QUESTION 2 What conclusion is most correct about the Experimental Design shown here with the response in the far right column?
|
|
|
- Oliver Ryan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 QUESTION 1 When a Belt Poka-Yoke's a defect out of the process entirely then she should track the activity with a robust SPC system on the characteristic of interest in the defect as an early warning system. QUESTION 2 What conclusion is most correct about the Experimental Design shown here with the response in the far right column? A. No factor has enough statistical confidence greater than 95% to have an impact on the response rate B. Constant, Adv and Bev are the only factors statistically affecting the response rate with 95% confidence or more C. If the Adv is increased from the low level to the high level, the response rate increases D. The response level is statistically concluded to only need the Adv and Bev factors set at the low level to get the largest response rate E. This design does not have enough experimental runs to conclude anything as evidenced by the lack of P- values in the MINITABTM output QUESTION 3 Which statement(s) are correct about the Factorial Plot shown here? (Note: There are 3 correct answers). A. When the cutting speed increased from low to high level, the tool age increases B. The coefficient of the metal hardness is positively related to the output of tool age C. The coded coefficient is lower for cutting speed than the cutting angle related to the output of tool age D. These plots prove a statistically significance factor with 95% confidence E. These plots are an example of interaction plots
2 QUESTION 4 Which statement(s) are correct about the Pareto Chart shown here for the DOE analysis? (Note: There are 2 correct answers). A. It is unknown from this graph how many factors were in the Experimental Design B. The factors to keep in the mathematical model are E, D, DE, BD and B with an alpha risk equal to 2.06 C. The effects to keep in the mathematical model are E, D, DE, BD and B with an alpha risk equal to 0.05 D. The factors to keep in the mathematical model with a 5% alpha risk are BE, AB, A and AD QUESTION 5 If in an experiment all possible variable pairs sum to zero the design is Orthogonal. QUESTION 6 The method of Steepest Ascent guides you toward a target inside the original inference space. QUESTION 7 Kaizens or Kaikakus and Six Sigma projects are intended to create incremental process improvements versus breakthrough, significant improvements.
3 QUESTION 8 SPC Charts are used extensively in different business and decision-making environments. In this example a vendor is being selected based on speed of delivery. Which of the conclusions would help you pick a vendor for your needs regarding lead-time of delivery from your vendors? (Note: There are 4 correct answers). A. Vendor A with a much shorter lead time in delivery B. Vendor B as it has a better consistency (lower variance) on lead time C. Vendor B as Vendor A shows a situation out of control as shown in red D. Vendor B as the Control Limits are much narrower than Vendor A E. Vendor B with higher lead time, but a process with much narrower Control Limits QUESTION 9 Fractional Factorial Designs are used to analyze factors to model the output as a function of inputs if Hypothesis Testing in the Analyze Phase was inadequate to sufficiently narrow the factors that significantly impact the output(s).
4 QUESTION 10 A Factorial Experiment based on a Level 2 Design with 6 factors would require 16 runs to fully assess the interactions. QUESTION 11 Screening experiments are the proper choice when a Belt is faced with the situation of highly Fractional Factorial Designs. QUESTION 12 Which statement(s) are correct about the DOE Factorial plot output here? (Note: There are 3 correct answers). A. Two factors were operated at 3 levels each B. The highest tool age was achieved with metal hardness at high level while keeping the cutting speed at the low level C. The design indicated above is a 32 factorial design D. The cutting speed and cutting angle are at the low level for the least tool age achieved E. All factors had 2 levels in the experiment QUESTION 13 Which statement(s) are incorrect for the Regression Analysis shown here? (Note: There are 2 correct answers). A. The air-fuel ratio explains most of the TurbineOutput variation B. The Regression explains over 98% of the process variation C. This Multiple Linear Regression has three statistically significant independent variables D. If the air-fuel ratio increases by 1, the TurbineOutput more than triples E. The SteamExitTemp explains the most variation of the TurbineOutput
5 QUESTION 14 Which statement(s) are most correct for the Regression Analysis shown here? A. The Regression explains 50.8% of the process variation B. The air-fuel ratio explains most of the TurbineOutput variation C. This Simple Linear Regression explains 98+% of the process variation D. This Multiple Linear Regression has four statistically significant independent variables QUESTION 15 A valid mathematical Regression represents all of the characteristics shown except. A. The residuals when plotted follow a Normal Distribution B. The sum of the residuals is zero C. All of the standardized residuals will be within ±3 Standard Deviations D. Most standardized residuals are within ±2 Standard Deviations
6 QUESTION 16 Which statement is NOT correct about the Fitted Line Plot shown here? A. The independent variable is the reactant B. If the reactant was 6 units, with 95 % confidence we would expect a minimum yield of 100 units C. With at least 95% confidence, we can expect less than 10 units of Yield when the reactant is at a value of 1 D. A reactant value between 2 and 4 units yields around 20 to 40 E. When the reactant increases, the expected yield would increase
7 QUESTION 17 Which statement(s) are correct about the Regression shown here? (Note: There are 2 correct answers). A. The dependent variable is the outside temperature B. The relationship between outside temperature and number of customers per hour is a Linear Regression C. The dashed lines indicate with 95% confidence where all of the process data should fall between D. The dashed lines indicate with 95% confidence the estimate for the Quadratic Regression Line E. The predicted number of customers per hour is close to 5 if the outside temperature is 10 deg C QUESTION 18 A Belt working in a supply chain environment has to make a decision to change suppliers of critical raw materials for a new product upgrade. The purchasing manager is depending on the Belt's effort requiring that the average cost of an internal critical raw material component be less than or equal to $4,200 in order to stay within budget. Using a sample of 35 first article components, a Mean of the new product upgrade price of $4,060, and a Standard Deviation of $98 was estimated. The Alternative Hypothesis in the above example is? A. The Standard Deviation is equal to $300. B. The Mean is less than $4,320. C. The Mean is equal to $4,060. D. The Mean is less than $4,200. E. The Mean is greater than $ 4,200. QUESTION 19 An ANOVA used across many dependent variables could increase the Beta risk. QUESTION 20 A Non-parametric Test should be used if just one distribution is not Normal out of the two or more gathered.
8 QUESTION 21 Contingency Tables are used to test for association, or dependency, between two or more classifications. QUESTION 22 For the data shown here which statement(s) are true? (Note: There are 2 correct answers). A. With 95% confidence, we cannot conclude if the samples are from three Normal Distributions. B. With greater than 95% confidence, we conclude the samples are from Non-normal Distributions. C. If we wanted to compare the Central Tendencies of these three samples we would use the one way ANOVA test. D. If we wanted to compare the Central Tendencies of these three samples we could use Mood's Median test. QUESTION 23 For the data set shown here which of these statements is/are true? A. Hypothesis Testing of Means or Medians cannot be done since there are an unequal number of observations for the 3 samples B. A Paired T-test would be applicable for comparing Grade B and Grade A since they follow each other in the data set C. Grade A has the lowest sample Mean of the 3 samples D. Grade A has a higher sample Mean than Grade B
9 QUESTION 24 Review the analysis shown here. Which statements are true about the process? (Note: There are 3 correct answers). A. The initial focus for this project would be to determine why the thicknesses are so frequently too low. B. The majority of the process is closer to the lower specification limit. C. This process is described with the Weibull Distribution. D. The process has more problems with Variation than Centering. E. The process follows a non-normal distribution with the given data. QUESTION 25
10 A Lean Six Sigma project is attempting to reduce inventory days. The Process Capability will be monitored as part of the Control Phase to track the sustainability of the improvement. Which distribution type is best used for performing the Capability Analysis? A. Weibull Distribution B. Normal Distribution C. Exponential Distribution D. Logistic Distribution E. Gaussian Distribution QUESTION 26 What conclusion is most correct about the Experimental Design shown here with the response in the far right column?
11 A. No factor has enough statistical confidence greater than 95% to have an impact on the response rate B. Constant, Adv and Bev are the only factors statistically affecting the response rate with 95% confidence or more C. If the Adv is increased from the low level to the high level, the response rate increases D. The response level is statistically concluded to only need the Adv and Bev factors set at the low level to get the largest response rate E. This design does not have enough experimental runs to conclude anything as evidenced by the lack of P- values in the MINITABTM output QUESTION 27 When conducting a Hypothesis Test using Continuous Data the proper sample size is influenced by the extent to which we need to assess a Difference to be detected and the inherent variation in the process. QUESTION 28 Statistical Difference is the magnitude of difference or change required to distinguish between a true difference, brought about by change or improvement, and one that could have occurred by chance. QUESTION 29 When the Inputs, X's, for your process are Normally Distributed about the Mean, the Outputs, Y's, will always be Normally Distributed. QUESTION 30 For a Normal Distribution as samples size increases the Range in Mean and Standard Deviation decrease relative to the Mean and Standard Deviation of the population. QUESTION 31 A statistical test or Hypothesis Test is performed to reject or fail to reject a stated hypothesis and it converts the Practical Problem into a Statistical Problem.
