IRON METABOLISM. Harper s Illustrated Biochemistry chapter 50
|
|
|
- Rose May
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IRON METABOLISM Harper s Illustrated Biochemistry chapter 50
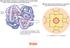
2 IRON 26th element in the periodic table Chemical Symbol: Fe MW = Electron Configuration: 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 6 Fourth most abundant mineral O > Si > Al Oxidation states = -2 to +6 Readily interconverted, i.e. redox active very useful for redox chemistry in the body very dangerous chemistry
3 IRON FUNCTIONS IN BIOLOGY Oxygen Transport and Storage Hemoglobin Myoglobin Electron Transport and Energy Metabolism Cytochromes Fe-S proteins Substrate Oxidation & Reduction Iron dependent enzyme: Ribonucleotide reductase Amino acid oxidases Fatty acid desaturases Nitric oxide synthetase Peroxidases Regulation of intracellular iron
4 IRON IN BIOLOGY Flavoproteins Heme Flavoproteins 2Fe-2S 4Fe-4S Enz Other Enz Transferrin & Others Ferritin & Hemosiderin Other Fe Proteins Fe-sulfur Enz Fe-Containing Proteins Hemeproteins Other Fe Enz Iron Activated Enz Other Enz Hemoglobin Myoglobin Cytochromes Other Enz
5 IRON FORMS IN DIET Heme Iron-porphyrin prosthetic group Hemoglobin, myoglobin, cytochromes Other iron-containing enzymes are ~3% body iron Aconitase, peroxidases 5-35% is absorbed Exist as Fe 2+ Nonheme >85% of iron in foods is non heme iron 2-20% is absorbed Exist as Fe 3+
6 ABSORPTION Nonheme Heme Iron solublized and ionized by stomach acid Chelation with small molecular weight compounds and mucin Protein digestion of hemoglobin and myoglobin releases heme Iron chelates pass through unstirred water layer bind to surface proteins and are internalized Heme transported as such into the cell Absorption all along the small intestine, but highest in duodenum
7 ABSORPTION Ferrous, Fe 2+, most soluble = most absorbable Each mechanism has 3 phases Iron uptake Intraenterocyte transport Storage and extraenterocyte transfer Dietary Iron: Iron is essential element and must be precisely regulated. On the lumen side of small intestine iron is reduced from its ferric form(fe 3+ ) to ferrous form(fe 2+ ). Ferrous iron is then transported in enterocytes by DMT1(divalent metal transporter).
8 ABSORPTION Heme iron is an important dietary sources of iron because it is more effectively absorbed than nonheme iron. From 5% to 35% of heme iron is absorbed from a single meal, whereas non-heme iron absorption from a single meal can range 2%-20%, depending on the iron status of the individual and the ratio of enhancers and promotors in the diet. Thus, although it constitutes about 10% of the iron found in the diet, heme iron may provide up to one-third of total absorbed dietary iron. The reason ascorbic acid promote iron absorption is ascorbic acid maintain iron in a reduced form and forms a soluble chelate with iron. These actions are shared by organic acids such as citric, lactic acids. A number of dietary factors influence iron absorption. Promotors Amino Acids Animal Proteins(for heme) Ascorbic Acid Hydrochloric Acid Organic Acids Sugars Mucin Inhibitors Carbonates Calcium (for heme) Egg yolk phosvitin Fiber Oxalates Phosphates Phytates Plant polyphenols Soy proteins
9 TRANSPORT Free iron is toxic because it catalyses the Fenton reaction generating free oxygen radicals. In biological systems iron is always bound to proteins to limit its toxicity. In plasma, it is bound to transferrin that plays a key role in iron transport to sites where it is required. Transferrin: Transport iron Single polypeptides composed of two iron binding half-site motifs, ~679 aas, ~76 kda MW; It is a glycoprotein synthesised in the liver; Bind 2 Fe 3+ and 2 HCO 3 Normally 25-50% saturated with iron Lactoferrin is iron binding protein in milk,plasma and mucus secretion such as tears Ovotransferrin is iron binding protein in bird s egg white Transferrin glycosilation is compromised in some disorders and in chronic alcholism, where carbohydrate-deficient transferrin, CDT, is decreased and can be monitored by isoelectric focusing (IEF). CDT is a marker for chronic alcholism
10 IRON TRANSPORT: TRANSFERRIN CYCLE Transferrin cycle: holotransferrin (Tf-Fe) binds to transferrin receptor 1 (TfR1) on cell surface. Clathrincoated vescicles form and endocitosis occurs forming endosomes where ph is acidic. The acidic ph causes iron release from transferrin. Apotransferrin (Apo.Tf) still binds to TfR1. Ferric iron is converted to ferrous iron by a iron reductase (Steap 3). Ferrous iron is transported in the cytosol trhough DMT-1. The TfR1-apo- Tf complex is recycled on cell surface where apo-tf is released and TfR1 can bind another Tf-Fe.
11 IRON TRANSPORT: TRANSFERRIN CYCLE Clathrin constitutes the coat of vesicles involved in three receptor-mediated intracellular transport pathways; the export of aggregated material from the trans-golgi network for regulated secretion, the transfer of lysosomal hydrolases from the trans-golgi network to lysosomes and receptor-mediated endocytosis at the plasma membrane. The clathrin subunits and the other major coat constituents, the adaptor polypeptides, interact in specific ways to build the characteristic polygonal clathrin lattice and to attach the coat to integral membrane receptors.
12 IRON TRANSPORT: TRANSFERRIN CYCLE TfR1 is present in almost all cells, especially in erythrocytes precursors There is a TfR2 (TfR2) that is mainly expressed on hepatocyte cells surface but it has a low affinity for Tf-Fe and it does not seem to be involved in iron uptake. It is one of the sensors for body iron stored levels Erythrocites half-life is around 60 days and they are engulfed by macrophages, where heme is degraded and iron is recycled and it is the highest iron source for the body (25 mg per day) whereas diet iron contributes with only 1-2 mg
13 STORAGE IRON Ferritin Major iron storage protein Apoferritin 24 polypeptide units in raspberry-like cluster Surrounds spherical cluster of hydrated ferric phosphate within its hollow center Can contain up to 4500 Fe atoms Liver contains ~60% of ferritin in the body Two types of subunits: Hemosiderin - H subunit: 22 kda, 182 aa, predominant in heart - L subunit: 20 kda, 174 aa, predominant in liver ~50% liver iron stores Reacts to ferritin antibodies - likely a degradation product Less available for mobilization
14 REGULATION OF INTRACELLULAR HOMEOSTASIS Synthesis of TfR1 and ferritin are linked to the intracellular iron content When iron levels are high, ferritin is synthesised for iron storage and TrF1 synthesis is inhibited When iron levels are low, ferritin synthesis is blocked whereas TrF1 is active Regulation of mrna stability is involved mrna for ferritin and TrF1 contain iron response elements (IREs) forming hairpins in the untranslated regions at the 5 and 3, respectively IREs are linked to iron regulatory proteins (IRPs) that are sensitive to intracellular iron levels and induced by low levels of the metal IRPs bind to IREs when iron levels are low IRPs binding to 5 UTR mrna blocks ferritin translation IRPs binding to 3 UTR mrna stabilises mrna and increases the synthesis of TrF1.
