277-3233;
Lateral Outflow from Supercritical Channels J. Coonrod 1, J. Ho 2 and N. Bernardo 3 1 Associate Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, NM 87131; PH (505) 277-3233;
On The Effect Of Various Design Factors On Wind-Induced Natural Ventilation Of Residential Buildings In Malaysia M. F. Mohamad 1,2*, A. Hagishima 2, J
 On The Effect Of Various Design Factors On Wind-Induced Natural Ventilation Of Residential Buildings In Malaysia M. F. Mohamad 1,2*, A. Hagishima 2, J. Tanimoto 2, N. Ikegaya 2, and A. R. Omar 1 1 Faculty
On The Effect Of Various Design Factors On Wind-Induced Natural Ventilation Of Residential Buildings In Malaysia M. F. Mohamad 1,2*, A. Hagishima 2, J. Tanimoto 2, N. Ikegaya 2, and A. R. Omar 1 1 Faculty
Atmospheric boundary layer simulation in a short wind tunnel
 Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. (2014) 11:59 68 DOI 10.1007/s13762-013-0371-4 ORIGINAL PAPER Atmospheric boundary layer simulation in a short wind tunnel S. M. N. Shojaee O. Uzol Ö. Kurç Received: 11 September
Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. (2014) 11:59 68 DOI 10.1007/s13762-013-0371-4 ORIGINAL PAPER Atmospheric boundary layer simulation in a short wind tunnel S. M. N. Shojaee O. Uzol Ö. Kurç Received: 11 September
MODELING THE STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS OF CHOSEN COMPONENTS OF THE HORIZONTAL AXIS WIND TURBINE
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 18, No. 2 2011 MODELING THE STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS OF CHOSEN COMPONENTS OF THE HORIZONTAL AXIS WIND TURBINE Mariusz Pawlak, Mariola Jureczko, Tomasz Czapla
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 18, No. 2 2011 MODELING THE STRUCTURAL DYNAMICS OF CHOSEN COMPONENTS OF THE HORIZONTAL AXIS WIND TURBINE Mariusz Pawlak, Mariola Jureczko, Tomasz Czapla
The influence of the lengths of turbine blades on the power produced by miniature wind turbines that operate in non-uniform flow fields
 World Transactions on Engineering and Technology Education Vol.10, No.2, 2012 2012 WIETE The influence of the lengths of turbine blades on the power produced by miniature wind turbines that operate in
World Transactions on Engineering and Technology Education Vol.10, No.2, 2012 2012 WIETE The influence of the lengths of turbine blades on the power produced by miniature wind turbines that operate in
GEKOM Ltd. Geophysical and Ecological Modeling 2 Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Naval Architecture 3
 Estimating urban wind characteristics via neural networks Josip Križan 1, Goran Gašparac 1, Hrvoje Kozmar 2, Oleg Antonić 3, Branko Grisogono 4 ggasparac@gekom.hr 1 GEKOM Ltd. Geophysical and Ecological
Estimating urban wind characteristics via neural networks Josip Križan 1, Goran Gašparac 1, Hrvoje Kozmar 2, Oleg Antonić 3, Branko Grisogono 4 ggasparac@gekom.hr 1 GEKOM Ltd. Geophysical and Ecological
Fotios Barmpas, Nicolas Moussiopoulos, Ioannis Ossanlis and Vassilis Akylas
 H14-292 DISPERSION OF TRAFFIC EMISSIONS IN THE LEOPOLD II ROAD TUNNEL IN BRUSSELS UNDER THE COMBINED INFLUENCE OF THE VENTILATION SYSTEM AND THE VEHICLE MOTION Fotios Barmpas, Nicolas Moussiopoulos, Ioannis
H14-292 DISPERSION OF TRAFFIC EMISSIONS IN THE LEOPOLD II ROAD TUNNEL IN BRUSSELS UNDER THE COMBINED INFLUENCE OF THE VENTILATION SYSTEM AND THE VEHICLE MOTION Fotios Barmpas, Nicolas Moussiopoulos, Ioannis
Modelling of the Performance of a Building- Mounted Ducted Wind Turbine
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Modelling of the Performance of a Building- Mounted Ducted Wind Turbine To cite this article: S J Watson et al 007 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 75 000 View the article online
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Modelling of the Performance of a Building- Mounted Ducted Wind Turbine To cite this article: S J Watson et al 007 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 75 000 View the article online
Wind Turbine Wakes and Wind Farms. Stefan Ivanell Director, Stand Up for Wind Centre
 Wind Turbine Wakes and Wind Farms Stefan Ivanell Director, Stand Up for Wind Centre Planning of lectures Lecture 1: Energy extraction and flow close to the blades Lecture 2: Flow behind the turbine, i.e.,
Wind Turbine Wakes and Wind Farms Stefan Ivanell Director, Stand Up for Wind Centre Planning of lectures Lecture 1: Energy extraction and flow close to the blades Lecture 2: Flow behind the turbine, i.e.,
Pressure Distribution Around Net Clad Scaffolds Using Computation Fluid Dynamics Techniques
 e-issn: 78-1684, p-issn: 30-334X PP 54-6 Pressure Distribution Around Net Clad Scaffolds Using Computation Fluid Dynamics Techniques Hassan Irtaza 1, R.G. Beale, M.H.R. Godley, A. Jameel 3 1 (Department
e-issn: 78-1684, p-issn: 30-334X PP 54-6 Pressure Distribution Around Net Clad Scaffolds Using Computation Fluid Dynamics Techniques Hassan Irtaza 1, R.G. Beale, M.H.R. Godley, A. Jameel 3 1 (Department
Numerical Investigation of Swirl's Effects in the Outer Annulus of a Reverse-flow Gas Turbine Combustor
 Numerical Investigation of Swirl's Effects in the Outer Annulus of a Reverse-flow Gas Turbine Combustor Mostafa Ghanei Tayeblou and Kavous Ariafar Department of Civil Engineering Islamic Azad University,
Numerical Investigation of Swirl's Effects in the Outer Annulus of a Reverse-flow Gas Turbine Combustor Mostafa Ghanei Tayeblou and Kavous Ariafar Department of Civil Engineering Islamic Azad University,