12 QUESTION 32 If an experiment has 5 factors and no replicates for a 2-level Experimental Design with 16 experimental runs which statement(s) are correct? (Note: There are 3 correct answers). A. The Main Effects for the 5 factors are not aliased or confounded but the 2-way interactions are confounded with the 3-way interactions B. The Main Effects are confounded with only 4-way interactions C. The Experimental Design is half-fractional D. The experiment has 8 experimental runs with the first factor at the high level E. The experiment has only 4 experimental runs with the 5th factor at the high level QUESTION 33 Which statement(s) are correct about the Pareto Chart shown here for the DOE analysis? (Note: There are 2 correct answers). A. It is unknown from this graph how many factors were in the Experimental Design B. The factors to keep in the mathematical model are E, D, DE, BD and B with an alpha risk equal to 2.06 C. The effects to keep in the mathematical model are E, D, DE, BD and B with an alpha risk equal to 0.05 D. The factors to keep in the mathematical model with a 5% alpha risk are BE, AB, A and AD
13 QUESTION 34 Accuracy can be assessed in several ways and a fairly accurate means of measurement is visual comparison. QUESTION 35 Appropriate measures means that measurements are. A. Representative B. Sufficient C. Contextual D. Relevant E. All of these answers are correct QUESTION 36 An operator checks that all boxes being packed contain enough products to fill the box. However, each box getting filled has a different number of products in it. This is a Reproducibility problem, not a Repeatability problem. QUESTION 37 For Attribute Data, Process Capability is defined as the average proportion of nonconforming products. QUESTION 38 Which statements are correct about the advanced Capability Analysis shown here?
14 (Note: There are 3 correct answers). A. This is a Poisson Capability Analysis. B. The average DPU with 95% confidence is between and C. The DPU does not seem to vary depending on sample size. D. The process shows only one instance of being out of control statistically so we have confidence in the estimated DPU of this process. E. The maximum DPU in one observation was nearly QUESTION 39 If in an experiment all possible variable pairs sum to zero the design is Orthogonal. QUESTION 40 The method of Steepest Ascent guides you toward a target inside the original inference space. QUESTION 41 Kaizens or Kaikakus and Six Sigma projects are intended to create breakthrough, significant process improvement versus minor, incremental improvements. QUESTION 42 SPC Charts are used extensively in different business and decision-making environments. In this example a vendor is being selected based on speed of delivery. Which of the conclusions would help you pick a vendor for your needs regarding lead-time of delivery from your vendors? (Note: There are 4 correct answers).
15 A. Vendor A with a much shorter lead time in delivery B. Vendor B as it has a better consistency (lower variance) on lead time C. Vendor B since Vendor A shows a situation out of control as shown in red D. Vendor B since the Control Limits are much narrower than Vendor A E. Vendor B has higher lead time, but a process with much narrower Control Limits QUESTION 43 If you can Poka-Yoke a defect out of the process entirely then you do not need use SPC on the characteristic of interest in the defect. QUESTION 44 When variation is removed from the output of a process then the process customer can have more confidence in the experience that results from the process. QUESTION 45 Which of these are examples of business metrics or Key Performance Indicators commonly referred to as KPI's? A. Cycle Time B. Defects C. No. of Units Reworked D. Labor Hours E. All of these answers are correct QUESTION 46 The Japanese born function of a Kanban event utilizes a specific, step-by-step approach meant to bring about major changes to a process. QUESTION 47 Two of the key deliverables for the Measure Phase are a robust description of the process and its flow and an assessment of the Management System. QUESTION 48 Which of the items listed do not define what an X-Y Diagram is? A. Created for every project B. Based on team's collective opinions C. Updated whenever a parameter is changed D. Used to show each step in a process E. A living document throughout project lifecycle
16 QUESTION 49 The two types of data that are to be used in Statistical Analysis are Attribute and Variance. QUESTION 50 Of the various types of data shown which is NOT representative of Variable Data. A. Child's height is 4 foot 3 inches B. Three employees wore hard hats C. Car burned 2.7 gallons of gasoline D. Train was going 140 kilometers per hour QUESTION 51 A fundamental rule is that both Standard Deviation and Variance can be added. QUESTION 52 Which statement(s) are correct about the Factorial Plot shown here? (Note: There are 3 correct answers). A. When the cutting speed increased from low to high level, the tool age increases B. The coefficient of the metal hardness is positively related to the output of tool age C. The coded coefficient is lower for cutting speed than the cutting angle related to the output of tool age D. These plots prove a statistically significance factor with 95% confidence E. These plots are an example of interaction plots
17 QUESTION 53 Which statement(s) are incorrect for the Regression Analysis shown here? (Note: There are 2 correct answers). A. The air-fuel ratio explains most of the TurbineOutput variation B. The Regression explains over 98% of the process variation C. This Multiple Linear Regression has three statistically significant independent variables D. If the air-fuel ratio increases by 1, the TurbineOutput more than triples E. The SteamExitTemp explains the most variation of the TurbineOutput QUESTION 54 Fractional Factorial Designs are used to analyze factors to model the output as a function of inputs if Hypothesis Testing in the Analyze Phase was inadequate to sufficiently narrow the factors that significantly impact the output(s). QUESTION 55 A Factorial Experiment based on a Level 2 Design with 4 factors would require 16 runs to fully assess the interactions. QUESTION 56 Screening experiments are the proper choice when a Belt is faced with the situation of highly Fractional Factorial Designs.
18 QUESTION 57 Which statement(s) are correct about the DOE Factorial plot output here? (Note: There are 3 correct answers). A. Two factors were operated at 3 levels each B. The highest tool age was achieved with metal hardness at high level while keeping the cutting speed at the low level C. The design indicated above is a 32 factorial design D. The cutting speed and cutting angle are at the low level for the least tool age achieved E. All factors had 2 levels in the experiment QUESTION 58 Which statement is most correct for the Regression Analysis shown here?
19 A. The Regression explains 50.8% of the process variation B. The air-fuel ratio explains most of the TurbineOutput variation C. This Simple Linear Regression explains 98+% of the process variation D. This Multiple Linear Regression has four statistically significant independent variables QUESTION 59 For the data set shown here which of these statements is/are true? A. Hypothesis Testing of Means or Medians cannot be done since there are an unequal number of observations for the 3 samples B. A Paired T-test would be applicable for comparing Grade B and Grade A since they follow each other in the data set C. Grade A has the lowest sample Mean of the 3 samples D. Grade A has a higher sample Mean than Grade B QUESTION 60 Choose those characteristics of a Simple Linear Regression (SLR) Analysis that are applicable. (Note: There are 3 correct answers). A. The Correlation Coefficient is always greater than the Regression Coefficient in a SLR B. General Regression Analysis deals only with Continuous Data C. Non-linear Regressions can explain curvature when with more statistical confidence than Linear Regressions D. SLR can help quantify the significance of variation in X that influences the variation in Y via a mathematical equation E. A Correlation does not explain causation but a Regression Analysis with a statistically valid mathematical equation does explain causation QUESTION 61 A valid Multiple Linear Regression (MLR) is characterized by all of these except? A. It is an assumption that the X's (inputs) are not correlated to each other B. The X's (inputs) are assumed to be independent of each other C. The Residuals from MLR analysis have to be Normally Distributed D. MLR is conducted based on a deliberate form of experimentation E. It is not possible to evaluate interactions in a MLR analysis
20 QUESTION 62 Which statement is NOT correct about the Fitted Line Plot shown here? A. The independent variable is the reactant B. If the reactant was 10 units, with 95% confidence we would expect a minimum yield of 148 units C. With at least 95% confidence, we can expect less than 10 units of Yield when the reactant is at a value of 1 D. A reactant value between 6 and 8 units yields around 40 to 60 E. When the reactant increases, the expected yield would increase QUESTION 63 Contingency Tables are used to test for association, or dependency, between two or more classifications. QUESTION 64 A valid mathematical Regression represents all of the characteristics shown except. A. All of the standardized residuals will be within ±3 Standard Deviations B. The sum of the residuals is zero C. The residuals when plotted follow a Normal Distribution D. Most standardized residuals are within ±2 Standard Deviations E. The Residual is equal to the difference between the observed and predicted values
21 QUESTION 65 Which statement(s) are correct about the Regression shown here? (Note: There are 2 correct answers). A. The dependent variable is the outside temperature B. The relationship between outside temperature and number of customers per hour is a Linear Regression C. The dashed lines indicate with 95% confidence where all of the process data should fall between D. The dashed lines indicate with 95% confidence the estimate for the Quadratic Regression Line E. The predicted number of customers per hour is close to 5 if the outside temperature is 10 deg C QUESTION 66 Review the analysis shown here. Which statements are true about the process? (Note: There are 3 correct answers).