15 HEPCIDIN It is a protein with a key role in iron homeostasis It is synthesised by liver as a pro-peptide of 84 aa (pro-hepicidin) The bioactive peptide contains 25 aa This peptide binds to the cellular iron exporter, ferroportin, and initiates internalization and degradation
16 HEPICIDIN: REGULATION The major mechanism of hepicidin is THE REGULATION OF TRANSMEMBRANE IRON TRANSPORT It binds to FERROPORTIN, forms hepicidin-ferroportin complex,which is degraded in the lysosomes and iron is locked inside the cells (mainly enterocytes, hepatocytes and macrophages). When hepicidin levels are low, iron exporting cells have abundant ferroportin and thus releases iron into plasma. When hepicidin concentration increases it binds to ferroportin and thus iron is retained in the cells.
Lec.1 Medical Physiology Blood Physiology Z.H.Kamil
 Hemoglobin The major function of red blood cells is to transport hemoglobin, which in turn carries oxygen from the lungs to the tissues. Hemoglobin, the protein that makes red blood cells red, binds easily
Hemoglobin The major function of red blood cells is to transport hemoglobin, which in turn carries oxygen from the lungs to the tissues. Hemoglobin, the protein that makes red blood cells red, binds easily
Microcytic Anemia: Iron Deficiency (IDA) and ACD*
 Microcytic Anemia: Iron Deficiency (IDA) and ACD* IDA: iron deficiency anemia *ACD: anemia of chronic disease Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com Microcytic Anemia, IDA and ACD Part One Anemia overview
Microcytic Anemia: Iron Deficiency (IDA) and ACD* IDA: iron deficiency anemia *ACD: anemia of chronic disease Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com Microcytic Anemia, IDA and ACD Part One Anemia overview
IRON METABOLISM R. Mohammadi Biochemist (Ph.D.) Faculty member of Medical Faculty
 IRON METABOLISM R. Mohammadi Biochemist (Ph.D.) Faculty member of Medical Faculty HEMPROTEINS Hemoglobin Myoglobin Cytochromes Peroxidases Trp Pyrrolase PG Synthase NO Synthase Guanylate Synthase NON-HEME
IRON METABOLISM R. Mohammadi Biochemist (Ph.D.) Faculty member of Medical Faculty HEMPROTEINS Hemoglobin Myoglobin Cytochromes Peroxidases Trp Pyrrolase PG Synthase NO Synthase Guanylate Synthase NON-HEME
IRON METABOLISM & CLINICAL IMPORTANCE
 Iron IRON METABOLISM & CLINICAL IMPORTANCE IRON METABOLISM LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, student should be able to; Know the biochemical proper1es of iron Enlist the func1ons of iron in
Iron IRON METABOLISM & CLINICAL IMPORTANCE IRON METABOLISM LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, student should be able to; Know the biochemical proper1es of iron Enlist the func1ons of iron in
SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
 1 SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL SEMINAR: IRON AND IRON BALANCE An Overview What are some of the vital functions
1 SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL SEMINAR: IRON AND IRON BALANCE An Overview What are some of the vital functions
Iron Regulation Gone Wrong
 Iron Regulation Gone Wrong Stephanie Blackburn, MHS, MLS(ASCP) CM Objectives Describe the function of proteins involved in iron regulation. Explain the development of iron deficiency. Evaluate cases involving
Iron Regulation Gone Wrong Stephanie Blackburn, MHS, MLS(ASCP) CM Objectives Describe the function of proteins involved in iron regulation. Explain the development of iron deficiency. Evaluate cases involving
ANEMIA OF CHRONIC DISEASE (ACD)
 ANEMIA OF CHRONIC DISEASE (ACD) seminar Martin Vokurka 2007 Unofficial study material 1 VERY COMMON!!! In hospitalized patients is the second most common after iron deficiency OFTEN NEGLECTED!! Unofficial
ANEMIA OF CHRONIC DISEASE (ACD) seminar Martin Vokurka 2007 Unofficial study material 1 VERY COMMON!!! In hospitalized patients is the second most common after iron deficiency OFTEN NEGLECTED!! Unofficial
Metabolic Liver Diseases (for the Boards)
 Metabolic Liver Diseases (for the Boards) HH Iron dysregulation (understand the factors involved) Multisystem (which systems?) Diagnostic Lab Studies and key stains? Complications Wilson s Copper dysregulation
Metabolic Liver Diseases (for the Boards) HH Iron dysregulation (understand the factors involved) Multisystem (which systems?) Diagnostic Lab Studies and key stains? Complications Wilson s Copper dysregulation
Iron metabolism. And. Anemia in chronic kidney disease
 Iron metabolism And Anemia in chronic kidney disease Chittima Sirijerachai Iron distribution Intracellular iron Intracellular ferrous iron Heme iron compound : Hb, myoglobin Iron containing enzyme Intracellular
Iron metabolism And Anemia in chronic kidney disease Chittima Sirijerachai Iron distribution Intracellular iron Intracellular ferrous iron Heme iron compound : Hb, myoglobin Iron containing enzyme Intracellular
Clinical Aspects and Laboratory Iron Metabolism, Anemias
 W Manfred Wick Wulf Pinggera Paul Lehmann Clinical Aspects and Laboratory Iron Metabolism, Anemias Concepts in the anemias of malignancies and renal and rheumatoid diseases Sixth, revised and updated edition
W Manfred Wick Wulf Pinggera Paul Lehmann Clinical Aspects and Laboratory Iron Metabolism, Anemias Concepts in the anemias of malignancies and renal and rheumatoid diseases Sixth, revised and updated edition
1/24/2012. Cell. Plasma Membrane
 Chapter 3 Outline Plasma Membrane Cytoplasm and Its Organelles Cell and Gene Expression Protein Synthesis and Secretion DNA Synthesis and Cell Division Cell Basic unit of structure and function in body
Chapter 3 Outline Plasma Membrane Cytoplasm and Its Organelles Cell and Gene Expression Protein Synthesis and Secretion DNA Synthesis and Cell Division Cell Basic unit of structure and function in body
Mobilization of Stored Iron in Mammals: A Review
 Nutrients 2013, 5, 4022-4050; doi:10.3390/nu5104022 Review OPEN ACCESS nutrients ISSN 2072-6643 www.mdpi.com/journal/nutrients Mobilization of Stored Iron in Mammals: A Review Maria C. Linder Department
Nutrients 2013, 5, 4022-4050; doi:10.3390/nu5104022 Review OPEN ACCESS nutrients ISSN 2072-6643 www.mdpi.com/journal/nutrients Mobilization of Stored Iron in Mammals: A Review Maria C. Linder Department
Red blood cells : Circulating Haemoglobin factories
 Red blood cells : Circulating Haemoglobin factories Haemoglobin : Oxygenated Oxygen is bound to the Fe in within Haem M1.2 Iron plays an essential role in several metabolic processes Heme iron compounds
Red blood cells : Circulating Haemoglobin factories Haemoglobin : Oxygenated Oxygen is bound to the Fe in within Haem M1.2 Iron plays an essential role in several metabolic processes Heme iron compounds
Lecture 11: Metalloproteins - I
 Lecture 11: Metalloproteins - I 1. Introduction A large number of biochemical reactions are known to be catalyzed by proteins. The reason behind their functions as catalysts is attributed to the side chains
Lecture 11: Metalloproteins - I 1. Introduction A large number of biochemical reactions are known to be catalyzed by proteins. The reason behind their functions as catalysts is attributed to the side chains
Chapter 2 Molecules to enzymes - Short answer [72 marks]
![Chapter 2 Molecules to enzymes - Short answer [72 marks] Chapter 2 Molecules to enzymes - Short answer [72 marks]](/thumbs/72/67260206.jpg) Chapter 2 Molecules to enzymes - Short answer [72 marks] 1a. Outline primary and quaternary protein structures. Primary protein structure: Quaternary protein structure: a. (primary structure) is sequence
Chapter 2 Molecules to enzymes - Short answer [72 marks] 1a. Outline primary and quaternary protein structures. Primary protein structure: Quaternary protein structure: a. (primary structure) is sequence
Iron Deficiency Anemia F I R S T Y E A R H E M A T O L O G Y M O D U L E
 Iron Deficiency Anemia F I R S T Y E A R H E M A T O L O G Y M O D U L E 2 0 1 3 Objectives By The end of this lecture, the student will be able to: describe briefly iron metabolism in human body. mention
Iron Deficiency Anemia F I R S T Y E A R H E M A T O L O G Y M O D U L E 2 0 1 3 Objectives By The end of this lecture, the student will be able to: describe briefly iron metabolism in human body. mention
Dr. Muaz Osman Fagere
 Dr. Muaz Osman Fagere In biology, pigments are defined as substances occurring in living matter that absorb visible light. Pigments are differ in origin, chemical constitution, and biological significance.
Dr. Muaz Osman Fagere In biology, pigments are defined as substances occurring in living matter that absorb visible light. Pigments are differ in origin, chemical constitution, and biological significance.
invited review Physiology of iron transport and the hemochromatosis gene
 Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 282: G403 G414, 2002; 10.1152/ajpgi.00404.2001. Physiology of iron transport and the hemochromatosis gene invited review ANTONELLO PIETRANGELO Unit for the Study
Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 282: G403 G414, 2002; 10.1152/ajpgi.00404.2001. Physiology of iron transport and the hemochromatosis gene invited review ANTONELLO PIETRANGELO Unit for the Study
STRUCTURE OF THE MEMBRANE PROXIMAL OXIDOREDUCTASE DOMAIN OF HUMAN STEAP3, THE DOMINANT FERRIREDUCTASE OF THE ERYTHROID TRANSFERRIN CYCLE
 STRUCTURE OF THE MEMBRANE PROXIMAL OXIDOREDUCTASE DOMAIN OF HUMAN STEAP3, THE DOMINANT FERRIREDUCTASE OF THE ERYTHROID TRANSFERRIN CYCLE by Anoop Kumar Balakrishnan Sendamarai ` A dissertation submitted
STRUCTURE OF THE MEMBRANE PROXIMAL OXIDOREDUCTASE DOMAIN OF HUMAN STEAP3, THE DOMINANT FERRIREDUCTASE OF THE ERYTHROID TRANSFERRIN CYCLE by Anoop Kumar Balakrishnan Sendamarai ` A dissertation submitted
Biochemistry study of the molecular basis of life
 Biochemistry : An Introduction Biochemistry study of the molecular basis of life n Study of the chemistry of living organisms Studies organic molecules & organic reactions in living organisms n Living
Biochemistry : An Introduction Biochemistry study of the molecular basis of life n Study of the chemistry of living organisms Studies organic molecules & organic reactions in living organisms n Living
Quantitative Determination Of Serum Iron, Unsaturated Iron Binding Capacity (UIBC), And Total Iron Binding Capacity (TIBC)
 Quantitative Determination Of Serum Iron, Unsaturated Iron Binding Capacity (UIBC), And Total Iron Binding Capacity (TIBC) Objectives To Determine The Normal Level Of Serum Iron. To Determine The Use Of
Quantitative Determination Of Serum Iron, Unsaturated Iron Binding Capacity (UIBC), And Total Iron Binding Capacity (TIBC) Objectives To Determine The Normal Level Of Serum Iron. To Determine The Use Of
A Computational Model of Liver Iron Metabolism
 Simon Mitchell 1, Pedro Mendes 1,2 * 1 School of Computer Science and Manchester Institute of Biotechnology, University of Manchester, Manchester, United Kingdom, 2 Virginia Bioinformatics Institute, Virginia
Simon Mitchell 1, Pedro Mendes 1,2 * 1 School of Computer Science and Manchester Institute of Biotechnology, University of Manchester, Manchester, United Kingdom, 2 Virginia Bioinformatics Institute, Virginia
1. Heme proteins in general
 1. Heme proteins in general 1 2 Cloning, expression and purification E. coli K-12 genome cloning (kda) pet21c overexpression purification 97 66 45 33 Full-length YddV 54 kda YddV contains a b-type heme
1. Heme proteins in general 1 2 Cloning, expression and purification E. coli K-12 genome cloning (kda) pet21c overexpression purification 97 66 45 33 Full-length YddV 54 kda YddV contains a b-type heme
The essential nature of iron usage and regulation
 Vol 23 o 15 642 Primer The essential nature of iron usage and regulation Jerry Kaplan and Diane M. Ward The facile ability of iron to gain and lose electrons has made iron an important participant in a
Vol 23 o 15 642 Primer The essential nature of iron usage and regulation Jerry Kaplan and Diane M. Ward The facile ability of iron to gain and lose electrons has made iron an important participant in a
C2006/F2402 '14 OUTLINE OF LECTURE #12
 C2006/F2402 '14 OUTLINE OF LECTURE #12 (c) 2014 Dr. Deborah Mowshowitz, Columbia University, New York, NY. Last update 03/04/2014 03:24 PM Handouts: 12-A -- mrna processing 12-B -- Alternative processing
C2006/F2402 '14 OUTLINE OF LECTURE #12 (c) 2014 Dr. Deborah Mowshowitz, Columbia University, New York, NY. Last update 03/04/2014 03:24 PM Handouts: 12-A -- mrna processing 12-B -- Alternative processing
Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism (Part I)
 Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism (Part I) Microbial Metabolism Metabolism refers to all chemical reactions that occur within a living organism. These chemical reactions are generally of two types: Catabolic:
Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism (Part I) Microbial Metabolism Metabolism refers to all chemical reactions that occur within a living organism. These chemical reactions are generally of two types: Catabolic:
2012 GENERAL [5 points]
![2012 GENERAL [5 points] 2012 GENERAL [5 points]](/thumbs/75/72452386.jpg) GENERAL [5 points] 2012 Mark all processes that are part of the 'standard dogma of molecular' [ ] DNA replication [ ] transcription [ ] translation [ ] reverse transposition [ ] DNA restriction [ ] DNA
GENERAL [5 points] 2012 Mark all processes that are part of the 'standard dogma of molecular' [ ] DNA replication [ ] transcription [ ] translation [ ] reverse transposition [ ] DNA restriction [ ] DNA
Dietary G6PD deficiency (Favism):
 Dietary G6PD deficiency (Favism): VICINE FAVA BEAN Stomach Acid (low ph) Glucose CH 2 OH O OH OH OH H OH O 2 + NH 2 Divicine (oxidized) N C N C HC NH 2 C O O Reductase Vicine is found in uncooked fava
Dietary G6PD deficiency (Favism): VICINE FAVA BEAN Stomach Acid (low ph) Glucose CH 2 OH O OH OH OH H OH O 2 + NH 2 Divicine (oxidized) N C N C HC NH 2 C O O Reductase Vicine is found in uncooked fava
Chemistry 1050 Exam 4 Study Guide
 Chapter 19 Chemistry 1050 Exam 4 Study Guide 19.1 and 19.2 Know there are 20 common amino acids that can polymerize into proteins. Know why amino acids are called alpha amino acids. Identify the charges
Chapter 19 Chemistry 1050 Exam 4 Study Guide 19.1 and 19.2 Know there are 20 common amino acids that can polymerize into proteins. Know why amino acids are called alpha amino acids. Identify the charges