22 A. The initial focus for this project would be to determine why the thicknesses are so frequently too low B. The majority of the process is closer to the lower specification limit C. This process is described with the Weibull Distribution D. The process has more problems with Variation than Centering E. The process follows a non-normal distribution with the given data QUESTION 67 A Lean Six Sigma project is attempting to reduce inventory days. The Process Capability will be monitored as part of the Control Phase to track the sustainability of the improvement. Which distribution type is best used for performing the Capability Analysis? A. Weibull Distribution B. Normal Distribution C. Exponential Distribution D. Logistic Distribution E. Gaussian Distribution
23 QUESTION 68 Which of these might contribute to similar distributions having Unequal Variance? A. Extreme tails B. Outliers C. Multiple Modes D. All of the above QUESTION 69 A Belt working in a supply chain environment has to make a decision to change suppliers of critical raw materials for a new product upgrade. The purchasing manager is depending on the Belt's effort requiring that the average cost of an internal critical raw material component be less than or equal to $4,200 in order to stay within budget. Using a sample of 35 first article components, a Mean of the new product upgrade price of $4,060, and a Standard Deviation of $98 was estimated. The Alternative Hypothesis in the above example is? A. The Standard Deviation is equal to $300 B. The Mean is less than $4,320 C. The Mean is equal to $4,060 D. The Mean is less than $4,200 E. The Mean is greater than $ 4,200 QUESTION 70 An ANOVA used across many dependent variables could increase the Beta risk. QUESTION 71 A Non-parametric Test should be used if just one distribution is not Normal out of the two or more gathered. QUESTION 72 Assessing process proportion as opposed to evaluating a process with respect to a set target can be done using one or more of these. (Note: There are 2 correct answers). A. Process proportion equals some desired value B. Process proportion equals some value range C. Target is current D. When we deal with Attribute type data E. Proportion of the tail is equal
24 QUESTION 73 For the data shown here which statement(s) are true? (Note: There are 2 correct answers). A. With 95% confidence, we cannot conclude if the samples are from three Normal Distributions B. With greater than 95% confidence, we conclude the samples are from Non-normal Distributions C. If we wanted to compare the Central Tendencies of these three samples we would use the one way ANOVA test D. If we wanted to compare the Central Tendencies of these three samples we could use Mood's Median test E. If we wanted to compare the Central Tendencies of all three samples we could use the Mann- Whitney test QUESTION 74 When conducting a Hypothesis Test using Continuous Data the proper sample size is influenced only by the extent to which we need to assess a Difference to be detected but not the inherent variation in the process. QUESTION 75 Statistical Difference is the magnitude of difference or change required to distinguish between a true difference, brought about by change or improvement, and one that could have occurred by chance. QUESTION 76 When the Inputs, X's, for your process are Normally Distributed about the Mean, the Outputs, Y's, will be Normally Distributed. QUESTION 77 For a Normal Distribution as samples size increases the Range in Mean and Standard Deviation decrease relative to the Mean and Standard Deviation of the population. QUESTION 78 A statistical test or Hypothesis Test is performed to reject or fail to reject a stated hypothesis and it converts the Practical Problem into a Statistical Problem.
25 QUESTION 79 The class score distribution of schools in a metropolitan area is shown here along with an analysis output. Comment on the statistical significance between the Means of the two distributions. Select the most appropriate statement. A. The two class Means are statistically different from each other B. The two class Means statistically not different from each other C. Inadequate information on class Means to make any statistical conclusions D. A visual comparison shows that class Means are not statistically different QUESTION 80 Accuracy can be assessed in several ways and a fairly accurate means of measurement is visual comparison.
26 QUESTION 81 An operator checks that all boxes being packed contain enough products to fill the box. However, each box getting filled has a different number of products in it. This is a Reproducibility problem, not a Repeatability problem. QUESTION 82 Which item(s) listed would impact the Process Capability for a process with a continuous output? (Note: There are 4 correct answers). A. Shape of process data distribution (e.g. Normal Distribution) B. Process Technology C. Process Standard Deviation D. Presence of Special Causes or solely Common Causes E. Seasonal variation in process QUESTION 83 For Attribute Data, Process Capability is defined as the average proportion of nonconforming products. QUESTION 84 Which statements are correct about the advanced Capability Analysis shown here? (Note: There are 3 correct answers). A. This is a Poisson Capability Analysis B. The average DPU with 95% confidence is between and C. The DPU does not seem to vary depending on sample size
27 D. The process shows only one instance of being out of control statistically so we have confidence in the estimated DPU of this process E. The maximum DPU in one observation was nearly QUESTION 85 When variation is removed from the output of a process then the process customer can have more confidence in the experience that results from the process. QUESTION 86 The Japanese born function of a Kaizen event utilizes a specific, step-by-step approach meant to bring about major changes to a process. QUESTION 87 Two of the key deliverables for the Measure Phase are a robust description of the process and its flow and an assessment of the Measurement System. QUESTION 88 One of the primary deliverables from performing a SIPOC is to begin to understand which outputs have the greatest affect on the customer most valued inputs. QUESTION 89 From this list select the items that define what an X-Y Diagram is. (Note: There are 4 correct answers). A. Created for every project B. Based on team's collective opinions C. Updated whenever a parameter is changed D. Used to show each step in a process E. A living document throughout project lifecycle QUESTION 90 The two types of data that can be used in Statistical Analysis are Attribute and Variable.
28 QUESTION 91 Which of these is not a primary cause for Non-normal Data? A. Skewness B. Mixed Distributions C. Kurtosis D. Formulosis E. Granularity QUESTION 92 The Mann-Whitney test is a powerful test and is unique to situations from which of the choices listed? (Note: There are 2 correct answers). A. Testing the identity of two populations B. Focuses on equality of the Median of the two populations C. Less powerful than the traditional "t-test" D. More widely applicable than the traditional "t-test" QUESTION 93 Special Cause Variation falls into which two categories? (Note: There are 2 correct answers). A. Natural B. Short term C. Assignable D. Pattern QUESTION 94 The English words used for the 5S's are Sorting, Straightening,, and Sustaining. (Note: There are 2 correct answers). A. Shaping B. Shining C. Standardizing D. Signing QUESTION 95 For a batch manufacturing process, while assessing short term process variation, which variation category(ies) should one need to focus on? (Note: There are 2 correct answers). A. Variation within consecutive pieces B. Variation among consecutive batches C. Variation among groups of pieces D. Variation among the completed product
29 QUESTION 96 The English words used for the 5S's are,, Shining, Standardizing and Sustaining. (Note: There are 2 correct answers). A. Shaping B. Sorting C. Shifting D. Straightening QUESTION 97 There are 14 different defects that can occur on a completed time card. The payroll department collects 328 cards and finds a total of 87 defects. DPMO =: A B. 87 (328 14) C D ,000,000 E F. 87 1,000,000 (14 328) QUESTION 98 A management team lists nine goals across the top of a rectangle and 15 activity initiatives along the left hand side of the rectangle. If one of the activities strongly supports one of the goals a circle is placed in the box where that activity's row intersects the goal's column. If the activity's support is very strong a "bulls eye" is placed in the box and if the support is weak a triangle is used. This best describes which problem solving tool? A. Affinity diagram B. Inter-relationship digraph C. Tree diagram D. Process decision program chart E. Matrix diagram
30 F. Prioritization matrix G. Activity network diagram QUESTION 99 The management team in the above problem assigns each goal a numerical value designating its importance. The "bulls eyes," circles and triangles are replaced by the values 3, 2 and 1 respectively. Entries are made in each box by multiplying the 3, 2 or 1 by the goal value. The importance of each activity is calculated by adding the entries in its row. A. Affinity diagram B. Inter-relationship digraph C. Tree diagram D. Process decision program chart E. Matrix diagram F. Prioritization matrix QUESTION 100. This table displays the inventory of fasteners in a storage cabinet. An item is selected at random from the fastener cabinet. Find the approximate probability it is a bolt.
31 A. 160 B..160 C..09 D..30 E. none of the above
Six Sigma Black Belt Study Guides
 Six Sigma Black Belt Study Guides 1 www.pmtutor.org Powered by POeT Solvers Limited. Overview of Six Sigma DMAIC Define Define the project targets and customer (internal and external) deliverables. Measure
Six Sigma Black Belt Study Guides 1 www.pmtutor.org Powered by POeT Solvers Limited. Overview of Six Sigma DMAIC Define Define the project targets and customer (internal and external) deliverables. Measure
Using Excel s Analysis ToolPak Add-In
 Using Excel s Analysis ToolPak Add-In Bijay Lal Pradhan, PhD Introduction I have a strong opinions that we can perform different quantitative analysis, including statistical analysis, in Excel. It is powerful,
Using Excel s Analysis ToolPak Add-In Bijay Lal Pradhan, PhD Introduction I have a strong opinions that we can perform different quantitative analysis, including statistical analysis, in Excel. It is powerful,
Quality Management (PQM01) Chapter 04 - Quality Control
 Quality Management (PQM01) Chapter 04 - Quality Control Slide 1 Slide 2 Involves monitoring specific project results to determine if they comply with relevant quality standards, and identifying ways to
Quality Management (PQM01) Chapter 04 - Quality Control Slide 1 Slide 2 Involves monitoring specific project results to determine if they comply with relevant quality standards, and identifying ways to
CREDIT RISK MODELLING Using SAS
 Basic Modelling Concepts Advance Credit Risk Model Development Scorecard Model Development Credit Risk Regulatory Guidelines 70 HOURS Practical Learning Live Online Classroom Weekends DexLab Certified
Basic Modelling Concepts Advance Credit Risk Model Development Scorecard Model Development Credit Risk Regulatory Guidelines 70 HOURS Practical Learning Live Online Classroom Weekends DexLab Certified
Online Student Guide Types of Control Charts
 Online Student Guide Types of Control Charts OpusWorks 2016, All Rights Reserved 1 Table of Contents LEARNING OBJECTIVES... 4 INTRODUCTION... 4 DETECTION VS. PREVENTION... 5 CONTROL CHART UTILIZATION...