Chemistry 1120 Exam 3 Study Guide
 Chemistry 1120 Exam 3 Study Guide Chapter 9 9.1 and 9.2 Know there are 20 common amino acids that can polymerize into proteins. Know why amino acids are called alpha amino acids. Identify the charges of
Chemistry 1120 Exam 3 Study Guide Chapter 9 9.1 and 9.2 Know there are 20 common amino acids that can polymerize into proteins. Know why amino acids are called alpha amino acids. Identify the charges of
Physiology Unit 3 HEMATOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 3 HEMATOLOGY In Physiology Today Hematocrit Percentage of blood volume that is erythrocytes 45% in men 42% in women Average blood volume in is 5 L Plasma Large amounts of organic/inorganic
Physiology Unit 3 HEMATOLOGY In Physiology Today Hematocrit Percentage of blood volume that is erythrocytes 45% in men 42% in women Average blood volume in is 5 L Plasma Large amounts of organic/inorganic
Metabolism BIOL 3702: Chapter 10
 Metabolism BIOL 3702: Chapter 10 Introduction to Metabolism u Metabolism is the sum total of all the chemical reactions occurring in a cell u Two major parts of metabolism: v Catabolism Ø Large, more complex
Metabolism BIOL 3702: Chapter 10 Introduction to Metabolism u Metabolism is the sum total of all the chemical reactions occurring in a cell u Two major parts of metabolism: v Catabolism Ø Large, more complex
Globular proteins. Myoglobin and hemoglobin. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester,
 Globular proteins Myoglobin and hemoglobin Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Functions of myoglobin and hemoglobin Myoglobin is storage of O 2 in muscles. During periods of oxygen deprivation,
Globular proteins Myoglobin and hemoglobin Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Functions of myoglobin and hemoglobin Myoglobin is storage of O 2 in muscles. During periods of oxygen deprivation,
Gene Expression: From Genes to Proteins
 The Flow of Genetic Information Gene Expression: From Genes to Proteins Chapter 9 Central Dogma in Molecular Biology molecule Gene 1 Strand to be transcribed Gene 2 Gene 3 strand Codon : Polymerase transcribes
The Flow of Genetic Information Gene Expression: From Genes to Proteins Chapter 9 Central Dogma in Molecular Biology molecule Gene 1 Strand to be transcribed Gene 2 Gene 3 strand Codon : Polymerase transcribes
G = H (T S) I. Cellular Metabolism & Reaction Coupling Figure 1: Metabolism
 I. Cellular Metabolism & Reaction Coupling Figure 1: Metabolism Metabolism represents the sum total of ALL chemical reactions within the cell. These reactions can be regarded as either catabolic or anabolic
I. Cellular Metabolism & Reaction Coupling Figure 1: Metabolism Metabolism represents the sum total of ALL chemical reactions within the cell. These reactions can be regarded as either catabolic or anabolic
Enzymes Part III: regulation I. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017
 Enzymes Part III: regulation I Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017 Mechanisms of regulation Expression of isoenzymes Regulation of enzymatic activity Inhibitors Conformational changes Allostery Modulators Reversible
Enzymes Part III: regulation I Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017 Mechanisms of regulation Expression of isoenzymes Regulation of enzymatic activity Inhibitors Conformational changes Allostery Modulators Reversible
Chapter 1 -- Life. Chapter 2 -- Atoms, Molecules and Bonds. Chapter 3 -- Water
 Chapter 1 -- Life In the beginning... Molecular evolution Heirarchy and organization levels of organization Form follows function Language in science Cell and Molecular Biology -- Biology 20A Chapter Outlines
Chapter 1 -- Life In the beginning... Molecular evolution Heirarchy and organization levels of organization Form follows function Language in science Cell and Molecular Biology -- Biology 20A Chapter Outlines
Chapter 3.5. Protein Synthesis
 Chapter 3.5 Protein Synthesis Summary of Protein Synthesis How chemical Information is transfer during protein synthesis DNA mrna protein transcription the step from DNA to mrna occurs in the nucleus where
Chapter 3.5 Protein Synthesis Summary of Protein Synthesis How chemical Information is transfer during protein synthesis DNA mrna protein transcription the step from DNA to mrna occurs in the nucleus where
Human Transferrin / TF ELISA Pair Set
 Human Transferrin / TF ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11019 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized in the
Human Transferrin / TF ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11019 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized in the
Bioinorganic Chemistry: Inorganic Elements in the Chemistry of Life
 Bioinorganic Chemistry: Inorganic Elements in the Chemistry of Life An Introduction and Guide Wolfgang Kaim Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany and Brigitte Schwederski Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart,
Bioinorganic Chemistry: Inorganic Elements in the Chemistry of Life An Introduction and Guide Wolfgang Kaim Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany and Brigitte Schwederski Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart,
Copper: Essential for Human Health
 BIOLOGY Copper: Essential for Human Health 14-16 YEARS Copper is an essential trace element vital to the health of all living organisms. Although the amount of copper found in the human body (50 120 milligrams
BIOLOGY Copper: Essential for Human Health 14-16 YEARS Copper is an essential trace element vital to the health of all living organisms. Although the amount of copper found in the human body (50 120 milligrams
Endothelium conference
 Endothelium conference Epithelium FUNCTIONS: COVER ORGANS, LINE VISCERA AND BLOOD VESSELS, SECRETORY CELLS OF GLANDS DISTINGUISHING FEATURES AND DISTRIBUTION: ALWAYS SIT ON A BASEMENT MEMBRANE, BUT COME
Endothelium conference Epithelium FUNCTIONS: COVER ORGANS, LINE VISCERA AND BLOOD VESSELS, SECRETORY CELLS OF GLANDS DISTINGUISHING FEATURES AND DISTRIBUTION: ALWAYS SIT ON A BASEMENT MEMBRANE, BUT COME
Gene Expression: Transcription
 Gene Expression: Transcription The majority of genes are expressed as the proteins they encode. The process occurs in two steps: Transcription = DNA RNA Translation = RNA protein Taken together, they make
Gene Expression: Transcription The majority of genes are expressed as the proteins they encode. The process occurs in two steps: Transcription = DNA RNA Translation = RNA protein Taken together, they make
35% of elements in the planet. In rock, found oxidised as haematite or magnetite
 35% of elements in the planet In rock, found oxidised as haematite or magnetite Iron sulphur clusters may have been central to the earliest life forms 3.5 billion years ago Bacterial membranes are minature
35% of elements in the planet In rock, found oxidised as haematite or magnetite Iron sulphur clusters may have been central to the earliest life forms 3.5 billion years ago Bacterial membranes are minature
B.Sc. I YEAR COURSE OUTCOMES. Understand biochemistry at the atomic level, draw molecules and reactions involved with biomolecules.
 B.Sc. I YEAR SEMESTER-I BS104 Chemistry Of DSC-1A 4T +2P = 6 4+1=5 Biomolecules After studying this paper, biochemistry graduate students will be able to: Understand biochemistry at the atomic level, draw
B.Sc. I YEAR SEMESTER-I BS104 Chemistry Of DSC-1A 4T +2P = 6 4+1=5 Biomolecules After studying this paper, biochemistry graduate students will be able to: Understand biochemistry at the atomic level, draw
Metabolism. BIOL 3702: Chapter 10. Introduction to Metabolism. Energy and Work. BIOL 3702: Chapter 10 AY Dr. Cooper 1. Metabolism (cont.
 Metabolism BIOL 3702: Chapter 10 Introduction to Metabolism u Metabolism is the sum total of all the chemical reactions occurring in a cell u Two major parts of metabolism: v Catabolism Ø Large, more complex
Metabolism BIOL 3702: Chapter 10 Introduction to Metabolism u Metabolism is the sum total of all the chemical reactions occurring in a cell u Two major parts of metabolism: v Catabolism Ø Large, more complex
A snapshot of bioinorganic chemistry
 A snapshot of bioinorganic chemistry Biological periodic table Metallobiomolecules The diverse coordination chemistry of the d block elements allows metallobiomolecules to be tuned for a wide array of
A snapshot of bioinorganic chemistry Biological periodic table Metallobiomolecules The diverse coordination chemistry of the d block elements allows metallobiomolecules to be tuned for a wide array of
4 Purification of ferritin from seeds of Vigna mungo (L.) Hepper
 4 Purification of ferritin from seeds of Vigna mungo (L.) Hepper 4.1 Introduction Iron is an essential element for all living organisms. It is required by many functional molecules involved in a great
4 Purification of ferritin from seeds of Vigna mungo (L.) Hepper 4.1 Introduction Iron is an essential element for all living organisms. It is required by many functional molecules involved in a great
CARENZA ED ECCESSO DI FERRO: nuove conoscenze ed approccio terapeutico. Ore 9,20-9,50 Fisiopatologia dei disordini del ferro E.
 CARENZA ED ECCESSO DI FERRO: nuove conoscenze ed approccio terapeutico Ore 9,20-9,50 Fisiopatologia dei disordini del ferro E. Angelucci- Genova Iron overload All things are poison, and nothing is without
CARENZA ED ECCESSO DI FERRO: nuove conoscenze ed approccio terapeutico Ore 9,20-9,50 Fisiopatologia dei disordini del ferro E. Angelucci- Genova Iron overload All things are poison, and nothing is without
EXPRESSION OF THE IRON EXPORTER FERROPORTIN IN RESPONSE TO COPPER DEFICIENCY AND IRON LOADING
 EXPRESSION OF THE IRON EXPORTER FERROPORTIN IN RESPONSE TO COPPER DEFICIENCY AND IRON LOADING By SUPAK JENKITKASEMWONG A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL
EXPRESSION OF THE IRON EXPORTER FERROPORTIN IN RESPONSE TO COPPER DEFICIENCY AND IRON LOADING By SUPAK JENKITKASEMWONG A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE SLIDES
 CHAPTER 13 LECTURE SLIDES Prepared by Brenda Leady University of Toledo To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off.
CHAPTER 13 LECTURE SLIDES Prepared by Brenda Leady University of Toledo To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off.