Online Student Guide Types of Control Charts OpusWorks 2016, All Rights Reserved 1 Table of Contents LEARNING OBJECTIVES... 4 INTRODUCTION... 4 DETECTION VS. PREVENTION... 5 CONTROL CHART UTILIZATION...
Six Sigma Dictionary
 Six Sigma Dictionary # 4M / 5M / 6M Framework for root cause brainstorming. Categorizes root causes by: Man, Methods, Machines, Material, (5M) Mother Nature and (6M) Measurement System Impact 8D Process
Six Sigma Dictionary # 4M / 5M / 6M Framework for root cause brainstorming. Categorizes root causes by: Man, Methods, Machines, Material, (5M) Mother Nature and (6M) Measurement System Impact 8D Process
Chapter 5 Introduction to Statistical Quality Control, 7th Edition by Douglas C. Montgomery. Copyright (c) 2012 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 1 Learning Objectives 2 Basic SPC Tools 3 5.2 Chance and Assignable Causes of Variation A process is operating with only chance causes of variation present is said to be in statistical control. A process
1 Learning Objectives 2 Basic SPC Tools 3 5.2 Chance and Assignable Causes of Variation A process is operating with only chance causes of variation present is said to be in statistical control. A process
Overview of Statistics used in QbD Throughout the Product Lifecycle
 Overview of Statistics used in QbD Throughout the Product Lifecycle August 2014 The Windshire Group, LLC Comprehensive CMC Consulting Presentation format and purpose Method name What it is used for and/or
Overview of Statistics used in QbD Throughout the Product Lifecycle August 2014 The Windshire Group, LLC Comprehensive CMC Consulting Presentation format and purpose Method name What it is used for and/or
LEAN SIX SIGMA BLACK BELT CHEAT SHEET
 GreyCampus LEAN SIX SIGMA BLACK BELT CHEAT SHEET 2 Includes formulas: what they are, when to use them, references CONTENTS ANOVA DOE (DESIGN OF EXPERIMENTS) One Factor At a Time (OFAT) Comparison Randomization
GreyCampus LEAN SIX SIGMA BLACK BELT CHEAT SHEET 2 Includes formulas: what they are, when to use them, references CONTENTS ANOVA DOE (DESIGN OF EXPERIMENTS) One Factor At a Time (OFAT) Comparison Randomization
August 24, Jean-Philippe Mathevet IAQG Performance Stream Leader SAFRAN Paris, France. Re: 2014 Supplier Performance Data Summary
 Page 1 of 27 August 24, 2105 Jean-Philippe Mathevet IAQG Performance Stream Leader SAFRAN Paris, France Re: 2014 Supplier Performance Data Summary Dear Jean-Philippe: The following report is a summary
Page 1 of 27 August 24, 2105 Jean-Philippe Mathevet IAQG Performance Stream Leader SAFRAN Paris, France Re: 2014 Supplier Performance Data Summary Dear Jean-Philippe: The following report is a summary
AcaStat How To Guide. AcaStat. Software. Copyright 2016, AcaStat Software. All rights Reserved.
 AcaStat How To Guide AcaStat Software Copyright 2016, AcaStat Software. All rights Reserved. http://www.acastat.com Table of Contents Frequencies... 3 List Variables... 4 Descriptives... 5 Explore Means...
AcaStat How To Guide AcaStat Software Copyright 2016, AcaStat Software. All rights Reserved. http://www.acastat.com Table of Contents Frequencies... 3 List Variables... 4 Descriptives... 5 Explore Means...
BODY OF KNOWLEDGE CERTIFIED QUALITY TECHNICIAN
 BODY OF KNOWLEDGE CERTIFIED QUALITY TECHNICIAN The topics in this Body of Knowledge include additional detail in the form of subtext explanations and the cognitive level at which the questions will be
BODY OF KNOWLEDGE CERTIFIED QUALITY TECHNICIAN The topics in this Body of Knowledge include additional detail in the form of subtext explanations and the cognitive level at which the questions will be
Business Intelligence, 4e (Sharda/Delen/Turban) Chapter 2 Descriptive Analytics I: Nature of Data, Statistical Modeling, and Visualization
 Business Intelligence, 4e (Sharda/Delen/Turban) Chapter 2 Descriptive Analytics I: Nature of Data, Statistical Modeling, and Visualization 1) One of SiriusXM's challenges was tracking potential customers
Business Intelligence, 4e (Sharda/Delen/Turban) Chapter 2 Descriptive Analytics I: Nature of Data, Statistical Modeling, and Visualization 1) One of SiriusXM's challenges was tracking potential customers
Continuous Improvement Toolkit. Risk Analysis. Continuous Improvement Toolkit.
 Continuous Improvement Toolkit Risk Analysis The Continuous Improvement Map Managing Risk FMEA Understanding Performance Check Sheets Data Collection PDPC RAID Log* Risk Analysis* Fault Tree Analysis Traffic
Continuous Improvement Toolkit Risk Analysis The Continuous Improvement Map Managing Risk FMEA Understanding Performance Check Sheets Data Collection PDPC RAID Log* Risk Analysis* Fault Tree Analysis Traffic
Ch 26 Just-In-Time and Lean Production. What is Lean Production? Structure of Lean Production System. Activities in Manufacturing.
 Ch 26 Just-In-Time and Lean Production Sections: 1. Lean Production and Waste in Manufacturing 2. Just-in-time Production Systems 3. Autonomation 4. Worker Involvement What is Lean Production? Lean production
Ch 26 Just-In-Time and Lean Production Sections: 1. Lean Production and Waste in Manufacturing 2. Just-in-time Production Systems 3. Autonomation 4. Worker Involvement What is Lean Production? Lean production
Practical Applications of Statistical Methods Under 2011 FDA Process Validation Guidance
 Practical Applications of Statistical Methods Under 2011 FDA Process Validation Guidance Abe Germansderfer Associate Director, Quality Control Gilead Sciences 2011 Process Validation Guidance In January
Practical Applications of Statistical Methods Under 2011 FDA Process Validation Guidance Abe Germansderfer Associate Director, Quality Control Gilead Sciences 2011 Process Validation Guidance In January
SECTION 11 ACUTE TOXICITY DATA ANALYSIS
 SECTION 11 ACUTE TOXICITY DATA ANALYSIS 11.1 INTRODUCTION 11.1.1 The objective of acute toxicity tests with effluents and receiving waters is to identify discharges of toxic effluents in acutely toxic
SECTION 11 ACUTE TOXICITY DATA ANALYSIS 11.1 INTRODUCTION 11.1.1 The objective of acute toxicity tests with effluents and receiving waters is to identify discharges of toxic effluents in acutely toxic
Experimental Design Day 2
 Experimental Design Day 2 Experiment Graphics Exploratory Data Analysis Final analytic approach Experiments with a Single Factor Example: Determine the effects of temperature on process yields Case I:
Experimental Design Day 2 Experiment Graphics Exploratory Data Analysis Final analytic approach Experiments with a Single Factor Example: Determine the effects of temperature on process yields Case I:
1. What is a key difference between an Affinity Diagram and other tools?
 1) AFFINITY DIAGRAM 1. What is a key difference between an Affinity Diagram and other tools? Affinity Diagram builds the hierarchy 'bottom-up', starting from the basic elements and working up, as opposed
1) AFFINITY DIAGRAM 1. What is a key difference between an Affinity Diagram and other tools? Affinity Diagram builds the hierarchy 'bottom-up', starting from the basic elements and working up, as opposed
Quality Control Charts
 Quality Control Charts General Purpose In all production processes, we need to monitor the extent to which our products meet specifications. In the most general terms, there are two "enemies" of product
Quality Control Charts General Purpose In all production processes, we need to monitor the extent to which our products meet specifications. In the most general terms, there are two "enemies" of product
Attachment 1. Categorical Summary of BMP Performance Data for Solids (TSS, TDS, and Turbidity) Contained in the International Stormwater BMP Database
 Attachment 1 Categorical Summary of BMP Performance Data for Solids (TSS, TDS, and Turbidity) Contained in the International Stormwater BMP Database Prepared by Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. Wright Water
Attachment 1 Categorical Summary of BMP Performance Data for Solids (TSS, TDS, and Turbidity) Contained in the International Stormwater BMP Database Prepared by Geosyntec Consultants, Inc. Wright Water
It is not essential for students to conduct an investigation for every question they generate or generate questions based on prior investigations.
 Scientific Inquiry 5-1 The student will demonstrate an understanding of scientific inquiry, including the foundations of technological design and the processes, skills, and mathematical thinking necessary
Scientific Inquiry 5-1 The student will demonstrate an understanding of scientific inquiry, including the foundations of technological design and the processes, skills, and mathematical thinking necessary
THE LEAD PROFILE AND OTHER NON-PARAMETRIC TOOLS TO EVALUATE SURVEY SERIES AS LEADING INDICATORS
 THE LEAD PROFILE AND OTHER NON-PARAMETRIC TOOLS TO EVALUATE SURVEY SERIES AS LEADING INDICATORS Anirvan Banerji New York 24th CIRET Conference Wellington, New Zealand March 17-20, 1999 Geoffrey H. Moore,
THE LEAD PROFILE AND OTHER NON-PARAMETRIC TOOLS TO EVALUATE SURVEY SERIES AS LEADING INDICATORS Anirvan Banerji New York 24th CIRET Conference Wellington, New Zealand March 17-20, 1999 Geoffrey H. Moore,
Multiple Regression. Dr. Tom Pierce Department of Psychology Radford University
 Multiple Regression Dr. Tom Pierce Department of Psychology Radford University In the previous chapter we talked about regression as a technique for using a person s score on one variable to make a best
Multiple Regression Dr. Tom Pierce Department of Psychology Radford University In the previous chapter we talked about regression as a technique for using a person s score on one variable to make a best
Leading High Reliability Organizations in Healthcare. Richard Morrow, MBA, MBB Author/Founder RPM Exec (847)
 Leading High Reliability Organizations in Healthcare Richard Morrow, MBA, MBB Author/Founder RPM Exec (847) 989-3333 rpm@rpmexec.com www.rpmexec.com 1 Baseline Performance Healthcare Compared 2 Organizations
Leading High Reliability Organizations in Healthcare Richard Morrow, MBA, MBB Author/Founder RPM Exec (847) 989-3333 rpm@rpmexec.com www.rpmexec.com 1 Baseline Performance Healthcare Compared 2 Organizations
Engenharia e Tecnologia Espaciais ETE Engenharia e Gerenciamento de Sistemas Espaciais
 Engenharia e Tecnologia Espaciais ETE Engenharia e Gerenciamento de Sistemas Espaciais SITEMA DE GESTÃO DA QUALIDADE SEIS SIGMA 14.12.2009 SUMÁRIO Introdução ao Sistema de Gestão da Qualidade SEIS SIGMA
Engenharia e Tecnologia Espaciais ETE Engenharia e Gerenciamento de Sistemas Espaciais SITEMA DE GESTÃO DA QUALIDADE SEIS SIGMA 14.12.2009 SUMÁRIO Introdução ao Sistema de Gestão da Qualidade SEIS SIGMA
Continuous Improvement Toolkit. RACI Matrix
 Continuous Improvement Toolkit RACI Matrix R A C I The Continuous Improvement Map Managing Risk FMEA Understanding Performance** Check Sheets Data Collection PDPC RAID Log* Risk Analysis* Benchmarking***
Continuous Improvement Toolkit RACI Matrix R A C I The Continuous Improvement Map Managing Risk FMEA Understanding Performance** Check Sheets Data Collection PDPC RAID Log* Risk Analysis* Benchmarking***
Continuous Improvement Toolkit. Traffic Light Assessment. Continuous Improvement Toolkit.
 Continuous Improvement Toolkit Traffic Light Assessment The Continuous Improvement Map Managing Risk FMEA Understanding Performance Check Sheets Data Collection PDPC RAID Log* Risk Assessment* Fault Tree
Continuous Improvement Toolkit Traffic Light Assessment The Continuous Improvement Map Managing Risk FMEA Understanding Performance Check Sheets Data Collection PDPC RAID Log* Risk Assessment* Fault Tree
Continuous Improvement Toolkit. Pareto Analysis. Continuous Improvement Toolkit.
 Continuous Improvement Toolkit Pareto Analysis The Continuous Improvement Map Managing Risk FMEA Understanding Performance Check Sheets Data Collection PDPC RAID Log* Risk Assessment* Fault Tree Analysis
Continuous Improvement Toolkit Pareto Analysis The Continuous Improvement Map Managing Risk FMEA Understanding Performance Check Sheets Data Collection PDPC RAID Log* Risk Assessment* Fault Tree Analysis
Continuous Improvement Toolkit. Relationship Mapping. Continuous Improvement Toolkit.
 Continuous Improvement Toolkit Relationship Mapping The Continuous Improvement Map Managing Risk FMEA Understanding Performance Check Sheets Data Collection PDPC RAID Log* Risk Assessment* Fault Tree Analysis
Continuous Improvement Toolkit Relationship Mapping The Continuous Improvement Map Managing Risk FMEA Understanding Performance Check Sheets Data Collection PDPC RAID Log* Risk Assessment* Fault Tree Analysis
Wrapper Line Improvement
 February 21, 2014 Wrapper Line Improvement Six Sigma Project Final Tollgate Presentation Define Measure Analyze Improve Control Alah Raqab Varun Nandakumar Scott Shepfer Rohit Subramanian Project Charter
February 21, 2014 Wrapper Line Improvement Six Sigma Project Final Tollgate Presentation Define Measure Analyze Improve Control Alah Raqab Varun Nandakumar Scott Shepfer Rohit Subramanian Project Charter
Spreadsheets in Education (ejsie)
 Spreadsheets in Education (ejsie) Volume 2, Issue 2 2005 Article 5 Forecasting with Excel: Suggestions for Managers Scott Nadler John F. Kros East Carolina University, nadlers@mail.ecu.edu East Carolina
Spreadsheets in Education (ejsie) Volume 2, Issue 2 2005 Article 5 Forecasting with Excel: Suggestions for Managers Scott Nadler John F. Kros East Carolina University, nadlers@mail.ecu.edu East Carolina
FMEA Failure Mode Effects Analysis. ASQ/APICS Joint Meeting May 10, 2017
 FMEA Failure Mode Effects Analysis ASQ/APICS Joint Meeting May 10, 2017 FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis) Failure Mode and Effects Analysis Agenda What is it? Motivation FMEA Methods Examples What
FMEA Failure Mode Effects Analysis ASQ/APICS Joint Meeting May 10, 2017 FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis) Failure Mode and Effects Analysis Agenda What is it? Motivation FMEA Methods Examples What
CERTIFIED QUALITY IMPROVEMENT ASSOCIATE
 CQIA CERTIFIED QUALITY IMPROVEMENT ASSOCIATE Quality excellence to enhance your career and boost your organization s bottom line asq.org/cert Certification from ASQ is considered a mark of quality excellence
CQIA CERTIFIED QUALITY IMPROVEMENT ASSOCIATE Quality excellence to enhance your career and boost your organization s bottom line asq.org/cert Certification from ASQ is considered a mark of quality excellence
Instructor Info: Dave Tucker, LSSMBB ProModel Senior Consultant Office:
 Instructor Info: Dave Tucker, LSSMBB ProModel Senior Consultant Office: 321.567.5642 dtucker@promodel.com 1 Understand how simulation models can be utilized within the DMAIC approach Examine a completed
Instructor Info: Dave Tucker, LSSMBB ProModel Senior Consultant Office: 321.567.5642 dtucker@promodel.com 1 Understand how simulation models can be utilized within the DMAIC approach Examine a completed
Regression diagnostics
 Regression diagnostics Biometry 755 Spring 2009 Regression diagnostics p. 1/48 Introduction Every statistical method is developed based on assumptions. The validity of results derived from a given method
Regression diagnostics Biometry 755 Spring 2009 Regression diagnostics p. 1/48 Introduction Every statistical method is developed based on assumptions. The validity of results derived from a given method
Consumer Math Unit Lesson Title Lesson Objectives 1 Basic Math Review Identify the stated goals of the unit and course
 Consumer Math Unit Lesson Title Lesson Objectives 1 Basic Math Review Introduction Identify the stated goals of the unit and course Number skills Signed numbers and Measurement scales A consumer application
Consumer Math Unit Lesson Title Lesson Objectives 1 Basic Math Review Introduction Identify the stated goals of the unit and course Number skills Signed numbers and Measurement scales A consumer application
Continuous Improvement Toolkit. Value Analysis
 Continuous Improvement Toolkit Value Analysis VA NVA The Continuous Improvement Map Managing Risk FMEA Understanding Performance** Check Sheets Data Collection PDPC RAID Log* Risk Analysis* Benchmarking***
Continuous Improvement Toolkit Value Analysis VA NVA The Continuous Improvement Map Managing Risk FMEA Understanding Performance** Check Sheets Data Collection PDPC RAID Log* Risk Analysis* Benchmarking***
MULTIMEDIA COLLEGE JALAN GURNEY KIRI KUALA LUMPUR
 STUDENT IDENTIFICATION NO MULTIMEDIA COLLEGE JALAN GURNEY KIRI 54100 KUALA LUMPUR FIFTH SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION, 2014/2015 SESSION MGT2063 TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT DMGW-E-F-1/13, DMGQ-E-F-1/13, DMGA-E-F-1/13,
STUDENT IDENTIFICATION NO MULTIMEDIA COLLEGE JALAN GURNEY KIRI 54100 KUALA LUMPUR FIFTH SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION, 2014/2015 SESSION MGT2063 TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT DMGW-E-F-1/13, DMGQ-E-F-1/13, DMGA-E-F-1/13,
ANALYSING QUANTITATIVE DATA
 9 ANALYSING QUANTITATIVE DATA Although, of course, there are other software packages that can be used for quantitative data analysis, including Microsoft Excel, SPSS is perhaps the one most commonly subscribed
9 ANALYSING QUANTITATIVE DATA Although, of course, there are other software packages that can be used for quantitative data analysis, including Microsoft Excel, SPSS is perhaps the one most commonly subscribed
Continuous Improvement Toolkit
 Continuous Improvement Toolkit Process Redesign Managing Risk PDPC Pros and Cons Importance-Urgency Mapping RACI Matrix Stakeholders Analysis FMEA RAID Logs Break-even Analysis Cost -Benefit Analysis PEST
Continuous Improvement Toolkit Process Redesign Managing Risk PDPC Pros and Cons Importance-Urgency Mapping RACI Matrix Stakeholders Analysis FMEA RAID Logs Break-even Analysis Cost -Benefit Analysis PEST
The Dummy s Guide to Data Analysis Using SPSS
 The Dummy s Guide to Data Analysis Using SPSS Univariate Statistics Scripps College Amy Gamble April, 2001 Amy Gamble 4/30/01 All Rights Rerserved Table of Contents PAGE Creating a Data File...3 1. Creating
The Dummy s Guide to Data Analysis Using SPSS Univariate Statistics Scripps College Amy Gamble April, 2001 Amy Gamble 4/30/01 All Rights Rerserved Table of Contents PAGE Creating a Data File...3 1. Creating
Overview. Presenter: Bill Cheney. Audience: Clinical Laboratory Professionals. Field Guide To Statistics for Blood Bankers
 Field Guide To Statistics for Blood Bankers A Basic Lesson in Understanding Data and P.A.C.E. Program: 605-022-09 Presenter: Bill Cheney Audience: Clinical Laboratory Professionals Overview Statistics
Field Guide To Statistics for Blood Bankers A Basic Lesson in Understanding Data and P.A.C.E. Program: 605-022-09 Presenter: Bill Cheney Audience: Clinical Laboratory Professionals Overview Statistics
Glossary of Standardized Testing Terms https://www.ets.org/understanding_testing/glossary/
 Glossary of Standardized Testing Terms https://www.ets.org/understanding_testing/glossary/ a parameter In item response theory (IRT), the a parameter is a number that indicates the discrimination of a
Glossary of Standardized Testing Terms https://www.ets.org/understanding_testing/glossary/ a parameter In item response theory (IRT), the a parameter is a number that indicates the discrimination of a
Lean Gold Certification Blueprint
 The Lean Certification Blueprint provides additional useful information beyond the Body of Knowledge. The Body of Knowledge specifies the competencies, topics, and subtopics required by different types
The Lean Certification Blueprint provides additional useful information beyond the Body of Knowledge. The Body of Knowledge specifies the competencies, topics, and subtopics required by different types
TDWI strives to provide course books that are contentrich and that serve as useful reference documents after a class has ended.