Protein shape and function is determined by the sequence of amino acids that make up the protein. Amino acids are held together by peptide bonds to
 Protein shape and function is determined by the sequence of amino acids that make up the protein. Amino acids are held together by peptide bonds to form peptides. Peptides are held together by hydrogen
Protein shape and function is determined by the sequence of amino acids that make up the protein. Amino acids are held together by peptide bonds to form peptides. Peptides are held together by hydrogen
Organelle Atlas APPENDIX TO CHAPTER 4 4A.1
 APPENDIX TO CHAPTER 4 This atlas contains images of cellular organelles visualized using a wide variety of reagents and techniques and demonstrates the diversity of methods for exploring the cell. The
APPENDIX TO CHAPTER 4 This atlas contains images of cellular organelles visualized using a wide variety of reagents and techniques and demonstrates the diversity of methods for exploring the cell. The
I. Enzyme Action Figure 1: Activation Energy (Ea) Activation Energy (Ea):
 I. Enzyme Action Figure 1: Activation Energy (Ea) *Activation energy represents an energy barrier that reactant molecules must overcome in order to react & form products. Think of an Olympic track star
I. Enzyme Action Figure 1: Activation Energy (Ea) *Activation energy represents an energy barrier that reactant molecules must overcome in order to react & form products. Think of an Olympic track star
Protein analysis. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 5
 Protein analysis Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2015-2016 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 5 Bases of protein separation Proteins can be purified on the basis Solubility
Protein analysis Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2015-2016 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 5 Bases of protein separation Proteins can be purified on the basis Solubility
Sheet #7 Dr. Mamoun Ahram 10/07/2014
 1 Recap: Globular Proteins - There are two types of proteins according to their structure: a. Fibrous proteins. b. Globular proteins: are globe-like (spherical) with three-dimensional compact structures
1 Recap: Globular Proteins - There are two types of proteins according to their structure: a. Fibrous proteins. b. Globular proteins: are globe-like (spherical) with three-dimensional compact structures
Gene Expression and Regulation - 1
 Gene Expression and Regulation - 1 We have been discussing the molecular structure of DNA and its function in DNA replication and in transcription. Earlier we discussed how genes interact in transmission
Gene Expression and Regulation - 1 We have been discussing the molecular structure of DNA and its function in DNA replication and in transcription. Earlier we discussed how genes interact in transmission
Examination I PHRM 836 Biochemistry for Pharmaceutical Sciences II September 29, 2015
 Examination I PHRM 836 Biochemistry for Pharmaceutical Sciences II September 29, 2015 PHRM 836 Exam I - 1 Name: Instructions 1. Check your exam to make certain that it has 9 pages including this cover
Examination I PHRM 836 Biochemistry for Pharmaceutical Sciences II September 29, 2015 PHRM 836 Exam I - 1 Name: Instructions 1. Check your exam to make certain that it has 9 pages including this cover
TIDES 2014 GalNAc-siRNA with Enhanced Stabilization Chemistry: ESC-GalNAc-siRNA. May 14, 2014 Muthiah Manoharan
 TIDES 2014 GalNAc-siRNA with Enhanced Stabilization Chemistry: ESC-GalNAc-siRNA May 14, 2014 Muthiah Manoharan Agenda sirna-galnac Conjugates: Background Standard Template Chemistry (STC)» Human POC of
TIDES 2014 GalNAc-siRNA with Enhanced Stabilization Chemistry: ESC-GalNAc-siRNA May 14, 2014 Muthiah Manoharan Agenda sirna-galnac Conjugates: Background Standard Template Chemistry (STC)» Human POC of
Enzymes and Coenzymes I
 Enzymes and Coenzymes I Objectives :- What are enzymes? Classification of enzymes and naming. Coenzymes, Cofactors, Isoenzymes. Enzyme activity and specificity. Factors affecting enzyme activity. Enzyme
Enzymes and Coenzymes I Objectives :- What are enzymes? Classification of enzymes and naming. Coenzymes, Cofactors, Isoenzymes. Enzyme activity and specificity. Factors affecting enzyme activity. Enzyme
Protein Structure/Function Relationships
 Protein Structure/Function Relationships W. M. Grogan, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. Describe and cite examples of fibrous and globular proteins. 2. Describe typical tertiary structural motifs found in proteins.
Protein Structure/Function Relationships W. M. Grogan, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. Describe and cite examples of fibrous and globular proteins. 2. Describe typical tertiary structural motifs found in proteins.
disaccharides = two mono-s linked together e.g. lactose = glucose + galactose sucrose = glucose + fructose
 involved in the degradation of molecules found in animal cells membrane limited varies in shape and size contains acid hydrolases (phosphatase, nucleases, proteases, etc.), enzymes that work only at acid
involved in the degradation of molecules found in animal cells membrane limited varies in shape and size contains acid hydrolases (phosphatase, nucleases, proteases, etc.), enzymes that work only at acid
Unit 2 Review: DNA, Protein Synthesis & Enzymes
 1. One of the functions of DNA is to A. secrete vacuoles.. make copies of itself.. join amino acids to each other. D. carry genetic information out of the nucleus. 2. Two sugars found in nucleic acids
1. One of the functions of DNA is to A. secrete vacuoles.. make copies of itself.. join amino acids to each other. D. carry genetic information out of the nucleus. 2. Two sugars found in nucleic acids
Key words: transferrin receptor, purification, affinity chromatography
 Vol. 42, No. 2, June 1997 BIOCHEMISTRY end MOLECULAR BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL Pages 309-314 ISOLATION OF THE TRANSFERRIN RECEPTOR FROM HUMAN PLACENTA Kanevsky V.Yu., Pozdnyakova L.P., Katukov V.Yu., Severin
Vol. 42, No. 2, June 1997 BIOCHEMISTRY end MOLECULAR BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL Pages 309-314 ISOLATION OF THE TRANSFERRIN RECEPTOR FROM HUMAN PLACENTA Kanevsky V.Yu., Pozdnyakova L.P., Katukov V.Yu., Severin
Amino Acids & Proteins
 Chemistry 131 Lecture 13: Protein Function; Amino Acids and Properties, Chirality & Handedness in Amino Acids, Primary Protein Structure Sections 18.1 18.7 in McMurry, Ballantine, et. al. 7 th edition
Chemistry 131 Lecture 13: Protein Function; Amino Acids and Properties, Chirality & Handedness in Amino Acids, Primary Protein Structure Sections 18.1 18.7 in McMurry, Ballantine, et. al. 7 th edition
Protein Metabolism (Chap 27)
 Protein Metabolism (Chap 27) Translation: nucleic acid language amino acid language The Genetic Code is the basis for this translation: aminoacyl-trna synthetase xxx xxx xxx trna + amino acid xxx amino
Protein Metabolism (Chap 27) Translation: nucleic acid language amino acid language The Genetic Code is the basis for this translation: aminoacyl-trna synthetase xxx xxx xxx trna + amino acid xxx amino
MOLECULAR GENETICS PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1
 AP BIOLOGY MOLECULAR GENETICS ACTIVITY #2 NAME DATE HOUR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1 GENETIC CODE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS OVERVIEW Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 2 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
AP BIOLOGY MOLECULAR GENETICS ACTIVITY #2 NAME DATE HOUR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 1 GENETIC CODE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS OVERVIEW Molecular Genetics Activity #2 page 2 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
Spectroscopic Studies of Methionine- and Histidine-Rich hctr1 Model Peptides
 Spectroscopic Studies of Methionine- and Histidine-Rich hctr1 Model Peptides Kathryn L. Haas and Katherine J. Franz Department of Chemistry, Duke University Abstract Mechanisms of copper homeostasis are
Spectroscopic Studies of Methionine- and Histidine-Rich hctr1 Model Peptides Kathryn L. Haas and Katherine J. Franz Department of Chemistry, Duke University Abstract Mechanisms of copper homeostasis are
The living things in an area interacting with their physical environment make up an.
 Standard 4 Review Sheet / Key Idea 1 Living Environment The living things in an area interacting with their physical environment make up an. Organisms which can make their own food by photosynthesis are
Standard 4 Review Sheet / Key Idea 1 Living Environment The living things in an area interacting with their physical environment make up an. Organisms which can make their own food by photosynthesis are
namibia UniVERSITY OF SC IEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES PAPER: THEORY
 namibia UniVERSITY OF SC IEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES QUALIFICATION CODE: SOBBMS LEVEL: 6 COURSE:
namibia UniVERSITY OF SC IEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES QUALIFICATION CODE: SOBBMS LEVEL: 6 COURSE:
Approaches to Nanoparticle Targeting. Mahmoud R. Jaafari, PhD Prof. of Pharmaceutics and Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology
 Approaches to Nanoparticle Targeting Mahmoud R. Jaafari, PhD Prof. of Pharmaceutics and Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology Principles of drug targeting Drug targeting is the systemic or local administration
Approaches to Nanoparticle Targeting Mahmoud R. Jaafari, PhD Prof. of Pharmaceutics and Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology Principles of drug targeting Drug targeting is the systemic or local administration
Synthetic cells: do bacteria need all its genes? No.