 Previews of TDWI course books offer an opportunity to see the quality of our material and help you to select the courses that best fit your needs. The previews cannot be printed. TDWI strives to provide
Previews of TDWI course books offer an opportunity to see the quality of our material and help you to select the courses that best fit your needs. The previews cannot be printed. TDWI strives to provide
FOR 274 Forest Measurements and Inventory. Written Take Home Exam
 FOR 274 Forest Measurements and Inventory Written Take Home Exam Instructions: This exam is comprehensive of the material covered within the Forest Resources 274 class curriculum. The first question is
FOR 274 Forest Measurements and Inventory Written Take Home Exam Instructions: This exam is comprehensive of the material covered within the Forest Resources 274 class curriculum. The first question is
Continuous Improvement Toolkit
 Continuous Improvement Toolkit Lean Measures Managing Risk PDPC Pros and Cons Importance-Urgency Mapping RACI Matrix Stakeholders Analysis FMEA RAID Logs Break-even Analysis Cost -Benefit Analysis PEST
Continuous Improvement Toolkit Lean Measures Managing Risk PDPC Pros and Cons Importance-Urgency Mapping RACI Matrix Stakeholders Analysis FMEA RAID Logs Break-even Analysis Cost -Benefit Analysis PEST
CHAPTER 8 T Tests. A number of t tests are available, including: The One-Sample T Test The Paired-Samples Test The Independent-Samples T Test
 CHAPTER 8 T Tests A number of t tests are available, including: The One-Sample T Test The Paired-Samples Test The Independent-Samples T Test 8.1. One-Sample T Test The One-Sample T Test procedure: Tests
CHAPTER 8 T Tests A number of t tests are available, including: The One-Sample T Test The Paired-Samples Test The Independent-Samples T Test 8.1. One-Sample T Test The One-Sample T Test procedure: Tests
WAYNE STATE UNIVERSITY Department of Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering May, 2010
 WAYNE STATE UNIVERSITY Department of Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering May, 2010 PhD Preliminary Examination Candidate Name: 1- Sensitivity Analysis (20 points) Answer ALL Questions Question 1-20
WAYNE STATE UNIVERSITY Department of Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering May, 2010 PhD Preliminary Examination Candidate Name: 1- Sensitivity Analysis (20 points) Answer ALL Questions Question 1-20
Descriptive Statistics Tutorial
 Descriptive Statistics Tutorial Measures of central tendency Mean, Median, and Mode Statistics is an important aspect of most fields of science and toxicology is certainly no exception. The rationale behind
Descriptive Statistics Tutorial Measures of central tendency Mean, Median, and Mode Statistics is an important aspect of most fields of science and toxicology is certainly no exception. The rationale behind
INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING
 1 P a g e AND OPERATION RESEARCH 1 BREAK EVEN ANALYSIS Introduction 5 Costs involved in production 5 Assumptions 5 Break- Even Point 6 Plotting Break even chart 7 Margin of safety 9 Effect of parameters
1 P a g e AND OPERATION RESEARCH 1 BREAK EVEN ANALYSIS Introduction 5 Costs involved in production 5 Assumptions 5 Break- Even Point 6 Plotting Break even chart 7 Margin of safety 9 Effect of parameters
Business Intelligence and Process Modelling
 Business Intelligence and Process Modelling F.W. Takes Universiteit Leiden Lecture 3: Business Intelligence & Visual Analytics BIPM Lecture 3: Business Intelligence & Visual Analytics 1 / 72 Business Intelligence
Business Intelligence and Process Modelling F.W. Takes Universiteit Leiden Lecture 3: Business Intelligence & Visual Analytics BIPM Lecture 3: Business Intelligence & Visual Analytics 1 / 72 Business Intelligence
Continuous Improvement Toolkit. QFD (Quality Function Deployment) Continuous Improvement Toolkit.
 Continuous Improvement Toolkit QFD (Quality Function Deployment) The Continuous Improvement Map Managing Risk FMEA Understanding Performance Check Sheets Data Collection PDPC RAID Log* Risk Assessment*
Continuous Improvement Toolkit QFD (Quality Function Deployment) The Continuous Improvement Map Managing Risk FMEA Understanding Performance Check Sheets Data Collection PDPC RAID Log* Risk Assessment*
EFFECTIVENESS OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING WITH REFERENCE TO TPM
 EFFECTIVENESS OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING WITH REFERENCE TO TPM V.K.AJAY 1 1. Assistant Professor & Research Scholar (Anna University Chennai, Department of Management Science, S.A.Engineering College, Poonamallee
EFFECTIVENESS OF EDUCATION AND TRAINING WITH REFERENCE TO TPM V.K.AJAY 1 1. Assistant Professor & Research Scholar (Anna University Chennai, Department of Management Science, S.A.Engineering College, Poonamallee
Use repeated addition to multiply fractions by whole numbers. is shown. is an improper fraction.
 Student book pages 0 Multiplying a Whole Number by a Fraction You will need counters Use repeated addition to multiply fractions by whole numbers You can use grids and counters to model fractions What
Student book pages 0 Multiplying a Whole Number by a Fraction You will need counters Use repeated addition to multiply fractions by whole numbers You can use grids and counters to model fractions What
GSU College of Business MBA Core Course Learning Outcomes. Updated 9/24/2015
 GSU College of Business MBA Core Course Learning Outcomes Updated 9/24/2015 ACCT 6100 ACCT 7101 ECON 6100 ECON 7500 FIN 7101 MIS 7101 MGMT 6100 MGMT 6700 MGMT 7400 MGMT 7500 MGMT 7600 MGMT 8900 MKTG 7100
GSU College of Business MBA Core Course Learning Outcomes Updated 9/24/2015 ACCT 6100 ACCT 7101 ECON 6100 ECON 7500 FIN 7101 MIS 7101 MGMT 6100 MGMT 6700 MGMT 7400 MGMT 7500 MGMT 7600 MGMT 8900 MKTG 7100
JIT and Lean Operations. JIT/Lean Operations
 5/7/2011 16 JIT and Lean Operations By : Sa Ed M. Salhieh, Salhieh, Ph.D. 16-1 JIT/Lean Operations Good production systems require that managers address three issues that are pervasive and fundamental
5/7/2011 16 JIT and Lean Operations By : Sa Ed M. Salhieh, Salhieh, Ph.D. 16-1 JIT/Lean Operations Good production systems require that managers address three issues that are pervasive and fundamental
Outline. Push-Pull Systems Global Company Profile: Toyota Motor Corporation Just-in-Time, the Toyota Production System, and Lean Operations
 JIT and Lean Operations Outline Push-Pull Systems Global Company Profile: Toyota Motor Corporation Just-in-Time, the Toyota Production System, and Lean Operations Eliminate Waste Remove Variability Improve
JIT and Lean Operations Outline Push-Pull Systems Global Company Profile: Toyota Motor Corporation Just-in-Time, the Toyota Production System, and Lean Operations Eliminate Waste Remove Variability Improve
Make the Jump from Business User to Data Analyst in SAS Visual Analytics
 SESUG 2016 Paper 200-2016 Make the Jump from Business User to Data Analyst in SAS Visual Analytics Ryan Kumpfmilller, Zencos Consulting ABSTRACT SAS Visual Analytics is effective in empowering the business
SESUG 2016 Paper 200-2016 Make the Jump from Business User to Data Analyst in SAS Visual Analytics Ryan Kumpfmilller, Zencos Consulting ABSTRACT SAS Visual Analytics is effective in empowering the business
THE GUIDE TO SPSS. David Le
 THE GUIDE TO SPSS David Le June 2013 1 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 How to Use this Guide... 3 Frequency Reports... 4 Key Definitions... 4 Example 1: Frequency report using a categorical variable
THE GUIDE TO SPSS David Le June 2013 1 Table of Contents Introduction... 3 How to Use this Guide... 3 Frequency Reports... 4 Key Definitions... 4 Example 1: Frequency report using a categorical variable
91 محرم الصفحة. Industrial Engineering Standards. Professional Engineer Exam Ι
 Industrial Engineering Standards 1 الصفحة Introduction Engineering standards are the set of knowledge, abilities, and professional attributes necessary to practice the engineering profession [3-5]. Every
Industrial Engineering Standards 1 الصفحة Introduction Engineering standards are the set of knowledge, abilities, and professional attributes necessary to practice the engineering profession [3-5]. Every
Measurement Systems Analysis
 Measurement Systems Analysis Components and Acceptance Criteria Rev: 11/06/2012 Purpose To understand key concepts of measurement systems analysis To understand potential sources of measurement error and
Measurement Systems Analysis Components and Acceptance Criteria Rev: 11/06/2012 Purpose To understand key concepts of measurement systems analysis To understand potential sources of measurement error and
EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS ON FRICTION WELDING PROCESS FOR DISSIMILAR MATERIALS USING DESIGN OF EXPERIMENTS
 137 Chapter 6 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS ON FRICTION WELDING PROCESS FOR DISSIMILAR MATERIALS USING DESIGN OF EXPERIMENTS 6.1 INTRODUCTION In the present section of research, three important aspects are
137 Chapter 6 EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATIONS ON FRICTION WELDING PROCESS FOR DISSIMILAR MATERIALS USING DESIGN OF EXPERIMENTS 6.1 INTRODUCTION In the present section of research, three important aspects are
Overview Three-Sigma Quality
 Manufacturing Environment Reliability: The Other Dimension of Quality Today s manufacturers face: William Q. Meeker Iowa State University Fall Technical Conference Youden Memorial Address October 7, 00
Manufacturing Environment Reliability: The Other Dimension of Quality Today s manufacturers face: William Q. Meeker Iowa State University Fall Technical Conference Youden Memorial Address October 7, 00
Hierarchical Linear Modeling: A Primer 1 (Measures Within People) R. C. Gardner Department of Psychology
 Hierarchical Linear Modeling: A Primer 1 (Measures Within People) R. C. Gardner Department of Psychology As noted previously, Hierarchical Linear Modeling (HLM) can be considered a particular instance
Hierarchical Linear Modeling: A Primer 1 (Measures Within People) R. C. Gardner Department of Psychology As noted previously, Hierarchical Linear Modeling (HLM) can be considered a particular instance
Ch.3 Quality Issues.
 Module 2 : Supply Environment. Ch.3 Quality Issues. Edited by Dr. Seung Hyun Lee (Ph.D., CPM) IEMS Research Center, E-mail : lkangsan@iems.co.kr Resolving Quality Problems. Documentation of Corrective
Module 2 : Supply Environment. Ch.3 Quality Issues. Edited by Dr. Seung Hyun Lee (Ph.D., CPM) IEMS Research Center, E-mail : lkangsan@iems.co.kr Resolving Quality Problems. Documentation of Corrective
Notes for Production and Operations Management- I
 Notes for Production and Operations Management- I Factors affecting Process Design Decisions Nature of product/service demand Degree of vertical integration Production Flexibility Degree of automation
Notes for Production and Operations Management- I Factors affecting Process Design Decisions Nature of product/service demand Degree of vertical integration Production Flexibility Degree of automation
Identify sampling methods and recognize biased samples
 9-1 Samples and Surveys Identify sampling methods and recognize biased samples Vocabulary population (p. 462) sample (p. 462) biased sample (p. 463) random sample (p. 462) systematic sample (p. 462) stratified
9-1 Samples and Surveys Identify sampling methods and recognize biased samples Vocabulary population (p. 462) sample (p. 462) biased sample (p. 463) random sample (p. 462) systematic sample (p. 462) stratified
SEMBIT SQA Unit Code F9JY 04 Developing visual management systems
 Overview This unit covers the competences required for developing and applying the principles and processes of visual management. It involves identifying the appropriate parts of the process or work area
Overview This unit covers the competences required for developing and applying the principles and processes of visual management. It involves identifying the appropriate parts of the process or work area
EST Accuracy of FEL 2 Estimates in Process Plants
 EST.2215 Accuracy of FEL 2 Estimates in Process Plants Melissa C. Matthews Abstract Estimators use a variety of practices to determine the cost of capital projects at the end of the select stage when only
EST.2215 Accuracy of FEL 2 Estimates in Process Plants Melissa C. Matthews Abstract Estimators use a variety of practices to determine the cost of capital projects at the end of the select stage when only
The combination of factors and their levels describe the battlespace conditions.
 Design of Experiments (DOE) is an acronym and a test technique increasingly being used in the T&E community. This will present a conceptual overview of what DOE is, how it compares to other testing techniques,
Design of Experiments (DOE) is an acronym and a test technique increasingly being used in the T&E community. This will present a conceptual overview of what DOE is, how it compares to other testing techniques,
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS (KEY) UNIT- I
 SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS (KEY) UNIT- I 1. Define quality. Quality is the totality of characteristics of an entity that bear on its ability to satisfy stated and implied needs. 2. What do you mean by quality
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS (KEY) UNIT- I 1. Define quality. Quality is the totality of characteristics of an entity that bear on its ability to satisfy stated and implied needs. 2. What do you mean by quality
LEAN CERTIFICATION BODY OF KNOWLEDGE RUBRIC VERSION 3.0
 MODULE 1 LEAN CERTIFICATION BODY OF KNOWLEDGE RUBRIC VERSION 3.0 1. Cultural Enablers 15% 20% 25% 1.1. Principles of Cultural Enablers 3% 4% 5% 1.1.1. Respect for the individual 1.1.2. Humility 1.2. Processes
MODULE 1 LEAN CERTIFICATION BODY OF KNOWLEDGE RUBRIC VERSION 3.0 1. Cultural Enablers 15% 20% 25% 1.1. Principles of Cultural Enablers 3% 4% 5% 1.1.1. Respect for the individual 1.1.2. Humility 1.2. Processes
Continuous Improvement Toolkit. Flow Process Chart. Continuous Improvement Toolkit.
 Continuous Improvement Toolkit Flow Process Chart The Continuous Improvement Map Managing Risk FMEA Understanding Performance Check Sheets Data Collection PDPC RAID Log* Risk Assessment* Fault Tree Analysis
Continuous Improvement Toolkit Flow Process Chart The Continuous Improvement Map Managing Risk FMEA Understanding Performance Check Sheets Data Collection PDPC RAID Log* Risk Assessment* Fault Tree Analysis
Process Capability Studies
 Definition The quality of a production process is subject to certain fluctuations. What are known as capability indexes are calculated so that these processes can be assessed, with a broad distinction
Definition The quality of a production process is subject to certain fluctuations. What are known as capability indexes are calculated so that these processes can be assessed, with a broad distinction
Multiple Choice (#1-9). Circle the letter corresponding to the best answer.
 !! AP Statistics Ch. 3 Practice Test!! Name: Multiple Choice (#1-9). Circle the letter corresponding to the best answer. 1. In a statistics course, a linear regression equation was computed to predict
!! AP Statistics Ch. 3 Practice Test!! Name: Multiple Choice (#1-9). Circle the letter corresponding to the best answer. 1. In a statistics course, a linear regression equation was computed to predict
STATISTICS PART Instructor: Dr. Samir Safi Name:
 STATISTICS PART Instructor: Dr. Samir Safi Name: ID Number: Question #1: (20 Points) For each of the situations described below, state the sample(s) type the statistical technique that you believe is the
STATISTICS PART Instructor: Dr. Samir Safi Name: ID Number: Question #1: (20 Points) For each of the situations described below, state the sample(s) type the statistical technique that you believe is the
Theoretical Condition Indices
 Theoretical Condition Indices By Eric Teicholz and Gary Evans Summary Research commissioned by the General Services Administration to develop and test a methodology to derive cost-effective, reasonably-accurate
Theoretical Condition Indices By Eric Teicholz and Gary Evans Summary Research commissioned by the General Services Administration to develop and test a methodology to derive cost-effective, reasonably-accurate
STAT/MATH Chapter3. Statistical Methods in Practice. Averages and Variation 1/27/2017. Measures of Central Tendency: Mode, Median, and Mean
 STAT/MATH 3379 Statistical Methods in Practice Dr. Ananda Manage Associate Professor of Statistics Department of Mathematics & Statistics SHSU 1 Chapter3 Averages and Variation Copyright Cengage Learning.