 NO NEED TO REFER TO THE SLIDES. بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Do we need all the non coding regions of the DNA? Two weeks ago, they discovered that the genome of a plant is very small (recall that plant genome
NO NEED TO REFER TO THE SLIDES. بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Do we need all the non coding regions of the DNA? Two weeks ago, they discovered that the genome of a plant is very small (recall that plant genome
Allosteric Effects & Cooperative Binding
 Allosteric Effects & Cooperative Binding The shape of the binding curve for oxygen to myoglobin is hyperbolic and follows the equation for non-cooperative binding: Y=[L]/(KD + [L]). The binding curve for
Allosteric Effects & Cooperative Binding The shape of the binding curve for oxygen to myoglobin is hyperbolic and follows the equation for non-cooperative binding: Y=[L]/(KD + [L]). The binding curve for
Proteins. Amino Acids (APK) Peptides (APK) 5/23/2012. Peptide bond. Acid. Amino
 Proteins Amino Acids (APK) Acid Amino Image courtesy of Biotech (biotech.chem.indiana.edu/pages/ protein_intro.html) Peptides (APK) Peptide bond 1 Proteins (polypeptides) Segment of a protein Peptide bonds
Proteins Amino Acids (APK) Acid Amino Image courtesy of Biotech (biotech.chem.indiana.edu/pages/ protein_intro.html) Peptides (APK) Peptide bond 1 Proteins (polypeptides) Segment of a protein Peptide bonds
Text Reference, Campbell v.8, chapter 17 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
 AP BIOLOGY Text Reference, Campbell v.8, chapter 17 ACTIVITY 1.22 NAME DATE HOUR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS GENETIC CODE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS OVERVIEW PROTEIN SYNTHESIS TRANSCRIPTION PROTEIN SYNTHESIS TRANSLATION
AP BIOLOGY Text Reference, Campbell v.8, chapter 17 ACTIVITY 1.22 NAME DATE HOUR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS GENETIC CODE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS OVERVIEW PROTEIN SYNTHESIS TRANSCRIPTION PROTEIN SYNTHESIS TRANSLATION
THE MATRIX IS ALWAYS COMPLEX!
 THE MATRIX IS ALWAYS COMPLEX! Prof. Kenneth Dawson Centre for BioNano Interactions University College Dublin http://www.ucd.ie/cbni/ 1 Around this month 2 NEW SCIENCE 3 Engineered Nanoscale written in
THE MATRIX IS ALWAYS COMPLEX! Prof. Kenneth Dawson Centre for BioNano Interactions University College Dublin http://www.ucd.ie/cbni/ 1 Around this month 2 NEW SCIENCE 3 Engineered Nanoscale written in
A. Incorrect! Enzymes are not altered or consumed by the reactions they catalyze.
 CLEP Biology - Problem Drill 04: Enzymes and Cellular Metabolism No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about enzymes is correct? (A) Enzymes are consumed in a reaction. (B) Enzymes act by lowering
CLEP Biology - Problem Drill 04: Enzymes and Cellular Metabolism No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about enzymes is correct? (A) Enzymes are consumed in a reaction. (B) Enzymes act by lowering
Conformational properties of enzymes
 Conformational properties of enzymes; Physics of enzyme substrate interactions; Electronic conformational interactions, cooperative properties of enzymes Mitesh Shrestha Conformational properties of enzymes
Conformational properties of enzymes; Physics of enzyme substrate interactions; Electronic conformational interactions, cooperative properties of enzymes Mitesh Shrestha Conformational properties of enzymes
Dissociation of Orthophosphoric Acid
 { Phosphorus General Essential for all living things Component of DNA, RNA, ADP, ATP, and bone Usually the most limiting nutrient in phytoplankton productivity Many forms Soluble inorganic, soluble organic,
{ Phosphorus General Essential for all living things Component of DNA, RNA, ADP, ATP, and bone Usually the most limiting nutrient in phytoplankton productivity Many forms Soluble inorganic, soluble organic,
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company. 5 Function of Globular Proteins
 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 5 Function of Globular Proteins CHAPTER 5: Function of Globular Proteins Key topics in protein function: Reversible binding of ligands is essential Specificity of ligands
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 5 Function of Globular Proteins CHAPTER 5: Function of Globular Proteins Key topics in protein function: Reversible binding of ligands is essential Specificity of ligands
Hypochromic/Microcytic Anemias
 Hypochromic/Microcytic Anemias (NORMO)/HYPOCHROMIC &/or (NORMO)/MICROCYTIC ANEMIAS 1. Disorders of iron utilization a. iron deficiency b. anemia of chronic disease 2. Disorders of globin synthesis a. Thalassemias
Hypochromic/Microcytic Anemias (NORMO)/HYPOCHROMIC &/or (NORMO)/MICROCYTIC ANEMIAS 1. Disorders of iron utilization a. iron deficiency b. anemia of chronic disease 2. Disorders of globin synthesis a. Thalassemias
HEMOGLOBIN: PHYSIOLOGICAL EXPRESSION AND EVOLUTION OF GENE CLUSTER
 HEMOGLOBIN: PHYSIOLOGICAL EXPRESSION AND EVOLUTION OF GENE CLUSTER I. Physiological Expression: HOW DO WE GET OXYGEN TO OUR BODY TISSUES? Oxygen has a low solubility in blood. During the course of animal
HEMOGLOBIN: PHYSIOLOGICAL EXPRESSION AND EVOLUTION OF GENE CLUSTER I. Physiological Expression: HOW DO WE GET OXYGEN TO OUR BODY TISSUES? Oxygen has a low solubility in blood. During the course of animal
Egg Whites. Spider Webs
 Put down pencils! Muscles Nails Horns Enzymes Hair Egg Whites Spider Webs What do proteins do? Transport Make Provide up Antibodies Structural in Support your Immune System Example: Hemoglobin carries
Put down pencils! Muscles Nails Horns Enzymes Hair Egg Whites Spider Webs What do proteins do? Transport Make Provide up Antibodies Structural in Support your Immune System Example: Hemoglobin carries
Specificity: Induced Fit
 Specificity: Induced Fit Conformational changes may occur upon ligand binding (Daniel Koshland in 1958) This adaptation is called the induced fit Induced fit allows for tighter binding of the ligand Induced
Specificity: Induced Fit Conformational changes may occur upon ligand binding (Daniel Koshland in 1958) This adaptation is called the induced fit Induced fit allows for tighter binding of the ligand Induced
Ferritin and ferritin isoforms I: Structure function relationships, synthesis, degradation and secretion
 Ferritin and ferritin isoforms I: Structure function relationships, synthesis, degradation and secretion A. M. KOORTS & M. VILJOEN Department of Physiology, School of Medicine, University of Pretoria,
Ferritin and ferritin isoforms I: Structure function relationships, synthesis, degradation and secretion A. M. KOORTS & M. VILJOEN Department of Physiology, School of Medicine, University of Pretoria,
Bioreaction Kinetics Seungwook Kim Chem. & Bio. Eng.
 Bioreaction Kinetics 2 2004 Seungwook Kim Chem. & Bio. Eng. Reference Chemistry and the Living Organism, 6 th edition, Molly M. Bloomfield, Lawrence J. Stephens, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Enzymes 1. Most
Bioreaction Kinetics 2 2004 Seungwook Kim Chem. & Bio. Eng. Reference Chemistry and the Living Organism, 6 th edition, Molly M. Bloomfield, Lawrence J. Stephens, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Enzymes 1. Most
Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Key Concepts 3.1 Nucleic Acids Are Informational Macromolecules 3.2 Proteins Are Polymers with Important Structural
3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Chapter 3 Nucleic Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes Key Concepts 3.1 Nucleic Acids Are Informational Macromolecules 3.2 Proteins Are Polymers with Important Structural
BIOINFORMATICS LABORATORY MANUAL 2 DEGREE IN BIOTECHNOLOGY
 BIOINFORMATICS LABORATORY MANUAL 2 DEGREE IN BIOTECHNOLOGY UNIVERSIDAD MIGUEL HERNÁNDEZ DE ELCHE Course 2010-2011 Course Instructor: Dr. Gregorio Fernández Ballester In order to do this exercise, you
BIOINFORMATICS LABORATORY MANUAL 2 DEGREE IN BIOTECHNOLOGY UNIVERSIDAD MIGUEL HERNÁNDEZ DE ELCHE Course 2010-2011 Course Instructor: Dr. Gregorio Fernández Ballester In order to do this exercise, you
Mechanisms of Mammalian Iron Homeostasis
 pubs.acs.org/biochemistry Mechanisms of Mammalian Iron Homeostasis Kostas Pantopoulos, Suheel Kumar Porwal, Alan Tartakoff, and L. Devireddy*, Lady Davis Institute for Medical Research, Jewish General
pubs.acs.org/biochemistry Mechanisms of Mammalian Iron Homeostasis Kostas Pantopoulos, Suheel Kumar Porwal, Alan Tartakoff, and L. Devireddy*, Lady Davis Institute for Medical Research, Jewish General
Globins. The Backbone structure of Myoglobin 2. The Heme complex in myoglobin. Lecture 10/01/2009. Role of the Globin.
 Globins Lecture 10/01/009 The Backbone structure of Myoglobin Myoglobin: 44 x 44 x 5 Å single subunit 153 amino acid residues 11 residues are in an a helix. Helices are named A, B, C, F. The heme pocket
Globins Lecture 10/01/009 The Backbone structure of Myoglobin Myoglobin: 44 x 44 x 5 Å single subunit 153 amino acid residues 11 residues are in an a helix. Helices are named A, B, C, F. The heme pocket
Review. The Molecular Biology of Human Iron Metabolism. The Iron Circuit
 The Molecular Biology of Human Iron Metabolism William E. Winter, MD, 1,2,3 * Lindsay A. L. Bazydlo, PhD, 1 and Neil S. Harris, MD 1 Lab Med Spring 2014;45:92-102 DOI: 10.1309/LMF28S2GIMXNWHMM ABSTRACT
The Molecular Biology of Human Iron Metabolism William E. Winter, MD, 1,2,3 * Lindsay A. L. Bazydlo, PhD, 1 and Neil S. Harris, MD 1 Lab Med Spring 2014;45:92-102 DOI: 10.1309/LMF28S2GIMXNWHMM ABSTRACT
Review. The Molecular Biology of Human Iron Metabolism. The Iron Circuit
 The Molecular Biology of Human Iron Metabolism William E. Winter, MD, 1,2,3 * Lindsay A. L. Bazydlo, PhD, 1 and Neil S. Harris, MD 1 Lab Med Spring 2014;45:92-102 DOI: 10.1309/LMF28S2GIMXNWHMM ABSTRACT
The Molecular Biology of Human Iron Metabolism William E. Winter, MD, 1,2,3 * Lindsay A. L. Bazydlo, PhD, 1 and Neil S. Harris, MD 1 Lab Med Spring 2014;45:92-102 DOI: 10.1309/LMF28S2GIMXNWHMM ABSTRACT
3-Carbon. Okazaki fragments
 DNA Replication DNA strands separate and the nucleotides in the cells come in and join the nitrogenous bases Enzyme Helicase unzips the DNA ready for replication Enzyme Primase adds an RNA Primer which
DNA Replication DNA strands separate and the nucleotides in the cells come in and join the nitrogenous bases Enzyme Helicase unzips the DNA ready for replication Enzyme Primase adds an RNA Primer which
Enzyme. Proteins with catalytic properties. A small group of catalytic RNA molecules
 بسمه تعالی کارشناسی ارشد بیوشیمی و بیولوژي سلول آنزیم ابراهیم قاسمی Enzyme Proteins with catalytic properties A small group of catalytic RNA molecules Catalyze reactions (degrade, conserve and transform
بسمه تعالی کارشناسی ارشد بیوشیمی و بیولوژي سلول آنزیم ابراهیم قاسمی Enzyme Proteins with catalytic properties A small group of catalytic RNA molecules Catalyze reactions (degrade, conserve and transform
Gene Expression: Transcription, Translation, RNAs and the Genetic Code
 Lecture 28-29 Gene Expression: Transcription, Translation, RNAs and the Genetic Code Central dogma of molecular biology During transcription, the information in a DNA sequence (a gene) is copied into a
Lecture 28-29 Gene Expression: Transcription, Translation, RNAs and the Genetic Code Central dogma of molecular biology During transcription, the information in a DNA sequence (a gene) is copied into a
Transferrin Human ELISA Kit
 Transferrin Human ELISA Kit Cat. No.:DEIA1523 Pkg.Size:96T Intended use For the quantitative measurement of Human Transferrin concentrations in cel culture supernatants, milk, saliva and urine. General
Transferrin Human ELISA Kit Cat. No.:DEIA1523 Pkg.Size:96T Intended use For the quantitative measurement of Human Transferrin concentrations in cel culture supernatants, milk, saliva and urine. General
REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION
 REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION Each cell of a living organism contains thousands of genes. But all genes do not function at a time. Genes function according to requirements of the cell. Genes control the
REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION Each cell of a living organism contains thousands of genes. But all genes do not function at a time. Genes function according to requirements of the cell. Genes control the