STAT/MATH 3379 Statistical Methods in Practice Dr. Ananda Manage Associate Professor of Statistics Department of Mathematics & Statistics SHSU 1 Chapter3 Averages and Variation Copyright Cengage Learning.
Reliability Lifecycle of GaN Power Devices
 WHITE PAPER Reliability Lifecycle of GaN Power Devices Kurt Smith & Ronald Barr March 2017 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction JEDEC Qualification High temperature switching operation test 4 Conclusion 5 Acknowledgements
WHITE PAPER Reliability Lifecycle of GaN Power Devices Kurt Smith & Ronald Barr March 2017 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction JEDEC Qualification High temperature switching operation test 4 Conclusion 5 Acknowledgements
Applying Regression Techniques For Predictive Analytics Paviya George Chemparathy
 Applying Regression Techniques For Predictive Analytics Paviya George Chemparathy AGENDA 1. Introduction 2. Use Cases 3. Popular Algorithms 4. Typical Approach 5. Case Study 2016 SAPIENT GLOBAL MARKETS
Applying Regression Techniques For Predictive Analytics Paviya George Chemparathy AGENDA 1. Introduction 2. Use Cases 3. Popular Algorithms 4. Typical Approach 5. Case Study 2016 SAPIENT GLOBAL MARKETS
PROJECT QUALITY MANAGEMENT
 PROJECT QUALITY MANAGEMENT http://www.tutorialspoint.com/pmp-exams/project_quality_management.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Here is a list of sample questions which would help you to understand the
PROJECT QUALITY MANAGEMENT http://www.tutorialspoint.com/pmp-exams/project_quality_management.htm Copyright tutorialspoint.com Here is a list of sample questions which would help you to understand the
Estoril Education Day
 Estoril Education Day -Experimental design in Proteomics October 23rd, 2010 Peter James Note Taking All the Powerpoint slides from the Talks are available for download from: http://www.immun.lth.se/education/
Estoril Education Day -Experimental design in Proteomics October 23rd, 2010 Peter James Note Taking All the Powerpoint slides from the Talks are available for download from: http://www.immun.lth.se/education/
Using Factor Analysis to Generate Clusters of Agile Practices
 Using Factor Analysis to Generate Clusters of Agile Practices (A Guide for Agile Process Improvement) Noura Abbas University of Southampton School of Electronics and Computer Science Southampton, UK, SO17
Using Factor Analysis to Generate Clusters of Agile Practices (A Guide for Agile Process Improvement) Noura Abbas University of Southampton School of Electronics and Computer Science Southampton, UK, SO17
Statistics Quality: Control - Statistical Process Control and Using Control Charts
 Statistics Quality: Control - Statistical Process Control and Using Control Charts Processes Processing an application for admission to a university and deciding whether or not to admit the student. Reviewing
Statistics Quality: Control - Statistical Process Control and Using Control Charts Processes Processing an application for admission to a university and deciding whether or not to admit the student. Reviewing
Find the sum of ALL of the terms in this sequence:
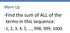 Warm Up Find the sum of ALL of the terms in this sequence: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,, 998, 999, 1000. GO OVER HOMEWORK QUIZZES Put this in Linear Section! Scatter Plot HW % vs. Grades Do you think there is a relationship
Warm Up Find the sum of ALL of the terms in this sequence: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,, 998, 999, 1000. GO OVER HOMEWORK QUIZZES Put this in Linear Section! Scatter Plot HW % vs. Grades Do you think there is a relationship
Statistics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test 1: Statistical Sampling
 Statistics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test 1: Statistical Sampling 1 a Explain what is meant by a census. b Write down two disadvantages of using a census rather than a sample. Each circuit board produced at GC
Statistics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test 1: Statistical Sampling 1 a Explain what is meant by a census. b Write down two disadvantages of using a census rather than a sample. Each circuit board produced at GC
Lifecycle Approach to Process Validation
 Lifecycle Approach to Process Validation Best Practices and Strategies July 19 th, 2016 Patrick Donohue, Drug Product Development, Janssen R&D Disclaimer The contents of this presentation are my personal
Lifecycle Approach to Process Validation Best Practices and Strategies July 19 th, 2016 Patrick Donohue, Drug Product Development, Janssen R&D Disclaimer The contents of this presentation are my personal
LEARNING TO SEE an introduction to lean thinking
 LEARNING TO SEE an introduction to lean thinking 2 Why Lean? Customer satisfaction Market share Costs 3 Where did Lean come from? Henry Ford First flow production line 1960s The term Lean originated International
LEARNING TO SEE an introduction to lean thinking 2 Why Lean? Customer satisfaction Market share Costs 3 Where did Lean come from? Henry Ford First flow production line 1960s The term Lean originated International
CERTIFIED RELIABILITY ENGINEER (CRE) BODY OF KNOWLEDGE MAP 2018
 CERTIFIED RELIABILITY ENGINEER (CRE) BODY OF KNOWLEDGE MAP 2018 The Certified Reliability Engineer (CRE) Body of Knowledge () has been updated to ensure that the most current state of reliability practice
CERTIFIED RELIABILITY ENGINEER (CRE) BODY OF KNOWLEDGE MAP 2018 The Certified Reliability Engineer (CRE) Body of Knowledge () has been updated to ensure that the most current state of reliability practice
Lean Flow Enterprise Elements
 "Lean Flow" describes the performance of organizations that are effective enough to win consistently in the competitive global marketplace. To understand how to get there, it s useful to focus on Lean
"Lean Flow" describes the performance of organizations that are effective enough to win consistently in the competitive global marketplace. To understand how to get there, it s useful to focus on Lean
1. Introduction to CQE
 About C.Q.E. 1. Introduction to CQE Certified Quality Engineer (CQE) Since 1968 The Certified Quality Engineer is a professional who understands the principles of product and service quality evaluation
About C.Q.E. 1. Introduction to CQE Certified Quality Engineer (CQE) Since 1968 The Certified Quality Engineer is a professional who understands the principles of product and service quality evaluation
A Process to Assess Rigor In Test and Evaluation Plans Best Practice
 A Process to Assess Rigor In Test and Evaluation Plans Best Practice Authored by: Michael Harman 30 April 2016 The goal of the STAT T&E COE is to assist in developing rigorous, defensible test strategies
A Process to Assess Rigor In Test and Evaluation Plans Best Practice Authored by: Michael Harman 30 April 2016 The goal of the STAT T&E COE is to assist in developing rigorous, defensible test strategies
Seven Basic Quality Tools. SE 450 Software Processes & Product Metrics 1
 Seven Basic Quality Tools SE 450 Software Processes & Product Metrics 1 The Seven Basic Tools Checklists (Checksheets) Pareto Diagrams Histograms Run Charts Scatter Diagrams (Scatter Plots) Control Charts
Seven Basic Quality Tools SE 450 Software Processes & Product Metrics 1 The Seven Basic Tools Checklists (Checksheets) Pareto Diagrams Histograms Run Charts Scatter Diagrams (Scatter Plots) Control Charts
SPRS EVALUATION CRITERIA (Revised JUL 2017)
 SPRS EVALUATION CRITERIA (Revised JUL 2017) 1. DELIVERY PERFORMANCE: A contractor s delivery performance will be based by Federal Supply Classification (FSC) or North American Industry Classification System
SPRS EVALUATION CRITERIA (Revised JUL 2017) 1. DELIVERY PERFORMANCE: A contractor s delivery performance will be based by Federal Supply Classification (FSC) or North American Industry Classification System
APPLICATION OF SEASONAL ADJUSTMENT FACTORS TO SUBSEQUENT YEAR DATA. Corresponding Author
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 APPLICATION OF SEASONAL ADJUSTMENT FACTORS TO SUBSEQUENT
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 APPLICATION OF SEASONAL ADJUSTMENT FACTORS TO SUBSEQUENT
OVERVIEW. AVL Reliability Engineering & Load Matrix
 AVL Reliability Engineering and Load Matrix OVERVIEW January 2006 Page 1 Content The Reliability Challenge AVL s Reliability Engineering Approach The Load Matrix Conclusions January 2006 Page 2 The Reliability
AVL Reliability Engineering and Load Matrix OVERVIEW January 2006 Page 1 Content The Reliability Challenge AVL s Reliability Engineering Approach The Load Matrix Conclusions January 2006 Page 2 The Reliability
An initiative of the Food Sector for the protection of the environment
 An initiative of the Food Sector for the protection of the environment LIFE+ FOODPRINT LIFE13 ENV/GR/000958 Action B.1: Development of a Carbon Footprint tool for the effective quantification of CO 2 equivalent
An initiative of the Food Sector for the protection of the environment LIFE+ FOODPRINT LIFE13 ENV/GR/000958 Action B.1: Development of a Carbon Footprint tool for the effective quantification of CO 2 equivalent
